Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD
|
|
|
- Bernard Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August 2009
2 Outline Background Concepts of Eutrophication and Dead-Zones Introduce Features of Chesapeake Bay Describe Hypoxia Patterns in Bay Explain Factors Regulating Hypoxia : Physical Flow, Stratification, Mixing Biological Nutrient Loading Ecological Responses to Hypoxia Concluding Comments Epilogue: Ecosystem Feedbacks and Restoration of Eutrophic Coastal Systems
3 Eutrophication Effects on Coastal Ecosystems Oligotrophic Eutrophic Stratification Dead Zone
4 Global Scale of Eutrophication Harmful Algal Blooms Seagrass Loss Hypoxia/Anoxia
5 Background Information Chesapeake Bay
6 Key Bay Features Large ratio of watershed to estuarine area (= 14:1) Deep, narrow channel is seasonally stratified Broad shallows flank channel (mean z = 6.5m) Most of Bay volume is in the mainstem Most of its surface area in tributaries & embayments Relatively long water residence time (~ 6 mo)
7 Watershed Changes: Land-Use & Population Exponential growth in watershed population Population x a) Human Population Land-use shift from forest to farm (thru 1850) to developed ( ) % of Total Land b) Land-Use Forest Agriculture Developed Year
8 Susquehanna River Flow is Large (Flood Flow At Conowingo Dam)
9 Watershed Changes & Variations: Flow & Fertilizer Large variations in river flow (~4X); wet and dry decades but no long-term trends Fertilizer use in basin has been increasing since 1950, tripling since 1960 Mean Flow m 3 s -1 kg N y -1 x c) Susquehanna Flow Tropical Storm Agnes Wet Drought d) Nitrogen F ertilizer Use Variable wet Year
10 Hypoxia Patterns in Chesapeake Bay
11 Summer Hypoxic Dead-Zone : Clear increasing trend in volume of severely hypoxic (O 2 < 1 mg/l) from Within long-term trend, hypoxia is greater in high flow years (wet = green dot) compared to low flow years (dry = red dot) Summer Low DO Volume (10 9 m 3 ) DO < 1 mg L -1 Wet Year Dry Year 1960 Tropical Storm Agnes Years ( Hagy et al 2004)
12 Location of Bay Hypoxic Zone mg/l Depth (m) /20/ km from Susquehanna River (Hagy 2002)
13 Seasonal Cycle of Algal Productivity, Temperature and Bottom Dissolved O 2 Hypoxia confined to summer (June-September) Hypoxia coincides with peak temperature and productivity
14 Spatial Distribution of Bay Hypoxia: 1959 vs (low flow) Longitudinal sections of summer dissolved oxygen for two years with similar (low flow) freshwater inputs No anoxic conditions in 1959 but large anoxic (dead) zone in summer of 1995 Upper oxic layer was much deeper in 1959 (10-12 m) compared to 1995 (5-10 m)
15 Factors Regulating Hypoxia Physical Factors Ecological Factors
16 Stratification Control of Hypoxia: Position & Intensity of Low O 2 Water Depth (m) Susq. R. MD/VA Atlantic Pycnocline Anoxic DO declines along landward bottom-layer flow
17 Vertical Exchange between Upper & Lower Layers 250 Distance from Atlantic (km) cm d Vertical exchange is minimal in mid-bay from May-August Corresponds to location and duration of hypoxia. How does it vary inter-annually? Month (Hagy 2002)
18 River Flow, Stratification, & Mixing ( ) 12 Stratification Stratification strongly correlated with river flow. cm d rad 2 s Vertical Exchange 1996 Vertical exchange relation to flow is weaker (buoyancy vs. mixing). High flow also delivers more nutrients Winter-Spring River Flow (m 3 s -1 ) (Hagy 2002)
19 Increasing Nitrogen in Susquehanna River: Seasonal and Long-Term Trends Long-term increases in nitrate levels & changes in seasonality seen over five decades Nov Sep Highest nitrate levels (yellow, red) occur in cold months Jul May Nitrate trends are closely related to total Nitrogen N-loads to Bay doubled from 1945 to 1970 Mar Jan (Hagy et al 2004)
20 Hypoxia Response to N Loading ( ): Unexpected Shifts in Ecosystem Processes Hypoxic Volume (10 9 m 3 ) (DO<1 mg l -1 ) Winter-Spring NO - 3 Loading (10 6 kg) Hypoxia increases with N loading. Equivalent N load since 1980 generates more hypoxia than in past. Is system less able to assimilate N-load? No clear explanation for regime shift. (Hagy et al. 2004)
21 Ecological Consequences of Hypoxia & Dead-Zones
22 Summary of Faunal Responses to Hypoxia in Mississippi River Plume (Rabalais et al. 2001)
23 Hypoxia Degrades Habitat for Benthic Fauna in Chesapeake Bay Comparing estuaries worldwide (#1-14), benthic animal abundance tends to be proportional to algal food produced in water Upper and lower Bay generally follow this trend, but hypoxic mid Bay has lower animal biomass than expected Loss of bottom habitat causes loss of important fish and invertebrate animals Macrobenthic Biomass (g AFDW m -2 ) Lower Bay Upper Bay Mid Bay Severe hypoxia Annual Phytoplankton Production (gc m -2 y -1 ) (Hagy 2002, Herman et al. 1999) 1
24 Degraded Bottom Habitats Cause Loss of Benthic Fauna in Hypoxic Regions of Bay With increasing nutrient enrichment and organic production, depth of sediment oxidized zone declines Fauna shift from diverse large deep-burrowing forms to few small surface-dwellers Sediment Profile Photos Conceptual Model Benthic macrofaunal abundance declines markedly Model derived in part from work of by Don Rhoads in LIS Benthic Community Change Disturbance Gradient (Nilsson and Rosenberg 2000)
25 Degraded Bottom Habitats Alter Fish Community Structure and Harvest Steady decrease in the proportion of fisheries harvest from bottomdwelling animals General degradation of bottom habitats in shallow (loss of SAV) and deep (hypoxia) waters Similar trends are being reported in other systems worldwide Possible loss of trophic efficiency (fish harvest per unit photosynthesis) (Houde in Kemp et al 2005)
26 Concluding Comments 1 Coastal eutrophication is a global scale phenomenon Many features of Chesapeake Bay make it susceptible to seasonal development and expansion of hypoxic dead zones Seasonal deep-water hypoxia is generally regulated by stratification and enhanced nutrient loading A dramatic upward shift in the size and intensity of Bay hypoxia occurred in the early 1980s Similar hypoxic regime shifts have been reported elsewhere Hypoxic dead zones result in reduced abundance, diversity and production of benthic invertebrates and demersal fish.
