State: MAHARASHTRA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SINDHUDURG
|
|
|
- Edward Heath
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Final Vetted by NBSS & LUP State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SINDHUDURG 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning Commission) Agro Climatic Zone (NARP) Central and south Sahyadris, hot moist, subhumid to humid eco-subregion(19.2) Western Coast Plains and Ghat region (XII) South Konkan Coastal Zone (MH-1) List all the districts or part thereof falling under the Ratnagiri and Sindhudurg NARP Zone Geographic coordinates of district headquarters Latitude Longitude Altitude Name and address of the concerned ZRS/ ZARS/ RARS/ RRS/ RRTTS 16 o N 73 o E 213 m Regional Fruit Research Station, Vengurle, Dist. Sindhudurg (M.S.) Mention the KVK located in the district Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Kirlos, Tal. Malvan, Dist. Sindhudurg (M.S.) Name and address of the nearest Agromet Field Unit for agro- advisories in the zone 1.2 Rainfall Normal RF(mm) Technical Officer, Integrated Agro Advisory Services, Agricultural Research Station, Mulde, Dist. Sindhudurg (M.S.) Normal Rainy days (number) Normal Onset ( specify week and month) Normal Cessation (specify week and month) SW monsoon (June-Sep): First week of June 2 nd week of October NE Monsoon(Oct-Dec): Post monsoon showers (Oct.- Dec) Winter (Nov-Feb) Summer (Mar-May) Annual
2 1.3 Land use pattern of the district (latest statistics) Area ( 000 ha) Geographical area Cultivable area Forest area Land under nonagricultural use Permanent pastures Cultivable wasteland Land under Misc. tree crops and groves Barren and uncultivable land Current fallows Source: District Socio-economic Review, 2010( Directorate of Economic & Statistics, Govt. of Maharashtra ) 1. 4 Major Soils (common names like red sandy loam deep soils (etc.,) Area ( 000 ha) Percent (%) of total Deep soils Medium deep soils Shallow soils Source :- NBSS & LUP, Nagpur 1.5 Agricultural land use Area ( 000 ha) Cropping intensity % Net sown area 163 Area sown more than once 4 Gross cropped area 167 Source District Socio-economic Review ( Directorate of Economic & Statistics, Govt. of Maharashtra ) Other fallows 2
3 3 1.6 Irrigation Area ( 000 ha) Net irrigated area 17 Gross irrigated area 20 Rainfed area 127 Sources of Irrigation Number Area ( 000 ha) Percentage of total irrigated area Canals Tanks Open wells Bore wells 88 Lift irrigation schemes 1561 Micro-irrigation Other sources (please specify) Total Irrigated Area 17.0 Pump sets No. of Tractors 35 Source District Socio-economic Review ( Directorate of Economic & Statistics, Govt. of Maharashtra ) Groundwater availability and use* (Data source: State/Central Ground water Department /Board) Over exploited Critical Semi- critical Safe Wastewater availability and use Ground water quality *over-exploited: groundwater utilization > 100%; critical: %; semi-critical: 70-90%; safe: <70% No. of blocks/ Tahasils (%) area Quality of water (specify the problem such as high levels of arsenic, fluoride, saline etc) 3
4 4 1.7 Area under major field crops & horticulture etc. ( ) 1.7 Major Field crops cultivated Area ( 000 ha) Kharif Rabi Summer Total Irrigated Rainfed Irrigated Rainfed Rice Finger millet Prosomillet Pulses (Lab lab bean, black gram, horse gram, cowpea, etc.) Groundnut Niger, sunflower Sugarcane Horticultural crops Fruits Total Area ( 000 ha) Mango 27.1 Cashew 60.6 Sapota 0.2 Other fruit crops 2.5 Horticulture crops Vegetables Okra, Brinjal, Chilli and Leafy vegetables etc ( ) Plantation crops Coconut 16.5 Arecanut 0.8 Fodder crops 3.9 ( ) Source :- Krishi Utpadan Karyakramachi Rupresha, Kharif and Rabi Hangam , Vibhagiy Sabha, Konkan Mahsul Vibhag. Dept. of Agriculture, Govt. of Maharashtra 4
5 5 Livestock Male Female Total 1.8 Non descriptive Cattle (local low yielding) Crossbred cattle Non descriptive Buffaloes (local low yielding) Graded Buffaloes Goat Sheep Others (Camel, Pig, Yak etc.) Commercial dairy farms (Number) 1.9 Poultry No. of farms Total No. of birds Commercial Backyard Source : Maharashtra Animal and Fisheries Science University, Nagpur 1.10 Fisheries (Data source: Chief Planning Officer) A. Capture i) Marine (Data Source: Fisheries Department) No. of fishermen Mechanized Boats Non-mechanized Mechanized (Trawl nets, Gill nets) Nets Nonmechanized (Shore Seines, Stake & trap nets) Storage facilities (Ice plants etc.) Number of processing unit ii) Inland (Data Source: Fisheries Department) No. Farmer owned ponds No. of Reservoirs No. of village tanks
6 6 B. Culture Water Spread Area ( 000 ha) Yield (t/ha) Production ( tons) i) Brackish water (Data Source: MPEDA/ Fisheries Department) ii) Fresh water (Data Source: Fisheries Department) Production and Productivity of major crops 1.11 Name of crop Kharif Rabi-Summer Summer Total Crop residue Produc tion ( 00 MT) Produc tivity (kg/ha) Produc tion ( 00 MT) Produc tivity (kg/ha) Produc tion ('00 M t) Produc tivity (kg/ha) Produc tion ( 00 MT ) Major Field crops (Crops to be identified based on total acreage) Rice Finger millet Prosomillet Pulses (Lab lab bean, black gram, horse gram, cowpea, etc.) Groundnut and other oil seed Produc ivity (kg/ha) (Groundnut) 1 others) Source :- Krishi Utpadan Karyakramachi Rupresha, Kharif and Rabi Hangam , Vibhagiy Sabha, Konkan Mahsul Vibhag. Dept. of Agriculture, Govt. of Maharashtra Major Horticultural crops (Crops to be identified based on total acreage) Mango MT/ha Cashew Coconuts nuts nuts/palm Sapota MT/ha as fodder ( 000 tons) 6
7 Sowing window for 5 major field crops Rice Finger millet Groundnut Niger (Karla) Sugarcane Kharif- Rainfed 3 rd week of June to 4 th week of June 3 rd week of June-4 th week of June 2 nd week of June - 2 nd week of July 2 nd week of June- 3 rd week of June - Kharif-Irrigated Rabi- Rainfed Rabi-Irrigated 2 nd week of Nov- 2 nd week of December. 2 nd week of December - 2 nd week of January 2 nd week of Oct - 2 nd week of Nov. (Cowpea, Wal, Horse gram, Sunflower) Green gram - February 2 nd week of December -2 nd week of January 1.13 What is the major contingency the district is prone to? (Tick mark) Regular Occasional None Drought Flood -- (June to August) -- Cyclone Hail storm -- - Heat wave - -- Cold wave Frost -- (Nov.-Dec.) -- Sea water intrusion - -- Pests and disease outbreak (specify for major pests and diseases) Rice:- Bacterial blight, Blast 2. Finger millet :_ Bacterial blight, Blast 3. Groundnut :- Leaf spot and rust of groundnut 4. Mango :- Hopper, Mealy bug, thrips, fruit fly, Anthracnose, Powdery mildew, Branch drying & post harvest rots 5. Cashew :- Tea mosquito bug, thrips, aphids, Anthracnose. 6. Coconut :- Rhinoceros beetle, eriophyid mite 7.Areca nut :- Koleroga, Inflorescence blight and Ganoderma rot. Others (specify)
8 Include Digital maps of the district for Location map of district within State as Annexure I Mean annual rainfall as Annexure 2 Soil map as Annexure 3 Enclosed: Yes Enclosed: yes Enclosed: Yes 8
9 Annexure I- Location map
10 Mean monthly rainfall (mm) of Sindhudurg District Annexure - 2 Rainfall (mm) January February March April May June July August September October November December Months Mean rainfall (mm) 10
11 11 Annexure - 3 Soil map Sindhudurg district (Source :- NBSS & LUP, Nagpur) 11
12 2.0 Strategies for weather related contingencies 2.1 Drought Rainfed situation Condition Suggested Contingency measures Early season drought (delayed onset) Major Farming situation Normal Crop / Cropping system Change in crop / cropping system including variety Agronomic measures Remarks on Implementation Delay by 2 weeks (3 rd week of June)* a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Rice Early variety (Ratnagiri 73, Ratnagiri 24, Ratnagiri- 1) Source of Seed : Maharashtra State Seed Corporation Finger millet No change Prosomillet No change Groundnut No change Niger No change Sugarcane No change b) Mid-land medium deep soils Rice Early duration variety (Ratnagiri 1, Karjat 3, Ratnagiri 24, Ratnagiri 5, Karjat-7.) Source of Seed : Maharashtra State Seed Corporation c) Low land deep soils Rice Mid-late duration variety (Ratnagiri 4, Palghar- 1, Palghar- 2, Karjat- 5 ) --- d) Hill slope shallow soils Finger millet No change --- Prosomillet No change ---
13 13 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Early season drought (delayed onset) Major Farming situation Normal Crop / Cropping system Change in crop / cropping system c including variety Agronomic measures Remarks on Implementation ** Delay by 4 weeks (1 st Week of July) a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Rice Finger millet Prosomillet Very early variety (Ratnagiri 73, Karjat -184) Grow pulses like cowpea (Var. Konkan Sadabahar), black gram Oil Seed like niger (Var. IGP 76) Dapog/mat nursery raising /sowing of sprouted seed Source of Seed : Maharashtra State Seed Corporation Groundnut Early duration variety -- (Phule Pragati) Niger No change -- Sugarcane No change Irrigation as per requirement b) Mid-land medium deep soils Rice Early duration variety (Ratnagiri 73, Karjat 184, Ratnagiri - 24) Young seedling transplanting Source of Seed : Maharashtra State Seed Corporation c) Low land deep soils Rice Mid-late duration variety (Ratnagiri 4, Palghar- 1 Palghar- 2, Karjat- 5 ) d) Hill slope shallow soils Finger millet Prosomillet Grow pulses like cowpea (Konkan Sadabahar), black gram Oil Seed like niger (Var. IGP 76) Note :- ** Generally such type of situation has not occurred during past years 13
14 14 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Early season drought (delayed onset) Major Farming situation Normal Crop / Cropping system Change in crop / cropping system including variety Agronomic measures Remarks on Implementation ** Delay by 6 weeks a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Not applicable Note :- ** Generally such type of situation has not occurred during past years (3 rd week of July) b) Mid-land medium deep soils c) Low land deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils Condition Suggested Contingency measures Early season drought (delayed onset) Major Farming situation Normal Crop / Cropping system Change in crop / cropping system including variety Agronomic measures Remarks on Implementation ** Delay by 8 weeks a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Not applicable Note :- ** Generally such type of situation has not occurred during past years (1 st Week of August) b) Mid-land medium deep soils c) Low land deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils 14
15 15 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Early season drought Major Farming Crop management (Normal onset) situation Normal onset followed by days dry spell after sowing leading to poor germination/crop stand etc. a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Normal Crop/cropping system Rice Re-raising nursery by mat technique Soil nutrient & moisture conservation measues Protective irrigation/ mulching between row of seedling with glyricidia Remarks on Implementation b) Mid-land medium deep soils c) Low land deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils Finger millet Use short duration variety (H.R. 374) and delay sowing till monsoon restart. Protective irrigation Groundnut Sow after monsoon restart --- Niger No change --- Sugarcane No change Protective irrigation Rice ---- Protective irrigation Rice ---- Protective irrigation Finger millet Prosomillet Use short duration variety and delay sowing till monsoon restart Protective irrigation Protective irrigation 15
