Yvan L Homme, Anne Leboeuf, Johanne Cameron. Abstract. Résumé
|
|
|
- Cornelia Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Article PrP genotype frequencies of Quebec sheep breeds determined by real-time PCR and molecular beacons Yvan L Homme, Anne Leboeuf, Johanne Cameron Abstract The allele and genotype frequencies of the prion protein gene (PrP), known to have an impact on scrapie susceptibility, were determined by real-time PCR for 500 Quebec purebred rams. Molecular beacons were very efficient in discriminating the 5 alleles investigated. Polymorphisms at coding positions 136, 154, and 171 of the PrP gene were analyzed using 3 separate real-time PCR reactions and a total of 7 molecular beacons. A total of 4 different alleles (ARQ, ARR, AHR, and VRQ) were observed at different frequencies among the 7 breeds of sheep investigated. Results show that more than 50% of the rams in every breed carried at least one ARR allele, which is considered the most resistant to scrapie. The susceptibility ARQ allele was also present in every breed and together with the ARR allele, they were the most frequent alleles found in Quebec rams. The VRQ allele associated with the highest susceptibility to scrapie occurred in 5 of the 7 breeds, although at low frequencies. Overall, the results indicate that the frequencies of PrP alleles and genotypes in common breeds of sheep in Quebec make it feasible to reduce scrapie risk by selective breeding. Résumé Les fréquences alléliques et génotypiques du gène de la protéine prion (PrP), reconnu pour avoir un impact sur la susceptibilité envers la tremblante, ont été déterminées par PCR en temps réel pour 500 béliers pur-sang du Québec. Des balises moléculaires étaient très efficaces pour discriminer les 5 allèles étudiés. Le polymorphisme aux positions codantes 136, 154 et 171 du gène PrP a été analysé à l aide de 3 analyses séparées de PCR en temps réel et un total de 7 balises moléculaires. Quatre allèles différents (ARQ, ARR, AHR et VRQ) ont été observés à des fréquences variables parmi les 7 races de moutons étudiées. Les résultats montrent que plus de 50 % des béliers dans chaque race sont porteurs d au moins un allèle ARR, considéré comme étant le plus résistant à la tremblante. L allèle de susceptibilité ARQ était également présent dans chaque race et avec l allèle ARR ils étaient les allèles les plus fréquemment rencontrés chez les béliers du Québec. L allèle VRQ associé avec la plus grande susceptibilité à la tremblante était rencontré chez 5 des 7 races, bien qu à des fréquences peu élevées. De manière générale, les résultats indiquent que la fréquence des allèles PrP et des génotypes chez les races de mouton communes au Québec rendent possible une réduction du risque de tremblante en effectuant des accouplements sélectifs. (Traduit par Docteur Serge Messier) Introduction Scrapie is a member of the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) which include bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattle, chronic wasting disease (CWD) in cervids, and Creutzfeldt-Jacob (CJD) disease in humans. While the exact etiology of TSEs is still debated, the disease is associated with the presence of an abnormal isoform of a host-encoded protein called a prion (1). In many species, including sheep, polymorphisms in the prion gene are associated with susceptibility to the disease. Considerable data now exist on the genetics of susceptibility to scrapie (2). It is generally accepted that susceptibility or resistance to scrapie is modulated by allelic variants of the prion protein (PrP) gene (3). Over 40 polymorphisms have been reported so far for the PrP gene, although only those at codons 136, 154, and 171 appear to be closely linked to scrapie susceptibility. These later polymorphisms give rise to 5 alleles that vary by 1 amino acid from what is considered to be the original or wild type allele (ARQ): ARR, AHQ, ARH, VRQ, and ARQ (4). Polymorphisms at codon 136 (alanine A or valine V) and at codon 171 (glutamine Q, histidine H, or arginine R) clearly influence susceptibility of developing scrapie (5 7). The association between the polymorphism at codon 154 (arginine R or histidine H) and susceptibility to scrapie is still unclear since some data suggest that a histidine at codon 154 offers some protection in certain breeds of sheep (7) but not in others (8). The genotype AA 136 RR 171 is associated with the highest resistance to scrapie, whereas the genotype VV 136 QQ 171 is associated with the highest susceptibility to infection (7). In breeds where the V 136 R 154 Q 171 allele is absent, TransBIOtech, 201 Mgr Bourget, Lévis, Québec G6V 9V6 (L Homme); Centre d expertise en production ovine du Québec, 1642, rue de la ferme La Pocatière, Québec G0R 1Z0 (Leboeuf, Cameron). Address all correspondence to Dr. Yvan L Homme; telephone: (450) , ext 102; fax: (450) ; lhommey@inspection.gc.ca Dr. l Homme s current address is Canadian Food Inspection Agency, St-Hyacinthe Laboratory, St-Hyacinthe, Québec J2S 8E3. Received May 16, Accepted September 27, The Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research 2008;72:
2 homozygous AA 136 QQ 171 animals are the most susceptible. Based on this linkage, a classification scheme has been established in the UK under the National Scrapie Plan (9), with NSP type 1 representing sheep that are genetically most resistant to scrapie and NSP type 5 representing those that are highly susceptible to scrapie and that should not be used for breeding. Several studies show that the distribution of scrapie genotypes varies widely according to breed or geographic origin. Several techniques have been used by different laboratories to genotype the PrP gene. These include polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphisms (PCR-RFLP), PCR followed by dot blot hybridization, sequencing and real-time PCR using Taqman technology. The novel method used in this study utilizes molecular beacons. This technique was selected because it offers very high specificity and high throughput capacity. Due to their hairpin structure, molecular beacons are uniquely suited for the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) because they are much more specific in their target recognition than linear probes (10,11). Moreover, since molecular beacons can possess different fluorophores, multiple targets can be detected in the same reaction tube (multiplex). Scrapie is widespread and is found in most parts of the world. Diagnosed in Canada for the first time in 1938, it was made a reportable disease in 1945, and a control program was put in place. Since 1984, over 140 infected and exposed flocks have been depopulated, mostly in Quebec. The control program has evolved since 1945 and genotyping is now part of the different strategies offered to the owner of an infected flock (12). There are over reproductive ewes in Quebec flocks, about to of which are purebred; there are approximately 3500 purebred rams. Most of the flocks are commercial flocks in which mainly crossbred or hybrid females are used with registered or nonregistered purebred rams; lambs are sold to the meat market. Rams are either terminal (meat) or maternal/ prolific type breeds. The aim of this study was to investigate prion gene polymorphisms at 3 codons of interest in common breeds of sheep in Quebec to provide information about their susceptibility to scrapie and about the genetic potential within each breed to reduce this susceptibility. Sheep Materials and methods A total of 500 purebred rams from 49 flocks were selected for this study (Table I). Rams were chosen because they are thought to represent the PrP genotypes found within each of their respective breeds. The rams were from the most common paternal (Suffolk, Hampshire, and Canadian Arcott), maternal (Dorset and Polypay) and prolific breeds (Rideau Arcott and Romanov) in Quebec. All flocks had to be participating in the Quebec genetic Scheme (GenOvis). The sampling size for each breed reflected the different proportion of these breeds in GenOvis ( ). In 2003, when the study took place, there were over 1100 rams and ram lambs available in 67 GenOvis participating flocks. Moreover, considering that maternal and prolific breeds have a larger incidence on the whole reproductive Table I. Number of rams sampled from each breed Breed Number of flocks Number of rams Canadian Arcott (CD) 5 28 Suffolk (SU) Hampshire (HA) 5 40 Dorset (DP) Polypay (PO) 7 97 Rideau Arcott (RI) 9 52 Romanov (RV) 6 57 Totals Note: There was more than one breed on some farms. population (breeding ewes), it was decided to have these breeds overrepresented. DNA samples All analyses were performed at TransBIOtech in Lévis, Québec. For each sheep, 5 ml of blood was collected by jugular venipuncture into an EDTA-vacutainer and kept cold until deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction. Genomic DNA was extracted from white blood cells in 200 ml of whole blood using the DNA blood kit (Qiagen, Mississauga, Ontario) following the manufacturer s instructions. Genotyping All primers and beacons were synthesized and purified by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) at Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Coralville, Iowa, USA. Three independent realtime PCR reactions were developed, 1 for each of the 3 codons of interest. Each reaction was optimized and validated with DNA from animals of known genotypes (ARQ/ARQ, ARQ/VRQ, VRQ/VRQ, AHQ/ARQ, AHQ/AHQ, ARR/ARQ, ARR/ARR, ARH/ARQ, ARH/ARR, ARH/ARH). For each reaction, the conditions were as follows: in a final volume of 25 ml, containing 100 mm of each nucleotide, 400 mm of each primer, 200 mm of each beacon, 3 mm MgCl 2, 100 mm Tris-HCl (ph 8.3), 50 mm KCl and 0.5U Platinum Taq (Invitrogen, Burlington, Ontario), ng of genomic DNA (determined at 260 nm in a spectrophotometer) was subjected to PCR amplification in an M p instrument (Stratagene, La Jolla, California). Each sample was tested in duplicate, and appropriate controls from animals whose genotypes were determined by automated sequencing were included in each run. Furthermore, 142 animals had their genotype determined in a blind fashion by TransBioTech Lévis, Quebec and a French accredited laboratory (Labogena, Jouy-en-Josas, France). All results were fully congruent. Codon 136 by 40 cycles at 94 C for 15 s, 62 C for 45 s, and 72 C for 30 s. as follows: Beacon 136A: 59 FAM - TCG GGC TGG GAA GTG CCA TGA GCA GGC GCC CGA - BHQ1 39, Beacon 136V: 59 - HEX AGC GAT TGG GAA GTG TCA TGA GCA GGA TCG CT - BHQ2 39, 2000;64:0 00 The Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research 321
