Water System Optimization: An Energy Efficiency View
|
|
|
- Shauna Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ABSTRACT Water System Optimization: An Energy Efficiency View Noah Mundt, Siemens Industry, Inc. James Dodenhoff, DNV GL Energy Services USA, Inc. Water and energy are inextricably linked in the hydrologic cycle, so a reduction in the use of one concurrently reduces the other. Nowhere in the United States is this cycle more important to future sustainability than in the state of Arizona. Arizona has a highly complex water supply and distribution system to provide for a rapidly growing state. Yet Arizona continues to experience extreme drought conditions that will only exacerbate water shortages. These water shortages will make the need for water system optimization critical in the years to come. The costs associated with the operation and maintenance of water distribution and treatment systems are large. The majority of operating costs are incurred through the purchase of electricity to power the motors and drives pressurizing the water distribution and transmission lines. Capital costs are driven by a need for enhanced infrastructure to offset system leakage, replace inefficient system components, and extend reach to obtain water. Optimization and calibration of the pressure required in water distribution systems offer significant annual energy cost savings, reduce direct water use, and provide indirect lowered water use in power generation. Utility incentive programs can play a key role to help reduce the first-time costs of these measures through utility-sponsored rebate programs. This paper quantifies and characterizes the energy savings of representative Arizona water system energy efficiency projects. The findings from this study will help water purveyors better understand the energy efficiency implications of capital improvements and guide future project adoption. Study Objectives and Methodology The four energy efficiency projects surveyed in this paper received ratepayer-funded incentives under the Arizona Public Service (APS) Solutions for Business program that began in DNV GL provides energy efficiency implementation services under contract to APS. These services include engineering support, technical review, and site surveys of energy efficiency project applications. In this paper, we provide an overview of the sources and uses of water in the state. We then draw from secondary literature to highlight the relationship between water use and energy use for water distribution systems. We also evaluate the current understanding of energy intensity for water systems and some recent trends that have impacted this understanding. The featured projects represent energy efficiency retrofit projects implemented across a broad array of Arizona municipal water distribution systems, all of which are unique in their water supply, population served, and system infrastructure. Key findings and observations from our work are shared and we provide recommendations for future opportunities for water system energy efficiency projects ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry 2-1
2 Overview of Arizona Sources and Uses of Water There are four categories of water sources available in Arizona: the Colorado River, surface water other than the Colorado River, groundwater, and reclaimed water (effluent). The use of each type of water depends on its quantity, quality, reliability, and economic feasibility. Water supplied through the Colorado River comes directly from the river and from a system of reservoirs on the river to harness its supplies for use in several states. Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Wyoming, and Mexico share the river, and it is the principal water supply for western Arizona. Additionally, the Central Arizona Project supplies 1.6 million acre-feet (MAF) to central and southern Arizona via a 336-mile diversion canal that originates in Lake Havasu City. Rights to use Colorado River water are quantified by a group of legal authorities known as the Law of the River, which grants Arizona the right to use 2.8 MAF annually. (Bureau of Reclamation, 2014) The second category of surface water comes from lakes, rivers, and streams; however, because of Arizona s desert climate, the amount of surface water available can vary dramatically from year to year, season to season, and place to place. In order to make the best use of the surface water, storage reservoirs and delivery systems have been constructed throughout the state. Almost all of the natural surface water in Arizona has been developed. Groundwater is a third source of water and is found beneath the earth s surface in natural reservoirs called aquifers. In most cases, the water stored in these reservoirs has been in place for millions of years. Historically, groundwater has been pumped out more rapidly than it is being replenished, creating a condition called overdraft. Though a large amount of water remains stored in Arizona s aquifers, its availability is limited by location, depth, and quality. Reclaimed water, or effluent, is an increasing water source in many states including Arizona. Reclaimed water is treated to a quality that can be used for a variety of purposes such as agriculture, golf courses, and industrial cooling. Arizona has grown from a population of 2.7 million people with an economy of approximately $30 billion in 1980 to nearly 6.6 million people with an economy of $260 billion in Annual water demand is expected to grow from the current estimate of 7.1 MAF in 2014 to between 8.2 to 8.6 MAF in 2035, between 8.6 and 9.1 MAF in 2060, and 9.9 to 10.5 MAF in 2110 (Arizona Department of Water Resources 2014). The demand for water by major user segment is approximately 70% agriculture, 8% industrial, and 22% municipal (Arizona Department of Water Resources 2015) A breakdown of the sources for annual usage is provided in Table 1: ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry
3 Table 1. Sources of Arizona s annual water supply. Source: State of Arizona, Department of Resources 2014 Annual Report. The Arizona Water Atlas (Atlas) was developed by the Arizona State Water Resources Department to support water planning and development efforts by providing water-related information on a local, regional and statewide level. The Atlas divides Arizona into seven planning areas (see Figure 1). Planning areas are composed of groundwater basins and are an organizational concept that provide for a regional perspective on water supply, demand and resource issues ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry 2-3
4 Figure 1. Arizona Regional Water Planning Areas Source: Arizona Department of Water Resources Arizona Water Atlas, Executive Summary, Volume 1 How Water Supply and Distribution Systems Use Energy Water supply involves the transportation of water from its source to treatment plants, storage facilities, and end users. Currently, most of the electricity used in water systems is for pumping; comparatively little is used in treatment. (Environmental Protection Agency 2013) Surface water treatment typically consists of chemical addition, coagulation, and settling, followed by filtration and disinfection. As drinking water regulations increase, a need arises to address contaminants of emerging concern. More energy-intensive, advanced treatment technologies including membrane filtration, ozonation, and ultraviolet irradiation have gained a greater share of the market since the mid-1990s and are likely to continue to grow market share. Water distribution accounts for most energy use. After treatment, water is usually pumped at high pressure to the distribution and storage system, which consists of storage tanks or reservoirs and, in some cases, additional pump stations to deliver water to other distribution zones. Distribution pumping and storage serves several operational purposes including: Overcoming pipe friction within the distribution system Providing adequate pressure for the water end-users ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry
5 Providing adequate storage volume and pressure for firefighting and other emergency uses Providing adequate equalization storage volume to meet water demand if the water needs in a system exceed constant pumping capacities High-service pumps and booster pumps provide the distribution system pumping by distributing water to users under adequate pipe pressure. High-service pumps are generally large horsepower (hp) pumps located at the water treatment plant that pump treated water into the service area under high head pressure conditions. Booster pumps are distributed throughout the distribution system and provide a similar function to deliver water to other distribution zones. What is considered adequate pressure can vary widely from one system to the next, with a typical range of pounds per square inch (psi) measured in the distribution mains. State health departments often specify a minimum pressure of 20 psi. With less than 40 psi, there may not be adequate pressure to provide minimal fire safety requirements in public and commercial buildings. High-rise buildings usually have their own booster pumps to serve upper floors. Water storage and system pressure are both tools that system operators can actively manage for electrical demand and electrical energy savings (Electric Power Research Institute [EPRI] 2013). Energy intensity will vary in terms of water system characteristics; however, pumping comprises the majority of energy usage for most surface water and groundwater distribution systems (Carns 2005). Given the large impact of pumping on overall system energy use, energy efficiency improvements should begin at the pumping systems. Table 2 shows estimated energy intensities (kwh/day) of three types of pumping processes used at three different pumping efficiencies and at different production rates. Table 2. Energy intensities of different processes and pumping efficiencies at different production rates. Source: Electricity Use and Management in the Municipal Water Supply and Wastewater Industries, EPRI, November 2013, p ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry 2-5
6 Survey of Water System Projects City of Yuma Surface Water Supply: Colorado River Yuma is nestled in the southwestern portion of Arizona, along the Arizona/California border and in the Lower Colorado River Water planning area. This area contains the driest and hottest portions of the state. Yuma is in the Low Elevation Climate Zone that consists of deserts ranging from 100 feet to 3,500 feet (Arizona Department of Water Resources 2015a). Annual precipitation in Yuma is 3.01 inches, with average summer maximum temperatures and winter minimum temperatures of 100º F and 45.8º F degrees, respectively. Yuma represents the last stop along the Colorado River s path as it winds out of the United States and into Mexico. The city has a population of 93,064 residents (2010). Given its location and extremely arid climate, Yuma is an especially interesting focal point when dealing with the hydrologic implications of water and energy usages. The water system serves square miles of city land and residential water use accounts for 60% of total water consumption in the region. The majority of the water used comes from the Colorado River through a series of canals called the All American Canal. Water is diverted from the Colorado River by the Imperial Dam, which is about 20 miles north of Yuma. The majority of water for the region comes through the All American Canal; however, recently, several groundwater wells have been installed and put into service. All water from the canals and the groundwater wells is sent to the water treatment plant operated by the city of Yuma to be treated prior to consumption. The water treatment plant treats and distributes approximately 14,000 acre-feet annually. Given such a large load and, more importantly, that all water coming in and going out of the plant has to be pumped, it becomes apparent that Yuma has a significant energy footprint related to water usage. Through the utility-sponsored program, the city of Yuma had a large portion of its pumps tested to determine current overall plant efficiency. This process led to a number of energy efficient upgrades including: Installing variable frequency drive (VFD) motors on three 500 hp pumps Installing VFDs on three 350 hp pumps Upgrading motors on three 350 hp pumps Following these installations, the plant improved its operating points from 60 hertz and 92 psi to 53 hertz and 80 psi. This step decrease in pressure offers enormous energy savings as well as maintenance and leak prevention implications. The total rebate for these energy conservation measures exceeded $154,000 with deemed energy savings claims of 6.5 million kwh. Based on these savings and the incentives offered by the utility, the overall simple payback for these projects was less than one year ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry
7 Table 3. City of Yuma project measures and estimated savings. Name of Organization Project Name City Type Status Requested Incentive Payment Annual kwh Savings kw Savings City of Yuma VSD Installation-City of Yuma Yuma Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Paid $51, $51, City of Yuma City of Yuma Pump Tests Yuma Technical Assistance & Studies Paid $2, $2, Zone 2 Booster Pump Station Upgrade City of Yuma Pumps 1-3 YUMA Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Paid $52, $52, City of Yuma Yuma Civic Center Main Hall Lights YUMA Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Paid $6, $6, Zone 2 Booster Pump Station upgrade City of Yuma Pumps 4 YUMA Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Paid $17, $17, City of Yuma VFD 500 HP high Speed YUMA Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Paid $24, $24, Source: APS Solutions for Business Program Operations Database City of Flagstaff Surface Water and Groundwater Supply Flagstaff is located in north central Arizona in the Eastern Plateau area. With a population of approximately 70,000 people and located at an altitude of 6,910 feet, the city has a dry semi-continental climate with snow in winter (average annual snowfall is 77 inches) and a dry, hot early summer (average temperatures of 80º F) followed by monsoons from July to September. (U.S. Climate Data 2015) The city represents a niche market for water use within the state of Arizona given its mountainous climate and elevations in the predominantly arid state. Historically, Flagstaff derived the bulk of its water use from two surface water sources, Lake Mary and Inner Basin, and one groundwater source, Woody Mountain well field. All three of these importation projects lie outside of the city limits, and it was not until 1990 that well fields were developed within the city limits. The final component of the city s total water supply is the reclaimed water from treatment plants, which in 2010 made up 18% of total water usage. Flagstaff s current water distribution volume is approximately 8,400 acre-feet per year Data from 2008 show Flagstaff has one of the lowest per capita residential usage rates in the state at 61 gallons per capita per day compared with, for instance, Phoenix at 123 gallons.(city of Flagstaff 2011). Over the past two decades, the city implemented many water conservation programs that led to a stabilized water consumption rate as the population grew. The APS Solutions for Business rebate program provided financial assistance to fund the technical assistance studies and audits completed on 13 well pumps and both of the city s wastewater reclamation facilities. These studies helped identify opportunities within the water distribution and treatment system for improved efficiencies based on capital improvements. Those projects submitted through the program included: Installing VFDs on two raw water pumps Installing VFDs on Lake Mary well 8 Installing VFDs on Fort Tuthill Well Resizing raw water pump station Installing shop well VFD Upgrading shop well pump, including a full pump and motor replacement These projects received incentives of more than $145,000, and provided estimated deemed energy savings of 5.8 GWh per year and annual cost savings of $300, ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry 2-7
8 Table 4. City of Flagstaff project measures and estimated savings. Source: APS Solutions for Business Program Operations Database City of Holbrook Groundwater Supply: Coconino Aquifer Holbrook is located in northeast Arizona in the Eastern Plateau area, and is in the High Elevation Climate Zone. This zone consists of cool plateau highlands at 4,000 6,000 feet and cold mountains at 6,000 8,000 feet. It is semi-arid to arid, but the highest elevations may receive up to 30 inches of precipitation annually (Arizona Department of Water Resources 2015b). The city operates a water supply and distribution system serving a community of approximately 5,800 people with approximately 1,000 acre-feet of water per year. The primary source of water is from the Coconino Aquifer (C-Aquifer), a groundwater supply. The water distribution system is relatively simple comprising seven wells that pump water from the C- Aquifer into a major water pipeline that flows to the southern end of the city and to three water tanks on top of a hill. Water flows from these tanks to supply the northern part of the city. A series of four energy efficiency projects for this water system comprised the following elements: Replacing City of Holbrook Well #3 and upgrading to a VFD Retrofitting City of Holbrook Well #5 to include a VFD Retrofitting City of Holbrook Well #7 to include a VFD Water conservation resulting from increased system efficiency was not the primary project objective; however, it is estimated that these capital improvements resulted in direct water conservation savings through reduced leakage. Furthermore, the estimated energy savings from improved pump and motor efficiency created indirect water savings of roughly 70 acre-feet from reduced power generation requirements at the nearby Cholla Power Plant. This savings is approximately 7% of the City of Holbrook s overall water use. These projects provided incentives to the City of Holbrook exceeding $45,000. Total estimated energy savings from these projects amounted to nearly 1.75 million kwh per year, or estimated energy cost savings of more than $100,000 per year ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry
9 Table 5. City of Holbrook project measures and estimated savings. Name of Organization Project Name Type Status Requested Incentive Payment Annual kwh Savings kw Savings City of Custom 8 Holbrook City of Holbrook Well 3 Measures - Paid $16, $16, City of Holbrook Holbrook Booster Plant Prescriptive Measures - Paid $10, $10, City of Prescriptive Holbrook Holbrook Well 5 VFD Measures - Paid $5, $5, City of Holbrook Wells 3 and 7 Prescriptive Holbrook WWTP VFD's Measures - Paid $15, $15, Source: APS Solutions for Business Program Operations Database Carefree Water Company Surface Water Supply (Central Arizona Project) and Groundwater Supply The town of Carefree is located in central Arizona, 33 miles northeast of Phoenix. Carefree is in a Low Elevation Climate Zone consisting of deserts at altitudes ranging from 100 to 3,500 feet. Annual precipitation is 3 to 12 inches. The Carefree Water Company operates a water supply and distribution system serving a community of approximately 3,500 people. It is equipped to supply up to 1,500 acre-feet of water per year. Peak daily usage occurs in the summer and is approximately 1,000,000 gallons. Approximately half of the total water use in this area is by the municipal sector, with the remainder used by agriculture and industry. Water storage reservoirs and the Central Arizona Project allocation of 1,200 acre-feet per year allow for a relatively high proportion of surface water use in some places. The remaining 30% of the total water supply is groundwater. (Carefree Water Company Web Site 2015) Over the past 10 years, the Carefree Water Company has completed many improvements to the storage and distribution system, including: Completing construction of a new 1,000,000 water storage reservoir Enhancing water wells for emergency supply capabilities Upgrading well to enhance efficiency Upgrading pumping system to enhance efficiency Installing VFD on selected pump Much of these system enhancements received incentives under the APS Solutions for Business program, inclusive of: Installing a new motor and pump on one of the wells Replacing a motor on the second well Replacing both the motor and bowl on one of the boosters Replacing just the bowl on two additional boosters Replacing just the motor on one additional booster The City of Carefree received an incentive of $33,000, realized estimated annual energy savings from these projects amounting to nearly 425,000 kwh per year, and estimated energy savings of more than $30,000 per year. Carefree receives most of its electric power from the Palo 2015 ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry 2-9
10 Verde Nuclear Generating (PVNG) Station. This power plant evaporates the water from the treated sewage from several nearby cities and towns to provide the cooling of the steam that it produces. Thus, the reduction in electricity consumption in Carefree reduces the use of effluent at PVNG. Table 6. Carefree Water Company project measures and estimated savings. Name of Organization Project Name Type Requested Status Incentive Payment Final Received CBusName Annual kwh Savings kw Savings Carefree Water 1 Company Carefree - Well 6 Upgrade Custom Measures - Retrofit Paid $11, $11, /20/2010 The Pump Co Town of Carefree Admin J.E. Bowen 4 Town of Carefree Office & Water Company Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Paid $2, $2, /9/2011 Construction Carefree Water 1 Company Carefree Pumping System Upgrade Custom Measures - Retrofit Paid $9, $6, /3/2011 The Pump Co Carefree Water 1 Company Carefree Pumping System Upgrade Phase 2 Custom Measures - Retrofit Paid $9, $ /2/2011 The Pump Co Carefree Water 1 Company Carefree Water Company - Well 2 Upgrade Custom Measures - Retrofit Paid $5, $5, /3/2014 The Pump Co Carefree Water Carefree Water Company Final 1 Company VFD Install Prescriptive Measures - Retrofit Appro $6, $6, /27/ Source: APS Solutions for Business Program Operations Database Key Findings and Observations Through our research we found Arizona to be an excellent laboratory for studying and developing technologies around the water-energy nexus due to the state s following characteristics: Diversity of climate Diversity of ecosystem Diversity of urban and rural water uses Diversity of water sources Well established policies governing water supply and use The learnings derived from Arizona can be applied broadly throughout the U.S. especially in areas that share one or more similar characteristics as the case studies reviewed. The systems that convey and distribute water are complex. Notably, we also found that water supply sources are systems unto themselves, inter-dependent, and highly complex, These water supply systems are impacted by many variables: climate, multiple uses, variability within use, geography, and dynamic public policy. These systems---both water distribution systems and water supply systems----must be managed thoughtfully with a deep understanding of these many variables, interdependent effects, and potential unintended consequences. Indirect water savings realized through thermal energy reductions can be material. We question whether they are fully or properly valued when an energy efficiency project is adopted. When that energy efficiency project also reduces direct water use, the combined water and energy savings can create a significantly reduced resource footprint inclusive of water reduction, energy reduction, and GHG emissions reduction. Given the system complexity we observed, we found that water distribution systems are inherently unique. Even within the State of Arizona, we found significant differences across supply, distribution systems, and use. Every water system has a story. Spending the time to ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry
11 understand the story and its history helps assure that efficiency and conservation enhancements are real, verifiable, and sustainable. Future Opportunities/Areas of Future Research At this time of severe drought in the West, we also find there to be significant areas for future research and analysis across many technical and policy parameters, including: References Understanding how the EPA Clean Power Plan may impact Arizona s water- energy systems Better correlation between system component changes (pumps/vfds) and overall system pressure changes; and a need to more tightly correlate system pressure changes to leak reductions Developing a clearer understanding of the wide variation in per capita water use and water conservation efforts; and determining the real and illusory cause and effect relationships that may or may not exist. Continued understanding of water system-energy use intensity to help enhance benchmarking Better understanding how energy efficiency improvements provide scalable benefits to water systems Enhancing integrated energy efficiency and water conservation program design around energy efficiency projects that serve water systems with the goal of expanding the value proposition to include reduced water use in power generation. Exploring lessons to be shared and learned between 1) electric grid enhancement and 2) water distribution system optimization Using pricing, tariffs, and economic incentives as tools to optimize water-energy projects and accompanying water-energy use Arizona Department of Water Resources. January Arizona s Next Century: A Strategic Vision for Water Supply Sustainability. Phoenix, AZ. Arizona Department of Water Resources. Accessed Securing Arizona s Water Future. Bureau of Reclamation, The Law of the River- Lower Colorado Region. Carefree Water Company website Frequently Asked Questions. Accessed March 15, Carns, K., EPRI Solutions. November 2, Bringing Energy Efficiency to the Water & Wastewater Industry: How Do We Get There? Presented at the Water Environment Federation s Annual Technical Exhibition and Conference (WEFTEC), Washington, DC ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry 2-11
12 City of Flagstaff Utilities Integrated Master Plan, Water History, Demand, Existing Supplies and Future Needs and Recommended Options. Flagstaff, AZ. EPRI (Electric Power Research Institute) with the Water Research Foundation. November Electricity Use and Management in the Municipal Water Supply and Wastewater Industries. Palo Alto, CA Environmental Protection Agency Energy Efficiency in Water and Wastewater Facilities A Guide to Developing and Implementing Greenhouse Gas Reduction Programs, Washington D.C. U.S.Climate Data. Accessed 2015, Climate Flagstaff Arizona September Arizona Water Atlas. 1_web.pdf a. Arizona Water Awareness: Yuma b. Arizona Water Awareness: Holbrook c. Arizona Water Awareness: Carefree ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Industry
Energy Management Strategies at Metropolitan Water District. Roy L Wolfe, Ph.D.
 Energy Management Strategies at Metropolitan Water District Roy L Wolfe, Ph.D. Japan U.S. Joint Conference on Drinking Water Quality Management and Wastewater Control California Water and Energy March
Energy Management Strategies at Metropolitan Water District Roy L Wolfe, Ph.D. Japan U.S. Joint Conference on Drinking Water Quality Management and Wastewater Control California Water and Energy March
Scottsdale Water Campus 20 Years of Sustainable Water Management. Brian K. Biesemeyer, PE Director, Scottsdale Water
 Scottsdale Water Campus 20 Years of Sustainable Water Management Brian K. Biesemeyer, PE Director, Scottsdale Water Agenda About Scottsdale Water 1980 Groundwater Management Act Water Campus Concept Recharge
Scottsdale Water Campus 20 Years of Sustainable Water Management Brian K. Biesemeyer, PE Director, Scottsdale Water Agenda About Scottsdale Water 1980 Groundwater Management Act Water Campus Concept Recharge
U.S. Water Budget. Figure Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources , Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council.
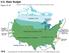 U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
Home to about 56 million people, the Southwest includes Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado and most of California.
 Climate change in the U.S. Southwest U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Overview The Southwest is the hottest and driest region in the nation. Extending from the Pacific Ocean east to the Rocky Mountains
Climate change in the U.S. Southwest U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Overview The Southwest is the hottest and driest region in the nation. Extending from the Pacific Ocean east to the Rocky Mountains
Analyzing the Water-Energy Nexus: Case Studies that Examine the Crucial Connection
 Analyzing the Water-Energy Nexus: Case Studies that Examine the Crucial Connection June 30, 2014 Ned Spang, Ph.D. Program Manager Heather Cooley Water Program Director Amanda Acheson Sustainable Building
Analyzing the Water-Energy Nexus: Case Studies that Examine the Crucial Connection June 30, 2014 Ned Spang, Ph.D. Program Manager Heather Cooley Water Program Director Amanda Acheson Sustainable Building
WaterSim: Supply and Demand Simulation Model for Metropolitan Phoenix
 WaterSim: Supply and Demand Simulation Model for Metropolitan Phoenix Teacher s Guide to Using WaterSim on the Web http://watersim.asu.edu Global Institute of Sustainability, Arizona State University Introduction:
WaterSim: Supply and Demand Simulation Model for Metropolitan Phoenix Teacher s Guide to Using WaterSim on the Web http://watersim.asu.edu Global Institute of Sustainability, Arizona State University Introduction:
The Pursuit of Sustainable & Reliable Water Supplies in the Desert. The Las Vegas Story
 The Pursuit of Sustainable & Reliable Water Supplies in the Desert The Las Vegas Story Richard B. Holmes Southern Nevada Water Authority February 16, 2010 SOUTHERN NEVADA Presentation Outline Early Las
The Pursuit of Sustainable & Reliable Water Supplies in the Desert The Las Vegas Story Richard B. Holmes Southern Nevada Water Authority February 16, 2010 SOUTHERN NEVADA Presentation Outline Early Las
SLIDES: Status of Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA): Third Intake into Lake Mead and Groundwater Project
 University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Western Water Law, Policy and Management: Ripples, Currents, and New Channels for Inquiry (Martz Summer Conference, June 3-5) Getches-Wilkinson
University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Western Water Law, Policy and Management: Ripples, Currents, and New Channels for Inquiry (Martz Summer Conference, June 3-5) Getches-Wilkinson
Northern Arizona Hydrogeology
 Northern Arizona Hydrogeology Some basics Coconino Plateau Hydrogeology Flagstaff and Coconino Plateau Water Resources Well development, City of Flagstaff Effluent discharge to the Rio de Flag from Wildcat
Northern Arizona Hydrogeology Some basics Coconino Plateau Hydrogeology Flagstaff and Coconino Plateau Water Resources Well development, City of Flagstaff Effluent discharge to the Rio de Flag from Wildcat
Colorado River Challenges Impacts to Southern Arizona
 Colorado River Challenges Impacts to Southern Arizona 2 3 4 5 Colorado River Basics 7 States, 2 Nations Annual Flow 15.0 MAF 40 Million People All of the Major Cities in Southwest 5.5m Irrigated Acres
Colorado River Challenges Impacts to Southern Arizona 2 3 4 5 Colorado River Basics 7 States, 2 Nations Annual Flow 15.0 MAF 40 Million People All of the Major Cities in Southwest 5.5m Irrigated Acres
New River Desert Hills Community Association Ben Graff CAP Board October 13, 2017
 New River Desert Hills Community Association Ben Graff CAP Board October 13, 2017 Central Arizona Project 336-mile aqueduct stretches from Lake Havasu to Tucson 14 pumping plants lift water nearly 3,000
New River Desert Hills Community Association Ben Graff CAP Board October 13, 2017 Central Arizona Project 336-mile aqueduct stretches from Lake Havasu to Tucson 14 pumping plants lift water nearly 3,000
G4: GEOGRAPHY REVISION Theme 2: Sustainable Water Supply
 G4: GEOGRAPHY REVISION Theme 2: Sustainable Water Supply What physical factors determine the supply of water? Water supply in the UK Plentiful supply of surface run-off and precipitation in the North and
G4: GEOGRAPHY REVISION Theme 2: Sustainable Water Supply What physical factors determine the supply of water? Water supply in the UK Plentiful supply of surface run-off and precipitation in the North and
Pipelines to Nowhere? Structural Responses to Climate Change and Population
 Pipelines to Nowhere? Structural Responses to Climate Change and Population Presented by James Lochhead, Esq. Brownstein Hyatt Farber Schreck, LLP bhfs.com Evolving Strategies of Water Supply Development
Pipelines to Nowhere? Structural Responses to Climate Change and Population Presented by James Lochhead, Esq. Brownstein Hyatt Farber Schreck, LLP bhfs.com Evolving Strategies of Water Supply Development
Facts. Groundwater. The big problem. Issues. Consequences of Subsidence. How can we help? 2 major aquifers. Louanne Nutile Mitch Jacobs Sam Bejarano
 Facts Groundwater Louanne Nutile Mitch Jacobs Sam Bejarano 2 major aquifers Tucson Basin Aquifer and the Arva Valley Aquifer There are 4 well fields Central, Southside, Santa Cruz, and Arva Valley well
Facts Groundwater Louanne Nutile Mitch Jacobs Sam Bejarano 2 major aquifers Tucson Basin Aquifer and the Arva Valley Aquifer There are 4 well fields Central, Southside, Santa Cruz, and Arva Valley well
Report. Office of the General Manager. Colorado River Management Report. Summary. Detailed Report
 Report Office of the General Manager Summary Colorado River Management Report This report provides a summary of the activities related to the Colorado River during April and a response to a request from
Report Office of the General Manager Summary Colorado River Management Report This report provides a summary of the activities related to the Colorado River during April and a response to a request from
California s s Water Supplies and Uses
 California s s Water Supplies and Uses Presented to Delta Stewardship Council Presented by Joe Grindstaff September 21 1 Place to Place: Most precipitation falls in the mountains in the north and east
California s s Water Supplies and Uses Presented to Delta Stewardship Council Presented by Joe Grindstaff September 21 1 Place to Place: Most precipitation falls in the mountains in the north and east
NGWA INFORMATION BRIEF
 Several techniques are employed to artificially recharge aquifers Streamflow is directed to an artificial recharge basin, where water percolates downward to the underlying aquifer. A recharge well is used
Several techniques are employed to artificially recharge aquifers Streamflow is directed to an artificial recharge basin, where water percolates downward to the underlying aquifer. A recharge well is used
Sustainable Water Future for the City of Los Angeles
 Sustainable Water Future for the City of Los Angeles National Research Council Pathways to Urban Sustainability: Challenges & Opportunities April 29, 2015 Nancy Sutley Chief Sustainability & Economic Development
Sustainable Water Future for the City of Los Angeles National Research Council Pathways to Urban Sustainability: Challenges & Opportunities April 29, 2015 Nancy Sutley Chief Sustainability & Economic Development
Water Reuse in Arizona
 Water Reuse in Arizona Driven by Need, Enabled by Legal Framework CIFA Conference November 2015 Tampa, Florida Water Infrastructure Finance Authority of Arizona Independent state agency Manage Arizona
Water Reuse in Arizona Driven by Need, Enabled by Legal Framework CIFA Conference November 2015 Tampa, Florida Water Infrastructure Finance Authority of Arizona Independent state agency Manage Arizona
Shortage on the Colorado River: Analysis of Impacts to Water Users in Central Arizona. Ken Seasholes
 Shortage on the Colorado River: Analysis of Impacts to Water Users in Central Arizona Ken Seasholes Manager, Resource Planning & Analysis AWRA Annual Conference, Denver November 19, 2015 Colorado River
Shortage on the Colorado River: Analysis of Impacts to Water Users in Central Arizona Ken Seasholes Manager, Resource Planning & Analysis AWRA Annual Conference, Denver November 19, 2015 Colorado River
Nevada 300,000. August 26, 2002 The CAP water in Arizona is allocated each year to cities and industries as follows: Phoenix 113,914
 Handout #3 CAP and Colorado River Facts & Figures The Colorado River is 1,450 miles long. It flows across 1,360 miles in the U.S. and 90 miles in Mexico. 1922 The Colorado River Compact divides water from
Handout #3 CAP and Colorado River Facts & Figures The Colorado River is 1,450 miles long. It flows across 1,360 miles in the U.S. and 90 miles in Mexico. 1922 The Colorado River Compact divides water from
A Look at Water Conditions in the Second-Driest State
 A Look at Water Conditions in the Second-Driest State September 18, 2008 Utah is the second-driest state in the nation and home to over 2.6 million people. When Utah experiences drought conditions, water
A Look at Water Conditions in the Second-Driest State September 18, 2008 Utah is the second-driest state in the nation and home to over 2.6 million people. When Utah experiences drought conditions, water
Securing and Protecting Water Rights and Uses in Arizona
 Securing and Protecting Water Rights and Uses in Arizona L. William Staudenmaier One Arizona Center 400 East Van Buren Street, Suite 1900 Phoenix, Arizona 85004 2202 602.382.6000 602.382 6070 (fax) www.swlaw.com
Securing and Protecting Water Rights and Uses in Arizona L. William Staudenmaier One Arizona Center 400 East Van Buren Street, Suite 1900 Phoenix, Arizona 85004 2202 602.382.6000 602.382 6070 (fax) www.swlaw.com
Coping With an Increase in Energy Usage. Cynthia Lane American Water Works Association
 Coping With an Increase in Energy Usage at Drinking Water Facilities Cynthia Lane American Water Works Association September 15, 2009 Today s Presentation Energy usage at drinking water utilities Data
Coping With an Increase in Energy Usage at Drinking Water Facilities Cynthia Lane American Water Works Association September 15, 2009 Today s Presentation Energy usage at drinking water utilities Data
Complexities Associated with Climate Change, Water, and Agriculture
 Introduction Complexities Associated with Climate Change, Water, and Agriculture Lou Swanson, Vice President for Engagement, Colorado State University Session Moderator Reagan Waskom, Director, Colorado
Introduction Complexities Associated with Climate Change, Water, and Agriculture Lou Swanson, Vice President for Engagement, Colorado State University Session Moderator Reagan Waskom, Director, Colorado
Description of Water Systems
 Description of Water Systems 1 WATER SYSTEM OWNERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT The City is a Washington State municipal corporation that owns and operates a Group A community water system within the boundaries of
Description of Water Systems 1 WATER SYSTEM OWNERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT The City is a Washington State municipal corporation that owns and operates a Group A community water system within the boundaries of
March 26, Colorado River Basin States. Colorado River overview and management. Basin States response to drought
 Integrated Resource Planning Advisory Committee March 26, 2014 Colorado River Basin States 1 Meeting Topics Colorado River overview and management Basin States response to drought U.S. Mexico Colorado
Integrated Resource Planning Advisory Committee March 26, 2014 Colorado River Basin States 1 Meeting Topics Colorado River overview and management Basin States response to drought U.S. Mexico Colorado
Maintaining Water Supply Resilience in Extreme Times
 Maintaining Water Supply Resilience in Extreme Times Presented to the Western Coalition of Arid States June 20, 2018 Presentation Outline: Snapshot of Reclamation Offices West-wide Precipitation and Storage
Maintaining Water Supply Resilience in Extreme Times Presented to the Western Coalition of Arid States June 20, 2018 Presentation Outline: Snapshot of Reclamation Offices West-wide Precipitation and Storage
Texas Municipal League Water Conference
 Texas Municipal League Water Conference January 8, 2015 Darron Leiker City Manager Wichita Falls, Texas Water Supply Summary Population served w/ water ~ 150,000 Includes 15 wholesale customers Area cities
Texas Municipal League Water Conference January 8, 2015 Darron Leiker City Manager Wichita Falls, Texas Water Supply Summary Population served w/ water ~ 150,000 Includes 15 wholesale customers Area cities
Water Users & Southern Arizona
 Water Users & Southern Arizona March 6, 2015 SOUTHERN ARIZONA WATER USERS Southern Arizona Water Users Association Water Experts & Professionals serving Southern Arizona Discuss & Analyze Issues One Voice
Water Users & Southern Arizona March 6, 2015 SOUTHERN ARIZONA WATER USERS Southern Arizona Water Users Association Water Experts & Professionals serving Southern Arizona Discuss & Analyze Issues One Voice
Arizona Department of Water Resources An Overview of Water Management in Arizona
 Arizona Department of Water Resources An Overview of Water Management in Arizona New River/Desert Hills Community Association Anthem, AZ January 9, 2015 Douglas W. Dunham Assistant to the Director Legislative
Arizona Department of Water Resources An Overview of Water Management in Arizona New River/Desert Hills Community Association Anthem, AZ January 9, 2015 Douglas W. Dunham Assistant to the Director Legislative
Beneficial Use of Produced Water: A Case Study of Projects in Colorado and Wyoming
 Beneficial Use of Produced Water: A Case Study of Projects in Colorado and Wyoming D. R. Stewart, PhD, PE* and L. Takichi, PE Review This paper discusses our combined experience in the beneficial use of
Beneficial Use of Produced Water: A Case Study of Projects in Colorado and Wyoming D. R. Stewart, PhD, PE* and L. Takichi, PE Review This paper discusses our combined experience in the beneficial use of
A Case Study: Imperial Valley, California
 University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Western Water: Expanding Uses/Finite Supplies (Summer Conference, June 2-4) Getches-Wilkinson Center Conferences, Workshops, and Hot Topics
University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Western Water: Expanding Uses/Finite Supplies (Summer Conference, June 2-4) Getches-Wilkinson Center Conferences, Workshops, and Hot Topics
Water Resources of Central Iron County and Washington County
 Water Resources of Central Iron County and Washington County An Alternative to the Lake Powell Pipeline Project Jesse Pope Instructor: Dr. Tarboton CEE 6440 2013 2 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION....3 Figure
Water Resources of Central Iron County and Washington County An Alternative to the Lake Powell Pipeline Project Jesse Pope Instructor: Dr. Tarboton CEE 6440 2013 2 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION....3 Figure
C I R P A C P R E S E N T A T I O N B Y R O N T H O M P S O N J U N E 1 6,
 WATER UPDATE C I R P A C P R E S E N T A T I O N B Y R O N T H O M P S O N J U N E 1 6, 2 0 1 6 W A T E R S U P P L Y, C O N S E R V A T I O N A N D D E V E L O P M E N T CURRENT WATER CONDITIONS 102%*
WATER UPDATE C I R P A C P R E S E N T A T I O N B Y R O N T H O M P S O N J U N E 1 6, 2 0 1 6 W A T E R S U P P L Y, C O N S E R V A T I O N A N D D E V E L O P M E N T CURRENT WATER CONDITIONS 102%*
The Quest for Long-Term Water Resource Planning
 The Quest for Long-Term Water Resource Planning Maricopa County Cooperative Extension April 29, 2009 Sharon B. Megdal, Ph.D. smegdal@cals.arizona.edu WRRC Mission The University of Arizona's Water Resources
The Quest for Long-Term Water Resource Planning Maricopa County Cooperative Extension April 29, 2009 Sharon B. Megdal, Ph.D. smegdal@cals.arizona.edu WRRC Mission The University of Arizona's Water Resources
Managed Aquifer Recharge for the Arizona Desert: The Development of Large Surface Water Spreading Facilities
 ABSTRACT & POWERPOINT PRESENTATION Managed Aquifer Recharge for the Arizona Desert: The Development of Large Surface Water Spreading Facilities Mario R. Lluria, Ph.D., P.G. Senior Professional Geohydrologist
ABSTRACT & POWERPOINT PRESENTATION Managed Aquifer Recharge for the Arizona Desert: The Development of Large Surface Water Spreading Facilities Mario R. Lluria, Ph.D., P.G. Senior Professional Geohydrologist
Preparing for the Future Near-Term Shortage and Long-Term Challenges
 Preparing for the Future Near-Term Shortage and Long-Term Challenges Coconino Plateau Watershed Partnership June 26, 2015 Dennis Rule Manager, CAGRD Central Arizona Project 336-mile aqueduct stretches
Preparing for the Future Near-Term Shortage and Long-Term Challenges Coconino Plateau Watershed Partnership June 26, 2015 Dennis Rule Manager, CAGRD Central Arizona Project 336-mile aqueduct stretches
Introduction and Background
 Securing Sustainable Water Supplies in Arizona Sharon B. Megdal, Ph.D. 1 The University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center IDS-Water 2004 Conference, May 2004 Introduction and Background Arizona
Securing Sustainable Water Supplies in Arizona Sharon B. Megdal, Ph.D. 1 The University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center IDS-Water 2004 Conference, May 2004 Introduction and Background Arizona
Wastewater Reuse - How Viable is It? Another Look
 Wastewater Reuse - How Viable is It? Another Look Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Chase, W. L.; Fulton, J. Publisher Arizona-Nevada Academy of Science Journal Hydrology and Water Resources in Arizona
Wastewater Reuse - How Viable is It? Another Look Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Chase, W. L.; Fulton, J. Publisher Arizona-Nevada Academy of Science Journal Hydrology and Water Resources in Arizona
Natural Resources of the West: Water and Drought
 Prowers Co., Colorado, 1937. (Western History Collection, University of Oklahoma) Natural Resources of the West: Water and Drought What is Drought? Thirsty corn in Iowa Drought in India Gigi A. Richard
Prowers Co., Colorado, 1937. (Western History Collection, University of Oklahoma) Natural Resources of the West: Water and Drought What is Drought? Thirsty corn in Iowa Drought in India Gigi A. Richard
light & power wastewater stormwater water fact book
 2015 fact book light & power stormwater wastewater water INSIDE UTILITIES Utilities revenue is fee based, not general fund (sales tax). Our intent: to deliver a level of service our customers expect in
2015 fact book light & power stormwater wastewater water INSIDE UTILITIES Utilities revenue is fee based, not general fund (sales tax). Our intent: to deliver a level of service our customers expect in
The Undiluted Cost of Energy and Water: From Rainfall to Outfall. Greg Harrington Professor and Associate Chair
 The Undiluted Cost of Energy and Water: From Rainfall to Outfall Greg Harrington Professor and Associate Chair Acknowledgments Graduate students Todd Elliott Irene Xagoraraki Ben Zeier Joshua Bohnert Mike
The Undiluted Cost of Energy and Water: From Rainfall to Outfall Greg Harrington Professor and Associate Chair Acknowledgments Graduate students Todd Elliott Irene Xagoraraki Ben Zeier Joshua Bohnert Mike
Water and Energy in Arizona
 Water and Energy in Arizona Bob Lo&s Arizona Public Service Company Mul: States Salinity Coali:on Summit 3/2/2017 1 Redhawk Power Plant (APS) 1,000 MW CC Mesquite Power Plant (SRP & Sempra) 1,000 MW CC
Water and Energy in Arizona Bob Lo&s Arizona Public Service Company Mul: States Salinity Coali:on Summit 3/2/2017 1 Redhawk Power Plant (APS) 1,000 MW CC Mesquite Power Plant (SRP & Sempra) 1,000 MW CC
Groundwater Management in the Sonoran Desert of Arizona: The Importance of Surface Supplies and Recharge
 Groundwater Management in the Sonoran Desert of Arizona: The Importance of Surface Supplies and Recharge Engalec 04 March 2004 XII Encuentro National de Ganaderos Lecheros Torreón, Coahuila México Sharon
Groundwater Management in the Sonoran Desert of Arizona: The Importance of Surface Supplies and Recharge Engalec 04 March 2004 XII Encuentro National de Ganaderos Lecheros Torreón, Coahuila México Sharon
Testimony David V. Modeer General Manager Central Arizona Project. House Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on Energy and Water Development
 Testimony David V. Modeer General Manager Central Arizona Project House Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on Energy and Water Development Support for $17.3 million in Fiscal Year 2015 Funding for
Testimony David V. Modeer General Manager Central Arizona Project House Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on Energy and Water Development Support for $17.3 million in Fiscal Year 2015 Funding for
HYDROLOGY NOTES LLAMA, LLAMA AND WRITE YOU NAME AND PERIOD AT THE TOP
 HYDROLOGY NOTES LLAMA, LLAMA AND WRITE YOU NAME AND PERIOD AT THE TOP QUIZ TIME: WHAT IS HYDROLOGY GOING TO BE ABOUT? A. A NATIVE AMERICAN MYTH ABOUT HYDROL THE SPIRIT WHO CONTROLS THE RAIN. B. AN EARLY
HYDROLOGY NOTES LLAMA, LLAMA AND WRITE YOU NAME AND PERIOD AT THE TOP QUIZ TIME: WHAT IS HYDROLOGY GOING TO BE ABOUT? A. A NATIVE AMERICAN MYTH ABOUT HYDROL THE SPIRIT WHO CONTROLS THE RAIN. B. AN EARLY
Raw water sources, facilities, and infrastructure
 WATER AND WASTEWATER SERVICES IN STEAMBOAT SPRINGS Prepared by Jay Gallagher, General Manager Mt. Werner Water and Sanitation District (February, 2015) Raw water sources, facilities, and infrastructure
WATER AND WASTEWATER SERVICES IN STEAMBOAT SPRINGS Prepared by Jay Gallagher, General Manager Mt. Werner Water and Sanitation District (February, 2015) Raw water sources, facilities, and infrastructure
The National Academy of Sciences Water Energy Nexus. Bob Lotts December
 The National Academy of Sciences Water Energy Nexus Bob Lotts December 5 2013 Recent Water Issues Affecting Power Plants Farley drought in ACF * River Basin Browns Ferry reduced power output due to water
The National Academy of Sciences Water Energy Nexus Bob Lotts December 5 2013 Recent Water Issues Affecting Power Plants Farley drought in ACF * River Basin Browns Ferry reduced power output due to water
Using GIS as the Backbone of the World's Largest Water Conservation Rebate Program
 Using GIS as the Backbone of the World's Largest Water Conservation Rebate Program Lou Reinbold Asst. Conservation Programs Coordinator, SNWA Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA) Member Agencies Big
Using GIS as the Backbone of the World's Largest Water Conservation Rebate Program Lou Reinbold Asst. Conservation Programs Coordinator, SNWA Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA) Member Agencies Big
LOS ANGELES DEPARTMENT OF WATER AND POWER
 LOS ANGELES DEPARTMENT OF WATER AND POWER FISCAL YEAR 2015-2016 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The goals and objectives of the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) for Fiscal Year 2015-16 are in alignment
LOS ANGELES DEPARTMENT OF WATER AND POWER FISCAL YEAR 2015-2016 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The goals and objectives of the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) for Fiscal Year 2015-16 are in alignment
Water Resources. Israel, Jordan and the United States a case study
 World Geography TEK (12) Economics. The student understands the economic importance of, and issues related to, the location and management of resources. The student is expected to: (A) analyze how the
World Geography TEK (12) Economics. The student understands the economic importance of, and issues related to, the location and management of resources. The student is expected to: (A) analyze how the
Profile of the South Platte River Basin
 Cooperative Extension, Colorado State University http://dare.agsci.colostate.edu/csuagecon/extension/pubstools.htm Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics, Fort Collins, CO 80523-1172 December
Cooperative Extension, Colorado State University http://dare.agsci.colostate.edu/csuagecon/extension/pubstools.htm Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics, Fort Collins, CO 80523-1172 December
Overview of US Water Sector
 Overview of US Water Sector The broadly defined US water sector represented approximately US$124 billion in revenues in 2008, growing 4-5% over 2007 figures. Water utilities (about 70% public sector) and
Overview of US Water Sector The broadly defined US water sector represented approximately US$124 billion in revenues in 2008, growing 4-5% over 2007 figures. Water utilities (about 70% public sector) and
Water Management in Arizona: An Introduction League of Arizona Cities and Towns September 1, 2004
 Water Management in Arizona: An Introduction League of Arizona Cities and Towns September 1, 2004 Sharon B. Megdal, Director Water Resources Research Center 350 N. Campbell Tucson, AZ 85721 520-792-9591,
Water Management in Arizona: An Introduction League of Arizona Cities and Towns September 1, 2004 Sharon B. Megdal, Director Water Resources Research Center 350 N. Campbell Tucson, AZ 85721 520-792-9591,
CHAPTER 3 THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
 Water Resources Water is an essential resource to sustain human life, a healthy environment, and a strong economy. Since its early days, Tucson has relied on the same underground water source. In the mid-1940s,
Water Resources Water is an essential resource to sustain human life, a healthy environment, and a strong economy. Since its early days, Tucson has relied on the same underground water source. In the mid-1940s,
Legislative Committee on Public Lands
 Legislative Committee on Public Lands EXHIBIT D2 May 28, 2004 EXHIBIT D2 Committee Name Lands Document consists of 74 Slides Entire document provided. Due to size limitations, pages provided. A copy of
Legislative Committee on Public Lands EXHIBIT D2 May 28, 2004 EXHIBIT D2 Committee Name Lands Document consists of 74 Slides Entire document provided. Due to size limitations, pages provided. A copy of
Ensuring Reliable Water Supplies for Central Arizona. Marie Pearthree, P.E. Assistant General Manager Central Arizona Project
 Ensuring Reliable Water Supplies for Central Arizona Marie Pearthree, P.E. Assistant General Manager Central Arizona Project WESTCAS Fall Conference October 28, 2009 A Drying West A Question of Power A
Ensuring Reliable Water Supplies for Central Arizona Marie Pearthree, P.E. Assistant General Manager Central Arizona Project WESTCAS Fall Conference October 28, 2009 A Drying West A Question of Power A
New Roles for the Bureau of Reclamation
 University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Books, Reports, and Studies Getches-Wilkinson Center for Natural Resources, Energy, and the Environment 1989 New Roles for the Bureau of
University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Books, Reports, and Studies Getches-Wilkinson Center for Natural Resources, Energy, and the Environment 1989 New Roles for the Bureau of
The State of the Colorado River
 April 2014 The State of the Colorado River Executive Summary The Colorado River Basin is now in its fifteenth year of drought. System runoff during this period has been comparable to or less than that
April 2014 The State of the Colorado River Executive Summary The Colorado River Basin is now in its fifteenth year of drought. System runoff during this period has been comparable to or less than that
CHAPTER. 14 Water Resources
 CHAPTER 14 Water Resources Looking for Water... in the Desert The 2300-kilometer Colorado River once flowed deep and wide across the Southwest to Mexico s Gulf of California. Since the Colorado River Compact,
CHAPTER 14 Water Resources Looking for Water... in the Desert The 2300-kilometer Colorado River once flowed deep and wide across the Southwest to Mexico s Gulf of California. Since the Colorado River Compact,
TGR EDU: EXPLORE MIDDLE SCHOOL PROJECT PIPELINE FRESHWATER IMPACT
 TGR EDU: EXPLORE PROJECT MIDDLE SCHL PIPELINE FRESHWATER IMPACT LESSON OVERVIEW: Did you know that only 3.5% of Earth s water is freshwater, and over 98% of that water is locked up in ice, glaciers,and
TGR EDU: EXPLORE PROJECT MIDDLE SCHL PIPELINE FRESHWATER IMPACT LESSON OVERVIEW: Did you know that only 3.5% of Earth s water is freshwater, and over 98% of that water is locked up in ice, glaciers,and
Anthropogenic Southwest Drying CMIP5 Style
 Anthropogenic Southwest Drying CMIP5 Style Richard Seager, Mingfang Ting, Cuihua Li, Ben Cook, Naomi Naik, Jennifer Nakamura, Haibo Liu Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University To recap...
Anthropogenic Southwest Drying CMIP5 Style Richard Seager, Mingfang Ting, Cuihua Li, Ben Cook, Naomi Naik, Jennifer Nakamura, Haibo Liu Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University To recap...
LOS ANGELES DEPARTMENT OF WATER AND POWER
 LOS ANGELES DEPARTMENT OF WATER AND POWER FISCAL YEAR 2016-2017 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The goals and objectives of the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) for Fiscal Year 2016-17 are in alignment
LOS ANGELES DEPARTMENT OF WATER AND POWER FISCAL YEAR 2016-2017 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The goals and objectives of the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) for Fiscal Year 2016-17 are in alignment
SLIDES: Perspectives on Water Management in Arizona
 University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Innovations in Managing Western Water: New Approaches for Balancing Environmental, Social and Economic Outcomes (Martz Summer Conference,
University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Innovations in Managing Western Water: New Approaches for Balancing Environmental, Social and Economic Outcomes (Martz Summer Conference,
APPENDIX C 2012 RECYCLED WATER FEASIBILITY STUDY PUBLIC COMMENT RESPONSES
 APPENDIX C 2012 RECYCLED WATER FEASIBILITY STUDY PUBLIC COMMENT RESPONSES Prepared by: Dennis Delzeit, P.E., Project Manager Reviewed by: Tom Falk, P.E., Dudek Date: April 26, 2012 1. Can the treated effluent
APPENDIX C 2012 RECYCLED WATER FEASIBILITY STUDY PUBLIC COMMENT RESPONSES Prepared by: Dennis Delzeit, P.E., Project Manager Reviewed by: Tom Falk, P.E., Dudek Date: April 26, 2012 1. Can the treated effluent
Water for Tucson s Future
 For more information about Tucson Water s Water Plan 2000-2050, call 791-4331 or visit their web site at www.cityoftucson.org/water. Para recibir esta informacíon en español, sírvase llamar al 791-4331.
For more information about Tucson Water s Water Plan 2000-2050, call 791-4331 or visit their web site at www.cityoftucson.org/water. Para recibir esta informacíon en español, sírvase llamar al 791-4331.
A deep dive into the water space
 A deep dive into the water space May 2018 Introduction Water is a life-sustaining resource with no substitute; humans, animals and plants alike all require water to survive. Water, and the infrastructure
A deep dive into the water space May 2018 Introduction Water is a life-sustaining resource with no substitute; humans, animals and plants alike all require water to survive. Water, and the infrastructure
SLIDES: Tightening Water Supplies
 University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Hard Times on the Colorado River: Drought, Growth and the Future of the Compact (Summer Conference, June 8-10) 2005 6-9-2005 SLIDES: Tightening
University of Colorado Law School Colorado Law Scholarly Commons Hard Times on the Colorado River: Drought, Growth and the Future of the Compact (Summer Conference, June 8-10) 2005 6-9-2005 SLIDES: Tightening
Monday July 27th, Flagstaff, Arizona
 Monday July 27th, 2015 Flagstaff, Arizona OVERVIEW Colorado River and Western Drought Challenges Increasing Water Storage Projects and Solutions Bureau of Reclamation Transparency Act Bill Williams Water
Monday July 27th, 2015 Flagstaff, Arizona OVERVIEW Colorado River and Western Drought Challenges Increasing Water Storage Projects and Solutions Bureau of Reclamation Transparency Act Bill Williams Water
(b) Water Engineering Basics
 NRRI Training for the Oklahoma Corporation Commission March 14-16, 2017 Topic 3 (b) Water Engineering Basics Kathryn J. Kline Research Associate National Regulatory Research Institute kkline@nrri.org Industry
NRRI Training for the Oklahoma Corporation Commission March 14-16, 2017 Topic 3 (b) Water Engineering Basics Kathryn J. Kline Research Associate National Regulatory Research Institute kkline@nrri.org Industry
Bottled Water: What s the problem?
 Bottled Water: What s the problem? Where does your water come from? Groundwater Reservoir River What is groundwater? Aquifers and Groundwater Groundwater: any water that is found underground in cracks
Bottled Water: What s the problem? Where does your water come from? Groundwater Reservoir River What is groundwater? Aquifers and Groundwater Groundwater: any water that is found underground in cracks
City of Ceres Water Conservation Program
 City of Ceres Water Conservation Program The City of Ceres continues to be committed to water conservation and our residents; making every effort to efficiently utilize our produced water supply while
City of Ceres Water Conservation Program The City of Ceres continues to be committed to water conservation and our residents; making every effort to efficiently utilize our produced water supply while
o Groundwater Groundwater use within AMAs (Active Management Areas) limited by GMA (groundwater management act) Page 1 of 10
 Workshop on Water and Growth: Future Water Supplies for Central Arizona Sponsored by the ASU Global Institute of Sustainability and the Sustainability Partnership Phoenix, Arizona June 21, 2006 Issues
Workshop on Water and Growth: Future Water Supplies for Central Arizona Sponsored by the ASU Global Institute of Sustainability and the Sustainability Partnership Phoenix, Arizona June 21, 2006 Issues
MAJOR THEMES IN ARIZONA S WATER FUTURE
 Chapter 2 MAJOR THEMES IN ARIZONA S WATER FUTURE KATHY JACOBS AND MARSHALL A. WORDEN Seven major themes or overarching concerns regarding Arizona s water future are discussed in succeeding chapters. Information
Chapter 2 MAJOR THEMES IN ARIZONA S WATER FUTURE KATHY JACOBS AND MARSHALL A. WORDEN Seven major themes or overarching concerns regarding Arizona s water future are discussed in succeeding chapters. Information
The Future of Water Supply for California s Cities. March 2, 2016
 The Future of Water Supply for California s Cities March 2, 2016 Current Situation End of a four-year drought? Supplies stretched but not broken Significant and unprecedented state action Relatively modest
The Future of Water Supply for California s Cities March 2, 2016 Current Situation End of a four-year drought? Supplies stretched but not broken Significant and unprecedented state action Relatively modest
Volume 1 Executive Summary
 2013 Cheyenne Water and Wastewater Master Plans Final November 27, 2013 Prepared for: City of Cheyenne Board of Public Utilities 2416 Snyder Ave. Cheyenne, WY 82001 Prepared by: HDR Engineering AMEC Earth
2013 Cheyenne Water and Wastewater Master Plans Final November 27, 2013 Prepared for: City of Cheyenne Board of Public Utilities 2416 Snyder Ave. Cheyenne, WY 82001 Prepared by: HDR Engineering AMEC Earth
Southern Nevada Water Briefing. John J. Entsminger, General Manager
 Southern Nevada Water Briefing John J. Entsminger, General Manager MAJOR RESPONSIBILITIES Regional water supply planning Conservation programming Water quality Managing and protecting environmental resources
Southern Nevada Water Briefing John J. Entsminger, General Manager MAJOR RESPONSIBILITIES Regional water supply planning Conservation programming Water quality Managing and protecting environmental resources
CHAPTER SEVEN: UTILITIES
 CHAPTER SEVEN: UTILITIES 7.1 Introduction The Water Works Board of the City of Auburn (AWWB) is the primary potable water service provider for the City of Auburn (City) and Auburn University. There are
CHAPTER SEVEN: UTILITIES 7.1 Introduction The Water Works Board of the City of Auburn (AWWB) is the primary potable water service provider for the City of Auburn (City) and Auburn University. There are
Detail on Concentrate Handling and Disposal Options
 Detail on Concentrate Handling and Disposal Options A number of options are available for disposing of concentrate including direct disposal as well as additional handling and/or treatment designed to
Detail on Concentrate Handling and Disposal Options A number of options are available for disposing of concentrate including direct disposal as well as additional handling and/or treatment designed to
Hydrologic Characteristics of the Owens River Basin below the Upper Owens River
 Appendix T. Hydrologic Characteristics of the Owens River Basin below the Upper Owens River The hydrology of Mono Basin is described in detail in Chapter 3A. This appendix describes the Owens River basin
Appendix T. Hydrologic Characteristics of the Owens River Basin below the Upper Owens River The hydrology of Mono Basin is described in detail in Chapter 3A. This appendix describes the Owens River basin
Government Involvement in Desalination
 Chapter 7 Government Involvement in Desalination provements in distillation technologies. Any future Federal funding for R&D could lead to further im- provements in membrane technology and desali- nation
Chapter 7 Government Involvement in Desalination provements in distillation technologies. Any future Federal funding for R&D could lead to further im- provements in membrane technology and desali- nation
BEFORE THE NEW MEXICO PUBLIC REGULATION COMMISSION
 BEFORE THE NEW MEXICO PUBLIC REGULATION COMMISSION IN THE MATTER OF THE APPLICATION OF ) PUBLIC SERVICE COMPANY OF NEW MEXICO ) FOR APPROVAL OF A CERTIFICATE OF PUBLIC ) CONVENIENCE AND NECESSITY FOR A
BEFORE THE NEW MEXICO PUBLIC REGULATION COMMISSION IN THE MATTER OF THE APPLICATION OF ) PUBLIC SERVICE COMPANY OF NEW MEXICO ) FOR APPROVAL OF A CERTIFICATE OF PUBLIC ) CONVENIENCE AND NECESSITY FOR A
Supplemental Water Supply Program and Fee Study. City of Coachella
 Supplemental Water Supply Program and Fee Study City of Coachella Prepared By: TKE Engineering, Inc. 2305 Chicago Avenue Riverside, CA 92507 (951) 680-0440 TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1 Coachella Water Authority...
Supplemental Water Supply Program and Fee Study City of Coachella Prepared By: TKE Engineering, Inc. 2305 Chicago Avenue Riverside, CA 92507 (951) 680-0440 TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1 Coachella Water Authority...
ADVERTISEMENT: REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL
 City of Cortez Service Center 110 West Progress Circle Cortez, CO 81321 PW-18-96 ADVERTISEMENT: REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL WATER TREATMENT PLANT PLC AND SCADA SYSTEM UPGRADE PROJECT SCOPE: The City of Cortez
City of Cortez Service Center 110 West Progress Circle Cortez, CO 81321 PW-18-96 ADVERTISEMENT: REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL WATER TREATMENT PLANT PLC AND SCADA SYSTEM UPGRADE PROJECT SCOPE: The City of Cortez
Santa Barbara County Region
 Attachment 3 Santa Barbara County Region IRWM Implementation Grant Proposal Attachment 3 consists of the following items:. Attachment 3 provides a project description, estimated physical benefits, technical
Attachment 3 Santa Barbara County Region IRWM Implementation Grant Proposal Attachment 3 consists of the following items:. Attachment 3 provides a project description, estimated physical benefits, technical
The Drainage Basin. From Peaks of Colorado to Mexico 1,400 miles Drains 242,000 square miles of Western US Colored River because of sediments
 HOOVER DAM Need arose to control the Colorado River flow and the cycles of flood and drought. Responsibility fell on the Department of the Interior s Bureau of Reclamation Colorado River Compact History
HOOVER DAM Need arose to control the Colorado River flow and the cycles of flood and drought. Responsibility fell on the Department of the Interior s Bureau of Reclamation Colorado River Compact History
Desalination Plans to Solve Water Scarcity
 Desalination Plans to Solve Water Scarcity Thomas Manaugh, PhD Integral Scientific Institute "A new type of thinking is essential if mankind is to survive and move toward higher levels. -- Albert Einstein
Desalination Plans to Solve Water Scarcity Thomas Manaugh, PhD Integral Scientific Institute "A new type of thinking is essential if mankind is to survive and move toward higher levels. -- Albert Einstein
A hot drought : Warming is driving much of the Colorado River s decline, scientists say
 A hot drought : Warming is driving much of the Colorado River s decline, scientists say Brinkwire September 8, 2018 Since 2000, the amount of water flowing in the Colorado River has dropped 19 percent
A hot drought : Warming is driving much of the Colorado River s decline, scientists say Brinkwire September 8, 2018 Since 2000, the amount of water flowing in the Colorado River has dropped 19 percent
DESERT ROSE H20. Final Design Report. Fredonia, AZ Water Safety Plan CENE 486C 12/14/2017
 DESERT ROSE H20 Final Design Report Fredonia, AZ Water Safety Plan CENE 486C 12/14/2017 This report shows the characterization of the Navajo Sandstone Aquifer, characterization of the water distribution
DESERT ROSE H20 Final Design Report Fredonia, AZ Water Safety Plan CENE 486C 12/14/2017 This report shows the characterization of the Navajo Sandstone Aquifer, characterization of the water distribution
WATER USE EFFICIENCY PROGRAM
 WATER USE EFFICIENCY PROGRAM The following describes the City s current water use efficiency (WUE) goals, current and future water conservation measures, and potential water savings from the City s WUE
WATER USE EFFICIENCY PROGRAM The following describes the City s current water use efficiency (WUE) goals, current and future water conservation measures, and potential water savings from the City s WUE
Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study. Leslie Meyers Coconino Plateau Water Advisory Council Strategic Planning Retreat April 26, 2013
 Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study Leslie Meyers Coconino Plateau Water Advisory Council Strategic Planning Retreat April 26, 2013 Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study Study
Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study Leslie Meyers Coconino Plateau Water Advisory Council Strategic Planning Retreat April 26, 2013 Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study Study
aka the basin study Eric Kuhn General Manager 2013 Upper Colorado River Basin Water Conference Colorado Mesa University November 7, 2013
 aka the basin study 2013 Upper Colorado River Basin Water Conference Colorado Mesa University November 7, 2013 Eric Kuhn General Manager THE STORYLINE OF THE COLORADO RIVER: Limited Supplies Competing
aka the basin study 2013 Upper Colorado River Basin Water Conference Colorado Mesa University November 7, 2013 Eric Kuhn General Manager THE STORYLINE OF THE COLORADO RIVER: Limited Supplies Competing
ENERGY FACILITY LICENSING PROCESS
 ENERGY FACILITY LICENSING PROCESS CALIFORNIA ENERGY COMMISSION Water Supply Information STAFF PAPER/DRAFT DECEMBER 2000 P700-00-017 STATE OF CALIFORNIA 1975 2000 ENERGY COMMISSION Gray Davis, Governor
ENERGY FACILITY LICENSING PROCESS CALIFORNIA ENERGY COMMISSION Water Supply Information STAFF PAPER/DRAFT DECEMBER 2000 P700-00-017 STATE OF CALIFORNIA 1975 2000 ENERGY COMMISSION Gray Davis, Governor
14 Water Resources. Looking for Water... in the Desert. Where Is Our Water? Lesson 1.1 Earth: The Water Planet
 CHAPTER 14 Water Resources Looking for Water... in the Desert The 2300-kilometer Colorado River once flowed deep and wide across the Southwest to Mexico s Gulf of California. Since the Colorado River Compact,
CHAPTER 14 Water Resources Looking for Water... in the Desert The 2300-kilometer Colorado River once flowed deep and wide across the Southwest to Mexico s Gulf of California. Since the Colorado River Compact,
Water Demand and Supply Outlook for Greater Chicago Area
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC 2009 Conference Proceedings 7-2009 Water Demand and Supply Outlook for Greater Chicago Area Ben Dziegielewski Southern Illinois University Carbondale Follow
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC 2009 Conference Proceedings 7-2009 Water Demand and Supply Outlook for Greater Chicago Area Ben Dziegielewski Southern Illinois University Carbondale Follow
Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet
 1 Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet Kerry Schwartz, Director, Arizona Project WET Protect Your Groundwater Day: Tuesday, September 9, 2014 What I Hope to Convey Groundwater
1 Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet Kerry Schwartz, Director, Arizona Project WET Protect Your Groundwater Day: Tuesday, September 9, 2014 What I Hope to Convey Groundwater
Water Resources of the Virgin River Basin
 Water Resources of the Virgin River Basin Michael Johnson, Chief Hydrologist Virgin Valley Water District for Legislative Committee on Public Lands January 22, 2010 Las Vegas, Nevada Virgin River Drainage
Water Resources of the Virgin River Basin Michael Johnson, Chief Hydrologist Virgin Valley Water District for Legislative Committee on Public Lands January 22, 2010 Las Vegas, Nevada Virgin River Drainage
TECHNICAL EVALUATION OF OPTIONS FOR LONG-TERM AUGMENTATION OF THE COLORADO RIVER SYSTEM RESERVOIR EVAPORATION CONTROL
 TECHNICAL EVALUATION OF OPTIONS FOR LONG-TERM AUGMENTATION OF THE COLORADO RIVER SYSTEM RESERVOIR EVAPORATION CONTROL BY: GREGG THOMPSON, PROJECT ENGINEER CH2M HILL JOSEPH LIN, STAFF ENGINEER CH2M HILL
TECHNICAL EVALUATION OF OPTIONS FOR LONG-TERM AUGMENTATION OF THE COLORADO RIVER SYSTEM RESERVOIR EVAPORATION CONTROL BY: GREGG THOMPSON, PROJECT ENGINEER CH2M HILL JOSEPH LIN, STAFF ENGINEER CH2M HILL
ORANGE WATER AND SEWER AUTHORITY Quality Service Since 1977
 ORANGE WATER AND SEWER AUTHORITY Quality Service Since 1977 Mayor Kevin Foy Town of Chapel Hill 306 North Columbia Street Chapel Hill, NC 27516 Chairman Barry Jacobs Orange County Board of Commissioners
ORANGE WATER AND SEWER AUTHORITY Quality Service Since 1977 Mayor Kevin Foy Town of Chapel Hill 306 North Columbia Street Chapel Hill, NC 27516 Chairman Barry Jacobs Orange County Board of Commissioners
