Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.4396
|
|
|
- Stephanie Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of technical replicate consistency between and across the standard ATAC-seq method, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. (a) Heatmap-based representation of ATAC-seq quality control metrics including library size (purple), percent of reads mapping to mitochondrial DNA (blue), and enrichment of signal at TSSs (orange) for each optimization made to produce the Omni-ATAC protocol. Deeper color is used to depict the most desirable value of each statistic. All values were determined from 100,000 random aligned reads. Data represents the average of two technical replicates per square. (b-d) Correlation of technical replicates from GM12878 ATAC-seq data generated using (b) the Omni-ATAC protocol, (c) the standard ATAC-seq protocol, and (d) DNase-seq. Data for standard ATAC-seq and DNase-seq were obtained from publicly available data. Each dot represents an individual peak. Peaks analyzed were derived from a union peak set using data from all three methods. Only 50,000 random peaks with more than 5 reads are shown. R value indicated at the top of each plot. (e,f) Correlation of GM12878 ATAC-seq data generated using (e) Omni-ATAC protocol and (f) the standard ATACseq protocol with DNase-seq as in (b-d). (g) Pearson correlation heatmap showing sample by sample unsupervised clustering on all peaks identified across all technical replicates from each method. Each sample represents an individual technical replicate. (h,i) CTCF meta-footprint across the top 20,000 ATAC-seq peaks containing a CTCF motif in data from GM12878 cells derived using (h) the standard ATAC-seq protocol and (i) the Omni-ATAC protocol. Data for standard ATAC-seq method derived from published data 1.
3 Supplementary Figure 2 Comparison of Omni-ATAC to the Fast-ATAC method in primary human T cells. (a-c) Correlation of technical replicates from primary human CD4+ T cells cells using (a) the Omni-ATAC protocol, (b) the Fast-ATAC protocol, and (c) the standard ATAC-seq protocol. All data shown was generated in this study from the same sample of T cells. Each dot represents an individual peak. Peaks analyzed were derived from a union peak set using data from all three methods. Only 50,000 random peaks with more than 5 reads are shown. R value indicated at the top of each plot. (d,e) Correlation of ATAC-seq data generated using the Omni-ATAC protocol with data generated using (d) the Fast-ATAC protocol or (e) the standard ATAC-seq protocol in CD4+ T cells as in (a-c). (f) Pearson correlation heatmap showing sample by sample unsupervised clustering on all peaks identified across all technical replicates of CD4+ T cells from each method.
4
5 Supplementary Figure 3 Comparison of Omni-ATAC to standard ATAC-seq and DNase-seq at the level of peaks. (a) The number of PCR cycles required to amplify ATAC-seq libraries to an absolute yield of 80 femtomoles (20 ul at 4 nm) using the standard ATAC-seq protocol, the Fast-ATAC protocol, and the Omni-ATAC protocol. N=28 for each box chart, representing 2 technical replicates from 14 distinct cell types and cell contexts (Supplementary Table 1). (b) Fraction of reads in peaks mapping to TSSs (+/- 500 bp of TSS) and distal elements (>500 bp from TSS) from GM12878 libraries generated in this study and from public repositories using the standard ATAC-seq protocol ( Standard ), the Fast-ATAC-seq protocol ( Fast ), the Omni-ATACseq protocol ( Omni-ATAC ), and DNase-seq 11 ( DNase ). Each bar represents the mean of 2 technical replicates with the exception of the previously published ATAC-seq data which had 4 technical replicates. Error bars represent standard deviation. **p < 0.01, ***p < by two-tailed unpaired students t-test comparing the fraction of reads in peaks to reads outside of peaks. All values were determined from 5 million random aligned de-duplicated reads. (c) Histogram comparing the distribution of macs2 peak scores (-log10(pvalue of peak call)) from peaks called from 20 million randomly selected aligned de-duplicated reads in GM12878 cells as in (d). (d,e) In silico simulation of peak calling from variable read depth using data derived from (d) GM12878 cells with the standard ATAC-seq protocol, DNase-seq, and the Omni-ATAC protocol or (e) CD4+ T cells with the standard ATAC-seq protocol, the Fast-ATAC protocol, and the Omni-ATAC protocol. Input reads were randomly selected from a pool of properly aligned, non-duplicate reads. All input reads were trimmed to equal length (36 bp) prior to alignment to match DNase-seq data. GM12878 data from the standard ATAC-seq protocol and DNase-seq were obtained from publicly available sources. All data for CD4+ T cells was generated from a single donor. Data points represent the mean of three individual down-sampled technical replicates. (f-h) Signal at peaks called as unique in the analysis presented in Figure 1c for (f) the standard ATAC-seq protocol, (g) the Omni-ATAC protocol, and (h) DNase-seq. Peak score is calculated in the same way as the TSS enrichment score but for a different set of specified peaks. (i-l) Input read normalized sequencing tracks at a control locus (i,j) and a B cell-related locus (k,l) from GM12878 cells derived using standard ATAC-seq, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. In each case, 60 million properly aligned, non-duplicate reads were used to allow for direct comparison. All tracks in each panel are shown on the same y-axis scale. Tracks shown in (j,l) depict the same regions shown in (i,k) but with a reduced y-axis scale to show the difference in signal-to-background in data generated using the Omni-ATAC protocol compared to the standard ATAC-seq protocol and DNase-seq. Peaks that pass above the 10 read y-axis limit are truncated at y=10. All input reads were trimmed to equal length (36 bp) prior to alignment to match DNase-seq. Regions shown represent (i,j) chr19:36,097,939-36,272,939, and (k,l) chr9:36,373,966-37,494,500.
6 Supplementary Figure 4 Omni-ATAC outperforms the standard ATAC-seq method in situations requiring low cell numbers. (a,b) Sequencing tracks of ATAC-seq data at (a) a control locus and (b) the PAX5 locus derived from the standard ATAC-seq protocol and the Omni-ATAC protocol using 500 GM12878 cells. No normalization was performed. All available filtered reads are shown under the assumption that the libraries have been sequenced to relatively complete depth. Each track represents an individual technical replicate. Data for standard ATAC-seq from Buenrostro et al Region shown represents (a) chr19:36,097,939-36,272,939 or (b) chr9:36,373,966-37,494,500. (c) The total raw reads, filtered reads, and the percent duplication (how completely the libraries have been sequenced) are shown for each library to the right. (d,e) Sequencing tracks shown in (a,b) but with a y-axis scale of 5 to show the difference in signal-to-background in data derived using the Omni-ATAC protocol compared to the standard ATAC-seq protocol. Peaks that pass above the 5 read y- axis limit are truncated at y=5. Each track represents an individual technical replicate. Region shown represents (d) chr19:36,097,939-36,272,939 or (e) chr9:36,373,966-37,494,500. (f) Fraction of reads in peaks mapping to TSSs (+/- 500 bp of TSS) and distal elements (>500 bp from TSS) from the libraries shown in (a-e). Each bar represents the mean of 3 technical replicates. Error bars represent standard deviation. ***p<0.001 by two-tailed unpaired students t-test. Data for standard ATAC-seq from Buenrostro et al (g) Metaplot showing
7 enrichment of reads at TSSs in data derived from 500 GM12878 cells using Omni-ATAC (N=3) compared to published data using standard ATAC-seq 1 (N=3). (h) Overlap of 500 cell GM12878 peaks called from all available reads using the standard ATAC-seq protocol and the Omni-ATAC protocol. Numbers represent the mean of three individual technical replicates in each case. Overlap was performed with a union set of GM12878 peaks identified by DNase-seq, standard ATAC-seq, and Omni-ATAC. Data for standard ATAC-seq from Buenrostro et al (i) Correlation of Omni-ATAC data from 500 GM12878 cells with Omni-ATAC data from 50,000 GM12878 cells. Each dot represents an individual peak. Peaks analyzed were derived from a union peak set using data from the standard ATAC-seq method, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. Only 50,000 random peaks with more than 5 reads are shown. R value indicated at the top of the plot. (j) Pearson correlation heatmap showing sample by sample unsupervised clustering on all peaks identified across all technical replicates of 500 and 50,000 GM12878 cells. Data for standard ATAC-seq for both 500 cell and 50,000 cell GM12878 data from Buenrostro et al DNase-seq was performed on an unknown number of cells.