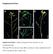
3 1/1 1/1 1/2 1/2 2/2 NTC 2/2 NTC Figure 1a. Amplification plots obtained with dual labelled molecular beacon A 136 (FAM) for PrP codon 136 genotyping. Results are shown for an AA 136 homozygote (1/1), a VA 136 heterozygote (1/2), a VV 136 homozygote (2/2) and a no template control (NTC). Figure 1b. Amplification plots obtained with dual labelled molecular beacon V 136 (HEX) for PrP codon 136 genotyping. Results are shown for a VV 136 homozygote (1/1), a VA 136 heterozygote (1/2), an AA 136 homozygote (2/2) and a no template control (NTC). sens-primer: ATG AAG CAT GTG GCA GGA GC - 39, anti sens primer: ACG GTC CTC ATA GTC ATT GCC Codon 154 by 40 cycles at 94 C for 15 s, 60 C for 45 s, and 72 C for 30 s. as follows: beacon 154H: 59 HEX - CGC GAG ACC GTT ACT ATC ATG AAA ACA TGT CGC G - BHQ2 39, beacon 154R: 59 FAM - CGC GAA CCG TTA CTA TCG TGA AAA CAT GTC GCG - BHQ 1 39, sens primer: 59 - ATG AAG CAT GTG GCA GGA GC - 39, anti-sens primer: 59 - CTG ATC CAC TGG TCT GTA GTA CAC Codon 171 by 40 cycles at 94 C for 15 s, 59 C for 45 s, and 72 C for 30 s. as follows: beacon 171Q: 59 - FAM CGC GAT CCA GTG GAT CAG TAT AGT AAC CAT CGC G - BHQ1 39, beacon 171R: 59 - HEX CGC GAT CCA GTG GAT CCG TAT AGT AAC CAT CGC G - BHQ2 39, beacon171h: 59 - CY5 CGC GAT CCA GTG GAT CAT TAT AGT AAC CAT CGC G - BHQ2 39, sens primer: 59 - CGT GAA AAC ATG TAC CGT TAC CCC - 39, and antisens primer: 59 - GGT GAC TGT GTG TTG CTT GAC TG Results All molecular beacons were very efficient in discriminating the single base mismatches responsible for the allelic differences under study. An example of the results obtained with codon 136 molecular beacons is shown in Figures 1a and 1b. The beacons only fluoresced and gave a strong signal in the presence of their perfectly complementary target making allele scoring unambiguous. In the absence of their perfectly complementary target, the probes remained dark and no or very weak signals were detected (samples 2/2 Figures 1a and 1b). Table II. Percentage frequencies of prion protein alleles (PrP) in 7 breeds of sheep in Quebec (n = 1000 alleles rams) Breed CD DP HA PO RI RV SU ARR AHQ ARQ VRQ CD Canadian Arcott; DP Dorset; HA Hampshire; PO Polypay; RI Rideau Arcott; RV Romanov; SU Suffolk. The PrP allelic frequencies of the 500 sampled rams are summarized for each breed in Table II. Four of the 5 PrP alleles associated with susceptibility or resistance to scrapie were found: ARR, ARQ, AHQ, and VRQ no ARH. Codon 171 was polymorphic (R/Q) in every breed but no histidine (H) was found meaning that every breed sampled has access to the ARR allele associated with the greatest resistance to scrapie. Codon 154 was also found to be polymorphic (R/H) in 4 of the breeds (Rideau Arcott, Polypay, Dorset, and Canadian Arcott) but with a very low proportion of the AHQ allele (, 2%). The remaining 3 breeds had only arginine (R) and no H at position 154. At codon 136, all breeds but 2 (Rideau Arcott and Polypay, which had no VRQ allele) were polymorphic (V/A) although the frequency of the VRQ allele (associated with the highest susceptibility to scrapie) was always very low. In all breeds, the dominant alleles were ARQ and ARR and the less frequent were AHQ and VRQ, but there was considerable variation among breeds. In all breeds, the frequency of the ARQ allele exceeded 30% and it reached 66.7% in Romanov. For the most resistant ARR allele, all breeds showed a relative frequency of. 25% and it reached or exceeded 50% for Canadian Arcott, Dorset, Suffolk, and Polypay. The VRQ allele, which is associated with the highest susceptibility to scrapie, was found at low frequencies (between 1.2% and 7.1%) in Suffolk, Hampshire, Romanov, Dorset, and Canadian Arcott. The AHQ allele was found in very low proportion (, 2%) in Canadian Arcott, Dorset, Polypay, and Rideau Arcott. 322 The Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research 2000;64:0 00
4 Table III. Percentage frequencies of prion protein (PrP) genotypes in 7 Quebec sheep breeds (n = 500 rams) All GENOTYPES breeds CD SU HA DP PO RI RV ARR/ARR ARR/AHQ ARR/ARQ ARR/VRQ AHQ/ARQ ARQ/ARQ ARQ/VRQ VRQ/VRQ CD Canadian Arcott; DP Dorset; HA Hampshire; PO Polypay; RI Rideau Arcott; RV Romanov; SU Suffolk. The PrP genotypes frequencies for the 7 breeds are shown in Table III. Eight different genotypes were identified in the sampled rams: ARR/ARR, ARR/ARQ, ARR/AHQ, ARQ/ARQ, ARQ/AHQ, ARR/VRQ, ARQ/VRQ, and VRQ/VRQ. Canadian Arcott, Dorset, and Polypay breeds had the highest percentage of the NSP type 1 genotype (ARR/ARR) (39%, 29%, and 27%, respectively), whereas the Romanov breed had the lowest percentage (7%) of the most resistant rams. Of note is that for all breeds,. 50% of the rams tested were of NSP type 1 (ARR/ARR) or 2 (ARR/ARQ and ARR/AHQ) which are all considered to confer resistance to scrapie. In most breeds, the cumulative frequencies of these 3 genotypes were over 70%. The most susceptible genotypes (VRQ/VRQ, VRQ/ARQ), which correspond to NSP type 5, were found in small proportions in Romanov (7.0%), Dorset (4.9%), Canadian Arcott (3.6%), and Suffolk (1.2%). Discussion Although their design is challenging, molecular beacons can be very efficient in distinguishing between single base pair mismatch allelic variants (Figures 1a and 1b). The fact that 142 samples from this study gave identical results in our laboratory and the French laboratory Labogena, supports this finding. The assays are simple, rapid, and amenable to multiplexing and automation which make them ideally suited for routine diagnosis. Moreover, since the amplification, hybridization, and analysis are all performed simultaneously in a closed tube, the risk of cross-contamination is greatly reduced. The first objective of this study was to estimate the frequencies of PrP alleles and genotypes among the major sheep breeds in Quebec. One other goal was to give breeders an indication of the genetic potential within each breed or flock in breeding animals with low genetic susceptibility to scrapie. This study represents a starting point for breeders interested in a breeding process that includes the selection of ARR/ARR animals and the elimination of VRQ-carrying animals. The ARR allele, which plays an important role in scrapie resistance, was found in each breed and more than 50% of the rams in every studied breed carried at least 1 copy of this allele (NSP type 1 and 2). The breeds with the highest proportion of ARR/ARR rams were the Canadian Arcott with 39.3%, Dorset with 28.9%, and Polypay with 26.8%. The high percentage of resistant rams in some breeds probably reflects the fact that some breeders in Quebec have been selecting for scrapie resistant rams for several years. Another explanation for this high percentage of ARR/ARR rams observed in some breeds might be the founder effect. This might be the case for the Canadian Arcott where, to our knowledge, no selection based on scrapie genotypes had been done prior to our study. In this particular breed, the relatively small size of the sample might also cause a bias (few source flocks and less genetic variability). Such high frequency of the ARR allele is common in many countries and in different breeds (12 15). The ARH allele was not found in any of the animals tested in this study, which is not unexpected since the ARH allele is usually found in a small proportion of animals of very few breeds like the Texel and Suffolk (16 18). VRQ-carrying animals are considered to be the most susceptible to scrapie. In the present study, the VRQ allele was found in 5 of the 7 breeds but at low frequency similar to what has been found in other sheep breeds around the world (12 15). With a proportion of 14.3% and 7.0% of VRQ-carrying rams respectively, the Canadian Arcott and the Romanov breeds had the highest frequency of highly susceptible animals. It is interesting to note that although the Canadian Arcott had the highest proportion (14.3%) of very susceptible VRQcarrying animals, it also had the highest proportion (39.3%) of the most resistant rams (ARR/ARR). In non-vrq breeds, animals with the ARQ/ARQ genotype are considered to be the most susceptible to scrapie. In this regard, Romanov and Hampshire rams must be considered at risk with a proportion of 42% and 40% of ARQ/ARQ animals, respectively. The proportion of ARQ homozygous rams in the other breeds was between 10% and 20%. Among the rams studied here, the Romanov and the Hampshire appeared to be the most susceptible to natural scrapie with 49.1% and 42.5% of rams being of susceptible genotypes respectively (NSP type 4 and 5). The Canadian Arcott rams also appeared to be at great risk with 14.3% of VRQ-carrying rams, but the high proportion of ARR-carrying rams in this breed (71.4%) makes it possible to rapidly diminish or eliminate the VRQ allele by selective breeding. The results reported here can serve as a starting point for Quebec breeders in developing breeding strategies to increase overall resistance to the common strains of scrapie. Breeding towards scrapie resistance is clearly possible for the 7 breeds included in this study. 2000;64:0 00 The Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research 323
5 However, it will certainly take more time in some breeds where less homozygous ARR rams are available. In these breeds, ARR heterozygous rams will have to be used for the first few generations. To ensure that no production trait is lost as the frequency of ARR allele is increased in the population, it is important to keep in mind that improving scrapie resistance should not be the sole, neither the first, selection criterion. So far, little or no association has been found between scrapie genotypes and important reproduction or production traits such as weight gain, ovulation rate, or litter size (19 21). When selecting toward genetic resistance to natural scrapie, one must also consider the occurrence of atypical scrapie, such as the Nor98 isolate, in usually resistant sheep (22,23). Even though these rare isolates have not yet been found in Canada, they confirm the fact that ARR/ARR resistance is relative and not absolute and that the selection process must continuously adjust to new scientific findings. Acknowledgments This project was financially supported by a grant from Le Conseil pour le développement de l agriculture du Québec (CDAQ). The authors wish to thank all the sheep producers that participated in the study. Special thanks are also given to Rebecca Guy for reviewing the manuscript. References 1. Prusiner SB. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie Science 1982;216: Baylis M, Goldmann W. The genetics of scrapie in sheep and goats. Curr Mol Med 2004;4: Hunter N, Goldmann W, Marshall E, O Neill G. Sheep and goats: Natural and experimental TSEs and factors influencing incidence of disease. Arch Virol Suppl 2000;16: Hunter N, Foster JD, Goldmann W, Stear MJ, Hope J, Bostock C. Natural scrapie in a closed flock of Cheviot sheep occurs only in specific PrP genotypes. Arch Virol 1996;141: Belt PB, Muileman IH, Schreuder BE, Bos-de Ruijter J, Gielkens AL, Smits MA. Identification of five allelic variants of the sheep PrP gene and their association with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol. 1995;76: Clouscard C, Beaudry P, Elsen JM, et al. Different allelic effects of the codons 136 and 171 of the prion protein gene in sheep with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol 1995;76: Elsen JM, Amigues Y, Schelcher F, et al. Genetic susceptibility and transmission factors in scrapie: Detailed analysis of an epidemic in a closed flock of Romanov. Arch Virol 1999;144: Billinis C, Psychas V, Leontides L, et al. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in healthy and scrapie-affected sheep in Greece. J Gen Virol 2004;85: Anonymous (2006) National Scrapie Plan for Great Britain. (NSP, DEFRA, 2006) [homepage on the Internet]. Available from Last accessed April 28, Tyagi S, Bratu DP, Kramer FR. Multicolor molecular beacons for allele discrimination. Nat Biotechnol 1998;16: Piatek AS, Tyagi S, Pol AC, et al. Molecular beacon sequence analysis for detecting drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Biotechnol 1998;16: Canadian Food Inspection Agency. [homepage on the Internet]. Available from heasan/man/scrtre/scrtree.shtml Last accessed April 26, Eglin RD, Warner R, Gubbins S, Sivam SK, Dawson M. Frequencies of PrP genotypes in 38 breeds of sheep sampled in the National Scrapie Plan for Great Britain. Vet Rec 2005;156: Holko I, Novackova A, Holkova T, Kmet V. PrP genotyping of sheep breeds in Slovakia. Vet Rec 2005;157: DeSilva U, Guo X, Kupfer DM, et al. Allelic variants of ovine prion protein gene (PRNP) in Oklahoma sheep. Cytogenet Genome Res 2003;102: Sild E, Volskiene R, Viinalass H, et al. Detection of prion protein gene polymorphisms in Baltic breeds of sheep. Vet Rec 2006;159: O Doherty E, Aherne M, Ennis S, Weavers E, Roche JF, Sweeney T. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in pedigree sheep in Ireland. Res Vet Sci 2001;70: Drögemüller C, Leeb T, Distl O. PrP genotype frequencies in German breeding sheep and the potential to breed for resistance to scrapie. Vet Rec 2001;149: de Vries F, Borchers N, Hamann H, et al. Associations between the prion protein genotype and performance traits of meat breeds of sheep. Vet Rec 2004;155: Vitezica ZG, Moreno CR, Bodin L, et al. No associations between PrP genotypes and reproduction traits in INRA 401 sheep. J Anim Sci 2006;84: Sweeney T, Hanrahan JP, O Doherty E. Is there a relationship between prion protein genotype and ovulation rate and litter size in sheep? Anim Reprod Sci 2007;101: Epub 2006, Dec Benestad SL, Sarradin P, Thu B, Schönheit J, Tranulis MA, Bratberg B. Cases of scrapie with unusual features in Norway and designation of a new type, Nor98. Vet Rec 2003;153: Le Dur A, Béringue V, Andréoletti O, et al. A newly identified type of scrapie agent can naturally infect sheep with resistant PrP genotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102: Epub 2005, Oct The Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research 2000;64:0 00
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Hes6. PPARα. PPARγ HNF4 CD36
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), , DOI: /bi00034a013
 Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
PCR analysis was performed to show the presence and the integrity of the var1csa and var-
 Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
PrP gene polymorphism and its variations among Bulgarian indigenous sheep breeds
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 2 (2015) pp. 466-474 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article PrP gene polymorphism and its variations among Bulgarian indigenous sheep breeds Tsvetoslav Koynarski
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 2 (2015) pp. 466-474 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article PrP gene polymorphism and its variations among Bulgarian indigenous sheep breeds Tsvetoslav Koynarski
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines
 Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Supplementary Figure 1A A404 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid
 Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells
 Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
NAME:... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:... Maximum marks: 50. Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer Science, UKZN
 COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering
 Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
II 0.95 DM2 (RPP1) DM3 (At3g61540) b
 Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
G+C content. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1. ΔPDD1 x wild type. 70 kd Pdd1. Pdd3
 Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Supplementary Information. Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins
 Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
ORFs and genes. Please sit in row K or forward
 ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
PCR-based Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation
 PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers
 DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
PrP genotypes of atypical scrapie cases in Great Britain
 Journal of General Virology (2006), 87, 3141 3149 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.81779-0 PrP genotypes of atypical scrapie cases in Great Britain G. C. Saunders, S. Cawthraw, S. J. Mountjoy, J. Hope and O. Windl Correspondence
Journal of General Virology (2006), 87, 3141 3149 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.81779-0 PrP genotypes of atypical scrapie cases in Great Britain G. C. Saunders, S. Cawthraw, S. J. Mountjoy, J. Hope and O. Windl Correspondence
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1
 Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
Legends for supplementary figures 1-3
 High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were
 1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
Homework. A bit about the nature of the atoms of interest. Project. The role of electronega<vity
 Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR
 Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification
 Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Supplemental Information. Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids. Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites. to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Protein Structure Analysis
 BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Iosif Vaisman COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOINFORMATICS STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS
BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Iosif Vaisman COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY COMPUTATIONAL MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOINFORMATICS STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS
S4B fluorescence (AU)
 A S4B fluorescence (AU) S4B fluorescence (AU) dsbb csgba csgd dsbb csgba bcsa 5000 * NS NS 4000 * 3000 2000 1000 0 ΔcsgBAΔbcsA ΔcsgDΔdsbBΔbcsA ΔcsgBA ΔdsbBΔcsgBA ΔcsgDΔdsbB B -1000 4000 * * NS 3500 * 3000
A S4B fluorescence (AU) S4B fluorescence (AU) dsbb csgba csgd dsbb csgba bcsa 5000 * NS NS 4000 * 3000 2000 1000 0 ΔcsgBAΔbcsA ΔcsgDΔdsbBΔbcsA ΔcsgBA ΔdsbBΔcsgBA ΔcsgDΔdsbB B -1000 4000 * * NS 3500 * 3000
Codon Bias with PRISM. 2IM24/25, Fall 2007
 Codon Bias with PRISM 2IM24/25, Fall 2007 from RNA to protein mrna vs. trna aminoacid trna anticodon mrna codon codon-anticodon matching Watson-Crick base pairing A U and C G binding first two nucleotide
Codon Bias with PRISM 2IM24/25, Fall 2007 from RNA to protein mrna vs. trna aminoacid trna anticodon mrna codon codon-anticodon matching Watson-Crick base pairing A U and C G binding first two nucleotide
Supplemental Data. Bennett et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
for Programmed Chemo-enzymatic Synthesis of Antigenic Oligosaccharides
 Supporting Information Design of α-transglucosidases of Controlled Specificity for Programmed Chemo-enzymatic Synthesis of Antigenic Oligosaccharides Elise Champion ±,,,, Isabelle André ±,,, Claire Moulis
Supporting Information Design of α-transglucosidases of Controlled Specificity for Programmed Chemo-enzymatic Synthesis of Antigenic Oligosaccharides Elise Champion ±,,,, Isabelle André ±,,, Claire Moulis
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Primer Design Workshop. École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria
 Primer Design Workshop École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria Scenario You have discovered the presence of a novel endophy5c organism living inside the cells
Primer Design Workshop École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria Scenario You have discovered the presence of a novel endophy5c organism living inside the cells
National PHL TB DST Reference Center PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents
 PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents Document Page Number PSQ for Rifampin 2-6 Comparison table for rpob Codon Numbering 2 rpob mutation list (new numbering system) 3-5 rpob interpretations 6 PSQ for
PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents Document Page Number PSQ for Rifampin 2-6 Comparison table for rpob Codon Numbering 2 rpob mutation list (new numbering system) 3-5 rpob interpretations 6 PSQ for
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR.
