A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells
|
|
|
- Alaina Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells ANTONIO COPPOLA From the Department ofpathology, College of Medicine, Downstate Medical Center, State University of New York, Brooklyn, NY 11203, USA SUMMARY A method is described whereby the time required for the processing of white blood cells for electron microscopy can be shortened from 36 to 3- hours. Because cells of the peripheral blood are not attached to each other, fixation, dehydration, and infiltration of the embedding medium is more rapid. This makes it possible for clinicians to use fine structural data for diagnosis as illustrated in three cases. In haematology little emphasis has been placed on electron microscopy for diagnostic purposes. One of the principal reasons may be that with standard methods for electron microscopy the time required for the fixation and embedding of the specimens is approximately 36 hours (Bessis, 1973). In haematology the electron microscope has therefore been considered primarily a tool for research purposes. It has been proposed, however, that in the study of the bone marrow, in addition to smears, sections of particles, bone biopsy, and cytochemistry, fine structural study should also be done if light microscopic methods fail to reveal the nature of the cells or if it is necessary to define cells ultrastructurally (Coppola and Athanassiades, 1977). However, the accepted procedures require hours for regular processing for electron microscopy. So it is convenient to have a rapid method for fine structural analysis of cells. It is the purpose of this paper to present evidence that haemopoietic cells can be processed for electron microscopy and examined in 31 hours. The clinician will thus have quick access to fine structural data which will aid in making the exact diagnosis in difficult haematological cases. Material and methods Electron microscopic examination of peripheral blood taken from patients with leukaemias was done by both the quick method of fixation and embedding and the standard method. Received for publication 19 July 1978 Two 5-mi aliquots of peripheral blood from each patient were placed into test tubes containing EDTA. The blood was kept for 30 minutes in the vertical position at 40C. The plasma layers rich in white blood cells (WBC) were then aspirated, placed into other test tubes, and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes in a Clay-Adams centrifuge. The plasma supernatants were discarded from each tube, and the two pellets from each patient were labelled for either the rapid experimental procedure or the control procedure. They were then processed as described below. Experimental procedure The cells were immediately resuspended in sodiumcacodylate buffered glutaraldehyde, ph 7*4 (Sabatini et al., 1963) and kept for 10 minutes at 4VC. After the primary aldehyde fixation, they were washed three times in sodium cacodylate buffer over six minutes, and then postosmicated in sodium-acetate-sodiumveronal-buffered osmium tetroxide, ph 7*4 (Palade, 1952) for 15 minutes. The cells were subsequently washed for three minutes in 35%, 50%, 70%, and 95% alcohol. The dehydration was further accomplished by two washes in absolute alcohol and two changes in propylene oxide washes over six minutes. After this last step the cells were suspended in a propylene-epon mixture for 10 minutes, and then placed into Beam capsules and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for five minutes. The propylene-epon mixture was then aspirated, and Epon was introduced into the capsules (Luft, 1961). The Beam capsules containing packed cells at the tip were kept at 370C for 162
2 A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells 45 minutes, and subsequently Epon polymerisation was carried out at 1000C for one hour. After cooling, the blocks were cut with glass and diamond knives. Thick sections were stained with toluidine blue (Trump et al., 1961) and thin sections with methanolic uranyl acetate (Stempak and Ward, 1964). CONTROL PROCEDURE WBC from the same patients were processed according to our routine method over a 24-hour period (Bessis, 1973; Coppola, 1973). In summary, the cell pellets were cut into blocks less than 1 mm3, fixed for one hour in buffered glutaraldehyde, and postfixed in osmium tetroxide for an additional hour. Subsequently, the cell pellets were dehydrated in graded alcohols and propylene oxide over 2 2 hours. Finally, the cell pellets were embedded in Epon 812 and polymerisation was performed at 60'C for hours. Results Complete polymerisation of the Epon blocks was obtained within one hour at 1000C. Thick sections were easily cut and were well stained with toluidine blue. No difficulties were encountered in cutting thin sections with a diamond knife. When the thin sections were cut, stained with uranyl acetate, and examined with the electron microscope we could see little difference between the rapid and the conventional methods. There was a slight decrease in the cytoplasmic translucency and the cytoplasm often appeared of increased density in the rapidly processed material. Cytoplasmic granules were darker and somewhat better defined in the conventionally fixed cells. However, with the rapid method there was very good preservation of both organelles and granules. The morphology of the granules was adequate for identification of cell types and their stage of maturation. Three illustrative cases follow. PATIENT 1 A 34-year-old woman with a two-year history of chronic myeloid leukaemia was admitted to hospital. While the patient was still in the emergency room, examination of the peripheral blood revealed a WBC of 79 x 109/l. The smear showed a total spectrum of granulocyte maturity, which was compatible with the diagnosis of chronic granulocytic leukaemia, but there were also 24% blast cells that were peroxidasenegative. The peripheral blood was prepared for electron microscopy in order better to define the nature of the blast cells. Ultrastructurally, these blast cells appeared to have an agranular cytoplasm, displaying the general appearance of lymphoblasts (Fig. 1). The occurrence of lymphoid cells in the blastic crisis of chronic granulocytic leukaemia has recently been stressed (Rosenthal et al., 1977). The structure of the other leukaemic cells was not unusual: their granules, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, plasma membranes, nuclear envelopes, chromatin, and nucleoli were similar to those usually seen in such cases (Figs 2, 3, 4). The diagnosis of chronic granulocytic leukaemia in blastic crisis was confirmed. PATIENT 2 A 64-year-old woman was admitted with purple macular lesions on the chest. In the emergency room her WBC was 10-5 x 109/l. The differential count showed 39 % monocytoid cells, some of which were immature. The peripheral blood was then studied by electron microscopy. Ultrastructurally, mature and immature monocytoid cells were seen (Fig. 5). These were characterised by kidney-shaped or irregularly shaped nuclei, which contained a variable amount of chromatin which rarely was seen attached and condensed against the nuclear envelope. Approximately 5% of them were markedly convoluted. The cytoplasm contained the usual organelles as seen in monocytes. Some cells displayed a variable number of pleomorphic granules and vacuoles. Also in this case on high power magnification there was an excellent resolution of the cytoplasmic organelles (Fig. 6). The diagnosis of acute monocytic leukaemia was made from this material, substantiating the diagnosis made on the light microscopic characters of the cells in the peripheral blood. PATIENT 3 A 67-year-old man was admitted to hospital with progressive pruritic dermatitis of four years' duration. The WBC in the emergency room was 120 x 109/l. Sezary's syndrome was suspected because 30% of lymphocytes had cerebriform, convoluted nuclei and cytoplasmic vacuoles. Ultrastructurally, the cells of this patient had the characteristic features of Sezary's cells, that is, cerebriform-shaped nuclei with condensed chromatin adjacent to the nuclear envelope. Occasionally large nucleoli were seen (Figs 7 and 8). Thus we were able to provide the clinician with accurate diagnostic data in a very short period of time. Discussion 163 Fixatives and embedding media for electron microscopy have been greatly improved over the past 20 years. In our experience, glutaraldehyde-osmium fixation gives the best cellular detail. The best embedding medium is the epoxy resin suggested by Luft (1961). The suggested time for fixation and
