Received 15 December 2003/Accepted 19 April 2004
|
|
|
- Silvia Hall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2004, p Vol. 78, No X/04/$ DOI: /JVI Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Adjuvant Activities of Novel Cytokines, Interleukin-23 (IL-23) and IL-27, for Induction of Hepatitis C Virus-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in HLA-A*0201 Transgenic Mice Masanori Matsui, 1 * Osamu Moriya, 1 Maria Laura Belladonna, 2 Sadahiro Kamiya, 3,4 François A. Lemonnier, 5 Takayuki Yoshimoto, 3 and Toshitaka Akatsuka 1 Department of Microbiology, Saitama Medical School, Saitama, 1 and Intractable Immune System Disease Research Center 3 and Department of Immunology, 4 Tokyo Medical University, Tokyo, Japan; Department of Experimental Medicine, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy 2 ; and Department of AIDS and Retrovirus, Pasteur Institute, Paris, France 5 Received 15 December 2003/Accepted 19 April 2004 Searching the sequence databases has revealed two novel cytokines: interleukin-23 (IL-23) and IL-27. These cytokines are quite similar to, but clearly distinct from IL-12 in their structures and T-cell stimulatory fashions. In contrast to IL-12, however, little is known about the roles of IL-23 and IL-27 in the immune regulation. Previously, we evaluated the prime-boost immunization consisting of priming and the first boosting with the hepatitis C virus (HCV)-core expression plasmid, followed by a second boosting with recombinant adenovirus expressing HCV core for induction of HCV core-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in BALB/c mice. The present study demonstrates that HCV-specific CTL induction was greatly enhanced by coinoculation of an IL-12 expression plasmid in the prime-boost immunization, indicating the potent adjuvant activity of IL-12. We investigated whether similar adjuvant effects could be exerted by either IL-23 or IL-27 in a prime-boost immunization with HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice. Coadministration of either an IL-23 or an IL-27 expression plasmid, as well as an IL-12 expression plasmid, in a prime-boost immunization enhanced induction of HCV-specific CTLs and led to dramatic increases in the numbers of gamma interferon (IFN- )- producing, HCV-specific CD8 cells. Further, preinjections of IL-12, IL-23, or IL-27 expression plasmids before immunization resulted in great increases in the number of IFN- -producing, HCV-specific CD8 cells in response to immunization with recombinant adenovirus. These data revealed that both IL-23 and IL-27, as well as IL-12, are potent adjuvants for epitope-specific CTL induction. The two novel cytokines might offer new prophylactic and therapeutic strategies against infectious pathogens such as HCV. CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) recognize virus-derived peptides in association with major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells and kill the virus-infected target cells. There are a number of evidences showing that CTLs play a central role in the clearance of pathogenic viruses (67). In case of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, vigorous HCV-specific CTL responses existed in the persons resolving acute HCV infection (27). In the experimental model, chimpanzees who cleared HCV generated strong CTL but poor antibody responses, whereas other chimpanzees developing chronic hepatitis generated much weaker CTL response (12). Thus, spontaneous resolution of HCV is likely to be associated with HCV-specific CTLs rather than neutralizing antibodies (12, 18, 27, 58). However, 60% of HCV-infected individuals turn out to have chronic hepatitis (1). Chronic HCV hepatitis eventually progresses to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (53). In the chronic stage, HCVspecific CTLs are detectable in both peripheral blood and liver, but the precursor frequency of HCV-specific CTLs is extremely low (27, 50, 51). Therefore, enhancement of HCVspecific CTL induction in HCV-infected individuals should be considered to be a strategy to clear the virus. * Corresponding author. Mailing address: Department of Microbiology, Saitama Medical School, Moroyama-Cho, Iruma-Gun, Saitama , Japan. Phone: Fax: mmatsui@saitama-med.ac.jp. DNA vaccination has been proven to be a useful strategy for inducing both humoral and cellular immune responses (19). DNA vaccine safely mimics the effect of live, attenuated virusbased vaccine to generate a long-lasting CTL response. However, the efficiency of DNA vaccine is sometimes quite low and, therefore, several modifications have been attempted in recent years (19). Thus far, the most successful protocol of DNA immunization for CTL induction is likely to be a consecutive immunization involving priming with plasmid DNA and boosting with recombinant virus (2, 24, 35, 43, 54). The rationale behind this strategy is that DNA priming elicits low-level but persistent immunity, followed by strong boosting with virus encoding the same recombinant antigen as the DNA encodes. This regimen of the consecutive immunization has been proven to be efficient for CTL induction by many groups (2, 24, 35, 37, 43, 54). Recently, McConkey et al. (37) have shown that the prime-boost immunization induced high frequencies of antigen-specific T-cell responses to malaria antigen and displayed partial protection in humans. Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a heterodimeric proinflammatory cytokine formed by a 35-kDa light chain (p35) and a 40-kDa heavy chain (p40) (57). This cytokine is a dominant factor in the differentiation of T helper type 1 (Th1) cells and plays an essential role in a link between innate and adaptive immunities (60). Recently, two novel polypeptides, p19 (42) and p28 (48), have been identified by searching the databases with a computationally derived profile of IL-6. These factors do not show 9093
2 9094 MATSUI ET AL. J. VIROL. any biological activity by themselves. However, p19 associates with a p40 subunit of IL-12 to form a biologically active, new heterodimeric cytokine, termed IL-23 (42). The IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) is composed of the IL-12R 1 subunit and a novel IL-23R subunit (44). On the other hand, p28 combines with Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3), which is an IL-12 p40-related protein, and shapes a new cytokine named IL-27 (48). It has recently been found that the orphan cytokine receptor WSX-1/TCCR, which is homologous to the IL-12R 2 subunit (48), and gp130 (47) constitute the IL-27R. In addition to the structural similarities, all three cytokines definitely favor the differentiation of Th1 cells. However, these three cytokines act at different stages during the Th1 development (52). Thus, IL-23 and IL-27 are similar to, but clearly distinct from IL-12. Although the effects of IL-12 in the regulation of immune response are well established (60), little is known about the roles of IL-23 and IL-27. We previously evaluated the prime-boost immunization consisting of an HCV core-expression plasmid and a recombinant adenovirus expressing HCV core for the induction of HCV core-specific CTLs in BALB/c mice (35). An IL-12 expression plasmid has been shown to be an effective adjuvant for CTL induction in the conventional DNA vaccine by several groups (25, 41, 49, 56, 61). We showed that coadministration of an IL-12 expression plasmid in a prime-boost immunization could enhance HCV-specific CTL induction (35). In the present study, we tested whether adjuvant effects could be exerted by either an IL-23 or an IL-27 expression plasmid, as well as an IL-12 expression plasmid, in a prime-boost immunization using human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen HLA-A 0201 transgenic mice. To circumvent uneven gene expression of the two subunits (32), genetically linked, single-chain IL-12 (scil- 12), scil-23, and scil-27 were used in the experiments. MATERIALS AND METHODS Mice. The HHD mice express a transgenic HLA-A*0201 monochain, designated HHD, in which human 2 -microglobulin is covalently linked to a chimeric heavy chain composed of HLA-A*0201 ( 1 and 2 domains) and H-2D b ( 3, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains) (46). Because the innate H-2D b and mouse 2 -microglobulin genes have been disrupted by homologous recombination, the only major histocompatibility complex class I molecule on the cell surface, HLA-A*0201, is efficiently utilized by HLA-A*0201-restricted CTLs in HHD mice. Six- to eight-week-old HHD mice were used for all experiments. Mice were housed in appropriate animal care facilities at Saitama Medical School, Saitama, Japan, and handled according to international guidelines for experiments with animals. Cell lines. The HHD gene-transfected mouse lymphoma cell line, RMA-HHD (H-2 b ), was previously described (46). The cell surface expression of the HHD molecule was confirmed by flow cytometry using the anti-hla-a2 monoclonal antibody BB7.2 (45) (data not shown). The adenovirus type 5 DNA-transformed, human kidney cell lines, 293 (16), and its derivative, 293T, were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, Md.). RMA-HHD cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) and 500 g of G418 (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.)/ml. 293 and 293T cells were cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium with 10% FCS. Synthetic peptides. Two HCV core-derived, three HCV NS3-derived, and two HCV NS4-derived, HLA-A*0201-restricted peptides were synthesized by Qiagen (Tokyo, Japan) by using Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethoxy carbonyl) chemistry (Table 1). These peptides were desalted and then analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Plasmid constructs. The cdnas encoding the p40 and p35 chains of mouse IL-12 and the EBI3 and p28 chains of mouse IL-27 were generated by reverse transcriptase PCR from total RNA of concanavalin A-activated mouse spleen cells. DNA constructs for scil-12 and scil-27 were then prepared as described previously (5). In brief, the p40 and p35 subunits of IL-12, or the EBI3 and p28 TABLE 1. HLA-A*0201-associated, HCV-derived CTL epitopes used in this study Name Region Residue Sequence Reference core-35 HCV-core YLLPRRGPRL 4 core-132 HCV-core DLMGYIPLV 4 NS HCV-NS CINGVCWTV 9 NS HCV-NS KLVALGINAV 9 NS HCV-NS YLVAYQATV 65 NS HCV-NS4A VLVGGVLAA 55 NS HCV-NS4B HMWNFISGI 55 subunits of IL-27 were genetically fused with a DNA linker encoding 15 amino acids, (Gly 4 Ser) 3 (5), by PCR amplification (scil-12 sense, 5 -AAGCTTATGT GGGAGCTGGAGAAA-3 ; scil-12 antisense, 5 -CTCGAGTCAGGCGGAG CTCAGATA-3 ; scil-27 sense, 5 -AAGCTTCCTGGTTACACTGAAACA-3 ; and scil-27 antisense, 5 -AGATCTTAGGAATCCCAGGCTGA-3 ). The linker sequences were synthesized as sense and antisense oligonucleotides spanning the sequence as reported by Huston et al. (22). The PCR products were subcloned into the pcr-blunt II-TOPO vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.). After digestion with HindIII and EcoRI for IL-12 or