Cataract Induction in Lenses Cultured With Transforming Growth Factor-/}
|
|
|
- Barnaby O’Connor’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cataract Induction in Lenses Cultured With Transforming Growth Factor-/} Angela M. Hales, Coral G. Chamberlain, and John W. McAvoy Purpose. Anterior subcapsular cataracts are characterized by the appearance of opaque plaques of abnormal cells. Distinctive spindle-shaped cells containing a-smooth muscle actin are present and are associated with wrinkling of the overlying lens capsule. Accumulations of extracellular matrix, including type I collagen, also are found. The authors previously reported that transforming growth factor-/? (TGF-0) induces similar aberrant morphologic changes in lens epithelial explants. More recently, they identified a-smooth muscle actin in explants cultured with TGF-/3. The aim of this study was to determine whether TGF-/? induces comparable cataractous changes in whole lenses and to examine the effects of this treatment on the transparency of the lens. Methods. Whole lenses from 21-day-old rats were cultured in defined serum-free medium with TGF-/32 or without added growth factors for 5 days. Lenses were then photographed and prepared for histology and immunolocalization. Results. Lenses cultured with TGF-/? developed distinct anterior opacities just beneath the lens capsule. Histologically, clumps of abnormal cells corresponded with these opacities. Spindle-shaped cells, which contained a-smooth muscle actin, were present, and the overlying capsule was often wrinkled. The clumps contained accumulations of type I collagen, laminin, and heparan sulphate proteoglycan. In contrast, lenses cultured without growth factors remained transparent, retained normal lens morphology, and did not accumulate a-smooth muscle actin or type I collagen. Conclusions. These results show that TGF-/? induces whole lenses to form opacities that contain morphologic and biochemical markers for subcapsular cataract. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995;36:17O v-«ataract, an opacity of the lens that may cause partial or total blindness, is one of the most prevalent eye diseases. Extracapsular cataract extraction, the most common treatment in Western countries, is not always successful; in 10% to 50% of patients, reclouding of the lens occurs within 5 years because of the formation of after-cataracts (also referred to as posterior capsular opacifications or secondary cataracts) that arise from lens cells left behind at the time of surgery. 1 " 3 Given the magnitude of the cataract problem From the Department of Anatomy and Histology, University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Supported by grants from the National Eye Institute, the Department of Health, Education and Welfare, and the National Health and Medical Research Council, Canberra, Australia, and by a University of Sydney Medical Faculty Postgraduate Scholarship (AMH). Submitted for publication November 28, 1994; revised March 13, 1995; accepted March 13, Proprietary interest category: N. Reprint requests: fohn W. McAvoy, Department of Anatomy and Histology, University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia worldwide (for example, 1.3 million cataract operations costing $5 billion were performed in the United States in 1991 ), 4 surprisingly little is known about its cause (s). Epidemiologic studies have identified numerous factors associated with increased risk of cataract (for example, aging, diabetes, malnutrition, ultraviolet light-sunlight, glaucoma, and ocular surgery), 5 and a protective role for antioxidant nutrients, vitamins, and minerals has been suggested but not proven. 6 However, little is known about mechanisms of cataractogenesis at the molecular or cellular level; this has hampered progress in clinical management. Previously, using rat lens epithelial explants, we showed that fibroblast growth factor plays a key role in normal events in mammalian lens growth and differentiation. 78 We reported recently 9 that, in contrast, transforming growth factor-/? (TGF-/5), a multifunctional growth factor, induces abnormal changes in explants, all of which can be blocked by a pan-specific Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, July 1995, Vol. 36, No. 8 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology 1709
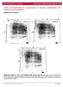
2 1710 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, July 1995, Vol. 36, No. 8 antibody against TGF-/?.10 These include the formation of spindle-shaped cells, capsule wrinkling, and accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM). Some or all of these changes are typically found in human siibcapsular cataracts and after-cataracts.11"14 The lens explants we use consist of epithelial cell monolayers peeled away from fiber cells (see Fig, 1C for normal lens morphology) and pinned out on culture dishes. Although this culture system is well suited to analyzing responses to TGF-/? at the cellular level, it does not allow assessment of the effects of TGF-/? on the most clinically significant feature of cataract induction, opacification of the lens. In this article, we show that whole rat lenses cultured with TGF-/? develop opacities that closely resemble anterior subcapsular cataract. MATERIALS AND METHODS All experimental procedures conformed to the ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research. Twenty-one-day-old rats were sacrificed by carbon dioxide asphyxiation, and eyes were removed and placed in approximately 4 ml serum-free culture medium (Ml99 with bovine serum albumin and antibiotics).15 Lenses were carefully removed by a posterior approach using plastic-coated forceps and fine scissors and were transferred to a culture dish containing 3 ml fresh medium (two lenses per dish). Transforming growth factor-/?2 (Genzyme, Cambridge, MA) was added to the culture medium at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml10; this was shown to be a saturating dose in studies using lens explants from 21-day-old rats (Liu J, Chamberlain C, McAvoyJ, unpublished data, 1993). Control lenses were cultured without TGF-/?. Lenses (six per treatment) were cultured for 5 days at 37 C in 5% CO2/air. Medium (with or without TGF-/?) was renewed on days 2 and 4. Lenses were photographed daily and fixed and embedded for routine histology on day 5. Results were confirmed in a replicate experiment. In supplementary experiments, lenses were cultured for longer periods. Beyond 5 days culture, there was no further progression of TGF-/?-induced changes; beyond 7 days, irrespective of treatment, deterioration of the lens fiber mass was observed. At the end of the culture period, whole lenses were fixed overnight in Carnoy'sfixative,10dehydrated in alcohol, cleared in xylol at room temperature, and embedded in paraffin. Serial 5-//m sections were dried onto slides overnight at 37 C and stained widi haematoxylin and eosin. Alternatively, immunofluorescent localization was performed using antibodies against a-smooth muscle actin (clone IA4; Sigma, St. Louis, MO),1617 laminin, heparan sulphate proteoglycan (HSPG), or rat type I collagen (Silenus, Hawthorn, Vic, Australia). Further details of localization methods FIGURE l. The effect of transforming growth factor (TGF)0 on lens transparency and morphology. Whole lenses were cultured for 5 days without TGF-/? (A,C) or with TGF-/? (B,D). Lenses were photographed through the posterior pole (A,B) Sagittal sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (C,D); the equator of the lens is at the bottom edge of the micrograph in each case. In the presence of TGF-/?, lenses developed anterior opacities (B) that corresponded with cellular plaques (D, arrowhead) underlying the lens capsule (ca). Without TGF-/?, lenses remained clear (A) and retained normal histology (C) with a monolayer of epithelial cells (ep) covered by the lens capsule overlying the fiber mass (fm). At the lens equator (arrow), cells began to elongate and to differentiate into fibers. Scale bars = 400 ^m (A,B), 250 pm (C,D). are given elsewhere.10 Appropriate nonimmune immunoglobulin or serum controls were included routinely. For collagen type I, preadsorption controls were also carried out. The specificity of die a-smooth muscle actin antibody has been established by Western blot analysis.1618 RESULTS When lenses from 21-day-old rats were maintained in medium without TGF-/? (controls), lenses remained transparent (Fig. 1A) and retained normal morphology during the 5-day culture period (Figs. 1C, 2A). When TGF-/? was included in the medium, however,