8 Supplementary Figure 5 Omni-ATAC enables the use of less amounts of transposase without decreasing data quality. (a) Heatmap-based representation of ATAC-seq quality control metrics including library size, percent of reads mapping to mitochondrial DNA, and enrichment of signal at TSSs. Deeper color is used to depict the most desirable value of each statistic. All values were determined from 5 million random aligned reads. Data represents two technical replicates per square. (b-d) Correlation of Omni-ATAC data generated with varying amounts of transposase enzyme. Technical replicates using (b) 100% Tn5 transposase input and (c) 20% transposase input are shown alongside (d) the correlation of 100% Tn5 transposase input with 20% Tn5 transposase input. Peaks analyzed were derived from DNase-seq data. Only 50,000 random peaks with more than 5 reads are shown. R value indicated at the top of each plot. (e) Fraction of reads in peaks mapping to TSSs (+/- 500 bp of TSS) and distal elements (>500 bp from TSS) for Omni-ATAC data performed with various amounts of Tn5 transposase input. Peak set used was derived from DNase-seq data. Each bar represents the mean of 2 technical replicates. Error bars represent standard deviation. NS = not significant.
9 Supplementary Figure 6 Application of Omni-ATAC to frozen post-mortem human brain samples yields robust data. (a) Representative phase contrast image of nuclei isolated from frozen post-mortem human brain. Scale bar represents 10 µm. Experiment was repeated 5 times with 5 total images collected. (b) Representative DAPI staining of the nuclei shown in (a). Scale bar represents 10 µm. (c) Three-dimensional principal component analysis showing the first 3 principal components from ATAC-seq data generated with the Omni-ATAC protocol in 5 different brain regions from 2 different biological donors, each with 2 technical replicates.
10 Different brain regions are indicated by color. CC = corpus callosum; CN = caudate nucleus; CB = cerebellum; HIP = hippocampus; MFG = middle frontal gyrus. (d) Differentially-accessible peaks defined as being at least 2 standard deviations away from the mean of all other regions. Transcription factors whose binding motifs are identified as enriched using the Hypergeometric Optimization of Motif Enrichment (Homer) algorithm in the accessible chromatin regions of each brain region are shown to the right. (e) Transcription factor deviation of all technical replicates and biological donors. TFs enriched in each cluster are shown to the right. Color scale represents the minimum and maximum of each row. Each row represents an individual TF motif. Each column represents an individual replicate of ATAC-seq using the Omni-ATAC protocol.
11 Supplementary Figure 7
12 GWAS analysis of ATAC-seq data from different brain regions provides key insights into the ontogeny of various brain diseases. (a) Box plot of the minimum empirical p value from all brain regions for each GWAS SNP set assayed. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired students t-test. (b) Significance of enrichment of disease-specific GWAS polymorphisms in the uniquely-accessible regions of the 5 different brain regions shown in Fig. 2b. The empirical p value is depicted colorimetrically with reference to association-based permutations of the GWAS SNPs. (c) Heatmap representation of the enrichment (left) and significance (right) of the enrichment of GWAS SNPs in the uniquely-accessible regions of each brain region. For enrichment, 0 values are represented colorimetrically the same as a log2(enrichment) of -3. Regions without significant associations are shown as white in the p value heatmap.
13 Supplementary Figure 8
14 The Omni-ATAC protocol enables generation of robust ATAC-seq data from 50-µm-thick frozen tissue sections. (a) Depth-normalized sequencing tracks surrounding amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease-associated SNP rs Tracks were normalized according to the total number of reads in peaks. Each individual replicate (N=4 technical replicates for each of 2 donors per tissue fragment, N=1 technical replicate for each of 2 donors for corpus callosum sections, and N=2 technical replicates for each of 2 donors for cerebellum sections) is displayed with 25% transparency to show consistency among technical replicates and biological donors. Region shown represents chr15:92,390,775-92,470,760. Data derived from 20 mg tissue fragments and 50 µm tissue sections are represented by a cartoon image to the right. (b-d) Depth normalized sequencing tracks from all replicates from all regions comparing ATAC-seq data generated using the Omni-ATAC protocol in 50 µm tissue sections and larger 20 mg tissue fragments. Each individual replicate (N=4 technical replicates for each of 2 donors per tissue fragment, N=1 technical replicate for each of 2 donors for corpus callosum sections, and N=2 technical replicates for each of 2 donors for cerebellum sections) is displayed with 25% transparency to show consistency among technical replicates and biological donors. Regions shown represent (c) chr2:182,378, ,585,768, (d) chr21:34,391,306-34,455,298, and (e) chr22:38,347,790-38,398,955. (e-f) Correlation of ATAC-seq data from 50 µm sections of (f) corpus callosum or (g) cerebellum with ATAC-seq data generated from a nearby 20 mg fragment of the same brain region from the same donor. Each dot represents an individual peak from a union set of peaks called from all technical replicates and biological donors of data derived from tissue fragments from the same brain region. Only 50,000 random peaks with more than 5 reads are shown. (g) Histology and immunohistochemistry of 5 µm frozen sections from cerebellum and corpus callosum immediately adjacent to the 50 µm section used for ATAC-seq shown in Figure 2d-e. Stains from left to right: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Nissl. Scale bar represents 100 µm in each image.
15
16 Supplementary Figure 9 Histology of tissue immediately adjacent to a 50-µm section used for ATAC-seq. (a,e) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of corpus callosum and cerebellum. Scale bar represents 1 mm. (b,f) Nissl staining of corpus callosum and cerebellum. Scale bar represents 1 mm. (c,g) Anti-NEUN immunohistochemistry of corpus callosum and cerebellum. Scale bar represents 1 mm. (d,h) Anti-SOX10 immunohistochemistry of corpus callosum and cerebellum. Scale bar represents 100 µm. All images represent same tissue shown in Figure 2d.
