Cyclin- Dependent Protein Kinase. Function
|
|
|
- Victoria McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complex Cyclin Cyclin- Dependent rotein Kinase Function promotes passage through restriction G1-CDK Complex Cyclin D CDK4 or CDK6 point in late G1 G1/S-CDK Complex Cyclin E CDK2 commits the cell to DA replication at the end of G1 S-CDK Complex Cyclin A CDK2 required for the initiation of DA replication M-CDK Complex Cyclin B CDK1 promotes the events of mitosis
2 C G T A H H H H H H Cyclin Cyclin Accessory roteins Cyclin Cyclin rigin of Replication (ri) Initiation Factors Replication Fork
3 Helicases Single Strand DA Binding roteins Topoisomerases DA Directed RA olymerase - rimase DA Directed DA olymerase Leading Strand Lagging Strand Lagging Strand Leading Strand Leading Strand Lagging Strand Lagging Strand Leading Strand rigin of Replication
4
5 Subunit Activity 2 α (alpha) polymerase activity 2 ε (epsilon) 3 exonuclease, the proof reading activity 2 θ (theta) function not precisely known, may be involved in α, ε assembly / scaffold protein 4 β (beta) forms sliding clamp holding enzyme to DA 2 τ (tau) assembly of holoenzyme on DA 2 γ (gamma) part of the gamma complex 1 δ (delta) part of the gamma complex 1 δ (delta prime) part of the gamma complex 1 χ (chi) part of the gamma complex 1 ψ (psi) part of the gamma complex
6 DA olymerase I 3 RA rimer Leading Strand Lagging Strand 3 Exonuclease Activity (rimer Removal) olymerase Activity 3 Exonuclease Activity (roofreading) 3 Leading Strand (Counterclockwise) TerG Clockwise Trap TerF TerB TerC To ri TerA TerD Counterclockwise Trap TerB 3 Leading Strand (Clockwise)
7 ol δ Replicator Cdt1 Cdc6 Cdc45 Cdt1 Cdc6 Cdc45 Cdc45 ol α Cdc45 ol α ol α Cdc45 ol δ CA ol α Cdc45 ol δ ol ol ol ol ol ol ol CA ol ol ol ol ol Rase H1 ol ol ol ol FE1/RTH1 ol ol ol ol DA Ligase ol ol ol ol TEL 3 Telomerase binds to the 3 end of the singlestranded region, and the RA template forms base pairs with the chromosomal DA. CUAACCCUAAC AACCCTAACCCTAA 3 ATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATT TEL 3 An additional repeat is added to the 3 end of the DA using the internal RA as a template. CUAACCCUAAC AACCCTAACCCTAA 3 ATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATT TEL 3 Telomerase shifts by six nucleotides and is positioned to synthesize another repeat. CUAACCCUAAC AACCCTAACCCTAA 3 ATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATTGGGATT
8 Correlation (Equivalency) Table for Replication Bacteria Eukaryotes Function DnaA rigin Recognition Complex 1-6 Recognizes and binds to the rigin of Replication or the (RC1 - RC6) Replicator Sequence. DnaB MCM Complex Helicase Activity DnaC Cell-division-cycle rotein 6 (Cdc6) Loads the Helicase into the Initiation Complex SSB Replication Licensing Factor (Cdt1) Replication Factor A () Single Strand Binding rotein rimase DA olymerase α Synthesizes RA primer DA olymerase III α, ε, & θ subunits DA olymerase III β subunits DA olymerase III δ, δ, χ & ψ subunits DA olymerase I 3 exonuclease DA olymerase I α, ε, & θ subunits DA olymerase I β subunits DA olymerase I δ, δ, χ & ψ subunits DA olymerase δ DA olymerase ε roliferating Cell uclear Antigen (CA) Replication Factor C () Rase H1 FE1/RTH1 DA olymerase ε roliferating Cell uclear Antigen (CA) Replication Factor C () The polymerase and the 3 exonuclease (proofreading) activities The sliding clamp that tethers the enzyme to the DA Clamp loading complex Removes the RA primers The polymerase and the 3 exonuclease (proofreading) activities The sliding clamp that tethers the enzyme to the DA Clamp loading complex DA Ligase DA Ligase Seals nicks between kasaki fragments How DA Is Damaged During Replication - Transitions or Transversions Deamination - A, C, or G Ionizing Radiation Base Alkylation Intercalating Agents H Z H S S S H 2 H 2 H H
9
10
11 (E 6 Homologs) MutS (E 5 Homologs) MutL
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. January 25, 2006
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 28, 2004
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 26, 2005
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
DNA replication. DNA replication. replication model. replication fork. chapter 6
 DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam
 Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam Chapter 9 Replication of DNA Question 1. Name the two substrates for DNA synthesis. Explain why each is necessary for DNA synthesis.
Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam Chapter 9 Replication of DNA Question 1. Name the two substrates for DNA synthesis. Explain why each is necessary for DNA synthesis.
DNA replication. DNA replication. replication model. replication fork. chapter 6
 DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
The flow of Genetic information
 The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
Chapter 30. Replication. Meselson Stahl Experiment. BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2 Conceptual Mechanism of.
 BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three
BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three
Fidelity of DNA polymerase
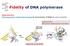 Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function. Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function Gary Peter Learning Objectives 1. List and explain the mechanisms by which E. coli DNA is replicated 2. Describe
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function Gary Peter Learning Objectives 1. List and explain the mechanisms by which E. coli DNA is replicated 2. Describe
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION
 DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 11 DNA Replication
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI REPLICATION - ENZYMES.
 ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
BIOL 5304 Molecular Biology Fall 2018 Name. Homework #1 Due Monday, September 10 at 10:00 AM. 80 points - 1 -
 BIOL 5304 Molecular Biology Fall 2018 ame omework #1 Due Monday, September 10 at 10:00 AM 80 points - 1 - 1. (20 points-maximum) For each item at the left, find all the descriptions on the right that apply
BIOL 5304 Molecular Biology Fall 2018 ame omework #1 Due Monday, September 10 at 10:00 AM 80 points - 1 - 1. (20 points-maximum) For each item at the left, find all the descriptions on the right that apply
Enzymes used in DNA Replication
 Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
Biologia Genômica. 2º Semestre, Replicação de DNA em Bactérias e no Núcleo Eucariótico. Prof. Marcos Túlio
 Biologia Genômica 2º Semestre, 2017 Replicação de DNA em Bactérias e no Núcleo Eucariótico Prof. Marcos Túlio mtoliveria@fcav.unesp.br Faculdade de Ciências Agrárias e Veterinárias de Jaboticabal Instituto
Biologia Genômica 2º Semestre, 2017 Replicação de DNA em Bactérias e no Núcleo Eucariótico Prof. Marcos Túlio mtoliveria@fcav.unesp.br Faculdade de Ciências Agrárias e Veterinárias de Jaboticabal Instituto
DNA replication. - proteins for initiation of replication; - proteins for polymerization of nucleotides.
 DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
The replication forks Summarising what we know:
 When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
Welcome to Class 18! Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives. Replication is semiconservative! Replication: DNA DNA! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
7.05 Recitation Schedule
 7.05 Spring 004 February 13, 004 7.05 Recitation Schedule Contact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, -13 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, -13 Spring 004 Calendar Sun Monday
7.05 Spring 004 February 13, 004 7.05 Recitation Schedule Contact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, -13 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, -13 Spring 004 Calendar Sun Monday
Molecular Biology (2)
 Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Fundamental Process. Unit Map. Unit
 Unit 3 Unit Map 3.A DNA replication, repair and recombination 120 3.B RNA synthesis and processing 137 3.C Protein synthesis and processing 151 3.D Control of gene expression at transcription and translation
Unit 3 Unit Map 3.A DNA replication, repair and recombination 120 3.B RNA synthesis and processing 137 3.C Protein synthesis and processing 151 3.D Control of gene expression at transcription and translation
DNA REPLICATION. Third Stage. Lec. 12 DNA Replication. Lecture No.: 12. A. Watson & Crick (1952) C. Cairns (1963) autoradiographic experiment
 Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES
 MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 28 II 32 III 32 IV 30 V 28 150 PLEASE WRITE your NAME or SID number on each page. This exam must be written
MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 28 II 32 III 32 IV 30 V 28 150 PLEASE WRITE your NAME or SID number on each page. This exam must be written
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
Chapter 12. DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 12 DNA Replication and Recombination I. DNA replication Three possible modes of replication A. Conservative entire original molecule maintained B. Semiconservative one strand is template for new
Chapter 12 DNA Replication and Recombination I. DNA replication Three possible modes of replication A. Conservative entire original molecule maintained B. Semiconservative one strand is template for new
Zoo-342 Molecular biology Lecture 2. DNA replication
 Zoo-342 Molecular biology Lecture 2 DNA replication DNA replication DNA replication is the process in which one doubled-stranded DNA molecule is used to create two double-stranded molecules with identical
Zoo-342 Molecular biology Lecture 2 DNA replication DNA replication DNA replication is the process in which one doubled-stranded DNA molecule is used to create two double-stranded molecules with identical
Replication. Obaidur Rahman
 Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
Hershey & Chase Avery, MacLeod, & McCarty DNA: The Genetic Material
 DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
Requirements for the Genetic Material
 Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two. Fig. 10-CO, p.240
 Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
Bacterial DNA replication
 Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
MCB 110 First Midterm SIX PAGES
 MCB 110 First Midterm SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 27 II 32 III 35 IV 33 V 24 151 This exam must be written in PEN if you want the option of a regrade. DO NOT USE WHITE
MCB 110 First Midterm SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 27 II 32 III 35 IV 33 V 24 151 This exam must be written in PEN if you want the option of a regrade. DO NOT USE WHITE
DNA Metabolism. I. DNA Replication. A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding
 DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
DNA REPLICATION NOTES
 DNA REPLICATION NOTES The Central Dogma Replication Facts DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied during the S or synthesis phase of interphase New cells will need identical DNA strands
DNA REPLICATION NOTES The Central Dogma Replication Facts DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied during the S or synthesis phase of interphase New cells will need identical DNA strands
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.8 DNA REPLICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
BS GENOMES. DNA replication and repair
 BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two. Fig. 10-CO, p.240
 Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE
 STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
You Should Be Able To
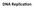 DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
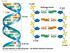 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication
 Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Initiation of Replication. This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication.
 Initiation of Replication This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication. Replicons and origins of replication The unit of DNA replication
Initiation of Replication This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication. Replicons and origins of replication The unit of DNA replication
Chapter Twelve: DNA Replication and Recombination
 This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
DNA Replication and Transcription: Biosynthesis of DNA and RNA 阮雪芬
 DNA Replication and Transcription: Biosynthesis of DNA and RNA 阮雪芬 2004/05/21 @NTU Outline Introduction Replication of DNA Action of DNA Polymerases DNA Damage and Repair Synthesis of RNA Post-transcriptional
DNA Replication and Transcription: Biosynthesis of DNA and RNA 阮雪芬 2004/05/21 @NTU Outline Introduction Replication of DNA Action of DNA Polymerases DNA Damage and Repair Synthesis of RNA Post-transcriptional
Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
DNA Replication and Repair
 DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
Biochemistry. DNA Polymerase. Structure and Function of Biomolecules II. Principal Investigator
 Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Biochemistry 302, February 11, 2004 Exam 1 (100 points) 1. What form of DNA is shown on this Nature Genetics cover? Z-DNA or left-handed DNA
 1 Biochemistry 302, February 11, 2004 Exam 1 (100 points) Name I. Structural recognition (very short answer, 2 points each) 1. What form of DNA is shown on this Nature Genetics cover? Z-DNA or left-handed
1 Biochemistry 302, February 11, 2004 Exam 1 (100 points) Name I. Structural recognition (very short answer, 2 points each) 1. What form of DNA is shown on this Nature Genetics cover? Z-DNA or left-handed
Lecture 24: DNA replication. Lecture Outline. Chromosomes. Review
 Lecture 4: D replication Lecture Outline Figure 6.7a, c nm (c) Space-filling model Overview of D replication D has polarity (5, 3 O) Rules of Replication Details of the replication machine roofreading
Lecture 4: D replication Lecture Outline Figure 6.7a, c nm (c) Space-filling model Overview of D replication D has polarity (5, 3 O) Rules of Replication Details of the replication machine roofreading
III. Detailed Examination of the Mechanism of Replication A. Initiation B. Priming C. Elongation D. Proofreading and Termination
 Outline for Replication I. General Features of Replication A. Semi-Conservative B. Starts at Origin C. Bidirectional D. Semi-Discontinuous II. Proteins and Enzymes of Replication III. Detailed Examination
Outline for Replication I. General Features of Replication A. Semi-Conservative B. Starts at Origin C. Bidirectional D. Semi-Discontinuous II. Proteins and Enzymes of Replication III. Detailed Examination
The Size and Packaging of Genomes
 DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
Biochemistry 674 Your Name: Nucleic Acids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 17, 2005
 Biochemistry 674 ucleic Acids Your ame: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) ovember 17, 2005 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under
Biochemistry 674 ucleic Acids Your ame: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) ovember 17, 2005 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under
Please write your name or student ID number on every page.
 MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 30 II 30 III 30 IV 38 V 22 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 30 II 30 III 30 IV 38 V 22 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA: Structure & Replication
 DNA Form & Function DNA: Structure & Replication Understanding DNA replication and the resulting transmission of genetic information from cell to cell, and generation to generation lays the groundwork
DNA Form & Function DNA: Structure & Replication Understanding DNA replication and the resulting transmission of genetic information from cell to cell, and generation to generation lays the groundwork
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 24, 2005
 DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11
 Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
DNA metabolism. DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination
 DNA metabolism DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology Central Dogma or Flow of genetic information
DNA metabolism DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology Central Dogma or Flow of genetic information
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
DNA and Replication 1
 DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
Please write your name or student ID number on every page.
 MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 36 II 35 III 27 IV 28 V 24 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 36 II 35 III 27 IV 28 V 24 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
DNA Replication. The Organization of DNA. Recall:
 Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
Players. Processes. Molecular Biology Recombinant DNA technology (So... you want to be a genetic engineer)
 lay Davis, 8/11/12 Molecular Biology Recombinant DN technology (So... you want to be a genetic engineer) Introduction, or, games to play with DN You have learned something of the structure of DN, its replication,
lay Davis, 8/11/12 Molecular Biology Recombinant DN technology (So... you want to be a genetic engineer) Introduction, or, games to play with DN You have learned something of the structure of DN, its replication,
copyright cmassengale 2
 1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division. DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis
 Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis The faithful transmission of genotype at cell division, illustrated by the behaviour of tumor cells Cell
Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis The faithful transmission of genotype at cell division, illustrated by the behaviour of tumor cells Cell
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number:
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 35 II 29 III 30 IV 32 V 24 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 35 II 29 III 30 IV 32 V 24 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
CSIR UGC NET, GATE (ENGINEERING), GATE (Science), IIT-JAM, UGC NET, TIFR, IISc, NIMCET, JEST etc. JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY
 JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY REPLICATION TYPE OF DNA REPLICATION REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES REPLICATION IN EUKARYOTES For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary Road,
JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY REPLICATION TYPE OF DNA REPLICATION REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES REPLICATION IN EUKARYOTES For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary Road,
1 Macromolecular Synthesis
 FID Figure 1.1 1 helical turn = 3.4 nm ydrogen bond Sugar-phosphate backbone Base FID Figure 1.2 Bases 1 2 6 7 5 8 4 9 3 urine 2 denine 2 uanine 4 2 3 5 3 2 1 6 yrimidine ytosine Uracil hymine Sugars 2
FID Figure 1.1 1 helical turn = 3.4 nm ydrogen bond Sugar-phosphate backbone Base FID Figure 1.2 Bases 1 2 6 7 5 8 4 9 3 urine 2 denine 2 uanine 4 2 3 5 3 2 1 6 yrimidine ytosine Uracil hymine Sugars 2
Prokaryotic Physiology. March 3, 2017
 1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins
 Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins I. Synthesis of DNA = REPLICATION A. Components of DNA (Fig. 11-1) 1. Composed of 4 different nucleotides that are joined by the
Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins I. Synthesis of DNA = REPLICATION A. Components of DNA (Fig. 11-1) 1. Composed of 4 different nucleotides that are joined by the
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
DNA Model Building and Replica3on
 DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis
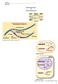 Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
DNA Replication. Rasime Kalkan,PhD.
 DNA Replication Rasime Kalkan,PhD. DNA Replication The process of copying one DNA molecule into two identical molecules is called DNA replication. DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied
DNA Replication Rasime Kalkan,PhD. DNA Replication The process of copying one DNA molecule into two identical molecules is called DNA replication. DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March :24 pm
 Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Proposed Models of DNA Replication. Conservative Model. Semi-Conservative Model. Dispersive model
 5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
DNA Replication. Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow!
 DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR
 DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA Replication: Prokaryotes and Yeast
 DNA Replication: Prokaryotes and Yeast Derek J Hoelz, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA Robert J Hickey, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA Linda H
DNA Replication: Prokaryotes and Yeast Derek J Hoelz, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA Robert J Hickey, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA Linda H
Eukaryotic DNA Replication Mechanism:
 Eukaryotic DNA Replication Mechanism: Eukaryotic cells are endowed with a very complicated but sophisticated regulation of cell division. Embryonic cells go through first seven to eight cell divisions
Eukaryotic DNA Replication Mechanism: Eukaryotic cells are endowed with a very complicated but sophisticated regulation of cell division. Embryonic cells go through first seven to eight cell divisions
DNA is a functional genetic material as it:
 DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information
 Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
