Marking Scheme Geography Junior Certificate Higher Level 2003
|
|
|
- Cameron Lynch
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. 1mark Marking Scheme Geography Junior Certificate Higher Level 2003 Upper/Young = 1mk Correct location = 1mk Increased = 1mk. 2. 1mark High between 1024 isobar = 1mk 968 = 1 mk Cold = 1mk Section 1 Folder Question 20 3 marks each = 60 marks 3A. 1mark Or 3B. Mid-Atlantic Ridge = 1 mk. The Pacific Ring of Fire = 1 mk. The Rockies = 1 mk. 4 correct = 3 marks 2 3 correct = 2 marks 1 correct = 1mk A 3 B 1 C 4 D 2 E marks 1,3,5 = 3mks marks A town where people live but work in another town. = 3mks 6.A OR 6.B 1mk 1 mark (i) C = 1mk (i) Hot Desert = 1mk (ii) 37.2 mm = 1 mk (ii) Equatorial = 1mk (iii) Day 7 = 1mk (iii) Boreal = 1mk 7. 1 mark Greater = 1 mk Greater = 1 mk One reason = 1mk. Suggested answer Outward migration/ cheaper housing/ cheaper land Page 1
2 8. 1 mark High Fluctuating = 1 mk Death Rate = 1 mk Developed Countries = 1 mk marks Needle-like leaves = 3 mks correct = 2 marks / 2correct = 3 marks Diagram on left = Humification = 2mks Diagram on right = Leaching = 1 mk. 11A. 3 mark Or 11B 3 marks Box (c) = 3marks Box (c) = 3marks 12 3marks Convectional Rainfall = 3 mks mark Less than 15 0 C = 1 mk Lower = 1 mk Decrease = 1 mk mk. Any 3 from Solar / Wave / Tidal / Hydro 15. 2marks + 1mk. (i)terrace (ii)bungalows Other (iii)two Storey detached Two Storey Semi-detached Page 2
3 16. 1mark Two 1mark. Developing = 1 mk. Male 19% Female 29% mark. County Dublin is the most urbanised = 3 mks marks Land use Coniferous forest Sewage Treatment Plant Factory Grid Square S6674 S7174 S mark N80 = 3 mks marks 3.6 kms 3.9 kms = 3 mks. Draw a small grid to Total Marks for each Question on the Folder. Mk X Qs = Total 3 X 11 = 33 2 X 6 = 12 1 X 2 = 2 0 X 1 = 0 20 = 47 Please enter the folder total mark on the top right corner of the first page of the candidate s script. When entering the mark on the front grid enter it as F = 47 as per example above. Page 3
4 Marking Scheme Geography Junior Certificate Higher Level 2003 Section 2 Question 1. Resources and Economic Activity A. Water (i) With the aid of the diagram of the Water Cycle explain how water is a renewable resource. (6) Three 2 marks each. (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (One Development must refer to the completion of the cycle) Suggested answers. The sun evaporates seawater, which rises and condenses into cloud. Clouds become cooler releasing moisture as precipitation. Some precipitation returns to the sea in the form of rivers. (ii) Water is a scarce resource in some parts of the world With reference to an Irrigation Scheme you have studied: Name the scheme. Outline its operation. Discuss two benefits of the scheme to the local population. Named Scheme = 2mks (10) Aswan Dam, Central California Valley, etc. Outline of Scheme 4 marks(st2mk + Dev 2Mks) Or (St 2mk + St 2mk) The Aswan Dam was built across the Nile Gorge to control flooding on the Nile and provide HEP. Page 4
5 Question 1.(continued) Two 2 marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) Suggested Answer. It supplies electricity Prevents flooding irrigation for crops all year provides lake for tourism. B. Peat (i) The use of technology has speeded up the rate of exploitation of the Irish peat lands. The diagram below shows the stages in the exploitation of a bog. Use this diagram to explain three ways technology has been used to exploit the bogs. (8) Three explanations 3mks(St 2mk + Dev1mk) 2mks(St 1mk + Dev 1mk) Suggested Answers. The bog is drained by digging deep drains with machines called Ditchers. The bog is leveled with machines called Graders Rail tracks are laid for transport. Peat is harvested with special Milling machines. Briquettes and Peat moss are marketed through various media e.g. TV, radio, print etc. (ii) In the future, Bord na Mona may use the Cutaway Bogs for wind farms. Suggest three advantages the Cutaway Bogs have for the location of wind farms. Three 2 marks each Suggested answers. Flat land - easy access Exposed landscape no shelter from wind. Infrastructure Narrow gauge railway Page 5
6 Question 1. (continued) Or Suggest three other ways in which the cutaway bogs might be used in the future. Three 2 marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (6) Suggested answers. Grassland for cattle, sheep Forestry Construction and furniture Wildlife - sanctuary. Page 6
7 Question 2. Population A. Examine the Population Pyramids of Ireland 2000 and Mali 2000 Identify the differences in the structures of these two populations. In your answer refer to: Birth Rates Death Rates Life Expectancy (12) Three differences 4 marks each. Statement of difference under each heading = 2marks Development of each statement = 2marks. Information from the Pyramids must be used to get the development marks. Birth rates in Mali are higher than Ireland The base is wider in Mali. Death Rate are higher in Mali the pyramid narrows more quickly. Life expectancy is greater in Ireland 85 + in Ireland. B. Examine the Population Pyramids for Ireland 2000 and Ireland Describe two contrasts between the actual population figures for Ireland in 2000 and the estimated figures for (10) Two 5 marks each. (St 2mks + Dev 2mks + Dev 1mk) Information from the Pyramids must be used to get the development marks. Birth rate is lower in ,000 in 2000, 220,000 in 2050 Much greater elderly population in 2050 e.g. 180,000 in 2050, 50,000 in 2000 Page 7
8 Question 2. (continued) C. Estimated population projections for the future. How do estimated figures such as the ones shown for Ireland in 2050 help in planning for: Health Services Education services. (8) One explanation under each 4 marks. (St 2mks + Dev 2mks) Many older people therefore more Hospital services needed. Number of young lower therefore less demand for school buildings and extra teachers Page 8
