III. Detailed Examination of the Mechanism of Replication A. Initiation B. Priming C. Elongation D. Proofreading and Termination
|
|
|
- Amice Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline for Replication I. General Features of Replication A. Semi-Conservative B. Starts at Origin C. Bidirectional D. Semi-Discontinuous II. Proteins and Enzymes of Replication III. Detailed Examination of the Mechanism of Replication A. Initiation B. Priming C. Elongation D. Proofreading and Termination
2 DNA replication with two forks
3 DNA replication Fork The polarity of DNA synthesis creates an asymmetry between the leading strand and the lagging strand at the replication fork
4 Protein complexes of the replication fork: DNA primase DNA Helicase ssdna binding protein DNA Ligase DNA Topoisomerase DNA polymerase RNaseH Sliding Clamp Clamp Loader
5 Replication caught in Action Topoisomerase
6 II. Identifying Proteins and Enzymes involved in Replication A. Combine Genetics and Biochemistry 1. Genetic Approach: Obtain Mutants that are defective in Replication a. Such mutations are Lethal! b. Conditional lethal c. Temperature sensitive (ts) lethal 2. Method: a. Mutagenize cells b. Plate the cells on agar plates and grow at 30 o C c. Replica plate and grow at 37 o C
7 2 classes of DNA replication mutants identified by Francis Jacob et al 1. Quick-stop mutants: major class Stop replication immediately upon increase in temperature. Defect in elongation enzymes, enzyme that makes precursors 2. Slow-stop mutants: small class Complete current round of replication but cannot start next one > Replication initiation defect
8 In vitro complementation: A technique used to identify the mutants in DNA Replication (dna mutants) Make extract from dna mutant grown at restrictive temperature and complement with wt components to identify dna defect ts mutant WT (fraction X) DNA DNA synthesis Purify DnaX component from fraction X 37C
9 Priming of DNA replication Examples: Replication Rolling circle Replication Protein A nicks X174 viral strand at ori
10 DNA primase Primase is a special RNA polymerase that makes RNA primer on a ssdna template Unlike DNA Polymerase, primase can start synthesis de novo Makes an RNA primer of 4-12 nucleotides Different from other RNA polymerase: no sequence specificity How is it regulated? Activated only when bound by DNA replication proteins like helicases PRIMOSOME: complex formed between primase and helicase DnaG is primase in E. coli; it associates with RF proteins at oric Primase is not rifampicin sensitive while RNA pol is sensitive EXCEPTION: M13 phage uses bacterial RNA pol for primer synthesis Yeast: PRI1 and PRI2 Humans: primase (PRIM1, 2) Primase also acts as a halting mechanism to prevent the leading strand from outpacing the lagging strand by halting the progression of the replication fork. LEADING STRAND synthesis needs only 1 RNA primer LAGGING STRAND requires multiple ( ) RNA primers
11 DNA Primer synthesis On Lagging strand
12 DNA Replication at the leading strand Lagging strand
13 DNA Helicase (essential for cell survival) separates or unwinds DNA strands in a double-helix using ATP hydrolysis (1 ATP/bp unwound); thus an ATPase Thus creates ssdna templates for replication Functions as a hexamer Forms a ring and translocates along ssdna Unidirectional (5 to 3 ) Acts processively: helicase remains bound to substrate for long time DnaB is helicase in E. coli (12 helicases in all): identified as quick stop mutant Yeast and humans: Mcm complex (2-7)
14 Structure of a DNA Helicase DNA replication fork and helicase to scale. (C) Detailed structure of the bacteriophage T7 replicative helicase,
15 DNA Helicase Assay
16 SSB: Single Strand DNA-binding Proteins, also called helix destabilizing proteins
17 SSB (essential gene) Binds and maintains templates in single-stranded state Binds ssdna as tetramer Sequence-independent binding Co-operative binding: binding of 1 SSB to DNA promotes binding of another SSB by inter-ssb interaction; ensures rapid coating of ssdna SSB binding makes ssdna into an extended conformation which inhibits formation of hydrogen bonds Types: SSB in E. coli Yeast and humans: RPA (Replication Protein A); heterotrimeric protein
18 Structure of human SSB Proteins bound to DNA DNA
19 Topoisomerases DNA unwinding by helicase creates positive supercoils ahead of Replication forks The supercoiling ahead of the fork needs to be relieved or tension would build up (like coiling as spring) and block fork progression.
20
21
22 Supercoiling is relieved by the action of Topoisomerases. Type I topoisomerases: no ATP required Make nicks in one DNA strands Can relieve supercoiling Type II topoisomersases: ATP-dependent reaction Make nicks in both DNA strands (double strand break) Can relieve supercoiling and untangle linked DNA helices Both types of enzyme form covalent intermediates with the DNA E. coli: Gyrase (TopoII-like enzyme), TopoI Eukaryotes: both I and II function in replication
23 DNA topoisomerase I
24 DNA topoisomerase II
25 RNAseH: A special DNA repair enzyme that recognizes an RNA strand in an RNA/DNA hybrid and degrades it; thus removes RNA primers; this leaves gaps that are filled in by DNA polymerase Nicks in phosphate backbone are sealed by DNA ligase. RNAseH from E.coli
26 DNA Ligase: Uses ATP energy to make phosphodiester bond 2-step reaction: 1. ligase-amp complex forms 2. AMP complex attaches to 5 phosphate at the nick then a phosphodiester bond is formed with the 3'-OH terminus of the nick, thus releasing AMP and enzyme.
27 Mammalian replication Fork (eucaryote, DNA polymerase (primase) a synthesize RNA/DNA, DNA polymerase delta is the real polymerase)
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 11 DNA Replication
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
The replication forks Summarising what we know:
 When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Enzymes used in DNA Replication
 Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
The flow of Genetic information
 The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
Replication. Obaidur Rahman
 Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. January 25, 2006
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI REPLICATION - ENZYMES.
 ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 28, 2004
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
Fidelity of DNA polymerase
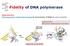 Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
Welcome to Class 18! Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives. Replication is semiconservative! Replication: DNA DNA! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
The Size and Packaging of Genomes
 DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA: Structure & Replication
 DNA Form & Function DNA: Structure & Replication Understanding DNA replication and the resulting transmission of genetic information from cell to cell, and generation to generation lays the groundwork
DNA Form & Function DNA: Structure & Replication Understanding DNA replication and the resulting transmission of genetic information from cell to cell, and generation to generation lays the groundwork
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 26, 2005
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Overall mechanism 2. Roles of Polymerases & other proteins 3. More mechanism: Initiation and Termination 4. Mitochondrial DNA replication DNA replication
Chapter Twelve: DNA Replication and Recombination
 This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
DNA REPLICATION. Third Stage. Lec. 12 DNA Replication. Lecture No.: 12. A. Watson & Crick (1952) C. Cairns (1963) autoradiographic experiment
 Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule.
 1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
Nucleic Acid Structure:
 Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
Molecular Biology (2)
 Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
Proposed Models of DNA Replication. Conservative Model. Semi-Conservative Model. Dispersive model
 5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
Covalently bonded sugar-phosphate backbone with relatively strong bonds keeps the nucleotides in the backbone connected in the correct sequence.
 Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
CSIR UGC NET, GATE (ENGINEERING), GATE (Science), IIT-JAM, UGC NET, TIFR, IISc, NIMCET, JEST etc. JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY
 JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY REPLICATION TYPE OF DNA REPLICATION REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES REPLICATION IN EUKARYOTES For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary Road,
JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY REPLICATION TYPE OF DNA REPLICATION REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES REPLICATION IN EUKARYOTES For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary Road,
Requirements for the Genetic Material
 Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
CH 4 - DNA. DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells
 CH 4 - DNA DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid» its structure was determined in the 1950 s (not too long ago).» scientists were already investigating
CH 4 - DNA DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid» its structure was determined in the 1950 s (not too long ago).» scientists were already investigating
DNA Replication and Repair
 DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DNA Metabolism. I. DNA Replication. A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding
 DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 24, 2005
 DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March :24 pm
 Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
Chapter 12. DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 12 DNA Replication and Recombination I. DNA replication Three possible modes of replication A. Conservative entire original molecule maintained B. Semiconservative one strand is template for new
Chapter 12 DNA Replication and Recombination I. DNA replication Three possible modes of replication A. Conservative entire original molecule maintained B. Semiconservative one strand is template for new
Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis is the key to expression of biological information - Structural Protein: bones, cartilage - Contractile Proteins: myosin, actin - Enzymes - Transport
Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis is the key to expression of biological information - Structural Protein: bones, cartilage - Contractile Proteins: myosin, actin - Enzymes - Transport
Zoo-342 Molecular biology Lecture 2. DNA replication
 Zoo-342 Molecular biology Lecture 2 DNA replication DNA replication DNA replication is the process in which one doubled-stranded DNA molecule is used to create two double-stranded molecules with identical
Zoo-342 Molecular biology Lecture 2 DNA replication DNA replication DNA replication is the process in which one doubled-stranded DNA molecule is used to create two double-stranded molecules with identical
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
DNA Structure. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES
 MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 28 II 32 III 32 IV 30 V 28 150 PLEASE WRITE your NAME or SID number on each page. This exam must be written
MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 28 II 32 III 32 IV 30 V 28 150 PLEASE WRITE your NAME or SID number on each page. This exam must be written
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
DNA replication. - proteins for initiation of replication; - proteins for polymerization of nucleotides.
 DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
Chapter 9. Topics - Genetics - Flow of Genetics - Regulation - Mutation - Recombination
 Chapter 9 Topics - Genetics - Flow of Genetics - Regulation - Mutation - Recombination 1 Genetics Genome Chromosome Gene Protein Genotype Phenotype 2 Terms and concepts gene Fundamental unit of heredity
Chapter 9 Topics - Genetics - Flow of Genetics - Regulation - Mutation - Recombination 1 Genetics Genome Chromosome Gene Protein Genotype Phenotype 2 Terms and concepts gene Fundamental unit of heredity
Genetic material must be able to:
 Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function. Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function Gary Peter Learning Objectives 1. List and explain the mechanisms by which E. coli DNA is replicated 2. Describe
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function Gary Peter Learning Objectives 1. List and explain the mechanisms by which E. coli DNA is replicated 2. Describe
Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam
 Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam Chapter 9 Replication of DNA Question 1. Name the two substrates for DNA synthesis. Explain why each is necessary for DNA synthesis.
Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam Chapter 9 Replication of DNA Question 1. Name the two substrates for DNA synthesis. Explain why each is necessary for DNA synthesis.
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
BS GENOMES. DNA replication and repair
 BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides
 Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11
 Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Replication of DNA Virus Genomes. Lecture 7 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2013
 Replication of DNA Virus Genomes Lecture 7 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2013 It s all about Initiation Problems faced by DNA replication machinery Viruses must replicate their genomes to make new progeny
Replication of DNA Virus Genomes Lecture 7 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2013 It s all about Initiation Problems faced by DNA replication machinery Viruses must replicate their genomes to make new progeny
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.8 DNA REPLICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number:
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 35 II 29 III 30 IV 32 V 24 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 35 II 29 III 30 IV 32 V 24 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
You Should Be Able To
 DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION
 DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
Hershey & Chase Avery, MacLeod, & McCarty DNA: The Genetic Material
 DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
Bacterial DNA replication
 Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR
 DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
DNA. Chapter 1. Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals, Methods and Clinical Applications Second Edition 1/29/2013. Copyright 2012 F.A.
 DNA Chapter 1 1 Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a genetic information storage system. A T G C T A C G DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. Nucleotides are phosphorylated nucleosides. DNA Nucleosides comprise
DNA Chapter 1 1 Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a genetic information storage system. A T G C T A C G DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. Nucleotides are phosphorylated nucleosides. DNA Nucleosides comprise
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis
 Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
DNA Replication. Rasime Kalkan,PhD.
 DNA Replication Rasime Kalkan,PhD. DNA Replication The process of copying one DNA molecule into two identical molecules is called DNA replication. DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied
DNA Replication Rasime Kalkan,PhD. DNA Replication The process of copying one DNA molecule into two identical molecules is called DNA replication. DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 The Genetic Material Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 The Genetic Material Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE
 STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
SCBC203 Cell Division & DNA Synthesis. Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318
 SCBC203 Cell Division & DNA Synthesis Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives 1. Explain the biological roles & significance
SCBC203 Cell Division & DNA Synthesis Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives 1. Explain the biological roles & significance
DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Double helix structure of DNA
 Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
IDTutorial: DNA Replication
 IDTutorial: DNA Replication Introduction In their report announcing the structure of the DNA molecule, Watson and Crick (Nature, 171: 737-738, 1953) observe, It has not escaped our notice that the specific
IDTutorial: DNA Replication Introduction In their report announcing the structure of the DNA molecule, Watson and Crick (Nature, 171: 737-738, 1953) observe, It has not escaped our notice that the specific
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material. The Nature of Genetic Material. Chemical Nature of Nucleic Acids. Chromosomes - DNA and protein
 Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
Replication of DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 9. Replication of DNA and Chromosomes 1. Semiconservative Replication 2. DNA Polymerases and DNA Synthesis In Vitro 3. The Complex Replication Apparatus 4. Unique Aspects of Eukaryotic Chromosome
Chapter 9. Replication of DNA and Chromosomes 1. Semiconservative Replication 2. DNA Polymerases and DNA Synthesis In Vitro 3. The Complex Replication Apparatus 4. Unique Aspects of Eukaryotic Chromosome
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
DNA Model Building and Replica3on
 DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Principle 2. Overview of Central. 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of
 Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of. Chapter 16. Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme
 Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
DNA and Replication 1
 DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
Please write your name or student ID number on every page.
 MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 36 II 35 III 27 IV 28 V 24 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 36 II 35 III 27 IV 28 V 24 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions!
 Page 1 of 5 Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions! 1. A mutation in which parts of two nonhomologous chromosomes change places is called a(n) A. translocation. B. transition.
Page 1 of 5 Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions! 1. A mutation in which parts of two nonhomologous chromosomes change places is called a(n) A. translocation. B. transition.
Wednesday, April 9 th. DNA The Genetic Material Replication. Chapter 16
 Wednesday, April 9 th DNA The Genetic Material Replication Chapter 16 Modified from Kim Foglia Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick
Wednesday, April 9 th DNA The Genetic Material Replication Chapter 16 Modified from Kim Foglia Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick
The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes:
 DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
Tala Saleh. Tamer Barakat ... Anas Abu. Humaidan
 7 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat... Anas Abu. Humaidan Some Information in this lecture may not be mentioned by the Dr. as thoroughly as this sheet. But they cannot be overlooked for a better understanding,
7 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat... Anas Abu. Humaidan Some Information in this lecture may not be mentioned by the Dr. as thoroughly as this sheet. But they cannot be overlooked for a better understanding,
