Y. T. Puyate* and Z. R. Yelebe**
|
|
|
- Archibald Adams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp Etimation Of Monod Kinetic Parameter During Aerobic Digetion Of Biodegradable Organic Wate, Part : Analyi Baed On Microbial Growth With Effect Of Bioaugmentation Y. T. Puyate* and Z. R. Yelebe** * Department of Chemical/Petro-chemical Engineering, River State Univerity of Science and Technology, P. M. B. 58, Port Harcourt, Nigeria. ** Department of Chemical/Petroleum Engineering, Niger-Delta Univerity, Wilberforce Iland Bayela State, Nigeria. ABSTRACT Monod kinetic parameter baed on microbial growth during aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate are etimated. The analyi involve non-bioaugmentation and bioaugmentation of aerobic biodegradation of organic wate in bioreactor labeled nonbioaugmented (i.e. control) bioreactor, and bioaugmented bioreactor repectively, uing a mixed culture of indigenou microorganim iolated from the wate for bioaugmentation. The maximum pecific growth rate ( m ) of microorganim during biodegradation of the wate are.17 and.15 day -1 for the control and bioaugmented bioreactor repectively. Dimenional yield coefficient ( ) for the control and bioaugmented bioreactor are cfu/mg and 3. 1 cfu/mg repectively. It i hown that the ubtrate aturation contant, K, in Monod equation varie with time and microbial denity during microbial growth. Model for predicting K a a function of time, and microbial denity a a function of K, are alo preented. Prediction of the model are compared with experimental data and good agreement i obtained. Key word: Aerobic digetion, Bioaugmentation, Biodegradation, Monod kinetic, Organic wate. 1. INTRODUCTION In mot developing countrie like Nigeria, handling and treatment of municipal olid wate (MSW) i a major concern to the government and the people. Nigeria for example, produce approximately million tonne of municipal olid wate annually baed on an average of.5 kg olid wate generated by every Nigerian per day [1], majority of which i dumped in municipal landfill and/or heaped openly on the earth urface at variou location in the citie. Thee method of dipoing olid wate which are commonly practiced in thi part of the world have left an inheritance of abandoned dumpite, contaminated oil and groundwater, poioned lake and tream, and dipoal ite with toxic wate and methane exploion potential in many location []. The development and implementation of better engineering ytem for proper handling of olid wate generated by man, rather than jut dumping them into the environment, i extremely important in protecting urface water, groundwater, oil, and maintaining air quality tandard. According to Ogunbiyi [1], not le than 65% of our dometic wate i vegita, while the remaining 35% i made up of platic, rubber, cotton, leather, metal, glae, etc. With the ever-increaing cot of land, increae in human population, and difficultie in permitting new landfill ite, exiting landfill pace i becoming a valuable commodity. Biodegradation (or microbial degradation) of organic pollutant i a biological treatment proce accomplihed primarily by microorganim which utilize organic matter for metabolim [3,4]. Biological treatment of olid wate i a cot effective alternative to other wate treatment technique and many expert regard biotreatment a the technology of the future [5]. Wate containing ubtantial amount of biodegradable organic compound can be treated biologically under aerobic condition. The biological oxidation of organic wate by micro-organim under aerobic condition to produce table wate, water, and a mixture of carbon dioxide and other gae, i known a aerobic digetion and i one of the mot common wate treatment technique [6]. Although aerobic digetion i ued worldwide for the treatment of indutrial, agricultural, and municipal watewater a well a ludge becaue of the proven feaibility of the proce and the multitude of environmental benefit, the technology i alo applied to the treatment of municipal olid wate in recent year [6,7]. Bioremediation involve the ue of microorganim to remove pollutant, and the proce i becoming an increaingly important remedial option [8,9]. Adding nutrient to a contaminated ite to timulate the growth of the indigenou microbial community i known a biotimulation and it i ued extenively for retoration of the environment at petroleum-polluted ite. Injecting microorganim with extenive degrading activity into a contaminated ite to breakdown a pollutant i known a 93 P a g e
2 Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp bioaugmentation. Biotimulation and bioaugmentation either in-itu or ex-itu are variou modification of bioremediation [9]. Monod growth kinetic [1] i widely ued in modeling biodegradation of organic compound and microbial growth in pure culture, wate treatment ytem, and the natural environment. When Monod equation i coupled with bioma yield and decay, a number of kinetic parameter are required to decribe the operation of a ytem. Studie have hown that the kinetic of microbial degradation i bet repreented by a batch culture [11], and a lot of work ha been done on etimation of the kinetic parameter in Monod equation for variou ytem. For example, Lin and Weber [1] propoed a non-linear regreion procedure for obtaining unbiaed etimate of all Monod kinetic parameter uing batch tet data. Igoni et al. [13] etimated contant value of the kinetic parameter in Monod equation during anaerobic digetion of MSW. Simkin and Alexander [14] etimated the parameter of Monod kinetic that bet decribe mineralization of everal ubtrate concentration by diimilar bacterial denitie. Robinon and Tiedje [15] etimated the Monod growth kinetic parameter from a ingle ubtrate depletion curve, while Dang et al. [16] tudied biodegradation kinetic with repirometric data. Literature on the biokinetic of aerobic digetion of MSW i carce. Yelebe and Puyate [17] preented an approximate model for predicting microbial denity during aerobic biodegradation of MSW, where the ubtrate aturation contant ( K ) in Monod equation wa neglected. Prediction of the model how ignificant deviation from experimental data, which wa attributed to the neglected K in the analyi. Puyate and Yelebe [18] etimated Monod kinetic parameter baed on ubtrate utilization during aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate with and without the effect of bioaugmentation. In thi current paper, all kinetic parameter in Monod equation are etimated from experimental data [19] baed on microbial growth during aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate in bioaugmented and non-bioaugmenetd batch reactor. The difference between the preent analyi and the one preented in Puyate and Yelebe [18] lie in the kinetic of ubtrate utilization and microbial growth during biodegradation of organic wate in a batch reactor. Alo, the ubtrate aturation contant ( K ) in Monod equation, ubtrate concentration, and microbial denity are predicted by different equation in the preent analyi and in Puyate and Yelebe [18] thereby providing general alternative procedure for etimating Monod kinetic parameter during aerobic biodegration proce. A mixed microbial culture iolated from the wate i ued for the bioaugmentation ince mixed microbial population compoed of many different bacterial pecie often achieve a greater degree of biodegradation [-] than pure culture which generally degrade only a limited number of the compound found in a pollutant [3].. MATERIALS AND METHOD Biodegradable organic wate compoed of food wate, wood/leave, and paper, wa collected, chopped manually, and mahed to homogenize the mixture. Ten-fold erial dilution method [4] of analyi wa ued to enumerate and iolate three type of bacteria (Bacillu pecie, Staphylococcu pecie, and Peudomona pecie) from the wate. The iolated bacteria were then ued to prepare a broth culture (conortium of bacteria) required for bioaugmentation of the biodegradation proce. Detail of the preparation of the liquid wate and broth culture ued in the tudy are preented in Yelebe [19]. Fifty batch reactor, each coniting of 5 ml round bottom flak, were ued for the experiment conducted in the Laboratory of the Department of Chemical/Petro-chemical Engineering, River State Univerity of Science and Technology, Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Twenty-five of the bioreactor were labeled bioaugmented and each bioreactor wa charged with 37 ml of the prepared liquid wate, while each of the remaining twenty-five bioreactor were labeled control and charged with 4 ml of the prepared liquid wate. Thirty millilitre (3 ml) of the prepared broth culture wa added to each of the bioaugmented bioreactor which increaed the volume of the liquid in each of thee bioreactor to 4 ml. The broth culture raied the initial microbial denity in each of the bioaugmented bioreactor to cfu/l, while the initial microbial denity in each of the twenty-five control-bioreactor with no 11 innoculum added wa cfu/l. The bioreactor and their content were intrumented to monitor preure, temperature, and airflow rate. Air wa injected to the bottom of each flak for proper aerobic treatment, and the ga produced during the microbial degradation proce wa vented out from the open end of each flak. The flow rate of air wa approximately.15 l/min per 4 ml of the organic wate olution, and thi airflow rate wa choen to enure proper mixing/bubbling of the olution in each flak without plahing on the wall of the flak. During the natural proce of organic matter degradation in landfill, contaminated water called leachate i formed. In the preent cae, the leachate produced during the biodegradation proce wa not withdrawn from the bioreactor, and the experimental etup wa allowed to run for 5 day. Every day, one bioaugmented-flak and one control-flak were dimantled and a ample wa taken from each flak and analyed for microbial denity and chemical oxygen demand (COD) uing tandard method in Ofunne [4] and Cleceri et al. 94 P a g e
3 Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp [5], noting that COD (taken here to repreent ubtrate concentration) i normally ued to determine the degree of degradation of wate [7]. The ph of the medium in each dimantled flak wa alo meaured at the ame time interval a the other parameter (i.e. COD and microbial denity) uing a digital ph meter. rate of ubtrate utilization i related to the rate of cell formation in the form d dc (4) dt dt where i the fraction of ubtrate converted to cell (mg/l of cell per mg/l of ubtrate) and range typically from.4 to.8 for aerobic ytem, and.8 The fractional converion of ubtrate ( X ) baed on the meaured COD wa calculated a to. for anaerobic ytem []. The yield coefficient Initial COD Final COD X may (1) alo be expreed a Initial COD c co The temperature in each bioreactor wa meaured (5) twice daily at 9 and 16 hour uing a o thermometer. which can be rearranged to give ( c co) o (6) 3. KINETICS OF MICROBIAL GROWTH IN A BATCH REACTOR where co i the initial ma concentration of The batch growth of microorganim microorganim, and o i the initial ma involve adding a mall quantity of the microorganim or their pore (the eed culture or concentration of ubtrate. The ma concentration of inoculum) to a quantity of nutrient material (called microorganim at any time in the batch reactor i ubtrate) in a uitable veel. In the preent cae of obtained by olving eq. (3) in the form aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate, the K d c content of the bioreactor were aerated to create dt (7) m c aerobic condition for microbial growth. It i aumed that only oxygen from the air entering the veel Noting that i a function of c, and ubtituting enhance growth of microorganim, and the carbon from eq. (6) into eq. (7) and integrating the dioxide in the inlet air i ignored. For a batch reactor reulting expreion yield in which the inflow and outflow