HindIII and BglII for IL-27, the PCR products were cloned into the p3xflag-cmv-9 (p3xflag) (Sigma) expression vector (p3xflag-il-12 and p3xflag-il-27). This vector encodes the preprotrypsin signal peptide and the FLAG epitope tag sequence (DYKDHD GDYKDHDIDYKDDDDK) upstream of the multiple cloning region and, hence, expresses a secreted N-terminal 3 FLAG fusion protein in mammalian cells. The cdna encoding the scil-23 composed of the p40 chain, a (Gly 4 Ser) 3 linker, and the p19 chain, was amplified from the scil-23 immunoglobulin (Ig) fusion protein expression plasmid (5). The following primers were used: sense, 5 -AAGCTTATGTGGGAGCTGGAGAAA-3 ; and antisense, 5 -CTCGAGTC AAGCTGTTGGCACTAA-3. The PCR product was subcloned into the pcr- Blunt II-TOPO vector (Invitrogen). After digestion with HindIII and EcoRI, the scil-23 cdna was cloned into p3xflag (p3xflag-il-23) as well. The nucleotide sequences of the inserts were confirmed by DNA sequencing. The plasmids expressing HCV-NS3 and -NS4 proteins were generated as described before (35, 36). Briefly, the two HCV-derived genes corresponding to amino acid residues 1018 to 1657, including the NS3 region, and amino acid residues 1607 to 1972 including the NS4 region, were amplified by PCR from the HCV cdna clone, pbrtm/hcv1-3011con (26), which was kindly provided by C. M. Rice (Rockefeller University, New York, N.Y.). The primers used here were as follows: NS3 sense, 5 -GCCGGATCCATGGTCTCCAAGGGGTGGA G-3 ; antisense, 5 -TCACGTGACGACCTCCAGGTCGGCC-3 ; NS4 sense, 5 - GTGGGGATCCATGTGGAAGTGTTTGATCC-3 ; and antisense, 5 -TCAGC ATGGAGTGGTACACTCCGAGC-3. The PCR-amplified genes were subcloned into the pcr2.1 vector in the TA cloning kit (Invitrogen), and the nucleotide sequences were verified to be identical to those in pbrtm/hcv1-3011con by DNA sequencing. After digestion with HindIII and NotI for NS3 or with BamHI for NS4, each of the genes was cloned into the multiple cloning site in the eukaryotic expression vector, pcep4 (Invitrogen; pcep4-ns3 and pcep4-ns4, respectively). pcep4 contains the Epstein-Barr virus origin of replication and the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen, permitting high-copy extrachromosomal replication, hygromycin B gene as the selectable marker, and cytomegalovirus promoter for gene expression. The pcep4-core plasmid expressing the HCV core protein was described previously (35). Purification of plasmid DNA for immunization was performed by ultracentrifugation to equilibrium in cesium chloride-ethidium bromide gradients. Detection of scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins. Each of p3xflag, p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, and p3xflag-il-27 plasmids was transiently transfected into 293T cells by using FuGENE 6 (Roche Diagnostics Co., Indianapolis, Ind.). Briefly, in an Eppendorf tube, 1.5 l of FuGENE 6 was diluted in 100 l of serum-free medium, and then 0.5 g of each DNA solution was added into the medium containing FuGENE 6. The mixture was incubated for 15 min at room temperature and then added to T cells in a well of a 12-well plate. After 2 days, the supernatant was collected. Fusion proteins in the supernatants were immunoprecipitated by using the anti-flag M2 monoclonal antibody (Sigma). In brief, 2 g of the M2 antibody was mixed with 20 l of 50% protein G-Sepharose solution (Pharmacia, Piscataway, N.J.) for 1hat4 C and then added into 100 l of each supernatant. After a 2- h incubation at 4 C, the immunoprecipitates were washed twice with 1 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Immunoprecipitated fusion proteins were then released from the protein G by boiling the samples for 3 min in 50 l of digest
3 VOL. 78, 2004 ADJUVANT EFFECTS OF IL-23 AND IL-27 FOR CTL INDUCTION 9095 FIG. 1. Schedule of the prime-boost immunization. HHD mice received the consecutive immunization consisting of priming and the first boosting with DNA followed by the second boosting with adenovirus. DNA, 100 g of either pcep4-core, pcep4-ns3, or pcep4-ns4 together with 10 to 100 g of either p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il- 23, or p3xflag-il-27; Virus, PFU of either Adex1SR3ST or Adex1CA3269. buffer composed of 0.01 M Na 2 HPO 4, 0.03% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and 0.1% Triton X-100. After immunoprecipitation, Western blotting of immunoprecipitated proteins was performed. Briefly, the released fusion proteins were separated by electrophoresis on a SDS 12% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked with PBS containing 5% nonfat milk. The blot was stained with 5 g of the M2 antibody (Sigma)/ml for 1hatroom temperature, followed by secondary staining with peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody. The protein bands were developed by the ECL system (Amersham, Piscataway, N.J.). STAT tyrosine phosphorylation assay. Mouse IL-12R 1 and IL-12R 2 cdnas were previously cloned into an expression vector, pme18s (pme18s- IL-12R 1 and pme18s-il-12r 2) (69). Mouse IL-23R, WSX-1/TCCR, and gp130 cdnas were isolated by reverse transcription-pcr from total RNA of concanavalin A-activated mouse spleen cells and cloned into the expression vector, p3xflag-cmv-14 (Sigma) (p3xflag-il-23r, p3xflag-wsx-1/ TCCR, and p3xflag-gp130). For detection of tyrosine phosphorylation (py) of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) triggered by either IL-12 or IL-23, 293T cells were transiently transfected with either pme18s-il-12r 1 plus pme18s-il-12r 2 or pme18s-il-12r 1 plus p3xflag-il-23r, together with the STAT4 expression vector as described by Visconti et al. (63) by using FuGENE 6 (Roche Diagnostics). For detection of py-stat1 induced by IL-27, 293T cells were transiently transfected with p3xflag-wsx-1/tccr, and p3xflag-gp130 by using FuGENE 6 (Roche Diagnostics). After 36 h, the transfectants were stimulated for 45 min with the culture supernatant of 293T cells transiently transfected with either p3xflag- IL-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27 at various concentrations of 0.5, 5.0, and 50%. The cells were then subjected to Western blotting with anti- STAT1, anti-stat4 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, Calif.), anti-py- STAT1 (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Beverly, Mass.), or anti-py-stat4 (Zymed Laboratories, Inc., South San Francisco, Calif.) antibody. Adenoviruses. The replication-defective recombinant adenoviruses expressing the HCV structural proteins (core, E1, and E2; Adex1SR3ST) and the HCV nonstructural proteins (NS3, NS4, and NS5A; Adex1CA3269) were previously described (33, 62). The wild-type adenovirus lacking the insert (Adex1w) was used as a negative control. Virus was amplified in 293 cells and titers were determined by standard plaque assays on 293 cells. All three adenoviruses were kindly provided by T. Miyamura (National Institute of Health, Tokyo, Japan). Immunization. Mice received the prime-boost immunization as described previously (35). Briefly, mice were intramuscularly immunized twice via the tibialis muscles with 100 g of either pcep4, pcep4-core, pcep4-ns3, or pcep4-ns4, together with either various amounts (10, 30, and 100 g) of p3xflag, p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, p3xflag-il-27, or the mixture of p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27 dissolved in PBS at 1 mg/ml and then immunized intraperitoneally with PFU recombinant adenovirus diluted in PBS at 10 8 PFU/ml (Fig. 1). The immunization interval was 2 weeks. CTL assay. After 2 to 3 weeks after immunization, mice were sacrificed and spleen cells were prepared. Spleen cells were then cultured for 6 to 7 days with equal numbers of irradiated (30 Gy), syngeneic naive spleen cells prepulsed with a10 M concentration of an appropriate peptide and used as effector cells. Cytotoxic activities were measured in standard 51 Cr release assays (34). In brief, 10 6 RMA-HHD cells were pulsed with a 10 M concentration of an appropriate peptide for 1 h,and then labeled with 100 Ci of Na 2 51 CrO 4 for 30 min. After being washed, the labeled target cells were plated in wells of a round-bottom 96-well plate at cells/well with or without effector cells at various effector/target (E:T) ratios. After a 4-h incubation at 37 C, supernatant from each well was harvested, and the radioactivity was counted. The results were calculated as the mean of a triplicate assay. The percent specific lysis was calculated according to the following formula: % specific lysis [(cpm sample cpm spontaneous )/(cpm maximum cpm spontaneous )] 100, where cpm stands for counts per minute. Spontaneous release represents the radioactivity released by target cells in the absence of effectors, and maximum release represents the radioactivity released by target cells lysed with 5% Triton X-100. At least three mice per group were used in each experiment. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. Intracellular IFN- staining. Three to five mice per group were immunized as described above. Spleen cells of immunized mice per group were pooled, and were resuspended in RPMI 1640 with 10% FCS. In each well of a 96-well round-bottom plate, cells were incubated with 1 l of brefeldin A (GolgiPlug, BD Pharmingen, San Diego, Calif.)/ml for 5 h at 37 C in the presence or absence of an antigenic peptide at a final concentration of 10 or 50 M. The cells were then washed once with ice-cold PBS containing 1% FCS and 15 mm sodium azide (fluorescence-activated cell-sorting buffer) and incubated for 10 min at 4 C with the rat anti-mouse CD16/CD32 monoclonal antibody (Fc Block; BD Pharmingen) at a concentration of 1 g/well to block FcR. After incubation, the cell surface was stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated rat anti-mouse CD8 monoclonal antibody (clone ; BD Pharmingen) at a concentration of 0.5 g/well for 30 min at 4 C. For detection of effector and memory CD8 T cells (21, 66), the cell surface was stained with CyChrome-conjugated anti-mouse CD8 monoclonal antibody (clone ), together with either FITC-conjugated rat anti-mouse CD11a antibody (clone 2D7; BD Pharmingen) or FITC-conjugated rat anti-mouse CD62L antibody (clone MEL-14; BD Pharmingen) at a concentration of 0.5 g/well. After two washes with fluorescence-activated cell-sorting buffer, the cells were fixed and permeabilized by using the Cytofix/Cytoperm kit (BD Pharmingen) and stained with phycoerythrin-conjugated rat anti-mouse gamma interferon (IFN- ) monoclonal antibody (clone XMG1.2; BD Pharmingen) to detect intracellular IFN- according to the manufacturer s instructions. Isotype-matched control antibodies were added to control wells to confirm the specificity of the staining. After removal of unbound antibody by a wash with the 1 Perm/Wash solution in the kit, flow cytometric analyses were performed. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. ELISPOT assay for IFN- -secreting cells. Detection of IFN- secreting cells was performed by using a mouse IFN- enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) set (BD Pharmingen). Each well of a sterile 96-well ImmunoSpot ELISPOT plate (BD Pharmingen) was precoated with 0.5 g of unlabeled anti-ifn- capture antibody (clone R4-6A2; BD Pharmingen)/well at 4 C overnight. Plates were washed and then blocked with RPMI 1640 containing 10% FCS for 2hat room temperature. Spleen cells from individual, immunized mice were prepared, and red blood cells were removed by treatment with ammonium chloride. After the blocking solution was discarded, effector spleen cells were added into wells at various cell densities (10 4 to 10 6 cells/well), along with 10 6 gamma-irradiated (30 Gy) syngeneic spleen cells. Cells were incubated with 100 U of human recombinant IL-2 (Cetus Corp., Emeryville, Calif.)/ml in the presence or absence of an appropriate peptide at a final concentration of 10 M at37 C for 2 days. Cells were then removed by five washes with PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20, followed by the addition of biotinylated anti-mouse IFN- detection antibody (clone SMG1.2; BD Pharmingen) at a concentration of 0.5 g/well. After a 2-h incubation at room temperature, the detection antibody was removed by three washes with PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20. Avidin-horseradish peroxidase was added into the wells. After the unbound avidin-hrp was washed, spots were developed by using freshly prepared substrate buffer (0.3 mg of 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole/ml and 0.015% H 2 O 2 in 0.1 M sodium acetate). Statistical analyses. Statistical analyses were performed with the Student t test. A P value of 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Expression and activity of the scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins. Mouse scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 genes were constructed and cloned into the mammalian expression vector. Each of the plasmids, p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27, and the empty vector, p3xflag, was transiently transfected into 293T cells. The proteins secreted into the culture supernatants were immunoprecipitated with the anti-flag monoclonal antibody, M2 (Sigma), since the p3xflag vector produces a secreted N-terminal 3XFLAG fusion protein in
4 9096 MATSUI ET AL. J. VIROL. mammalian cells. The immunoprecipitated fusion proteins were then subjected to Western blot analysis with the M2 antibody. As shown in Fig. 2A, the scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins were clearly detected in the lanes as single polypeptide bands of 76, 74, and 66 kda, respectively. In order to examine whether these cytokine fusion proteins are functional, STAT tyrosine phosphorylation assays were carried out (Fig. 2B to D). As shown in Fig. 2C, STAT4 in 293T cells expressing IL-12R 1 and IL-23R was phosphorylated on tyrosine in response to scil-23 but not by either scil-12 or scil-27. STAT1 in cells expressing WSX-1/TCCR and gp130 was phosphorylated on tyrosine by the addition of scil-27 but not by either scil-12 or scil-23 (Fig. 2D). Further, the scil-12 fusion protein induced STAT4 tyrosine phosphorylation in cells expressing IL-12R 1 and IL-12R 2 (Fig. 2B). Taken together, these data indicate that the scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins are functional. Enhanced induction of HCV-specific CTLs by coadministration of either p3xflag-il-23 or p3xflag-il-27 in the prime-boost immunization. We then tested whether adjuvant effects could be exerted by these cytokine expression plasmids in the prime-boost immunization for induction of HCV-specific CTLs. As shown in Fig. 1, HHD mice received the primeboost immunization consisting of priming and the first boosting with 100 g of either pcep4-core, pcep4-ns3, or pcep4-ns4, together with 100 g of any one of p3xflag, p3xflag- IL-12, p3xflag-il-23, and p3xflag-il-27, followed by the second boosting with either Adex1SR3ST for core-specific CTL induction or Adex1CA3269 for NS3 and NS4-specific CTL induction. Spleen cells were then stimulated in vitro with appropriate peptide-pulsed syngeneic spleen cells. One week later, CTL assays were performed at various E:T ratios. In agreement with the previous results (35), the induction of CTLs specific for various HCV-derived epitopes, including core-132 (Fig. 3A), NS (Fig. 3B), NS (Fig. 3C), and NS (Fig. 3D), was greatly enhanced by coinoculation of p3xflag-il-12 in conjunction with the prime-boost immunization in comparison with coinoculation of the empty vector, p3xflag. It was also found that coadministration of either p3xflag-il-23 or p3xflag-il-27 in the primeboost immunization greatly enhanced induction of CTLs specific for these epitopes (Fig. 3) relative to coinoculation of the empty vector. These results clearly demonstrate that both p3xflag-il-23 and p3xflag-il-27, as well as p3xflag- IL-12, have potent adjuvant activities to induce high levels of HCV-specific CTLs in the prime-boost immunization. Because it has been reported that an inhibitory effect was observed by inoculation with an IL-12 expression plasmid at a dose as high as 200 g (61), we tested the adjuvant activities of p3xflag- IL-12, p3xflag-il-23, and p3xflag-il-27 at lower doses than 100 g. However, significantly greater boosting was not observed at the lower doses (Fig. 4A), indicating that there was no inhibitory effect at a dose of 100 g in our experimental system. Hence, an inoculation dose of 100 g was used in the following experiments. On the other hand, the combination of p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, and p3xflag-il-27 led to a synergistic adjuvant effect in comparison to an equal amount of p3xflag-il-12 (Fig. 4B). Quantification of IFN- -producing cells in response to HCVderived peptides by intracellular IFN- staining and ELISPOT. FIG. 2. Expression and activity of the scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins. (A) p3xflag-il-12 (IL-12), p3xflag-il-23 (IL- 23), p3xflag-il-27 (IL-27), and p3xflag (vector) were transiently transfected into 293T cells. Proteins secreted in the supernatants were immunoprecipitated with the anti-flag antibody. The immunoprecipitated proteins were separated on by SDS 12% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and subjected to Western blotting analysis with the anti-flag antibody. The positions of protein molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown in the figure, and the three arrows indicate the bands of the scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins. (B to D) STAT tyrosine phosphorylation assay. 293T cells were transiently transfected with either pme18s-il-12r 1 plus pme18s-il-12r 1 (B), pme18s-il-12r 1 plus p3xflag-il-23r (C), or p3xflag-wsx-1/tccr plus p3xflag-gp130 (D). After 36 h, the cells were stimulated for 45 min with the culture supernatant containing either scil-12 (IL-12) (B), scil-23 (IL-23) (C), or scil-27 (IL-27) (D) at final concentrations of 0, 0.5, 5, and 50%. As negative controls, the cells were stimulated for 45 min with the culture supernatant containing either scil-23/scil-27 (B), scil-12/scil-27 (C), or scil-12/scil-23 (D) at a final concentration of 50%. The cells were then subjected to Western blotting with anti-stat1 (Total STAT1) (D), anti-stat4 (Total STAT4) (B and C), antipy-stat1 (py-stat1) (D), and anti-py-stat4 (py-stat4) (B and C) antibodies.
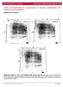
5 VOL. 78, 2004 ADJUVANT EFFECTS OF IL-23 AND IL-27 FOR CTL INDUCTION 9097 FIG. 3. Enhancement of HCV-specific CTL induction by coadministration of either p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27 in the prime-boost immunization. Mice were immunized as follows: priming and the first boosting with 100 g of either pcep4-core (A), pcep4-ns3 (B), or pcep4-ns4 (C and D), together with 100 g of either p3xflag-il-12 (circles), p3xflag-il-23 (triangles), p3xflag- IL-27 (squares), or p3xflag (diamonds), followed by the second boosting with PFU of either Adex1SR3ST (A) or Adex1CA3269 (B to D). The interval between immunizations was 2 weeks. At 2 to 3 weeks after the last immunization, spleen cells were prepared and stimulated in vitro with syngeneic spleen cells pulsed with 10 M concentrations of core-132 (A), NS (B), NS (C), or NS (D). After 1 week, 51 Cr release assays were performed at various E:T ratios with RMA-HHD cells pulsed with (open symbols) or without (solid symbols) 10 M concentrations of core-132 (A), NS (B), NS (C), or NS (D) as targets. The data are representative of one of three independent experiments and are shown as the mean the standard deviation (SD) of triplicate wells. Similar results were obtained in the three independent experiments. To further address the adjuvant activities of p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27, we next examined the numbers of HCVspecific CD8 T cells by staining for antigen-induced intracellular IFN- in spleen cells of HHD mice immunized by the prime-boost immunization in combination with either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27. Since the cells were stimulated in vitro with an appropriate peptide for only 5hin this assay, the possibility of substantial in vitro expansion of responder cells is precluded (8). After the consecutive immunization involving priming and the first boosting with pcep4-core, along with p3xflag, followed by a second boosting with Adex1SR3ST (pcep4-core/p3xflag 2 Adex1SR3ST), 6.5% of the CD8 spleen cells produced IFN- in response to stimulation with core-132 (Fig. 5D), whereas the frequency of IFN- -producing CD8 cells was very low (1.1%) in nonimmunized mice (Fig. 5B). On the other hand, the percentages of IFN- -producing CD8 cells in response to core-132 were 23.9, 18.3, and 20.2% in mice immunized with pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-12 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 5F), pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-23 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 5H), and pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-27 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 5J), respectively. Furthermore, similar patterns were also observed in stimulations with NS As shown in Fig. 5K to T, coinoculation of either p3xflag-il- 12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 in the prime-boost immunization resulted in significant expansions of the IFN- -producing CD8 spleen cells in response to NS Differences in the increase of the HCV-specific CD8 response in Fig. 5 to NS compared to core-132 could be explained by a difference in the immunogenicity between the two epitopes (unpublished data). The IFN- -producing CD8 T cells in response to core-132 were further stained with either anti-cd11a or anti-cd62l antibody. The IFN- -producing CD8 T cells expressed the CD11a high /CD62L low effector phenotype (21, 66) in mice immunized with either pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-12 2 Adex1SR3ST (99.5%/94.4%), pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-23 2 Adex1SR3ST (98.7%/95.5%), or pcep4-core/p3xflag- IL-27 2 Adex1SR3ST (99.0%/93.1%).