17 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1 ATAC-seq Quality Assessment Cumulative experience has demonstrated that the original ATAC-seq method performs suboptimally on certain cell types and cell contexts. The primary metrics used to determine the quality of ATAC-seq data are (i) enrichment of signal at transcriptional start sites (TSSs), (ii) a low percentage of reads mapping to non-chromatinized mitochondrial DNA, (iii) high library complexity, and (iv) an insert size distribution that follows a nucleosomal spacing periodicity. In this work, we also use the fraction of reads in peaks as a measure of data quality; however, we note that this requires a priori knowledge of peak locations and is correlated with the TSS enrichment score. We also note that the value of the TSS enrichment score is dependent on the set of TSSs that is used. We have chosen to use RefSeq-defined TSSs as downloaded from the UCSC Genome Browser. Rationale and Efficacy of Chosen Optimizations The individual optimizations made to the original ATAC-seq protocol that comprise the Omni- ATAC protocol are as follows: (1) The addition of 0.1% Tween-20 and 0.01% digitonin to the NP40-based lysis buffer (2) Washing lysed cells in a resuspension buffer containing 0.1% Tween-20 (3) The addition of PBS, 0.1% Tween-20, and 0.01% digitonin to the transposition mix These optimizations were rationally designed to improve the overall quality (as described above) of the ATAC-seq data and improve the breadth of applications to which ATAC-seq can be applied without individualized protocol alterations. The addition of Tween-20 and digitonin to the NP40-based lysis buffer (i) leads to a reduction in mitochondrial reads and an increase in library complexity and (ii) enables lysis in a wider array of cell types. Washing of lysed cells in resuspension buffer containing Tween-20 on its own does not improve data quality, but in the context of lysis with Tween-20, digitonin, and NP40, further increases the library complexity and further reduces reads from mitochondrial DNA. The addition of PBS to the transposition reaction on its own increases the enrichment of signal at TSSs by 48% on average (Supplementary Fig. 1a). Collectively, these optimizations (i) improve ATAC-seq data quality in cell types and cell contexts that were already tractable with the standard ATAC-seq protocol and (ii) make ATAC-seq possible in cell types and cell contexts that were not possible with the standard ATAC-seq protocol. Decreasing Transposase Concentration in the ATAC-seq Reaction We have found that the amount of Tn5 transposase added per ATAC-seq reaction can be reduced without changes in data quality. Titration of Tn5 input from 100 nm to 10 nm in mouse embryonic stem cells (mescs) showed no appreciable change in fragment enrichment at open chromatin or total fragment yield, except in the lowest Tn5 concentration of 10 nm, which shows a reduction in library size (Supplementary Fig. 5a-e and Supplementary Table 1). Thus, the Omni-ATAC protocol can provide high-quality ATAC-seq data with a reduced per-reaction cost. However, we note that this was performed using homemade Tn5 transposase that may have different properties than Tn5 transposase purchased from Illumina. Additionally, transposase requirements may vary between different cell types and we have only tested mouse embryonic stem cells here. Aside from
18 Supplementary Fig. 5, all ATAC-seq reactions performed in this manuscript used the standard 2.5 µl Tn5 transposase per 50 µl ATAC-seq reaction. We encourage users to test the result of reducing Tn5 transposase concentration in their system of interest.
Supplementary Table 1: Oligo designs. A list of ATAC-seq oligos used for PCR.
 Ad1_noMX: Ad2.1_TAAGGCGA Ad2.2_CGTACTAG Ad2.3_AGGCAGAA Ad2.4_TCCTGAGC Ad2.5_GGACTCCT Ad2.6_TAGGCATG Ad2.7_CTCTCTAC Ad2.8_CAGAGAGG Ad2.9_GCTACGCT Ad2.10_CGAGGCTG Ad2.11_AAGAGGCA Ad2.12_GTAGAGGA Ad2.13_GTCGTGAT
Ad1_noMX: Ad2.1_TAAGGCGA Ad2.2_CGTACTAG Ad2.3_AGGCAGAA Ad2.4_TCCTGAGC Ad2.5_GGACTCCT Ad2.6_TAGGCATG Ad2.7_CTCTCTAC Ad2.8_CAGAGAGG Ad2.9_GCTACGCT Ad2.10_CGAGGCTG Ad2.11_AAGAGGCA Ad2.12_GTAGAGGA Ad2.13_GTCGTGAT
Supplementary Figure 1. HiChIP provides confident 1D factor binding information.
 Supplementary Figure 1 HiChIP provides confident 1D factor binding information. a, Reads supporting contacts called using the Mango pipeline 19 for GM12878 Smc1a HiChIP and GM12878 CTCF Advanced ChIA-PET
Supplementary Figure 1 HiChIP provides confident 1D factor binding information. a, Reads supporting contacts called using the Mango pipeline 19 for GM12878 Smc1a HiChIP and GM12878 CTCF Advanced ChIA-PET
Introduction to genome biology
 Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs We ve found most genes; but what about the rest of the genome? Genome size* 12 Mb 95 Mb 170 Mb 1500 Mb 2700 Mb 3200 Mb #coding genes ~7000 ~20000 ~14000 ~26000
Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs We ve found most genes; but what about the rest of the genome? Genome size* 12 Mb 95 Mb 170 Mb 1500 Mb 2700 Mb 3200 Mb #coding genes ~7000 ~20000 ~14000 ~26000
Green Center Computational Core ChIP- Seq Pipeline, Just a Click Away
 Green Center Computational Core ChIP- Seq Pipeline, Just a Click Away Venkat Malladi Computational Biologist Computational Core Cecil H. and Ida Green Center for Reproductive Biology Science Introduc
Green Center Computational Core ChIP- Seq Pipeline, Just a Click Away Venkat Malladi Computational Biologist Computational Core Cecil H. and Ida Green Center for Reproductive Biology Science Introduc
Chromosome-scale scaffolding of de novo genome assemblies based on chromatin interactions. Supplementary Material
 Chromosome-scale scaffolding of de novo genome assemblies based on chromatin interactions Joshua N. Burton 1, Andrew Adey 1, Rupali P. Patwardhan 1, Ruolan Qiu 1, Jacob O. Kitzman 1, Jay Shendure 1 1 Department
Chromosome-scale scaffolding of de novo genome assemblies based on chromatin interactions Joshua N. Burton 1, Andrew Adey 1, Rupali P. Patwardhan 1, Ruolan Qiu 1, Jacob O. Kitzman 1, Jay Shendure 1 1 Department
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Processing of mutations and generation of simulated controls. On the left, a diagram illustrates the manner in which covariate-matched simulated mutations were obtained, filtered
Supplementary Figure 1 Processing of mutations and generation of simulated controls. On the left, a diagram illustrates the manner in which covariate-matched simulated mutations were obtained, filtered
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Retention of RNA with LabelX.
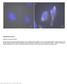 Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
1 Najafabadi, H. S. et al. C2H2 zinc finger proteins greatly expand the human regulatory lexicon. Nat Biotechnol doi: /nbt.3128 (2015).
 F op-scoring motif Optimized motifs E Input sequences entral 1 bp region Dinucleotideshuffled seqs B D ll B1H-R predicted motifs Enriched B1H- R predicted motifs L!=!7! L!=!6! L!=5! L!=!4! L!=!3! L!=!2!
F op-scoring motif Optimized motifs E Input sequences entral 1 bp region Dinucleotideshuffled seqs B D ll B1H-R predicted motifs Enriched B1H- R predicted motifs L!=!7! L!=!6! L!=5! L!=!4! L!=!3! L!=!2!
Supplementary Figure 1
 Nucleotide Content E. coli End. Neb. Tr. End. Neb. Tr. Supplementary Figure 1 Fragmentation Site Profiles CRW1 End. Son. Tr. End. Son. Tr. Human PA1 Position Fragmentation site profiles. Nucleotide content
Nucleotide Content E. coli End. Neb. Tr. End. Neb. Tr. Supplementary Figure 1 Fragmentation Site Profiles CRW1 End. Son. Tr. End. Son. Tr. Human PA1 Position Fragmentation site profiles. Nucleotide content
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2239 Hepatocytes (Endoderm) Foreskin fibroblasts (Mesoderm) Melanocytes (Ectoderm) +Dox rtta TetO CMV O,S,M,K & N H1 hes H7 hes H9 hes H1 hes-derived EBs H7 hes-derived EBs H9 hes-derived
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2239 Hepatocytes (Endoderm) Foreskin fibroblasts (Mesoderm) Melanocytes (Ectoderm) +Dox rtta TetO CMV O,S,M,K & N H1 hes H7 hes H9 hes H1 hes-derived EBs H7 hes-derived EBs H9 hes-derived
The ENCODE Encyclopedia. & Variant Annotation Using RegulomeDB and HaploReg
 The ENCODE Encyclopedia & Variant Annotation Using RegulomeDB and HaploReg Jill E. Moore Weng Lab University of Massachusetts Medical School October 10, 2015 Where s the Encyclopedia? ENCODE: Encyclopedia
The ENCODE Encyclopedia & Variant Annotation Using RegulomeDB and HaploReg Jill E. Moore Weng Lab University of Massachusetts Medical School October 10, 2015 Where s the Encyclopedia? ENCODE: Encyclopedia
The ChIP-Seq project. Giovanna Ambrosini, Philipp Bucher. April 19, 2010 Lausanne. EPFL-SV Bucher Group
 The ChIP-Seq project Giovanna Ambrosini, Philipp Bucher EPFL-SV Bucher Group April 19, 2010 Lausanne Overview Focus on technical aspects Description of applications (C programs) Where to find binaries,
The ChIP-Seq project Giovanna Ambrosini, Philipp Bucher EPFL-SV Bucher Group April 19, 2010 Lausanne Overview Focus on technical aspects Description of applications (C programs) Where to find binaries,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Origin use and efficiency are similar among WT, rrm3, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2; rrm3 strains. A. Analysis of fork progression around confirmed and likely origins (from cerevisiae.oridb.org).
Supplementary Figure 1 Origin use and efficiency are similar among WT, rrm3, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2; rrm3 strains. A. Analysis of fork progression around confirmed and likely origins (from cerevisiae.oridb.org).
Myers Lab ChIP-seq Protocol v Modified January 10, 2014
 Myers Lab ChIP-seq Protocol V011014 1 Contact information: Dr. Florencia Pauli Behn HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology 601 Genome Way Huntsville, AL 35806 Telephone: 256-327-5229 Email: fpauli@hudsonalpha.org
Myers Lab ChIP-seq Protocol V011014 1 Contact information: Dr. Florencia Pauli Behn HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology 601 Genome Way Huntsville, AL 35806 Telephone: 256-327-5229 Email: fpauli@hudsonalpha.org
PIP-seq. Cells. Permanganate ChIP-Seq
 PIP-seq ells Formaldehyde Permanganate 5 Harvest Lyse Sonicate First dapter Ligation 3 3 5 hip Elute Reverse rosslinks Piperidine cleavage 5 3 3 5 Primer Extension Second dapter Ligation 5 3 3 5 Deep Sequencing
PIP-seq ells Formaldehyde Permanganate 5 Harvest Lyse Sonicate First dapter Ligation 3 3 5 hip Elute Reverse rosslinks Piperidine cleavage 5 3 3 5 Primer Extension Second dapter Ligation 5 3 3 5 Deep Sequencing
From Variants to Pathways: Agilent GeneSpring GX s Variant Analysis Workflow
 From Variants to Pathways: Agilent GeneSpring GX s Variant Analysis Workflow Technical Overview Import VCF Introduction Next-generation sequencing (NGS) studies have created unanticipated challenges with
From Variants to Pathways: Agilent GeneSpring GX s Variant Analysis Workflow Technical Overview Import VCF Introduction Next-generation sequencing (NGS) studies have created unanticipated challenges with
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna
 Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Data and Metadata Models Recommendations Version 1.2 Developed by the IHEC Metadata Standards Workgroup
 Data and Metadata Models Recommendations Version 1.2 Developed by the IHEC Metadata Standards Workgroup 1. Introduction The data produced by IHEC is illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. The space of epigenomic
Data and Metadata Models Recommendations Version 1.2 Developed by the IHEC Metadata Standards Workgroup 1. Introduction The data produced by IHEC is illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. The space of epigenomic
Applying Immunohistochemistry & Reverse Transcription PCR to Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Animal Model
 Applying Immunohistochemistry & Reverse Transcription PCR to Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Animal Model Sprague Dawley Rat (Rattus norvegicus ) Olga Paley Working with: Professor Dawn Elliott
Applying Immunohistochemistry & Reverse Transcription PCR to Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in an Animal Model Sprague Dawley Rat (Rattus norvegicus ) Olga Paley Working with: Professor Dawn Elliott
RIPTIDE HIGH THROUGHPUT RAPID LIBRARY PREP (HT-RLP)
 Application Note: RIPTIDE HIGH THROUGHPUT RAPID LIBRARY PREP (HT-RLP) Introduction: Innovations in DNA sequencing during the 21st century have revolutionized our ability to obtain nucleotide information
Application Note: RIPTIDE HIGH THROUGHPUT RAPID LIBRARY PREP (HT-RLP) Introduction: Innovations in DNA sequencing during the 21st century have revolutionized our ability to obtain nucleotide information
Quality Measures for CytoChip Microarrays
 Quality Measures for CytoChip Microarrays How to evaluate CytoChip Oligo data quality in BlueFuse Multi software. Data quality is one of the most important aspects of any microarray experiment. This technical
Quality Measures for CytoChip Microarrays How to evaluate CytoChip Oligo data quality in BlueFuse Multi software. Data quality is one of the most important aspects of any microarray experiment. This technical
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Quality Control Assessment in Genotyping Console
 Quality Control Assessment in Genotyping Console Introduction Prior to the release of Genotyping Console (GTC) 2.1, quality control (QC) assessment of the SNP Array 6.0 assay was performed using the Dynamic
Quality Control Assessment in Genotyping Console Introduction Prior to the release of Genotyping Console (GTC) 2.1, quality control (QC) assessment of the SNP Array 6.0 assay was performed using the Dynamic
Simultaneous profiling of transcriptome and DNA methylome from a single cell
 Additional file 1: Supplementary materials Simultaneous profiling of transcriptome and DNA methylome from a single cell Youjin Hu 1, 2, Kevin Huang 1, 3, Qin An 1, Guizhen Du 1, Ganlu Hu 2, Jinfeng Xue
Additional file 1: Supplementary materials Simultaneous profiling of transcriptome and DNA methylome from a single cell Youjin Hu 1, 2, Kevin Huang 1, 3, Qin An 1, Guizhen Du 1, Ganlu Hu 2, Jinfeng Xue
Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Illumina RNA- Seq Data. Ryan Peters Field Application Specialist
 Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Illumina RNA- Seq Data Ryan Peters Field Application Specialist Partek GS in your NGS Pipeline Your Start-to-Finish Solution for Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data
Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Illumina RNA- Seq Data Ryan Peters Field Application Specialist Partek GS in your NGS Pipeline Your Start-to-Finish Solution for Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data
Analysis of a Tiling Regulation Study in Partek Genomics Suite 6.6
 Analysis of a Tiling Regulation Study in Partek Genomics Suite 6.6 The example data set used in this tutorial consists of 6 technical replicates from the same human cell line, 3 are SP1 treated, and 3
Analysis of a Tiling Regulation Study in Partek Genomics Suite 6.6 The example data set used in this tutorial consists of 6 technical replicates from the same human cell line, 3 are SP1 treated, and 3
Supplementary Data for DNA sequence+shape kernel enables alignment-free modeling of transcription factor binding.
