WHO EBOLA SCIENCE COMMITTEE
|
|
|
- Harry Barnaby Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHO EBOLA SCIENCE COMMITTEE Prioritized Research Agenda World Health Organization 19 October 2015 The epidemic of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in West Africa found the world unprepared, lacking critical knowledge and proven disease control interventions. This provided a sharp reminder that investing in research is vital for ensuring effective control and prevention of future outbreaks of filoviruses and other severe emerging infectious diseases. In the spring of 2015, WHO convened the Ebola Science Committee (see Annex 1) to define the necessary research, and the requirements for its successful implementation. This research agenda provides a framework for future research activities on EVD and other filoviruses by identifying broad thematic research priorities and key research foci for the development of specific proposals, and articulating the relationship between them. Sustained delivery of this agenda depends on the necessary infrastructure, funding, and support, and must foster the integration of this research into wider efforts to strengthen public health capacity, including health research capacity, in affected countries and globally. As part of broader WHO efforts to develop a research and development Blueprint for public health emergencies, this will involve providing key knowledge and human capacity to address future EVD outbreaks, as well as to leverage linkages with efforts to address other ebolavirus species, other filoviruses, and other severe emerging diseases from the perspectives of scientific and operational research. I. Objectives This research agenda is intended to facilitate progress towards: A. An effective global emerging disease surveillance and response system B. Vaccine(s) to prevent EVD acquisition and to prevent or reduce virus transmission; 1 C. Therapeutics to treat EVD and reduce or prevent sequelae in EVD survivors; 1 D. Validated EVD treatment algorithms; E. Robust diagnostics, including for use at point of care; 1 F. An ethical framework for research in epidemic situations; G. Effective community engagement and mobilization strategies; H. Response and research capacity building for resilient health systems in currently and potentially-affected countries. 1 Detailed development of vaccines, therapeutics and diagnostics is being addressed through the WHO STAC- EE but has been included in this research agenda as a prioritized objective. 1
2 II. Research priorities Seven areas of research were identified as priorities: 2 1. Genomics and implications of viral genetic diversity The current EVD outbreak has highlighted the importance of genetic diversity. Variations in sequence could impact many different facets of the outbreak, from transmissibility to clinical outcomes. Linkages between sequence differences at different geographic locations may provide critical insights into molecular epidemiology. Genome data can further help shape control measures and therapeutic interventions. It could also offer novel insights into developing drugs and vaccines. 2. Biomarkers - This term has multiple uses, but in this context is considered to encompass immunological, virological, biochemical, and metabolic indices as well as other clinical parameters or host genotypic markers. Identifying and monitoring biomarkers may reveal patterns characteristic of different syndromes and stages of illness, and be of use for improving future responses, by improving diagnosis and enhancing the timing of therapeutic and public health interventions. 3. Public health practice - Further research is needed into the impact and improvement of public health measures and practices in three broad areas: transmission dynamics and ecologic factors, such as the impact of activities and understandings amongst health workers, the impact of different clinical manifestations, how best to break transmission chains, relevant human-animal interactions and predictive tools; surveillance, such as improvements to case definitions, monitoring methods, rapid detection capabilities and contact tracing; as well as prevention strategies, such as determining what interventions led to diminution of cases, how they were perceived, what metrics might be needed to assess efficacy, and how this impacts measures to prevent international spread. In addition, the value of research into the recovery and resilience of public healthcare systems was also emphasised. 4. Data, information and knowledge The outbreak highlighted a number of missed opportunities for collecting data during a public health emergency which could be important for subsequent research, for example, meta-data associated with biological samples. It also highlighted a need to develop systems to better link data being generated by different facets of a response, for example epidemiological, virological, and clinical data. More work is also needed to ensure that information and knowledge generated from data collected during an outbreak can be usefully fed back into those communities which produced the data. 2 The First Meeting of the Ebola Science Committee identified a number of different areas of potential interest, they were further refined into this format at the Second Meeting. For more details of this process, see the relevant meeting reports. 2
3 5. Social and community interactions - Whilst noting that they are distinct concepts, there are important roles for research both in social science and community engagement. Connecting these, community-engaged research, following a participatory paradigm, is important to ensure that the views and knowledge of those affected are heard, and can influence the response and future research. Whenever possible, research encompassing these topics should be community-led. To this end, there is particular value in using exploratory and participatory methods and tools within communities (for example, rapid ethnography, participatory appraisal methods and mixed-group dialogues), as well as systematic, representative and quantitative research approaches. 6. Safeguarding future research - There is a need to ensure that studies in pursuit of the priorities identified in this agenda are undertaken in such a way to promote robust, scalable, excellence in research practice whilst minimizing accidental or deliberate risks to those undertaking the research, in the facilities in which they are working, in the communities in which those facilities are situated, and society more broadly, as well as the environment. 7. Implementation science - To facilitate future response readiness and ensure that opportunities to learn from the current outbreak are not missed, the efficacy of, and impact of interactions between, key interventions should be researched. For these research activities to contribute to achieving the objectives listed above, they will have to be coordinated with each other around matters of common concern. The implication is that there will be important cross-disciplinary elements which must be facilitated so that the value chain connecting original research to practical outcomes is optimised. A number of specific research questions in each of these areas were also identified, and have been included in Annex 2. III. Implementation of the research agenda The research agenda is intended to be a living document, evolving to meet changing needs over time. It will require revisiting and revision on a regular basis. A number of specific actions to facilitate the implementation of this research agenda have been included in Annex 3. A number of key factors were identified for translating this agenda into effective action. The need for ongoing work in this space will necessitate the development of a dedicated infrastructure. Implementation of this agenda will also need to be integrated into broader efforts to strengthen public health capacity. Wherever possible, efforts should increase preparedness and response planning for future events. Fostering and leveraging relevant research capacity in affected countries is an overarching principal for ensuring that this research agenda contributes to efforts to ensure the world is better prepared for the next EVD outbreak. Research under this agenda will require rigorous ethical oversight, and support to enhance relevant ethics review capacity may be needed. Data and knowledge management capacities will also require augmentation. 3
4 If this research agenda is to encourage the best use of available resources, prevent unnecessary duplication of effort and unethical exposure of subjects to avoidable harm, it will be necessary to improve information flow. Appropriate relationships will play a key role in identifying research underway and being planned. Appropriate relationships can also help in accessing data both for research purposes, and to help shape responses. Strengthening relevant relationships and timely data-sharing practices would help ensure access to necessary data in a timeframe which can positively inform practice and the design of further necessary research. Practices, systems and relationships can also be formed around access to resources critical for future research. In particular, many of those involved in research in pursuit of this agenda will likely need access to the same resources, including sequence data, non-infectious cloned material, inactivated virus samples, virus isolates, and, sometimes, original clinical samples. Whilst informal relationships will evolve naturally, a more structured approach would help maintain the focus on urgent research for the benefit of the affected countries, so that limited resources are not wasted, and promote longer-term sustainability. Research proposals developed in pursuit of this agenda are expected to follow best practice in research conduct and ethics. When developing specific research projects in pursuit of elements in this agenda, researchers are expected to have considered how the planned research links to objectives and priorities of this agenda, explored appropriate partnerships and collaborations, reviewed existing capabilities and identified opportunities for capacity building. It is essential that both forethought and postresearch reflection be given to how, and to whom, the results will be communicated, and how they might influence future work and identified public health considerations. A more detailed exploration of the specific actions, necessary partnerships, and responsibilities of researchers, to facilitate the implementation of this research agenda can be found in Annex 3. IV. Elements for future action Through its work on a research and development Blueprint for public health emergencies, WHO should develop an action plan to ensure that this research agenda results in effective outcomes, including by considering that: (i) (ii) (iii) management of a research agenda requires active review of both research in progress and research completed. Basic, applied, and implementation research must all be addressed. at regular intervals, the research findings and achievements should be reviewed, and a new gap analysis performed. mechanisms are needed to enable relevant stakeholders to review and reassess the priorities in the light of these analyses, and in the contemporaneous context of global readiness, surveillance and response capacity. This will entail representation from intensely affected and other involved countries, the R&D community, other relevant agencies, institutions and NGOs, and science foundations and funders. 4