9 Question 3. GEOGRAPHICAL MIX Answer THREE of the following A, B, C, D Mark all if answered by candidates, but credit marks for the best three only. Square bracket the surplus question A. Greenhouse Effect I Climatic Change. (i) Describe the causes of the increase in global temperatures. You may use a diagram to help in the explanation. (4) Two marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) Burning of fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide gases producing greenhouse effect. Increase in animal farming means more methane gas Deforestation means less carbon dioxide being absorbed. (ii) Explain how TWO of the following might help to ease the problem of global warming: Energy Conservation. Use of Renewable energy sources. Increase the area planted with trees. (6) Two 3 marks each. (St 2mks + Dev 1mk) More people using Public transport cutting down on gas emissions. Tidal, wave, solar, wind or HEP do not emit gases. Trees absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen. Page 9
10 Question 3. (continued) B. World Inequalities. Examine the chart comparing Ireland and Nigeria and answer the questions that follow: (6) (i) Select from the chart three statistics showing that Nigeria is less developed than Ireland. (6) Three 2marks each (St 1mk + Stat 1mk) Nigeria has a smaller GDP - $853 compared to $25,918 Ireland has a higher life expectancy 76.4 years as compared to 51.5 years. (ii) Outline two types of aid Ireland could provide to Nigeria to help it develop. In your answer name the type of aid and discuss the likely effects of each. (4) Two types of 2 marks.(st 1mk + Dev 1mk) Bilateral aid could be used to improve education or health services. NGO aid like that supplied by Concern could be used to improve farm production. Page 10
11 Question 3. (continued) C. Urban Geography. Examine the diagram of the cross-section of a city and answer the questions that follow: (i) With reference to the diagram, state which part of the city has the highest land values. Explain two reasons why land values are high in that part of the city. (4) Statement = 2 mark Two 1 mark each. A or CDB has the highest land value Land here is used intensively. It is used mostly by businesses that can afford high rents. (ii) Use the photograph of Carlow town to answer this part of the question. Parts of an urban area are given over to particular land uses. With reference to the photograph of Carlow town, locate and describe two land-uses in the town. (6) (Note: As it is not a vertical photograph, refer to places as background, right foreground etc.) Two land 3 marks each. (St 1mk + Dev 1mk + Loc 1mk) There is a residential area where people live in the left background. There is a car park for shoppers in the right middle distance. There is a recreational area where people might walk in the right background. Page 11
12 Question 3. (continued) D. Soil (i) Explain two ways soil is important to humans. (4) Two 2 marks each. (St 1m + Dev 1mk) It is used by farmers to grow crops for food. Different types of trees for construction grow on different types of soil. Without soil plants could not grow / without plants there would be no food for humans. (ii) With reference to two of the following factors explain their role in soil formation. Original rock, Climate, Micro-organisms, Vegetation. (6) Two 3 marks each (St 2 mks + Dev 1mk) Materials from which soils are formed, physical / chemical weathering breaks rocks into mineral particles the minerals contain calcium / potassium which are essential foods for plants. Climate is important as different amounts of moisture and temperature determine certain soil types. Micro-organisms break down plant litter to form humus, bacteria change nitrogen into a form which plants can absorb. Fungi change organic matter into humus. Certain types of vegetation influence soil type e.g. Coniferous forest lead to podzols while deciduous forest lead to brown earths. Page 12
13 Question 4. ORDNANCE SURVEY AND AERIAL PHOTOGRAPH Study the Ordnance Survey map and the legend (key) supplied. A. Draw a sketch map of the area shown on the Ordnance Survey map. Mark and identify the following features: The river Barrow and one named tributary. One National Primary road and one National Secondary road. The town of Carlow An area above 300 meters Two antiquities (12) Five 2 marks each. (Location = 1 mk + Named 1 mk) Frame = 1mk + Correct orientation = 1mk. Graveyard B N80 Castle A Barrow N A Fushoge B N 9 Motte C D Burial ground And Cross A. Barrow + Fushoge B. N 9 + N 80 C. Carlow D. Area above 300metres E. Antiquities Named Burial ground B N9 A Barrow Moated site Page 13
14 Question 4. (continued) B. The Local Authority has made efforts to reduce traffic congestion in the town of Carlow. Using the photograph only describe two such measures. (6) Two 3 marks each. (St 1mk + Dev 1mk + Loc 1mk) The yellow box at the cross roads in the left foreground helps prevent congestion by vehicles turning. Off street car parks like the one in right middle keep traffic flowing. Street lanes with direction arrows like those in the left foreground help control traffic flow. Double yellow lines, no parking right foreground C. Using both the map and the photograph explain three reasons why the town of Carlow developed at this location. (12) Three 4 marks each. (St 2mks + Dev 1mk + Loc 1mk) (Evidence from both Photo and Map must be given to obtain full marks.) Carlow grew up as a crossing point on the river Barrow because of the bridge in the left background. The town is at the meeting point of many roads making it a nodal point e.g. N80, N9,R417 and the R430. It may have developed as a defence settlement in the past as there is evidence of a castle at S Carlow has developed as a tourist town e.g. there is boating on the river at S Page 14
15 Question5. TOURISM Climatic data for Dublin and Lanzarote (Canary Islands) A. With reference to the information above explain why Lanzarote would be a better choice than Dublin for the location of a beach holiday. (10) Two 5 marks each. (St. 2mks + Dev 2mks + Dev 1mk) (Both explanations must use weather information supplied.) Lanzarote has higher temperatures in the summer than Dublin e.g. it is 30 0 C in July in Lanzarote while it is 18 0 C in July in Dublin There are more hours sunshine in Lanzarote e.g. 11 hours in July while Dublin only has 5 hours. Longer periods of sunshine in June/July/August in Lanzarotte than in Dublin, which tourists prefer in order to relax at beaches/ sunbathe. Temperature higher / warmer in Lanzarotte than in Dublin, 9 0 average difference over 7 months. B Tourists are attracted to locations other than beaches for a holiday, these include: Areas of Natural Beauty Cities Sporting and Recreation facilities. With reference to specific examples you have studied discuss two of these attractions. (10) Two 2 marks. (Loc 1mk + Loc 1mk) Two attractions 4 marks each, (St. 2mk + Dev 2mk) The Burren landscape features flora fauna history/culture Dublin Museums theatres/cinemas shopping parks etc. Page 15
16 Question5. (continued) C. Tourism may have positive and negative effects on people and the environment With reference to the diagram provided discuss two of these effects. In your answer refer to both positive and negative effects. (10) One positive 5 marks. (St. 2mks + Dev 2mks + 1mk) One negative 5 marks. (St. 2mks + Dev 2mks + 1mk) There is increased employment in transport, accommodation and catering thus improving the standard of living for local people. Roads, water services, electricity etc are improved to cater for the tourists, these benefit the local people. The cost of living rises for the local people as the cost of food, services and property increase. The high-rise hotels, which are being built, are extremely ugly and out of character with the landscape, they are poorly built and usually dominate the skyline. Page 16
17 Summary Marking Scheme Question 1. Resources and Economic Activity A. (i) Three 2 marks each. (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (6) (ii) Named Scheme = 2mks Outline of Scheme 4 marks (St2mk + Dev 2Mks) or (St2mk + Dev 2Mks) Two 2 marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (10) B. (i) Three explanations 3mks(St 2mk + Dev1mk) 2mks(St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (8) (ii) Three 2 marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (6) Or (ii) Three 2 marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (6) Question 2. Population A. Three differences 4 marks each.(st 2 mks + Dev 2 mks) (12) B. Two 5 marks each. (St 2mks + Dev 2mks + Dev 1mk) (10) C. One explanation under each 4 marks. (St 2mks + Dev 2mks) (8) Question 3. GEOGRAPHICAL MIX Answer THREE of the following A, B, C, D Mark all if answered by candidates, but credit marks for the best three only. Square bracket the surplus question A. (i) Two marks each (St 1mk + Dev 1mk) (4) (ii)two 3 marks each. (St 2mks + Dev 1mk) (6) B. (i) Three 2marks each (St 1mk + Stat 1mk) (6) (ii)two types of 2 marks.(st 1mk + Dev 1mk). (4) C. (i) Statement = 2 mark Two 1 mark each. (4) (ii)two land 3 marks each. (St 1mk + Dev 1mk + Loc 1mk) (6) D. `(i)two 2 marks each. (St 1m + Dev 1mk) (4) (ii)two 3 marks each (St 2 mks + Dev 1mk) (6) Question 4. ORDNANCE SURVEY AND AERIAL PHOTOGRAPH A. Five 2 marks each. (Loc = 1 mk + Named 1 mk) Frame = 1mk + Correct orientation = 1mk. (12) B. Two 3 marks each. (St 1mk + Dev 1mk + Loc 1mk) (6) C. Three 4 marks each. (St 2mks + Dev 1mk + Loc 1mk) (12) Question 5. TOURISM A. Two 5 marks each. (St. 2mks + Dev 2mks + Dev 1mk) (10) B. Two 2 marks. (Loc 1mk + Loc 1mk) Two attractions 4 marks each, (St. 2mk + Dev 2mk) (10) C. One positive 5 marks. (St. 2mks + Dev 2mks + 1mk) One negative 5 marks. (St. 2mks + Dev 2mks + 1mk) (10) Page 17
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations
 GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education Geography Extended Marking Scheme Higher Level Time Allowed: 2 hours Answer all questions in the spaces provided Total marks for the
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education Geography Extended Marking Scheme Higher Level Time Allowed: 2 hours Answer all questions in the spaces provided Total marks for the
Paper Reference. 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F. Foundation Tier. Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F Foundation Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F Foundation Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
2015 Higher Level Geography Exam Answers JC-Learn. JC-Learn. Geography Higher Level 2015 Exam Answers
 2015 Higher Level Geography Exam Answers JC-Learn JC-Learn Geography Higher Level 2015 Exam Answers 1 2015 Higher Level Geography Exam Answers JC-Learn 2 Section 1 Allow 20 Questions @ 3 marks each = 60
2015 Higher Level Geography Exam Answers JC-Learn JC-Learn Geography Higher Level 2015 Exam Answers 1 2015 Higher Level Geography Exam Answers JC-Learn 2 Section 1 Allow 20 Questions @ 3 marks each = 60
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2003 1 hour 45 minutes
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2003 1 hour 45 minutes
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2003 1 hour 45 minutes
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2003 1 hour 45 minutes
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2003 1 hour 45 minutes
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2003 1 hour 45 minutes
Renewable and non-renewable resources (Marking Scheme: 5 2 marks for each definition and 1 mark example.)