6 9098 MATSUI ET AL. J. VIROL. FIG. 4. (A) Dose-response curves for the adjuvant plasmids p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27. Mice were primed and boosted with 100 g of pcep4-core, together with various doses (0, 10, 30, and 100 g) of either p3xflag-il-12 (circles), p3xflag-il-23 (inverted triangles), or p3xflag-il-27 (squares), followed by the second boosting with PFU of Adex1SR3ST. (B) Synergistic effect of the combination of p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27. Mice were primed and boosted with 100 g of pcep4-core, together with 100 g of either p3xflag, p3xflag-il-12 (IL-12), or the combination of p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27 (33 g each) (IL-12/23/27), followed by a second boosting with PFU of Adex1SR3ST. At 2 to 3 weeks after the last immunization of either the experiment A or B, spleen cells were prepared and stimulated in vitro with syngeneic spleen cells pulsed with 10 M concentrations of core-132. After 1 week, 51 Cr release assays were performed at an E:T ratio of 50 with RMA-HHD cells pulsed with (open symbols or bars) or without (solid symbols or bars) 10 M core-132 as targets. The data are shown as the mean the SD of triplicate wells. To confirm the expansions of IFN- -producing cells in response to HCV-derived peptides, the numbers of IFN- -producing cells were determined in ELISPOT assays. As shown in Table 2, coinoculation of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 in the prime-boost immunization augmented the numbers of IFN- -secreting cells in response to any of the HCVderived epitopes tested, including core-35, core-132, NS3-1073, NS3-1406, and NS In support of the data in CTL assays (Fig. 3), these results indicate that coadministration of either p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27 in the prime-boost immunization leads to dramatic expansions of IFN- -producing cells in response to HCV-derived peptides. Taken together, these data have revealed that both IL-23 and IL-27, as well as IL-12, are potent adjuvants for the induction of HCV-specific CTLs. Preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 enhance the efficiency of HCV-specific CTL induction raised by immunization with the recombinant adenovirus. To obtain control data for Fig. 5, we examined the frequencies of CD8 T cells producing antigen-induced intracellular IFN- in spleen cells of mice primed and boosted with the empty vector, pcep4, together with p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag- IL-23, or p3xflag-il-27, followed by a second boosting with Adex1SR3ST. As shown in Fig. 6, the percentages of the IFN- -producing CD8 cells were 7.3, 9.0, and 4.5% in mice immunized with pcep4/p3xflag-il-12 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 6L), pcep4/p3xflag-il-23 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 6N), and pcep4/p3xflag-il-27 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 6P), respectively. These values were much higher than that (1.3%) in mice immunized with pcep4-core/ p3xflag 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 6B), although these values were clearly less than, but comparable to those in mice immunized with pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-12 2 Adex1SR3ST (18.3%) (Fig. 6D), pcep4-core/p3xflag- IL-23 2 Adex1SR3ST (22.3%) (Fig. 6F), and pcep4-core/ p3xflag-il-27 2 Adex1SR3ST (16.4%) (Fig. 6H), respectively. Furthermore, killing response by core-132-specific CTLs was greatly enhanced by double preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 without pcep4-core but with pcep4, followed by immunization with Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 7). These results indicate that preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 enhance the efficiency of HCV-core-specific CTL induction raised by immunization with Adex1SR3ST. To further confirm these results in Fig. 6, we performed similar experiments accompanied with supplementary controls. In accordance with the data in Fig. 6, the frequency of IFN- producing CD8 cells in mice immunized with pcep4-core 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 8D) was higher than that in mice immunized with p3xflag 2 Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 8F) but lower than in mice that received double preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12 (Fig. 8H), -IL-23 (Fig. 8J), or -IL-27 (Fig. 8L) without pcep4, followed by immunization with Adex1SR3ST. In contrast, IFN- -secreting CD8 cells in response to core-132 were not practically detected in mice that received double preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL- 23, or -IL-27, followed by injection of Adex1w (Fig. 8M to R). These data confirm that preinjections of either p3xflag-il- 12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 enhance induction of HCV-specific CTLs raised by immunization with the recombinant adenovirus. In addition, preinjections of p3xflag-il-27 marginally enhanced induction of peptide-specific IFN- -secreting CD8 cells in mice immunized with pcep4-core (Fig. 8V), as well as preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12 or -IL-23 (data not shown).
7 VOL. 78, 2004 ADJUVANT EFFECTS OF IL-23 AND IL-27 FOR CTL INDUCTION 9099 FIG. 5. Intracellular IFN- staining of HCV-specific CD8 cells in spleen cells of mice that received coinoculation of either p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27 in the prime-boost immunization. HHD mice were immunized as follows: priming and first boosting with 100 g of either pcep4-core (C to J) or pcep4-ns3 (M to T), along with 100 g of either p3xflag (C, D, M, and N), p3xflag-il-12 (E, F, O, and P), p3xflag-il-23 (G, H, Q, and R), or p3xflag-il-27 (I, J, S, and T); followed by second boosting with PFU Adex1SR3ST (C to J) or Adex1CA3269 (M to T). Nonimmunized mice (naive) (A, B, K, and L) were used as a negative control. At 2 to 3 weeks after the last immunization, spleen cells were prepared and cultured for 5hinthepresence or absence (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O, Q, and S) of 10 M core-132 (B, D, F, H, and J), or 50 M NS (L, N, P, R, and T). After stimulation, cells were stained for their surface expression of CD8 (x axis) and their intracellular expression of IFN- (y axis). The numbers shown indicate the percentages of CD8 cells that are positive for intracellular IFN-. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. Three to five mice per group were used in each experiment, and the spleen cells of the mice per group were pooled. Taken together, these data also support the idea that the novel cytokines IL-23 and IL-27, as well as IL-12, have potent adjuvant activities for the induction of HCV-specific CTLs. DISCUSSION It was previously demonstrated that p40-deficient mice are more susceptible to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (11) and Cryptococcus neoformans (14) than p35-deficient mice. In addition, p35-deficient mice are quite resistant to Listeria monocytogenes at low doses of infection (7). Because p35-deficient mice do not produce IL-12 but can make IL-23 composed of p40 and p19, these observations suggest that IL-23 plays a crucial role in the clearance of pathogens. Furthermore, mice lacking one subunit of the IL-27 receptor, WSX-1/TCCR, were remarkably susceptible to Leishmania major infection and showed impaired IFN- production early in the infection (68). Thus, these data strongly suggest that both IL-23 and IL-27 are crucial for T-cell-mediated immunity against various infectious agents. In the present study, we have demonstrated that the coadministration of either p3xflag-il-23 or p3xflag-il-27, as well as p3xflag-il-12, in the prime-boost immunization enhanced induction of CTLs specific for various HCV-derived epitopes (Fig. 3) and led to dramatic expansions of IFN- producing cells in response to HCV-derived, CTL epitopes (Fig. 5 and Table 2). We have also shown that preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 resulted in great increases in IFN- -producing, HCV-specific CD8 cells induced by immunization with the recombinant adenovirus. Since p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, and -IL-27 produce high amounts of scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins in mammalian cells, respectively (Fig. 1), all of these data indicate that the secreted scil-23 and scil-27, as well as scil-12
8 9100 MATSUI ET AL. J. VIROL. TABLE 2. Quantitation of IFN- -secreting cells by ELISPOT in spleens of HHD mice immunized by the prime-boost immunization a Expt and immunization b Mean no. of IFN- -secreting cells/10 6 cells SD stimulated with: No peptide core-35 core-132 NS NS NS Expt 1 pcep4-core/p3xflag 2 Adex1SR3ST pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-12 2 Adex1SR3ST * * pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-23 2 Adex1SR3ST * 1, * pcep4-core/p3xflag-il-27 2 Adex1SR3ST ** ** Expt 2 pcep4-ns3/p3xflag 2 Adex1CA pcep4-ns3/p3xflag-il-12 2 Adex1CA * * pcep4-ns3/p3xflag-il-23 2 Adex1CA * * * pcep4-ns3/p3xflag-il-27 2 Adex1CA * * a Spleen cells were prepared from mice immunized by the prime-boost immunization, and the numbers of IFN- -secreting cells in response to the indicated peptides were determined by ELISPOT. Data represent results from individual mice and are shown as the mean of six determinations (n 6). *, P 0.001; **, P 0.005;, P 0.01 compared to the pcep4-core/p3xflag 2 Adex1SR3ST or the pcep4-ns3/p3xflag 2 Adex1CA3269 regime in response to each peptide. b Mice received priming and the first boost with 100 g of either pcep4-core or pcep4-ns3, along with 100 g of either p3xflag, p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27, followed by a second boost with PFU of recombinant adenovirus (Adex1SR3ST or Adex1CA3269). are potent adjuvants for the induction of HCV-specific CTLs. Each of the single-chain cytokines is composed of two appropriate subunits connected by a flexible 15-amino-acid linker. Using the same (5) or a similar (31) peptide linker, the previously described scil-12 and scil-23 fusion proteins showed comparable biological activity to those of the native heterodimeric IL-12 and IL-23, respectively. Furthermore, we have shown that the scil-12, scil-23, and scil-27 fusion proteins could induce tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT via IL-12R 1/ IL-12R 2, IL-12R 1/IL-23R, and WSX-1/gp130, respectively (Fig. 2B to D). Taken together, the current data have revealed that two novel cytokines, IL-23 and IL-27, possess potent ad- FIG. 6. Intracellular IFN- staining of HCV core-specific CD8 cells in spleen cells of mice that received preinjections with either p3xflag- IL-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27, followed by immunization with Adex1SR3ST. HHD mice were primed and boosted with 100 g of either pcep4-core (A to H) or pcep4 (K to P), together with 100 g of either p3xflag (A and B), p3xflag-il-12 (C, D, K, and L), p3xflag-il-23 (E, F, M, and N), or p3xflag-il-27 (G, H, O, and P), followed by the second boosting with PFU Adex1SR3ST (A to H and K to P). At 2 to 3 weeks after the last immunization, spleen cells were prepared and cultured for 5hinthepresence (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, and P) or absence (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, and O) of 10 M core-132. After stimulation, cells were stained for their surface expression of CD8 (x axis) and their intracellular expression of IFN- (y axis). The numbers shown indicate the percentages of CD8 cells that are positive for intracellular IFN-. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. We analyzed all data of the three experiments and concluded that the difference between panel B and either panel L (P 0.005), N (P 0.038), or P (P 0.003) was statistically significant as determined by applying the Student t test. At least three mice per group were used in each experiment, and spleen cells of mice per group were pooled.