27 Epilogue: Ecosystem Feedbacks and Restoration of Eutrophic Coastal Ecosystems
28 Bottom-Water Hypoxia Enhances Recycling of Benthic Nutrients Benthic nutrient (PO 4 & NH 4 ) recycling sustains algal production and hypoxia thru summer Hypoxia causes higher rates nutrient recycling rates Thus, hypoxia promotes more algal growth per nutrient input to the Bay For N & P recycling, same effect of low O 2 but different mechanisms Benthic DIP-Recycling (Boynton in Kemp et al. 2005) DIN-Recycling Efficiency (Cornwell in Kemp et al. 2005)
29 Seagrass (SAV) Decline: Loss of Particle & Nutrient Trapping Dramatic decline in SAV between 1962 & 1982 throughout the Bay Many factors contributed to decline, but increased nutrients was primary factor Plants (kg m -2 ) Response Nutrient to Nutrient ResponseLoads Plant Epi Phyto Control Low High
30 Excess Nutrients Inhibit SAV Survival But Healthy Beds are Nutrient Sinks Historical Bay SAV beds were capable of removing ~45% of current N Loading Primary pathways of N removal would be trapping particulate N & direct assimilation Calculation only considers mainstem upper (MD) Bay N removal rates would be larger if whole Bay were considered Percent of Total N-Sources Atmosphere Diffuse Sources Point Sources N-Sources Particulate Nitrogen Trapping Plant Uptake N-Sinks (SAV Beds) Denitrification ( Kemp et al 2005)
31 Oyster Decline: Loss of Particle Filtration Decline in oyster abundance has caused loss of nutrient filtration capacity Oyster declines due primarily to overfishing and disease Historic oyster populations were able to filter Bay water volume in days WetMeatWeight(kgx10 6 ) Virginia Maryland Time (days) Days to Filter Maryland's Portion of Chesapeake Bay (Newell 1988) Current oyster populations filter Bay water in months-years Oyster restoration would help mitigate eutrophication effects Time (years) (Kemp et al 2005)
32 Oyster Filtration Effects on Bottom Hypoxia Oyster restoration to meet management mandate (10x), and to estimated precolonial conditions (100x) Dramatic declines in phytoplankton with restoration throughout Bay Small improvements in bottom O 2 with oyster restoration (~ effects of reduced nutrient loading) Phytoplankton Chlorophyll-a Time (days) Days to Filter Maryland's Portion of Chesapeake Bay Dissolved O Restoration improves water clarity (& SAV cover) 10x restoration ~ 50% effect of 100x restoration mid- Bay Large Trib Small Trib Whole Bay mid- Bay Large Trib Small Trib Whole Bay (Cerco and Noel 2007)
33 Tidal Marshes Expanding with Soil Erosion, But Contracting with Sea-Level Rise Tidal marshes are important features of Bay watershed Marsh area expanded since colonial times due to increased soil erosion from watershed Marshes have served as buffers filtering nutrient inputs from watershed Marsh area is declining due to sea level rise and reduced soil erosion Pre-Colonial (hypothetical)
34 Tidal Marshes Serve as Nutrient Filters at Watershed-Estuary Margins Tidal marshes have enormous capacity to filter sediments & nutrients Nitrogen removal capacity measured in experimental marsh ecosystems 80% of N-inputs from land and estuary removed in three year-old marshes Similar effects on N-loading for diverse (brackish) and mono-specific (salt) marshes Marsh restoration would help re-establish lost filtration capacity Nitrogen Removal (% Inputs) Time (years) Brackish (High diversity) Saline (Low diversity)
35 Ecosystem Feedbacks affect Bay Response to Nutrient Management Positive & negative feedbacks control paths of ecosystem change with Bay degradation Among other mechanisms, N & P inputs affect hypoxia & light Hypoxia leads to more nutrients, more algae, & more hypoxia Turbidity leads to less SAV causing more turbidity, less SAV Oysters & marshes tend to reinforce these feedbacks Processes reverse w/ restoration, thus reinforcing trends (Kemp et al. 2005)
36 Concluding Comments 2 Dead-zones are an expanding problem that is linked to coastal eutrophication at global scales Although some systems are more susceptible to hypoxia due to inherent physics, anthropogenic nutrient loading is a key driving factor Restoration of Bays and estuaries worldwide requires reduction in nutrient loading to coastal systems Diverse ecological feedback processes complicate Bay restoration Hypoxia stimulates more algal growth thru enhanced nutrient recycling Loss of SAV, tidal marshes and oyster beds causes reduced natural filtration of nutrients from coastal waters Ecological positive feedbacks reinforce both coastal ecosystem degradation and restoration Thresholds and delayed responses may be expected with loading,
37
38 Fishery Responses to Eutrophication Stages of Fish respond to nutrient enrichment? (1) (2) (3) First: Fishery production increases with nutrients Second: Fishery does not respond to nutrients Third: Fishery production declines with nutrients (Caddy 1993)
39 Volume of Summer Hypoxic Water is Related to River flow and Nitrate Loading, with Regime Shift in Early 1980s Volumes of summer hypoxic (O 2 < 1 mg/l) and anoxic (O 2 < 0.5 mg/l) clearly related to winter-spring river flow Hypoxia vs. River Flow Abrupt increase in slope of time trend from (blue line) to (magenta line). Currently, there is more hypoxia per unit NO 3 Loading Hypoxia vs. NO 3 Loading What factors have contributed to this abrupt regime shift leading to more hypoxia per loading? Positive feedback mechanisms at work? (Hagy et al 2004, Kemp et al 2005)
40 Dissolved O 2 in Low-Flow Years Susquehanna River Atlantic Ocean mg/l Major differences between conditions in 1950s and present are -- increased intensity -- seaward expansion. (Hagy 2002)
41 Dissolved O 2 in High-Flow Years Susquehanna River Atlantic Ocean mg/l Major difference between earlier years and present years is -- seaward expansion -- deeper hypoxic area (Hagy 2002)
42 Oxygen Budget for Mid Bay mg l -1 Average Flow (1990) 21% 79% 34% 66% 56% 44% Vertical Diffusion Net Horizontal Advection
43 Chesapeake Bay System: Watershed area = 116,000 km 2 Water surface area = 11,500 km 2 Land-Use in Watershed: Susquehanna R. (55 % of flow) 58 % 28 % Agriculture Barren Developed Forest Water Wetland
44 Concluding Thoughts Restoration Implications
45 Salinity and O 2 Seasonal and Vertical Distributions (Kemp et al. 1992)