3 1711 TGF-/J Induces Anterior Subcapsular Cataracts In Vitro ITS? FIGURE 2. Micrographs of lenses cultured without transforming growth factor (TGF)-/? (A,C) or with TGF-/3 (B,C) for 5 days. Serial sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (A,B) or used for immunofluorescent localization of a-smooth muscle actin (C,D). Control lenses retained normal lens architecture with a monolayer of cuboidal epithelium overlying the fiber mass (A); no reactivity for a-smooth muscle acti'": was detectable (C). Subcapsular plaques containing spindle-shaped cells (closed arrow) developed in lenses cultured with TGF-/?, and between the plaques (open arrow), abnormal celts replaced the cuboidal epithelium (B). Insets show the region indicated by the open arrow in B and the corresponding region in A at higher magnification. Spindle-shaped cells within and outside the plaques showed strong reactivity for a-smooth muscle actin (D) Scale bar = 30 tm (insets, 20 distinct subcapsular opacities formed across the anterior surface of every lens (Fig. IB), whereas the fiber cells that comprised the bulk of the lens remained transparent. The opacities, first noticed at 3 days, became larger and more opaque with time. They appeared to correspond with subcapsular clumps or *'plaques" of aberrant cells distributed across the anterior surface of the lens (Figs. ID, 2B). Between the plaques, spindle-shaped cells were arranged parallel to the capsule; no normal cuboidal epithelial cells remained (Figs. 2A, 2B). The spindle-shaped cells were generally present in multilayers two to five cells deep, and the thickest regions tended to be associated with wrinkling of the overlying capsule (Fig. 3). There FIGURE 3. Micrograph of a lens cultured with transforming growth factor-/? for 5 days and stained with hematoxylin and eosin, showing wrinkling of the capsule (ca) and spindleshaped cells (arrowhead). Scale bar = 17 /xm. FIGURE 4. Micrographs of lenses cultured without transforming growth factor (TGF)-/? (A,C,E) and with TGF-/? (B,D,F,). Serial sections were used for immunofluorescent localization of extracellular matrix components: laminin (A,B), heparan sulphate proteoglycan (C,D), or type I collagen (E,F). Control lenses displayed a normal distribution of laminin (A) and heparan sulphate proteoglycan (HSPG) (C) in the lens capsule and showed no reactivity for type I collagen (E). Lenses cultured with TGF-/? showed strong reactivity for laminin (B) and HSPG (D) in the subcapsular plaques and the lens capsule. Reactivity for type I collagen was present within these plaques and in association with the spindle-shaped cells diat replaced the normal epithelium (F). Scale bar = 30 fim. also were regions devoid of these cells, in which the capsule abutted directly onto the fiber mass. Some of the abnormal cells in the subcapsular plaques also appeared to be spindle shaped (Fig. 2B), Lenses cultured with TGF-/? showed strong reactivity for a-smooth muscle actin within and outside the plaques (Fig. 2D) in regions in which spindleshaped cells were present. Corresponding sections treated with normal mouse immunoglobulin G instead of the a-smoodi muscle actin primary antibody (to test for nonspecific fluorescence) showed no reactivity for a-smooth muscle actin (not shown). No reactivity for a-smooth muscle actin was detected in control lenses (Fig. 2C). In lenses cultured with TGF-/5, the subcapsular plaques were shown to contain accumulations of laminin and HSPG (Figs. 4B, 4D), ECM components normally present in lens capsule.19 Strong reactivity for laminin was present throughout the plaques, but HSPG reactivity was concentrated in the central regions (Figs. 4B, 4D). In control lenses, laminin and
4 1712 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, July 1995, Vol. 36, No. 8 HSPG were detected in the capsule only (Figs. 4A, 4C). In addition, type I collagen, which is not generally found in the lens, 20 was detected within the plaques and in association with spindle-shaped cells outside the plaques (Fig. 4F). In control lenses, no specific fluorescence for type I collagen was detected (Fig. 4E). Corresponding sections treated with normal rabbit immunoglobulin G instead of any of the specific antibodies, to test for nonspecific fluorescence, showed no reactivity either in the plaques or in the lens capsule. For type I collagen, specific reactivity was virtually abolished by preadsorbing the antibody with type I collagen (not shown). DISCUSSION In this study, we identified a molecule present in the eye that induces cataractous changes in the lens in vitro. Subcapsular opacities histologically indistinguishable from early stages of human anterior subcapsular cataracts develop in whole rat lenses cultured with TGF-/32 for 5 days. This form of cataract is seen first as small, opaque flecks or dots underlying the capsule and overlying the transparent fiber mass. 14 Histologically, these opacities consist of plaques of abnormal cells, including spindle-shaped cells, and accumulations of ECM; the capsule overlying the plaques often is wrinkled Type I collagen and a-smooth muscle actin, proteins not normally found in the lens, also are found in this form of cataract In the opaque subcapsular plaques induced by TGF-/?, abnormal accumulations of laminin and HSPG were present (Figs. 4A to 4D; see ref. 10); these are normal lens capsule components. 19 Type I collagen also accumulates in these plaques (Fig. 4F). The latter finding is supported by an earlier study in which type I collagen was localized in TGF- /3-induced cellular aggregations in postnatal rat lens explants (LiuJ, Chamberlain C, McAvoyJ, unpublished data, 1994). Type I collagen is an ECM component known to accumulate in anterior subcapsular cataracts and after-cataracts. 20 ' 21 It is not usually expressed in the lens, 20 although it has been detected in the capsule of some elderly patients. 22 Thus, TGF-/? induces cataract-like accumulation of ECM components, including a marker for cataract. The cytoskeletal protein a-smooth muscle actin has been localized in the spindle-shaped cells of anterior subcapsular cataracts 17 and after-cataracts 23 ; however, it is not present in the normal mammalian lens. 24 Recently, we showed that this marker for cataract is induced in lens explants by TGF-/?. 16 In this article, we show that a-smooth muscle actin is present in the spindle-shaped cells and cataract-like subcapsular plaques induced in whole lenses by TGF-/? (Figs. 2C, 2D). Transforming growth factor-/? and its mrna have been detected in the mammalian eye. 25 " 27 Furthermore, several studies have shown that the ocular media that bathe the lens contain TGF-/?, and they suggest that, under normal conditions, this TGF-/3 is present predominantly in a latent form. 28 " 31 A major increase in vitreous TGF-/3 levels has been detected in proliferative vitreoretinopathy, and unusually high levels of active TGF-/? have been reported in another study in which aqueous was collected only from patients with cataract. 30 In addition, latent TGF-/? may become activated for example, after eye surgery. 32 In summary, this study of whole lenses has identified a molecule capable of inducing lens opacification and early events in cataractogenesis. The opacities induced by TGF-/? are indistinguishable from classic textbook representations of early stages of anterior subcapsular cataract, and they contain two molecules known to be markers for this form of cataract and for after-cataract. Moreover, this study has established that, at least in vitro, lens cells can receive a TGF-/? stimulus across the intact lens capsule, which must happen if elevations in ocular media TGF-/? activity are involved in the induction of anterior subcapsular cataract in situ. All these findings are consistent with a key role for TGF-/? in the etiology of major forms of cataract. Key Words a-smooth muscle actin, cataractogenesis, lens opacities, transforming growth factor-/?, type I collagen Acknowledgments The authors thank Dr. F. Lovicu for assistance with the type I collagen preadsorption control. The authors also thank R. Smith for assisting with photography and Dr. M. Dziadek for supplying the heparan sulphate proteoglycan antibody. References 1. Zaturinsky B, Naveh N, Saks D, Solomon AS. Prevention of posterior capsular opacification by cryolysis and the use of heparinized irrigating solution during extracapsular lens extraction in rabbits. Ophthalmic Surg. 1990;21: Hutz W. Prospective study of cataract after five year intraocular lenses with and without laser ridge. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd. 1993;203: Kappelhof JP, Vrensen, GFJM. The pathology of aftercataract. Ada Ophthalmol. 1992;205(suppl): Bullimore MA, Bailey IL. Foreword: Clarifying cataract. Optom Vis Sci. 1993; 70: Harding J. Cataract: Biochemistry, Epidemiology and Pharmacology. London: Chapman and Hall; The National Advisory Eye Council/US Department of Health and Human Services. Vision Research: A National Plan Washington, DC: US Depart-