5 (iv) (v) dedicated support and knowledge management infrastructure are needed for effective implementation. leveraging linkages with efforts to address other severe emerging diseases is essential to obtain the greatest benefits for future disease control strategies. 5
6 ANNEX 1 Members of the WHO EBOLA Science Committee Professor Peter Piot, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, UK (Chair) Dr Sylvain Baize, Institut Pasteur, France Dr Daniel Bausch, Tulane University, USA Dr Philippe Calaine, MSF, Suisse Professor Jean-Francois Delfraissy, INSERM Dr Scott Dowell, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, USA Dr John Edmunds, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, UK Dr Robert Fowler, Sunnybrook Medical Centre, USA Professor Stephan Günther, BNI, University of Hamburg, Germany Dr Lisa Hensley, National Institutes of Health, USA Dr Peter Jahrling, National Institutes of Health, USA Dr Gary Kobinger, Public Health Agency of Canada, Canada Dr Mandy Kader Konde, Chair of Ebola Research Committee, Guinea Professor Jean-Jacques Muyembe, INRB Kinshasa, DRC Dr Abdulsalami Nasidi, Center for Disease Control, Nigeria Dr Stuart Nichol, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, USA 6
7 ANNEX 2 Specific research questions associated with identified research priorities The Ebola Science Committee concluded that urgent research was indicated in the areas of (1) genomics and the implications of viral diversity, and (2) biomarkers, as these would have an immediate impact on many aspects of outbreak control and in patient care. They also identified a range of key research questions relating to public health practice; data, information and knowledge; social and community interactions; safeguarding future research; and implementation science. The principal questions in each of these categories are listed in this annex. Genomics and implications of viral genetic divergence Five research questions were identified: 1. How much viral genetic diversity has arisen throughout the course of this epidemic across the affected countries? Are different viral genotypes or viral clades associated with different mortality rates, the epidemiology of the outbreak or other variations in the clinical course of infection? 2. How are variations in disease transmissibility, immunopathology, clinical features and outcomes, or intra-host pathogen dynamics linked to particular changes in specific viral genes? 3. Can the patterns of genetic diversification be used to infer the geographic patterns of virus spread, identify missed opportunities for control, and estimate the number of unreported infections? 4. How do mutations in key viral genes affect the accuracy of diagnostic assays in current use? Or the expected utility of vaccine candidates? Or the utility of therapeutic strategies, including antibody-based therapeutics, and immune modulators? 5. How does attenuation affect evaluation of Ebola interventions in animal and in vitro models? What, if any, are the implications for humans of the observed 7U/8U switch? 6. What other non-gp conserved viral targets are there for vaccine design, therapeutics, or diagnostics? How can we identify the most suitable targets? Biomarkers Nine research questions identified were: 1. What biomarkers are associated with (or predict) effective control, or outcome (or lack thereof), of an infection or viral replication at early, middle or late stages in the course of illness? 2. What biomarkers are associated with (or predict) different viral loads? 3. What biomarkers are associated with immunity to re-infection? 4. What biomarkers are associated with (or predict) subclinical or mild infections? 7
8 5. What biomarkers could be used for diagnosis prior to onset of clinical manifestations in exposed persons, or those with early, non-specific symptoms? 6. What biomarkers are associated with (or which could predict) infectivity, transmissibility or virulence? 7. What early biomarkers are associated with (or which could differentiate between) different presentations and syndromes? 8. Which biomarkers, including reductions in viral loads, differ in human recipients of different vaccines and therapies compared to those observed in infections without previous immunization or treatment? 9. What are the functional correlates of immunity following natural infection and post-vaccination? What biomarkers are associated with (or predict) effective post-immunization protection? Public health practice Specific research questions identified included: Transmission dynamics and ecologic factors 1. With regards to healthcare workers in an affected community (including alternative medicine practitioners): What role do they play in amplifying an epidemic? How effective are current infection prevention and control (IPC) practices, including personal protective equipment (PPE) selection, use, and training? 2. How did health workers and other potentially exposed professionals (especially from affected communities) understand the duty, or freedom, to provide care? 3. What is the potential infectivity of people with subclinical, mild or more severe infections, and the potential impact of different syndromes on transmission risk? 4. What are the viral, host, behavioural, and social factors explaining the heterogeneity in transmission and susceptibility including super-spreading events? 5. What are the effective and ethically acceptable approaches for follow up of contacts in order to prevent further transmission (e.g. temperature, or symptom monitoring, quarantine in households or villages, quarantine in healthcare or hotel setting, self-imposed verses system imposed measures)? 6. How do we integrate genomic sequencing into new case investigation and contact tracing to differentiate chains of transmission (e.g. late transmission from recovered patients) and distinguish new zoonotic transmission events? 7. What therapeutic options may be indicated to prevent or interrupt infection of contacts (e.g. vaccine, drugs for post-exposure prophylaxis)? 8. How can efforts to predict future outbreaks be improved? What outbreak characteristics might be employed in forecasting and modelling future outbreaks? 9. What are the relevant human-animal interactions in their ecological and social contexts? What are the animal reservoirs and how can they be monitored 8
9 Surveillance efficiently for risk of zoonotic transmission events? What can the urban nature of this epidemic tell us about potential animal reservoirs relevant to such settings? 10. How do we use the clinical and outbreak data to revise and risk-stratify the case definition, as might be indicated over the course of an outbreak? 11. What are feasible methods to monitor and detect EVD in a low frequency transmission state during outbreaks (e.g. event-based surveillance, targeted post-mortem swabs, skin biopsy, verbal autopsy)? 12. How can we develop and employ rapid detection assays for screening in primary care facilities, within communities, and at mass gatherings that balance needs to maximize case detection while allowing the progress of common life-saving care (e.g., motor vehicle accident trauma response, management of maternal haemorrhage)? 13. How important is contact tracing, how could relevant methodologies be improved, and what procedures and practices should be used during future epidemics? Prevention strategies 14. What factors and sequences had the strongest associations with decreases in cases in each of the countries with sustained transmission of Ebola (e.g. prevention and mitigation strategies, policy decisions, community learning, resources)? How can procedures and practices to identify such factors, and integrate them to prevention, mitigation, response and post-response efforts be improved in advance of the next outbreak? 15. How did survivors and patient s relatives understand isolation and quarantine orders (in terms of rationale, choices, coercion, etc.), and what was the impact and roles of case finders? 16. What metrics, such as those linked to patient and community outcomes, can be reproducibly assessed for community engagement and risk communications? How did these vary by community according to cultural, ethnic and political context, and what lessons emerge from using those metrics regarding the best approaches? 17. Which strategies are most practical and effective to prevent international spread during an outbreak, including quarantine measures and temperature monitoring? Data, information and knowledge Four research questions were identified: 1. How best to develop a system to link or integrate laboratory, epidemiological, and clinical data? 2. How best to develop a strategy to collect meta-data connected to individual physical samples, and design the databases connected to them? 9