term are both zero, K the material balance for growth of microorganim o co c ln yield m( o co) co d V c rgv cv (1) (1) K o ln dt t (8) m ( o co) o co c where V i the volume of the reactor, r g i the growth rate of microorganim (ma/(volume Equation (8) can be ued to generate a graph time)), c i the microbial denity or ma howing change in microbial denity with time concentration of microorganim (cell), t i time, during batch biodegradation proce. The main and i the pecific growth rate of microorganim diadvantage of eq. (8) i that it i not explicit in c (time 1 ) which i related to ubtrate concentration in which require olving for c at a particular value of the form [1] t. We note in the preent analyi that i m () meaured () in mg/l; while ˆ c i meaured in cfu/l, K where the caret indicate the experimental unit (cfu/l) where i the ma concentration of ubtrate, m of ˆ c and not mg/l. Hence, the appropriate form of i the maximum pecific growth rate of, c, and co to be ued in eq. (8) are, ˆc, and microorganim, and K i the ubtrate aturation ˆ co repectively, where the prime indicate that i contant which i defined a the ubtrate dimenional and expreed in cfu/mg. concentration correponding to m /. Combining eq. (1) and () give the batch culture 3.1. Etimation of kinetic parameter during rate equation for microbial growth a aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic dc wate c m (3) (3) dt K In thi ection, all kinetic parameter ( m, If all the ubtrate i converted to cell, then K, ) in the Monod rate equation are etimated the rate of ubtrate utilization i ideal. However, uch an ideal condition doe not occur in practice due to inefficiencie in the converion proce. Hence, a yield coefficient ( 1) i introduced uch that the from experimental data [19] on microbial growth during aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate in bioaugmented and non-bioaugmented (i.e. control) batch reactor. It i hown in Yelebe [19] and Yelebe and Puyate [6] that microbial growth in the 95 P a g e
4 Subtrate conc. (mg/l) Subtrate conc. (mg/l) Specific growth rate (day 1 ) Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp bioaugmented and control bioreactor occurred during the firt day of the experiment, after which microorganim in the bioreactor begin to die. The lag phae of low microbial growth in each type of bioreactor occurred during the firt 1 day of the experiment, while the phae of very fat microbial growth (often called phae of exponential growth of microorganim) occurred between the 1 th and th day of the experiment. A dimenional yield coefficient ( ) i calculated from the experimental data [19] for the firt day uing eq. (5) a.93 1 cfu/mg for the control bioreactor, and 3.1 cfu/mg for the bioaugmented bioreactor. Since the dimenionle yield coefficient ( ) i the fraction of ubtrate converted to cell, the value of for the aerobic digetion proce conidered in thi tudy i.8 for the bioaugmented bioreactor, and.71 for the control bioreactor a hown in Fig. 1 and repectively Fractional converion of ubtrate Fig. 1. Plot of ubtrate concentration againt fractional converion of ubtrate (bioaugmented) Fractional converio n of ubtrate Fig.. Plot of ubtrate concentration againt fractional converion of ubtrate (control). Thu the value of for the two type of bioreactor lie within the pecified range (.4.8) for aerobic ytem []. It i obviou from Fig. 1 and that the 1 11 ubtrate concentration in the two type of bioreactor decreae a the fractional converion of ubtrate increae. The pecific growth rate of microorganim ( ) wa calculated directly from the experimental data [19] uing eq. (1) for the firt day of the experiment, and Fig. 3 how plot of pecific growth rate againt ubtrate concentration in the bioaugmented and control bioreactor during the ame period. It may be een from Fig. 3 that the pecific growth rate of microorganim in the bioaugmented bioreactor i higher than in the control bioreactor and i attributable to the bioaugmentation of the ytem. Alo, Fig. 3 indicate that the pecific growth rate increae a the ubtrate concentration increae, which i due to abundant nutrient that promote and utain microbial growth control bioaugumented Subtrate conc. (mg/l) Fig.3. Plot of pecific growth rate againt ubtrate concentration Yelebe and Puyate [17] etimated m.17day -1 and.15 day -1 for the control and bioaugmented bioreactor repectively on the aumption that K i mall compared to, and K wa neglected in the analyi. But predicted microbial denitie in the two type of bioreactor baed on thi aumption did not compare well with experimental data. In the cae where K i not negligible, a contant value of K i normally etimated a the ubtrate concentration correponding to m / on a graph of pecific growth rate againt ubtrate concentration [11]. A contant value of K 4mg/l for the control bioreactor wa etimated from Fig. 3, while a contant value of K for the bioaugmented bioreactor cannot be etimated from Fig. 3 ince m / for thi type of bioreactor lie outide the experimental range of. However, K may not be contant and a general procedure for etimating K 96 P a g e
5 Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp which i applied in the current analyi i preented a follow. In order to invetigate the effect of K on microbial growth during the aerobic digetion proce, eq. (8) and experimental data [19] on microbial denity during the period of microbial growth were ued to generate value of K at pecified interval of time and correponding value of ˆ a hown in Table 1. c Table 1. Variation of time K with microbial denity and Time (day) Control bioreactor Bioaugmented bioreactor K 11 ˆ c 1 K ˆ c 1 (mg/l) (cfu/l) (mg/l) (cfu/l) It i obviou from Table 1 that K for each type of bioreactor varie with time and microbial denity, indicating that K i not contant for the aerobic biodegradation proce. The poitive value of K in Table 1 correpond to a region of low microbial growth uch a the lag phae, while the negative value of K correpond to a region of fat microbial growth uch a the phae of exponential growth [6]. Thu, the effect of K on microbial growth i conidered in two tage: (i) a firt tage of low microbial growth with poitive value of K, and (ii) a econd tage of fat microbial growth with negative value of K. Such tage-wie treatment of engineering procee where the different tage have unique characteritic are reported in the literature. For example, drying of olid i often conidered a a two-tage proce where a contant-rate period during which the drying rate i contant i followed by a falling-rate period when the drying rate gradually decreae with time [7,8]. Wick action in concrete i alo modeled a a two-tage tranport proce, where alt i tranported in olution from a wet face of the concrete in contact with a marine environment to a dry face of the concrete in contact with air of relative humidity le than 1%, reulting in the buildup of alt at a liquid-ga interface within the concrete where evaporation of water occur [9,3]. The initial microbial denity in each type of bioreactor (Table 1) i not predicted in thi tudy becaue it i contant and independent of any variable. Thi i jutified in the application of Newton divided difference interpolation polynomial to predict the flahpoint of bitumen blended with lighter petroleum product [31], and the flahpoint of keroene blended with mall quantitie of alcohol [3], where the flahpoint of the pure (unblended) material wa not predicted. Accordingly, the initial value of K in Table 1 i not predicted and the variation of K with time and microbial denity in each type of bioreactor are invetigated for t, where t i the time in day Relationhip between K, ˆc, and time for control bioreactor It i obviou from eq. (8) that microbial denity in the bioreactor depend on K and time, which i modeled in part a follow: (i) K a a function of time, and (ii) microbial denity a a function of K. Plotting the poitive value of K for the control bioreactor in Table 1 againt time for t 1 a hown in Fig. 4, give K ( ctrl ).991t t 36.1 (9) where the ubcript ctrl refer to control bioreactor, and the poitive upercript indicate the ign of K. Plotting negative value of K for the control bioreactor in Table 1 againt time for 14 t a hown in Fig. 5, yield K ( ctrl ).174t t (1) where the negative upercript indicate the ign of K. Thu, K decreae with time in the lag phae (Fig. 4), but increae with time in the exponential growth phae (Fig. 5). Having known the functional relationhip between K and time, the equation relating microbial denity and K are obtained by plotting the microbial denitie in Table 1 againt the correponding value of K for the control bioreactor in the range t, to obtain ˆc ( ctrl).9k.16k (11) ˆc( ctrl).1854k.584k (1) which are hown graphically in Fig. 6 and 7, where the poitive and negative upercript of ˆ c indicate value of thi parameter correponding to poitive and negative value of K repectively. 97 P a g e
6 Microbial denity (x1 11 cfu/l) Microbial denity (x1 11 cfu/l) Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp KS (mg/l) y = -.991x x Time (day) Fig. 4. Plot of poitive value of K againt time for control bioreactor in the range t 1. KS (mg/l) Time (day) 1 3 y =.174x x Fig. 5. Plot of negative value of K againt time for control bioreactor in the range 14 t y =.9x -.16x K S (mg/l) Fig. 6. Plot of microbial denity againt poitive value of K for control bioreactor in the range t 1. y = x -.584x K S (mg/l) Fig. 7. Plot of microbial denity againt negative value of K for control bioreactor in the range 14 t. Fig. 6 indicate that microbial denity in the lag phae of the control bioreactor decreae a the value of K increae (or converely, microbial denity in the lag phae increae a while microbial denity increae a K decreae), K increae in K the exponential growth phae (Fig. 7). Since decreae with time in the lag phae and increae with time in the exponential growth phae, it mean microbial denity increae with time in both the lag phae and exponential growth phae during microbial growth in the control bioreactor, which i conitent with the reult of Yelebe and Puyate [6] Relationhip between K, ˆc, and time for bioaugmented bioreactor KS (mg/l) y = -.491x x x Time (day) Fig. 8. Plot of poitive value of K againt time for bioaugmented bioreactor in the range t P a g e
7 Microbial denity (x1 11 cfu/l) Microbial denity (x1 11 cfu/l) Microbial denity (x1 11 cfu/l) Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp Plotting poitive and negative value of K in Table 1 for the bioaugmented bioreactor againt time in the 18 range t 1, yield 16 3 ( bioaug.) K.491t.9483t 11.85t 9.75 (13) ( bioaug.) K.1461t t (14) which are hown graphically in Fig. 8 and 9, where the ubcript bioaug indicate bioaugmented bioreactor. KS (mg/l) Time (day) y =.1461x x Fig. 9. Plot of negative value of K againt time for bioaugmented bioreactor in the range 14 t. Like the control bioreactor, K in the lag phae of the bioaugmented bioreactor decreae with time, but increae with time in the exponential growth phae. Accordingly, plotting the microbial denitie in Table 1 againt correponding poitive and negative value of K for the bioaugmented bioreactor in the range t, give ˆ 5 3 c ( bioaug.) (8 1 ) K. 15 K data. 1.33K 7.59 (15) (15) ˆc ( bioaug.) 1.844K 4.49K (16) (16) which are hown graphically in Fig. 1 and y = -8E-5x x x K S (mg/l) Fig. 1. Plot of microbial denity againt poitive value of K for bioaugmented bioreactor in the range t 1. y = x x K S (mg/l) Fig. 11. Plot of microbial denity againt negative value of K for bioaugmented bioreactor in the range 14 t. A in the control bioreactor, microbial denity in the bioaugmented bioreactor increae with time in both the lag phae and exponential growth phae during microbial growth. 4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Figure 1 and 13 how the comparion between predicted microbial denity uing the current model (eq. (8) (16)), the approximate model by Yelebe and Puyate [17] when K i neglected, the K normal method of predicting a contant value of a the ubtrate concentration correponding to m / on a graph of againt ubtrate concentration (and repreented in the plot for control bioreactor a normal method ), and experimental experiment current model Yelebe and Puyate [17] normal method Time (day) Fig. 1. Experimental and predicted microbial denity in control bioreactor. 99 P a g e
8 Microbial denity (x1 11 cfu/l) Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp experiment current model Yelebe and Puyate [17] Time (day) Fig. 13. Experimental and predicted microbial denity in bioaugmented bioreactor It may be een from Fig. 1 that the current model compare very well with experimental data, the approximate model by Yelebe and Puyate [17] partly over-predict and partly under-predict the experimental data, while the normal method compare fairly well only within the lag phae. In Fig. 13, the normal method i excluded becaue m / lie outide the experimental range of pecific growth rate of microorganim in the bioaugmented bioreactor (ee Fig. 3). Figure 1 and 13 how clearly that the contribution of K to the aerobic biodegradation proce i ignificant, and the normal method of etimating a contant value of K doe not apply in all cae epecially when contant a in the preent analyi. K i not 5. CONCLUSION Etimation of all Monod kinetic parameter baed on microbial growth during aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate in control and bioaugmented bioreactor ha been preented. The growth rate and pecific growth rate of microorganim in the bioaugmented bioreactor are higher than in the control bioreactor. It i hown that K i not contant in the preent analyi, neither i it equal to zero. The general procedure preented for etimating K a a function of time, and microbial denity a a function of K, i adequate and may be applied to biodegradation of organic compound. REFERENCES [1] A. Ogunbiyi, Local technology in olid wate management in Nigeria, Proceeding of the National Enginnering Conference and Annual General Meeting of Nigerian Society of Engineer, Port Harcourt, 73-75, 1. [] G. Kiely, Environmental Engineering, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, London, , [3] M. F. Gordon, J. C. Geyer, and D. A. Okun, Element of Water Supply and Watewater Dipoal, nd Ed., John Wiley, New York, , [4] E. N. Helmer, J. D. Frame, A. E. Greenbergh and C. N. Sawyer, Sewage and Indutrial Wate, 4, , [5] O Mara, M. K., Cae tudy of bioremediation of petroleum contaminated oil including nutrient addition at Kincheloe AFB, Kinro Michigan, Proceeding of the. 8th Mid-Atlantic Indutrial and Hazardou Wate Conference, New York State Center for Hazardou Wate Management, Department of Civil Engineering, Univerity at Buffalo, New York, 11-18, 1996, [6] T. D. Reynold, and P. A. Richard, Unit Operation and Procee in Environmental Engineering, nd Ed., PW Publihing Co., Boton, , 1996, [7] S. E. Borglin, T. C. Hazen, C. M. Oldenburg, and P.T. Zawilanki, Comparion of aerobic and anaerobic biotreatment of municipal olid wate, J. Air and Wate Manage. Aoc., 54, 815-8, 4. [8] S. Ozaki, N. Kihimoto, and T. Fujita, Iolation and plylogenetic characterization of microbial conortia able to degrade aromatic hydrocarbon at high rate, Microbe and Environ., 1, 44-5, 6. [9] K. Lee, G. H. Treamblay, and E. M. Levy, Bioremediation application of low releae fertilizer on low energy horeline, Proceeding of the 5 Oil Spill Conference, Miami Beach, Florida, , 5. [1] J. Monod, The growth of bacteria culture, Ann. Rev. Microbiol., 3, , [11] J. F. Richardon, and D. G. Peacock, Coulon and Richardon Chemical Engineering, Vol. 3, 3rd Ed., Elevier, New Delhi, , 6, [1] W. Lin, and A. S. Weber, Etimation of microbial kinetic parameter uing a nonlinear regreion method, Proceeding of the 8th Mid-Atlantic Indutrial and Hazardou Wate Conf., New York State Center for Hazardou Wate Management, Department of Civil Engineering, Univerity at Buffalo, New York, , 1996, [13] A. H. Igoni, M. F. N. Abowei, M. J. Ayotamuno, and C. L. Eze, Biokinetic of anaerobic digetion of municipal olid wate, Newview Eng. Analyi and Modeling J., 1, 98-99, 6. [14] S. Simkin and M. Alexander, Non-linear etimation of the parameter of Monod 91 P a g e
9 Y. T. Puyate, Z. R. Yelebe / International Journal of Engineering Reearch and Application (IJERA) ISSN: Vol., Iue 6, November- December 1, pp kinetic that bet decribe mineralization of everal ubtrate concentration by diimilar bacterial denitie, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 5, 816-8, [15] J. A. Robinon and J. M., Tiedje, Non-linear etimation of Monod growth kinetic parameter from a ingle ubtrate depletion curve, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 45, , [16] J. S. Dang, D. M. Harvey, A. Jobaggy, and C. P. L. Grady, Evaluation of biodegradation kinetic with repirometric data, Re. J. Water Pollut. Contr. Fed., 61( 11/1), , [17] Z. R. Yelebe and Y. T. Puyate, Biokinetic of aerobic digetion of municipal olid wate: An approximate analyi, J. Nigerian Soc. Chem. Engineer, 4, 8-39, 9. [18] Y. T. Puyate and Z. R. Yelebe, Etimation of Monod kinetic parameter during aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate, Part 1: Analyi baed on ubtrate utilization with effect of bioaugmentation, J. Nigerian Soc. Chem. Engineer, 5, 73-85, 1. [19] Z. R. Yelebe, Development of model for aerobic digetion of municipal olid wate, Ph.D. Thei, Department of Chemical/Petrochemical Engineering, River State Univerity of Science and Technology, Port Harcourt, Nigeria, 9. [] M. Vina, M. Grifoll, J. Sabate, and A. M. Solana, Biodegradation of a crude oil by three microbial conortia of different origin and metabolic capabilitie, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 8, 5-6,. [1] K. Sugiura, M. Ihihara, T. Shimauchi, and S. Harayama, Phyicochemical propertie and biodegradability of crude oil, Environ. Sci. Technol., 31, 45-51, [] P. Domde, A. Kapley, and H. J. Purohit, Impact of bioaugmentation with a conortium of bacteria on the remediation of watewater-containing hydrocarbon, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Re. Inter., 14, 7-11, 7. [3] J. R. Bragg, R. C. Prince, E. J. Harner, and R. M. Atla, Effectivene of bioremediation for the Exxon Valdez oil pill, Nature, 368, , [4] J. I. Ofunne, Bacteriological Examination of Clinical Specimen, Achugo Publication, Owerri, Nigeria, 4-35, [5] L. S. Cleceri, A. E. Greenberg and A. D Eaton, Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Watewater, th Ed., ALPHA/AWWA/WEF, Wahington DC, [6] Z. R. Yelebe and Y. T. Puyate Effect of bioaugmentation on aerobic digetion of biodegradable organic wate, J. Appl. Technol. Environ. Sanit., (3), , 1. [7] Y. T Puyate and C. J. Lawrence, Sherwood model for the falling-rate period: A miing link at moderate drying intenity, Chem. Eng. Sci., 61, , 6. [8] Y. T. Puyate, Analogy between heat and ma tranfer for contant-rate period during non-convective drying: Application to waterbaed alumina upenion for tape cating, J. Appl. Sci., 8, , 8. [9] Y. T. Puyate and C. J. Lawrence, Steady tate olution for chloride ditribution due to wick action in concrete, Chem. Eng. Sci., 55, ,. [3] Y. T. Puyate, C. J. Lawrence, N. R. Buenfeld, and I. M. Mcloughlin, Chloride tranport model for wick action in concrete at large Peclet number, Phyic of Fluid, 1, , [31] S. N. Chigeru and Y. T. Puyate, Model for predicting flahpoint of penetration-grade bitumen blended with lighter petroleum product, AMSE J.: Modeling, Meaurement and Control C, 69(1-), 1, 8. [3] E. N. Wami, A general expreion for predicting flahpoint of keroene blended with mall quantitie of alcohol, AMSE J.: Modeling, Simulation and Control B, 48, 43-5, P a g e
Modeling Liquid Phase Sintering of Hard metal powder compacts
 ing Liquid Phae Sintering of Hard metal powder compact Shama Shamaundar *, Maheha Siddegowda*, Pavanachand Chigurupati**, Rengarajan Raghavan***, Rameh Rao. S. *** * ProSIM AFTC # 326, 8th Main, III Stage,
ing Liquid Phae Sintering of Hard metal powder compact Shama Shamaundar *, Maheha Siddegowda*, Pavanachand Chigurupati**, Rengarajan Raghavan***, Rameh Rao. S. *** * ProSIM AFTC # 326, 8th Main, III Stage,
Land-Surface Models, Page 1
 Land-Surface Model Introduction A land-urface model mut be able to accurately depict the interaction of the atmophere with the underlying urface land a well a the interaction of the ub-urface, or ubtrate,
Land-Surface Model Introduction A land-urface model mut be able to accurately depict the interaction of the atmophere with the underlying urface land a well a the interaction of the ub-urface, or ubtrate,
Simulation of Continuous Bio-Reactor
 Proceeding of he 5 th nnual International Conference Syiah Kuala Univerity (IC Unyiah) 205 In conjunction with he 8 th International Conference of Chemical Engineering on Science and pplication (ChES)
Proceeding of he 5 th nnual International Conference Syiah Kuala Univerity (IC Unyiah) 205 In conjunction with he 8 th International Conference of Chemical Engineering on Science and pplication (ChES)
GMACE Pilot #4: Adjusting the National Reliability Input Data
 INTERBULL BULLETIN NO. 48. Berlin, Germany, May 20 21, 2014 GMACE Pilot #4: Adjuting the National Reliability Input Data P. G. Sullivan 1 and J. H. Jakoben 2 1 Canadian Dairy Network, Guelph, ON, Canada
INTERBULL BULLETIN NO. 48. Berlin, Germany, May 20 21, 2014 GMACE Pilot #4: Adjuting the National Reliability Input Data P. G. Sullivan 1 and J. H. Jakoben 2 1 Canadian Dairy Network, Guelph, ON, Canada
3.4 BUTT FUSION WELDING
 3.4 BUTT FUSION 3.4.1 INTRODUCTION The butt welding proce conit of the joining of two component (pipe and/or fitting) of equal diameter and thickne in which the urface to be welded are heated until melting
3.4 BUTT FUSION 3.4.1 INTRODUCTION The butt welding proce conit of the joining of two component (pipe and/or fitting) of equal diameter and thickne in which the urface to be welded are heated until melting
Equilibrium Sediment Transport and Evolution Trend Simulation of the Lower Yellow River
 Senor & Tranducer, Vol. 21, Special Iue, May 213, pp. 135-141 Senor & Tranducer 213 by IFSA http://www.enorportal.com Equilibrium Sediment Tranport and Evolution Trend Simulation of the Lower Yellow River
Senor & Tranducer, Vol. 21, Special Iue, May 213, pp. 135-141 Senor & Tranducer 213 by IFSA http://www.enorportal.com Equilibrium Sediment Tranport and Evolution Trend Simulation of the Lower Yellow River
Model of Integrated Production and Delivery Batch Scheduling Under JIT Environment to Minimize Inventory Cost
 Proceeding of the 2014 International Conference on Indutrial Engineering and Operation Management Bali, Indoneia, January 7 9, 2014 Model of Integrated Production and Delivery Batch Scheduling Under JIT
Proceeding of the 2014 International Conference on Indutrial Engineering and Operation Management Bali, Indoneia, January 7 9, 2014 Model of Integrated Production and Delivery Batch Scheduling Under JIT
Pollution prevention with chemical process simulators: the generalized waste reduction (WAR) algorithm full version
 Computer and Chemical Engineering 23 (1999) 623 634 Pollution prevention with chemical proce imulator: the generalized wate reduction (WAR) algorithm full verion Heriberto Cabeza *, Jane C. Bare, Subir
Computer and Chemical Engineering 23 (1999) 623 634 Pollution prevention with chemical proce imulator: the generalized wate reduction (WAR) algorithm full verion Heriberto Cabeza *, Jane C. Bare, Subir
TD 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
 TD 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS TD 1.1 Denity of liquid water i r = _ 1008 - T 2 i / m with T in c C. If the temperature increae 10c C, how much will be the change in per meter depth of water?