16 16 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Early season drought (Normal onset) Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Crop management Soil nutrient & moisture conservation measures Remarks on Implementation Normal onset followed by days dry spell at the time of transplanting a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Rice Increase number of seedling per hill (5 to 6) Increase 25% nitrogen dose Adopt closer spacing (15 x15 cm) For shortage of seedling prepare seedling by mat nursery using short duration variety. Protective irrigation for nursery Use water from the outside sources like farm ponds, nalas, streams, rivers for puddling operation Finger millet Increase 25% nitrogen dose Prosomillet Adopt closer spacing (15 x15 cm) Protective irrigation after transplanting Use water from the outside sources like farm ponds, nalas, streams, rivers, etc. Groundnut No change --- Niger --- Sugarcane Protective irrigation b) Mid-land medium deep soils c) Low land Rice Increase number of seedling per hill (5 to 6) Increase 25% nitrogen dose Adopt closer spacing Rice Protective irrigation Use water from the outside sources like farm ponds, nalas, streams, rivers for puddling operation deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils Finger millet Increase 25% nitrogen dose Prosomillet Adopt closer spacing Protective irrigation 16
17 17 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Mid season drought (long dry spell, consecutive 2 weeks rainless (>2.5 mm) period) At vegetative stage Major Farming situation a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Normal Crop/cropping system Crop management Rice Apply split dose of Nitrogen after restart of rains Finger millet Adopt weed management Prosomillet practice Groundnut Mulching with tree lopping or glyricidia leaves Adopt weed management practice with dry land weeder Niger No change Soil nutrient & moisture conservation measures Protective irrigation Protective irrigation Remarks on Implementation b) Mid-land medium deep soils c) Low land deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils Sugarcane --- Protective irrigation Rice Apply split dose of Nitrogen after restart of rains Adopt weed management Rice practices Finger millet Apply split dose of Nitrogen after Prosomillet restart of rains Adopt weed management practices Maintain the existing water level in the field. Protective irrigation Give protective irrigation if possible 17
18 18 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Mid season drought (long dry spell) At flowering/ fruiting stage Major Farming situation a) Upland medium deep to shallow soils Normal Crop/cropping system Crop management Soil nutrient & moisture conservation measure Rice -- Protective Finger millet irrigation Prosomillet Groundnut -- Protective irrigation Remarks on Implementation b) Mid-land medium deep soils c) Low land deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils Niger -- Sugarcane --- Protective irrigation Rice Rice - - Maintain the existing water level in the field. Protective irrigation Finger millet - Protective Prosomillet irrigation. 18
19 19 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Terminal drought Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Crop management Rabi crop planting Remarks on Implementation (Early withdrawal of a) Upland Rice Harvest crop at Groundnut, cowpea, water Use of farm pound monsoon) physiological maturity melons, leafy vegetables, for protective medium deep to shallow Finger millet Harvest crop at raising of seedling for irrigation of crops soils Prosomillet physiological maturity chilli, brinjal, cabbage, Groundnut Protective irrigation knol kol Niger No change Sugarcane No change Protective irrigation b) Mid-land Rice Protective irrigation Horse gram, cowpea, Harvest crop at water melons medium deep soils physiological maturity cucurbitaceous crops Leafy vegetables, Raising of seedling for chilli, brinjal, cabbage, knol kol c) Low land deep soils d) Hill slope shallow soils Rice Finger millet Harvest crop at Prosomillet physiological maturity Sow field bean, horse gram, cowpea, mustard green gram on residual moisture
20 Irrigated situation Condition Suggested Contingency measures Delayed release of water in canals due to low rainfall Major Farming situation Mid and low land Medium deep to deep soils Normal Crop/cropping system Rice (Rabi season) Groundnut Pulses (Cowpea, Horsegram, Green gram) Vegetables Change in crop/cropping system Agronomic measures Remarks on Implementation Early duration variety (Ratnagiri 73) or Grow short duration pulses viz. cowpea (Var. Konkan Sadabahar), under control irrigation and tail end area Short duration variety (Phule pragati) or Grow short duration pulses viz. cowpea (Var. Konkan Sadabahar), No change Short duration vegetable and leafy vegetables Dapog/mat technique of nursery raising, SRI Technique If other source of irrigation is available sow the crop as per schedule. Water melon -- Use black polythene mulch Sugarcane --- If other source of irrigation is available sow the crop as per schedule. Source of Seed Maharashtra State seed corporation Source of Seed Maharashtra State seed corporation Condition Suggested Contingency measures Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Change in crop/cropping system Agronomic measures Limited release of Mid and low land Rice (Rabi season) Early duration variety in Use SRI Technique of water in canals due Medium deep to low land situation rice cultivation to low rainfall deep soils Grow short duration pulses, groundnut, vegetables in midland situation Groundnut Short duration variety (Phule Mulching, Protective Pulses (Cowpea, Horsegram, Green gram) Pragati) irrigation No change Protective irrigation Remarks on Implementation 20
21 21 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Change in crop/cropping system Agronomic measures Vegetables Leafy vegetables, cucumber Water melon Short duration pulses Sugarcane No change Protective irrigation Remarks on Implementation Condition Suggested Contingency measures Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Change in crop/cropping system Agronomic measures Non release of Mid and low land Rice (Rabi season) Field bean, horse gram, black Minimum tillage and water in canals Medium deep to gram, cowpea, mustard on sowing of seed by under delayed deep soils residual moisture under low dibbling. Relay onset of monsoon land situation cropping in catchment Groundnut Minimum tillage Pulses (Cowpea, horsegram, green gram) Vegetables Water melon If farm pond water is available go for short duration pulses and leafy vegetables Sugarcane -- Protective irrigation Remarks on Implementation 21
22 22 Condition Suggested Contingency measures Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Change in crop/cropping system Agronomic measures Lack of inflows Mid and low land Rice (Rabi season) Wal (lablab bean), horse gram Minimum tillage and into tanks due to Medium deep to on residual moisture under low sowing of seed by insufficient deep soils land situation dibbling, relay cropping /delayed onset of Groundnut Minimum tillage monsoon Pulses (Cowpea, horsegram, green gram) Vegetables Water melon If farm pond water is available go for short duration pulses, Leafy vegetables Sugarcane Protective irrigation Remarks on Implementation Condition Suggested Contingency measures Major Farming situation Normal Crop/cropping system Change in crop/cropping system Agronomic measures Insufficient groundwater recharge due to low rainfall Mid and low land Medium deep to deep soils Not applicable 2.2 Unusual rains (untimely, unseasonal etc) (for both rainfed and irrigated situations) Remarks on Implementation Condition Suggested contingency measure Continuous high rainfall in a short span leading to water logging Rice - - Drain out water and harvest the crop before lodging Vegetative stage Flowering stage Crop maturity stage Post harvest Immediate threshing and drying in shed Fingermillets - - Harvest the crop before lodging Immediate threshing and dryinh in shed Groundnut Drain out excess water Drain out excess water Drain out water and harvest the crop immediately Separate the pod immediately and dry in shed Niger
23 Sugarcane Drain out excess water Tie the sugarcane at grand growth stage Drain out excess water Drain out water and harvest at physiological maturity stage Send immediately for crushing Horticulture Cucurbitaceous crop Drain out excess water Drain out excess Drain out excess water water Mango If heavy rainfall is occur during th July to 15 th Aug. postpone paclabutrazol application till congenial condition arrives (Dose of of 0.75 g/ a.i. per meter average canopy diameter) Cashew Banana Drain out excess water Drain out excess Drain out excess water Drain out excess water water Pineapple Drain out excess water Drain out excess water Drain out excess water ---- Heavy rainfall with high speed winds in a short span 2 Rice - - Drain out water and harvest the crop at maturity immediately if lodging take place Fingermillets - - Drain out all water and harvest the crop at maturity immediately Groundnut Drain out excess water Drain out excess Drain out water and harvest the crop water at maturity immediately Immediate threshing and drying in shed Immediate threshing and drying in shed Separate the pod immediately and dry in shed Niger Sugarcane Drain out excess water Drain out excess Drain out water and harvest at Send immediately for Tie the sugarcane at grand water physiological maturity stage crushing growth stage Horticulture Cucurbitaceous crop Drain out excess water Drain out excess water Mango Prune the broken branches and apply carbaryl (50WP) mixed Drain out excess water Collect and utilize fallen fruit immediately for suitable processing
24 Cashew Banana with Bordeaux paste on cut surface and trunk. Drain out excess water Do staking Flowers of broken plants may be used for vegetables Fruit of broken plants may be used as vegetable. Pineapple Drain out excess water Drain out excess Drain out excess water ---- water Outbreak of pests and diseases due to unseasonal rains Rice Spraying of Carbendazim 0.1% Spraying of - - or Copper oxy chloride 0.25% or tricyclazole 0.1% to control blast disease Carbendazim 0.1% or Copper oxy chloride 0.25% or tricyclazole 0.1% to control blast disease Fingermillet Groundnut Spraying with carbendazim 0.1% or Propiconazole 0.1% or Tridemorph 0.1% to control early and late leaf spot Spraying with carbendazim 0.1% or Propiconazole 0.1% or Tridemorph 0.1% to control early and late leaf spot Niger Sugarcane Horticulture Cucurbitaceous crop Install rakshak I trap to control fruit fly ---- Mango Take 2 sprays at 15 days interval of Phosalone 0.05% and carbaryl 0.2 % for control of mango hopper, shoot borer. Spraying with 1% Bordeaux mixture or 0.1% carbendazim or 0.1% thiophenate methyl to control anthracnose, Spraying with 0.2% W.P. sulphur dust or 0.05% hexaconazol or 0.1% Tridemorph to control powdery mildew Install Rakshak I trap to control fruit fly 24 Dipping fruits in 0.05% carbendazim for 10 min. after harvest to control post harvest rot Cashew Spay with carbaryl 0.2 % after
25 25 the rains to control tea mosquito bug. Acecanut - Spraying with 1% Bordeaux mixture or 0.37% copper oxychloride or root feeding four times at monthly intetvals (June to sept.) with fosetyl AL 0.3% to control kolerog Sapota ---- Spraying of Metalaxyl + Mancozeb containing complex 0.2% to control fruit drop Floods Condition Suggested contingency measure Transient water logging/ Seedling / nursery stage Vegetative stage Reproductive stage At harvest partial inundation 1 Rice If wash out resowing of nursery by using mat nursery/ sowing of sprouted seed on puddled field Drain out excess water Drain out excess water Immediate harvesting, threshing and dry in shed Fingermillets Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Groundnut Niger Sugarcane Horticulture (Vegetables) Cucurbitaceous crop Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Continuous submergence for more than 2 days 2 Rice If wash out resowing of nursery by Drain out excess water Drain out excess water Immediate harvesting, 25