10 3. How best to develop a strategy to transition knowledge and technological capacity to affected countries and countries which might potentially be affected in future outbreaks? 4. How best to develop strategies to further the harmonization, accessibility, and interpretation of data and dissemination of findings in a timely fashion? Social and community interactions Nine research questions were identified: 1. How have social, cultural and epidemiological dynamics interacted over the course of the epidemic, how has this varied from place to place, and what have been the consequences? 2. What have communities learned during the outbreak so far about managing EVD risk, and what do they see as the key priorities for knowledge or intervention? 3. How have social and behavioural norms (for example around visits, care and funerals) changed in the short- and longer-term during the course of the outbreak, and what have been the respective roles of community learning, externally-led social mobilization, and interactions between these? 4. How do people perceive and judge the effectiveness of interventions whether around outbreak control, treatment trials, vaccination studies, laboratories, and social mobilization efforts - in the context of local social understandings and dynamics around disease and social life? 5. How did patients who participated in interventional research (such as treatment trials or vaccination studies) understand consent, risks, benefits and choices? How were such concepts communicated to them? 6. What perceptions and experiences underlie community anxieties, resistances and rumours, and what political and economic factors shape these? What broader lessons are suggested for future governance, trust-building and development policy in the affected countries? 7. How do these perceptions and experiences differ between communities (for example, by region, rural-urban areas, and ethnic group), and within them (for example, by gender, age, ethnicity/religion, wealth)? 8. Which local actors and institutions are best positioned to convey and build trust and community ownership in messages and interventions around epidemic control? What are the roles of, for example, local societies, youth groups, local health workers, or survivors? 9. How can community engagement and trust be built and reinforced during the re-building of health systems following the epidemic? Safeguarding future research Research is needed into: 1. How to develop capacity to rapidly scale up research in response to epidemics and to integrate the results of such efforts into preparedness, mitigation, response and post-response efforts in as close to real time as possible? 10
11 2. In varied resource settings and in partnership with relevant practitioners, how best to develop a comprehensive strategy to implement and expand practices for safe handling, methods for inactivation, and disposal of samples and waste in both outbreak settings and containment facility settings? 3. What strategies ensure that necessary safety and security practices are in place and implemented in all relevant facilities, including those used in emergency response operations which may be widely distributed and mobile? 4. What strategies should be used to engage with other communities (such as biosafety, biosecurity professionals, law enforcement, transportation official or customs officers) to work together to ensure that the needs of all stakeholders are met, for example when moving material and personnel into and out of affected areas? Implementation Science Further research is needed into the efficacy of, and impact of interactions between, key interventions, including: 1. Quarantine; 2. Isolation at home; 3. Isolation at health facilities; 4. Infection prevention and control in health facilities; 5. Infection prevention and control at home; 6. Prevention of mass gatherings; 7. Local or national travel restrictions; 8. International travel restrictions; 9. Temperature monitoring; 10. Safe burials; 11. Entry into the Healthcare System, including effective triaging; 12. Use of near-patient or point-of-care tests; 13. Real-time quality assurance and quality control of field use of near patient and point of care tests; 14. Data, information and knowledge gathering, curation, integrations and dissemination; 15. Ethics and regulatory systems during a crisis; 16. Epidemic intelligence; 17. Projection and modelling; 18. Optimal IPC practice. 11
12 ANNEX 3 Specific actions to aid in the implementation of the research agenda The Ebola Science Committee described a set of factors to be addressed to ensure that implementation of the research agenda would yield progress toward the desired outcomes of better prevention and control of EVD, and eventually for other severe emerging infectious diseases. The Committee also discussed how partnerships and stakeholder engagement could support and sustain the necessary work. Finally, they reviewed the role of researchers, and the matters researchers should consider when developing research proposals Key factors to facilitate implementation Nine factors will assist in transitioning from talk to action: 1. Ensuring dedicated infrastructure to provide key support and engender sustainability, including development of sample biobanks and data repositories; 2. Including research considerations in mainstream public health sector development throughout future work in affected countries in order to effectively prepare and respond to EVD and other severe disease outbreaks which may occur; 3. Addressing longer-term sustainability of human resources and key resources, such as reagents and relevant supplies and equipment for research activities; 4. Approved and funded protocols for key activities and needs, on the shelf and ready to use ; 5. Leveraging research and researchers to strengthen response planning, including participation of senior biomedical investigators, anthropologists and social scientists in such responses; 6. Fostering strong and full involvement of national and local researchers in contributing their expertise, and ensuring appropriate ownership of research questions, processes, findings and translation into policy and practice; 7. Ensuring the presence of robust ethical and regulatory capacity in countries, including mechanisms to provide, upon request, advice on research, as well as model material transfer agreements to be used for exporting samples; 8. Enabling ethical reviews at all stages of international studies, including exploring, where feasible, joint reviews at the regional or sub-regional level; 9. Strengthening knowledge and data management, to provide a clearer picture of what research has been conducted (including the reporting of negative results) as well as what is planned Building partnerships Stronger relationships are necessary between stakeholders, including the scientific research community, government health agencies from affected and responding countries, NGOs and other operational partners, scientific foundations, funding agencies as well as recovered patients and their communities. The unique convening power of the WHO to bring together such diverse constituencies will be of particular importance. 12
13 Some models for innovative partnerships already exist, such as the Global Research Collaboration for Infectious Disease Preparedness (GloPID-R), which brings together 11 major preparedness research funders 3. The goal of is to facilitate collaboration and coordination among funders during the inter-epidemic period, so that a rapid and effective research response is ready to be deployed in the case of a significant outbreak. There may be other models for the alignment of diverse stakeholder groups to be found in different spheres. During a crisis, it is difficult to form new operational networks to link researchers to country surveillance, for example. There is value in developing pre-existing frameworks for forming such connections and networks, so that there will be no interference with field operations in emergency conditions, and at the same time avoid hindering access to data and samples for essential research. In some cases, existing networks, such as the Emerging and Dangerous Pathogens Laboratory Network(EDPLN), The Emerging Disease Clinical and Research Network(EDCARN), ISARIC, and others, could be leveraged to improve systematic data collection, integration and information flow. In other areas, such as for clinical data or biobanking of samples, new networks with dedicated infrastructure and governance may be necessary. It is desirable that geographical participation be as wide as possible in such networks. Given the importance of data and resources, there is an urgent need to identify and promote the added value for partners and global public health in the early sharing of data, and for open access to data and results. In particular, cooperative resource collection and management confers an increased responsibility to ensure that affected and at risk communities realize benefit from such arrangements. Considerations when developing research proposals When developing projects to address the priorities in this research agenda, researchers should attempt to address: How the research being planned connects to the research agenda, or how the proposal would enable progress towards addressing the priorities; Which national and international partners will be involved; What capacities need to be in place with which partners, and who is intended to provide such capacities; How the research will help to build relevant capacity in countries and among partners, including helping set priorities for patients and sites for research, and the use of limited funds. Who needs the results of the research and why it represents a priority. How the outcomes of the research will be shared and communicated. 3 European Commission, CIHR, Canada, U.S. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, INSERM/IMMI/AVIESAN France, FIOCRUZ and BUTANTAN Institutes Brazil, Instituto de Salud Carlos III Spain, NRF Korea, South African Medical Research Council and Department of Science and Technology South Africa, Institut Pasteur Korea, Thai National Institute of Health, Department of Medical Sciences (Thai NIH, DMSc. MoPH) Thailand, National Health and Medical Research Council Australia. Mexico is currently in the process of joining the initiative. 13
