WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS. LESSON 6 Nutrient No-No s
|
|
|
- Benedict Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 Nutrient No-No s
2 Lesson 6: Nutrient No-No s Subject Overview: Fresh water streams, rivers, and lakes contain varying amounts of nutrients. These nutrients supply living organisms with the basic materials they need to grow and reproduce. Nitrogen and phosphorus are essential to the growth of aquatic plants which in turn become a food source to other organisms. Excess nitrogen and phosphorus, however, can lead to excess plant growth in water, most notably in the form of algae. Large mats of algae block sunlight from reaching more beneficial photosynthetic organisms just below the water s surface. As algae dies and begins to decompose, oxygen levels in the water decrease as the molecules are utilized in the decomposition process, resulting in less available oxygen for fish and other aquatic organisms. Minimizing the input of excess nutrients from fertilizer applications and landscape clippings reduces the occurrences of algae mats and the negative impact of decomposition. Nitrogen and phosphorus are essential nutrients for the growth of aquatic and terrestrial plants. Plant growth and appearance can be significantly improved with the addition of these nutrients in the form of fertilizers. Nitrogen is found in environment in a number of different forms with nitrate being the form most available for plants for uptake and utilization for growth. Phosphorus is also available in many forms, but plants utilize the soluble form phosphate. In most dry environments, nitrogen is the limiting nutrient to growth as phosphorus is present at sufficient levels. Urban environments, through the use of fertilizers, increase the input of soluble nitrate and phosphate into streams and creeks adapted to lower nutrient levels. Algae growth normally limited by the lack of sufficient nitrogen is increased, resulting in algal blooms floating on the surface of creeks, streams, and rivers. Decomposing plant material sinks to the bottom of the water and begins to utilize the oxygen in the water to break down the plant material. Significant decomposition in a lake or river robs fish of oxygen resulting in what are called fish kills. Excess algae also reduce the quality of recreational activities such as boating, swimming, and fishing. This process is called eutrophication. (Western Pennsylvania Conservancy To Fertilize or Not To Fertilize ) In order to grow, plants require essential minerals and elements, along with sunlight and water. If the soil doesn t provide enough nutrients for plants to grow, fertilizers may need to be added. A fertile soil has adequate amounts of the major plant nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium; a sufficiency of the micronutrients (sometimes called trace minerals) zinc, manganese, boron, iron, sulfur, an abundance of organic matter, and humus. To be fertile, the soil must also have a nearly neutral soil ph as well as good structure and drainage. 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [1]
3 Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium can be obtained from natural sources (animal and vegetable matter) or from inorganic fertilizers that are chemically produced. When you buy fertilizers commercially, most are labeled with a formula that states the percentage of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium that the preparations contain. The chemical symbols for these three elements are N, P and K respectively, and the elements are referred to by their symbols on fertilizer bags. If a bag of fertilizer says it is , for example, that means that it contains 5 percent N, 10 percent P and 5 percent K. For example, a 100-pound bag of would supply 5 pounds of nitrogen to your garden, 10 pounds of phosphorous and 5 pounds of potassium. The rest is inert filler. Both organic and inorganic commercial fertilizers are labeled using these initial letters. Amounts of these elements can vary in fertilizer depending on what you want or need the plant to do. Nitrogen maintains plants green color and is largely responsible for good leaf and stem growth. Nitrogen provides a quick boost of energy to a plant just like a candy bar does to us. It is very soluble in water and thus leaches out of the soil quickly. If your plants run out of nitrogen you will see pale foliage and spindly growth. Phosphorous is especially important to the root development of a plant. It also helps the plant to produce fruit and seeds and resist disease. Root crops and flower bulbs require a lot of phosphorous. It is not highly soluble and can be applied in the fall. Potassium is essential for plant growth and for resistance to disease. It is highly soluble and leaches out quickly so must be applied from time to time. Did you know that if you forget which element is P and which is K, you can use a memory device such as Phosphorus is P because the word has two P s in it? Activity Concepts: nutrients, eutrophication, nitrogen cycle Subject Links: Science: chemistry, ecology Vocabulary: eutrophication, nitrogen, phosphorus, and decomposition Purpose of activities: Youth will have the opportunity to learn about the composition of fertilizers and how nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) from fertilizers impacts aquatic organisms. Overview of activities: Youth will explore nutrients through hands-on activities. Time Required: Approximately minutes (Activity 1); approximately minutes (Activity 2). 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [2]
4 LESSON HANDOUT 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [3]
5 Activity #1: Nutrient Math Experiencing (Procedure): Using the color/ingredient key, ask the group to appropriately label the jars. Allow the group minutes to discuss their answers. Discuss the need for different rates of fertilizers. Sharing, Processing, and Generalizing: Discuss the questions below: What are the advantages of using organic fertilizers compared to inorganic fertilizers? Are there any disadvantages to utilizing manures as a fertilizer? If so, explain. Getting Ready: Or Assign one colored candy to represent each of the following: Nitrogen Phosphorous Potassium Inert Filler Apply a blank label to each jar. Count out candies; fill and close each jar accordingly: (Balanced) : 16 Nitrogen 16 Phosphorous 16 Potassium 52 Inert Filler (High Nitrogen): 21 Nitrogen 79 Inert Filler (High Phosphorous): 12 Nitrogen 55 Phosphorous 6 Potassium 27 Inert Filler (Organic: Cottonseed Meal) : 7 Nitrogen 3 Phosphorous 2 Potassium 88 Inert Filler (Organic: Manure): 1 Nitrogen 1 Phosphorous 1 Potassium 97 Inert Filler 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [4]
6 Materials Needed: (4) 32oz. Clear Jars with Lids 400 pieces each of (4) different colored candies: (Example: Red Hots, Lemon Heads, Good and Plenty (colors separated), M&Ms (colors separated), Baked Beans, Mike and Ikes (colors separated), Sugar Babies etc. Printout: (4) Labels: Fertilizer Fertilizer Fertilizer Fertilizer or Fertilizer Key for paired color and fertilizer ingredients. Opening Questions: Ask the youths to provide their answers on the flip chart paper provided. What is a fertilizer? What do the numbers on the product bag represent? What is the difference between organic and inorganic fertilizers? Why is Nitrogen necessary for plant health? Phosphorous? Potassium? In what situation might you use a fertilizer with more Nitrogen? Phosphorous? 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [5]
7 ACTIVITY #2: Fertilizer Foolishness Suggested Grouping: Pairs or small groups no larger than 4-6 individuals Materials Needed per Group: Glass bowl slightly larger than 1 quart Potable (drinking) water Bulk Super Snow (Dunecraft.com or Lakeshore Learning) Measuring spoons (1/2 teaspoon and 1 teaspoon) Flip chart paper and markers Lesson Handout - Water Quality Scenario Getting Ready: Fill glass bowl with 1 quart of water representing a lake or pond. Provide youth with at least a tablespoon of Super Snow that represents nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer (algae) and a set of measuring spoons containing ½ teaspoon and 1 teaspoon. Green Super Snow can be created by adding food dye to hydrated mixture and then drying in an oven at a low temperature to prevent burning. Trash bag to dispose of Super Snow once activity is complete. Material will dry in 4-6 weeks and can be utilized again. Opening Questions: 1. Ask youth how they think nutrients are obtained and utilized by plants. Ask them to explain their thoughts. Ask them to record their thoughts and ideas on the flip chart paper provided. 2. Ask the youth: Why are fertilizers added to lawns and agricultural crops? Where does fertilizer end up if it is not utilized by plants? Ask them to record their thoughts and ideas on the flip chart paper provided. [Facilitator s Tip: This question is trying to get to the point of water runoff and how it carries nutrients applied to agricultural lands or urban impervious surfaces (sidewalks, driveway, and streets) and landscapes into a body of water.] 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [6]
8 Experiencing (Procedure): Provide each pair/small group with the four scenarios provided below (pp. 8 & 9). Within their groups, ask them to read the scenarios aloud and follow the directions. Ask them to record the amount of Super Snow crystals they add to the glass bowl that represents a lake, pond or bay. Youth should observe and record how the Super Snow would make it difficult for fish to swim, boats to navigate, and other recreational activities. Sharing, Processing, & Generalizing: Ask the youth to use their words to explain what happened in the activity. Ask them to share the data they recorded and record additional thoughts on the flip chart paper provided. Ask the youth how they think nutrients might affect freshwater animals, marine animals, or estuarine environments (areas where freshwater and marine waters mix). Ask them to record their thoughts on the flip chart paper provided. If necessary, use more targeted questions as prompts to get to specific points. Additional questions might include: How can humans to reduce their contribution of nutrients to fresh water stream and creeks? Do they think nutrients impact rivers, streams, and the ocean differently at different times of the year? Concept and Term Introduction: At this point, facilitators need to ensure that the concepts and terms eutrophication, nitrogen, and phosphorus have been introduced. Note: The goal is to have the youth develop these concepts through their exploration and define the terms using their own words. The facilitator also needs to ensure that: The youth understand the concept of eutrophication and how excess nutrients impact waters. The youth have identified (from the scenarios) major sources of nutrients in surface runoff. Concept Application (Optional Activities): Take a field trip to a lake, pond, stream, or coastal area. Have the youth observe the different plants and animals. Identify whether the plants growing in the water are invasive or native. Have the youth predict how a food web would be affected if the nutrients in a fresh water stream suddenly increased during the rainy season (e.g. impact on insect population, plants, and fish). 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [7]
9 Water Quality Scenarios Scenario 1: You decide your lawn is just not green enough and you hear on the radio that tomorrow it is supposed to rain. You figure today is a good time to fertilize your front yard since the expected rain will water it down into the roots. Unfortunately, the rain is a downpour and your entire lawn floods and much of the fertilizer is carried off into the gutter. (Add ½ teaspoon of Super Snow fertilizer to glass bowl.) Scenario 2: The weather is warming and your grass, trees, and shrubs are starting to put on spring growth so you decide to head to the nursery and pick up a bag of fertilizer to feed your plants. You have an old hand-held spreader that you plan on using to spread the fertilizer. After ripping open the bag you lift it up to pour enough fertilizer into the spreader to fill it up completely, but the fertilizer pours out too quickly and you spill fertilizer all over the driveway. You pick up what you can and put it back into the bag, but granules are small and it is just taking too long. You grab the hose and wash the fertilizer off the driveway in to the gutter since the fertilizer bag warns that it will stain concrete surfaces.cal streams. (Add 1 teaspoon of Super Snow fertilizer to the glass bowl.) Scenario 3: You are a busy person and do not really like to mow and edge the lawn so you hire a gardener. The gardener always does a great job and the neighbors comment on how green and healthy your lawn looks. One day you come home early to see the gardener cleaning up after mowing and edging but he is blowing the clippings down to the street and into the storm drain. (Add 1 teaspoon of Super Snow fertilizer to glass bowl.) Scenario 4: The local sports park near your home is utilized year round for soccer, baseball, and football practice and games so the turf requires a lot of attention by the city landscapers. The turf fields are designed to drain well so that practice and game schedules are not affected by irrigation and rain events. This required the installation of an elaborate landscape drain system that allows runoff to leave the field and enter the storm drain. When the city fertilizes, however, they do not cover these drains and fertilizer falls directly into the drains. (Add 1/2 teaspoon of Super Snow fertilizer to glass bowl.) LESSON HANDOUT 4H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [8]
10 Resources: The University of California prohibits discrimination or harassment of any person on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex, gender identity, pregnancy (including childbirth, and medical conditions related to pregnancy or childbirth), physical or mental disability, medical condition (cancer-related or genetic characteristics), ancestry, marital status, age, sexual orientation, citizenship, or service in the uniformed services (as defined by the Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act of 1994: service in the uniformed services includes membership, application for membership, performance of service, application for service, or obligation for service in the uniformed services) in any of its programs or activities. University policy also prohibits reprisal or retaliation against any person in any of its programs or activities for making a complaint of discrimination or sexual harassment or for using or participating in the investigation or resolution process of any such complaint. University policy is intended to be consistent with the provisions of applicable State and Federal laws. Inquiries regarding the University s nondiscrimination policies may be directed to the Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Director, University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources, 1111 Franklin Street, 6 th Floor, Oakland, CA 94607, (510) H SET: WATER QUALITY AWARENESS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENTS LESSON 6 [9]
Orange County Fertilizer Application Education Course for Citizens
 Orange County Fertilizer Application Education Course for Citizens Thanks for taking the time to learn how to keep Central Florida beautiful while protecting our water quality! Why is Orange County Requiring
Orange County Fertilizer Application Education Course for Citizens Thanks for taking the time to learn how to keep Central Florida beautiful while protecting our water quality! Why is Orange County Requiring
City of Texarkana, Arkansas. Storm Water Pollution
 City of Texarkana, Arkansas Storm Water Pollution STORM WATER GUIDE What is Storm Water Pollution? Stormwater can provide a toxic discharge which can enter into a lake, river or coastal water system. As
City of Texarkana, Arkansas Storm Water Pollution STORM WATER GUIDE What is Storm Water Pollution? Stormwater can provide a toxic discharge which can enter into a lake, river or coastal water system. As
How does human activity impact water quality in New York Harbor? (8)
 How does human activity impact water quality in New York Harbor? (8) Amy Goods, MS 447 Adapted from The Water Sourcebooks www.epa.gov Summary/Overview: Students will add common household production/chemical
How does human activity impact water quality in New York Harbor? (8) Amy Goods, MS 447 Adapted from The Water Sourcebooks www.epa.gov Summary/Overview: Students will add common household production/chemical
Source Water Protection Practices Bulletin Managing Turfgrass and Garden Fertilizer Application to Prevent Contamination of Drinking Water
 United States Office of Water EPA 816-F-01-029 Environmental Protection (4606) July 2001 Agency Source Water Protection Practices Bulletin Managing Turfgrass and Garden Fertilizer Application to Prevent
United States Office of Water EPA 816-F-01-029 Environmental Protection (4606) July 2001 Agency Source Water Protection Practices Bulletin Managing Turfgrass and Garden Fertilizer Application to Prevent
Thirsty, anyone? Lesson Focus: The effect of humans on our water supply and environment, specifically non-point source pollution.
 Thirsty, anyone? Lesson Focus: The effect of humans on our water supply and environment, specifically non-point source pollution. Learning objectives: Students will learn how humans effect the environment
Thirsty, anyone? Lesson Focus: The effect of humans on our water supply and environment, specifically non-point source pollution. Learning objectives: Students will learn how humans effect the environment
Balancing the Nitrogen Budget
 University of California Tulare County Cooperative Extension Balancing the Nitrogen Budget Bill Peacock Pub. NG2-96 Sources of nitrogen in the soil/water system other than fertilizer should be considered
University of California Tulare County Cooperative Extension Balancing the Nitrogen Budget Bill Peacock Pub. NG2-96 Sources of nitrogen in the soil/water system other than fertilizer should be considered
Understanding Nutrients and Their Affects on the Environment
 Understanding Nutrients and Their Affects on the Environment Humans & Ecosystems Humans are just like ecosystems, too much or too little of a nutrient is bad for the system. Nutrient management is a balancing
Understanding Nutrients and Their Affects on the Environment Humans & Ecosystems Humans are just like ecosystems, too much or too little of a nutrient is bad for the system. Nutrient management is a balancing
EUTROPHICATION. Student Lab Workbook
 EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
Plum Creek. The Plum Creek Watershed. Your Water, Your Home. Watershed Partnership
 The Watershed Your Water, Your Home, Extension Water Quality Program Specialist I Mark McFarland, Professor and Extension Specialist Nikki Dictson, Extension Water Quality Program Specialist II Department
The Watershed Your Water, Your Home, Extension Water Quality Program Specialist I Mark McFarland, Professor and Extension Specialist Nikki Dictson, Extension Water Quality Program Specialist II Department
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico
 The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
Earth Systems and Interactions
 CHAPTER The Earth System Earth Systems and Interactions What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
CHAPTER The Earth System Earth Systems and Interactions What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
recycling in Oregon To learn more about biosolids recycling EC 1471 Reprinted February 2002
 Biosolids in the backyard Some treatment plants produce composted biosolids products that are suitable for use by landscape contractors and the public. These products must meet the most stringent EPA standards
Biosolids in the backyard Some treatment plants produce composted biosolids products that are suitable for use by landscape contractors and the public. These products must meet the most stringent EPA standards
Dirty Water. Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, Grade Level: all. Duration: 1-2 class periods
 Dirty Water Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Grade Level: all Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom or laboratory Summary:
Dirty Water Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Grade Level: all Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom or laboratory Summary:
Introduction to Water Quality Parameters
 Introduction to Water Quality Parameters Directions: Your group will be assigned one or two Water Quality (WQ) parameters to read about and present to the class. 1. Read the explanations for your assigned
Introduction to Water Quality Parameters Directions: Your group will be assigned one or two Water Quality (WQ) parameters to read about and present to the class. 1. Read the explanations for your assigned
Frequently Asked Questions - Fertilizers -
 What is fertilizer? What is phosphorus? What is nitrogen? How do I know if the fertilizer is phosphorus or nitrogen free? Which number on the bag of fertilizer is phosphorus and which is nitrogen? Is low
What is fertilizer? What is phosphorus? What is nitrogen? How do I know if the fertilizer is phosphorus or nitrogen free? Which number on the bag of fertilizer is phosphorus and which is nitrogen? Is low
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Life Depends on the Sun Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Life Depends on the Sun Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
How Ecosystems Work Section 2. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so..where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so..where do essential
How Ecosystems Work Section 2
 Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work
 Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Start by put the words sustainable and conventional methods on the flip chart. Brainstorm ideas then synthesize those that seem to fit the best.
 TITLE: Introduction to Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems OBJECTIVES: To introduce the principles of sustainable agriculture and how they are used on the farm. To introduce the terms industrial/global
TITLE: Introduction to Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems OBJECTIVES: To introduce the principles of sustainable agriculture and how they are used on the farm. To introduce the terms industrial/global
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
You re the Solution to Water Pollution!
 You re the Solution to Water Pollution! Storm Drains Did you know that stormdrains deliver surface water run-off directly to the nearest pond or creek, and eventually to the Bay? Major Pollutants: Soil
You re the Solution to Water Pollution! Storm Drains Did you know that stormdrains deliver surface water run-off directly to the nearest pond or creek, and eventually to the Bay? Major Pollutants: Soil
The Science of Maryland Agriculture
 Edition 3 (2016) GOAL STATEMENT: Students will understand how Maryland farmers and developers can use conservation techniques to reduce environmental damage. OBJECTIVES: Students will identify ways agriculture
Edition 3 (2016) GOAL STATEMENT: Students will understand how Maryland farmers and developers can use conservation techniques to reduce environmental damage. OBJECTIVES: Students will identify ways agriculture
Good Housekeeping Pollution Prevention
 Good Housekeeping Pollution Prevention Oak Meadow Golf and Banquet September 12, 2008 Richard Hentschel Extension Specialist Green Industry Programming University of Illinois Sensible turf management limits
Good Housekeeping Pollution Prevention Oak Meadow Golf and Banquet September 12, 2008 Richard Hentschel Extension Specialist Green Industry Programming University of Illinois Sensible turf management limits
AP Environmental Science
 Name AP Environmental Science DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic
Name AP Environmental Science DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic
Hubbard County Water Quality and You Celebrating 20 Years of Water Quality Testing in Hubbard County!
 Hubbard County Water Quality and You Celebrating 20 Years of Water Quality Testing in Hubbard County! A Collaborative Effort by: Citizen Volunteers Hubbard County Coalition of Lake Associations (HC COLA)
Hubbard County Water Quality and You Celebrating 20 Years of Water Quality Testing in Hubbard County! A Collaborative Effort by: Citizen Volunteers Hubbard County Coalition of Lake Associations (HC COLA)
The Biosphere Chapter 3. What Is Ecology? Section 3-1
 The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
Organic Manures and Fertilizers for Vegetable Crops
 Organic Manures and Fertilizers for Vegetable Crops Brent Rowell, Extension Vegetable Specialist and Robert Hadad Animal manures contribute more to the soil than just nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Organic Manures and Fertilizers for Vegetable Crops Brent Rowell, Extension Vegetable Specialist and Robert Hadad Animal manures contribute more to the soil than just nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials
 Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
The Science of Maryland Agriculture
 The Science of Maryland Agriculture GOAL STATEMENT: Students will learn about soil as a natural resource, what its components are, how it is used, and whether it is renewable. OBJECTIVES: Students will
The Science of Maryland Agriculture GOAL STATEMENT: Students will learn about soil as a natural resource, what its components are, how it is used, and whether it is renewable. OBJECTIVES: Students will
Water Quality: The Basics
 Water Quality: The Basics Environmental Science Why is Water Quality Important? Effects all humans Safe drinking water Allows for food productions and SAFE food products Effects Wildlife Health domestic
Water Quality: The Basics Environmental Science Why is Water Quality Important? Effects all humans Safe drinking water Allows for food productions and SAFE food products Effects Wildlife Health domestic
Unit F: Soil Fertility and Moisture Management. Lesson 2: Determining the Value of Manure and Compost
 Unit F: Soil Fertility and Moisture Management Lesson 2: Determining the Value of Manure and Compost 1 Terms Compost Fertilizer Global climate change Greenhouse effect Manure Methane Nitrate Organic matter
Unit F: Soil Fertility and Moisture Management Lesson 2: Determining the Value of Manure and Compost 1 Terms Compost Fertilizer Global climate change Greenhouse effect Manure Methane Nitrate Organic matter
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality
 Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
Lesson Objectives. Core Content Objectives. Language Arts Objectives. Core Vocabulary
 The Seasons of Farming 8 Lesson Objectives Core Content Objectives Students will: Describe a farmer s job Sequence the seasonal rhythm of planting, growing, and harvesting Describe how farmers protect
The Seasons of Farming 8 Lesson Objectives Core Content Objectives Students will: Describe a farmer s job Sequence the seasonal rhythm of planting, growing, and harvesting Describe how farmers protect
Aquatic Science Unit 2. Water Quality and Water Pollution
 Aquatic Science Unit 2 Water Quality and Water Pollution What is a healthy water body? In your own words, take a moment to describe what you believe are some of the characteristics of a healthy stream
Aquatic Science Unit 2 Water Quality and Water Pollution What is a healthy water body? In your own words, take a moment to describe what you believe are some of the characteristics of a healthy stream
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
BUILD A WATERSHED. DESIGN CHALLENGE Build a 3-D model of a watershed and experiment to see how human and natural activities can affect it.
 Grades 3 5, 6 8 60 minutes BUILD A WATERSHED DESIGN CHALLENGE Build a 3-D model of a watershed and experiment to see how human and natural activities can affect it. SUPPLIES AND EQUIPMENT Per whole group:
Grades 3 5, 6 8 60 minutes BUILD A WATERSHED DESIGN CHALLENGE Build a 3-D model of a watershed and experiment to see how human and natural activities can affect it. SUPPLIES AND EQUIPMENT Per whole group:
Science Enhanced Scope and Sequence Grade 6. Water Quality
 Water Quality Strand Topic Living Systems Investigating water quality Primary SOL 6.7 The student will investigate and understand the natural processes and human interactions that affect watershed systems.
Water Quality Strand Topic Living Systems Investigating water quality Primary SOL 6.7 The student will investigate and understand the natural processes and human interactions that affect watershed systems.
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles
 Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Information regarding the contents and levels of metals in this product is available on the Internet at:
 FERTILIZER WITH 0.069% BIFENTHRIN Insect Control 17-0-5 Guaranteed Analysis Total Nitrogen (N)...17% 17.0% Urea Nitrogen* Soluble Potash (K 2 O)... 5% Sulfur (S)...1.6% 1.6% Free Sulfur Derived From: Urea,
FERTILIZER WITH 0.069% BIFENTHRIN Insect Control 17-0-5 Guaranteed Analysis Total Nitrogen (N)...17% 17.0% Urea Nitrogen* Soluble Potash (K 2 O)... 5% Sulfur (S)...1.6% 1.6% Free Sulfur Derived From: Urea,
You are the solution to water pollution. A guide for preventing water pollution in your own backyard
 You are the solution to water pollution A guide for preventing water pollution in your own backyard Even if you live miles away from a river or stream, you may be polluting the water without even knowing
You are the solution to water pollution A guide for preventing water pollution in your own backyard Even if you live miles away from a river or stream, you may be polluting the water without even knowing
Clean water. From nature.
 Clean water. From nature. Natural Treatment System Save water. Do your part. Did you know that over watering or a broken sprinkler on your property can contribute to ocean pollution? Excess watering creates
Clean water. From nature. Natural Treatment System Save water. Do your part. Did you know that over watering or a broken sprinkler on your property can contribute to ocean pollution? Excess watering creates
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Agriculture and Natural Resources Newsletter
 SEPTEMBER - NOVEMBER 2018 Agriculture and Natural Resources Newsletter WHITLEY COUNTY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Important Dates: Sept. 27th-Whitley Co. Cattlemen's Association Meeting, 7 pm Oct. 2nd-Cattle
SEPTEMBER - NOVEMBER 2018 Agriculture and Natural Resources Newsletter WHITLEY COUNTY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Important Dates: Sept. 27th-Whitley Co. Cattlemen's Association Meeting, 7 pm Oct. 2nd-Cattle
Factsheet: City of West Haven Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: City of West Haven Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: City of West Haven Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
STORMWATER POLLUTION PREVENTION
 STORMWATER POLLUTION PREVENTION WHAT IS STORMWATER? STORMWATER IS RAINWATER RUNOFF STREETS SIDEWALKS ROOFTOPS DRIVEWAYS PARKING LOTS STORMWATER IS NOT TREATED BEFORE IT GETS DISCHARGED INTO A LOCAL WATER
STORMWATER POLLUTION PREVENTION WHAT IS STORMWATER? STORMWATER IS RAINWATER RUNOFF STREETS SIDEWALKS ROOFTOPS DRIVEWAYS PARKING LOTS STORMWATER IS NOT TREATED BEFORE IT GETS DISCHARGED INTO A LOCAL WATER
The Snapshot CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT
 CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT ABOVE: CONODOGUINET CREEK AT RT 74 BRIDGE FACING DOWNSTREAM The Snapshot The Conodoguinet Watershed Snapshot was a collaborative effort to engage local citizens in
CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT ABOVE: CONODOGUINET CREEK AT RT 74 BRIDGE FACING DOWNSTREAM The Snapshot The Conodoguinet Watershed Snapshot was a collaborative effort to engage local citizens in
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems. Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid?
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
Reducing Nutrient Contributions from urban and rural residential sources
 Help Protect our Rivers and Lakes Proposed approaches to Reducing Nutrient Contributions from urban and rural residential sources Fertilizer application Household cleaning products Background document
Help Protect our Rivers and Lakes Proposed approaches to Reducing Nutrient Contributions from urban and rural residential sources Fertilizer application Household cleaning products Background document
WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein!
 Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nueces River Watershed
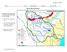 Name period Date assigned date due date returned Directions: You will color parts of the on the next page: 1. Trace the rivers and lakes in blue 2. Trace the outside edge of the watershed in red (it s
Name period Date assigned date due date returned Directions: You will color parts of the on the next page: 1. Trace the rivers and lakes in blue 2. Trace the outside edge of the watershed in red (it s
8/11/2015 BY KOREE POMPEY
 8/11/2015 BY KOREE POMPEY Water Basics AVAILABLE WATER ON EARTH Salt water Fresh water Ground water Surface water Saltwater Saltwater, is a geological term that refers to naturally occurring solutions
8/11/2015 BY KOREE POMPEY Water Basics AVAILABLE WATER ON EARTH Salt water Fresh water Ground water Surface water Saltwater Saltwater, is a geological term that refers to naturally occurring solutions
HOME PRACTICES TO PROMOTE WATER QUALITY
 November 2004 HOME PRACTICES TO PROMOTE WATER QUALITY There are four major watersheds in the Mid- Atlantic: the Ohio River basin draining to the Gulf of Mexico, the Delaware Bay, the Roanoke and Chowan
November 2004 HOME PRACTICES TO PROMOTE WATER QUALITY There are four major watersheds in the Mid- Atlantic: the Ohio River basin draining to the Gulf of Mexico, the Delaware Bay, the Roanoke and Chowan
Drought Irrigation Strategies for Alfalfa
 Making a Difference for California University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources http://anrcatalog.ucdavis.edu Publication 8448 June 211 Drought Irrigation Strategies for Alfalfa BLAINE HANSON,
Making a Difference for California University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources http://anrcatalog.ucdavis.edu Publication 8448 June 211 Drought Irrigation Strategies for Alfalfa BLAINE HANSON,
Youth make a solution of food coloring with a concentration of one part per million and discuss clean water standards.
 One in a Million Overview: Youth make a solution of food coloring with a concentration of one part per million and discuss clean water standards. Substances dissolved in water can be present in very tiny
One in a Million Overview: Youth make a solution of food coloring with a concentration of one part per million and discuss clean water standards. Substances dissolved in water can be present in very tiny
Root Stimulator & Starter Solution
 CONCENTRATE Root Stimulator & Starter Solution 5-15-5 For Newly Planted Flowers, Shrubs and Trees Around The Home KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN CAUTION See Booklet For Additional Precautionary Statements
CONCENTRATE Root Stimulator & Starter Solution 5-15-5 For Newly Planted Flowers, Shrubs and Trees Around The Home KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN CAUTION See Booklet For Additional Precautionary Statements
Big Chetac and the Red Cedar River Watershed. Dan Zerr University of Wisconsin-Extension Natural Resource Educator
 Big Chetac and the Red Cedar River Watershed Dan Zerr University of Wisconsin-Extension Natural Resource Educator The Water Cycle An area that all drains to a particular stream, river, lake, or ocean.
Big Chetac and the Red Cedar River Watershed Dan Zerr University of Wisconsin-Extension Natural Resource Educator The Water Cycle An area that all drains to a particular stream, river, lake, or ocean.
The Importance of Riparian Forests
 The Importance of Riparian Forests By Jean Llewellyn Monroe County is the second fastest growing county in Pennsylvania. This rapid growth can be problematic because uncontrolled and unregulated growth
The Importance of Riparian Forests By Jean Llewellyn Monroe County is the second fastest growing county in Pennsylvania. This rapid growth can be problematic because uncontrolled and unregulated growth
ARE ALL fertilizers the same? Of
 Fertilizer Formulations ARE ALL fertilizers the same? Of course not, but how do they differ? Knowing the types of fertilizers available is important to producers for economic and environmental reasons.
Fertilizer Formulations ARE ALL fertilizers the same? Of course not, but how do they differ? Knowing the types of fertilizers available is important to producers for economic and environmental reasons.
Factsheet: Town of Deep River Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Deep River Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Deep River Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
BC Science Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems
 BC Science 10 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Notes Nutrients are chemicals required for growth and other life processes. Nutrients move through the biosphere in nutrient cycles (n.c), or exchanges.
BC Science 10 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Notes Nutrients are chemicals required for growth and other life processes. Nutrients move through the biosphere in nutrient cycles (n.c), or exchanges.
General Recommendations for Fertilization of Turfgrasses on Florida Soils 1
 SL1 General Recommendations for Fertilization of Turfgrasses on Florida Soils 1 J.B. Sartain In many neighborhoods, people envy the individual with the most beautiful lawn and think they cannot grow a
SL1 General Recommendations for Fertilization of Turfgrasses on Florida Soils 1 J.B. Sartain In many neighborhoods, people envy the individual with the most beautiful lawn and think they cannot grow a
2/11/16. Materials in ecosystems are constantly reused Three cycles: The Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle
 Materials in ecosystems are constantly reused Three cycles: The Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle The Cycle Carbon is essential in proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, which make up all organisms Carbon cycle
Materials in ecosystems are constantly reused Three cycles: The Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle The Cycle Carbon is essential in proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, which make up all organisms Carbon cycle
Whole Soil Fertility Step-by-Step
 Whole Soil Fertility Step-by-Step A guide to using the whole soil fertility worksheet What the soil needs Our first step is to estimate plant and soil needs. For this, we use 1. Plant nitrogen requirements
Whole Soil Fertility Step-by-Step A guide to using the whole soil fertility worksheet What the soil needs Our first step is to estimate plant and soil needs. For this, we use 1. Plant nitrogen requirements
To Pesticide Use Around the Home and Garden
 To Pesticide Use Around the Home and Garden Pests in the home and garden can cause damage to homes and landscapes, cause health problems, and decrease fruit and vegetable production. The use of pesticides
To Pesticide Use Around the Home and Garden Pests in the home and garden can cause damage to homes and landscapes, cause health problems, and decrease fruit and vegetable production. The use of pesticides
4-H Ham Radio Communication Proficiency Program A Member s Guide
 4-H Ham Radio Communication Proficiency Program A Member s Guide OVERVIEW The 4-H Ham Radio Communication Proficiency program helps you learn what you need to know about your 4-H project. Your project
4-H Ham Radio Communication Proficiency Program A Member s Guide OVERVIEW The 4-H Ham Radio Communication Proficiency program helps you learn what you need to know about your 4-H project. Your project
UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS
 UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Chapter 2 Biogeochemical Cycles Science 10 Change & Recovery in Ecosystems (you do not need to copy) What happens to the materials that make up a truck when it begins to rust?
UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Chapter 2 Biogeochemical Cycles Science 10 Change & Recovery in Ecosystems (you do not need to copy) What happens to the materials that make up a truck when it begins to rust?
CNY Stormwater Coalition. Gardens and Gutters. Looking for Blue and Seeing Green?
 CNY Stormwater Coalition Gardens and Gutters A Central New Yorker s Guide to Managing Stormwater Runoff Volume 3 Issue 2 Summer 2015 Looking for Blue and Seeing Green? Inside this issue: New State Law
CNY Stormwater Coalition Gardens and Gutters A Central New Yorker s Guide to Managing Stormwater Runoff Volume 3 Issue 2 Summer 2015 Looking for Blue and Seeing Green? Inside this issue: New State Law
AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench)
 Name AP Biology AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic Primary
Name AP Biology AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic Primary
The effects of pollution. What is stormwater runoff? Why is stormwater runoff a problem?
 What is stormwater runoff? Stormwater runoff occurs when precipitation from rain or snowmelt flows over the ground. Impervious surfaces like driveways, sidewalks, and streets prevent stormwater from naturally
What is stormwater runoff? Stormwater runoff occurs when precipitation from rain or snowmelt flows over the ground. Impervious surfaces like driveways, sidewalks, and streets prevent stormwater from naturally
Freshwater Ecosystems
 Freshwater Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are mainly determined by the water s salinity. As a result, aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and marine ecosystems. Freshwater
Freshwater Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are mainly determined by the water s salinity. As a result, aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and marine ecosystems. Freshwater
Soil Quality How can we improve soil quality?
 Activitydevelop Soil Quality How can we improve soil quality? Overview Students explore the conditions that make high-quality soils. Using data from field research and interactive computational models,
Activitydevelop Soil Quality How can we improve soil quality? Overview Students explore the conditions that make high-quality soils. Using data from field research and interactive computational models,
CLMP+ Report on Grass Lake (Anoka County) Lake ID# CLMP+ Data Summary
 CLMP+ Report on Grass Lake (Anoka County) Lake ID# 02-0113-00 2012-2013 CLMP+ Data Summary October 2014 Authors Shannon Martin, MPCA Editing and graphic design Public Information Office Staff The (MPCA)
CLMP+ Report on Grass Lake (Anoka County) Lake ID# 02-0113-00 2012-2013 CLMP+ Data Summary October 2014 Authors Shannon Martin, MPCA Editing and graphic design Public Information Office Staff The (MPCA)
Nitrogen Dynamics Feeding the Crops that Feed Us
 Nitrogen Dynamics Feeding the Crops that Feed Us Overview All plants require nitrogen in relatively large amounts and nitrogen is the most commonly limiting nutrient in agriculture. Consequences of insufficient
Nitrogen Dynamics Feeding the Crops that Feed Us Overview All plants require nitrogen in relatively large amounts and nitrogen is the most commonly limiting nutrient in agriculture. Consequences of insufficient
Coastal Water Ways. Want to Know How to Protect Your Water Quality? Volume 1, Issue 1. Coastal Waccamaw Stormwater Education Consortium
 Volume 1, Issue 1 Want to Know How to Protect Your Water Quality? We re going to help! This article is the first in a series of informational and educational tools for property owners concerned about water
Volume 1, Issue 1 Want to Know How to Protect Your Water Quality? We re going to help! This article is the first in a series of informational and educational tools for property owners concerned about water
Land Use Activities Potential Pollution Problems. Land Disposal septic system bacteria, nitrate, phosphate
 If Bugs Could Talk PURPOSE: To describe and identify the link between land use activities within a watershed and water quality. Students will also understand the link between aquatic macroinvertebrates
If Bugs Could Talk PURPOSE: To describe and identify the link between land use activities within a watershed and water quality. Students will also understand the link between aquatic macroinvertebrates
GI BMP Training Program Review Worksheets
 GI BMP Training Program Review Worksheets 2/7/2013 Version 1 ANSWER KEY Instructions: Use the worksheets as a guide to review key learning points and information provided during the training program. Depending
GI BMP Training Program Review Worksheets 2/7/2013 Version 1 ANSWER KEY Instructions: Use the worksheets as a guide to review key learning points and information provided during the training program. Depending
Factsheet: Town of East Lyme Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of East Lyme Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of East Lyme Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Observe and document the application of differing water conservation efforts of golf courses.
 First Green is an innovative environmental and STEM education outreach program using golf courses as environmental learning labs. Water Water comprises 80 to 85% of the weight of a grass plant. In most
First Green is an innovative environmental and STEM education outreach program using golf courses as environmental learning labs. Water Water comprises 80 to 85% of the weight of a grass plant. In most
Chapter: The Nonliving Environment
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Nonliving Environment Section 1: Abiotic Factors Section 2: Cycles in Nature Section 3: Energy Flow Abiotic Factors 1 Environmental Factors The features of the environment
Table of Contents Chapter: The Nonliving Environment Section 1: Abiotic Factors Section 2: Cycles in Nature Section 3: Energy Flow Abiotic Factors 1 Environmental Factors The features of the environment
CITY OF TOMBALL MUNICIPAL SEPARATE STORM SEWER SYSTEM (MS4) PERMIT SUMMER 2015
 What is stormwater runoff? 1 CITY OF TOMBALL MUNICIPAL SEPARATE STORM SEWER SYSTEM (MS4) PERMIT SUMMER 2015 Stormwater is any precipitation from a storm event (rain, snow, sleet, etc). Stormwater runoff
What is stormwater runoff? 1 CITY OF TOMBALL MUNICIPAL SEPARATE STORM SEWER SYSTEM (MS4) PERMIT SUMMER 2015 Stormwater is any precipitation from a storm event (rain, snow, sleet, etc). Stormwater runoff
Factsheet: Town of Hamden Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Hamden Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each town
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Hamden Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each town
Stormwater BMP Maintenance
 Stormwater BMP Maintenance Background and Definitions What is Stormwater Runoff? Stormwater Stormwater is the result of precipitation that flows overland to streams and other bodies of water Stormwater
Stormwater BMP Maintenance Background and Definitions What is Stormwater Runoff? Stormwater Stormwater is the result of precipitation that flows overland to streams and other bodies of water Stormwater
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems CARBON CYCLE A. Carbon Facts: Carbon is found in all living matter. Places that carbon is found are called stores or sinks Short-term Stores Long-term Stores - living
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems CARBON CYCLE A. Carbon Facts: Carbon is found in all living matter. Places that carbon is found are called stores or sinks Short-term Stores Long-term Stores - living
A Guide to Collecting Soil Samples for Farms and Gardens
 A Guide to Collecting Soil Samples for Farms and Gardens M. Fery and E. Murphy Without a soil analysis, it s nearly impossible to determine what a soil needs in order to be productive. Laboratory soil
A Guide to Collecting Soil Samples for Farms and Gardens M. Fery and E. Murphy Without a soil analysis, it s nearly impossible to determine what a soil needs in order to be productive. Laboratory soil
CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION. INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico
 CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico SAVING THE BAY Teams of researchers try to pin down what s choking the Chesapeake Water pollution
CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico SAVING THE BAY Teams of researchers try to pin down what s choking the Chesapeake Water pollution
Ecosystems Full of Matter, Energy, and Entropy
 Living Environment Ecosystems Ecosystems Full of Matter, Energy, and Entropy 2017-07-18 www.njctl.org Table of Contents: Ecosystems Full of Matter, Energy, and Entropy Click on a topic to go to that section
Living Environment Ecosystems Ecosystems Full of Matter, Energy, and Entropy 2017-07-18 www.njctl.org Table of Contents: Ecosystems Full of Matter, Energy, and Entropy Click on a topic to go to that section
Water Pollution Overview. Sewage dumping
 Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Sewage dumping Ocean Pollution Water Pollution Overview Urban Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Water Pollution Overview Urban Runoff Water Pollution Overview
Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Sewage dumping Ocean Pollution Water Pollution Overview Urban Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Water Pollution Overview Urban Runoff Water Pollution Overview
Subject Index. See for options on how to legitimately share published articles.
 INDEX 279 Subject Index Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on December 24, 2018 at 05:54:08 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Acid-base
INDEX 279 Subject Index Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on December 24, 2018 at 05:54:08 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Acid-base
Natural Ecosystem Change
 Environmental Science Set 3 of 9 Natural Ecosystem Change Presentation MEDIA Version 2 BIOZONE International 2009, 2013 Processes in Carbon Cycling Carbon cycles between the living (biotic) and non-living
Environmental Science Set 3 of 9 Natural Ecosystem Change Presentation MEDIA Version 2 BIOZONE International 2009, 2013 Processes in Carbon Cycling Carbon cycles between the living (biotic) and non-living
Matter Cycles How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems?
 9. In order to continually use the same area of land for agriculture, some farmers apply fertilizers to improve the level of nitrates in the soil. An alternative to this intensive use of fertilizer is
9. In order to continually use the same area of land for agriculture, some farmers apply fertilizers to improve the level of nitrates in the soil. An alternative to this intensive use of fertilizer is
PURDUE PESTICIDE PROGRAMS
 PPP-39 PURDUE PESTICIDE PROGRAMS Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service PESTICIDE SAFETY AND CALIBRATION MATH FOR THE HOMEOWNER Fred Whitford, Coordinator, Purdue Pesticide Programs Andrew Martin,
PPP-39 PURDUE PESTICIDE PROGRAMS Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service PESTICIDE SAFETY AND CALIBRATION MATH FOR THE HOMEOWNER Fred Whitford, Coordinator, Purdue Pesticide Programs Andrew Martin,
Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production
 Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production Richard Smith, Farm Advisor Monterey County Farm Water Quality Planning Project UC Cooperative Extension/ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Fertilizers
Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production Richard Smith, Farm Advisor Monterey County Farm Water Quality Planning Project UC Cooperative Extension/ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Fertilizers
The Nitrogen Cycle. ) in the atmosphere is converted into ammonium ions ( NH 4 + ).
 The Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen is essential for many processes; it is crucial for all life on Earth. It is in all amino acids, is incorporated into proteins, and is present in the bases that make up nucleic
The Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen is essential for many processes; it is crucial for all life on Earth. It is in all amino acids, is incorporated into proteins, and is present in the bases that make up nucleic
Soil Testing and Nutrient Management. Craig Cogger Soil Scientist WSU Puyallup
 Soil Testing and Nutrient Management Craig Cogger Soil Scientist WSU Puyallup Soil Testing Nutrients Soil Quality Contaminants Biological Simple Soil Quality Tests Texture Structure Color Texture: Proportions
Soil Testing and Nutrient Management Craig Cogger Soil Scientist WSU Puyallup Soil Testing Nutrients Soil Quality Contaminants Biological Simple Soil Quality Tests Texture Structure Color Texture: Proportions
