Content. River Tank Set Up Building a Watershed Model Exploring Stream Tables Fertilizer and ph Investigations...
|
|
|
- Ginger White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teacher Resources
2 Content Teacher Resources River Tank Set Up Building a Watershed Model Exploring Stream Tables Fertilizer and ph Investigations TG 278 Teacher Guide/Resources
3 Teacher Resources RIVER TANK SET UP Figure 1 Side view The water in the aquarium is pumped through the flexible tubing to the upper end of the plastic trough. The water flows down through the trough. It is IMPORTANT to keep water flowing through the system at all times if you intend to keep anything alive in the tank. The trough needs to be set at a very small downward slope which requires a little playing around until the proper slope for that particular pump is achieved (e.g. you don t want the water to flow too quickly through the trough). A small cap can be used on the down slope side to keep the trough from running dry. Assorted rocks and benthic macro-invertebrates collected from a riffle area can be placed in the trough. Adjust the placement of rocks to ensure a turbulent flow of water. Figure 2 Top View As the little stream cascades from the end of the trough into the aquarium, it becomes further aerated. The aquarium pool can be outfitted with stream gravel, aquatic plants, rocks and even a small fish or two (no more than 1 fish per gallon of water). Don t purchase aquarium fish from a pet store - these are not native to your ecosystem. Instead, bait stores which carry live minnows are a good source for a variety of stream shiners and chubs. Occasionally they will capture a small perch, bluegill or bass which are not suitable as bait fish but make good predators in a classroom model river. Teacher Guide/Resources TG 279
4 BUILDING WATERSHED MODEL Teacher Resources Build a Watershed of Your Own Trouble shoot challenges that students may have in building their watershed. Setting up a Material Station Student groups will need a set of watershed materials. Do not give the students the spray bottle yet. Preparing Spray Bottles Add enough Tempora paint or food coloring (red, blue or green) to the water so that when sprayed on the butcher paper the color is clearly evident. Drawing Elevation Map Using a piece of notebook paper, draw an elevation map of your model. Sketch a bird s-eye view of your model by standing over the model and looking down. Mark the high areas with H s and the low areas with L s. Observing Model Building Watershed Model Place newspaper under the tray. Arrange a tall object near one edge of the tray and arrange the shorter objects toward the center of the tray. Crumple up a piece of butcher paper. Be careful not to rip any holes in the paper. Carefully cover the tall and short objects with the sheet of butcher paper pressing the paper down so that it looks like tall and shorter hills. Use pieces of tape to keep the paper from lifting up from the tray. Use a colored marker to draw arrows that predict how the water will flow. Using a different color pen draw on your map how the water flows over your model and where the water accumulates. Note the pattern of how the water flows over your model, how smaller rivers join to form larger rivers and how rivers flow into lakes. Hold the spray bottle about 5 inches from your model and spray for several minutes until you get a continual flow of water. Take turns spraying your model. Alternate where each person sprays. Teacher Guide/Resources TG 281
5 EXPLORING STREAM TABLES How to buid our stream table? Materials Spray bottles Stream table pan of earth materials Two water supply containers 1 waste water catch basin 2 wooden slats (ruler or paint stick) 1 wooden angle 1 large (2L) pop bottle filled with water 1 package transparency markers 1 tray cover (plexiglass) 1 magnifying glass Paper towels and a lot of newspapers Procedure 1. Cover the work area with a lot of newspapers. 2. Place the tray flat on top of the newspapers. Position the tray so that the drain hole is off the table. 3. Place opened newspapers on the floor. Teacher Resources that it bridges the wooden slat and the tray edge. The hole of the container should be over the earth materials. 8. Using your pointer finger, make a curved finger nail deep river bed from the ruler to the end of the earth material. Smooth the sides of the river channel with your fingers. 9. Sketch a copy of your river on your worksheet. 10.Place your finger over the hole of the normal water supply container and begin to fill the container with water to the line from the 2L pop bottle. Once filled, place the water supply so that it bridges the edge of the tray and the wooden slant. 4. Position the waste water catch basin on the newspapers. The drain hole of the tray should be over the catch basin. 5. Push the earth materials to the end of the tray opposite the drain hole. 6. Flatten the earth materials at a slight slant downward and ending in a cliff. Use the wooden angle (ruler) to flatten and pack down the earth materials.the materials should fill 3/4 of the length of the tray. 11.Now it is time to observe your river. Watch what happens to the water and the earth materials. Release your finger from the hole. Let the water run for a slow count of 20 seconds and make your observations. 12.Place the wooden angle under the tray. Repeat steps 7. Lay the ruler or wooden slat across the tray about 5 cm from the end. Position the water supply container labeled normal so Teacher Guide/Resources TG 283
6 Procedure 1. Tip the tray so a as much water as possible runs out of the tray. 2. Push all of the earth materials to the end opposite the drain using the wooden angle. 3. Drain off more of the water. Some of the earth materials may drain with the water into the catch basin. These materials can be retrieved at a later time. 4. When as much of the water is drained as possible, flatten the earth materials. 5. Place 1 layer of paper towels on the surface of the earth materials and then about 3 thick sections of newspaper. 6. Carry the trays to a designated storage space. 7. Clean any earth materials off the equipment and throw out the soggy news papers. If they are not soggy, they can be left for the next group. 8. Do not throw the waste water down the drain!! The waste water will be poured into a designated waste water pail. TG 284 Teacher Guide/Resources
7 The Rural Setting 1. Set-up the stream table and place the stream table on the wooden angle so that the stream table is on a slant or a slope. 2. Using your pointer finger, make a smooth, curved, finger nail-deep river bed from the ruler to the end of the earth material. Smooth the sides of the river with your fingers. Scoop out a lake to the right of the river. 3. Place some cubes along the right side of the river to represent houses. Put some near the river and some farther away. Pour a small amount of water into the lake. water down the river for a slow count of 20 seconds. Record observations again. 9. Clean-up pollution. Use a spoon to remove the polluted soil. Place the polluted soil into a waste container. The Residential Setting 1. A developer comes in and builds houses along the left side of the river. There is a lot of grass around the houses. Place some grass and houses on the left side of the river. 2. Have teacher check your set-up and then sketch your stream table on the next page. 3. Spray your model until you see water running along the surface into the river and lake. Houses and Grass The Rural Setting 4. Have teacher check your set-up and then sketch your stream table on the next page. 5. Let one container of water flow continuously down the river. Record observations. 6. Spray your model with water. Record observations. 7. The houses around the right side of the river decide to spray their lawn with a combination of fertilizers and weed killers. Use the spray bottle with colored water and spray 3 strokes from a height of about 5 inches over the houses on the right side of the river. Record observations. 8. It rains right afterward. Spray the same area with 5 or so sprays of clear water and run 4. Observe what happens to the water as you spray your model and count the number of sprays needed to create surface run-off 5. Clean-up and remove grass and houses. The Urban Setting 1. A land developer decides to put in buildings streets and parking lots. On the left side of the river use the laminated black paper to represent pavement and then add buildings. 2. Have teacher check your set-up and then sketch your stream table on the next page. 3. Spray your model until you see water running along the surface into the river and lake. 4. Observe what happens to the water as you spray your model and count the number of sprays needed to create surface run-off. 5. Clean-up and remove pavement and houses. Teacher Guide/Resources TG 285
8 FERTILIZER AND ph INVESTIGATION Materials needed - 4 baby food jars or 100 ml beakers - distilled water or "aged" tap water gals of river water healthy duckweed plants (10/jar) - fertilizer solution - clear plastic wrap 4" x 4" squares rubber bands Preparing the fertilizer solution Pick up a commercial garden or house plant fertilizer from a local garden center or hardware store. Recommended strengths are or (N/nitrate, P/phosphate, K/potassium ratio.) Follow the directions on the package for mixing the fertilizer solution. Setting-up the experiment 1. Label each jar with a number (1-4). 2. Set-up four jars as follows: JAR 1 (No Fertilizer) - 50 mls distilled water JAR 2 (Low Fertilizer) - 25 mls distilled water - 25 mls fertilizer solution JAR 3 (High Fertilizer) - 50 mls fertilizer solution JAR 4 (River Water) - 50 mls river water 3. Add the same amount of duckweed to each jar. (Approximately ten duckweed plants) 4. Place the jars in a well lit area of the room. 5. With your students, develop an organized way to collect data for two weeks. 6. After adding materials to each jar, cover tightly with clear plastic wrap and secure with rubber band. Teacher Resources Materials needed (per group) baby food jars or 100 ml beakers - distilled water or "aged" tap water gals of river water healthy duckweed plants (10/jar) - 1 gallon distilled vinegar per class - clear plastic wrap.4" x 4" squares rubber bands - aquatic plants (duckweed, elodea) Preparing the acid (vinegar) solution This experiment uses 4 levels of acid (vinegar solution; neutral, weak acid, medium acid, and strong acid). These may be prepared ahead of time or at the time when the different treatments (jars) are set up. Neutral solution = 100% distilled water (dh2o) Weak Acid = 3 parts vinegar to 7 parts dh20 Medium Acid = 7 parts vinegar to 3 parts dh20 Strong Acid = 100% distilled vinegar Setting-up the experiment 1. Label each jar with a number (1-5). 2. Set-up four jars as follows: JAR 1 (Neutral) - 50 mls distilled water JAR 2 (Weak Acid) - 35 mls distilled water - 15 mls vinegar JAR 3 (Medium Acid) - 15 mls distilled water - 35 mls vinegar JAR 4 (Strong Acid) - 50 mls vinegar JAR 5 (River Water) - 50 mls river water 3. Add the same amount of duckweed to each jar. (Approximately ten duckweed plants) 4. Place the jars in a well lit area of the room. Investigating what affect will ph have on 5. With your students develop an organized aquatic plants. way to collect data for two weeks. 6. After adding materials to each jar, cover tightly with clear plastic wrap and secure with rubber band. Teacher Guide/Resources TG 287
Building a Watershed Model
 9 Building a Watershed Model Purpose Students will build a model to identify the characteristics of a watershed. Students will learn how elevation determines the flow of water within a watershed. Overview
9 Building a Watershed Model Purpose Students will build a model to identify the characteristics of a watershed. Students will learn how elevation determines the flow of water within a watershed. Overview
When it Rains it Pours
 Lesson Summary: Students will understand how water is absorbed into the ground. They will also be able to explain the difference between pervious and impervious surfaces. Students will also learn about
Lesson Summary: Students will understand how water is absorbed into the ground. They will also be able to explain the difference between pervious and impervious surfaces. Students will also learn about
GROUNDWATER. Narrative
 GROUNDWATER Narrative BIG IDEAS: Groundwater. is between the grains of sand and gravel.. moves because gravity works underground just like it does above ground.. is connected to surface water. 4. is part
GROUNDWATER Narrative BIG IDEAS: Groundwater. is between the grains of sand and gravel.. moves because gravity works underground just like it does above ground.. is connected to surface water. 4. is part
Florida Watersheds Video Southwest Florida Water Management District
 Teacher s Guide Florida Watersheds Video Download at: http://www.watermatters.org/watershedvideo Middle School Video Length: 11 minutes Lesson Time: One block or class period (approximately 45 minutes)
Teacher s Guide Florida Watersheds Video Download at: http://www.watermatters.org/watershedvideo Middle School Video Length: 11 minutes Lesson Time: One block or class period (approximately 45 minutes)
Materials. Materials. NOTE Delta Education Customer Service can be reached at
 w Weather and Water Measuring Matter Materials Materials Contents Kit Inventory List... 42 Materials Supplied by the Teacher... 45 Preparing the Kit for Your Classroom... 47 Care, Reuse, and Recycling...
w Weather and Water Measuring Matter Materials Materials Contents Kit Inventory List... 42 Materials Supplied by the Teacher... 45 Preparing the Kit for Your Classroom... 47 Care, Reuse, and Recycling...
What is a Watershed? Summary. Background. Chicago River Classroom Activity
 Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They will then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They will then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Module 4.3. Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? CT Science Framework Topics
 Module 4.3 Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? Science Content Standard 4.3 CT Science Framework Topics 1. Water is continuously moving
Module 4.3 Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? Science Content Standard 4.3 CT Science Framework Topics 1. Water is continuously moving
Lesson Plan: Stream Table Investigation By: Lauri Dahlin
 Lesson Plan: Stream Table Investigation By: Lauri Dahlin Target Grade: 4 th Teacher Prep Time: 1 hour Lesson Time: 3½ hours (We recommend doing this lesson over 4 days.) Day 1 o 15 min. Beginning Thoughts
Lesson Plan: Stream Table Investigation By: Lauri Dahlin Target Grade: 4 th Teacher Prep Time: 1 hour Lesson Time: 3½ hours (We recommend doing this lesson over 4 days.) Day 1 o 15 min. Beginning Thoughts
GREENHOUSE LAB EXPERIMENTAL FOUNDATIONS OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE BROUGHT ON BY CARBON DIOXIDE POLLUTION
 GREENHOUSE LAB EXPERIMENTAL FOUNDATIONS OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE BROUGHT ON BY CARBON DIOXIDE POLLUTION STUDENT VERSION: PART 1...1-10 PART 2...11-14 PART 3...15-17 TEACHER INFORMATION PAGES: PART 1...18-26
GREENHOUSE LAB EXPERIMENTAL FOUNDATIONS OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE BROUGHT ON BY CARBON DIOXIDE POLLUTION STUDENT VERSION: PART 1...1-10 PART 2...11-14 PART 3...15-17 TEACHER INFORMATION PAGES: PART 1...18-26
Analyzing Groundwater
 Analyzing Groundwater SUBJECTS: Science GRADE LEVELS: 7 th DURATION: approximately two 60 minute periods ACTIVITY SUMMARY: Students will compare the properties of different soil types including texture
Analyzing Groundwater SUBJECTS: Science GRADE LEVELS: 7 th DURATION: approximately two 60 minute periods ACTIVITY SUMMARY: Students will compare the properties of different soil types including texture
Methods: Record the date and time in the data book.
 Chemical Station Materials & Methods Materials: 3 Tall Plastic Vials with Caps 1 Small Glass Vial with Cap 1 Nitrate Tablet #1 1 ph Tablet 1 Nitrate Tablet #2 1 Phosphate Tablet 2 Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
Chemical Station Materials & Methods Materials: 3 Tall Plastic Vials with Caps 1 Small Glass Vial with Cap 1 Nitrate Tablet #1 1 ph Tablet 1 Nitrate Tablet #2 1 Phosphate Tablet 2 Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
Key Concept One. The Okanagan Watershed
 Key Concept One The Okanagan Watershed Poster Panels, Activities and Essential Learnings for Key Concept One The Okanagan Watershed or Basin includes all the water within and the land surrounding the streams
Key Concept One The Okanagan Watershed Poster Panels, Activities and Essential Learnings for Key Concept One The Okanagan Watershed or Basin includes all the water within and the land surrounding the streams
The Science of Maryland Agriculture
 Edition 3 (2016) The Science of Maryland Agriculture GOAL STATEMENT: Students will develop an understanding of ways in which human activities can cause nonpoint pollution within a watershed. OBJECTIVES:
Edition 3 (2016) The Science of Maryland Agriculture GOAL STATEMENT: Students will develop an understanding of ways in which human activities can cause nonpoint pollution within a watershed. OBJECTIVES:
Objectives: 1. Students. will be able 2. Students 3. Students pollution. 4. Students. Materials: Newspaper. you like. powder. students: Standards:
 Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They willl then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They willl then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
THE CLEAN WATER FACTORY:
 THE CLEAN WATER FACTORY: Green infrastructure in Our Watersheds KEY CONCEPTS METHOD SUSTAINABILITY OF WATER RESOURCES REQUIRES CONSERVATION AND BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES. RESPONSIBILITY FOR WATER IS EVERYONE
THE CLEAN WATER FACTORY: Green infrastructure in Our Watersheds KEY CONCEPTS METHOD SUSTAINABILITY OF WATER RESOURCES REQUIRES CONSERVATION AND BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES. RESPONSIBILITY FOR WATER IS EVERYONE
What Are Floods? Floods 3 5 Flood Science LESSON PLAN 2. Key Terms and Concepts. Purpose. Objectives. Activities
 Flood Science The relationship of floods to the hydrologic cycle, terrain and types of soil can help children understand the risk of flood. Key Terms and Concepts flash flood flood flood plain flood stage
Flood Science The relationship of floods to the hydrologic cycle, terrain and types of soil can help children understand the risk of flood. Key Terms and Concepts flash flood flood flood plain flood stage
What in the World is a Watershed?
 What in the World is a Watershed? LESSON GRADE LEVEL 4-9 CATEGORY Water, Wetlands and Watersheds TOPIC Watersheds and Watercycle LENGTH Part 1: a 60-minute period Part 2: two 60-minute periods SETTING
What in the World is a Watershed? LESSON GRADE LEVEL 4-9 CATEGORY Water, Wetlands and Watersheds TOPIC Watersheds and Watercycle LENGTH Part 1: a 60-minute period Part 2: two 60-minute periods SETTING
Science in the Schoolyard Guide: FOSS California Water Planet. Investigation 3 Evaporation Locations
 Water Planet Water Planet > Investigation 3: Water Vapor > Part 2: Evaporation Locations, page 120 Evaporation Locations Following Part 2, take students outside to expand this investigation. Refer to the
Water Planet Water Planet > Investigation 3: Water Vapor > Part 2: Evaporation Locations, page 120 Evaporation Locations Following Part 2, take students outside to expand this investigation. Refer to the
Reading the River, Summer A Study of Duck Creek Grades 7-8. Jim Young St. Joseph School Campbell County, Kentucky
 Reading the River, Summer 2002 A Study of Duck Creek Grades 7-8 Jim Young St. Joseph School Campbell County, Kentucky Study of Duck Creek The eighth and seventh grade students at Saint Joseph School, Cold
Reading the River, Summer 2002 A Study of Duck Creek Grades 7-8 Jim Young St. Joseph School Campbell County, Kentucky Study of Duck Creek The eighth and seventh grade students at Saint Joseph School, Cold
BACKGROUND: The following is adapted from the Watershed Cruzin Guide:
 GOALS: To introduce students to the Watsonville Wetlands water system To help students identify sources of water pollution and learn how they can avoid polluting the environment To discuss the importance
GOALS: To introduce students to the Watsonville Wetlands water system To help students identify sources of water pollution and learn how they can avoid polluting the environment To discuss the importance
Biochemical Oxygen Demand
 Biochemical Oxygen Demand Computer 20 Oxygen available to aquatic organisms is found in the form of dissolved oxygen. Oxygen gas is dissolved in a stream through aeration, diffusion from the atmosphere,
Biochemical Oxygen Demand Computer 20 Oxygen available to aquatic organisms is found in the form of dissolved oxygen. Oxygen gas is dissolved in a stream through aeration, diffusion from the atmosphere,
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12
 Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12 NR/WQ/2012-5 SET-UP Please allow time to practice using the groundwater model before conducting demonstrations. 1. Remove the groundwater
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12 NR/WQ/2012-5 SET-UP Please allow time to practice using the groundwater model before conducting demonstrations. 1. Remove the groundwater
POLLUTION POLLUTION. Name(s)
 POLLUTION Name(s) Many of the changes that occur on the earth are caused by human intervention. While some of these changes are beneficial to humans and other life forms, others are not. Pollution refers
POLLUTION Name(s) Many of the changes that occur on the earth are caused by human intervention. While some of these changes are beneficial to humans and other life forms, others are not. Pollution refers
Introduction to Water Quality Monitoring Life Science: Grades 4-8
 Introduction to Water Quality Monitoring Life : Grades 4-8 Enduring Understandings 1. Understand and be able to list and describe important water quality factors (temperature, transparency, ph, electrical
Introduction to Water Quality Monitoring Life : Grades 4-8 Enduring Understandings 1. Understand and be able to list and describe important water quality factors (temperature, transparency, ph, electrical
Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds
 Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds Objectives: Students will be able to: describe what happens to water when it hits the ground. recognize that bodies of water are the end product of drainage
Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds Objectives: Students will be able to: describe what happens to water when it hits the ground. recognize that bodies of water are the end product of drainage
There s a Watershed in My Backyard
 There s a Watershed in My Backyard www.ksagclassroom.org There s a Watershed in My Backyard Grade Level: 3-5,6-8 Academic Area(s): Science, Social Studies Topic(s): Earth Science, Geography Rev. August/2017
There s a Watershed in My Backyard www.ksagclassroom.org There s a Watershed in My Backyard Grade Level: 3-5,6-8 Academic Area(s): Science, Social Studies Topic(s): Earth Science, Geography Rev. August/2017
Take the:: By Doing: Using: Seeing Watersheds, warm up Branching Out. By Doing: Using: Water Models. By Doing: Using:
 Take the: Attend the:: Take the:: Thank you for participating in the Arizona Water Festival program! Our program assessment shows that students who experience the entire Water Festival unit, from pre-lessons
Take the: Attend the:: Take the:: Thank you for participating in the Arizona Water Festival program! Our program assessment shows that students who experience the entire Water Festival unit, from pre-lessons
Comprehending Currents II Density-Driven Ocean Currents
 II Density-Driven Ocean Currents Adapted from NASA s visit to an Ocean Planet Curriculum http://topex-www.jpl.nasa.gov/education/activities.html Currents in the ocean are important because they transport
II Density-Driven Ocean Currents Adapted from NASA s visit to an Ocean Planet Curriculum http://topex-www.jpl.nasa.gov/education/activities.html Currents in the ocean are important because they transport
Underwater Avalanche: Turbidity Currents Investigating Density Currents
 Underwater Avalanche: Turbidity Currents Investigating Density Currents OBJECTIVE Students will investigate how changes in density affect the rate at which slurry moves down a slope and what effect changes
Underwater Avalanche: Turbidity Currents Investigating Density Currents OBJECTIVE Students will investigate how changes in density affect the rate at which slurry moves down a slope and what effect changes
Albemarle County Public Schools K-5 Science Program
 Albemarle County Public Schools K-5 Science Program Inventory list of curricular materials by grade level objective from the 1997 K-5 Science Adoption to be carried over into the 2003 K-5 Science Adoption.
Albemarle County Public Schools K-5 Science Program Inventory list of curricular materials by grade level objective from the 1997 K-5 Science Adoption to be carried over into the 2003 K-5 Science Adoption.
OCEAN ACIDIFICATION SUPPLIES AND EQUIPMENT. Per whole group. Per participant. Per team. Grades 6 8, minutes.
 OCEAN Grades 6 8, 9 12 60 minutes ACIDIFICATION DESIGN CHALLENGE Participants design and build a system that uses bubbles to reduce the amount of dissolved carbon dioxide in water, thereby changing the
OCEAN Grades 6 8, 9 12 60 minutes ACIDIFICATION DESIGN CHALLENGE Participants design and build a system that uses bubbles to reduce the amount of dissolved carbon dioxide in water, thereby changing the
Stepping Stone. Name: Date:
 Stepping Stone Name: Date: Description: The project is useful for landscaping. Measurements of the right amount of Portland cement, water, sand, and course aggregates will be used to construct this project.
Stepping Stone Name: Date: Description: The project is useful for landscaping. Measurements of the right amount of Portland cement, water, sand, and course aggregates will be used to construct this project.
InstallatIon. Guidelines. Relax More. A C T G L O B A L. C O M / X T R E M E L A W N E M A I L : X T R M E L A W A C T G L O B A L.
 InstallatIon Guidelines Relax More. Installation Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. Required Materials 1. Xtreme Lawn 2. Shovel or gas powered sod cutter 3. Vibrating plate compactor 4. Weed barrier mesh 5. Rock aggregate
InstallatIon Guidelines Relax More. Installation Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. Required Materials 1. Xtreme Lawn 2. Shovel or gas powered sod cutter 3. Vibrating plate compactor 4. Weed barrier mesh 5. Rock aggregate
Science Unit: Surface Water and Groundwater
 Science Unit: Lesson 2: Water Surface Water and Groundwater School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School
Science Unit: Lesson 2: Water Surface Water and Groundwater School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School
GOOEY GARBAGE. Dear Presenter,
 Dear Presenter, This is a 20 to 25 minute presentation and HANDS-ON activity for approximately 25-30 ten year-old children. You MUST do this activity at home BEFORE you attempt to lead the activity during
Dear Presenter, This is a 20 to 25 minute presentation and HANDS-ON activity for approximately 25-30 ten year-old children. You MUST do this activity at home BEFORE you attempt to lead the activity during
Lesson. Conductors: Testing the Transfer of Heat Energy A QUICK LOOK. Overview. Big Idea. Process Skills Key Notes
 ENERGY CLUSTER 3 HEAT ENERGY TRANSFERS Lesson 62 Conductors: Testing the Transfer of Heat Energy A QUICK LOOK Big Idea Warmer things lose heat, or transfer heat energy, to cooler things. Some materials
ENERGY CLUSTER 3 HEAT ENERGY TRANSFERS Lesson 62 Conductors: Testing the Transfer of Heat Energy A QUICK LOOK Big Idea Warmer things lose heat, or transfer heat energy, to cooler things. Some materials
BUILDING A WATERSHED MODEL
 BUILDING A WATERSHED MODEL OBJECTIVES Define a watershed and describe how it functions Identify that students live in a watershed within the San Antonio River Basin TOPICS Watersheds Runoff TEKS ALIGNMENT
BUILDING A WATERSHED MODEL OBJECTIVES Define a watershed and describe how it functions Identify that students live in a watershed within the San Antonio River Basin TOPICS Watersheds Runoff TEKS ALIGNMENT
Student Instructions for Modeling the Water Cycle
 Student Instructions for Modeling the Water Cycle 1. Cover your work space with the large absorbent pad. Make sure the absorbent side faces up and the plastic side is down. 2. Place the small absorbent
Student Instructions for Modeling the Water Cycle 1. Cover your work space with the large absorbent pad. Make sure the absorbent side faces up and the plastic side is down. 2. Place the small absorbent
THE ADVENTURES OF FRED FISH PART I:
 THE ADVENTURES OF FRED FISH PART I: Students will demonstrate the affects of pollution on water using a story of Fred Fish. Materials: Small paper cups with the following: (2 T unless specified) 2. Soil
THE ADVENTURES OF FRED FISH PART I: Students will demonstrate the affects of pollution on water using a story of Fred Fish. Materials: Small paper cups with the following: (2 T unless specified) 2. Soil
Where Does Our Drinking Water Come From?
 Reading Selection Where Does Our Drinking Water Come From? Have you been keeping track of how much water you use each day? Just think of all the ways you use water. You use it to wash your face after you
Reading Selection Where Does Our Drinking Water Come From? Have you been keeping track of how much water you use each day? Just think of all the ways you use water. You use it to wash your face after you
Construct a Watershed Model Adapted from A MyScienceBox Lesson Plan by Irene Salter (
 Construct a Watershed Model Adapted from A MyScienceBox Lesson Plan by Irene Salter (http://www.mysciencebox.org) Summary Simple materials are turned into models of wetlands and watersheds in this simple
Construct a Watershed Model Adapted from A MyScienceBox Lesson Plan by Irene Salter (http://www.mysciencebox.org) Summary Simple materials are turned into models of wetlands and watersheds in this simple
15A Carbon Dioxide and Living Things
 Carbon Dioxide and Living Things Investigation 15A 15A Carbon Dioxide and Living Things How do living things exchange carbon dioxide? The carbon cycle is a series of pathways through which carbon atoms
Carbon Dioxide and Living Things Investigation 15A 15A Carbon Dioxide and Living Things How do living things exchange carbon dioxide? The carbon cycle is a series of pathways through which carbon atoms
Nueces River Watershed
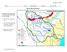 Name period Date assigned date due date returned Directions: You will color parts of the on the next page: 1. Trace the rivers and lakes in blue 2. Trace the outside edge of the watershed in red (it s
Name period Date assigned date due date returned Directions: You will color parts of the on the next page: 1. Trace the rivers and lakes in blue 2. Trace the outside edge of the watershed in red (it s
Activity 1: Flood Storage
 Activity 1: Flood Storage Overview Background Students will observe how different soil components peat, sand, gravel, and potting soil vary in their capacity to absorb and hold water. They will observe
Activity 1: Flood Storage Overview Background Students will observe how different soil components peat, sand, gravel, and potting soil vary in their capacity to absorb and hold water. They will observe
Bulk Density Protocol
 Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the bulk density of each horizon in a soil profile Overview In the field, students collect three soil samples from each horizon in a soil profile using a container
Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the bulk density of each horizon in a soil profile Overview In the field, students collect three soil samples from each horizon in a soil profile using a container
Lesson Title: How Natural Areas Filter Water
 Lesson Title: How Natural Areas Filter Water Essential question: Science Topic: Natural Resources How do paved areas impact the filtration of rainwater? Lesson Overview: Students learn about the importance
Lesson Title: How Natural Areas Filter Water Essential question: Science Topic: Natural Resources How do paved areas impact the filtration of rainwater? Lesson Overview: Students learn about the importance
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 Water Sampler # 15010 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Purpose: Contents: For the collection of water samples at varying depths or distances away from a shoreline. One (1) Assembled Water Sampler One (1) Cord (15
Water Sampler # 15010 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Purpose: Contents: For the collection of water samples at varying depths or distances away from a shoreline. One (1) Assembled Water Sampler One (1) Cord (15
Dirty Water. Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, Grade Level: all. Duration: 1-2 class periods
 Dirty Water Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Grade Level: all Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom or laboratory Summary:
Dirty Water Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Grade Level: all Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom or laboratory Summary:
Macroinvertebrate Investigation
 Macroinvertebrate Investigation PURPOSE: To introduce students to living aquatic macroinvertebrates in a field setting. SUMMARY: Students will collect live macroinvertebrates from a river or stream. They
Macroinvertebrate Investigation PURPOSE: To introduce students to living aquatic macroinvertebrates in a field setting. SUMMARY: Students will collect live macroinvertebrates from a river or stream. They
Lesson Focus: watershed and non point source pollution
 From Brook to Ocean Lesson Focus: watershed and non point source pollution Lesson objectives: To create an understanding that everyone is part of a watershed and that humans can affect that watershed in
From Brook to Ocean Lesson Focus: watershed and non point source pollution Lesson objectives: To create an understanding that everyone is part of a watershed and that humans can affect that watershed in
AT HOME SCIENTIST! SHARKS
 SHARKS Sharks are amazing and often misunderstood creatures of the sea. Without them, the ocean food chain would be affected, and the balance of life in the ocean would be disrupted. Have you wondered
SHARKS Sharks are amazing and often misunderstood creatures of the sea. Without them, the ocean food chain would be affected, and the balance of life in the ocean would be disrupted. Have you wondered
A DIVISION OF INSTALLATION. Guide. Relax More.
 A DIVISION OF INSTALLATION Guide Relax More. Turfscape Installation Guide Required Materials Turfscape Shovel or gas powered sod puller Vibrating plate compactor Weed barrier mesh Rock aggregate Utility
A DIVISION OF INSTALLATION Guide Relax More. Turfscape Installation Guide Required Materials Turfscape Shovel or gas powered sod puller Vibrating plate compactor Weed barrier mesh Rock aggregate Utility
Reading the River Summer 2004 July 31, A Unit for Grade 8 Science An Adventure in Water. Karyl White Rowan County Middle School Rowan County
 Reading the River Summer 2004 July 31, 2004 A Unit for Grade 8 Science An Adventure in Water Karyl White Rowan County Middle School Rowan County Grade Level: 8 Create a Model Filtration System to Purify
Reading the River Summer 2004 July 31, 2004 A Unit for Grade 8 Science An Adventure in Water Karyl White Rowan County Middle School Rowan County Grade Level: 8 Create a Model Filtration System to Purify
Grade 5 Hands-on activities
 Grade 5 Hands-on activities Hands-on investigation Hands-on learning is at the heart of Amplify Science, and is integrated into every unit. Each hands-on activity provides clear instructions for the teacher,
Grade 5 Hands-on activities Hands-on investigation Hands-on learning is at the heart of Amplify Science, and is integrated into every unit. Each hands-on activity provides clear instructions for the teacher,
Unit 2M.2: Investigating Materials
 Unit 2M.2: Investigation (1) Waterproof Materials Bendy and Flexible Materials (2) Shiny and Dull Materials Transparent and Opaque Materials. Science skills: Classifying Observing Predicting Measuring
Unit 2M.2: Investigation (1) Waterproof Materials Bendy and Flexible Materials (2) Shiny and Dull Materials Transparent and Opaque Materials. Science skills: Classifying Observing Predicting Measuring
Advanced Water Quality Monitoring and Analysis Life Science: Grades 7-12
 Advanced Water Quality Monitoring and Analysis Life : Grades 7-12 Enduring Understandings 1. Understand and be able to list and describe important water quality factors (temperature, transparency, ph,
Advanced Water Quality Monitoring and Analysis Life : Grades 7-12 Enduring Understandings 1. Understand and be able to list and describe important water quality factors (temperature, transparency, ph,
Evaluation copy. Managing Garden Soil Moisture. Experiment OBJECTIVES MATERIALS PROCEDURE
 Managing Garden Soil Moisture Experiment 6 Compost, aerobically decomposed remnants of organic materials, is commonly mixed into soil to improve soil fertility and water holding capacity. Grass clippings,
Managing Garden Soil Moisture Experiment 6 Compost, aerobically decomposed remnants of organic materials, is commonly mixed into soil to improve soil fertility and water holding capacity. Grass clippings,
Lesson 1 Introduction to Unit
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Unit Teacher instructions for Lesson One Overview Lesson One introduces sedimentation as a nonpoint source of pollution involving soils in runoff from the watershed into the surface
Lesson 1 Introduction to Unit Teacher instructions for Lesson One Overview Lesson One introduces sedimentation as a nonpoint source of pollution involving soils in runoff from the watershed into the surface
Make Every Breath Count
 QuickLab Make Every Breath Count MATERIALS beaker, 250 ml bromthymol blue Elodea, sprig graduated cylinder stopper straw test tube,large water, 100 ml SAFETY PROCEDURE 1. Pour 100 ml of water from a graduated
QuickLab Make Every Breath Count MATERIALS beaker, 250 ml bromthymol blue Elodea, sprig graduated cylinder stopper straw test tube,large water, 100 ml SAFETY PROCEDURE 1. Pour 100 ml of water from a graduated
Benthic Macroinvertebrate Monitoring
 Benthic Macroinvertebrate Monitoring "In the end, we will conserve only what we love, we will love only what we understand, we will understand only what we are taught." - Bada Dioum, Senegalese conservationist
Benthic Macroinvertebrate Monitoring "In the end, we will conserve only what we love, we will love only what we understand, we will understand only what we are taught." - Bada Dioum, Senegalese conservationist
When Rain Hits the Land Experimenting with Runoff
 When Rain Hits the Land Experimenting with Runoff Overview In this activity students will do an experiment to determine how land surfaces affect the flow of rain water as it flows through the watershed.
When Rain Hits the Land Experimenting with Runoff Overview In this activity students will do an experiment to determine how land surfaces affect the flow of rain water as it flows through the watershed.
Chapter 13 Water Resources
 Chapter 13 Water Resources Where does your drinking water come from? I. Earth s Water Supply A. Where is Earth s water? 1. 97.2% - oceans 2. 2.2% - icecaps and glaciers 3. 0.6% - surface or groundwater
Chapter 13 Water Resources Where does your drinking water come from? I. Earth s Water Supply A. Where is Earth s water? 1. 97.2% - oceans 2. 2.2% - icecaps and glaciers 3. 0.6% - surface or groundwater
Water, Water Everywhere
 Water, Water Everywhere Overview: Students explore the location of water on Earth using a terrarium to model the water cycle. (NOTE: This lesson requires two separate days.) Level I Grades K-2 Objectives:
Water, Water Everywhere Overview: Students explore the location of water on Earth using a terrarium to model the water cycle. (NOTE: This lesson requires two separate days.) Level I Grades K-2 Objectives:
Bulk Density Protocol
 Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the soil bulk density of each horizon in your soil profile. Overview Students obtain a soil sample in the field using a container with a measured volume. The soil
Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the soil bulk density of each horizon in your soil profile. Overview Students obtain a soil sample in the field using a container with a measured volume. The soil
Just Passing Through. Suggested Grade Level 6-8. Estimated Time 45 minutes. Objectives Students will be able to:
 Just Passing Through Overview Students will investigate soils and observe how water moves through soil, how soil properties affect flow rate and water holding capacity. Students time the flow of water
Just Passing Through Overview Students will investigate soils and observe how water moves through soil, how soil properties affect flow rate and water holding capacity. Students time the flow of water
Lesson Plan Title: Batteries One Option in Energy Storage
 Jody Smith Paris Cooperative High School Paris, IL June 25, 2014 Lesson Plan Title: Batteries One Option in Energy Storage Introduction: This lesson plan will allow students to learn about the use of batteries
Jody Smith Paris Cooperative High School Paris, IL June 25, 2014 Lesson Plan Title: Batteries One Option in Energy Storage Introduction: This lesson plan will allow students to learn about the use of batteries
Shower Curtain Watershed
 Topic Watersheds Shower Curtain Watershed Grades 3-5 Sites Outdoors, Indoors Duration 30 minutes Materials Watershed pictures Labels or index cards Clear plastic shower curtain Spray bottles with water
Topic Watersheds Shower Curtain Watershed Grades 3-5 Sites Outdoors, Indoors Duration 30 minutes Materials Watershed pictures Labels or index cards Clear plastic shower curtain Spray bottles with water
6x5. Assembly Manual CAUTION. Sharp Edges PATENTS ARE PENDING. Building Dimensions. Approximate Size. Storage Area. Interior Dimensions
 Assembly Manual 6x5 PATENTS ARE PENDING Building Dimensions Approximate Size Storage Area Exterior Dimensions Interior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge Wall to Wall Sq. Ft. Cu. Ft. Width Depth Height
Assembly Manual 6x5 PATENTS ARE PENDING Building Dimensions Approximate Size Storage Area Exterior Dimensions Interior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge Wall to Wall Sq. Ft. Cu. Ft. Width Depth Height
Water Habitat Experiment
 outcome Materials Water Habitat Experiment! 2 medium-sized tanks or tubs (preferably transparent), labelled! Habitat lll and Habitat 2! Bin filled with sand and a scoop! Bin filled with rocks and a scoop!
outcome Materials Water Habitat Experiment! 2 medium-sized tanks or tubs (preferably transparent), labelled! Habitat lll and Habitat 2! Bin filled with sand and a scoop! Bin filled with rocks and a scoop!
WATER PROTECTION: DOWN THE SEWER
 ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION: This activity introduces students to the idea that many household chemicals are classified as hazardous waste. It also informs students that the water and other substances/items that
ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION: This activity introduces students to the idea that many household chemicals are classified as hazardous waste. It also informs students that the water and other substances/items that
Watershed Tarp Activity
 Watershed Tarp Activity Grade Level: 3 rd High School Duration: Prep: 15 minutes Activity: 25-35 minutes Objectives: Students will be able to define a watershed, identify the physical boundary of a watershed
Watershed Tarp Activity Grade Level: 3 rd High School Duration: Prep: 15 minutes Activity: 25-35 minutes Objectives: Students will be able to define a watershed, identify the physical boundary of a watershed
Name. Your Handbook and Journal of. Lake name. Lake Water Quality
 Your Handbook and Journal of Name Lake name Lake Water Quality Table of Contents Page # Section 1 Why do we care about clean water?... 4 How do lakes work?... 5 Section 2 How do we measure the health of
Your Handbook and Journal of Name Lake name Lake Water Quality Table of Contents Page # Section 1 Why do we care about clean water?... 4 How do lakes work?... 5 Section 2 How do we measure the health of
Science Supply Lists
 2014-2015 Science Supply Lists Earth Science 2014 Glynlyon, Inc Table of Contents UNIT 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 2: FORCES AND FEATURES OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 3: FEATURES OF EARTH'S CRUST...
2014-2015 Science Supply Lists Earth Science 2014 Glynlyon, Inc Table of Contents UNIT 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 2: FORCES AND FEATURES OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 3: FEATURES OF EARTH'S CRUST...
Where does your water shed? National Association of Conservation Districts (NACD) Poster Contest Promotion 2013 Contest
 Slide 1 Where does your water shed? National Association of Conservation Districts (NACD) Poster Contest Promotion 2013 Contest 1 Slide 2 Where does your water shed? Share an activity to show how water
Slide 1 Where does your water shed? National Association of Conservation Districts (NACD) Poster Contest Promotion 2013 Contest 1 Slide 2 Where does your water shed? Share an activity to show how water
National Aquatic Monitoring Center (NAMC): Protocol for the Collection of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Samples
 National Aquatic Monitoring Center (NAMC): Protocol for the Collection of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Samples Overview The described sampling protocol was designed to generate data sufficient to characterize
National Aquatic Monitoring Center (NAMC): Protocol for the Collection of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Samples Overview The described sampling protocol was designed to generate data sufficient to characterize
Effects of Turbulence on Dissolved Oxygen
 Effects of Turbulence on Dissolved Oxygen Lesson Focus: This lesson focuses on the importance of dissolved oxygen to a healthy aquatic ecosystem and how dissolved oxygen in water can be increased. This
Effects of Turbulence on Dissolved Oxygen Lesson Focus: This lesson focuses on the importance of dissolved oxygen to a healthy aquatic ecosystem and how dissolved oxygen in water can be increased. This
Grades 3 & 4 Biogas As A Source Of Energy
 Grades 3 & 4 Biogas As A Source Of Energy Objectives The students will: Analyze the importance of energy and how they use energy in their lives. Describe the difference between renewable and non renewable
Grades 3 & 4 Biogas As A Source Of Energy Objectives The students will: Analyze the importance of energy and how they use energy in their lives. Describe the difference between renewable and non renewable
When the Oxygen is Gone
 When the Oxygen is Gone Need for Oxygen Adapted from: Activity 24 "When the oxygen is gone" in Living in Water. The National Aquarium in Baltimore. 1997 Grade Level: Intermediate Duration: 1 class period
When the Oxygen is Gone Need for Oxygen Adapted from: Activity 24 "When the oxygen is gone" in Living in Water. The National Aquarium in Baltimore. 1997 Grade Level: Intermediate Duration: 1 class period
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality
 Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
Aquatic Species Diversity and Water Quality
 Aquatic Species Diversity and Water Quality Reference: Wagner & Sanford. Environmental Science. Wiley & Sons, 2005 Introduction: Freshwater is only a small part of the Earth s supply of water, yet it is
Aquatic Species Diversity and Water Quality Reference: Wagner & Sanford. Environmental Science. Wiley & Sons, 2005 Introduction: Freshwater is only a small part of the Earth s supply of water, yet it is
Step-by-Step Instructions for Lesson and Materials List
 Step-by-Step Instructions for Lesson and Materials List Materials: Modeling clay (beige, terra cotta, dark brown, green) 1 - Roll the beige, dark brown, and green modeling clay into flat layers using a
Step-by-Step Instructions for Lesson and Materials List Materials: Modeling clay (beige, terra cotta, dark brown, green) 1 - Roll the beige, dark brown, and green modeling clay into flat layers using a
Mosquito Larvae Protocol Mosquito Larvae Sampling Field Guide
 Mosquito Larvae Protocol Mosquito Larvae Sampling Field Guide Task Collect and identify mosquito larvae to the genus level. Samples can be taken for species level identification in the lab. What You Need
Mosquito Larvae Protocol Mosquito Larvae Sampling Field Guide Task Collect and identify mosquito larvae to the genus level. Samples can be taken for species level identification in the lab. What You Need
OIMB GK12 CURRICULUM
 3 rd Grade 45 minutes MARSHES AS FILTERS Oregon Science Content Standards: 3.1 Structure and Function: Living and non-living things vary in their characteristics and properties. 3.2 Interaction and Change:
3 rd Grade 45 minutes MARSHES AS FILTERS Oregon Science Content Standards: 3.1 Structure and Function: Living and non-living things vary in their characteristics and properties. 3.2 Interaction and Change:
Objectives Introduction restriction endonucleases Examples: Hind III: Eco RI: Pst I:
 Objectives Before doing this lab you should understand how gel electrophoresis separates DNA molecules present in a mixture and how restriction endonucleases function. After doing this lab you should be
Objectives Before doing this lab you should understand how gel electrophoresis separates DNA molecules present in a mixture and how restriction endonucleases function. After doing this lab you should be
1. Students will become familiar with the sources of water pollution
 Educators, Please Note! WLSSD education staff is available to present the Water Drop program upon request, call Sarah at (218) 740-4784 to schedule an appointment. Lesson Plan: River Rangers Water Quality
Educators, Please Note! WLSSD education staff is available to present the Water Drop program upon request, call Sarah at (218) 740-4784 to schedule an appointment. Lesson Plan: River Rangers Water Quality
BEFORE YOU GET STARTED...
 BEFORE YOU GET STARTED... We re con dent you ll love your gorgeous new Next furniture. However, it s worth making absolutely certain before you put it all together. So, let s quickly run through these
BEFORE YOU GET STARTED... We re con dent you ll love your gorgeous new Next furniture. However, it s worth making absolutely certain before you put it all together. So, let s quickly run through these
That Sinking Feeling: Density Currents Lab
 Details That Sinking Feeling: Density Currents Lab Completion Time: About 1 period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Overview Density currents drive 3D movements within the world s oceans that dwarf
Details That Sinking Feeling: Density Currents Lab Completion Time: About 1 period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Overview Density currents drive 3D movements within the world s oceans that dwarf
LESSON 1 CONCEPTS: (pre-tour) WATER YOU NEED. Activity Overview: Vocabulary: Students will learn: Time Requirement: Materials: Preparation:
 LESSON 1 (pre-tour) WATER YOU NEED CONCEPTS: Students will learn: how the hydrologic cycle works and why it is important how much fresh water is available on Earth how much water we use for various activities
LESSON 1 (pre-tour) WATER YOU NEED CONCEPTS: Students will learn: how the hydrologic cycle works and why it is important how much fresh water is available on Earth how much water we use for various activities
1850 x 40/50mm Raised Shower Tray Kit
 Installation Instructions 850 x 40/50mm Raised Shower Tray Kit Parts Supplied Description Qty Shower Tray Shower Tray Extension Parts Required (Fitting Kit) Materials Required Description Qty Description
Installation Instructions 850 x 40/50mm Raised Shower Tray Kit Parts Supplied Description Qty Shower Tray Shower Tray Extension Parts Required (Fitting Kit) Materials Required Description Qty Description
PATENTS ARE PENDING. Building Dimensions. Exterior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge
 Assembly Manual 8x5 PATENTS ARE PENDING Approximate Size 7980303 Storage Area Building Dimensions Exterior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge Interior Dimensions Wall to Wall Sq. Ft. Cu. Ft. Width Depth
Assembly Manual 8x5 PATENTS ARE PENDING Approximate Size 7980303 Storage Area Building Dimensions Exterior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge Interior Dimensions Wall to Wall Sq. Ft. Cu. Ft. Width Depth
Eutrophication: Too Much of a Good Thing?
 Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab DATASHEET FOR IN-TEXT LAB Eutrophication: Too Much of a Good Thing? Plants depend on nutrients such as phosphates and nitrates to survive. However, when people release
Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab DATASHEET FOR IN-TEXT LAB Eutrophication: Too Much of a Good Thing? Plants depend on nutrients such as phosphates and nitrates to survive. However, when people release
Rain Forests. America's. Water Wonders. Rain Forest Ecology. Prince William Network's OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES SUBJECTS
 Rain Forest Ecology National Science Education Standards Standard B: Physical Science Transfer of energy. Standard B: Physical Science Properties and changes of properties in matter. Standard C: Life Sciences
Rain Forest Ecology National Science Education Standards Standard B: Physical Science Transfer of energy. Standard B: Physical Science Properties and changes of properties in matter. Standard C: Life Sciences
Name Lab Section Date. Sediment Lab
 Name Lab Section Date. Investigating Stokes Law Sediment Lab ds = density of solid, g/cm dw = density of water, g/cm g = gravity, 980 cm/second 2 D = particle diameter in centimeters μ = molecular viscosity,
Name Lab Section Date. Investigating Stokes Law Sediment Lab ds = density of solid, g/cm dw = density of water, g/cm g = gravity, 980 cm/second 2 D = particle diameter in centimeters μ = molecular viscosity,
Multi-plate Sampling
 Multi-plate Sampling Sampling method multi-plate sampler Adapted from: Field Manual for Water Quality Monitoring, Aquatic Entomology, and State of Ohio Environmental Protection Agency: Biological Criteria
Multi-plate Sampling Sampling method multi-plate sampler Adapted from: Field Manual for Water Quality Monitoring, Aquatic Entomology, and State of Ohio Environmental Protection Agency: Biological Criteria
Water, Water Everywhere
 Water, Water Everywhere Overview: Students explore the location of water on Earth using a terrarium to model the water cycle. (NOTE: This lesson requires two separate days.) Grades 3-4 Objectives: The
Water, Water Everywhere Overview: Students explore the location of water on Earth using a terrarium to model the water cycle. (NOTE: This lesson requires two separate days.) Grades 3-4 Objectives: The
PATENTS ARE PENDING. Building Dimensions. Exterior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge
 Assembly Manual 8x9 PATENTS ARE PENDING Approximate Size 7640303 Storage Area Building Dimensions Exterior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge Interior Dimensions Wall to Wall Sq. Ft. Cu. Ft. Width Depth
Assembly Manual 8x9 PATENTS ARE PENDING Approximate Size 7640303 Storage Area Building Dimensions Exterior Dimensions Roof Edge to Roof Edge Interior Dimensions Wall to Wall Sq. Ft. Cu. Ft. Width Depth
Can water pressure influence water flow?
 Unit 2 How is Flowing Water an Energy Source? Activity B Can water pressure influence water flow? Introduction Water pressure influences the rate of water flow. As pressure increases, so does the rate
Unit 2 How is Flowing Water an Energy Source? Activity B Can water pressure influence water flow? Introduction Water pressure influences the rate of water flow. As pressure increases, so does the rate
DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF
 DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF THE LEAKY FAUCET Outcome (lesson objective) Students will gather scientific data and be able to utilize the data to generalize the results over a long period of time. Student/Class
DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF THE LEAKY FAUCET Outcome (lesson objective) Students will gather scientific data and be able to utilize the data to generalize the results over a long period of time. Student/Class
Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D.
 Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
Illustrations: Janet Moneymaker Rebecca W. Keller, Ph.D. Copyright 2011 Gravitas Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
What in the World is a Watershed? There s a Watershed in My Backyard - Activity 1
 Soil & Water What in the World is a Watershed? There s a Watershed in My Backyard - Activity 1 Science, Geography Materials Umbrella Spray bottle with water Large bath towel Supplemental watershed diagram
Soil & Water What in the World is a Watershed? There s a Watershed in My Backyard - Activity 1 Science, Geography Materials Umbrella Spray bottle with water Large bath towel Supplemental watershed diagram