5 TGF-/3 Induces Anterior Subcapsular Cataracts In Vitro 1713 ment of Health and Human Services; NIH publication : McAvoyJW, Chamberlain CG, de Iongh RU, et al. The role of fibroblast growth factor in eye lens development. Ann NYAcad Sti. 1991; 638: Schulz MW, Chamberlain CG, de Iongh RU, McAvoy JW. Acidic and basic FGF in ocular media and lens: Implications for lens polarity and growth patterns. Development. 1993; 118: Laiho M, Keski-Oja J. Transforming growth factors- P as regulators of cellular growth and phenotype. Crit Rev Oncogenesis. 1992;3: Liu J, Hales AM, Chamberlain CG, McAvoyJW. Induction of cataract-like changes in rat lens epithelial explants by transforming growth factor-/?. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sti. 1994; 35: Font RL, Brownstein S. A light and electron microscopic study of anterior subcapsular cataracts. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974; 78: Novotny GEK, Pau H. Myofibroblast-like cells in human anterior capsular cataract. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat]. 1984; 404: Green WR, McDonnell PJ. Opacification of the posterior capsule. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK. 1985; 104: Worgul BV. Lens. In: Jakobiec FA, ed. Ocular Anatomy, Embryology, and Teratology. Philadelphia: Harper & Row; 1982: Hales A, Chamberlain CG, McAvoyJW. Measurement of lens epithelial cell migration on a laminin substratum using image analysis. / Comput Assist Microsc. 1992;4: Hales AM, Schulz MW, Chamberlain CG, McAvoyJW. TGF-/?1 induces lens cells to accumulate a-smooth muscle actin, a marker for subcapsular cataracts. Curr Eye Res. 1994; 13: Schmitt-Graff A, Pau H, Spahr R, et al. Appearance of alpha-smooth muscle actin in human eye lens cells of anterior capsular cataract and in cultured bovine lens-forming cells. Differentiation. 1990; 43: Skalli O, Ropraz P, Trzeciak A, Benzonana G, Gillessen D, Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against a- smooth muscle actin: A new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. / Cell Biol. 1986; 103: Mohan PS, Spiro RG. Macromolecular organization of basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986; 261: Hatae T, Ishibashi T, Yoshitomo F, Shibata Y. Immunocytochemistry of types I-IV collagen in human anterior subcapsular cataracts. Graefe's Arch ClinExp Ophthalmol. 1993;231: Namiki M, Tagami Y, Morino I, et al. Findings from slit lamp and histological examination of the anterior capsule in patients with severe anterior capsular shrinkage and opacities after implantation of intraocular lenses. JJpn Ophthalmol Soc. 1993;97:7l Marshall GE, Konstas AGP, Bechrakis NE, Lee WR. Macromolecular organization of basement membranes, characterization and comparison of glomerular basement membrane and lens capsule components by immunochemical and lectin affinity procedures. ExpEyeRes. 1992;54: Frezzotti R, Caporossi A, Mastrangelo D, et al. Pathogenesis of posterior capsular opacification: II: Histopathological and in vitro culture findings. / Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16: Rafferty NS, Rafferty KA. Lens cytoskeleton and aftercataract. Ada Ophthalmol. 1992; 205(suppl): Millan FA, Denhez F, Kondaiah P, Akhurst RJ. Embryonic gene expression patterns of TGF- beta 1, beta 2 and beta 3 suggest different developmental functions in vivo. Development. 1991; 111: Pelton RW, Saxena B, Jones M, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of TGF/?1, TGF/52, and TGF/?3, in the mouse embryo: Expression patterns suggest multiple roles during embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 1991;115: Pasquale LR, Dorman-Pease ME, Lutty GA, et al. Immunolocalization of TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2 and TGFbeta 3 in the anterior segment of the human eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sti. 1993;34: Connor TB, Roberts AB, Sporn MB, et al. Correlation of fibrosis and transforming growth factor-/? type 2 levels in the eye.jclin Invest. 1989;83: Granstein RD, Staszewski R, Knisely TL, et al. Aqueous humor contains transforming growth factor-/? and a small (< 3500 daltons) inhibitor of thymocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1990; 144: Jampel HD, Roche N, Stark WJ, Roberts AB. Transforming growth factor-/3 in human aqueous humour. Curr Eye Res. 1990;9: Cousins SW, McCabe MM, Danielpour D, Streilein JW. Identification of transforming growth factor-beta as an immunosuppressive factor in aqueous humor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sti. 1991;32: Tripathi RC, Borisuth NSC, Tripathi BJ. Growth factors in the aqueous humor and their therapeutic implications in glaucoma and anterior segment disorders of the human eye. Drug Develop Res. 1991; 22:1-23.
Cell biology of posterior capsular opacification
 Cell biology of posterior capsular opacification JULIA M. MARCANTONIO, GIJS F.J.M. VRENSEN J.M. Marcantonio School of Biological Sciences University of East Anglia Norwich NR4 7TJ, UK Fax +44 (0)1603 592250
Cell biology of posterior capsular opacification JULIA M. MARCANTONIO, GIJS F.J.M. VRENSEN J.M. Marcantonio School of Biological Sciences University of East Anglia Norwich NR4 7TJ, UK Fax +44 (0)1603 592250
Anterior subcapsular (or anterior polar) cataracts are
 Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin Expression in Cultured Lens Epithelial Cells Toshiyuki Nagamoto, 1,2 Goro Eguchi, 1,3 and David C. Beebe 2 PURPOSE. Lens epithelial cells transdifferentiate to myofibroblasts
Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin Expression in Cultured Lens Epithelial Cells Toshiyuki Nagamoto, 1,2 Goro Eguchi, 1,3 and David C. Beebe 2 PURPOSE. Lens epithelial cells transdifferentiate to myofibroblasts
Vitronectin is present in epithelial cells of the intact lens and promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition in lens epithelial explants
 Received 13 February 2006 Accepted 9 October 2006 Published 26 October 2006 Vitronectin is present in epithelial cells of the intact lens and promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition in lens epithelial
Received 13 February 2006 Accepted 9 October 2006 Published 26 October 2006 Vitronectin is present in epithelial cells of the intact lens and promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition in lens epithelial
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Experimental traumatic cataract
 Experimental traumatic cataract II. A transmission electron microscopy and extracellular tracer study P. P. Fagerholm and B. T. Philipson Lens changes caused by injury to the anterior part of the lens
Experimental traumatic cataract II. A transmission electron microscopy and extracellular tracer study P. P. Fagerholm and B. T. Philipson Lens changes caused by injury to the anterior part of the lens
Effects of dexamethasone on posterior capsule opacification-like changes in a rat lens explant model
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2004 Effects of dexamethasone on posterior capsule opacification-like changes
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2004 Effects of dexamethasone on posterior capsule opacification-like changes
10:10-10:22. YIA-1 A study of newly established human peripheral blood monocyte-derived ips cell line used in allergy research 10:22-10:32
 10:10-10:22 YIA-1 A study of newly established human peripheral blood monocyte-derived ips cell line used in allergy research 10:22-10:32 EPA-1 Integration of conventional cell viability assays- recruiting
10:10-10:22 YIA-1 A study of newly established human peripheral blood monocyte-derived ips cell line used in allergy research 10:22-10:32 EPA-1 Integration of conventional cell viability assays- recruiting
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Cataract is a consequence of the aging of the lens and is the. A Fully Human In Vitro Capsular Bag Model to Permit Intraocular Lens Evaluation.