26 using mat nursery/ sowing of sprouted seed on puddled field Apply dose of nitrogen after submergence is over threshing and dry in shed Fingermillet Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Groundnut Niger Sugarcane Horticulture (Vegetables) Cucurbitaceous crop Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Sea water intrusion 3 Rice Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out, If wash out resowing of nursery with salt tolerant varieties like Panvel -1 and Panvel -2 Fingermillets Groundnut Niger Sugarcane Horticulture (Vegetables) Not applicable Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out Cucurbitaceous crop Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable Coconut Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out Mound the crop with soil. Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out 26 Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out Strengthening of creek bund and sea wall to prevent sea water intrusion Drain out sea water, Irrigate the affected area with fresh water and drain out 26
27 Extreme events: Heat wave / Cold wave/frost/ Hailstorm /Cyclone Extreme event type Heat Wave Mango Cashew Coconut Arecanut Cold wave Not applicable Frost Not applicable Hailstorm Suggested contingency measure Seedling / nursery stage Vegetative stage Reproductive stage At harvest Cover with shed net /Protective irrigation Water spray Cover with shed net /Protective irrigation Water spray Cover with shed net /Protective irrigation, Water spray Cover with shed net /Protective irrigation Water spray Water spray/ 1% potassium nitrate spray Collect dropped fruits and use it for suitable processing Collect dropped fruits and use it for suitable processing Protective irrigation Protective irrigation ---- Frequent irrigation Frequent irrigation Frequent irrigation Mango Collect and destroy the fallen fruit to avoid the further built-up of pest and disease Cyclone Mango Support the young seedling/grafts Proper pruning of damage or broken branches Cashew Support the young seedling/grafts Proper pruning of damage or broken branches Proper pruning of damage or broken branches Collect dropped fruits and use it for suitable processing Proper pruning of damage or broken branches Collect fallen tender nuts market it. Coconut Support the young seedling ---- Collect fallen tender nuts market it. Collect the fallen fruit to avoid the further built-up of pest and disease Proper pruning of damage or broken branches Collect dropped fruits and use it for suitable processing Proper pruning of damage or broken branches Collect fallen nuts and store Collect fallen tender nuts market it. 27
28 28 Arecanut Support the young seedling ---- Collect fallen tender nuts market Collect fallen tender nuts market it. 2.5 Contingent strategies for Livestock, Poultry & Fisheries Livestock Suggested contingency measures Drought Before the event s During the event After the event Feed and Conservation of green fodder as silage dry fodder as hay Judicious use of feed resources Green fodder fodder in flush season for utilization in lean period processed as per type of livestock production in next availability Dry fodder available should be processed i.e. Urea possessed by the livestock owners. Kharip season treatment of crop residues to enhance their nutritive Distribution of fodder, UMMB needs to be value. For this inputs such as training of livestock blocks, other feed resources stored undertaken as a owners, material like urea, polythene sheet etc may be provided free of cost to the livestock owners. Judicial use of available feed resources by the livestock in the affected area to the livestock owners as per the number and type of livestock possessed. source of fodder at earliest. Mineral owners. Mineral supplementation Supplementation Non conventional feed resources such as Neem seed Mineral mixture be provided for should be Cake/ Sal seed Meal/ Mango seed Kernels/ Babul pods the livestock@50 g/day/anim. continued. etc should be collected and stored. Disposal/Transfer of the animals Concentrate feeding Concentrate ingredients such as Grains, brans, chunnies in the area having feed resources for productive & oilseed cakes, low grade grains, Govt. Godowns availability. animals so as to wastes, grains unfit for human consumption etc. should Concentrate feeding for productive compensate the be procured for productive animals. animals to support minimum body condition and Urea molasses mineral blocks (UMMB) may be reserved with NDDB, Anand, Gujarat for emergency supply as production & life saving of the important animals. production. The animals must concentrate. Other non productive animals are be brought into Sugarcane bagasse, cane tops and molasses form to be fed at subsistence level. cyclic stage for important byproducts. Sugarcane bagasse- is an Use of food grains for biodisel and reproduction. important feed resource for ruminants. distillaries should be stopped and Young crossbred Tree leaves are easily available. Leaves of neem, mango, the grains be spared for productive livestock needs to banyan, pipal, babul, subabul, mahuva, etc. can be used animals. be attended as green fodder. Tree leaves are good source of protein, Bypass protein concentrate properly so as to calcium, Vitamin A and hence should be reserved for ingredients may be provided in harness the high feeding during drought. order to harvest maximum productivity. Cactus is primarily found in deserts hence it is easily nutrients for productive animals Adlib. feeding may available during scarcity also. As such it is not used for particularly high productive be practiced with feeding animals but during scarcity it can be used. crossbred cows. balancing the Mineral mixture should be procured and stored for Top feeds should be used during nutrients required. 28
29 supply. Fodder Banks: Grasses & tree leaves: Grasses from periphery of forest area wastelands & farmlands & Dry fallen forest tree leaves may be harvested & stored as hay in bales. Fodder Bank: Crop Residues: The major cereals like rice & wheat straws are more important for this purpose. Next are coarse cereals, legumes, haulms left after removing grains from the crops. These may be stored in these banks to be established at each Taluka in the drought area. Govt. should provide support to farmers for making stacks, bailing & storage. State Animal feed resources Grid needs to be established so as to provide feed resources during scarcity period. Cattle camp sites needs to be identified. NGOs/Gorakshan Sanstha etc. needs to be identified. Anticipated number of livestock & feed resources to be provided needs to be assessed. Livestock registration should be compulsory with identification by tagging Preparedness of veterinary services to drought prone areas. Encourage farmers to cultivate fodder crops. Identification of the site for fodder depot. Facility to store fodder by creating centralized silage making facility with provision for transport. Forage production and storage of fodder in irrigated areas. Assessment of risk and vulnerability. Formation of village Disaster Management Committee. Establishment of drought monitoring system or early warning system. scarcity period only. Oil seed cakes are good source of proteins and hence should be used for productive animals only. Feed supplements/ Additives needs to be used widely for productive animals. Establishment of Cattle camps at identified sites. NGOs/Gorakshan Sanstha etc. identified to be involved for participation/ implementation. Feed 7 kg.dry fodder/ day/adult animal for maintenance 2.0 kg. concentrate mixture/day/adult animal for supporting minimum milk production. Adaptation of proper distribution policy as per requirement with transport facility. Regular rest periods for working animals particularly bulls during hot period of the day. Capture and care of stray animals. The unproductive/surplus livestock needs to be culled/disposed. Sale of feed and fodder from the affected area to non affected area should be banned. Distribute fodder at reasonable rate. Monitoring feed and fodder prices. 29 The unproductive/surplu s livestock needs to be culled/disposed. Livestock suitable with the farming system practiced only should be maintained. Mechanization in agriculture needs to be encouraged. Feed processing needs to be encouraged in order to minimize the wastage of feed resources. In-situ storage and feeding of processed animal feed resources by the livestock owners needs to be encouraged. Readiness for feed and fodder bank as and when required for each districts with transport facility. Review of shortfalls in planning and refining action plan the before and during event. 29
30 Suggested contingency measures Drought Before the event s During the event After the event Drinking water Water resources as in general are inadequate and hence the resources should be trapped and increased. Available rain water harvesting technique should be adopted i.e. farm ponds etc. Water conservations measures be adopted to increase water table like recharging of bore wells. Available water resources should be tapped and reserved. Water harvesting measures like farm ponds alternative water sources, Nala bunding/check dams etc. needs to be undertaken. Judicious use of water in agriculture i.e. through drip/sprinkler irrigation. Wastage of water needs to be curbed. Rain water harvesting measures needs to be implemented at village level. Proper utilization of Water to save water. Equal water distribution plan may be implemented. Cloud seeding desalination, recycle sewage water, transvasment river project etc. Special distribution and carrying capacity should be implemented from other available resources. Water should be used as per the requirement of animals (@10-15 lit/ 100 kg body weight). Drinking water should not be used for washing animals. Clean and chlorinated water be provided to prevent water borne diseases. Special distribution and carrying capacity should be supplemented from other available resources. Water for irrigation should be stopped. Judicious use of water for livestock. Supply of water through tankers during contingency. Private water resources such as wells shall be used for drinking water. Proper utilization of Water to save water. In vicinity of animal camp or chavani creation of borewell. Permanent water resources should 30 be developed with campaign for public awareness. Steps should be taken to conserve water. Ensure fresh clean and cold water supply to livestock. Suggested contingency measures Drought Before the event s During the event After the event Health and disease management Routine Personnel should be trained for health and disease management through trainings and list of trained personnel should be available at each district head quarter with stock of life saving medicine for livestock. Vaccination of animals for various diseases according to season. Deworming and spraying be done to get rid of endoparasites and ectoparasites to keep the health of animals in good condition. Services of trained personnel need to be made available in affected area with sufficient supply of life saving medicine of livestock. A team of veterinary experts be deployed for health management of drought hit livestock. During occurrence of disease, affected animals should be kept isolated and treated properly and promptly. Vaccination against contagious diseases like HS, FMD, Theileriosis be carried out. training programme as a refresher course need to be implemented in relation to health and disease management during drought with stock of life saving medicine for livestock. There will be stress on animals due to deterioration of health 30
31 Personnels should be trained for health and disease management through training List of trained personnel should be available at each district head quarter. Feedadditives/Tonics/ Vitamin supplements should be stocked. Vaccines, Insecticides, disinfectants and dewormers needs to be stocked. Records/PM/ Carcass disposal arrangements needs to be ensured. Training of farmers for maintaining optimum health of animals, balance ration and recognize early signs of disease and managemental shortfalls. Create temporary shade shelters to prevent heat stress on the animals. (animal camps) Supply of Mineral and Vitamins mixture. Application of preventive and control measures of SP & MD. Mineral mixture be provided to take care of deficiency disorders. Tick control measures be undertaken to prevent tick borne diseases in animals under stress. Deworming should be carried out. Feed additives/tonics/vitamin supplements should be provided. Post Mortem /record keeping/carcass disposal arrangements be effected. Restriction on movement of the animals to prevent the spread of diseases. Periodic disinfection and disinfestations of premises where animals are kept. Permission of only healthy and vaccinated animals in cattle market. By proper treatment with supervision and exercise over starvation. Special transport facility of mobile van for veterinary team be deployed. 31 during drought period. Concentrates and vitaminmineral supplements be provided to minimize the stress on animals. The animals should be observed for signs of contagious diseases or deficiency disorders. Vaccination spraying and deworming programme needs to be undertaken. Record of affected livestock to be submitted for compensation of the loss. Farm disinfection and disinfestations. Assessment of losses due to mortality if any. Suggested contingency measures Floods Before the event s During the event After the event Feed and Identification of flood prone zones and flood Quick evacuation of livestock Green fodder fodder forecasting. from flood plane areas before area production in next availability Installation of early warning systems. become flooded Kharip season Steps to prevent spoilage of food and water supply due Prevent outflow of manure pit in needs to be to flood water. river undertaken as a Dedicated helpline to emergency contact and Proper feed, vaccine, drugs, source of fodder at communication at taluka level. disinfecrants and feed supplement earliest. Fodder Avoid construction of farm buildings in flood risk distribution policy adopted with seed of improved areas. transport facility. fodder crop Local ponds and canals regularly inspected and cleared off from obstruction Adequate stock of Tetanus toxoid. Change cropping pattern according to flood risk Prevent spoilage of food and water supply Judicious use of feed resources processed as per type of livestock varieties needs to be distributed. Mineral Supplementation periods. possessed by the livestock should be 31
32 Storage of available fodder at safe place before rainy season. Training of local personnel for disaster management. Dry fodder available should be processed i.e. Urea treatment of crop residues to enhance their nutritive value. For this inputs such as training of livestock owners, material like urea, polythene sheet etc may be provided free of cost to the livestock owners. Judicial use of available feed resources by the livestock owners. Non conventional feed resources such as Neem seed Cake/ Sal seed Meal/ Mango seed Kernels/ Babul pods etc should be collected and stored. Concentrate ingredients such as Grains, brans, chunnies & oilseed cakes,low grade grains, Govt Godowns wastes, grains unfit for human consumption etc. should be procured for productive animals. Urea molasses mineral blocks (UMMB) may be reserved with NDDB, Anand, Gujarat for emergency supply as concentrate. Sugarcane bagasse, cane tops and molasses form important byproducts. Sugarcane bagasse- is an important feed resource for ruminants. Tree leaves are easily available. Leaves of neem, mango, banyan, pipal, babul, subabul, mahuva, etc. can be used as green fodder.tree leaves are good source of protein, calcium, Vitamin A&hence should be reserved for feeding during drought. Cactus is primarily found in deserts hence it is easily available during scarcity also. As such it is not used for feeding animals but during scarcity it can be used. Mineral mixture should be procured and stored for supply. Fodder Banks: Grasses & tree leaves: Grasses from periphery of forest area wastelands & farmlands & Dry fallen forest tree leaves may be harvested & stored as hay in bales. Fodder Bank: Crop Residues: The major cereals like rice & wheat straws are more important for this purpose. Next are coarse cereals, legumes, haulms left after removing grains from the crops. These may be owners. Distribution of fodder, UMMB blocks, other feed resources stored in the affected area to the livestock owners as per the number and type of livestock possessed. Mineral supplementation Mineral mixture be provided for the g/day/anim. Disposal/Transfer of the animals in the area having feed resources availability. Concentrate feeding for productive animals to support minimum production & life saving of the important animals. Other non productive animals are to be fed at subsistence level. Use of food grains for biodisel and distillaries should be stopped and the grains be spared for productive animals. Bypass protein concentrate ingredints may be provided in order to harvest maximum nutrients for productive animals particularly high productive crossbred cows. Top feeds should be used during scarcity period only. Oil seed cakes are good source of proteins and hence should be used for productive animals only. Feed supplements/ Additives needs to be used widely for productive animals. Establishment of Cattle camps at identified sites. NGOs/Gorakshan Sanstha etc. identified to be involved for 32 continued. Concentrate feeding for productive animals so as to compensate the body condition and production. The animals must be brought into cyclic stage for reproduction. Young crossbred livestock needs to be attended properly so as to harness the high productivity. Adlib. feeding may be practiced with balancing the nutrients required. The unproductive/surpl us livestock needs to be culled/disposed. Livestock suitable with the farming system practiced only should be maintained. Mechanization in agriculture needs to be encouraged. Feed processing needs to be encouraged in order to minimize the wastage of feed resources. 32
33 stored in these banksto be established at each Taluka in the drought area. Govt. should provide support to farmers for making stacks, bailing & storage. State Animal feed resources Grid needs to be established so as to provide feed resources during scarcity period. Cattle camp sites needs to be identified. NGOs/Gorakshan Sanstha etc. needs to be identified. Anticipated number of livestock & feed resources to be provided needs to be assessed. Information at every district head quarter regarding availability of fodder resources from other areas for exploitation should be made available. A storehouse can be prepared at a highest point in the city where feeds & fodder (silage) can be stored for emergency use. participation/ implementation. Feed 7 kg.dry fodder/day/adult animal for maintainance 2.0 kg. concentrate mixture/day/adult animal for supporting minimum milk production. The stored feeds & fodder can be used to feed the animals & if it is short then Fodder resources should be exploited with sufficient transport facilities from other areas of the district. 33 In-situ storage and feeding of processed animal feed resources by the livestock owners needs to be encouraged. Fodder resources should be exploited with sufficient transport facilities from other areas of the district even after the event. Suggested contingency measures Floods Before the event s During the event After the event Drinking water Sufficient storage capacity should be made available Sufficient facility for transportation Sufficient particularly during rainy season in view of the with advanced proper planning infrastructure forecasting of the flood. Rain water harvesting should should be made in the areas of each facility for be done in all districts. Every district should be made district. transportation with self-sufficient. Every district gas plenty of rain water During flood condition there will be advanced proper which should be harvested so that these areas should become self-sufficient & if required they should be able to provide water to other dry areas too. The rain water polluted water, whatever potable drinking water source is available should be used with almost care. planning should be made in the areas of each district. should not be wasted in sea. Disinfection of drinking water i.e. Clean disinfected Shelters & temporary camps should be set up at a height chlorination of water should be water from bore in city area as well as in suburbs after choosing the right carried out Stop use of drinking well or rain location for each area. Same provisions should be done water for animals from contaminated harvested water in other Konkan districts. water resources. may be supplied to Bore well facilities should be exploited in districts for Disinfection of the water for the animals as supply of clean water. Contamination of local water resources due to flood water should be prevented consumption of the animals should be carried out to prevent water-borne water-borne infections are Potable drinking water source should be there to supply diseases. Aerosol spray of the common after water to animals. Every society should implement rain harvesting system, disinfectant for preventing spread of airborne infections should be carried floods. Sources of potable 33
34 so that water can be stored for use whole year long. Water problem likely to be faced in future. Water harvesting measures like farm ponds alternative water sources, Nala bunding/check dams etc. needs to be undertaken. Judicious use of water in agriculture i.e. through drip/sprinkler irrigation. Wastage of water needs to be curbed. Rain water harvesting measures needs to be implemented even at village level with establishment of water Storage and Purification facility out. Shelters & temporary camps for displaced animals should be set up with proper sanitation facilities. Judicious use of water for livestock. Water tankers provision Private water resources such as wells shall be used for drinking water availability only. 34 drinking water should be tapped for its proper use. Permanent water resources should be developed with campaign for public awareness. Water storage facility created away from the flooded area. Suggested contingency measures Floods Before the event s During the event After the event Health and disease management Personnel should be trained for health and disease management through trainings and list of trained personnel should be available at each district head quarter for flood affected areas with stock of life saving medicine for livestock. Vaccination of animals for various diseases according to season. Deworming and spraying be done to get rid of endoparasites and ectoparasites to keep the health of animals in good condition. Stock of life saving medicine be made. Disaster management team of veterinarians be constituted at district/taluka/panchayat level. Training to veterinarians in health and disease management during flood disaster be given. Awareness amongst farmers regarding health care practices during flood disaster be Services of trained personnel need to be made available in affected area with sufficient supply of life saving medicine of livestock. Shifting of the animals at suitable place for temporary shelter. Disaster management team of veterinarians be deployed. Makeshift Veterinary medical facilities should be created at the site nearer to disaster place. Various referral centres in the disease diagnostics should be roped in for detection of infections which cannot be diagnosed at field level. Various diagnostic facility with modern techniques should be made available at Tahsil level besides district level so that more number of farmers may approach for diagnosis & treatment. Adequate nutrition including vitamin-mineral supplements should be given to animals to keep their health in proper condition. During occurrence of contagious diseases, affected animals should be kept isolated and treated properly. Isolation and treatment of ailing animals viz. hypothermia, wound, diarrhoea and pneumonia be undertaken. Routine training programme as a refresher course need to be implemented in relation to health and disease management during flood with stock of life saving medicine for livestock. After flood condition there are chances of occurrence of specific diseases. Preventive measures should be taken to reduce occurrence of diseases. Vaccination and deworming programme needs to be undertaken. Animals should closely be observed for new/re-emerging diseases. Proper disposal of carcass is very important in flood affected areas from public health point of view Methods of disposing of dead animals include burning, burying and 34
State: MAHARASHTRA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: RATNAGIRI
 State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: RATNAGIRI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning
State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: RATNAGIRI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning
State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: THANE
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: THANE Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Western Ghats And Coastal Plain,
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: THANE Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Western Ghats And Coastal Plain,
State: RAJASTHAN. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: JAIPUR
 State: RAJASTHAN Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: JAIPUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Northern Plain and Central highlands
State: RAJASTHAN Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: JAIPUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Northern Plain and Central highlands
State: GUJARAT. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SURAT
 State: GUJARAT Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SURAT 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Central Highlands (Malwa), Gujarat plain
State: GUJARAT Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SURAT 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Central Highlands (Malwa), Gujarat plain
State: TAMILNADU. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Theni
 State: TAMILNADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Theni 1.0 District Agriculture Profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Ghats And Tamil Nadu
State: TAMILNADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Theni 1.0 District Agriculture Profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Ghats And Tamil Nadu
STATE: KARNATAKA AGRICULTURE CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR DISTRICT: UDUPI
 STATE: KARNATAKA AGRICULTURE CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR DISTRICT: UDUPI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Western Ghats And Coastal Plain, Hot
STATE: KARNATAKA AGRICULTURE CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR DISTRICT: UDUPI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Western Ghats And Coastal Plain, Hot
State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Banda
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Banda Central Plain Zone Agro-Climatic
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Banda Central Plain Zone Agro-Climatic
State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Amethi
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Amethi North plain zone Agro-Climatic
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Amethi North plain zone Agro-Climatic
Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Shopian
 State: Jammu and Kashmir Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Shopian 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning
State: Jammu and Kashmir Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Shopian 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning
State: Uttarakhand Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Haridwar
 State: Uttarakhand Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Haridwar 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Northern Plain, Hot Subhumib (Dry) Eco-Region (9.1) Agro-Climatic
State: Uttarakhand Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Haridwar 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Northern Plain, Hot Subhumib (Dry) Eco-Region (9.1) Agro-Climatic
State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Jalaun
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Jalaun Central Plain Zone Agro-Climatic
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Jalaun Central Plain Zone Agro-Climatic
State: TAMIL NADU. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: TIRUPPUR
 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region /Sub Region (ICAR) State: TAMIL NADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: TIRUPPUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile Eastern Ghat (TN uplands
1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region /Sub Region (ICAR) State: TAMIL NADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: TIRUPPUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile Eastern Ghat (TN uplands
State: Jammu and Kashmir. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Pulwama
 State: Jammu and Kashmir Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Pulwama 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning
State: Jammu and Kashmir Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Pulwama 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning
State: KERALA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KANNUR
 State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KANNUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Northern Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Konkan, Karnataka and
State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KANNUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Northern Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Konkan, Karnataka and
STATE: MANIPUR. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: UKHRUL
 STATE: MANIPUR Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: UKHRUL 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) North-Eastern Hills (Purvachal), Warm
STATE: MANIPUR Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: UKHRUL 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) North-Eastern Hills (Purvachal), Warm
State: TAMILNADU. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KANYAKUMARI
 State: TAMILNADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KANYAKUMARI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Region
State: TAMILNADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KANYAKUMARI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Region
State: Uttar Pradesh. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Basti
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning Commission) Agro-Climatic Zone (NARP) List all the districts falling the
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/ Ecological Zone Agro-Ecological Sub Region(ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning Commission) Agro-Climatic Zone (NARP) List all the districts falling the
State: TAMIL NADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: ERODE. 1.0 District Agriculture profile
 State: TAMIL NADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: ERODE 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Region (Planning Commission) Agro Climatic
State: TAMIL NADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: ERODE 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Region (Planning Commission) Agro Climatic
State: KERALA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: THRISSUR
 State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: THRISSUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Konkan, Karnataka and Kerala Coastal
State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: THRISSUR 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Konkan, Karnataka and Kerala Coastal
State: Nagaland Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: LONGLENG District
 State: Nagaland Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: LONGLENG District 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Tropical to sub-tropical Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR)
State: Nagaland Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: LONGLENG District 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Tropical to sub-tropical Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR)
Sreedhar Patil 5/30/2013
 Farming in India Sreedhar Patil 5/30/2013 Location of India in World Map States in India Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA 28 states and seven union territories Annual Rainfall in India Rivers in India River
Farming in India Sreedhar Patil 5/30/2013 Location of India in World Map States in India Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA 28 states and seven union territories Annual Rainfall in India Rivers in India River
State: NAGALAND Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: MON
 State: NAGALAND Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: MON 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Temperate to subtropical hill zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) 17.1,D2A9,
State: NAGALAND Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: MON 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Temperate to subtropical hill zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) 17.1,D2A9,
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTIVE CROP PRODUCTION STRATEGIES IN HIGH ALTITUDE AND TRIBAL AREAS OF VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, A.P
 CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTIVE CROP PRODUCTION STRATEGIES IN HIGH ALTITUDE AND TRIBAL AREAS OF VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, A.P K. SASIKALA * and P. ASHOK Regional Agricultural Research Station, Chintapalli, Visakhapatnam
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTIVE CROP PRODUCTION STRATEGIES IN HIGH ALTITUDE AND TRIBAL AREAS OF VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, A.P K. SASIKALA * and P. ASHOK Regional Agricultural Research Station, Chintapalli, Visakhapatnam
State: WEST BENGAL Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: JALPAIGURI
 1.0 District Agriculture profile State: WEST BENGAL Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: JALPAIGURI 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Assam And Bengal Plain, Hot
1.0 District Agriculture profile State: WEST BENGAL Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: JALPAIGURI 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Assam And Bengal Plain, Hot
GRAMIN KRISHI MAUSAM SEWA
 GRAMIN KRISHI MAUSAM SEWA INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT NORTH EASTERN GAHAT ZONE RRTTS, G.UDAYAGIRI, OUAT, KANDHMAL, ODISHA-762100 MULTIMODEL ENSEMBLE BASED DISTRICT LEVEL WEATHER FORECAST FOR THE STATE:
GRAMIN KRISHI MAUSAM SEWA INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT NORTH EASTERN GAHAT ZONE RRTTS, G.UDAYAGIRI, OUAT, KANDHMAL, ODISHA-762100 MULTIMODEL ENSEMBLE BASED DISTRICT LEVEL WEATHER FORECAST FOR THE STATE:
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM
 STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 7 TH April 2015 9 TH APRIL 2015 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON TUESDAY 7 TH
