Principles of Management. Lecture - 8
|
|
|
- Adam Farmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Management Lecture - 8
2 LEADERSHIP THEORIES TRAIT THEORY GHISELLI BASES OF INFLUENCE (POWER) FRENCH & RAVEN BEHAVIORAL THEORIES OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BLAKE & MOUTON CONTINGENCY THEORIES FIEDLER HOUSE & MITCHELL VROOM & YETTON ROLE THEORIES MINTZBERG
3 TRAIT APPROACHES TO LEADERSHIP GHISELLI LEADERS ARE BORN, NOT MADE PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS APPEARANCE, HEIGHT, AGE PERSONALITY EXTROVERSION, PERSISTENCE, SELF-ASSURANCE, DECISIVENESS INTELLIGENCE KNOWLEDGE, ABILITY, JUDGMENT SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS TACT, DIPLOMACY, SOCIABILITY, FLUENCY THE BIG FIVE PERSONALITY TRAITS *** EXTROVERSION (AMBITION, ENERGY) ** CONSCIENTIOUSNESS ** OPENNESS TO EXPERIENCE * EMOTIONAL STABILITY (SELF-CONFIDENCE) AGREEABLENESS
4 Trait Theories Traits Theories of Leadership Theories that consider personality, social, physical, or intellectual traits to differentiate leaders from nonleaders. Leadership Traits: Ambition and energy The desire to lead Honest and integrity Self-confidence Intelligence High self-monitoring Job-relevant knowledge
5 Trait Theories Limitations: No universal traits found that predict leadership in all situations. Traits predict behavior better in weak than strong situations. Unclear evidence of the cause and effect of relationship of leadership and traits. Better predictor of the appearance of leadership than distinguishing effective and ineffective leaders.
6 Behavioral Theories Behavioral Theories of Leadership Theories proposing that specific behaviors differentiate leaders from nonleaders. Trait theory: Leaders are born, not made. Behavioral theory: Leadership traits can be taught.
7 Ohio State Studies Initiating Structure The extent to which a leader is likely to define and structure his or her role and those of subordinates in the search for goal attainment. Consideration The extent to which a leader is likely to have job relationships characterized by mutual trust, respect for subordinate s ideas, and regard for their feelings.
8 University of Michigan Studies Employee-Oriented Leader Emphasizing interpersonal relations; taking a personal interest in the needs of employees and accepting individual differences among members. Production-Oriented Leader One who emphasizes technical or task aspects of the job.
9 The Managerial Grid (Blake and Mouton)
10 THE MANAGERIAL GRID BLAKE & MOUTON (64) COUNTRY-CLUB TEAM (1,9) (9,9) CONCERN FOR PEOPLE (5,5) MIDDLE OF ROAD IMPOVERISHED TASK 1 (1,1) (9,1) CONCERN FOR PRODUCTION
11 Scandinavian Studies Development-Oriented Leader One who values experimentation, seeking new ideas, and generating and implementing change. Researchers in Finland and Sweden question whether there are only two dimensions (production-orientation and employee-orientation) that capture the essence of leadership behavior. Their premise is that in a changing world, effective leaders would exhibit development-oriented behavior.
12 Contingency Theories Fiedler s Contingency Model The theory that effective groups depend on a proper match between a leader s style of interacting with subordinates and the degree to which the situation gives control and influence to the leader. Least Preferred Co-Worker (LPC) Questionnaire An instrument that purports to measure whether a person is taskor relationship-oriented.
13 Fiedler s Model: Defining the Situation Leader-Member Relations The degree of confidence, trust, and respect subordinates have in their leader. Task Structure The degree to which the job assignments are procedurized. Position Power Influence derived from one s formal structural position in the organization; includes power to hire, fire, discipline, promote, and give salary increases.
14 Findings from Fiedler Model
15 Cognitive Resource Theory Cognitive Resource Theory A theory of leadership that states that stress can unfavorably affect a situation and that intelligence and experience can lessen the influence of stress on the leader. Research Support: Less intelligent individuals perform better in leadership roles under high stress than do more intelligent individuals. Less experienced people perform better in leadership roles under low stress than do more experienced people.
16 Hersey and Blanchard s Situational Leadership Theory Situational Leadership Theory (SLT) A contingency theory that focuses on followers readiness. Unable and Unwilling Unable but Willing Able and Unwilling Able and Willing Follower readiness: ability and willingness Leader: decreasing need for support and supervision Directive High Task and Relationship Orientations Supportive Participative Monitoring
17 Leadership Styles and Follower Follower Readiness Readiness (Hersey and Blanchard) Unwilling Willing Able Supportive Participative Monitoring Unable Directive Leadership Styles High Task and Relationship Orientations
18 Leader Member Exchange Theory Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory Leaders create in-groups and out-groups, and subordinates with in-group status will have higher performance ratings, less turnover, and greater job satisfaction.
19 Path-Goal Theory Path-Goal Theory The theory that it is the leader s job to assist followers in attaining their goals and to provide them the necessary direction and/or support to ensure that their goals are compatible with the overall objectives of the group or organization.
20 The Path-Goal Theory
21 Leader-Participation Model Leader-Participation Model (Vroom and Yetton) A leadership theory that provides a set of rules to determine the form and amount of participative decision making in different situations.
22 Factors Affecting Style Leadership style may be dependent on various factors: Risk - decision making and change initiatives based on degree of risk involved Type of business creative business or supply driven? How important change is change for change s sake? Organisational culture may be long embedded and difficult to change Nature of the task needing cooperation? Direction? Structure?
23 4 Leadership styles S1: Telling S2: Selling S3: Participating S4: Delegating 4 Levels of Maturity M1: Low, Immature M2: Low to Moderate M3: Moderate to High M4: High, Mature Low Moderate 4 Levels of Maturity of Followers High M1 M2 M3 M4 Telling Selling Participating Delegating
24 4 Development Levels D1: Low competence, High commitment D2: Some competence, Low commitment D3: High competence, Variable commitment D4: High competence, High commitment Low Moderate High Development Levels of Followers D1 D2 D3 D4 S1: Tell S2:Sell S3: Participate S4: Delegate
25 Supportive Behavior Directive Behavior Participating Q3 S3: High Relationship Low Task D3: Able but unwilling or insecure Delegating Q4 S4: Low Relationship Low Task D4: Able/competent & willing/confident Mature Selling Q2 S2: High Relationship High Task D2: Unable but willing or confident Telling Q1 S1: Low Relationship High Task D1: Unable & unwilling or insecure Immature
26 Summary of Leadership Theories Theory Trait Theory Behavioral Theory Leadership Based On Leaders born with leadership traits Initial structure and consideration - Role Theory Shaped by culture, training, modeling - Managerial Grid Concern for production and concern for people Participative Leadership More people involved = better collaboration - Lewin s Style Autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire - Likert s Style Task oriented, relationship oriented, participative style Contingency Theories No one best leadership style - Fiedler s LPC Theory Task focus v. relationship focus - Cognitive Resource Theory Intelligence and experience make a difference - House s Path Goal Theory Help followers make their goals compatible with organizational goals Situational Leadership Similar to contingency theory - Hersey and Blanchard Based on relationship between leader and follower and task behavior - Vroom & Yetton Decision quality and decision acceptance
27 Motivation, Satisfaction, and Performance
28 Introduction (Cont.) Motivation is the psychological process that leads to Choice of behavior that results in Some level of job performance The Motivation-Behavior-Job Performance Sequence
29 Motivation Motivation is anything that provides direction, intensity, and persistence to behavior.
30 Needs Theories Maslow Herzberg Self-Actualisation Esteem Motivators Social Safety Hygiene Factors Physiological
31 Theories of Motivation Needs theories Maslow s hierarchy of needs Herzberg s two factor theory Process theories Expectancy Theory Goal Setting Theory
32 Expectancy Theory (Vroom) Individual Effort 1 2 Individual Performance Organisational Rewards 3 1. Effort-Performance relationship = Expectancy 2. Performance-Rewards relationship = Instrumentality 3. Rewards-Personal goals relationship = Valence Personal Goals Chapter 6
33 How Expectancy Theory Works Your tutor offers you 1 million if you memorise the textbook by tomorrow morning. Expectancy Instrumentality Valence Effort - Performance Link No matter how much effort you put in, probably not possible to memorise the text in 24 hours E=0 Performance - Rewards Link Your tutor does not look like someone who has 1 million I=0 Rewards - Personal Goals Link There are a lot of wonderful things you could do with 1 million V=1 Conclusion: Though you value the reward, you will not be motivated to do this task.