14 How the research will impact future work (including any new avenues of research it may open). How the research will be fed back into preparedness, response, recovery planning and activities, or future system-building. How the research results will be fed back into refining the research agenda. 14
Ebola virus disease outbreak in western Africa
 Action Plan Strategic Objectives 6. Promote innovation and research on new drugs International surveillance networks and information sharing on promising research Active role in research for governments
Action Plan Strategic Objectives 6. Promote innovation and research on new drugs International surveillance networks and information sharing on promising research Active role in research for governments
Notes for the record: Consultation on Monitored Emergency Use of Unregistered and Investigational Interventions for Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
 Notes for the record: Consultation on Monitored Emergency Use of Unregistered and Investigational Interventions for Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) A group of independent scientific experts convened by the WHO
Notes for the record: Consultation on Monitored Emergency Use of Unregistered and Investigational Interventions for Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) A group of independent scientific experts convened by the WHO
EBOLA RESPONSE PHASE 3
 EBOLA RESPONSE PHASE 3 Framework for achieving and sustaining a resilient zero SEPTEMBER 2015 Photo: WHO/M. Winkler WHO/EVD/Guidance/Strategy/15.3 World Health Organization 2015 All rights reserved. The
EBOLA RESPONSE PHASE 3 Framework for achieving and sustaining a resilient zero SEPTEMBER 2015 Photo: WHO/M. Winkler WHO/EVD/Guidance/Strategy/15.3 World Health Organization 2015 All rights reserved. The
Ebola outbreak in West Africa : Shift in paradigm
 Ebola outbreak in West Africa : Shift in paradigm Dr S.C Briand, Director Pandemic and Epidemic Diseases department, WHO Geneva EVD West Africa: many "first time" Enormous epidemic in the affected countries
Ebola outbreak in West Africa : Shift in paradigm Dr S.C Briand, Director Pandemic and Epidemic Diseases department, WHO Geneva EVD West Africa: many "first time" Enormous epidemic in the affected countries
Guidance on Request for Information on Rapid Response Platform Technologies for Epidemic Preparedness
 Guidance on Request for Information on Rapid Response Platform Technologies for Epidemic Preparedness Purpose of this request for information The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF; also referred to
Guidance on Request for Information on Rapid Response Platform Technologies for Epidemic Preparedness Purpose of this request for information The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF; also referred to
Combating Infectious Diseases Takes a Community: Lessons From the Ebola Epidemic
 Combating Infectious Diseases Takes a Community: Lessons From the 2014 2015 Ebola Epidemic May 1, 2015 Nahid Bhadelia, MD, MA Director of Infection Control and Medical Response, National Emerging Infectious
Combating Infectious Diseases Takes a Community: Lessons From the 2014 2015 Ebola Epidemic May 1, 2015 Nahid Bhadelia, MD, MA Director of Infection Control and Medical Response, National Emerging Infectious
Vector control. REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 8.4. SEA/RC70/10 Maldives 6 10 September July Seventieth Session
 REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 8.4 Seventieth Session SEA/RC70/10 Maldives 6 10 September 2017 18 July 2017 Vector control Major vector-borne diseases account for an estimated 17% of the global
REGIONAL COMMITTEE Provisional Agenda item 8.4 Seventieth Session SEA/RC70/10 Maldives 6 10 September 2017 18 July 2017 Vector control Major vector-borne diseases account for an estimated 17% of the global
Ebola Virus disease in West Africa : challenges and lessons learned
 Ebola Virus disease in West Africa : challenges and lessons learned Pr N. Shindo Dr S.C. Briand Pandemic and Epidemic Diseases Department WHO Geneva EVD outbreak in West Africa in Numbers From24 March
Ebola Virus disease in West Africa : challenges and lessons learned Pr N. Shindo Dr S.C. Briand Pandemic and Epidemic Diseases Department WHO Geneva EVD outbreak in West Africa in Numbers From24 March
The response of research: from the field to the lab. K. Victoir PhD
 The response of research: from the field to the lab K. Victoir PhD Outline Responses to the Ebola outbreak: a nations response (France) and an institutional response (IP) Overview of the Field actions
The response of research: from the field to the lab K. Victoir PhD Outline Responses to the Ebola outbreak: a nations response (France) and an institutional response (IP) Overview of the Field actions
Dialogue 1: Partnerships in support of strengthening health systems: Building resilience to pandemics 1
 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL PARTNERSHIPS FORUM Dialogue 1: Partnerships in support of strengthening health systems: Building resilience to pandemics 1 Introduction 28 May 2015, 11:00 a.m. 1:00 p.m. UN
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL PARTNERSHIPS FORUM Dialogue 1: Partnerships in support of strengthening health systems: Building resilience to pandemics 1 Introduction 28 May 2015, 11:00 a.m. 1:00 p.m. UN
EBOLA IN DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO (DRC) CRISIS INFO #2 06/06/2018
 EBOLA IN DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO (DRC) CRISIS INFO #2 06/06/2018 1. Global overview 1.1. Context So far, the outbreak (officially declared on 8 th of May) has affected the Bikoro (Bikoro and Ikoko
EBOLA IN DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO (DRC) CRISIS INFO #2 06/06/2018 1. Global overview 1.1. Context So far, the outbreak (officially declared on 8 th of May) has affected the Bikoro (Bikoro and Ikoko
Overview of Nigeria s R & D Plan for Lassa fever
 Overview of Nigeria s R & D Plan for Lassa fever Presented by Bola Olayinka Preparing for Lassa Vaccine Clinical Trials with Targeted Epidemiology Studies Workshop 08 November 2018, Accra, Ghana Introduction
Overview of Nigeria s R & D Plan for Lassa fever Presented by Bola Olayinka Preparing for Lassa Vaccine Clinical Trials with Targeted Epidemiology Studies Workshop 08 November 2018, Accra, Ghana Introduction
STATUS OF REVIEWS, AUTHORIZATIONS AND OVERSIGHT FOR CLINICAL TRIALS IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION. Technical Document
 30 August 2017 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-seventh session Victoria Falls, Republic of Zimbabwe, 28 August 1 September 2017 Agenda item 17 STATUS OF REVIEWS, AUTHORIZATIONS AND
30 August 2017 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-seventh session Victoria Falls, Republic of Zimbabwe, 28 August 1 September 2017 Agenda item 17 STATUS OF REVIEWS, AUTHORIZATIONS AND
Personalized. Health in Canada
 Personalized Health in Canada Canadian Institutes of Health Research Personalized Medicine Signature Initiative 2010-2013 0 Dr. Morag Park CIHR Institute of Cancer Research Dr. Paul Lasko CIHR Institute
Personalized Health in Canada Canadian Institutes of Health Research Personalized Medicine Signature Initiative 2010-2013 0 Dr. Morag Park CIHR Institute of Cancer Research Dr. Paul Lasko CIHR Institute
STATUS OF REVIEWS, AUTHORIZATIONS AND OVERSIGHT FOR CLINICAL TRIALS IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION. Technical Document
 15 June 2017 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-seventh session Victoria Falls, Republic of Zimbabwe, 28 August 1 September 2017 Provisional agenda item 17 STATUS OF REVIEWS, AUTHORIZATIONS
15 June 2017 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-seventh session Victoria Falls, Republic of Zimbabwe, 28 August 1 September 2017 Provisional agenda item 17 STATUS OF REVIEWS, AUTHORIZATIONS
R&D for potential vaccines for the Ebola virus
 R&D for potential vaccines for the Ebola virus Update 4 March 2015 Roberto Bertollini MD MPH Chief Scientist and WHO Representative to the EU Gathering knowledge Since August 2014, series of consultations
R&D for potential vaccines for the Ebola virus Update 4 March 2015 Roberto Bertollini MD MPH Chief Scientist and WHO Representative to the EU Gathering knowledge Since August 2014, series of consultations
Malaria Research Capability Strengthening in Africa
 July 2005 UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research & Training in Tropical Diseases (TDR) Multilateral Initiative on Malaria (MIM) Malaria Research Capability Strengthening in Africa INTRODUCTION
July 2005 UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research & Training in Tropical Diseases (TDR) Multilateral Initiative on Malaria (MIM) Malaria Research Capability Strengthening in Africa INTRODUCTION
Ebola Virus Disease in West Africa: From Crisis to More Resilient Health Systems
 Ebola Virus Disease in West Africa: From Crisis to More Resilient Health Systems Patricio V. Marquez Lead Health Specialist World Bank Health, Nutrition and Population Global Practice April 15, 2015 Outline
Ebola Virus Disease in West Africa: From Crisis to More Resilient Health Systems Patricio V. Marquez Lead Health Specialist World Bank Health, Nutrition and Population Global Practice April 15, 2015 Outline
UNITED STATES ARMY MEDICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
 UNITED STATES ARMY MEDICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Biodefense solutions to protect our nation Forward genomic surveillance advances DoD biomedical research toward combating high-consequence
UNITED STATES ARMY MEDICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Biodefense solutions to protect our nation Forward genomic surveillance advances DoD biomedical research toward combating high-consequence
Emergencies preparedness, response Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic
 1 von 5 05.12.2018, 08:43 Emergencies preparedness, response Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic of the Congo Disease outbreak news: Update 29 November 2018 As the Ebola virus disease (EVD) outbreak
1 von 5 05.12.2018, 08:43 Emergencies preparedness, response Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic of the Congo Disease outbreak news: Update 29 November 2018 As the Ebola virus disease (EVD) outbreak
One Year Later, Where Does the U.S. Response to Ebola Stand?