9 VOL. 78, 2004 ADJUVANT EFFECTS OF IL-23 AND IL-27 FOR CTL INDUCTION 9101 FIG. 7. Enhancement of CTL induction specific for HCV-core by preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27, followed by immunization with Adex1SR3ST. Mice were preinjected twice with either p3xflag-il-12 (circles), p3xflag-il-23 (inverted triangles), or p3xflag-il-27 (squares), along with pcep4, followed by immunization with Adex1SR3ST. As a control, mice were primed and boosted with pcep4-core, together with p3xflag, followed by second boosting with Adex1SR3ST (diamonds). The injection doses were 100 g of plasmid DNA and PFU of virus, and the interval between immunizations was 2 weeks. After the last immunization, spleen cells were prepared and stimulated in vitro with syngeneic spleen cells pulsed with 10 M core-132. After 1 week, 51 Cr release assays were performed at various E:T ratios with RMA-HHD cells pulsed with (open symbols) or without (solid symbols) 10 M core-132 as targets. The data are representative of one of three independent experiments and are shown as the mean the SD of triplicate wells. Similar results were obtained in the three independent experiments. juvant activities for induction of antigen-specific CTLs, as well as IL-12. As far as we know, this is the first report of the adjuvant effect of IL-27 on epitope-specific CTL induction and the second one, following the study described by Lo et al. (31), for IL-23. The present data, however, do not show whether these cytokines act directly on CTL or not. In some sense, it is easily predictable that IL-23 and IL-27 possess adjuvant activities for CTL induction because they are in many aspects closely related to IL-12. IL-12 has been shown to be a potent adjuvant for CTL induction by a number of groups including us (6, 20, 25, 35, 38, 41, 49, 56, 59, 61). First, all three cytokines are heterodimers that consist of related subunits (42, 48). Second, the subunits of their receptors are also closely related (42, 48). In addition to the structural similarity, they display biological homology. All three cytokines are dominant factors in the development of the Th1 phenotype and do not support the Th2 development (52, 60). However, they act on T cells at different stages during the development of Th1-mediated immune response. The activities of IL-23 are preferentially restricted to memory CD4 T cells, whereas IL-12 mainly acts on naive CD4 T cells. In contrast, IL-27 does not affect memory CD4 T cells at all but acts on naive CD4 T cells at an earlier stage than does IL-12 (52, 60). In addition, it is known that IL-27 synergizes with IL-12 to produce IFN- in naive T cells (48). Accordingly, it is likely that mechanisms of the enhancement in HCV-specific CTL induction are different between the three cytokines and, therefore, the combined and sequential use of the three cytokines should be more effective for antigen-specific CTL induction than the single use. Actually, it was reported that the combined exposure of IL-12 and IL-23 resulted in additive effects on cytokine production from dendritic cells (5). We also showed that the combination of p3xflag-il-12, p3xflag-il-23, and p3xflag-il-27 led to a synergistic adjuvant effect for induction of HCV-specific CTLs (Fig. 4B). It is surprising that double preinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 have potent adjuvant effects on the induction of HCV-specific CTLs raised by immunization with Adex1SR3ST (Fig. 6 to 8), although the increases in HCV-specific CD8 cells in this case were substantially less than in mice that received coinjections of either p3xflag-il-12, -IL-23, or -IL-27 in conjunction with the prime-boost immunization (Fig. 6). It is possible to explain that the persistently secreted, single-chain cytokine was sufficiently left in mice and enhanced the cell-mediated immunity elicited by the recombinant adenovirus. In contrast, double preinjections of a different IL-12 expression plasmid, named pcaggs-il-12, did not significantly enhance HCV-specific CTL induction raised by immunization with Adex1SR3ST, although coinjections of pcaggs-il-12 in the prime-boost immunization did lead to dramatic enhancement of HCV-specific CTL induction (35). In pcaggs- IL-12, the gene named IRES (for internal ribosome entry site) of the encephalomyocarditis virus exists between p35 and p40 cdnas and allows the two subunits to coexpress in cells (35, 40). The genetically linked scil-12 is presumably more stable than the natively associated, heterodimeric IL-12 produced by pcaggs-il-12. In addition, the monomeric nature of the single-chain fusion protein ensures equimolar expression of each subunit, thereby avoiding the formation of inhibitory p40 dimers (32). These differences might be able to explain the discrepancy of the opposite results. If this is the case, an artificial single-chain forms of IL-12, IL-23, or IL-27 might be more suitable as an adjuvant than a native form. On the other hand, negative effects of these cytokines should be considered. Actually, the first clinical trial of IL-12 resulted in the death of 2 persons and caused severe toxic effects in 15 others (23, 28). It is noteworthy that artificial mutant IL-12 reduced toxicity without reducing the adjuvant activity (20). IL-12 has also been considered to be related to several autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (15). Many data on a major role for IL-12 in multiple sclerosis have been obtained from rodent studies of the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. However, most of the experiments were performed primarily through the use of neutralizing antibodies against p40 that affect both IL-12 and IL-23 (10, 29, 30). Recently, Cua et al. (13) compared the susceptibility of mice
10 9102 MATSUI ET AL. J. VIROL. FIG. 8. Intracellular IFN- staining of HCV core-specific CD8 cells in spleen cells of mice that received preinjections with either p3xflag- IL-12, p3xflag-il-23, or p3xflag-il-27, followed by immunization with either recombinant adenovirus or plasmid DNA. HHD mice were injected with various combinations of 100 g of plasmid DNA and/or PFU of recombinant adenovirus as follows: priming and the first boosting with pcep4-core, followed by the second boosting with Adex1SR3ST (C and D); preinjections twice with either p3xflag (E, F, S, and T), p3xflag-il-12 (G, H, M, and N), p3xflag-il-23 (I, J, O, and P), or p3xflag-il-27 (K, L, Q, R, and U-X), followed by immunization with Adex1SR3ST (C-L), Adex1w (M-R), pcep4-core (S-V), or pcep4 (W and X). At 2 to 3 weeks after the last immunization, spleen cells were prepared and cultured for 5hinthepresence (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, P, R, T, V, and X) or absence (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O, Q, S, U, and W) of 10 M core-132. After in vitro stimulation, the cells were stained for their surface expression of CD8 (x axis) and their intracellular expression of IFN- (y axis). The numbers shown indicate the percentages of CD8 cells that are positive for intracellular IFN-. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. We analyzed all data of the three experiments and concluded that the difference between panel D and either panel H (P 0.002), J (P 0.015), or L (P 0.001) was statistically significant as determined from the Student t test. At least three mice per group were used in each experiment, and spleen cells of mice per group were pooled. lacking either IL-12 alone (p35 deficient), IL-23 alone (p19 deficient), or both cytokines (p40 deficient) to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and showed that IL-23 rather than IL-12 is the crucial factor for the disease. Although no side effects of IL-27 have been reported, too much activation by IL-27 might cause toxicity and/or autoimmunity. In the chronic HCV infection, the precursor frequency of HCV-specific CTLs is quite low (27, 50, 51). Therefore, people believe that this is one of the major reasons why HCV-specific CTLs cannot clear the virus in the chronic stage. In addition to the quantitative aspect, several groups have suggested that the impaired T-cell-mediated immune response may establish chronicity in HCV infection. In fact, it has been reported that HCV-specific CD8 T cells in the chronic HCV infection show less proliferation after antigen stimulation, less production of IFN- and TNF-, and less HCV-specific cytotoxicity (17, 64). Further, Bain et al. (3) demonstrated the impaired stimulatory function of dendritic cells in chronic HCV infections. The mechanisms of the dysfunctional immune response are still unclear (39, 57). However, supplementation of the vaccine
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3554
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: Generation, purification and characterization of recombinant mouse IL-35 (ril-35). High-Five insect cells expressing high levels of the bicistronic
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: Generation, purification and characterization of recombinant mouse IL-35 (ril-35). High-Five insect cells expressing high levels of the bicistronic
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology
 CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology
 CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
Solutions for Your Research
 Solutions for Your Research Custom Antibody Services Polyclonal Monoclonal The service we offer is very complete starting from rabbits, mice and rats. The different formats provided by Primm depend on
Solutions for Your Research Custom Antibody Services Polyclonal Monoclonal The service we offer is very complete starting from rabbits, mice and rats. The different formats provided by Primm depend on
Recombinant DNA Technology. The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology. yeast. Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology.