34 Goal Setting Goals Specific Difficult Accepted Effects on Person Directs attention Energises Encourages persistency New strategies developed Performance Feedback
35 Self-Motivation Self-fulfilment and satisfaction Difficult goals lead to higher performance Motivation to act depends on the attractiveness of the outcome
36 Motivation Direction Intensity Persistence
37 Defining Motivation Key Elements 1. Intensity: how hard a person tries 2. Direction: toward beneficial goal 3. Persistence: how long a person tries
38 Performance Performance concerns those behaviors directed toward the organization s mission or goals, or the products and services resulting from those behaviors.
39 Job satisfaction Job satisfaction deals with one s attitudes or feelings about the job itself, pay, promotion, or educational opportunities, supervision, co-workers, workload, and so on.
40 Three Major Needs Theories Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs ERG Theory Herzberg s Two-Factor Theory
41 MASLOW S Hierarchy Of Needs Self- Actualization Esteem Needs Belongingness & Love Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs
42 Hierarchy of Needs The hierarchy has five levels: Physiological Needs: oxygen, water, protein, salt, sugar, calcium and other minerals and vitamins, shelter and sleep etc. Safety Needs: security, stability, protection from physical and emotional harm Belongingness & Love Needs: affection, belonging, acceptance, friendship, community Esteem Needs: (Internal ones are need for self-respect, confidence, autonomy, and achievement. External ones are need for respect of others, status, fame, glory, recognition and attention.) Maslow feels these are the roots to many, if not most of our psychological problems. Self-actualization: (doing that which maximizes one s potential and fulfills one s innate aspirations)
43 DEFICIT (D-NEEDS) If you don t have enough of something you have a deficit (need) Maslow's hierarchy seems to follow the life cycle. A baby's needs are almost entirely physiological. As the baby grows, it needs safety, then love. Toddlers are eager for social interaction, attention and affection. Teenagers are anxious about social needs, young adults are concerned with esteem and only more mature people transcend the first four levels to spend much time self-actualizing. Under stressful conditions, or when survival is threatened, we can regress to a lower level need.
44 BEING NEEDS (SELF-ACTUALIZATION) Needs that do not involve balance Once engaged, they continue to be felt Continuous desire to fulfill potentials ( be all you can be ) You need to have lower needs taken care of, at least to a considerable extent Only a small percentage of the population is truly, self-actualizing (approximately 2%)
45 Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs
46 E.R.G. Theory A variation of Maslow's hierarchy of needs Three groups of needs Existence needs: physical and material wants Relatedness needs: desires for interpersonal relationships Growth needs: desires to be creative and productive; to use one s skills
47 E.R.G. Theory (Cont.) Maslow hierarchy E.R.G. Theory Selfactualization Esteem Growth needs Relationship of Maslow s hierarchy to E.R.G. Theory. Belongingness and love Relatedness needs Safety Physiological Existence needs
48 E.R.G. Theory (Cont.) Both similar to and different from Maslow's need hierarchy Satisfied and unsatisfied needs operate in much the same way Movement upward is the same Movement downward is new
49 E.R.G. Theory (Cont.) Satisfaction-progression: move up the hierarchy as needs are satisfied Frustration-regression: move down the hierarchy when a need is frustrated Deficiency cycle: more strongly desire existence needs when they are unsatisfied Enrichment cycle: more strongly desire growth needs when they are satisfied
50 ERG Theory Alderfer s ERG Theory Existence Needs are desires for physiological and material well-being. Relatedness needs are desires for satis-fying interpersonal relationships. Relatedness Needs are desires for satisfying interpersonal relationships. Growth Needs are desires for continued psychological growth and development.
51 Herzberg s Two-factor Theory Herzberg s Two-factor Theory Hygiene Factor is found in the job context, such as working conditions, interpersonal relations, organizational policies, and salary. Motivator Factor is found in job content, such as a sense of achievement, recognition, responsibility, advancement, or personal growth.
52 Herzberg s Motivator-Hygiene Theory Early interview research with engineers and accountants Negative events: mostly involved a person's job context such as company policy and supervision Positive events: described aspects of the job and feelings of achievement Salary mentioned about the same number of times in negative and positive reports
53 Herzberg s Motivator-Hygiene Theory (Cont.) Dissatisfiers: items predominantly found in descriptions of negative events Could lead to high levels of employee dissatisfaction Improve the dissatisfiers and reduce dissatisfaction Not get higher satisfaction
54 Herzberg s Motivator-Hygiene Theory (Cont.) Satisfiers: items predominantly found in descriptions of positive events Could lead to high levels of employee satisfaction Their absence, or a person's failure to experience them, would not produce dissatisfaction
55 Herzberg s Motivator-Hygiene Theory (Cont.) Two distinct continua: one for satisfaction and one for dissatisfaction Not a single continuum with dissatisfaction on one end and satisfaction on the other Herzberg eventually called the satisfiers motivators; the dissatisfiers hygiene factors
56 Herzberg s Motivators Motivator-Hygiene Theory Achievement Recognition Work itself Hygiene factors (Cont.) Company policies and their administration Quality of supervision Working conditions
57 Herzberg s Motivator-Hygiene Theory (Cont.) Dissatisfiers distracted from the motivators Once the work context is improved, the manager can try to provide the motivators Use a process called job enrichment Add more responsibility and autonomy to the job Creates opportunity for employee to experience the motivators
58 Herzberg s Motivator-Hygiene Theory Empirical research Mixed results Methodological issues See the text book for details (Cont.)
59 Theory X and Theory Y (Douglas McGregor)
60 Functions of Communication Control Motivation Emotional Expression Information
61 The Communication Process Source Encoding Channel Decoding Receiver Feedback
62 Communication Fundamentals Direction: Downward Upward Crosswise Networks: Formal vs. Informal
63 Communication Networks Chain Wheel All Channels
64 Barriers to Effective Communication Filtering Selective Perception Emotions Language
65 Key Communication Skills Listening Skills Feedback Skills Presentation skills
66 Basic Communication Skills Profile Communication Order Learned Extent Used Extent Taught Listening First First Fourth Speaking Second Second Third Reading Third Third Second Writing Fourth Fourth First
67 Stages of the Listening Process Hearing Focusing on the message Comprehending and interpreting Analyzing and Evaluating Responding Remembering
68 Barriers to Active Listening Environmental barriers Physiological barriers Psychological barriers Selective Listening Negative Listening Attitudes Personal Reactions Poor Motivation
69 How to Be an Effective Listener What You Think about Listening? Understand the complexities of listening Prepare to listen Adjust to the situation Focus on ideas or key points Capitalize on the speed differential Organize material for learning
70 Communication Process Model Sender Transmit Message Receiver Form message Encode message Receive encoded message Decode message Noise Decode feedback Receive feedback Encode feedback Form feedback Transmit Feedback
71 Communication Barriers Perceptions Filtering Language Jargon Ambiguity Information Overload
72 The HURIER Model: Components of Effective Listening Hearing (paying careful attention to what is being said) Understanding (comprehending the messages being sent) Remembering (being able to recall the message being sent) Effective Listening Responding (replying to the sender, letting him or her know you are paying attention) Evaluating (not immediately passing judgment on the message being sent) Interpreting (not reading anything into the message the sender is communicating)
73 Information Overload Episodes of information overload Information Load Employee s information processing capacity Time
74 Problem: Overload: Problem Solved Overload (too many messages reaching a person at once) Message A Message B Message C Person Solutions: Use gatekeepers to control the number of incoming messages received Message A Message B Message C Gatekeeper Message C Person Use queuing to present messages in order Message A Message B Message C Person
75 Mean Percentage of Managers Preferring Media Oral vs. Written Communication: Preference for Media Depends on the Message Oral media are preferred for sending ambiguous messages. Written media are preferred for sending clear messages (88.3) (11.3) (32.1) (67.9) Oral Media Written Media Extremely ambiguous messages Extremely clear messages
76 Communicating Through Advantages of Messages quickly formed, edited, sent, and stored Needs little coordination Random information access Fewer social status barriers Problems with Information overload Flaming Interpreting emotions Lacks empathy or social support
77 Nonverbal Communication Actions, gestures, facial expressions, etc. Transmits most info in face-to-face meetings Influences meaning of verbal and written symbols Less rule bound than verbal communication Important part of emotional labour
78 Hierarchy of Media Richness Rich Media Richness Overloaded Zone Newsletters Face-to-face Telephone Oversimplified Zone Lean Routine/ Clear Situation Nonroutine/ Ambiguous
79 Communicating in Hierarchies Workspace design Employee surveys Newsletters and e-zines Management by walking around
80 Grapevine Characteristics Transmits information very rapidly in all directions Relatively accurate, but deletes details and exaggerates key points More active in homogeneous groups who easy communication access Most active when employees are anxious Usually follows a cluster chain pattern
81 Personal Communication Style The Nobel (someone who says what s on his or her mind) The Magistrate (blend between Noble and Socratic) The Senator (sometimes Noble and sometimes Reflective) The Socratic (someone who likes to argue his or her points fully) The Reflective (someone who would rather say nothing than to hurt someone else s feelings) The Candidate (blend between Socratic and Reflective)
82 Relative Proportion of Statements Internal vs. External Communications: Is There a Difference? More Statements Threats were used more than opportunities when communicating internally. Opportunities were used more than threats when communicating externally. External statements Fewer Statements Internal statements Threats Focus of Statements Opportunities
83 Cross-Cultural Communication Verbal differences Language Nonverbal differences Voice intonation Interpreting nonverbal meaning Importance of verbal versus nonverbal Silence and conversational overlaps
84 Gender Communication Differences Men Report talk Women Rapport talk Gives advice quickly and directly Gives advice indirectly and reluctantly Avoids asking for information Frequently asks for information Less sensitive to nonverbal cues More sensitive to nonverbal cues
85 Gender Issues in Leadership Male and female leaders have similar taskand people-oriented leadership. Participative leadership is used more often by female leaders. Women rated less favourably than equivalent male leaders due to stereotyping.
86 Getting Your Message Across Empathize Repeat the message Use timing effectively Be descriptive
87 Active Listening Process and Strategies SENSING Postpone evaluation Avoid interruptions Maintain interest RESPONDING Show interest Clarify the message ACTIVE LISTENING EVALUATING Empathize Organize information
88 Persuasive Communication Communicator Characteristics Expert Credibility Attractive Communication Medium Message Content Present all sides Few arguments Emotional appeals Inoculation effect Audience Characteristics Self-esteem Inoculated
Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management
 Subject Name Paper Name Paper No. 14 Module Name/Title Module Id Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management Organizational Leadership FT/FBM/09 Objectives To know about difference between
Subject Name Paper Name Paper No. 14 Module Name/Title Module Id Description of Module Food Technology Food Business Management Organizational Leadership FT/FBM/09 Objectives To know about difference between
Determinants of Performance
 MOTIVATION 1 Determinants of Performance Person: Ability Motivation Accurate Role Perceptions Situation: Environmental (Constraints and Facilitators) Performance 2 Fundamentals of Motivation Motivation
MOTIVATION 1 Determinants of Performance Person: Ability Motivation Accurate Role Perceptions Situation: Environmental (Constraints and Facilitators) Performance 2 Fundamentals of Motivation Motivation
Management. Part IV: Leading Ch. 13. Leadership
 Management Part IV: Leading Ch. 13. Leadership Dan C. Lungescu, PhD, assistant professor 2015-2016 Course outline Management Part I: Introduction Part II: Planning Part III: Organizing Part IV: Leading
Management Part IV: Leading Ch. 13. Leadership Dan C. Lungescu, PhD, assistant professor 2015-2016 Course outline Management Part I: Introduction Part II: Planning Part III: Organizing Part IV: Leading
Unit 5 Motivation. "Motivation is the set of forces that causes people to behave in certain ways." R.W. Griffin
 Unit 5 Motivation Concept and Process Since motivation influences productivity, supervisors need to understand what motivates employees to reach peak performance. It is not an easy task to increase employee
Unit 5 Motivation Concept and Process Since motivation influences productivity, supervisors need to understand what motivates employees to reach peak performance. It is not an easy task to increase employee
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA CENTRE FOR OPEN AND LIFELONG LEARNING OFFICE MANAGEMENT & TECHNOLOGY ADMINISTRATIVE MANAGEMENT B (ADM720S) FEEDBACK LETTER NO. 1 FOR SECOND SEMESTER 2015 COMPILED BY: DDJ FREDERICKS
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA CENTRE FOR OPEN AND LIFELONG LEARNING OFFICE MANAGEMENT & TECHNOLOGY ADMINISTRATIVE MANAGEMENT B (ADM720S) FEEDBACK LETTER NO. 1 FOR SECOND SEMESTER 2015 COMPILED BY: DDJ FREDERICKS
Motivation Through Needs, Job Design Involve? & Intrinsic Rewards
 6 Motivation Through Needs, Job Design Involve? & Intrinsic Rewards Chapter What Does Motivation Need Theories of Motivation Motivating Employees Through Job Design Leading Others Toward Intrinsic Motivation
6 Motivation Through Needs, Job Design Involve? & Intrinsic Rewards Chapter What Does Motivation Need Theories of Motivation Motivating Employees Through Job Design Leading Others Toward Intrinsic Motivation
Leadership In Organizations: National Implications
 VOLUME 7, NUMBER 1, 2004 Leadership In Organizations: National Implications Alicia Kritsonis MBA Graduate Student California State University, Dominquez Hills ABSTRACT The purpose of this article is to
VOLUME 7, NUMBER 1, 2004 Leadership In Organizations: National Implications Alicia Kritsonis MBA Graduate Student California State University, Dominquez Hills ABSTRACT The purpose of this article is to
Theories of Motivation. 2. Introduction. 2.1 Overview. Notes: Copyright 2016 Educational Design Technology (EDT) background music
 Theories of Motivation 2. Introduction 2.1 Overview background music 2.2 Learning Objectives background music 1. Motivation 1.1 Motivation no audio 1.2 Definition of Motivation Motivation is the psychological
Theories of Motivation 2. Introduction 2.1 Overview background music 2.2 Learning Objectives background music 1. Motivation 1.1 Motivation no audio 1.2 Definition of Motivation Motivation is the psychological
MOTIVATION FEM3104 DR SA ODAH BINTI AHMAD JPMPK/FEM/UPM
 MOTIVATION FEM3104 DR SA ODAH BINTI AHMAD JPMPK/FEM/UPM LEARNING OUTCOME 1. To learn the basic concepts of work motivation 2. To learn theories of motivation at work 3. To compare differences and similarity
MOTIVATION FEM3104 DR SA ODAH BINTI AHMAD JPMPK/FEM/UPM LEARNING OUTCOME 1. To learn the basic concepts of work motivation 2. To learn theories of motivation at work 3. To compare differences and similarity
Manager versus Leader not the same Ideally all managers should be leaders. Not all leaders can be managers (appointed formally)
 LEADERSHIP Manager versus Leader not the same Ideally all managers should be leaders. Not all leaders can be managers (appointed formally) Define leaders as those able to influence and possess managerial
LEADERSHIP Manager versus Leader not the same Ideally all managers should be leaders. Not all leaders can be managers (appointed formally) Define leaders as those able to influence and possess managerial
Foodservice Organizations
 Foodservice Organizations Ninth Edition CHAPTER 10 Leadership and Organizational Change Learning Objectives 10.1 Describe theories of motivation and their application to foodservice management. 10.2 Discuss
Foodservice Organizations Ninth Edition CHAPTER 10 Leadership and Organizational Change Learning Objectives 10.1 Describe theories of motivation and their application to foodservice management. 10.2 Discuss
Basic Motivation Concepts
 Basic Motivation Concepts 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR S T E P H E N P. R O B B I N S E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N W W W. P R E N H A L L. C O M / R O B B I N S
Basic Motivation Concepts 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR S T E P H E N P. R O B B I N S E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N W W W. P R E N H A L L. C O M / R O B B I N S
General Management (MNG2601) Mari Vrba
 General Management (MNG2601) Mari Vrba CONTENTS OF THE LECTURE Introduction to general management The evolution of management theory Managing in a changing environment Planning Managerial decision making
General Management (MNG2601) Mari Vrba CONTENTS OF THE LECTURE Introduction to general management The evolution of management theory Managing in a changing environment Planning Managerial decision making
Lesson:-20 MOTIVATION & ITS THEORIES
 Lesson:-20 MOTIVATION & ITS THEORIES Welcome to today s lesson on motivation. We have appreciated earlier the importance of motivation in determining human behaviour. In today s module we will review the
Lesson:-20 MOTIVATION & ITS THEORIES Welcome to today s lesson on motivation. We have appreciated earlier the importance of motivation in determining human behaviour. In today s module we will review the
Motivation. Motivating is a management process of influencing other people s behavior based on the knowledge of what makes people tick
 Motivation Motivation is a human psychological characteristic that contributes to a person s degree of commitment. It includes the factors that cause, channel and sustain human behavior in a particular
Motivation Motivation is a human psychological characteristic that contributes to a person s degree of commitment. It includes the factors that cause, channel and sustain human behavior in a particular
Management. Part IV: Leading Ch. 12. Motivation
 Management Part IV: Leading Ch. 12. Motivation Dan C. Lungescu, PhD, assistant professor 2015-2016 Course outline Management Part I: Introduction Part II: Planning Part III: Organizing Part IV: Leading
Management Part IV: Leading Ch. 12. Motivation Dan C. Lungescu, PhD, assistant professor 2015-2016 Course outline Management Part I: Introduction Part II: Planning Part III: Organizing Part IV: Leading
D. Organizing planning leading controlling. E. Leading organizing planning controlling. C GT Fa
 Multiple Choice Questions CHAPTER INTRODUCTION 156. Which of the following statements accurately characterize effective leaders in the contemporary world? A. Leaders understand the diversity of people
Multiple Choice Questions CHAPTER INTRODUCTION 156. Which of the following statements accurately characterize effective leaders in the contemporary world? A. Leaders understand the diversity of people
Basic Concepts of Supervisory Skills for Transportation Officials
 Puerto Rico Transportation Technology Transfer Center Department of Civil Engineering and Surveying University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez PO Box 9000 * Mayagüez, PR 00681 Tel. 787-834- 6385 * Fax: 787-265-
Puerto Rico Transportation Technology Transfer Center Department of Civil Engineering and Surveying University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez PO Box 9000 * Mayagüez, PR 00681 Tel. 787-834- 6385 * Fax: 787-265-
STUDY UNIY 5 MOTIVATION
 STUDY UNIY 5 MOTIVATION OUTCOMES On successful completion of this study unit, students will be able to: o Describe the different theories of motivation o See and explain the interrelatedness between the
STUDY UNIY 5 MOTIVATION OUTCOMES On successful completion of this study unit, students will be able to: o Describe the different theories of motivation o See and explain the interrelatedness between the
Chapter 11. Motivation at Work. Copyright 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 11 Motivation at Work Copyright 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved. Definition of Motivation Motivation - the process of arousing and sustaining goal-directed
Chapter 11 Motivation at Work Copyright 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved. Definition of Motivation Motivation - the process of arousing and sustaining goal-directed
An Examination of the Situational Leadership Approach: Strengths and Weaknesses
 Cross-Currents: An International Peer-Reviewed Journal on Humanities & Social Sciences ISSN 2394-451X (Print) http://crosscurrentpublisher.com/ An Examination of the Situational Leadership Approach: Strengths
Cross-Currents: An International Peer-Reviewed Journal on Humanities & Social Sciences ISSN 2394-451X (Print) http://crosscurrentpublisher.com/ An Examination of the Situational Leadership Approach: Strengths
Motivation the internal and external factors that lead an individual to engage in goal-oriented behavior.
 Motivation the internal and external factors that lead an individual to engage in goal-oriented behavior. The theories of motivation fall into two main categories: 1. Needs theories. They describe the
Motivation the internal and external factors that lead an individual to engage in goal-oriented behavior. The theories of motivation fall into two main categories: 1. Needs theories. They describe the
Chapter 9. Top Performance through Empowerment, Teamwork, and Communication
 Chapter 9 Top Performance through Empowerment, Teamwork, and Communication Learning Objectives 1 Discuss empowering employees. 5 Describe team conflict. Distinguish the five types of teams. 2 3 Identify
Chapter 9 Top Performance through Empowerment, Teamwork, and Communication Learning Objectives 1 Discuss empowering employees. 5 Describe team conflict. Distinguish the five types of teams. 2 3 Identify
Chapter 7 Management and leadership
 Chapter 7 Management and leadership Leadership and management Definitions of leadership Leadership means giving a lead to others. A leader gives guidance and direction, and other ( followers ) follow the
Chapter 7 Management and leadership Leadership and management Definitions of leadership Leadership means giving a lead to others. A leader gives guidance and direction, and other ( followers ) follow the
Power, Influence, and Leadership. 2. Introduction. 2.1 Overview. Notes: Copyright 2016 Educational Design Technology (EDT) background music
 Power, Influence, and Leadership 2. Introduction 2.1 Overview background music 2.2 Learning Objectives No audio 1. Scene 1 1.1 Aspects of Leadership no audio 1.2 Power & Influence Power is an integral
Power, Influence, and Leadership 2. Introduction 2.1 Overview background music 2.2 Learning Objectives No audio 1. Scene 1 1.1 Aspects of Leadership no audio 1.2 Power & Influence Power is an integral
Motivation HRM in Construction
 Motivation HRM in Construction Dr. Nabil I. El Sawalhi Construction Management 1 1. Content theory Motivation Herzberg s Motivation-Hygiene ) )الوقائية Theory Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs McClelland s Learned
Motivation HRM in Construction Dr. Nabil I. El Sawalhi Construction Management 1 1. Content theory Motivation Herzberg s Motivation-Hygiene ) )الوقائية Theory Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs McClelland s Learned
5.1 Leadership Versus Management 5.2 Transactional Leadership 5.3 Transformational Leadership 5.4 Situational Leadership
 5. Leading 5.1 Leadership Versus Management 5.2 Transactional Leadership 5.3 Transformational Leadership 5.4 Situational Leadership 5.5 Personality Types 5.6 Power in Organizations 5.7 Leadership in Teams
5. Leading 5.1 Leadership Versus Management 5.2 Transactional Leadership 5.3 Transformational Leadership 5.4 Situational Leadership 5.5 Personality Types 5.6 Power in Organizations 5.7 Leadership in Teams
MOTIVATION. Definition of Motivation The will to achieve. Factor that cause, channel & sustain an individual s behavior (Stoner).
 Definition of Motivation The will to achieve MOTIVATION Factor that cause, channel & sustain an individual s behavior (Stoner). The willingness to put forth effort in the pursuit of organizational goals
Definition of Motivation The will to achieve MOTIVATION Factor that cause, channel & sustain an individual s behavior (Stoner). The willingness to put forth effort in the pursuit of organizational goals
Page 1 of 12 Saylor URL:
 This text was adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work s original creator or licensee. Saylor
This text was adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work s original creator or licensee. Saylor
Realize. The Theories Behind Management
 Realize The Theories Behind Management 2 Table of Contents Introduction... 5 Ch. 1: Employee-Centered Management... 6 Ch. 2: Managerial Grid... 10 Ch. 3: Motivation... 16 Ch. 4: The Contingency Model...
Realize The Theories Behind Management 2 Table of Contents Introduction... 5 Ch. 1: Employee-Centered Management... 6 Ch. 2: Managerial Grid... 10 Ch. 3: Motivation... 16 Ch. 4: The Contingency Model...
Working in Groups 6 th edition
 Working in Groups 6 th edition Isa N. Engleberg Prince George s Community College Dianna R. Wynn Nash Community College This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following
Working in Groups 6 th edition Isa N. Engleberg Prince George s Community College Dianna R. Wynn Nash Community College This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following
2. What does the Human Resource Plan describe? 3. List three items included in the Staffing Management Plan.
 CSC 310 Program Management California State University Dominguez Hills Spring 2017 Instructor: Howard Rosenthal Assignment 3c Chapter 3 What Are The Project Management Process Groups Answer Sheet 1. Who
CSC 310 Program Management California State University Dominguez Hills Spring 2017 Instructor: Howard Rosenthal Assignment 3c Chapter 3 What Are The Project Management Process Groups Answer Sheet 1. Who
Chapter 16 Motivating Employees
 Chapter 16 Motivating Employees TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS A MANAGER S DILEMMA 1. According to the company profile in A Manager s Dilemma, the majority of employees at Group M consist of highly educated professionals
Chapter 16 Motivating Employees TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS A MANAGER S DILEMMA 1. According to the company profile in A Manager s Dilemma, the majority of employees at Group M consist of highly educated professionals
Chapter 12 - Leadership in Organizational Settings Competency Perspective of Leadership Competency Perspective Limitations
 Chapter 12 - Leadership in Organizational Settings Leadership - influencing, motivating, and enabling others to contribute toward the effectiveness and success of the organizations of which they are members;
Chapter 12 - Leadership in Organizational Settings Leadership - influencing, motivating, and enabling others to contribute toward the effectiveness and success of the organizations of which they are members;
MOTIVATION Concept of Motivation 02 - Definition of Motivation 02 - Motivation and Morale Relationship 02 THEORIES OF MOTIVATION 03
 Contents MOTIVATION 02 - Concept of Motivation 02 - Definition of Motivation 02 - Motivation and Morale Relationship 02 THEORIES OF MOTIVATION 03 - Masslow s Need Hierarchy Model 03 - Douglas McGregor
Contents MOTIVATION 02 - Concept of Motivation 02 - Definition of Motivation 02 - Motivation and Morale Relationship 02 THEORIES OF MOTIVATION 03 - Masslow s Need Hierarchy Model 03 - Douglas McGregor
Motivation and Empowerment
 Chapter 8 Motivation and Empowerment 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 1 Your Leadership
Chapter 8 Motivation and Empowerment 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 1 Your Leadership
Lesson-21. Leadership-- Some More Leadership Theories. This lesson is an insight into the following topics related to leadership:
 Lesson-21 Leadership-- Some More Leadership Theories Learning Objectives This lesson is an insight into the following topics related to leadership: Some more leadership theories Leadership styles Leadership
Lesson-21 Leadership-- Some More Leadership Theories Learning Objectives This lesson is an insight into the following topics related to leadership: Some more leadership theories Leadership styles Leadership
Needs the fundamental ingredient of individual motivation
 Employee Motivation Motivation is a set of forces that directs an individual to the behavior that results in better job performance. A motivated employee might work harder than expected to complete the
Employee Motivation Motivation is a set of forces that directs an individual to the behavior that results in better job performance. A motivated employee might work harder than expected to complete the
Topic 5 Contingency and Situational Leadership
 Topic 5 Contingency and Situational Leadership Introduction This week we discuss specific guidelines about which leadership style to use in specific circumstances. Leaders are most effective when they
Topic 5 Contingency and Situational Leadership Introduction This week we discuss specific guidelines about which leadership style to use in specific circumstances. Leaders are most effective when they
4. ADMINISTRATIVE BEHAVIOUR
 4. ADMINISTRATIVE BEHAVIOUR 4.1 DECISION-MAKING Decision-making is a common everyday phenomenon. Decision-making is the basis of all organisations be it Public or Private. It is the essence of management.
4. ADMINISTRATIVE BEHAVIOUR 4.1 DECISION-MAKING Decision-making is a common everyday phenomenon. Decision-making is the basis of all organisations be it Public or Private. It is the essence of management.
Chapter 3. Motivation, Leadership and Entrepreneurship
 Chapter 3 Motivation, Leadership and Entrepreneurship 3.1 Motivation Introduction Process of influencing or stimulating a person to take action by creating a work atmosphere wherein the goals of the organization
Chapter 3 Motivation, Leadership and Entrepreneurship 3.1 Motivation Introduction Process of influencing or stimulating a person to take action by creating a work atmosphere wherein the goals of the organization
Faculty of Business and Economics SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT AND PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION MG 201DFL: ORGANISATION BEHAVIOUR FINAL EXAMINATION SEMESTER 1, 2009
 The University of the South Pacific Serving the Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, Niue, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu. Faculty of Business and Economics
The University of the South Pacific Serving the Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, Niue, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu. Faculty of Business and Economics
1/16/2009. Chapter Sixteen. Learning Objectives. The Nature of Motivation. Managing Employee Motivation and Performance
 Chapter Sixteen Managing Employee Motivation and Performance Slide content created by Charlie Cook, The University of West Alabama Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives
Chapter Sixteen Managing Employee Motivation and Performance Slide content created by Charlie Cook, The University of West Alabama Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives
Chapter 16 Motivation
 Chapter 16 Motivation TRUE/FALSE. 1) The definition of motivation has three key elements: energy, direction, and persistence. 8) According to the goal-setting theory, a generalized goal of "do your best"
Chapter 16 Motivation TRUE/FALSE. 1) The definition of motivation has three key elements: energy, direction, and persistence. 8) According to the goal-setting theory, a generalized goal of "do your best"
4.1 Organizational Charts and Designs 4.2 Centralized and Decentralized Organization 4.3 Span of Control
 4. Organizing 4.1 Organizational Charts and Designs 4.2 Centralized and Decentralized Organization 4.3 Span of Control 4.4 Authority and Unity of Command 4.5 Incentives and Motivation Tools 4.6 Maslow
4. Organizing 4.1 Organizational Charts and Designs 4.2 Centralized and Decentralized Organization 4.3 Span of Control 4.4 Authority and Unity of Command 4.5 Incentives and Motivation Tools 4.6 Maslow
 Types of Planning? Informal Planning 1. Nothing is written down 2.Little or no sharing of goals 3.General and lacking in continuity Formal Planning 1.Written and defined specific goals 2.Specific action
Types of Planning? Informal Planning 1. Nothing is written down 2.Little or no sharing of goals 3.General and lacking in continuity Formal Planning 1.Written and defined specific goals 2.Specific action
The Supervisor as Leader
 Chapter 8 The Supervisor as Leader Before you are a leader, success is all about growing yourself. When you become a leader, success is all about growing others. - Jack Welch What is Leadership? Leadership-the
Chapter 8 The Supervisor as Leader Before you are a leader, success is all about growing yourself. When you become a leader, success is all about growing others. - Jack Welch What is Leadership? Leadership-the
Chapter 4: Theories of Motivation
 Chapter 4: Theories of Motivation Organizational Behaviour 5 th Canadian Edition Langton / Robbins / Judge Copyright 2010 Pearson Education Canada 4-1 Chapter Outline What Is Motivation? Needs Theories
Chapter 4: Theories of Motivation Organizational Behaviour 5 th Canadian Edition Langton / Robbins / Judge Copyright 2010 Pearson Education Canada 4-1 Chapter Outline What Is Motivation? Needs Theories
A leader lives in each of us. Leadership is one of the four functions of management.
 MODULE 16 A leader lives in each of us MODULE GUIDE 16.1 What are the foundations for effective leadership? What are current issues and directions in leadership development? Leadership is one of the four
MODULE 16 A leader lives in each of us MODULE GUIDE 16.1 What are the foundations for effective leadership? What are current issues and directions in leadership development? Leadership is one of the four
UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey. Prepared for: University of Alaska, Fairbanks Administrative Services
 UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University of Alaska, Fairbanks Administrative Services July 2009 UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University
UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University of Alaska, Fairbanks Administrative Services July 2009 UAF Administrative Services Work Environment Survey Prepared for: University
Chapter 1. Leadership CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Leadership CHAPTER OUTLINE Chapter 1 I. THE NATURE OF LEADERSHIP A. Leadership is the process by which a person exerts influence over other people and inspires, motivates, and directs their activities
Leadership CHAPTER OUTLINE Chapter 1 I. THE NATURE OF LEADERSHIP A. Leadership is the process by which a person exerts influence over other people and inspires, motivates, and directs their activities
Motivation the internal and external factors that lead an individual to engage in goal-oriented behavior.
 Motivation the internal and external factors that lead an individual to engage in goal-oriented behavior. The theories of motivation fall into the following categories: 1. Needs theories. They describe
Motivation the internal and external factors that lead an individual to engage in goal-oriented behavior. The theories of motivation fall into the following categories: 1. Needs theories. They describe
Leadership & Management
 W1: Introduc-on Leadership & Management What is then Leadership? The Evolu-on of Leadership Research 1900: Traits approaches 1950: Behavioral theories 1990s 1960: Contingency theories Conflict Ppaper Construc-ve
W1: Introduc-on Leadership & Management What is then Leadership? The Evolu-on of Leadership Research 1900: Traits approaches 1950: Behavioral theories 1990s 1960: Contingency theories Conflict Ppaper Construc-ve
A. OVERVIEW OF THE COMPETENCIES BY CLUSTER
 A. OVERVIEW OF THE COMPETENCIES BY CLUSTER Marketing Representative Competency Model I. Communication and Influence II. Task Management III. Self Management 1. Interpersonal Awareness: The ability to notice,
A. OVERVIEW OF THE COMPETENCIES BY CLUSTER Marketing Representative Competency Model I. Communication and Influence II. Task Management III. Self Management 1. Interpersonal Awareness: The ability to notice,
CHAPTER 3. Motivating People. Myron D. Fottler, Stephen J. O Connor, Mattia J. Gilmartin, and Thomas A. D Aunno
 sho01910_ch03 10/21/05 12:46 PM Page 21 CHAPTER 3 Motivating People Myron D. Fottler, Stephen J. O Connor, Mattia J. Gilmartin, and Thomas A. D Aunno LECTURE OUTLINE A. Chapter Purpose The objective of
sho01910_ch03 10/21/05 12:46 PM Page 21 CHAPTER 3 Motivating People Myron D. Fottler, Stephen J. O Connor, Mattia J. Gilmartin, and Thomas A. D Aunno LECTURE OUTLINE A. Chapter Purpose The objective of
identify different types of needs and factors contributing to motivation; distinguish between Maslow and Herzberg s theories of motivation;
 UNIT 10 MOTIVATION Structure 10.0 Objectives 10.1 Introduction 2.2 Concept of Motivation 2.3 Motivators 10.4 Theories of Motivation 10.4.1 Maslow s Need Hierarchy Theory 10.4.2 Herzberg s Two Factors Theory
UNIT 10 MOTIVATION Structure 10.0 Objectives 10.1 Introduction 2.2 Concept of Motivation 2.3 Motivators 10.4 Theories of Motivation 10.4.1 Maslow s Need Hierarchy Theory 10.4.2 Herzberg s Two Factors Theory
We have three choices
 NURSING LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM Robin A. Bleier, RN, LHRM, CLC RB Health Partners, Inc. 4.2016 We have three choices Lead Follow or Get Out of the Way? Ben Roethlisberger Defines a True Winner Ben
NURSING LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM Robin A. Bleier, RN, LHRM, CLC RB Health Partners, Inc. 4.2016 We have three choices Lead Follow or Get Out of the Way? Ben Roethlisberger Defines a True Winner Ben
Chapter Ten. Motivating Employees. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Ten Motivating Employees McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. INTRINSIC REWARDS The Value of Motivation Intrinsic Rewards -- Personal satisfaction
Chapter Ten Motivating Employees McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. INTRINSIC REWARDS The Value of Motivation Intrinsic Rewards -- Personal satisfaction
TEAM WORK IN SA COMPANY - BUILDING AND MOTIVATION
 TEAM WORK IN SA COMPANY - BUILDING AND MOTIVATION PhD Student Simona LUPULEAC Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, E-mail:anomisw@yahoo.com The purpose /Objectives/ Methodology: To analyze of
TEAM WORK IN SA COMPANY - BUILDING AND MOTIVATION PhD Student Simona LUPULEAC Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, E-mail:anomisw@yahoo.com The purpose /Objectives/ Methodology: To analyze of
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit VI
 UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Motivation and Leadership Reading Assignment Chapter 13: Motivation and Performance Chapter 14: Leadership Suggested Reading See information below. Learning Activities (Non-Graded)
UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Motivation and Leadership Reading Assignment Chapter 13: Motivation and Performance Chapter 14: Leadership Suggested Reading See information below. Learning Activities (Non-Graded)
Employee Value Proposition (EVP) February 2016
 Employee Value Proposition (EVP) February 2016 Why is important an EVP? EVP Talent Development & Career Compensation & Benefits Attracting and Retaining Talent Strategy TO ATTRACT TALENT Nowadays is more
Employee Value Proposition (EVP) February 2016 Why is important an EVP? EVP Talent Development & Career Compensation & Benefits Attracting and Retaining Talent Strategy TO ATTRACT TALENT Nowadays is more
Leadership: A Framework for Thinking and Acting
 sho01910_ch04 10/21/05 12:46 PM Page 28 CHAPTER 4 Leadership: A Framework for Thinking and Acting Dennis D. Pointer LECTURE OUTLINE A. Chapter Purpose The purpose of this chapter is to develop an understanding
sho01910_ch04 10/21/05 12:46 PM Page 28 CHAPTER 4 Leadership: A Framework for Thinking and Acting Dennis D. Pointer LECTURE OUTLINE A. Chapter Purpose The purpose of this chapter is to develop an understanding
Management 301 Exam 2 Review
 Chapter 1: The Exceptional Manager pg. 4 29 Management 301 Exam 2 Review What are the challenges to being a star manager? Challenge 1: Managing for Competitive Advantage Staying Ahead of Rivals o Being
Chapter 1: The Exceptional Manager pg. 4 29 Management 301 Exam 2 Review What are the challenges to being a star manager? Challenge 1: Managing for Competitive Advantage Staying Ahead of Rivals o Being
1. is the set of forces that energize, direct, and sustain behavior. a. Motivation b. Expectancy c. Empowerment d. Socialization
 CHAPTER 10: MOTIVATION Multiple Choice Questions 1. is the set of forces that energize, direct, and sustain behavior. a. Motivation b. Expectancy c. Empowerment d. Socialization Answer: a (p. 277, easy,
CHAPTER 10: MOTIVATION Multiple Choice Questions 1. is the set of forces that energize, direct, and sustain behavior. a. Motivation b. Expectancy c. Empowerment d. Socialization Answer: a (p. 277, easy,
BBS Notes - Human Resource Management Unit-6 Motivation
 Unit-6 Motivation The term motivation is developed from the English word motive which is itself derived from the Latin word movere. Movere means to move.motive may be defined as needs, wants, drives or
Unit-6 Motivation The term motivation is developed from the English word motive which is itself derived from the Latin word movere. Movere means to move.motive may be defined as needs, wants, drives or
INTERPERSONAL SKILLS FOR
 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS FOR PROJECT MANAGERS Dr Anthony Yeong DBA MBA PMP PRINCE2 Practitioner July 2011 AGENDA Why Interpersonal Skills? Leadership Team building Motivation Communication Influencing Decision
INTERPERSONAL SKILLS FOR PROJECT MANAGERS Dr Anthony Yeong DBA MBA PMP PRINCE2 Practitioner July 2011 AGENDA Why Interpersonal Skills? Leadership Team building Motivation Communication Influencing Decision
Organizationa Behavior and Management
 Organizationa Behavior and Management Ninth Edition John M. Ivancevich Hugli Roy and Lillie Cram Cullen Chair and Professor of Organizational Behavior and Management, C. T. Bauer College of Business, University
Organizationa Behavior and Management Ninth Edition John M. Ivancevich Hugli Roy and Lillie Cram Cullen Chair and Professor of Organizational Behavior and Management, C. T. Bauer College of Business, University
LEADERSHIP POTENTIAL INDICATOR
 LEADERSHIP POTENTIAL INDICATOR Personal Report John Smith 2017 MySkillsProfile. All rights reserved. Introduction The (LPI) measures aspects of your leadership style by asking you questions about your
LEADERSHIP POTENTIAL INDICATOR Personal Report John Smith 2017 MySkillsProfile. All rights reserved. Introduction The (LPI) measures aspects of your leadership style by asking you questions about your
PART B UNIT 5 MOTIVATION AND BEHAVIOR. N.Venkatesh, MITE
 PART B UNIT 5 MOTIVATION AND BEHAVIOR Hawthorne studies Elton Mayo conducted the famous experiment at Howthorne plant of western electric company between 1924 and 1932 The study revealed the influence
PART B UNIT 5 MOTIVATION AND BEHAVIOR Hawthorne studies Elton Mayo conducted the famous experiment at Howthorne plant of western electric company between 1924 and 1932 The study revealed the influence
Nelson Mandela s Influence Using Organizational Behaviour Techniques
 Nelson Mandela s Influence Using Organizational Behaviour Techniques Leadership and Motivation Megan Latzkowski A leader is like a shepherd. He stays behind the flock, letting them go out ahead, not realizing
Nelson Mandela s Influence Using Organizational Behaviour Techniques Leadership and Motivation Megan Latzkowski A leader is like a shepherd. He stays behind the flock, letting them go out ahead, not realizing
Creative Leadership Questionnaire (CLQ)
 MSP Feedback Guide 2009 Creative Leadership Questionnaire (CLQ) Feedback to Test Takers www.myskillsprofile.com Introduction (page 2 of the report) Key points to make The Creative Leadership Questionnaire
MSP Feedback Guide 2009 Creative Leadership Questionnaire (CLQ) Feedback to Test Takers www.myskillsprofile.com Introduction (page 2 of the report) Key points to make The Creative Leadership Questionnaire
Justice Administration Police, Courts, and Corrections Management
 Justice Administration Police, Courts, and Corrections Management EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 2 Organization and Administration: Principles and Practices Defining Organizations Like supervision and management,
Justice Administration Police, Courts, and Corrections Management EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 2 Organization and Administration: Principles and Practices Defining Organizations Like supervision and management,
Management. tenth edition. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 2 1
 Management tenth edition Stephen P. Robbins Mary Coulter Chapter 2 Management History 2 1 Learning Outcomes 2.1 Historical Background Of Management. Explain why studying management history is important.
Management tenth edition Stephen P. Robbins Mary Coulter Chapter 2 Management History 2 1 Learning Outcomes 2.1 Historical Background Of Management. Explain why studying management history is important.
PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT BUSN 2330
 PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT BUSN 2330 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0.0 Revised: Fall 2014 Catalog Course Description: This course
PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT BUSN 2330 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0.0 Revised: Fall 2014 Catalog Course Description: This course
Motivation. The Nature of Human Relations. Companies Giving Employees Incentives to Improve Productivity. Ray Kaupp
 Motivation The Nature of Human Relations What motivates employees to perform on the job is the focus of human relations The study of the behavior of individuals and groups in organizational settings Motivation
Motivation The Nature of Human Relations What motivates employees to perform on the job is the focus of human relations The study of the behavior of individuals and groups in organizational settings Motivation
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FOURTH SEMESTER MG6851 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT QUESTION BANK UNIT I - INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT AND
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FOURTH SEMESTER MG6851 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT QUESTION BANK UNIT I - INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONS (2 MARKS) 1. What is Management? (M-12) Management
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FOURTH SEMESTER MG6851 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT QUESTION BANK UNIT I - INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONS (2 MARKS) 1. What is Management? (M-12) Management
Getting Engaged - What is Employee Engagement and Why Does it Matter?
 Getting Engaged - What is Employee Engagement and Why Does it Matter? Employee engagement is critical for the success of any business. It is about having a workforce who wants to be there, who like what
Getting Engaged - What is Employee Engagement and Why Does it Matter? Employee engagement is critical for the success of any business. It is about having a workforce who wants to be there, who like what
UNIT 10 LEADERSHIP IN ORGANIZATIONS MODULE - 3
 UNIT 10 LEADERSHIP IN ORGANIZATIONS MODULE - 3 UNIT 10 LEADERSHIP IN ORGANIZATIONS Leadership in Organizatons Structure 10.0 Introduction 10.1 Unit Objectives 10.2 Leadership: An Overview 10.3 Formal and
UNIT 10 LEADERSHIP IN ORGANIZATIONS MODULE - 3 UNIT 10 LEADERSHIP IN ORGANIZATIONS Leadership in Organizatons Structure 10.0 Introduction 10.1 Unit Objectives 10.2 Leadership: An Overview 10.3 Formal and
Business Studies - Management Notes. Business Studies Study Notes
 Business Studies - Management Notes Business Studies Study Notes The Nature of Management: Definition of Management: The process of working with and through other people to achieve business goals in a
Business Studies - Management Notes Business Studies Study Notes The Nature of Management: Definition of Management: The process of working with and through other people to achieve business goals in a
Motivating the Demotivated Checklist 221
 Motivating the Demotivated Checklist 221 Introduction Some would argue that people are not unmotivated; it s just that the right motivation triggers have not yet been found. It s largely a question of
Motivating the Demotivated Checklist 221 Introduction Some would argue that people are not unmotivated; it s just that the right motivation triggers have not yet been found. It s largely a question of
Mentors: Measuring Success
 Mentors: Measuring Success Your success is measured by many milestones. Your Mentee may realize for the first time that he/she has potential is confident and self-assured values education and the learning
Mentors: Measuring Success Your success is measured by many milestones. Your Mentee may realize for the first time that he/she has potential is confident and self-assured values education and the learning
Supervising for Excellence Training Participant Guide Part II/Module Eleven 22-Jun-06 1
 Part II/Module Eleven 22-Jun-06 1 Course Objectives Situational Leadership/Delegation and Empowerment v v v Discuss the Situational Leadership model as it applies to your role as a supervisor. Identify
Part II/Module Eleven 22-Jun-06 1 Course Objectives Situational Leadership/Delegation and Empowerment v v v Discuss the Situational Leadership model as it applies to your role as a supervisor. Identify
FOURTH EDITION. BUSINESS REVIEW BOOKS Management. Patrick J. Montana. Bruce H. Charnov BARRON'S
 BUSINESS REVIEW BOOKS Management FOURTH EDITION Patrick J. Montana Professor of Management Fordham University Schools of Business Bruce H. Charnov Associate Professor of Management Frank G. Zarb School
BUSINESS REVIEW BOOKS Management FOURTH EDITION Patrick J. Montana Professor of Management Fordham University Schools of Business Bruce H. Charnov Associate Professor of Management Frank G. Zarb School
Employee Motivation: A Tool for Organizational Productivity Improvement.
 Employee Motivation: A Tool for Organizational Productivity Improvement. Samuel Maina Mari, Zubaida Ben Waffy and Babagana Modu Aji National Productivity Centre Maiduguri ABSTRACT Methods of motivating
Employee Motivation: A Tool for Organizational Productivity Improvement. Samuel Maina Mari, Zubaida Ben Waffy and Babagana Modu Aji National Productivity Centre Maiduguri ABSTRACT Methods of motivating
Mentoring Toolkit Additional Resources
 Mentoring Toolkit Additional Resources University of Edinburgh Mentoring Connections Programme Table of Contents Mentoring Connections at the University of Edinburgh... 4 General information on the mentoring
Mentoring Toolkit Additional Resources University of Edinburgh Mentoring Connections Programme Table of Contents Mentoring Connections at the University of Edinburgh... 4 General information on the mentoring
E.M.S Leadership Development. Objectives. Leadership Development 11/4/2012. Drew Fried, EMT-CC CHEP, CHSP. Help explain leadership techniques
 E.M.S Leadership Development Drew Fried, EMT-CC CHEP, CHSP Objectives Help explain leadership techniques Define the role of officers as a manager How to use good communication skills Leadership Development
E.M.S Leadership Development Drew Fried, EMT-CC CHEP, CHSP Objectives Help explain leadership techniques Define the role of officers as a manager How to use good communication skills Leadership Development
Innovation in Human Resources A theorethical advancement on employee motivation and organisational innovation
 2011 2 nd International Conference on Economics, Business and Management IPEDR vol.22 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Innovation in Human Resources A theorethical advancement on employee motivation
2011 2 nd International Conference on Economics, Business and Management IPEDR vol.22 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Innovation in Human Resources A theorethical advancement on employee motivation
The Servant Leader:! Enabling Exceptional Performance
 The Servant Leader: Enabling Exceptional Performance Chris De Santis with help from Warren Bennis, Robert Thomas, Daniel Goleman, Robert Greenleaf, Peter Drucker, Joseph Nye, Sylvia Hewlett, Carol Dweck
The Servant Leader: Enabling Exceptional Performance Chris De Santis with help from Warren Bennis, Robert Thomas, Daniel Goleman, Robert Greenleaf, Peter Drucker, Joseph Nye, Sylvia Hewlett, Carol Dweck
Project Human Resource Management
 Project Human Resource Management Study Notes PMI, PMP, CAPM, PMBOK, PM Network and the PMI Registered Education Provider logo are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc. Points to Note
Project Human Resource Management Study Notes PMI, PMP, CAPM, PMBOK, PM Network and the PMI Registered Education Provider logo are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc. Points to Note
Work in the 21 st Century: An Introduction to Industrial- Organizational Psychology. Chapter 9. The Motivation to Work
 Work in the 21 st Century: An Introduction to Industrial- Organizational Psychology By Frank J. Landy & Jeffrey M. Conte 1 Copyright The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 9 The Motivation to
Work in the 21 st Century: An Introduction to Industrial- Organizational Psychology By Frank J. Landy & Jeffrey M. Conte 1 Copyright The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 9 The Motivation to
Leadership and Decision Making
 Slide 1 BA-101 Introduction to Business Leadership and Decision Making Chapter Nine 1-1 Slide 2 The Nature of Leadership Leadership the processes and behaviors used by someone, such as a manager, to motivate,
Slide 1 BA-101 Introduction to Business Leadership and Decision Making Chapter Nine 1-1 Slide 2 The Nature of Leadership Leadership the processes and behaviors used by someone, such as a manager, to motivate,
TTI TriMetrix HD Talent Report
 TTI TriMetrix HD Talent Report Test TEST 11-4-3 INTRODUCTION Where Opportunity Meets Talent Research has proven that job-related talents are directly related to job satisfaction and personal performance.
TTI TriMetrix HD Talent Report Test TEST 11-4-3 INTRODUCTION Where Opportunity Meets Talent Research has proven that job-related talents are directly related to job satisfaction and personal performance.
EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT. Administrative Office Circuit Court of Lake County, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey. Employee Growth & Development
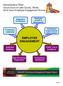 Administrative Office, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey Supportive Co-Workers Employee Growth & Development Trustworthy Leadership Continuous Organizational Improvement EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
Administrative Office, Illinois 2014 Court Employee Engagement Survey Supportive Co-Workers Employee Growth & Development Trustworthy Leadership Continuous Organizational Improvement EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
Project Manager: Superman or Entrepreneur?
 Project Manager: Superman or Entrepreneur? Nina Alimpić, PMP nina@saga.rs Dragana Milojević, PMP dragana.milojevic@pmi-yu.org Belgrade, November 18, 2009 What is Project Management? What is not Project
Project Manager: Superman or Entrepreneur? Nina Alimpić, PMP nina@saga.rs Dragana Milojević, PMP dragana.milojevic@pmi-yu.org Belgrade, November 18, 2009 What is Project Management? What is not Project
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Chapter 09 - Project Human Resource Management
 Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Chapter 09 - Project Human Resource Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Chapter 09 - Project Human Resource Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO
Leading and Managing People and Processes
 Leading and Managing People and Processes APA 16 May 2017 John A. Kline, PhD Troy University Managing People and Processes Armed Forces Comptroller, 53-1 (Winter 2008), 35-38 Gave Seven Points 1. Demonstrate
Leading and Managing People and Processes APA 16 May 2017 John A. Kline, PhD Troy University Managing People and Processes Armed Forces Comptroller, 53-1 (Winter 2008), 35-38 Gave Seven Points 1. Demonstrate
COURSE CATALOG. vadoinc.net
 COURSE CATALOG 2018 vadoinc.net Welcome Welcome to the Vado 2018 Course Catalog. Vado provides any organization or learner numerous opportunities to build the skills needed to lead and manage others, as
COURSE CATALOG 2018 vadoinc.net Welcome Welcome to the Vado 2018 Course Catalog. Vado provides any organization or learner numerous opportunities to build the skills needed to lead and manage others, as
BUILDING A CULTURE OF ENGAGEMENT: THE IMPORTANCE OF SENIOR LEADERSHIP
 BUILDING A CULTURE OF ENGAGEMENT: THE IMPORTANCE OF SENIOR LEADERSHIP Dale Carnegie Training White Paper Copyright 2012 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. All rights reserved. Senior_leadership_121412_wp
BUILDING A CULTURE OF ENGAGEMENT: THE IMPORTANCE OF SENIOR LEADERSHIP Dale Carnegie Training White Paper Copyright 2012 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. All rights reserved. Senior_leadership_121412_wp
CORE COMPETENCIES. For all faculty and staff
 SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
The slightest perception of something negative happening can affect an employee s emotional state.
 Employee feedback is the core of personal and professional growth. Feedback can help an employee get better at what they do, and surprisingly employees crave feedback. Most managers don t provide enough
Employee feedback is the core of personal and professional growth. Feedback can help an employee get better at what they do, and surprisingly employees crave feedback. Most managers don t provide enough