 One Year Later, Where Does the U.S. Response to Ebola Stand? Kaiser Family Foundation, Washington, DC Jen Kates, PhD Vice President & Director, Global Health & HIV Policy Kaiser Family Foundation jkates@kff.org
One Year Later, Where Does the U.S. Response to Ebola Stand? Kaiser Family Foundation, Washington, DC Jen Kates, PhD Vice President & Director, Global Health & HIV Policy Kaiser Family Foundation jkates@kff.org
IMI2 Ebola and other filoviral haemorrhagic fevers programme. Webinar for SRG and SC 3 November 2014
 IMI2 Ebola and other filoviral haemorrhagic fevers programme Webinar for SRG and SC 3 November 2014 Background Ebola virus diseases (EVD) is a rare and deadly disease Filoviruses such as Ebola spread directly
IMI2 Ebola and other filoviral haemorrhagic fevers programme Webinar for SRG and SC 3 November 2014 Background Ebola virus diseases (EVD) is a rare and deadly disease Filoviruses such as Ebola spread directly
A surveillance of Ebola outbreak at Télimélé, Guinea Conakry 2014
 A surveillance of Ebola outbreak at Télimélé, Guinea Conakry 2014 Jean Marie Vianney Namahoro Postgraduate student Stellenbosch University Fakulteit Geneeskunde en Gesondheidswetenskappe Faculty of Medicine
A surveillance of Ebola outbreak at Télimélé, Guinea Conakry 2014 Jean Marie Vianney Namahoro Postgraduate student Stellenbosch University Fakulteit Geneeskunde en Gesondheidswetenskappe Faculty of Medicine
WHO Blood Regulators Network (BRN)
 Distribution: General English only WHO Blood Regulators Network (BRN) Position Paper on Use of Convalescent Plasma, Serum or Immune Globulin Concentrates as an Element in Response to an Emerging Virus*
Distribution: General English only WHO Blood Regulators Network (BRN) Position Paper on Use of Convalescent Plasma, Serum or Immune Globulin Concentrates as an Element in Response to an Emerging Virus*
CEPI Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations. CEPI a model for funding other initiatives and areas
 CEPI Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations CEPI a model for funding other initiatives and areas Foto: Daniel Berehulak, The New York Times Testing of an Ebola vaccine a successful but suboptimal
CEPI Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations CEPI a model for funding other initiatives and areas Foto: Daniel Berehulak, The New York Times Testing of an Ebola vaccine a successful but suboptimal
Licenced Ebola Vaccine
 The Market Shaping Goal Shape vaccine markets to ensure adequate supply of appropriate, quality vaccines at low and sustainable prices for developing countries. Supply and Procurement Roadmap Licenced
The Market Shaping Goal Shape vaccine markets to ensure adequate supply of appropriate, quality vaccines at low and sustainable prices for developing countries. Supply and Procurement Roadmap Licenced
Democratic Republic of Congo: Ebola update May 2018
 Democratic Republic of Congo: Ebola update May 2018 30 May 2018 Summary Since the Ebola epidemic in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) was declared on 8 May 2018, 54 people who presented symptoms of haemorrhagic
Democratic Republic of Congo: Ebola update May 2018 30 May 2018 Summary Since the Ebola epidemic in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) was declared on 8 May 2018, 54 people who presented symptoms of haemorrhagic
PUI PROPOSAL TO SUPPORT ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES RELATED TO:
 PUI PROPOSAL TO SUPPORT ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES RELATED TO: ENHANCING CAPACITY OF NATIONAL MONITORING TEAMS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE (EVD) UNDER HIGH BIO-SAFETY CONDITIONS UNDER TC PROJECT RAF/0/042
PUI PROPOSAL TO SUPPORT ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES RELATED TO: ENHANCING CAPACITY OF NATIONAL MONITORING TEAMS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE (EVD) UNDER HIGH BIO-SAFETY CONDITIONS UNDER TC PROJECT RAF/0/042
Preparations for Ebola Vaccine Deployment
 Preparations for Ebola Vaccine Deployment Ebola vaccine and vaccination - Session 8 Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) Geneva, 14 16 April 2015 Dr Marie-Pierre Preziosi,
Preparations for Ebola Vaccine Deployment Ebola vaccine and vaccination - Session 8 Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) Geneva, 14 16 April 2015 Dr Marie-Pierre Preziosi,
UPDATE #20 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Issued on 27 January 2015 at 16:00
 UPDATE #20 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Issued on 27 January 2015 at 16:00 1. NUMBER OF CASES AND FATALITIES West Africa and Incorporating the International Situation Data issued by the World Health Organization
UPDATE #20 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Issued on 27 January 2015 at 16:00 1. NUMBER OF CASES AND FATALITIES West Africa and Incorporating the International Situation Data issued by the World Health Organization
FOREST INVESTMENT PROGRAM DESIGN DOCUMENT. (Prepared by the Forest Investment Program Working Group)
 CIF/DMFIP.2/2 February 24, 2009 Second Design Meeting on the Forest Investment Program Washington, D.C. March 5-6, 2009 FOREST INVESTMENT PROGRAM DESIGN DOCUMENT (Prepared by the Forest Investment Program
CIF/DMFIP.2/2 February 24, 2009 Second Design Meeting on the Forest Investment Program Washington, D.C. March 5-6, 2009 FOREST INVESTMENT PROGRAM DESIGN DOCUMENT (Prepared by the Forest Investment Program
Introduction to Lassa fever
 Introduction to Lassa fever Managing infectious hazards Store food in containers with lids OpenWHO.org WHO2017 1 Learning objectives Describe signs, symptoms, and transmission of Lassa fever List 4 preventive
Introduction to Lassa fever Managing infectious hazards Store food in containers with lids OpenWHO.org WHO2017 1 Learning objectives Describe signs, symptoms, and transmission of Lassa fever List 4 preventive
Exploring Good Clinical Practice guidance in clinical trials meeting summary
 Exploring Good Clinical Practice guidance in clinical trials meeting summary Summary The ICH Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines are currently being revised, providing an opportunity to review the
Exploring Good Clinical Practice guidance in clinical trials meeting summary Summary The ICH Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines are currently being revised, providing an opportunity to review the
Development of plasma therapies for emerging infectious diseases. Dr Glenn Smith Biological Science Section Scientific Evaluation Branch
 Development of plasma therapies for emerging infectious diseases Dr Glenn Smith Biological Science Section Scientific Evaluation Branch June 2017 Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) A part of the Australian
Development of plasma therapies for emerging infectious diseases Dr Glenn Smith Biological Science Section Scientific Evaluation Branch June 2017 Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) A part of the Australian
Selection and use of Ebola in vitro diagnostic (IVD) assays
 EMERGENCY GUIDANCE Selection and use of Ebola in vitro diagnostic (IVD) assays June 2015 World Health Organization 2015. All rights reserved. The designations employed and the presentation of the material
EMERGENCY GUIDANCE Selection and use of Ebola in vitro diagnostic (IVD) assays June 2015 World Health Organization 2015. All rights reserved. The designations employed and the presentation of the material
Malaria Research Capability Strengthening in Africa
 October 2004 UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research & Training in Tropical Diseases (TDR) Multilateral Initiative on Malaria (MIM) Malaria Research Capability Strengthening in Africa
October 2004 UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research & Training in Tropical Diseases (TDR) Multilateral Initiative on Malaria (MIM) Malaria Research Capability Strengthening in Africa
Conference conclusions and Action Agenda
 PRE- FINAL VERSION AS OF 16:00 CET, FRIDAY 8 JULY 2016 FINAL VERSION TO BE AVAILABLE ONLINE FROM TUESDAY 12 JULY 2016 Conference conclusions and Action Agenda The Paris Agreement, adopted on 12 th December
PRE- FINAL VERSION AS OF 16:00 CET, FRIDAY 8 JULY 2016 FINAL VERSION TO BE AVAILABLE ONLINE FROM TUESDAY 12 JULY 2016 Conference conclusions and Action Agenda The Paris Agreement, adopted on 12 th December
Highlights from BIO 2015
 Volume 2-4th Quarter 2015 Highlights from BIO 2015 Africabio Enterprises Inc The BIO International Convention was in full swing in June 2015 as CEOs, scientists, researchers, economic development professionals,
Volume 2-4th Quarter 2015 Highlights from BIO 2015 Africabio Enterprises Inc The BIO International Convention was in full swing in June 2015 as CEOs, scientists, researchers, economic development professionals,
Why the private sector matters for development effectiveness
 Why the private sector matters for development effectiveness Hadiza Sidikou African Development Bank The development paradigm has shifted towards private investment and during the last decade, the private
Why the private sector matters for development effectiveness Hadiza Sidikou African Development Bank The development paradigm has shifted towards private investment and during the last decade, the private
Data & Materials Sharing Agreement. Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery. Clinical Trials Data Sharing Addendum & Related Information
 Data & Materials Sharing Agreement Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery Clinical Trials Data Sharing Addendum & Related Information I. Overview of this Document The primary purpose of this document
Data & Materials Sharing Agreement Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery Clinical Trials Data Sharing Addendum & Related Information I. Overview of this Document The primary purpose of this document
Stem Cell Research: Identifying emerging high priority policy issues
 The state stem cell agency Stem Cell Research: Identifying emerging high priority policy issues Ellen G. Feigal, M.D. SVP, Research and Development National Cancer Policy Summit Washington, DC November
The state stem cell agency Stem Cell Research: Identifying emerging high priority policy issues Ellen G. Feigal, M.D. SVP, Research and Development National Cancer Policy Summit Washington, DC November
Anticipating Epidemics Science and Research December Dr Marie-Paule Kieny Assistant Director-General Health Systems and Innovation
 Anticipating Epidemics Science and Research December 2015 Dr Marie-Paule Kieny Assistant Director-General Health Systems and Innovation Preparing for the inevitable With more frequent travel, globalized
Anticipating Epidemics Science and Research December 2015 Dr Marie-Paule Kieny Assistant Director-General Health Systems and Innovation Preparing for the inevitable With more frequent travel, globalized
IHR Emergency Committee on the 2014 / 15 Ebola outbreak in West Africa
 IHR Emergency Committee on the 2014 / 15 Ebola outbreak in West Africa April, 2015 Dr Peter Gaturuku Capacity Building and Training Health Security and Emergencies Cluster WHO Regional Office for Africa,
IHR Emergency Committee on the 2014 / 15 Ebola outbreak in West Africa April, 2015 Dr Peter Gaturuku Capacity Building and Training Health Security and Emergencies Cluster WHO Regional Office for Africa,
Current context and challenges; stopping the epidemic; and preparedness in non-affected countries and regions
 EXECUTIVE BOARD Special session on Ebola Provisional agenda item 3 EBSS/3/2 EXECUTIVE BOARD 136th session 9 January 2015 Provisional agenda item 9.4 Current context and challenges; stopping the epidemic;
EXECUTIVE BOARD Special session on Ebola Provisional agenda item 3 EBSS/3/2 EXECUTIVE BOARD 136th session 9 January 2015 Provisional agenda item 9.4 Current context and challenges; stopping the epidemic;
BOARD PAPER - NHS ENGLAND. Purpose of Paper: To inform the Board of the development of an NHS England Personalised Medicine Strategy.
