Surface water flood risk mapping in the UK - approaches and challenges
|
|
|
- Alvin Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slide 1 Surface water flood risk mapping in the UK - approaches and challenges Slide 2 Surface water flood risk mapping in the UK Chris Elms, Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs Selena Peters, Environment Agency (England) Kirsten Thorburn, Scottish Environment Protection Agency Linda MacHugh, Northern Ireland Department for Infrastructure Flood risk management is a devolved matter in the UK. Each of the four nations England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland - is responsible for risk assessment, mapping and plans. Working Group F Pluvial flood risk, Berlin, October We have many players involved in the Floods Directive in the United Kingdom and flood risk management is a devolved matter. Each of the four nations- England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland is responsible for the risk assessment, mapping and plans Defra co-ordinates reporting and delivery of the requirements of the Directives such as PFRAs and FRMPs. The UK government delegates responsibility for preparation and publication of the PFRAs, FRMPs etc in England to the Environment Agency, as its competent authority. Similar arrangements apply in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
2 Local authorities are responsible for the management of pluvial flood risk as they are best placed to deal with the impact of surface water flooding in local areas My colleagues will outline our respective approaches to understanding and managing the risks from pluvial flooding. It is important to note that though we have common needs and there are common theme, each nation has adapted its approach to deal most effectively with the issues for them, and this flexibility provided by the Directive is important. For example, in England and Wales we mapped for surface water flooding on a national basis before the Directive came into force following extensive flooding in 2007 which led to new legal responsibilities for local authorities in respect of assessing, mapping and planning for flood risk and has informed our approach. Slide 3 Common needs Develop understanding of pluvial flooding Inform FRMP and support decision making investment in structural defences improve emergency response land use planning Raise public awareness Understand future impacts adapting to climate change Working Group F Pluvial flood risk, Berlin, October The common needs which we all share are: Firstly the need to develop our understanding of pluvial flooding We need this to inform our Flood Risk Management Plans and support our decision making in respect of our investment in structural defences, to improve our emergency response and for the purposes of land use planning We also need to raise public awareness and understand future impacts, in particular how we adapt to climate change.
3 Slide 4 Approach to modelling and mapping surface water flood risk in England (and Wales) Manning s n (0.02, 0.03, 0.1) 68% LiDAR 2m resolution Local modelling Cleaning Local validation No defences Extent Surface 91,000 manual structure edits Roads lowered (0.125m) Buildings raised (0.3m) 50% summer rainfall profile 3 annual frequencies (30, 100, 1000) National legislation definition Water Current day scenario Urban/rural adjustments Suitability Outputs Depth Communication 3 storm durations (1,3,6hr) Hazard Velocity Surface Water Mapping history in England (and Wales until April 2013): 2008: Areas Susceptible to surface water flooding (AStSWF) The Government s Pitt Review following flooding of 2007 which focused on surface water flooding, previously not such an issue. The map was produced independently by Jeremy Benn Associates and we licenced its use. 2010: Our first Flood Map for Surface Water (FMfSW) a step forward from AStSWF, however still a national scale model with no local input. We used this map to determine our Flood Risk Areas in the PFRA 1 st cycle. 2012: updated Flood Map for Surface Water (ufmfsw) improvements to both data and method. We published it in December 2013, now called Risk of Flooding from Surface Water (RoFW). Water (Hydrology) National legislation defines surface water flooding as surface runoff from rainwater (Flood and Water Management Act, 2010: flooding that takes place from the 'surface runoff' generated by rainwater (including snow and other precipitation) which: (a) is on the surface
4 of the ground (whether or not it is moving), and (b) has not yet entered a watercourse, drainage system or public sewer ) Current day scenario only Urban vs rural adjustments for effective rainfall. Urban assumptions of 70% rainfall infiltration and drainage rate 12mm/hr. 3 storm durations 1 hr, 3 hrs and 6 hrs results merged together to form worst case and to give a better chance that the frequency of the flood is appropriate. 3 annual frequencies 1 in 30 chance of happening in any given year, 1 in 100 and 1 in 1000 (annual exceedance probabilities) Surface (DTM) Ground surface made up of LiDAR downgraded to a 2m resolution for national consistency Maintained flowpaths where possible: 2m resolution to pick up small structures Raised buildings and lowered roads Things that weren t picked up automatically, we edited manually (eg tunnels through rail embankments) No defences included Roughness values varied according to land use Ran using a 2D model Then included results of any local modelling from local authorities better quality outputs produced in line with EU Directive requirements (Article 6) plus an additional output we called suitability which is a measure of confidence in the outputs and the reliability of the outputs if used at various scales cleaning remove isolated flooding (>100m 3 ), filled in dry areas <50m 3, remove anything below defined hazard threshold (0.575) to create an outline local validation we shared the outputs online with local authorities for their comment and confidence communication published on our website in December 2013 (next slide for progress), available to non-commercial and commercial companies with a licence (data free of charge since April) Documents available describing our Risk of Flooding from Surface Water (RoFSW) information: (Using the RoFSW Information dataset documentation)
5 Slide 5 How we communicate national SW flood risk to the public (ANIMATED SLIDE): Published our Flood Risk Maps. Showing the adverse impacts of flooding. The slide shows the page and map from the Thames Basin District where the Flood Risk Area is London. The image on the slide shows Risk to People. Others available are Economic Activity, Natural and Historic Environment. Previously map based as only method of communication (currently running in parallel to new method) &y=355134#x=357683&y=355134&scale=2
6 Now we have the Long Term Flood Risk Information: postcode search for flood risk information focussed on action before risk (R&D telling us what people are interested in) and simpler map visuals with a slider from basic to more detailed information New approach to communicating risk, now live but running in parallel to the above (Long Term Flood Risk Information): Research report into communicating flood risk (Sciencewise):
7 The actions that are listed in the report change order and/or content according to the relative risk of the sources of flooding
8 Slide 6 National pluvial rapid flood spreading modelling All Scotland Data in Assumption s Digital Terrain Model (NextMap) Topographic map Rainfall urban and rural areas Runoff Drainage Rainfall (profile, duration, return period, climate change) Outputs Extent Depth In high risk areas Regional pluvial 2D hydraulic modelling Outputs Data in Assumption s Digital Terrain Model (LiDAR) Topographic map Rainfall Land cover map Runoff Drainage mannings Rainfall (profile, duration, return period, climate change) Extent Depth Velocity Hazard rating Water company flood hazard from sewer system 1D Sewer model and 2D spreading Locations of flooding, extents and depths Scotland pluvial flood modelling Before the floods directive and our national legislation in Scotland we had no national understanding of pluvial flood risk 2011 National pluvial modelling. For the preliminary flood risk assessment in 2011 we developed a national pluvial flood model covering the whole of Scotland this was based on relatively simple modelling software - rapid flood spreading model giving higher level and strategic outputs to enable us to consider pluvial flood risk in our pfra. We did this because we had experienced some significant pluvial flood events (e.g. Glasgow 2002 and the pluvial floods in England in 2007) The data we needed to input to this modelling was: o DTM (we had an existing national Digital Terrain Model based on NEXT map not as accurate as LiDAR) o Detailed topographic map to add surface features to DTM (e.g. buildings, roads, remove false blockages) o Rainfall data (from Centre of Ecology and Hydrology (CEH)) o Map showing urban and rural areas for applying different model assumptions What it was used for
9 o The 2011 pluvial modelling gave us an understanding of the scale of pluvial flood risk in Scotland (based on economic damages to homes and businesses pluvial flooding accounted for 38% of damages, fluvial flooding 45%, coastal flooding 17%) o It provided information on pluvial flood risk in each ASFR o It was used to identify those areas with higher pluvial flood risk where more detailed pluvial modelling was carried out. By 2013 we then carried out more detailed pluvial modelling in the highest risk areas (covers 11% of Scotland), this informed our hazard and risk mapping for areas of significant flood risk and the flood risk management plans. This used more detailed modelling software 2D hydraulic modelling giving more outputs, as well as extent and depth we also have velocity and hazard rating. It also gives us more confidence in the outputs. The water company also provided some modelling of the drainage network. The key new data needed to do this more detailed modelling was o improving the accuracy of the DTM using LiDAR, and o land use cover map to determine mannings and more detailed identification of urban and rural areas. What it was used for o Provided an updated understanding of the scale of pluvial flood risk in Scotland (based on economic damages pluvial flooding accounted for 23% of damages, fluvial flooding 56%, coastal flooding 21%) o Informed the FRMP in consultation with local authorities (was used to identify those towns and cities with greatest pluvial flood risk where local authorities would lead on the management of this risk) o Was provided to local authorities to inform management of pluvial flood risk (local authorities will validate in detail and do more detailed modelling where required) o Was provided to land use planning authorities to inform new development. Scotland has policy for pluvial flooding and new developments - new developments must be designed to ensure that buildings are not at risk of pluvial flooding and that it does not increase the risk of flooding out with the development. This is different to planning policy for fluvial and coastal flooding where new development is not allowed in the flood extent Environment/planning/Policy Pluvial flood hazard maps made publically available online.
10 Slide 7 Scotland National pluvial modelling Scotland Regional pluvial modelling Coverage All Scotland In high risk areas Modelling software Rapid flood spreading model (ISIS Fast) 2D hydraulic modelling (Jflow+) Data inputs required Digital Terrain Model (Next Map) 0.7m vertical accuracy, 5m resolution (Based on topographic map) - Buildings raised 0.3m, roads lowered 0.1m, false blockages removed Digital Terrain Model (LiDAR) 0.15m vertical accuracy, 1-2m resolution (Based on topographic map) - Buildings raised 0.3m, false blockages removed No flood defences No flood defences Map showing urban and rural areas Land Cover Map Detailed topographic map Detailed topographic map Rainfall data Rainfall data Assumptions Urban Rural Urban Rural Model resolution 5m 5m 2m 5m Runoff 70% 55% 70% 55% Mannings Does not take into Does not take into Based on land cover Based on land cover map account roughness account roughness map Drainage capacity 12mm/hr 0mm/hr 1in5yr rainfall return 0mm/hr Rainfall Profile 50% summer profile 50% summer profile 50% summer profile 50% summer profile Rainfall duration 1hr 3hr 1hr, 3hr 1hr, 3hr Rainfall return period Climate change uplifts Post processing 10yr,30yr,30yrCC, 50yr, 100yr, 200yr, 200yrCC 10yr,30yr,30yrCC, 50yr, 100yr, 200yr, 200yrCC 10yr,30yr,30yrCC, 50yr, 100yr, 200yr, 200yrCC 10yr,30yr,30yrCC, 50yr, 100yr, 200yr, 200yrCC 20% uplift in rainfall intensity based on UK Climate Projections 2009 (UKCP09) and review of other studies in the UK. Applying depth thresholds, removing small ponded areas Outputs Extents, depths Extents, depths, velocity, hazard rating Working Group F Pluvial flood risk, Berlin, October This slide shows more information about the data used for the modelling and assumptions made.
11 Slide 8 Adverse consequences of flooding Example of adverse consequences of pluvial flooding risk (1in200yr shown here) GIS analysi s damage (based on depth) for homes, businesses and roads Flood Hazard Research Centre Working Group F Pluvial flood risk, Berlin, October Scotland, how we assessed the adverse consequences of flooding (Animated Slide) Using our flood hazard maps we then assessed the adverse consequences of flooding (higher level assessment done for pfra in 2011, more detailed assessment done for maps of ASFR in 2013) Data needed for this: o Hazard outputs from modelling (extent, depth) o Dataset on a national scale with information on receptors of flooding (e.g. properties, cultural heritage, roads, rail etc and information on these e.g. property type (home, business, community facility), floor area, areas more socially vulnerable to flooding, The adverse consequences assed included (done for all return periods): o Number of residential properties at risk and damage to residential properties o Number of residential properties at risk in areas that are more socially vulnerable to flooding o Number of non-residential properties at risk and damage o Number and type of community facilities at risk Number and type of cultural heritage buildings and sites at risk o Infrastructure at risk (roads, rail, airports, energy distribution infrastructure, water and waste water infrastructure) o Impact on environmental designated sites was not done for pluvial flooding as risk not significant more detailed local modelling needed to understand environmental risks for pluvial flooding. Methods for identifying adverse consequences based on manual from flood hazard research centre at Middlesex University including economic damage based on depth of flooding in. We have found the numbers of properties at risk from pluvial flooding is very sensitive to how buildings are represented in the Digital Terrain Model and the method used to identify what properties are within the flood extent.
12 Slide 9 Approach to modelling and mapping surface water flooding in Northern Ireland NI methodology for creating Surface Water Flood maps similar to England & Wales NI focus is on Flood Hazard only Maps for all of NI communicated via Flood Maps (NI) website NI Viewer presents interactive map with linked PDF maps showing depth information for high, medium, low probability flood scenarios Information is presented for present day & climate change epochs Working Group F Pluvial flood risk, Berlin, October NI methodology for creating the Surface Water Flood maps is very similar to England & Wales (as illustrated on other slides of the presentation). NI Surface Water maps focus on flood hazard only. The maps are communicated via the Flood Maps (NI) website - The map viewer presents an interactive map for all of NI, along with preformatted PDF maps showing depth information for all 3 flood scenarios (high, medium, low probability). Information is presented for both present day and climate change epochs. The maps are used within the planning process to trigger drainage assessments where appropriate. Stats are produced at a NI (and parliamentary boundary) scale to indicate the number of properties that are impacted by surface water flooding.
13 Slide 10 Sharing Licencing Large dataset size Understanding Strengths and limitations Fluvial vs pluvial Language for risk Precision vs accuracy Improving Amendments Keeping up to date with developments Using Counting properties Receptor datasets Suitability Creating DTM Calibration and verification Drainage and runoff rates What we re working on in surface water modelling and mapping Creating DTM LiDAR coverage challenges. LiDAR vs NEXTMAP - cost vs benefit of having a more accurate DTM where there is lower risk (rural areas) Calibration/Verification limited history, unreliable records, how/when to record, mixed sources, quick onset and recession Drainage and runoff rates various possible approaches: blanket drainage capacity based on defined rainfall rate regionally variable capacity based on a local rainfall capacity (eg SEPA: 5yr) locally derived drainage rates based on local knowledge (Environment Agency Research & Development) Runoff rates urban vs rural variations Using Counting properties this is very sensitive to the methods used modelling includes buildings, so using a property point counting method significantly underestimates property counts.
14 Alternative method: perimeter method buffering issues/internal boundaries eg. Terraced houses, what counts as being at risk? Receptor datasets availability of and confidence in national receptor/property datasets is important to get consistent and comparable impact assessments Suitability what level of scale is it appropriate to use the data? A key question to enable practitioners to understand the reliability of decisions based on the information. Not property level. Recommended for use for surface water management plans (strategic level) England country-county-town level only except where local model outputs included. Advise to always check with local authorities for detail Scotland our more detailed regional hazard and risk data may be appropriate to identify streets and neighbourhoods at higher risk when combined with local authority knowledge and verification at a more local level. Sharing Licencing restricting our ability to make the information Open Data (available unrestricted to all) England includes local models which need local authorities permission for us to share as Open Data progress being made Scotland challenges for local authorities sharing the data with consultants as part of further investigation of surface water flooding as well as where water companies local modelling has been included. Large dataset size means difficultly sharing and storing. (England total size = 550GB too big for sensible download times) Understanding appreciating the strengths and limitations of surface water modelling and mapping is key to effective sharing and use we produce documentation to support local authorities in using the information in an informed way Fluvial vs pluvial pluvial flooding is a different kind of flooding all together ground variations at a very local level can have a significant impact, therefore modelling is a lot more unreliable. This is not always appreciated by users (and the public) who assume reliability is the same as for fluvial modelling. rainfall inputs may be more accurate than fluvial flow inputs due to the longer record history, but this may not outweigh the ground variation challenge Pluvial mapping may produce more reliable outputs for very small watercourses where fluvial modelling is uncertain dangerous to silo sources Language for risk it s vital that we can communicate the size of a flood / the amount of risk. Need to be taken seriously for people to act! An area that we are doing lots of work on at the moment. Probabilities Using technical terms 1 in 100 or 1% are not effective. Some possible strategies are to compare to previous floods, or in terms of relative time frames eg. X times in the duration of a house mortgage (about 30yrs) or lifetime etc Uncertainty how can we easily communicate uncertainty?
15 England Suitability/Reliability table (linked to the above) Precision vs accuracy resolution 2m doesn t mean it s accurate to that level Improving Amendments how can we update the maps if it needs changing in particular locations? England not very easily. The local authorities must (re)model the local area and submit the outputs for us to update. Modelling must be compatible (guidance issued). Keeping up to date with developments: A challenge to keep current as knowledge, information and datasets develop Climate change UK Climate Projections 2009 has limitations but it currently being updated for National Rainfall Data Scotland - The changes to the Depth-Duration-Flow grids that support the rainfall input to national models is likely to have a significant impact on pluvial maps. This will require model re-runs and, where changes are significant, represents a challenge of communication as well as re-evaluation of pluvial impacts. Forecasting (notes only) Scotland - pilot of the Surface Water Alert scheme in 2014 in Glasgow. Brings together flood hazard and risk modelling for pluvial flooding in an operational arena. Further work needed before a national system is available. England Flood Forecasting Centre (joint MetOffice Environment Agency) issue high level extreme rainfall alerts on a Flood Guidance Statement Current Research and Development include impact forecasting using the surface water maps now in operational test phase
East Riding of Yorkshire Council STRATEGIC FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT (SFRA) Level 1. APPENDIX C Surface Water Flood Hazard Mapping
 APPENDIX C Surface Water Flood Hazard Mapping (this page intentionally left blank) Introduction Surface water or pluvial flooding can be defined as flooding which results from rainfall generated overland
APPENDIX C Surface Water Flood Hazard Mapping (this page intentionally left blank) Introduction Surface water or pluvial flooding can be defined as flooding which results from rainfall generated overland
Scottish Hydrological Group Meeting, 13 th November Surface water management plans in action Case studies in Kent.
 Scottish Hydrological Group Meeting, 13 th November 2013. Surface water management plans in action Case studies in Kent Paul Eccleston Topics Prioritisation and broad-scale surface water mapping Case study
Scottish Hydrological Group Meeting, 13 th November 2013. Surface water management plans in action Case studies in Kent Paul Eccleston Topics Prioritisation and broad-scale surface water mapping Case study
Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act
 Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act Flood Hazard Maps Mark McLaughlin, Principal Hydrologist, SEPA British Hydrological Society Symposium Birmingham, 4 September 2014 1 Long-term process Risk-based and
Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act Flood Hazard Maps Mark McLaughlin, Principal Hydrologist, SEPA British Hydrological Society Symposium Birmingham, 4 September 2014 1 Long-term process Risk-based and
Flood hazard assessment in the Raval District of Barcelona using a 1D/2D coupled model
 9 th International Conference on Urban Drainage Modelling Belgrade 2012 Flood hazard assessment in the Raval District of Barcelona using a 1D/2D coupled model Beniamino Russo, David Suñer, Marc Velasco,
9 th International Conference on Urban Drainage Modelling Belgrade 2012 Flood hazard assessment in the Raval District of Barcelona using a 1D/2D coupled model Beniamino Russo, David Suñer, Marc Velasco,
Surface Water Guidance for Developers
 Surface Water Guidance for Developers Contents Overview of Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS)... 2 Information Required in a Flood Risk Assessment or Drainage Strategy... 3 Outline Planning Applications...
Surface Water Guidance for Developers Contents Overview of Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS)... 2 Information Required in a Flood Risk Assessment or Drainage Strategy... 3 Outline Planning Applications...
Flood Modelling Guidance for Responsible Authorities Version 1.1
 Flood Modelling Guidance for Responsible Authorities Version 1.1 1 Executive Summary Developing our knowledge of flooding and how we can effectively assess potential impacts on our communities is essential
Flood Modelling Guidance for Responsible Authorities Version 1.1 1 Executive Summary Developing our knowledge of flooding and how we can effectively assess potential impacts on our communities is essential
FEWS-Risk: A step towards risk-based flood forecasting A pilot application in Dumfries, Scotland
 FEWS-Risk: A step towards risk-based flood forecasting A pilot application in Dumfries, Scotland Tavendale A., Brown E., Stuparu D. 27 th October 2016, FEWS-User Days Project team SEPA Amy Tavendale, Michael
FEWS-Risk: A step towards risk-based flood forecasting A pilot application in Dumfries, Scotland Tavendale A., Brown E., Stuparu D. 27 th October 2016, FEWS-User Days Project team SEPA Amy Tavendale, Michael
16 th September 2016 BRIM Workshop Loughborough. Richard Allitt
 16 th September 2016 BRIM Workshop Loughborough Richard Allitt Contents Uncertainties in Flood Risk Modelling 4 components Catchment wetness Asset data Rainfall Modelling Regulatory regime AMP1 to AMP5
16 th September 2016 BRIM Workshop Loughborough Richard Allitt Contents Uncertainties in Flood Risk Modelling 4 components Catchment wetness Asset data Rainfall Modelling Regulatory regime AMP1 to AMP5
Rutherglen (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/14) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Glasgow City Council, South Lanarkshire Counc
 Rutherglen (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/14) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Glasgow City Council, South Lanarkshire Council Main catchment Cityford Burn Summary of flooding
Rutherglen (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/14) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Glasgow City Council, South Lanarkshire Council Main catchment Cityford Burn Summary of flooding
REAL-TIME HAZARD IMPACT MODELLING OF SURFACE WATER FLOODING: SOME UK DEVELOPMENTS
 REAL-TIME HAZARD IMPACT MODELLING OF SURFACE WATER FLOODING: SOME UK DEVELOPMENTS Steven J. Cole 1,*, Robert J. Moore 1, Timothy Aldridge 2, Andy Lane 3,4, Stefan Laeger 3 1 Centre for Ecology & Hydrology,
REAL-TIME HAZARD IMPACT MODELLING OF SURFACE WATER FLOODING: SOME UK DEVELOPMENTS Steven J. Cole 1,*, Robert J. Moore 1, Timothy Aldridge 2, Andy Lane 3,4, Stefan Laeger 3 1 Centre for Ecology & Hydrology,
Presentation structure
 www.gov.uk/hs2 Presentation structure HS2 overview Design vision Policy drivers Flood risk management aims and approach Case study from Phase 2a (Fradley to Crewe) Integrated assessment and design approach
www.gov.uk/hs2 Presentation structure HS2 overview Design vision Policy drivers Flood risk management aims and approach Case study from Phase 2a (Fradley to Crewe) Integrated assessment and design approach
Science for the future management of floods and droughts. Prof. Alan Jenkins
 Science for the future management of floods and droughts Prof. Alan Jenkins Outline Floods Droughts The future Types of flooding Fluvial Pluvial Coastal Groundwater Snowmelt 2007 Floods & the Pitt Review
Science for the future management of floods and droughts Prof. Alan Jenkins Outline Floods Droughts The future Types of flooding Fluvial Pluvial Coastal Groundwater Snowmelt 2007 Floods & the Pitt Review
FLOOD WARNING & EVACUATION PLAN LIMEHOUSE MARINA, LONDON DECEMBER 2010
 FLOOD WARNING & EVACUATION PLAN LIMEHOUSE MARINA, LONDON DECEMBER 2010 No 2 Smithy Farm Chapel Lane Bruera Chester CH3 6EW Tel: 01244 677060 Fax: 01244 620431 info@weetwood.net www.weetwood.net SIGNATURE
FLOOD WARNING & EVACUATION PLAN LIMEHOUSE MARINA, LONDON DECEMBER 2010 No 2 Smithy Farm Chapel Lane Bruera Chester CH3 6EW Tel: 01244 677060 Fax: 01244 620431 info@weetwood.net www.weetwood.net SIGNATURE
Development of an operational, riskbased approach to surface water flood forecasting. Presenter: Graeme Boyce
 Development of an operational, riskbased approach to surface water flood forecasting Presenter: Graeme Boyce Surface Water Flooding (SWF) SWF major hazard in UK: ~4 million properties at risk Summer 2007
Development of an operational, riskbased approach to surface water flood forecasting Presenter: Graeme Boyce Surface Water Flooding (SWF) SWF major hazard in UK: ~4 million properties at risk Summer 2007
Analysing the cascading effects on critical infrastructure in Torbay coastal/pluvial flooding with climate change
 EPiC Series in Engineering Volume 3, 2018, Pages 780 787 HIC 2018. 13th International Conference on Hydroinformatics Engineering Analysing the cascading effects on critical infrastructure in Torbay coastal/pluvial
EPiC Series in Engineering Volume 3, 2018, Pages 780 787 HIC 2018. 13th International Conference on Hydroinformatics Engineering Analysing the cascading effects on critical infrastructure in Torbay coastal/pluvial
Irvine to Troon (Potentially Vulnerable Area 12/07) Local Plan District Local authority Main catchment North Ayrshire Council, Ayrshire Monkton to Irv
 Irvine to Troon (Potentially Vulnerable Area 12/07) Local Plan District Ayrshire Local authority North Ayrshire Council, South Ayrshire Council Main catchment Monkton to Irvine coastal Summary of flooding
Irvine to Troon (Potentially Vulnerable Area 12/07) Local Plan District Ayrshire Local authority North Ayrshire Council, South Ayrshire Council Main catchment Monkton to Irvine coastal Summary of flooding
Flood Consequence Assessment. Proposed Commercial Development, Tank Farm Way, Sully
 Flood Consequence Assessment Proposed Commercial Development, Tank Farm Way, Sully Client O Reilly Concrete Group Larchfield Kingscourt County Cavan Ireland By RVW Consulting 6 Neptune Court Vanguard Way
Flood Consequence Assessment Proposed Commercial Development, Tank Farm Way, Sully Client O Reilly Concrete Group Larchfield Kingscourt County Cavan Ireland By RVW Consulting 6 Neptune Court Vanguard Way
PROPOSALS FOR A GROUNDWATER CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION IN REGULATION. Final Report (SR1 2007)
 UK Technical Advisory Group on the Water Framework Directive PROPOSALS FOR A GROUNDWATER CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION IN REGULATION Final Report (SR1 2007) October 2007 Contents INTRODUCTION...
UK Technical Advisory Group on the Water Framework Directive PROPOSALS FOR A GROUNDWATER CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION IN REGULATION Final Report (SR1 2007) October 2007 Contents INTRODUCTION...
Loughton, Buckhurst Hill and Theydon Bois
 Loughton, Buckhurst Hill and Theydon Bois Surface Water Management Plan ` Final Report June 2016 Revision Schedule DOCUMENT INFORMATION Title: Owner: Essex County Council Version: 4 Status: Final Project
Loughton, Buckhurst Hill and Theydon Bois Surface Water Management Plan ` Final Report June 2016 Revision Schedule DOCUMENT INFORMATION Title: Owner: Essex County Council Version: 4 Status: Final Project
Title Advanced Hydraulic Modeling to Support Emergency Action Plans
 Title Advanced Hydraulic Modeling to Support Emergency Action Plans Abstract Freese and Nichols, Inc. (FNI) developed an Emergency Action Plan (EAP) for a Levee Improvement District (LID) located in a
Title Advanced Hydraulic Modeling to Support Emergency Action Plans Abstract Freese and Nichols, Inc. (FNI) developed an Emergency Action Plan (EAP) for a Levee Improvement District (LID) located in a
Stormwater: Too Simple?
 Stormwater: Too Simple? Getting Closer to Advertised Level of Service Brandon Klenzendorf, Ph.D., P.E. 13 December 2017 - CWEA Fall Seminar Introduction Traditional approaches to solving stormwater problems
Stormwater: Too Simple? Getting Closer to Advertised Level of Service Brandon Klenzendorf, Ph.D., P.E. 13 December 2017 - CWEA Fall Seminar Introduction Traditional approaches to solving stormwater problems
Volume Two. City wide Pluvial Flood Risk Assessment
 EU Interreg IVB FloodResilienCity Project Final Report Dublin Volume Two City wide Pluvial Flood Risk Assessment Document control sheet BPP 04 F8 Client: Project: Document Title: Dublin City Council EU
EU Interreg IVB FloodResilienCity Project Final Report Dublin Volume Two City wide Pluvial Flood Risk Assessment Document control sheet BPP 04 F8 Client: Project: Document Title: Dublin City Council EU
ASFPM 2015 Atlanta. Automated Hydrological and Hydraulic (2D and 1D-2D) Model Construction, Model Running, and Flood Map Production
 ASFPM 2015 Atlanta Automated Hydrological and Hydraulic (2D and 1D-2D) Model Construction, Model Running, and Flood Map Production Dr Richard Crowder Elise Ibendahl Content The challenge and opportunities
ASFPM 2015 Atlanta Automated Hydrological and Hydraulic (2D and 1D-2D) Model Construction, Model Running, and Flood Map Production Dr Richard Crowder Elise Ibendahl Content The challenge and opportunities
Guildford Surface Water Management Plan
 Guildford Surface Water Management Plan Document: 1 Version: 4 Guildford Borough Council In partnership with Surrey County Council, the Environment Agency and Thames Water November 2013 Guildford Surface
Guildford Surface Water Management Plan Document: 1 Version: 4 Guildford Borough Council In partnership with Surrey County Council, the Environment Agency and Thames Water November 2013 Guildford Surface
Drainage design tools
 Drainage design tools Richard Kellagher This presentation Designing drainage systems > Conveyance >Storage > Infiltration > Interception > Exceedence Assessing outline designs (planning) Checking detailed
Drainage design tools Richard Kellagher This presentation Designing drainage systems > Conveyance >Storage > Infiltration > Interception > Exceedence Assessing outline designs (planning) Checking detailed
Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet. Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet. Catchment: Catchment: Catchment:
 Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Local Plan District: : 01/04 : 01/04 01/04 Local Plan District: 1 Highl Argyll Local Plan
Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Potentially Vulnerable Area Datasheet Local Plan District: : 01/04 : 01/04 01/04 Local Plan District: 1 Highl Argyll Local Plan
Prestwick and Ayr (Potentially Vulnerable Area 12/09) Local Plan District Ayrshire Local authority South Ayrshire Council Main catchment Doonfoot to M
 Prestwick and Ayr (Potentially Vulnerable Area 12/09) Local Plan District Ayrshire Local authority South Ayrshire Council Main catchment Doonfoot to Monkton coastal Summary of flooding impacts At risk
Prestwick and Ayr (Potentially Vulnerable Area 12/09) Local Plan District Ayrshire Local authority South Ayrshire Council Main catchment Doonfoot to Monkton coastal Summary of flooding impacts At risk
Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: Northing: PFRA database comments (in italics):
 Location: Aughinish CHP and ESB Sub Station Co. Limerick Unique ID: 240366 (from PFRA database) Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: 129250 Northing: 153000 River / Catchment / Sub-catchment
Location: Aughinish CHP and ESB Sub Station Co. Limerick Unique ID: 240366 (from PFRA database) Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: 129250 Northing: 153000 River / Catchment / Sub-catchment
Guildford Surface Water Management Plan
 Guildford Surface Water Management Plan Document: 1 Version: 5 Guildford Borough Council In partnership with Surrey County Council, the Environment Agency and Thames Water October 2014 Halcrow Group Ltd
Guildford Surface Water Management Plan Document: 1 Version: 5 Guildford Borough Council In partnership with Surrey County Council, the Environment Agency and Thames Water October 2014 Halcrow Group Ltd
Rising Sun. Scaffold Hill. Flood Risk Assessment
 Rising Sun Scaffold Hill Flood Risk Assessment August 2010 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Site Description... 5 3.0 Legislative Framework... 6 4.0 Flood Risk... 10 5.0 Surface Water Drainage... 11
Rising Sun Scaffold Hill Flood Risk Assessment August 2010 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Site Description... 5 3.0 Legislative Framework... 6 4.0 Flood Risk... 10 5.0 Surface Water Drainage... 11
FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT AND THE OPW IN 2012 (How We Do Business)
 FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT AND THE OPW IN 2012 (How We Do Business) TOPICS Legislative Framework Preliminary Flood Risk Assessment (PFRA) Catchment Flood Risk Assessment and Management Plans (CFRAM) Flood Relief
FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT AND THE OPW IN 2012 (How We Do Business) TOPICS Legislative Framework Preliminary Flood Risk Assessment (PFRA) Catchment Flood Risk Assessment and Management Plans (CFRAM) Flood Relief
EU IVB FloodResilienCity Project Final Report - Dublin
 Final Report - Dublin Non-Technical Summary September 2012 Tom Leahy, FRC Project Director, Tony Maguire, FRC Project Manager. Dublin City Council is one of eleven partner organisations, drawn from eight
Final Report - Dublin Non-Technical Summary September 2012 Tom Leahy, FRC Project Director, Tony Maguire, FRC Project Manager. Dublin City Council is one of eleven partner organisations, drawn from eight
Cambridgeshire Flood Risk Management Partnership St Neots Surface Water Management Plan
 Cambridgeshire Flood Risk Management Partnership St Neots Surface Water Management Plan Detailed Assessment and Options Appraisal Report Final Hyder Consulting (UK) Limited 2212959 Aston Cross Business
Cambridgeshire Flood Risk Management Partnership St Neots Surface Water Management Plan Detailed Assessment and Options Appraisal Report Final Hyder Consulting (UK) Limited 2212959 Aston Cross Business
IDENTIFYING FLOOD CONTROL LOTS IN THE HORNSBY LGA
 IDENTIFYING FLOOD CONTROL LOTS IN THE HORNSBY LGA B.C. Phillips 1, R.S. Thomson 1, T. Fang 1, S. Yu 1, A. Boyd 2 1 Cardno (NSW/ACT) Pty Ltd, Sydney, NSW 2 Hornsby Shire Council, Hornsby, NSW Introduction
IDENTIFYING FLOOD CONTROL LOTS IN THE HORNSBY LGA B.C. Phillips 1, R.S. Thomson 1, T. Fang 1, S. Yu 1, A. Boyd 2 1 Cardno (NSW/ACT) Pty Ltd, Sydney, NSW 2 Hornsby Shire Council, Hornsby, NSW Introduction
Attachment 12 Stage 1 Flood Risk Assessment (IE RP-0001)
 IE0311133-22-RP-0001, Issue A 17/10/2013 Attachment 12 Stage 1 Flood Risk Assessment (IE0311133-30-RP-0001) IE0311133-22-RP-0001_A_02.DOC Flood Risk Assessment Celebrating 40 Years in Business Jazz Pharmaceuticals
IE0311133-22-RP-0001, Issue A 17/10/2013 Attachment 12 Stage 1 Flood Risk Assessment (IE0311133-30-RP-0001) IE0311133-22-RP-0001_A_02.DOC Flood Risk Assessment Celebrating 40 Years in Business Jazz Pharmaceuticals
21 ST CENTURY DRAINAGE PROGRAMME CAPACITY ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 21 ST CENTURY DRAINAGE PROGRAMME CAPACITY ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Report Ref. No. 21CDP.CAF Programme Area & Reference Report Title Project Management Contractor Sub-Contractor Author of
21 ST CENTURY DRAINAGE PROGRAMME CAPACITY ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Report Ref. No. 21CDP.CAF Programme Area & Reference Report Title Project Management Contractor Sub-Contractor Author of
Urban drainage models for flood forecasting: 1D/1D, 1D/2D and hybrid models
 Urban drainage models for flood forecasting: 1D/1D, 1D/2D and hybrid models N. Simões 1,2 *, S. Ochoa 1, J. P. Leitão 3, R. Pina 4, A. Sá Marques 2, Č. Maksimović 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental
Urban drainage models for flood forecasting: 1D/1D, 1D/2D and hybrid models N. Simões 1,2 *, S. Ochoa 1, J. P. Leitão 3, R. Pina 4, A. Sá Marques 2, Č. Maksimović 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental
Microgeneration Installation Standard MIS 3006
 Microgeneration Installation Standard MIS 3006 REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTRACTORS UNDERTAKING THE SUPPLY, DESIGN, INSTALLATION, SET TO WORK COMMISSIONING AND HANDOVER OF MICRO-HYDROPOWER SYSTEMS Issue 1.1 This
Microgeneration Installation Standard MIS 3006 REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTRACTORS UNDERTAKING THE SUPPLY, DESIGN, INSTALLATION, SET TO WORK COMMISSIONING AND HANDOVER OF MICRO-HYDROPOWER SYSTEMS Issue 1.1 This
Respond! Housing Association. Residential Development at Flinters Field, Athy, Co. Kildare. Engineering Report. Job No. : Date: April 2017
 Job No. : 16036 Date: April 2017 Respond! Housing Association Residential Development at Flinters Field, Athy, Co. Kildare Engineering Report 2B Richview Office Park Clonskeagh Dublin 14 Contents Amendment
Job No. : 16036 Date: April 2017 Respond! Housing Association Residential Development at Flinters Field, Athy, Co. Kildare Engineering Report 2B Richview Office Park Clonskeagh Dublin 14 Contents Amendment
Unique ID: (from PFRA database) Location: Newport, Co. Tipperary. Stage 1: Desktop Review
 Location: Newport, Co. Tipperary Unique ID: 240433 (from PFRA database) Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: 172620 Northing: 162375 River / Catchment / Sub-catchment Newport/Mulcair
Location: Newport, Co. Tipperary Unique ID: 240433 (from PFRA database) Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: 172620 Northing: 162375 River / Catchment / Sub-catchment Newport/Mulcair
Phase 1 FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT
 Phase 1 FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PREPARED FOR: REFERENCE #: 1916 MS Power Projects Ltd DATE: February 2014 Page 1 of 24 AMBIENTAL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS LTD. DOCUMENT ISSUE RECORD PROJECT: PHASE 1 FLOOD
Phase 1 FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT PREPARED FOR: REFERENCE #: 1916 MS Power Projects Ltd DATE: February 2014 Page 1 of 24 AMBIENTAL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS LTD. DOCUMENT ISSUE RECORD PROJECT: PHASE 1 FLOOD
Country report. UK bathing water quality in United Kingdom. May Photo: Peter Kristensen
 Country report UK bathing water quality in 2016 United Kingdom May 2017 Photo: Peter Kristensen BWD Report For the Bathing Season 2016 The United Kingdom The report gives a general overview of information
Country report UK bathing water quality in 2016 United Kingdom May 2017 Photo: Peter Kristensen BWD Report For the Bathing Season 2016 The United Kingdom The report gives a general overview of information
Natural Hazards Partnership Surface Water Flooding Hazard Impact Model: Phase 2 Final Report
 Natural Hazards Partnership Surface Water Flooding Hazard Impact Model: Phase 2 Final Report The NHP is a consortium of 17 public bodies (mainly government departments and agencies, trading funds and public
Natural Hazards Partnership Surface Water Flooding Hazard Impact Model: Phase 2 Final Report The NHP is a consortium of 17 public bodies (mainly government departments and agencies, trading funds and public
Storm Water Management
 Storm Water Management Policy September 2014 2 Sustainable drainage feature designed to control and manage flows through a series of check dams 3 Document Name: Storm Water Management Controlled Copy No:
Storm Water Management Policy September 2014 2 Sustainable drainage feature designed to control and manage flows through a series of check dams 3 Document Name: Storm Water Management Controlled Copy No:
Flow estimate for a Site in South Wales
 April 2011 Flow estimate for a Site in South Wales Wallingford HydroSolutions Limited For and on behalf of Wallingford HydroSolutions Ltd Client Prepared by Approved by Position Click here to enter text.
April 2011 Flow estimate for a Site in South Wales Wallingford HydroSolutions Limited For and on behalf of Wallingford HydroSolutions Ltd Client Prepared by Approved by Position Click here to enter text.
Risk-based assessment of climate change impact on storm drainage system
 Flood Recovery, Innovation and Response II 13 Risk-based assessment of climate change impact on storm drainage system Z. Alsaqqaf, H. Zhang & S. Mohamed Griffith School of Engineering, Griffith University,
Flood Recovery, Innovation and Response II 13 Risk-based assessment of climate change impact on storm drainage system Z. Alsaqqaf, H. Zhang & S. Mohamed Griffith School of Engineering, Griffith University,
Cheshire East Council Strategic Flood Risk Assessment
 Cheshire East Council Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Final Report August 2013 Cheshire East Council Spatial Planning Team 1st Floor Westfields Sandbach CW11 1HZ JBA Project Manager Chris Isherwood JBA
Cheshire East Council Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Final Report August 2013 Cheshire East Council Spatial Planning Team 1st Floor Westfields Sandbach CW11 1HZ JBA Project Manager Chris Isherwood JBA
RTPI Flooding & SUDS. Implementing Flood Management. Christian Lomax - AECOM. Structure of Presentation. Introduction. Background
 RTPI Flooding & SUDS Implementing Flood Management Christian Lomax - AECOM Structure of Presentation Introduction Background Working in Partnership Water Cycle Studies Surface Water Management Plans AECOM
RTPI Flooding & SUDS Implementing Flood Management Christian Lomax - AECOM Structure of Presentation Introduction Background Working in Partnership Water Cycle Studies Surface Water Management Plans AECOM
SuDS design criteria for catchment flood protection Are current criteria appropriate?
 SuDS design criteria for catchment flood protection Are current criteria appropriate? Richard Kellagher SuDS Drainage design for catchment flood protection All countries of UK (roughly) in alignment, BUT
SuDS design criteria for catchment flood protection Are current criteria appropriate? Richard Kellagher SuDS Drainage design for catchment flood protection All countries of UK (roughly) in alignment, BUT
Microgeneration Installation Standard MIS 3006
 Microgeneration Installation Standard MIS 3006 REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTRACTORS UNDERTAKING THE SUPPLY, DESIGN, INSTALLATION, SET TO WORK COMMISSIONING AND HANDOVER OF MICRO-HYDROPOWER SYSTEMS Issue 2.0 This
Microgeneration Installation Standard MIS 3006 REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTRACTORS UNDERTAKING THE SUPPLY, DESIGN, INSTALLATION, SET TO WORK COMMISSIONING AND HANDOVER OF MICRO-HYDROPOWER SYSTEMS Issue 2.0 This
Unique ID: (from PFRA database) Location: Clonfert, Co. Galway. Stage 1: Desktop Review
 Location: Clonfert, Co. Galway Unique ID: 252906 (from PFRA database) Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: 197134 Northing: 221731 River / Catchment / Sub-catchment Un-named minor
Location: Clonfert, Co. Galway Unique ID: 252906 (from PFRA database) Initial OPW Designation APSR AFRR IRR Co-ordinates Easting: 197134 Northing: 221731 River / Catchment / Sub-catchment Un-named minor
Modelling landscape opportunities, multiple benefits and impacts
 In partnership with: Modelling landscape opportunities, multiple benefits and impacts Iain Craigen and Charlotte Beattie Natural Flood Management and Working With Natural Processes There is a growing evidence
In partnership with: Modelling landscape opportunities, multiple benefits and impacts Iain Craigen and Charlotte Beattie Natural Flood Management and Working With Natural Processes There is a growing evidence
Global flood inundation forecasting combining GloFAS and flood hazard maps: A case study of the 2017 Brahmaputra floods
 Global flood inundation forecasting combining GloFAS and flood hazard maps: A case study of the 2017 Brahmaputra floods Hydrological Services for Business 8 th May 2018 John Bevington, Beatriz Revilla-Romero,
Global flood inundation forecasting combining GloFAS and flood hazard maps: A case study of the 2017 Brahmaputra floods Hydrological Services for Business 8 th May 2018 John Bevington, Beatriz Revilla-Romero,
A Hydrologic Study of the. Ryerson Creek Watershed
 A Hydrologic Study of the Ryerson Creek Watershed Dave Fongers Hydrologic Studies Unit Land and Water Management Division Michigan Department of Environmental Quality May 8, 2002 Table of Contents Summary...2
A Hydrologic Study of the Ryerson Creek Watershed Dave Fongers Hydrologic Studies Unit Land and Water Management Division Michigan Department of Environmental Quality May 8, 2002 Table of Contents Summary...2
Flood Risk and Drainage Assessment.
 Flood Risk and Drainage Assessment. Change of Use off land to Leisure Complex At, Caersws, Powys, SY17 5SB October 2018 Statement prepared for: Mr T Bebb By Woodsyde Developments Ltd Woodsyde Developments
Flood Risk and Drainage Assessment. Change of Use off land to Leisure Complex At, Caersws, Powys, SY17 5SB October 2018 Statement prepared for: Mr T Bebb By Woodsyde Developments Ltd Woodsyde Developments
A part of BMT in Energy and Environment Kosciusko Avenue Main Drain Catchment Drainage / Flood Study Draft Report
 A part of BMT in Energy and Environment Kosciusko Avenue Main Drain Catchment Drainage / Flood Study Draft Report R.M7299.003.00.DraftReport January 2011 Kosciusko Avenue Main Drain Catchment Drainage
A part of BMT in Energy and Environment Kosciusko Avenue Main Drain Catchment Drainage / Flood Study Draft Report R.M7299.003.00.DraftReport January 2011 Kosciusko Avenue Main Drain Catchment Drainage
Chapter 2 - Policy TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 2 - POLICY... 2-1 2.1 Overview... 2-1 2.1.1 Introduction... 2-1 2.1.2 Policy vs. Criteria... 2-1 2.1.3 Location of Policy and Criteria... 2-2 2.2 General Hydraulic Design Policies...
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 2 - POLICY... 2-1 2.1 Overview... 2-1 2.1.1 Introduction... 2-1 2.1.2 Policy vs. Criteria... 2-1 2.1.3 Location of Policy and Criteria... 2-2 2.2 General Hydraulic Design Policies...
Redevelopment Introduction
 Redevelopment 11 11.1 Introduction Design standards for new development sites have been established in previous chapters of this document. Redevelopment sites, however, often present unique challenges
Redevelopment 11 11.1 Introduction Design standards for new development sites have been established in previous chapters of this document. Redevelopment sites, however, often present unique challenges
GRIMSBY TIDAL DEFENCES: WAVE OVERTOPPING AND COASTAL FLOODING
 14 May 2013 GRIMSBY TIDAL DEFENCES: WAVE OVERTOPPING AND COASTAL FLOODING EMAY TOHA B&V WATER INTRODUCTION, CONTENTS AND WHY GRIMSBY? 2 I N T R O D U C T I O N S & C O N T E N T S INTRODUCTIONS Senior
14 May 2013 GRIMSBY TIDAL DEFENCES: WAVE OVERTOPPING AND COASTAL FLOODING EMAY TOHA B&V WATER INTRODUCTION, CONTENTS AND WHY GRIMSBY? 2 I N T R O D U C T I O N S & C O N T E N T S INTRODUCTIONS Senior
Isle of Wight Strategic Flood Risk Assessment MK2. Appendix P Newport
 Isle of Wight Strategic Flood Risk Assessment MK2 Appendix P June 2010 Isle of Wight Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Overview Please review this discussion in conjunction with the mapping provided in this
Isle of Wight Strategic Flood Risk Assessment MK2 Appendix P June 2010 Isle of Wight Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Overview Please review this discussion in conjunction with the mapping provided in this
Adaptation to climate change
 Adaptation to climate change Adaptation in the UK at the local level Helsinki 10 th March 2011 Laurie Newton UK Climate Impacts Programme Contents UK Climate Impacts Programme (UKCIP) UK climate change
Adaptation to climate change Adaptation in the UK at the local level Helsinki 10 th March 2011 Laurie Newton UK Climate Impacts Programme Contents UK Climate Impacts Programme (UKCIP) UK climate change
HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION
 HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION A watershed is an area of land that captures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed where the
HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION A watershed is an area of land that captures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed where the
Climate Change in Europe s Cities
 in Europe s Cities Copernicus for Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu WHY IS COPERNICUS NEEDED IN EUROPE S CITIES? Climate Copernicus Climate Service
in Europe s Cities Copernicus for Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu WHY IS COPERNICUS NEEDED IN EUROPE S CITIES? Climate Copernicus Climate Service
Integrated Catchment Modelling
 Integrated Catchment Modelling Modelling the whole water cycle in one package Ann Pugh Integrated Water Planning Historically water, wastewater and stormwater modelling occurred in silos with little integration
Integrated Catchment Modelling Modelling the whole water cycle in one package Ann Pugh Integrated Water Planning Historically water, wastewater and stormwater modelling occurred in silos with little integration
Making Space for Water
 Making Space for Water Groundwater flooding records collation, monitoring and risk assessment (reference HA5) The UK Groundwater Forum, London May 23 rd 2007 (Climate change: the future for groundwater
Making Space for Water Groundwater flooding records collation, monitoring and risk assessment (reference HA5) The UK Groundwater Forum, London May 23 rd 2007 (Climate change: the future for groundwater
Climate change adaptation and rail. Dr Kate Avery Sustainability Specialist (Climate Change Adaptation) 23 rd January 2013
 Climate change adaptation and rail Dr Kate Avery Sustainability Specialist (Climate Change Adaptation) 23 rd January 2013 1 Contents The challenge Our approach Opportunities and hurdles The Challenge Asset
Climate change adaptation and rail Dr Kate Avery Sustainability Specialist (Climate Change Adaptation) 23 rd January 2013 1 Contents The challenge Our approach Opportunities and hurdles The Challenge Asset
TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III - MINIMUM DESIGN STANDARDS Section 105 DRAINAGE SYSTEM DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS AND SCOPE 105.1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III - MINIMUM DESIGN STANDARDS Section 105 DRAINAGE SYSTEM DESIGN SECTION TITLE PAGE 105.1. SPECIFICATIONS AND SCOPE 105.1 105.2. METHODS OF ANALYSIS 105.1 105.2.1. Rational Method
TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III - MINIMUM DESIGN STANDARDS Section 105 DRAINAGE SYSTEM DESIGN SECTION TITLE PAGE 105.1. SPECIFICATIONS AND SCOPE 105.1 105.2. METHODS OF ANALYSIS 105.1 105.2.1. Rational Method
Under a Changing Climate:
 Engineering Methods for Precipitation Under a Changing Climate: Outline of the Problem J. Rolf Olsen Institute for Water Resources U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Alexandria, Virginia ASCE Committee on Adaptation
Engineering Methods for Precipitation Under a Changing Climate: Outline of the Problem J. Rolf Olsen Institute for Water Resources U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Alexandria, Virginia ASCE Committee on Adaptation
Impacts of Rainfall Event Pattern and Land-Use Change on River Basin Hydrological Response: a Case in Malaysia
 International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, Vol. 93 (2016) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2016. V93. 23 Impacts of Rainfall Event Pattern and Land-Use Change on River Basin Hydrological
International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, Vol. 93 (2016) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2016. V93. 23 Impacts of Rainfall Event Pattern and Land-Use Change on River Basin Hydrological
A 25 Year Strategic Plan
 A 25 Year Strategic Plan The challenges which face the provision of water services are identified as: Meeting Customer Needs at an Affordable Cost Providing Safe Water Supplies Managing Wastewater Protecting
A 25 Year Strategic Plan The challenges which face the provision of water services are identified as: Meeting Customer Needs at an Affordable Cost Providing Safe Water Supplies Managing Wastewater Protecting
UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2017: Summary of ASC-commissioned research projects
 UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2017: Summary of ASC-commissioned research projects The Adaptation Sub-Committee (ASC) of the Committee on Climate Change has been asked by the Government to lead the
UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2017: Summary of ASC-commissioned research projects The Adaptation Sub-Committee (ASC) of the Committee on Climate Change has been asked by the Government to lead the
Distribution Restriction Statement Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 CECW-EH-Y Regulation No. 1110-2-1464 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 Engineering and Design HYDROLOGIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHED RUNOFF Distribution Restriction
CECW-EH-Y Regulation No. 1110-2-1464 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 Engineering and Design HYDROLOGIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHED RUNOFF Distribution Restriction
Latest headline evidence from the Defra Multi-objective Flood Management Demonstration Projects:
 Latest headline evidence from the Defra Multi-objective Flood Management Demonstration Projects: Land use and management can make a significant contribution to reducing flood risk Primary aims In 2009
Latest headline evidence from the Defra Multi-objective Flood Management Demonstration Projects: Land use and management can make a significant contribution to reducing flood risk Primary aims In 2009
Estimating the 100-year Peak Flow for Ungagged Middle Creek Watershed in Northern California, USA
 American Journal of Water Resources, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 4, 99-105 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajwr/2/4/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajwr-2-4-3 Estimating the 100-year
American Journal of Water Resources, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 4, 99-105 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajwr/2/4/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajwr-2-4-3 Estimating the 100-year
PLUVIAL FLOOD MODELLING AND HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR LARGE SCALE URBAN AREAS
 10 th International Conference on Hydroinformatics HIC 2012, Hamburg, GERMANY PLUVIAL FLOOD MODELLING AND HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR LARGE SCALE URBAN AREAS ALBERT S. CHEN, SLOBODAN DJORDJEVIĆ Centre for Water
10 th International Conference on Hydroinformatics HIC 2012, Hamburg, GERMANY PLUVIAL FLOOD MODELLING AND HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR LARGE SCALE URBAN AREAS ALBERT S. CHEN, SLOBODAN DJORDJEVIĆ Centre for Water
Dynamic Inundation Mapping for Emergency Planning and Disaster Response
 Dynamic Inundation Mapping for Emergency Planning and Disaster Response Ross Gordon, LEED AP October 29, 2008 Presentation Overview Introduce MIKE FLOOD Rice / TMC Case Study Emergency Planning Disaster
Dynamic Inundation Mapping for Emergency Planning and Disaster Response Ross Gordon, LEED AP October 29, 2008 Presentation Overview Introduce MIKE FLOOD Rice / TMC Case Study Emergency Planning Disaster
Whole of Water Cycle Modelling Pilot Study
 Whole of Water Cycle Modelling Pilot Study Presentation Outline Background Model development Water and Sewer Stormwater Advantages of Integrated Modelling Challenges and Limitations Project Aims To investigate
Whole of Water Cycle Modelling Pilot Study Presentation Outline Background Model development Water and Sewer Stormwater Advantages of Integrated Modelling Challenges and Limitations Project Aims To investigate
CORFU project FLOOD HAZARD ASSESSMENT CONSIDERING CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS: APPLICATION TO BARCELONA CASE STUDY USING A 1D/2D DETAILED COUPLED MODEL
 Exeter (UK), September 2013 CORFU project FLOOD HAZARD ASSESSMENT CONSIDERING CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS: APPLICATION TO BARCELONA CASE STUDY USING A 1D/2D DETAILED COUPLED MODEL Beniamino Russo PhD, Civil
Exeter (UK), September 2013 CORFU project FLOOD HAZARD ASSESSMENT CONSIDERING CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS: APPLICATION TO BARCELONA CASE STUDY USING A 1D/2D DETAILED COUPLED MODEL Beniamino Russo PhD, Civil
Using Rapid Flood Inundation Modeling to Make Informed Decisions and Optimize Investments
 Using Rapid Flood Inundation Modeling to Make Informed Decisions and Optimize Investments Chris Niforatos, P.E. Client Account Manager chris.niforatos@ch2m.com So what is Rapid Inundation? Being able to
Using Rapid Flood Inundation Modeling to Make Informed Decisions and Optimize Investments Chris Niforatos, P.E. Client Account Manager chris.niforatos@ch2m.com So what is Rapid Inundation? Being able to
Urban Flood Modelling Dissemination Seminar. 25 th Jan University of Sheffield James Shucksmith
 Urban Flood Modelling Dissemination Seminar 25 th Jan University of Sheffield James Shucksmith Aims of the Event Present and discuss ongoing research in the area of urban flood modelling, including 1.
Urban Flood Modelling Dissemination Seminar 25 th Jan University of Sheffield James Shucksmith Aims of the Event Present and discuss ongoing research in the area of urban flood modelling, including 1.
APPENDIX J-3 Technical Report on Airport Drainage, Northern Sector Airport and Ordinance Creek Watershed, Airport Creek Hydrologic Models
 APPENDIX J-3 Technical Report on Airport Drainage, Northern Sector Airport and Ordinance Creek Watershed, Airport Creek Hydrologic Models Introduction Technical Report on Airport Drainage Appendix J-3:
APPENDIX J-3 Technical Report on Airport Drainage, Northern Sector Airport and Ordinance Creek Watershed, Airport Creek Hydrologic Models Introduction Technical Report on Airport Drainage Appendix J-3:
This document was endorsed by Cambridgeshire County Council (CCC) in its capacity as Lead Local Flood Authority on 14 July 2016.
 Note to the reader Note to the reader This document was endorsed by Cambridgeshire County Council (CCC) in its capacity as Lead Local Flood Authority on 14 July 2016. Once adopted as a Supplementary Planning
Note to the reader Note to the reader This document was endorsed by Cambridgeshire County Council (CCC) in its capacity as Lead Local Flood Authority on 14 July 2016. Once adopted as a Supplementary Planning
Bristol City Surface Water Management Plan Development and Application. Patrick Goodey Bristol City Council Paul Davies Ove Arup & partners Ltd
 Bristol City Surface Water Management Plan Development and Application Patrick Goodey Bristol City Council Paul Davies Ove Arup & partners Ltd City of Bristol Bristol city, population of over 433,000 incorporating
Bristol City Surface Water Management Plan Development and Application Patrick Goodey Bristol City Council Paul Davies Ove Arup & partners Ltd City of Bristol Bristol city, population of over 433,000 incorporating
Flood Risks to CMT Estates
 s Executive Summary Whilst the proximity of Chatham Maritime to the tidal Medway tends to lead people to worry about flooding from the river, the risk of this happening is considered to be very low. Parts
s Executive Summary Whilst the proximity of Chatham Maritime to the tidal Medway tends to lead people to worry about flooding from the river, the risk of this happening is considered to be very low. Parts
Three Waters Modelling Programme Hamilton City Council 29 October Flood Hazard Report. Prepared by AECOM in Association with:
 Three Waters Modelling Programme Hamilton City Council 29 October 2012 Flood Hazard Report Prepared by AECOM in Association with: Three Waters Modelling Programme Flood Hazard Report Flood Hazard Report
Three Waters Modelling Programme Hamilton City Council 29 October 2012 Flood Hazard Report Prepared by AECOM in Association with: Three Waters Modelling Programme Flood Hazard Report Flood Hazard Report
Preliminary Rainfall Runoff Management for Developments EA/Defra Report Procedure W5-074/A Summary Guidance for Developers and Engineers
 Preliminary Rainfall Runoff Management for Developments EA/Defra Report Procedure W5-074/A Summary Guidance for Developers and Engineers 1. Objective of this guidance and Procedure W5-074/A is to assist
Preliminary Rainfall Runoff Management for Developments EA/Defra Report Procedure W5-074/A Summary Guidance for Developers and Engineers 1. Objective of this guidance and Procedure W5-074/A is to assist
Integrated Watershed Modeling of the Alewife Brook: Developing the Right Tools for Climate Change Preparedness
 Integrated Watershed Modeling of the Alewife Brook: Developing the Right Tools for Climate Change Preparedness David Bedoya, PhD, PE Yovanni Cataño-Lopera, PhD, PE Nicholas Stepina, PE Date Presentation
Integrated Watershed Modeling of the Alewife Brook: Developing the Right Tools for Climate Change Preparedness David Bedoya, PhD, PE Yovanni Cataño-Lopera, PhD, PE Nicholas Stepina, PE Date Presentation
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FROM THE UK TO SUPPORT FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT
 NEW TECHNOLOGIES FROM THE UK TO SUPPORT FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT Jon Wicks 1, Rob Berry 1, Paul Wilkinson 2, Beccy Dunn 2, Frazer Rhodes 3 1 Halcrow Group Ltd, UK, wicksjm@halcrow.com 2 Halcrow Group Ltd,
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FROM THE UK TO SUPPORT FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT Jon Wicks 1, Rob Berry 1, Paul Wilkinson 2, Beccy Dunn 2, Frazer Rhodes 3 1 Halcrow Group Ltd, UK, wicksjm@halcrow.com 2 Halcrow Group Ltd,
Engineers Ireland Presentation
 Engineers Ireland Presentation Kevin Gallagher Chartered Engineer Senior Executive Engineer Cork City Council Local Authority Response to Flooding in an Urban Area INTRODUCTION: Context Flooding Types
Engineers Ireland Presentation Kevin Gallagher Chartered Engineer Senior Executive Engineer Cork City Council Local Authority Response to Flooding in an Urban Area INTRODUCTION: Context Flooding Types
A Climate Change Impact Assessment of Urban Infrastructure by a Grid-Based Flood Model Focusing on Stream and Road Facilities
 A Climate Change Impact Assessment of Urban Infrastructure by a Grid-Based Flood Model Focusing on Stream and Road Facilities D. Lee, K. Oh, and B. Park Abstract Local governments in Korea are facing increasing
A Climate Change Impact Assessment of Urban Infrastructure by a Grid-Based Flood Model Focusing on Stream and Road Facilities D. Lee, K. Oh, and B. Park Abstract Local governments in Korea are facing increasing
0.0. Pervious CN = 40. (Unconnected impervious) (Total impervious) Total impervious area (percent) Composite CN
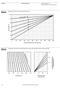 Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
UMLALAZI-NKANDLA SMART GROWTH DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PROVISION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SERVICES
 UMLALAZI-NKANDLA SMART GROWTH DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PROVISION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SERVICES PROPOSED STORMWATER RETICULATION DESIGN AND MANAGEMENT DATE: OCTOBER 2011 PREPARED FOR: PREPARED BY: DEPARTMENT
UMLALAZI-NKANDLA SMART GROWTH DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PROVISION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SERVICES PROPOSED STORMWATER RETICULATION DESIGN AND MANAGEMENT DATE: OCTOBER 2011 PREPARED FOR: PREPARED BY: DEPARTMENT
ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE 2 ND ROUND REPORT
 ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE 2 ND ROUND REPORT Western Power Distribution May 2015 Contents 1 Executive Summary... 4 Introduction...4 Understanding Risk...4 Understanding Uncertainties...4 Details of Actions...4
ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE 2 ND ROUND REPORT Western Power Distribution May 2015 Contents 1 Executive Summary... 4 Introduction...4 Understanding Risk...4 Understanding Uncertainties...4 Details of Actions...4
SWMPs and SFRAs Sa S m m W ingfifeld
 SWMPs and SFRAs Sam Wingfield Introduction 1. Introduction to the Cumbria SWMP. Impact on future development and types of actions that will be proposed. 2. Flood risk mitigation options for future development
SWMPs and SFRAs Sam Wingfield Introduction 1. Introduction to the Cumbria SWMP. Impact on future development and types of actions that will be proposed. 2. Flood risk mitigation options for future development
APPENDIX E APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS
 APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
Flood Forecasting - What Can You Do With Your Data?
 Flood Forecasting - What Can You Do With Your Data? C Druery 1, D McConnell,2 1 WorleyParsons, Sydney, NSW 2 WorleyParsons, Sydney, NSW Abstract Driven by the large scale flooding over the past several
Flood Forecasting - What Can You Do With Your Data? C Druery 1, D McConnell,2 1 WorleyParsons, Sydney, NSW 2 WorleyParsons, Sydney, NSW Abstract Driven by the large scale flooding over the past several
TULLAMORE FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT STUDY
 TULLAMORE FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT STUDY FINAL HYDRAULICS REPORT 1794/RP/004/C June 2008 FRAM Section Engineering Services Office of Public Works Doc. No. 1794/RP/004/C ii June 2008 INDEX OF
TULLAMORE FLOOD RISK ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT STUDY FINAL HYDRAULICS REPORT 1794/RP/004/C June 2008 FRAM Section Engineering Services Office of Public Works Doc. No. 1794/RP/004/C ii June 2008 INDEX OF
USE OF LONG TERM MONITORING DATA FOR DEFINING BASELINE SOUND LEVELS
 23 rd International Congress on Sound & Vibration Athens, Greece 10-14 July 2016 ICSV23 USE OF LONG TERM MONITORING DATA FOR DEFINING BASELINE SOUND LEVELS Chris Skinner, Paul Shields and Yuyou Liu AECOM,
23 rd International Congress on Sound & Vibration Athens, Greece 10-14 July 2016 ICSV23 USE OF LONG TERM MONITORING DATA FOR DEFINING BASELINE SOUND LEVELS Chris Skinner, Paul Shields and Yuyou Liu AECOM,
Building Resilience to Climate Change What are the Risks?
 Building Resilience to Climate Change What are the Risks? Summary of the UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2012 & Reflections on methods and tools for addressing social and environmental impacts Dr. Steven
Building Resilience to Climate Change What are the Risks? Summary of the UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2012 & Reflections on methods and tools for addressing social and environmental impacts Dr. Steven
Tomorrow s Railway and Climate Change
 Tomorrow s Railway and Climate Change John Dora CEng FICE FRMetS FPWI Northern Hub and Beyond - PWI Technical Seminar, March 2017 Images and material by kind permission from the IPCC, Met Office, Network
Tomorrow s Railway and Climate Change John Dora CEng FICE FRMetS FPWI Northern Hub and Beyond - PWI Technical Seminar, March 2017 Images and material by kind permission from the IPCC, Met Office, Network
