On colouring epon-embedded tissue sections with Sudan black B or Nile blue A for light microscopy
|
|
|
- Luke Griffith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 109 On colouring epon-embedded tissue sections with Sudan black B or Nile blue A for light microscopy By S. M. McGEE-RUSSELL and N. B. SMALE (From the Electron Microscopy Laboratory, Virus Research Unit, Medical Research Council Laboratories, Carshalton, Surrey) With one plate (fig. i) Summary Sections of osmium-fixed tissues embedded in epon 812 colour with either Sudan black B or Nile blue A solutions to reveal a variety of detail by direct microscopy with normal apochromatic or semi-apochromatic objectives. The clarity of the coloration gives a picture fully comparable to that seen by phase-contrast microscopy. The plastic is not removed, i-p sections or thinner sections down to green or gold, are mounted on clean glass slides by drying down from 20% acetone/water after flattening on a hot plate. Colouring is carried out at room temperature in Sudan black B (saturated solution in 70% alcohol) for 1 to 2 h. The result is a reversed or negative effect, for the epon plastic takes the stain avidly, but dense elements of the tissue do not, and appear white against a blue background of stained plastic. Lipid droplets retain a capacity to colour, becoming dark blue to blue-black. Nile blue sulphate (1% aqueous solution) colours thin sections of tissue in 1 to 2 h at 6o C, acting apparently as a basic dye on most cell elements, and also colours lipid droplets dark blue. After both techniques the sections are mounted in Farrants's medium. Introduction Material and methods.... Colouring epon sections with Sudan black B Solutions required.... Schedule Result Comments Colouring epon sections with Nile blue A Solutions required.... Schedule Result Comments References Contents page 09 Introduction THE recent publication by Luft (1961) of a simple and reliable method for the embedding of tissue for electron microscopy in epoxy resin, epon 812, and the work of Glauert, Rogers, and Glauert (1956), Glauert and Glauert (1958), Kushida (1959), and Finck (i960), mark a most significant step forward in [Quart. J. micr. Sci., Vol. 104, pt. 1, pp , 1963.]
2 no McGee-Russell and Smale Colouring epon sections for technique, and many laboratories have all but eliminated from their procedures the use of methacrylate. In the last decade various staining methods have been applied to tissues embedded in methacrylate, since it is possible to achieve some staining of structures without removal of the plastic; a greater number of techniques succeed after removal of the plastic, which is comparatively simple. It is not, however, so easy to remove epoxy resins from sections of tissue. Routine inspection of i- to 2-JJ. sections with the light microscope is an important part of the technique of thin sectioning. It is very satisfactorily carried out using positive phase-contrast objectives and 'anoptral' contrast objectives (commercially made by Reichert after Wilska, 1953), see Palay and others (1962). However, not all laboratories are equipped for this type of observation, and it is desirable that there should be available some simple staining techniques for use on epon-embedded material, without removal of the plastic, which will yield the same type of information when studied with ordinary objectives by direct microscopy. We have established two such techniques: either colouring with Sudan black B, or with Nile blue A, which give results of such clarity that they can be highly recommended. The information to be derived from their use is fully comparable to that obtained by phase-contrast microscopy and, indeed, it has already proved possible to detect, by the use of Nile blue A, structures known to exist from electron micrographs but not noticed by phase contrast. Material and methods Sections of material embedded in epon 812 (obtained as epikote 812, Shell Chemical Company Limited, 15/17 Great Marlborough Street, London, W. 1. batch 3 and batch 10) according to the procedure of Luft (1961), were cut on 'Huxley' ultramicrotomes (Huxley, 1957) at a thickness of 1 p or less using glass knives. This was done more quickly and easily on a modified prototype (McGee-Russell and others, 1962) but could also be done satisfactorily on the commercially obtainable machine (Cambridge Instrument Company). Two principal types of tissue were used: either Krebs II ascites cells pelleted by centrifugation in buffered osmium tetroxide, or cerebral ganglion of the snail Helix pomatia, fixed by immersion fixation in buffered osmium (exact constitution of the fixative, and the proportion of added calcium chloride as recorded by Palay and others, 1962). With both types of material results were similar. The sections were floated on to a droplet of 20% acetone/distilled water, and warmed for 5 to 10 sec on a hot plate in order to flatten them. The fluid was drained off and the sections were allowed to dry down on to the warm, clean, glass slide. With no further treatment, the slides were placed in staining solutions for different lengths of time. Results were unsatisfactory with toluidine blue and Sudan IV for periods of staining up to 22 h, no striking differentiation of elements being obtained. However, the following two techniques, arrived at after similar tests, can be recommended.
3 Solutions required light microscopy Colouring epon sections with Sudan black B Sudan black B in 70% alcohol, saturated solution prepared by refluxing in the normal way. Filter before use. (Sample used in the tests: B.D.H. standard reagent); Farrants's medium (Baker, i960). Schedule Place epon sections of osmium-fixed tissues (thickness preferably i/ior less) mounted on clean glass slides directly into the solution of Sudan black B in a Coplin jar. Allow to stain for 1 to 2 h at room temperature. Remove the slide from the Coplin jar and rinse off the remaining Sudan black with a gentle stream of distilled water. Drain off the excess water and mount beneath a coverslip in Farrants's medium. View with an intense light source. Result The epon plastic colours intensely with Sudan black to give a bright blue colour, when viewed with high intensity transmitted illumination. This appears as a general background colour against which the densest elements of the tissue, such as the nucleoli, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, and so on (from which, presumably, the plastic is largely excluded) appear as clear white objects, almost as if viewed by dark ground microscopy. It is a startling image (fig. 1, A). Other, presumably less dense elements, partially penetrated by the plastic, such as the general cytoplasm and mitochondria, appear in pale shades of greyish blue. Granules such as the yellow granules of the neurone of the snail Helix (Chou, 1957 a, b), which have intrinsic colour, may remain completely uncoloured by Sudan black and stand out clearly (fig. 1, A). Large lipid granules, such as those observed in ascites tumour cells (Ross, 1961), or vertebrate liver cells, or the same snail neurones, retain a capacity to colour with the Sudan black, and become intensely blue-black. The histochemical specificity of this coloration has not been established firmly, but the site of coloration appears to be the same as that determined by valid histochemical techniques, using Sudan reagents. Comments Some difficulty may be experienced when using the Sudan black solution, as the sections are liable to float off in the liquid. This can be overcome by pre-coating the slide with a very thin film of 'complete resin mixture' (Luft, 1961) made extremely dilute with acetone. Such a film dries quickly and can be sufficiently hardened in a 6o C oven in 10 to 15 min. Sections dried down on to such a film from acetone/water become firmly attached, and will not be lost during treatment with Sudan black solutions. The thin film of plastic will, however, stain, and although this does not disturb the result so far as the m
4 ii2 McGee-Russell and Smale Colouring epon sections for section is concerned, it gives a less pleasing slide. Clean slides normally ensure adhesion of the sections. The unusual result of this use of Sudan black immediately makes one ask whether it is a property of this compound alone. Tests carried out with Sudan IV solutions showed that over periods up to 20 h the plastic colours slightly pink. There is no striking differentiation of cellular elements. There is no colouring of large lipid droplets. Hence the capacity of the two Sudan reagents to colour lipids would not appear to be related to their ability to colour the plastic. The slightly basic nature of Sudan black may be significant. One may also inquire whether the result with Sudan black is restricted to this particular resin mixture. Tests were carried out on sections cut from blocks of tissue embedded in methacrylate, vestopal (Ryter and Kellenberger, 1958), araldite (Glauert and Glauert, 1958), and X 133/2097 (Staubli, i960). None gave as satisfactory a result as the epon-embedded material. The methacrylate-embedded tissue (newt intestine) showed slight coloration: the microvillar border of the intestinal epithelial cells coloured a pale blue, and the goblet cells developed some colour. The epoxy and polyester resins showed a fair degree of staining with Sudan black, but the time required for the uptake of the dye varied. Staubli's X 133/2097 gave a result very similar to the epon, in 1 h. Vestopal took 3 to 4 h to achieve some coloration of the plastic. Araldite showed some colour only after immersion for 22 h, and even after FIG. 1 (plate), i-y. sections of cerebral ganglion of the snail H. pomatiafixedin buffered osmium and embedded in epon 812. The photomicrographs were made on a Reichert Zetopan microscope with a Reichert 18 mm apochromatic X 100 oil-immersion objective, and plan eyepiece X 8, on Polaroid Land type 55 P/N 4 X 5 in. film, using the polaroidfilmholder model 500 in a special camera mount manufactured in the workshop of these laboratories by Mr. B. Firmager, under the direction of Mr. R. Emery. The final prints used here were made by normal photographic enlargement from polaroid negatives. A, epon section of snail nerve-cells coloured with Sudan black B. Dense elements of the cells such as the nuclear membranes, chromatin, nucleoli, and some cytoplasmic inclusions stand out in reversed contrast as white objects against the dark background of the plastic which is coloured deep blue. Lipid granules (Ig) colour dark blue to blue-black. General cytoplasm is differentiated in shades of greyish blue. Certain cytoplasmic inclusions which have intrinsic colour are unstained, and stand out prominently because of their own colour, e.g. the complex yellow granules (yg), chracteristic of these cells. The particle marked yg is a clear demonstration of the position of small dense particles within the body of the complex yellow granule. Some authors (e.g. Chou, 1957) have emphasized the occurrence of external 'satellites' associated with the cytoplasmic inclusions of snail neurones; internal densities would appear to be equally prominent. This photomicrograph demonstrates that the Sudan black technique enables one to detect sectioning artifacts easily: tramlines indicative of a deteriorating knife edge run from the top right to the bottom left of the picture. B, epon section of snail nerve-cells coloured with Nile blue A. A delicate coloration of most of the cellular elements is achieved. Nuclear membrane, chromatin,filamentouselements in the cytoplasm, cytoplasmic granules, and cell membranes are all differentiated in shades of blue. Background plastic is colourless. Note that the large lipid granules (Ig) are coloured a dark blue, and that, also, the complex granules (yg) are coloured blue. A tiny punctate granule (pg) about O-6 n in diameter can be detected easily in this type of preparation. These granules can barely be distinguished in unstained plastic sections of similar cells by phase-contrast microscopy, but are prominent in electron micrographs (observations to be published). They are not mitochondria, which in electron micrographs of these cells show profiles which would indicate that the majority of the mitochondria are filamentous.
5 FIG. I S. M. McGEE-RUSSELL and N. B. SMALE
6 light microscopy h araldite did not colour as darkly as the epon after 2 h. However, a similar reversed effect was achieved, and dense elements such as sperm-heads and basement membranes showed up white against the pale blue plastic. It remains to be shown which components in the embedding media are responsible for these colorations with Sudan black. Colouring epon sections with Nile blue A Solutions required 1 % aqueous solution of Nile blue A. Filter before use. (Sample used in this work: Nile blue sulphate, Hopkin and Williams Ltd., Chadwell Heath, batch no , kindly given to us by Dr. G. David); Farrants's medium. Schedule Place the epon sections (1 /J. or less in thickness) of osmium-fixed tissue, mounted on glass slides, directly into the solution of Nile blue A in a Coplin jar. Allow to colour in a 6o C oven for 1 to 2 h. Remove the slide from the warm Nile blue solution and rinse with a gentle stream of distilled water. Drain and mount in Farrants's medium. Result The majority of the elements of the cells of the tissue are dyed with delicacy and clarity in different shades of blue. The plastic is almost uncoloured, although a very faint pink may be discerned. The nuclear membrane, chromatin, chromosomes, cell membrane, mitochondria, and cytoplasmic inclusions are all well shown. There is a remarkable correspondence between the stained image and the image seen by phase-contrast microscopy of the same stained section; the Nile blue in fact enhances the phase-contrast image, and it is a useful exercise to go rapidly from phase contrast to bright field, and back again, whilst viewing the material. The colouring of lipid inclusions is worthy of comment. In snail neurones (fig. 1, B) and in ascites tumour cells, it is apparent that the lipid droplets coloured by the Sudan black technique are coloured by the Nile blue, but that the Nile blue also colours other lipid-containing granules, for example the yellow granules of complex character found in the cytoplasm of the Helix neurone (yg in fig. 1). It colours more generally than Sudan black, when used on plastic sections, and gives a most satisfactory morphological picture. Comments We have experienced no difficulty with sections detaching during staining with Nile blue A solutions, and no special precautions need be taken. Brief experience suggests that it is possible to dehydrate the Nile-bluecoloured sections rapidly in acetone, pass them through xylol, and mount them in Canada balsam to achieve what may be a permanent preparation.
7 ii4 McGee-Russell and Smale Colouring epon sections for This is not possible after Sudan black. The degree of permanence, however, has still to be established by the passage of time. The questions posed for the effect obtained with Sudan black must be considered again for Nile blue A. Is the colouring effect a special property of this dyestuff? Does Nile blue A produce a coloration with tissue supported in other embedding mixtures? Coloration with Nile blue is well known to be a complex process. The oxazine component of the dyestuff can act as a basic dye. Resistance of the stained sections to acetone, mentioned above, suggests that it is the basic property of the dyestuff which is significant in the reaction with epon-embedded tissue. We therefore tested the ability of another wellknown basic dye, toluidine blue, to stain sections of this kind. Ascites tumour cells are intensely basiphilic after normal methods of preparation either as smears, or in paraffin sections, and stain heavily with toluidine blue. This property cannot be shown after fixation in osmium tetroxide and embedding in epon 812, and we were unable to obtain any satisfactory staining of the plastic sections with toluidine blue. The basic character of the dyestuff would not, therefore, appear to be the cause of the colouring effect with Nile blue A. We tested the same variety of tissues and embedding media to determine the effect upon the Nile blue colouring. The Nile blue method produces pleasing results with methacrylate, araldite, and vestopal sections in 1 to 2 h, and acts as an excellent general colouring agent for most of the cellular elements. With Staubli's X 133/2097 (tissue: digestive gland of Helix) in 1 to 2 h there is some uptake of Nile blue on to the plastic, which colours pink, but the elements of the tissue, nuclear membrane, chromatin, and complex cytoplasmic granules, dye in well-differentiated shades of blue, and stand out distinctly. The background pink coloration does not obscure the informative dyeing effect. These results would appear to indicate that the colouring with Nile blue A is dependent upon the properties of the embedded tissue rather than upon the nature of the embedding plastic. The Nile blue technique can be recommended as an excellent general method for the study of plastic embedded tissues. It is a pleasure to acknowledge the hard work of Dr. W. C. de Bruyn, of the University of Leiden, who co-operated with the senior author (S. M. M. R.) in a survey of embedding media, and prepared the blocks of material embedded in araldite, vestopal, and X 133/2097, whilst visiting the Department of Zoology, Birkbeck College, University of London, during It is also a pleasure to thank Dr. F. K. Sanders for his enthusiasm and initiative in encouraging work in electron microscopy in these laboratories. References BAKER, J. R., Cytological technique, 4th edition. London (Methuen). CHOU, J. T. Y., 1957a. Quart J. micr. Sci., 98, *- Ibid., 98, 59. FINCK, H., i960. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., 7, 27.
8 light microscopy 115 GLAUERT, A. M., ROGERS, G. E., and GLAUERT, R. H,, Nature, Lond., 178, 803. and GLAUERT, R. H., J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., 4, 191. HUXLEY, A. F., J. Physiol., 173, 73P. KUSHIDA, H., Electron Microscopy, 8, 72. LUFT, J. H., J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., 9, 409. MCGEE-RUSSELL, S. M., ROBERTS, F. H., and JACOBS, J. K., Quart. J. micr. Sci. (In press). PALAY, S. L., MCGEE-RUSSELL, S. M., GORDON, S., and GRILLO, M. A., J. Cell Biol. (formerly J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.), 12, 385. Ross, K. F. A., Quart. J. micr. Sci., 102, 59. RYTER, A., and KELLENBERGER, E., J. Infrastructure Res., 2, 200. STAUBLI, W., i960. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris., 250, WiLSKA, A., Nature, Lond., 171, 697.
Preparation of tissues for study
 Preparation of tissues for study HISTOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic
Preparation of tissues for study HISTOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic
A Study of Potassium Permanganate 'Fixation' for Electron Microscopy
 241 A Study of Potassium Permanganate 'Fixation' for Electron Microscopy By S. BRADBURY AND G. A. MEEK (From the Department of Human Anatomy, South Parks Road, Oxford) With five plates (figs, i, 2, 4,
241 A Study of Potassium Permanganate 'Fixation' for Electron Microscopy By S. BRADBURY AND G. A. MEEK (From the Department of Human Anatomy, South Parks Road, Oxford) With five plates (figs, i, 2, 4,
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION. TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D
 BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D Why do we need EM for biological samples? (O'Connor and Adams, 2010) Why do we need EM for biological samples?
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D Why do we need EM for biological samples? (O'Connor and Adams, 2010) Why do we need EM for biological samples?
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS
 PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
Electron Microscopy (EM) Grid
 Anirban Som 25-01-14 Instrumental technique presentation Electron Microscopy (EM) Grid What I will talk about Some basic topics about EM grid Home-made grid preparation Grid cleaning Carbon coating and
Anirban Som 25-01-14 Instrumental technique presentation Electron Microscopy (EM) Grid What I will talk about Some basic topics about EM grid Home-made grid preparation Grid cleaning Carbon coating and
Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM
 Collaborative Research Center (SFB 1278) Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM Rainer Heintzmann, Fengjiao Ma, Institute of Physical Chemistry Stephanie Höppener, Martin
Collaborative Research Center (SFB 1278) Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM Rainer Heintzmann, Fengjiao Ma, Institute of Physical Chemistry Stephanie Höppener, Martin
THE USE OF LEAD CITRATE AT HIGH ph AS AN ELECTRON-OPAQUE STAIN IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
 THE USE OF LEAD CITRATE AT HIGH ph AS AN ELECTRON-OPAQUE STAIN IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY EDWARD S. REYNOLDS. From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston Aqueous solutions of lead salts
THE USE OF LEAD CITRATE AT HIGH ph AS AN ELECTRON-OPAQUE STAIN IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY EDWARD S. REYNOLDS. From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston Aqueous solutions of lead salts
BrdU IHC Kit. For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells
 K-ASSAY BrdU IHC Kit For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-077 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in
K-ASSAY BrdU IHC Kit For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-077 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in
Manufactured by. Zyagen Barnes Canyon Road San Diego, CA 92121, USA
 Alkaline Phosphatase Immunohistochemistry Detection kits For detection of mouse, rabbit, goat, rat, sheep, chicken, guinea pig, and human primary antibodies Size: 500 Tests Catalog #: AK-011, Mouse Kit
Alkaline Phosphatase Immunohistochemistry Detection kits For detection of mouse, rabbit, goat, rat, sheep, chicken, guinea pig, and human primary antibodies Size: 500 Tests Catalog #: AK-011, Mouse Kit
Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count
 2014-09- 01 Blood Page 1 of 5 Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count Aim: Learn to count cells, observe and identify different blood cells in a smear, quantify their proportions and count RBCs per µl (mm^3) using
2014-09- 01 Blood Page 1 of 5 Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count Aim: Learn to count cells, observe and identify different blood cells in a smear, quantify their proportions and count RBCs per µl (mm^3) using
Working Reagent Preparation 1:1,000 dilution in standard Alcoholic Ortho- Phosphoric acid staining solution
 www.smobio.com Product Information FluoroStain Protein Fluorescent Staining Dye (Red, 1,000X) PS1000 1 ml x 1 PS1001 1 ml x 5 Storage Protected from light -20 C for 24 months Working Reagent Preparation
www.smobio.com Product Information FluoroStain Protein Fluorescent Staining Dye (Red, 1,000X) PS1000 1 ml x 1 PS1001 1 ml x 5 Storage Protected from light -20 C for 24 months Working Reagent Preparation
Baraa Ayed AL-Odat. Israa Ayed. Heba kalbouneh
 1 Baraa Ayed AL-Odat Israa Ayed Heba kalbouneh Introduction: "lecture #1" The name " histology " is derived from the Greek words: "histo" means a tissue and "logos" means the study of. So, Histology mean
1 Baraa Ayed AL-Odat Israa Ayed Heba kalbouneh Introduction: "lecture #1" The name " histology " is derived from the Greek words: "histo" means a tissue and "logos" means the study of. So, Histology mean
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes
 Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 162-1 67 A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells ANTONIO COPPOLA From the Department ofpathology, College of Medicine, Downstate Medical
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 162-1 67 A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells ANTONIO COPPOLA From the Department ofpathology, College of Medicine, Downstate Medical
Fluorescence Microscopy. Terms and concepts to know: 10/11/2011. Visible spectrum (of light) and energy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Louisiana Tech University Ruston, Louisiana Microscopy Workshop Dr. Mark DeCoster Associate Professor Biomedical Engineering 1 Terms and concepts to know: Signal to Noise Excitation
Fluorescence Microscopy Louisiana Tech University Ruston, Louisiana Microscopy Workshop Dr. Mark DeCoster Associate Professor Biomedical Engineering 1 Terms and concepts to know: Signal to Noise Excitation
Label Tape FAQs and Technical Information Pertaining to Brother Label Printers PT-9700PC and PT-9800PCN
 1-800-777-7020 www.cybermetrics.com Label Tape FAQs and Technical Information Pertaining to Brother Label Printers PT-9700PC and PT-9800PCN Label Tape FAQs Can I use these labels outside? If the label
1-800-777-7020 www.cybermetrics.com Label Tape FAQs and Technical Information Pertaining to Brother Label Printers PT-9700PC and PT-9800PCN Label Tape FAQs Can I use these labels outside? If the label
haematology DDKItalia Stains for blood and bone marrow classic staining methods, fast stain and foil staining haematology
 DDKItalia Stains for blood and bone marrow classic staining methods, fast stain and foil staining haematology Haematological staining methods All reagents from one source Fast and safe processes Easy to
DDKItalia Stains for blood and bone marrow classic staining methods, fast stain and foil staining haematology Haematological staining methods All reagents from one source Fast and safe processes Easy to
KCC Path-Core Page 1 of 5
 Instructions for Sample preparation for Paraffin embedding PLEASE NOTE: There is no one-size-fits-all method of tissue preparation for all experimental designs. Before harvesting tissue, you need to assess
Instructions for Sample preparation for Paraffin embedding PLEASE NOTE: There is no one-size-fits-all method of tissue preparation for all experimental designs. Before harvesting tissue, you need to assess
Electron Microscopy of Proteus vulgaris Exposed to
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 1968, p. 1956-1960 Copyright ( 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 95, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Electron Microscopy of Proteus vulgaris Exposed to Cephalothin' NICHOLAS
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 1968, p. 1956-1960 Copyright ( 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 95, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Electron Microscopy of Proteus vulgaris Exposed to Cephalothin' NICHOLAS
ab BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit
 ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
ZytoDot. 2C SPEC HER2/CEN 17 Probe
 ZytoDot 2C SPEC HER2/CEN 17 Probe C-3032-400 C-3032-100 40 (0.4 ml) 10 (0.1 ml) For the detection of the human HER2 gene and alphasatellites of chromosome 17 by chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH)....
ZytoDot 2C SPEC HER2/CEN 17 Probe C-3032-400 C-3032-100 40 (0.4 ml) 10 (0.1 ml) For the detection of the human HER2 gene and alphasatellites of chromosome 17 by chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH)....
Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them
 Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them Focus on: Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Osmium tetroxide M. Kuwajima/Kristen Harris Lab EM processing and
Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them Focus on: Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Osmium tetroxide M. Kuwajima/Kristen Harris Lab EM processing and
In-Gel Western Detection Using Near-Infrared Fluorescence
 In-Gel Western Detection Using Near-Infrared Fluorescence Developed for: Aerius, and Odyssey Family of Imagers Please refer to your manual to confirm that this protocol is appropriate for the applications
In-Gel Western Detection Using Near-Infrared Fluorescence Developed for: Aerius, and Odyssey Family of Imagers Please refer to your manual to confirm that this protocol is appropriate for the applications
Electron Microscopic Study of a Slime Layer
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1969, p. 316-325 Copyright @ 1969 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 99, No. I Printed in U.S.A. Electron Microscopic Study of a Slime Layer H. C. JONES, I. L. ROTH, AND
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1969, p. 316-325 Copyright @ 1969 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 99, No. I Printed in U.S.A. Electron Microscopic Study of a Slime Layer H. C. JONES, I. L. ROTH, AND
Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001
 INSTRUCTIONS Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001 Highlights Easily isolates genomic DNA in any targeted microscopic tissue area on a slide. The simple procedure combines Pinpoint tissue
INSTRUCTIONS Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001 Highlights Easily isolates genomic DNA in any targeted microscopic tissue area on a slide. The simple procedure combines Pinpoint tissue
Visualization of Normal & Transformed Cells - Kit 1. Introduction. Your kit includes the following materials:
 Visualization of Normal & Transformed Cells - Kit 1 CellServ@FAES/NIH www.cellservkits.com Introduction Cells in culture may assume a variety of morphologies, most often quite different from their shape
Visualization of Normal & Transformed Cells - Kit 1 CellServ@FAES/NIH www.cellservkits.com Introduction Cells in culture may assume a variety of morphologies, most often quite different from their shape
Activity 2.1. Activity 2.2. Looking at animal cells. Looking at plant cells
 Activity 2.1 Looking at animal cells Skills C1, C2 a source of animal cells, for example some macerated liver or scrapings from the lining of the trachea from a set of sheep or other lungs (obtainable
Activity 2.1 Looking at animal cells Skills C1, C2 a source of animal cells, for example some macerated liver or scrapings from the lining of the trachea from a set of sheep or other lungs (obtainable
Gaskamine 240 Improvement of Curing Performance under Low Temperature Condition
 Technical Service Report No. 03021H Ver. 1.0 Gaskamine 240 Improvement of Curing Performance under Low Temperature Condition MITSUBISHI GAS CHEMICAL COMPANY, INC. HIRATSUKA RESEARCH LABORATORY -CONTENTS-
Technical Service Report No. 03021H Ver. 1.0 Gaskamine 240 Improvement of Curing Performance under Low Temperature Condition MITSUBISHI GAS CHEMICAL COMPANY, INC. HIRATSUKA RESEARCH LABORATORY -CONTENTS-
Department of Microbiology, Lab 016 instructions
 Protocol for standard FISH and DOPE-FISH for prokaryotes (slightly modified from Amann, 1995, note, for other modifications or other microorganisms like eukaryotes, consult special literature or check
Protocol for standard FISH and DOPE-FISH for prokaryotes (slightly modified from Amann, 1995, note, for other modifications or other microorganisms like eukaryotes, consult special literature or check
CHEMICALS. CHEMICALS resin kits. Standard Resin Kits. Araldite/TAAB 812 Resin Kit. Clear Casting Resin C. Durcupan ACM Epoxy Kit
 resin kits Standard Resin Kits Clear Casting Resin C An unsaturated polyester resin in styrene monomer. Ideal for clear casting og biological and medical specimens for display or, when mixed with styrene
resin kits Standard Resin Kits Clear Casting Resin C An unsaturated polyester resin in styrene monomer. Ideal for clear casting og biological and medical specimens for display or, when mixed with styrene
Methods of Culturing Microorganisms. Chapter 3. Five Basic Techniques of Culturing Bacteria. Topics
 Chapter 3 Topics Methods of Culturing Microorganisms Microscope (History, Types, Definitions) Staining (Gram s) Methods of Culturing Microorganisms Five basic techniques of culturing Media Microbial growth
Chapter 3 Topics Methods of Culturing Microorganisms Microscope (History, Types, Definitions) Staining (Gram s) Methods of Culturing Microorganisms Five basic techniques of culturing Media Microbial growth
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable
 Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Protocol INTRODUCTION RELATED INFORMATION MATERIALS. Histological Preparation of Embryonic and Adult Zebrafish Eyes
 Please cite as: CSH Protocols; 2007; doi:10.1101/pdb.prot4846 Protocol Histological Preparation of Embryonic and Adult Zebrafish Eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3,4 1 Section of Molecular
Please cite as: CSH Protocols; 2007; doi:10.1101/pdb.prot4846 Protocol Histological Preparation of Embryonic and Adult Zebrafish Eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3,4 1 Section of Molecular
Instructions. Fuse-It-siRNA. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
ASE SYSTEMS. EPOXY RESIN FLOOR Prep / REPAIR SYSTEM For Air Caster Load Moving Equipment
 ASE SYSTEMS The Ergonomics & Productivity Specialists! 5611 Guhn Road Ste: A1 * Houston Texas 77040 *al@asesystems.com 713-462-3072 * fax: 713-462-3540 * www.asesystems.com The following Epoxy Resins &
ASE SYSTEMS The Ergonomics & Productivity Specialists! 5611 Guhn Road Ste: A1 * Houston Texas 77040 *al@asesystems.com 713-462-3072 * fax: 713-462-3540 * www.asesystems.com The following Epoxy Resins &
Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 8: Biochemistry
 Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 8: Biochemistry Name Date Section 1. List the 3 basic components of a DNA nucleotide, and draw a simple picture to show how they interact. 2. Consider the amine bases in DNA. List
Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 8: Biochemistry Name Date Section 1. List the 3 basic components of a DNA nucleotide, and draw a simple picture to show how they interact. 2. Consider the amine bases in DNA. List
Name Date Block LAB: Exploring Plant & Animal Cells
 Name Date Block LAB: Exploring Plant & Animal Cells Background Information: One of the first scientists to look at cells under a microscope was an English scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed
Name Date Block LAB: Exploring Plant & Animal Cells Background Information: One of the first scientists to look at cells under a microscope was an English scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed
Isolation & Characterization of Bacteria
 PR025 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Isolation & Characterization of Bacteria Teacher s Handbook (Cat. # BE 204) think proteins!
PR025 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Isolation & Characterization of Bacteria Teacher s Handbook (Cat. # BE 204) think proteins!
666 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY' VOLUME 71, 1976" pages
 ph-dependent BINDING OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS TO INTESTINAL CELLS OF THE NEONATAL RAT RICHARD RODEWALD. From the Department of Biology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia 22901. Neonatal rats
ph-dependent BINDING OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS TO INTESTINAL CELLS OF THE NEONATAL RAT RICHARD RODEWALD. From the Department of Biology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia 22901. Neonatal rats
ZytoLight SPEC FGFR3 Dual Color Break Apart Probe
 ZytoLight SPEC FGFR3 Dual Color Break Apart Probe Z-2170-200 20 (0.2 ml) For the detection of translocations involving the FGFR3 gene at 4p16.3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).... In vitro
ZytoLight SPEC FGFR3 Dual Color Break Apart Probe Z-2170-200 20 (0.2 ml) For the detection of translocations involving the FGFR3 gene at 4p16.3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).... In vitro
1. Paraffin section slides can be stored at room temperature for a long time.
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocols Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocol of Paraffin Section 1. Fix dissected tissues with 10% formalin for no less than 48 hours at room temperature. Inadequately fixation
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocols Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Protocol of Paraffin Section 1. Fix dissected tissues with 10% formalin for no less than 48 hours at room temperature. Inadequately fixation
Nuclear Condensation Assay Kit Green Fluorescence
 ab139479 Nuclear Condensation Assay Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to assay chromatin condensation in live cells using an intercalating dye which is excitable with a standard 488nm
ab139479 Nuclear Condensation Assay Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to assay chromatin condensation in live cells using an intercalating dye which is excitable with a standard 488nm
Engineering Branch Assets Delivery Group
 F.1 SCOPE This Technical Specification shall apply to Fibre Reinforced Plastics or Glass Reinforced Plastics (hereinafter referred to as FRP or GRP) structures and the materials used in their manufacture,
F.1 SCOPE This Technical Specification shall apply to Fibre Reinforced Plastics or Glass Reinforced Plastics (hereinafter referred to as FRP or GRP) structures and the materials used in their manufacture,
THE PATTERNED ORGANIZATION OF THICK AND THIN MICROFILAMENTS IN THE CONTRACTING PSEUDOPOD OF DIFFLUGIA
 y. Ceii sd. 13,727-739 (1973) 727 Printed in Great Britain THE PATTERNED ORGANIZATION OF THICK AND THIN MICROFILAMENTS IN THE CONTRACTING PSEUDOPOD OF DIFFLUGIA B. S. ECKERT* AND S. M. MCGEE-RUSSELL Department
y. Ceii sd. 13,727-739 (1973) 727 Printed in Great Britain THE PATTERNED ORGANIZATION OF THICK AND THIN MICROFILAMENTS IN THE CONTRACTING PSEUDOPOD OF DIFFLUGIA B. S. ECKERT* AND S. M. MCGEE-RUSSELL Department
Methodology for Immunohistochemistry. Learning Objectives:
 Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9
 Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9 Resolution, Detection Magnification Interaction of Light with matter: Absorbtion, Refraction, Reflection, Fluorescence Light Microscopy Absorbtion
Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9 Resolution, Detection Magnification Interaction of Light with matter: Absorbtion, Refraction, Reflection, Fluorescence Light Microscopy Absorbtion
Instructions DAKO In situ Hybridization Detection System for Fluorescein-Labelled Probes
 Instructions DAKO In situ Hybridization Detection System for Fluorescein-Labelled Probes Code No. K0607 Size 15mL FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 1. INTENDED USE FOR RESEARCH
Instructions DAKO In situ Hybridization Detection System for Fluorescein-Labelled Probes Code No. K0607 Size 15mL FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 1. INTENDED USE FOR RESEARCH
ZytoFast HPV type 6/11/16/18/31/33/35 Screening Probe (Bio
 ZytoFast HPV type 6/11/16/18/31/33/35 Screening Probe (Bio iotin in-labeled labeled) T-1044-400 40 (0.4 ml) For the detection of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) type 6/11/16/18/31/33/35 DNA by chromogenic
ZytoFast HPV type 6/11/16/18/31/33/35 Screening Probe (Bio iotin in-labeled labeled) T-1044-400 40 (0.4 ml) For the detection of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) type 6/11/16/18/31/33/35 DNA by chromogenic
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A FISSION YEAST,
 JOURNAL OF BACTER10LOGY Vo. 88, No. 5, p. 1459-1466 November, 1964 Copyright 1964 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A FISSION YEAST, SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE NORMAN
JOURNAL OF BACTER10LOGY Vo. 88, No. 5, p. 1459-1466 November, 1964 Copyright 1964 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A FISSION YEAST, SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE NORMAN
Protocol. Nexterion Slide A+ MPX 16. DNA-application
 Seite: 1/12 1 Introduction...2 2 Storage and handling...3 3 General precautions...3 4 Reagents required...3 5 Equipment required...4 6 Array printing...4 7 Printing guidelines...5 8 DNA immobilization...6
Seite: 1/12 1 Introduction...2 2 Storage and handling...3 3 General precautions...3 4 Reagents required...3 5 Equipment required...4 6 Array printing...4 7 Printing guidelines...5 8 DNA immobilization...6
***************************************************************************************************************
 09330 QUARRY TILE *************************************************************************************************************** SPECIFIER: CSI MasterFormat 2004 number 09 30 16 ***************************************************************************************************************
09330 QUARRY TILE *************************************************************************************************************** SPECIFIER: CSI MasterFormat 2004 number 09 30 16 ***************************************************************************************************************
Histology FISH Accessory Kit Step-by-Step Procedure
 PROCEDURE Histology FISH Accessory Kit Step-by-Step Procedure Code K5799 For probes diluted in Formamide based hybridization buffer Reagent Preparation Equilibration Deparaffinization/Rehydration Prepare
PROCEDURE Histology FISH Accessory Kit Step-by-Step Procedure Code K5799 For probes diluted in Formamide based hybridization buffer Reagent Preparation Equilibration Deparaffinization/Rehydration Prepare
TACS XL TM. In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit. Catalog Number: TA200. DAB Kit. 30 tests FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES.
 TACS XL TM In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number: TA200 DAB Kit 30 tests This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC
TACS XL TM In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number: TA200 DAB Kit 30 tests This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC
BIO 315 Lab Exam I. Section #: Name:
 Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
LAMININ. For Immunohistochemical Demonstration of Laminin in Paraffin-embedded and Frozen Human Tissue Sections Stock No. IMMH-7
 LAMININ For Immunohistochemical Demonstration of Laminin in Paraffin-embedded and Frozen Human Tissue Sections Stock No. IMMH-7 TABLE OF CONTENTS BACKGROUND AND PRINCIPLE... 4 REAGENTS AND EQUIPMENT PROVIDED...
LAMININ For Immunohistochemical Demonstration of Laminin in Paraffin-embedded and Frozen Human Tissue Sections Stock No. IMMH-7 TABLE OF CONTENTS BACKGROUND AND PRINCIPLE... 4 REAGENTS AND EQUIPMENT PROVIDED...
for New Energy Materials and Devices; Beijing National Laboratory for Condense Matter Physics,
 Electronic Supplementary Information Highly efficient core shell CuInS 2 /Mn doped CdS quantum dots sensitized solar cells Jianheng Luo, a Huiyun Wei, a Qingli Huang, a Xing Hu, a Haofei Zhao, b Richeng
Electronic Supplementary Information Highly efficient core shell CuInS 2 /Mn doped CdS quantum dots sensitized solar cells Jianheng Luo, a Huiyun Wei, a Qingli Huang, a Xing Hu, a Haofei Zhao, b Richeng
Hon. Rinenart and Winston, inc. 383 Madison Avenue, New York DNA AND CHROMOSOMES CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION INTERACTING SYSTEMS IN
 CELLS AND ORGANELLES Alex B Novikoff, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Yeshiva University, and Eric Holtzman, Columbia University Providing the most modern approach to the study of cell structure yet
CELLS AND ORGANELLES Alex B Novikoff, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Yeshiva University, and Eric Holtzman, Columbia University Providing the most modern approach to the study of cell structure yet
No.5605, No.5605BN* Tape thickness: 0.05mm
 Double-coated adhesive tape No.5605, No.5605BN Outline Nitto Denko No. 5605 and No. 5605BN are 0.05mm-thick polyester film based double-coated adhesive tapes with acrylic adhesive. Using a polyester film
Double-coated adhesive tape No.5605, No.5605BN Outline Nitto Denko No. 5605 and No. 5605BN are 0.05mm-thick polyester film based double-coated adhesive tapes with acrylic adhesive. Using a polyester film
Web Based Promotion! 10% Off any initial product order. Mention promo code 1204!
 Web Based Promotion! 10% Off any initial product order. Mention promo code 1204! Volume 2, Number 2 1998 FROM PATIENT TO EMBEDDING CENTER IN TWO HOURS OR LESS The single biggest factor in health care today
Web Based Promotion! 10% Off any initial product order. Mention promo code 1204! Volume 2, Number 2 1998 FROM PATIENT TO EMBEDDING CENTER IN TWO HOURS OR LESS The single biggest factor in health care today
Activity 5.1.4: Gram Staining
 Activity 5.1.4: Gram Staining Introduction In the last activity, you isolated the bacteria that was responsible for Anna s illness and performed a gross examination of the resultant colonies. While gross
Activity 5.1.4: Gram Staining Introduction In the last activity, you isolated the bacteria that was responsible for Anna s illness and performed a gross examination of the resultant colonies. While gross
Protocol. Micronucleus Assay. with
 with Page 2 of 8 Content 1. Background 3 2. Basic Procedure 3 3. Materials 4 3.1. epics kit components 4 3.2. Additionally needed materials and laboratory equipment 4 4. Method 5 4.1. Tissue and Medium
with Page 2 of 8 Content 1. Background 3 2. Basic Procedure 3 3. Materials 4 3.1. epics kit components 4 3.2. Additionally needed materials and laboratory equipment 4 4. Method 5 4.1. Tissue and Medium
Dr: RAWIA BADR Associate Professor of Microbiology&Immunology
 Dr: RAWIA BADR Associate Professor of Microbiology&Immunology Cell culture Commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, while the more specific term plant tissue.culture is used only for
Dr: RAWIA BADR Associate Professor of Microbiology&Immunology Cell culture Commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, while the more specific term plant tissue.culture is used only for
PreAnalytiX Supplementary Protocol
 PreAnalytiX Supplementary Protocol Purification of full-length proteins from sections of PAXgene Tissue fixed, paraffin-embedded (PFPE) tissue This protocol describes using the Qproteome FFPE Tissue kit
PreAnalytiX Supplementary Protocol Purification of full-length proteins from sections of PAXgene Tissue fixed, paraffin-embedded (PFPE) tissue This protocol describes using the Qproteome FFPE Tissue kit
Cell Culture, Transfection and Microscopy in one Slide
 www.biontex.com www.ibidi.com µ Transfection Kit VI Cell Culture, Transfection and Microscopy in one Slide The µ Transfection Kit VI combines the efficient transfection of METAFECTENE µ (Biontex Laboratories
www.biontex.com www.ibidi.com µ Transfection Kit VI Cell Culture, Transfection and Microscopy in one Slide The µ Transfection Kit VI combines the efficient transfection of METAFECTENE µ (Biontex Laboratories
Self-Cleaning/ Anti-Fouling Coating
 Anti-Static, Super-Hydrophilic and Inorganic Self-Cleaning/ Anti-Fouling Coating SKETCH CO.,LTD. 2012.12 1 Contents: The Background of the Development of SKETCH Anti-Static, Super-Hydrophilic and Inorganic
Anti-Static, Super-Hydrophilic and Inorganic Self-Cleaning/ Anti-Fouling Coating SKETCH CO.,LTD. 2012.12 1 Contents: The Background of the Development of SKETCH Anti-Static, Super-Hydrophilic and Inorganic
A Level. A Level Biology. Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter
An Investigation of the Histochemical Technique for the Localization of Acid Phosphomonoesterase By FRANCES MACDONALD
 3*5 An Investigation of the Histochemical Technique for the Localization of Acid Phosphomonoesterase By FRANCES MACDONALD (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With one Plate
3*5 An Investigation of the Histochemical Technique for the Localization of Acid Phosphomonoesterase By FRANCES MACDONALD (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With one Plate
6.2 Chromatin is divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin
 6.2 Chromatin is divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin Individual chromosomes can be seen only during mitosis. During interphase, the general mass of chromatin is in the form of euchromatin. Euchromatin
6.2 Chromatin is divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin Individual chromosomes can be seen only during mitosis. During interphase, the general mass of chromatin is in the form of euchromatin. Euchromatin
Transmission Electron Microscopic Study of Antibiotic Action on Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilm
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 2002, p. 2679 2683 Vol. 46, No. 8 0066-4804/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.8.2679 2683.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 2002, p. 2679 2683 Vol. 46, No. 8 0066-4804/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.8.2679 2683.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
FONTANA-MASSON SILVER METHOD - MELANIN PURPOSE:
 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - MINERALS AND PIGMENTS Page: 1 of 3 FONTANA-MASSON SILVER METHOD - MELANIN PURPOSE: To identify argentaffin granules and melanin. Melanin is a nonlipid,
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - MINERALS AND PIGMENTS Page: 1 of 3 FONTANA-MASSON SILVER METHOD - MELANIN PURPOSE: To identify argentaffin granules and melanin. Melanin is a nonlipid,
Low Odour Acrylic Adhesives DP8805NS Green DP8810NS Green DP8825NS Green. Preliminary Technical Data Sheet May 2017
 Scotch-Weld Preliminary Technical Data Sheet May 2017 Product Description 3M Scotch-Weld are high-performance, two-part acrylic adhesives with lower odour than most acrylic adhesives. These toughened products
Scotch-Weld Preliminary Technical Data Sheet May 2017 Product Description 3M Scotch-Weld are high-performance, two-part acrylic adhesives with lower odour than most acrylic adhesives. These toughened products
A Comparison of Techniques Useful for Preparing Nematodes for Scanning Electron Microscopy 1
 Journal of Nematology 18(4):479-487. 1986. The Society of Nematologists 1986. A Comparison of Techniques Useful for Preparing Nematodes for Scanning Electron Microscopy 1 J. D. EISENBACK ~ Abstract: Second-stage
Journal of Nematology 18(4):479-487. 1986. The Society of Nematologists 1986. A Comparison of Techniques Useful for Preparing Nematodes for Scanning Electron Microscopy 1 J. D. EISENBACK ~ Abstract: Second-stage
Marabu. Mara Pur PU. Field of Application. Characteristics
 Solvent-based screen printing ink for pretreated polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), thermosetting plastics, metals, and coated surfaces High gloss, high opacity, fast drying twocomponent ink, resistant
Solvent-based screen printing ink for pretreated polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), thermosetting plastics, metals, and coated surfaces High gloss, high opacity, fast drying twocomponent ink, resistant
Partner: Cathy 22 March Separation and Qualitative Determination of Cations and Anions
 Partner: Cathy 22 March 2012 Separation and Qualitative Determination of Cations and Anions Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to identify the cations and anions components in the unknown solution. This
Partner: Cathy 22 March 2012 Separation and Qualitative Determination of Cations and Anions Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to identify the cations and anions components in the unknown solution. This
Resin Efficiency in Particleboard As Influenced by Density, Atomization and Resin Content
 Resin Efficiency in Particleboard As Influenced by Density, Atomization and Resin Content William F. Lehmann Abstract Resin efficiency in particleboards was studied using a Douglas-fir flake-particle mixture.
Resin Efficiency in Particleboard As Influenced by Density, Atomization and Resin Content William F. Lehmann Abstract Resin efficiency in particleboards was studied using a Douglas-fir flake-particle mixture.
CHAPTER 3 CHARACTERIZATION OF MANUFACTURED SAND
 41 CHAPTER 3 CHARACTERIZATION OF MANUFACTURED SAND 3.1 GENERAL The characteristics of concrete mainly depend upon the properties of materials used. Grading, mineralogical composition, shape and texture
41 CHAPTER 3 CHARACTERIZATION OF MANUFACTURED SAND 3.1 GENERAL The characteristics of concrete mainly depend upon the properties of materials used. Grading, mineralogical composition, shape and texture
IMPROVEMENT OF IMPREGNATION AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CFRTP COMPOSITES BY MICRO-BRAIDED YARNS
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS IMPROVEMENT OF IMPREGNATION AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CFRTP COMPOSITES BY MICRO-BRAIDED YARNS P. Wongsriraksa 1 *, A. Nakai 2, K. Uzawa 1 and
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS IMPROVEMENT OF IMPREGNATION AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CFRTP COMPOSITES BY MICRO-BRAIDED YARNS P. Wongsriraksa 1 *, A. Nakai 2, K. Uzawa 1 and
TRANSLUX D 150 CLEAR EPOXY CASTING RESIN
 Crystal Clear resin Simple to hand cast Good UV stability Easy pigmentation Perfect matching of other pigmented liquids like wine, coffee etc... Good UV stability CLEAR EPOXY CASTING RESIN Crystal Clear
Crystal Clear resin Simple to hand cast Good UV stability Easy pigmentation Perfect matching of other pigmented liquids like wine, coffee etc... Good UV stability CLEAR EPOXY CASTING RESIN Crystal Clear
StemXVivo. Mesoderm Kit. Catalog Number SC030B. Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm.
 StemXVivo Mesoderm Kit Catalog Number SC030B Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
StemXVivo Mesoderm Kit Catalog Number SC030B Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
ZytoLight SPEC ABL2 Dual Color Break Apart Probe
 ZytoLight SPEC ABL2 Dual Color Break Apart Probe Z-2200-200 20 (0.2 ml) For the detection of translocations involving the ABL2 gene at 1q25.2 by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).... In vitro diagnostic
ZytoLight SPEC ABL2 Dual Color Break Apart Probe Z-2200-200 20 (0.2 ml) For the detection of translocations involving the ABL2 gene at 1q25.2 by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).... In vitro diagnostic
EZ-Vision DNA Dye as Loading Buffer
 EZ-Vision DNA Dye as Loading Buffer Code Description Size N472-SAMPLE EZ-VIsion One, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N650-SAMPLE EZ-Vision Two, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N313-SAMPLE EZ-Vision
EZ-Vision DNA Dye as Loading Buffer Code Description Size N472-SAMPLE EZ-VIsion One, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N650-SAMPLE EZ-Vision Two, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N313-SAMPLE EZ-Vision
ab CytoPainter Mitochondrial Staining Kit NIR Fluorescence
 ab176747 CytoPainter Mitochondrial Staining Kit NIR Fluorescence Instructions for Use For staining Mitochondria in live cells with our proprietary NIR probe. This product is for research use only and is
ab176747 CytoPainter Mitochondrial Staining Kit NIR Fluorescence Instructions for Use For staining Mitochondria in live cells with our proprietary NIR probe. This product is for research use only and is
Optimized Immunohistochemistry Workflow Facilitated by New Dako Autostainer Link 48 Software
 Optimized Immunohistochemistry Workflow Facilitated by New Dako Autostainer Link 48 Software * Corresponding Author E-mail: ronald.stead@holburn.com This e-mail address can be published Elizabeth C. Colley,
Optimized Immunohistochemistry Workflow Facilitated by New Dako Autostainer Link 48 Software * Corresponding Author E-mail: ronald.stead@holburn.com This e-mail address can be published Elizabeth C. Colley,
Product Permission Document (PPD) of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Injection Ph.Eur Purified Neurotoxin Complex
 Product Permission Document (PPD) of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Injection Ph.Eur Purified Neurotoxin Complex Brand Name : BOTO GENIE 1. Introduction : BOTO GENIE (Botulinum Toxin Type A for Injection Ph.Eur)
Product Permission Document (PPD) of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Injection Ph.Eur Purified Neurotoxin Complex Brand Name : BOTO GENIE 1. Introduction : BOTO GENIE (Botulinum Toxin Type A for Injection Ph.Eur)
SEM Immunocytochemistry for Cells & Materials
 SEM Immunocytochemistry for Cells & Materials R. Geoff Richards AO Research Institute, AO Foundation, Davos, Switzerland. Immunohistochemistry Immunocytochemistry can be performed on a biological specimen,
SEM Immunocytochemistry for Cells & Materials R. Geoff Richards AO Research Institute, AO Foundation, Davos, Switzerland. Immunohistochemistry Immunocytochemistry can be performed on a biological specimen,
Staining Techniques. Staining Techniques. There are many dyes. Histochemical Stains: chemical reactions. Feulgen reaction -DNA
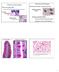 Staining Techniques There are many dyes. http://medinfo.ufl.edu/~dental/denhisto/stains.html Examples: Sudan black -Lipids Myelinated axons- blue ihcworld.com/imagegallery/displayimage.php?al... Weigert
Staining Techniques There are many dyes. http://medinfo.ufl.edu/~dental/denhisto/stains.html Examples: Sudan black -Lipids Myelinated axons- blue ihcworld.com/imagegallery/displayimage.php?al... Weigert
ab In situ Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab206386 In situ Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For detection of apoptotic cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 8 Last Updated 6 February
ab206386 In situ Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For detection of apoptotic cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 8 Last Updated 6 February
Raychem brand S1125 Adhesive
 RK-6619 Revision 9 Page 1 of 6 Date Printed 11-Nov-10 RK-6619 Revision 9 Raychem brand S1125 Adhesive SCOPE This Quality Assurance Specification establishes the quality standard for a two-part epoxy adhesive
RK-6619 Revision 9 Page 1 of 6 Date Printed 11-Nov-10 RK-6619 Revision 9 Raychem brand S1125 Adhesive SCOPE This Quality Assurance Specification establishes the quality standard for a two-part epoxy adhesive
LIQUID PENETRANTS USER S MANUAL in accordance to specifications: EN 571, ASTME 1417, AMS 2644, MIL, ASME, DIN, UNI, BS, AFNOR, etc..
 LIQUID PENETRANTS USER S MANUAL in accordance to specifications: EN 571, ASTME 1417, AMS 2644, MIL, ASME, DIN, UNI, BS, AFNOR, etc.. The liquid penetrant examination method is an effective means for detecting
LIQUID PENETRANTS USER S MANUAL in accordance to specifications: EN 571, ASTME 1417, AMS 2644, MIL, ASME, DIN, UNI, BS, AFNOR, etc.. The liquid penetrant examination method is an effective means for detecting
DRAFT EAST AFRICAN STANDARD
 DEAS 340: 2012 ICS 71.100.70 HC 3304 99 20 DRAFT EAST AFRICAN STANDARD Nail Polish Specifications EAST AFRICAN COUNITY EAS 2012 First Edition 2012 DEAS 340: 2012 Copyright notice This EAC document is
DEAS 340: 2012 ICS 71.100.70 HC 3304 99 20 DRAFT EAST AFRICAN STANDARD Nail Polish Specifications EAST AFRICAN COUNITY EAS 2012 First Edition 2012 DEAS 340: 2012 Copyright notice This EAC document is
Procedure for Stool Routine & Microscopy
 Procedure for Stool Routine & Microscopy : To perform Gross & Physical examination of Stool Variables : Specimen collection, Labelling of specimen, Name, Identifying number, date, time Gross Examination
Procedure for Stool Routine & Microscopy : To perform Gross & Physical examination of Stool Variables : Specimen collection, Labelling of specimen, Name, Identifying number, date, time Gross Examination
Protocol. Nexterion HiSens E. DNA application
 Seite: 1/12 1 Introduction... 2 2 Product overview... 2 3 Storage and handling... 4 4 Array printing... 4 5 DNA immobilization... 4 6 Handling of printed arrays... 5 7 Washing... 5 8 Blocking... 5 9 Hybridization...
Seite: 1/12 1 Introduction... 2 2 Product overview... 2 3 Storage and handling... 4 4 Array printing... 4 5 DNA immobilization... 4 6 Handling of printed arrays... 5 7 Washing... 5 8 Blocking... 5 9 Hybridization...
INSTRUCTION FOR BONDING TECHNOLOGY Fibermarine / Fibermarine HighLine
 INSTRUCTION FOR BONDING TECHNOLOGY Fibermarine / Fibermarine HighLine GRE and GRVE Pipe and Fitting by TPR Fiberdur GmbH & Co. KG 2014 1. BONDING TECHNOLOGY 1.1 Working Procedure 1.2 Handling Adhesive
INSTRUCTION FOR BONDING TECHNOLOGY Fibermarine / Fibermarine HighLine GRE and GRVE Pipe and Fitting by TPR Fiberdur GmbH & Co. KG 2014 1. BONDING TECHNOLOGY 1.1 Working Procedure 1.2 Handling Adhesive
Comparing the Quality of Fixation for Gel-based Formalin (Formagel) versus Traditional Liquid-Based Formalin for Immunohistochemistry
 Comparing the Quality of Fixation for Gel-based Formalin (Formagel) versus Traditional Liquid-Based Formalin for Immunohistochemistry Brian H. Le, M.D., Reading Hospital Reviewed by Michael R. LaFrinere,
Comparing the Quality of Fixation for Gel-based Formalin (Formagel) versus Traditional Liquid-Based Formalin for Immunohistochemistry Brian H. Le, M.D., Reading Hospital Reviewed by Michael R. LaFrinere,
I. Conditions for Phagocytosis: Phagocytosis of Paramecium by Pelomyxa carolinensis Amoeba
 Bio 219 Homepage I. Conditions for Phagocytosis: Phagocytosis of Paramecium by Pelomyxa carolinensis Amoeba Michael Smith Wheaton College Norton, MA 02766 In collaboration with Samara Audet Original Post:
Bio 219 Homepage I. Conditions for Phagocytosis: Phagocytosis of Paramecium by Pelomyxa carolinensis Amoeba Michael Smith Wheaton College Norton, MA 02766 In collaboration with Samara Audet Original Post:
MEASUREMENT OF THICKNESS OF DISPERSED CLAY FLAKES WITH THE
 MEASUREMENT OF THICKNESS OF DISPERSED CLAY FLAKES WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE by A, H. WEIR, H. L. NIXON AND R. D. WOODS Rothamsted Experimental Station, ttarpenden, England ABSTRACT The shadow lengths
MEASUREMENT OF THICKNESS OF DISPERSED CLAY FLAKES WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE by A, H. WEIR, H. L. NIXON AND R. D. WOODS Rothamsted Experimental Station, ttarpenden, England ABSTRACT The shadow lengths
CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence
 ab139483 CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed for the detection of Golgi bodies by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139483 CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed for the detection of Golgi bodies by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