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
Quality Control Assays
 QUALITY CONTROL An integral part of the Penn Vector Core is its robust quality control program which is carried out by a separate quality control group. Quality control assays have been developed and optimized
QUALITY CONTROL An integral part of the Penn Vector Core is its robust quality control program which is carried out by a separate quality control group. Quality control assays have been developed and optimized
Short- and Long-Term Immune Responses of CD-1 Outbred Mice to the Scrub Typhus DNA Vaccine Candidate: p47kp
 Short- and Long-Term Immune Responses of CD-1 Outbred Mice to the Scrub Typhus DNA Vaccine Candidate: p47kp GUANG XU, a SUCHISMITA CHATTOPADHYAY, a JU JIANG, a TEIK-CHYE CHAN, a CHIEN-CHUNG CHAO, a WEI-MEI
Short- and Long-Term Immune Responses of CD-1 Outbred Mice to the Scrub Typhus DNA Vaccine Candidate: p47kp GUANG XU, a SUCHISMITA CHATTOPADHYAY, a JU JIANG, a TEIK-CHYE CHAN, a CHIEN-CHUNG CHAO, a WEI-MEI
isolated from ctr and pictreated mice. Activation of effector CD4 +
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bystander inflammation conditioned T reg cells have normal functional suppressive activity and ex vivo phenotype. WT Balb/c mice were treated with polyi:c (pic) or PBS (ctr) via
Supplementary Figure 1 Bystander inflammation conditioned T reg cells have normal functional suppressive activity and ex vivo phenotype. WT Balb/c mice were treated with polyi:c (pic) or PBS (ctr) via
Mouse CD30L ELISA Kit
 Product Information Sheet Catalog No. BO0150 Size 96T Range 15.6pg/ml-1000pg/ml Sensitivity < 1pg/ml Specificity No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. Storage Store at 4 for frequent
Product Information Sheet Catalog No. BO0150 Size 96T Range 15.6pg/ml-1000pg/ml Sensitivity < 1pg/ml Specificity No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. Storage Store at 4 for frequent
LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS.
 Supplemental Data: LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS. Scott Jepson, Bryan Vought, Christian H.
Supplemental Data: LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS. Scott Jepson, Bryan Vought, Christian H.
NS5 MTases. Recombinant wild type and mutant E218A MTase domain of WNV NS5
 doi:10.1038/nature09489 Supplementary Figure 1. Methylation pattern of wild type and mutant WNV NS5 MTases. Recombinant wild type and mutant E218A MTase domain of WNV NS5 (N-terminal 300 amino acids) were
doi:10.1038/nature09489 Supplementary Figure 1. Methylation pattern of wild type and mutant WNV NS5 MTases. Recombinant wild type and mutant E218A MTase domain of WNV NS5 (N-terminal 300 amino acids) were
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tal et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807694106 SI Materials and Methods VSV Infection and Quantification. Infection was carried out by seeding 5 10 5 MEF cells per well in a 6-well plate and
Supporting Information Tal et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807694106 SI Materials and Methods VSV Infection and Quantification. Infection was carried out by seeding 5 10 5 MEF cells per well in a 6-well plate and
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC.
 TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
INVESTIGATION OF THE BINDING SPECIFICITY OF IGF-IR USING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
 INVESTIGATION OF THE BINDING SPECIFICITY OF IGF-IR USING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES By Mehrnaz Keyhanfar, Pharm.D. A thesis submitted to the University of Adelaide, South Australia in fulfilment of the requirements
INVESTIGATION OF THE BINDING SPECIFICITY OF IGF-IR USING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES By Mehrnaz Keyhanfar, Pharm.D. A thesis submitted to the University of Adelaide, South Australia in fulfilment of the requirements
Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing. 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology
 Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Immunization Chapter Reading pp. 505-511 What is Immunization? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Immunization Chapter Reading pp. 505-511 What is Immunization? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
1. Immunization. What is Immunization? 12/9/2016. Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing. 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology
 Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Immunization Chapter Reading pp. 505-511 What is Immunization? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Immunization Chapter Reading pp. 505-511 What is Immunization? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Examination in Immunotechnology, 30 May 2011, 8-13
 Examination in Immunotechnology, 30 May 2011, 8-13 1 Each question can give 5p, with a total of 10 questions (i.e. 50 points in total). 2 Write name and personal number on ALL pages (including the cover).
Examination in Immunotechnology, 30 May 2011, 8-13 1 Each question can give 5p, with a total of 10 questions (i.e. 50 points in total). 2 Write name and personal number on ALL pages (including the cover).
Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: sales@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit Catalog No GWB-ZZD063 Size
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: sales@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit Catalog No GWB-ZZD063 Size
Human IL10RB ELISA Pair Set ( CRFB4 )
 Human IL10RB ELISA Pair Set ( CRFB4 ) Catalog Number : SEK10945 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the
Human IL10RB ELISA Pair Set ( CRFB4 ) Catalog Number : SEK10945 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the
(Supplementary Methods online)
 (Supplementary Methods online) Production and purification of either LC-antisense or control molecules Recombinant phagemids and the phagemid vector were transformed into XL-1 Blue competent bacterial
(Supplementary Methods online) Production and purification of either LC-antisense or control molecules Recombinant phagemids and the phagemid vector were transformed into XL-1 Blue competent bacterial
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
BD IMag. Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM. Technical Data Sheet. Product Information
 Technical Data Sheet Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM Product Information Material Number: Size: Storage Buffer: 557812 5 ml Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Description
Technical Data Sheet Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM Product Information Material Number: Size: Storage Buffer: 557812 5 ml Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Description
Supporting Information for. Bongseo Choi, 1, Hyojin Moon, 1, Sung Joon Hong, 1 Changsik Shin, 1 Yoonkyung Do, 1 Seongho Ryu, 2,* Sebyung Kang 1,*
 Supporting Information for Effective Delivery of Antigen-Encapsulin Nanoparticle Fusions to Dendritic Cells Leads to Antigen-Specific Cytotoxic T Cell Activation and Tumor Rejection Bongseo Choi, 1, Hyojin
Supporting Information for Effective Delivery of Antigen-Encapsulin Nanoparticle Fusions to Dendritic Cells Leads to Antigen-Specific Cytotoxic T Cell Activation and Tumor Rejection Bongseo Choi, 1, Hyojin
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4086
 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3
Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3 p815 p815-hcd2 Ag (-) anti-cd3
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells
 Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Siglec-7 Engagement by GBS -protein Suppresses Pyroptotic Cell Death of Natural Killer Cells Jerry J. Fong a,b, Chih-Ming Tsai a,b, Sudeshna Saha a,b, Victor Nizet a,c,d Ajit
Supplementary Information for Siglec-7 Engagement by GBS -protein Suppresses Pyroptotic Cell Death of Natural Killer Cells Jerry J. Fong a,b, Chih-Ming Tsai a,b, Sudeshna Saha a,b, Victor Nizet a,c,d Ajit
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS NOTE FOR GUIDANCE 1 : DNA VACCINES NON-AMPLIFIABLE IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS FOR VETERINARY USE
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Veterinary Use CVMP/IWP/07/98-FINAL COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS NOTE FOR GUIDANCE 1 : DNA VACCINES
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Veterinary Use CVMP/IWP/07/98-FINAL COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS NOTE FOR GUIDANCE 1 : DNA VACCINES
Find 1 cell in 100,000 with ELISpot
 Find 1 cell in 100,000 with ELISpot ELISpot is a sensitive assay used to quantify cytokine- or immunoglobulin-secreting cells at the single-cell level. ELISpot has been widely applied to investigate specific
Find 1 cell in 100,000 with ELISpot ELISpot is a sensitive assay used to quantify cytokine- or immunoglobulin-secreting cells at the single-cell level. ELISpot has been widely applied to investigate specific
Human IL-6 ELISA. For the quantitative determination of IL-6 in human cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA, citrate)
 K-ASSAY Human IL-6 ELISA For the quantitative determination of IL-6 in human cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA, citrate) Cat. No. KT-1348 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic
K-ASSAY Human IL-6 ELISA For the quantitative determination of IL-6 in human cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA, citrate) Cat. No. KT-1348 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic
Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of
 Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB525334 effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of different concentrations of SB525334. Cells were lysed and
Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB525334 effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of different concentrations of SB525334. Cells were lysed and