 Paper: PB.24.09.15/05 Title: Personalised Medicine Strategy. From: Sir Bruce Keogh, National Medical Director. BOARD PAPER - NHS ENGLAND Purpose of Paper: To inform the Board of the development of an NHS
Paper: PB.24.09.15/05 Title: Personalised Medicine Strategy. From: Sir Bruce Keogh, National Medical Director. BOARD PAPER - NHS ENGLAND Purpose of Paper: To inform the Board of the development of an NHS
AFM Corporate Governance Code
 AFM Corporate Governance Code January 2019 Ó Association of Financial Mutuals About this document The AFM Corporate Governance Code (AFM Code) takes effect from 1 January 2019. This means AFM members should
AFM Corporate Governance Code January 2019 Ó Association of Financial Mutuals About this document The AFM Corporate Governance Code (AFM Code) takes effect from 1 January 2019. This means AFM members should
Boosting Decent Employment for Africa s Youth. Request for Concept Notes
 Boosting Decent Employment for Africa s Youth Request for Concept Notes Submission deadline: October 8, 2018 i Table of Contents 1. About the partner organizations... 1 2. Background and rationale... 2
Boosting Decent Employment for Africa s Youth Request for Concept Notes Submission deadline: October 8, 2018 i Table of Contents 1. About the partner organizations... 1 2. Background and rationale... 2
Marburg and Ebola viruses. Stephan Becker Philipps-Universität Marburg
 Marburg and Ebola viruses Stephan Becker Philipps-Universität Marburg Filoviridae (order Mononegavirales) Matrix (VP40) Surface glycoprotein (GP) Lipid envelope Ribonucleoprotein complex (vrna, NP, VP35,
Marburg and Ebola viruses Stephan Becker Philipps-Universität Marburg Filoviridae (order Mononegavirales) Matrix (VP40) Surface glycoprotein (GP) Lipid envelope Ribonucleoprotein complex (vrna, NP, VP35,
Foreword... iii. 2 Situation Analysis... 1 Current status... 3 Key issues affecting Health Systems Global... 3
 Strategic Plan 2013 2015 Table of Contents Foreword... iii 1. Introduction... 1 Overview of Health Systems Global... 1 Purpose of the strategic plan... 1 How the strategic plan was developed... 1 2 Situation
Strategic Plan 2013 2015 Table of Contents Foreword... iii 1. Introduction... 1 Overview of Health Systems Global... 1 Purpose of the strategic plan... 1 How the strategic plan was developed... 1 2 Situation
to protect human health throughout the life-cycle of medicinal products;
 ICMRA Communications Strategy: 2018-2020 Introduction The International Coalition of Medicines Regulatory Authorities (ICMRA) is a voluntary, highlevel, strategic coordinating, advocacy and leadership
ICMRA Communications Strategy: 2018-2020 Introduction The International Coalition of Medicines Regulatory Authorities (ICMRA) is a voluntary, highlevel, strategic coordinating, advocacy and leadership
Australian Medical Research and Innovation Priorities Determination 2018
 Australian Medical Research and Innovation Priorities 2018 2020 Determination 2018 I, Ian Frazer, Chair of the Australian Medical Research Advisory Board, make the following instrument on behalf of the
Australian Medical Research and Innovation Priorities 2018 2020 Determination 2018 I, Ian Frazer, Chair of the Australian Medical Research Advisory Board, make the following instrument on behalf of the
THREE -YEAR STRATEGIC PLAN
 THREE -YEAR STRATEGIC PLAN 2017 18 2019 20 About ICES Population-based health research that makes a difference Since its inception in 1992, the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) has led
THREE -YEAR STRATEGIC PLAN 2017 18 2019 20 About ICES Population-based health research that makes a difference Since its inception in 1992, the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) has led
NHS ENGLAND BOARD PAPER
 NHS ENGLAND BOARD PAPER Paper: PB.30.03.2017/06 Title: Creating a genomic medicine service to lay the foundations to deliver personalised interventions and treatments Lead Director: Professor Sir Bruce
NHS ENGLAND BOARD PAPER Paper: PB.30.03.2017/06 Title: Creating a genomic medicine service to lay the foundations to deliver personalised interventions and treatments Lead Director: Professor Sir Bruce
Terms of Reference of CGIAR s Independent Science for Development Council (ISDC)
 Approved by the System Council with effect from 4 October 2018 (Decision Ref: SC/M6/EDP2) Terms of Reference of CGIAR s Independent Science for Development Council (ISDC) 1. Background 1.1 The Independent
Approved by the System Council with effect from 4 October 2018 (Decision Ref: SC/M6/EDP2) Terms of Reference of CGIAR s Independent Science for Development Council (ISDC) 1. Background 1.1 The Independent
Personalised Medicine Regulatory Issues
 Personalised Medicine Regulatory Issues INFRAFRONTIER / IMPC Stakeholder Meeting Presented by Marisa Papaluca on 14 November 2017 Senior Scientific Advisor, Scientific Committees Regulatory Science Strategy
Personalised Medicine Regulatory Issues INFRAFRONTIER / IMPC Stakeholder Meeting Presented by Marisa Papaluca on 14 November 2017 Senior Scientific Advisor, Scientific Committees Regulatory Science Strategy
The Quality Principles: Alcohol & Drug Partnership (ADP) Validated Self- Assessment and Improvement Mid and East Lothian
 The Quality Principles: Alcohol & Drug Partnership (ADP) Validated Self- Assessment and Improvement Mid and East Lothian Introduction To support effective implementation of the Quality Principles, the
The Quality Principles: Alcohol & Drug Partnership (ADP) Validated Self- Assessment and Improvement Mid and East Lothian Introduction To support effective implementation of the Quality Principles, the
Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP)
 E CDIP/21/11 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: MARCH 16, 2018 Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP) Twenty-First Session Geneva, May 14 to 18, 2018 COMPILATION OF MEMBER STATE INPUTS ON THE MODALITIES
E CDIP/21/11 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: MARCH 16, 2018 Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP) Twenty-First Session Geneva, May 14 to 18, 2018 COMPILATION OF MEMBER STATE INPUTS ON THE MODALITIES
Webinar IMI2 - Call 9 Data quality in preclinical research and development. Thomas Steckler IMI webinar
 Webinar IMI2 - Call 9 Data quality in preclinical research and development Thomas Steckler 11.04.2016 IMI webinar Need for public-private collaboration Low quality data hamper innovation and progress in
Webinar IMI2 - Call 9 Data quality in preclinical research and development Thomas Steckler 11.04.2016 IMI webinar Need for public-private collaboration Low quality data hamper innovation and progress in
Genomics and personalised medicine
 Genomics and personalised medicine Dr Tom Fowler, Deputy Chief Scientist & Director of Public Health WHO Symposium on the Future of Digital Health Systems in the European Region February 2019 About me
Genomics and personalised medicine Dr Tom Fowler, Deputy Chief Scientist & Director of Public Health WHO Symposium on the Future of Digital Health Systems in the European Region February 2019 About me
Classroom Discussion Guide on Ethics and Public Health Emergencies
 Classroom Discussion Guide on Ethics and Public Health Emergencies This guide provides discussion questions and topics based on the Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues report, Ethics
Classroom Discussion Guide on Ethics and Public Health Emergencies This guide provides discussion questions and topics based on the Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues report, Ethics
FAO STRATEGY FOR FORESTS AND FORESTRY
 FAO STRATEGY FOR FORESTS AND FORESTRY Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome, 2010 FAO STRATEGY FOR FORESTS AND FORESTRY THE CHALLENGES AHEAD The forest sector continues to be affected
FAO STRATEGY FOR FORESTS AND FORESTRY Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome, 2010 FAO STRATEGY FOR FORESTS AND FORESTRY THE CHALLENGES AHEAD The forest sector continues to be affected
The Power of Partnership
 The Foundation for Science and Technology 25 March, 2015 London Debate on from the Response to the Ebola Outbreak Chapter One The Power of Partnership 2 1 Some Key Points So Far Dec 2013 First Ebola case
The Foundation for Science and Technology 25 March, 2015 London Debate on from the Response to the Ebola Outbreak Chapter One The Power of Partnership 2 1 Some Key Points So Far Dec 2013 First Ebola case
Ebola Virus Disease. West Africa Dr Sylvie Briand. Pandemic and Epidemic Diseases department
 Ebola Virus Disease West Africa - 2014 Dr Sylvie Briand 1 Haemorrhagic fever Incubation period: 2 21 days Symptoms: start with fever, intense weakness, muscle pain, headache and sore throat. Followed by
Ebola Virus Disease West Africa - 2014 Dr Sylvie Briand 1 Haemorrhagic fever Incubation period: 2 21 days Symptoms: start with fever, intense weakness, muscle pain, headache and sore throat. Followed by
Joint Evaluation of Joint Programmes on Gender Equality in the United Nations System Management Response
 drafted by: Working Group (UN Women, UNDP, UNFPA, UNICEF, MDGF/UNDP) Date: 5/16/2014 Overall : The interagency group which commissioned the Joint Evaluation of Joint Programmes on Gender Equality in the
drafted by: Working Group (UN Women, UNDP, UNFPA, UNICEF, MDGF/UNDP) Date: 5/16/2014 Overall : The interagency group which commissioned the Joint Evaluation of Joint Programmes on Gender Equality in the
Preparedness for the inevitable: overcoming obstacles to a timely and effective R&D response. The WHO Blueprint Team
 Preparedness for the inevitable: overcoming obstacles to a timely and effective R&D response The WHO Blueprint Team Context of the Blueprint WHO Executive Board 1 (January 2015) WHO Summit on Ebola R&D
Preparedness for the inevitable: overcoming obstacles to a timely and effective R&D response The WHO Blueprint Team Context of the Blueprint WHO Executive Board 1 (January 2015) WHO Summit on Ebola R&D
Internal Oversight Division. Internal Audit Strategy
 Internal Oversight Division Internal Audit Strategy 2018-2020 Date: January 24, 2018 page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF ACRONYMS 3 1. BACKGROUND 4 2. PURPOSE 4 3. WIPO STRATEGIC REALIGNMENT PROGRAM 5 (A)
Internal Oversight Division Internal Audit Strategy 2018-2020 Date: January 24, 2018 page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF ACRONYMS 3 1. BACKGROUND 4 2. PURPOSE 4 3. WIPO STRATEGIC REALIGNMENT PROGRAM 5 (A)
The role of PHE s AMRHAI Reference Unit
 The role of PHE s AMRHAI Reference Unit Professor Neil Woodford Antimicrobial Resistance & Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit Crown copyright What does AMRHAI offer? Susceptibility
The role of PHE s AMRHAI Reference Unit Professor Neil Woodford Antimicrobial Resistance & Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit Crown copyright What does AMRHAI offer? Susceptibility
VALUE OF COMPANION DIAGNOSTICS IN PERSONALISED MEDICINE
 VALUE OF COMPANION DIAGNOSTICS IN PERSONALISED MEDICINE Stimulating innovation for improving health through companion diagnostics 5 March 2015 I. Introduction Personalised healthcare provides targeted
VALUE OF COMPANION DIAGNOSTICS IN PERSONALISED MEDICINE Stimulating innovation for improving health through companion diagnostics 5 March 2015 I. Introduction Personalised healthcare provides targeted
May 9, Meeting Summary. Facilitating Antibacterial Drug Development
 May 9, 2012 Meeting Summary Facilitating Antibacterial Drug Development Origins of the Current Public Health Crisis of Antibacterial Resistance Antibacterial drugs play a critical role in the ability to
May 9, 2012 Meeting Summary Facilitating Antibacterial Drug Development Origins of the Current Public Health Crisis of Antibacterial Resistance Antibacterial drugs play a critical role in the ability to
ANNEX E. Emerging Green Technologies
 ANNEX E Emerging Green Technologies APEC Regulatory Cooperation Advancement Mechanism: Revised Recommendations on Smart Grid Interoperability Standards Background As called for by the APEC Regulatory Cooperation
ANNEX E Emerging Green Technologies APEC Regulatory Cooperation Advancement Mechanism: Revised Recommendations on Smart Grid Interoperability Standards Background As called for by the APEC Regulatory Cooperation
Alliances for Action
 Context Alliances for Action Summary Paper With the adoption of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by the United Nations, the political commitment to eradicate poverty in all its forms and dimensions
Context Alliances for Action Summary Paper With the adoption of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by the United Nations, the political commitment to eradicate poverty in all its forms and dimensions
JOB DESCRIPTION. Job title: Epidemiologist Location: Maputo, Mozambique frequent visits to Provinces
 JOB DESCRIPTION Job title: Epidemiologist Location: Maputo, Mozambique frequent visits to Provinces Department: Technical Length of contract: 4 years Role type: National Grade: 9 Travel involved: Up to
JOB DESCRIPTION Job title: Epidemiologist Location: Maputo, Mozambique frequent visits to Provinces Department: Technical Length of contract: 4 years Role type: National Grade: 9 Travel involved: Up to
Point-of-care diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in low-resource settings
 Society for Applied Microbiology Point-of-care diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in low-resource settings Thursday 7 June 2018 Room B308 B309 ASM Microbe Georgia World Congress Center Atlanta
Society for Applied Microbiology Point-of-care diagnostic testing for infectious diseases in low-resource settings Thursday 7 June 2018 Room B308 B309 ASM Microbe Georgia World Congress Center Atlanta
Emergencies preparedness, response Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic
 1 von 5 26.11.2018, 08:41 Emergencies preparedness, response Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic of the Congo Disease outbreak news: Update 22 November 2018 Containing the ongoing Ebola virus disease
1 von 5 26.11.2018, 08:41 Emergencies preparedness, response Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic of the Congo Disease outbreak news: Update 22 November 2018 Containing the ongoing Ebola virus disease
A new Model of Vaccine R&D Global Health Public Private Partnership : The Global Health Vaccine Center of Innovation (GHVCI)
 A new Model of Vaccine R&D Global Health Public Private Partnership : The Global Health Vaccine Center of Innovation (GHVCI) Jean Lang avp R&D sanofi pasteur 9eme Rencontre Nationale des Directeurs de
A new Model of Vaccine R&D Global Health Public Private Partnership : The Global Health Vaccine Center of Innovation (GHVCI) Jean Lang avp R&D sanofi pasteur 9eme Rencontre Nationale des Directeurs de
6 th November
 6 th November 207 ACCOUNTABILITY FRAMEWORK FOR THE INTER-AGENCY STANDING COMMITTEE POLICY ON GENDER EQUALITY AND THE EMPOWERMENT OF WOMEN AND GIRLS IN HUMANITARIAN ACTION - A. PURPOSE AND RATIONALE The
6 th November 207 ACCOUNTABILITY FRAMEWORK FOR THE INTER-AGENCY STANDING COMMITTEE POLICY ON GENDER EQUALITY AND THE EMPOWERMENT OF WOMEN AND GIRLS IN HUMANITARIAN ACTION - A. PURPOSE AND RATIONALE The
Developing a 5 Year Strategic Framework: Charting a New Course for Malaria Communication. July 26-27, 2011 Southern Sun Hotel Nairobi, Kenya
 Developing a 5 Year Strategic Framework: Charting a New Course for Malaria Communication July 26-27, 2011 Southern Sun Hotel Nairobi, Kenya Agenda Day 1 Welcome and Introductions Outline and Synopsis of
Developing a 5 Year Strategic Framework: Charting a New Course for Malaria Communication July 26-27, 2011 Southern Sun Hotel Nairobi, Kenya Agenda Day 1 Welcome and Introductions Outline and Synopsis of
Standards of proficiency. Biomedical scientists
 Standards of proficiency Biomedical scientists Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of proficiency
Standards of proficiency Biomedical scientists Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of proficiency
Human Genome Editing: Science, Ethics, and Governance Highlights for Industry Stakeholders
 Human Genome Editing: Science, Ethics, and Governance Highlights for Industry Stakeholders Background Advances in genome editing, especially the CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system, have generated tremendous
Human Genome Editing: Science, Ethics, and Governance Highlights for Industry Stakeholders Background Advances in genome editing, especially the CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system, have generated tremendous
Evaluation and Regulation of Biomarkers A Public Health Perspective
 Evaluation and Regulation of Biomarkers A Public Health Perspective Dr Ron Zimmern MA, FRCP, FFPHM Executive Director, PHG Foundation OECD Workshop on Policy Issues for the Development and Use of Biomarkers
Evaluation and Regulation of Biomarkers A Public Health Perspective Dr Ron Zimmern MA, FRCP, FFPHM Executive Director, PHG Foundation OECD Workshop on Policy Issues for the Development and Use of Biomarkers
Enabling the adoption of new diagnostics within the UK healthcare system:
 Enabling the adoption of new diagnostics within the UK healthcare system: The key role of diagnostics in the AMR challenge Fiona Carragher FRCPath @DepCSOFiona Deputy Chief Scientific Officer for England
Enabling the adoption of new diagnostics within the UK healthcare system: The key role of diagnostics in the AMR challenge Fiona Carragher FRCPath @DepCSOFiona Deputy Chief Scientific Officer for England
Towards a sustainable health workforce in the WHO European Region: framework for action
 Regional Committee for Europe 67th session EUR/RC67/10 +EUR/RC67/Conf.Doc./5 Budapest, Hungary, 11 14 September 2017 1 August 2017 170677 Provisional agenda item 5(c) ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Towards a sustainable
