Derivation of Demand and Price Elasticities for Food and Non Food Consumption in Tamil Nadu
|
|
|
- Blaze Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Gowri and Shanmugam Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (1): (2017) ISSN: DOI: ISSN: Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (1): (2017) Research Article Derivation of Demand and Price Elasticities for Food and Non Food Consumption in Tamil Nadu M. Uma Gowri * and T.R. Shanmugam Department of Agricultural Economics, Centre for Agricultural and Development Studies, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore , India *Corresponding Author umanomics@gmail.com Received: Revised: Accepted: ABSTRACT Food is a basic need for human life which carries enormous social, cultural, political, symbolic and nutritional significance of all societies. Rapid economic and income growth, urbanization and globalization along with technological developments lead to a dramatic shift of diets away from staples and increasingly towards livestock and dairy products, vegetable and fruit and fat and oil. The specific objectives of the study were to analyze the demand and price elasticities of food and non-food consumption pattern and to study the consumption pattern/expenditure share of the households besides conventional analysis, advanced econometric model of Almost Ideal Demand System, which formed the basis to derive the own price and expenditure elasticities was used to analyze the data. The % of food expenditure for rural worked out to 51.06, and % respectively, among LIG, MIG and HIGs, and it was 50.27, and % respectively for urban LIG, MIG and HIGs. The % of non-food expenditure was 48.94, and in rural and 49.73, and % in urban areas for LIG, MIG and HIGs, respectively. Own price elasticities for most of the food commodity indicated that any increase in the prices of food commodity had a strong income effect and reduced the intake of the food items for LIG. The expenditure elasticity for rice and other cereals followed the Engel's law of household consumption for MIG and HIG in both the sectors. The income elasticity of vegetables for LIG in both sectors was inelastic. Key words: Expenditure Share, Elasticity, Income, Price, Consumption Pattern INTRODUCTION Recent trends indicate that the composition of nutritional intake in India is fast changing. The per capita food grain consumption has been decreasing in both rural and urban population and the non-grain crops and animal products (dairy and poultry) are increasing their share of the daily nutritional intake 7. It is expected that the share of calorie supply of food grains, non-grain crops and animal products will change from 63:29:8 %s in 2000 to 48:36:16 %s by A much of the total grain demand increase in the future will be due to feed grain demand increase. Cite this article: Gowri, M.U. and Shanmugam, T.R., Derivation of Demand and Price Elasticities for Food and Non Food Consumption in Tamil Nadu, Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5(1): (2017). doi: Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 236
2 The per capita total food grain consumption in again at random. The final stage of sampling the rural areas is projected to decrease from unit consisted of selection of households kg month -1 in 2000 to kg month -1 Totally, 180 rural and 180 urban households by 2050, and in the urban area food grain were selected. Based on the report Chapter on consumption decreases only slightly from Housing Requirement Projection for IX plan to kg month -1, for the same period. ( ), the selected households were Due to rapid urbanization, the food grain post stratified into three groups viz., Low consumption per person in India will decrease Income Group (LIG) earning less than Rs. from to kg month -1 over the next 7300 month per month, Middle Income Group 50 years. However, with the rapid increase in (MIG) earning Rs per month and feed grain demand, the total food grain High Income Group HIG earning more than demand is projected to increase from to Rs per month kg month -1 over the next 50 years. Of Tools of analysis the total increase in demand, the food and feed Empirical frame work of AIDS model grain demand increase comprised of 38 % and The following form of AIDS model was used 58 %, respectively 1. in the present analysis to estimate the system Changing crop demand would of demand functions for food items like significantly increase the income opportunities cereals, pulses, oils, fruits and vegetables, of the agriculture dependent population. The sugar, meat products, milk, spices and total grain demand will increase from 201 condiments. From the estimated demand million metric tonnes in 2000 to about 291 and functions price and income elasticities were 377 million metric tonnes by 2025 and 2050 derived. Following Deaton and Muellbauer 3, respectively. The demand for non-grain crops the linear approximate AIDS model was used. is projected to increase significantly; oil crops W i = a i +Σb ij ln P j +c i ln (X/P * ) from 42 to 115 million metric tonnes; Where, W i - Average budget share of the i th vegetables from 70 to 180 million metric commodity, P j - Price of the j th commodity tonnes; and fruits from 40 to 106 million X - Expenditure per capita on food metric tonnes 12. Hence an attempt is made to commodities (rice, other cereals, pulses, oil derive the demand and price elasticity in Tamil and fat, vegetables, fruits, meat, milk, sugar, Nadu region. The objectives of the study are processed food and health drinks, others) To derive the demand and price elasticities of food and non-food consumption pattern in Tamil Nadu To study the consumption pattern/expenditure share of the households in the study area To suggest suitable policy measures MATERIALS AND METHODS Coimbatore, Erode and Tiruppur districts was chosen for the study. Multistage random sampling technique was followed. In first stage, one block was selected at random from each of the districts. For the urban category, sample households residing in the city limit and around five km radius from city was selected. To compare the consumption of rural and urban households in the study area, three villages from each of the blocks were selected, Ln P * - Price Index, b ij, c i Parameters, i. j - 1, For the Aids to be consistent with the properties of consumer demand theory the structural parameters of AIDS model were estimated subjected to Engel aggregation, homogeneity and symmetry restrictions. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Household consumption expenditure on food and non-food commodities The consumption expenditure on food items as well as on non-food items was a direct function of income and it varies among income groups. In the present analysis, consumption expenditure was worked out for 11 major food and 11 non-food items (Table 1). Saving was assumed as exogenous and the total expenditure was used as a proxy for Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 237
3 income. In both the sectors, the proportion of consumer theory indicated that the expenditure food expenditure to total consumption on non-food items increased with income. expenditure was more in LIG than in MIG and Absolute level of expenditure on non-food HIG, while the proportion of non-food items were more in the urban sector than in the expenditure was more in middle and high rural sector among the income groups. In a income groups. It could be seen that the high similar study by Dzioubinski and Chipman 4 on and middle income groups in both rural and Trends in Consumption and Production: urban sectors, spent relatively larger per cent Household Energy Consumption, they found of income on non-food commodities. that there had been a clear shift in recent Moreover, as income increased, the per cent of decades from the grain consumption to non expenditure on food items had decreased. This grain food and animal products consumption. is the well known Engel Phenomenon. It could The per capita grain consumption had shown a be observed that food expenditure accounted declining trend since 1980 s because of for Rs. 1732, Rs and Rs month -1 increasing income, changes in life style, in LIG,MIG and HIG, respectively, in the rural changes in relative prices and availability of sectors and out of which, they spent Rs. 211, non grain food at affordable cost etc. Rs. 774 and Rs for rice and other cereals Expenditure shares alone. Thus, rice and other cereals accounted The proportion of expenditure made on food for 6.23 %, 7.52 % and 6.41 % to the total and non-food items are reported in Table 2. It food budget in the LIG, MIG and HIG, is evident from the table that the budget share respectively which was 5.90 %, 7.24 % and on food items was more in LIG, while the 6.56 % in urban sector. LIG availed major share of non-food expenditure was more in the portion of food grain (rice) by free rice supply MIG and HIG in both sectors. The income scheme through Public Distribution System. group-wise expenditure shares revealed that The government encourages the food security the per cent of food expenditure was 51.06, through PDS by distributing rice free of cost to and in the rural sector and 50.27, LIG and % in the urban sector among In general, the proportion of food the low, middle and high income groups, expenditure is less and the absolute level of respectively. The average budget share on expenditure on total food is more in the urban non-food commodities also increased with sector in all the three income groups. Because income. One striking feature was that the rural of the urbanization, the consumption of oil, LIG spent 6.23 % on other cereals, whereas, fruits and vegetables, milk, processed food and all other groups incurred only 2.92 % to 3.87 health drinks and meat were more in urban % for other cereals. Wheat was the major than in rural. One had to bear in mind that one cereal among other cereals, and its supply was more element which enhanced the urban made through Public Distribution System household budget was the higher priced they (PDS). As regards milk, the proportion of per paid i.e. they bought high quality product at capita expenditure spent on milk remained premium price. On the contrary, rural people almost similar across groups. In the case of oil consumed substantially their farm produced also, the figures did not exhibit much products especially in case of rural MIG and difference among groups. rural HIG. In the non-food items, the The expenditure share on vegetable expenditure on beverage, narcotics and alcohol increased with income and the urban people were more among the low income groups in spent more than the rural groups. The both the sectors. Expenditure on education, expenditure share on processed food and fuel, transport and social and religious health drinks was more in the urban sector activities were high in middle and high income than in the rural sector. The prices of these groups of both the sectors indicated the better items were moderately higher in the rural than quality of life they enjoyed. The established in the urban sector, because the rural traders Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 238
4 purchase only in urban centres and offer for milk, the share was only % in rural LIG sale at higher price. The expenditure share of as against % among the urban HIG. In meat, fish and eggs were approximately six per high income groups, the processed food and cent of the total expenditure, irrespective of health drinks constituted 8.62 to 8.88 % of the income groups. The meat price was more food expenditure in both the areas. The or less same in both rural and urban sectors. It expenditure share on sugar was high in both is observed that the low income people LIG compared to MIG and HIG. consumed more quantity of less priced meat The table 4 summarizes the like pork and beef but the high income groups expenditure behaviour of the households on consumed high priced meat such as goat and non-food commodities. Fuel, transport, chicken. Hence expenditure share for meat and clothing and education were by far the most meat products were more or less the same, but important non-food commodities in the total it was significantly different in absolute values non-food budget. These items accounted about (Table 1). The expenditure on non-food items 19 % to 30 % of the household expenditure in ranged from % to % in rural all the income groups both in urban and rural sector. It ranged from % to % in areas. There was a remarkable similarity the urban sector among income groups. Also, across income groups in the budget shares on the % of expenditure on non-food items to electricity. Surprisingly, the share of total consumption expenditure, increased with expenditure on medical expenses tended to the enhancement in income, while the per cent decrease with increased income. The LIG of food expenditure declined with the increase spends 7.74 % and 6.82 % in rural and urban in income. Thus it is in conformity with the sectors, respectively, on social and religious Engel's propositions. Rao 11, in his study on functions which was higher than that in the Declining demand for food grains in rural MIG. But in absolute terms MIG spent more India: Causes and Implications, where they than the LIG. The major expenditure incurred found that there had been a clear shift in recent by LIG on recreation was towards cinema. But decades from the grain consumption to non the MIG and HIG people spent on newspapers, grain food and animal products consumption. cinema, weekly magazine and purchase of Distribution of food expenditure video and audio cassettes. The food budget share is reported in Table 3. In general, LIG in both the sectors An average household spent about 12 to 15 % spent more on beverages and narcotics than of the total food expenditure on food grains. the HIG. Since more number of people in the Thus, among the other cereals, wheat occupied LIG consumes liquor and resort to smoking, the most important position. In the total food the expenditure on beverages and narcotics expenditure animal product (meat products) were higher. MIG and HIG spent more on occupied to % followed by fruits education, religious and social functions. In a (11.14 to %) and vegetables with study by Jain and Patel (1996) on % to % across household groups in both Consumption Pattern of Food and Nonareas. The rural LIG spent % for other Food items in Haryana state using NSSO cereals and their counterpart in urban areas data, found that the average per capita spent about 6.07 %. The expenditure on pulses expenditure of urban households was higher was more (9.65 %) in urban LIG. Lowest per compared to rural households. The expenditure cent of spending was done by the rural and share on food was 71 % and 64 %, urban HIG. This is because high income group respectively in the two above mentioned in the rural and urban would spend more on sections animal protein, which substitutes the pulses. Derivation of income elasticities As one expects, the consumption of milk, milk The income elasticities based on AIDS for products and meat and meat products major food and non food commodities are increased with income levels. In the case of reported in Table 5. It could be seen from the Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 239
5 table that the income elasticities for rice in rural sector were and for MIG and HIG, respectively. The LIG availed rice at free of cost from Public Distribution System. expenditure on sugar as the income increased. It was due to the fact that their needs were met by subsidy sugar itself. The elasticities for processed food and health drinks were highly The results confirmed to the demand theory elastic and almost same for the HIG in both that the income elasticity (expenditure the sectors. But, the average value of budget share referred in Table 5 on processed food elasticity) for basic necessities decline at the and health drinks were more in the urban higher income levels. The rural expenditure sector. In general income elasticities for most elasticities were consistently higher than those of the food items in all the expenditure class of urban, for rice. As could be expected, the were positive and elastic. This implied that an expenditure elasticity for rice was elastic for increased in household income was led to an MIG in both the sectors. It was inelastic in HIG. It followed the Engel's law of household increased in household expenditure on each and every item. consumption. Similar trend was observed in The expenditure elasticity on other cereals. It was showed the prevalence of cereal consumption in rural than in urban. It was a remarkable and expected result and the income elasticity was as low as for beverages was negative in the LIG in both the sectors and it was high (1.3351) for the urban MIG. Except the rural MIG, the income elasticity on narcotics was inelastic. The urban HIG, implied that their group preferred income elasticity on clothing was inelastic for rural LIG since it is a necessity for that group. higher quality cereals and better quality food The expenditure elasticities were elastic for items. In general, pulses were income elastic other groups who were more conscious in the for all expenditure groups. These elasticities use of good dresses. were higher in urban when compared to rural. The income elasticities on fuel were It might due to the awareness shown by the elastic for all groups. The urban groups tend to urban people on the nutritive value of pulses. use more of fuel as their income increased as For oil, the income elasticities were higher in MIG, indicated that one per cent increase in income would increase the more than one per cent of oil consumption. The income elasticity of vegetables for LIG in both sectors was inelastic and elastic in the MIG. It was also high in HIG. The expenditure elasticity for fruits was elastic in in the case of rural, this might be due to the availability of substitutes for fuel. Transport and electricity were expenditure inelastic in the rural sector. However it was expenditure elastic in urban sector, showed higher demand for transport and electricity. As could be expected education were inelastic among the rural LIG and MIG; elastic in HIG and LIG, all the income groups. It was very high in the MIG, HIG in the urban sector. The urban sector than in the rural sector in the respective income groups. In urban sector, the MIG and HIG had high elasticity and LIG had expenditure on health was elastic in all, except LIG in urban. It shows the fact that the LIG in urban had accessibility towards public health. relatively low elasticities. This shows For the social and religious expenses, MIG and importance given by the urban sector people for fruits. The income elasticity on meat and meat products was elastic for urban HIG. The HIG were elastic and the low income groups inelastic in both the sectors. Derivation of own price elasticities elasticities for milk and milk products were The direct price elasticities were also higher for all income groups. It indicated the importance given by all categories of people for milk and milk products. The positive impact of well organized supply system of milk through operation flood programme might recognized by the policy makers in the evolution of policies relating to milk industry. The inelastic nature of sugar for rural LIG showed that they were not increasing their computed at the mean level and given in Table 6. The direct price response was high in the urban than the rural for other cereals and it needed some explanation. In this category, the urban people consumed mainly wheat but rural people take other cereals and subsidy wheat. Hence any rise in the price of wheat would shift the consumption of wheat mainly in the urban. The own price elasticity on pulses were Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 240
6 rather mixed among the different income shown one per cent increase in price of fuel, groups. It was high among rural LIG and the consumption of fuel would increase less urban HIG. That was changed in the prices of than one per cent. The cost of education had no pulses had real income effect for this groups. effect on HIG and urban MIG. Since these There was much responsiveness for the change groups were prepare to invest on education by in the price of oil on the part of the LIG of sending their wards to private institutions for both sectors and urban MIG. social reasons even at high incremental cost. For milk and milk products the direct Similar results were obtained in a study by price elasticity was positive in the urban HIG Samad and Hossain 13 on Estimation of and however it was inelastic. The direct price Income and Expenditure Elasticities for Major elasticities for processed food and health drinks Consumption Items in Bangladesh for both and meat and meat products followed the law rural and urban categories over two periods of demand. The demand for sugar had negative between and The study relationship with price of all in income groups revealed that meat and sugar were found to be except urban MIG. The own price elasticity high elastic consumption items. The was positive only for rural LIG because it was corresponding elasticities in the case of urban a necessity. The direct price elasticity for fuel area also showed an increase over those in rural was positive in LIG in both the sectors. area. However, the coefficients were small. This Table 1: Monthly food and non-food consumption expenditure (Rupees/Household) Food items A. Total food Rice Other cereals Pulses Oil and fat Vegetables Fruits Meat Milk Sugar Processed food and Health drinks Others B. Total non food Beverages Narcotics Alcohol Clothing Fuel Transport Electricity Education Health Social and Religious Others Total Expenditure (A+B) Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 241