Gα i Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
Human ICAM-2 ELISA Kit
 OriGene Technologies, Inc 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: Human ICAM-2 ELISA Kit Catalog No. EA100643
OriGene Technologies, Inc 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: Human ICAM-2 ELISA Kit Catalog No. EA100643
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1302 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1302 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Anti-HB-EGF (Human) mab
 Page 1 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. CODE No. D308-3 Anti-HB-EGF (Human) mab CLONALITY CLONE ISOTYPE QUANTITY SOURCE IMMUNOGEN FORMURATION STORAGE Monoclonal 3H4 Mouse IgG1
Page 1 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. CODE No. D308-3 Anti-HB-EGF (Human) mab CLONALITY CLONE ISOTYPE QUANTITY SOURCE IMMUNOGEN FORMURATION STORAGE Monoclonal 3H4 Mouse IgG1
ReliaBLOT TM. IP/Western Blot Reagents Cat. No. WB120, rabbit
 ReliaBLOT TM Introduction: IP/Western Blot Reagents Cat. No. WB120, rabbit ReliaBLOT TM IP/Western Blot Reagents and Procedures (patent pending) provide an improved method for the detection of immunoprecipitated
ReliaBLOT TM Introduction: IP/Western Blot Reagents Cat. No. WB120, rabbit ReliaBLOT TM IP/Western Blot Reagents and Procedures (patent pending) provide an improved method for the detection of immunoprecipitated
Discovery and Humanization of Novel High Affinity Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies to Human IL-17A
 Discovery and Humanization of Novel High Affinity Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies to Human IL-17A Contacts: Marty Simonetti martysimonetti@gmail.com Kirby Alton kirby.alton@abeomecorp.com Rick Shimkets
Discovery and Humanization of Novel High Affinity Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies to Human IL-17A Contacts: Marty Simonetti martysimonetti@gmail.com Kirby Alton kirby.alton@abeomecorp.com Rick Shimkets
In general, 8- to 10-week-old adult females were ovariectomized and rested for 10 days
 Animal injections and tissue processing In general, 8- to 10-week-old adult females were ovariectomized and rested for 10 days before they received any injections. Mice were injected with sesame seed oil
Animal injections and tissue processing In general, 8- to 10-week-old adult females were ovariectomized and rested for 10 days before they received any injections. Mice were injected with sesame seed oil
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods. Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered
 Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in TNN lysis buffer (50mM Tris at ph 8.0, 120mM NaCl
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in TNN lysis buffer (50mM Tris at ph 8.0, 120mM NaCl
7.012 Problem Set 5. Question 1
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 5 Question 1 While studying the problem of infertility, you attempt to isolate a hypothetical rabbit gene that accounts for the prolific reproduction of rabbits. After much
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 5 Question 1 While studying the problem of infertility, you attempt to isolate a hypothetical rabbit gene that accounts for the prolific reproduction of rabbits. After much
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa)
 Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
Arf6 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Arf6 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 82401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Arf6 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 82401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
ICH Considerations. Oncolytic Viruses September 17, 2009
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH Considerations Oncolytic Viruses September 17, 2009 1. Introduction Oncolytic viruses
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH Considerations Oncolytic Viruses September 17, 2009 1. Introduction Oncolytic viruses
Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Western Blotting Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using T-PER tissue protein extraction buffer. Protein concentrations were determined
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Western Blotting Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using T-PER tissue protein extraction buffer. Protein concentrations were determined
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
Custom Antibodies Services. GeneCust Europe. GeneCust Europe
 GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 2 route de Remich L-5690 Ellange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com Custom
GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 2 route de Remich L-5690 Ellange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com Custom
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis. Mitesh Shrestha
 Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
SI Appendix. Tumor-specific CD8 + Tc9 cells are superior effector than Tc1 cells for. adoptive immunotherapy of cancers
 SI Appendix Tumor-specific CD8 + Tc9 cells are superior effector than Tc1 cells for adoptive immunotherapy of cancers Yong Lu, Bangxing Hong, Haiyan Li, Yuhuan Zheng, Mingjun Zhang, Siqing Wang, Jianfei
SI Appendix Tumor-specific CD8 + Tc9 cells are superior effector than Tc1 cells for adoptive immunotherapy of cancers Yong Lu, Bangxing Hong, Haiyan Li, Yuhuan Zheng, Mingjun Zhang, Siqing Wang, Jianfei
For quantitative detection of mouse IGF-1 in serum, body fluids, tissue lysates or cell culture supernatants.
 Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit (migf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0378 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit (migf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0378 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Quantifying small numbers of antibodies with a near-universal protein-dna chimera
 Quantifying small numbers of antibodies with a near-universal protein-dna chimera Ian Burbulis, Kumiko Yamaguchi, Richard Yu, Orna Resnekov & Roger Brent Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary figure
Quantifying small numbers of antibodies with a near-universal protein-dna chimera Ian Burbulis, Kumiko Yamaguchi, Richard Yu, Orna Resnekov & Roger Brent Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary figure
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of the POP2 transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory elements. (A) POP2 nucleotide sequence
 1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of the POP transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory elements. (A) POP nucleotide sequence depicting the consensus sequence for
1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of the POP transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory elements. (A) POP nucleotide sequence depicting the consensus sequence for
RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by. 5 AGACACAAACACCAUUGUCACACUCCACAGC; Rand-2 OMe,
 Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
RheB Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based RheB Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 81201 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 FAX: 610-945-2008 Table
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based RheB Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 81201 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 FAX: 610-945-2008 Table
Mouse PECAM-1/CD31 ELISA Kit (mpecam-elisa)
 Mouse PECAM-1/CD31 ELISA Kit (mpecam-elisa) Cat. No. EK0874 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) is an important target GP in DITP. 1 PECAM-1/CD31
Mouse PECAM-1/CD31 ELISA Kit (mpecam-elisa) Cat. No. EK0874 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) is an important target GP in DITP. 1 PECAM-1/CD31
FDA Perspective on the Preclinical Development of Cancer Vaccines
 FDA Perspective on the Preclinical Development of Cancer Vaccines Richard D. McFarland Ph.D., M.D. Medical Officer CBER/OCTGT/DCEPT mcfarlandr@cber.fda.gov Cancer Vaccine Clinical Trials Workshop Alexandria,
FDA Perspective on the Preclinical Development of Cancer Vaccines Richard D. McFarland Ph.D., M.D. Medical Officer CBER/OCTGT/DCEPT mcfarlandr@cber.fda.gov Cancer Vaccine Clinical Trials Workshop Alexandria,
Monoclonal Antibody Generation. Ivo Lorenz Tri-Institutional Therapeutics Discovery Institute
 Monoclonal Antibody Generation Ivo Lorenz Tri-Institutional Therapeutics Discovery Institute Common Antibody Formats Heavy chain VL VH Light chain Fab CL CH1 VH VL Linker CH2 VH VL Fc CH3 IgG Immunoglobulin
Monoclonal Antibody Generation Ivo Lorenz Tri-Institutional Therapeutics Discovery Institute Common Antibody Formats Heavy chain VL VH Light chain Fab CL CH1 VH VL Linker CH2 VH VL Fc CH3 IgG Immunoglobulin
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental Methods:
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Pre-made expression Adenovirus product manual
 Pre-made expression Adenovirus product manual Catalog# Product Name Amounts AVP001 RFP adenovirus AVP002 AVP004 AVP005 AVP011 AVP012 AVP017 AVP010 AVP013 AVP014 AVP015 AVP016 AVP-Null AVP001-PBS AVP002-PBS
Pre-made expression Adenovirus product manual Catalog# Product Name Amounts AVP001 RFP adenovirus AVP002 AVP004 AVP005 AVP011 AVP012 AVP017 AVP010 AVP013 AVP014 AVP015 AVP016 AVP-Null AVP001-PBS AVP002-PBS
Store samples to be assayed within 24 hours at 2-8 C. For long-term storage, aliquot and freeze samples at -20 C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
 Human Retinol Binding Protein 4, RBP4 ELISA Kit Preparation Plate Washing Discard the solution in the plate without touching the side walls. Blot the plate onto paper towels or other absorbent material.
Human Retinol Binding Protein 4, RBP4 ELISA Kit Preparation Plate Washing Discard the solution in the plate without touching the side walls. Blot the plate onto paper towels or other absorbent material.
OX40 MARKET LANDSCAPE
 OX40 Agonist OX40 MARKET LANDSCAPE OX40 (a.k.a. CD134) is a costimulatory molecule belonging to the TNF receptor family expressed primarily on activated effector T (T eff) cells and naive regulatory T
OX40 Agonist OX40 MARKET LANDSCAPE OX40 (a.k.a. CD134) is a costimulatory molecule belonging to the TNF receptor family expressed primarily on activated effector T (T eff) cells and naive regulatory T
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 (Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
(Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
T-cell response. Taken from NIAID: s.aspx
 T-cell receptor T-cell response 1. Macrophage or dendritic cell digest antigen bacteria, virus 2. Fragments of Ag bind to major histo-compatiblity (MHC) proteins in macrophage. 3. MHC I-Ag fragment expressed
T-cell receptor T-cell response 1. Macrophage or dendritic cell digest antigen bacteria, virus 2. Fragments of Ag bind to major histo-compatiblity (MHC) proteins in macrophage. 3. MHC I-Ag fragment expressed
ELISPOT antibody pair Technical Data Sheet
 ELISPOT antibody pair Technical Data Sheet 10-plate and 20-plate format For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. This Technical Data Sheet applies for the following U-CyTech
ELISPOT antibody pair Technical Data Sheet 10-plate and 20-plate format For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. This Technical Data Sheet applies for the following U-CyTech
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT - Reporter - Jurkat Recombinant Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT - Reporter - Jurkat Recombinant Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT - Reporter - Jurkat Recombinant Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements
Data Sheet. TCR activator / PD-L1 - CHO Recombinant Cell line Cat. #: 60536
 Data Sheet TCR activator / PD-L1 - CHO Recombinant Cell line Cat. #: 60536 Product Description Recombinant CHO-K1 cells constitutively expressing human PD-L1 (Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1, CD274, B7
Data Sheet TCR activator / PD-L1 - CHO Recombinant Cell line Cat. #: 60536 Product Description Recombinant CHO-K1 cells constitutively expressing human PD-L1 (Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1, CD274, B7
Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B
 Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B Yohei Kanamori, Makoto Sugiyama, Osamu Hashimoto, Masaru Murakami, Tohru Matsui and Masayuki Funaba Supplemental methods Liver cell separation
Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B Yohei Kanamori, Makoto Sugiyama, Osamu Hashimoto, Masaru Murakami, Tohru Matsui and Masayuki Funaba Supplemental methods Liver cell separation
Product Data Sheet - TRUEMAB
 888.267.4436 techsupport@origene.com www.origene.com Name:IL6 mouse monoclonal antibody, clone OTI3G9 (formerly 3G9) Product Data Sheet - TRUEMAB Catalog: TA500067 Components: IL6 mouse monoclonal antibody,
888.267.4436 techsupport@origene.com www.origene.com Name:IL6 mouse monoclonal antibody, clone OTI3G9 (formerly 3G9) Product Data Sheet - TRUEMAB Catalog: TA500067 Components: IL6 mouse monoclonal antibody,
Find 1 cell in 100,000 with ELISpot
 Find 1 cell in 100,000 with ELISpot Interest in any of the products, request or order them at io-connect Diagnostics. io-connect Diagnostics.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 60 T E +32 (0)2 502 12 53 egonialaan
Find 1 cell in 100,000 with ELISpot Interest in any of the products, request or order them at io-connect Diagnostics. io-connect Diagnostics.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 60 T E +32 (0)2 502 12 53 egonialaan
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Nuclear extracts were. oligonucleotide spanning the NF-kB site (5 -GATCC-
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Nuclear extracts were prepared as previously described. (1) A [ 32 P] datp-labeled doublestranded oligonucleotide spanning
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Nuclear extracts were prepared as previously described. (1) A [ 32 P] datp-labeled doublestranded oligonucleotide spanning
Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289
 Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289 Background Human CD137 (4-1BB; TNFRS9) is an inducible co-stimulatory molecule that activates T cells. CD137:CD137L-mediated
Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289 Background Human CD137 (4-1BB; TNFRS9) is an inducible co-stimulatory molecule that activates T cells. CD137:CD137L-mediated
Rab5 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Rab5 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 83701 20 assays 24 Whitewoods Lane 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Rab5 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 83701 20 assays 24 Whitewoods Lane 1 Table of Content Product
The Biotechnology Toolbox
 Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Immunoglobulins. (1 of 2)
 Immunoglobulins (1 of 2) Immunoglobulins (Igs) = antibodies Each B cell synthesizes Igs of single specificity for a specific epitope B cell receptors (BCRs) are the Igs on B cell surface Humoral immunity
Immunoglobulins (1 of 2) Immunoglobulins (Igs) = antibodies Each B cell synthesizes Igs of single specificity for a specific epitope B cell receptors (BCRs) are the Igs on B cell surface Humoral immunity
1 Name. 1. (3 pts) What is apoptosis and how does it differ from necrosis? Which is more likely to trigger inflammation?
 1 Name MCB 150 Midterm Eam #1 (100 points total) Please write your full name on each page of the eam!! The eam consists of 17 questions (6 pages). Each has a different point count as indicated. Please
1 Name MCB 150 Midterm Eam #1 (100 points total) Please write your full name on each page of the eam!! The eam consists of 17 questions (6 pages). Each has a different point count as indicated. Please
Porcine IL-12/IL-23 p40 ELISA kit
 Porcine IL-12/IL-23 p40 ELISA kit Catalog number: NB-E50014 (96 wells) The kit is designed to quantitatively detect the levels of Porcine IL-12/IL-23 p40 in cell culture supernatants. FOR RESEARCH USE
Porcine IL-12/IL-23 p40 ELISA kit Catalog number: NB-E50014 (96 wells) The kit is designed to quantitatively detect the levels of Porcine IL-12/IL-23 p40 in cell culture supernatants. FOR RESEARCH USE
Rhesus CD16 / FCGR3 ELISA Pair Set
 Rhesus CD16 / FCGR3 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK90013 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the General
Rhesus CD16 / FCGR3 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK90013 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the General
Human IL-10 ELISA MAX Set Deluxe
 Human IL-10 ELISA MAX Set Deluxe Cat. No. 430604 (5 plates) 430605 (10 plates) 430606 (20 plates) ELISA Set for Accurate Cytokine Quantification from Cell Culture Supernatant, Serum, Plasma or Other Body
Human IL-10 ELISA MAX Set Deluxe Cat. No. 430604 (5 plates) 430605 (10 plates) 430606 (20 plates) ELISA Set for Accurate Cytokine Quantification from Cell Culture Supernatant, Serum, Plasma or Other Body
Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg
![Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg](/thumbs/84/90687567.jpg) Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Mouse Betacellulin/BTC ELISA Kit
 OriGene Technologies, Inc 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: Mouse Betacellulin/BTC ELISA Kit Catalog No.
OriGene Technologies, Inc 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: Mouse Betacellulin/BTC ELISA Kit Catalog No.
A novel therapeutic strategy to rescue the immune effector function of proteolyticallyinactivated
 A novel therapeutic strategy to rescue the immune effector function of proteolyticallyinactivated cancer therapeutic antibodies Supplemental Data File in this Data Supplement: Supplementary Figure 1-4
A novel therapeutic strategy to rescue the immune effector function of proteolyticallyinactivated cancer therapeutic antibodies Supplemental Data File in this Data Supplement: Supplementary Figure 1-4
The presence of T cell epitopes is important for induction of antibody
 The presence of T cell epitopes is important for induction of antibody responses against antigens directed to DEC25 + dendritic cells Kelly N. S. Amorim, Eline V. Rampazo, Renan Antonialli, Marcio M. Yamamoto,
The presence of T cell epitopes is important for induction of antibody responses against antigens directed to DEC25 + dendritic cells Kelly N. S. Amorim, Eline V. Rampazo, Renan Antonialli, Marcio M. Yamamoto,
Human IFN-γ. Pre-Coated ELISA Kit
 Human IFN-γ (Interferon Gamma) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2067 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 15.6 1000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 9.4 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
Human IFN-γ (Interferon Gamma) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2067 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 15.6 1000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 9.4 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
SouthernBiotech Custom Services
 SouthernBiotech Custom Services Quality Antibodies for Quality Research Peptide Synthesis for Antibody Production SouthernBiotech provides complete services for production of immunogenic peptides for antibody
SouthernBiotech Custom Services Quality Antibodies for Quality Research Peptide Synthesis for Antibody Production SouthernBiotech provides complete services for production of immunogenic peptides for antibody
Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development
 Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development Rebecca Brunette, PhD Scientist, Analytical Biology SNBL USA Preclinical Immunotoxicology The study of evaluating adverse effects
Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development Rebecca Brunette, PhD Scientist, Analytical Biology SNBL USA Preclinical Immunotoxicology The study of evaluating adverse effects
MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam will have 40 multiple choice questions.
 MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
a. Hypoxanthine was present in the media. MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No.
 MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
Monoclonal Antibodies
 Monoclonal Antibodies Homogeneous antibody preparations produced in the laboratory by hybridomas. Produced by identical type of B cell clones. Recognize a signal epitope on an antigen. Hybridoma Technology
Monoclonal Antibodies Homogeneous antibody preparations produced in the laboratory by hybridomas. Produced by identical type of B cell clones. Recognize a signal epitope on an antigen. Hybridoma Technology
Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1.
 Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1. UTK1 inhibits the second EGF-induced wave of lamellipodia formation in TT cells. A and B, EGF-induced lamellipodia formation in TT cells,
Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1. UTK1 inhibits the second EGF-induced wave of lamellipodia formation in TT cells. A and B, EGF-induced lamellipodia formation in TT cells,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Powell and Xu 10.1073/pnas.0807274105 SI Methods Design of Estrogen Receptor (ER) Fusion Constructs for Use in Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) Assay. Because the
Supporting Information Powell and Xu 10.1073/pnas.0807274105 SI Methods Design of Estrogen Receptor (ER) Fusion Constructs for Use in Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) Assay. Because the
Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells Niklas Engels, Lars Morten König, Christina Heemann, Johannes
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells Niklas Engels, Lars Morten König, Christina Heemann, Johannes
DC enriched CD103. CD11b. CD11c. Spleen. DC enriched. CD11c. DC enriched. CD11c MLN
 CD CD11 + CD + CD11 d g CD CD11 + CD + CD11 CD + CD11 + Events (% of max) Events (% of max) CD + CD11 Events (% of max) Spleen CLN MLN Irf fl/fl e Irf fl/fl h Irf fl/fl DC enriched CD CD11 Spleen DC enriched
CD CD11 + CD + CD11 d g CD CD11 + CD + CD11 CD + CD11 + Events (% of max) Events (% of max) CD + CD11 Events (% of max) Spleen CLN MLN Irf fl/fl e Irf fl/fl h Irf fl/fl DC enriched CD CD11 Spleen DC enriched
ICH CONSIDERATIONS Oncolytic Viruses
 European Medicines Agency Pre-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ICH CONSIDERATIONS Oncolytic Viruses 20 November 2008 EMEA/CHMP/GTWP/607698/2008
European Medicines Agency Pre-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ICH CONSIDERATIONS Oncolytic Viruses 20 November 2008 EMEA/CHMP/GTWP/607698/2008
Human TGF-beta1 ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human TGF-beta1 ELISA For the quantitative determination of TGF-beta1 in human cell culture supernates, serum, plasma (EDTA) and urine Cat. No. KT-1471 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic
K-ASSAY Human TGF-beta1 ELISA For the quantitative determination of TGF-beta1 in human cell culture supernates, serum, plasma (EDTA) and urine Cat. No. KT-1471 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic
