From Prehistory to end of River Valley Civilization Era. Chapters 1-3
|
|
|
- Felix Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From Prehistory to end of River Valley Civilization Era Chapters 1-3
2 Use the Rule of Three when reading your book Read your book three times BEFORE taking a quiz or test. 1. Quick Glance - Skim through important sections 2. Slow Reading - Read carefully and do written work 3. Review - Reread only the important sections that were discussed in class and review your classroom notes on the same topics.
3 Let s do Step 1 1. Quick Glance - Skim through important sections 1-2 on board means Chapter 1 Section 2 Also look at:
4 EESPRITE E = Era - years - century - period E = Environment - region - country S = Social developments P = political developments - government R = Religious beliefs I = Ideologies they believe in T = Technology developed E = Economic activities
5 Before Agriculture: nomads hunter-gatherers also called foragers Write down definitions
6 Neolithic Revolution circa 8,000 B.C.E. Man discovers how to: farm domesticate animals but not all changed to farming 2-1
7 Big Change: Farming Villages developed into... Civilizations 1 3 vocab: civilization specialization scribes cuneiform Bronze Age ziggurat
8 Where did it happen? River Valley Civilizations go to page 27
9 skim first then read Mesopotamia E = BCE 2-1 E = Middle East (Fertile Crescent) follow order in book Tigris and Euphrates River unpredictable flooding of river combined with periods of little or no rain; crossroads of civilization; limited natural resources S = rulers, priests, nobles = landowners artisans, merchants, landless peasants, Slaves; women could: work as merchants, farmers, or artisans P = Decentralized city-states: Sumer, Babylon kings - not divine supported by priests Hammurabi s Code of Law-first written laws Important Vocabulary: Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia city-state dynasty cultural diffusion polytheism empire Hammurabi Hammurabi s Code of Law
10 skim first then read Mesopotamia 2-1 follow order in book R = Polytheistic Beliefs storm-god most powerful Epic of Gilgamesh reveals gloomy and dark afterlife human king seen as an intermediary between gods and humans ziggurats priests Important Vocabulary: Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia city-state dynasty cultural diffusion polytheism empire Hammurabi Hammurabi s Code of Law I = Hammurabi s Code of Law, Sumerian Science and Technology: arithmetic and geometry,
11 skim first then read Mesopotamia 2-1 follow order in book T = architectural innovations (arches, columns, ramps, pyramid (ziggarat); system of writing (cuneiform) E = Middle East Tigris and Euphrates River unpredictable flooding of river crossroads of civilization Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia city-state dynasty cultural diffusion polytheism empire Hammurabi Hammurabi s Code of Law Important Vocabulary:
12 EESPRITE-ing Mesopotamia Era: 3, B.C.E. Government: Decentralized city-states: Sumer, Babylon kings - not divine supported by priests Hammurabi s Code of Law Environment: Middle East Tigris and Euphrates River unpredictable flooding of river crossroads of civilization Polytheistic Beliefs storm-god most powerful Epic of Gilgamesh reveals gloomy and dark afterlife human king seen as an intermediary between gods and humans ziggurats priests Economy: Middle East Tigris and Euphrates River unpredictable flooding of river crossroads of civilization rulers, priests, nobles = landowners artisans, merchants landless peasants slaves
13 skim first then read E = bc Egypt 2-2 Important Vocabulary: pharaoh theocracy pyramid mummification deity Book of the Dead hieroglyphics papyrus E = along the Nile River; dry parched desert land with distant mountains, plateaus, and lakes S = women have many rights as men; slaves; four classes- royal family; upper class; middle class; lower class (largest of classes) P = pharaohs considered gods on earth; stood at the center of religion, government, and army
14 skim first then read 2-2 Egypt Important Vocabulary: pharaoh theocracy pyramid mummification deity Book of the Dead hieroglyphics papyrus R = polytheistic; god Re (sun god); Osiris (god of death); Anubis (guide of underworld); believed in mummification; believed in after life I = developed form of writing (hieroglyphics); T = papyrus (paper-like substance for writing; medicine; calendar; pyramids; writing numbers for counting, adding, and subtracting (for taxes) E = collected taxes; armies; priesthoods
15 2-3 Indus River Valley Civ. E = b.c. important vocabulary: subcontinent monsoons Harappan civilization E = India; along Indus and Ganges Rivers; deserts, tall mountains, fertile plains; monsoons dominate India s climate; yearly flooding spread rich soil, but are unpredictable; river sometimes change course; monsoon winds are unpredictable; large land mass S = diverse languages (not as yet deciphered by scientists) P = government may have been a theocracy
16 2-3 Indus River Valley Civ. R = Hindu god Shiva; worshipped a bull; priest prayed for good harvest and safety from floods. I = planned cities (grid system) capital cities of Harrapa and Mohenjo-Daro; developed a written language; schools T = plumbing and sewage systems (Mohenjo-Daro) E = link to the sea for trade regionally and distant (gold, silver, jewelry, cotton cloth) important vocabulary: subcontinent monsoons Harappan civilization
17 2-4 E = B.C. China Important vocabulary: loess Shang Dynasty oracle bones dynastic cycle Zhou Dynasty Mandate of Heaven feudalism Warring States Era E = isolated by natural barriers caused Chinese to believe that it was the the center of the civilized world; early settlers had to supply their own goods due to the isolation; Yellow River (Huang He); fertile soil (loess); could have disastrous floods; 10% of the land suitable for farming; S = dynastic cycle; family central to Chinese society; elder men controlled property and made important decisions; women-treated as inferiors (expected to obey all males even young boys); social classes: ruling warrior-nobles (land owners) and peasants. P = dynastic cycle; Shang Dynasty: first family of Chinese rulers to leave written records; dynastic cycle of rule as dictated by the Mandate of Heaven (vocabulary);
18 China 2-4 R = family closely linked to religion; did not regard spirits as mighty gods; consulted gods through spirits of ancestors; Shang kings use oracle bones to ask questions of the gods I = writing system that people all over China could learn regardless of language; feudalism (look at vocabulary list); Important vocabulary: loess Shang Dynasty oracle bones dynastic cycle Zhou Dynasty Mandate of Heaven feudalism Warring States Era T = Zhou Dynasty: roads and canals for trade and agriculture; blast furnaces for production of cast iron for weapons (daggers, axes, swords; sickles, knives, spades for farming; coined money E = agriculture
19 3-1 E = B.C. E = Indus River Valley; Indus River Valley - Aryan migration Important Vocabulary: Indo-Europeans steppes migrations ( explain push-pull factor) Aryans Vedas Brahmins castes Mahabharata S = Indo-Europeans a group of nomadic peoples from steppes of the Caucasus Mountain regions; Indo-European language-aryans are an Indo- European group that migrated to the Indus River Valley of India. Aryans were organized into four groups based on occupation: Brahmins (priests), warriors, traders and landowners, and peasants or traders; group determined life in society. P =
20 3-1 Indus River Valley - Aryan migration R = Vedas (four collections of prayers, magical spells, and instructions for performing rituals. I = Vedas (sacred literature); Caste System; Mahabharata (great epic of India) T = tames horses; rode into battle in two-wheeled chariots; E = pastoral: herded sheep, cattle, and goats Important Vocabulary: Indo- Europeans steppes migrations ( explain push-pull factor) Aryans Vedas Brahmins castes Mahabharata
21 Phoenicians 3-3 Important E =1100 B.C. E = in area known as Lebanon on the Mediterranean Sea. S = Vocabulary: Minoans Aegean Sea Knossos King Minos Phoenicians P = never united into a country; founded a number of wealthy city-states that sometimes competed with one another R = I = alphabet (was spread around to others through trade) it made learning more accessible to more people T = round boat a ship that was very wide and had a rounded bottom (for cargo storage E = trade (trading center cities: Byblos, Tyre, Sidon); shipbuilders, seafarers (first to venture beyond the Strait of Gibraltar); set up trading posts
22 Monuments and sculpture of Early Civilizations ziggurats streets, roads, sewage and water systems pyramids Olmec sculpture
AP WORLD HISTORY PERIOD 1: C BCE T E C H N O L O G I C A L A N D E N V I R O N M E N T A L T R A N S F O R M A T I O N S
 AP WORLD HISTORY PERIOD 1: C. 8000 600 BCE T E C H N O L O G I C A L A N D E N V I R O N M E N T A L T R A N S F O R M A T I O N S KEY CONCEPT 1.1 BIG GEOGRAPHY & THE PEOPLING OF THE EARTH Big Bang (13.75
AP WORLD HISTORY PERIOD 1: C. 8000 600 BCE T E C H N O L O G I C A L A N D E N V I R O N M E N T A L T R A N S F O R M A T I O N S KEY CONCEPT 1.1 BIG GEOGRAPHY & THE PEOPLING OF THE EARTH Big Bang (13.75
AP WORLD HISTORY PERIOD 1: C BCE
 AP WORLD HISTORY PERIOD 1: C. 8000 600 BCE Technological and Environmental Transformations Key Concept 1.1 Big Geography & the Peopling of the Earth Big Bang (13.75 Billion Years Ago) Human-like creatures
AP WORLD HISTORY PERIOD 1: C. 8000 600 BCE Technological and Environmental Transformations Key Concept 1.1 Big Geography & the Peopling of the Earth Big Bang (13.75 Billion Years Ago) Human-like creatures
Bell Ringer: September (5)6, 2017
 Announcements: 1: Check your grades! You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: River Valley Civilizations Map/Anchor Chart Assignment Bell Ringer: September (5)6, 2017 1. Get out your notes from last
Announcements: 1: Check your grades! You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: River Valley Civilizations Map/Anchor Chart Assignment Bell Ringer: September (5)6, 2017 1. Get out your notes from last
Unit 1 Packet: Beginnings in History
 Unit 1 Packet: Beginnings in History c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! (This must be kept in a separate 3 ring binder 1-inch) 1 Timeline
Unit 1 Packet: Beginnings in History c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! (This must be kept in a separate 3 ring binder 1-inch) 1 Timeline
Seventh Grade Social Studies: Early World History Unit 3: Early Civilizations and the Emergence of Pastoral Peoples ( B.C.E.
 Lesson 2 Ongoing development as represented in the feedback loop above resulted in larger groups of people living in cities with social hierarchies and intensified agriculture. The first known examples
Lesson 2 Ongoing development as represented in the feedback loop above resulted in larger groups of people living in cities with social hierarchies and intensified agriculture. The first known examples
Mesopotamia Study Guide
 Mesopotamia Study Guide Name: KEY Period: Date of Test: _OCTOBER 28 TH -I can explain why civilizations developed near rivers. (THIS) -I can describe how the environment helps shape human civilizations.
Mesopotamia Study Guide Name: KEY Period: Date of Test: _OCTOBER 28 TH -I can explain why civilizations developed near rivers. (THIS) -I can describe how the environment helps shape human civilizations.
Culture Hearths & World Religions Steven A. Stofferahn Department of History
 & World Religions Steven A. Stofferahn Department of History Geography and History of the World Seminar Indiana State University July 2007 GHW 1.1 DEFINITION Culture Hearth: - heartland - source area -
& World Religions Steven A. Stofferahn Department of History Geography and History of the World Seminar Indiana State University July 2007 GHW 1.1 DEFINITION Culture Hearth: - heartland - source area -
Ch. 2 Ancient Middle East and Egypt Test
 Name: Date: 1. The Fertile Cresent that lies between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers has had a significant impact on the Middle East because this area was the site of the A. establishment of the first
Name: Date: 1. The Fertile Cresent that lies between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers has had a significant impact on the Middle East because this area was the site of the A. establishment of the first
Why does this revolution occur anyway? Climatic change drought- caused scarcity of food supplies (12,000 BCE) especially in Southwest Asia Population
 Why does this revolution occur anyway? Climatic change drought- caused scarcity of food supplies (12,000 BCE) especially in Southwest Asia Population pressure perhaps saturation point for hunter-gatherers
Why does this revolution occur anyway? Climatic change drought- caused scarcity of food supplies (12,000 BCE) especially in Southwest Asia Population pressure perhaps saturation point for hunter-gatherers
Period 1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, to c. 600 B.C.E. Key Concept 1.1. Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth
 AP World History Curriculum Framework Period 1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, to c. 600 B.C.E. Key Concept 1.1. Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth The term Big Geography draws
AP World History Curriculum Framework Period 1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, to c. 600 B.C.E. Key Concept 1.1. Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth The term Big Geography draws
Social Studies Review. Geography & Early Man
 Geography & Early Man Word Bank: Barter Latitude Basic needs Fresh water Culture Primary source Peninsula Good soil (fertile land) Longitude Directions: Fill in the blanks using the word bank above. 1.
Geography & Early Man Word Bank: Barter Latitude Basic needs Fresh water Culture Primary source Peninsula Good soil (fertile land) Longitude Directions: Fill in the blanks using the word bank above. 1.
Civilization in Sumer
 Civilization in Sumer Vocabulary Words innovation division of labor surplus monarchy absolute authority bureaucracy pictograph cuneiform social class merchant INNOVATION A new way of doing things. Division
Civilization in Sumer Vocabulary Words innovation division of labor surplus monarchy absolute authority bureaucracy pictograph cuneiform social class merchant INNOVATION A new way of doing things. Division
NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION (BEGINNINGS-600 BCE) 1.2 APWH Unit 1 - Technological and Environmental Transformations, c B.C.E. to c.
 NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION (BEGINNINGS-600 BCE) 1.2 APWH Unit 1 - Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8000 B.C.E. to c. 600 Learning Objectives Become aware that agriculture evolved independently
NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION (BEGINNINGS-600 BCE) 1.2 APWH Unit 1 - Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8000 B.C.E. to c. 600 Learning Objectives Become aware that agriculture evolved independently
Chapter 8: African Civilizations, 1500 B.C. A.D. 700
 Name Chapter 8: African Civilizations, 1500 B.C. A.D. 700 Period African Civilizations Diverse Societies in Africa Terms and Names Sahara Large desert in Africa savanna Grassy plain Sahel Land at the
Name Chapter 8: African Civilizations, 1500 B.C. A.D. 700 Period African Civilizations Diverse Societies in Africa Terms and Names Sahara Large desert in Africa savanna Grassy plain Sahel Land at the
Student's Name appears here Course Name appears here QuizStar
 Quiz Preview Go back Student's Name appears here Course Name appears here QuizStar 3rd Quarter Final (PGES- 2016) Quiz Directions Directions: 1. Answer the questions below by clicking the button next to
Quiz Preview Go back Student's Name appears here Course Name appears here QuizStar 3rd Quarter Final (PGES- 2016) Quiz Directions Directions: 1. Answer the questions below by clicking the button next to
Lesson Objectives. Part I Core Content Objectives. Language Arts Objectives
 Lesson Objectives The Indus River Valley, 1 Part I Core Content Objectives Students will: Identify Asia as the largest continent with the most populous countries in the world Locate Asia and India on a
Lesson Objectives The Indus River Valley, 1 Part I Core Content Objectives Students will: Identify Asia as the largest continent with the most populous countries in the world Locate Asia and India on a
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent If YOU were there You are a farmer in Southwest Asia about 6,000 years ago. You live near a slow-moving river, with many shallow lakes and marshes. The river makes
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent If YOU were there You are a farmer in Southwest Asia about 6,000 years ago. You live near a slow-moving river, with many shallow lakes and marshes. The river makes
6. Base your answer to question on the quotation below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 1. During which period did the domestication of animals and growing of crops first occur? A) Iron Age B) Paleolithic Period C) Neolithic Revolution D) Scientific Revolution 2. Where does the archaeological
1. During which period did the domestication of animals and growing of crops first occur? A) Iron Age B) Paleolithic Period C) Neolithic Revolution D) Scientific Revolution 2. Where does the archaeological
7 AGRICULTURE & CIVILIZATION WAS FARMING AN IMPROVEMENT OVER FORAGING?
 7 AGRICULTURE & CIVILIZATION WAS FARMING AN IMPROVEMENT OVER FORAGING? UNIT 7 AGRICULTURE & CIVILIZATION CONTENTS UNIT 7 BASICS 3 Unit 7 Overview 4 Unit 7 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 7 Lessons 6 Unit 7 Key
7 AGRICULTURE & CIVILIZATION WAS FARMING AN IMPROVEMENT OVER FORAGING? UNIT 7 AGRICULTURE & CIVILIZATION CONTENTS UNIT 7 BASICS 3 Unit 7 Overview 4 Unit 7 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 7 Lessons 6 Unit 7 Key
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT. Chapter 3 Section 1
 MESOPOTAMIA GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT Chapter 3 Section 1 Land Between Two Rivers The Tigris and Euphrates rivers are the most important physical features of the region sometimes known as Mesopotamia
MESOPOTAMIA GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT Chapter 3 Section 1 Land Between Two Rivers The Tigris and Euphrates rivers are the most important physical features of the region sometimes known as Mesopotamia
MODELS OF GOVERNANCE: PALEOLITHIC ANCIENT ERA
 Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
Was the Development of Agriculture Good for Humans? Advanced Social Studies
 Was the Development of Agriculture Good for Humans? Advanced Social Studies Essential Question for this Inquiry Essential Question for this Inquiry Was the development of agriculture good for humans? Supporting
Was the Development of Agriculture Good for Humans? Advanced Social Studies Essential Question for this Inquiry Essential Question for this Inquiry Was the development of agriculture good for humans? Supporting
Geography of the Fertile Crescent
 Geography of the Fertile Crescent If YOU were there You are a farmer in Southwest Asia about 6,000 years ago. You live near a slowmoving river, with many shallow lakes and marshes. The river makes the
Geography of the Fertile Crescent If YOU were there You are a farmer in Southwest Asia about 6,000 years ago. You live near a slowmoving river, with many shallow lakes and marshes. The river makes the
The First Civilizations Emerge on the World Stage
 The First Civilizations Emerge on the World Stage By Cynthia Stokes Brown, Big History Project on 07.30.16 Word Count 1,556 Level MAX An Egyptian fresco, circa 1306 1290 BCE. BELOW: A map of Mesopotamia.
The First Civilizations Emerge on the World Stage By Cynthia Stokes Brown, Big History Project on 07.30.16 Word Count 1,556 Level MAX An Egyptian fresco, circa 1306 1290 BCE. BELOW: A map of Mesopotamia.
Geography of the. If YOU were there... Rivers Support the Growth of Civilization. How can you control the waters of the river?
 ECTION 1 What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. The rivers of outhwest Asia supported the growth of civilization. 2. New farming techniques led to the growth of cities. The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris
ECTION 1 What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. The rivers of outhwest Asia supported the growth of civilization. 2. New farming techniques led to the growth of cities. The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris
Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States. How did geographic challenges lead to the rise of city-states in Mesopotamia?
 Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States How did geographic challenges lead to the rise of city-states in Mesopotamia? 4.1. Introduction In Chapter 3, you learned how people in the Fertile Crescent began
Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States How did geographic challenges lead to the rise of city-states in Mesopotamia? 4.1. Introduction In Chapter 3, you learned how people in the Fertile Crescent began
5.1 Uses of the Nile River pp Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Standards 6.15 and 6.19.
 5.1 Uses of the Nile River pp. 101-104 Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Standards 6.15 and 6.19 3 days Part 1 Success Criteria I can describe geographic features of
5.1 Uses of the Nile River pp. 101-104 Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Standards 6.15 and 6.19 3 days Part 1 Success Criteria I can describe geographic features of
01 The Neolithic Revolution 10,000 BCE 3,000 BCE
 01 The Neolithic Revolution 10,000 BCE 3,000 BCE The Agricultural Revolution in World History Summer Terms Gathering and hunting Neolithic or Agricultural Revolution Domestication Innovation Diffusion
01 The Neolithic Revolution 10,000 BCE 3,000 BCE The Agricultural Revolution in World History Summer Terms Gathering and hunting Neolithic or Agricultural Revolution Domestication Innovation Diffusion
Bell Ringer: August 26(30), 2016
 Bell Ringer: August 26(30), 2016 In your own words, describe the changes that came about during the Neolithic Revolution. What might have been some problems that people faced by building permanent settlements
Bell Ringer: August 26(30), 2016 In your own words, describe the changes that came about during the Neolithic Revolution. What might have been some problems that people faced by building permanent settlements
Seventh Grade Social Studies: Early World History Unit 3: Early Civilizations and the Emergence of Pastoral Peoples ( B.C.E.
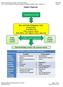 Graphic Organizer Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum Page 1 of 24 Big Idea Card Big Ideas of Lesson 7, Unit 3 Era 2 was characterized by the rise and fall of kingdoms with strong monarchs, powerful
Graphic Organizer Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum Page 1 of 24 Big Idea Card Big Ideas of Lesson 7, Unit 3 Era 2 was characterized by the rise and fall of kingdoms with strong monarchs, powerful
4/21/2009. Chapter 7. What Is Adaptation? People Adapt
 Chapter 7 Patterns of Subsistence What Is Adaptation? Adaptation refers to beneficial adjustments of organisms to their environment. This process leads to changes in the organisms and impacts their environment.
Chapter 7 Patterns of Subsistence What Is Adaptation? Adaptation refers to beneficial adjustments of organisms to their environment. This process leads to changes in the organisms and impacts their environment.
Chapter 4. The Rise of Sumerian City-States
 Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States How did geographic challenges lead to the rise of city-states in Mesopotamia? 4.1 Introduction Early people who lived
Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States Chapter 4 The Rise of Sumerian City-States How did geographic challenges lead to the rise of city-states in Mesopotamia? 4.1 Introduction Early people who lived
Unit 1 Foundations of Civilization
 Unit 1 Foundations of Civilization Questions to Ponder 1. How did the development of agriculture lead to the development of civilization? 2. How does geography and climate impact the development of civilization?
Unit 1 Foundations of Civilization Questions to Ponder 1. How did the development of agriculture lead to the development of civilization? 2. How does geography and climate impact the development of civilization?
Scenario: You awake in the morning and the world as you know it has totally changed. There are no cities, no stores, no houses, no cars, no money, no
 Scenario: You awake in the morning and the world as you know it has totally changed. There are no cities, no stores, no houses, no cars, no money, no government - nothing man-made. There is nothing but
Scenario: You awake in the morning and the world as you know it has totally changed. There are no cities, no stores, no houses, no cars, no money, no government - nothing man-made. There is nothing but
Kush. Piankhi. Meroë. smelting. Lesson Main Ideas. The Region of Nubia. Upper and Lower Nubia. The Kush Civilization
 Grade 6 World History: Ancient Civilizations Chapter 6: Kush and Other African Kingdoms Lesson 1: Nubia and the Land of Kush Objectives 1. Describe the geographic features of Nubia. 2. Summarize the development
Grade 6 World History: Ancient Civilizations Chapter 6: Kush and Other African Kingdoms Lesson 1: Nubia and the Land of Kush Objectives 1. Describe the geographic features of Nubia. 2. Summarize the development
Unit 2 Neolithic Revolution
 Unit 2 Neolithic Revolution Announcements : Posted unit 2 activities Midterm handed out Thursday of week 5, May 10th Wrap up unit 2 Beginnings of agriculture SRC research Board work today s indigenous
Unit 2 Neolithic Revolution Announcements : Posted unit 2 activities Midterm handed out Thursday of week 5, May 10th Wrap up unit 2 Beginnings of agriculture SRC research Board work today s indigenous
Pollution of the Yangtze and Ganges Rivers & Air Pollution and Flooding in India and China
 Pollution of the Yangtze and Ganges Rivers & Air Pollution and Flooding in India and China Pollution of the Yangtze and Ganges Rivers & Air Pollution and Flooding in India and China fdsafs The Ganges
Pollution of the Yangtze and Ganges Rivers & Air Pollution and Flooding in India and China Pollution of the Yangtze and Ganges Rivers & Air Pollution and Flooding in India and China fdsafs The Ganges
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1
 Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the ancient foundations of the state in Athens, in Rome, and in the feudal system. 2. Analyze the rise of sovereign states. 3.
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the ancient foundations of the state in Athens, in Rome, and in the feudal system. 2. Analyze the rise of sovereign states. 3.
The Beginning of Agriculture
 The Beginning of Agriculture Many Neolithic settlements were located in the Fertile Crescent, where the land was fertile. Here, people built towns such as Jericho, Catal Hoyuk, and Jarmo. Complex hunter-gatherer
The Beginning of Agriculture Many Neolithic settlements were located in the Fertile Crescent, where the land was fertile. Here, people built towns such as Jericho, Catal Hoyuk, and Jarmo. Complex hunter-gatherer
Geography in Ancient Egypt
 Geography in Ancient Egypt GRADE 6 This sample task contains a set of primary and authentic sources about the impact of geography on the development of civilization in Ancient Egypt. Alignment The questions
Geography in Ancient Egypt GRADE 6 This sample task contains a set of primary and authentic sources about the impact of geography on the development of civilization in Ancient Egypt. Alignment The questions
Steps to Civilization. Paleolithic Age Farming Revolution Permanent settlements Division of labor Specialization of labor Technology Trade Cities
 Paleolithic Age Farming Revolution Permanent settlements Division of labor Specialization of labor Technology Trade Cities Paleolithic Age nomadic hunters and gatherers clan groups: 15-20 clan leader
Paleolithic Age Farming Revolution Permanent settlements Division of labor Specialization of labor Technology Trade Cities Paleolithic Age nomadic hunters and gatherers clan groups: 15-20 clan leader
The Rise of Democracy
 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES. Student Name
 Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST LARGE PRINT GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES. Student Name
 Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST LARGE PRINT GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age,
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST LARGE PRINT GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1816531560* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/22 Paper 2 October/November 2014
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1816531560* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/22 Paper 2 October/November 2014
Medieval China and the Power of Learning
 Medieval China and the Power of Learning By Big History Project, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.06.17 Word Count 861 These terraced rice paddies are located in Yunnan province, China. Under the Song Dynasty,
Medieval China and the Power of Learning By Big History Project, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.06.17 Word Count 861 These terraced rice paddies are located in Yunnan province, China. Under the Song Dynasty,
The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural. Fastest growing part of the economy was trade of goods. Those manufactured in Europe
 13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
Neolithic Revolution Announcements: Unit 2 wrap up Unit 3 Artist as Scientist
 Neolithic Revolution Announcements: Mon. assign. Folder update will be posted Next Weds. 2 nd art session next Weds. midterm will be handed out units 1-3 + art session 2- due in 1 week Weds. Nov. 1st Unit
Neolithic Revolution Announcements: Mon. assign. Folder update will be posted Next Weds. 2 nd art session next Weds. midterm will be handed out units 1-3 + art session 2- due in 1 week Weds. Nov. 1st Unit
T H E I N D U S T R I A L R E V O L U T I O N
 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! When and where did the Industrial Revolution begin? Why did it begin in this country? How was work organized before the Industrial Revolution?
1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! When and where did the Industrial Revolution begin? Why did it begin in this country? How was work organized before the Industrial Revolution?
Mediterranean Landscape Dynamics Project (Medland)
 Mediterranean Landscape Dynamics Project (Medland) K-12 Education Outreach Group What are some ways people change landscapes? How has the Phoenix landscape changed? 1912 2003 1912 2000 Add Water Bring
Mediterranean Landscape Dynamics Project (Medland) K-12 Education Outreach Group What are some ways people change landscapes? How has the Phoenix landscape changed? 1912 2003 1912 2000 Add Water Bring
Prof. Dr. Ulrich Menzel. Water Politics
 Summer School on Water and International Relations Sept. 5 - Sept. 15, 2011 Technical University of Braunschweig www-public.tu-bs.de:8080/~umenzel www.ulrich-menzel.de Contents 1) The Hydraulic Theory
Summer School on Water and International Relations Sept. 5 - Sept. 15, 2011 Technical University of Braunschweig www-public.tu-bs.de:8080/~umenzel www.ulrich-menzel.de Contents 1) The Hydraulic Theory
The Industrial Revolution ( )
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
Human Adaptations. ESP 30 Lecture 4
 Human Adaptations ESP 30 Lecture 4 Evolution of Human Adaptations Humans face basically the same adaptive challenges as all organisms But humans are unique in having most of their adaptations transmitted
Human Adaptations ESP 30 Lecture 4 Evolution of Human Adaptations Humans face basically the same adaptive challenges as all organisms But humans are unique in having most of their adaptations transmitted
Social Studies World Geography Unit 10: South Asia
 Social Studies World eography Unit 10: South Asia 2012 2013 1 An earthquake takes place in which sphere? A atmosphere B lithosphere biosphere D hydrosphere 2 Which physical process is most responsible
Social Studies World eography Unit 10: South Asia 2012 2013 1 An earthquake takes place in which sphere? A atmosphere B lithosphere biosphere D hydrosphere 2 Which physical process is most responsible
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science History : Chapter 6 Peasants and Farmers
 NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science History : Chapter 6 Peasants and Farmers Activities Question 1. Draw a timeline from 1650 to 1930 showing the significant agricultural changes which you have
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science History : Chapter 6 Peasants and Farmers Activities Question 1. Draw a timeline from 1650 to 1930 showing the significant agricultural changes which you have
Chapter 3-2: Examples for 14 C Dating Applications in Archaeology
 Chapter 3-2: Examples for 14 C Dating Applications in Archaeology 1. The roots of iron age (technological and demographic change) 2. Stonehenge (site analysis and site development) 3. Cherchen Man (Migration
Chapter 3-2: Examples for 14 C Dating Applications in Archaeology 1. The roots of iron age (technological and demographic change) 2. Stonehenge (site analysis and site development) 3. Cherchen Man (Migration
THE DEVELOPMENT AND PROSPECT OF CHINESE GRASSLAND ECONOMIC SYSTEM. H. Fuzeng Chinese Grassland Society, Beijing Abstract
 THE DEVELOPMENT AND PROSPECT OF CHINESE GRASSLAND ECONOMIC SYSTEM H. Fuzeng Chinese Grassland Society, Beijing 100094 Abstract China is a country with an old agriculture civilization of the world. The
THE DEVELOPMENT AND PROSPECT OF CHINESE GRASSLAND ECONOMIC SYSTEM H. Fuzeng Chinese Grassland Society, Beijing 100094 Abstract China is a country with an old agriculture civilization of the world. The
Industrial Revolution. Great Britain: How and Why It Happened
 Industrial Revolution Great Britain: How and Why It Happened Birth of the Industrial Revolution, Part One THE SEEDS Early 1700s: Great Britain What do you notice about this woman? Imagine how she might
Industrial Revolution Great Britain: How and Why It Happened Birth of the Industrial Revolution, Part One THE SEEDS Early 1700s: Great Britain What do you notice about this woman? Imagine how she might
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The Neolithic Revolution (?)
 The Neolithic Revolution (?) Books to read Robert J. Wenke. Patterns in Prehistory: Humankind s First Three Million Years Charles Keith Maisels. The Emergence of Civilization: From Hunting and Gathering
The Neolithic Revolution (?) Books to read Robert J. Wenke. Patterns in Prehistory: Humankind s First Three Million Years Charles Keith Maisels. The Emergence of Civilization: From Hunting and Gathering
The Industrial Revolution. Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization.
 The Industrial Revolution Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 What do you own that
The Industrial Revolution Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 What do you own that
History. Objectives: Vocabulary: Development of lesson: Introduction
 History Objectives: To enable the children to 1. Get a brief introduction to the history of agriculture 2. Appreciate how the first villages were formed 3. Get an overview of the history of farming in
History Objectives: To enable the children to 1. Get a brief introduction to the history of agriculture 2. Appreciate how the first villages were formed 3. Get an overview of the history of farming in
STUDY GUIDE. Living in Southeast Asia. Chapter 31, Section 1. Terms to Know DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCE ORGANIZING YOUR THOUGHTS
 Chapter 31, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 759 765. Living in Southeast Asia Terms to Know paddy A flooded field in which rice is grown (page 760) sickle A long, sharp, curved knife (page 760) subsistence
Chapter 31, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 759 765. Living in Southeast Asia Terms to Know paddy A flooded field in which rice is grown (page 760) sickle A long, sharp, curved knife (page 760) subsistence
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *4255872845* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/21 Paper 2 May/June 2017 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *4255872845* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/21 Paper 2 May/June 2017 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Tragedy of the commons Population Ecology and
 Tragedy of the commons Population Ecology and Tragedy of the Commons v The over-use of common-property or free access resources v Includes clean air and atmosphere, water, land, ocean, wildlife v v Thinking.The
Tragedy of the commons Population Ecology and Tragedy of the Commons v The over-use of common-property or free access resources v Includes clean air and atmosphere, water, land, ocean, wildlife v v Thinking.The
AN OHIO WATER MILL. Learning Objective. Video Synopsis. Teacher Background
 Learning Objective Students will be able to analyze primary source documents and conduct research to make inferences about technological innovations made during the nineteenth century. Video Synopsis In
Learning Objective Students will be able to analyze primary source documents and conduct research to make inferences about technological innovations made during the nineteenth century. Video Synopsis In
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007
 Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
 Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne Warmup Which group of people followed a code of chivalry? If you don t know, ask your neighbor Medieval Europe Middle Ages (also called The Dark Ages) 500-1500
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne Warmup Which group of people followed a code of chivalry? If you don t know, ask your neighbor Medieval Europe Middle Ages (also called The Dark Ages) 500-1500
Map of North and South America
 PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
Warm-up. don t know you may use a dictionary or dictionary.com on your phones)
 Warm-up 1. A state that conquers other lands and rules over them is known as an 2. What does republic mean? And where have you heard it used before? (If you don t know you may use a dictionary or dictionary.com
Warm-up 1. A state that conquers other lands and rules over them is known as an 2. What does republic mean? And where have you heard it used before? (If you don t know you may use a dictionary or dictionary.com
(additional)
 A new dam - Teacher notes A new dam (Lesson 1 of 5) About this lesson This lesson provides examples of dams in the past and today, and helps to identify some key geographical factors behind the contemporary
A new dam - Teacher notes A new dam (Lesson 1 of 5) About this lesson This lesson provides examples of dams in the past and today, and helps to identify some key geographical factors behind the contemporary
Th F e rench Revolution
 The French Revolution 1789-1799 The Old Regime (Ancien Regime) Old Regime social & political system which existed in most of Europe during the 18 th century Countries were ruled by absolutism Divine Right
The French Revolution 1789-1799 The Old Regime (Ancien Regime) Old Regime social & political system which existed in most of Europe during the 18 th century Countries were ruled by absolutism Divine Right
The Human Socio-cultural System
 Marin Burgos 1 Marin Burgos, Carlos Survey of Anthropology 11/05/2007 The Human Socio-cultural System 1) The Issue:- To describe culture, system and superstructure, structure, and infrastructure as components
Marin Burgos 1 Marin Burgos, Carlos Survey of Anthropology 11/05/2007 The Human Socio-cultural System 1) The Issue:- To describe culture, system and superstructure, structure, and infrastructure as components
IMPACT OF CLIMATIC CHANGE & DECAY OF AN URBAN CIVILIZATION
 IMPACT OF CLIMATIC CHANGE & DECAY OF AN URBAN CIVILIZATION Dr. VIDYA H N HOD & Associate professor in History, Government Arts College, Hassan -573201 ABSTRACT Global history is replete with several disappearances
IMPACT OF CLIMATIC CHANGE & DECAY OF AN URBAN CIVILIZATION Dr. VIDYA H N HOD & Associate professor in History, Government Arts College, Hassan -573201 ABSTRACT Global history is replete with several disappearances
-a series of wars between European Christians and Arab Muslims over the Holy Land. -Europeans went for adventure, gain wealth, & forgiveness of sins
 Review The Dark Ages -education is minimal -peasants live in a feudalistic society -invaders attack often -personal hygiene is lacking -knights protect their cities and fight in tournaments The Plague
Review The Dark Ages -education is minimal -peasants live in a feudalistic society -invaders attack often -personal hygiene is lacking -knights protect their cities and fight in tournaments The Plague
Urban Planning in Pre-Industrial China. Urban Planning in Pre-Industrial China. US-China Review, Vol. XII No. 2 pp
 Urban Planning in Pre-Industrial China US-China Review, Vol. XII No. 2 pp. 17-21 1988 by Charles M. Nelson, Ph.D. In this article Dr. Nelson discusses the importance of the political and ideological dimensions
Urban Planning in Pre-Industrial China US-China Review, Vol. XII No. 2 pp. 17-21 1988 by Charles M. Nelson, Ph.D. In this article Dr. Nelson discusses the importance of the political and ideological dimensions
The Industrial Revolution
 1760-1910 The Industrial Revolution Biggest change in human lifestyles since the development of farming during the Neolithic Revolution!!! (New Stone Age) It will all begin with an Agricultural Revolution
1760-1910 The Industrial Revolution Biggest change in human lifestyles since the development of farming during the Neolithic Revolution!!! (New Stone Age) It will all begin with an Agricultural Revolution
2/16/2015. Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs. French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution
 Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution 1 Constructive Response Questions 1. Describe what an absolute monarch is and provide two examples: 2 What Will We
Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution 1 Constructive Response Questions 1. Describe what an absolute monarch is and provide two examples: 2 What Will We
Monday, January 23 rd
 Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
GEOGRAPHY TODAY BOOK 3 REVISED EDITION
 GEOGRAPHY TODAY BOOK 3 REVISED EDITION TOPIC: AGRICULTURE ( Pg No : 61-72 ) Q.1 Fill in the blanks. 1. Pakistan has held agricultural censuses in 1960, 1972, and 2. In the 1950s, agriculture was largely
GEOGRAPHY TODAY BOOK 3 REVISED EDITION TOPIC: AGRICULTURE ( Pg No : 61-72 ) Q.1 Fill in the blanks. 1. Pakistan has held agricultural censuses in 1960, 1972, and 2. In the 1950s, agriculture was largely
Power of information in the Indian rural set up an analysis
 Power of information in the Indian rural set up an analysis Debadutta Kumar Panda Jasmine Mohanty Director Operations Managing Director MP Associates MP Associates (Development Consulting & Research Company)
Power of information in the Indian rural set up an analysis Debadutta Kumar Panda Jasmine Mohanty Director Operations Managing Director MP Associates MP Associates (Development Consulting & Research Company)
Principles of Cultural Geography
 Agriculture Agriculture: Terms Agriculture is the deliberate modification of the Earth s surface through cultivation of plants and rearing of animals to obtain sustenance or economic gain. Cultivate means
Agriculture Agriculture: Terms Agriculture is the deliberate modification of the Earth s surface through cultivation of plants and rearing of animals to obtain sustenance or economic gain. Cultivate means
Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars
 Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars Key Concept 2.1 Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. Key Concept 2.1.I In much of Europe, absolute
Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars Key Concept 2.1 Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. Key Concept 2.1.I In much of Europe, absolute
TOPICS AND ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS GENIUS HOUR PROJECT
 TOPICS AND ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS GENIUS HOUR PROJECT TOPICS Michigan History from Civil War to present Geography Civics (how to be a responsible citizen) and Government Economics (what Michigan Companies
TOPICS AND ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS GENIUS HOUR PROJECT TOPICS Michigan History from Civil War to present Geography Civics (how to be a responsible citizen) and Government Economics (what Michigan Companies
Section 2. Objectives
 Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power. Identify Louis XIV s
Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power. Identify Louis XIV s
Name Date Class. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia
 For use with textbook pages 463 468. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia Terms to Know arable Suitable for farming (page 464) commodity An economic product (page 465) petrochemical
For use with textbook pages 463 468. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia Terms to Know arable Suitable for farming (page 464) commodity An economic product (page 465) petrochemical
Government in Athens
 SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
Wind. Wind Basics. The Daily Wind Cycle
 Wind Electrieit7 Generation from Wind Where Wind is Harnessed >) Types of Wind Turbines ~> History of Wind Power )> Wind Energy & the Environment Wind Basics Energy from Moving Air How Uneven Heating of
Wind Electrieit7 Generation from Wind Where Wind is Harnessed >) Types of Wind Turbines ~> History of Wind Power )> Wind Energy & the Environment Wind Basics Energy from Moving Air How Uneven Heating of
Religious War and Henry IV
 Ch 18.2 Synopsis After Protestant Reformation, France was a divided country. Henry IV became king by a religious compromise and brought limited religious tolerance into France in order to promote healing.
Ch 18.2 Synopsis After Protestant Reformation, France was a divided country. Henry IV became king by a religious compromise and brought limited religious tolerance into France in order to promote healing.
Social Studies Grade 7
 Name 1 st enchmark for 2008-2009 Social Studies Grade 7 Secure for Local Use Edition 2007 ll rights reserved. This document may not be reproduced by any means, in whole or in part, without the express
Name 1 st enchmark for 2008-2009 Social Studies Grade 7 Secure for Local Use Edition 2007 ll rights reserved. This document may not be reproduced by any means, in whole or in part, without the express
EC 165: Economics of the Middle East
 EC 165: Economics of the Middle East Why Middle East Economics? Human Development Indicators Source: UNDP, Arab Human Development Report, 2002. Oil Economics of the Middle East 1. Economic History 2. Demographics
EC 165: Economics of the Middle East Why Middle East Economics? Human Development Indicators Source: UNDP, Arab Human Development Report, 2002. Oil Economics of the Middle East 1. Economic History 2. Demographics
Early Agricultural Regions AGRICULTURE 2. Climate and Agriculture. Map of Agriculture. Areas of Naturally Fertile Soil 4/20/2015.
 GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Early Agricultural Regions AGRICULTURE 2 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2015 What accounts for this distribution? 2 World Climates Köppen Climate Classification
GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Early Agricultural Regions AGRICULTURE 2 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2015 What accounts for this distribution? 2 World Climates Köppen Climate Classification
Agriculture AGRICULTURE. Agriculture. More Terms TERMS. Agricultural Revolutions 11/20/2017. What is it? Why and where did it begin?
 GEOG 247 Cultural Geography AGRICULTURE 1 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2017 Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 1117 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior
GEOG 247 Cultural Geography AGRICULTURE 1 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2017 Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 1117 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior
Flood Plain Functions
 Flood Plain Functions Lesson Abstract Summary: MO GLE: Subject Areas: Students will connect knowledge from previous watershed lessons to understand the functions of flood plains by participating in group
Flood Plain Functions Lesson Abstract Summary: MO GLE: Subject Areas: Students will connect knowledge from previous watershed lessons to understand the functions of flood plains by participating in group
Enrichment Essay Ancient Greece and Rome and Their Influence on Modern Western Civilization (HA)
 Enrichment Essay Ancient Greece and Rome and Their Influence on Modern Western Civilization (HA) This essay examines the political, economic, and social structures of ancient Greece and Rome and explores
Enrichment Essay Ancient Greece and Rome and Their Influence on Modern Western Civilization (HA) This essay examines the political, economic, and social structures of ancient Greece and Rome and explores
Lesson Two. Aims. Context. In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families
 Lesson Two England and the civil wars Aims In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families how Parliament was able to win the war what happened after the execution
Lesson Two England and the civil wars Aims In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families how Parliament was able to win the war what happened after the execution
MISSION OF JNV MORADABAD TREE PLANTATION UPTO 2020
 MISSION OF JNV MORADABAD TREE PLANTATION UPTO 2020 By the next three years, the school will achieve plantation of 500 trees in the area surrounding the school and in the city to spread awareness among
MISSION OF JNV MORADABAD TREE PLANTATION UPTO 2020 By the next three years, the school will achieve plantation of 500 trees in the area surrounding the school and in the city to spread awareness among