 Lens A Fully Human In Vitro Capsular Bag Model to Permit Intraocular Lens Evaluation Lucy J. Dawes, 1,2 Christopher D. Illingworth, 3 and I. Michael Wormstone 1 PURPOSE. To establish a fully human in vitro
Lens A Fully Human In Vitro Capsular Bag Model to Permit Intraocular Lens Evaluation Lucy J. Dawes, 1,2 Christopher D. Illingworth, 3 and I. Michael Wormstone 1 PURPOSE. To establish a fully human in vitro
Resveratrol inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal. pigment epithelium and development of proliferative vitreoretinopathy
 Resveratrol inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal pigment epithelium and development of proliferative vitreoretinopathy Keijiro Ishikawa, 1,2 Shikun He, 2, 3 Hiroto Terasaki, 1 Hossein
Resveratrol inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal pigment epithelium and development of proliferative vitreoretinopathy Keijiro Ishikawa, 1,2 Shikun He, 2, 3 Hiroto Terasaki, 1 Hossein
Introduction to histology and its methods of study
 Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
BD BioCoat Growth Factor Reduced. MATRIGEL Invasion Chamber. Catalog No Lot No Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
 BD BioCoat Growth Factor Reduced MATRIGEL Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354483 Lot No. 47169 Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 1996 Becton Dickinson and Company
BD BioCoat Growth Factor Reduced MATRIGEL Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354483 Lot No. 47169 Guidelines for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 1996 Becton Dickinson and Company
The effects of three-piece or single-piece acrylic intraocular lens implantation on posterior capsule opacification
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 14 no. 5, 2004 / pp. 375-380 The effects of three-piece or single-piece acrylic intraocular lens implantation on posterior capsule opacification A.H. BİLGE 1, Ü.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 14 no. 5, 2004 / pp. 375-380 The effects of three-piece or single-piece acrylic intraocular lens implantation on posterior capsule opacification A.H. BİLGE 1, Ü.
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin
 Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
Scanning electron microscopy of corneal wound healing in the rabbit. Barrett G. Haik and Marilyn L. Zimny
 Scanning electron microscopy of corneal wound healing in the rabbit Barrett G. Haik and Marilyn L. Zimny Corneal lesions 7.5 mm. in diameter were made with an ocidar trephine in rabbits. The time periods
Scanning electron microscopy of corneal wound healing in the rabbit Barrett G. Haik and Marilyn L. Zimny Corneal lesions 7.5 mm. in diameter were made with an ocidar trephine in rabbits. The time periods
Table of Contents. 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components Additional Required Reagents Required Equipment...
 i Table of Contents 1.0 Overview of the NeuroCult NCFC Assay 2.0 Materials 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components... 4 2.2 Additional Required Reagents... 4 2.3 Required Equipment... 4 3.0 Preparation
i Table of Contents 1.0 Overview of the NeuroCult NCFC Assay 2.0 Materials 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components... 4 2.2 Additional Required Reagents... 4 2.3 Required Equipment... 4 3.0 Preparation
An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation
 Lens An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation Julie A. Eldred, 1 Jiyun Zheng, 2 Sulin Chen, 2 and I. Michael Wormstone
Lens An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation Julie A. Eldred, 1 Jiyun Zheng, 2 Sulin Chen, 2 and I. Michael Wormstone
An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation
 Lens An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation Julie A. Eldred, 1 Jiyun Zheng, 2 Sulin Chen, 2 and I. Michael Wormstone
Lens An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation Julie A. Eldred, 1 Jiyun Zheng, 2 Sulin Chen, 2 and I. Michael Wormstone
bronchial epithelial cells (I). Bronchi are outlined with dashed line. Scale bars = 25 µm, if not
 Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Requirement for TGFβ receptor signaling during terminal lens fiber differentiation
 Development 128, 3995-4010 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV4569 3995 Requirement for TGFβ receptor signaling during terminal lens fiber differentiation Robbert
Development 128, 3995-4010 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV4569 3995 Requirement for TGFβ receptor signaling during terminal lens fiber differentiation Robbert
Dr: RAWIA BADR Associate Professor of Microbiology&Immunology
 Dr: RAWIA BADR Associate Professor of Microbiology&Immunology Cell culture Commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, while the more specific term plant tissue.culture is used only for
Dr: RAWIA BADR Associate Professor of Microbiology&Immunology Cell culture Commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, while the more specific term plant tissue.culture is used only for
Differentiation in Cultured Limbal Epithelium as Defined by Keratin Expression
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32, No. 12, November 1991 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Differentiation in Cultured Limbal Epithelium as Defined by Keratin
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32, No. 12, November 1991 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Differentiation in Cultured Limbal Epithelium as Defined by Keratin
Supplementary Figures and supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary Figures and supplementary figure legends Figure S1. Effect of different percentage of FGF signaling knockdown on TGF signaling and EndMT marker gene expression. HUVECs were subjected to different
Supplementary Figures and supplementary figure legends Figure S1. Effect of different percentage of FGF signaling knockdown on TGF signaling and EndMT marker gene expression. HUVECs were subjected to different
Application Note. BD PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Collagen I Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animal-free Surface for Culture of Human Keratinocytes
 Page 1 BD PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Collagen I Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animal-free Surface for Culture of Human Keratinocytes Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Elizabeth Abraham, Paula Flaherty,
Page 1 BD PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Collagen I Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animal-free Surface for Culture of Human Keratinocytes Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Elizabeth Abraham, Paula Flaherty,
Light Microscopic Variation of Fiber Cell Size, Shape and Ordering in the Equatorial Plane of Bovine and Human Lenses
 Molecular Vision 3 : 2, 1997 Received 21 Dec 96 Accepted 22 Jan 1997 Published 2 Feb 1997 Light Microscopic Variation of Fiber Cell Size, Shape and Ordering in
Molecular Vision 3 : 2, 1997 Received 21 Dec 96 Accepted 22 Jan 1997 Published 2 Feb 1997 Light Microscopic Variation of Fiber Cell Size, Shape and Ordering in
IT S A GLOBAL LEADER. IT S PROVEN.
 isert Preloaded IOL System IT S A GLOBAL LEADER. IT S PROVEN. IT S isert. isert delivers the combination of simple operation, outstanding visual quality, and procedural efficiency. LEADERSHIP, WITH VISION
isert Preloaded IOL System IT S A GLOBAL LEADER. IT S PROVEN. IT S isert. isert delivers the combination of simple operation, outstanding visual quality, and procedural efficiency. LEADERSHIP, WITH VISION
Basics of 3D Cell Culture: Forming spheroids in the presence of extracellular matrix
 Basics of 3D Cell Culture: Forming spheroids in the presence of extracellular matrix 3D Cell Culture Core (3D3C ) Facility Birck Nanotechnology Center, Discovery Park Drs. Sophie Lelièvre, Shirisha Chittiboyina,
Basics of 3D Cell Culture: Forming spheroids in the presence of extracellular matrix 3D Cell Culture Core (3D3C ) Facility Birck Nanotechnology Center, Discovery Park Drs. Sophie Lelièvre, Shirisha Chittiboyina,
PROTOCOL. Collagen I Thin Gel Coating of Alvetex Scaffold. Introduction. Method. Page 1
 Page 1 Introduction Extra-cellular matrix (ECM) coating of in vitro culture surfaces is commonly used to enhance cellsubstrate adhesion, encourage cell-matrix signalling and to protect shear-sensitive
Page 1 Introduction Extra-cellular matrix (ECM) coating of in vitro culture surfaces is commonly used to enhance cellsubstrate adhesion, encourage cell-matrix signalling and to protect shear-sensitive
Contents. The Right Surface for Every Cell Extracellular Matrices and Biologically Coated Surfaces ECM Mimetic and Advanced Surfaces...
 Contents The Right Surface for Every Cell... 1 Extracellular Matrices and Biologically Coated Surfaces... 2 Corning Matrigel Matrix... 2 Corning BioCoat Cultureware... 3 ECM Mimetic and Advanced Surfaces...
Contents The Right Surface for Every Cell... 1 Extracellular Matrices and Biologically Coated Surfaces... 2 Corning Matrigel Matrix... 2 Corning BioCoat Cultureware... 3 ECM Mimetic and Advanced Surfaces...
Introduction to Histology
 Introduction to Histology Histology The term "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of Histology : Is the study of tissues and how they are arranged
Introduction to Histology Histology The term "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of Histology : Is the study of tissues and how they are arranged
TheraLin. Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology
 TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology Contents Page # TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative 3 Introduction 5 Easy
TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology Contents Page # TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative 3 Introduction 5 Easy
A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING
 A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING Umadevi Kandalam, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry College of Dental Medicine Nova Southeastern University Fort Lauderdale, Florida
A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING Umadevi Kandalam, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry College of Dental Medicine Nova Southeastern University Fort Lauderdale, Florida
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Tissue Preparation and Microscopy. General Concepts. Chemical Fixation CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Tissue Preparation and Microscopy General Concepts I. Biological tissues must undergo a series of treatments to be observed with light and electron microscopes. The process begins by stabilization
CHAPTER 1 Tissue Preparation and Microscopy General Concepts I. Biological tissues must undergo a series of treatments to be observed with light and electron microscopes. The process begins by stabilization
Sélection Internationale Ens Ulm 2012, Cell Biology
 Sélection Internationale Ens Ulm 2012, Cell Biology Please read the whole subject before starting. Questions 1-8 and 12-14 are general biology questions. In questions 9, 10, 11 and15, we ask you to interpret
Sélection Internationale Ens Ulm 2012, Cell Biology Please read the whole subject before starting. Questions 1-8 and 12-14 are general biology questions. In questions 9, 10, 11 and15, we ask you to interpret
Cataract is a consequence of the ageing of the lens and is the
 Lens An In Vitro Evaluation of the Anew Zephyr Open-Bag IOL in the Prevention of Posterior Capsule Opacification Using a Human Capsular Bag Model Julie A. Eldred, 1 David J. Spalton, 1,2 and I. Michael
Lens An In Vitro Evaluation of the Anew Zephyr Open-Bag IOL in the Prevention of Posterior Capsule Opacification Using a Human Capsular Bag Model Julie A. Eldred, 1 David J. Spalton, 1,2 and I. Michael
Cataract is a consequence of the ageing of the lens and is the
 Lens An In Vitro Evaluation of the Anew Zephyr Open-Bag IOL in the Prevention of Posterior Capsule Opacification Using a Human Capsular Bag Model Julie A. Eldred, 1 David J. Spalton, 1,2 and I. Michael
Lens An In Vitro Evaluation of the Anew Zephyr Open-Bag IOL in the Prevention of Posterior Capsule Opacification Using a Human Capsular Bag Model Julie A. Eldred, 1 David J. Spalton, 1,2 and I. Michael
MATERIAL & DESIGN MAKE THE DIFFERENCE
 First-in-class material & unique patented design make the difference 01 Easy and reproducible injection 02 2.4 mm incision 03 100% glistening free 04 Long-term axial, radial and torsional stability 05
First-in-class material & unique patented design make the difference 01 Easy and reproducible injection 02 2.4 mm incision 03 100% glistening free 04 Long-term axial, radial and torsional stability 05
Heparanase Modulates Chondrogenic Factor Signaling And Is Upregulated In Ectopic Cartilage
 Heparanase Modulates Chondrogenic Factor Signaling And Is Upregulated In Ectopic Cartilage Julianne Huegel, Motomi Enomoto-Iwamoto, PhD, Federica Sgariglia, Tricia Bhatti, Eiki Koyama, Maurizio Pacifici.
Heparanase Modulates Chondrogenic Factor Signaling And Is Upregulated In Ectopic Cartilage Julianne Huegel, Motomi Enomoto-Iwamoto, PhD, Federica Sgariglia, Tricia Bhatti, Eiki Koyama, Maurizio Pacifici.
Application Note 493
 Corning PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Collagen I Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animal-free Surface for Culture of Human Keratinocytes Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Elizabeth Abraham, Paula Flaherty, Susan
Corning PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Collagen I Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animal-free Surface for Culture of Human Keratinocytes Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Elizabeth Abraham, Paula Flaherty, Susan
Honours and PostDoctorate Research Projects. Lions Eye Institute, Perth
 Honours and PostDoctorate Research Projects Available from 1 st Semester, 2018 Lions Eye Institute, Perth 1 About the Lions Eye Institute. The Lions Eye Institute is a not-for-profit centre of excellence
Honours and PostDoctorate Research Projects Available from 1 st Semester, 2018 Lions Eye Institute, Perth 1 About the Lions Eye Institute. The Lions Eye Institute is a not-for-profit centre of excellence
Supplementary Methods. Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to. graft disease propagation
 1 Supplementary Methods Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to graft disease propagation Neural transplantation and clinical assessment Detailed information
1 Supplementary Methods Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to graft disease propagation Neural transplantation and clinical assessment Detailed information
Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde
 Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Supplementary Figure S1. Expression of complement components in E4 chick eyes. (a) A
 Supplementary Figure S1. Expression of complement components in E4 chick eyes. (a) A schematic of the eye showing the ciliary margin (CM) of the anterior region, and the neuroepithelium (NE) and retinal
Supplementary Figure S1. Expression of complement components in E4 chick eyes. (a) A schematic of the eye showing the ciliary margin (CM) of the anterior region, and the neuroepithelium (NE) and retinal
Lens Regeneration in New Zealand Albino Rabbits After Endocapsular Cataract Extraction
 Lens Regeneration in New Zealand Albino Rabbits After Endocapsular Cataract Extraction Arlene Gwon,* Lawrence Gruber, Christine Mantras, and Crystal Cunanan Purpose. To evaluate the regenerative capacity
Lens Regeneration in New Zealand Albino Rabbits After Endocapsular Cataract Extraction Arlene Gwon,* Lawrence Gruber, Christine Mantras, and Crystal Cunanan Purpose. To evaluate the regenerative capacity
Mechanical Testing of Urothelial Cells in Voided Urine as a Possible Test for Early Detection of Glaucoma
 Mechanical Testing of Urothelial Cells in Voided Urine as a Possible Test for Early Detection of Glaucoma Duong Nguyễn, Nicole Seddon, Michell Kim 4, Crystal K. Santillanes 4, Arun Sharma,5, Angelo P.