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 7 TH April 2015 9 TH APRIL 2015 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON TUESDAY 7 TH
State: West Bengal Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: CoochBehar
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: West Bengal Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: CoochBehar Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Assam And Bengal Plain, Hot
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: West Bengal Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: CoochBehar Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Assam And Bengal Plain, Hot
STATE: KARNATAKA AGRICULTURE CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR DISTRICT: GULBARGA
 STATE: KARNATAKA AGRICULTURE CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR DISTRICT: GULBARGA 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Semi arid Deccan Plateau, hot arid
STATE: KARNATAKA AGRICULTURE CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR DISTRICT: GULBARGA 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Semi arid Deccan Plateau, hot arid
State: KERALA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KASARAGOD
 State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KASARAGOD 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Konkan, Karnataka and Kerala Coastal
State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: KASARAGOD 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Konkan, Karnataka and Kerala Coastal
State: UTTAR PRADESH. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: VARANASI
 State: UTTAR PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: VARANASI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Northern Plain (And Central
State: UTTAR PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: VARANASI 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Northern Plain (And Central
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 25 TH MARCH to 28 TH MARCH 2016
 STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 25 TH MARCH to 28 TH MARCH 2016 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON FRIDAY 25 TH
STATE COMPOSITE AGRO-MET ADVISORY BULLETIN FOR THE STATE OF SIKKIM PERIOD: 25 TH MARCH to 28 TH MARCH 2016 IMD, GANGTOK IN COLLABORATION WITH ICAR, GANGTOK, FSAD AND HCCD, GANGTOK ISSUED ON FRIDAY 25 TH
State: KERALA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: MALAPPURAM
 State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: MALAPPURAM 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Central Zone 1.0 District Agriculture profile Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) High lands: Central
State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: MALAPPURAM 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Central Zone 1.0 District Agriculture profile Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) High lands: Central
CARE Climate Change Adaptation(CCA) Plan
 CARE Climate Change Adaptation(CCA) Plan a. Introduction: b. Background: The project Reversing Environmental Degradation and Rural Poverty through Adaptation to Climate Change in Drought Stricken Areas
CARE Climate Change Adaptation(CCA) Plan a. Introduction: b. Background: The project Reversing Environmental Degradation and Rural Poverty through Adaptation to Climate Change in Drought Stricken Areas
KRISHI VIGYAN KENDRA GURDASPUR ANNUAL TRAINING SCHEDULE ( ) DIRECTORATE OF EXTENSION EDUCATION PUNJAB AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY LUDHIANA
 KRISHI VIGYAN KENDRA GURDASPUR ANNUAL TRAINING SCHEDULE (2016-17) DIRECTORATE OF EXTENSION EDUCATION PUNJAB AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY LUDHIANA INDEX Sr. No Discipline Page 1. TRAININGS FOR FARMERS AND FARM
KRISHI VIGYAN KENDRA GURDASPUR ANNUAL TRAINING SCHEDULE (2016-17) DIRECTORATE OF EXTENSION EDUCATION PUNJAB AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY LUDHIANA INDEX Sr. No Discipline Page 1. TRAININGS FOR FARMERS AND FARM
DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT
 DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT Cropping Seasons in India Agriculture in India also follows three distinct cropping seasons i.e. rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown from October to December
DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT Cropping Seasons in India Agriculture in India also follows three distinct cropping seasons i.e. rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown from October to December
State: Uttar Pradesh. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Ballia
 State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Ballia 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Plain, Hot Subhumid (moist)
State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Ballia 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Plain, Hot Subhumid (moist)
State: KERALA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PALAKKAD
 State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PALAKKAD 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Western Ghats And Coastal Plain, Hot
State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PALAKKAD 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Western Ghats And Coastal Plain, Hot
Climate Change Impact on Paddy Farming in Erode and Tiruchirapalli Districts of Tamil Nadu
 Journal of Extension Education Vol. 27 No. 4, 2015 Climate Change Impact on Paddy Farming in Erode and Tiruchirapalli Districts of Tamil Nadu P. Sivaraj 1 and H. Philip 2 ABSTRACT Climate change implies
Journal of Extension Education Vol. 27 No. 4, 2015 Climate Change Impact on Paddy Farming in Erode and Tiruchirapalli Districts of Tamil Nadu P. Sivaraj 1 and H. Philip 2 ABSTRACT Climate change implies
State: ASSAM. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: DIBRUGARH. Zone 2 (Eastern Himalayan Division) RARS: Titabor, Assam Agricultural University
 State: ASSAM Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: DIBRUGARH 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Zone 2 Humid Bengal- Assam Basin Agro-Climatic
State: ASSAM Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: DIBRUGARH 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Zone 2 Humid Bengal- Assam Basin Agro-Climatic
Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops
 LECTURE 1 Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops Importance of cereals Grains are generally classified as
LECTURE 1 Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops Importance of cereals Grains are generally classified as
PROPOSED ACTION KVK, FARIDKOT ( ) Directorate of Extension Education Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana
 PROPOSED ACTION PLAN OF KVK, FARIDKOT (2018-19) Directorate of Extension Education Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana 141 001 0 INDEX Sr. Discipline Pages of trainings 1. TRAINING COURSES FOR FARMERS
PROPOSED ACTION PLAN OF KVK, FARIDKOT (2018-19) Directorate of Extension Education Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana 141 001 0 INDEX Sr. Discipline Pages of trainings 1. TRAINING COURSES FOR FARMERS
State: WEST BENGAL Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SOUTH 24-PARGANAS
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: WEST BENGAL Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SOUTH 24-PARGANAS Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Coastal Plain,
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: WEST BENGAL Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: SOUTH 24-PARGANAS Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Coastal Plain,
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]
![AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]](/thumbs/79/79737240.jpg) AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
Common millet management
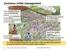 Common millet management Soil compaction due to tracking animals and tractors No protection measures against wind and soil erosion Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of harvested fields No soil water
Common millet management Soil compaction due to tracking animals and tractors No protection measures against wind and soil erosion Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of harvested fields No soil water
Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.
 Cropping 101 Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.edu This overview provides summaries of 1. Key
Cropping 101 Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.edu This overview provides summaries of 1. Key
Calibre BMR Forage Sorghum
 Calibre BMR Forage Sorghum Sorghum bicolor x sudanese Early to mid maturing, Brown Mid Rib sorghum x Sudan grass hybrid 12 gene BMR now delivering new high quality in the forage market Low Lignin = highly
Calibre BMR Forage Sorghum Sorghum bicolor x sudanese Early to mid maturing, Brown Mid Rib sorghum x Sudan grass hybrid 12 gene BMR now delivering new high quality in the forage market Low Lignin = highly
Impact of Water Harvesting Structures on water Availability-A A Case Study of. Maharashtra
 Impact of Water Harvesting Structures on water Availability-A A Case Study of Kokarda Watershed, Nagpur District, Maharashtra V. Ramamurthy National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning Amravati Road,
Impact of Water Harvesting Structures on water Availability-A A Case Study of Kokarda Watershed, Nagpur District, Maharashtra V. Ramamurthy National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning Amravati Road,
State: ANDHRA PRADESH. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PRAKASAM
 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: ANDHRA PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PRAKASAM 1.0 District Agriculture profile Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Coastal plain, hot
1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: ANDHRA PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PRAKASAM 1.0 District Agriculture profile Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Coastal plain, hot
On-Farm Testing (OFT) :
 On-Farm Testing (OFT) : The technologies which are in the pipeline or to be released for wide scale diffusion in the farmers field need to be tested for adaptability without modifying its scalability and
On-Farm Testing (OFT) : The technologies which are in the pipeline or to be released for wide scale diffusion in the farmers field need to be tested for adaptability without modifying its scalability and
Sorghum Farming. Introduction
 Sorghum Farming Introduction For a very long time, sorghum has been the mostly cultivated cereal crop especially in semi arid areas. It is rich in vitamins and carbohydrates which keep families strong
Sorghum Farming Introduction For a very long time, sorghum has been the mostly cultivated cereal crop especially in semi arid areas. It is rich in vitamins and carbohydrates which keep families strong
State: KARNATAKA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: CHITRADURGA
 State: KARNATAKA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: CHITRADURGA 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone 1.0 District Agriculture profile Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Ghats And Tamil Nadu
State: KARNATAKA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: CHITRADURGA 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone 1.0 District Agriculture profile Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Ghats And Tamil Nadu
UPL Group of Companies
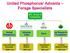 UPL Group of Companies United Phosphorus Advanta India Tatva Jai Research Foundation Crop Protection Chemicals Seeds & Biotech Environment Services Contract Research (CRO) ` 12000 crore ` 1000 crore `
UPL Group of Companies United Phosphorus Advanta India Tatva Jai Research Foundation Crop Protection Chemicals Seeds & Biotech Environment Services Contract Research (CRO) ` 12000 crore ` 1000 crore `
State: Uttar Pradesh. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Faizabad
 State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Faizabad 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Plain, Hot Subhumid
State: Uttar Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Faizabad 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Plain, Hot Subhumid
MAIZE (Zea mays L.) Family Poaecea(Gramineae) By Dr. S A. Abolusoro
 MAIZE (Zea mays L.) Family Poaecea(Gramineae) By Dr. S A. Abolusoro Origin Maize was domesticated in Southern Mexico around 4000BC. On arrival of European in America,maize had already spread from chile
MAIZE (Zea mays L.) Family Poaecea(Gramineae) By Dr. S A. Abolusoro Origin Maize was domesticated in Southern Mexico around 4000BC. On arrival of European in America,maize had already spread from chile
Crops. Information contained in this presentation came from the National Engineering Handbook Irrigation Guide
 Crops Information contained in this presentation came from the National Engineering Handbook Irrigation Guide Crops The purpose of irrigation is to supplement natural precipitation so that the moisture
Crops Information contained in this presentation came from the National Engineering Handbook Irrigation Guide Crops The purpose of irrigation is to supplement natural precipitation so that the moisture
The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect
 Chapter 2 The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect 2.1 Introduction Sugarcane growing countries of the world are lying between the latitude 36.70 0 north and 31.00 0 south of the equator extending from tropical
Chapter 2 The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect 2.1 Introduction Sugarcane growing countries of the world are lying between the latitude 36.70 0 north and 31.00 0 south of the equator extending from tropical
Rice growing environments
 Rice growing environments 2 Rice production by region Global rice production area by region Other 2% Africa 3% Latin America 4% East Asia 33% South Asia 31% Southeast Asia 27% IRRI 2011 2 3 Rice Production
Rice growing environments 2 Rice production by region Global rice production area by region Other 2% Africa 3% Latin America 4% East Asia 33% South Asia 31% Southeast Asia 27% IRRI 2011 2 3 Rice Production
State: Bihar. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District:Banka
 State: Bihar Agriculture Contingency Plan for District:Banka 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Plain, Hot Subhumid (moist) Eco-sub
State: Bihar Agriculture Contingency Plan for District:Banka 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Plain, Hot Subhumid (moist) Eco-sub
State: MAHARASHTRA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: GONDIA
 State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: GONDIA 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning Commission)
State: MAHARASHTRA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: GONDIA 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Zone (Planning Commission)
12. Water Management Technology Options for Non-Rice Crops
 12. Water Management Technology Options for Non-Rice Crops Special irrigation techniques for non-rice crops: Paired row technique: It is a method in which accommodating crop rows on both sides of furrow
12. Water Management Technology Options for Non-Rice Crops Special irrigation techniques for non-rice crops: Paired row technique: It is a method in which accommodating crop rows on both sides of furrow
State: HARYANA. Agriculture Contingency Plan: KURUKSHETRA
 State: HARYA Agriculture Contingency Plan: KURUKSHETRA 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Punjab and Rohilkhand plains, hot dry, subhumid
State: HARYA Agriculture Contingency Plan: KURUKSHETRA 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Punjab and Rohilkhand plains, hot dry, subhumid
State: KARNATAKA. Agriculture Contingency Plan: District YADGIR
 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: KARNATAKA Agriculture Contingency Plan: District YADGIR Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Semi and Deccan plateau, Hot and Eco
1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: KARNATAKA Agriculture Contingency Plan: District YADGIR Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Semi and Deccan plateau, Hot and Eco
Improved Water Management Practices in the Rice-Wheat Zone of Sind, Pakistan
 Improved Water Management Practices in the Rice-Wheat Zone of Sind, Pakistan T he current yields of rice and wheat in Sind, Pakistan are far below their potential yields partly due to improper water management
Improved Water Management Practices in the Rice-Wheat Zone of Sind, Pakistan T he current yields of rice and wheat in Sind, Pakistan are far below their potential yields partly due to improper water management
Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum
 Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum Importance o It is regarded as queen of oilseeds Because of its quality (fatty acid composition) Its resistance to oxidation and rancidity o India is considered as basic
Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum Importance o It is regarded as queen of oilseeds Because of its quality (fatty acid composition) Its resistance to oxidation and rancidity o India is considered as basic
Site specific enterprise planning and implementation for developing farming system model
 Site specific enterprise planning and implementation for developing farming system model L E C T U R E 7 S S R A N A S R S C I E N T I S T Determinants of Farming Systems Natural Resources and Climate
Site specific enterprise planning and implementation for developing farming system model L E C T U R E 7 S S R A N A S R S C I E N T I S T Determinants of Farming Systems Natural Resources and Climate
ANNEX 1. Climate change risks, adverse impacts, adaptation, mitigation strategies and possible government action in Agriculture and Fisheries
 ANNEX 1. Climate change risks, adverse impacts, adaptation, mitigation strategies and possible government action in Agriculture and Fisheries CHANGING WEATHER PATTERNS LANDSLIDES Failure on crop establishment
ANNEX 1. Climate change risks, adverse impacts, adaptation, mitigation strategies and possible government action in Agriculture and Fisheries CHANGING WEATHER PATTERNS LANDSLIDES Failure on crop establishment
Sorghum grown under poor management
 Sorghum grown under poor management Compaction of soil with tracking animals and tractors Use of poor seeds No hedges to protect the soil from erosion by wind Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of
Sorghum grown under poor management Compaction of soil with tracking animals and tractors Use of poor seeds No hedges to protect the soil from erosion by wind Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of
Growth and yield of faba bean (Vicia faba.l) under rain fed and irrigated conditions in Jordan.
 Research Article ISISnet Publishers Bioscience Research, 6(1): 35-39, 2009 www.isisn.org Growth and yield of faba bean (Vicia faba.l) under rain fed and irrigated conditions in Jordan. Talal Thalji* Seed
Research Article ISISnet Publishers Bioscience Research, 6(1): 35-39, 2009 www.isisn.org Growth and yield of faba bean (Vicia faba.l) under rain fed and irrigated conditions in Jordan. Talal Thalji* Seed
State: ARUNACHAL PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: LOHIT
 1.0 District Agriculture profile* 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: ARUNACHAL PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: LOHIT Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Himalayas, Warm Perhumid
1.0 District Agriculture profile* 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone State: ARUNACHAL PRADESH Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: LOHIT Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Eastern Himalayas, Warm Perhumid
Thematic Brief 2 Water Productivity
 Thematic Brief 2 Water Productivity Brief prepared for the Entry phase of the project: Strengthening Agricultural Water Efficiency and Productivity on the African and Global Level The Project The GCP/INT/166/SWI
Thematic Brief 2 Water Productivity Brief prepared for the Entry phase of the project: Strengthening Agricultural Water Efficiency and Productivity on the African and Global Level The Project The GCP/INT/166/SWI
10. Demographic details
 DISTRICT PROFILE 1. Name of the District : Ramanagara 2. District Head Quarters: Ramanagara 3. Rural Population: 815484 4. Net sown area: 169052 ha 5. Soil type: Sandly Clay Loam 6. Agro Climatic Zone:
DISTRICT PROFILE 1. Name of the District : Ramanagara 2. District Head Quarters: Ramanagara 3. Rural Population: 815484 4. Net sown area: 169052 ha 5. Soil type: Sandly Clay Loam 6. Agro Climatic Zone:
State: KERALA. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PATHANAMTHITTA
 1.0 District Agriculture profile State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PATHANAMTHITTA 1. 1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Central and south Sahyadris,
1.0 District Agriculture profile State: KERALA Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: PATHANAMTHITTA 1. 1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Central and south Sahyadris,
State: TAMILNADU. Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Vellore
 State: TAMILNADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Vellore 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Region (Planning
State: TAMILNADU Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Vellore 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Region / Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic Region (Planning
Climate Smart Agriculture: evidence based technologies and enabling policy frameworks
 Climate Smart Agriculture: evidence based technologies and enabling policy frameworks 2014, LIFT Annual Forum, NPT Udaya Sekhar Nagothu Director (International Projects), The Norwegian Institute of Agriculture
Climate Smart Agriculture: evidence based technologies and enabling policy frameworks 2014, LIFT Annual Forum, NPT Udaya Sekhar Nagothu Director (International Projects), The Norwegian Institute of Agriculture
TIPS OF THE DAY TIPS 1: TIPS 2: TIPS 3: TIPS 4 TIPS 5
 TIPS OF THE DAY TIPS 1: To control Rhinocerous Beetle in coconut, 5 kg cowdung and 1kg Castor can be mixed in water and kept in pots at the 4 corners of the Farm. This will attract the Beetles in to the
TIPS OF THE DAY TIPS 1: To control Rhinocerous Beetle in coconut, 5 kg cowdung and 1kg Castor can be mixed in water and kept in pots at the 4 corners of the Farm. This will attract the Beetles in to the
1._. Crop Production and Management. Lesson at a Glance
 1._ Crop Production and Management Lesson at a Glance Agriculture: The applied branch of biology which deals with cultivation of plants and rearing of animals is called agriculture. Generally, the art
1._ Crop Production and Management Lesson at a Glance Agriculture: The applied branch of biology which deals with cultivation of plants and rearing of animals is called agriculture. Generally, the art
Group 3: Anuradha Rucku Gupta Marvis Dan Xiao Duong Nguyen Van
 Group 3: Anuradha Rucku Gupta Marvis Dan Xiao Duong Nguyen Van Introduction Agriculture has been the basic source for the subsistence of man for thousand of years. Even today, it provides livelihood to
Group 3: Anuradha Rucku Gupta Marvis Dan Xiao Duong Nguyen Van Introduction Agriculture has been the basic source for the subsistence of man for thousand of years. Even today, it provides livelihood to
14 FARMING PRACTICES Land preparation. - To control the growth of weeds; - To shape the seedbed (into ridges, beds, or mounds).
 14 FARMING PRACTICES An enumerator working in farm surveys needs a basic understanding of the agricultural operations done by the farmers during the crop season. It is on these subjects that he will be
14 FARMING PRACTICES An enumerator working in farm surveys needs a basic understanding of the agricultural operations done by the farmers during the crop season. It is on these subjects that he will be
Nutrient Budgeting. An Overview of What, How and Why. June 2014
 Nutrient Budgeting An Overview of What, How and Why 2014 Topics to Cover 1. Why the need for nutrient budgets 2. What is OVERSEER? 3. Principles Behind OVERSEER 4. User Inputs 5. Importance of accurate
Nutrient Budgeting An Overview of What, How and Why 2014 Topics to Cover 1. Why the need for nutrient budgets 2. What is OVERSEER? 3. Principles Behind OVERSEER 4. User Inputs 5. Importance of accurate
State: HARYANA. Agriculture Contingency Plan: KARNAL
 State: HARYANA Agriculture Contingency Plan: KARNAL 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) North Punjab plain, Ganga-Yamuna Doab and Rajasthan
State: HARYANA Agriculture Contingency Plan: KARNAL 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) North Punjab plain, Ganga-Yamuna Doab and Rajasthan
Crop Calendar for Ri Bhoi District, Meghalaya (For areas located at an altitude of m from mean sea level)
 Crop Calendar for Ri Bhoi District, Meghalaya (For areas located at an altitude of 800-1400 m from mean sea level) Technical Bulletin (ICARNEH/NICRA/2013) US Saikia, RK Singh, DJ Rajkhowa, B Goswami and
Crop Calendar for Ri Bhoi District, Meghalaya (For areas located at an altitude of 800-1400 m from mean sea level) Technical Bulletin (ICARNEH/NICRA/2013) US Saikia, RK Singh, DJ Rajkhowa, B Goswami and
State: Madhya Pradesh. Agriculture Contingency Plan: Alirajpur
 State: Madhya Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan: Alirajpur 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Central Plateau and Hills Region Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic
State: Madhya Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan: Alirajpur 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Central Plateau and Hills Region Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Agro-Climatic
Technology Demonstration Component National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA)
 Technology Demonstration Component National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) Dr V. K. Sachan, Programme Coordinator/ PI KRISHI VIGYAN KENDRA (ICAR-VPKAS) CHINYALISAUR, UTTARKASHI-249196
Technology Demonstration Component National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) Dr V. K. Sachan, Programme Coordinator/ PI KRISHI VIGYAN KENDRA (ICAR-VPKAS) CHINYALISAUR, UTTARKASHI-249196
Chapter 15: Improvement in Food Resources Science
 Chapter 15: Improvement in Food Resources Science Page No: 204 1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source of energy.
Chapter 15: Improvement in Food Resources Science Page No: 204 1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables? Cereals provide us with carbohydrates. Also, they are a rich source of energy.
Environmental Guideline on livestock rearing including cattle, goat and sheep (up to 20 cattle heads, 50 goat heads and 50 sheep heads)
 2018 No.29 Environmental Guideline on livestock rearing including cattle, goat and sheep (up to 20 cattle heads, 50 goat heads and 50 sheep heads) Department of Environment The purpose of this environmental
2018 No.29 Environmental Guideline on livestock rearing including cattle, goat and sheep (up to 20 cattle heads, 50 goat heads and 50 sheep heads) Department of Environment The purpose of this environmental
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture.
 1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
Nutrient management. Cassava
 Nutrient management Cassava Fertilizer use By applying mineral fertilizers to their cassava, smallholder farmers can increase their yields from about 10 tonnes to as much as 16 tonnes of fresh roots per
Nutrient management Cassava Fertilizer use By applying mineral fertilizers to their cassava, smallholder farmers can increase their yields from about 10 tonnes to as much as 16 tonnes of fresh roots per
Application of 50 kg K2O/ha, 30 days prior to harvesting of plant cane with irrigation water, resulted in better sprouting of winter harvested cane.
 AGRONOMY Agronomical requirements for sugarcane varieties CoH 35, CoS 8436, CoH 99, CoH 92, CoH 110 and CoH 119 released for cultivation in Haryana and also for CoH 92 released at national level have been
AGRONOMY Agronomical requirements for sugarcane varieties CoH 35, CoS 8436, CoH 99, CoH 92, CoH 110 and CoH 119 released for cultivation in Haryana and also for CoH 92 released at national level have been
What is organic farming?
 Vietnam Farmers Union What is organic farming? Ha noi, January 2016 1 What is organic farming? Organic farming is not use: - Chemical fertilizer or human manure. - Herbicide and pesticides that harmful
Vietnam Farmers Union What is organic farming? Ha noi, January 2016 1 What is organic farming? Organic farming is not use: - Chemical fertilizer or human manure. - Herbicide and pesticides that harmful
CHAPTER - VIII SAMPLE SURVEY MICRO LEVEL CASE STUDIES This chapter is devoted to study the sample villages at micro level selected from each of the
 CHAPTER - VIII SAMPLE SURVEY MICRO LEVEL CASE STUDIES This chapter is devoted to study the sample villages at micro level selected from each of the crop combination zone. This helps to evaluate the interactions
CHAPTER - VIII SAMPLE SURVEY MICRO LEVEL CASE STUDIES This chapter is devoted to study the sample villages at micro level selected from each of the crop combination zone. This helps to evaluate the interactions
(A) garden (B) agriculture (C) crop (D) all of the above
 CROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT 1.Why storage of food is done? 2.Write any two sources of irrigation? 3.What are the two common forms by which we add nutrients in soil? 4.What do you mean by seed drill?
CROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT 1.Why storage of food is done? 2.Write any two sources of irrigation? 3.What are the two common forms by which we add nutrients in soil? 4.What do you mean by seed drill?
NICRA (National Innovations on Climate Resilient Agriculture)
 NICRA (National Innovations on Climate Resilient Agriculture) Climate change has become an important area of concern for India to ensure food and nutritional security for growing population. The impacts
NICRA (National Innovations on Climate Resilient Agriculture) Climate change has become an important area of concern for India to ensure food and nutritional security for growing population. The impacts
Supplier # NITROGEN RECORDING PAGES
 Supplier # NITROGEN RECORDING PAGES NITROGEN RECORDING PAGES The information you provide in this form will be entered into Overseer and used to generate a report. This report will provide you with ongoing
Supplier # NITROGEN RECORDING PAGES NITROGEN RECORDING PAGES The information you provide in this form will be entered into Overseer and used to generate a report. This report will provide you with ongoing
State: Madhya Pradesh. Agriculture Contingency Plan: Jhabua District
 State: Madhya Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan: Jhabua District 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Central Plateau and Hills Region Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR)
State: Madhya Pradesh Agriculture Contingency Plan: Jhabua District 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Central Plateau and Hills Region Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR)
State: HARYANA. Agriculture Contingency Plan District: JIND
 State: HARYANA Agriculture Contingency Plan District: JIND 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Northern Plain (And Central Highlands) (4.1)
State: HARYANA Agriculture Contingency Plan District: JIND 1.0 District Agriculture profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological Zone Agro Ecological Sub Region (ICAR) Northern Plain (And Central Highlands) (4.1)
Details of Training Programmes Soil Sampling and its importance 28 19
 Details of Training Programmes 200- Training Area 04.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 28 2 Soil science 0.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 29 3 22.02.20 Soil Sampling and its importance 28
Details of Training Programmes 200- Training Area 04.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 28 2 Soil science 0.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 29 3 22.02.20 Soil Sampling and its importance 28
Field Problems in Direct-Seeded Rice Using Drumseeder -- and Solutions
 Field Problems in Direct-Seeded Rice Using Drumseeder -- and Solutions Dr. P. Bala Hussain Reddy, SMS (Agrl. Extension), Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Nellore District, Andhra Pradesh, India S. Sreenivasulu, SMS
Field Problems in Direct-Seeded Rice Using Drumseeder -- and Solutions Dr. P. Bala Hussain Reddy, SMS (Agrl. Extension), Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Nellore District, Andhra Pradesh, India S. Sreenivasulu, SMS
Country report on rice
 Country report on rice cultivation practice: Myanmar Dr. Khin Lay Swe Pro Rector (Retd.) Yezin Agricultural University Expert Meeting 2 3 June 2011 Bangkok, Thailand 1 Country Profile: Export: US$ 6.8billi
Country report on rice cultivation practice: Myanmar Dr. Khin Lay Swe Pro Rector (Retd.) Yezin Agricultural University Expert Meeting 2 3 June 2011 Bangkok, Thailand 1 Country Profile: Export: US$ 6.8billi
By: Jane Kugonza, Ronald Wabwire, Pius Lutakome, Ben Lukuyu and Josephine Kirui
 Characterisation of the livestock production system and potential for enhancing productivity through improved feeding in Kiryandongo Dairy Farmers Business Association in Kiryandango district of Uganda.
Characterisation of the livestock production system and potential for enhancing productivity through improved feeding in Kiryandongo Dairy Farmers Business Association in Kiryandango district of Uganda.
Good Practices in Addressing Climate Change Adaptation Deficits due to Extreme Climate Events Perspectives from Asia. Ramasamy Selvaraju
 Good Practices in Addressing Climate Change Adaptation Deficits due to Extreme Climate Events Perspectives from Asia Ramasamy Selvaraju Hazard and Vulnerability Asian region accounts for 40% of the total
Good Practices in Addressing Climate Change Adaptation Deficits due to Extreme Climate Events Perspectives from Asia Ramasamy Selvaraju Hazard and Vulnerability Asian region accounts for 40% of the total