7 Table 2: Share of food and non - food consumption expenditure(%) Food items A. Total food Rice Other cereals Pulses Oil and fat Vegetables Fruits Meat Milk Sugar Processed food and Health drinks Others B. Total non food Beverages Narcotics Alcohol Clothing Fuel Transport Electricity Education Health Social and religious Others C. Total expenditure share (A+B) Share of total expenditure to total income Table 3: Share of expenditure on food commodities (%) Food items Rice Other cereals Pulses Oil and Fat Vegetables Fruits Meat Milk Sugar Processed food and health Drinks Others Total Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 242
8 Table 4: Share of expenditure on non-food commodities (%) Non Food Beverages Narcotics Alcohol Clothing Fuel Transport Electricity Education Health Social and religious Others Total Table 5: Expenditure elasticities derived from AIDS for different socio economic groups Commodity A. Food groups Rice Other cereals Pulses Oil and Fat Vegetables Fruits Meat Milk Sugar Processed food and Health drinks Others B. Non-food groups Beverages Narcotics Alcohol Clothing Fuel Transport Electricity Education Health Social and religious Others Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 243
9 Table 6: Own price elasticities based on the AIDS for different socio economic groups Commodity A. Food groups Rice Other cereals Pulses Oil and Fat Vegetables Fruits Meat Milk Sugar Processed food and Health drinks Others B. Non Food groups Beverages Narcotics Alcohol Clothing Fuel Transport Electricity Education Health Social and religious Others CONCLUSION The present study was undertaken to derive the demand and price elasticities in Tamil Nadu. The expenditure pattern of rural and urban households was studied by estimating the % share of expenses on rice, other cereals, pulses, oil, vegetables, fruits, meat and meat products, milk and milk products, sugar, processed food and health drinks and others in the food groups. And in the non-food group, it included the beverages, narcotics, alcohol, clothing, fuel, transport, electricity, education, health, social and religious functions and others. As expected, the results of expenditure pattern had revealed that as income increased the per cent of expenditure on food commodities decreased and non-food commodities increased. The rice was supplied at subsidized (zero) price for LIG and hence no expenditure elasticity was estimated. The expenditure elasticity for rice was elastic for MIG in both the sectors. It was inelastic in HIG. It followed the Engel's law of household consumption. Similar trend was observed in other cereals. It showed the more prevalence of cereal consumption in rural than in urban areas. The own price elasticities behaved in an expected manner with negative signs except in a very few cases. The own price elasticities numerically decreased from LIG to HIG in both the sectors for most of the food items. This indicated that any increase in the price of food commodity had a strong income effect and reduced the intake of the food items for LIG. POLICY IMPLICATIONS To have a better quality of life, their expenditure towards on non-food items should be enhanced. This could be accomplished by providing more income and employment generating opportunities to the poor. Anti-poverty programmes and employment generating programmes such as TRYSEM, NREP and IRDP could be strengthened further to accomplish this task. Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 244
10 To generate self employment for poor in both rural and urban sectors, the institutional financing should be liberally provided with more flexibility. Poor households met their total rice consumption through Free Rice Scheme by the Government of Tamil Nadu. Further strengthening of this scheme would ensure food and nutritional security at the grass root level population. Pulses were the predominant and cheapest source of calorie and vegetable protein for the majority of the poor households. Hence the quantity of pulses supplied through PDS should be enhanced to ensure adequate intake of nutrition by the people. In poor households, the expenditure share on alcohol, beverages and narcotics was found more. So, impositions of regulatory measures like tax indirectly reduce the expenditure on these items and divert a share of the income towards essential food commodities which would enhance the standard of living of the poor. REFERENCES 1. Berkman, L.F., The role of social relations in health promotion. Psychosomatic Medicine, 573: (2010). 2. Cranfield, A.L., John, T.W., Hertel, J.E., Eales and Preckel, P.V., Changes in the structure of global food demand. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 80(5): (1998). 3. Deaton, A. and Muellbauer, J., An almost ideal demand system. American Economic Review, 70: (1980). 4. Dzioubinski and Chipman, R., Trends in consumption and production: household energy consumption. DESA Discussion paper No. 6 (2011). 5. Faber, M.C.W. and Drimie, S., Committee based agricultural interventions in the context of food and nutrition security in South Africa. South African Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 241: 32-41(2011). 6. Gilbert, C.C., Hall, G., Hegyi, A., Lehoux, C., Sanchez, M. and Astrom, A., Leveraging agriculture for improving nutrition and health, 2020 conference. International Food Policy and Research Institute, New Delhi, India (2010). 7. Haque, M.S., Determinants of household healthcare expenditure in Chittagong, Bangaldesh. Journal of Applied Economics, 54(24): 230 (2010). 8. Luke, O., Binam, J. and Fatunbioluwole., An assessment of farm input demand in the sudan saranna of Nigeria: The influence of the innovation platform systems of the integrated agricultural research for development learning publics. Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Studies, 21: (2010). 9. Mittal, S., What affect changes in cereal consumption?. Economic and Political Weekly February, 3: pp (2007). 10. Praduman, K., Estimation of demand elasticity for food commodities in India. Agricultural Economics Research Review, 24: 1-14 (2011). 11. Rao, C.H., Declining demand for food grains in rural India: causes and implications. Economic and Political Weekly, pp (2000). 12. Rosegrant, M.W., Paisner, M.S., Meijer, S. and Witcover, J., Emerging trends and alternative futures. International Food Policy Research Institute, (2001). 13. Samad, Q.A. and Hossain, M.Z., Estimation of income and expenditure elasticities for major consumption items in Bangladesh. Indian Journal of Agricultural Economics, 481: (1992). 14. Shenngen, F., Changing role of agriculture and food sector in Asia. International Food Policy and Research Institute. 15. Sorensen, L.B., Moller, P., Flint, A., Martens, M. and Raben, A., Effect of sensory perception of foods on appetite and food intake: a review of studies on humans. International Journal of Obesity Related Metabolic Disorder, 27: (2010). Copyright February, 2017; IJPAB 245
Effects of Subsidy on Food Consumption Pattern in Rural and Urban Households of Western Tamil Nadu, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 2112-2124 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.249
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 2112-2124 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.249
Chapter-5 Conclusions and Suggestions
 Chapter-5 Conclusions and Suggestions 147 Chapter 5 Conclusions and Suggestions The present study has been undertaken with the core objective of deriving the demand parameters and making demand projections
Chapter-5 Conclusions and Suggestions 147 Chapter 5 Conclusions and Suggestions The present study has been undertaken with the core objective of deriving the demand parameters and making demand projections
FOOD CONSUMPTION AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF VULNERABLE PEOPLE REARING LIVESTOCK IN BANGLADESH
 Bangladesh J. Agric. Econs, XXXIII, 1 & 2(2010) 41-56 FOOD CONSUMPTION AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF VULNERABLE PEOPLE REARING LIVESTOCK IN BANGLADESH K. M. M. Rahman 1 A. Sousa-Poza 2 ABSTRACT This study
Bangladesh J. Agric. Econs, XXXIII, 1 & 2(2010) 41-56 FOOD CONSUMPTION AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF VULNERABLE PEOPLE REARING LIVESTOCK IN BANGLADESH K. M. M. Rahman 1 A. Sousa-Poza 2 ABSTRACT This study
Demand vs Supply of Food in India - Futuristic Projection
 Published Online on 22 December 2016 Proc Indian Natn Sci Acad 82 No. 5 December 2016 pp. 1579-1586 Printed in India. DOI: 10.16943/ptinsa /2016/48889 Demand vs Supply of Food in India - Futuristic Projection
Published Online on 22 December 2016 Proc Indian Natn Sci Acad 82 No. 5 December 2016 pp. 1579-1586 Printed in India. DOI: 10.16943/ptinsa /2016/48889 Demand vs Supply of Food in India - Futuristic Projection
Price Shocks, Volatility and Household Welfare: A Cross-Country Inquiry
 Understanding and coping with food markets volatility towards more stable World and EU food systems. POLICY BRIEFING No 05 April 2015 Objectives 1. Measuring the welfare consequences of price changes and
Understanding and coping with food markets volatility towards more stable World and EU food systems. POLICY BRIEFING No 05 April 2015 Objectives 1. Measuring the welfare consequences of price changes and
Employment, Income and Labour Supply Decision of Rural Households : An Economic Analysis of MGNREGS in Tamil Nadu
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 24 (Conference Number) 2011 pp 473-484 Employment, Income and Labour Supply Decision of Rural Households : An Economic Analysis of MGNREGS in Tamil Nadu T. Sivasakthi
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 24 (Conference Number) 2011 pp 473-484 Employment, Income and Labour Supply Decision of Rural Households : An Economic Analysis of MGNREGS in Tamil Nadu T. Sivasakthi
Assessing the Impact of Southeast Asia's Increasing Meat Demand on Global Feed Demand and Prices
 Assessing the Impact of Southeast Asia's Increasing Meat Demand on Global Feed Demand and Prices Jim Hansen United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, MTED, 355 E Street. S.W.,
Assessing the Impact of Southeast Asia's Increasing Meat Demand on Global Feed Demand and Prices Jim Hansen United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, MTED, 355 E Street. S.W.,
The Application and Extension of Jiangsu Agricultural Policy Analysis Model ( JAPA )
 ACIAR China Grain Market Policy Project Paper No. 2 The Application and Extension of Jiangsu Agricultural Policy Analysis Model ( JAPA ) Shudong Zhou College of Economics and Trade, Nanjing Agricultural
ACIAR China Grain Market Policy Project Paper No. 2 The Application and Extension of Jiangsu Agricultural Policy Analysis Model ( JAPA ) Shudong Zhou College of Economics and Trade, Nanjing Agricultural
RISING FOOD PRICE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES
 RISING FOOD PRICE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES Hem Raj Regmi (Msc) 19 ABSTRACT Agricultural prices have risen worldwide sharply in the last two years, which has been a dilemma especially to policy makers. Higher
RISING FOOD PRICE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES Hem Raj Regmi (Msc) 19 ABSTRACT Agricultural prices have risen worldwide sharply in the last two years, which has been a dilemma especially to policy makers. Higher
CONCEPT NOTE ON FOOD SECURITY IN NIGERIA
 CONCEPT NOTE ON FOOD SECURITY IN NIGERIA O.O. Olayiwola Research Fellow, Development Policy Centre, Nigeria Email: olaniyi_2008@yahoo.com ABSTRACT The study of food problems would appear to have acquired
CONCEPT NOTE ON FOOD SECURITY IN NIGERIA O.O. Olayiwola Research Fellow, Development Policy Centre, Nigeria Email: olaniyi_2008@yahoo.com ABSTRACT The study of food problems would appear to have acquired
Trends in Growth Rates of Major Agricultural Crops in Karnataka
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/23207051.7220 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (6): 913917 (2018) Research Article Trends in Growth Rates of Major Agricultural
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/23207051.7220 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (6): 913917 (2018) Research Article Trends in Growth Rates of Major Agricultural
Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis
 Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis Dr Waheeda Sunny Thomas Faculty Economics, SEMCOM, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT First millennium development goal is to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis Dr Waheeda Sunny Thomas Faculty Economics, SEMCOM, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT First millennium development goal is to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
An Economic Analysis of Cumbu Napier Grass Farm Using Treated Wastewater in Karur District of Tamil Nadu
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Sathaiah et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (2): 1318-1322 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6309 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Sathaiah et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (2): 1318-1322 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6309 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Food and Nutritional Insecurity and its Determinants in Food Surplus Areas: The Case Study of Punjab State
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 21 January-June 2008 pp 91-98 Food and Nutritional Insecurity and its Determinants in Food Surplus Areas: The Case Study of Punjab State R.S. Sidhu a *, Inderpreet
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 21 January-June 2008 pp 91-98 Food and Nutritional Insecurity and its Determinants in Food Surplus Areas: The Case Study of Punjab State R.S. Sidhu a *, Inderpreet
CHAPTER V DEMAND VERSUS SUPPLY OF FOOD GRAINS IN INDIA: FUTURE SCENARIO
 139 CHAPTER V DEMAND VERSUS SUPPLY OF FOOD GRAINS IN INDIA: FUTURE SCENARIO To project the future food security scenario of India is the objective of this chapter for which future demand and supply of
139 CHAPTER V DEMAND VERSUS SUPPLY OF FOOD GRAINS IN INDIA: FUTURE SCENARIO To project the future food security scenario of India is the objective of this chapter for which future demand and supply of
Income Distribution Effects of Food Prices Increases. Trade and Pro-Poor Growth Thematic Working Group. Dr. I. Mogotsi.
 Trade and Pro-Poor Growth Thematic Working Group Income Distribution Effects of Food Prices Increases Dr. I. Mogotsi December 2009 indigenous growth 1. INTRODUCTION Over the past 2 3 years: 2006 2008,
Trade and Pro-Poor Growth Thematic Working Group Income Distribution Effects of Food Prices Increases Dr. I. Mogotsi December 2009 indigenous growth 1. INTRODUCTION Over the past 2 3 years: 2006 2008,
FARM POLICY AND OBESITY IN THE UNITED STATES
 3rd Quarter 2010 25(3) FARM POLICY AND OBESITY IN THE UNITED STATES Julian M. Alston, Bradley J. Rickard, and Abigail M. Okrent JEL Classifications: I18, Q18 Many commentators including prominent economists,
3rd Quarter 2010 25(3) FARM POLICY AND OBESITY IN THE UNITED STATES Julian M. Alston, Bradley J. Rickard, and Abigail M. Okrent JEL Classifications: I18, Q18 Many commentators including prominent economists,
FOOD MARKET IN POLAND (current state and trends)
 2009 Creativity, Innovation and Management Proceedings of the 10th International Conference Sousse, Tunisia, 25 28 November FOOD MARKET IN POLAND (current state and trends) Prof. Szwacka-Mokrzycka Joanna
2009 Creativity, Innovation and Management Proceedings of the 10th International Conference Sousse, Tunisia, 25 28 November FOOD MARKET IN POLAND (current state and trends) Prof. Szwacka-Mokrzycka Joanna
Agriculture in China - Successes, Challenges, and Prospects. Prof. Zhihao Zheng College of Economics & Management China Agricultural University
 Agriculture in China - Successes, Challenges, and Prospects Prof. Zhihao Zheng College of Economics & Management China Agricultural University I. Success 1. For the past three decades (1978-2010), China
Agriculture in China - Successes, Challenges, and Prospects Prof. Zhihao Zheng College of Economics & Management China Agricultural University I. Success 1. For the past three decades (1978-2010), China
The Empirical Analysis of Income and Food Consumption Structure of Urban Residents in China
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(13): 3594-3598, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: July 27, 2012 Accepted: September
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(13): 3594-3598, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: July 27, 2012 Accepted: September
Sumiter Singh BROCA. Policy Officer. Ensuring Resilient Food Systems in Asian cities Bangkok Nov Contents
 Food security for the urban poor: Mitigating the impact of food price volatility Sumiter Singh BROCA Policy Officer FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Ensuring Resilient Food Systems in Asian
Food security for the urban poor: Mitigating the impact of food price volatility Sumiter Singh BROCA Policy Officer FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Ensuring Resilient Food Systems in Asian
COST AND RETURN FROM MILK PRODUCTION AMONG TRIBALS (GUJJARS) IN DIFFERENT DISTRICTS OF JAMMU REGION OF J&K STATE IN INDIA
 Received: 16 th August-2012 Revised: 19 th August -2012 Accepted: 24 th August -2012 Research article COST AND RETURN FROM MILK PRODUCTION AMONG TRIBALS (GUJJARS) IN DIFFERENT DISTRICTS OF JAMMU REGION
Received: 16 th August-2012 Revised: 19 th August -2012 Accepted: 24 th August -2012 Research article COST AND RETURN FROM MILK PRODUCTION AMONG TRIBALS (GUJJARS) IN DIFFERENT DISTRICTS OF JAMMU REGION
National Integrated Food Security and Nutrition Policy (NIFSNP) Manoj Thibbotuwawa, Research Economist
 National Integrated Food Security and Nutrition Policy (NIFSNP) Manoj Thibbotuwawa, Research Economist Food Security When all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe
National Integrated Food Security and Nutrition Policy (NIFSNP) Manoj Thibbotuwawa, Research Economist Food Security When all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe
Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India
 Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Does Urbanisation Influence Agricultural Activities? A Case Study of Andhra Pradesh
 Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.64, No.3, July-Sept. 2009 SUBJECT II URBANISATION AND ITS IMPACT ON FARM SECTOR Does Urbanisation Influence Agricultural Activities? A Case Study of Andhra Pradesh P. Parthasarathy
Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.64, No.3, July-Sept. 2009 SUBJECT II URBANISATION AND ITS IMPACT ON FARM SECTOR Does Urbanisation Influence Agricultural Activities? A Case Study of Andhra Pradesh P. Parthasarathy
The Food Security Statistics of Iran
 The Food Security Statistics of Iran R. Hosseinpour Samim Mamaghani Statistician of Information Technology and Communication Center, Ministry of Jahad Agriculture Tehran Iran K. Ahmadi Someeh Head of Information
The Food Security Statistics of Iran R. Hosseinpour Samim Mamaghani Statistician of Information Technology and Communication Center, Ministry of Jahad Agriculture Tehran Iran K. Ahmadi Someeh Head of Information
Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives
 THE WORLD BANK WORKSHOP Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives Session I Food Inflation: Drivers and Policy Implications Subir Gokarn Reserve Bank of India January 12, 212 The Claridges
THE WORLD BANK WORKSHOP Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives Session I Food Inflation: Drivers and Policy Implications Subir Gokarn Reserve Bank of India January 12, 212 The Claridges
China s Meat Consumption: An Income Elasticity Analysis and Long-Term Projections
 China s Meat Consumption: An Income Elasticity Analysis and Long-Term Projections Tadayoshi Masuda 1 and Peter D. Goldsmith 2 1 National Soybean Research Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
China s Meat Consumption: An Income Elasticity Analysis and Long-Term Projections Tadayoshi Masuda 1 and Peter D. Goldsmith 2 1 National Soybean Research Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Livestock and Climate Change in South Asia. Carolyn Opio 26 August 2008 Dhaka
 Livestock and Climate Change in South Asia Carolyn Opio 26 August 2008 Dhaka Content The Livestock sector in South Asia Livestock and climate change Mitigation and Adaptation Policy options and conclusions
Livestock and Climate Change in South Asia Carolyn Opio 26 August 2008 Dhaka Content The Livestock sector in South Asia Livestock and climate change Mitigation and Adaptation Policy options and conclusions
Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India
 Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India Kiresur V.R and Melinamani V.P. Paper prepared for presentation at the 12 th EAAE Congress People,
Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India Kiresur V.R and Melinamani V.P. Paper prepared for presentation at the 12 th EAAE Congress People,
Input Subsidy vs Farm Technology Which is More Important for Agricultural Development?