Mechanical Testing of Urothelial Cells in Voided Urine as a Possible Test for Early Detection of Glaucoma Duong Nguyễn, Nicole Seddon, Michell Kim 4, Crystal K. Santillanes 4, Arun Sharma,5, Angelo P.
TITLE: Enhancement of Skeletal Muscle Repair by the Urokinase Type Plasminogen Activator System
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0159 TITLE: Enhancement of Skeletal Muscle Repair by the Urokinase Type Plasminogen Activator System PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Timothy J. Koh, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0159 TITLE: Enhancement of Skeletal Muscle Repair by the Urokinase Type Plasminogen Activator System PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Timothy J. Koh, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Expression and role of E- and P-cadherin adhesion molecules in embryonic histogenesis
 Development 105, 271-277 (1989) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 271 Expression and role of E- and P-cadherin adhesion molecules in embryonic histogenesis II. Skin morphogenesis
Development 105, 271-277 (1989) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 271 Expression and role of E- and P-cadherin adhesion molecules in embryonic histogenesis II. Skin morphogenesis
Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: on October 30, 2018 jcb.rupress.org Downloaded from
 Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.1.197 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on October 30, 2018 BRIEF NOTES 197 The Use of Potassium Permanganate as an Electron-Dense
Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.1.197 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on October 30, 2018 BRIEF NOTES 197 The Use of Potassium Permanganate as an Electron-Dense
Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cortex (area 1 as defined in Fig. 2a), and corpus
Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cortex (area 1 as defined in Fig. 2a), and corpus
Identification of heavy-molecular-weight soluble protein in aqueous humor in human phacolytic glaucoma
 Identification of heavy-molecular-weight soluble protein in aqueous humor in human phacolytic glaucoma David L. Epstein, Judith A. Jedziniak, and W. Morton Grant Aqueous humor was obtained by paracentesis
Identification of heavy-molecular-weight soluble protein in aqueous humor in human phacolytic glaucoma David L. Epstein, Judith A. Jedziniak, and W. Morton Grant Aqueous humor was obtained by paracentesis
The Construction of Cell-Density Controlled Three- Dimensional Tissues by Coating Micrometer-Sized Collagen. Fiber Matrices on Single Cell Surfaces
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Page S1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for RSC Advances The Construction of Cell-Density
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Page S1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for RSC Advances The Construction of Cell-Density
Elevated tropomyosin expression is associated with epithelial mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells
 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 17, No 1, 2013 pp. 212-221 Elevated tropomyosin expression is associated with epithelial mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells Eri Kubo a, *, Nailia Hasanova a, Nigar Fatma
J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 17, No 1, 2013 pp. 212-221 Elevated tropomyosin expression is associated with epithelial mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells Eri Kubo a, *, Nailia Hasanova a, Nigar Fatma
Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds
 Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds Claudia Fischbach, Ruth Chen, Takuya Matsumoto, Tobias Schmelzle, Joan S Brugge, Peter J Polverini & David J Mooney Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure
Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds Claudia Fischbach, Ruth Chen, Takuya Matsumoto, Tobias Schmelzle, Joan S Brugge, Peter J Polverini & David J Mooney Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure
Laser Cataract Refractive Surgery. Robert Maloney, MD
 Laser Cataract Refractive Surgery Robert Maloney, MD Traditional Cataract Surgery!!!! Capsulotomy size directly related to Effective Lens Position1,2 Corneal incisions are manually executed and imprecise
Laser Cataract Refractive Surgery Robert Maloney, MD Traditional Cataract Surgery!!!! Capsulotomy size directly related to Effective Lens Position1,2 Corneal incisions are manually executed and imprecise
Cells Culture Techniques Marta Czernik
 Cells Culture Techniques 13.03.2018 Marta Czernik Why we need the cell/tissue culture Research To overcome problems in studying cellular behaviour such as: - confounding effects of the surrounding tissues
Cells Culture Techniques 13.03.2018 Marta Czernik Why we need the cell/tissue culture Research To overcome problems in studying cellular behaviour such as: - confounding effects of the surrounding tissues
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) induces different responses in lens epithelial cells depending on its concentration
 Development 107, 221-228 (1989) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 221 Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) induces different responses in lens epithelial cells depending on its
Development 107, 221-228 (1989) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 221 Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) induces different responses in lens epithelial cells depending on its
Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc. Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications
 Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications NutriStem Defined, xeno-free (XF), serum-free media (SFM) specially formulated for growth and
Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications NutriStem Defined, xeno-free (XF), serum-free media (SFM) specially formulated for growth and
INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS. IntestiCult and STEMdiff Media for Intestinal Organoid Culture. Scientists Helping Scientists
 INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS IntestiCult and STEMdiff Media for Intestinal Organoid Culture Scientists Helping Scientists WWW.STEMCELL.COM CULTURING INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 Introduction 4 IntestiCult
INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS IntestiCult and STEMdiff Media for Intestinal Organoid Culture Scientists Helping Scientists WWW.STEMCELL.COM CULTURING INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 Introduction 4 IntestiCult
UK +44 (0) CH +41 (0) DE +49 (0) US
 UK +44 (0) 1235 232100- CH +41 (0) 91 604 5522 - DE +49 (0) 69 779099 - US +1 855 267 2464 Featured Product Areas Stem Cell Fate Regulators and Synthetic Retinoid ec23 Recombinant Growth Factor Mimetics
UK +44 (0) 1235 232100- CH +41 (0) 91 604 5522 - DE +49 (0) 69 779099 - US +1 855 267 2464 Featured Product Areas Stem Cell Fate Regulators and Synthetic Retinoid ec23 Recombinant Growth Factor Mimetics
Supplementary Table-1: List of genes that were identically matched between the ST2 and
 Supplementary data Supplementary Table-1: List of genes that were identically matched between the ST2 and ST3. Supplementary Table-2: List of genes that were differentially expressed in GD2 + cells compared
Supplementary data Supplementary Table-1: List of genes that were identically matched between the ST2 and ST3. Supplementary Table-2: List of genes that were differentially expressed in GD2 + cells compared
Activation of Src Kinases Signals Induction of Posterior Capsule Opacification
 Activation of Src Kinases Signals Induction of Posterior Capsule Opacification Janice L. Walker, Iris M. Wolff, Liping Zhang, and A. Sue Menko PURPOSE. Posterior capsule opacification (PCO) is a complication
Activation of Src Kinases Signals Induction of Posterior Capsule Opacification Janice L. Walker, Iris M. Wolff, Liping Zhang, and A. Sue Menko PURPOSE. Posterior capsule opacification (PCO) is a complication
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information
 Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Product Datasheet. Vinculin Antibody (hvin-1) NB Unit Size: 0.1 ml
 Product Datasheet Vinculin Antibody (hvin-1) NB600-1293 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 2 Protocols, Publications,
Product Datasheet Vinculin Antibody (hvin-1) NB600-1293 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 2 Protocols, Publications,
Smooth Muscle-Specific Expression of ipla 2 β Participates in the Initiation and Early Progression of Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation
 Smooth Muscle-Specific Expression of ipla 2 β Participates in the Initiation and Early Progression of Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation Shu Liu 1, Zhongwen Xie 2, Qingwei Zhao 2, Huan Pang
Smooth Muscle-Specific Expression of ipla 2 β Participates in the Initiation and Early Progression of Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation Shu Liu 1, Zhongwen Xie 2, Qingwei Zhao 2, Huan Pang
Factors modulating mouse lens epithelial cell morphology with differentiation and development of a lentoid structure in vitro
 Development 99, 25-32 (1987) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 25 Factors modulating mouse lens epithelial cell morphology with differentiation and development of a lentoid
Development 99, 25-32 (1987) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 25 Factors modulating mouse lens epithelial cell morphology with differentiation and development of a lentoid
Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
Electromagnetical stimulation of human articular chondrocytes by. the Algonix device.
 Electromagnetical stimulation of human articular chondrocytes by the Algonix device. Karsten Gavénis 1*, Stefan Andereya 1, Bernhard Schmidt-Rohlfing 2, Ralf Mueller-Rath 1, Jiri Silny 3, Ulrich Schneider
Electromagnetical stimulation of human articular chondrocytes by the Algonix device. Karsten Gavénis 1*, Stefan Andereya 1, Bernhard Schmidt-Rohlfing 2, Ralf Mueller-Rath 1, Jiri Silny 3, Ulrich Schneider
Exome Sequencing Exome sequencing is a technique that is used to examine all of the protein-coding regions of the genome.
 Glossary of Terms Genetics is a term that refers to the study of genes and their role in inheritance the way certain traits are passed down from one generation to another. Genomics is the study of all
Glossary of Terms Genetics is a term that refers to the study of genes and their role in inheritance the way certain traits are passed down from one generation to another. Genomics is the study of all
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3101
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Plvap / mice. (a) Schematic presentation of the targeting construct as well as the wild-type and targeted Plvap alleles]. PuroR, puromycin resistance. The location
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Plvap / mice. (a) Schematic presentation of the targeting construct as well as the wild-type and targeted Plvap alleles]. PuroR, puromycin resistance. The location
2-step or indirect immunofluorescence 1. Substrate on which cells are plated: plastic vs. glass; coating vs. non
 Variables in standard immunostaining protocol 2-step or indirect immunofluorescence 1. Substrate on which cells are plated: plastic vs. glass; coating vs. non 2. Plating density: sparse vs. confluent 3.
Variables in standard immunostaining protocol 2-step or indirect immunofluorescence 1. Substrate on which cells are plated: plastic vs. glass; coating vs. non 2. Plating density: sparse vs. confluent 3.
Comparing the Quality of Fixation for Gel-based Formalin (Formagel) versus Traditional Liquid-Based Formalin for Immunohistochemistry
 Comparing the Quality of Fixation for Gel-based Formalin (Formagel) versus Traditional Liquid-Based Formalin for Immunohistochemistry Brian H. Le, M.D., Reading Hospital Reviewed by Michael R. LaFrinere,
Comparing the Quality of Fixation for Gel-based Formalin (Formagel) versus Traditional Liquid-Based Formalin for Immunohistochemistry Brian H. Le, M.D., Reading Hospital Reviewed by Michael R. LaFrinere,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Svegliati Baroni S, Santillo M, Bevilacqua F, et al. Stimulatory
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Svegliati Baroni S, Santillo M, Bevilacqua F, et al. Stimulatory
The Thermo Scientific Nunclon Sphera surface supports formation of embryoid bodies from pluripotent stem cells
 1 The Thermo Scientific surface supports formation of embryoid bodies from pluripotent stem cells Louise Gaarn, Amy Sinor-Anderson, Robert Scott, Cindy Neeley, Joseph Granchelli, and Tina Marwood Application
1 The Thermo Scientific surface supports formation of embryoid bodies from pluripotent stem cells Louise Gaarn, Amy Sinor-Anderson, Robert Scott, Cindy Neeley, Joseph Granchelli, and Tina Marwood Application
Methodology for Immunohistochemistry. Learning Objectives:
 Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
The effect of endotoxin-induced intraocular inflammation on the rat lens epithelium
 The effect of endotoxin-induced intraocular inflammation on the rat lens epithelium Basil V. Worgul and George R. Merriam, Jr. Intraocular inflammation induced by an intravitreal injection o/shigella endotoxin
The effect of endotoxin-induced intraocular inflammation on the rat lens epithelium Basil V. Worgul and George R. Merriam, Jr. Intraocular inflammation induced by an intravitreal injection o/shigella endotoxin
Description of supplementary material file
 Description of supplementary material file In the supplementary results we show that the VHL-fibronectin interaction is indirect, mediated by fibronectin binding to COL4A2. This provides additional information
Description of supplementary material file In the supplementary results we show that the VHL-fibronectin interaction is indirect, mediated by fibronectin binding to COL4A2. This provides additional information
Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit
 Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit Catalog No. SCR019 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23 8026 2233
Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit Catalog No. SCR019 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23 8026 2233
Detection of Ocular & Systemic Disease
 Disclosures: Lyndon Jones Biosensing & Drug Delivery Lyndon Jones PhD FCOptom FAAO FCAHS Professor & University Research Chair School of Optometry & Vision Science Director, Centre for Ocular Research
Disclosures: Lyndon Jones Biosensing & Drug Delivery Lyndon Jones PhD FCOptom FAAO FCAHS Professor & University Research Chair School of Optometry & Vision Science Director, Centre for Ocular Research
Myosin was extracted from rabbit EOMs (all recti and inferior oblique. muscles), tongue, vastus lateralis, atria and ventricles of the heart.