3 Fig. 2 A myelocyte displaying normal cytoplasmic granules and nuclear chromatin. Ag = azurophilic granules; N = nucleus. Uranyl acetate x w,. *-Z;tSS-2'Gx ti<st~~~~~~~l ~~~~~~~~~j.a..'.;..mjs$. Fig. 3 Note excellent preser vation of the nucleus, nucleolus, and cytoplasmic organelles of this leukaemic = rough endoplasmic reticulum; N = nucleus. Uranyl acetate x mtyelocyte. ER Fig. I An agranular malignant cell with morphological characteristics of a lymphoblast. M = mitochondria. Uranyl acetate x
4 .* <. =. * t.i/,.. <.,,.<,... <,5. 4%i.. f P` 'O KA flis'xx; r.<,eeer..., _^ *_;J ); ~; F:. Fig. 5 A malignant monocyte showing a bizarre shape of the nucleus and abundance ofazurophilic granules along with other cytoplasmic organelles. Ag = azurophilic granules; N = nucleus. Uranyl acetate x , Fig. 4 The structure of the mitochondria and profiles of the rough endoplasmic reticulum are clearly delineated in this myeloid cell. ER = rough endoplasmic reticulum; M = mitochondria. Uranyl acetate x
5 :-:;..Ut ^e 4~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ d<a Fig. 6 At this magnification ribosomes, centriole, anid membranous structures of the Golgi apparatus (G) are clearly demonstrated. C = centriole; Uranyl acetate x Fig. 7 A lymphoid cell of Sezary type with characteristic cerebriform-shaped nucleus. A large nucleolus is also seen. Nu = nucleolus. Uranyl acetate x Fig. 8 A high-power view of a Sezary cell. C = centriole; N = nucleuis. Urany l acetate x 31 21! Voaker
6 A rapid method for electron microscopic examination of blood cells 167 dehydration is approximately 7 hours and the time required for the Epon infiltration and polymerisation is about 24 hours (Bessis, 1973). With the present modified procedure, we have shown that the time required for the entire processing for electron microscopy can be shortened to 31 hours provided that the temperature for the Epon polymerisation is raised to 100 C. In our experience, using this method in many cases, no appreciable cell distortion nor artifacts have been noted. The only inconvenience is that, because of the centrifugation that follows every step, only one specimen can be processed at a time. We have therefore limited our procedure to those cases in which electron microscopy is of immediate diagnostic value. An analogous method has already proved to be excellent for tissue biopsies (Rowden et al., 1974). Since we are dealing not with solid tissue but with buffy coat, the fixation, dehydration, and embedding steps can be rapidly achieved even when there is a large pellet. Despite the high temperature used for the polymerisation of the resin, there is no detectable cellular distortion nor shrinkage of cells (Rowden et al., 1974). We recommend the use of the rapid procedure so that the clinical haematologist may add evaluation of the fine structural detail to the other information he has available before making the final diagnosis. I am indebted to Thomas J. Athanassiades and Dr Joanna Sher for their critical review of the manuscript. The technical assistance of Alan Lieberman and Nilda Stahl is also appreciated. The generous support of the project by Dr John D. Broome, Professor and Chairman, Department of Pathology, is also gratefully acknowledged. References Bessis, M. (1973). Living Blood Cells and their Ultrastructure, translated by R. I. Weed, p Springer, New York and Berlin. Coppola, A. (1973). A transplantable mouse lymphoma with unusual azurophilic granules. American Journal of Pathology, 73, Coppola, A., and Athanassiades, T. J. (1977). The relative merits of bone marrow biopsy and particle section technics (Letter). American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 67, 309. Luft, J. H. (1961). Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. Journal of Biophysical and Biochemical Cytology, 9, Palade, G. E. (1952). A study of fixation for electron microscopy. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 95, Rosenthal, S., Canellos, G. P., Whang-Peng, J., and Gralnick, H. R. (1977). Blast crisis of chronic granulocytic leukemia: morphologic variants and therapeutic implications. American Journal of Medicine, 63, Sabatini, D. D., Bensch, K.. and Barrnett, R. J. (1963). Cytochemistry and electron microscopy: the preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. Journal of Cell Biology, 17, Rowden, G., and Lewis, M. G. (1974). Experience with a three hour electron microscopy biopsy service. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 27, Stempak, J. G., and Ward, R. T. (1964). An improved staining method for electron microscopy. Journal of Cell Biology, 22, Trump, B. F., Smuckler, E. A., and Benditt, E. P. (1961). A method for staining epoxy sections for light microscopy. Journal of Ultrastructure Research, 5, Requests for reprints to: Dr Antonio Coppola, Department of Pathology, Downstate Medical Center, State University of New York, 450 Clarkson Avenue, Brooklyn, New York 11203, USA. J Clin Pathol: first published as /jcp on 1 February Downloaded from on 7 May 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Chapter. Methods for and. Analysis of Plant Cell Tissue Ultrastructure. Contents. 1.1 Introduction. John E. Mayfield and William V.
 In: Dashek, William V., ed. Methods in plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press: pp. 3-11. Chapter 1. 1997. Chapter Methods for and Analysis of Plant Cell Tissue Ultrastructure
In: Dashek, William V., ed. Methods in plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press: pp. 3-11. Chapter 1. 1997. Chapter Methods for and Analysis of Plant Cell Tissue Ultrastructure
Rapid processing of renal glomeruli for electron microscopy
 516 Rapid processing of renal glomeruli for electron microscopy H. HELIN1, A. PASTERNACK2, and I. RANTALA2 Departments of 1Biomedical and 2Clinical Sciences, University of Tampere, Box 607, SF-33101 Tampere
516 Rapid processing of renal glomeruli for electron microscopy H. HELIN1, A. PASTERNACK2, and I. RANTALA2 Departments of 1Biomedical and 2Clinical Sciences, University of Tampere, Box 607, SF-33101 Tampere
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Tissue Preparation and Microscopy. General Concepts. Chemical Fixation CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Tissue Preparation and Microscopy General Concepts I. Biological tissues must undergo a series of treatments to be observed with light and electron microscopes. The process begins by stabilization
CHAPTER 1 Tissue Preparation and Microscopy General Concepts I. Biological tissues must undergo a series of treatments to be observed with light and electron microscopes. The process begins by stabilization
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION. TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D
 BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D Why do we need EM for biological samples? (O'Connor and Adams, 2010) Why do we need EM for biological samples?