46 Concluding Comments Coastal eutrophication is a global scale problem, and Chesapeake Bay is a system that is inherently susceptible to effects of nutrient enrichment Eutrophication effects first evident 200 years ago, with intense hypoxia and dramatic SAV loss first occurring in the 1950s and 1960s A dramatic upward shift in the hypoxic zone size occurred around 1980, with more hypoxia generated per nutrient loading now compared to past Increased turbidity with eutrophication has caused large reductions in benthic primary production (algal & SAV) Changes in abundance and community composition of demersal fish and benthic invertebrates have occurred in response to bottom habitat losses Human-induced changes of oyster and marshes habitats further stimulate Bay ecosystem response to nutrient enrichment and nutrient abatement Ecological positive feedbacks reinforce both Bay degradation response to nutrient enrichment, and Bay restoration response to nutrient reductions Thresholds and delayed responses may be expected with reduced nutrient loading, but habitat restoration may tend stimulate recovery
Eutrophication. A Synthesis for Scientific Understanding and Management Applications. W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory
 Eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay: A Synthesis for Scientific Understanding and Management Applications W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Work supported by UMCES,
Eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay: A Synthesis for Scientific Understanding and Management Applications W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Work supported by UMCES,
Thresholds in Recovery of Eutrophic Bay Sub-Systems: Five Case-Studies
 Thresholds in Recovery of Eutrophic Bay Sub-Systems: Five Case-Studies W. Michael Kemp, Walter Boynton, and Denise Breitburg University of Maryland CES & SERC (Collaborators: J. Testa, Y. Lee, J. Hagy,
Thresholds in Recovery of Eutrophic Bay Sub-Systems: Five Case-Studies W. Michael Kemp, Walter Boynton, and Denise Breitburg University of Maryland CES & SERC (Collaborators: J. Testa, Y. Lee, J. Hagy,
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014
 Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
Mid-Bay Dissolved Oxygen Trends as a. Function of Nutrient Loads and Strength of Stratification
 Mid-Bay Dissolved Oxygen Trends as a William P. Ball 1, Damian C. Brady 3, Dominic D. DiToro 4, W. Michael Kemp 2, Rebecca R. Murphy 1, Jeremy M. Testa 2 (and others) 1 Dept. of Geography and Environmental
Mid-Bay Dissolved Oxygen Trends as a William P. Ball 1, Damian C. Brady 3, Dominic D. DiToro 4, W. Michael Kemp 2, Rebecca R. Murphy 1, Jeremy M. Testa 2 (and others) 1 Dept. of Geography and Environmental
Chesapeake Bay Nitrogen Assessments
 Chesapeake Bay Nitrogen Assessments May 20, 2010 Workshop on Nitrogen Assessment Science in the USA Thomas E. Jordan Chesapeake Bay Watershed Area=167,000 km 2 Spans 6 states + DC 6 physiographic provinces
Chesapeake Bay Nitrogen Assessments May 20, 2010 Workshop on Nitrogen Assessment Science in the USA Thomas E. Jordan Chesapeake Bay Watershed Area=167,000 km 2 Spans 6 states + DC 6 physiographic provinces
How global warming and climate change may be accelerating losses of Chesapeake Bay seagrasses.
 How global warming and climate change may be accelerating losses of Chesapeake Bay seagrasses. Dr. Ken Moore The Virginia Institute of Marine Science School of Marine Science College of William and Mary
How global warming and climate change may be accelerating losses of Chesapeake Bay seagrasses. Dr. Ken Moore The Virginia Institute of Marine Science School of Marine Science College of William and Mary
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters. Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU
 Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Chesapeake Bay Restora/on Effort
 Chesapeake Bay Restora/on Effort Dave Nemazie Associate VP for External Affairs 15 April 2015 Leadership Maryland A Shallow Bay with a Large Watershed Watershed: 64,000 m 2 Ave Depth: 6 m Max Depth: 50
Chesapeake Bay Restora/on Effort Dave Nemazie Associate VP for External Affairs 15 April 2015 Leadership Maryland A Shallow Bay with a Large Watershed Watershed: 64,000 m 2 Ave Depth: 6 m Max Depth: 50
Implications of global climate change for estuarine & coastal ecosystems (Gulf of Mexico in particular)
 - The cumulative effects of global change, including climate change, increased population, & more intense industrialization & agribusiness, will likely continue & intensify the course of eutrophication
- The cumulative effects of global change, including climate change, increased population, & more intense industrialization & agribusiness, will likely continue & intensify the course of eutrophication
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia
 Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Water Quality Monitoring Stations
 Water Quality Monitoring Stations Eastern Basin Race Narrows Western Basin Central Basin The CT Department of Environmental Protection (CT DEP) conducts a water quality CT DEP monitoring program for the
Water Quality Monitoring Stations Eastern Basin Race Narrows Western Basin Central Basin The CT Department of Environmental Protection (CT DEP) conducts a water quality CT DEP monitoring program for the
Climate Change and Plankton Communities: Disruptions at the Base of the Food Web
 Climate Change and Plankton Communities: Disruptions at the Base of the Food Web Walker O. Smith, Jr. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary With contributions from D. Steinberg,
Climate Change and Plankton Communities: Disruptions at the Base of the Food Web Walker O. Smith, Jr. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary With contributions from D. Steinberg,
SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY
 SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY CENTRAL CASE STUDY: STARVING THE LOUISIANA COAST OF SEDIMENT LOUISIANA IS LOSING 25MI2 OF COASTAL WETLANDS ANNUALLY WETLANDS SUPPORT A DIVERSITY OF
SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY CENTRAL CASE STUDY: STARVING THE LOUISIANA COAST OF SEDIMENT LOUISIANA IS LOSING 25MI2 OF COASTAL WETLANDS ANNUALLY WETLANDS SUPPORT A DIVERSITY OF
CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION. INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico
 CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico SAVING THE BAY Teams of researchers try to pin down what s choking the Chesapeake Water pollution
CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico SAVING THE BAY Teams of researchers try to pin down what s choking the Chesapeake Water pollution
STATE OF THE BAY IN 2012
 9 10 11 STATE OF THE BAY IN 2012 Nitrogen &!Phosphorus Bay-wide nitrogen loads were similar to 2010, but phosphorus loads decreased. These loads are highly elated to river flows and stormwater runoff that
9 10 11 STATE OF THE BAY IN 2012 Nitrogen &!Phosphorus Bay-wide nitrogen loads were similar to 2010, but phosphorus loads decreased. These loads are highly elated to river flows and stormwater runoff that
Nancy Rabalais Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium
 Eutrophication, Coastal Hypoxia, Carbon & Climate Nancy Rabalais Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium nrabalais@lumcon.edu http://www.gulfhypoxia.net Charismatically stressed and dead benthic fauna
Eutrophication, Coastal Hypoxia, Carbon & Climate Nancy Rabalais Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium nrabalais@lumcon.edu http://www.gulfhypoxia.net Charismatically stressed and dead benthic fauna
Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts. SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE
 Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE Introduction Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of the intermediate-depth eastern tropical oceans. Oxygen-poor
Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE Introduction Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of the intermediate-depth eastern tropical oceans. Oxygen-poor
PRESS RELEASE. LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM July 28, Abstract
 PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM July 28, 2013 Abstract The 2013 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 15,120 square kilometers (= 5,800 square miles) in this
PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM July 28, 2013 Abstract The 2013 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 15,120 square kilometers (= 5,800 square miles) in this
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Coastal Ecosystems: Saving Chesapeake Bay. Note the highest pigment concentrations (red) in coastal regions, especially estuaries
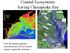 Coastal Ecosystems: Saving Chesapeake Bay Note the highest pigment concentrations (red) in coastal regions, especially estuaries Coastal Ecosystems: human impacts Humans severely impact the coastal zone
Coastal Ecosystems: Saving Chesapeake Bay Note the highest pigment concentrations (red) in coastal regions, especially estuaries Coastal Ecosystems: human impacts Humans severely impact the coastal zone
Finalizing the Chesapeake Bay Health Index (BHI)
 Finalizing the Chesapeake Bay Health Index (BHI) Part 1: Water Quality Index Part 2: Biotic Index Bill Dennison Ben Longstaff, Michael Williams, Claire Buchanan, Roberto Llansó, and Peter Bergstrom On
Finalizing the Chesapeake Bay Health Index (BHI) Part 1: Water Quality Index Part 2: Biotic Index Bill Dennison Ben Longstaff, Michael Williams, Claire Buchanan, Roberto Llansó, and Peter Bergstrom On
Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter. European MedSeA
 Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter European MedSeA 21 ST CENTURY CLIMATE CHANGE AND SUBMERGED AQUATIC VEGETATION IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY The 20 th century story: nutrient pollution, eutrophication,
Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter European MedSeA 21 ST CENTURY CLIMATE CHANGE AND SUBMERGED AQUATIC VEGETATION IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY The 20 th century story: nutrient pollution, eutrophication,
Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton. Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
 Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science 1 Data and Method Summer Hypoxia Dissolve Oxygen Patterns
Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science 1 Data and Method Summer Hypoxia Dissolve Oxygen Patterns
Modeling the water quality benefits of tributary-scale oyster reef restoration
 Modeling the water quality benefits of tributary-scale oyster reef restoration Lisa Kellogg, Mark Brush and Jeff Cornwell Sustainable Fisheries Goal Implementation Team December 17, 2018 Reef Restoration
Modeling the water quality benefits of tributary-scale oyster reef restoration Lisa Kellogg, Mark Brush and Jeff Cornwell Sustainable Fisheries Goal Implementation Team December 17, 2018 Reef Restoration
Nutrients in Chesapeake Bay: The Nutrient Diet is Working!
 Nutrients in Chesapeake Bay: The Nutrient Diet is Working! SERC 2017 Bay Optimism Lecture Series June, 2017 14:1 Large Drainage Basin Only 0.2 acres per person for dilution of wastes Walt Boynton and Many
Nutrients in Chesapeake Bay: The Nutrient Diet is Working! SERC 2017 Bay Optimism Lecture Series June, 2017 14:1 Large Drainage Basin Only 0.2 acres per person for dilution of wastes Walt Boynton and Many
CBF Water Quality Interactive Map
 CBF Water Quality Interactive Map Student and adult groups that take part Often, they measure the water chemistry to evaluate the be doing it when you come out with us! By compiling these points on a map
CBF Water Quality Interactive Map Student and adult groups that take part Often, they measure the water chemistry to evaluate the be doing it when you come out with us! By compiling these points on a map
Chesapeake Bay. report card
 Chesapeake Bay report card 2010 C- C Healthy water quality provides better habitat conditions for crabs, fish, and other aquatic species. issolved oxygen is essential to the survival of all these organisms;
Chesapeake Bay report card 2010 C- C Healthy water quality provides better habitat conditions for crabs, fish, and other aquatic species. issolved oxygen is essential to the survival of all these organisms;
Chapter Seven: Factors Affecting the Impact of Nutrient Enrichment on the Lower Estuary
 Chapter Seven: Factors Affecting the Impact of Nutrient Enrichment on the Lower Estuary As presented in Chapter Six, the water quality data for the upper stations of the tidal freshwater Potomac Estuary
Chapter Seven: Factors Affecting the Impact of Nutrient Enrichment on the Lower Estuary As presented in Chapter Six, the water quality data for the upper stations of the tidal freshwater Potomac Estuary
IMPROVEMENTS IN WATER QUALITY OF A DANISH ESTUARY FOLLOWING NUTRIENT REDUCTIONS
 IMPROVEMENTS IN WATER QUALITY OF A DANISH ESTUARY FOLLOWING NUTRIENT REDUCTIONS Peter Stæhr 1, Jeremy Testa 2, Jacob Carstensen 1 1 Dept. Bioscience,, Denmark 2 Chesapeake Biological Laboratory, Univ.
IMPROVEMENTS IN WATER QUALITY OF A DANISH ESTUARY FOLLOWING NUTRIENT REDUCTIONS Peter Stæhr 1, Jeremy Testa 2, Jacob Carstensen 1 1 Dept. Bioscience,, Denmark 2 Chesapeake Biological Laboratory, Univ.