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS DATA 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 Electrophoretic and immunoblotting analysis of MyHCs Myosin was extracted from rabbit EOMs (all recti and inferior oblique muscles), tongue, vastus lateralis,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS DATA 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 Electrophoretic and immunoblotting analysis of MyHCs Myosin was extracted from rabbit EOMs (all recti and inferior oblique muscles), tongue, vastus lateralis,
Matrices Sourcebook Life Technologies extracellular matrices products
 Matrices Sourcebook Life Technologies extracellular matrices products Introduction Our Gibco products, including extracellular matrices, 3D scaffolds, and attachment proteins, are essential tools for providing
Matrices Sourcebook Life Technologies extracellular matrices products Introduction Our Gibco products, including extracellular matrices, 3D scaffolds, and attachment proteins, are essential tools for providing
Applying Immunohistochemistry & Reverse Transcription PCR to Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Animal Model
 Applying Immunohistochemistry & Reverse Transcription PCR to Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Animal Model Sprague Dawley Rat (Rattus norvegicus ) Olga Paley Working with: Professor Dawn Elliott
Applying Immunohistochemistry & Reverse Transcription PCR to Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Animal Model Sprague Dawley Rat (Rattus norvegicus ) Olga Paley Working with: Professor Dawn Elliott
Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor, P21 Is Not Essential For Endochondral Ossification
 Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor, P21 Is Not Essential For Endochondral Ossification Nobuaki Chinzei, Shinya Hayashi, Shingo Hashimoto, Noriyuki Kanzaki, Kenjiro Iwasa, Shuhei Sakata, Shinsuke Kihara,
Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor, P21 Is Not Essential For Endochondral Ossification Nobuaki Chinzei, Shinya Hayashi, Shingo Hashimoto, Noriyuki Kanzaki, Kenjiro Iwasa, Shuhei Sakata, Shinsuke Kihara,
Modeling Periodic Aspect of Limb Pattern Formation
 Forum Forma, 27, S33 S37, 2012 Takashi Miura Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Yoshida Konoe-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan E-mail address:
Forum Forma, 27, S33 S37, 2012 Takashi Miura Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Yoshida Konoe-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan E-mail address:
Materials and Methods Materials Required for Fixing, Embedding and Sectioning. OCT embedding matrix (Thermo Scientific, LAMB/OCT)
 Page 1 Introduction Tissue freezing and sectioning is a rapid method of generating tissue samples (cryosections) for histological analysis, and obviates the need for wax embedding. The method is popular
Page 1 Introduction Tissue freezing and sectioning is a rapid method of generating tissue samples (cryosections) for histological analysis, and obviates the need for wax embedding. The method is popular
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information PDGFRα plays a crucial role in connective tissue remodeling Shinjiro Horikawa 1,2, Yoko Ishii 1, Takeru Hamashima 1, Seiji Yamamoto 1,*, Hisashi Mori 3, Toshihiko Fujimori 4,
Supplementary Information PDGFRα plays a crucial role in connective tissue remodeling Shinjiro Horikawa 1,2, Yoko Ishii 1, Takeru Hamashima 1, Seiji Yamamoto 1,*, Hisashi Mori 3, Toshihiko Fujimori 4,
Introducing the envista IOL. Dr Kerrie Meades PersonalEYES Pty Ltd
 Introducing the envista IOL Dr Kerrie Meades PersonalEYES Pty Ltd envista IOL Basic Features Hydrophobic acrylic IOL, single piece 6.0mm aspheric neutral optic, modified C haptic 12.5mm overall length
Introducing the envista IOL Dr Kerrie Meades PersonalEYES Pty Ltd envista IOL Basic Features Hydrophobic acrylic IOL, single piece 6.0mm aspheric neutral optic, modified C haptic 12.5mm overall length
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0516 TITLE: Cadherin-11 Regulation of Fibrosis through Modulation of Epithelial-to- Mesenchymal Transition: Implications for Pulmonary Fibrosis in Scleroderma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0516 TITLE: Cadherin-11 Regulation of Fibrosis through Modulation of Epithelial-to- Mesenchymal Transition: Implications for Pulmonary Fibrosis in Scleroderma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
Developmental Reprogramming in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Human Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Developmental Reprogramming in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Human Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Diptiman Chanda 1*, Ashish Kurundkar 1, Sunad Rangarajan 1, Morgan Locy 1, Karen Bernard 1,
Developmental Reprogramming in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Human Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Diptiman Chanda 1*, Ashish Kurundkar 1, Sunad Rangarajan 1, Morgan Locy 1, Karen Bernard 1,
Well Insert Holder in Deep Petri Dish - AVP015
 Well Insert Holder in Deep Petri Dish - AVP015 Product Information Leaflet Technology for Routine Three Dimensional (3D) Cell Culture t: +44 (0)1740 625266 f: +44 (0)1740 625251 e: info@reinnervate.com
Well Insert Holder in Deep Petri Dish - AVP015 Product Information Leaflet Technology for Routine Three Dimensional (3D) Cell Culture t: +44 (0)1740 625266 f: +44 (0)1740 625251 e: info@reinnervate.com
Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy findings in explanted PMMA and hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lenses
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 19 no. 1, 2009 / pp. 28-36 Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy findings in explanted PMMA and hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lenses
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 19 no. 1, 2009 / pp. 28-36 Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy findings in explanted PMMA and hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lenses
Supplementary Information. Bone marrow-on-a-chip replicates hematopoietic niche physiology in vitro
 Supplementary Information Bone marrow-on-a-chip replicates hematopoietic niche physiology in vitro Yu-suke Torisawa 1, Catherine S. Spina 1,2, Tadanori Mammoto 3, Akiko Mammoto 3, James C. Weaver 1, Tracy
Supplementary Information Bone marrow-on-a-chip replicates hematopoietic niche physiology in vitro Yu-suke Torisawa 1, Catherine S. Spina 1,2, Tadanori Mammoto 3, Akiko Mammoto 3, James C. Weaver 1, Tracy
Matrices sourcebook. Your guide to Gibco extracellular matrices products
 Matrices sourcebook Your guide to Gibco extracellular matrices products Introduction Gibco products, including extracellular matrices, 3D scaffolds, and attachment proteins, are essential tools for providing
Matrices sourcebook Your guide to Gibco extracellular matrices products Introduction Gibco products, including extracellular matrices, 3D scaffolds, and attachment proteins, are essential tools for providing
Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing
 Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing Dong-Hwee Kim 1,2, Shyam B. Khatau 1,2, Yunfeng Feng 1,3, Sam Walcott 1,4, Sean X. Sun 1,2,4, Gregory D. Longmore
Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing Dong-Hwee Kim 1,2, Shyam B. Khatau 1,2, Yunfeng Feng 1,3, Sam Walcott 1,4, Sean X. Sun 1,2,4, Gregory D. Longmore
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FILE
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FILE Existence of a microrna pathway in anucleate platelets Patricia Landry, Isabelle Plante, Dominique L. Ouellet, Marjorie P. Perron, Guy Rousseau & Patrick Provost 1. SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FILE Existence of a microrna pathway in anucleate platelets Patricia Landry, Isabelle Plante, Dominique L. Ouellet, Marjorie P. Perron, Guy Rousseau & Patrick Provost 1. SUPPLEMENTARY
Identification of the 2A10 Antigen of Retinal Pigment Epithelium as a /31 Subunit of Integrin
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32. No. 6. May 1991 Copyright Association lor Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Identification of the 2A10 Antigen of Retinal Pigment Epithelium as
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32. No. 6. May 1991 Copyright Association lor Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Identification of the 2A10 Antigen of Retinal Pigment Epithelium as
Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney
 1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
Studying the effect of shear stress on human corneal epithelial cells
 Studying the effect of shear stress on human corneal epithelial cells Wulff, David J (University of Waterloo) Molladavoodi, Sara (University of Waterloo) Gorbet, Maud (University of Waterloo) Introduction
Studying the effect of shear stress on human corneal epithelial cells Wulff, David J (University of Waterloo) Molladavoodi, Sara (University of Waterloo) Gorbet, Maud (University of Waterloo) Introduction
Effects of Growth Factors on Proliferation and Differentiation in Human Lens Epithelial Cells in Early Subculture
 Effects of Growth Factors on Proliferation and Differentiation in Human Lens Epithelial Cells in Early Subculture Nobuhiro Ibaraki, Li-Ren Lin, and Venkat N. Reddy Purpose. A successful method to subculture
Effects of Growth Factors on Proliferation and Differentiation in Human Lens Epithelial Cells in Early Subculture Nobuhiro Ibaraki, Li-Ren Lin, and Venkat N. Reddy Purpose. A successful method to subculture
Supplemental Figure 1: Podocyte specific knockdown of Klf4 in Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox mice was confirmed. (A) Primary glomerular epithelial cells
 Supplemental Figure 1: Podocyte specific knockdown of Klf4 in Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox mice was confirmed. (A) Primary glomerular epithelial cells were isolated from 10-week old Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox
Supplemental Figure 1: Podocyte specific knockdown of Klf4 in Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox mice was confirmed. (A) Primary glomerular epithelial cells were isolated from 10-week old Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox