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D Why do we need EM for biological samples? (O'Connor and Adams, 2010) Why do we need EM for biological samples?
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS
 PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
identified by light microscopy but were readily recognized-by the presence of brush bordersusing
 Gut, 1970, 11, 217-222 Cell loss from small intestinal mucosa: a morphological study1 I. J. PINK, D. N. CROFT, AND B. CREAMER From the Gastrointestinal Laboratory, St. Thomas' Hospital, London SUMMARY
Gut, 1970, 11, 217-222 Cell loss from small intestinal mucosa: a morphological study1 I. J. PINK, D. N. CROFT, AND B. CREAMER From the Gastrointestinal Laboratory, St. Thomas' Hospital, London SUMMARY
(From the Department of Pathology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Yeshiva University, New York)
 PRESERVATION OF THE FINE STRUCTURE OF ISOLATED LIVER CELL PARTICULATES WITH POLYVINYLPYRROLLIDONE- SUCROSE* BY ALEX B. NOVIKOFF, 1M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine,
PRESERVATION OF THE FINE STRUCTURE OF ISOLATED LIVER CELL PARTICULATES WITH POLYVINYLPYRROLLIDONE- SUCROSE* BY ALEX B. NOVIKOFF, 1M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine,
Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM
 Collaborative Research Center (SFB 1278) Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM Rainer Heintzmann, Fengjiao Ma, Institute of Physical Chemistry Stephanie Höppener, Martin
Collaborative Research Center (SFB 1278) Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM Rainer Heintzmann, Fengjiao Ma, Institute of Physical Chemistry Stephanie Höppener, Martin
EXPERIMENT 2 Cell Fractionation and DNA Isolation
 EXPERIMENT 2 Cell Fractionation and DNA Isolation Background Information A. The Eukaryotic Cell Cells are frequently classified into two basic types: prokaryotic and eukar yotic. The prokaryotic cell,
EXPERIMENT 2 Cell Fractionation and DNA Isolation Background Information A. The Eukaryotic Cell Cells are frequently classified into two basic types: prokaryotic and eukar yotic. The prokaryotic cell,
Improved Method of Embedding with Epoxy Resin 'Quetol
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6): 661-674, March 1982 Improved Method of Embedding with Epoxy Resin 'Quetol 651' for Both Light and Electron Microscopic Observation of Identical Sites in Semi-thin Sections
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6): 661-674, March 1982 Improved Method of Embedding with Epoxy Resin 'Quetol 651' for Both Light and Electron Microscopic Observation of Identical Sites in Semi-thin Sections
Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count
 2014-09- 01 Blood Page 1 of 5 Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count Aim: Learn to count cells, observe and identify different blood cells in a smear, quantify their proportions and count RBCs per µl (mm^3) using
2014-09- 01 Blood Page 1 of 5 Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count Aim: Learn to count cells, observe and identify different blood cells in a smear, quantify their proportions and count RBCs per µl (mm^3) using
Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: on October 30, 2018 jcb.rupress.org Downloaded from
 Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.1.197 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on October 30, 2018 BRIEF NOTES 197 The Use of Potassium Permanganate as an Electron-Dense
Published Online: 1 February, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.1.197 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on October 30, 2018 BRIEF NOTES 197 The Use of Potassium Permanganate as an Electron-Dense
Preparation of tissues for study
 Preparation of tissues for study HISTOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic
Preparation of tissues for study HISTOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic
2. Know the parts of a light microscope and general rules for using and focusing a microscope, such as:
 SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
THE USE OF LEAD CITRATE AT HIGH ph AS AN ELECTRON-OPAQUE STAIN IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
 THE USE OF LEAD CITRATE AT HIGH ph AS AN ELECTRON-OPAQUE STAIN IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY EDWARD S. REYNOLDS. From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston Aqueous solutions of lead salts
THE USE OF LEAD CITRATE AT HIGH ph AS AN ELECTRON-OPAQUE STAIN IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY EDWARD S. REYNOLDS. From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston Aqueous solutions of lead salts
2. Know the parts of a light microscope and general rules for using and focusing a microscope, such as:
 SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Biology Mounting medium Telophase Organelle Cell Theory Cell cycle Cytokinesis
Evaluation of the Automated Immature Granulocyte Count (IG) on Sysmex XE-2100 Automated Haematology Analyser vs. Visual Microscopy (NCCLS H20-A)
 Evaluation of the Automated Immature Granulocyte Count (IG) on Sysmex XE-21 Automated Haematology Analyser vs. Visual Microscopy (NCCLS H2-A) Th WEILAND *1, H KALKMAN *2, and H HEIHN *1 *1 Central Laboratory,
Evaluation of the Automated Immature Granulocyte Count (IG) on Sysmex XE-21 Automated Haematology Analyser vs. Visual Microscopy (NCCLS H2-A) Th WEILAND *1, H KALKMAN *2, and H HEIHN *1 *1 Central Laboratory,
CHAPTER 1. Aspects of the Three-Dimensional Intracellular Organization of Mesocarp Cells as Revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy
 CHAPTER 1 Aspects of the Three-Dimensional Intracellular Organization of Mesocarp Cells as Revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy Reprinted from Protoplasma by permission of Springer-Verlag Publishers,
CHAPTER 1 Aspects of the Three-Dimensional Intracellular Organization of Mesocarp Cells as Revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy Reprinted from Protoplasma by permission of Springer-Verlag Publishers,
to take a full thickness biopsy of epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. phosphate buffer) for conventional EM and/ or in paraformaldehyde for immuno-em
 INSTITUTE BORN-BUNGE-University of Antwerpen (UA) Laboratory of Ultrastructural Neuropathology (LUN) Head: C. Ceuterick-de Groote Universiteitsplein 1, B-2610 WILRIJK-Antwerpen (Belgium) Phone: 00 32 3
INSTITUTE BORN-BUNGE-University of Antwerpen (UA) Laboratory of Ultrastructural Neuropathology (LUN) Head: C. Ceuterick-de Groote Universiteitsplein 1, B-2610 WILRIJK-Antwerpen (Belgium) Phone: 00 32 3
Introduction to Histology
 Introduction to Histology Histology The term "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of Histology : Is the study of tissues and how they are arranged
Introduction to Histology Histology The term "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of Histology : Is the study of tissues and how they are arranged
scatter electrons and can easily he distinguished
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIOATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1968 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. PERCUTANEOUS ABSORPTION OF MERCURY IN MAN 1. A STUDY BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIOATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1968 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. PERCUTANEOUS ABSORPTION OF MERCURY IN MAN 1. A STUDY BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE
 -------------------------------------- Biology Name Summary Sbeet Cell Structure Lab Class Date --------------------~ ---------- A. Cork Cells: Wet mount I Higb Power 1. Is it easier to see individual
-------------------------------------- Biology Name Summary Sbeet Cell Structure Lab Class Date --------------------~ ---------- A. Cork Cells: Wet mount I Higb Power 1. Is it easier to see individual
LABORATORY ASSESSMENT OF HAEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY IMMUNOPHENOTYPING. First Edition Australasian Cytometry Society Laboratory Assessment Document
 LABORATORY ASSESSMENT OF HAEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY IMMUNOPHENOTYPING First Edition 2018 Australasian Cytometry Society Laboratory Assessment Document Paper-based publications This work is copyright. You may
LABORATORY ASSESSMENT OF HAEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY IMMUNOPHENOTYPING First Edition 2018 Australasian Cytometry Society Laboratory Assessment Document Paper-based publications This work is copyright. You may
Blood and Tissue Parasites Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 13, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director Review Date:
 Section: Policy # MI\PAR\11\01\v01 Page 1 of 5 Subject Title: Laboratory Procedures for Blood and Tissue Parasites Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 13, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director
Section: Policy # MI\PAR\11\01\v01 Page 1 of 5 Subject Title: Laboratory Procedures for Blood and Tissue Parasites Issued by: LABORATORY MANAGER Original Date: March 13, 2000 Approved by: Laboratory Director
ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF POLYOMA VIRUS-TRANSFORMED MOUSE CELLS TREATED WITH SPECIFIC IMMUNE SERUM
 J. Cell Sci. 7, 711-718(1970) 7II Printed in Great Britain ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF POLYOMA VIRUS-TRANSFORMED MOUSE CELLS TREATED WITH SPECIFIC IMMUNE SERUM G.NEGRONI AND RITA TILLY Department
J. Cell Sci. 7, 711-718(1970) 7II Printed in Great Britain ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF POLYOMA VIRUS-TRANSFORMED MOUSE CELLS TREATED WITH SPECIFIC IMMUNE SERUM G.NEGRONI AND RITA TILLY Department
1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench
 The Microscope Operating the compound light microscope 1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench 2. Check that lenses
The Microscope Operating the compound light microscope 1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench 2. Check that lenses
EMS MICROSCOPY ACADEMY BIOLOGICAL TEM WORKSHOP: A COMPLETE PICTURE
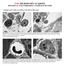 Examples of the endless possibilities in the field of Microscopy Bone Marrow: Transmission electron microscope image of a thin section cut through an area of bone marrow area near the cartilage/bone interface
Examples of the endless possibilities in the field of Microscopy Bone Marrow: Transmission electron microscope image of a thin section cut through an area of bone marrow area near the cartilage/bone interface
BIMM18 Dec 20 th - Flow cytometry in clinical diagnostics
 BIMM18 Dec 20 th - Flow cytometry in clinical diagnostics I. B cell leukemia and lymphomas Immunophenotyping as part of the diagnostic work- up of hematologic malignancies offers a rapid and effective
BIMM18 Dec 20 th - Flow cytometry in clinical diagnostics I. B cell leukemia and lymphomas Immunophenotyping as part of the diagnostic work- up of hematologic malignancies offers a rapid and effective
TELE-HEMATOLOGY: CRITICAL DETERMINANTS FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION
 Blood First Edition From Paper, www.bloodjournal.org prepublished by online guest on September July 4, 2018. 11, For 2003; personal DOI use 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1615 only. TELE-HEMATOLOGY: CRITICAL DETERMINANTS
Blood First Edition From Paper, www.bloodjournal.org prepublished by online guest on September July 4, 2018. 11, For 2003; personal DOI use 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1615 only. TELE-HEMATOLOGY: CRITICAL DETERMINANTS
Supporting Protocols
 Supporting Protocols This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec ECM Hydrogels. Introduction Cells and organoids may form complex
Supporting Protocols This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec ECM Hydrogels. Introduction Cells and organoids may form complex
Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No
 SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No 5 2012 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory The purpose of this newsletter is to provide an overview
SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No 5 2012 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory The purpose of this newsletter is to provide an overview
THE MAGNITUDE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS OF SUPERFICIAL AND DEEP REGIONS OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
 J. Cell Sci. 6, 793-805 (1970) 793 Printed in Great Britain THE MAGNITUDE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS OF SUPERFICIAL AND DEEP REGIONS OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX A. VAN HARREVELD AND
J. Cell Sci. 6, 793-805 (1970) 793 Printed in Great Britain THE MAGNITUDE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS OF SUPERFICIAL AND DEEP REGIONS OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX A. VAN HARREVELD AND
Introduction to histology and its methods of study
 Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
THE COMBINED LOM/AFM STUDY OF HUMAN BLOOD CELLS
 THE COMBINED LOM/AFM STUDY OF HUMAN BLOOD CELLS Pavel KEJZLAR 1,2, Eva MACAJOVÁ 1, Lukáš VOLESKÝ 1,2, Lenka BERGEROVÁ 3 1 Department of Material Science, Technical University of Liberec, Studentska 1402/2,
THE COMBINED LOM/AFM STUDY OF HUMAN BLOOD CELLS Pavel KEJZLAR 1,2, Eva MACAJOVÁ 1, Lukáš VOLESKÝ 1,2, Lenka BERGEROVÁ 3 1 Department of Material Science, Technical University of Liberec, Studentska 1402/2,
Improved Fixation of Cellulose-Acetate Reverse-Osmosis Membrane for Scanning Electron Microscopy
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1985, p. 446450 0099-2240/85/020446-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 49, No. 2 Improved Fixation of Cellulose-Acetate Reverse-Osmosis
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1985, p. 446450 0099-2240/85/020446-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 49, No. 2 Improved Fixation of Cellulose-Acetate Reverse-Osmosis
ADDITIONAL SPECIMEN TRANSPORT GUIDELINES
 ADDITIONAL SPECIMEN TRANSPORT GUIDELINES SPECIMEN TYPE / DEPARTMENT FLOOR/HOSPITAL (ROOM NUMBER) HOURS OF OPERATION COLOR**** If applicable BIOREPOSITORY Surgical Pathology 2 nd Floor/ School of Medicine
ADDITIONAL SPECIMEN TRANSPORT GUIDELINES SPECIMEN TYPE / DEPARTMENT FLOOR/HOSPITAL (ROOM NUMBER) HOURS OF OPERATION COLOR**** If applicable BIOREPOSITORY Surgical Pathology 2 nd Floor/ School of Medicine
CLEARLLAB LS LYMPHOID SCREEN REAGENT
 CLEARLLAB LS LYMPHOID SCREEN REAGENT CE MARKED ANTIBODY COMBINATION FOR LEUKEMIA / LYMPHOMA ANALYSIS Because Your Patient is Her Everything BECAUSE YOUR PATIENT IS HER EVERYTHING ClearLLab LS Lymphoid
CLEARLLAB LS LYMPHOID SCREEN REAGENT CE MARKED ANTIBODY COMBINATION FOR LEUKEMIA / LYMPHOMA ANALYSIS Because Your Patient is Her Everything BECAUSE YOUR PATIENT IS HER EVERYTHING ClearLLab LS Lymphoid
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes
 Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Monday: Y42 G53 Tuesday: Y42 G53 Wednesday: Y42 J11
 Locations: Irchel building 42, Level H and F Locations: Irchel building 42, Level H and F Self-study sessions: Monday: Y42 G53 Tuesday: Y42 G53 Wednesday: Y42 J11 1 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
Locations: Irchel building 42, Level H and F Locations: Irchel building 42, Level H and F Self-study sessions: Monday: Y42 G53 Tuesday: Y42 G53 Wednesday: Y42 J11 1 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
CELL ORGANELLES AT UNCOATED CRYOFRACTURED SURFACES AS VIEWED WITH THE SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
 J. Cell Sci. 21, 47-58 (1976) 47 Printed in Great Britain CELL ORGANELLES AT UNCOATED CRYOFRACTURED SURFACES AS VIEWED WITH THE SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE P. S. WOODS AND MYRON C. LEDBETTER Biology Department,
J. Cell Sci. 21, 47-58 (1976) 47 Printed in Great Britain CELL ORGANELLES AT UNCOATED CRYOFRACTURED SURFACES AS VIEWED WITH THE SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE P. S. WOODS AND MYRON C. LEDBETTER Biology Department,
Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them
 Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them Focus on: Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Osmium tetroxide M. Kuwajima/Kristen Harris Lab EM processing and
Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them Focus on: Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Osmium tetroxide M. Kuwajima/Kristen Harris Lab EM processing and
NEW STAINS IN TISSUE DIAGNOSIS
 NEW STAINS IN TISSUE DIAGNOSIS CHARLES F. GESCHICKTER, M.D. (Prom the Surgical Pathological Lahoratory of the Johns Hopkins Hospital ami Univel'sily, Baltimore, Maryland) The use of stains has long been
NEW STAINS IN TISSUE DIAGNOSIS CHARLES F. GESCHICKTER, M.D. (Prom the Surgical Pathological Lahoratory of the Johns Hopkins Hospital ami Univel'sily, Baltimore, Maryland) The use of stains has long been
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 26, 2014 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 September 26, 2014 1 / 21 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 26, 2014 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 September 26, 2014 1 / 21 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood RNA Purification Mini Kit #K0761
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood RNA Purification Mini Kit #K0761 www.thermoscientific.com/onebio #K0761 Lot Exp. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood
PRODUCT INFORMATION Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood RNA Purification Mini Kit #K0761 www.thermoscientific.com/onebio #K0761 Lot Exp. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood
PLASTINATION OF OLD FORMALIN-FIXED SPECIMENS
 1 J Int Soc Plastination, Vol 5:11-15, 1991 PLASTINATION OF OLD FORMALIN-FIXED SPECIMENS Mario Cannas and Paolo Fuda University of Torino, Department of Human Anatomy and Physiology, C.so M. D' Azeglio
1 J Int Soc Plastination, Vol 5:11-15, 1991 PLASTINATION OF OLD FORMALIN-FIXED SPECIMENS Mario Cannas and Paolo Fuda University of Torino, Department of Human Anatomy and Physiology, C.so M. D' Azeglio
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF NUCLEOCYTOPLASMIC INTERACTIONS
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF NUCLEOCYTOPLASMIC INTERACTIONS CARL M. FELDHERR. From the Department of Anatomical Sciences, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32601 It is evident that the pores of the
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF NUCLEOCYTOPLASMIC INTERACTIONS CARL M. FELDHERR. From the Department of Anatomical Sciences, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32601 It is evident that the pores of the
ab CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence
 ab139482 CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to detect Human endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139482 CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to detect Human endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Cells and Tissues. Overview CELLS
 Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Staining and Embedding the Whole Mouse Brain for Electron Microscopy
 Staining and Embedding the Whole Mouse Brain for Electron Microscopy Shawn Mikula, Jonas Binding, Winfried Denk Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Table 1 Supplementary Table 2 Supplementary
Staining and Embedding the Whole Mouse Brain for Electron Microscopy Shawn Mikula, Jonas Binding, Winfried Denk Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Table 1 Supplementary Table 2 Supplementary
Pushing limits in routine laboratory haematology with the XT-4000i
 Pushing limits in routine laboratory haematology with the XT-4000i Sysmex Xtra Online December 2013 Fig. 1 The XT-4000i haematology system With the launch of the XE-5000, Sysmex set new standards in haematology.
Pushing limits in routine laboratory haematology with the XT-4000i Sysmex Xtra Online December 2013 Fig. 1 The XT-4000i haematology system With the launch of the XE-5000, Sysmex set new standards in haematology.
CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence
 ab139483 CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed for the detection of Golgi bodies by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139483 CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed for the detection of Golgi bodies by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
XS-1000i New Sysmex 5-part diff haematology analyser with fluorescence technology
 XS-1000i New Sysmex 5-part diff haematology analyser Fig. 1: sysmex xs-1000i Since the introduction of fluorescence technology for leukocyte differentiation by sysmex in the year 1999, thousands of laboratories
XS-1000i New Sysmex 5-part diff haematology analyser Fig. 1: sysmex xs-1000i Since the introduction of fluorescence technology for leukocyte differentiation by sysmex in the year 1999, thousands of laboratories
Growth of crypt cell nodules in duodenal mucosa in
 J Clin Pathol 1985;38:1388-1393 Growth of crypt cell nodules in duodenal mucosa in man during organ culture in vitro DN CHALLACOMBE, EE WHEELER From the Somerset Children's Research Unit, Musgrove Park
J Clin Pathol 1985;38:1388-1393 Growth of crypt cell nodules in duodenal mucosa in man during organ culture in vitro DN CHALLACOMBE, EE WHEELER From the Somerset Children's Research Unit, Musgrove Park
Which hydrogel preparation for immunostaining protocol should I use?
 Protocol: Preparation of TissueSpec hydrogels for immunostaining This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec matrix hydrogels.
Protocol: Preparation of TissueSpec hydrogels for immunostaining This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec matrix hydrogels.
Thermal damage behaviour of human dental pulp stem cells
 S C I E N T I F I C Thermal damage behaviour of human dental pulp stem cells Karsten König 1 and Anton Kasenbacher 2 Objective This study was designed to examine the influence of temperatures ranging from
S C I E N T I F I C Thermal damage behaviour of human dental pulp stem cells Karsten König 1 and Anton Kasenbacher 2 Objective This study was designed to examine the influence of temperatures ranging from
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1302 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1302 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Light and transmission electron microscopy
 TECHNICAL NOTE Processing scarce biological samples for light and transmission electron microscopy P. Taupin 1,2,3 1 National Neuroscience Institute; 2 National University of Singapore; 3 Nanyang Technological
TECHNICAL NOTE Processing scarce biological samples for light and transmission electron microscopy P. Taupin 1,2,3 1 National Neuroscience Institute; 2 National University of Singapore; 3 Nanyang Technological
3.1 GENERAL SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS See test menu for test-specific requirements
 3.1 GENERAL SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS See test menu for test-specific requirements For all cases, include the following (see test-specific specimen requirements below): A. Completed PhenoPath requisition form
3.1 GENERAL SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS See test menu for test-specific requirements For all cases, include the following (see test-specific specimen requirements below): A. Completed PhenoPath requisition form
Histology Series Part 1. Choosing the Right Fixative to Preserve 3D Cell Cultures
 Introduction These histology protocols contain a series of detailed methods that will allow the user to examine the morphology of their cultured cells subsequent to 3D growth. These are not in any way
Introduction These histology protocols contain a series of detailed methods that will allow the user to examine the morphology of their cultured cells subsequent to 3D growth. These are not in any way
ADAPTIVE BIOTECHNOLOGIES DIAGNOSTIC PORTAL: ACCOUNT LOGIN
 ACCOUNT LOGIN 1. Create an account. To set up your account for our online order entry and reporting system, please go to: https://diagnostics.adaptivebiotech.com/account/login. After signing up, please
ACCOUNT LOGIN 1. Create an account. To set up your account for our online order entry and reporting system, please go to: https://diagnostics.adaptivebiotech.com/account/login. After signing up, please
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 19/May 12, 2014 Page 5083
 CORRELATION STUDY BETWEEN BONE MARROW IRON AND SERUM IRON AND SERUM FERRITIN IN PATIENTS OF MODERATE TO SEVERE ANEMIA Ankita Tripathi 1, R. K. Nigam 2, Reeni Malik 3, P. Jain 4, Atul Shrivastava 5 HOW
CORRELATION STUDY BETWEEN BONE MARROW IRON AND SERUM IRON AND SERUM FERRITIN IN PATIENTS OF MODERATE TO SEVERE ANEMIA Ankita Tripathi 1, R. K. Nigam 2, Reeni Malik 3, P. Jain 4, Atul Shrivastava 5 HOW
Wednesday 11 January 2012 Morning
 Wednesday 11 January 2012 Morning AS GCE BIOLOGY F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport *F210010111* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Insert (inserted) Other materials required:
Wednesday 11 January 2012 Morning AS GCE BIOLOGY F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport *F210010111* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Insert (inserted) Other materials required:
LaboPass TM Blood mini
 LaboPass TM Blood mini Protocol Book LaboPass TM Blood Mini Introduction LaboPass TM Blood Mini Kit provides a fast and convenient method for the isolation of total DNA from up to 400μLof fresh and frozen
LaboPass TM Blood mini Protocol Book LaboPass TM Blood Mini Introduction LaboPass TM Blood Mini Kit provides a fast and convenient method for the isolation of total DNA from up to 400μLof fresh and frozen
Title. Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto; FURUHATA, Kitao; KUDO, Norio; MIFU. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 15(4): 153- Issue Date
 Title CRYSTALLINE INCLUSIONS IN ENDOTHELIAL CELLS OF POST- LYMPH NODES Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto; FURUHATA, Kitao; KUDO, Norio; MIFU CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 15(4): 153- Issue Date
Title CRYSTALLINE INCLUSIONS IN ENDOTHELIAL CELLS OF POST- LYMPH NODES Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto; FURUHATA, Kitao; KUDO, Norio; MIFU CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 15(4): 153- Issue Date
Immunophenotyping of Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Cells by Flow Cytometry *Akanni EO and # Palini A.
 Immunophenotyping of Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Cells by Flow Cytometry *Akanni EO and # Palini A. * Department of Haematology & Blood Transfusion,College of Health Science, Ladoke Akintola University
Immunophenotyping of Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Cells by Flow Cytometry *Akanni EO and # Palini A. * Department of Haematology & Blood Transfusion,College of Health Science, Ladoke Akintola University
celldatasci.com/rnastorm RNAstorm RNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples Sample Kit (20 extractions)
 celldatasci.com/rnastorm info@celldatasci.com RNAstorm RNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples Sample Kit (20 extractions) Support: Email: support@celldatasci.com Phone: 650.285.2376 (option 2) Toll-free:
celldatasci.com/rnastorm info@celldatasci.com RNAstorm RNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples Sample Kit (20 extractions) Support: Email: support@celldatasci.com Phone: 650.285.2376 (option 2) Toll-free:
SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions:
 SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Apoptosis Cancer Cell membrane Cell specialization Cell wall Centriole Chloroplast
SNC 2DI Exam Review: Biology Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Apoptosis Cancer Cell membrane Cell specialization Cell wall Centriole Chloroplast
Introduction to Electron Microscopy Andres Kaech
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Introduction to Electron Microscopy Andres Kaech The types of electron microscopes Transmission electron microscope (TEM) Scanning electron microscope (SEM) 1 The
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Introduction to Electron Microscopy Andres Kaech The types of electron microscopes Transmission electron microscope (TEM) Scanning electron microscope (SEM) 1 The
Permanganate Fixation of Plant Cells
 Permanganate Fiation of Plant Cells By HILTON H. MOLLENHAUER, Ph.D. (From The University of Teas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas) PLATES 222 ~O 224 (Received for publication, June 22, 1959) ABSTRACT
Permanganate Fiation of Plant Cells By HILTON H. MOLLENHAUER, Ph.D. (From The University of Teas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas) PLATES 222 ~O 224 (Received for publication, June 22, 1959) ABSTRACT
Upon completion of the Clinical Hematology rotation, the MLS student will be able to:
 Clinical Performance Objectives in Clinical Hematology Department of Medical and Research Technology University of Maryland School of Medicine Spring 2015 Upon completion of the Clinical Hematology rotation,
Clinical Performance Objectives in Clinical Hematology Department of Medical and Research Technology University of Maryland School of Medicine Spring 2015 Upon completion of the Clinical Hematology rotation,
INFECTIOUS MURINE TYPE-C VIRUSES RELEASED FROM HUMAN CANCER CELLS TRANSPLANTED INTO NUDE MICE
 INFECTIOUS MURINE TYPE-C VIRUSES RELEASED FROM HUMAN CANCER CELLS TRANSPLANTED INTO NUDE MICE Toshimitsu SUZUKI,*1 Kazuyoshi YANAGIHARA,*2 Koichi YOSHIDA,*2 Tsutomu SEIDO,*1 Norito KUGA,*3 Yukio SHIMOSATO,*2
INFECTIOUS MURINE TYPE-C VIRUSES RELEASED FROM HUMAN CANCER CELLS TRANSPLANTED INTO NUDE MICE Toshimitsu SUZUKI,*1 Kazuyoshi YANAGIHARA,*2 Koichi YOSHIDA,*2 Tsutomu SEIDO,*1 Norito KUGA,*3 Yukio SHIMOSATO,*2
IT appears to be the general consensus of opinion that initial cooling or
 25 1 The Initial Cooling of Tissues in the Freezing-drying Technique By I. ZLOTNIK, PH.D., B.V.SC, M.R.C.V.S. (From the Moredun Research Institute, Gilmerton, Edinburgh) With one plate (fig. 2) SUMMARY
25 1 The Initial Cooling of Tissues in the Freezing-drying Technique By I. ZLOTNIK, PH.D., B.V.SC, M.R.C.V.S. (From the Moredun Research Institute, Gilmerton, Edinburgh) With one plate (fig. 2) SUMMARY
PHAGOCYTOSIS OF CONCANAVALIN A IN NORMAL AND ENUCLEATED CULTURES OF MAMMALIAN CELLS
 J. Cell Sci. aa, 623-632 (1976) 623 Printed in Great Britain PHAGOCYTOSIS OF CONCANAVALIN A IN NORMAL AND ENUCLEATED CULTURES OF MAMMALIAN CELLS GARY E. WISE Department of Biological Structure, University
J. Cell Sci. aa, 623-632 (1976) 623 Printed in Great Britain PHAGOCYTOSIS OF CONCANAVALIN A IN NORMAL AND ENUCLEATED CULTURES OF MAMMALIAN CELLS GARY E. WISE Department of Biological Structure, University
Introduction to Histology
 Introduction to Histology The name "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of It is tightly bounded to molecular biology, genetics, immunology and other
Introduction to Histology The name "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of It is tightly bounded to molecular biology, genetics, immunology and other
Dark-Field Electron Microscopy of Thin Sections of
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1974, p. 527-531 Copyright 0 1974 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 120, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Dark-Field Electron Microscopy of Thin Sections of Trichosporon cutaneum
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1974, p. 527-531 Copyright 0 1974 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 120, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Dark-Field Electron Microscopy of Thin Sections of Trichosporon cutaneum
CORRELATION OF CELL DIVISION AND SPECIFIC PROTEIN PRODUCTION DURING THE COURSE OF LYMPHOID CELL DIFFERENTIATION
 CORRELATION OF CELL DIVISION AND SPECIFIC PROTEIN PRODUCTION DURING THE COURSE OF LYMPHOID CELL DIFFERENTIATION W. D. KUHLMANN, M. BOUTEILLE, and S. AVRAMEAS Immunocytochemistry SFB 136 and Institut für
CORRELATION OF CELL DIVISION AND SPECIFIC PROTEIN PRODUCTION DURING THE COURSE OF LYMPHOID CELL DIFFERENTIATION W. D. KUHLMANN, M. BOUTEILLE, and S. AVRAMEAS Immunocytochemistry SFB 136 and Institut für
Phagocytosis Assay Kit (IgG PE)
 Phagocytosis Assay Kit (IgG PE) Item No. 600540 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Phagocytosis Assay Kit (IgG PE) Item No. 600540 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Image Analysis. Tools for basic and translational research. visualize analyze interpret report archive customize
 Image Analysis Tools for basic and translational research visualize analyze interpret report archive customize Unlock the benefits of image analysis. Image analysis is an integrated part of Aperio s digital
Image Analysis Tools for basic and translational research visualize analyze interpret report archive customize Unlock the benefits of image analysis. Image analysis is an integrated part of Aperio s digital
Electron microscopy technology of reticulocytes after sorting with
 Electron microscopy technology of reticulocytes after sorting with magnetic beads The Cell Analysis Center Scientific Bulletin Part 2 For efficient analysis of cells, sorting of the target cells is crucial.
Electron microscopy technology of reticulocytes after sorting with magnetic beads The Cell Analysis Center Scientific Bulletin Part 2 For efficient analysis of cells, sorting of the target cells is crucial.
TheraLin. Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology
 TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology Contents Page # TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative 3 Introduction 5 Easy
TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative Enabling Molecular Pathology Contents Page # TheraLin Universal Tissue Fixative 3 Introduction 5 Easy
2111: ALL Post-HCT. Add/ Remove/ Modify. Manual Section. Date. Description. Comprehensive Disease- Specific Manuals
 2111: ALL Post-HCT The Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Post-HCT Data Form is one of the Comprehensive Report Forms. This form captures ALL-specific post-hct data such as: planned treatments post-hct, the
2111: ALL Post-HCT The Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Post-HCT Data Form is one of the Comprehensive Report Forms. This form captures ALL-specific post-hct data such as: planned treatments post-hct, the
EVALUATION OF LIQUID-PREP TM ENCAPSULATION METHOD FOR LIQUID-BASED CYTOLOGY: CELL LOSS ESTIMATES DURING PROCESSING ABSTRACT
 EVALUATION OF LIQUID-PREP TM ENCAPSULATION METHOD FOR LIQUID-BASED CYTOLOGY: CELL LOSS ESTIMATES DURING PROCESSING James Geyer, Ph.D., James Marino, CMIAC, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA Seacoast Pathology,
EVALUATION OF LIQUID-PREP TM ENCAPSULATION METHOD FOR LIQUID-BASED CYTOLOGY: CELL LOSS ESTIMATES DURING PROCESSING James Geyer, Ph.D., James Marino, CMIAC, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA Seacoast Pathology,
PROTOCOL. Histology Series Part 1: Choosing the Right Fixative to Preserve 3D Cell Cultures. Introduction. Fixation methods.
 Page 1 Introduction These histology protocols contain a series of detailed methods that will allow the user to examine the morphology of their cultured cells subsequent to 3D growth. These are not in any
Page 1 Introduction These histology protocols contain a series of detailed methods that will allow the user to examine the morphology of their cultured cells subsequent to 3D growth. These are not in any
celldatasci.com/dnastorm DNAstorm DNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples 50 extractions (CD502)
 celldatasci.com/dnastorm info@celldatasci.com DNAstorm DNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples 50 extractions (CD502) Support: Email: support@celldatasci.com Phone: 650.285.2376 (option 2) Toll-free:
celldatasci.com/dnastorm info@celldatasci.com DNAstorm DNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples 50 extractions (CD502) Support: Email: support@celldatasci.com Phone: 650.285.2376 (option 2) Toll-free:
Biology unit. Big Idea. Cells are derived from cells Part 1 Review, what s in a cell!?
 Biology unit Big Idea Cells are derived from cells Part 1 Review, what s in a cell!? (cell nucleus and DNA-Gr 10 material for next year) http://www.popsci.com/science/article/2013-03/watch-absolutely-beautiful-animatedexplainer-dna
Biology unit Big Idea Cells are derived from cells Part 1 Review, what s in a cell!? (cell nucleus and DNA-Gr 10 material for next year) http://www.popsci.com/science/article/2013-03/watch-absolutely-beautiful-animatedexplainer-dna
MaxPar Cytoplasmic/Secreted Antigen Staining Protocol
 MaxPar Cytoplasmic/Secreted Antigen Staining Protocol CHEMICAL HAZARD: Before handling any chemicals, refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) provided by the manufacturer, and observe all relevant
MaxPar Cytoplasmic/Secreted Antigen Staining Protocol CHEMICAL HAZARD: Before handling any chemicals, refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) provided by the manufacturer, and observe all relevant
How to Get Well-Preserved Samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy
 pissn 2287-5123 eissn 2287-4445 https://doi.org/10.9729/am.2016.46.4.188 Review Article How to Get Well-Preserved Samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy Chang-Hyun Park*, Hyun-Wook Kim, Im Joo Rhyu
pissn 2287-5123 eissn 2287-4445 https://doi.org/10.9729/am.2016.46.4.188 Review Article How to Get Well-Preserved Samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy Chang-Hyun Park*, Hyun-Wook Kim, Im Joo Rhyu
ExKine Total Protein Extraction Kit
 ExKine Total Protein Extraction Kit Item NO. KTP3006 Product Name ExKine Total Protein Extraction Kit ATTENTION For laboratory research use only. Not for clinical or diagnostic use Version 201811 TABLE
ExKine Total Protein Extraction Kit Item NO. KTP3006 Product Name ExKine Total Protein Extraction Kit ATTENTION For laboratory research use only. Not for clinical or diagnostic use Version 201811 TABLE
PALM User Protocols. Laser Capture Microdissection (LCM): Live cells and molecular analysis. Microdissection from Carl Zeiss
 Microdissection from Carl Zeiss PALM User Protocols PALM Laboratories A unique service of Carl Zeiss 1 Sample Preparation 3 1.1 Cultivation of adherent cells 3 1.2 Cytospin preparation of cells in suspension
Microdissection from Carl Zeiss PALM User Protocols PALM Laboratories A unique service of Carl Zeiss 1 Sample Preparation 3 1.1 Cultivation of adherent cells 3 1.2 Cytospin preparation of cells in suspension
Conditions Critical for Optimal Visualization of Bacteriophage
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1975, p. 1498-1503 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 15, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Conditions Critical for Optimal Visualization of Bacteriophage Adsorbed
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1975, p. 1498-1503 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 15, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Conditions Critical for Optimal Visualization of Bacteriophage Adsorbed
Manual For Blood Cells Atlas Morphology Download
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with manual for blood cells
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with manual for blood cells
Biology Assessment Study Sheet. Estimating the size of Red Blood Cells
 Biology Assessment Study Sheet Perform a first-hand investigation using a light microscope and prepared slides to gather information to estimate the size of red and white blood cells and draw scaled diagrams
Biology Assessment Study Sheet Perform a first-hand investigation using a light microscope and prepared slides to gather information to estimate the size of red and white blood cells and draw scaled diagrams
KCC Path-Core Page 1 of 5
 Instructions for Sample preparation for Paraffin embedding PLEASE NOTE: There is no one-size-fits-all method of tissue preparation for all experimental designs. Before harvesting tissue, you need to assess
Instructions for Sample preparation for Paraffin embedding PLEASE NOTE: There is no one-size-fits-all method of tissue preparation for all experimental designs. Before harvesting tissue, you need to assess
Prelinzirwry and Short Report
 Prelinzirwry and Short Report ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF INFECTED HAIRS IN TRICHOMYCOSIS AXILLARIS* LEOPOLDO F. MONTES, M.D., CESAR VASQUEZ, M.D.' AND MARTA S. CATALDI, PH.D.' The etiologic agent of
Prelinzirwry and Short Report ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF INFECTED HAIRS IN TRICHOMYCOSIS AXILLARIS* LEOPOLDO F. MONTES, M.D., CESAR VASQUEZ, M.D.' AND MARTA S. CATALDI, PH.D.' The etiologic agent of
RNAstorm FFPE. RNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples. Kit Manual. 20 extractions (CD201) 50 extractions (CD501) rev. 1.3
 https://celldatasci.com info@celldatasci.com RNAstorm FFPE RNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples Kit Manual 20 extractions (CD201) 50 extractions (CD501) rev. 1.3 Support: Email: support@celldatasci.com
https://celldatasci.com info@celldatasci.com RNAstorm FFPE RNA Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissue Samples Kit Manual 20 extractions (CD201) 50 extractions (CD501) rev. 1.3 Support: Email: support@celldatasci.com
Using Human Tissue in Translational Research and Clinical Trials
 Using Human Tissue in Translational Research and Clinical Trials Dr Bridget S Wilkins NCRI Clinical Lead for Pathology Engagement (Consultant Histopathologist, St Thomas Hospital, London) Cellular and
Using Human Tissue in Translational Research and Clinical Trials Dr Bridget S Wilkins NCRI Clinical Lead for Pathology Engagement (Consultant Histopathologist, St Thomas Hospital, London) Cellular and
XN Hematology Case Studies Every Picture Tells a Story
 XN Hematology Case Studies Every Picture Tells a Story Barbara J Connell MS, MT(ASCP)SH Senior Product Manager Technical Marketing & Communications Sysmex America, Inc Objectives Describe the advantages
XN Hematology Case Studies Every Picture Tells a Story Barbara J Connell MS, MT(ASCP)SH Senior Product Manager Technical Marketing & Communications Sysmex America, Inc Objectives Describe the advantages
(nuclear diameter / heterochromatin condensation / leukaemic granulocytes) Institute of Haematology and Blood Transfusion, Prague, Czech Republic
 Original Article Morphometric and Densitometric Analysis of Heterochromatin during Cell Differentiation Using the Leukaemic Granulocytic Lineage as a Convenient Model (nuclear diameter / heterochromatin
Original Article Morphometric and Densitometric Analysis of Heterochromatin during Cell Differentiation Using the Leukaemic Granulocytic Lineage as a Convenient Model (nuclear diameter / heterochromatin