 Supplementary Data for DNA sequence+shape kernel enables alignment-free modeling of transcription factor binding. Wenxiu Ma 1, Lin Yang 2, Remo Rohs 2, and William Stafford Noble 3 1 Department of Statistics,
Supplementary Data for DNA sequence+shape kernel enables alignment-free modeling of transcription factor binding. Wenxiu Ma 1, Lin Yang 2, Remo Rohs 2, and William Stafford Noble 3 1 Department of Statistics,
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis. J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday 15 June 2015
 ChIP-Seq Data Analysis J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday 15 June 2015 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind DNA
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday 15 June 2015 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind DNA
Gap hunting to characterize clustered probe signals in Illumina methylation array data
 DOI 10.1186/s13072-016-0107-z Epigenetics & Chromatin RESEARCH Gap hunting to characterize clustered probe signals in Illumina methylation array data Shan V. Andrews 1,2, Christine Ladd Acosta 1,2,3, Andrew
DOI 10.1186/s13072-016-0107-z Epigenetics & Chromatin RESEARCH Gap hunting to characterize clustered probe signals in Illumina methylation array data Shan V. Andrews 1,2, Christine Ladd Acosta 1,2,3, Andrew
Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human. cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis. Supplementary Information
 Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis in HeLa S3 cells Liang Wu 1, Xiaolong Zhang 1,2, Zhikun Zhao 1,3,4, Ling Wang 5, Bo
Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis in HeLa S3 cells Liang Wu 1, Xiaolong Zhang 1,2, Zhikun Zhao 1,3,4, Ling Wang 5, Bo
Assay Standards Working Group Nov 2012 Assay Standards Working Group Recommendations, November 2012
 Assay Standards Working Group Recommendations, November 2012 Contents Assay Standards Working Group Recommendations, August 2012... 1 Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 1: Reference Epigenome Criteria...
Assay Standards Working Group Recommendations, November 2012 Contents Assay Standards Working Group Recommendations, August 2012... 1 Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 1: Reference Epigenome Criteria...
Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology
 STUDY DESIGNS Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology Clifford A. Meyer and X. Shirley Liu Abstract Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have
STUDY DESIGNS Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology Clifford A. Meyer and X. Shirley Liu Abstract Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have
B&DA Committee Bioinformatics and Data Analysis. PAG January 2016
 B&DA Committee Bioinformatics and Data Analysis PAG January 2016 B&DA progress so far Aim: to define standard bfx pipelines for FAANG data Group has skyped many times We have a Wiki: hosted by EBI Sub-groups
B&DA Committee Bioinformatics and Data Analysis PAG January 2016 B&DA progress so far Aim: to define standard bfx pipelines for FAANG data Group has skyped many times We have a Wiki: hosted by EBI Sub-groups
Impact of gdna Integrity on the Outcome of DNA Methylation Studies
 Impact of gdna Integrity on the Outcome of DNA Methylation Studies Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Authors Emily Putnam, Keith Booher, and Xueguang Sun Zymo Research Corporation, Irvine, CA, USA
Impact of gdna Integrity on the Outcome of DNA Methylation Studies Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Authors Emily Putnam, Keith Booher, and Xueguang Sun Zymo Research Corporation, Irvine, CA, USA
Figure S1. Unrearranged locus. Rearranged locus. Concordant read pairs. Region1. Region2. Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle
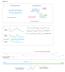 Figure S1 a Unrearranged locus Rearranged locus Concordant read pairs Region1 Concordant read pairs Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle Region2 Concordant read pairs b Physical coverage 5 4 3 2 1
Figure S1 a Unrearranged locus Rearranged locus Concordant read pairs Region1 Concordant read pairs Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle Region2 Concordant read pairs b Physical coverage 5 4 3 2 1
Validation Study of FUJIFILM QuickGene System for Affymetrix GeneChip
 Validation Study of FUJIFILM QuickGene System for Affymetrix GeneChip Reproducibility of Extraction of Genomic DNA from Whole Blood samples in EDTA using FUJIFILM membrane technology on the QuickGene-810
Validation Study of FUJIFILM QuickGene System for Affymetrix GeneChip Reproducibility of Extraction of Genomic DNA from Whole Blood samples in EDTA using FUJIFILM membrane technology on the QuickGene-810
Perm-seq: Mapping Protein-DNA Interactions in Segmental Duplication and Highly Repetitive Regions of Genomes with Prior- Enhanced Read Mapping
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Perm-seq: Mapping Protein-DNA Interactions in Segmental Duplication and Highly Repetitive Regions of Genomes with Prior- Enhanced Read Mapping Xin Zeng 1,BoLi 2, Rene Welch 1, Constanza
RESEARCH ARTICLE Perm-seq: Mapping Protein-DNA Interactions in Segmental Duplication and Highly Repetitive Regions of Genomes with Prior- Enhanced Read Mapping Xin Zeng 1,BoLi 2, Rene Welch 1, Constanza
Base Composition of Sequencing Reads of Chromium Single Cell 3 v2 Libraries
 TECHNICAL NOTE Base Composition of Sequencing Reads of Chromium Single Cell 3 v2 Libraries INTRODUCTION The Chromium Single Cell 3 v2 Protocol (CG00052) produces Single Cell 3 libraries, ready for Illumina
TECHNICAL NOTE Base Composition of Sequencing Reads of Chromium Single Cell 3 v2 Libraries INTRODUCTION The Chromium Single Cell 3 v2 Protocol (CG00052) produces Single Cell 3 libraries, ready for Illumina
High-yield, Scalable Library Preparation with the NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit
 be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE TECHNICAL NOTE High-yield, Scalable Library Preparation with the NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit Improving performance, ease of use and reliability of
be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE TECHNICAL NOTE High-yield, Scalable Library Preparation with the NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit Improving performance, ease of use and reliability of
You use the UCSC Genome Browser (www.genome.ucsc.edu) to assess the exonintron structure of each gene. You use four tracks to show each gene:
 CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Part 1: You would like to rapidly generate two different knockout mice using CRISPR-Cas9. The genes to be knocked out are Pcsk9 and Apoc3, both involved in lipid metabolism.
