Zero Background Cloning Kit
|
|
|
- Jonah Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 user guide Zero Background Cloning Kit (pzero -1 Vector) Catalog number K Revision date 29 March 2012 Publication part number MAN For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use.
2 ii
3 Contents Experienced Users Guide... iv Kit Contents and Storage... vi Introduction...1 Description of the System... 1 Methods...3 Clone into pzero Transformation Troubleshooting Appendix...17 Recipes Zeocin Selective Antibiotic Protocol for Chemically Competent Cells Protocol for Electrocompetent Cells pzero -1 Vector Accessory Products Technical Support Purchaser Notification References iii
4 Experienced Users Guide Introduction The following procedure is designed to get experienced users quickly started with the Zero Background Kit. Information is provided elsewhere in the manual if you need help with any of the steps. Before starting 1. Prepare Low Salt LB plates containing 50 μg/ml Zeocin (Low Salt LB- Zeocin, see page 17). Store the plates at 4 C. Plan on using 2 plates per transformation. If using a cell line carrying the laci q gene, include IPTG in the plating medium to achieve complete induction. 2. Prepare Low Salt LB or SOB liquid medium containing 50 μg/ml Zeocin for DNA minipreps. 3. Prepare or purchase chemically competent or electrocompetent TOP10 cells. See page 22 for protocols to prepare competent cells. The minimal efficiencies required are cfu/μg DNA for chemically competent cells and cfu/μg DNA for electrocompetent cells. Note: For convenient high-efficiency transformation, we recommend One Shot TOP10 Chemically Competent E. coli or One Shot TOP10 Electrocompetent Cells, which are available separately (see page 28 for ordering information). 4. Determine a cloning strategy for ligation into pzero -1. Refer to the details of the multiple cloning site (page 5) for help. Ligate into pzero -1 Note: Be sure to include a "no DNA", a "cells only", and linearized vector only controls. 1. Digest 1 μg each of pzero -1 supercoiled vector (1 μl) and your DNA in total volumes of 10 μl using the recommended buffer, temperature, and reaction conditions described by the manufacturer of the restriction enzyme. Optimal digestion time is minutes. Do not digest for longer than 30 minutes. 2. Inactivate the restriction enzyme(s) by heating the reaction at 65 C for minutes or by phenol extraction. Dilute the cut vector to 10 ng/μl with TE buffer (provided). If the enzyme is not heat inactivated (e.g. EcoR V), phenol-extract the enzyme. 3. Ethanol-precipitate the DNA and resuspend it in 90 μl of sterile water or TE buffer. We recommend that you use the linearized DNA immediately. You may store the DNA at 20 C for 1 2 weeks, but the cloning efficiency may decrease. Procedure continued on next page Continued on next page iv
5 Experienced Users Guide, Continued Ligate into pzero -1, Continued Procedure continued from previous page 4. Prepare the ligation reaction. If ligating cohesive-ends, use a 2:1 insert: vector molar ratio; if ligating blunt-ends, use an insert: vector molar ratio between 3:1 10:1. See page 7 to determine how much insert you need. Set up the following 10 μl ligation reaction using the reagents supplied in the kit: Digested vector (~10 ng) Digested DNA insert Sterile water 10X Ligation Buffer (with ATP) T4 DNA Ligase (4 U/μL) Total Volume 1 μl x μl to 8.5 μl 1 μl 0.5 μl 10 μl 5. Incubate the reaction at 16 C for 30 minutes (cohesive-end ligations) or 60 minutes (blunt-end ligations). Do not ligate at room temperature or exceed 1 hour for ligation, and do not add PEG to the ligation reaction. Increased background levels have been observed under these conditions. Proceed to Transformation in the following section. Transformation For more information on transformation methods, see pages Add 2 μl of each ligation reaction to a separate tube of competent cells (40 50 μl), and transform using your method of choice. 2. Plate μl of each transformation mix on Low Salt LB-Zeocin plates. Let the liquid absorb, invert the plate, and incubate at 37 C for hours. Proceed to Analyzing Transformants in the following section. Analyze transformants 1. Remove the plates from the incubator. Pick at least 10 Zeocin resistant transformants, and inoculate into 2 ml Low Salt SOB medium containing 50 μg/ml Zeocin. Grow 6 8 hours or overnight at 37 C. 2. Isolate the plasmid DNA by miniprep for restriction analysis or sequencing. Remember to purify the desired clone by streaking for single colonies and reconfirm the presence of insert before making a glycerol stock. 3. Prepare a glycerol stock of your desired clone for long-term storage by combining 0.85 ml of an overnight bacterial culture with 0.15 ml of sterile 100% glycerol. Mix by vortexing and transfer to a labeled storage tube. Freeze the tube in liquid nitrogen or a dry ice/ethanol bath and store at 70 C. 4. After you isolate the desired clone, proceed with further subcloning and/or analyzing your insert. v
6 Kit Contents and Storage Kit Contents The Zero Background Cloning Kit contains the following reagents: Item Concentration Storage pzero -1 vector, supercoiled, 1 μg/μl in TE Buffer, 30 C to 10 C 25 μg ph 7.5 Sterile water, 1 ml Nuclease-free water 30 C to 10 C 10X Ligation Buffer, 100 μl 60 mm Tris-HCl, ph C to 10 C 60 mm MgCl 2 50 mm NaCl 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin 70 mm β-mercaptoethanol 1 mm ATP 20 mm dithiothreitol 10 mm spermidine T4 DNA Ligase, 25 μl 4.0 Weiss units/μl 30 C to 10 C TE Buffer, 2 ml 10 mm Tris-HCl, ph C to 10 C 1 mm EDTA TOP10 cells, 1 stab 2 C to 8 C Zeocin antibiotic, 125 mg 100 mg/ml in water 30 C to 10 C Test Inserts, Blunt Ended ΦΧ174 Hae III DNA, 10 μl 20 ng/μl in TE buffer, ph 7.5 *TE buffer, ph 7.5: 10 mm Tris-HCl, 1 mm EDTA, ph C to 10 C Genotype of TOP10 F mcra Δ(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) φ80laczδm15 ΔlacX74 reca1 arad139 Δ(ara-leu)7697 galu galk rpsl enda1 nupg Prepare TOP10 E. coli glycerol stocks We recommend that you prepare a set of 5 10 TOP10 E. coli glycerol master stocks within 2 weeks of receiving the kit: 1. Streak a small portion of the TOP10 cells that you have received as a stab on an LB plate. 2. Invert the plate and incubate it at 37 C overnight. 3. Isolate a single colony and inoculate into 5 10 ml of LB medium. 4. Grow the culture to stationary phase (OD 600 = 1 2). 5. Mix 0.8 ml of the culture with 0.2 ml of sterile glycerol, and transfer to a cryovial. 6. Store the vials at 80 C. Use one master stock to create working stocks for regular use. Product Use For research use only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. vi
7 Description of the System Introduction System Overview This kit is designed to clone cohesive or blunt-ended DNA fragments with a low background of non-recombinants. The technology described here is based on vectors containing the lethal E. coli gene, ccdb (Bernard, et al., 1994). The cloning vector, pzero -1, contains the ccdb gene fused to the C-terminus of LacZα. Insertion of a DNA fragment disrupts the expression of the laczα-ccdb gene fusion, permitting growth of only positive recombinants. Cells that contain nonrecombinant vector are killed. Using the pzero -1 vector, very high cloning efficiencies (~95%) are often achieved without the need for exotic strains, X-Gal, calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP), or other components. The vector also contains: the Zeocin resistance gene for selection in E. coli the f1 origin of replication for single strand rescue a versatile multiple cloning site with 17 sites flanking Sp6 and T7 RNA promoter/priming sites for in vitro transcription all M13 universal primer sites for sequencing Recommended E. coli host TOP10 E. coli is the recommended strain for general use of pzero -1, but other host strains may also be used. Because the TOP10 E. coli strain does not carry the laci q gene, the ccdb gene is constitutively expressed without the need for IPTG induction. If you use a strain that contains the laci q gene, you must induce the expression of the ccdb gene with 1 mm IPTG. Strains that contain an F plasmid are not recommended for transformation and selection of recombinant clones. The F plasmid encodes the CcdA protein that acts as an inhibitor of the CcdB protein (see page 2 for a more detailed explanation). Any E. coli strain that contains the complete Tn5 transposable element (i.e. DH5αF IQ, SURE, SURE2) encodes the ble (bleomycin) resistance genes. These strains will confer resistance to Zeocin. For the most efficient selection, choose an E. coli strain that does not contain the Tn5 gene (e.g. TOP10, DH5, DH10). Do not use INVαF cells. The transformation efficiency of INVαF is very low using pzero -2 and selection on kanamycin. Continued on next page 1
8 Description of the System, Continued Mechanism of action of the CcdB protein The CcdB protein acts by poisoning bacterial DNA-gyrase (topoisomerase II), an essential enzyme that catalyzes the ATP-dependent negative supercoiling of DNA. DNA gyrase acts by creating a transient double-strand nick in the DNA substrate, passing the DNA helix through the break to decrease the linking number, and then resealing the nick. During the breaking-resealing reaction, the 5 phosphate termini are covalently linked to a tyrosine residue in the A subunit of DNA gyrase (gyra). This gyrase-dna intermediate is called the cleavable complex. The CcdB protein has been shown both in vivo (Bernard and Couturier, 1992) and in vitro (Bernard, et al., 1993) to poison the cleavable complex by inhibiting the resealing of the double-strand nick in the DNA. This causes DNA breakage and cell death. ccdb gene The ccdb gene is found in the ccd (control of cell death) locus on the F plasmid. This locus contains two genes, ccda and ccdb, which encode proteins of 72 and 101 amino acids respectively (Karoui, et al., 1983; Ogura and Hiraga, 1983; and Miki, et al., 1984). The ccd locus participates in stable maintenance of F plasmid by post-segregational killing of cells that do not contain the F plasmid (Jaffé, et al., 1985). The CcdB protein is a potent cell-killing protein when the CcdA protein does not inhibit its action. The half-life of the CcdA protein is shorter than that of the CcdB protein. Persistence of the CcdB protein leads to death of bacterial segregants that do not contain the F plasmid. Overexpression of the CcdB protein causes cell death when its action is not prevented by sufficient CcdA protein (Van Melderen, et al., 1994). Mechanism of action of Zeocin Zeocin is a member of the bleomycin family of cytotoxins that kills a wide range of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by binding chromosomal DNA and causing random double-stranded breaks. A Zeocin resistance gene, ble, has been isolated from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus. The ble gene product inactivates Zeocin by binding directly to it in a stoichiometric fashion and preventing chromosomal DNA from being bound and cleaved. The Zeocin resistance gene is included in this cloning vector as an alternative to β-lactamase. Since the Zeocin resistance protein is overproduced in the cytoplasm and not secreted like β-lactamase, there is no danger of Zeo S satellite colonies arising. For more information on Zeocin, see page 20. 2
9 Methods Clone into pzero -1 Introduction Selecting cloned inserts using the Zero Background technique is extremely powerful; however, because of the nature of selection, we do not recommend propagating the vector in common laboratory strains. We have developed ligation and transformation procedures to optimize the use of the pzero -1 vector provided in this kit. The kit contains enough vector for ~25 restriction digestions and ~2,000 ligations. Important Zeocin is inactivated by >110 mm salt concentrations. The salt concentration must either be reduced or the concentration of Zeocin increased to compensate. It is also important to maintain the ph between to prevent inactivation of the drug. Failure to lower the salt content and maintain the ph of your medium between will result in non-selection due to inactivation of Zeocin. To prevent inactivation of Zeocin, use Low Salt LB-Zeocin medium when plating transformation reactions. We recommend growing positive recombinants in Low Salt SOB-Zeocin liquid medium for better growth and higher plasmid yields. Using other liquid media such as Low Salt LB, YT, or TB may produce unsatisfactory results. The table below summarizes the media you can use. Technique Media (see Recipes, page 17) Plating transformation Low Salt LB-Zeocin (50 μg/ml Zeocin ) reaction YT-Zeocin (50 μg/ml Zeocin ) Growing positive Low Salt SOB-Zeocin (50 μg/ml Zeocin ) transformants in liquid culture Continued on next page 3
10 Clone into pzero -1, Continued Before starting 1. Prepare Low Salt LB-Zeocin plates (50 μg/ml) (see page 17). Store the plates at 4 C. If using cells carrying the laci q gene, include 1 mm IPTG in the plating medium to achieve complete induction. 2. Prepare Low Salt SOB-Zeocin (50 μg/ml) liquid medium for DNA minipreps. 3. Prepare or purchase chemically competent or electrocompetent TOP10 cells. See pages for protocols to prepare competent cells. The minimal efficiencies required are cfu/μg DNA for chemically competent and cfu/μg DNA for electrocompetent cells. Note: For high-efficiency and convenient transformation, we recommend One Shot TOP10 Chemically Competent E. coli or One Shot TOP10 Electrocompetent Cells, which are available separately (see page 28 for ordering information). 4. Determine a strategy for cloning into pzero -1. See the details of the multiple cloning site (page 5) for help. Continued on next page 4
11 Clone into pzero -1, Continued Detail of the multiple cloning site The following diagram shows the pzero -1 multiple cloning site and surrounding sequences. Restriction sites indicate where the enzyme cuts. Cloning into the multiple cloning site disrupts expression of the ccdb gene. The pzero -1 vector is a cloning vector; it is not designed to be an expression or fusion vector. 95 P lac-laco region GCGCAACGCA ATTAATGTGA GTTAGCTCAC TCATTAGGCA CCCCAGGCTT TACACTTTAT M13 Reverse primer lacza ORF GCTTCCGGCT CGTATGTTGT GTGGAATTGT GAGCGAATAA CAATTTCACA CAGGAAACAG CT ATG Sp6 Promoter/Priming site Met Nsi I * ACC ATG ATT ACG CCA AGC TAT TTA GGT GAC ACT ATA GAA TAC TCA AGC TAT GCA Thr Met Ile Thr Pro Ser Tyr Leu Gly Asp Thr Ile Glu Tyr Ser Ser Tyr Ala Hind III Asp718 I Kpn I Sac I BamH I/Bst I Spe I Eco RI TCA AGC TTG GTA CCG AGC TCG GAT CCA CTA GTA ACG GCC GCC AGT GTG CTG GAA Ser Ser Leu Val Pro Ser Ser Asp Pro Leu Val Thr Ala Ala Ser Val Leu Glu Pst I EcoR V Not I Xho I Sph I Nsi I * Xba I Apa I TTC TGC AGA TAT CCA TCA CAC TGG CGG CCG CTC GAG CAT GCA TCT AGA GGG CCC Phe Cys Arg Tyr Pro Ser His Trp Arg Pro Leu Glu His Ala Ser Arg Gly Pro T7 Promoter/Priming site M13 (-20) Foward priming site AAT TCG CCC TAT AGT GAG TCG TAT TAC AAT TCA CTG GCC GTC GTT TTA CAA CGT Asn Ser Pro Tyr Ser Glu Ser Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Leu Ala Val Val Leu Gln Arg CGT GAC TGG GAA AAC CCT GGC GTT ACC CAA CTT AAT CGC CTT GCA GCA CAT CCC Arg Asp Trp Glu Asn Pro Gly Val Thr Gln Leu Asn Arg Leu Ala Ala His Pro CCT TTC GCC AGC TGG CGT AAT AGC GAA GAG GCC CGC ACC GAT CGC CCT TCC CAA Pro Phe Ala Ser Trp Arg Asn Ser Glu Glu Ala Arg Thr Asp Arg Pro Ser Gln LacZa/ccdB Fusion joint CAG TTG CGC AGC CTA TAC GTA CGG CAG TTT AAG GTT TAC ACC TAT AAA AGA GAG Gln Leu Arg Ser Leu Tyr Val Arg Gln Phe Lys Val Tyr Thr Tyr Lys Arg Glu AGC CGT TAT CGT CTG TTT GTG GAT GTA CAG AGT GAT ATT ATT GAC ACG CCG GGG Ser Arg Tyr Arg Leu Phe Val Asp Val Gln Ser Asp Ile Ile Asp Thr Pro Gly ccdb ORF CGA CGG ATG GTG ATC CCC CTG GCC AGT GCA CGT CTG CTG TCA GAT AAA GTC TCC Arg Arg Met Val Ile Pro Leu Ala Ser Ala Arg Leu Leu Ser Asp Lys Val Ser CGT GAA CTT TAC CCG GTG GTG CAT ATC GGG GAT GAA AGC TGG CGC ATG ATG ACC Arg Glu Leu Tyr Pro Val Val His Ile Gly Asp Glu Ser Trp Arg Met Met Thr ACC GAT ATG GCC AGT GTG CCG GTC TCC GTT ATC GGG GAA GAA GTG GCT GAT CTC Thr Asp Met Ala Ser Val Pro Val Ser Val Ile Gly Glu Glu Val Ala Asp Leu AGC CAC CGC GAA AAT GAC ATC AAA AAC GCC ATT AAC CTG ATG TTC TGG GGA ATA Ser His Arg Glu Asn Asp Ile Lys Asn Ala Ile Asn Leu Met Phe Trp Gly Ile TAA ATG TCA GGC *** Continued on next page 5
12 Clone into pzero -1, Continued Isolate and Purify inserts For best results, phenol-extract PCR products and precipitate the DNA before ligating PCR products into pzero -1. If you gel-purify your insert before ligating into pzero -1, you may see a higher background of colonies without insert because of nuclease contamination. To reduce nuclease contamination, do not use communal ethidium bromide baths. Use solutions that are free of nucleases, and high quality agarose. Important considerations Do not dephosphorylate pzero -1. Do not overdigest pzero -1 or your insert with restriction enzymes, and take precautions to prevent nuclease contamination. Autoclave or extensively boil for 5 10 minutes in a microwave oven all water and buffers used in the experiments to ensure that they are nucleasefree. We recommend that you use the sterile, nuclease-free water and buffers provided with the kit. Exonuclease digestion of vector ends may cause a frameshift mutation resulting in disruption of the laczα-ccdb gene if the vector self-ligates. This results in a high background of non-recombinants. Ligate into pzero -1 Be sure to include a "no cells", a "cells only", and linearized vector controls. 1. Digest 1 μg each of pzero -1 supercoiled vector (1 μl) and your DNA in total volumes of 10 μl for minutes using the recommended buffer, temperature, and reaction conditions described by the manufacturer of the restriction enzyme. Do not overdigest. To ligate blunt fragments, digest pzero -1 with units of EcoR V for minutes. Adjusting insert: vector quantities to a molar ratio of 2:1 for a cohesive-end ligation and between 3:1 0:1 for a blunt-end ligation increases ligation efficiency. Adjust digestion quantities accordingly. 2. For enzymes that are inactivated by heat, add TE buffer to a final volume of 100 μl and incubate the reaction mix at 70 C for 10 minutes. Cool to room temperature, then place the reaction on ice. The final concentration of the reaction will be 10 ng/μl. You may use the enzyme digestion directly in the ligation reaction (step 4 of this procedure) unless the enzyme is not fully inactivated by heat. If the enzyme(s) are not fully inactivated by heat (e.g. BamH I, EcoR V, Kpn I, Pst I), extract the digest with 10 μl phenol/chloroform and precipitate the DNA with 1/10 volume 3 M sodium acetate, ph 5.6, and 2 volumes 100% ethanol. Centrifuge the tube containing precipitated DNA, and carefully wash the pellet with 80% ethanol. Air-dry the pellet and resuspend in 90 μl of TE buffer. Assuming 90% recovery, the DNA concentration will be 10 ng/μl. Procedure continued on next page Continued on next page 6
13 Cloning into pzero -1, Continued Ligate into pzero -1, Continued 3. To verify complete digestion and estimate recovery, run an aliquot of the digestion mixture on a 1% agarose gel. 4. If you are ligating cohesive-ends, use 2:1 insert: vector molar ratio. If you are ligating blunt-ends, increase the insert: vector molar ratio to between 3:1 10:1. See the following section, Calculate molar ratios, to determine how much insert you need. Set up the following 10 μl ligation reaction using the reagents supplied in the kit: Digested vector (~10 ng) 1 μl Digested DNA insert x μl Sterile water to a final volume of 8.5 μl 10X Ligation Buffer (with ATP) 1 μl T4 DNA Ligase (4 U/μL) 0.5 μl Total Volume 10 μl 5. Incubate at 16 C for 30 minutes (cohesive-end ligations) or 60 minutes (blunt-end ligations). Do not ligate at room temperature. Place the vials on ice. Proceed to Transformation, page 11. Calculate molar ratios To clone your insert into pzero -1, you need to know the concentration of your insert DNA solution. You may determine the concentration by OD 260, agarose gel electrophoresis, or fluorescence. Use the concentration to calculate the volume required to achieve a particular molar ratio of vector to insert. 1. Determine the concentration of the insert in μg/ml. 2. Use the following formula to calculate the amount of insert needed to give a molar ratio of 2:1 between insert and linearized pzero -1 (see the following Note). Note that the amount of pzero -1 is 10 ng. x ng insert = (2) (bp insert) (10 ng linearized pzero -1) (2,808 bp pzero -1) Note: If you are performing a blunt-ended ligation, calculate the insert: vector molar ratio to be between 3:1 10:1 by replacing the 2 with the appropriate molar ratio in the above equation. 3. Based on the preceding calculation, calculate the volumes needed for the ligation reaction. Continued on next page 7
14 Clone into pzero -1, Continued General guidelines for control reactions The following table gives some suggestions for possible control reactions for the experiments presented in this manual. It is useful to have control data to evaluate your experiments or if you need to contact Technical Support (page 29) for assistance. Experiment Control Reason Ligation and No DNA Checks for contamination of ligation Transformation reagents. Linearized vector only Cells only Supercoiled vector (e.g. puc19) Test Inserts Checks for uncut or self-ligated vector. If the vector religates, it will probably be lethal and very few transformants should arise. Checks for the presence of antibiotic in the plates and for contamination of competent cells and S.O.C. medium. Checks the efficiency of the competent cells. See Transformation, page 11. Checks general ligation conditions, and confirms disruption of ccdb expression. See Use the test inserts, page 9. Continued on next page 8
15 Clone into pzero -1, Continued Using the test inserts Use the test inserts to check the general ligation conditions and to confirm the lack of ccdb function when its expression is disrupted. To use the test inserts, digest the pzero -1 vector with EcoR V, and ligate the test inserts (Hae III digested ΦΧ174 DNA) into the vector. Transform the ligation mixture into competent TOP10 cells, and plate the transformation mix onto Low Salt LB-Zeocin plates. 1. Digest 1 μg of pzero -1 with EcoR V (10 units) for minutes. 2. EcoR V is not heat inactivated. Extract the digested vector with phenol/chloroform, and precipitate the DNA in the aqueous layer with 1/10 volume of 3 M sodium acetate ph 5.6 and 2 volumes of ethanol. Carefully wash the pellet with 80% ethanol and let the pellet air dry. 3. Resuspend the DNA pellet in 90 μl TE buffer. 4. Set up the following 10 μl ligation reaction: Digested vector (~10 ng) 1 μl Test inserts (blunt-ended ΦΧ174 DNA, 20 ng/μl) 1 μl Sterile water 6.5 μl 10X ligation buffer 1 μl T4 DNA Ligase (4 U/μL) 0.5 μl Total Volume 10 μl 5. Set up a "vector only" ligation reaction: Digested vector (~10 ng) 1 μl Sterile water 7.5 μl 10X ligation buffer 1 μl T4 DNA Ligase (4 U/μL) 0.5 μl Total Volume 10 μl 6. Incubate the ligation reactions at 16 C for 1 hour. Longer incubation times may increase the yield of ligated products. Proceed to Transformation, page 10. Use 2 μl of the ligation reaction to transform TOP10 cells. To determine the cloning efficiency, pick colonies and isolate plasmid DNA. To release the test inserts, digest with Nsi I or a combination of other enzymes. Digesting a recombinant plasmid will release one of 11 possible ΦΧ174 DNA fragments (bp): 72, 118, 194, 234, 271, 281, 310, 603, 872, 1078, or Note that tandem inserts may occur. This will not affect disruption of ccdb expression. ΦΧ174 DNA has no sites for Apa I, BamH I, EcoR I, Hind III, Kpn I, Not I, Spe I, Sph I, or Xba I. The cloning efficiency should be ~95%. Continued on next page 9
16 Clone into pzero -1, Continued Analyze clones To determine the cloning efficiency, pick colonies and isolate plasmid DNA. To release the test inserts, digest with Nsi I or a combination of other enzymes. Digestion of a recombinant plasmid containing the test insert will release one of 11 possible ΦΧ174 DNA fragments (bp): 72, 118, 194, 234, 271, 281, 310, 603, 872, 1078, or Note that tandem inserts may occur. This will not affect disruption of ccdb expression. ΦΧ174 DNA has no sites for Apa I, BamH I, EcoR I, Hind III, Kpn I, Not I, Spe I, Sph I, or Xba I. The cloning efficiency should be ~95%. Determine cloning efficiency To determine the cloning efficiency, compare the number of colonies produced in the test insert ligation (10 50 μl per plate) to the total number of colonies seen on the test insert ligation plate plus the number of colonies on the vector only plate. Be sure to correct for the volume plated. cloning efficiency = (colonies on test insert plate/μl plated) (100%) (colonies on test insert plate/μl plated) + (colonies on vector only plate/μl plated) 10
17 Transformation Introduction After performing the cloning reaction, chemically transform or electroporate your pzero -1 construct into competent TOP10 E. coli, and plate the transformed cells onto Low Salt LB-Zeocin plates (see Recipes, page 17). After incubating the plates for 24 hours, analyze Zeocin resistant colonies by DNA miniprep and restriction mapping to find the desired clones. This section includes protocols to transform chemically competent or electrocompetent E. coli. For a high-efficiency and convenient transformation, we recommend One Shot TOP10 Chemically Competent E. coli or One Shot TOP10 Electrocompetent Cells, which are available separately (see page 28 for ordering information). For instructions on preparing chemically competent or electrocompetent cells, see pages 22 and 24, respectively. Controls See the section on Control Reactions (page 8) to determine which controls you wish to include. RECOMMENDATION We recommend that you test the efficiency of the competent cells contained in the One Shot Kit using the puc19 control plasmid: 1. Prepare LB agar plates containing 50 μg/μl ampicillin. 2. Dilute the 10 ng/μl puc19 stock solution (provided with the One Shot Kit) 1:10 in sterile water to prepare a 1 ng/μl solution. 3. Prepare a 10 pg/μl puc10 working solution by transferring 1 μl of the 1 ng/μl stock into 99 μl of sterile water. 4. Transform 1 μl (10 pg) of the working vector solution into 50 μl of competent cells according to the transformation protocol next page. 5. Calculate the transformation efficiency as transformants per 1 μg of plasmid. The cells should have an efficiency of 10 9 transformants/μg of the control plasmid. Handling competent cells Be extremely gentle when working with competent cells. Competent cells are highly sensitive to changes in temperature or mechanical stress caused by pipetting. Start the transformation procedure immediately following the thawing of the cells on ice, and perform all mixing by stirring with a pipette tip, not by pipetting up and down. Important If using cells that carry a laci q gene (i.e. TOP10F, DH5αF ), IPTG is required to induce expression from the lac promoter. Be sure to include IPTG in the agar medium at a final concentration of 1 mm. Do not spread IPTG on the plate. Continued on next page 11
18 Transformation, Continued Before starting Equilibrate a water bath to 42 C. Warm 1 vial of S.O.C. medium to room temperature. Place an appropriate number of 10-cm diameter Low Salt LB-Zeocin agar plates in a 37 C incubator to remove excess moisture (use 1 plate for each transformation). Obtain a test tube rack (float) that will hold all transformation tubes to allow simultaneous heat shock in the water bath at 42 C. One Shot TOP10 chemical transformation protocol 1. Centrifuge the vial(s) containing the ligation reaction(s) briefly and place on ice. 2. Thaw, on ice, one 50 μl vial of One Shot cells for each ligation/transformation. 3. Pipet 2 μl of each ligation reaction directly into the competent cells, and mix by tapping gently. Use 1 μl of diluted control plasmid for the transformation control. You can store the remaining ligation mixture(s) at 20 C. 4. Incubate the vial(s) on ice for 15 minutes. 5. Incubate the vial(s) for seconds in the 42 C water bath (i.e. heat shock). Do not mix or shake. 6. Remove vial(s) from the 42 C bath and quickly place them on ice for 1 minute. 7. Add 250 μl of pre-warmed S.O.C. medium to each vial. (S.O.C. is a rich medium; you must practice good sterile technique to avoid contamination.) 8. Place the vial(s) in a microcentrifuge rack on its side, and secure them with tape to avoid loss of the vial(s). Shake the vial(s) at 37 C for exactly 1 hour at 225 rpm in a shaking incubator. 9. Place the vial(s) with the transformed cells on ice. 10. Spread μl from each transformation vial on separate, labeled Low Salt LB-Zeocin agar plates. We recommend that you plate 2 different volumes to ensure well-spaced colonies. For plating smaller volumes, add 20 μl S.O.C. to ensure even spreading. Note: Plate the puc19 control transformation on LB plates containing 50 μg/ml ampicillin. 11. Invert the plate(s) and incubate at 37 C overnight. Proceed to Analyze Transformants, page 15. Continued on next page 12
19 Transformation, Continued One Shot electroporation protocol Use ONLY electrocompetent cells for electroporation to avoid arcing. Do not use the One Shot TOP10 chemically competent cells for electroporation. 1. Add 2 μl of the ligation reaction into a sterile microcentrifuge tube containing 50 μl of electrocompetent E. coli and mix gently. Do not mix by pipetting up and down. Avoid formation of bubbles. Transfer the cells to a 0.1-cm cuvette. 2. Electroporate your samples using your own protocol and your electroporator. Note: If you have problems with arcing, see page Immediately add 250 μl of room temperature S.O.C. Medium. 4. Transfer the solution to a 15-mL snap-cap tube (e.g. Falcon) and shake at 37 C for 1 hour. 5. Spread μl from each transformation on a pre-warmed selective plate and incubate overnight at 37 C. To ensure even spreading of small volumes, add 20 μl of S.O.C. Medium. We recommend that you plate 2 different volumes to ensure that at least 1 plate will have well-spaced colonies. 6. Invert the plate(s) and incubate at 37 C overnight. Proceed to Analyze transformants, page 15. Chemical transformation Use the following chemical transformation procedure if you have generated your own competent cells from the TOP10 E. coli provided as a stab with the kit. You may not have the same high degree of transformation efficiency regularly attained when using One Shot chemically competent cells. Note: You need to prepare additional S.O.C. for this procedure (see Recipes, page 17). 1. Equilibrate a water bath or heat block to 42 C. Remove the appropriate number of tubes of frozen TOP10 chemically competent cells (50 μl each) and thaw on ice. 2. Add 2 5 μl of each ligation reaction to a separate tube of competent cells. Mix gently with the pipette tip. Do not pipette up and down. Repeat for all ligations. Note: If the cell competency is < cfu/μg, you may need to use more of the ligation mixture. 3. For control reactions, add 1 μl (10 ng) of each supercoiled plasmid (e.g. puc19) to a separate tube of cells. 4. Incubate all tubes on ice 20 minutes. 5. Transfer all tubes to 42 C heat block or water bath and incubate for 1 minute, then place on ice for 1 minute. 6. Add 450 μl of room temperature S.O.C. medium to each tube and shake at 225 rpm for 60 minutes at 37 C. Place on ice. Place the tubes horizontally in the shaker to maximize aeration, and secure them with tape. 7. Plate 25 and 100 μl of each transformation mix on Low Salt LB-Zeocin plates. Let all the liquid absorb into agar, invert the plate(s), and incubate at 37 C for hours. Proceed to Analyze Transformants, page 15. Note: If the cell competency is < cfu/μg, you may need to plate more of each transformation mix. Continued on next page 13
20 Transformation, Continued Electroporation transformation You need to prepare additional S.O.C. for this procedure (see Recipes, page 17). 1. Remove the appropriate number of microcentrifuge tubes of TOP10 electrocompetent cells from the 80 C freezer, and thaw the cells on ice. Chill the electroporation cuvettes on ice. 2. Set up your electroporation device for electroporation of bacteria using the manufacturer's instructions. 3. Dilute ligation reaction with 10 μl of sterile water and place at 65 C for 5 minutes. Note: Ligation reactions are diluted to reduce the salt concentration. Excess salt may cause arcing during electroporation. Heating to 65 C inactivates the ligase. 4. Add 2 μl of the ligation reaction to each tube containing 80 μl competent cells. Repeat for all ligation reactions. 5. For the control reactions, add 1 μl (10 ng) of each supercoiled plasmid (e.g. puc19) to a separate tube of 40 μl competent cells. 6. Incubate all tubes on ice for 1 minute. 7. Take one sample at a time and transfer the cell/dna mix to an electroporation cuvette. Be sure not to trap air bubbles in the sample. Place the cuvette in the chamber, and discharge the electrical pulse. 8. Remove the cuvette, and immediately add 450 μl of room temperature S.O.C. medium into the cuvette. Transfer the contents of the cuvette to a 15-mL snap-cap polypropylene tube (Falcon 2059 or similar), and place the tube on ice. Repeat Steps 7 8 until all samples have been transferred to 15-mL tubes. 9. Incubate the tubes with shaking ( rpm) at 37 C for 60 minutes. Place the tubes horizontally in the shaker to maximize aeration, and secure them with tape. 10. Plate 25 μl and 100 μl of the transformation mix on Low Salt LB-Zeocin agar plates. After the liquid is absorbed into the agar, invert the plates, and incubate them at 37 C for hours. Continued on next page 14
21 Transformation, Continued Analyze Transformants 1. Remove plates from the incubator. Pick 10 Zeocin resistant transformants and inoculate into 2 ml SOB-Zeocin medium with 50 μg/ml Zeocin. Grow 6 8 hours or overnight at 37 C. Using SOB-Zeocin medium is crucial for optimal growth and plasmid yield. 2. Purify plasmid DNA by miniprep for restriction analysis. Remember to isolate the desired clone by streaking for single colonies, and reconfirm the presence of insert before making a glycerol stock. 3. Prepare a glycerol stock of your desired clone for long-term storage by combining 0.85 ml of an overnight bacterial culture with 0.15 ml of sterile 100% glycerol in a labeled cryovial. Mix the contents of the cryovial by vortexing, and freeze the tube in liquid nitrogen or a dry ice/ethanol bath. Store the glycerol stocks at 80 C. 4. After isolating the desired clone, you may proceed with further subcloning and/or analyzing your insert. If you need ultra-pure plasmid DNA for automated or manual sequencing, we recommend using the PureLink HQ Mini Plasmid Purification Kit or the PureLink HiPure Plasmid Miniprep Kit (see page 28 for ordering information). Refer to or contact Technical Support (page 29) for more information on a large selection of plasmid purification columns. 15
22 Troubleshooting Troubleshooting The table below provides solutions to possible problems you might encounter. Observation Reason Solution Very few or no transformants arise High background of transformants which do not contain inserts Thin "lawn" of cells on plate DNA migrates anomalously on agarose gels (bands run at a larger molecular weight than expected and seem slightly smeared) Loss of DNA during precipitation Insert not ligating properly Incorrect insert to vector molar ratio Low transformation efficiency of E. coli strain Overdigestion of vector with restriction enzymes Nuclease contamination in reagents If using a cell line carrying the laci q gene, there may be an insufficient amount of IPTG in plate medium Insufficient amount of Zeocin in plate medium High salt in LB medium Protein bound to DNA Be careful not to lose the DNA pellet when precipitating and washing. Check your subcloning strategy. Determine the concentration of insert and calculate the correct molar ratio. Check transformation efficiency with the puc19 control vector (page 10). Chemically competent cells should yield > transformants/μg DNA. Electrocompetent cells should yield > transformants/μg DNA. Limit digests to minutes. Use the reagents supplied with the kit or autoclave all reagents used for cloning (especially water). IPTG must be in excess to achieve proper induction and killing of background colonies without inserts. Be sure to add the correct amount of Zeocin to the plate medium and let medium cool sufficiently before adding. Make sure you make LB medium with 5 g/liter NaCl. Extract the DNA with phenol/chloroform during preparation of plasmid or after restriction digest. 16
23 Appendix Recipes Low Salt LB Agar Plates with Zeocin Low Salt LB Medium (per liter) 1% Tryptone 0.5% Yeast Extract 0.5% NaCl 1.5% Agar ph For 1 liter, dissolve 10 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 5 g NaCl in 950 ml of deionized water. 2. Adjust the ph of the solution to 7.5 with 5 M NaOH, add 15 g agar, and bring the volume to 1 liter. 3. Autoclave for 20 minutes on liquid cycle. 4. Let agar cool to ~55 C. Thaw the 100 mg/ml Zeocin stock solution and add to a final concentration of 50 μg/ml (500 μl/liter of medium). Sufficient Zeocin is provided to make 2 liters of 50 μg/ml Zeocin medium. If using a cell line carrying a laci q gene, add IPTG to a final concentration of 1 mm (1 ml/liter). 5. Pour the agar into 10-cm Petri dishes. Let the plates harden, then invert and store them at 4 C. Plates containing Zeocin are stable for 1 2 weeks. YT-Zeocin Plates YT medium (per liter) 0.8% Tryptone 0.5% Yeast extract 0.25% NaCl 1.5% agar 1. For 1 liter, dissolve 8 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 2.5 g NaCl in 900 ml of deionized water. 2. Adjust the ph to 7.5 with 5 M NaOH, add 15 g agar, and bring up the volume to 1 liter. 3. Autoclave for 20 minutes on liquid cycle. 4. Cool to the medium to ~55 C. Thaw the 100 mg/ml Zeocin stock solution. 5. Add Zeocin to 50 μg/ml final concentration (500 μl). Continued on next page 17
24 Recipes, Continued SOB Medium with Zeocin SOB (per liter) 2% Tryptone 0.5% Yeast Extract 0.05% NaCl 2.5 mm KCl 10 mm MgCl 2 1. Dissolve 20 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 0.5 g NaCl in 950 ml of deionized water. 2. Make a 250 mm KCl solution by dissolving 1.86 g of KCl in 100 ml of deionized water. Add 10 ml of this stock KCl solution to the solution in step Adjust the ph to 7.5 with 5 M NaOH, and bring up the volume to 1 liter with deionized water. 4. Autoclave this solution, cool to ~55 C, and add 10 ml of sterile 1 M MgCl If preparing medium with Zeocin, add Zeocin to a final concentration of 50 μg/ml. 6. Store the medium at room temperature or 4 C. S.O.C. Medium S.O.C. (per liter) SOB 20 mm glucose 1. After making SOB medium (see above), add 7.2 ml of 50% glucose after step Store the medium at room temperature or 4 C. Do not add Zeocin. Continued on next page 18
25 Recipes, Continued FSB Transformation Solution 10 mm Potassium acetate, ph mm MnCl 2-4H 2 O 10 mm CaCl 2-2H 2 O 100 mm KCl 3 mm Hexaamminecobalt chloride (Aldrich # ; to order) 10% glycerol 1. Prepare 100 ml of 1 M potassium acetate by dissolving 9.82 g in 90 ml deionized water. Adjust ph to 7.5 with 2 M acetic acid. Bring the volume up to 100 ml. 2. For 100 ml of FSB transformation solution, combine the following ingredients: 1 ml 1 M Potassium acetate, ph mg MnCl 2-4H 2 O 150 mg CaCl 2-2H 2 O 750 mg KCl 80 mg Hexaamminecobalt chloride 10 ml 100% glycerol 80 ml deionized water 3. Carefully adjust ph to 6.4 with 0.1 N HCl. If you go past the correct ph, remake the solution. Do not readjust ph with base. 4. Adjust the final volume to 100 ml with deionized water, and filter sterilize the solution. Store at 4 C. DMSO It is very important to use fresh, analytical grade DMSO. If you routinely transform cells by chemical means using the method of Hanahan, 1983, you probably have frozen aliquots of DMSO in your laboratory; if not, then follow this procedure: 1. Order the smallest amount of analytical grade DMSO you can. 2. When the DMSO arrives, take 5 10 ml and aliquot μl per microcentrifuge tube. You may use the rest of the DMSO for other applications or you may aliquot the remainder for competent cells. It depends on whether you plan to use the method described in this manual on a routine basis. 3. Freeze these tubes at 20 C and use one tube per preparation of competent cells. Discard any remaining DMSO in the tube. Use a fresh tube for every preparation of competent cells. 19
26 O HO Zeocin Selective Antibiotic Description Zeocin selective antibiotic belongs to a family of structurally related bleomycin/phleomycin-type antibiotics isolated from Streptomyces. Antibiotics in this family are broad spectrum antibiotics that act as strong antibacterial and antitumor drugs. They show strong toxicity against bacteria, fungi (including yeast), plants, and mammalian cells. Zeocin selective antibiotic is not as toxic as bleomycin on fungi. As a broad-spectrum antibiotic Zeocin selective antibiotic is particularly useful, allowing selection in a number of cell types containing vectors with a Zeocin resistance gene. Chemical properties Zeocin selective antibiotic is a basic, water-soluble compound isolated from Streptomyces verticillus as a copper-chelated glycopeptide. The presence of copper gives the solution its blue color. The chemical formula for Zeocin selective antibiotic is C 55 H 86 O 21 N 20 S 2 Cu-HCl and the molecular weight is It contains several unique amino acids, sugars, and aliphatic amines. For general information about the family of bleomycin antibiotics, see (Berdy, 1980) (Reference section). The general structure of Zeocin selective antibiotic is shown below. H N H N H 2 N H 2 N O CONH2 N ++ Cu N H 2 N CH 3 H N O NH 2 N H HO O O N H CH 3 O CH 3 HO OH OH O H N O NH CH 3 R = HN N S N S H N O NH R NH 2 O O HO HO OH O Continued on next page 20
27 Zeocin Selective Antibiotic, Continued Mechanism of action The exact mechanism of action of Zeocin selective antibiotic is not known; however, it is thought to be the same as bleomycin and phleomycin due to its similarity to these drugs and its inhibition by the Sh ble resistance protein (see the following section). The copper/glycopeptide complex is selective and involves chelation of copper (Cu 2+ ) by the amino group of the α-carboxamide, single nitrogen atoms of both the pyrimidine chromophore and the imidazole moiety, and the carbamoyl group of mannose. The copper-chelated form is inactive. When the antibiotic enters the cell, the copper cation is reduced from Cu 2+ to Cu + and removed by sulfhydryl compounds in the cell. Upon removal of the copper, Zeocin selective antibiotic is activated to bind DNA and cleave it causing cell death (Berdy, 1980). Salt concentrations greater than 110 mm and acidity or basicity inactivate Zeocin selective antibiotic; therefore, it is necessary to reduce the salt in bacterial medium and adjust the ph to 7.5 to make sure the drug remains active. Resistance to Zeocin Selective Antibiotic A Zeocin resistance protein has been isolated and characterized (Gatignol, et al., 1988; Drocourt, et al., 1990). This protein, the product of the Sh ble gene (Streptoalloteichus hindustanus bleomycin gene), is a 13,665 D protein that binds Zeocin selective antibiotic in a stoichiometric manner. The binding of Zeocin selective antibiotic inhibits its DNA strand cleavage activity. Expression of this protein in eukaryotic and prokaryotic hosts confers resistance to the Zeocin selective antibiotic. The Sh ble gene can be excised from pzero -1 without the promoter using PmL I or with the bla (β-lactamase) promoter using Ssp I and Dra I. 21
28 Protocol for Chemically Competent Cells Introduction The following protocol describes how to make chemically competent cells for transformation with plasmid DNA (Hanahan, 1983). These cells are not a substitute for electrocompetent cells used for electroporation. To make chemically competent cells, grow the cells to mid-log phase, wash them with FSB solution, and treat them with DMSO. Freeze the competent cells in a dry ice/ethanol bath and stored at 80 C. Yield This protocol yields enough cells for approximately 60 transformations. The expected efficiency of chemically competent TOP10 cells is cfu/μg of supercoiled DNA. This is also the minimum efficiency needed to obtain colonies per 100 μl transformation mix. Important Sterile technique is absolutely essential to avoid contaminating the competent cells. Remember to use sterile solutions, medium, and supplies. Solutions required For each batch of chemically competent cells, prepare the following solutions (see Recipes, page 17): 5 ml SOB medium in a sterile culture tube 250 ml SOB medium in a sterile 500-mL or 1-liter culture flask FSB solution (~25 ml) Fresh, reagent grade DMSO Protocol for chemically competent cells Day 1: 1. Streak TOP10 E. coli on an LB plate, invert the plate, and incubate at 37 C overnight. Day 2: 2. Inoculate 5 ml of SOB medium in a sterile culture tube with one colony from the LB plate. 3. Grow the cells overnight (12 16 hours) in a shaking incubator ( rpm) at 37 C. Day 3: 4. For each preparation, place the following items on ice or at 4 C. Two 250-mL sterile centrifuge bottles Two 50-mL sterile centrifuge tubes Two 5-mL sterile pipettes 5. Inoculate 250 ml of fresh SOB medium in a 500-mL or 1-liter culture flask with 2.5 ml of the overnight culture. 6. Grow the culture at 37 C at rpm in a shaking incubator until the OD 550 reaches between (2 3 hours). Procedure continued on next page Continued on next page 22
29 Protocol for Chemically Competent Cells, Continued Protocol for chemically competent cells, Continued Day 3, Continued: 7. Divide the culture between the two cold (0 4 C), sterile 250-mL centrifuge bottles, and place on ice for 30 minutes. 8. Centrifuge the 250-mL bottles at 2,000 g for minutes at 0 4 C. 9. Decant the medium, and resuspend each pellet in 10 ml of cold (0 4 C) FSB solution. Transfer the resuspended cells to two cold, sterile, 50-mL centrifuge tubes. Incubate the tubes on ice for 15 minutes. 10. Centrifuge the tubes at 2,000 g for minutes at 0 4 C. 11. Decant the buffer, and resuspend each pellet in 1.8 ml cold FSB solution using a sterile 5-mL pipette. 12. While gently swirling the tubes, slowly add 65 μl of DMSO drop by drop to each tube. Incubate the tubes on ice for 15 minutes. 13. While gently swirling the tubes, slowly add an additional 65 μl of DMSO drop by drop to each tube. 14. Combine the cell suspensions from both tubes into one, and incubate the tube on ice for 15 minutes. Keep on ice. 15. Prepare a dry ice/ethanol bath. 16. For each preparation, place approximately sixty 1.5-mL microcentrifuge tubes on ice. Keep cell suspension on ice. 17. Pipette 50 μl of cell suspension into each tube. 18. As soon as all of the cell suspension is aliquoted, quick-freeze the tubes in the dry ice/ethanol bath and store at 80 C. 23
30 Protocol for Electrocompetent Cells Introduction The following procedure describes how to prepare cells for transformation with plasmid DNA by electroporation. The washing step in the protocol ensures that salts are removed from the cell solution to reduce the conductivity. High conductivity may result in arcing during electroporation. Use electrocompetent cells only for electroporation. Do not use them for any other transformation procedure. Yield The following procedure yields enough electrocompetent cells for approximately 30 transformations. The expected efficiency of the electrocompetent TOP10 cells is cfu/μg of supercoiled DNA. This is the minimum efficiency needed to obtain colonies per 100 μl of the transformation reaction. Important Sterile technique is absolutely essential to avoid contaminating the electrocompetent cells. Protocol for electrocompetent cells Day 1: 1. Streak TOP10 E. coli on an LB plate, invert the plate, and incubate at 37 C overnight. 2. Prepare the following solutions. Store the LB media at room temperature, and the glycerol solution and water at 4 C. 50 ml LB medium in a 250-mL sterile culture flask 1 liter of LB medium in a 2-liter or 4-liter sterile culture flask 50 ml of sterile 10% glycerol 1 liter of sterile water Day 2: 3. Inoculate the 50 ml of LB medium in a 250-mL culture flask with a single colony from the LB plate and incubate at 37 C with shaking ( rpm) for hours (overnight). Day 3: 4. For each preparation, pre-chill on ice or at 4 C: Two sterile 500-mL centrifuge bottles Two sterile 50-mL centrifuge tubes Two sterile 25-mL pipettes One sterile 5-mL pipette 5. Inoculate 1 liter of LB medium in a 2-liter or 4-liter flask with the 50 ml of overnight culture. Grow the 1 liter culture in a shaking incubator ( rpm) at 37 C until the OD 550 is between (approximately 2 3 hours). Procedure continued on next page Continued on next page 24
31 Protocol for Electrocompetent Cells, Continued Protocol for electrocompetent cells, Continued Day 3, Continued: 6. Transfer the 1 liter culture to the 2 chilled, sterile 500-mL centrifuge bottles, and incubate on ice for 30 minutes. 7. Centrifuge the cultures at 2,000 g for 15 minutes at 0 4 C. Keep the cell pellet, and decant the broth. Place the bottles back on ice. 8. Resuspend the cell pellet in each bottle in approximately 500 ml of ice cold sterile water. 9. Centrifuge cells at 2,000 g for 15 minutes at 0 4 C. Keep the pellet, and decant the water. Place the bottles back on ice. 10. Resuspend the cells in each bottle in approximately 250 ml of ice cold sterile water. 11. Centrifuge cells at 2,000 g for 15 minutes at 0 4 C. Decant the water and place the bottles back on ice. 12. Using a pre-chilled sterile 25-mL pipette, resuspend the cells in each bottle in 20 ml of ice cold sterile 10% glycerol. Transfer each cell suspension to a chilled sterile 50-mL centrifuge tube. 13. Centrifuge the cells at 4,000 g for 15 minutes at 0 4 C. Decant the 10% glycerol, and place the tubes on ice. 14. Resuspend each cell pellet in 1 ml of ice cold sterile 10% glycerol. Using a pre-chilled 5-mL pipette, pool the cells into one of the 50-mL tubes. Keep the tubes containing the cells on ice. 15. Prepare a dry ice/ethanol bath. 16. For each preparation, place thirty-five to forty 1.5-mL microcentrifuge tubes on ice, and pipet 40 μl of the cell suspension into each tube. Keep the cell suspension and tubes on ice until you have aliquoted all of the cell solution. 17. After you have aliquoted all of the cell solution, quick-freeze the tubes in the dry ice/ethanol bath. Store the electrocompetent cells at 80 C until ready for use. 25
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual
 MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
ITS Sequencing in Millepora. 10/09 Subcloning DNA Fragments into pbluescript Preparation of pbluescript Vector
 Page 1 of 5 10/09 Subcloning DNA Fragments into pbluescript Preparation of pbluescript Vector 1. Digest 1 µg of pbluescript with Eco RI 2. Following digestion, add 0.1 volumes of 3M sodium acetate (ph
Page 1 of 5 10/09 Subcloning DNA Fragments into pbluescript Preparation of pbluescript Vector 1. Digest 1 µg of pbluescript with Eco RI 2. Following digestion, add 0.1 volumes of 3M sodium acetate (ph
pgm-t Cloning Kit For direct cloning of PCR products generated by Taq DNA polymerases For research use only Cat. # : GVT202 Size : 20 Reactions
 pgm-t Cloning Kit For direct cloning of PCR products generated by Taq DNA polymerases Cat. # : GVT202 Size : 20 Reactions Store at -20 For research use only 1 pgm-t Cloning Kit Cat. No.: GVT202 Kit Contents
pgm-t Cloning Kit For direct cloning of PCR products generated by Taq DNA polymerases Cat. # : GVT202 Size : 20 Reactions Store at -20 For research use only 1 pgm-t Cloning Kit Cat. No.: GVT202 Kit Contents
E. cloni 10G BAC-Optimized Electrocompetent cells
 E. cloni 10G BAC-Optimized Electrocompetent cells Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012 custserv@lucigen.com techserv@lucigen.com
E. cloni 10G BAC-Optimized Electrocompetent cells Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012 custserv@lucigen.com techserv@lucigen.com
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
One Shot TOP10 Competent Cells
 One Shot TOP10 Competent Cells Catalog nos. C4040-10, C4040-03, C4040-06, C4040-50, and C4040-52 Version M 6 April 2004 28-0126 www.invitrogen.com tech_service@invitrogen.com Important Information Introduction
One Shot TOP10 Competent Cells Catalog nos. C4040-10, C4040-03, C4040-06, C4040-50, and C4040-52 Version M 6 April 2004 28-0126 www.invitrogen.com tech_service@invitrogen.com Important Information Introduction
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
E. cloni EXPRESS Electrocompetent Cells
 E. cloni EXPRESS Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX:
E. cloni EXPRESS Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX:
pgm-t Cloning Kit Cat. # : GVT202 Size : 20 Reactions Store at -20
 pgm-t Cloning Kit Cat. # : GVT202 Size : 20 Reactions Store at -20 1 Kit Contents Contents pgm-t Cloning Kit pgm-t Vector (50 ng/μl) 20 μl T4 DNA Ligase (3 U/μl) 20 μl 10X T4 DNA Ligation Buffer 30 μl
pgm-t Cloning Kit Cat. # : GVT202 Size : 20 Reactions Store at -20 1 Kit Contents Contents pgm-t Cloning Kit pgm-t Vector (50 ng/μl) 20 μl T4 DNA Ligase (3 U/μl) 20 μl 10X T4 DNA Ligation Buffer 30 μl
Expression of Recombinant Proteins
 Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Endura Chemically Competent and Electrocompetent Cells
 Endura Chemically Competent and Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE. Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608)
Endura Chemically Competent and Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE. Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608)
One Shot TOP10F Competent Cells
 One Shot TOP10F Competent Cells Catalog nos. C3030-03, C3030-06 Version I 6 April 2004 28-0124 www.invitrogen.com tech_service@invitrogen.com 2 Overview Contents 21 tubes of competent TOP10F E. coli in
One Shot TOP10F Competent Cells Catalog nos. C3030-03, C3030-06 Version I 6 April 2004 28-0124 www.invitrogen.com tech_service@invitrogen.com 2 Overview Contents 21 tubes of competent TOP10F E. coli in
Molecular Techniques Third-year Biology
 PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
ORFs and genes. Please sit in row K or forward
 ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
HI-Control BL21(DE3) & HI-Control 10G Chemically Competent Cells
 HI-Control BL21(DE3) & HI-Control 10G Chemically Competent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE MA156 Rev.31OCT2016 Table of Contents Components & Storage Conditions... 3 HI-Control
HI-Control BL21(DE3) & HI-Control 10G Chemically Competent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE MA156 Rev.31OCT2016 Table of Contents Components & Storage Conditions... 3 HI-Control
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
CopyCutter EPI400 Electrocompetent E. coli CopyCutter EPI400 Chemically Competent E. coli CopyCutter Induction Solution
 CopyCutter EPI400 Electrocompetent E. coli CopyCutter EPI400 Chemically Competent E. coli CopyCutter Induction Solution Cat. Nos. C400EL10, C400CH10, and CIS40025 Available exclusively thru Lucigen. lucigen.com/epibio
CopyCutter EPI400 Electrocompetent E. coli CopyCutter EPI400 Chemically Competent E. coli CopyCutter Induction Solution Cat. Nos. C400EL10, C400CH10, and CIS40025 Available exclusively thru Lucigen. lucigen.com/epibio
Electrocomp GeneHogs E. coli One Shot Electrocomp GeneHogs E. coli
 Electrocomp GeneHogs E. coli One Shot Electrocomp GeneHogs E. coli Catalog nos. C8080-10, C8080-03, C800-05 Version E 17 May 2007 25-0387 www.invitrogen.com Overview Introduction The information in this
Electrocomp GeneHogs E. coli One Shot Electrocomp GeneHogs E. coli Catalog nos. C8080-10, C8080-03, C800-05 Version E 17 May 2007 25-0387 www.invitrogen.com Overview Introduction The information in this
CopyCutter EPI400 Electrocompetent E. coli. CopyCutter EPI400 Chemically Competent E. coli
 Cat. Nos. C400EL10, C400CH10, and CIS40025 CopyCutter EPI400 Electrocompetent and Chemically Competent E. coli* cells were developed to significantly lower the copy number of a wide variety of common vectors
Cat. Nos. C400EL10, C400CH10, and CIS40025 CopyCutter EPI400 Electrocompetent and Chemically Competent E. coli* cells were developed to significantly lower the copy number of a wide variety of common vectors
GeNei TM Transformation Teaching Kit Manual
 Teaching Kit Manual Cat No. New Cat No. KT07 107385 KT07A 106220 Revision No.: 00060505 CONTENTS Page No. Objective 3 Principle 3 Kit Description 6 Materials Provided 7 Procedure 9 Observation & Interpretation
Teaching Kit Manual Cat No. New Cat No. KT07 107385 KT07A 106220 Revision No.: 00060505 CONTENTS Page No. Objective 3 Principle 3 Kit Description 6 Materials Provided 7 Procedure 9 Observation & Interpretation
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines
 Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
MC1061 F- Electrocompetent Cells
 MC1061 F- Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608)
MC1061 F- Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608)
TransforMax EPI300 Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 Chemically Competent E. coli
 TransforMax EPI300 Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 Chemically Competent E. coli Cat. Nos. EC300102, EC300110, EC300150, and C300C105 Available exclusively thru Lucigen. lucigen.com/epibio www.lucigen.com
TransforMax EPI300 Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 Chemically Competent E. coli Cat. Nos. EC300102, EC300110, EC300150, and C300C105 Available exclusively thru Lucigen. lucigen.com/epibio www.lucigen.com
An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
TD-P Revision 3.0 Creation Date: 6/9/2016 Revision Date: 8/16/2018
 Protocol TD-P Revision 3.0 Creation Date: 6/9/2016 Revision Date: 8/16/2018 Electrotransformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Modified from Methods in Molecular Biology Vol. 47 Introduction Agrobacterium
Protocol TD-P Revision 3.0 Creation Date: 6/9/2016 Revision Date: 8/16/2018 Electrotransformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Modified from Methods in Molecular Biology Vol. 47 Introduction Agrobacterium
High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria
 High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria Eric R Geertsma & Bert Poolman Supplementary text and figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of SfiI sites yielding identical 3 extensions
High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria Eric R Geertsma & Bert Poolman Supplementary text and figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of SfiI sites yielding identical 3 extensions
Phage T1-Resistant TransforMax EPI300 -T1 R Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 -T1 R Chemically Competent E. coli
 Phage T1-Resistant TransforMax EPI300 -T1 R Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 -T1 R Chemically Competent E. coli Cat. Nos. EC02T15, EC02T110, and CT1C0210 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com),
Phage T1-Resistant TransforMax EPI300 -T1 R Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 -T1 R Chemically Competent E. coli Cat. Nos. EC02T15, EC02T110, and CT1C0210 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com),
Presto Mini Plasmid Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 03.06.17 For Research Use Only Presto Mini Plasmid Kit PDH004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) PDH100 (100 Preparation Kit) PDH300 (300 Preparation Kit) Advantages Sample: 1-7 ml of cultured
Instruction Manual Ver. 03.06.17 For Research Use Only Presto Mini Plasmid Kit PDH004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) PDH100 (100 Preparation Kit) PDH300 (300 Preparation Kit) Advantages Sample: 1-7 ml of cultured
Hetero-Stagger PCR Cloning Kit
 Product Name: Code No: Size: DynaExpress Hetero-Stagger PCR Cloning Kit DS150 20 reactions Kit Components: Box 1 (-20 ) phst-1 Vector, linearized Annealing Buffer Ligase Mixture phst Forward Sequence Primer
Product Name: Code No: Size: DynaExpress Hetero-Stagger PCR Cloning Kit DS150 20 reactions Kit Components: Box 1 (-20 ) phst-1 Vector, linearized Annealing Buffer Ligase Mixture phst Forward Sequence Primer
pbluescript II RI Predigested Vector
 pbluescript II RI Predigested Vector INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #212250 Revision A For In Vitro Use Only 212250-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this product.
pbluescript II RI Predigested Vector INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #212250 Revision A For In Vitro Use Only 212250-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this product.
ElectroTen-Blue Electroporation Competent Cells
 ElectroTen-Blue Electroporation Competent Cells Instruction Manual Catalog #200159 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 200159-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty
ElectroTen-Blue Electroporation Competent Cells Instruction Manual Catalog #200159 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 200159-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty
NAME:... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:... Maximum marks: 50. Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer Science, UKZN
 COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
Hurricane Miniprep Kit PROTOCOL
 Hurricane Miniprep Kit PROTOCOL Description: The Hurricane Miniprep Kit is designed for purification of up to 25 ug of high purity plasmid DNA from a starting volume of 2-5 ml of bacterial culture. The
Hurricane Miniprep Kit PROTOCOL Description: The Hurricane Miniprep Kit is designed for purification of up to 25 ug of high purity plasmid DNA from a starting volume of 2-5 ml of bacterial culture. The
GenBuilder TM Plus Cloning Kit User Manual
 GenBuilder TM Plus Cloning Kit User Manual Cat. No. L00744 Version 11242017 Ⅰ. Introduction... 2 I.1 Product Information... 2 I.2 Kit Contents and Storage... 2 I.3 GenBuilder Cloning Kit Workflow... 2
GenBuilder TM Plus Cloning Kit User Manual Cat. No. L00744 Version 11242017 Ⅰ. Introduction... 2 I.1 Product Information... 2 I.2 Kit Contents and Storage... 2 I.3 GenBuilder Cloning Kit Workflow... 2
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
TransforMax EPI300 Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 Chemically Competent E. coli
 TransforMax EPI300 Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 Chemically Competent E. coli Cat. Nos. EC300105, EC300110, EC300150, and C300C105 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com),
TransforMax EPI300 Electrocompetent E. coli TransforMax EPI300 Chemically Competent E. coli Cat. Nos. EC300105, EC300110, EC300150, and C300C105 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com),
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
HE Swift Cloning Kit
 HE Swift Cloning Kit For high-efficient cloning of PCR products either blunt or sticky-end Kit Contents Contents VTT-BB05 phe Vector (35 ng/µl) 20 µl T4 DNA Ligase (3 U/µl) 20 µl 2 Reaction Buffer 100
HE Swift Cloning Kit For high-efficient cloning of PCR products either blunt or sticky-end Kit Contents Contents VTT-BB05 phe Vector (35 ng/µl) 20 µl T4 DNA Ligase (3 U/µl) 20 µl 2 Reaction Buffer 100
Five-minute cloning of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products
 TOPO TA Cloning Version Q July 21, 2003 25-0184 TOPO TA Cloning Five-minute cloning of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products Catalog nos. K4500-01, K4500-40, K4510-20, K4520-01, K4520-40, K4550-01, K4550-40,
TOPO TA Cloning Version Q July 21, 2003 25-0184 TOPO TA Cloning Five-minute cloning of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products Catalog nos. K4500-01, K4500-40, K4510-20, K4520-01, K4520-40, K4550-01, K4550-40,
GenBuilder TM Cloning Kit User Manual
 GenBuilder TM Cloning Kit User Manual Cat.no L00701 Version 11242017 Ⅰ. Introduction... 2 I.1 Product Information... 2 I.2 Kit Contents and Storage... 2 I.3 GenBuilder Cloning Kit Workflow... 2 Ⅱ. DNA
GenBuilder TM Cloning Kit User Manual Cat.no L00701 Version 11242017 Ⅰ. Introduction... 2 I.1 Product Information... 2 I.2 Kit Contents and Storage... 2 I.3 GenBuilder Cloning Kit Workflow... 2 Ⅱ. DNA
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
GenBuilder TM Plus Cloning Kit User Manual
 GenBuilder TM Plus Cloning Kit User Manual Cat.no L00744 Version 11242017 Ⅰ. Introduction... 2 I.1 Product Information... 2 I.2 Kit Contents and Storage... 2 I.3 GenBuilder Cloning Kit Workflow... 2 Ⅱ.
GenBuilder TM Plus Cloning Kit User Manual Cat.no L00744 Version 11242017 Ⅰ. Introduction... 2 I.1 Product Information... 2 I.2 Kit Contents and Storage... 2 I.3 GenBuilder Cloning Kit Workflow... 2 Ⅱ.
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
G+C content. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
CJ236 Electrocompetent Cells
 CJ236 Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012
CJ236 Electrocompetent Cells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012
Geneaid Maxi Plasmid Kit & Geneaid Maxi Plasmid Kit (Endotoxin Free)
 Geneaid Maxi Plasmid Kit & Geneaid Maxi Plasmid Kit (Endotoxin Free) PM002, PME02 (2 Preparation Sample Kit) PM010, PME10 (10 Preparation Kit) PM025, PME25 (25 Preparation Kit) Instruction Manual Ver.
Geneaid Maxi Plasmid Kit & Geneaid Maxi Plasmid Kit (Endotoxin Free) PM002, PME02 (2 Preparation Sample Kit) PM010, PME10 (10 Preparation Kit) PM025, PME25 (25 Preparation Kit) Instruction Manual Ver.
I-Blue Midi Plasmid Kit. I-Blue Midi Plasmid Kit. (Endotoxin Free) IBI SCIENTIFIC. Instruction Manual Ver For Research Use Only.
 Instruction Manual Ver. 05.11.17 For Research Use Only I-Blue Midi Plasmid Kit & I-Blue Midi Plasmid Kit (Endotoxin Free) IB47180, IB47190 (2 Preparation Sample Kit) IB47181, IB47191 (25 Preparation Kit)
Instruction Manual Ver. 05.11.17 For Research Use Only I-Blue Midi Plasmid Kit & I-Blue Midi Plasmid Kit (Endotoxin Free) IB47180, IB47190 (2 Preparation Sample Kit) IB47181, IB47191 (25 Preparation Kit)
Biol/Chem 475 Spring 2007
 Biol/Chem 475 Spring 2007 Goal of lab: For most of the quarter, we will be exploring a gene family that was first discovered in fruitlfies and then found to be present in humans and worms and fish and
Biol/Chem 475 Spring 2007 Goal of lab: For most of the quarter, we will be exploring a gene family that was first discovered in fruitlfies and then found to be present in humans and worms and fish and
Transforming Bacteria
 Properties of E. coli Strains for Subcloning Common laboratory strains of E. coli, like JM109, DH5α, and XL-1 Blue, are different from their wildtype counterparts. These strains carry some mutations designed
Properties of E. coli Strains for Subcloning Common laboratory strains of E. coli, like JM109, DH5α, and XL-1 Blue, are different from their wildtype counterparts. These strains carry some mutations designed
Subcloning 1. Overview 2. Method
 Subcloning 1. Overview: 1.1. Digest plasmids for vector + insert 1.2. CIP treat vector 1.3. Gel purify vector + insert 1.4. Ligate 1.5. Transform bacteria with ligation reactions 1.6. Qiagen or Eppendorf
Subcloning 1. Overview: 1.1. Digest plasmids for vector + insert 1.2. CIP treat vector 1.3. Gel purify vector + insert 1.4. Ligate 1.5. Transform bacteria with ligation reactions 1.6. Qiagen or Eppendorf
Cat # Box1 Box2. DH5a Competent E. coli cells CCK-20 (20 rxns) 40 µl 40 µl 50 µl x 20 tubes. Choo-Choo Cloning TM Enzyme Mix
 Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
ProductInformation. Genomic DNA Isolation Kit. Product No. GDI-3 Technical Bulletin No. MB-275 May 2000 TECHNICAL BULLETIN
 Genomic DNA Isolation Kit Product No. GDI-3 Technical Bulletin No. MB-275 May 2000 TECHNICAL BULLETIN ProductInformation Product Description Sigma s Genomic DNA Isolation Kit isolates genomic DNA from
Genomic DNA Isolation Kit Product No. GDI-3 Technical Bulletin No. MB-275 May 2000 TECHNICAL BULLETIN ProductInformation Product Description Sigma s Genomic DNA Isolation Kit isolates genomic DNA from
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
FosmidMAX DNA Purification Kit
 Cat. No. FMAX046 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook (facebook.com/epicentrebio), and Twitter (@EpicentreBio). www.epicentre.com Lit. # 204 10/2012 1 EPILIT204 Rev. A
Cat. No. FMAX046 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook (facebook.com/epicentrebio), and Twitter (@EpicentreBio). www.epicentre.com Lit. # 204 10/2012 1 EPILIT204 Rev. A
Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
Protein Expression. TrcHis. A Manual of Methods for Expression of Polyhistidine - Containing Recombinant Proteins Using the ptrchis Vector System
 Xpress System Protein Expression TrcHis Version E 000920 25-0038 Xpress System Protein Expression TrcHis A Manual of Methods for Expression of Polyhistidine - Containing Recombinant Proteins Using the
Xpress System Protein Expression TrcHis Version E 000920 25-0038 Xpress System Protein Expression TrcHis A Manual of Methods for Expression of Polyhistidine - Containing Recombinant Proteins Using the
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
VDL101.3 CLONING TRANSGENE INTO pad5f35
 Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this protocol is to transfer a transgene from the pshuttlex plasmid to pad5/f35. 1.2. The starting material is 10 μg plasmid DNA. 1.3. This procedure is routinely performed
Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this protocol is to transfer a transgene from the pshuttlex plasmid to pad5/f35. 1.2. The starting material is 10 μg plasmid DNA. 1.3. This procedure is routinely performed
Transformation (The method of CaCl 2 )
 PROTOCOLS E. coli Transformation (The method of CaCl 2 ) Ligation PRODUCTION competent cells of E. COLI. (Rubidium cells). Gel DNA Recovery Kit Electroporation Digestiones Plasmid purification (The method
PROTOCOLS E. coli Transformation (The method of CaCl 2 ) Ligation PRODUCTION competent cells of E. COLI. (Rubidium cells). Gel DNA Recovery Kit Electroporation Digestiones Plasmid purification (The method
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Homework. A bit about the nature of the atoms of interest. Project. The role of electronega<vity
 Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
BP-reaction (recombination of PCR products into entry vector) Created on: 06/01/10 Version: 1.1 No.: 1 Page 1 of 6
 Created on: 06/01/10 Version: 1.1 No.: 1 Page 1 of 6 1. Background This reaction generates bacteria that contain recombinant Gateway-compatible entry plasmid. The PCRamplified ORFs (SOPs ORF-PCR 1 (two
Created on: 06/01/10 Version: 1.1 No.: 1 Page 1 of 6 1. Background This reaction generates bacteria that contain recombinant Gateway-compatible entry plasmid. The PCRamplified ORFs (SOPs ORF-PCR 1 (two
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Primer Design Workshop. École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria
 Primer Design Workshop École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria Scenario You have discovered the presence of a novel endophy5c organism living inside the cells
Primer Design Workshop École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria Scenario You have discovered the presence of a novel endophy5c organism living inside the cells
BACMAX DNA Purification Kit
 Cat. No. BMAX044 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook (facebook.com/epicentrebio), and Twitter (@EpicentreBio). www.epicentre.com Lit. # 212 10/2012 1 EPILIT212 Rev. A
Cat. No. BMAX044 Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook (facebook.com/epicentrebio), and Twitter (@EpicentreBio). www.epicentre.com Lit. # 212 10/2012 1 EPILIT212 Rev. A
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
National PHL TB DST Reference Center PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents
 PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents Document Page Number PSQ for Rifampin 2-6 Comparison table for rpob Codon Numbering 2 rpob mutation list (new numbering system) 3-5 rpob interpretations 6 PSQ for
PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents Document Page Number PSQ for Rifampin 2-6 Comparison table for rpob Codon Numbering 2 rpob mutation list (new numbering system) 3-5 rpob interpretations 6 PSQ for
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
PCR Polishing Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Catalog # Revision A. For In Vitro Use Only
 PCR Polishing Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #200409 Revision A For In Vitro Use Only 200409-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this product. No other warranties
PCR Polishing Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #200409 Revision A For In Vitro Use Only 200409-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this product. No other warranties
Experiment (CSS451, 2010) 1. It is the. the amount. a. The ph of the. reaction solution, be stored at 4. VERY. -20oC. They. conditions.
 Experiment 3: Plasmid Digestion, Ligation, E coli. Transformation, and Selection (CSS451, 2010) GENERAL COMMENTS 1. It is the accepted convention that 1 unit of restriction endonuclease corresponds to
Experiment 3: Plasmid Digestion, Ligation, E coli. Transformation, and Selection (CSS451, 2010) GENERAL COMMENTS 1. It is the accepted convention that 1 unit of restriction endonuclease corresponds to
Lambda DNA Purification Kit
 Lambda DNA Purification Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #200391 and #200392 Revision A For In Vitro Use Only 200391-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this
Lambda DNA Purification Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #200391 and #200392 Revision A For In Vitro Use Only 200391-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this
Figure 1. Map of cloning vector pgem T-Easy (bacterial plasmid DNA)
 Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi CHEM4402 Biochemistry II Laboratory Laboratory 6: Ligation & Bacterial Transformation (Bring your text and laptop to class if you wish to work on your assignment during
Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi CHEM4402 Biochemistry II Laboratory Laboratory 6: Ligation & Bacterial Transformation (Bring your text and laptop to class if you wish to work on your assignment during
TA Cloning Kit. Catalog nos. K and K Catalog nos. K and K Catalog nos. K and K
 TA Cloning Kit Version T August 20, 2002 25-0024 TA Cloning Kit Catalog nos. K2000-01 and K2000-40 Catalog nos. K2030-01 and K2030-40 Catalog nos. K2040-01 and K2040-40 A Limited Label License covers this
TA Cloning Kit Version T August 20, 2002 25-0024 TA Cloning Kit Catalog nos. K2000-01 and K2000-40 Catalog nos. K2030-01 and K2030-40 Catalog nos. K2040-01 and K2040-40 A Limited Label License covers this
Table of Contents. i. Insertion of DNA fragments into plasmid vector...4. ii. Self-circularization of linear blunt-ended DNA...4
 Table of Contents I. Description...2 II. Kit Components...2 III. Storage...2 IIV. Notes...2 V. Reference...3 VI. PROCEDURES A. Dephosphorylation of vector DNA...3 B. Blunting reaction...3 C. Ligation reaction
Table of Contents I. Description...2 II. Kit Components...2 III. Storage...2 IIV. Notes...2 V. Reference...3 VI. PROCEDURES A. Dephosphorylation of vector DNA...3 B. Blunting reaction...3 C. Ligation reaction
Rapid DNA Ligation & Transformation Kit
 1 Rapid DNA Ligation & Transformation Kit (#K1432 for 30 reactions) INTRODUCTION The Rapid DNA Ligation & Transformation Kit enables ligation of any type of DNA in 5 minutes at ambient temperature followed
1 Rapid DNA Ligation & Transformation Kit (#K1432 for 30 reactions) INTRODUCTION The Rapid DNA Ligation & Transformation Kit enables ligation of any type of DNA in 5 minutes at ambient temperature followed
His-Patch ThioFusion Expression System
 user guide His-Patch ThioFusion Expression System Catalog number K360-01 Revision date 19 January 2012 Publication Part number 25-0120 MAN0000029 For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human
user guide His-Patch ThioFusion Expression System Catalog number K360-01 Revision date 19 January 2012 Publication Part number 25-0120 MAN0000029 For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human
TOPO TA Cloning. TOPO TA Cloning. Five-minute cloning of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products
 TOPO TA Cloning Version O 011102 25-0184 TOPO TA Cloning Five-minute cloning of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products Catalog nos. K4500-01, K4500-40, K4520-01, K4520-40, K4550-01, K4550-40, K4560-01 (pcr
TOPO TA Cloning Version O 011102 25-0184 TOPO TA Cloning Five-minute cloning of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products Catalog nos. K4500-01, K4500-40, K4520-01, K4520-40, K4550-01, K4550-40, K4560-01 (pcr
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification
 Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
DNA Ligation Kit Ver. 1 Manual
 Table of content Description... 2 Procedures and Examples A. Insertion of DNA into plasmid vectors... 3 B. Insertion of DNA into λ phage vectors... 4 C. Self-circulization of linear DNA... 4 D. Linker
Table of content Description... 2 Procedures and Examples A. Insertion of DNA into plasmid vectors... 3 B. Insertion of DNA into λ phage vectors... 4 C. Self-circulization of linear DNA... 4 D. Linker
HiPer Transformation Teaching Kit
 HiPer Transformation Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM017 Number of experiments that can be performed: 10 Duration of Experiment: 4 days Day 1- Preparation of media and revival of E. coli Host Day 2- Inoculation
HiPer Transformation Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM017 Number of experiments that can be performed: 10 Duration of Experiment: 4 days Day 1- Preparation of media and revival of E. coli Host Day 2- Inoculation
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Protein Structure Analysis
 BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Iosif Vaisman COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOINFORMATICS STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS
BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Iosif Vaisman COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOINFORMATICS STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS
Product Information (1) General Information
 Table of Contents Product Information 2 (1) General Information 2 (2) Features 3 (3) Kit Contents 3 (4) Storage and Expiration 3 Standard Protocol for Preparation of Competent Cells 4 Instant Protocol
Table of Contents Product Information 2 (1) General Information 2 (2) Features 3 (3) Kit Contents 3 (4) Storage and Expiration 3 Standard Protocol for Preparation of Competent Cells 4 Instant Protocol
Genlantis A division of Gene Therapy Systems, Inc Telesis Court San Diego, CA USA Telephone: or (US toll free)
 TurboCells BL21(DE3) TurboCells BL21(DE3)pLysS Chemically Competent E. coli Instruction Manual Catalog Numbers C302020 C303020 A division of Gene Therapy Systems, Inc. 10190 Telesis Court San Diego, CA
TurboCells BL21(DE3) TurboCells BL21(DE3)pLysS Chemically Competent E. coli Instruction Manual Catalog Numbers C302020 C303020 A division of Gene Therapy Systems, Inc. 10190 Telesis Court San Diego, CA
TaKaRa MiniBEST Plasmid Purification Kit Ver.4.0
 Cat. # 9760 For Research Use TaKaRa MiniBEST Plasmid Purification Kit Ver.4.0 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Kit Components... 3 III. Shipping and Storage... 4 IV. Preparation
Cat. # 9760 For Research Use TaKaRa MiniBEST Plasmid Purification Kit Ver.4.0 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Kit Components... 3 III. Shipping and Storage... 4 IV. Preparation
Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit
 Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MX-P10/ DP01MX-P20 Size : 10/20 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit provides simple,
Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MX-P10/ DP01MX-P20 Size : 10/20 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit provides simple,
Creation of A Caspese-3 Sensing System Using A Combination of Split- GFP and Split-Intein
 Supplementary Information Creation of A Caspese-3 Sensing System Using A Combination of Split- GFP and Split-Intein Seiji Sakamoto,* Mika Terauchi, Anna Hugo, Tanner Kim, Yasuyuki Araki and Takehiko Wada*
Supplementary Information Creation of A Caspese-3 Sensing System Using A Combination of Split- GFP and Split-Intein Seiji Sakamoto,* Mika Terauchi, Anna Hugo, Tanner Kim, Yasuyuki Araki and Takehiko Wada*
HiPer Plasmid DNA Cloning Teaching Kit
 HiPer Plasmid DNA Cloning Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM022 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: 4 days Day 1- Preparation of media and revival of E. coli Host Day2-
HiPer Plasmid DNA Cloning Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM022 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: 4 days Day 1- Preparation of media and revival of E. coli Host Day2-
Zero Blunt TOPO PCR Cloning Kit
 user guide Zero Blunt TOPO PCR Cloning Kit Five-minute cloning of blunt-end PCR products Catalog numbers K2800-20, K2800-40, K2820-20, K2820-40, K2830-20, K2860-20, K2860-40, K2800-02, 450245 Publication
user guide Zero Blunt TOPO PCR Cloning Kit Five-minute cloning of blunt-end PCR products Catalog numbers K2800-20, K2800-40, K2820-20, K2820-40, K2830-20, K2860-20, K2860-40, K2800-02, 450245 Publication
PCR Cloning II fusion domains for purification His 6 GST chitin binding protein MBP
 PCR cloning : why secondary amplification? May 26, 2009 secondary amplification amplification of the coding sequence alone or of defined fragments ligation into expression vector insertion of fusion domains
PCR cloning : why secondary amplification? May 26, 2009 secondary amplification amplification of the coding sequence alone or of defined fragments ligation into expression vector insertion of fusion domains
Ready_to_use Fast Seamless Cloning Kit. User Manual
 For general laboratory use. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. Ready_to_use Fast Seamless Cloning Kit User Manual 1 / 6 Tel: 021-58975266 Fax: 021-50800270 Email:tech@dogene.com
For general laboratory use. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. Ready_to_use Fast Seamless Cloning Kit User Manual 1 / 6 Tel: 021-58975266 Fax: 021-50800270 Email:tech@dogene.com
Recombineering Manual
 Recombineering Manual Anthony Popkie The Phiel Laboratory The Research Institute at Nationwide Childrenʼs Hospital 1 BAC Transformation BACs may be transformed into either DY380, EL250 or EL350 cells.
Recombineering Manual Anthony Popkie The Phiel Laboratory The Research Institute at Nationwide Childrenʼs Hospital 1 BAC Transformation BACs may be transformed into either DY380, EL250 or EL350 cells.
Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit. Cat. # : DP01MX-P10/ DP01MX-P20 Size : 10/20 Reactions Store at RT For research use only
 Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MX-P10/ DP01MX-P20 Size : 10/20 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit provides simple,
Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MX-P10/ DP01MX-P20 Size : 10/20 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Maxiprep Plus Purification Kit provides simple,
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
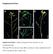 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
pcmv6-neo Vector Application Guide Table of Contents Package Contents and Storage Conditions Each kit comes with the following components:
 pcmv6-neo Vector Application Guide Table of Contents Package Contents and Storage Conditions... 1 Product Description... 1 Introduction... 1 Production and Quality Assurance... 2 Methods... 2 Other required
pcmv6-neo Vector Application Guide Table of Contents Package Contents and Storage Conditions... 1 Product Description... 1 Introduction... 1 Production and Quality Assurance... 2 Methods... 2 Other required
Plasmid Midiprep Purification Kit
 Plasmid Midiprep Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MD/ DP01MD-100 Size : 20/100 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Midiprep Purification Kit provides simple rapid protocol
Plasmid Midiprep Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MD/ DP01MD-100 Size : 20/100 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Midiprep Purification Kit provides simple rapid protocol
