Wetland Soils. Lecture outline: Importance of wetland soils
|
|
|
- Joanna Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Importance of wetland soils Wetland Soils Chemical transformations Chemical (nutrient) storage These affect plant growth and peat formation Lecture outline: What are soils? How does inundation change upland soils into hydric soils? What are the important distinguishing characteristics of hydric soils? What are the implications of the unique characteristics of hydric soils for plants and chemical transformations?
2 What are soils? = study of the components and formation of soils Soil mapping is done by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), a branch of the USDA. Soil Definitions: Early definition of soil: the material capable of supporting the growth of land plants. A natural body comprised of solids (minerals and organic matter), liquid, and gases that occurs on the land surface, occupies space, and is characterized by one or more of the following: horizons, or layers, that are distinguishable from the initial material as a result of additions, losses, transfers, and transformations of energy or the ability to support rooted plants in a natural environment. (Soil Survey Staff 1998)
3 What are NOT soils? Bedrock Rocky outcrops & plateaus Salt flats Sand beaches and sand bars Muddy shores Unconsolidated material lacking any vegetation cover Permanently flooded bottoms (this is SUBSTRATE) Can you have a wetland if you don t have soil? Tiner 1999: Tidal mud flats, sandy intertidal beaches, and rocky shores are examples of nonvegetated wetlands occurring on nonsoils.
4 Soil Types Two main types of soil: organic and mineral % C = half the amount of % organic material, ~ > 40% organic material by weight Organic matter must be 40 cm for a soil to be a histosol (organic soil); otherwise, it is a mineral soil with an organic layer (horizon) on the top. Sprecher In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds, Wetland Soils.
5 Organic Soils = Histosols Formed when decomposition & mineralization of organic matter is greatly slowed due to either anaerobic conditions or cool-cold humid conditions. Decomposition 3 of the 4 types of organic soils form due to hydric conditions: Fibrists = peat less than ¼ decomposed, mostly identifiable plant fibers Hemists = mucky peat (peaty muck); intermediate decomposition and identifiability. Saprists = muck; mostly decomposed, mostly unidentifiable. Folists = non-hydric organic soils of boreal & tropical mountain areas
6 Mineral soil is comprised of particles < 2 mm in size Sand Silt Clay Sprecher In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds, Wetland Soils.
7
8 Soil Horizons Soil is studied only to a depth of about 2 m O = organic horizon: Oa = sapric Oe = hemic Oi = fibric A = top mineral horizon E = light colored horizon depleted in clay, other minerals B = mineral subsoil horizon C = parent material R = unweathered rock Horizons are often missing in natural soil profiles Sprecher In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds, Wetland Soils.
9 Mineral soil, non-hydric Histosol, hydric Limnic Haplosaprist
10 E horizon
11 Comparison of organic & mineral soil properties Soil Property Organic soil Mineral soil Organic C content > 12-18% < 12-18% Bulk density < 0.6 g/cm g/cm 3 Porosity > 80% 45-55% ph < Fens > 7.0 Nutrient availability Low Low high Cation exchange capacity High Low high Plant available water High Low high Hydraulic conductivity Moderate rapid Very low very rapid Collins & Kuehl In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds, Wetland Soils.
12 Soil Formation Factors: organisms, topography, climate, parent material, time. Processes: additions, deletions, transformations, translocations Richardson, Arndt, & Montgomery In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds, Wetland Soils.
13 Hydrarch Succession Tiner 1998
14 Hydric soils Definition: A hydric soil is a soil that is formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to develop anaerobic conditions in the upper part. (Federal Register, Feb. 24, 1995, Vol 60, No. 37, p ). (Upper part = rooting zone of non-tree vegetation; typically 2 ft). Length of inundation: Extended inundation anaerobic conditions slowed decomposition organic matter buildup = organic soils Wet-dry cycles mineral soils with unique characteristics caused by aerobic/anaerobic cycles. Anaerobic conditions develop due to (all are required for hydric soil): Slow diffusion of oxygen into water-filled soil pores (stagnant water) Microbial respiration Presence of organic material (microbe substrate) Sufficient temperature for biological activity in soil (0 2 C)
15 Oxidation-reduction process Typical respiration (a redox reaction): C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O Half-reactions: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6H 2 O 6CO e H + (Oxidation = losing electrons, becoming more positive) 6O e H + 12H 2 O Alternate e - acceptors: NO 3 - MnO 2 Fe(OH) 3 SO 4-2 CO 2 (Reduction = gaining electrons, becoming more negative)
16 Oxidation-reduction process Relative concentration Reducing conditions Inundation Mitsch & Gosselink 2000.
17 Oxidation-reduction process Terminal e- Reduction Reaction Soil colors acceptor Oxygen O 2 + 4e - + 4H + 2H 2 O red, yellow, brown Nitrate 2NO e H + N 2 + 6H 2 O no change Manganese MnO 2 + 2e - + 4H + Oxides Mn H 2 O loss of mineral blacks Iron Fe(OH) 3 + e - + 3H + Fe H 2 O gray, greenish, bluish Oxides Sulfate SO e H + H 2 S + 4H 2 O no change Carbon CO 2 + 8e - + 8H + CH 4 + 2H 2 O no change Dioxide Vepraskas & Faulkner In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds. Wetland soils.
18 Hydric soil colors Non-hydric Gleization, Gleys Pore linings Oxidized rhizospheres Redoxomorphic Redox depletions
19 O 2 Soil drains Fe 2+ Fe masses form when Fe 2+ is oxidized Oxygen moves into soil Color of depletion is gray Reduced Fe diffuses into matrix,
20 Munsell Color Charts
21 Oxidation-reduction cont. Relative concentration Mitsch & Gosselink 2000.
22 Oxidation-reduction cont. Craft In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds. Wetland soils.
23 Oxidation-reduction cont. Process Electron acceptor Energy (- G kj/mole e - )* Redox potential (Eh) in (mv)** Aerobic O > 300 Nitrate reduction NO Manganese reduction MnO Iron reduction Fe(OH) (-100) Sulfate reduction SO (-200) Methanogenesis CO < -200 * Reddy & D Angelo In Mitsch, ed, Global wetlands. ** Redox potentials are rough estimates, they vary depending on ph and temperature. Mitsch & Gosselink 2000.
24 Facultatitve Oxidation-reduction cont. Aerobic Anaerobic Craft In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds. Wetland soils.
25 Faust & Aly Chemistry of Natural Waters. Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Stoneham MA
26 Hypothetical changes in redox potential over a wet-dry cycle Vepraskas In Richardson & Vepraskas, eds. Wetland soils.
Lecture 21: Soil Redox; Hydric Soils; Wetlands
 Lecture 21: Soil Redox; Hydric Soils; Wetlands Soil Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Many Elements Exist in Multiple Oxidation States in Soils Oxygen: O 2 (0), H 2 O (-2) Carbon: CH 4 (-4), Organic C (-3 to
Lecture 21: Soil Redox; Hydric Soils; Wetlands Soil Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Many Elements Exist in Multiple Oxidation States in Soils Oxygen: O 2 (0), H 2 O (-2) Carbon: CH 4 (-4), Organic C (-3 to
Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical, & biological processes
 OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
HYDRIC SOILS. By Neal Svendsen Resource Soil Scientist Natural Resources Conservation Service Sept 2006
 HYDRIC SOILS By Neal Svendsen Resource Soil Scientist Natural Resources Conservation Service Sept 2006 Wetlands and Hydric Soils The term hydric soils proposed by Cowardin in 1979 Classification of Wetlands
HYDRIC SOILS By Neal Svendsen Resource Soil Scientist Natural Resources Conservation Service Sept 2006 Wetlands and Hydric Soils The term hydric soils proposed by Cowardin in 1979 Classification of Wetlands
Reactions & Processes Influenced by Soil Wetness. Topics for Consideration. Reactions and Processes Influenced by Soil Wetness
 Reactions & Processes Influenced by Soil Wetness Topics for Consideration A. Organic matter (OM) accumulation B. Some reduction effects induced by soil saturation C. Redoximorphic features D. Calcium carbonate
Reactions & Processes Influenced by Soil Wetness Topics for Consideration A. Organic matter (OM) accumulation B. Some reduction effects induced by soil saturation C. Redoximorphic features D. Calcium carbonate
Submerged Soils for Rice Production
 Submerged Soils for Rice Production What is soil composed of? If you were to divide soil into its component parts, you would have: a mineral component organic matter and pore space composed of air and
Submerged Soils for Rice Production What is soil composed of? If you were to divide soil into its component parts, you would have: a mineral component organic matter and pore space composed of air and
ACT PRESENTATION 5 AN INTRODUCTION TO HYDRIC SOILS AND HYDRIC SOIL TERMINOLOGY OCTOBER 2011
 ACT PRESENTATION 5 AN INTRODUCTION TO HYDRIC SOILS AND HYDRIC SOIL TERMINOLOGY OCTOBER 2011 An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology by: Wade Hurt, USDA, NRCS, NSSC/ University of Florida,
ACT PRESENTATION 5 AN INTRODUCTION TO HYDRIC SOILS AND HYDRIC SOIL TERMINOLOGY OCTOBER 2011 An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology by: Wade Hurt, USDA, NRCS, NSSC/ University of Florida,
This is the 2 nd module of training course titled: Submerged Soils for Rice Production
 How are soil properties affected when soil is submerged? This is the 2 nd module of training course titled: Submerged Soils for Rice Production An interactive version of this presentation can be viewed
How are soil properties affected when soil is submerged? This is the 2 nd module of training course titled: Submerged Soils for Rice Production An interactive version of this presentation can be viewed
Redoximorphic Features
 Redoximorphic Features Redoximorphic Features for Identifying Aquic Conditions, Technical Bulletin 301 NCSU, Raleigh, North Carolina. Order from: Dept. of Ag. Comm., Box 7603, NCSU, Raleigh, NC 27695-7603
Redoximorphic Features Redoximorphic Features for Identifying Aquic Conditions, Technical Bulletin 301 NCSU, Raleigh, North Carolina. Order from: Dept. of Ag. Comm., Box 7603, NCSU, Raleigh, NC 27695-7603
Biogeochemistry of Wetlands
 Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Biogeochemical Properties of Wetlands Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science
Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Biogeochemical Properties of Wetlands Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science
HYDROLOGIC CRITERION FOR HYDRIC SOILS. M. J. Vepraskas, NC State University
 HYDROLOGIC CRITERION FOR HYDRIC SOILS M. J. Vepraskas, NC State University Is this a hydric soil? Yes, because it meets the definition of a hydric soil. Definition A hydric soil is a soil that formed under
HYDROLOGIC CRITERION FOR HYDRIC SOILS M. J. Vepraskas, NC State University Is this a hydric soil? Yes, because it meets the definition of a hydric soil. Definition A hydric soil is a soil that formed under
An Explanation of the Hydric Soil Technical Standard and Normal Precipitation
 An Explanation of the Hydric Soil Technical Standard and Normal Precipitation From: National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils. 2001. Hydric Soil Technical Standard (Technical Note 11). http://soils.usda.gov/soil_us
An Explanation of the Hydric Soil Technical Standard and Normal Precipitation From: National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils. 2001. Hydric Soil Technical Standard (Technical Note 11). http://soils.usda.gov/soil_us
Mineral Hydric Soil Morphology Part 1 of 2
 Mineral Hydric Soil Morphology Part 1 of 2 Ch. 7 Richardson & Vepraskas Outline: 1. Redox Reactions and Associated Soil Conditions 2. Principal Types of Morphological Features in Hydric Soils September
Mineral Hydric Soil Morphology Part 1 of 2 Ch. 7 Richardson & Vepraskas Outline: 1. Redox Reactions and Associated Soil Conditions 2. Principal Types of Morphological Features in Hydric Soils September
A Short Course on Soil McDaniel s Nut Grove Wednesday, October 12 th, Soil Characteristics
 A Short Course on Soil McDaniel s Nut Grove Wednesday, October 12 th, 2005 Soils are unconsolidated natural mineral and organic materials at the earth s surface, differentiated by weathering and decomposition
A Short Course on Soil McDaniel s Nut Grove Wednesday, October 12 th, 2005 Soils are unconsolidated natural mineral and organic materials at the earth s surface, differentiated by weathering and decomposition
An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology. Based on deliberations of: The National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCHS).
 An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology Based on deliberations of: The National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCHS). A word about the NTCHS The National Technical Committee
An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology Based on deliberations of: The National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCHS). A word about the NTCHS The National Technical Committee
An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology. A word about the NTCHS. Wetlands
 An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology Based on deliberations of: The National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCHS). A word about the NTCHS The National Technical Committee
An Introduction to Hydric Soils and Hydric Soil Terminology Based on deliberations of: The National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCHS). A word about the NTCHS The National Technical Committee
Lecture 5. Exchange Reactions. Cation exchange Salt/Sodium Affected Soils Acid Soils
 Lecture 5 Exchange Reactions Cation exchange Salt/Sodium Affected Soils Acid Soils General Classes (layer build-up) of Phyllosilicate Minerals: Layer Type Charge Trioctahedral Dioctahedral 1 octahedra
Lecture 5 Exchange Reactions Cation exchange Salt/Sodium Affected Soils Acid Soils General Classes (layer build-up) of Phyllosilicate Minerals: Layer Type Charge Trioctahedral Dioctahedral 1 octahedra
Soils of Great Salt Lake Wetlands: Hydric Indicators and Common Features
 Soils of Great Salt Lake Wetlands: Hydric Indicators and Common Features Christine Rohal, Karin Kettenring, Rebekah Downard, and Mark Larese-Casanova Department of Watershed Sciences, Quinney College of
Soils of Great Salt Lake Wetlands: Hydric Indicators and Common Features Christine Rohal, Karin Kettenring, Rebekah Downard, and Mark Larese-Casanova Department of Watershed Sciences, Quinney College of
Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts
 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts Version 3.1 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program August, 2018 This document is a compilation
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts Version 3.1 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program August, 2018 This document is a compilation
WETLAND SOILS. Soil consists of :
 WETLAND SOILS 1) Soil environment generally 2) Wetland soils and their characteristics 3) Redox 4) Nitrogen transformation 5) Mn, Fe, SO4 transformation 6) CH4 production 7) Phosphorus Soil consists of
WETLAND SOILS 1) Soil environment generally 2) Wetland soils and their characteristics 3) Redox 4) Nitrogen transformation 5) Mn, Fe, SO4 transformation 6) CH4 production 7) Phosphorus Soil consists of
Wetland Soils, Hydrology, and Geomorphology
 TWO Wetland Soils, Hydrology, and Geomorphology C. RHETT JACKSON, JAMES A. THOMPSON, and RANDALL K. KOLKA WETLAND SOILS Landscape Position Soil Properties Soil Profiles Soil Processes Legal Differentiation
TWO Wetland Soils, Hydrology, and Geomorphology C. RHETT JACKSON, JAMES A. THOMPSON, and RANDALL K. KOLKA WETLAND SOILS Landscape Position Soil Properties Soil Profiles Soil Processes Legal Differentiation
ABSTRACT. although little research has evaluated the effects of organic additions on the development
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: REDOXIMORPHIC FEATURES INDUCED BY ORGANIC AMENDMENTS AND SIMULATED WETLAND HYDROLOGY Adam Lincoln Gray, Master of Science, 2010 Directed By: Professor Martin C. Rabenhorst,
ABSTRACT Title of Document: REDOXIMORPHIC FEATURES INDUCED BY ORGANIC AMENDMENTS AND SIMULATED WETLAND HYDROLOGY Adam Lincoln Gray, Master of Science, 2010 Directed By: Professor Martin C. Rabenhorst,
Urban Soil Conservation and Management
 Urban Soil Conservation and Management Urban Soil include those located in: Cities in park areas Recreation areas Community gardens Green belts Lawns Septic absorption fields Sediment basins We need a
Urban Soil Conservation and Management Urban Soil include those located in: Cities in park areas Recreation areas Community gardens Green belts Lawns Septic absorption fields Sediment basins We need a
WETLAND GEOMORPHOLOGY, SOILS, AND FORMATIVE PROCESSES
 2 WETLAND GEOMORPHOLOGY, SOILS, AND FORMATIVE PROCESSES Randy K. Kolka and James A. Thompson The soil is where many of the hydrologic and biogeochemical processes that influence wetland function and ecology
2 WETLAND GEOMORPHOLOGY, SOILS, AND FORMATIVE PROCESSES Randy K. Kolka and James A. Thompson The soil is where many of the hydrologic and biogeochemical processes that influence wetland function and ecology
The Relationship between the Properties and Features of Wetland Soils and the Adjacent Uplands
 The Relationship between the Properties and Features of Wetland Soils and the Adjacent Uplands By USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Connecticut Staff Wetlands and watercourses are features of
The Relationship between the Properties and Features of Wetland Soils and the Adjacent Uplands By USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Connecticut Staff Wetlands and watercourses are features of
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts. Version 2.1
 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts Version 2.1 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program November, 2014 This document is a
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts Version 2.1 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program November, 2014 This document is a
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts. Version 2
 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts Version 2 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program March, 2014 This document is a compilation
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts Version 2 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program March, 2014 This document is a compilation
Soil, Landscape, Hydrology Relationships
 Soil, Landscape, Hydrology Relationships Soil Hydrologic Cycle Unsaturated Soils with Suction (Tension) Forces Water under a suction, pulls particles together. This water is not free water, it is not free
Soil, Landscape, Hydrology Relationships Soil Hydrologic Cycle Unsaturated Soils with Suction (Tension) Forces Water under a suction, pulls particles together. This water is not free water, it is not free
Freshwater Wetlands: Functions & Conservation. ENVIRTHON Workshop 2016 University of Massachusetts Amherst Deborah J.
 Freshwater Wetlands: Functions & Conservation ENVIRTHON Workshop 2016 University of Massachusetts Amherst Deborah J. Henson, PhD, CPSS What is a Wetland? Legal Definition:...those areas that are inundated
Freshwater Wetlands: Functions & Conservation ENVIRTHON Workshop 2016 University of Massachusetts Amherst Deborah J. Henson, PhD, CPSS What is a Wetland? Legal Definition:...those areas that are inundated
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts
 The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program September, 2013 This document is largely taken
The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program Pocket Guide to Hydric Soils for Wetland Delineations in Massachusetts The Buzzards Bay National Estuary Program September, 2013 This document is largely taken
The History and Use of Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States
 The History and Use of Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States Lenore Matula Vasilas Soil Scientist USDA NRCS Beltsville, MD 1970s Soil Taxonomy incorporates wet soils into the classification
The History and Use of Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States Lenore Matula Vasilas Soil Scientist USDA NRCS Beltsville, MD 1970s Soil Taxonomy incorporates wet soils into the classification
What is a Wetland? Common Wetland Names. Wetlands: Ecotones between Upland and Aquatic Systems. Matthew J. Gray University of Tennessee.
 What is a Wetland? Matthew J. Gray University of Tennessee Common Wetland Names Backwater swamps Peatland Estuary Vernal Pools Marsh Playa Fen Bog Bayou Spring Seep Humedales Wetlands: Ecotones between
What is a Wetland? Matthew J. Gray University of Tennessee Common Wetland Names Backwater swamps Peatland Estuary Vernal Pools Marsh Playa Fen Bog Bayou Spring Seep Humedales Wetlands: Ecotones between
2008 Southern Regional Cooperative Soil Survey Conference. Ad Hoc Committee on Subaqueous Soil Interpretations July 14, 2008
 2008 Southern Regional Cooperative Soil Survey Conference Ad Hoc Committee on Subaqueous Soil Interpretations July 14, 2008 Soil scientists are now investigating aquatic bottoms. USDA-NRCS aims to survey
2008 Southern Regional Cooperative Soil Survey Conference Ad Hoc Committee on Subaqueous Soil Interpretations July 14, 2008 Soil scientists are now investigating aquatic bottoms. USDA-NRCS aims to survey
The Hydric Soil Technical Standard. Deliberations of: National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCSH)
 The Hydric Soil Technical Standard Deliberations of: National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCSH) NTCHS Recommendation for Application of the HSTS The NTCHS recommends that the HSTS be used to:
The Hydric Soil Technical Standard Deliberations of: National Technical Committee for Hydric Soils (NTCSH) NTCHS Recommendation for Application of the HSTS The NTCHS recommends that the HSTS be used to:
Wetland Delineation. Richard L. Darden, Ph.D. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Charleston District October 3, 2012 BUILDING STRONG
 Wetland Delineation Richard L. Darden, Ph.D. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Charleston District October 3, 2012 Why Delineate Wetlands? To define the limits of federal jurisdiction, in accordance with current
Wetland Delineation Richard L. Darden, Ph.D. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Charleston District October 3, 2012 Why Delineate Wetlands? To define the limits of federal jurisdiction, in accordance with current
Soil Quality: manifestations, mechanisms and measurement
 Soil Quality: manifestations, mechanisms and measurement John Witty and Lance Mytton Why is soil quality important? 54 The impact of biology on soil quality 54 Oxygen status in soils 55 Effect of oxygen
Soil Quality: manifestations, mechanisms and measurement John Witty and Lance Mytton Why is soil quality important? 54 The impact of biology on soil quality 54 Oxygen status in soils 55 Effect of oxygen
Revelations in Lentic Soils:
 Revelations in Lentic Soils: Deciphering System Processes and Resource Conditions from Mud, Muck, and Peat Mark A. Gonzalez National Riparian Service Team Prineville, Oregon Calvin and Hobbes by Bill Watterson
Revelations in Lentic Soils: Deciphering System Processes and Resource Conditions from Mud, Muck, and Peat Mark A. Gonzalez National Riparian Service Team Prineville, Oregon Calvin and Hobbes by Bill Watterson
Soil Physical Properties and Wastewater Treatment
 Soil Physical Properties and Wastewater Treatment John R. Buchanan, Ph.D., P. E. Associate Professor Biosystems Engineering and Soil Science Department Soil Physical Properties and Wastewater Treatment
Soil Physical Properties and Wastewater Treatment John R. Buchanan, Ph.D., P. E. Associate Professor Biosystems Engineering and Soil Science Department Soil Physical Properties and Wastewater Treatment
3 Parameters Federal/Corps. Wetland Delineation. Vegetation. Monterey County Wetlands Workshop 2/24/2014
 3 Parameters Federal/Corps Vegetation Wetland Delineation Soils Hydrology 3 Parameters but only 1 needed for State/Coastal Commission Vegetation Vegetation Soils Hydrology Sponsor: Elkhorn Slough Coastal
3 Parameters Federal/Corps Vegetation Wetland Delineation Soils Hydrology 3 Parameters but only 1 needed for State/Coastal Commission Vegetation Vegetation Soils Hydrology Sponsor: Elkhorn Slough Coastal
Hydric soil development in the Olentangy River Experimental Wetlands after five years of inundation
 Soils! 113 Hydric soil development in the Olentangy River Experimental Wetlands after five years of inundation Ashish P. Deshmukh and William J. Mitsch Environmental Science Graduate Program, The Ohio
Soils! 113 Hydric soil development in the Olentangy River Experimental Wetlands after five years of inundation Ashish P. Deshmukh and William J. Mitsch Environmental Science Graduate Program, The Ohio
Installing Equipment for the Hydric Soil Technical Standard
 Installing Equipment for the Hydric Soil Technical Standard Mike Vepraskas, NC State Univ. April 2005 Procedure: 1. Sites: Select at least two spots to monitor. One should be within a hydric soil, or at
Installing Equipment for the Hydric Soil Technical Standard Mike Vepraskas, NC State Univ. April 2005 Procedure: 1. Sites: Select at least two spots to monitor. One should be within a hydric soil, or at
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry
 Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 9 April 2013 Reading: Seitzinger & Mayorga (2008) 2013 Frank Sansone 1. Global coastal zone Outline 2. Nutrient loading in estuaries
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 9 April 2013 Reading: Seitzinger & Mayorga (2008) 2013 Frank Sansone 1. Global coastal zone Outline 2. Nutrient loading in estuaries
The Revolving (Evolving) Door of Hydric Soil Indicators
 The Revolving (Evolving) Door of Hydric Soil Indicators A brief history lesson in Hydric Soil Identification (I) Cowardin et al. (1979; Classification of Wetlands and Deepwater Habitats of the US) coined
The Revolving (Evolving) Door of Hydric Soil Indicators A brief history lesson in Hydric Soil Identification (I) Cowardin et al. (1979; Classification of Wetlands and Deepwater Habitats of the US) coined
Coastal Wetlands Formation, Functions, and Susceptibility. John Marton CWC Gulf Lagniappe November 23, 2013
 Coastal Wetlands Formation, Functions, and Susceptibility John Marton CWC Gulf Lagniappe November 23, 2013 What is a wetland? Wetlands are distinguished by the presence of water, either at the surface
Coastal Wetlands Formation, Functions, and Susceptibility John Marton CWC Gulf Lagniappe November 23, 2013 What is a wetland? Wetlands are distinguished by the presence of water, either at the surface
Lecture 5: Earth Environment
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Environmental Engineering Department Environmental Microbiology (EENV-2321) Lecture 5: Earth Environment Prepared by Husam Al-Najar 1 Earth Living Skin: The complexity of
The Islamic University of Gaza- Environmental Engineering Department Environmental Microbiology (EENV-2321) Lecture 5: Earth Environment Prepared by Husam Al-Najar 1 Earth Living Skin: The complexity of
WETLAND DETERMINATION DATA FORM Eastern Mountains and Piedmont
 WETLAND DETERMINATION DATA FORM Eastern Mountains and Piedmont Project/Site: PIK-104-10.62 (PID: 83667) City/County: Pike Sampling Date: 5.30.13 Applicant/Owner: ODOT State: OH Sampling Point: 36 Investigator(s):
WETLAND DETERMINATION DATA FORM Eastern Mountains and Piedmont Project/Site: PIK-104-10.62 (PID: 83667) City/County: Pike Sampling Date: 5.30.13 Applicant/Owner: ODOT State: OH Sampling Point: 36 Investigator(s):
Wastewater Treatment in Soils
 Wastewater Treatment in Soils James L. Anderson, PhD David Gustafson Aziz Amoozegar, PhD David Lindbo, PhD Model Decentralized Wastewater Practitioner Curriculum NDWRCDP Disclaimer This work was supported
Wastewater Treatment in Soils James L. Anderson, PhD David Gustafson Aziz Amoozegar, PhD David Lindbo, PhD Model Decentralized Wastewater Practitioner Curriculum NDWRCDP Disclaimer This work was supported
Supplemental Guide for Seasonal High Water Table Indicators in Georgia s Onsite. Wastewater Manual Section C: Flatwoods Region.
 Supplemental Guide for Seasonal High Water Table Indicators in Georgia s Onsite Wastewater Manual Section C: Flatwoods Region Brant Phelps Non-Thesis Research Paper Advisor: Dr. Willie Harris November
Supplemental Guide for Seasonal High Water Table Indicators in Georgia s Onsite Wastewater Manual Section C: Flatwoods Region Brant Phelps Non-Thesis Research Paper Advisor: Dr. Willie Harris November
Swamp School. Eastern Mountains and Piedmont Region. Hydric Soil and Wetland Hydrology Indicators
 Scope Reference Materials The purpose of this procedure is to provide information on the hydric and Wetland Hydrology indicators for the Eastern Mountains and Piedmont Region. This procedure should be
Scope Reference Materials The purpose of this procedure is to provide information on the hydric and Wetland Hydrology indicators for the Eastern Mountains and Piedmont Region. This procedure should be
The soil is a very. The soil can. The manure. Soil Characteristics. effective manure treatment system if manures are applied at the proper rate.
 The soil is a very effective manure treatment system if manures are applied at the proper rate. The soil can filter pollutants and prevent them from reaching groundwater. The manure application rate should
The soil is a very effective manure treatment system if manures are applied at the proper rate. The soil can filter pollutants and prevent them from reaching groundwater. The manure application rate should
Deep River-Portage Burns Waterway Watershed 2015
 2.4 Soils Soil development is the product of the interaction of parent material, topography, climate, organisms and time. Understanding the types of soils that exist within a watershed and their characteristics
2.4 Soils Soil development is the product of the interaction of parent material, topography, climate, organisms and time. Understanding the types of soils that exist within a watershed and their characteristics
14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride
 Sulfur 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride Development of an oxygenated atmosphere facilitated this
Sulfur 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride Development of an oxygenated atmosphere facilitated this
Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States: Loamy and Clayey Soils
 Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States: Loamy and Clayey Soils Field Indicators The publication Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the US (Vasilas, Hurt, and Noble 2010) is the reference
Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States: Loamy and Clayey Soils Field Indicators The publication Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the US (Vasilas, Hurt, and Noble 2010) is the reference
Introduction. Wetland System. A Wetland Scene at Lorne C. Henderson Conservation Area near Petrolia
 Wetland Treatment of Wastewater This monograph, one in a series of single issue documents that deal with our local environment, has been prepared by the Sarnia-Lambton Environmental Association in co-operation
Wetland Treatment of Wastewater This monograph, one in a series of single issue documents that deal with our local environment, has been prepared by the Sarnia-Lambton Environmental Association in co-operation
Trip Report New Mexico Study of Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States 6/23 6/27/2008
 Trip Report New Mexico Study of Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States 6/23 6/27/2008 Objective Lenore Vasilas, NRCS, HQ; Jim Herrington, EPA, TX; Ken Scheffe, NRCS, NM; and Bob Hill, NRCS,
Trip Report New Mexico Study of Field Indicators of Hydric Soils in the United States 6/23 6/27/2008 Objective Lenore Vasilas, NRCS, HQ; Jim Herrington, EPA, TX; Ken Scheffe, NRCS, NM; and Bob Hill, NRCS,
Who cares? You do! In India, one child dies every minute from severe acute malnutrition.
 Soil & Agriculture Who cares? You do! In India, one child dies every minute from severe acute malnutrition. Case Study: The Dust Bowl In the dirty thirties a large area of cropland was abandoned due to
Soil & Agriculture Who cares? You do! In India, one child dies every minute from severe acute malnutrition. Case Study: The Dust Bowl In the dirty thirties a large area of cropland was abandoned due to
Biochar Soil Amendment Opportunities
 Biochar Soil Amendment Opportunities Curtis Dell Research Soil Scientist, USDA ARS and Adjunct Associate Professor, Ecosystems Science and Management Department, PSU Soils 101 Important soil properties
Biochar Soil Amendment Opportunities Curtis Dell Research Soil Scientist, USDA ARS and Adjunct Associate Professor, Ecosystems Science and Management Department, PSU Soils 101 Important soil properties
Hydrologic Indicators
 Hydrologic Indicators Courtney M. Stevens Regulatory Specialist Coastal Branch December 8, 2011 US Army Corps of Engineers HYDROLOGY Some Factors that Influence the Wetness of a Site Climate Landscape
Hydrologic Indicators Courtney M. Stevens Regulatory Specialist Coastal Branch December 8, 2011 US Army Corps of Engineers HYDROLOGY Some Factors that Influence the Wetness of a Site Climate Landscape
Western Mountains, Valleys, and Coast Interim Regional Supplement to the 1987 Wetlands Delineation Manual
 Western Mountains, Valleys, and Coast Interim Regional Supplement to the 1987 Wetlands Delineation Manual Bill Kirchner, PWS, US Fish & Wildlife Service Janet Morlan, PWS, Department of State Lands Mike
Western Mountains, Valleys, and Coast Interim Regional Supplement to the 1987 Wetlands Delineation Manual Bill Kirchner, PWS, US Fish & Wildlife Service Janet Morlan, PWS, Department of State Lands Mike
CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles. Environmental Microbiology
 Updated: 1 October 015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #13 Environmental Biology II Metabolism Reading: Davis & Masten, Chapter 3 David Reckhow CEE 370 L#13 1 Environmental
Updated: 1 October 015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #13 Environmental Biology II Metabolism Reading: Davis & Masten, Chapter 3 David Reckhow CEE 370 L#13 1 Environmental
If you have an extra electron where do you put it?
 If you have an extra electron where do you put it? Jouni Lehtoranta Finnish Environment Institute Marine Research Center Systems Ecological Perspectives on Sustainability Conference 25.09.2014 Spatial
If you have an extra electron where do you put it? Jouni Lehtoranta Finnish Environment Institute Marine Research Center Systems Ecological Perspectives on Sustainability Conference 25.09.2014 Spatial
Lab today Finish Inventory work at Rest Area Site
 Lubrecht Forest, Montana NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Day 23 Nov 10, 2009 Nutrient Cycling (Chapters 16-18) Lab today Finish Inventory work at Rest Area Site Quiz on Thursday Also record trees & shrubs
Lubrecht Forest, Montana NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Day 23 Nov 10, 2009 Nutrient Cycling (Chapters 16-18) Lab today Finish Inventory work at Rest Area Site Quiz on Thursday Also record trees & shrubs
Soils and Wetlands. What s About to Hit the Pit
 Soils and Wetlands What s About to Hit the Pit http://www.usace.army.mil/cw/cecwo/reg/reg_supp.htm Why Regionalize? Recommendations A new and consistent system of wetland delineation regions is needed,
Soils and Wetlands What s About to Hit the Pit http://www.usace.army.mil/cw/cecwo/reg/reg_supp.htm Why Regionalize? Recommendations A new and consistent system of wetland delineation regions is needed,
CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles
 Updated: 12 October 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #13 Environmental Biology II Metabolism Reading: Davis & Masten, Chapter 3 David Reckhow CEE 370 L#13 1 Environmental
Updated: 12 October 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #13 Environmental Biology II Metabolism Reading: Davis & Masten, Chapter 3 David Reckhow CEE 370 L#13 1 Environmental
Regulatory and Assessment Challenges for Muskeg Soil at Oil and Gas Sites in Northeast BC
 Regulatory and Assessment Challenges for Muskeg Soil at Oil and Gas Sites in Northeast BC Tom Frkovich, P.Geo. SynergyAspen Environmental 2013 Remediation Technologies Symposium Regulatory and Assessment
Regulatory and Assessment Challenges for Muskeg Soil at Oil and Gas Sites in Northeast BC Tom Frkovich, P.Geo. SynergyAspen Environmental 2013 Remediation Technologies Symposium Regulatory and Assessment
SITE ANALYSIS. 1. Hydrophytic Vegetation: A predominance of plants that are typically adapted for life in saturated soils.
 Soil Mapping The soil mapping inventory completed by the Natural Resource Conservation Service was reviewed as a part of this assessment (fig. 4). This mapping identified the soils generally throughout
Soil Mapping The soil mapping inventory completed by the Natural Resource Conservation Service was reviewed as a part of this assessment (fig. 4). This mapping identified the soils generally throughout
ATTACHMENT 4 USDA NRCS HYDRIC SOIL UNIT DESCRIPTIONS
 ATTACHMENT 4 USDA NRCS HYDRIC SOIL UNIT DESCRIPTIONS USDA NRCS descriptions of the 23 wetland soil units (hydric soils and soils with hydric inclusions) That occur within the proposed Marble River Wind
ATTACHMENT 4 USDA NRCS HYDRIC SOIL UNIT DESCRIPTIONS USDA NRCS descriptions of the 23 wetland soil units (hydric soils and soils with hydric inclusions) That occur within the proposed Marble River Wind
Inherent Factors Affecting Soil Respiration
 Soil respiration is a measure of the carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) released from soil. It is released as a result of decomposition of soil organic matter (SOM) and plant litter by soil microbes and through plant
Soil respiration is a measure of the carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) released from soil. It is released as a result of decomposition of soil organic matter (SOM) and plant litter by soil microbes and through plant
Biogeochemistry of C
 Biogeochemistry of C NREM 665 CO 2 CO 2 CH 4 diffusion & ebullition CO 2 Organic-C accretion DOC CH 4 methanogenesis C Biogeochemistry I.Forms of C in WTLs & Coastal Ecosystems Molecule Oxidation State
Biogeochemistry of C NREM 665 CO 2 CO 2 CH 4 diffusion & ebullition CO 2 Organic-C accretion DOC CH 4 methanogenesis C Biogeochemistry I.Forms of C in WTLs & Coastal Ecosystems Molecule Oxidation State
Ecosystems. 6.L.2.2 Explain how plants respond to external stimuli (including dormancy and forms of tropism) to enhance survival in an environment.
 Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Municipal Stadium Wetland
 W A T E R S H E D F A C T S Total watershed area 140 mi 2 Average annual rainfall 38 in Average annual temperature 58 F Elevation Max 1321 ft Min 899 ft C. J. Brown Reservoir controls flow from 83 mi 2
W A T E R S H E D F A C T S Total watershed area 140 mi 2 Average annual rainfall 38 in Average annual temperature 58 F Elevation Max 1321 ft Min 899 ft C. J. Brown Reservoir controls flow from 83 mi 2
Legal Perspectives on Florida Wetland Jurisdiction
 Legal Perspectives on Florida Wetland Jurisdiction Timothy J. Perry, Esq. Oertel, Fernandez, Bryant & Atkinson, P.A. Tallahassee, Florida tperry@ohfc.com History 1993 Florida Environmental Reorganization
Legal Perspectives on Florida Wetland Jurisdiction Timothy J. Perry, Esq. Oertel, Fernandez, Bryant & Atkinson, P.A. Tallahassee, Florida tperry@ohfc.com History 1993 Florida Environmental Reorganization
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the influence of reducing conditions on
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the influence of reducing conditions on organic C bound to Fe. Under aerobic conditions, a significant fraction of soil C may be associated with Fe(III)
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the influence of reducing conditions on organic C bound to Fe. Under aerobic conditions, a significant fraction of soil C may be associated with Fe(III)
Wetland Functions in the Watershed: Part 1 Watershed Elements. USDA NRCS Module Name 1
 Wetland Functions in the Watershed: Part 1 Watershed Elements USDA NRCS Module Name 1 Objectives Define Landscape Elements in the Watershed Describe Hydrologic Connections Between Elements Introduce Soil
Wetland Functions in the Watershed: Part 1 Watershed Elements USDA NRCS Module Name 1 Objectives Define Landscape Elements in the Watershed Describe Hydrologic Connections Between Elements Introduce Soil
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
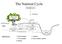 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
Soils and their Sustainable Management (2016) Trish Steinhilber extension.umd.edu/anmp
 Soils and their Sustainable Management (2016) Trish Steinhilber psteinhi@umd.edu extension.umd.edu/anmp What is Soil? the living skin of the Earth (Ian Pepper, soil microbiologist) crucible of terrestrial
Soils and their Sustainable Management (2016) Trish Steinhilber psteinhi@umd.edu extension.umd.edu/anmp What is Soil? the living skin of the Earth (Ian Pepper, soil microbiologist) crucible of terrestrial
Soil Composition and Importance p. 1 Preview and Important Facts p. 1 What Is Soil? p. 1 Components of Soil p. 3 Historical Perspectives p.
 Preface p. xvii Soil Composition and Importance p. 1 Preview and Important Facts p. 1 What Is Soil? p. 1 Components of Soil p. 3 Historical Perspectives p. 8 Soil-A Precious Resource p. 13 Soil Quality
Preface p. xvii Soil Composition and Importance p. 1 Preview and Important Facts p. 1 What Is Soil? p. 1 Components of Soil p. 3 Historical Perspectives p. 8 Soil-A Precious Resource p. 13 Soil Quality
Impacts of a Zero Valent Iron PRB on Downgradient Biodegradation Processes. John E. Vidumsky DuPont Corporate Remediation Group
 Impacts of a Zero Valent Iron PRB on Downgradient Biodegradation Processes John E. Vidumsky DuPont Corporate Remediation Group Why is Downgradient Biodegradation Important? Significant contaminant mass
Impacts of a Zero Valent Iron PRB on Downgradient Biodegradation Processes John E. Vidumsky DuPont Corporate Remediation Group Why is Downgradient Biodegradation Important? Significant contaminant mass
River transport and chemistry. Lecture Outline
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.12.17) (Schlesinger & Bernhardt: Chapter 8) River transport and chemistry Lecture Outline 1. Introduction Overview 2. Soil Hydraulics & Stream Hydrology 3. Stream Load
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.12.17) (Schlesinger & Bernhardt: Chapter 8) River transport and chemistry Lecture Outline 1. Introduction Overview 2. Soil Hydraulics & Stream Hydrology 3. Stream Load
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry
 Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 2 April 2015 Readings: Seitzinger& Mayorga(2008) Jeandelet al.(2011) 2015 Frank Sansone and S.V. Smith 1. Global coastal zone Outline
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 2 April 2015 Readings: Seitzinger& Mayorga(2008) Jeandelet al.(2011) 2015 Frank Sansone and S.V. Smith 1. Global coastal zone Outline
Characterization and Remediation of Diesel in a Fractured Rock Aquifer with a Nutrient-Flushing System
 Characterization and Remediation of Diesel in a Fractured Rock Aquifer with a Nutrient-Flushing System Presentation by David Thomson and Stefan Humphries 31-Oct-07 Authors and Collaborators Presenting
Characterization and Remediation of Diesel in a Fractured Rock Aquifer with a Nutrient-Flushing System Presentation by David Thomson and Stefan Humphries 31-Oct-07 Authors and Collaborators Presenting
ABSTRACT. SEVERSON, ERIK. Evaluation of Several Methods of Predicting Historic Water Table Levels (Under the direction of Dr.
 ABSTRACT SEVERSON, ERIK. Evaluation of Several Methods of Predicting Historic Water Table Levels (Under the direction of Dr. David Lindbo) Redoximorphic features (iron depletions) and their location in
ABSTRACT SEVERSON, ERIK. Evaluation of Several Methods of Predicting Historic Water Table Levels (Under the direction of Dr. David Lindbo) Redoximorphic features (iron depletions) and their location in
Biogeochemistry of Wetlands
 Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Wetland Communities Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science Department University
Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Wetland Communities Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science Department University
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY BIOGEOCHEMISTR Y OF N NREM
 BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF N NREM 665 Dominant Pathways for N Cycling Plant Uptake: assimilation of NH + - 4 and NO 3 into biomass N Fixation: Conversion of gaseous N 2 to NH 3 Ammonia Volatilization: NH 4+ NH
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF N NREM 665 Dominant Pathways for N Cycling Plant Uptake: assimilation of NH + - 4 and NO 3 into biomass N Fixation: Conversion of gaseous N 2 to NH 3 Ammonia Volatilization: NH 4+ NH
Managing Crops for Excess Water Stress
 27 Managing Crops for Excess Water Stress Curtis Cavers* and John Heard Manitoba Agriculture & Food, Soils & Crops Branch, Box 1149 Carman, MB RG J (ccavers@gov.mb.ca) A review of literature on the effect
27 Managing Crops for Excess Water Stress Curtis Cavers* and John Heard Manitoba Agriculture & Food, Soils & Crops Branch, Box 1149 Carman, MB RG J (ccavers@gov.mb.ca) A review of literature on the effect
MMG 301 Dr. Frank Dazzo Microbial Ecology: Methodology & Soil Microbiology. Some methods used to study microbes in natural habitats:
 MMG 301 Dr. Frank Dazzo Microbial Ecology: Methodology & Soil Microbiology Some methods used to study microbes in natural habitats: Microbial abundance: microscopy, computer-assisted image analysis measurement
MMG 301 Dr. Frank Dazzo Microbial Ecology: Methodology & Soil Microbiology Some methods used to study microbes in natural habitats: Microbial abundance: microscopy, computer-assisted image analysis measurement
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Hana Santruckova Introduction in the topic of the IP Soil & Water :
 ERASMUS Soil & Water Protokoll Montag 17.09.2012 Hana Santruckova Introduction in the topic of the IP Soil & Water : Soil-Water-Interactions water retention capacity of soil: water doesn't evaporate in
ERASMUS Soil & Water Protokoll Montag 17.09.2012 Hana Santruckova Introduction in the topic of the IP Soil & Water : Soil-Water-Interactions water retention capacity of soil: water doesn't evaporate in
Describe/characterize some Microclimate & Soil parameters
 Objectives/Goals Describe/characterize some Microclimate & Soil parameters Assess microclimate and soils at 4 sites Quantitatively - using basic methods Qualitatively visually Compare soils at 4 sites
Objectives/Goals Describe/characterize some Microclimate & Soil parameters Assess microclimate and soils at 4 sites Quantitatively - using basic methods Qualitatively visually Compare soils at 4 sites
Agricultural Interpretations Database Description
 Agricultural Interpretations Database Description Date of last update: 31-Mar-2003 Field Field Name Type Width Dec Index 1 AREA Numeric 18 5 N 2 PERIMETER Numeric 18 5 N 3 SOIL_ Numeric 11 N 4 SOIL_ID
Agricultural Interpretations Database Description Date of last update: 31-Mar-2003 Field Field Name Type Width Dec Index 1 AREA Numeric 18 5 N 2 PERIMETER Numeric 18 5 N 3 SOIL_ Numeric 11 N 4 SOIL_ID
Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases
 Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases Content Atmospheric Composition Composition of the Earth s Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases The Radiative Forcing bar chart: AR5 version Natural Greenhouse Gases Water
Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases Content Atmospheric Composition Composition of the Earth s Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases The Radiative Forcing bar chart: AR5 version Natural Greenhouse Gases Water
Brianna Richards Chris Craft
 Brianna Richards Chris Craft June 8, 2012 Wetland ecosystem services Flood abatement and water storage Nutrient Removal Biodiversity Habitat C sequestration Wetland Losses Conversion to ag Example: Great
Brianna Richards Chris Craft June 8, 2012 Wetland ecosystem services Flood abatement and water storage Nutrient Removal Biodiversity Habitat C sequestration Wetland Losses Conversion to ag Example: Great
Appendix E Preliminary Jurisdictional Wetland Delineation Report, JYL 2008
 Appendix E Preliminary Jurisdictional Wetland Delineation Report, JYL 2008 PRELIMINARY JURISDICTIONAL WETLAND DELINEATION REPORT A portion of USS 3819 and 2664: Horton Lot and Statter Harbor Juneau, Alaska
Appendix E Preliminary Jurisdictional Wetland Delineation Report, JYL 2008 PRELIMINARY JURISDICTIONAL WETLAND DELINEATION REPORT A portion of USS 3819 and 2664: Horton Lot and Statter Harbor Juneau, Alaska
Wetland Observations
 Wetland Observations What is a wetland?/ Wetland Delineation Adapted from: Run for the Border and Do You Dig Wetland Soil in WOW! Wonders of Wetlands: An Educator s Guide. Bozeman: The Watercourse and
Wetland Observations What is a wetland?/ Wetland Delineation Adapted from: Run for the Border and Do You Dig Wetland Soil in WOW! Wonders of Wetlands: An Educator s Guide. Bozeman: The Watercourse and
Why Water Quality? FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE March 26, 2013
 Nutrients Nutrients Microbes Rulers of the World Microbes and Redox Potential Dissolved Oxygen Nitrogen Cycle From Waste to Gas Phosphorus Cycle or Recycle Algae The Miracle of Life Stormwater - Loadings
Nutrients Nutrients Microbes Rulers of the World Microbes and Redox Potential Dissolved Oxygen Nitrogen Cycle From Waste to Gas Phosphorus Cycle or Recycle Algae The Miracle of Life Stormwater - Loadings
Aquatic Science Unit 2. Water Quality and Water Pollution
 Aquatic Science Unit 2 Water Quality and Water Pollution What is a healthy water body? In your own words, take a moment to describe what you believe are some of the characteristics of a healthy stream
Aquatic Science Unit 2 Water Quality and Water Pollution What is a healthy water body? In your own words, take a moment to describe what you believe are some of the characteristics of a healthy stream
What to do with extra electrons how combating eutrophication may affect mineralization pathways
 What to do with extra electrons how combating eutrophication may affect mineralization pathways Jouni Lehtoranta Finnish Environment Institute Marine Research Centre Sun e - Energy goes through the system
What to do with extra electrons how combating eutrophication may affect mineralization pathways Jouni Lehtoranta Finnish Environment Institute Marine Research Centre Sun e - Energy goes through the system
RIS Swedish National Forest Inventory. RIS MI Swedish Forest Soil Inventory. Integrated Monitoring - IM
 RIS Swedish National Forest Inventory RIS MI Swedish Forest Soil Inventory Integrated Monitoring - IM Ecosystem monitoring Forest Environment Integrated Monitoring IM & RIS MI Swedish Soil Survey * Land
RIS Swedish National Forest Inventory RIS MI Swedish Forest Soil Inventory Integrated Monitoring - IM Ecosystem monitoring Forest Environment Integrated Monitoring IM & RIS MI Swedish Soil Survey * Land
A BRIEF HISTORY ON SOIL MICROCOSMS AS AN EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS FOR BIOGEOCHEMICAL RESEARCH
 Chapter A BRIEF HISTORY ON SOIL MICROCOSMS AS AN EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS FOR BIOGEOCHEMICAL RESEARCH Kewei Yu a and Ronald D. DeLaune b a Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences, Troy University,
Chapter A BRIEF HISTORY ON SOIL MICROCOSMS AS AN EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS FOR BIOGEOCHEMICAL RESEARCH Kewei Yu a and Ronald D. DeLaune b a Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences, Troy University,
MANAGING CROPS FOR EXCESS WATER STRESS
 MANAGING CROPS FOR EXCESS WATER STRESS A review of literature on the effect of mid-season excess moisture on a growing crop was conducted to understand the processes affected by excess water and to quantify
MANAGING CROPS FOR EXCESS WATER STRESS A review of literature on the effect of mid-season excess moisture on a growing crop was conducted to understand the processes affected by excess water and to quantify
David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology
 How does carbon influence nitrogen availability and losses? David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology Outline Carbon cycle Global carbon cycle Soil carbon 3
How does carbon influence nitrogen availability and losses? David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology Outline Carbon cycle Global carbon cycle Soil carbon 3