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 27 (No.1) January-June 2014 pp 1-18 DOI: 10.5958/j.0974-0279.27.1.001 Input Subsidy vs Farm Technology Which is More Important for Agricultural Development?
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 27 (No.1) January-June 2014 pp 1-18 DOI: 10.5958/j.0974-0279.27.1.001 Input Subsidy vs Farm Technology Which is More Important for Agricultural Development?
Economic Analysis of Tribal Farm in Gadchiroli District of Maharashtra, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 07 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.707.247
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 07 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.707.247
CHANGING DIMENSIONS OF LIVESTOCK SECTOR IN TAMIL NAIDU - AN ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
 CHANGING DIMENSIONS OF LIVESTOCK SECTOR IN TAMIL NAIDU - AN ECONOMIC ANALYSIS Prabu M., Selvakumar K.N., Serma Saravana Pandian A., G. Senthilkumar and B. Jaya Varathan Department of Animal Husbandry Economics
CHANGING DIMENSIONS OF LIVESTOCK SECTOR IN TAMIL NAIDU - AN ECONOMIC ANALYSIS Prabu M., Selvakumar K.N., Serma Saravana Pandian A., G. Senthilkumar and B. Jaya Varathan Department of Animal Husbandry Economics
FOOD BASKET PRICE MONTHLY May 2018
 Issue 29 May/2018 FOOD BASKET PRICE MONTHLY May 2018 The basket of food products included in this publication is derived from the Income and Expenditure Survey (IES) of 2014/15, compiled by Statistics
Issue 29 May/2018 FOOD BASKET PRICE MONTHLY May 2018 The basket of food products included in this publication is derived from the Income and Expenditure Survey (IES) of 2014/15, compiled by Statistics
INDIAN COUNCIL FOR RESEARCH ON INTERNATIONAL ECONOMIC RELATIONS
 Working Paper No. 184 Structural Shift in Demand for Food: Projections for 2020 Surabhi Mittal August 2006 INDIAN COUNCIL FOR RESEARCH ON INTERNATIONAL ECONOMIC RELATIONS CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES...iii
Working Paper No. 184 Structural Shift in Demand for Food: Projections for 2020 Surabhi Mittal August 2006 INDIAN COUNCIL FOR RESEARCH ON INTERNATIONAL ECONOMIC RELATIONS CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES...iii
AMBER WAVES VOLUME 6 ISSUE 1
 VOLUME 6 ISSUE 1 10 Jupiterimages Corporation (gas pump and corn field); PhotoDisc (grocery bags) ECONOMIC RESEARCH SERVICE/USDA Corn Prices Near Record High, But What About Food Costs? FEBRUARY 2008 Ephraim
VOLUME 6 ISSUE 1 10 Jupiterimages Corporation (gas pump and corn field); PhotoDisc (grocery bags) ECONOMIC RESEARCH SERVICE/USDA Corn Prices Near Record High, But What About Food Costs? FEBRUARY 2008 Ephraim
Impact of Grain Legume (Groundnut) on Energy and Nutritional Levels of Tribal Farm Households in Koraput (Orissa)
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 21 January-June 2008 pp 54-59 Impact of Grain Legume (Groundnut) on Energy and Nutritional Levels of Tribal Farm Households in Koraput (Orissa) G. Govindaraj*,
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 21 January-June 2008 pp 54-59 Impact of Grain Legume (Groundnut) on Energy and Nutritional Levels of Tribal Farm Households in Koraput (Orissa) G. Govindaraj*,
FOOD CONSUMPTION PARAMETERS IN BANGLADESH IMPLICATIONS FOR FOOD POLICY
 Bangladesh J. Agric. Econ. XllI, 1 & 2( December 1990 ) 43-66 FOOD CONSUMPTION PARAMETERS IN BANGLADESH IMPLICATIONS FOR FOOD POLICY R. K. Talukder ABSTRACT Food consumption parameters have been estimated
Bangladesh J. Agric. Econ. XllI, 1 & 2( December 1990 ) 43-66 FOOD CONSUMPTION PARAMETERS IN BANGLADESH IMPLICATIONS FOR FOOD POLICY R. K. Talukder ABSTRACT Food consumption parameters have been estimated
China s Role in the Future Food Security Situation of Asia: A Threat or An Ally
 China s Role in the Future Food Security Situation of Asia: A Threat or An Ally Jikun Huang Center for Chinese Agricultural Policy Chinese Academy of Sciences Presented at International Conference on Asian
China s Role in the Future Food Security Situation of Asia: A Threat or An Ally Jikun Huang Center for Chinese Agricultural Policy Chinese Academy of Sciences Presented at International Conference on Asian
FOOD SECURITY MONITORING, TAJIKISTAN
 Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19 Tajikistan Food Security Monitoring FOOD SECURITY MONITORING, TAJIKISTAN July 2017 - ISSUE 19 Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19
Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19 Tajikistan Food Security Monitoring FOOD SECURITY MONITORING, TAJIKISTAN July 2017 - ISSUE 19 Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19
FOOD DEMAND PATTERNS IN PAKISTANI PUNJAB
 305 FOOD DEMAND PATTERNS IN PAKISTANI PUNJAB ZAHOOR UL HAQ*, HINA NAZLI**, KARL MEILKE**, MUHAMMAD ISHAQ***, AMJAD KHATTAK****, ARSHAD H. HASHMI***** and FASIH UR REHMAN****** * ** *** **** ***** ******
305 FOOD DEMAND PATTERNS IN PAKISTANI PUNJAB ZAHOOR UL HAQ*, HINA NAZLI**, KARL MEILKE**, MUHAMMAD ISHAQ***, AMJAD KHATTAK****, ARSHAD H. HASHMI***** and FASIH UR REHMAN****** * ** *** **** ***** ******
Determinants of Ruminant Meat Demand in Maiduguri, Borno State, Nigeria
 Greener Journal of Agricultural Sciences ISSN: 2276-7770; ICV: 6.15 Vol. 2(8), pp. 381-385, December, 2012 Copyright 2017, the copyright of this article is retained by the author(s) http://gjournals.org/gjas
Greener Journal of Agricultural Sciences ISSN: 2276-7770; ICV: 6.15 Vol. 2(8), pp. 381-385, December, 2012 Copyright 2017, the copyright of this article is retained by the author(s) http://gjournals.org/gjas
FOOD BASKET PRICE MONTHLY April 2018
 Issue 28 April/2018 FOOD BASKET PRICE MONTHLY April 2018 The basket of food products included in this publication is derived from the Income and Expenditure Survey (IES) of 2014/15, compiled by Statistics
Issue 28 April/2018 FOOD BASKET PRICE MONTHLY April 2018 The basket of food products included in this publication is derived from the Income and Expenditure Survey (IES) of 2014/15, compiled by Statistics
Milk Production and Resource Use Efficiency in Madurai District of Tamil Nadu: An Economic Analysis
 Journal of Community Mobilization and Sustainable Development Vol. 6(1), 025-030, January-June, 2011 Milk Production and Resource Use Efficiency in Madurai District of Tamil Nadu: An Economic Analysis
Journal of Community Mobilization and Sustainable Development Vol. 6(1), 025-030, January-June, 2011 Milk Production and Resource Use Efficiency in Madurai District of Tamil Nadu: An Economic Analysis
Results.
 Results Maps of production, consumption and production surplus of bovine meat in 2 are shown in Figure 1 for Africa, along with the growth in demand from 2 to 23. The full collection of maps is freely
Results Maps of production, consumption and production surplus of bovine meat in 2 are shown in Figure 1 for Africa, along with the growth in demand from 2 to 23. The full collection of maps is freely
Structural Growth and Development of Livestock Sector in North-Eastern Karnataka An Economic Analysis
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 27 (No.2) July-December 2014 pp 319-325 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2014.00036.6 Research Note Structural Growth and Development of Livestock Sector in North-Eastern
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 27 (No.2) July-December 2014 pp 319-325 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2014.00036.6 Research Note Structural Growth and Development of Livestock Sector in North-Eastern
Date File No. Our ref. Food Team Case No.
 Date 29-03-2012 File No. Our ref. Food Team Case No. 1. Summary... 3 2. Macroeconomic indicators... 3 3. Consumption of major food products... 4 4. Urban and rural consumption patterns... 6 5. Imported
Date 29-03-2012 File No. Our ref. Food Team Case No. 1. Summary... 3 2. Macroeconomic indicators... 3 3. Consumption of major food products... 4 4. Urban and rural consumption patterns... 6 5. Imported
Minimum Core Data Set
 Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Minimum Core Data Set Regional Office for the Asia-Pacific Regional Action Plan to Improve Agricultural and Rural Statistics
Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Minimum Core Data Set Regional Office for the Asia-Pacific Regional Action Plan to Improve Agricultural and Rural Statistics
Urban Agriculture and Nutrition. Empirical Evidence from a Sample of Developing Countries
 Urban Agriculture and Nutrition. Empirical Evidence from a Sample of Developing Countries Alberto Zezza and Luca Tasciotti Food and Agriculture Organization 24/09/2009 What is urban agriculture? Urban
Urban Agriculture and Nutrition. Empirical Evidence from a Sample of Developing Countries Alberto Zezza and Luca Tasciotti Food and Agriculture Organization 24/09/2009 What is urban agriculture? Urban
Identifying Investment Priorities for Malawian Agriculture
 Identifying Investment Priorities for Malawian Agriculture Rui Benfica (IFAD) and James Thurlow (IFPRI) Presentation to the Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Water Development Lilongwe, 8 February
Identifying Investment Priorities for Malawian Agriculture Rui Benfica (IFAD) and James Thurlow (IFPRI) Presentation to the Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Water Development Lilongwe, 8 February
How Do We Face Rising Food Prices
 March 2, 2011 How Do We Face Rising Food Prices Studies Directorate بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم " صدق اهلل العظيم )األعراف 31 ( 2 This presentation addresses the following questions: What is the situation of
March 2, 2011 How Do We Face Rising Food Prices Studies Directorate بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم " صدق اهلل العظيم )األعراف 31 ( 2 This presentation addresses the following questions: What is the situation of
Efficient Rural Development Strategies for the Improvement of Indian Economy
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Maurya and Kaushal Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 566-570 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5462 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Maurya and Kaushal Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 566-570 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5462 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
MSSD DISCUSSION PAPER NO. 19 THE IMPACT OF LIVESTOCK AND FISHERIES ON FOOD AVAILABILITY AND DEMAND IN 2020
 MSSD DISCUSSION PAPER NO. 19 THE IMPACT OF LIVESTOCK AND FISHERIES ON FOOD AVAILABILITY AND DEMAND IN 2020 by Christopher L. Delgado (IFPRI) Pierre Crosson (Resources for the Future) and Claude Courbois
MSSD DISCUSSION PAPER NO. 19 THE IMPACT OF LIVESTOCK AND FISHERIES ON FOOD AVAILABILITY AND DEMAND IN 2020 by Christopher L. Delgado (IFPRI) Pierre Crosson (Resources for the Future) and Claude Courbois
THE BRAZILIAN A LOOK AHEAD. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Economic Research Service. By John Earl Hutchison
 FILE COPY ONL'G Do Not Remove FDCD ERS THE BRAZILIAN ~--- :\\~~~-~ -% AtitCVfitJtAL\SITUATION: o;;;'i:j'.'...... - r ', A LOOK AHEAD i By John Earl Hutchison FOREIGN REGIONAl ANALYSIS DIVISION SEPTEMBER
FILE COPY ONL'G Do Not Remove FDCD ERS THE BRAZILIAN ~--- :\\~~~-~ -% AtitCVfitJtAL\SITUATION: o;;;'i:j'.'...... - r ', A LOOK AHEAD i By John Earl Hutchison FOREIGN REGIONAl ANALYSIS DIVISION SEPTEMBER
07. Engel s Law of family expenditure and significance. - Consumer's surplus estimation and applications.
 07. Engel s Law of family expenditure and significance. - Consumer's surplus estimation and applications. Engel s Law on Family Expenditure Every family has to spend money on necessaries of life, education,
07. Engel s Law of family expenditure and significance. - Consumer's surplus estimation and applications. Engel s Law on Family Expenditure Every family has to spend money on necessaries of life, education,
SOCIO ECONOMIC FACTORS AFFECTING FOOD CONSUMPTION PATTERN IN RURAL AREA OF DISTRICT NOWSHERA, PAKISTAN
 Sarhad J. Agric, Vol. 26, No.4, 2010 649 SOCIO ECONOMIC FACTORS AFFECTING FOOD CONSUMPTION PATTERN IN RURAL AREA OF DISTRICT NOWSHERA, PAKISTAN SAFIA BEGUM*, MUNIR KHAN**, MUHAMMAD FAROOQ***, NASIHA BEGUM****
Sarhad J. Agric, Vol. 26, No.4, 2010 649 SOCIO ECONOMIC FACTORS AFFECTING FOOD CONSUMPTION PATTERN IN RURAL AREA OF DISTRICT NOWSHERA, PAKISTAN SAFIA BEGUM*, MUNIR KHAN**, MUHAMMAD FAROOQ***, NASIHA BEGUM****
DEMAND FOR FRUITS AND VEGETABLES IN INDIA
 Agric. Econ. Res. Rev., Vol. 8(2), pp. 7-17 (1995) DEMAND FOR FRUITS AND VEGETABLES IN INDIA Praduman Kumar and Mruthyunjaya Division of Agricultural Economics, IARI, New Delhi India is a vast country,
Agric. Econ. Res. Rev., Vol. 8(2), pp. 7-17 (1995) DEMAND FOR FRUITS AND VEGETABLES IN INDIA Praduman Kumar and Mruthyunjaya Division of Agricultural Economics, IARI, New Delhi India is a vast country,
AFRICA S UNFOLDING DIET TRANSFORMATION:
 AFRICA S UNFOLDING DIET TRANSFORMATION: WHAT DO WE KNOW, WHAT DO WE NEED TO KNOW, AND WHAT ROLE FOR POLICY? David Tschirley Presented at the World Bank Washington, DC, 30 March 2017 Co-hosted by African
AFRICA S UNFOLDING DIET TRANSFORMATION: WHAT DO WE KNOW, WHAT DO WE NEED TO KNOW, AND WHAT ROLE FOR POLICY? David Tschirley Presented at the World Bank Washington, DC, 30 March 2017 Co-hosted by African
Impact of Fish Farming on Household Income: A Case Study from Mymensingh District
 Journal of Social Sciences 7 (2): 127-131, 2011 ISSN 1549-3652 2010 Science Publications Impact of Fish Farming on Household Income: A Case Study from Mymensingh District 1 Syed Mohammad Aminur Rahman,
Journal of Social Sciences 7 (2): 127-131, 2011 ISSN 1549-3652 2010 Science Publications Impact of Fish Farming on Household Income: A Case Study from Mymensingh District 1 Syed Mohammad Aminur Rahman,
Is urbanization a grand opportunity for rural economic growth in developing countries? Peter Richards Bureau for Food Security USAID
 Is urbanization a grand opportunity for rural economic growth in developing countries? Peter Richards Bureau for Food Security USAID 1 U.S. Government s Feed the Future Initiative Initiated in 2010 Launched
Is urbanization a grand opportunity for rural economic growth in developing countries? Peter Richards Bureau for Food Security USAID 1 U.S. Government s Feed the Future Initiative Initiated in 2010 Launched
iafor The International Academic Forum
 Demand on Commodities Contributor of Poverty in Aceh Province-Indonesia: Analyses on Urban Households Chenny Seftarita, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia Dr. Aliasuddin, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
Demand on Commodities Contributor of Poverty in Aceh Province-Indonesia: Analyses on Urban Households Chenny Seftarita, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia Dr. Aliasuddin, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
Public Policy Responses to the Food Security Challenges in East Asia: The Case of Malaysia
 Public Policy Responses to the Food Security Challenges in East Asia: The Case of Malaysia Fatimah Mohamed Arshad Institute of Agricultural and Food Policy Studies Institut Kajian Dasar Pertanian dan Makanan
Public Policy Responses to the Food Security Challenges in East Asia: The Case of Malaysia Fatimah Mohamed Arshad Institute of Agricultural and Food Policy Studies Institut Kajian Dasar Pertanian dan Makanan
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR FOOD AND AGRICULTURE IN THE 21 ST CENTURY
 CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR FOOD AND AGRICULTURE IN THE 21 ST CENTURY Catherine Moreddu Trade and Agriculture Directorate Agricultural Higher Education in the 21st Century, Zaragoza, Spain, 15-17
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR FOOD AND AGRICULTURE IN THE 21 ST CENTURY Catherine Moreddu Trade and Agriculture Directorate Agricultural Higher Education in the 21st Century, Zaragoza, Spain, 15-17
Using ERS Food Price Forecasts to Estimate Food Expenditures for American Households
 Using ERS Food Price Forecasts to Estimate Food Expenditures for American Households Annemarie Kuhns Economic Research Service, USDA Food Markets Branch Food Economics Division Agenda Introduction Overview
Using ERS Food Price Forecasts to Estimate Food Expenditures for American Households Annemarie Kuhns Economic Research Service, USDA Food Markets Branch Food Economics Division Agenda Introduction Overview
FSC Brief No Summary. 2. Introduction and background. 3. Main challenges
 Demand for livestock enterprises for employment creation and food security for farm households in vulnerable regions of Bangladesh Livestock is one of the major assets of rural households for livelihood
Demand for livestock enterprises for employment creation and food security for farm households in vulnerable regions of Bangladesh Livestock is one of the major assets of rural households for livelihood
3.5 Total factor productivity growth and agricultural production growth
 Figure 24: Output per worker Source: FAOSTAT 3.5 Total factor productivity growth and agricultural production growth If land and labour productivity growth occurred in both subregions (particularly in
Figure 24: Output per worker Source: FAOSTAT 3.5 Total factor productivity growth and agricultural production growth If land and labour productivity growth occurred in both subregions (particularly in
The future(s) of food
 The future(s) of food Tim Benton University of Leeds and Royal Institute of International Affairs, Chatham House t.g.benton@leeds.ac.uk tbenton@chathamhouse.org @timgbenton What is a food system? waste
The future(s) of food Tim Benton University of Leeds and Royal Institute of International Affairs, Chatham House t.g.benton@leeds.ac.uk tbenton@chathamhouse.org @timgbenton What is a food system? waste
A Study on Socio-Economic Status of the Farm Women of Tumakuru District of Karnataka State, India
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Yadav and Revanna Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 309-314 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5048 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Yadav and Revanna Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 309-314 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5048 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Global Strategy. Session 1.2: Minimum Set of Core Data Items. Module 1: Sampling in the Context of the Global Minimum Set of Core Data Items
 Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Module 1: Sampling in the Context of the Global Minimum Set of Core Data Items Session 1.2: Minimum Set of Core Data Items 13
Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Module 1: Sampling in the Context of the Global Minimum Set of Core Data Items Session 1.2: Minimum Set of Core Data Items 13
A STUDY ON COSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS IN COIMBATORE
 A STUDY ON COSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS IN COIMBATORE Mr. A. KARUPPUSAMY Research Scholar, Department of Management Studies SNR and Sons College, Peelamedu, Coimbatore E-Mail:
A STUDY ON COSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS IN COIMBATORE Mr. A. KARUPPUSAMY Research Scholar, Department of Management Studies SNR and Sons College, Peelamedu, Coimbatore E-Mail:
Centre for Economic Policy Research. Working Paper on Role of food processing industry in Indian economy
 Centre for Economic Policy Research Working Paper on Role of food processing industry in Indian economy Food Processing industry has emerged as a vital part of Indian economy both in generating GDP and
Centre for Economic Policy Research Working Paper on Role of food processing industry in Indian economy Food Processing industry has emerged as a vital part of Indian economy both in generating GDP and
Towards a Simplified Food Balance Sheet
 APCAS/08/14 June 2008 Agenda Item 10c ASIA AND PACIFIC COMMISSION ON AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS TWENTY-SECOND SESSION Kuching, Malaysia, 9-13 June 2008 Towards a Simplified Food Balance Sheet Robert Mayo
APCAS/08/14 June 2008 Agenda Item 10c ASIA AND PACIFIC COMMISSION ON AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS TWENTY-SECOND SESSION Kuching, Malaysia, 9-13 June 2008 Towards a Simplified Food Balance Sheet Robert Mayo
DEMAND AND SUPPLY PROJECTIONS OF PEARL MILLET IN RAJASTHAN
 DEMAND AND SUPPLY PROJECTIONS OF PEARL MILLET IN RAJASTHAN Shirish Sharma, I.P. Singh and Parvinder Jeet Kaur INDIAN JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS AND DEVELOPMENT Volume 9 July-September 2013 No.3 Indian J Econ
DEMAND AND SUPPLY PROJECTIONS OF PEARL MILLET IN RAJASTHAN Shirish Sharma, I.P. Singh and Parvinder Jeet Kaur INDIAN JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS AND DEVELOPMENT Volume 9 July-September 2013 No.3 Indian J Econ
Food and Energy Demand: African Situation and Outlook. Alex Winter Nelson ACE/UIUC March 5, 2009
 Food and Energy Demand: African Situation and Outlook Alex Winter Nelson ACE/UIUC March 5, 2009 Outline Introduction: Global Demand and Africa Africa s Impact on World Food Demand Population Income Scale
Food and Energy Demand: African Situation and Outlook Alex Winter Nelson ACE/UIUC March 5, 2009 Outline Introduction: Global Demand and Africa Africa s Impact on World Food Demand Population Income Scale
CHANGING DEMOGRAPHICS AND NUTRITION PATTERNS
 CHANGING DEMOGRAPHICS AND NUTRITION PATTERNS Margaret Gill Macaulay Land Use Research Institute Aberdeen, Scotland ABSTRACT The predictions for the rate of increase in the human population have been revised
CHANGING DEMOGRAPHICS AND NUTRITION PATTERNS Margaret Gill Macaulay Land Use Research Institute Aberdeen, Scotland ABSTRACT The predictions for the rate of increase in the human population have been revised
Estimating Demand Elasticities of Meat Demand in Slovakia
 Estimating Demand Elasticities of Meat Demand in Slovakia Daniela Hupkova (1) - Peter Bielik (2) (1) (2) Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra, Faculty of Economics and Management, Department of Economics,
Estimating Demand Elasticities of Meat Demand in Slovakia Daniela Hupkova (1) - Peter Bielik (2) (1) (2) Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra, Faculty of Economics and Management, Department of Economics,
Voluntary Report - Public distribution Date: 5/5/2008 GAIN Report Number: E48051
 GAIN Report Global Agriculture Information Network Template Version 2.09 Voluntary Report - Public distribution Date: 5/5/2008 GAIN Report Number: E48051 E48051 EU-27 Market Development Reports Impact
GAIN Report Global Agriculture Information Network Template Version 2.09 Voluntary Report - Public distribution Date: 5/5/2008 GAIN Report Number: E48051 E48051 EU-27 Market Development Reports Impact
Rising World Food Prices and Poverty in Fiji: A Developing Country Micro Perspective 1
 Contributed Paper Presented to 53 rd Annual Conference of the Australian Agricultural and Resource Economics Society, Cairns, Cairns International Hotel, 1 13 February 29. Rising World Food Prices and
Contributed Paper Presented to 53 rd Annual Conference of the Australian Agricultural and Resource Economics Society, Cairns, Cairns International Hotel, 1 13 February 29. Rising World Food Prices and
Structural Transformation in an Open Economy with Trade in all Three Sectors: Statistical Evidence from India
 International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 8-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.08.002
International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 8-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.08.002
THE AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY WORKING PAPERS IN ECONOMICS AND ECONOMETRICS
 THE AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY WORKING PAPERS IN ECONOMICS AND ECONOMETRICS Global Population Forecast Errors, Economic Performance and Food Demand: Preliminary Simulations* Brett Graham Trade Analysis
THE AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY WORKING PAPERS IN ECONOMICS AND ECONOMETRICS Global Population Forecast Errors, Economic Performance and Food Demand: Preliminary Simulations* Brett Graham Trade Analysis
Performance of Agriculture sector in India with Special Reference to Food grains
 IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 19, Issue 9, Ver. V (Sep. 2014), PP 18-28 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. Performance of Agriculture sector in India with Special
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 19, Issue 9, Ver. V (Sep. 2014), PP 18-28 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. Performance of Agriculture sector in India with Special
THE FUTURE OF GLOBAL MEAT DEMAND IMPLICATIONS FOR THE GRAIN MARKET
 1 THE FUTURE OF GLOBAL MEAT DEMAND IMPLICATIONS FOR THE GRAIN MARKET Mitsui Global Strategic Studies Industrial Studies Dept. II Yukiko Nozaki In the 2000s, the growing demand for meat pushed up the demand
1 THE FUTURE OF GLOBAL MEAT DEMAND IMPLICATIONS FOR THE GRAIN MARKET Mitsui Global Strategic Studies Industrial Studies Dept. II Yukiko Nozaki In the 2000s, the growing demand for meat pushed up the demand
Table 1. U.S. Agricultural Exports as a Share of Production, 1992
 Export markets are important to U.S. agriculture, absorbing a substantial portion of total production of many important commodities. During the last two decades there have been periods of expansion and
Export markets are important to U.S. agriculture, absorbing a substantial portion of total production of many important commodities. During the last two decades there have been periods of expansion and
Constraints and Suggestions as Percived by the Kisan Call Center Beneficiaries
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Kavitha and Anandaraja Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 1725-1729 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5623 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Kavitha and Anandaraja Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 1725-1729 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5623 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App.
AGRICULTURE IN BANGLADESH A NOTE ON FOOD SECURITY BY ENHANCING PRODUCTIVITY
 AGRICULTURE IN BANGLADESH A NOTE ON FOOD SECURITY BY ENHANCING PRODUCTIVITY Summary Awami League s Election Manifesto 2008 appropriately recognizes the importance of ensuring food security for all in Bangladesh.
AGRICULTURE IN BANGLADESH A NOTE ON FOOD SECURITY BY ENHANCING PRODUCTIVITY Summary Awami League s Election Manifesto 2008 appropriately recognizes the importance of ensuring food security for all in Bangladesh.
Why pulses? Source: Principles of Nutrition and Dietetics, primary research
 Why pulses? Pulses as a source of protein: It s a fact that Indians today are consuming far less protein than they used to. Protein consumption in rural India has dropped from 63.5g / capita / day in 1983
Why pulses? Pulses as a source of protein: It s a fact that Indians today are consuming far less protein than they used to. Protein consumption in rural India has dropped from 63.5g / capita / day in 1983
WFP in Bangladesh 2011 in Review
 Fighting Fighting Hunger Hunger Worldwide Worldwide WFP in Bangladesh 2011 in Review West Darfur, Sudan Food Security Monitoring, ruary FEBRUARY Executive Summary The overall food security situation deteriorated
Fighting Fighting Hunger Hunger Worldwide Worldwide WFP in Bangladesh 2011 in Review West Darfur, Sudan Food Security Monitoring, ruary FEBRUARY Executive Summary The overall food security situation deteriorated
The India Consumption Report
 The India Consumption Report 2005-2012 March 2016 Prepared by IMA India Disclaimer The India Consumption Report contains IMA India s analysis of data generated by two rounds of household consumer expenditure
The India Consumption Report 2005-2012 March 2016 Prepared by IMA India Disclaimer The India Consumption Report contains IMA India s analysis of data generated by two rounds of household consumer expenditure
How to feed the world: Is reducing meat consumption part of the solution?
 How to feed the world: Is reducing meat consumption part of the solution? C. Le Mouël (INRA-SAE2, Rennes), E. Marajo-Petitzon (INRA-SAE2, Rennes), P. Dumas (CIRAD, Paris), S. Manceron (INRA-DEPE, Paris),
How to feed the world: Is reducing meat consumption part of the solution? C. Le Mouël (INRA-SAE2, Rennes), E. Marajo-Petitzon (INRA-SAE2, Rennes), P. Dumas (CIRAD, Paris), S. Manceron (INRA-DEPE, Paris),
SUPPLY MANAGEMENT QUALITY. WATER, AGRICULTURE & FOOD Opportunities and Challenges
 SUPPLY MANAGEMENT QUALITY WATER, AGRICULTURE & FOOD Opportunities and Challenges Water and Alberta s Agriculture Industry Alberta is at a water management crossroads, and critical decisions are needed
SUPPLY MANAGEMENT QUALITY WATER, AGRICULTURE & FOOD Opportunities and Challenges Water and Alberta s Agriculture Industry Alberta is at a water management crossroads, and critical decisions are needed
Impact of urbanization on West African food systems
 Impact of urbanization on West African food systems John Staatz Michigan State University Presentation to Sahel & West Africa Week 26 October 2015 Milan Key drivers of West African urban food demand Rapid
Impact of urbanization on West African food systems John Staatz Michigan State University Presentation to Sahel & West Africa Week 26 October 2015 Milan Key drivers of West African urban food demand Rapid
CHAPTER 8. Agriculture and the Malaysian Economy
 CHAPTER 8 Agriculture and the Malaysian Economy 8.1 Contribution of agriculture to the gross domestic product (GDP) Agriculture is part of the primary sector in the Malaysian economy which contributes
CHAPTER 8 Agriculture and the Malaysian Economy 8.1 Contribution of agriculture to the gross domestic product (GDP) Agriculture is part of the primary sector in the Malaysian economy which contributes
Consumption Pattern of Fish in Uttar Pradesh, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 2854-2861 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.350
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 2854-2861 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.350
Status of growth in area, production and productivity of major crops in Jammu province of J&K State
 Indian J. Agric. Res., 51 (4) 2017 : 333-338 Print ISSN:0367-8245 / Online ISSN:0976-058X AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijarjournal.com Status of growth in area, production
Indian J. Agric. Res., 51 (4) 2017 : 333-338 Print ISSN:0367-8245 / Online ISSN:0976-058X AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijarjournal.com Status of growth in area, production
GROWTH OF THE AGRICULTURAL SECTOR OF INDIA UNDER THE GLOBALISATION ERA
 GROWTH OF THE AGRICULTURAL SECTOR OF INDIA UNDER THE GLOBALISATION ERA Dr.M.James Antony Associate Professor, Centre for Research, Arul Anandar College, Karumathur 625 514, Madurai (Dist), Tamil Nadu.
GROWTH OF THE AGRICULTURAL SECTOR OF INDIA UNDER THE GLOBALISATION ERA Dr.M.James Antony Associate Professor, Centre for Research, Arul Anandar College, Karumathur 625 514, Madurai (Dist), Tamil Nadu.
Analysis of Resource Use efficiency in Bt. Cotton and American Cotton in Sri Ganganagar District of Rajasthan
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6922 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (5): 462-466 (2018) Research Article Analysis of Resource Use efficiency in
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6922 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (5): 462-466 (2018) Research Article Analysis of Resource Use efficiency in
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UTTAR PRADESH ABSTRACT
 SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UTTAR PRADESH ABSTRACT Agriculture is a critical sector of the Indian economy. It forms the backbone of development in the country. An average
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UTTAR PRADESH ABSTRACT Agriculture is a critical sector of the Indian economy. It forms the backbone of development in the country. An average
Country Profile: Food Security Indicators
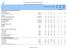 Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment 10 14 13 7 5.9-0.8-10.6 Number of undernourished millions 2.1 3.1
Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment 10 14 13 7 5.9-0.8-10.6 Number of undernourished millions 2.1 3.1
Status and trends in milk production world wide
 Milk production is a very important element of the whole dairy chain. In this part of the value chain the major share of a) the costs, b) resources used, c) emissions created and d) the political challenges
Milk production is a very important element of the whole dairy chain. In this part of the value chain the major share of a) the costs, b) resources used, c) emissions created and d) the political challenges
Socio-Economic, Psychological Characteristics and Constraints Faced by Farmers in Marketing of Coloured Broiler Birds in Karnataka
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Lavanya et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 00000 (0) ISSN: 0 0 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0./00. ISSN: 0 0 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 00000 (0) Research Article SocioEconomic,
Available online at www.ijpab.com Lavanya et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 00000 (0) ISSN: 0 0 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0./00. ISSN: 0 0 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 00000 (0) Research Article SocioEconomic,