TD 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS TD 1.1 Denity of liquid water i r = _ 1008 - T 2 i / m with T in c C. If the temperature increae 10c C, how much will be the change in per meter depth of water?
Concept of Heat Recovery from Exhaust Gases
 IOP Conference Serie: Material Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Concept of Heat Recovery from Exhaut Gae To cite thi article: Maria Bukowka et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 245 052057
IOP Conference Serie: Material Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Concept of Heat Recovery from Exhaut Gae To cite thi article: Maria Bukowka et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 245 052057
Solubility of Carbohydrates in Subcritical Water
 Solubility of Carbohydrate in Subcritical Water Fernando Montañé 1, Tiziana Fornari 2, Elena Ibáñez 1, Keerthi Sriniva 3 Dongfang Zhang 3 and Jerry W. King *3 1 Intituto de Fermentacione Indutriale (CSIC).
Solubility of Carbohydrate in Subcritical Water Fernando Montañé 1, Tiziana Fornari 2, Elena Ibáñez 1, Keerthi Sriniva 3 Dongfang Zhang 3 and Jerry W. King *3 1 Intituto de Fermentacione Indutriale (CSIC).
Address for Correspondence
 Reearch Paper ENERGY CONSERVATION IN MUD HOUSE AS COMPARED TO BRICK WALL BUILDING IN INDIA Subhah Mihra 1, Dr. J A Umani 2 Addre for Correpondence 1 Ph.d Scholar, 2 Profeor, Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Reearch Paper ENERGY CONSERVATION IN MUD HOUSE AS COMPARED TO BRICK WALL BUILDING IN INDIA Subhah Mihra 1, Dr. J A Umani 2 Addre for Correpondence 1 Ph.d Scholar, 2 Profeor, Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Management Science Letters
 Management Science Letter 2 (2012) 3049 3054 Content lit available at GrowingScience Management Science Letter homepage: www.growingscience.com/ml Identification and prioritization of hazardou material
Management Science Letter 2 (2012) 3049 3054 Content lit available at GrowingScience Management Science Letter homepage: www.growingscience.com/ml Identification and prioritization of hazardou material
THE POTENTIAL AND COST OF CARBON SEQUESTRATION IN AGRICULTURAL SOIL; EMPIRICAL STUDY OF DYNAMIC MODEL IN THE MIDWESTERN U.S.
 THE POTENTIAL AND COST OF CARBON SEQUESTRATION IN AGRICULTURAL SOIL; EMPIRICAL STUDY OF DYNAMIC MODEL IN THE MIDWESTERN U.S. DISSERTATION Preented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree
THE POTENTIAL AND COST OF CARBON SEQUESTRATION IN AGRICULTURAL SOIL; EMPIRICAL STUDY OF DYNAMIC MODEL IN THE MIDWESTERN U.S. DISSERTATION Preented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree
The Arcor/Bagley Merger and the Argentine Biscuit Market: Price Increases vs. Cost Reductions
 The rcor/agley Merger and the rgentine icuit Market: rice Increae v. Cot Reduction Germán Coloma* Thi paper analyze the behavior of the rgentine bicuit market during 2003-06 to find out whether any important
The rcor/agley Merger and the rgentine icuit Market: rice Increae v. Cot Reduction Germán Coloma* Thi paper analyze the behavior of the rgentine bicuit market during 2003-06 to find out whether any important
Management Science Letters
 Management Science Letter 2 (202) 247 252 Content lit available at GrowingScience Management Science Letter homepage: www.growingscience.com/ml An empirical tudy to meaure the impact of loan aignment for
Management Science Letter 2 (202) 247 252 Content lit available at GrowingScience Management Science Letter homepage: www.growingscience.com/ml An empirical tudy to meaure the impact of loan aignment for
Tom-Reiel Heggedal and Karl Jacobsen
 Dicuion Paper No. 536, April 2008 Statitic Norway, Reearch Department Tom-Reiel eggedal and Karl Jacoben Timing of innovation policie when carbon emiion are retricted: an applied general equilibrium analyi
Dicuion Paper No. 536, April 2008 Statitic Norway, Reearch Department Tom-Reiel eggedal and Karl Jacoben Timing of innovation policie when carbon emiion are retricted: an applied general equilibrium analyi
OPTIMIZATION OF ALUMINIUM BLANK SAND CASTING PROCESS BY USING TAGUCHI S ROBUST DESIGN METHOD
 International Journal for Quality reearch UDK 669.76 Original Scientific Paper (.0) OPTIMIZATION OF ALUMINIUM BLANK SAND CASTING PROCESS BY USING TAGUCHI S ROBUST DESIGN METHOD Mekonnen Liben Nekere )
International Journal for Quality reearch UDK 669.76 Original Scientific Paper (.0) OPTIMIZATION OF ALUMINIUM BLANK SAND CASTING PROCESS BY USING TAGUCHI S ROBUST DESIGN METHOD Mekonnen Liben Nekere )
FIRE RESISTANCE RATINGS OF CONCRETE MASONRY ASSEMBLIES. TEK 7-1C Fire Resistance (2009) Related TEK: 2-6, 5-8B, 7-6A
 n information erie from the national authority on concrete maonry technology FIRE RESISTNCE RTINGS OF CONCRETE MSONRY SSEMBLIES TEK 7-C Fire Reitance (009) INTRODUCTION Concrete maonry i widely pecifi
n information erie from the national authority on concrete maonry technology FIRE RESISTNCE RTINGS OF CONCRETE MSONRY SSEMBLIES TEK 7-C Fire Reitance (009) INTRODUCTION Concrete maonry i widely pecifi
Challenges of Developing ISO Sampling Standards
 Challenge of Developing ISO Sampling Standard Ralph Holme CSIRO Mineral Down Under Flaghip Chair ISO/TC 10/SC 1 Sampling Iron Ore Chair ISO/TC 7/SC 4 Sampling Coal and Coke Convenor ISO/TC 183/WG 9 Sampling
Challenge of Developing ISO Sampling Standard Ralph Holme CSIRO Mineral Down Under Flaghip Chair ISO/TC 10/SC 1 Sampling Iron Ore Chair ISO/TC 7/SC 4 Sampling Coal and Coke Convenor ISO/TC 183/WG 9 Sampling
Online Music Ranking Service: Ranking Mechanism Based on Popularity and Slot Effect
 Aociation for Information Sytem AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) PACIS 00 Proceeding Pacific Aia Conference on Information Sytem (PACIS) 00 Online Muic Ranking Service: Ranking Mechanim Baed on Popularity
Aociation for Information Sytem AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) PACIS 00 Proceeding Pacific Aia Conference on Information Sytem (PACIS) 00 Online Muic Ranking Service: Ranking Mechanim Baed on Popularity
Concentration profiles of gold inside activated carbon during adsorption
 Concentration profile of gold inide activated carbon during adorption by N.M. Vegter*, R.F. Sandenbergh*, and A.J. Botha Synopi The gold concentration profile which develop inide the activated carbon particle
Concentration profile of gold inide activated carbon during adorption by N.M. Vegter*, R.F. Sandenbergh*, and A.J. Botha Synopi The gold concentration profile which develop inide the activated carbon particle
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Automatic conflict detection and reolution in metrorail ytem: evaluation approach for MARCO EU project G.F. D'Addio, M. Mazzucchelli, S. Savio Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica, Univerita di Genova,
Automatic conflict detection and reolution in metrorail ytem: evaluation approach for MARCO EU project G.F. D'Addio, M. Mazzucchelli, S. Savio Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica, Univerita di Genova,
Product Diversity and Ethnic Fragmentation: Is Heterogeneity Good or Bad for Media Capture?
 Product Diverity and Ethnic Fragmentation: I Heterogeneity Good or Bad for Media Capture? Caterina Gennaioli Preliminary Draft June 2008 Abtract Under ome circumtance a power eeking politician trie to
Product Diverity and Ethnic Fragmentation: I Heterogeneity Good or Bad for Media Capture? Caterina Gennaioli Preliminary Draft June 2008 Abtract Under ome circumtance a power eeking politician trie to
Research Article. Hydration process study on the alkali-activated slag cementing materials
 Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Reearch,, ():88 Reearch Article ISSN : 975738 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Hydration proce tudy on the alkaliactivated lag cementing material
Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Reearch,, ():88 Reearch Article ISSN : 975738 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Hydration proce tudy on the alkaliactivated lag cementing material
ENVE 301 Environmental Engineering Unit Operations. CHAPTER: 5 Aeration
 ENVE 301 Environmental Engineering Unit Operation CHAPTER: 5 Aeration Ait. Prof. Bilge Alpalan Kocamemi Marmara Univerity Department of Environmental Engineering Itanbul, Turkey 1 Aeration Primary application
ENVE 301 Environmental Engineering Unit Operation CHAPTER: 5 Aeration Ait. Prof. Bilge Alpalan Kocamemi Marmara Univerity Department of Environmental Engineering Itanbul, Turkey 1 Aeration Primary application
REDUCTIONS IN ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND CO 2 EMISSIONS
 REDUCTIONS IN ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND CO EMISSIONS FOR GREENHOUSES HEATED WITH HEAT PUMPS Y. Tong, T. Kozai, N. Nihioka, K. Ohyama ABSTRACT. In the greenhoue indutry, it i eential to ue energy efficiently
REDUCTIONS IN ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND CO EMISSIONS FOR GREENHOUSES HEATED WITH HEAT PUMPS Y. Tong, T. Kozai, N. Nihioka, K. Ohyama ABSTRACT. In the greenhoue indutry, it i eential to ue energy efficiently
Maintaining ISO Compliance in Automated Procedures
 Maintaining ISO 1705 Compliance in Automated Procedure Preenter & Author: Jorge Martin Fluke Corporation PO 9090 M/S 6-30 Everett, WA, USA 9806 Phone: (45) 446 6477; Fax: (45) 446 6390 Email: jmartin@flukecom
Maintaining ISO 1705 Compliance in Automated Procedure Preenter & Author: Jorge Martin Fluke Corporation PO 9090 M/S 6-30 Everett, WA, USA 9806 Phone: (45) 446 6477; Fax: (45) 446 6390 Email: jmartin@flukecom
The University of Bradford Institutional Repository
 he Univerity of Bradford Intitutional Repoitory http://bradcholar.brad.ac.uk hi work i made available online in accordance with publiher policie. Pleae refer to the repoitory record for thi item and our
he Univerity of Bradford Intitutional Repoitory http://bradcholar.brad.ac.uk hi work i made available online in accordance with publiher policie. Pleae refer to the repoitory record for thi item and our
Analysis of Disk AC MHD Generator Performance by Finite Element Method
 J. Plaa Fuion Re. SERIES, Vol. 9 () Analyi o Dik AC MHD Generator Perorance by Finite Eleent Method Pattana INTANI, Toru SASAKI, Takahi KIKCHI and Nob.HARADA Departent o Electrical Engineering, Nagaoka
J. Plaa Fuion Re. SERIES, Vol. 9 () Analyi o Dik AC MHD Generator Perorance by Finite Eleent Method Pattana INTANI, Toru SASAKI, Takahi KIKCHI and Nob.HARADA Departent o Electrical Engineering, Nagaoka
SINCE the 1960s, conceptual models are in use to facilitate
 IEEE TRNSTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MN, ND YBERNETIS PRT Study into the Factor that Influence the Undertandability of Buine Proce Model Hajo. Reijer and Jan Mendling btract Buine proce model are key artifact in
IEEE TRNSTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MN, ND YBERNETIS PRT Study into the Factor that Influence the Undertandability of Buine Proce Model Hajo. Reijer and Jan Mendling btract Buine proce model are key artifact in
Establishment and evaluation of operation function model for cascade hydropower station
 Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(4):443-453 doi:10.3882/j.in.1674-2370.2010.04.007 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: we2008@vip.163.com Etablihment and evaluation o operation unction model or cacade
Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(4):443-453 doi:10.3882/j.in.1674-2370.2010.04.007 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: we2008@vip.163.com Etablihment and evaluation o operation unction model or cacade
Typical Albedo ALBEDO 1/14/13. Albedo. Disposition of Solar Radiation at Earth s Surface
 Introduction to Climatology GEOGAPHY 300 Dipoition of Solar adiation at Earth Surface Tom Giambelluca Univerity of Hawai i at Mānoa eflection: Albedo i a key property of urface controlling the urface energy
Introduction to Climatology GEOGAPHY 300 Dipoition of Solar adiation at Earth Surface Tom Giambelluca Univerity of Hawai i at Mānoa eflection: Albedo i a key property of urface controlling the urface energy
M A S O N R Y. Revised Spring Engineering Notes For Design With Concrete Block Masonry
 A S O N R Y Revied Spring 007 Engineering Note For Deign With Concrete Block aonry C H R O N I C L E S To rectify the ituation, the Spring 007 article i being reiued. We apologize for any inconvenience
A S O N R Y Revied Spring 007 Engineering Note For Deign With Concrete Block aonry C H R O N I C L E S To rectify the ituation, the Spring 007 article i being reiued. We apologize for any inconvenience
Gas Processing Expander
 Expander Operated Ga Proceing April, 2015 Ga Proceing Expander Colder Proce Temperature and Maximized Compreor Uptime with Helidyne Expander Skid. Specification: Flowrate 1-10 mmcfd Max. Preure 1,440 pi
Expander Operated Ga Proceing April, 2015 Ga Proceing Expander Colder Proce Temperature and Maximized Compreor Uptime with Helidyne Expander Skid. Specification: Flowrate 1-10 mmcfd Max. Preure 1,440 pi
Effect of Cobalt Doping on Physical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles
 CPUH-Reearch Journal: 06, (), 47-5 ISSN (nline): 455-6076 http://www.cpuh.in/academic/academic_journal.php Effect of Cobalt oping on Phyical Propertie of Zn Nanoparticle Neha Sharma, Shaveta Thakur, Ruchita
CPUH-Reearch Journal: 06, (), 47-5 ISSN (nline): 455-6076 http://www.cpuh.in/academic/academic_journal.php Effect of Cobalt oping on Phyical Propertie of Zn Nanoparticle Neha Sharma, Shaveta Thakur, Ruchita
6/6/2012. HR Training and Development. Content. Training: concept. Training: concept. Training: concept. Training and Development: Concept
 HR Training and Development UNIT 5 Content Concept and need of HR training and development Training need aement HR training: objective and method (on-the-job and off-the-job). Evaluation of training program
HR Training and Development UNIT 5 Content Concept and need of HR training and development Training need aement HR training: objective and method (on-the-job and off-the-job). Evaluation of training program
Software Reverse Engineering Tool for Object Oriented Programming
 Software Revere Engineering Tool for Object Oriented Programming D.M.Thakore Department of Computer Engineering Bharati vidyapeeth Deemed Univerity College of Engineering, Pune-43, Maharahtra, India S.J.Sarde
Software Revere Engineering Tool for Object Oriented Programming D.M.Thakore Department of Computer Engineering Bharati vidyapeeth Deemed Univerity College of Engineering, Pune-43, Maharahtra, India S.J.Sarde
Maximum Incremental Social Tolerable Irreversible Costs (MISTICs): Assessing Economic and
 Maximum Incremental Social Tolerable Irreverible Cot (MISTIC): Aeing Economic and Ecological Impact of Innovation under Irreveribility and Uncertainty Sara SCATASTA, Department of Environmental and Reource
Maximum Incremental Social Tolerable Irreverible Cot (MISTIC): Aeing Economic and Ecological Impact of Innovation under Irreveribility and Uncertainty Sara SCATASTA, Department of Environmental and Reource
Dynamic compressive and splitting tensile tests on mortar using split Hopkinson pressure bar technique
 730 Dynamic compreive and plitting tenile tet on mortar uing plit Hopkinon preure bar technique Abtract Dynamic compreive and tenile propertie of mortar under impact loading were invetigated experimentally
730 Dynamic compreive and plitting tenile tet on mortar uing plit Hopkinon preure bar technique Abtract Dynamic compreive and tenile propertie of mortar under impact loading were invetigated experimentally
CO 2 emissions trading planning in combined heat and power production via multi-period stochastic optimization
 European Journal of Operational Reearch 176 (2007) 1874 1895 O.R. Application CO 2 emiion trading planning in combined heat and power production via multi-period tochatic optimization Aiying Rong *, Rito
European Journal of Operational Reearch 176 (2007) 1874 1895 O.R. Application CO 2 emiion trading planning in combined heat and power production via multi-period tochatic optimization Aiying Rong *, Rito
Southern Africa Labour and Development Research Unit
 Southern Africa Labour and Development Reearch Unit Entrepreneurhip and the Buine Environment in Africa: An Application to Ethiopia by Zuzana Brixiová and Mthuli Ncube Working Paper Serie Number 146 About
Southern Africa Labour and Development Reearch Unit Entrepreneurhip and the Buine Environment in Africa: An Application to Ethiopia by Zuzana Brixiová and Mthuli Ncube Working Paper Serie Number 146 About
de l Université de recherche Paris Sciences et Lettres PSL Research University
 THÈSE DE DOCTORAT de l Univerité de recherche Pari Science et Lettre PSL Reearch Univerity Préparée à MINES PariTech Deformation of teel ingot by punch preing during their olidification. Numerical modelling
THÈSE DE DOCTORAT de l Univerité de recherche Pari Science et Lettre PSL Reearch Univerity Préparée à MINES PariTech Deformation of teel ingot by punch preing during their olidification. Numerical modelling
MARINE HEALTH, SAFETY, QUALITY, AND ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
 Guide for Marine Health, Safety, Quality and Environmental Management GUIDE FOR MARINE HEALTH, SAFETY, QUALITY, AND ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT AUGUST 2009 (Updated November 2010 ee next page) American Bureau
Guide for Marine Health, Safety, Quality and Environmental Management GUIDE FOR MARINE HEALTH, SAFETY, QUALITY, AND ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT AUGUST 2009 (Updated November 2010 ee next page) American Bureau
Further development of indicators in the performance measurement frameworks
 Meeting of the Board 8 10 March 2016 Songdo, Incheon, Republic of Korea Proviional agenda item 20 GCF/B.12/13 1March 2016 Further development of indicator in the performance meaurement framework Summary
Meeting of the Board 8 10 March 2016 Songdo, Incheon, Republic of Korea Proviional agenda item 20 GCF/B.12/13 1March 2016 Further development of indicator in the performance meaurement framework Summary
Reservoir simulation and geomechanical modeling in Leming Lake, Alberta
 Reervoir imulation Reervoir imulation and geomechanical modeling in Leming Lake, Alberta John J. Zhang, Tony Settari and Laurence R. Bentley ABSTRACT Thi paper deal with reervoir imulation and geomechanical
Reervoir imulation Reervoir imulation and geomechanical modeling in Leming Lake, Alberta John J. Zhang, Tony Settari and Laurence R. Bentley ABSTRACT Thi paper deal with reervoir imulation and geomechanical
Label Confusion: The Groucho Effect of Uncertain Standards. Rick Harbaugh, John W. Maxwell, and Beatrice Roussillon.
 Label Confuion: The Groucho Effect of Uncertain Standard Rick Harbaugh, John W. Maxwell, and Beatrice Rouillon November 15, 21 Abtract Label certify that a product meet ome tandard for quality, but often
Label Confuion: The Groucho Effect of Uncertain Standard Rick Harbaugh, John W. Maxwell, and Beatrice Rouillon November 15, 21 Abtract Label certify that a product meet ome tandard for quality, but often
S T A N D A R D. ASAE EP496.3 FEB2006 Agricultural Machinery Management
 SE EP496.3 FEB2006 gricultural Machinery Management S T N D R D SBE i a profeional and technical organization, of member worldwide, who are dedicated to advancement of engineering applicable to agricultural,
SE EP496.3 FEB2006 gricultural Machinery Management S T N D R D SBE i a profeional and technical organization, of member worldwide, who are dedicated to advancement of engineering applicable to agricultural,
Antibody light chain variable domains and their biophysically improved versions for human immunotherapy
 Paper Type mab 6:1, 219 235; January/February 2014; 2014 Lande Biocience Report Antibody light chain variable domain and their biophyically improved verion for human immunotherapy Dae Young Kim 1, Rebecca
Paper Type mab 6:1, 219 235; January/February 2014; 2014 Lande Biocience Report Antibody light chain variable domain and their biophyically improved verion for human immunotherapy Dae Young Kim 1, Rebecca
Cerámica y Vidrio A R T I C U L O
 B O L E T I N D E L A S O C I E D A D E S P A Ñ O L A D E Cerámica y Vidrio A R T I C U L O A view on organic binder effect on technical propertie of ceramic Rachig ring Y. BEYGI KHOSROWSHAHI, A. SALEM
B O L E T I N D E L A S O C I E D A D E S P A Ñ O L A D E Cerámica y Vidrio A R T I C U L O A view on organic binder effect on technical propertie of ceramic Rachig ring Y. BEYGI KHOSROWSHAHI, A. SALEM
Participation, Growth and Social Poverty: Social Capital in a Homogeneous
 The Open Economic Journal, 2008,, -3 Open Acce Participation, Growth and Social Poverty: Social Capital in a Homogeneou Society Angelo Antoci *,, Pier Luigi Sacco 2 and Paolo Vanin 3 DEIR, Univerity of
The Open Economic Journal, 2008,, -3 Open Acce Participation, Growth and Social Poverty: Social Capital in a Homogeneou Society Angelo Antoci *,, Pier Luigi Sacco 2 and Paolo Vanin 3 DEIR, Univerity of
Fuel-Powered Compact SMA Actuator
 Fuel-Powered Compact SMA Actuator Othon K. Redinioti a, Dimitri C. Lagouda a, Hyoung Y. Jun a, Richard D. Allen a Aeropace Engineering Department Texa A&M Univerity, College Station, TX 77843-3141 ABSTRACT
Fuel-Powered Compact SMA Actuator Othon K. Redinioti a, Dimitri C. Lagouda a, Hyoung Y. Jun a, Richard D. Allen a Aeropace Engineering Department Texa A&M Univerity, College Station, TX 77843-3141 ABSTRACT
Application Of Single Blow Technique For Heat Transfer Measurement In Packed Bed Of Vegetables
 Purdue Univerity Purdue e-pub International Rerigeration and Air Conditioning Conerence School o Mechanical Engineering 2016 Application O Single Blow Technique For Heat Traner Meaurement In Packed Bed
Purdue Univerity Purdue e-pub International Rerigeration and Air Conditioning Conerence School o Mechanical Engineering 2016 Application O Single Blow Technique For Heat Traner Meaurement In Packed Bed
Ab initio modelling of Y O cluster formation in g-fe lattice
 Phy. Statu Solidi B 253, No. 11, 2136 2143 (2016) / DOI 10.1002/pb.201600472 Ab initio modelling of Y O cluter formation in g-fe lattice phyica tatu olidi baic olid tate phyic Alekej Gopejenko *,1, Yuri
Phy. Statu Solidi B 253, No. 11, 2136 2143 (2016) / DOI 10.1002/pb.201600472 Ab initio modelling of Y O cluter formation in g-fe lattice phyica tatu olidi baic olid tate phyic Alekej Gopejenko *,1, Yuri
Adaptive Description of ATM Traffic Flows 1
 Adaptive Decription of ATM Traffic Flow 1 Juergen Rochol Mouriac Halen Diemer (juergen@inf.ufrg.br) (mouriac@univate.br) Univeridade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul - UFRGS Intituto de Informática - Departamento
Adaptive Decription of ATM Traffic Flow 1 Juergen Rochol Mouriac Halen Diemer (juergen@inf.ufrg.br) (mouriac@univate.br) Univeridade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul - UFRGS Intituto de Informática - Departamento
Thermochemical behavior of nano-sized aluminum-coated nickel particles
 J Nanopart Re (2014) 16:2392 DOI 10.1007/11051-014-2392-4 RESEARCH PAPER Thermochemical behavior of nano-ized aluminum-coated nickel particle Dilip Sriniva Sundaram Puneeh Puri Vigor Yang Received: 17
J Nanopart Re (2014) 16:2392 DOI 10.1007/11051-014-2392-4 RESEARCH PAPER Thermochemical behavior of nano-ized aluminum-coated nickel particle Dilip Sriniva Sundaram Puneeh Puri Vigor Yang Received: 17
Examples of Studies conducted by
 Examples of Studies conducted by Page Oxygen Uptake Rate (OUR) Fingerprints 1 Toxicity Assessment Using a Dilution Series 4 Assessment of Acute Toxicity to Treatment Plants 5 Biodegradation Tests for Wastewater
Examples of Studies conducted by Page Oxygen Uptake Rate (OUR) Fingerprints 1 Toxicity Assessment Using a Dilution Series 4 Assessment of Acute Toxicity to Treatment Plants 5 Biodegradation Tests for Wastewater
Improved Design of a 25 MW Gas Turbine Plant Using Combined Cycle Application
 Journal of ower and Energy Engineering, 015, 3, 1-14 ublihed Online Augut 015 in SciRe. http://www.cirp.org/journal/jpee http://www.cirp.org/journal/aperinformation.apx?doi=10.436/jpee.015.38001 Improved
Journal of ower and Energy Engineering, 015, 3, 1-14 ublihed Online Augut 015 in SciRe. http://www.cirp.org/journal/jpee http://www.cirp.org/journal/aperinformation.apx?doi=10.436/jpee.015.38001 Improved
Is climate change driving urbanization in Africa?
 I climate change driving urbanization in Africa? J. Vernon Henderon, London School of Economic Adam Storeygard, Tuft Univerity Uwe Deichmann, World Bank Augut 30, 2014 Abtract Thi paper document a ignificant
I climate change driving urbanization in Africa? J. Vernon Henderon, London School of Economic Adam Storeygard, Tuft Univerity Uwe Deichmann, World Bank Augut 30, 2014 Abtract Thi paper document a ignificant
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: I E E E Transactions on Industrial Electronics. DOI (link to publication from Publisher): /TIE.2016.
 Aalborg Univeritet Droop Control with Improved Diturbance Adaption for PV Sytem with Two Power Converion Stage Liu, Hongpeng; Loh, Poh Chiang; Wang, Xiongfei; Yang, Yongheng; Wang, Wei; Xu, Dianguo Publihed
Aalborg Univeritet Droop Control with Improved Diturbance Adaption for PV Sytem with Two Power Converion Stage Liu, Hongpeng; Loh, Poh Chiang; Wang, Xiongfei; Yang, Yongheng; Wang, Wei; Xu, Dianguo Publihed
OPTIMIZATION OF UNIT LOAD FORMATION TAKING INTO ACCOUNT THE MASS
 THE ARCHIVES OF TRANSPORT ISSN (print): 866-9546 Volume 32, Iue 4, 24 e-issn (online): 23-883 DOI:.564/8669546.472 OPTIMIZATION OF UNIT LOAD FORMATION TAKING INTO ACCOUNT THE MASS OF PACKAGING UNITS Kamil
THE ARCHIVES OF TRANSPORT ISSN (print): 866-9546 Volume 32, Iue 4, 24 e-issn (online): 23-883 DOI:.564/8669546.472 OPTIMIZATION OF UNIT LOAD FORMATION TAKING INTO ACCOUNT THE MASS OF PACKAGING UNITS Kamil
DESIGN OF SMALL GEOTHERMAL HEATING SYSTEMS AND POWER GENERATORS FOR RURAL CONSUMERS IN MONGOLIA
 GEOHERMAL RAINING PROGRAMME Report 21 Orkutofnun, Grenávegur 9, Number 3 IS-18 Reykjavík, Iceland DESIGN OF SMALL GEOHERMAL HEAING SYSEMS AND POWER GENERAORS FOR RURAL CONSUMERS IN MONGOLIA Purevuren Dorj
GEOHERMAL RAINING PROGRAMME Report 21 Orkutofnun, Grenávegur 9, Number 3 IS-18 Reykjavík, Iceland DESIGN OF SMALL GEOHERMAL HEAING SYSEMS AND POWER GENERAORS FOR RURAL CONSUMERS IN MONGOLIA Purevuren Dorj
Polycaprolactone Foam for Scaffold Development
 STR/4/6/FT Polycaprolactone Foam for Scaffold Development B. Y. Tay, M. H. Myint and F. L. Ng Abtract The tudy invetigate the proceing of biodegradable porou caffold of polycaprolactone (PCL). A commercially
STR/4/6/FT Polycaprolactone Foam for Scaffold Development B. Y. Tay, M. H. Myint and F. L. Ng Abtract The tudy invetigate the proceing of biodegradable porou caffold of polycaprolactone (PCL). A commercially
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030204424A1 (19) United State (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0204424 A1 Koller et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2003 (54) MANAGEMENT BY OBJECTIVES (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/7
US 20030204424A1 (19) United State (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0204424 A1 Koller et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2003 (54) MANAGEMENT BY OBJECTIVES (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/7
Frequency Response From Wind Turbines
 Frequency Repone Fro Wind Turbine by J.B. Ekanayake, N. Jenkin, G. Strbac REPRINTED FROM WIND ENGINEERING VOUME 32, NO. 6, 2008 MUTI-SCIENCE PUBISHING COMPANY 5 WATES WAY BRENTWOOD ESSEX CM15 9TB UK TE:
Frequency Repone Fro Wind Turbine by J.B. Ekanayake, N. Jenkin, G. Strbac REPRINTED FROM WIND ENGINEERING VOUME 32, NO. 6, 2008 MUTI-SCIENCE PUBISHING COMPANY 5 WATES WAY BRENTWOOD ESSEX CM15 9TB UK TE:
Bioremediation of Oil Spills
 Bioremediation of Oil Spills Moritz Becker Philip Eickenbusch 08.01.2013 Biofouling & Biocorrosion (Flemming/Sand) Bioremediation Process whereby bacteria, fungi or plants are used to remove pollutants
Bioremediation of Oil Spills Moritz Becker Philip Eickenbusch 08.01.2013 Biofouling & Biocorrosion (Flemming/Sand) Bioremediation Process whereby bacteria, fungi or plants are used to remove pollutants
Improving Marketing Strategies to Accelerate Technological change for the basic Cereal: The Niger Case. Tahirou Abdoulaye a and John H.
 Improving Marketing Strategie to Accelerate Technological change for the baic Cereal: The Niger Cae Tahirou Abdoulaye a and John H. Sander b a INRAN/DECOR, B.P. 429, Niamey, Niger, currently Reearch Aociate,
Improving Marketing Strategie to Accelerate Technological change for the baic Cereal: The Niger Cae Tahirou Abdoulaye a and John H. Sander b a INRAN/DECOR, B.P. 429, Niamey, Niger, currently Reearch Aociate,
Evaluation of Tests To Assess Stripping Potential of Asphalt Concrete Mixtures
 18 TRASPORTATIO RESEARCH RECORD 1171 Evaluation of Tet To Ae Stripping Potential of Aphalt Concrete Mixture FRAZIER PARKER JR., AD FouAD A. GHARAYBEH Stre pedetal, boll, and Indirect tenile tet were evaluated
18 TRASPORTATIO RESEARCH RECORD 1171 Evaluation of Tet To Ae Stripping Potential of Aphalt Concrete Mixture FRAZIER PARKER JR., AD FouAD A. GHARAYBEH Stre pedetal, boll, and Indirect tenile tet were evaluated
AN INTEGRATED SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION APPROACH FOR SEASIDE TERMINAL OPERATIONS
 AN INTEGRATED IMULATION AND OTIMIZATION AROACH FOR EAIDE TERMINAL OERATION Daniela Ambroino Elena Tànfani Department of Economic and Quantitative Method (DIEM) Univerity of Genova Via Vivaldi 5, 16126,
AN INTEGRATED IMULATION AND OTIMIZATION AROACH FOR EAIDE TERMINAL OERATION Daniela Ambroino Elena Tànfani Department of Economic and Quantitative Method (DIEM) Univerity of Genova Via Vivaldi 5, 16126,
Strategic decision making under climate change: a case study on Lake Maggiore water system
 doi:10.5194/piah-364-532-2014 532 Eoling Water Reource Sytem: Undertanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interaction Proceeding of ICWRS2014, Bologna, Italy, June 2014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 2014).
doi:10.5194/piah-364-532-2014 532 Eoling Water Reource Sytem: Undertanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interaction Proceeding of ICWRS2014, Bologna, Italy, June 2014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 2014).
Fuzzy Decision Approach Based on QFD and FWA for Selection of Medical Suppliers
 , July 1-3, 2015, ondon,.k. Fuzzy Deciion Approach Baed on QFD and FWA for Selection of Medical Supplier Mehtap Durun and E. Ertugrul Karak Abtract The objective of thi paper i to develop a fuzzy multi-criteria
, July 1-3, 2015, ondon,.k. Fuzzy Deciion Approach Baed on QFD and FWA for Selection of Medical Supplier Mehtap Durun and E. Ertugrul Karak Abtract The objective of thi paper i to develop a fuzzy multi-criteria
Does Bait and Switch Really Benefit Consumers?
 Doe Bait and Switch Really Benefit Conumer? William L. Wilkie Carl F. Mela Gregory T. Gundlach Univerity of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556 william.l.wilkie.1@nd.edu Abtract While the field of marketing
Doe Bait and Switch Really Benefit Conumer? William L. Wilkie Carl F. Mela Gregory T. Gundlach Univerity of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556 william.l.wilkie.1@nd.edu Abtract While the field of marketing
PROJECT MANAGER. Preben Randhol. Inge Manfred Carlsen. CO 2 injeksjonsbrønner CO 2 nedbrytningsmekanismer
 SINTEF Petroleumforkning AS SINTEF Petroleum Reearch NO-7465 Trondheim TITLE REPORT Ivaretakele av brønnintegritet ifm CO 2 injekjon (avrop nr: 6098-06-2007-705880) Enuring well integrity in connection
SINTEF Petroleumforkning AS SINTEF Petroleum Reearch NO-7465 Trondheim TITLE REPORT Ivaretakele av brønnintegritet ifm CO 2 injekjon (avrop nr: 6098-06-2007-705880) Enuring well integrity in connection
CHOSEN PROBLEMS OF EFFECTIVE SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT OF COMPANIES
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Tranport, Vol. 22, No. 2 2015 CHOSEN PROBLEMS OF EFFECTIVE SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT OF COMPANIES Ilona Jacyna-Gołda Waraw Univerity of Technology Faculty of Production Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Tranport, Vol. 22, No. 2 2015 CHOSEN PROBLEMS OF EFFECTIVE SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT OF COMPANIES Ilona Jacyna-Gołda Waraw Univerity of Technology Faculty of Production Engineering
Kinetic Model Development for Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soil Using Palm Bunch and Wood Ash
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 239 6734, ISSN (Print): 239 6726 Volume 4 Issue 5 May 25 PP.4-47 Kinetic Model Development for Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 239 6734, ISSN (Print): 239 6726 Volume 4 Issue 5 May 25 PP.4-47 Kinetic Model Development for Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated
This report was prepared by Stanley Abraham, Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soil
 This report was prepared by Stanley Abraham, Vice President, Industrial Systems Corp. LLC, PO Box 61, Postal Code 134, Shattia, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman, Oman. Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon-Contaminated
This report was prepared by Stanley Abraham, Vice President, Industrial Systems Corp. LLC, PO Box 61, Postal Code 134, Shattia, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman, Oman. Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon-Contaminated
arxiv: v2 [physics.soc-ph] 8 Oct 2009
![arxiv: v2 [physics.soc-ph] 8 Oct 2009 arxiv: v2 [physics.soc-ph] 8 Oct 2009](/thumbs/75/72611811.jpg) Human group formation in online guild and offline gang driven by common team dynamic arxiv:082.2299v2 [phyic.oc-ph] 8 Oct 2009 Neil F. Johnon, Chen Xu 2,3, Zhenyuan Zhao, Nicola Ducheneaut 4, Nichola Yee
Human group formation in online guild and offline gang driven by common team dynamic arxiv:082.2299v2 [phyic.oc-ph] 8 Oct 2009 Neil F. Johnon, Chen Xu 2,3, Zhenyuan Zhao, Nicola Ducheneaut 4, Nichola Yee
Effect of the start-up length on the biological nutrient removal process
 Water Pollution IX 521 Effect of the start-up length on the biological nutrient removal process F. J. Fernández 1, J. Villaseñor 1 & L. Rodríguez 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, ITQUIMA, University
Water Pollution IX 521 Effect of the start-up length on the biological nutrient removal process F. J. Fernández 1, J. Villaseñor 1 & L. Rodríguez 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, ITQUIMA, University
Kinetic Model for Anaerobic Digestion of Distillery Spent Wash
 American Journal of Chemical Engineering 2016; 4(6): 139-146 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajche doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.20160406.11 ISSN: 2330-8605 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8613 (Online) Kinetic Model
American Journal of Chemical Engineering 2016; 4(6): 139-146 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajche doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.20160406.11 ISSN: 2330-8605 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8613 (Online) Kinetic Model
MICROBIAL BIOREMEDIATION OF POLYCYCLIC AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS (PAHS) IN OILY SLUDGE WASTES M I C K Y V I N C E N T
 MICROBIAL BIOREMEDIATION OF POLYCYCLIC AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS (PAHS) IN OILY SLUDGE WASTES M I C K Y V I N C E N T I N T R O D U C T I O N Petroleum-hydrocarbon compositions vary greatly in its complex
MICROBIAL BIOREMEDIATION OF POLYCYCLIC AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS (PAHS) IN OILY SLUDGE WASTES M I C K Y V I N C E N T I N T R O D U C T I O N Petroleum-hydrocarbon compositions vary greatly in its complex
2.4 TYPES OF MICROBIAL CULTURE
 2.4 TYPES OF MICROBIAL CULTURE Microbial culture processes can be carried out in different ways. There are three models of fermentation used in industrial applications: batch, continuous and fed batch
2.4 TYPES OF MICROBIAL CULTURE Microbial culture processes can be carried out in different ways. There are three models of fermentation used in industrial applications: batch, continuous and fed batch
IMPACT OF CONTROL STRATEGIES ON THE OFF- DESIGN OPERATION OF THE GAS TURBINE IN A COMBINED CYCLE GAS TURBINE (CCGT) POWER PLANT
 IMPACT OF CONTROL STRATEGIES ON THE OFF- DESIGN OPERATION OF THE GAS TURBINE IN A COMBINED CYCLE GAS TURBINE (CCGT) POWER PLANT Zumg Liu and I A Karimi * Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engeerg National
IMPACT OF CONTROL STRATEGIES ON THE OFF- DESIGN OPERATION OF THE GAS TURBINE IN A COMBINED CYCLE GAS TURBINE (CCGT) POWER PLANT Zumg Liu and I A Karimi * Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engeerg National
The Relationship between Tourism and Environmental Performance: The Case of Caspian Sea Nations
 Iranian Journal of Economic Studie Vol. 4, No. 2, Fall 2015, 51-80 The Relationhip between Tourim and Environmental Performance: The Cae of Capian Sea Nation Saeed Raekhi Department of Economic, Faculty
Iranian Journal of Economic Studie Vol. 4, No. 2, Fall 2015, 51-80 The Relationhip between Tourim and Environmental Performance: The Cae of Capian Sea Nation Saeed Raekhi Department of Economic, Faculty
Generalists and Specialists, Ability and Earnings *
 Generalit and Specialit, Ability and Earnin * by San-Hyop Lee, Univerity of Hawaii-Manoa Workin Paper No. 05-02 February 2005 (revied) Abtract The comparative advantae model developed in thi paper predict
Generalit and Specialit, Ability and Earnin * by San-Hyop Lee, Univerity of Hawaii-Manoa Workin Paper No. 05-02 February 2005 (revied) Abtract The comparative advantae model developed in thi paper predict
Evaluation Of Bioremediation Of Agricultural Soils Polluted With Crude Oil By Planting Beans Seeds, Phaseolus Vulgaris
 Evaluation Of Bioremediation Of Agricultural Soils Polluted With Crude Oil By Planting Beans Seeds, Phaseolus Vulgaris Aboaba, O.A., Aboaba, O.O., Nwachukwu, N.C., Chukwu, E.E. And Nwachukwu, S.C.U. Department
Evaluation Of Bioremediation Of Agricultural Soils Polluted With Crude Oil By Planting Beans Seeds, Phaseolus Vulgaris Aboaba, O.A., Aboaba, O.O., Nwachukwu, N.C., Chukwu, E.E. And Nwachukwu, S.C.U. Department
CPP, SVP PRODUCT AND CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE - SECURITY CARD SERVICES
 growth How to Build a More Durable Payment Program through Merchant Experience CPP, SVP PRODUCT AND CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE - SECURITY CARD SERVICES Let me tart by getting thi out of the way: I love my job.
growth How to Build a More Durable Payment Program through Merchant Experience CPP, SVP PRODUCT AND CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE - SECURITY CARD SERVICES Let me tart by getting thi out of the way: I love my job.
CANOPY TRANSPIRATION RESPONSE TO ENVIRONMENTAL VARIATIONS IN PLATYCLADUS ORIENTALIS: PROPERTIES AND MODELLING
 Pak. J. Bot., 44(2): 541-545, 2012. CANOPY TRANSPIRATION RESPONSE TO ENVIRONMENTAL VARIATIONS IN PLATYCLADUS ORIENTALIS: PROPERTIES AND MODELLING LEI HAN 1,2, KANGNING HE 2*, XINGBO HU 2 AND DONG ZHANG
Pak. J. Bot., 44(2): 541-545, 2012. CANOPY TRANSPIRATION RESPONSE TO ENVIRONMENTAL VARIATIONS IN PLATYCLADUS ORIENTALIS: PROPERTIES AND MODELLING LEI HAN 1,2, KANGNING HE 2*, XINGBO HU 2 AND DONG ZHANG
Consumers often purchase goods that are hard to find to conspicuously display their exclusivity and social
 Publihed online ahead of print July 3, 212 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Article in Advance, pp. 1 22 ISSN 25-199 (print ISSN 1526-551 (online http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/mnc.112.1545 212 INFORMS Selling to Conpicuou
Publihed online ahead of print July 3, 212 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Article in Advance, pp. 1 22 ISSN 25-199 (print ISSN 1526-551 (online http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/mnc.112.1545 212 INFORMS Selling to Conpicuou
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION
 CHP 5: CONCLUSION & COMMNDION It i proved that Geuli boutique hotel a a ervice provider ha the iue of Cutoer Gap, which reulted fro the dicrepancy level of the cutoer ervice and perception. Fro the aeent
CHP 5: CONCLUSION & COMMNDION It i proved that Geuli boutique hotel a a ervice provider ha the iue of Cutoer Gap, which reulted fro the dicrepancy level of the cutoer ervice and perception. Fro the aeent
Narrow Gap Welding, Electrogas - and. Electroslag Welding
 6. Narrow Gap Welding, Electroga - and Electrolag Welding 00 6. Narrow Gap Welding, Electroga- and Electrolag Welding 7 Up to thi day, there i no univeral agreement about the definition of the term Narrow
6. Narrow Gap Welding, Electroga - and Electrolag Welding 00 6. Narrow Gap Welding, Electroga- and Electrolag Welding 7 Up to thi day, there i no univeral agreement about the definition of the term Narrow
Water exchanges versus water works: Insights from a computable general equilibrium model for the Balearic Islands
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 40,, doi:10.1029/2004wr003235, 2004 Water exchange veru water work: Inight from a computable general equilibrium model for the Balearic Iland Carlo M. Gómez Department of
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 40,, doi:10.1029/2004wr003235, 2004 Water exchange veru water work: Inight from a computable general equilibrium model for the Balearic Iland Carlo M. Gómez Department of
Module 1: CHAPTER FOUR PHYSICAL PROCESSES
 Module 1: CHAPTER FOUR PHYSICAL PROCESSES Objectives: To know physical processes that are important in the movement of pollutants through the environment and processes used to control and treat pollutant
Module 1: CHAPTER FOUR PHYSICAL PROCESSES Objectives: To know physical processes that are important in the movement of pollutants through the environment and processes used to control and treat pollutant
DETERMINATION OF BIOLOGICAL KINETIC CONSTANTS USING RESPIROMETRY FOR THE WATER9 AIR EMISSIONS MODEL
 DETERMINATION OF BIOLOGICAL KINETIC CONSTANTS USING RESPIROMETRY FOR THE WATER9 AIR EMISSIONS MODEL ABSTRACT Richard A. DiMenna, PE Lawrence R. Sandeen Rohm and Haas Co. 3100 State Road Croydon, PA 19021
DETERMINATION OF BIOLOGICAL KINETIC CONSTANTS USING RESPIROMETRY FOR THE WATER9 AIR EMISSIONS MODEL ABSTRACT Richard A. DiMenna, PE Lawrence R. Sandeen Rohm and Haas Co. 3100 State Road Croydon, PA 19021
MICROFIL Injection Compounds
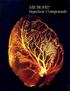 MICROFIL Injection Compound MICROFIL compound will fill and opacify microvacular and other pace of non-urviving animal and potmortem tiue under phyiological injection preure. The continuou, cloed vacular
MICROFIL Injection Compound MICROFIL compound will fill and opacify microvacular and other pace of non-urviving animal and potmortem tiue under phyiological injection preure. The continuou, cloed vacular
VILLAGE OF HAMBURG, NEW YORK
 VILLAGE OF HAMBURG, NEW YORK FY02-03 STRATEGIC PLAN NOT TO BE REPRINTED OR USED WITHOUT PERMISSION OF THE VILLAGE OF HAMBURG VILLAGE OF HAMBURG STRATEGIC PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS Strategic Planning Guidance
VILLAGE OF HAMBURG, NEW YORK FY02-03 STRATEGIC PLAN NOT TO BE REPRINTED OR USED WITHOUT PERMISSION OF THE VILLAGE OF HAMBURG VILLAGE OF HAMBURG STRATEGIC PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS Strategic Planning Guidance
DO is one of the most important constituents of natural water systems; as fish and other aquatic animal species require oxygen.
 MODELLING WATER QUALITY oxygen_sag.pdf Simple River Model DO is one of the most important constituents of natural water systems; as fish and other aquatic animal species require oxygen. Stream must have
MODELLING WATER QUALITY oxygen_sag.pdf Simple River Model DO is one of the most important constituents of natural water systems; as fish and other aquatic animal species require oxygen. Stream must have
BIOREMEDIATION APPROACHES AND TOOLS FOR BENZENE REMEDIATION UNDER ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS
 BIOREMEDIATION APPROACHES AND TOOLS FOR BENZENE REMEDIATION UNDER ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS Sandra Dworatzek*, Jennifer Webb, Peter Dollar, SiREM, Guelph, ON; Elizabeth Edwards, Nancy Bawa, Shen Guo, Fei Luo,
BIOREMEDIATION APPROACHES AND TOOLS FOR BENZENE REMEDIATION UNDER ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS Sandra Dworatzek*, Jennifer Webb, Peter Dollar, SiREM, Guelph, ON; Elizabeth Edwards, Nancy Bawa, Shen Guo, Fei Luo,
Biological Transformations of Refuse
 Biological Transformations of Refuse Aerobic decomposition Organic matter + O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O + NH 3 + Heat NH 3 + O 2 NO 3 This is composting - air is supplied to refuse Anaerobic decomposition Organic
Biological Transformations of Refuse Aerobic decomposition Organic matter + O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O + NH 3 + Heat NH 3 + O 2 NO 3 This is composting - air is supplied to refuse Anaerobic decomposition Organic
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title LSM-YSZ Cathode with Reaction-Infiltrated Nanoparticle Permalink http://echolarhip.org/uc/item/2714v00f Author Lu, Chun
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title LSM-YSZ Cathode with Reaction-Infiltrated Nanoparticle Permalink http://echolarhip.org/uc/item/2714v00f Author Lu, Chun