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry
 Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 9 April 2013 Reading: Seitzinger & Mayorga (2008) 2013 Frank Sansone 1. Global coastal zone Outline 2. Nutrient loading in estuaries
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 9 April 2013 Reading: Seitzinger & Mayorga (2008) 2013 Frank Sansone 1. Global coastal zone Outline 2. Nutrient loading in estuaries
Qian Zhang (UMCES / CBPO) Joel Blomquist (USGS / ITAT)
 CBP STAC Water Clarity Workshop Solomons, MD, 02/06/2017 Long-term Riverine Inputs from Major Tributaries to Chesapeake Bay Relevant to Water Clarity Qian Zhang (UMCES / CBPO) Joel Blomquist (USGS / ITAT)
CBP STAC Water Clarity Workshop Solomons, MD, 02/06/2017 Long-term Riverine Inputs from Major Tributaries to Chesapeake Bay Relevant to Water Clarity Qian Zhang (UMCES / CBPO) Joel Blomquist (USGS / ITAT)
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Triblet Characteristics & Responses
 Triblet Characteristics & Responses K.G. Sellner 1, W.R. Boynton 2, J. Testa 2, T. Rosen 3, R.J. Orth 4, D. Dauer 5, and J. Uphoff 6 1 Center for Coastal & Watershed Studies, Hood College 2 UMCES-CBL 3
Triblet Characteristics & Responses K.G. Sellner 1, W.R. Boynton 2, J. Testa 2, T. Rosen 3, R.J. Orth 4, D. Dauer 5, and J. Uphoff 6 1 Center for Coastal & Watershed Studies, Hood College 2 UMCES-CBL 3
7.9 Nitrogenous Nutrients and Plankton Production in Jamaica Bay, NY
 7.9 Nitrogenous Nutrients and Plankton Production in Jamaica Bay, NY Ray Sambrotto 7.9.1 SUMMARY Two blooms characterize phytoplankton growth in Jamaica Bay: the winter/spring bloom, between February and
7.9 Nitrogenous Nutrients and Plankton Production in Jamaica Bay, NY Ray Sambrotto 7.9.1 SUMMARY Two blooms characterize phytoplankton growth in Jamaica Bay: the winter/spring bloom, between February and
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine
 Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES
 GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES Suhas E.P RVCE (VTU) No. 4/1 Golden Residency, Rmv 2 stage, Sanjaynagar, Bangalore SYNOPSIS Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of
GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES Suhas E.P RVCE (VTU) No. 4/1 Golden Residency, Rmv 2 stage, Sanjaynagar, Bangalore SYNOPSIS Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary
 Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
Cultural accelerated by anthropogenic activities
 EUTROPHICATION IMPLICATIONS OF N & P Intent of this lecture? Link our discussions of terrestrial N & P dynamics with its influences on receiving water bodies How the relative amounts of N & P can influence
EUTROPHICATION IMPLICATIONS OF N & P Intent of this lecture? Link our discussions of terrestrial N & P dynamics with its influences on receiving water bodies How the relative amounts of N & P can influence
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Scientific overview: Water quality functions of coastal buffers
 Scientific overview: Water quality functions of coastal buffers Caitlin Chaffee, Coastal Policy Analyst RI Coastal Resources Management Council November 21, 2013 Buffer Zone Setback = Minimum Distance
Scientific overview: Water quality functions of coastal buffers Caitlin Chaffee, Coastal Policy Analyst RI Coastal Resources Management Council November 21, 2013 Buffer Zone Setback = Minimum Distance
Classification of systems. Aquatic Ecosystems. Lakes 9/9/2013. Chapter 25
 Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Using the Chesapeake Bay Program Interpolator to analyze Chesapeake Bay monitoring program data
 Using the Chesapeake Bay Program Interpolator to analyze Chesapeake Bay monitoring program data Bill Romano & Mark Trice MD Dept. of Natural Resources bromano@dnr.state.md.us mtrice@dnr.state.md.us www.eyesonthebay.net
Using the Chesapeake Bay Program Interpolator to analyze Chesapeake Bay monitoring program data Bill Romano & Mark Trice MD Dept. of Natural Resources bromano@dnr.state.md.us mtrice@dnr.state.md.us www.eyesonthebay.net
MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture Dan Cogalniceanu Course content Overview of marine systems
 Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Benefits and Challenges of Using Multiple Models to Inform Management Decisions
 Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Benefits and Challenges of Using Multiple Models to Inform Management Decisions Multiple Models for Management (M3.2) in the Chesapeake Bay February 25, 2013 Annapolis MD
Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Benefits and Challenges of Using Multiple Models to Inform Management Decisions Multiple Models for Management (M3.2) in the Chesapeake Bay February 25, 2013 Annapolis MD
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry
 Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 2 April 2015 Readings: Seitzinger& Mayorga(2008) Jeandelet al.(2011) 2015 Frank Sansone and S.V. Smith 1. Global coastal zone Outline
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 2 April 2015 Readings: Seitzinger& Mayorga(2008) Jeandelet al.(2011) 2015 Frank Sansone and S.V. Smith 1. Global coastal zone Outline
Management Modeling of Suspended Solids and Living Resource Interactions
 Management Modeling of Suspended Solids and Living Resource Interactions Carl Cerco 1, Mark Noel 1, Sung-Chan Kim 2 1 Environmental Laboratory, US Army ERDC, Vicksburg MS, USA 2 Coastal and Hydraulics
Management Modeling of Suspended Solids and Living Resource Interactions Carl Cerco 1, Mark Noel 1, Sung-Chan Kim 2 1 Environmental Laboratory, US Army ERDC, Vicksburg MS, USA 2 Coastal and Hydraulics
Climate Change, Marsh Erosion and the Chesapeake Bay TMDL
 Climate Change, Marsh Erosion and the Chesapeake Bay TMDL Rising sea level in Chesapeake Bay is inexorable. One environmental effect associated with sea level rise is marsh erosion. Marsh erosion can impact
Climate Change, Marsh Erosion and the Chesapeake Bay TMDL Rising sea level in Chesapeake Bay is inexorable. One environmental effect associated with sea level rise is marsh erosion. Marsh erosion can impact
Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong
 Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong Prof. Paul J. Harrison Atmospheric, Marine & Coastal Environment Program Institute for the Environment HK University of Science & Technology Outline Background
Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong Prof. Paul J. Harrison Atmospheric, Marine & Coastal Environment Program Institute for the Environment HK University of Science & Technology Outline Background
Research Question What ecological and other services do coastal wetlands provide?
 Bringing Wetlands to Market Part 1 Introduction Blue, Green, and Bountiful: Wetlands and carbon Estuary Principle Principle 5: Humans, even those living far from the coast, rely on goods and services supplied
Bringing Wetlands to Market Part 1 Introduction Blue, Green, and Bountiful: Wetlands and carbon Estuary Principle Principle 5: Humans, even those living far from the coast, rely on goods and services supplied
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico
 The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
Fig. 1. Map for location
 The Asian Journal of Biology Education (2002) Number 1 3 Faculty of Education, Shiga University 2--1 Hiratsu, Otsu, 20-0862. Japan. Introduction Lake Biwa (Fig. 1) is the largest lake in Japan and one
The Asian Journal of Biology Education (2002) Number 1 3 Faculty of Education, Shiga University 2--1 Hiratsu, Otsu, 20-0862. Japan. Introduction Lake Biwa (Fig. 1) is the largest lake in Japan and one
PRESS RELEASE. LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 2, 2017 SUMMARY
 PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 2, 2017 SUMMARY The 2017 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 22,720 square kilometers (= 8,776 square miles) is the
PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 2, 2017 SUMMARY The 2017 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 22,720 square kilometers (= 8,776 square miles) is the
Low Dissolved Oxygen HYPOXIA. What is Hypoxia?
 HYPOXIA Low Dissolved Oxygen What is Hypoxia? Hypoxia or low dissolved oxygen has been identified as the most critical issue facing the Sound. Just as we breathe oxygen, the fish and other marine life
HYPOXIA Low Dissolved Oxygen What is Hypoxia? Hypoxia or low dissolved oxygen has been identified as the most critical issue facing the Sound. Just as we breathe oxygen, the fish and other marine life
Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats
 Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats Donna Marie Bilkovic STAC Chesapeake Bay Forage Base Workshop 12 November 2014 http://www.chesapeake.org/stac/ Virginia Institute of Marine Science www.ccrm.vims.edu
Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats Donna Marie Bilkovic STAC Chesapeake Bay Forage Base Workshop 12 November 2014 http://www.chesapeake.org/stac/ Virginia Institute of Marine Science www.ccrm.vims.edu
EUTROPHICATION. Student Lab Workbook
 EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
HYPOXIA Definition: ~63 µm; 2 mg l -1 ; 1.4 ml l -1 ; 30 %
 HYPOXIA Definition: ~63 µm; 2 mg l -1 ; 1.4 ml l -1 ; 30 % Consequences of hypoxia Reduce habitat for living resources Change biogeochemical processes P released from sediments Denitrification reduced
HYPOXIA Definition: ~63 µm; 2 mg l -1 ; 1.4 ml l -1 ; 30 % Consequences of hypoxia Reduce habitat for living resources Change biogeochemical processes P released from sediments Denitrification reduced
Productivity and fisheries. Energy flow. Biological pyramids. Why study production processes?
 Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Documenting the Cause of a Fish Kill on the Neuse River Estuary
 Documenting the Cause of a Fish Kill on the Neuse River Estuary On October 23, 2006, a resident living on Upper Broad Creek noticed fish gulping for air at the surface. The next day, October 24 th, the
Documenting the Cause of a Fish Kill on the Neuse River Estuary On October 23, 2006, a resident living on Upper Broad Creek noticed fish gulping for air at the surface. The next day, October 24 th, the
Commonwealth Champions VA TeCH
 Commonwealth Champions VA TeCH Assessing Coastal Habitat Vulnerability to Local Climate Stressors within the York River Estuary CCVATCH-CBNERR Workshop December 5, 2013 Gloucester Point, Virginia Chesapeake
Commonwealth Champions VA TeCH Assessing Coastal Habitat Vulnerability to Local Climate Stressors within the York River Estuary CCVATCH-CBNERR Workshop December 5, 2013 Gloucester Point, Virginia Chesapeake
ITAT Workshop on Integrating Findings to Explain Water Quality Change
 ITAT Workshop on Integrating Findings to Explain Water Quality Change December 12-13, 2017 Annapolis, MD STAC publication 18-005 1 Workshop Purpose Interdisciplinary Dialogue To convene research synthesis
ITAT Workshop on Integrating Findings to Explain Water Quality Change December 12-13, 2017 Annapolis, MD STAC publication 18-005 1 Workshop Purpose Interdisciplinary Dialogue To convene research synthesis
Examining Human Impacts on Global Biogeochemical Cycling via the Coastal Zone & Ocean Margins
 Examining Human Impacts on Global Biogeochemical Cycling via the Coastal Zone & Ocean Margins L. Talaue-McManus Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science University of Miami JGOFS Open Science
Examining Human Impacts on Global Biogeochemical Cycling via the Coastal Zone & Ocean Margins L. Talaue-McManus Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science University of Miami JGOFS Open Science
Environmental Science 101 Water. Fall Learning Objectives: Reading Assignment:
 Environmental Science 101 Water Fall 2012 1 Lecture Outline: 16. SURFACE WATER OLLUTION A. Two Kinds of Aquatic lants B. Upsetting the Balance by Nutrient Enrichment C. Idaho Examples D. Sources of Nutrients
Environmental Science 101 Water Fall 2012 1 Lecture Outline: 16. SURFACE WATER OLLUTION A. Two Kinds of Aquatic lants B. Upsetting the Balance by Nutrient Enrichment C. Idaho Examples D. Sources of Nutrients
Student Data Sheet 1
 Student Data Sheet 1 Name Date Latitude (e.g. 75 o N) Longitude (e.g.18 o W) Recent weather conditions: Current weather (circle one) Clear Partly Cloudy Fog Overcast Rain Snow Air Temperature C or F Wind
Student Data Sheet 1 Name Date Latitude (e.g. 75 o N) Longitude (e.g.18 o W) Recent weather conditions: Current weather (circle one) Clear Partly Cloudy Fog Overcast Rain Snow Air Temperature C or F Wind
Drones: A New Tool for Water Monitoring
 Drones: A New Tool for Water Monitoring Donglai Gong Carl Friedrichs, Ryan Carnegie Outline What are the goals of water monitoring (from marine scientist s perspective)? Healthy ecosystem? Fisheries /
Drones: A New Tool for Water Monitoring Donglai Gong Carl Friedrichs, Ryan Carnegie Outline What are the goals of water monitoring (from marine scientist s perspective)? Healthy ecosystem? Fisheries /
Buffer Zone = Area of Undisturbed Vegetation
 Scientific overview: Water quality functions of coastal buffers Caitlin Chaffee, Coastal Policy Analyst RI Coastal Resources Management Council November 29, 2012 Buffer Zone Setback = Minimum i Distance
Scientific overview: Water quality functions of coastal buffers Caitlin Chaffee, Coastal Policy Analyst RI Coastal Resources Management Council November 29, 2012 Buffer Zone Setback = Minimum i Distance
Reducing Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment Pollution Progress Update. Jeff Corbin, Senior Advisor to the EPA Administrator
 Reducing Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment Pollution Progress Update Jeff Corbin, Senior Advisor to the EPA Administrator Reducing Pollution Briefing Package Overview 1. 29-11 Milestones 2. 211 Progress
Reducing Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment Pollution Progress Update Jeff Corbin, Senior Advisor to the EPA Administrator Reducing Pollution Briefing Package Overview 1. 29-11 Milestones 2. 211 Progress
Interpreting Lake Data
 Interpreting Lake Data Indiana Clean Lakes Program The Indiana Clean Lakes Program was created in 1989 as a program within the Indiana Department of Environmental Management's (IDEM) Office of Water Management.
Interpreting Lake Data Indiana Clean Lakes Program The Indiana Clean Lakes Program was created in 1989 as a program within the Indiana Department of Environmental Management's (IDEM) Office of Water Management.
Lecture 10. Nutrient and BOD Overloading in Fresh Waters
 Last Time Lecture 10 Nutrient and BOD Overloading in Fresh Waters 1.Nutrients and Nutrient Overloading Today 2. Organic Matter ( OM ) discharge and BOD Overloading a. general watershed effects b. point
Last Time Lecture 10 Nutrient and BOD Overloading in Fresh Waters 1.Nutrients and Nutrient Overloading Today 2. Organic Matter ( OM ) discharge and BOD Overloading a. general watershed effects b. point
Understanding Nutrients and Their Affects on the Environment
 Understanding Nutrients and Their Affects on the Environment Humans & Ecosystems Humans are just like ecosystems, too much or too little of a nutrient is bad for the system. Nutrient management is a balancing
Understanding Nutrients and Their Affects on the Environment Humans & Ecosystems Humans are just like ecosystems, too much or too little of a nutrient is bad for the system. Nutrient management is a balancing
Estimated Influence of 2050 Climate Change on Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Standards.
 Estimated Influence of 2050 Climate Change on Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Standards. Water Quality Goal Implementation Team Meeting NCTC Shepherdstown, WV December 14, 2015 Lewis Linker 1, Gopal Bhatt
Estimated Influence of 2050 Climate Change on Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Standards. Water Quality Goal Implementation Team Meeting NCTC Shepherdstown, WV December 14, 2015 Lewis Linker 1, Gopal Bhatt
Eutrophication and the Saltwater Hudson River
 Eutrophication and the Saltwater Hudson River Part 1: Primary Production and Eutrophication in the Hudson Since the Industrial Revolution, the Hudson River has had problems with pollution, yet the challenges
Eutrophication and the Saltwater Hudson River Part 1: Primary Production and Eutrophication in the Hudson Since the Industrial Revolution, the Hudson River has had problems with pollution, yet the challenges
Science of the Causes of Hypoxia Nancy Rabalais et al.
 Science of the Causes of Hypoxia Nancy Rabalais et al. In support of overview of diversions and hypoxia, and context for refining science needs; July 14, 2014 Scientific Curiosity Hypothesis Testing Management
Science of the Causes of Hypoxia Nancy Rabalais et al. In support of overview of diversions and hypoxia, and context for refining science needs; July 14, 2014 Scientific Curiosity Hypothesis Testing Management
Jeffrey Cornwell, Michael Owens, Lisa Kellogg Thanks to RIE Newell and K Paynter
 Jeffrey Cornwell, Michael Owens, Lisa Kellogg Thanks to RIE Newell and K Paynter Source: Tom Toles (2013) The Washington Post. 2014 Funding: Kellogg, M. L., J. C. Cornwell, M. S. Owens, and K. T. Paynter.
Jeffrey Cornwell, Michael Owens, Lisa Kellogg Thanks to RIE Newell and K Paynter Source: Tom Toles (2013) The Washington Post. 2014 Funding: Kellogg, M. L., J. C. Cornwell, M. S. Owens, and K. T. Paynter.
Climate Change and Ecological Forecasting in the Chesapeake Bay
 Climate Change and Ecological Forecasting in the Chesapeake Bay Howard Townsend NOAA/NMFS/Habitat Conservation Chesapeake Bay Office STAC Climate Workshop March 7-8, 2016 Annapolis, MD Ecological Factors
Climate Change and Ecological Forecasting in the Chesapeake Bay Howard Townsend NOAA/NMFS/Habitat Conservation Chesapeake Bay Office STAC Climate Workshop March 7-8, 2016 Annapolis, MD Ecological Factors
Ocean Water Buoyancy and Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico. Definitions. Hypoxia in the Headlines. Joe Smith. ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company
 Ocean Water Buoyancy and Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Joe Smith ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company Joe Smith 2004 Hypoxia NOAA Coastal Data Development Center Definitions Hypoxia is a term meaning low
Ocean Water Buoyancy and Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Joe Smith ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company Joe Smith 2004 Hypoxia NOAA Coastal Data Development Center Definitions Hypoxia is a term meaning low
Barnegat Bay-Little Egg Harbor: Ecosystem Condition. Michael J. Kennish Institute of Marine and Coastal Sciences Rutgers University
 Barnegat Bay-Little Egg Harbor: Ecosystem Condition Michael J. Kennish Institute of Marine and Coastal Sciences Rutgers University Coastal Lagoons Barnegat Bay- Little Egg Harbor ANTHROPOGENIC EFFECTS*
Barnegat Bay-Little Egg Harbor: Ecosystem Condition Michael J. Kennish Institute of Marine and Coastal Sciences Rutgers University Coastal Lagoons Barnegat Bay- Little Egg Harbor ANTHROPOGENIC EFFECTS*
The Dead Zone. Use the notes provided (attached to this sheet) to answer the following questions.
 The Dead Zone Use the notes provided (attached to this sheet) to answer the following questions. 1. Re-define Eutrophication: 2. What are the risks associated with an excess of Nitrogen? 3. What is a Dead
The Dead Zone Use the notes provided (attached to this sheet) to answer the following questions. 1. Re-define Eutrophication: 2. What are the risks associated with an excess of Nitrogen? 3. What is a Dead
Background. Eutrophication - an increase in the rate of supply of organic matter to an ecosystem. - Scott Nixon (1995)
 Background Estuaries are among the most productive ecosystems on earth. They can produce organic material at rates comparable to those in the most intensively cultivated farm fields. Generally, high productivity
Background Estuaries are among the most productive ecosystems on earth. They can produce organic material at rates comparable to those in the most intensively cultivated farm fields. Generally, high productivity
6 TH. Most of the Earth Is Covered with Water (2) Most Aquatic Species Live in Top, Middle, or Bottom Layers of Water (1)
 A Healthy Coral Reef in the Red Sea MILLER/SPOOLMAN ESSENTIALS OF ECOLOGY 6 TH Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Fig. 8 1, p. 168 Most of the Earth Is Covered with Water (2) Aquatic life zones Saltwater life
A Healthy Coral Reef in the Red Sea MILLER/SPOOLMAN ESSENTIALS OF ECOLOGY 6 TH Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Fig. 8 1, p. 168 Most of the Earth Is Covered with Water (2) Aquatic life zones Saltwater life
Hypoxia Effects on Demersal and Benthic Fauna
 Hypoxia Effects on Demersal and Benthic Fauna Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research,
Hypoxia Effects on Demersal and Benthic Fauna Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research,
Why is the Benthos Important? OR Pre- and Post- Salt Pond Restoration Assessment of Benthic Communities in South San Francisco Bay
 Why is the Benthos Important? OR Pre- and Post- Salt Pond Restoration Assessment of Benthic Communities in South San Francisco Bay Jan Thompson and Francis Parchaso Menlo Park, USGS Benthic communities
Why is the Benthos Important? OR Pre- and Post- Salt Pond Restoration Assessment of Benthic Communities in South San Francisco Bay Jan Thompson and Francis Parchaso Menlo Park, USGS Benthic communities
Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems
 Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems Location Bact. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) Phyto. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) BactB: PhytoB BactP (mg C m -2 d -1 ) 1 o Pro (mg
Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems Location Bact. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) Phyto. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) BactB: PhytoB BactP (mg C m -2 d -1 ) 1 o Pro (mg
Effects of Winds on Hypoxia Formation in the Pearl River Estuarine Coastal Waters
 The 1th International Estuarine Biogeochemistry Symposium May 19-22, 28, Xiamen China Effects of Winds on Hypoxia Formation in the Pearl River Estuarine Coastal Waters Kedong YIN 1,2,3, Paul J. Harrison
The 1th International Estuarine Biogeochemistry Symposium May 19-22, 28, Xiamen China Effects of Winds on Hypoxia Formation in the Pearl River Estuarine Coastal Waters Kedong YIN 1,2,3, Paul J. Harrison
PRESS RELEASE. LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 4, 2013
 PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 4, 2013 The 2014 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 13,080 square kilometers (= 5,052 square miles) as of Aug 1,
PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 4, 2013 The 2014 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 13,080 square kilometers (= 5,052 square miles) as of Aug 1,
What Characterizes the Taninim Estuary in Relation to Other Mediterranean Microestuaries in Israel and Implications for the River rehabilitation
 What Characterizes the Taninim Estuary in Relation to Other Mediterranean Microestuaries in Israel and Implications for the River rehabilitation Sarig Gafny (sarig@ruppin.ac.il) The RIME team: Gitai Yahel,
What Characterizes the Taninim Estuary in Relation to Other Mediterranean Microestuaries in Israel and Implications for the River rehabilitation Sarig Gafny (sarig@ruppin.ac.il) The RIME team: Gitai Yahel,
CLMP+ Report on Fleming Lake (Aitkin County)
 CLMP+ Report on Fleming Lake (Aitkin County) Lake ID# -5-5-6 CLMP+ Data Summary July 7 Authors Shannon Martin Contributors/acknowledgements Terry Dahlberg Sandy Dahlberg Pam Anderson For questions regarding
CLMP+ Report on Fleming Lake (Aitkin County) Lake ID# -5-5-6 CLMP+ Data Summary July 7 Authors Shannon Martin Contributors/acknowledgements Terry Dahlberg Sandy Dahlberg Pam Anderson For questions regarding
St. Lucie Estuary: Analysis of Annual Cycles and Integrated Water Column Productivity
 St. Lucie Estuary: Analysis of Annual Cycles and Integrated Water Column Productivity Tom Gallo, Malcolm Pirnie Inc. Clifton Bell, Malcolm Pirnie Inc. Peter Doering, South Florida Water Management District
St. Lucie Estuary: Analysis of Annual Cycles and Integrated Water Column Productivity Tom Gallo, Malcolm Pirnie Inc. Clifton Bell, Malcolm Pirnie Inc. Peter Doering, South Florida Water Management District
NERRS Science. Collaborative Project
 NERRS Science Collaborative Project Detecting non point nitrogen sources and transport pathways in the Great Bay watershed and engaging decision makers in the science Investigators: Dr. William H. McDowell,
NERRS Science Collaborative Project Detecting non point nitrogen sources and transport pathways in the Great Bay watershed and engaging decision makers in the science Investigators: Dr. William H. McDowell,
Osher Course. What Lies Beneath the Inland Bays?
 Osher Course What Lies Beneath the Inland Bays? Objectives for Course Describe the Delaware Inland Bays and their tributaries Illustrate the ecology and importance of estuaries Demonstrate the threats
Osher Course What Lies Beneath the Inland Bays? Objectives for Course Describe the Delaware Inland Bays and their tributaries Illustrate the ecology and importance of estuaries Demonstrate the threats
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling
 Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
CHESAPEAKE BAY COMPREHENSIVE WATER RESOURCES AND RESTORATION PLAN - UPDATE. Update to Chesapeake Bay Program STAR January 25, 2018
 CHESAPEAKE BAY COMPREHENSIVE WATER RESOURCES AND RESTORATION 255 255 255 237 237 237 0 0 0 217 217 217 163 163 163 200 200 200 PLAN - UPDATE 131 132 122 239 65 53 80 119 27 110 135 120 252 174.59 112 92
CHESAPEAKE BAY COMPREHENSIVE WATER RESOURCES AND RESTORATION 255 255 255 237 237 237 0 0 0 217 217 217 163 163 163 200 200 200 PLAN - UPDATE 131 132 122 239 65 53 80 119 27 110 135 120 252 174.59 112 92
 Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition: An increasingly Important Source of new Nitrogen Supporting Coastal Eutrophication H Paerl 1, D. Whitall 2 and R. Dennis 3 1 UNC-CH CH Institute of Marine Sciences, Morehead
Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition: An increasingly Important Source of new Nitrogen Supporting Coastal Eutrophication H Paerl 1, D. Whitall 2 and R. Dennis 3 1 UNC-CH CH Institute of Marine Sciences, Morehead
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Southern California Bight 2008 Regional Monitoring Program: Volume VIII. Estuarine Eutrophication
 Technical Report 0711 Southern California Bight 2008 Regional Monitoring Program: Volume VIII. Estuarine Eutrophication K. McLaughlin 1, M. Sutula 1, L. Busse 2, S. Anderson 3, J. Crooks 4, R. Dagit 5,
Technical Report 0711 Southern California Bight 2008 Regional Monitoring Program: Volume VIII. Estuarine Eutrophication K. McLaughlin 1, M. Sutula 1, L. Busse 2, S. Anderson 3, J. Crooks 4, R. Dagit 5,
Submersed Aquatic Vegetation Restoration and Management from the Biologist and Resource Perspective
 Submersed Aquatic Vegetation Restoration and Management from the Biologist and Resource Perspective Carol Franze, LA Sea Grant/LSU AgCenter cfranze@agcenter.lsu.edu and Michael Poirrier, University of
Submersed Aquatic Vegetation Restoration and Management from the Biologist and Resource Perspective Carol Franze, LA Sea Grant/LSU AgCenter cfranze@agcenter.lsu.edu and Michael Poirrier, University of
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Environmental Science 101. Chapter 11 Water Pollution
 Environmental Science 101 Chapter 11 Water Pollution Water Pollution Any change in water quality that causes harm to humans and other living organisms. Review Renewable vs nonrenewable Hydrological cycle
Environmental Science 101 Chapter 11 Water Pollution Water Pollution Any change in water quality that causes harm to humans and other living organisms. Review Renewable vs nonrenewable Hydrological cycle
Linking Ecosystem Indicators to Ecosystem Services
 Linking Ecosystem Indicators to Ecosystem Services Christine Davis* G. Van Houtven, C. Mansfield, M. Cutrofello, and M. O Neil *Health and Environmental Impacts Division, OAQPS U.S. Environmental Protection
Linking Ecosystem Indicators to Ecosystem Services Christine Davis* G. Van Houtven, C. Mansfield, M. Cutrofello, and M. O Neil *Health and Environmental Impacts Division, OAQPS U.S. Environmental Protection
EUTROPHICATION PHENOMENA IN RESERVOIRS
 EUTROPHICATION PHENOMENA IN RESERVOIRS D. TIMOFTI 1, C. DOLTU 2, M. TROFIN 3 ABSTRACT Eutrophication phenomena in reservoirs. If in the last few decades eutrophication represented an isolated incident
EUTROPHICATION PHENOMENA IN RESERVOIRS D. TIMOFTI 1, C. DOLTU 2, M. TROFIN 3 ABSTRACT Eutrophication phenomena in reservoirs. If in the last few decades eutrophication represented an isolated incident
