Lecture 3: Section 1.2 Linear Functions and Applications
|
|
|
- Felix Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 L3-1 Lecture 3: Section 1.2 Linear Functions and Applications In Lecture 2, we explored linear equations of the form Ax + By = C. Solving for y, we have the equivalent form y = mx + b. This is a functional relationship: an equation which associates to a given value of the independent variable x exactly one value of the dependent variable y. Specific functions are designated by letters such as f, g, etc. For a given function f, we define f(x) to be the unique value of y associated with a given x value. Def. A linear function is a function defined by y = f(x) = mx + b for real numbers m and b.
2 L3-2 ex. Express the given linear equation as a linear function, and then find f( 2). 1) 3x + 4y 6 = 0 2) 2y 5 = 0 ex. 2x + 3 = 0 NOTE: If B = 0 in the equation Ax + By = C, we do not have a function.
3 L3-3 Supply and Demand An important idea in economics is the relationship between the price of an item and the number of items sold or produced. The relationship between the price of an item p and quantity q can often be represented as a linear function, at least approximately. A demand function expresses the relationship between price p and q, the number of items that can be sold. For most examples, we let q be the independent variable, so p is the price at which q items will sell. ex. When a graphing calculator is priced at $90, a district manager at Office Depot observes that monthly sales average 480 units in his stores. When the price is reduced periodically for a special sale, his average monthly sales increase by 40 calculators per $4 price decrease. 1) The relationship between price p and quantity q appears to be linear. Why?
4 2) Find the linear demand function denoted p = D(q) which expresses this relationship. L3-4 Why is slope negative? 3) Find the demand for calculators when the price is set at $100.
5 L3-5 A supply function expresses the price p at which a producer is willing to supply q items. ex. Suppose that the price p at which the producer will supply q calculators is given by the supply function p = S(q) = 1 5 q ) Why is slope positive? 2) If the price is set at $100, how many calculators will be supplied to the Office Depot stores? Looking at both supply and demand at $100, what should happen to the price of a calculator?
6 L3-6 For our example, find the equilibrium quantity at which the supply equals demand. What is the equilibrium price?
7 L3-7 Break Even Analysis ex. An inventor would like to market his latest gadget. Each item costs $2.50 to produce, and his fixed costs of production are $1200. He plans to sell his gadget for $10. If the inventor thinks he can sell 150 items, should he put the gadget on the market? To answer the question, we consider the following ideas: 1) Find C(x), which gives the total cost of producing x items. Marginal Cost 2) Find the revenue function R(x).
8 L3-8 3) Find the break-even point. Should the inventor move ahead with production of his gadget? 4) Find the profit function P (x). What is the marginal profit?
9 L3-9 Additional Topic: Section 1.3 Least Squares Line and Linear Regression Consider the following data relating food availability in daily calorie supply and life expectancy for various countries: Country Calories(x) Life Expectancy (y) Belize Cambodia France India Mexico New Zealand Peru Sweden Tanzania United States Look at a scatter plot of this data. Does it appear to be linear?
10 L3-10 To find the linear model which best fits the set of data, we use the least squares line. This line is based on the vertical distance between an actual data point and the line; those distances for each point are summed and then minimized using calculus (you will learn how to do this in MAC 2234). If the least squares line has the form y = ax + b, the formulas for finding a and b are listed in your text, on page 27. A calculator or Excel spreadsheet can compute these values for a given set of data. In our case, the line of best fit has the formula y = x ex. Use your linear model to find the life expectancy of a citizen of the United Kingdom, with a daily calorie supply of (The actual life expectancy is 79.0 years). The Correlation Coefficient r, whose formula is given on page 30, is a measure of the accuracy of the line of best fit to the actual data. It lies between the numbers 1 and 1, and the closer r is to 1, the more linear the data and the better the fit. It can be computed on a calculator or spreadsheet.
11 L3-11 ex. For our example, r =
12 L3-12 Now you try it! 1. Suppose that Avis leases a Ford Focus for $32 per day plus 45 cents per mile, while Enterprise leases the same car for $23 per day plus 60 cents per mile. If a customer plans to rent the car for a one day trip of 100 miles, which company should she use to minimize her cost? Find the number of miles for which the charge is the same for the two companies. 2. According to the US Department of Agriculture, the per capita consumption of beef in the United States decreased from lb. in 1974 to 92.9 lb in Assuming that the consumption is decreasing linearly, write the function C(t) which expresses yearly consumption C in pounds as a function of t, the number of years since 1950 (so t = 0 in 1950). Round the slope to 2 decimal places. Using this model and rounding to the nearest whole number, in what year should the per capita consumption drop to 100 pounds? 3. For a certain product, the cost function is linear with fixed costs of $480. If the product will sell for $25 per unit and the break even quantity is 80 units, find the marginal cost and marginal profit for the product. Remember that marginal refers to the rate of change of the function if one more item is sold. How is it found? 4. Suppose the supply and demand functions for a given product are S(q) = 3.6q + 86 and D(q) = 2.8q (a) How many items will the supplier provide for a price of $86? (b) Find the equilibrium quantity and price. 5. A marketing firm wants to test a new weight loss product. (a) Find the linear supply function if the manufacturer will provide pill samples at a unit price of $40, and 100 samples if the price is $60 each. (b) The marketing firm has determined that demand for the 10-pill sample can be modeled by the demand function p = 1.3q Find the equilibrium quantity and price. 6. Projected spending on home care and medical equipment (in billions of dollars) from 2004 to 2016 is given in the following table. Year x Spending y (a) Find the least squares line and the correlation coefficient. (b) Use the regression line to find the projected spending in (c) If you have graphing capability, draw a scatterplot and add the least squares line.
Linear Cost, Revenue, Profit, Supply, and Demand
 Linear Cost, Revenue, Profit, Supply, and Demand Complete the following questions to investigate different types of linear models. Record your responses on this worksheet and the answer sheet. Turn in
Linear Cost, Revenue, Profit, Supply, and Demand Complete the following questions to investigate different types of linear models. Record your responses on this worksheet and the answer sheet. Turn in
Cost, Revenue, and Profit Functions
 Cost, Revenue, and Profit Functions In this lecture, we will study three functions fundamental in economy and business: the cost, the revenue and the profit function. Throughout the year, we will use these
Cost, Revenue, and Profit Functions In this lecture, we will study three functions fundamental in economy and business: the cost, the revenue and the profit function. Throughout the year, we will use these
. This function gives the supplier s behavior with respect to price and quantity.
 Demand and supply functions are used to describe the consumer and manufacturer behavior with respect to the price of a product or service and the quantity of a product or service. Different textbooks may
Demand and supply functions are used to describe the consumer and manufacturer behavior with respect to the price of a product or service and the quantity of a product or service. Different textbooks may
Math 1314 Lesson 8 Business Applications: Break Even Analysis, Equilibrium Quantity/Price
 Math 1314 Lesson 8 Business Applications: Break Even Analysis, Equilibrium Quantity/Price Three functions of importance in business are cost functions, revenue functions and profit functions. Cost functions
Math 1314 Lesson 8 Business Applications: Break Even Analysis, Equilibrium Quantity/Price Three functions of importance in business are cost functions, revenue functions and profit functions. Cost functions
Quadratic Regressions Group Acitivity 2 Business Project Week #4
 Quadratic Regressions Group Acitivity 2 Business Project Week #4 In activity 1 we created a scatter plot on the calculator using a table of values that were given. Some of you were able to create a linear
Quadratic Regressions Group Acitivity 2 Business Project Week #4 In activity 1 we created a scatter plot on the calculator using a table of values that were given. Some of you were able to create a linear
Activity A: Sidewalk Replacement.
 Activity A: Sidewalk Replacement. The following activity is from Introductory Algebra and focuses and synthesizes reading a graph with writing an equation. The piecewise function is typical in real world
Activity A: Sidewalk Replacement. The following activity is from Introductory Algebra and focuses and synthesizes reading a graph with writing an equation. The piecewise function is typical in real world
Math 1314 Lesson 9: Marginal Analysis. Marginal Cost
 Math 1314 Lesson 9: Marginal Analysis Marginal Cost Suppose a business owner is operating a plant that manufactures a certain product at a known level. Sometimes the business owner will want to know how
Math 1314 Lesson 9: Marginal Analysis Marginal Cost Suppose a business owner is operating a plant that manufactures a certain product at a known level. Sometimes the business owner will want to know how
15 (See Example E later in this lab)
 Tallahassee Community College APPLICATIONS OF ADDITION, SUBTRACTION, MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION In an earlier chapter, you learned some of the basics of working with applications. Many of the prior applications
Tallahassee Community College APPLICATIONS OF ADDITION, SUBTRACTION, MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION In an earlier chapter, you learned some of the basics of working with applications. Many of the prior applications
Chapter 5 Notes Page 1
 Chapter 5 Notes Page 1 COST BEHAVIOR When dealing with costs, it helps for you to determine what drives the cost in question. A Cost Driver (also called Cost Base) is an activity that is associated with,
Chapter 5 Notes Page 1 COST BEHAVIOR When dealing with costs, it helps for you to determine what drives the cost in question. A Cost Driver (also called Cost Base) is an activity that is associated with,
AS/ECON AF Answers to Assignment 1 October 2007
 AS/ECON 4070 3.0AF Answers to Assignment 1 October 2007 Q1. Find all the efficient allocations in the following 2 person, 2 good, 2 input economy. The 2 goods, food and clothing, are produced using labour
AS/ECON 4070 3.0AF Answers to Assignment 1 October 2007 Q1. Find all the efficient allocations in the following 2 person, 2 good, 2 input economy. The 2 goods, food and clothing, are produced using labour
1. You are given the following joint PPF for 3 individuals: Sarah, John, and Michael.
 Economics 102 Fall 2017 Answers to Homework #2 Due 10/10/17 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework
Economics 102 Fall 2017 Answers to Homework #2 Due 10/10/17 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework
Commerce 295 Midterm Answers
 Commerce 295 Midterm Answers October 27, 2010 PART I MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Each question has one correct response. Please circle the letter in front of the correct response for each question. There
Commerce 295 Midterm Answers October 27, 2010 PART I MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Each question has one correct response. Please circle the letter in front of the correct response for each question. There
Multiple Choice (#1-9). Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer.
 !! AP Statistics Ch. 3 Practice Test!! Name: Multiple Choice (#1-9). Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. In a statistics course, a linear regression equation was computed to predict
!! AP Statistics Ch. 3 Practice Test!! Name: Multiple Choice (#1-9). Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. In a statistics course, a linear regression equation was computed to predict
Part I: Math Review Remember to show all of your work. Also remember that calculators are not permitted on exams, so you should try these by hand.
 Economics 101 Fall 2013 Answers to Homework #1 Due Tuesday, September 17, 2013 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number
Economics 101 Fall 2013 Answers to Homework #1 Due Tuesday, September 17, 2013 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number
Algebra I Sample Questions. 4 On the set of axes below, graph the function represented by y = 3 x 2 for the domain
 4 On the set of axes below, graph the function represented by y = 3 x 2 for the domain 6 x 10. 11 5 Solve 8m 2 20m 12 for m by factoring. 13 6 Ryker is given the graph of the function y = 1 2 x2 4. He
4 On the set of axes below, graph the function represented by y = 3 x 2 for the domain 6 x 10. 11 5 Solve 8m 2 20m 12 for m by factoring. 13 6 Ryker is given the graph of the function y = 1 2 x2 4. He
Economics 101 Fall 2013 Answers to Homework #6 Due Tuesday, Dec 10, 2013
 Economics 101 Fall 2013 Answers to Homework #6 Due Tuesday, Dec 10, 2013 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top
Economics 101 Fall 2013 Answers to Homework #6 Due Tuesday, Dec 10, 2013 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top
EXAMINATION 3 VERSION A "Choices Underlying Supply and Demand" November 6, 2015
 Signature: William M. Boal Printed name: EXAMINATION 3 VERSION A "Choices Underlying Supply and Demand" November 6, 215 INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed-book, closed-notes. Simple calculators are permitted,
Signature: William M. Boal Printed name: EXAMINATION 3 VERSION A "Choices Underlying Supply and Demand" November 6, 215 INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed-book, closed-notes. Simple calculators are permitted,
Lesson Linear Models Answering Various Types of Questions Algebraically
 STTWY STUDENT HNDOUT STUDENT NME DTE INTRODUCTION Many people make small items at home to sell at craft sales or on ebay or through web pages. In some cases, their costs and revenues are easily determined.
STTWY STUDENT HNDOUT STUDENT NME DTE INTRODUCTION Many people make small items at home to sell at craft sales or on ebay or through web pages. In some cases, their costs and revenues are easily determined.
Lesson 7: Cost, Revenue and Profit Functions
 Lesson 7: Cost, Revenue and Profit Functions OBJECTIVE In today s lesson, we will study study three functions fundamental in economy and business: the cost, the revenue and the profit functions. Pay close
Lesson 7: Cost, Revenue and Profit Functions OBJECTIVE In today s lesson, we will study study three functions fundamental in economy and business: the cost, the revenue and the profit functions. Pay close
Chapter 2 - Introduction to Spreadsheet Modeling
 1. Which of the following is not one of the components of a mathematical model? a. Inputs b. Outputs c. Decision variables d. None of these options 2. Which of the following is not one of the features
1. Which of the following is not one of the components of a mathematical model? a. Inputs b. Outputs c. Decision variables d. None of these options 2. Which of the following is not one of the features
2014 $1.75 $10.00 $ $1.50 $10.50 $ $1.65 $11.00 $ $2.00 $11.50 $150
 Economics 101 Fall Homework #4 Due Tuesday, November 14, Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name, and section number on top of the homework
Economics 101 Fall Homework #4 Due Tuesday, November 14, Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name, and section number on top of the homework
Economics 101 Fall 2017 Answers to Homework 5 Due:12/12/17
 Economics 101 Fall 2017 Answers to Homework 5 Due:12/12/17 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name, and section number on top of the homework
Economics 101 Fall 2017 Answers to Homework 5 Due:12/12/17 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name, and section number on top of the homework
CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior
 3-1 CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior Objectives 3-2 1. Define cost behavior After studying for fixed, this variable, and mixed costs. chapter, you should 2. Explain the role be of the able resource to: usage
3-1 CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior Objectives 3-2 1. Define cost behavior After studying for fixed, this variable, and mixed costs. chapter, you should 2. Explain the role be of the able resource to: usage
consumption function
 1 Every day you make choices on what to do with the money you have. Should you splurge on a restaurant meal or save money by eating at home? Should you buy a new car, if so how expensive of a model? Should
1 Every day you make choices on what to do with the money you have. Should you splurge on a restaurant meal or save money by eating at home? Should you buy a new car, if so how expensive of a model? Should
1. Fill in the missing blanks ( XXXXXXXXXXX means that there is nothing to fill in this spot):
 1. Fill in the missing blanks ( XXXXXXXXXXX means that there is nothing to fill in this spot): Quantity Total utility Marginal utility 0 0 XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX 200 0 = 200 1 200 XXXXXXXXXXX
1. Fill in the missing blanks ( XXXXXXXXXXX means that there is nothing to fill in this spot): Quantity Total utility Marginal utility 0 0 XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX 200 0 = 200 1 200 XXXXXXXXXXX
MATH 2070 Mixed Practice Sections
 Name: Directions: For each question, show the specific mathematical notation that leads to your answer. Round final answers to three decimals unless the context dictates otherwise. 1. The demand for board
Name: Directions: For each question, show the specific mathematical notation that leads to your answer. Round final answers to three decimals unless the context dictates otherwise. 1. The demand for board
Calculating consumer s surplus and the change in consumer s surplus Calculating compensating and equivalent variations
 In this chapter you will study ways to measure a consumer s valuation of a good given the consumer s demand curve for it The basic logic is as follows: The height of the demand curve measures how much
In this chapter you will study ways to measure a consumer s valuation of a good given the consumer s demand curve for it The basic logic is as follows: The height of the demand curve measures how much
Name: Eddie Jackson. Course & Section: BU Mid-term
 Name: Eddie Jackson Course & Section: BU204 02 Mid-term Date: July 1st, 2012 Questions: 1. Atlantis is a small, isolated island in the South Atlantic. The inhabitants grow potatoes and catch fresh fish.
Name: Eddie Jackson Course & Section: BU204 02 Mid-term Date: July 1st, 2012 Questions: 1. Atlantis is a small, isolated island in the South Atlantic. The inhabitants grow potatoes and catch fresh fish.
CHAPTER. Activity Cost Behavior
 3-1 CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior 3-2 Objectives 1. Define cost behavior After for fixed, variable, and studying this mixed costs. chapter, you should 2. Explain the role of be the resource usage model
3-1 CHAPTER Activity Cost Behavior 3-2 Objectives 1. Define cost behavior After for fixed, variable, and studying this mixed costs. chapter, you should 2. Explain the role of be the resource usage model
Intermediate Microeconomics Midterm
 Econ 201 Spring 2016 Name: Student ID: Intermediate Microeconomics Midterm Thursday April 21, 2016 Beomsoo Kim There are 7 questions and 130 possible points. There are 2 pages to this exam. Please write
Econ 201 Spring 2016 Name: Student ID: Intermediate Microeconomics Midterm Thursday April 21, 2016 Beomsoo Kim There are 7 questions and 130 possible points. There are 2 pages to this exam. Please write
S-ID Used Subaru Foresters I
 S-ID Used Subaru Foresters I Alignments to Content Standards: S-ID.B.6 Task Jane wants to sell her Subaru Forester, but doesn t know what the listing price should be. She checks on craigslist.com and finds
S-ID Used Subaru Foresters I Alignments to Content Standards: S-ID.B.6 Task Jane wants to sell her Subaru Forester, but doesn t know what the listing price should be. She checks on craigslist.com and finds
Consumer and Producer Surplus and Deadweight Loss
 Consumer and Producer Surplus and Deadweight Loss The deadweight loss, value of lost time or quantity waste problem requires several steps. A ceiling or floor price must be given. We call that price the
Consumer and Producer Surplus and Deadweight Loss The deadweight loss, value of lost time or quantity waste problem requires several steps. A ceiling or floor price must be given. We call that price the
1. III. COST BEHAVIOR
 Chapter 3 Cost Behavior Page 1 1. III. COST BEHAVIOR In this chapter we discuss the manner in which costs behave. We will discuss fixed and variable costs. As part of this discussion, we will discuss learning
Chapter 3 Cost Behavior Page 1 1. III. COST BEHAVIOR In this chapter we discuss the manner in which costs behave. We will discuss fixed and variable costs. As part of this discussion, we will discuss learning
Question 4: How do you find cost and revenue functions?
 Question 4: How do you find cost and revenue functions? All businesses produce some kind of product. That product may be something that you can hold in your hand like an MP3 player or it may be a service
Question 4: How do you find cost and revenue functions? All businesses produce some kind of product. That product may be something that you can hold in your hand like an MP3 player or it may be a service
Elasticity and Its Applications
 Elasticity and Its Applications 1. In general, elasticity is a. a measure of the competitive nature of a market. b. the friction that develops between buyer and seller in a market. c. a measure of how
Elasticity and Its Applications 1. In general, elasticity is a. a measure of the competitive nature of a market. b. the friction that develops between buyer and seller in a market. c. a measure of how
WRITTEN PRELIMINARY Ph.D. EXAMINATION. Department of Applied Economics. University of Minnesota. June 16, 2014 MANAGERIAL, FINANCIAL, MARKETING
 WRITTEN PRELIMINARY Ph.D. EXAMINATION Department of Applied Economics University of Minnesota June 16, 2014 MANAGERIAL, FINANCIAL, MARKETING AND PRODUCTION ECONOMICS FIELD Instructions: Write your code
WRITTEN PRELIMINARY Ph.D. EXAMINATION Department of Applied Economics University of Minnesota June 16, 2014 MANAGERIAL, FINANCIAL, MARKETING AND PRODUCTION ECONOMICS FIELD Instructions: Write your code
Mixture Problems in 2 & 3 variables
 Mixture Problems in 2 & 3 variables A common type of problem in multiple variables is a mixture problem. The problems involve one equation describing the mixture: the weights of the individual variables
Mixture Problems in 2 & 3 variables A common type of problem in multiple variables is a mixture problem. The problems involve one equation describing the mixture: the weights of the individual variables
Intermediate Macroeconomics
 Intermediate Macroeconomics ECON 3312 Lecture 2 William J. Crowder Ph.D. Mercantilism Economic Nationalism Beggar-thy-neighbor policies Bullionism Regulate everything! Trade restrictions Monopoly rights
Intermediate Macroeconomics ECON 3312 Lecture 2 William J. Crowder Ph.D. Mercantilism Economic Nationalism Beggar-thy-neighbor policies Bullionism Regulate everything! Trade restrictions Monopoly rights
Final Exam: ECON-100A Intermediate Microeconomics Bob Baden Section I: Answer at least two questions (answer all parts of the questions you choose)
 Final Exam: ECON-100A Intermediate Microeconomics Bob Baden Section I: Answer at least two questions (answer all parts of the questions you choose) Question 1: (16 points) Donald Fribble is a stamp collector.
Final Exam: ECON-100A Intermediate Microeconomics Bob Baden Section I: Answer at least two questions (answer all parts of the questions you choose) Question 1: (16 points) Donald Fribble is a stamp collector.
FEEDBACK TUTORIAL LETTER ASSIGNMENT 1 INTERMEDIATE MICRO-ECONOMICS IMI611S
 FEEDBACK TUTORIAL LETTER 1 st SEMESTER 2017 ASSIGNMENT 1 INTERMEDIATE MICRO-ECONOMICS IMI611S 1 Solutions and explanations to the questions are provided in italics Question One [30 marks] The current world
FEEDBACK TUTORIAL LETTER 1 st SEMESTER 2017 ASSIGNMENT 1 INTERMEDIATE MICRO-ECONOMICS IMI611S 1 Solutions and explanations to the questions are provided in italics Question One [30 marks] The current world
Part I: PPF, Opportunity Cost, Trading prices, Comparative and Absolute Advantage
 Economics 101 Spring 2018 Homework #2 Due Thursday, February 22, 2018 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name, and section number on top
Economics 101 Spring 2018 Homework #2 Due Thursday, February 22, 2018 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name, and section number on top
Distance = Rate x Time
 Math 233A Chapter 2.4: More Application Problems Objectives: Finding distance, rate, and time for going in the same direction Finding distance, rate, and time for going in towards each other Finding distance
Math 233A Chapter 2.4: More Application Problems Objectives: Finding distance, rate, and time for going in the same direction Finding distance, rate, and time for going in towards each other Finding distance
Figure 4 1 Price Quantity Quantity Per Pair Demanded Supplied $ $ $ $ $10 2 8
 Econ 101 Summer 2005 In class Assignment 2 Please select the correct answer from the ones given Figure 4 1 Price Quantity Quantity Per Pair Demanded Supplied $ 2 18 3 $ 4 14 4 $ 6 10 5 $ 8 6 6 $10 2 8
Econ 101 Summer 2005 In class Assignment 2 Please select the correct answer from the ones given Figure 4 1 Price Quantity Quantity Per Pair Demanded Supplied $ 2 18 3 $ 4 14 4 $ 6 10 5 $ 8 6 6 $10 2 8
System of two quadratic inequalities
 Lesson Plan Lecture Version System of two quadratic inequalities Objectives: Students will: Graph a quadratic inequality and describe its solution set Solve a system of quadratic equalities graphically
Lesson Plan Lecture Version System of two quadratic inequalities Objectives: Students will: Graph a quadratic inequality and describe its solution set Solve a system of quadratic equalities graphically
17 19 Best Fit Line.notebook September 19, a graph of a set of data pairs used to help you recognize and make.
 Learning Target: I can draw a best fit line on a scatter plot and use it to make predictions. p.17 Remember what a scatter plot is? a graph of a set of data pairs used to help you recognize and make. Patterns
Learning Target: I can draw a best fit line on a scatter plot and use it to make predictions. p.17 Remember what a scatter plot is? a graph of a set of data pairs used to help you recognize and make. Patterns
Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives
 CHAPTER 11 Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 11.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets (pages 369 371) Explain what a perfectly competitive market is and why a perfect
CHAPTER 11 Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 11.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets (pages 369 371) Explain what a perfectly competitive market is and why a perfect
Practice Midterm Exam Microeconomics: Professor Owen Zidar
 Practice Midterm Exam Microeconomics: 33001 Professor Owen Zidar This exam is comprised of 3 questions. The exam is scheduled for 1 hour and 30 minutes. This is a closed-book, closed-note exam. There is
Practice Midterm Exam Microeconomics: 33001 Professor Owen Zidar This exam is comprised of 3 questions. The exam is scheduled for 1 hour and 30 minutes. This is a closed-book, closed-note exam. There is
PARTITION AND ITERATION
 PARTITION AND ITERATION Nick Wasserman Marymount School of New York Ph.D. Candidate, Teachers College, Columbia University AMTNYS Annual Conference Saratoga Springs, NY LINEARITY Take a few moments and
PARTITION AND ITERATION Nick Wasserman Marymount School of New York Ph.D. Candidate, Teachers College, Columbia University AMTNYS Annual Conference Saratoga Springs, NY LINEARITY Take a few moments and
Algebra 1 CCSS Regents Exam 0814 Page 1
 Algebra 1 CCSS Regents Exam 0814 Page 1 1 Which statement is not always true? The product of two irrational numbers is irrational. The product of two rational numbers is rational. The sum of two rational
Algebra 1 CCSS Regents Exam 0814 Page 1 1 Which statement is not always true? The product of two irrational numbers is irrational. The product of two rational numbers is rational. The sum of two rational
Pricing with Market Power
 Chapter 7 Pricing with Market Power 7.1 Motives and objectives Broadly The model of perfect competition is extreme (and hence wonderfully powerful and simple) because of its assumption that each firm believes
Chapter 7 Pricing with Market Power 7.1 Motives and objectives Broadly The model of perfect competition is extreme (and hence wonderfully powerful and simple) because of its assumption that each firm believes
MICROECONOMICS II - REVIEW QUESTIONS I
 MICROECONOMICS II - REVIEW QUESTIONS I. What is a production function? How does a long-run production function differ from a short-run production function? A production function represents how inputs are
MICROECONOMICS II - REVIEW QUESTIONS I. What is a production function? How does a long-run production function differ from a short-run production function? A production function represents how inputs are
Chapter 6 Lecture - Elasticity: The Responsiveness of Demand and Supply
 Chapter 6 Lecture - Elasticity: The Responsiveness of Demand and Supply 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Measurement We define price elasticity of demand and understand how to measure it. Although
Chapter 6 Lecture - Elasticity: The Responsiveness of Demand and Supply 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Measurement We define price elasticity of demand and understand how to measure it. Although
EXAMINATION 1 VERSION A "Labor Supply and Demand" February 27, 2018
 William M. Boal Signature: Printed name: EXAMINATION 1 VERSION A "Labor Supply and Demand" February 27, 2018 INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed-book, closed-notes. Simple calculators are permitted, but
William M. Boal Signature: Printed name: EXAMINATION 1 VERSION A "Labor Supply and Demand" February 27, 2018 INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed-book, closed-notes. Simple calculators are permitted, but
Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts
 Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Chapter 2 PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright
Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Chapter 2 PowerPoint Authors: Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA Copyright
Section I, Multiple Choice (40 points)
 ECO 230, Final Exam Name: Summer I, 2003 Eastern Kentucky University Dr. Ruppel Section I, Multiple Choice (40 points): Circle the letter in front of the best answer. 1. If Canada can increase its production
ECO 230, Final Exam Name: Summer I, 2003 Eastern Kentucky University Dr. Ruppel Section I, Multiple Choice (40 points): Circle the letter in front of the best answer. 1. If Canada can increase its production
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 2 Lesson 2. It s Time for a Round-Up Rounding Amounts of Money
 Suggested time: 45 minutes Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 2 Lesson 2 It s Time for a Round-Up Rounding Amounts of Money What s important in this lesson: It is important for you to fully understand place
Suggested time: 45 minutes Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 2 Lesson 2 It s Time for a Round-Up Rounding Amounts of Money What s important in this lesson: It is important for you to fully understand place
Basics of Economics. Alvin Lin. Principles of Microeconomics: August December 2016
 Basics of Economics Alvin Lin Principles of Microeconomics: August 2016 - December 2016 1 Markets and Efficiency How are goods allocated efficiently? How are goods allocated fairly? A normative statement
Basics of Economics Alvin Lin Principles of Microeconomics: August 2016 - December 2016 1 Markets and Efficiency How are goods allocated efficiently? How are goods allocated fairly? A normative statement
Q - water 3. Q - water. Q - water. Q - water. A new equimarginal condition. Lecture 21 & 22. A single farmer. A single farmer.
 Lecture 21 & 22 A new equimarginal condition First Second The efficient allocation of a resource at one point in time, the case of surface water. Third - The MNB to every user should be equal at the efficient
Lecture 21 & 22 A new equimarginal condition First Second The efficient allocation of a resource at one point in time, the case of surface water. Third - The MNB to every user should be equal at the efficient
Find the sum of ALL of the terms in this sequence:
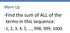 Warm Up Find the sum of ALL of the terms in this sequence: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,, 998, 999, 1000. GO OVER HOMEWORK QUIZZES Put this in Linear Section! Scatter Plot HW % vs. Grades Do you think there is a relationship
Warm Up Find the sum of ALL of the terms in this sequence: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,, 998, 999, 1000. GO OVER HOMEWORK QUIZZES Put this in Linear Section! Scatter Plot HW % vs. Grades Do you think there is a relationship
Imperfect Competition
 Imperfect Competition 6.1 There are only two firms producing a particular product. The demand for the product is given by the relation p = 24 Q, where p denotes the price (in dollars per unit) and Q denotes
Imperfect Competition 6.1 There are only two firms producing a particular product. The demand for the product is given by the relation p = 24 Q, where p denotes the price (in dollars per unit) and Q denotes
STATISTICAL TECHNIQUES. Data Analysis and Modelling
 STATISTICAL TECHNIQUES Data Analysis and Modelling DATA ANALYSIS & MODELLING Data collection and presentation Many of us probably some of the methods involved in collecting raw data. Once the data has
STATISTICAL TECHNIQUES Data Analysis and Modelling DATA ANALYSIS & MODELLING Data collection and presentation Many of us probably some of the methods involved in collecting raw data. Once the data has
Ex. p.17. Summary: a graph of a set of data pairs used to help you recognize and make.
 Learning Target: I can draw a best fit line on a scatter plot and use it to make predictions. p.17 Remember what a scatter plot is? a graph of a set of data pairs used to help you recognize and make. Patterns
Learning Target: I can draw a best fit line on a scatter plot and use it to make predictions. p.17 Remember what a scatter plot is? a graph of a set of data pairs used to help you recognize and make. Patterns
Eco 202 Exam 2 Spring 2014
 Eco 202 Exam 2 Spring 2014 PLEASE ANSWER 50 OF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. 1. Jon Brooks quit his job in a bicycle shop, where he earned $15,000 per year, to become a graduate student in economics. At the
Eco 202 Exam 2 Spring 2014 PLEASE ANSWER 50 OF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. 1. Jon Brooks quit his job in a bicycle shop, where he earned $15,000 per year, to become a graduate student in economics. At the
Response Modeling Marketing Engineering Technical Note 1
 Response Modeling Marketing Engineering Technical Note 1 Table of Contents Introduction Some Simple Market Response Models Linear model Power series model Fractional root model Semilog model Exponential
Response Modeling Marketing Engineering Technical Note 1 Table of Contents Introduction Some Simple Market Response Models Linear model Power series model Fractional root model Semilog model Exponential
Using this information, we then write the output of a firm as
 Economists typically assume that firms or a firm s owners try to maximize their profit. et R be revenues of the firm, and C be the cost of production, then a firm s profit can be represented as follows,
Economists typically assume that firms or a firm s owners try to maximize their profit. et R be revenues of the firm, and C be the cost of production, then a firm s profit can be represented as follows,
Demand The Demand curve answers this question: What quantity of a good would consumers buy at each possible price?
 1 of 6 30.4.2006 20:25 DANBY IA&S 324 Demand, Supply, and Surpluses Demand, Supply, and Surpluses Demand The Demand curve answers this question: What quantity of a good would consumers buy at each possible
1 of 6 30.4.2006 20:25 DANBY IA&S 324 Demand, Supply, and Surpluses Demand, Supply, and Surpluses Demand The Demand curve answers this question: What quantity of a good would consumers buy at each possible
MATHEMATICS High School Assessment Program Release Items
 High School Assessment Program Release Items Directions There are 20 questions on this test. Questions 1-16 are multiple-choice. Questions 17-20 are constructed-response. You must mark or write all answers
High School Assessment Program Release Items Directions There are 20 questions on this test. Questions 1-16 are multiple-choice. Questions 17-20 are constructed-response. You must mark or write all answers
Economics E201 (Professor Self) Sample Questions for Exam Two, Fall 2013
 , Fall 2013 Your exam will have two parts covering the topics in chapters 4 (page 91 through end of chapter), 5 and 6 from the Parkin chapters and chapter 10 (up to page 317, up to but not including the
, Fall 2013 Your exam will have two parts covering the topics in chapters 4 (page 91 through end of chapter), 5 and 6 from the Parkin chapters and chapter 10 (up to page 317, up to but not including the
Analyzing Accumulated Change Integrals in Action. Improper Integral
 Analyzing Accumulated Change Integrals in Action 6.1 -Perpetual Accumulation and Improper Integrals Improper Integral Definite integrals have specific numbers for both the upper limit and the lower limit.
Analyzing Accumulated Change Integrals in Action 6.1 -Perpetual Accumulation and Improper Integrals Improper Integral Definite integrals have specific numbers for both the upper limit and the lower limit.
Bremen School District 228 Social Studies Common Assessment 2: Midterm
 Bremen School District 228 Social Studies Common Assessment 2: Midterm AP Microeconomics 55 Minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements in this exam is followed by five
Bremen School District 228 Social Studies Common Assessment 2: Midterm AP Microeconomics 55 Minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements in this exam is followed by five
Managerial Economics
 Managerial Economics Estimating Demand Functions Rudolf Winter-Ebmer Johannes Kepler University Linz Winter Term 2014 Winter-Ebmer, Managerial Economics: Unit 2 - Demand Estimation 1 / 21 Why do you need
Managerial Economics Estimating Demand Functions Rudolf Winter-Ebmer Johannes Kepler University Linz Winter Term 2014 Winter-Ebmer, Managerial Economics: Unit 2 - Demand Estimation 1 / 21 Why do you need
Demand & Supply of Resources
 Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Week 1 (Part 1) Introduction Econ 101
 Week 1 (art 1) Introduction Econ 101 reliminary Concepts (Chapter 2 g 38-41 & 47-50) Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use scarce resources that nature and previous generations
Week 1 (art 1) Introduction Econ 101 reliminary Concepts (Chapter 2 g 38-41 & 47-50) Economics is the study of how individuals and societies choose to use scarce resources that nature and previous generations
Chapter 13. Microeconomics. Monopolistic Competition: The Competitive Model in a More Realistic Setting
 Microeconomics Modified by: Yun Wang Florida International University Spring, 2018 1 Chapter 13 Monopolistic Competition: The Competitive Model in a More Realistic Setting Chapter Outline 13.1 Demand and
Microeconomics Modified by: Yun Wang Florida International University Spring, 2018 1 Chapter 13 Monopolistic Competition: The Competitive Model in a More Realistic Setting Chapter Outline 13.1 Demand and
The exam has a total of 50 questions (100 points). You will have 75 minutes to complete the exam. Good Luck!
 Econ 111 Practice Midterm 1 The exam has a total of 50 questions (100 points). You will have 75 minutes to complete the exam. Good Luck! Print your Name Sign the honor Pledge affirming that you have neither
Econ 111 Practice Midterm 1 The exam has a total of 50 questions (100 points). You will have 75 minutes to complete the exam. Good Luck! Print your Name Sign the honor Pledge affirming that you have neither
Keystone Exam Project Based Assessment
 Keystone Exam Project Based Assessment Title: Winter Fun Fair Keystone Exam: Algebra 1 Module: 2 Linear Functions and Data Organizations Eligible Content Assessed: A1.2.1.1.1 Analyze a set of data for
Keystone Exam Project Based Assessment Title: Winter Fun Fair Keystone Exam: Algebra 1 Module: 2 Linear Functions and Data Organizations Eligible Content Assessed: A1.2.1.1.1 Analyze a set of data for
Ratios and Proportional Relationships: Lessons 7-10
 Unit 7-1 Lessons 7-10 Ratios and Proportional Relationships: Lessons 7-10 Name Date Homework Book Math 7: Mr. Sanford Lessons 7-10: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1-7 Lesson 7: Unit Rate as the Constant
Unit 7-1 Lessons 7-10 Ratios and Proportional Relationships: Lessons 7-10 Name Date Homework Book Math 7: Mr. Sanford Lessons 7-10: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1-7 Lesson 7: Unit Rate as the Constant
3. Pierre says that he will spend exactly $5.00 a day on candy bars, regardless of the price of candy bars. Pierre s demand for candy bars is:
 Each Multiple-Choice Question is worth 3 points (Total 60 points). 1. An economy s production of two goods is efficient if: a. both goods are unit elastic. b. all members of society consume equal portions
Each Multiple-Choice Question is worth 3 points (Total 60 points). 1. An economy s production of two goods is efficient if: a. both goods are unit elastic. b. all members of society consume equal portions
Problem Set 3 Eco 112, Spring 2011 Chapters covered: Ch. 6 and Ch. 7 Due date: March 3, 2011
 Problem Set 3 Eco 112, Spring 2011 Chapters covered: Ch. 6 and Ch. 7 Due date: March 3, 2011 There are 30 multiple choice questions in this problem set. Answer these questions by the beginning of the class
Problem Set 3 Eco 112, Spring 2011 Chapters covered: Ch. 6 and Ch. 7 Due date: March 3, 2011 There are 30 multiple choice questions in this problem set. Answer these questions by the beginning of the class
Section 4.2 Applications and Modeling of Quadratic Functions
 Section 4.2 Applications and Modeling of Quadratic Functions Objectives Set up a quadratic function to model certain "real life" situations. Use quadratic models and interpret results in "real life" terms.
Section 4.2 Applications and Modeling of Quadratic Functions Objectives Set up a quadratic function to model certain "real life" situations. Use quadratic models and interpret results in "real life" terms.
Economics, 2 nd edition N. Gregory Mankiw and Mark P. Taylor ISBN Cengage Learning EMEA
 1. The following information describes the value Lauren Landlord places on having her five houses repainted. She values the repainting of each house at a different amount depending on how badly it needs
1. The following information describes the value Lauren Landlord places on having her five houses repainted. She values the repainting of each house at a different amount depending on how badly it needs
Unit 4: Consumer choice
 Unit 4: Consumer choice In accordance with the APT programme the objective of the lecture is to help You to: gain an understanding of the basic postulates underlying consumer choice: utility, the law of
Unit 4: Consumer choice In accordance with the APT programme the objective of the lecture is to help You to: gain an understanding of the basic postulates underlying consumer choice: utility, the law of
Examining the Correlation Between GDP per Capita and Deforestation in 2005 in 38 Countries
 Examining the Correlation Between GDP per Capita and Deforestation in 2005 in 38 Countries Introduction A country s treatment of its environment is dictated by a multitude of factors the domestic economy,
Examining the Correlation Between GDP per Capita and Deforestation in 2005 in 38 Countries Introduction A country s treatment of its environment is dictated by a multitude of factors the domestic economy,
6. In the early part of 1998, crude oil prices fell to a nine-year low at $13.28 a barrel.
 Questions 1. Delta Software earned $10 million this year. Suppose the growth rate of Delta's profits and the interest rate are both constant and Delta will be in business forever. Determine the value of
Questions 1. Delta Software earned $10 million this year. Suppose the growth rate of Delta's profits and the interest rate are both constant and Delta will be in business forever. Determine the value of
In-class Practice questions for Perfect Competitive Market
 In-class Practice questions for Perfect Competitive Market 0. Assume that a very large number of firms in an industry all have access to the same production technology. The total cost function associated
In-class Practice questions for Perfect Competitive Market 0. Assume that a very large number of firms in an industry all have access to the same production technology. The total cost function associated
Exam 1 Version A A = 4; A- = 3.7; B+ = 3.3; B = 3.0; B- = 2.7; C+ = 2.3; C = 2.0; C- = 1.7; D+ = 1.3; D = 1.0; F = 0
 BA 210 Exam 1 Version A Dr. Jon Burke This is a 100-minute exam (1hr. 40 min.). There are 8 questions (12.5 minutes per question). The exam begins exactly at the normal time that class starts. To avoid
BA 210 Exam 1 Version A Dr. Jon Burke This is a 100-minute exam (1hr. 40 min.). There are 8 questions (12.5 minutes per question). The exam begins exactly at the normal time that class starts. To avoid
Practice Problems. Skills Practice
 Practice Problems Skills Practice 1. Solve the proportions. Simplify your answers. Round answers to the nearest hundredth as needed. Show all work. 28 3.5 p 12 a. b. x 5 5 50 c. 11 m c. 20 6 4 5 8 10 w
Practice Problems Skills Practice 1. Solve the proportions. Simplify your answers. Round answers to the nearest hundredth as needed. Show all work. 28 3.5 p 12 a. b. x 5 5 50 c. 11 m c. 20 6 4 5 8 10 w
ELASTICITY. Chapt er. Key Concepts
 Chapt er 4 ELASTICITY Key Concepts Price Elasticity of Demand The price elasticity of demand is a units-free measure of responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price when all
Chapt er 4 ELASTICITY Key Concepts Price Elasticity of Demand The price elasticity of demand is a units-free measure of responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price when all
學號 姓名 學號 姓名 學號 姓名 學號 姓名 學號 姓名
 小組成員 Section I. Multiple Choice Questions 1. If there is pollution in producing a product, then the market equilibrium price A) is too high and equilibrium quantity is too low. B) and equilibrium quantity
小組成員 Section I. Multiple Choice Questions 1. If there is pollution in producing a product, then the market equilibrium price A) is too high and equilibrium quantity is too low. B) and equilibrium quantity
Getting Started with OptQuest
 Getting Started with OptQuest What OptQuest does Futura Apartments model example Portfolio Allocation model example Defining decision variables in Crystal Ball Running OptQuest Specifying decision variable
Getting Started with OptQuest What OptQuest does Futura Apartments model example Portfolio Allocation model example Defining decision variables in Crystal Ball Running OptQuest Specifying decision variable
STAT/MATH Chapter3. Statistical Methods in Practice. Averages and Variation 1/27/2017. Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean
 STAT/MATH 3379 Statistical Methods in Practice Dr. Ananda Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics SHSU 1 Chapter3 Averages and Variation Copyright Cengage Learning.
STAT/MATH 3379 Statistical Methods in Practice Dr. Ananda Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics SHSU 1 Chapter3 Averages and Variation Copyright Cengage Learning.
I enjoy teaching this class. Good luck and have a nice Holiday!!
 ECON 202-501 Fall 2008 Xiaoyong Cao Final Exam Form A Instructions: The exam consists of 2 parts. Part I has 35 multiple choice problems. You need to fill the answers in the table given in Part II of the
ECON 202-501 Fall 2008 Xiaoyong Cao Final Exam Form A Instructions: The exam consists of 2 parts. Part I has 35 multiple choice problems. You need to fill the answers in the table given in Part II of the
Managerial Economics 2013 Block Course by MFZ,TUT CH 3& 4 in your text book. Please you need text book okay??
 CH 3& 4 in your text book. Please you need text book okay?? ! " " " #! $! % % & & & ' ( ) # % !* + % ( , % % !* + % ( ' -."/." 01. ! 2 3, ) 4 " 4 " 5 3, ) %, % ", % " " " " #!! % 3 ) ' " !* + % ( , % %
CH 3& 4 in your text book. Please you need text book okay?? ! " " " #! $! % % & & & ' ( ) # % !* + % ( , % % !* + % ( ' -."/." 01. ! 2 3, ) 4 " 4 " 5 3, ) %, % ", % " " " " #!! % 3 ) ' " !* + % ( , % %
Slide Set 3: Consumer Choice Market Demand & Elasticity
 Economics 10 Slide Set 3: Consumer Choice Market Demand & Elasticity University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Lecture Outline Consumer preferences, Utility diminishing marginal utility Marginal Benefit,
Economics 10 Slide Set 3: Consumer Choice Market Demand & Elasticity University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Lecture Outline Consumer preferences, Utility diminishing marginal utility Marginal Benefit,
2.6 Price elasticity of demand
 2.6 Price elasticity of demand Part 1 - PED is a measure of the responsiveness of consumers to a change in the price of a particular good. With data from a demand schedule, we can calculate the PED for
2.6 Price elasticity of demand Part 1 - PED is a measure of the responsiveness of consumers to a change in the price of a particular good. With data from a demand schedule, we can calculate the PED for
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 2 Lesson % OFF Sale Today Only! Percent and Discounts
 Suggested time: 45 minutes Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 2 Lesson 6 100% OFF Sale Today Only! Percent and Discounts What s important in this lesson: It is important for you to have a solid understanding
Suggested time: 45 minutes Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 2 Lesson 6 100% OFF Sale Today Only! Percent and Discounts What s important in this lesson: It is important for you to have a solid understanding
Name: R Number: Roster #:
 ECO 2305-002 ** TEST 2 ** Ibrahim Ozayturk Name: R Number: Roster #: Use the following to answer question 1: Figure: Consumer Surplus 1. (Figure: Consumer Surplus) In the figure, when the price falls from
ECO 2305-002 ** TEST 2 ** Ibrahim Ozayturk Name: R Number: Roster #: Use the following to answer question 1: Figure: Consumer Surplus 1. (Figure: Consumer Surplus) In the figure, when the price falls from
Chapter 6 Perfectly Competitive Markets
 Chapter 6 Perfectly Competitive Markets 1. A firm sells a product in a perfectly competitive market, at a price of $50. The firm has a fixed cost of $30. Fill in the following table and indicate the level
Chapter 6 Perfectly Competitive Markets 1. A firm sells a product in a perfectly competitive market, at a price of $50. The firm has a fixed cost of $30. Fill in the following table and indicate the level
9.7 Getting Schooled. A Solidify Understanding Task
 35 9.7 Getting Schooled A Solidify Understanding Task In Getting More $, Leo and Araceli noticed a difference in men s and women s salaries. Araceli thought that it was unfair that women were paid less
35 9.7 Getting Schooled A Solidify Understanding Task In Getting More $, Leo and Araceli noticed a difference in men s and women s salaries. Araceli thought that it was unfair that women were paid less
a) What is the opportunity cost of producing the first 5 coconuts? b) What is the opportunity cost of producing the first 2 fish?
 Economics 101 Fall 2012 Answers to Homework #2 Due 10/9/12 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework
Economics 101 Fall 2012 Answers to Homework #2 Due 10/9/12 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework
