AP Environmental Science Summer Assignments Mrs. Lena Agulian
|
|
|
- Amelia Sherman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mrs. Lena Agulian Hello! I hope that you have an enjoyable, exciting, and educational summer! Here are some activities that you need do this summer to prepare for AP Environmental Science(APES) in the fall. The objective of this summer assignment is to get you thinking environmentally and to refresh some math skills. Please note that these assignment will be collected for a grade at the end of the first week of school. There are 8 tasks to complete. All of your work is to be done in your APES Binder on 8 ½ x 11 inch college ruled loose leaf paper ( no exceptions). Write in ink except for any math you need to do. These assignments will have their own section in your binder, tabbed summer. Each task must begin on a new sheet of paper CONSIDER finding recycled paper- you are an environmentally conscientious consumer. DO YOUR OWN WORK, it s worth more to me as your instructor to hear your voice and your genuine effort lands well with me! Do Not Procrastinate- tackle a bit each week. August 18 th is our first day back- and we all know time FLIES. Task 1: Read the essay Tragedy of the Commons by Garrett Hardin. Here is a link: hen you have completed the reading, please respond to the following in complete sentences: a. What is Garrett Hardin s central idea in this essay? b. Do you personally agree with Hardin s central idea? c. Is the Tragedy of the Commons unavoidable? d. Identify one commons in your own life (at school, home, work) and explain how it is (or is not) being managed wisely to avoid the situation described in the essay. Task 2: Math Assignment. Please complete the following problems, showing all work and units. a. How many square centimeters are there in a square meter? b. How many square inches are there in a square meter? c. You may someday purchase a house that has 2500 square feet of living space. How many square meters of living space is this? d. If a calorie is equivalent to joules, how many joules are contained in that 200 kilocalorie slice of pizza? e. If a city of 10,000 experiences 100 births, 30 deaths, 10 immigrants, and 20 emigrants in the course of a year, what is its net annual percentage growth rate?
2 Task 3: Fruits and Vegetables on the Move! At some point over the summer, look around your house and identify a piece of fruit or vegetable that has travelled to be a part of your diet. Usually there is a sticker on the item telling you its country of origin or you could go to a food store and browse. (hint: do not use the tomato you picked out of the garden that morning) For the item you select: a. Record date, item, and its country of origin b. Use internet resources or other sources to estimate the distance from where the item was grown to your home. Do the best estimate you can obviously it is difficult/impossible to tell where in Mexico that cantaloupe came from c. List the most likely modes of transportation (hint: there are probably more than one of them) used to move that item from the field where it was growing to your kitchen. d. Respond to the following in a paragraph or two: What are the environmental impacts of shipping fresh produce over long distances? What are the health benefits/health costs of having a wide variety of fresh produce available at all times? Is it worth it?
3 Mrs. Lena Agulian Task #4 Because we will be discussing environmental issues throughout the world, a working knowledge of world geography is essential. All AP Environmental Science students must know the names and locations of the following on a map of the world: all continents, all oceans, major seas and lakes (Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, Mediterranean Sea, Arabian Sea, Black Sea, all 5 Great Lakes, Caspian Sea, Aral Sea), major rivers and river systems (Amazon, Nile, Mississippi (also Missouri and Ohio Rivers), Yangtze, Ganges, Yellow), major mountain chains (Rockies, Andes, Appalachians, Alps, Urals, Himalayas), and approximate locations of some major world cities (New York, Los Angeles, Mexico City, London, Tokyo, Shanghai). Students should also be able to draw the equator on a map of the world within 10 degrees of latitude. A map quiz will be given during the first week of school. To do this find a blank world map online- print it out and label as best you can. Using color will earn you maximum points here. FIND how to label a map on the internet follow the guidelines ( for example, things should be labeled horizontally) Task #5 Make flashcards of the attached vocabulary and become familiar with and be able to use the attached Prerequisite Basic Mathematical Skills. Task #6 Go to There are 10 questions on this web site and answers to these questions. The answers for each question are presented in 3 different levels of depth which allows readers to explore as deeply or as superficially as they like. You should read the first Summary level answers for all 10 questions and be prepared for a quiz on the first level answers the second day of school. You are encouraged to read the second Details level if your background in ecology/ecosystems is weak. Task #7 The AP Environmental Science exam will have some mathematical calculations in the multiple choice section, and one of the free response questions always involves mathematical calculations. No calculators are allowed during the exam. Therefore, a thorough knowledge of scientific notation, metric and English systems of measurement, and basic computational skills to be performed without a calculator is necessary. Review the information below and complete the problems to be turned in the first day of class. Also, expect a quiz on the metric system, percentages, units (conversion factors will be supplied to you if needed on the quiz) and scientific notation during the first week of school to be done without a calculator. Task #8 Online video resources.
4 a. Bozeman AP Environmental Science at - watch the FIRST 2 videos and take notes. Also make a list of the videos available in the notes, it is optional to watch additional videos. b. Watch the video Emerging Science: Ecological Economics at - watch the video and take notes. c. Watch the TED Talk Pavan Sukhdev: Put a value on nature at - watch the video and take notes. d. Crash Course Ecology at make a list of the videos available in the notes, it is optional to watch the ones you are most interested in.
5 Mrs. Lena Agulian Prerequisite Basic Mathematical Skills Percentage 17% = 17/100 =.17 - Remember that percent literally means divided by Percentage is a measure of the part of the whole, or part divided by whole. - Ex. 15 million is what percentage of the US population? 15 million / 300 million =.05 = 5% - What is 20% of this $15 bill so that I can give a good tip? $15 x.20 = $15 x 20/100 = $3 Rates Rise Y2-Y1 slope change y=mx+b dx Run X2-X1 time dt - All of the above are ways to look at rates. The second equation is the easiest way to calculate a rate, especially from looking at a graph. Rates will often be written using the word per followed by a unit of time, such as cases per year, grams per minute or miles per hour. The word per means to divide, so miles per gallon is actually the number of miles driven divided by one gallon. - Rates are calculating how much an amount changes in a given amount of time. Scientific Notation Thousand = 103 =1,000 Million = 106 =1,000,000 (people in the US) Billion = 109 =1,000,000,000 (people on Earth) Trillion = 1012 =1,000,000,000,000 (National debt) - When using very large numbers, scientific notation is often easiest to manipulate. For example, the US population is 300 million people or 300x106 or 3x108 - When adding or subtracting, exponents must be the same. Add the numbers in front of the ten and keep the exponent the same. - When multiplying or dividing, multiply or divide the number in front of the ten and add the exponents if multiplying or subtract the exponents if dividing - Online tutorial: Ex. 9x106 / 3x102 = (9/3) x 10(6-2) = 3 x 104 Dimensional Analysis You should be able to convert any unit into any other unit accurately if given the conversion factor. Online tutorials are available:
6 Prefixes m (milli) =1/1000 =10-3 c (cent) =1/100 =10-2 k (kilo) =1000 =103 M (mega) =1,000,000 =106 G (giga) =1,000,000,000 =109 T (tera) =1,000,000,000,000 =1012 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignments Long Division and Multiplication You should be able to do these calculations by hand, including values with decimals and scientific notation. Many students struggle in this area because calculators are not allowed on the AP exam. Online tutorials are available: Vocabulary Terms On each flash card, write a definition and sentence/example for each the following vocabulary terms in the context of environmental science.
7 1. Environment 2. environmental studies 3. ecosystem services 4. ecology 5. ecosystem 6. environmentalist 7. biodiversity 8. genetic diversity 9. species 10. species diversity 11. speciation 12. background 13. extinction rate 14. anthropogenic 15. greenhouse gases 16. sustainable development 17. sustainability 18. Biophilia 19. Ecological footprint 20. Scientific method 21. Null hypothesis 22. Hypothesis 23. Replication 24. Accuracy 25. Precision 26. Uncertainty 27. Control group 28. Natural experiment 29. Matter 30. Mass 31. Atom 32. Element 33. Periodic table 34. Molecule 35. Compound 36. Atomic number 37. Mass number 38. Isotopes 39. Radioactive decay 40. Half-life 41. Covalent bond 42. Ionic bond 43. Hydrogen bond 44. Polar molecule 45. Surface tension 46. Capillary action 47. Acid 48. Base 49. ph 50. chemical reaction 51. law of conservation of matter 52. inorganic compounds 53. organic compounds 54. carbohydrates 55. lipids 56. protein 57. DNA 58. RNA 59. nucleic acids 60. cell 61. energy 62. joule 63. power 64. electromagnetic radiation 65. photon 66. potential energy 67. chemical energy 68. kinetic energy 69. temperature 70. natural capital 71. natural resources 72. nutrient cycling 73. per capita resource 74. conservation 75. sustainable 76. yield 77. environmental degradation 78. tragedy of the commons 79. pollution 80. point source 81. nonpoint source output pollution 82. control 83. input pollution 84. control 85. natural experiment 86. fracking
8 Summer Assignments Math problems to be turned in the first day of class. Answer the questions. Use a separate sheet of paper to show all work. 1) What is ten thousand times one hundred million? Show your work in scientific notation. Give the answer in scientific notation and in words. 2) A population of deer had 325 individuals. If the population grows by 16% in one year, how many deer will there be the next year? 3) One year I had 124 AP Environmental Science students and the next year I had 87 Environmental Science students. What percentage did the population of APES students decrease by (round to the nearest tenth)? 4) Electricity costs 7 cents per kilowatt hour. In one month one home uses 1.8 megawatt hours of electricity. How much will the electric bill be? 5) Your car gets 21 miles to the gallon and your friend s car gets 28 miles to the gallon. You decide to go on a road trip to the University of Virginia, which is 175 miles away. If gas costs $4 per gallon and you decide to split the gas money, how much money will each of you save in gas by driving your friend s car? 6) Virginia Beach is about 20 miles wide and 28 miles long. If one inch of rain falls on Virginia Beach, how many cubic feet of rain fell on Virginia Beach? (Hint: convert all units to feet first). 7) The concentration of mercury in a water supply changes from 10ppm (parts per million) to 56ppm over a ten-year period. What is the percentage change of the mercury concentration? 8) Consider a wind turbine that is rated at 1.5 MW (megawatts) per hour. This means that with sufficiently high winds, it will produce 1.5 MW or 1,500 kw (kilowatts) of power. If this wind turbine runs at its rated power of 100% of the time for a full year, how much energy would it produce in a year? Give your answer in kwh/year (kilowatt hours per year). 9) Show your work for the following multiplication and division problems. You can use a calculator to check your work, but I want to see that you understand how to solve these problems by hand. Just like on the AP exam, no credit is given if you don t show your work. a x 16.9 b x.0718 c. 5.80x10-3 x 2.17 d / 71.9 e..08 /.0094 f. 4.60x104/.0530
AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment
 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment Congratulation on your decision to challenge yourself by taking APES. I am looking forward to work with you on mastering the concepts and preparing for the AP
AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment Congratulation on your decision to challenge yourself by taking APES. I am looking forward to work with you on mastering the concepts and preparing for the AP
AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment
 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment Dear AP Environmental Science Classes of 2014-2015, Welcome to AP Environmental Science!!! Students who enroll in APES should be ready and willing to devote sufficient
AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment Dear AP Environmental Science Classes of 2014-2015, Welcome to AP Environmental Science!!! Students who enroll in APES should be ready and willing to devote sufficient
Name: 2017 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment
 P a g e 1 Name: 2017 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment The Summer Assignment is due on the first day of class. P a g e 2 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment (This assignment is due on the
P a g e 1 Name: 2017 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment The Summer Assignment is due on the first day of class. P a g e 2 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment (This assignment is due on the
AP* Environmental Science Mastering the Math
 AP* Environmental Science Mastering the Math Part I: Dimensional Analysis (aka Factor-Label or Unit Cancellation Method) Sample Problem 1 A large, coal-fired electric power plant produces 12 million kilowatt-hours
AP* Environmental Science Mastering the Math Part I: Dimensional Analysis (aka Factor-Label or Unit Cancellation Method) Sample Problem 1 A large, coal-fired electric power plant produces 12 million kilowatt-hours
Environmental Problems, Causes, & Sustainability
 CHAPTER 1 Environmental Problems, Causes, & Sustainability Core Case Study: Living in an Exponential Age Describe exponential growth and what the graph would look like. Human population is experiencing
CHAPTER 1 Environmental Problems, Causes, & Sustainability Core Case Study: Living in an Exponential Age Describe exponential growth and what the graph would look like. Human population is experiencing
Unit 1. Science and the Environment
 Unit 1 Science and the Environment Part 1 Understanding Our Environment Part 1 This section describes the fields that contribute to environmental science. It also explores the history of humans in the
Unit 1 Science and the Environment Part 1 Understanding Our Environment Part 1 This section describes the fields that contribute to environmental science. It also explores the history of humans in the
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use.
 This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
Constant of Proportionality
 Constant of Proportionality LAUNCH (6 MIN) Before How can you use the titles on the axes to help you understand the meaning of the graph? Does this graph show a proportional relationship? How can you tell?
Constant of Proportionality LAUNCH (6 MIN) Before How can you use the titles on the axes to help you understand the meaning of the graph? Does this graph show a proportional relationship? How can you tell?
What is (are) the types of pollution discussed in your article? How does this pollution affect people and the environment?
 Pollution Work Sheet Read the article that has been assigned to your group and then, as a group, answer the following questions. At the end of class, each group will present on what they read. Name of
Pollution Work Sheet Read the article that has been assigned to your group and then, as a group, answer the following questions. At the end of class, each group will present on what they read. Name of
Pre-lab Homework Lab 10: Global Warming Prior to lab, answer the following questions to help you become prepared for the lab.
 Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework Prior to lab, answer the following questions to help you become prepared for the lab. 1. You will be calculating your carbon footprint as part of lab (an estimate of
Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework Prior to lab, answer the following questions to help you become prepared for the lab. 1. You will be calculating your carbon footprint as part of lab (an estimate of
Ecology Unit Guide Due October 2nd Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 14 Biochemistry Test Corrections
 Ecology Unit Guide Due October 2nd Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 14 Biochemistry Test Corrections 15 Introduce Part 1 - Choose & Research Country 16 Continue Part 1 17 Part 2 Climate Experiment
Ecology Unit Guide Due October 2nd Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 14 Biochemistry Test Corrections 15 Introduce Part 1 - Choose & Research Country 16 Continue Part 1 17 Part 2 Climate Experiment
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS
 ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
Reading Your Electric Meter
 AK Reading Your Electric Meter Target grades: 3-5 AK GLEs: Science Math [3/4/5] SA1.1 [3] E&C-4 [3/4/5] SA1.2 [4/5] E&C-3 [3/4] SA2.1 [3/4/5] S&P-2 Reading [3/4/5] 1.6.1 [3] 1.6.2 Set up time: 15 minutes
AK Reading Your Electric Meter Target grades: 3-5 AK GLEs: Science Math [3/4/5] SA1.1 [3] E&C-4 [3/4/5] SA1.2 [4/5] E&C-3 [3/4] SA2.1 [3/4/5] S&P-2 Reading [3/4/5] 1.6.1 [3] 1.6.2 Set up time: 15 minutes
Environmental Geography
 Environmental Geography Lecture 13 Water Pollution Lecture 13: Water Pollution I. Water Pollution A. Groundwater B. Surface Water C. Regulation II. Water Use in California 1 I. Water Pollution Types of
Environmental Geography Lecture 13 Water Pollution Lecture 13: Water Pollution I. Water Pollution A. Groundwater B. Surface Water C. Regulation II. Water Use in California 1 I. Water Pollution Types of
Starting Your Own Business
 Grade Five Starting Your Own Business Overview Students listen to several chapters from The Toothpaste Millionaire, by Jean Merrill, to learn about starting a business and earning a profit. They complete
Grade Five Starting Your Own Business Overview Students listen to several chapters from The Toothpaste Millionaire, by Jean Merrill, to learn about starting a business and earning a profit. They complete
Electric Power from Sun and Wind
 Electric Power from Sun and Wind Fred Loxsom Eastern Connecticut State University Willimantic, Connecticut Many environmental problems are related to energy consumption. A college-level environmental science
Electric Power from Sun and Wind Fred Loxsom Eastern Connecticut State University Willimantic, Connecticut Many environmental problems are related to energy consumption. A college-level environmental science
Environmental Science Curriculum Pacing Guide
 Unit 1 - Introduction to the Environmental Science 2 days Lab Safety Scientific Methods Statistics and Models Making Informed Choices The Environment and Society Lab Safety Linebacker Video Skills Practice
Unit 1 - Introduction to the Environmental Science 2 days Lab Safety Scientific Methods Statistics and Models Making Informed Choices The Environment and Society Lab Safety Linebacker Video Skills Practice
Elementary Education Subtest II (103)
 Elementary Education Subtest II (103) Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved. NES, the NES logo, Pearson, the Pearson logo, and National Evaluation Series are trademarks,
Elementary Education Subtest II (103) Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved. NES, the NES logo, Pearson, the Pearson logo, and National Evaluation Series are trademarks,
Reading Utility Bills
 Reading Utility Bills Summary: Students recognize and interpret electricity and natural gas use patterns for one year by reading a set of utility bills. Objectives Students will be able to read and interpret
Reading Utility Bills Summary: Students recognize and interpret electricity and natural gas use patterns for one year by reading a set of utility bills. Objectives Students will be able to read and interpret
EE80J: Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources. EE180J: Advanced Renewable Energy Sources. Instructors: Mike Isaacson Oxana Pantchenko
 1 EE80J: Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources EE180J: Advanced Renewable Energy Sources Instructors: Mike Isaacson Oxana Pantchenko 2 Welcome This is an introduction to energy conversion and storage
1 EE80J: Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources EE180J: Advanced Renewable Energy Sources Instructors: Mike Isaacson Oxana Pantchenko 2 Welcome This is an introduction to energy conversion and storage
PERCENTS - Teacher Notes Unit 6-7 th grade
 PERCENTS - Teacher Notes Unit 6-7 th grade Percents are special fractions whose denominators are. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written, but understood
PERCENTS - Teacher Notes Unit 6-7 th grade Percents are special fractions whose denominators are. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written, but understood
Practice Problems. Skills Practice
 Practice Problems Skills Practice 1. Solve the proportions. Simplify your answers. Round answers to the nearest hundredth as needed. Show all work. 28 3.5 p 12 a. b. x 5 5 50 c. 11 m c. 20 6 4 5 8 10 w
Practice Problems Skills Practice 1. Solve the proportions. Simplify your answers. Round answers to the nearest hundredth as needed. Show all work. 28 3.5 p 12 a. b. x 5 5 50 c. 11 m c. 20 6 4 5 8 10 w
MATH 1030, Review for Exam 1
 MATH 1030, Review for Exam 1 Name: I. Venn Diagrams and Arguments For problems 1-5, draw and label a Venn diagram for the given statement. 1. Some philosophers did not live in Greece. 2. Herman hates spiders.
MATH 1030, Review for Exam 1 Name: I. Venn Diagrams and Arguments For problems 1-5, draw and label a Venn diagram for the given statement. 1. Some philosophers did not live in Greece. 2. Herman hates spiders.
An Energy Primer for the AP Environmental Science Student by Thomas B. Cobb Bowling Green State University Bowling Green, Ohio
 Close Here is the article in a print-friendly format. Click the button above to print this page. An Energy Primer for the AP Environmental Science Student by Thomas B. Cobb Bowling Green State University
Close Here is the article in a print-friendly format. Click the button above to print this page. An Energy Primer for the AP Environmental Science Student by Thomas B. Cobb Bowling Green State University
Running on Renewables (Lesson Plan) (Utilizing HOMER: Modeling Software for Hybrid Electric Power Systems)
 Running on Renewables (Lesson Plan) (Utilizing HOMER: Modeling Software for Hybrid Electric Power Systems) Suggested Grade Level 9-12 Overview Students utilize software developed by the National Renewable
Running on Renewables (Lesson Plan) (Utilizing HOMER: Modeling Software for Hybrid Electric Power Systems) Suggested Grade Level 9-12 Overview Students utilize software developed by the National Renewable
Advanced Placement Environmental Science Course Introduction and Summer Assignment
 Advanced Placement Environmental Science 2015-2016 Course Introduction and Summer Assignment Welcome to college. Ensure you read this package thoroughly before summer break in case there are any questions.
Advanced Placement Environmental Science 2015-2016 Course Introduction and Summer Assignment Welcome to college. Ensure you read this package thoroughly before summer break in case there are any questions.
Fossil Fuel Consumption: United States and China
 Fossil Fuel : and Name Per. 1. Go to the Energy Information Administration s website at http://www.eia.gov/cfapps/ipdbproject/iedindex3.cfm and open up each category under. Select World, and the and set
Fossil Fuel : and Name Per. 1. Go to the Energy Information Administration s website at http://www.eia.gov/cfapps/ipdbproject/iedindex3.cfm and open up each category under. Select World, and the and set
Senior 2, Cluster 1: Dynamics of Ecosystems
 Senior 2, Cluster 1: Dynamics of Ecosystems In this cluster, students examine the complex relationships present in ecosystems in order to further investigate issues of sustainability. The large scale cycling
Senior 2, Cluster 1: Dynamics of Ecosystems In this cluster, students examine the complex relationships present in ecosystems in order to further investigate issues of sustainability. The large scale cycling
Water Utility Science Water Math and Hydraulics 050. Name: Date:
 Water Utility Science Water Math and Hydraulics 050 Name: Date: Note: Please show all of your calculations for each problem no matter how simple the problem may seem. Please use the accompanying pieces
Water Utility Science Water Math and Hydraulics 050 Name: Date: Note: Please show all of your calculations for each problem no matter how simple the problem may seem. Please use the accompanying pieces
Scope and Sequence for Environmental Systems Incorporating Essential Learning Outcomes. Prepared by Michael Delesantro Science Academy of South Texas
 Scope Sequence for Environmental Systems Incorporating Essential Learning Outcomes Prepared by Michael Delesantro Science Academy of South Texas April 27, 2009 Environmental Systems - Scope Sequence -
Scope Sequence for Environmental Systems Incorporating Essential Learning Outcomes Prepared by Michael Delesantro Science Academy of South Texas April 27, 2009 Environmental Systems - Scope Sequence -
Writing Quotients with Mixed Numbers
 LESSON 8 Writing Quotients with Mixed Numbers Power Up facts mental math Power Up G a. Estimation: Round 8 8 in. to the nearest inch. 9 in. b. Estimation: Round 8 in. to the nearest inch. in. c. Estimation:
LESSON 8 Writing Quotients with Mixed Numbers Power Up facts mental math Power Up G a. Estimation: Round 8 8 in. to the nearest inch. 9 in. b. Estimation: Round 8 in. to the nearest inch. in. c. Estimation:
Rough Values of Power of Various Processes (watts)
 Rough Values of Power of Various Processes (watts) Solar power in all directions 10 27 Solar power incident on earth 10 17 Solar power avg. on U.S. 10 15 Solar power consumed in photosynthesis 10 14 U.S.
Rough Values of Power of Various Processes (watts) Solar power in all directions 10 27 Solar power incident on earth 10 17 Solar power avg. on U.S. 10 15 Solar power consumed in photosynthesis 10 14 U.S.
Integrated Skills in English ISE II
 Integrated Skills in English Reading & Writing exam Sample paper 10am 12pm Your full name: (BLOCK CAPITALS) Candidate number: Centre: Time allowed: 2 hours Instructions to candidates 1. Write your name,
Integrated Skills in English Reading & Writing exam Sample paper 10am 12pm Your full name: (BLOCK CAPITALS) Candidate number: Centre: Time allowed: 2 hours Instructions to candidates 1. Write your name,
Generators supply electrical energy.
 Page of 5 KY CONCPT Generators supply electrical energy. BFOR, you learned Magnetism is a force exerted by magnets A moving magnetic field can generate an electric current in a conductor Generators use
Page of 5 KY CONCPT Generators supply electrical energy. BFOR, you learned Magnetism is a force exerted by magnets A moving magnetic field can generate an electric current in a conductor Generators use
Lesson 1b: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
 Lesson 1b: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change SUBJECTS Earth Science Life Science Physical Science GRADE LEVELS 4 8 CA SCIENCE STANDARDS Grade 6: Heat (Thermal Energy) (Physical Sciences). 3. Heat
Lesson 1b: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change SUBJECTS Earth Science Life Science Physical Science GRADE LEVELS 4 8 CA SCIENCE STANDARDS Grade 6: Heat (Thermal Energy) (Physical Sciences). 3. Heat
Estuary Adventures. Background. Objective
 Estuary Adventures Objective Students will work in groups to understand the concept of estuaries, their importance, and the role that density plays in the mixing of fresh and salt water. Students will
Estuary Adventures Objective Students will work in groups to understand the concept of estuaries, their importance, and the role that density plays in the mixing of fresh and salt water. Students will
LESSON 3: Prescribe a Pollution Diet
 LESSON 3: Prescribe a Pollution Diet LESSON OVERVIEW Pollutey Judy drives everywhere and never carpools. She drives her vehicle that runs on gas out of convenience and does not realize the impact her choices
LESSON 3: Prescribe a Pollution Diet LESSON OVERVIEW Pollutey Judy drives everywhere and never carpools. She drives her vehicle that runs on gas out of convenience and does not realize the impact her choices
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science s Keys Nevada State Science s High School 12 Nature of Science N Earth and Space E Physical Science P Life Science L Science s High School Unifying Concepts Science as Inquiry
AP Environmental Science s Keys Nevada State Science s High School 12 Nature of Science N Earth and Space E Physical Science P Life Science L Science s High School Unifying Concepts Science as Inquiry
19. MORE UNIT CONVERSION
 9 MORE UNIT CONVERSION multi-step conversions filling a sandbox ft ft ( ft)( ft)( ft) ft cubic foot ft Unit conversion problems are widespread You ll encounter them not only in math classes, but also in
9 MORE UNIT CONVERSION multi-step conversions filling a sandbox ft ft ( ft)( ft)( ft) ft cubic foot ft Unit conversion problems are widespread You ll encounter them not only in math classes, but also in
II. STRESSES ON ECOSYSTEMS
 II. STRESSES ON ECOSYSTEMS GENERAL TRENDS Recent research published in the journal Nature defines, for eight earth biophysical subsystems or processes, safe threshold boundaries that should not be exceeded
II. STRESSES ON ECOSYSTEMS GENERAL TRENDS Recent research published in the journal Nature defines, for eight earth biophysical subsystems or processes, safe threshold boundaries that should not be exceeded
Overview of Science Units & Major Resources: GRADE 5
 Overview of Science Units & Major : GRADE 5 Unit 1: Physical Science Simple Machines Mysterious Machine Interact Unit Teacher Guide and Student Journals Intermediate Simple Machines DVD (one per building)
Overview of Science Units & Major : GRADE 5 Unit 1: Physical Science Simple Machines Mysterious Machine Interact Unit Teacher Guide and Student Journals Intermediate Simple Machines DVD (one per building)
Environmental Science and Engineering Toolbox
 Environmental Science and Engineering Toolbox 1. Material balances 2. Energy balances 3. Equilibrium relations 4. Rate equations Reactions Mixing and transport Growth 5. Design for pollution control and
Environmental Science and Engineering Toolbox 1. Material balances 2. Energy balances 3. Equilibrium relations 4. Rate equations Reactions Mixing and transport Growth 5. Design for pollution control and
Bioreactors Prof G. K. Suraishkumar Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 02 Sterilization
 Bioreactors Prof G. K. Suraishkumar Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 02 Sterilization Welcome, to this second lecture on Bioreactors. This is a mooc on Bioreactors.
Bioreactors Prof G. K. Suraishkumar Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 02 Sterilization Welcome, to this second lecture on Bioreactors. This is a mooc on Bioreactors.
Focus: This lesson will provide a basic overview of wind energy and wind turbines. Grade Level: 9 th Grade to 12 th Grade Time: 50 minutes
 Wind Energy 101 Focus: This lesson will provide a basic overview of wind energy and wind turbines. Grade Level: 9 th Grade to 12 th Grade Time: 50 minutes 1. Have students brainstorm a list of ways we
Wind Energy 101 Focus: This lesson will provide a basic overview of wind energy and wind turbines. Grade Level: 9 th Grade to 12 th Grade Time: 50 minutes 1. Have students brainstorm a list of ways we
Acid Rain. National Science Education Standards
 Acid Rain Grades 6-7-8-9-10 National Science Education Standards SCIENCE AS INQUIRY STANDARDS LEVELS 5-8 LEVELS 9-12 Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry
Acid Rain Grades 6-7-8-9-10 National Science Education Standards SCIENCE AS INQUIRY STANDARDS LEVELS 5-8 LEVELS 9-12 Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry
Measuring School Electronics Energy at Work 1
 1 GRADE LEVEL 6-12 TIME NEEDED FOR COMPLETION 2 class periods or 1.5-2 hours STANDARDS LA GLEs and NGSS alignments are found in the Appendix starting on page A-1 MATERIALS 6 energy monitoring devices.
1 GRADE LEVEL 6-12 TIME NEEDED FOR COMPLETION 2 class periods or 1.5-2 hours STANDARDS LA GLEs and NGSS alignments are found in the Appendix starting on page A-1 MATERIALS 6 energy monitoring devices.
MATH 2070 Mixed Practice Sections
 Name: Directions: For each question, show the specific mathematical notation that leads to your answer. Round final answers to three decimals unless the context dictates otherwise. 1. The demand for board
Name: Directions: For each question, show the specific mathematical notation that leads to your answer. Round final answers to three decimals unless the context dictates otherwise. 1. The demand for board
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Lab: Ocean Salinity and Density M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Maths Level 2. Sample. Functional Skills. Mark Scheme and Marking Guidance. Assessment Code: FSML2AA/P
 Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Sample Mark Scheme and Marking Guidance The following documents are included in this marking guidance: General marking guidance and assessment principles. Mark schemes and
Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Sample Mark Scheme and Marking Guidance The following documents are included in this marking guidance: General marking guidance and assessment principles. Mark schemes and
TOPIC TEACHER GRADE. How do humans impact the Earth
 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE (1,5) Human Impact on Earth TOPIC TEACHER GRADE Subject Teacher s name Student s grade KEY LEARNING(S) UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS OPTIONAL INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS deforestation, desertification,
7 TH GRADE SCIENCE (1,5) Human Impact on Earth TOPIC TEACHER GRADE Subject Teacher s name Student s grade KEY LEARNING(S) UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS OPTIONAL INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS deforestation, desertification,
Section 1. Electricity and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology
 Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form B
 DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form B Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form B Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
Global Warming: Life in a Greenhouse (Aug. 2003) Lesson by Rebecca Field, Ph.D. Ecology professor, Colby-Sawyer College, New London, NH
 actionbioscience.org lesson To accompany the peer-reviewed article by Jeffrey Chanton, Ph.D.: Global Warming & Rising Oceans (Oct. 2002) http://www.actionbioscience.org/environment/chanton.html Global
actionbioscience.org lesson To accompany the peer-reviewed article by Jeffrey Chanton, Ph.D.: Global Warming & Rising Oceans (Oct. 2002) http://www.actionbioscience.org/environment/chanton.html Global
Exploring Economics. Standards. Multiple Intelligences Utilized. Teaching Lightning Bolt Books. Titles in this series: Economics.
 Teaching Lightning Bolt Books Exploring Economics TM K 2nd Grade Interest Level 2nd Grade ing Level Titles in this series: Do I Need It? Or Do I Want It? Making Budget Choices What Can You Do With Money?
Teaching Lightning Bolt Books Exploring Economics TM K 2nd Grade Interest Level 2nd Grade ing Level Titles in this series: Do I Need It? Or Do I Want It? Making Budget Choices What Can You Do With Money?
Compare body symmetry, movement, and organ systems in various animals. Consider some causes and effects of variation in the animal kingdom.
 Animals In Animals, students learn classification systems and the place of animals (including humans) within them. They explore physical and lifestyle characteristics of invertebrates and vertebrates through
Animals In Animals, students learn classification systems and the place of animals (including humans) within them. They explore physical and lifestyle characteristics of invertebrates and vertebrates through
What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment.
 Chapter 18 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment. What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity is the sum
Chapter 18 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment. What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity is the sum
What does each part of the equation mean? q=cm T
 Assignment #10 Energy Pyramids LO: I can define trophic levels and explain the energy flow. I can apply those ideas to food webs EQ: Where does all the energy from the sun go? (4-5 sentences) LEVEL ZERO
Assignment #10 Energy Pyramids LO: I can define trophic levels and explain the energy flow. I can apply those ideas to food webs EQ: Where does all the energy from the sun go? (4-5 sentences) LEVEL ZERO
BIO 2 GO! THE CARBON CYCLE Carbon and carbon dioxide are continuously recycled between living organisms and their environment.
 BIO 2 GO! THE CARBON CYCLE 3132 Carbon and carbon dioxide are continuously recycled between living organisms and their environment. At the end of this unit, you should be able to do the following: 1. Draw
BIO 2 GO! THE CARBON CYCLE 3132 Carbon and carbon dioxide are continuously recycled between living organisms and their environment. At the end of this unit, you should be able to do the following: 1. Draw
APES Review Worksheet #1
 APES Review Worksheet #1 1. Name the following: NO NO 2 NO 2 NO 3 NO 2 N 2 O N 2 NH 3 + NH 4 HNO 3 NO x 2. In the box to the right, sketch a house and the surroundings of a house that is designed to make
APES Review Worksheet #1 1. Name the following: NO NO 2 NO 2 NO 3 NO 2 N 2 O N 2 NH 3 + NH 4 HNO 3 NO x 2. In the box to the right, sketch a house and the surroundings of a house that is designed to make
Chapter 6 Section 1: Interconnected Planet. Key Vocabulary Terms 1
 Chapter 6 Section 1: Interconnected Planet Key Vocabulary Terms 1 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Nonrenewable energy resource formed from the remains of organisms that lived long ago; oil coal and natural
Chapter 6 Section 1: Interconnected Planet Key Vocabulary Terms 1 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Nonrenewable energy resource formed from the remains of organisms that lived long ago; oil coal and natural
Total Test Questions: 66 Levels: Grades Units of Credit: 1.0 STANDARD 2. Demonstrate appropriate use of personal protective devices.
 DESCRIPTION Biotechnology is designed to create an awareness of career possibilities in the field of biotechnology. Students are introduced to diagnostic and therapeutic laboratory procedures that support
DESCRIPTION Biotechnology is designed to create an awareness of career possibilities in the field of biotechnology. Students are introduced to diagnostic and therapeutic laboratory procedures that support
Using the Percent Equation
 Using the Percent Equation LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How can your personality affect a decision like this one? During What are the advantages of Offer A? Offer B? After Which option would you choose? KEY CONCEPT
Using the Percent Equation LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How can your personality affect a decision like this one? During What are the advantages of Offer A? Offer B? After Which option would you choose? KEY CONCEPT
ENERGY. 1. Non-renewable or finite energy resources are. 2. Renewable or infinite energy resources are source of
 Energy is the ability to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed: it can only be transformed, from one type into another. Energy can be either potential or kinetic. Kinetic energy is found in anything
Energy is the ability to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed: it can only be transformed, from one type into another. Energy can be either potential or kinetic. Kinetic energy is found in anything
Honors Algebra Midterm Study Guide
 Honors Algebra Midterm Study Guide Short Answer What is an algebraic expression for the word phrase? 1. the sum of n and 11 2. the quotient of d and 5 3. 2 times the sum of g and f 4. the quotient of 9
Honors Algebra Midterm Study Guide Short Answer What is an algebraic expression for the word phrase? 1. the sum of n and 11 2. the quotient of d and 5 3. 2 times the sum of g and f 4. the quotient of 9
SPRING-BREAK PACKET 7 th grade mathematics
 M.S. 181 PABLO CASALS CHRISTOPHER WARNOCK, PRINCIPAL 800 BAYCHESTER AVENUE, BRONX, NY 10475 PHONE: 718-904-5600 Conceive, it, Believe it, Achieve it SPRING-BREAK PACKET 7 th grade mathematics (New York
M.S. 181 PABLO CASALS CHRISTOPHER WARNOCK, PRINCIPAL 800 BAYCHESTER AVENUE, BRONX, NY 10475 PHONE: 718-904-5600 Conceive, it, Believe it, Achieve it SPRING-BREAK PACKET 7 th grade mathematics (New York
Water is everywhere on Earth oceans, glaciers, rivers, lakes, air,
 Section 6.1 6.1 Running Water 1 FOCUS Section Objectives 6.1 Explain how the water cycle circulates Earth s water supply in an unending cycle. 6.2 Explain how the water cycle is kept in balance. 6.3 Describe
Section 6.1 6.1 Running Water 1 FOCUS Section Objectives 6.1 Explain how the water cycle circulates Earth s water supply in an unending cycle. 6.2 Explain how the water cycle is kept in balance. 6.3 Describe
2.3 Density and Density Calculations
 2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
PE PLE WHO POLLUTED THE RIVER?
 UNIT 7 PEOPLE AND WASTE WHO POLLUTED THE RIVER? COUNTING ON PE PLE K-5 Activities for Global Citizenship METHOD Through an interactive story, K-2 students experience the pollution of a local river over
UNIT 7 PEOPLE AND WASTE WHO POLLUTED THE RIVER? COUNTING ON PE PLE K-5 Activities for Global Citizenship METHOD Through an interactive story, K-2 students experience the pollution of a local river over
Hydro Electric Power (Hydel Power)
 Operating Principle Hydro Electric Power (Hydel Power) Hydro-electric power is generated by the flow of water through turbine, turning the blades of the turbine. A generator shaft connected to this turbine
Operating Principle Hydro Electric Power (Hydel Power) Hydro-electric power is generated by the flow of water through turbine, turning the blades of the turbine. A generator shaft connected to this turbine
Period 25: Energy from Wind and Biomass
 Period 25: Energy from Wind and Biomass Activity 25.1: Causes of Winds 1) The Earth s winds a) What causes wind circulation from the equator to the high latitudes? The uneven heating of the Earth s surface
Period 25: Energy from Wind and Biomass Activity 25.1: Causes of Winds 1) The Earth s winds a) What causes wind circulation from the equator to the high latitudes? The uneven heating of the Earth s surface
Agriscience Standards
 Agriscience Standards 1) Synthesize research on the historical importance and purpose of agriculture and agriculture organizations, identifying major events, opportunities and technological developments
Agriscience Standards 1) Synthesize research on the historical importance and purpose of agriculture and agriculture organizations, identifying major events, opportunities and technological developments
6.RP (Ratios and Proportional Relationships)
 6.RP (Ratios and Proportional Relationships) 2014 by emathtest, Inc. emathtest, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected by Copyright and permission
6.RP (Ratios and Proportional Relationships) 2014 by emathtest, Inc. emathtest, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected by Copyright and permission
Math Entrance Exam is scheduled for Wednesday, January 6:00 p.m.
 Pharmacy Technician Study Guide Practice Math Packet This packet is designed to help prepare you for the Pharmacy Technician Math Entrance Exam. The key has been included to allow the student to check
Pharmacy Technician Study Guide Practice Math Packet This packet is designed to help prepare you for the Pharmacy Technician Math Entrance Exam. The key has been included to allow the student to check
The Nonliving Environment
 Chapter Review The Nonliving Environment Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Write the correct term in the spaces beside each definition. Unscramble the boxed letters to find a word that describes a
Chapter Review The Nonliving Environment Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Write the correct term in the spaces beside each definition. Unscramble the boxed letters to find a word that describes a
APES Introduction Assignment Save 3-5 clear plastic 2- liter bottles with caps from some soda other than Coca- Cola products
 APES Introduction Assignment 2016-17 Welcome to AP Environmental Science. There are three things I'd like you to do as we begin the semester: I. Save 3-5 clear plastic 2- liter bottles with caps from some
APES Introduction Assignment 2016-17 Welcome to AP Environmental Science. There are three things I'd like you to do as we begin the semester: I. Save 3-5 clear plastic 2- liter bottles with caps from some
CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH)
 CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH) Related lesson plan Fresh and Seawater Density What is this sensor? CTD is an acronym for Conductivity, Temperature and Depth. However, this is somewhat misleading
CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH) Related lesson plan Fresh and Seawater Density What is this sensor? CTD is an acronym for Conductivity, Temperature and Depth. However, this is somewhat misleading
Identification Label TIMSS Teacher Questionnaire. <Grade 4> <TIMSS> <National Research Center Name> <Address>
 Identification Label TIMSS 2011 Teacher Questionnaire IEA, 2011 Teacher Questionnaire Your school has agreed to participate in TIMSS 2011 (Trends
Identification Label TIMSS 2011 Teacher Questionnaire IEA, 2011 Teacher Questionnaire Your school has agreed to participate in TIMSS 2011 (Trends
Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Climate
 1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
Curriculum Guide. National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science
 National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Biomass. Coal. 10 Intermediate Energy Infobook Activities. Description of biomass: Renewable or nonrenewable: Description of photosynthesis:
 Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Lesson 3 Energy Resources
 Lesson 3 Energy Resources Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 44 Content Vocabulary 45 Lesson Outline 46 MiniLab 48 Content Practice A 49 Content Practice B 50 Language Arts Support 51 Math Skills
Lesson 3 Energy Resources Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 44 Content Vocabulary 45 Lesson Outline 46 MiniLab 48 Content Practice A 49 Content Practice B 50 Language Arts Support 51 Math Skills
There are 2 different types of numbers Exact -Measured
 Significant Figures When measuring or using our calculators we must determine the correct answer; our calculators are mindless drones and don t know the correct answer. There are 2 different types of numbers
Significant Figures When measuring or using our calculators we must determine the correct answer; our calculators are mindless drones and don t know the correct answer. There are 2 different types of numbers
Physics 171, Physics and Society Quiz 1 1pm Thurs Sept 14, 2017 Each question has one correct answer, or none (choose e on the clicker). 1.
 Physics 171, Physics and Society Quiz 1 1pm Thurs Sept 14, 2017 Each question has one correct answer, or none (choose e on the clicker). 1. Maria is riding her bicycle on a flat road at 10 mi/hr. Then
Physics 171, Physics and Society Quiz 1 1pm Thurs Sept 14, 2017 Each question has one correct answer, or none (choose e on the clicker). 1. Maria is riding her bicycle on a flat road at 10 mi/hr. Then
Basics Course. Montana. Introduction to Drinking Water Systems. for small public drinking water systems serving less than 3,300 people
 Basics Course for small public drinking water systems serving less than 3,300 people Montana Montana Basics Course for Small Public Drinking Water Systems -1 Introduction to Drinking Water Systems Welcome
Basics Course for small public drinking water systems serving less than 3,300 people Montana Montana Basics Course for Small Public Drinking Water Systems -1 Introduction to Drinking Water Systems Welcome
Permeability Field Investigation
 Permeability Field Investigation Using the scientific method to guide this outdoor investigation, students test the permeability of different school-ground areas, record and organize the results with maps
Permeability Field Investigation Using the scientific method to guide this outdoor investigation, students test the permeability of different school-ground areas, record and organize the results with maps
Introducing Environmental Science and Sustainability
 1 Introducing Environmental Science and Sustainability Overview of Chapter 1 Human Impacts on The Environment Population, Resources and the Environment Sustainability Environmental Science Addressing Environmental
1 Introducing Environmental Science and Sustainability Overview of Chapter 1 Human Impacts on The Environment Population, Resources and the Environment Sustainability Environmental Science Addressing Environmental
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers,
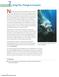 7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
1. The characteristics of populations are shaped by the interactions between individuals and their environment
 1. The characteristics of populations are shaped by the interactions between individuals and their environment Populations have size and geographical boundaries. The density of a population is measured
1. The characteristics of populations are shaped by the interactions between individuals and their environment Populations have size and geographical boundaries. The density of a population is measured
Packet questions # Packet questions # Packet questions # Packet questions # Microscope worksheet 3.
 NAME PER ECOLOGY HW PACKET POINTS SCORES Packet questions #1-32 6 Packet questions #33-38 3 Packet questions #39-51 4 Packet questions #52-58 3 Microscope worksheet 3 Ecology Interactions Activity 6 Test
NAME PER ECOLOGY HW PACKET POINTS SCORES Packet questions #1-32 6 Packet questions #33-38 3 Packet questions #39-51 4 Packet questions #52-58 3 Microscope worksheet 3 Ecology Interactions Activity 6 Test
Turbine subsystems include: What is wind energy? What is a wind turbine and how does it work?
 What is wind energy? In reality, wind energy is a converted form of solar energy. The sun's radiation heats different parts of the earth at different rates-most notably during the day and night, but also
What is wind energy? In reality, wind energy is a converted form of solar energy. The sun's radiation heats different parts of the earth at different rates-most notably during the day and night, but also
DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF
 DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF THE LEAKY FAUCET Outcome (lesson objective) Students will gather scientific data and be able to utilize the data to generalize the results over a long period of time. Student/Class
DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF THE LEAKY FAUCET Outcome (lesson objective) Students will gather scientific data and be able to utilize the data to generalize the results over a long period of time. Student/Class
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle
 Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Chapter 2. Table of Contents. Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships. Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem. Section 3 Cycling of Matter
 Ecosystems Table of Contents Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem Section 3 Cycling of Matter Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Interactions
Ecosystems Table of Contents Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem Section 3 Cycling of Matter Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Interactions
THE CASE OF THE MYSTERIOUS RENTERS
 THE CASE OF THE MYSTERIOUS RENTERS Objectives: The student will be able to: Identify ways in which water is used Determine how much water families use each day Recognize the importance of conserving water
THE CASE OF THE MYSTERIOUS RENTERS Objectives: The student will be able to: Identify ways in which water is used Determine how much water families use each day Recognize the importance of conserving water
Louis Pasteur STEM Project
 Louis Pasteur 2015-2016 STEM Project Project 1: Living Environment Project Overview: The Effects of oil spills Oil is an organic fluid that has a lower density than water. When oil is spilled on water,
Louis Pasteur 2015-2016 STEM Project Project 1: Living Environment Project Overview: The Effects of oil spills Oil is an organic fluid that has a lower density than water. When oil is spilled on water,
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S
 LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