 Primary Economic Activities Revision Notes Primary Economic Activities Primary economic activities are when people take resources from the earth e.g. mining, farming and forestry. If a country is mainly
Primary Economic Activities Revision Notes Primary Economic Activities Primary economic activities are when people take resources from the earth e.g. mining, farming and forestry. If a country is mainly
Paper Reference. 1313/4H Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 4H. Higher Tier. Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/4H Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 4H Higher Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1 3
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/4H Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 4H Higher Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1 3
8291 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 8291 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 8291/22 Paper
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 8291 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 8291/22 Paper
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
GEOGRAPHY Grade 7 Term
 1 GEOGRAPHY Grade 7 Term 4 2016 Table of Contents Topic: Natural resources and conservation in South Africa Page Content 2 Natural resources 8 Management of resources 11 Water in South Africa 2 NATURAL
1 GEOGRAPHY Grade 7 Term 4 2016 Table of Contents Topic: Natural resources and conservation in South Africa Page Content 2 Natural resources 8 Management of resources 11 Water in South Africa 2 NATURAL
Grade 7 Geography Term
 1 Grade 7 Geography Term 4 2018 Contents NATURAL RESOURCES... 2 Activity 1... 2 Water... 3 AIR... 3 SOIL... 3 Forests... 4 Animals and marine life... 4 Activity 2... 5 Use and abuse of natural resources...
1 Grade 7 Geography Term 4 2018 Contents NATURAL RESOURCES... 2 Activity 1... 2 Water... 3 AIR... 3 SOIL... 3 Forests... 4 Animals and marine life... 4 Activity 2... 5 Use and abuse of natural resources...
Control and Management. The Biosphere SG Biology
 Control and Management The Biosphere SG Biology Learning Outcomes 1 State that pollution affects air, fresh water, sea and land. State that the main sources of pollution are domestic, agricultural and
Control and Management The Biosphere SG Biology Learning Outcomes 1 State that pollution affects air, fresh water, sea and land. State that the main sources of pollution are domestic, agricultural and
cars power plants cows horses carbon dioxide CFCs global warming sea level rise
 2018 United States Geography Olympiad - Written Examination (Elementary) Student Name School General instructions - Respond to each of examination questions in the space provided. Only answers written
2018 United States Geography Olympiad - Written Examination (Elementary) Student Name School General instructions - Respond to each of examination questions in the space provided. Only answers written
Section 6.1 & 6.2 A changing Landscape
 Section 6.1 & 6.2 A changing Landscape Human Population and Natural Resource Use With increased human population, we are using more and more of the Earth s natural resources. Two types of Resources are:
Section 6.1 & 6.2 A changing Landscape Human Population and Natural Resource Use With increased human population, we are using more and more of the Earth s natural resources. Two types of Resources are:
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education * 4 0 9 5 0 7 6 1 2 0 * GEOGRAPHY 0460/12 Paper 1 May/June 2015 Candidates answer on the Question
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education * 4 0 9 5 0 7 6 1 2 0 * GEOGRAPHY 0460/12 Paper 1 May/June 2015 Candidates answer on the Question
0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
Year 11 Revision Booklet
 Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Energy
Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Energy
3rd Year Geography Higher Level
 3rd Year Geography Higher Level Rivers No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without
3rd Year Geography Higher Level Rivers No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without
Year GCSE 11 Revision Booklet
 Year GCSE 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Section A: Urban issues and challenges Section B: The changing economic world Question 2 Section C: The challenge of resource
Year GCSE 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Section A: Urban issues and challenges Section B: The changing economic world Question 2 Section C: The challenge of resource
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4211472946* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 October/November 2017 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4211472946* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 October/November 2017 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 060/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2006 1 hour
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 060/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2006 1 hour
Resources that can be replaced, given a sufficient amount of time. Nonrenewable Resources: Food, oxygen, wood, wind, water.
 What are the different types of resources? Renewable Resources- Resources that can be replaced, given a sufficient amount of time Ex: Food, oxygen, wood, wind, water Nonrenewable Resources: Once used up,
What are the different types of resources? Renewable Resources- Resources that can be replaced, given a sufficient amount of time Ex: Food, oxygen, wood, wind, water Nonrenewable Resources: Once used up,
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision sheets
 Academic Year 2016-2017 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Grade:8 Date: Section: (A) Science Practice : Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Coal is a natural
Academic Year 2016-2017 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Grade:8 Date: Section: (A) Science Practice : Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Coal is a natural
Final Exam Review. (a) Ecosystems (b) Human systems (c) Natural systems (d) Synergy
 Canadian Geography 1202 Final Exam Review Name: Part A Multiple Choice: Circle the correct response 1. Which term is used to describe the circulation of water in the ocean, weather and climate systems,
Canadian Geography 1202 Final Exam Review Name: Part A Multiple Choice: Circle the correct response 1. Which term is used to describe the circulation of water in the ocean, weather and climate systems,
20 Global Climate Change
 20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2 Options Geography
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2 Options Geography A.M. MONDAY, 18 June 2012 1 hour 15 minutes For s Use Only Theme 7 Section
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2 Options Geography A.M. MONDAY, 18 June 2012 1 hour 15 minutes For s Use Only Theme 7 Section
NATURAL. Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 14 NATURAL RESOURCES Multiple Choice Questions 1. The atmosphere of the earth is heated by radiations which are mainly (a) radiated by the sun (b) re-radiated by land (c) re-radiated by water (d)
Chapter 14 NATURAL RESOURCES Multiple Choice Questions 1. The atmosphere of the earth is heated by radiations which are mainly (a) radiated by the sun (b) re-radiated by land (c) re-radiated by water (d)
Chapter 21 Global Climate Change
 Chapter 21 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 21 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation
Chapter 21 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 21 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation
Coal is obtained from mines. It's a black solid material that must be transported by ships, trains or big trucks to the power plants where it's burnt
 Energy Sources Fossil Fuels Coal, Oil and Gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric plants and animals. They provide most of the world's total
Energy Sources Fossil Fuels Coal, Oil and Gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric plants and animals. They provide most of the world's total
Suitable for grades 3-5. atmospheric composition. solar radiation. climate variability and change. volcanoes. clouds. carbon cycle.
 Color and Understand the Global Climate System atmospheric composition solar radiation climate variability and change H 2 0, CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, O 3, etc. aerosols volcanoes clouds atmosphere-ice interaction
Color and Understand the Global Climate System atmospheric composition solar radiation climate variability and change H 2 0, CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, O 3, etc. aerosols volcanoes clouds atmosphere-ice interaction
0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/12 Paper 1, maximum raw
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/12 Paper 1, maximum raw
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
PERSONALISED LEARNING CHECKLISTS
 Area of Study: Physical Landscapes in the UK I can describe the location of the major upland and lowland areas within the UK I can describe the location of the major river systems within the UK Area of
Area of Study: Physical Landscapes in the UK I can describe the location of the major upland and lowland areas within the UK I can describe the location of the major river systems within the UK Area of
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3075807527* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/11 Paper 1 October/November 2011
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3075807527* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/11 Paper 1 October/November 2011
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS. Student driven research
 ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS Student driven research First Step Take out your notebook and label page 24 Environmental Factors On this page you will answer questions that are asked on the following slides. Make
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS Student driven research First Step Take out your notebook and label page 24 Environmental Factors On this page you will answer questions that are asked on the following slides. Make
Transition Year Geography Lesson
 Transition Year Geography Lesson Biodiversity and Wetlands Wetlands are a vital component of the water cycle. The complex interaction of their elements - water, soil, plants and animals fulfil many important
Transition Year Geography Lesson Biodiversity and Wetlands Wetlands are a vital component of the water cycle. The complex interaction of their elements - water, soil, plants and animals fulfil many important
PROBLEM SOLVING GEOGRAPHY SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY B Sample Assessment Materials 45 GCSE GEOGRAPHY B COMPONENT 2 PROBLEM SOLVING GEOGRAPHY SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes For examiner s use only SPaG Part A 32 0 Part B 28 0
GCSE GEOGRAPHY B Sample Assessment Materials 45 GCSE GEOGRAPHY B COMPONENT 2 PROBLEM SOLVING GEOGRAPHY SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes For examiner s use only SPaG Part A 32 0 Part B 28 0
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN. Climate Disruption. Cengage Learning 2015
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 19 Climate Disruption 19-1 How Is the Earth s Climate Changing? Considerable scientific evidence indicates that the earth s atmosphere is
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 19 Climate Disruption 19-1 How Is the Earth s Climate Changing? Considerable scientific evidence indicates that the earth s atmosphere is
Year 11 Revision Booklet
 Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Food
Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Food
GCSE 4242/02 GEOGRAPHY SPECIFICATION B FOUNDATION TIER UNIT 2 SECTION B
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4242/02 GEOGRAPHY SPECIFICATION B FOUNDATION TIER UNIT 2 SECTION B A.M. WEDNESDAY, 12 June 2013 1 hour 30 minutes For examiner s use only Part
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4242/02 GEOGRAPHY SPECIFICATION B FOUNDATION TIER UNIT 2 SECTION B A.M. WEDNESDAY, 12 June 2013 1 hour 30 minutes For examiner s use only Part
Bellringer. What Lies Beneath? Natural Resources
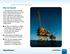 What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Period 24 Solutions: Energy and Water
 Period 24 Solutions: Energy and Water 24.1 The Earth s Water Cycle 1) Components of the Earth s water cycle a) What can happen to some of the water in lakes, rivers, oceans, and in the soil as the Sun
Period 24 Solutions: Energy and Water 24.1 The Earth s Water Cycle 1) Components of the Earth s water cycle a) What can happen to some of the water in lakes, rivers, oceans, and in the soil as the Sun
Earth Systems and Interactions
 CHAPTER The Earth System Earth Systems and Interactions What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
CHAPTER The Earth System Earth Systems and Interactions What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Generating Electricity
 Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
CLIMATE CHANGE AND ACID RAIN. Mr. Banks 7 th Grade Science
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND ACID RAIN Mr. Banks 7 th Grade Science COMPOSITION OF AIR? COMPOSITION OF AIR? 78% Nitrogen 21% Oxygen 0.93% Argon and other noble gases 0.04% carbon dioxide Variable amounts of water
CLIMATE CHANGE AND ACID RAIN Mr. Banks 7 th Grade Science COMPOSITION OF AIR? COMPOSITION OF AIR? 78% Nitrogen 21% Oxygen 0.93% Argon and other noble gases 0.04% carbon dioxide Variable amounts of water
Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Climate
 1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *2101029845* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/11 Paper 1 October/November 2013 Candidates answer on the Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *2101029845* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/11 Paper 1 October/November 2013 Candidates answer on the Question
the Environment the Atmosphere
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 People and the Environment Impacts on the Land Impacts on Water Chapter Wrap-Up Impacts on the Atmosphere How do human activities impact the environment?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 People and the Environment Impacts on the Land Impacts on Water Chapter Wrap-Up Impacts on the Atmosphere How do human activities impact the environment?
Atmosphere. The layer of gas surrounding the Earth
 Earth and Space Notes: Atmosphere Atmosphere The layer of gas surrounding the Earth Breakdown: Nitrogen (~79%) Oxygen (~21%) Argon, CO2, methane, ozone, water, nitrous oxides, sulphur dioxide, etc Gases
Earth and Space Notes: Atmosphere Atmosphere The layer of gas surrounding the Earth Breakdown: Nitrogen (~79%) Oxygen (~21%) Argon, CO2, methane, ozone, water, nitrous oxides, sulphur dioxide, etc Gases
RAG RAG RAG RAG Natural hazards Tectonic hazards Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are the result of physical processes.
 3.1.1 Section A: The challenge of natural hazards 3.1.1.1 Natural hazards Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition of a natural hazard. Types of natural hazard. Factors affecting
3.1.1 Section A: The challenge of natural hazards 3.1.1.1 Natural hazards Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition of a natural hazard. Types of natural hazard. Factors affecting
Chapter: The Nonliving Environment
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Nonliving Environment Section 1: Abiotic Factors Section 2: Cycles in Nature Section 3: Energy Flow Abiotic Factors 1 Environmental Factors The features of the environment
Table of Contents Chapter: The Nonliving Environment Section 1: Abiotic Factors Section 2: Cycles in Nature Section 3: Energy Flow Abiotic Factors 1 Environmental Factors The features of the environment
Lesson 3.1. Canada's Biomes. As you go down the list, the terms include more and more biotic and abiotic factors. 3.1 Canada's Biomes.
 Lesson 3.1 Canada's Biomes Jun 4 7:26 PM As you go down the list, the terms include more and more biotic and abiotic factors. May 17 2:04 PM 1 Biome a large geographic area with a similar climate Biosphere
Lesson 3.1 Canada's Biomes Jun 4 7:26 PM As you go down the list, the terms include more and more biotic and abiotic factors. May 17 2:04 PM 1 Biome a large geographic area with a similar climate Biosphere
The Greenhouse Effect
 Name: #: Date: 5.8 The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect traps heat in the atmosphere. This helps the Earth remain warm enough for humans. Without the greenhouse effect, human would not be able to
Name: #: Date: 5.8 The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect traps heat in the atmosphere. This helps the Earth remain warm enough for humans. Without the greenhouse effect, human would not be able to
Unit 1: Geographical Skills and Challenges
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Geography A Unit 1: Geographical Skills and Challenges Candidate Number Monday 14 June 2010 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Resource
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Geography A Unit 1: Geographical Skills and Challenges Candidate Number Monday 14 June 2010 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Resource
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *1336574734* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/12 Paper 1 October/November 2012 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *1336574734* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/12 Paper 1 October/November 2012 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates
Activity 3 Information sheet
 Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
WJEC PATHWAYS - ENTRY QUALIFICATIONS
 WJEC PATHWAYS - ENTRY QUALIFICATIONS Title Unit Ref. No. Entry Code Climate Change: Causes, Effects and Human Responses T/617/3317 A/617/3318 6234/E2 6234/E3 Level Entry 2/3 Credit Value 3 Unit aim This
WJEC PATHWAYS - ENTRY QUALIFICATIONS Title Unit Ref. No. Entry Code Climate Change: Causes, Effects and Human Responses T/617/3317 A/617/3318 6234/E2 6234/E3 Level Entry 2/3 Credit Value 3 Unit aim This
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry. Lesson 3: Recognizing the Importance of Forests
 Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 3: Recognizing the Importance of Forests 1 Terms Forest Forest canopy Piling Pulpwood Timberland Total forest land Urban forestry Veneer Reserved forest land 2 What
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 3: Recognizing the Importance of Forests 1 Terms Forest Forest canopy Piling Pulpwood Timberland Total forest land Urban forestry Veneer Reserved forest land 2 What
Unit 1: Geographical Skills and Challenges
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Geography A Unit 1: Geographical Skills and Challenges Candidate Number Monday 13 June 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Resource
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Geography A Unit 1: Geographical Skills and Challenges Candidate Number Monday 13 June 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Resource
Greenhouse Effect. How we stay warm
 Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0719333938* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/12 Paper 1 October/November 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0719333938* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/12 Paper 1 October/November 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No
CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES
 Natural Resources CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES NATURAL RESOURCES Exhaustible natural resources Inexhaustible natural resources Renewable Partly renewable Nonrenewable Inexhaustible Conditionally
Natural Resources CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES NATURAL RESOURCES Exhaustible natural resources Inexhaustible natural resources Renewable Partly renewable Nonrenewable Inexhaustible Conditionally
Chapter Introduction. Matter. Ecosystems. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
water, forestry, fossil fuels, metallic and non-metallic minerals
 water, forestry, fossil fuels, metallic and non-metallic minerals Faith / spirituality (water baptisms, FNMI water stories, etc) Sustains us / necessary for life Sanitation Transportation (canoe, boat,
water, forestry, fossil fuels, metallic and non-metallic minerals Faith / spirituality (water baptisms, FNMI water stories, etc) Sustains us / necessary for life Sanitation Transportation (canoe, boat,
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6278238366* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 May/June 2012 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6278238366* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 May/June 2012 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6278238366* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 May/June 2012 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6278238366* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 May/June 2012 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the
RENEWABLE ENERGY NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY
 Hydro Solar Biomass RENEWABLE ENERGY The motion associated with rapidly falling water, waves and tidal currents can be harnessed to drive turbines and generate electricity. RENEWABLE ENERGY Energy from
Hydro Solar Biomass RENEWABLE ENERGY The motion associated with rapidly falling water, waves and tidal currents can be harnessed to drive turbines and generate electricity. RENEWABLE ENERGY Energy from
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *2097927584* GEOGRAPHY 2217/13 Paper 1 May/June 2012 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *2097927584* GEOGRAPHY 2217/13 Paper 1 May/June 2012 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the Question
20 Global Climate Change
 20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
CHAPTER 8 Energy Efficiency, and Renewable Energy. Kildare County Development Plan , Volume 1
 Chapter 6 Rural Housing Strategy CHAPTER 8 Energy Efficiency, and Renewable Energy 157 8 ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY 8.1 Background The development of renewable energy sources is a priority
Chapter 6 Rural Housing Strategy CHAPTER 8 Energy Efficiency, and Renewable Energy 157 8 ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY 8.1 Background The development of renewable energy sources is a priority
GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2: Options Geography
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2: Options Geography A.M. THURSDAY, 22 May 2014 1 hour 15 minutes For s use Theme Maximum
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2: Options Geography A.M. THURSDAY, 22 May 2014 1 hour 15 minutes For s use Theme Maximum
Rock/ soil type and altitude differences.
 How does climate affect an ecosystem? The Earth s climate depends on energy from the sun. It affects growing conditions for vegetation and affects the location and characteristics of large scale eco-systems.
How does climate affect an ecosystem? The Earth s climate depends on energy from the sun. It affects growing conditions for vegetation and affects the location and characteristics of large scale eco-systems.
Ecosystems. 6.L.2.2 Explain how plants respond to external stimuli (including dormancy and forms of tropism) to enhance survival in an environment.
 Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Normal equatorial flow. Climate Variability. El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources
 Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
National Quali cations 2015
 H National Quali cations 2015 X733/76/11 Geography THURSDAY, 21 MAY 9:00 AM 11:15 AM Total marks 60 SECTION 1 PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks Attempt ALL questions. SECTION 2 HUMAN ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks
H National Quali cations 2015 X733/76/11 Geography THURSDAY, 21 MAY 9:00 AM 11:15 AM Total marks 60 SECTION 1 PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks Attempt ALL questions. SECTION 2 HUMAN ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks
Module 3 Educator s Guide Investigation 2
 Module 3 Educator s Guide Investigation 2 What s hot at the mall? Investigation Overview This investigation examines how shopping malls change natural environments. Studying NASA thermal images of a mall
Module 3 Educator s Guide Investigation 2 What s hot at the mall? Investigation Overview This investigation examines how shopping malls change natural environments. Studying NASA thermal images of a mall
CLIMATE CHANGE. Impacts, Vulnerabilities and EPA
 CLIMATE CHANGE Impacts, Vulnerabilities and EPA WHAT IS CLIMATE CHANGE? noun a long-term change in the earth's climate, especially a change due to an increase in the average atmospheric temperature. WHAT'S
CLIMATE CHANGE Impacts, Vulnerabilities and EPA WHAT IS CLIMATE CHANGE? noun a long-term change in the earth's climate, especially a change due to an increase in the average atmospheric temperature. WHAT'S
0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/12 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 60
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/12 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 60
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/21 Paper 2 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/21 Paper 2 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2717811529* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/13 Paper 1 October/November 2010
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2717811529* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/13 Paper 1 October/November 2010
Environmental Science Diagnostic Practice Exam
 Name: Period: Environmental Science Diagnostic Practice Exam * This test will be used to determine your current levels of understanding on Environmental Science topics. You will be graded based on effort
Name: Period: Environmental Science Diagnostic Practice Exam * This test will be used to determine your current levels of understanding on Environmental Science topics. You will be graded based on effort
! Ural Mountains. Please SAVE and PRINT the document file transferred to you when you logged in to help you take notes during class. !
 Europe s Climate and Environment Teacher: Mrs. Moody Class begins at: 10:05 Learning Targets: I I CAN describe the major environmental concerns facing Europe today. While you wait: Work on your USA Test
Europe s Climate and Environment Teacher: Mrs. Moody Class begins at: 10:05 Learning Targets: I I CAN describe the major environmental concerns facing Europe today. While you wait: Work on your USA Test
Earth s Dynamic Climate
 UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ
 Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ Instructions: The questions and answers below have been scrambled. Cut the answers and questions apart. Separate
Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ Instructions: The questions and answers below have been scrambled. Cut the answers and questions apart. Separate
Unit 1 Natural and Human Systems We Live in a World of Systems
 Unit 1 Natural and Human Systems We Live in a World of Systems The Big Ideas Systems The interaction of natural and human systems on the Earth shapes the environment in which you live. Natural system
Unit 1 Natural and Human Systems We Live in a World of Systems The Big Ideas Systems The interaction of natural and human systems on the Earth shapes the environment in which you live. Natural system
Page 2. Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon. Methane. Nitrogen.
 Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. (a) Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon Methane Nitrogen Oxygen (b) An increase in global temperature will cause climate change.
Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. (a) Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon Methane Nitrogen Oxygen (b) An increase in global temperature will cause climate change.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5927851245* GEOGRAPHY 0460/22 Paper 2 October/November 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5927851245* GEOGRAPHY 0460/22 Paper 2 October/November 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0606218973* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/11 Paper 1 October/November 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0606218973* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/11 Paper 1 October/November 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No
GCSE Geography Paper 2 Revision Checklist. Section A Urban Issues and Challenges
 GCSE Geography Paper 2 Revision Checklist Section A Urban Issues and Challenges A growing % of the world s urban population lives in urban areas. The global pattern of urban change. Urban trends in different
GCSE Geography Paper 2 Revision Checklist Section A Urban Issues and Challenges A growing % of the world s urban population lives in urban areas. The global pattern of urban change. Urban trends in different
Main Anthropogenic Sources of Greenhouse Gases Agriculture, Fire, Change in Land Use and Transport
 Main Anthropogenic Sources of Greenhouse Gases Agriculture, Fire, Change in Land Use and Transport Content GHG Emissions from AFOLU GHG Emissions from Transport Land Use & Forestry as a Source of GHG Transport
Main Anthropogenic Sources of Greenhouse Gases Agriculture, Fire, Change in Land Use and Transport Content GHG Emissions from AFOLU GHG Emissions from Transport Land Use & Forestry as a Source of GHG Transport
Inputs. Outputs. Component/store. Section of a system where material or energy is held. Something that enters the system (material or energy)
 .. Inputs Something that enters the system (material or energy) Outputs Something that leaves the system (material or energy) Component/store Section of a system where material or energy is held Transfer/flow
.. Inputs Something that enters the system (material or energy) Outputs Something that leaves the system (material or energy) Component/store Section of a system where material or energy is held Transfer/flow
Unit 3: The hydrosphere
 Unit 3: The hydrosphere 1. The water on the Earth 2. The water cycle 3. Water in the oceans 4. Water on the continents 5. Importance of water Think and answer? a. Where can water be found in our planet?
Unit 3: The hydrosphere 1. The water on the Earth 2. The water cycle 3. Water in the oceans 4. Water on the continents 5. Importance of water Think and answer? a. Where can water be found in our planet?
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
Impacts of Climate Change on Ecosystems
 Introduction The main objective of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is to stabilise greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level which will avoid dangerous human interference
Introduction The main objective of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is to stabilise greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level which will avoid dangerous human interference
Ecology. AQA Biology topic 7
 Ecology AQA Biology topic 7 7.1 Adaptations, Interdependence and Competition Ecosystems Definition: An ecosystem is the total interaction of a community of living organisms (biotic) with the non-living
Ecology AQA Biology topic 7 7.1 Adaptations, Interdependence and Competition Ecosystems Definition: An ecosystem is the total interaction of a community of living organisms (biotic) with the non-living
TOPIC: The Challenge of Natural Hazards Climate change section Slide 1: Evidence for climate change
 Slide 1: Evidence for climate change What is climate change? AQA definition: A long-term change in the earth's climate, normally associated with temperature change. The Earth is 4.5 billion years old.
Slide 1: Evidence for climate change What is climate change? AQA definition: A long-term change in the earth's climate, normally associated with temperature change. The Earth is 4.5 billion years old.
Ecosystems SOW. Environmentalist, scientist
 Key idea Distribution and characteristics of large scale ecosystems: Tropical, Temperate and boreal forests, tropical and temperate grasslands, deserts and tundra The role of climate and local factors
Key idea Distribution and characteristics of large scale ecosystems: Tropical, Temperate and boreal forests, tropical and temperate grasslands, deserts and tundra The role of climate and local factors
GCSE Geography. Case studies and examples
 GCSE Geography Case studies and examples Paper 1: Living with the physical environment Section A: The challenge of natural hazards Tectonic hazards 1) Use named examples to show how the effects and responses
GCSE Geography Case studies and examples Paper 1: Living with the physical environment Section A: The challenge of natural hazards Tectonic hazards 1) Use named examples to show how the effects and responses