Regional Committee for Europe 67th session EUR/RC67/10 +EUR/RC67/Conf.Doc./5 Budapest, Hungary, 11 14 September 2017 1 August 2017 170677 Provisional agenda item 5(c) ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Towards a sustainable
- OMICS IN PERSONALISED MEDICINE
 SUMMARY REPORT - OMICS IN PERSONALISED MEDICINE Workshop to explore the role of -omics in the development of personalised medicine European Commission, DG Research - Brussels, 29-30 April 2010 Page 2 Summary
SUMMARY REPORT - OMICS IN PERSONALISED MEDICINE Workshop to explore the role of -omics in the development of personalised medicine European Commission, DG Research - Brussels, 29-30 April 2010 Page 2 Summary
Job description and person specification
 Job description and person specification Position Job title Head of Genomics Unit Directorate Finance, Commercial and Specialised Commissioning Pay band AFC Band 9 Responsible to Director of Strategy and
Job description and person specification Position Job title Head of Genomics Unit Directorate Finance, Commercial and Specialised Commissioning Pay band AFC Band 9 Responsible to Director of Strategy and
RESEARCH SUPPORT SERVICES FRAMEWORK. Streamlining the management and governance of R&D studies in the NHS
 RESEARCH SUPPORT SERVICES FRAMEWORK Streamlining the management and governance of R&D studies in the NHS Page 1 of 22 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 How to use this document... 3 Background... 4 Purpose
RESEARCH SUPPORT SERVICES FRAMEWORK Streamlining the management and governance of R&D studies in the NHS Page 1 of 22 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 How to use this document... 3 Background... 4 Purpose
European Technology Platform for Global Animal Health. Action Plan
 European Technology Platform for Global Animal Health Action Plan European Technology T Platform for Global Animal Health Action Plan 2 Table of contents Executive Summary 7 Chapter 1: The Action Plan
European Technology Platform for Global Animal Health Action Plan European Technology T Platform for Global Animal Health Action Plan 2 Table of contents Executive Summary 7 Chapter 1: The Action Plan
2017 NON FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS GPEI DONOR CONTRIBUTIONS
 2017 NON FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS GPEI DONOR CONTRIBUTIONS Background The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) is financed through a range of public and private donations. The Financial Resource
2017 NON FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS GPEI DONOR CONTRIBUTIONS Background The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) is financed through a range of public and private donations. The Financial Resource
SIAPS assistance is grouped into four technical areas
 Our specific approaches to each of the five result areas follows Governance Under SIAPS, our approach to improving governance and accountability focuses on establishing transparent management systems grounded
Our specific approaches to each of the five result areas follows Governance Under SIAPS, our approach to improving governance and accountability focuses on establishing transparent management systems grounded
ARTICLE X OF THE BIOLOGICAL AND TOXIN WEAPONS CONVENTION (BTWC)
 SIXTH REVIEW CONFERENCE OF THE STATES PARTIES TO THE CONVENTION ON THE PROHIBITION OF THE DEVELOPMENT, PRODUCTION AND STOCKPILING OF BACTERIOLOGICAL (BIOLOGICAL) AND TOXIN WEAPONS AND ON THEIR DESTRUCTION
SIXTH REVIEW CONFERENCE OF THE STATES PARTIES TO THE CONVENTION ON THE PROHIBITION OF THE DEVELOPMENT, PRODUCTION AND STOCKPILING OF BACTERIOLOGICAL (BIOLOGICAL) AND TOXIN WEAPONS AND ON THEIR DESTRUCTION
Management response to the evaluation of UNDP contribution to environmental management for poverty reduction: the povertyenvironment
 United Nations DP/2011/9 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 17 December 2010 Original: English First regular session 2011
United Nations DP/2011/9 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 17 December 2010 Original: English First regular session 2011
Monitoring and Evaluation Policy
 Monitoring and Evaluation Policy 1 M&E Policy Last Updated October 2017 1. Introduction The Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) policy will apply to the global C&A Foundation including Fundación C&A in Mexico
Monitoring and Evaluation Policy 1 M&E Policy Last Updated October 2017 1. Introduction The Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) policy will apply to the global C&A Foundation including Fundación C&A in Mexico
Aims and challenges of clinical trial data sharing
 Aims and challenges of clinical trial data sharing Facilitating data access to non-industry funded research UCL and Yale meeting: 9 October 2015 London Dr Trish Groves Head of research,
Aims and challenges of clinical trial data sharing Facilitating data access to non-industry funded research UCL and Yale meeting: 9 October 2015 London Dr Trish Groves Head of research,
The Intersection of Genomics Research and the IDE Regulation
 The Intersection of Genomics Research and the IDE Regulation Katherine Donigan, Ph.D. Personalized Medicine Staff FDA/CDRH/OIR October 19, 2017 1 In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Regulation Through the 1976 medical
The Intersection of Genomics Research and the IDE Regulation Katherine Donigan, Ph.D. Personalized Medicine Staff FDA/CDRH/OIR October 19, 2017 1 In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Regulation Through the 1976 medical
WHO s IMS Organizational Structure Overview
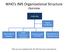 WHO s IMS Organizational Structure Overview Leadership Partner Coordination Information & Planning Health Expertise & Operations Operations Support and Logistics Management & Administration *this structure
WHO s IMS Organizational Structure Overview Leadership Partner Coordination Information & Planning Health Expertise & Operations Operations Support and Logistics Management & Administration *this structure
LABORATORY TRAINING LOGBOOK
 REGISTRATION TRAINING PORTFOLIO FOR THE IBMS CERTIFICATE OF COMPETENCE LABORATORY TRAINING LOGBOOK Version 4.1 www.ibms.org Trainee record details Registration Training Portfolio Case No: Surname: First
REGISTRATION TRAINING PORTFOLIO FOR THE IBMS CERTIFICATE OF COMPETENCE LABORATORY TRAINING LOGBOOK Version 4.1 www.ibms.org Trainee record details Registration Training Portfolio Case No: Surname: First
Discussion paper and expected outcomes Concept Note of IWG meeting
 Discussion paper and expected outcomes Concept Note of IWG meeting Document 01- For Discussion and Approval EIGHTH INTERNATIONAL DIALOGUE WORKING GROUP MEETING ON NEW DEAL IMPLEMENTATION 1-2 June 2016,
Discussion paper and expected outcomes Concept Note of IWG meeting Document 01- For Discussion and Approval EIGHTH INTERNATIONAL DIALOGUE WORKING GROUP MEETING ON NEW DEAL IMPLEMENTATION 1-2 June 2016,
7TH E-NEWSLETTER. 7 th EBOVAC2. e-newsletter
 7 th EBOVAC2 e-newsletter November 2018 1 Welcome to the EBOVAC2 e-newsletter! EBOVAC2: Getting up to date The EBOVAC2 project is one of 8 projects funded under the IMI Ebola+ program that was launched
7 th EBOVAC2 e-newsletter November 2018 1 Welcome to the EBOVAC2 e-newsletter! EBOVAC2: Getting up to date The EBOVAC2 project is one of 8 projects funded under the IMI Ebola+ program that was launched
1. Enhancing relevance of TVET
 Shanghai Consensus: Recommendations of the Third International Congress on Technical and Vocational Education and Training Transforming TVET: Building skills for work and life Shanghai, People s Republic
Shanghai Consensus: Recommendations of the Third International Congress on Technical and Vocational Education and Training Transforming TVET: Building skills for work and life Shanghai, People s Republic
Competencies Checklist for CE. Tier 1 Core Public Health Competencies Checklist
 Competencies Checklist for CE Student Name: Area of Concentration: Project Title: Tier 1 Core Public Health Competencies Checklist Domain #1: Analytic/Assessment Skills Describes factors affecting the
Competencies Checklist for CE Student Name: Area of Concentration: Project Title: Tier 1 Core Public Health Competencies Checklist Domain #1: Analytic/Assessment Skills Describes factors affecting the
Frequently Asked Questions About Ebola Virus Disease
 Frequently Asked Questions About Ebola Virus Disease Note that many of the answers below are accurate at an identified point in time. For the most recent information, please visit www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ebola Virus Disease Note that many of the answers below are accurate at an identified point in time. For the most recent information, please visit www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola.