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Part 1: You would like to rapidly generate two different knockout mice using CRISPR-Cas9. The genes to be knocked out are Pcsk9 and Apoc3, both involved in lipid metabolism.
Nextera DNA Sample Prep Kit
 Nextera DNA Sample Prep Kit (Roche FLX-compatible) Cat. Nos. FL09115, FL091120, and FLBC0950 * Covered by patents issued and pending. Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook
Nextera DNA Sample Prep Kit (Roche FLX-compatible) Cat. Nos. FL09115, FL091120, and FLBC0950 * Covered by patents issued and pending. Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
Complete Sample to Analysis Solutions for DNA Methylation Discovery using Next Generation Sequencing
 Complete Sample to Analysis Solutions for DNA Methylation Discovery using Next Generation Sequencing SureSelect Human/Mouse Methyl-Seq Kyeong Jeong PhD February 5, 2013 CAG EMEAI DGG/GSD/GFO Agilent Restricted
Complete Sample to Analysis Solutions for DNA Methylation Discovery using Next Generation Sequencing SureSelect Human/Mouse Methyl-Seq Kyeong Jeong PhD February 5, 2013 CAG EMEAI DGG/GSD/GFO Agilent Restricted
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit
 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Human Granulin / GRN / Progranulin ELISA Pair Set
 Human Granulin / GRN / Progranulin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEKA10826 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Granulin / GRN / Progranulin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEKA10826 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Mouse ICAM-1 / CD54 ELISA Pair Set
 Mouse ICAM-1 / CD54 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK50440 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the General
Mouse ICAM-1 / CD54 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK50440 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the General
Incorporating Molecular ID Technology. Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits
 Incorporating Molecular ID Technology Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits Molecular Identifiers (MIDs) MIDs are indices used to label unique library molecules MIDs can assess duplicate molecules in sequencing
Incorporating Molecular ID Technology Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits Molecular Identifiers (MIDs) MIDs are indices used to label unique library molecules MIDs can assess duplicate molecules in sequencing
SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC.
 TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
ChIP-seq/Functional Genomics/Epigenomics. CBSU/3CPG/CVG Next-Gen Sequencing Workshop. Josh Waterfall. March 31, 2010
 ChIP-seq/Functional Genomics/Epigenomics CBSU/3CPG/CVG Next-Gen Sequencing Workshop Josh Waterfall March 31, 2010 Outline Introduction to ChIP-seq Control data sets Peak/enriched region identification
ChIP-seq/Functional Genomics/Epigenomics CBSU/3CPG/CVG Next-Gen Sequencing Workshop Josh Waterfall March 31, 2010 Outline Introduction to ChIP-seq Control data sets Peak/enriched region identification
A comprehensive assessment of RNA-seq accuracy, reproducibility and information content by the Sequencing Quality Control Consortium
 A comprehensive assessment of RNA-seq accuracy, reproducibility and information content by the Sequencing Quality Control Consortium SEQC/MAQC-III Consortium* 214 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
A comprehensive assessment of RNA-seq accuracy, reproducibility and information content by the Sequencing Quality Control Consortium SEQC/MAQC-III Consortium* 214 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ho et al. 1.173/pnas.81288816 SI Methods Sequences of shrna hairpins: Brg shrna #1: ccggcggctcaagaaggaagttgaactcgagttcaacttccttcttgacgnttttg (TRCN71383; Open Biosystems). Brg shrna
Supporting Information Ho et al. 1.173/pnas.81288816 SI Methods Sequences of shrna hairpins: Brg shrna #1: ccggcggctcaagaaggaagttgaactcgagttcaacttccttcttgacgnttttg (TRCN71383; Open Biosystems). Brg shrna
Chapter 1 Analysis of ChIP-Seq Data with Partek Genomics Suite 6.6
 Chapter 1 Analysis of ChIP-Seq Data with Partek Genomics Suite 6.6 Overview ChIP-Sequencing technology (ChIP-Seq) uses high-throughput DNA sequencing to map protein-dna interactions across the entire genome.
Chapter 1 Analysis of ChIP-Seq Data with Partek Genomics Suite 6.6 Overview ChIP-Sequencing technology (ChIP-Seq) uses high-throughput DNA sequencing to map protein-dna interactions across the entire genome.
Introduction to ChIP Seq data analyses. Acknowledgement: slides taken from Dr. H
 Introduction to ChIP Seq data analyses Acknowledgement: slides taken from Dr. H Wu @Emory ChIP seq: Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation it ti + sequencing Same biological motivation as ChIP chip: measure specific
Introduction to ChIP Seq data analyses Acknowledgement: slides taken from Dr. H Wu @Emory ChIP seq: Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation it ti + sequencing Same biological motivation as ChIP chip: measure specific
For the rapid isolation of Mitochondrial DNA in various cell and tissue samples.
 ab65321 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid isolation of Mitochondrial DNA in various cell and tissue samples. This product is for research use only and is not intended for
ab65321 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid isolation of Mitochondrial DNA in various cell and tissue samples. This product is for research use only and is not intended for
IQFISH on Dako Omnis. Panel for Lung Cancer. Dako FAST RESULTS. ALK, ROS1, RET and MET IQFISH. Dako Omnis. Agilent Pathology Solutions
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Dako Omnis ALK, ROS1, RET and MET IQFISH Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH on Dako Omnis Panel for Lung Cancer FAST RESULTS Fast, high-quality FISH Integrated into your IHC workflow
PRODUCT INFORMATION Dako Omnis ALK, ROS1, RET and MET IQFISH Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH on Dako Omnis Panel for Lung Cancer FAST RESULTS Fast, high-quality FISH Integrated into your IHC workflow
SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for Illumina Sequencing Two powerful technologies combine to enable sequencing with ultra-low levels of RNA
 SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for Illumina Sequencing Two powerful technologies combine to enable sequencing with ultra-low levels of RNA The most sensitive cdna synthesis technology, combined with next-generation
SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for Illumina Sequencing Two powerful technologies combine to enable sequencing with ultra-low levels of RNA The most sensitive cdna synthesis technology, combined with next-generation
Precise quantification of Ion Torrent libraries on the QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System
 APPLICATION NOTE QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System Precise quantification of Ion Torrent libraries on the QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System Introduction The template preparation step in the next-generation
APPLICATION NOTE QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System Precise quantification of Ion Torrent libraries on the QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System Introduction The template preparation step in the next-generation
RNA-Sequencing analysis
 RNA-Sequencing analysis Markus Kreuz 25. 04. 2012 Institut für Medizinische Informatik, Statistik und Epidemiologie Content: Biological background Overview transcriptomics RNA-Seq RNA-Seq technology Challenges
RNA-Sequencing analysis Markus Kreuz 25. 04. 2012 Institut für Medizinische Informatik, Statistik und Epidemiologie Content: Biological background Overview transcriptomics RNA-Seq RNA-Seq technology Challenges
Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene
 SUPPLEMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Some HPr-1AR ARE-containing Genes Are Unresponsive to Androgen Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene specific. For
SUPPLEMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Some HPr-1AR ARE-containing Genes Are Unresponsive to Androgen Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene specific. For
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of DHS STARR-seq in the P5424 cell line.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DHS STARR-seq in the P5424 cell line. (a) Luciferase enhancer assays of proximal DHSs defined as active or inactive enhancers by STARR-seq in P5424 cells. For each candidate,
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DHS STARR-seq in the P5424 cell line. (a) Luciferase enhancer assays of proximal DHSs defined as active or inactive enhancers by STARR-seq in P5424 cells. For each candidate,
Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde
 Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
PeakSeq enables systematic scoring of ChIP-seq experiments relative to controls
 PeakSeq enables systematic scoring of ChIP-seq experiments relative to controls Joel Rozowsky, Ghia Euskirchen 2, Raymond K Auerbach 3, Zhengdong D Zhang, Theodore Gibson, Robert Bjornson 4, Nicholas Carriero
PeakSeq enables systematic scoring of ChIP-seq experiments relative to controls Joel Rozowsky, Ghia Euskirchen 2, Raymond K Auerbach 3, Zhengdong D Zhang, Theodore Gibson, Robert Bjornson 4, Nicholas Carriero
Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures
 Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures Table S1. Summary of 16 SNP tagged loci from the combined 50K and 250K MSNP screens with independently validated ASM. PBL, total peripheral blood leukocytes;
Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures Table S1. Summary of 16 SNP tagged loci from the combined 50K and 250K MSNP screens with independently validated ASM. PBL, total peripheral blood leukocytes;
Analysis of Microarray Data
 Analysis of Microarray Data Lecture 3: Visualization and Functional Analysis George Bell, Ph.D. Senior Bioinformatics Scientist Bioinformatics and Research Computing Whitehead Institute Outline Review
Analysis of Microarray Data Lecture 3: Visualization and Functional Analysis George Bell, Ph.D. Senior Bioinformatics Scientist Bioinformatics and Research Computing Whitehead Institute Outline Review
CS273B: Deep Learning in Genomics and Biomedicine. Recitation 1 30/9/2016
 CS273B: Deep Learning in Genomics and Biomedicine. Recitation 1 30/9/2016 Topics Genetic variation Population structure Linkage disequilibrium Natural disease variants Genome Wide Association Studies Gene
CS273B: Deep Learning in Genomics and Biomedicine. Recitation 1 30/9/2016 Topics Genetic variation Population structure Linkage disequilibrium Natural disease variants Genome Wide Association Studies Gene
Different Potential of Extracellular Vesicles to Support Thrombin Generation: Contributions of Phosphatidylserine, Tissue Factor, and Cellular Origin
 Different Potential of Extracellular Vesicles to Support Thrombin Generation: Contributions of Phosphatidylserine, Tissue Factor, and Cellular Origin Carla Tripisciano 1, René Weiss 1, Tanja Eichhorn 1,
Different Potential of Extracellular Vesicles to Support Thrombin Generation: Contributions of Phosphatidylserine, Tissue Factor, and Cellular Origin Carla Tripisciano 1, René Weiss 1, Tanja Eichhorn 1,
Agilent Genomic Workbench 7.0
 Agilent Genomic Workbench 7.0 Product Overview Guide Agilent Technologies Notices Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2012, 2015 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic
Agilent Genomic Workbench 7.0 Product Overview Guide Agilent Technologies Notices Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2012, 2015 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic
New Statistical Algorithms for Monitoring Gene Expression on GeneChip Probe Arrays
 GENE EXPRESSION MONITORING TECHNICAL NOTE New Statistical Algorithms for Monitoring Gene Expression on GeneChip Probe Arrays Introduction Affymetrix has designed new algorithms for monitoring GeneChip
GENE EXPRESSION MONITORING TECHNICAL NOTE New Statistical Algorithms for Monitoring Gene Expression on GeneChip Probe Arrays Introduction Affymetrix has designed new algorithms for monitoring GeneChip
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Fluorometric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA1539 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA1539 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Supplemental Information. Antagonistic Activities of Sox2. and Brachyury Control the Fate Choice. of Neuro-Mesodermal Progenitors
 Developmental Cell, Volume 42 Supplemental Information Antagonistic Activities of Sox2 and Brachyury Control the Fate Choice of Neuro-Mesodermal Progenitors Frederic Koch, Manuela Scholze, Lars Wittler,
Developmental Cell, Volume 42 Supplemental Information Antagonistic Activities of Sox2 and Brachyury Control the Fate Choice of Neuro-Mesodermal Progenitors Frederic Koch, Manuela Scholze, Lars Wittler,
Leveraging biological replicates to improve analysis in ChIP-seq experiments
 , http://dx.doi.org/10.5936/csbj.201401002 CSBJ Leveraging biological replicates to improve analysis in ChIP-seq experiments Yajie Yang a,b, Justin Fear a,b, Jianhong Hu c, Irina Haecker d, Lei Zhou a,
, http://dx.doi.org/10.5936/csbj.201401002 CSBJ Leveraging biological replicates to improve analysis in ChIP-seq experiments Yajie Yang a,b, Justin Fear a,b, Jianhong Hu c, Irina Haecker d, Lei Zhou a,
Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1
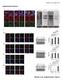 Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Supplement Figure 1. Characterization of the moab. (A) A series of moabs that are anti-hαiib-specific were tested for their ability to bind to
 Supplement Figure 1. Characterization of the 312.8 moab. (A) A series of moabs that are anti-hαiib-specific were tested for their ability to bind to platelets. The black line represents the 312.8 moab
Supplement Figure 1. Characterization of the 312.8 moab. (A) A series of moabs that are anti-hαiib-specific were tested for their ability to bind to platelets. The black line represents the 312.8 moab
2 x 30 mg for 2 x 1.5 ml working solution. 1 x 60 ml (final volume 1 x 200 ml)
 InviMag Blood DNA Mini Kit / KingFisher 96 for extraction of genomic DNA from up to 200 µl of whole blood sample using KingFisher 96 instrument (Thermo Electron) 1 Kit components (storage at room temperature)
InviMag Blood DNA Mini Kit / KingFisher 96 for extraction of genomic DNA from up to 200 µl of whole blood sample using KingFisher 96 instrument (Thermo Electron) 1 Kit components (storage at room temperature)
ab Hypoxic Response Human Flow Cytometry Kit
 ab126585 Hypoxic Response Human Flow Cytometry Kit Instructions for Use For measuring protein levels by flow cytometry: hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A) and BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kda proteininteracting
ab126585 Hypoxic Response Human Flow Cytometry Kit Instructions for Use For measuring protein levels by flow cytometry: hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A) and BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kda proteininteracting
InviMag Forensic Kit / KingFisher 96 for extractions of genomic DNA from forensic samples using KingFisher 96 instrument (Thermo Electron)
 InviMag Forensic Kit / KingFisher 96 for extractions of genomic DNA from forensic samples using KingFisher 96 instrument (Thermo Electron) Kit components (storage at room temperature) Important: Store
InviMag Forensic Kit / KingFisher 96 for extractions of genomic DNA from forensic samples using KingFisher 96 instrument (Thermo Electron) Kit components (storage at room temperature) Important: Store
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
BayesPI-BAR: a new biophysical model for characterization of regulatory sequence variations
 Published online 21 July 2015 Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, Vol. 43, No. 21 e147 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv733 BayesPI-BAR: a new biophysical model for characterization of regulatory sequence variations Junbai
Published online 21 July 2015 Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, Vol. 43, No. 21 e147 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv733 BayesPI-BAR: a new biophysical model for characterization of regulatory sequence variations Junbai
Genomics xxx (2011) xxx xxx. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Genomics. journal homepage:
 YGENO-08338; No. of pages: 11; 4C: 4, 5, 7 Genomics xxx (2011) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Genomics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygeno Distant cis-regulatory
YGENO-08338; No. of pages: 11; 4C: 4, 5, 7 Genomics xxx (2011) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Genomics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygeno Distant cis-regulatory
Supplementary File 3: DNA and RNA isolation
 Supplementary File 3: DNA and RNA isolation Q-CROC-02 Biopsy protocol For the purposes of this protocol, four needle core biopsies (NCBs) of lymph node tissue are isolated from each patient using a 16G
Supplementary File 3: DNA and RNA isolation Q-CROC-02 Biopsy protocol For the purposes of this protocol, four needle core biopsies (NCBs) of lymph node tissue are isolated from each patient using a 16G
What we ll do today. Types of stem cells. Do engineered ips and ES cells have. What genes are special in stem cells?
 Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? What we ll do today Research questions in stem cell biology Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells asuring gene expression
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? What we ll do today Research questions in stem cell biology Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells asuring gene expression
BIO 315 Lab Exam I. Section #: Name:
 Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Lecture 7: April 7, 2005
 Analysis of Gene Expression Data Spring Semester, 2005 Lecture 7: April 7, 2005 Lecturer: R.Shamir and C.Linhart Scribe: A.Mosseri, E.Hirsh and Z.Bronstein 1 7.1 Promoter Analysis 7.1.1 Introduction to
Analysis of Gene Expression Data Spring Semester, 2005 Lecture 7: April 7, 2005 Lecturer: R.Shamir and C.Linhart Scribe: A.Mosseri, E.Hirsh and Z.Bronstein 1 7.1 Promoter Analysis 7.1.1 Introduction to
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Amplification of HEV ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3 genome regions Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl EDTA plasma using Cobas AmpliPrep total nucleic acid isolation kit (Roche,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Amplification of HEV ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3 genome regions Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl EDTA plasma using Cobas AmpliPrep total nucleic acid isolation kit (Roche,
ab Methylated DNA Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
 ab117128 Methylated DNA Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Instructions for Use For the measurement of global DNA methylation status using DNA isolated from any species such as mammalians, plants, fungi,
ab117128 Methylated DNA Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Instructions for Use For the measurement of global DNA methylation status using DNA isolated from any species such as mammalians, plants, fungi,
ChroMoS Guide (version 1.2)
 ChroMoS Guide (version 1.2) Background Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) reveal increasing number of disease-associated SNPs. Since majority of these SNPs are located in intergenic and intronic regions
ChroMoS Guide (version 1.2) Background Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) reveal increasing number of disease-associated SNPs. Since majority of these SNPs are located in intergenic and intronic regions
scgem Workflow Experimental Design Single cell DNA methylation primer design
 scgem Workflow Experimental Design Single cell DNA methylation primer design The scgem DNA methylation assay uses qpcr to measure digestion of target loci by the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease
scgem Workflow Experimental Design Single cell DNA methylation primer design The scgem DNA methylation assay uses qpcr to measure digestion of target loci by the methylation sensitive restriction endonuclease
Gene Signal Estimates from Exon Arrays
 Gene Signal Estimates from Exon Arrays I. Introduction: With exon arrays like the GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST Array, researchers can examine the transcriptional profile of an entire gene (Figure 1). Being
Gene Signal Estimates from Exon Arrays I. Introduction: With exon arrays like the GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST Array, researchers can examine the transcriptional profile of an entire gene (Figure 1). Being
Next Gen Sequencing. Expansion of sequencing technology. Contents
 Next Gen Sequencing Contents 1 Expansion of sequencing technology 2 The Next Generation of Sequencing: High-Throughput Technologies 3 High Throughput Sequencing Applied to Genome Sequencing (TEDed CC BY-NC-ND
Next Gen Sequencing Contents 1 Expansion of sequencing technology 2 The Next Generation of Sequencing: High-Throughput Technologies 3 High Throughput Sequencing Applied to Genome Sequencing (TEDed CC BY-NC-ND
Supplemental File 1: Modified Nextera XT DNA Sample Preparation Guide (Illumina, USA, Part # rev. C, October 2012).
 Supplemental File 1: Modified Nextera XT DNA Sample Preparation Guide (Illumina, USA, Part # 15031942 rev. C, October 2012). Required Kit content: Box1 ATM Amplicon Tagment Mix TD Tagment DNA Buffer NPM
Supplemental File 1: Modified Nextera XT DNA Sample Preparation Guide (Illumina, USA, Part # 15031942 rev. C, October 2012). Required Kit content: Box1 ATM Amplicon Tagment Mix TD Tagment DNA Buffer NPM
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures?
 Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells George Bell, Ph.D. Bioinformatics and Research Computing 2012 Spring Lecture Series
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells George Bell, Ph.D. Bioinformatics and Research Computing 2012 Spring Lecture Series
Mentor: Dr. Bino John
 MAT Shiksha Mantri Mentor: Dr. Bino John Model-based Analysis y of Tiling-arrays g y for ChIP-chip X. Shirley Liu et al., PNAS (2006) vol. 103 no. 33 12457 12462 Tiling Arrays Subtype of microarray chips
MAT Shiksha Mantri Mentor: Dr. Bino John Model-based Analysis y of Tiling-arrays g y for ChIP-chip X. Shirley Liu et al., PNAS (2006) vol. 103 no. 33 12457 12462 Tiling Arrays Subtype of microarray chips
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELL (hesc) ASSESSMENT BY REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR)
 HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELL (hesc) ASSESSMENT BY REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) OBJECTIVE: is performed to analyze gene expression of human Embryonic Stem Cells (hescs) in culture. Real-Time PCR
HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELL (hesc) ASSESSMENT BY REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) OBJECTIVE: is performed to analyze gene expression of human Embryonic Stem Cells (hescs) in culture. Real-Time PCR
1. Paraffin section slides can be stored at room temperature for a long time.
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocols Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocol of Paraffin Section 1. Fix dissected tissues with 10% formalin for no less than 48 hours at room temperature. Inadequately fixation
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocols Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocol of Paraffin Section 1. Fix dissected tissues with 10% formalin for no less than 48 hours at room temperature. Inadequately fixation
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation
 Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
3C bioscience. ProbeSure Genotyping Master Mix User Guide. P a g e 1 ProbeSure User Guide v1.0
 3C bioscience r ProbeSure Genotyping Master Mix User Guide P a g e 1 www.3crbio.com ProbeSure User Guide v1.0 Content: 1. Product details 2. Description 3. Storage and shelf Life 4. Safety warnings and
3C bioscience r ProbeSure Genotyping Master Mix User Guide P a g e 1 www.3crbio.com ProbeSure User Guide v1.0 Content: 1. Product details 2. Description 3. Storage and shelf Life 4. Safety warnings and