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer
 TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
evaluated with UAS CLB eliciting UAS CIT -N Libraries increase in the
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE-/- hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE+/+
 ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
Overexpression Normal expression Overexpression Normal expression. 26 (21.1%) N (%) P-value a N (%)
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
Appendix 1a. Microsatellite analysis of P1-hyg, P2-neo and their. Amplified cdna (base pairs) P1-hyg P2-neo All progeny A A
 Supplementary information Appendix 1a. Microsatellite analysis of P1-hyg, P2-neo and their double drug resistant progeny (ABI 377). Primer set a,b Amplified cdna (base pairs) P1-hyg P2-neo All progeny
Supplementary information Appendix 1a. Microsatellite analysis of P1-hyg, P2-neo and their double drug resistant progeny (ABI 377). Primer set a,b Amplified cdna (base pairs) P1-hyg P2-neo All progeny
RPA-AB RPA-C Supplemental Figure S1: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification.
 RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING All of the patients and control subjects were sequenced and genotyped in the same way. Shotgun libraries of approximately 250 bp
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING All of the patients and control subjects were sequenced and genotyped in the same way. Shotgun libraries of approximately 250 bp
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FILE
 Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
11th Meeting of the Science Working Group. Lima, Peru, October 2012 SWG-11-JM-11
 11th Meeting of the Science Working Group Lima, Peru, 15-19 October 2012 Russian population genetics studies of jack mackerel in the South Pacific P.K.Afanasiev M.A.Rabchun A.I.Glubokov Introduction. In
11th Meeting of the Science Working Group Lima, Peru, 15-19 October 2012 Russian population genetics studies of jack mackerel in the South Pacific P.K.Afanasiev M.A.Rabchun A.I.Glubokov Introduction. In
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS. E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual
 MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR
 Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Causes and Effects of N-Terminal Codon Bias in Bacterial Genes. Mikk Eelmets Journal Club
 Causes and Effects of N-Terminal Codon Bias in Bacterial Genes Mikk Eelmets Journal Club 21.2.214 Introduction Ribosomes were first observed in the mid-195s (Nobel Prize in 1974) Nobel Prize in 29 for
Causes and Effects of N-Terminal Codon Bias in Bacterial Genes Mikk Eelmets Journal Club 21.2.214 Introduction Ribosomes were first observed in the mid-195s (Nobel Prize in 1974) Nobel Prize in 29 for
DNA Computing Circuits Using Libraries of. DNAzyme Subunits
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information for the paper: DNA Computing Circuits Using Libraries of DNAzyme Subunits Johann Elbaz a, Oleg lioubashevski a, Fuan Wang a, Françoise Remacle b, Raphael
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information for the paper: DNA Computing Circuits Using Libraries of DNAzyme Subunits Johann Elbaz a, Oleg lioubashevski a, Fuan Wang a, Françoise Remacle b, Raphael
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide
 PART A. Read the following: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the
PART A. Read the following: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. RNA/DNA sequences used in this study 2. Height and stiffness measurements on hybridized molecules 3. Stiffness maps at varying concentrations of target DNA 4. Stiffness measurements on RNA/DNA hybrids.
1. RNA/DNA sequences used in this study 2. Height and stiffness measurements on hybridized molecules 3. Stiffness maps at varying concentrations of target DNA 4. Stiffness measurements on RNA/DNA hybrids.
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system
 Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
BIOSTAT516 Statistical Methods in Genetic Epidemiology Autumn 2005 Handout1, prepared by Kathleen Kerr and Stephanie Monks
 Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include: to identify the genetic causes of phenotypic variation develop genetic tests o benefits to individuals and to society are still uncertain
Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include: to identify the genetic causes of phenotypic variation develop genetic tests o benefits to individuals and to society are still uncertain
Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus Replication by GS-6620, A Potent C-Nucleoside Monophosphate Prodrug
 Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus Replication by, A Potent C-Nucleoside Monophosphate Prodrug Running Title: In Vitro Pharmacology of Authors: Joy Y. Feng et al. Supplementary Information Table S1. RNA primer
Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus Replication by, A Potent C-Nucleoside Monophosphate Prodrug Running Title: In Vitro Pharmacology of Authors: Joy Y. Feng et al. Supplementary Information Table S1. RNA primer
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table S1: Water sampling sites in Brisbane River and their characteristics Sampling sites GPS coordinates Site characteristics Suspected source of fecal pollution
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table S1: Water sampling sites in Brisbane River and their characteristics Sampling sites GPS coordinates Site characteristics Suspected source of fecal pollution
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples
 NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples VERSION 2.0 SUMMARY This procedure describes the use of nested Sequence-Based
NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples VERSION 2.0 SUMMARY This procedure describes the use of nested Sequence-Based
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions
 Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions Vered Israeli-Ruimy 1,*, Pedro Bule 2,*, Sadanari Jindou 3, Bareket Dassa
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions Vered Israeli-Ruimy 1,*, Pedro Bule 2,*, Sadanari Jindou 3, Bareket Dassa
An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base. excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps
 Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature11496 Cl. 8 Cl. E93 Rag1 -/- 3H9 + BM Rag1 -/- BM CD CD c-kit c-kit c-kit wt Spleen c-kit B22 B22 IgM IgM IgM Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of single-cell-derived pre-b cell clones.
doi:1.138/nature11496 Cl. 8 Cl. E93 Rag1 -/- 3H9 + BM Rag1 -/- BM CD CD c-kit c-kit c-kit wt Spleen c-kit B22 B22 IgM IgM IgM Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of single-cell-derived pre-b cell clones.
Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURB
 Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURBO DNA-free Kit (Ambion). One µg of total RNA was reverse
Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURBO DNA-free Kit (Ambion). One µg of total RNA was reverse
dsxf - wt wt dsxf bp 2493bp Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4245 Supplementary Figure 1
 5 3 2493bp 2426bp attp GFP 3xP3 attp CDS dsxf - wt wt dsxf - Supplementary Figure 1 Molecular confirmation of the correct integration of the HDR-mediated event to generate dsxf PCRs were performed to verify
5 3 2493bp 2426bp attp GFP 3xP3 attp CDS dsxf - wt wt dsxf - Supplementary Figure 1 Molecular confirmation of the correct integration of the HDR-mediated event to generate dsxf PCRs were performed to verify
Supporting Information. Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy
 Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Xie YL, Chakravorty S, Armstrong DT, et al. Evaluation of a
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Xie YL, Chakravorty S, Armstrong DT, et al. Evaluation of a
IDENTIFICATION OF BETA- LACTOGLOBULIN AND KAPPA-CASEIN GENOTYPES USING PCR-RFLP IN HOLSTEIN CATTLE
 IDENTIFICATION OF BETA- LACTOGLOBULIN AND KAPPA-CASEIN GENOTYPES USING PCR-RFLP IN HOLSTEIN CATTLE Yasemin GEDİK, Mehmet Ali YILDIZ, Orhan KAVUNCU Ankara University Agriculture Faculty Animal Science Biometry
IDENTIFICATION OF BETA- LACTOGLOBULIN AND KAPPA-CASEIN GENOTYPES USING PCR-RFLP IN HOLSTEIN CATTLE Yasemin GEDİK, Mehmet Ali YILDIZ, Orhan KAVUNCU Ankara University Agriculture Faculty Animal Science Biometry
Amplified Analysis of DNA by the Autonomous Assembly of Polymers Consisting of DNAzyme Wires
 Supporting information for the paper: Amplified Analysis of DNA by the Autonomous Assembly of Polymers Consisting of DNAzyme Wires Fuan Wang, Johann Elbaz, Ron Orbach, Nimrod Magen and Itamar Willner*
Supporting information for the paper: Amplified Analysis of DNA by the Autonomous Assembly of Polymers Consisting of DNAzyme Wires Fuan Wang, Johann Elbaz, Ron Orbach, Nimrod Magen and Itamar Willner*
GENETIC STRUCTURE AT THE PRION PROTEIN LOCUS
 GENETIC STRUCTURE AT THE PRION PROTEIN LOCUS (PrP) OF BOTOSANI KARAKUL SHEEP POPULATIONS IN RELATION TO THE ACCURACY AND INTENSITY OF SELECTION MECHANISMS Gh. Hrincă 1*, S.E. Georgescu 2, G. Vicovan 3,
GENETIC STRUCTURE AT THE PRION PROTEIN LOCUS (PrP) OF BOTOSANI KARAKUL SHEEP POPULATIONS IN RELATION TO THE ACCURACY AND INTENSITY OF SELECTION MECHANISMS Gh. Hrincă 1*, S.E. Georgescu 2, G. Vicovan 3,
-15 diopter negative lenses in wild-type and homozygous CHRM2-deleted mice, and
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1: Myopia induction was performed using uniocular -10 and -15 diopter negative lenses in wild-type and homozygous CHRM2-deleted mice, and results at 2, 4 and
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1: Myopia induction was performed using uniocular -10 and -15 diopter negative lenses in wild-type and homozygous CHRM2-deleted mice, and results at 2, 4 and
Supplemental Information. Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous. MicroRNAs in C. elegans. Inventory of Supplementary Information
 Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide
 The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide Shaozhou Zhu 1,2, Christopher D. Fage 1, Julian D. Hegemann 1, Andreas Mielcarek 1, Dushan Yan 1, Uwe Linne 1 & Mohamed A. Marahiel*,1 1 Department
The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide Shaozhou Zhu 1,2, Christopher D. Fage 1, Julian D. Hegemann 1, Andreas Mielcarek 1, Dushan Yan 1, Uwe Linne 1 & Mohamed A. Marahiel*,1 1 Department
A high efficient electrochemiluminescence resonance energy. transfer system in one nanostructure: its application for
 Supporting Information for A high efficient electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system in one nanostructure: its application for ultrasensitive detection of microrna in cancer cells Zhaoyang
Supporting Information for A high efficient electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system in one nanostructure: its application for ultrasensitive detection of microrna in cancer cells Zhaoyang
Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit
 Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit Mariko Suzuki 1, Saki Kondo 1, Manabu Yamasaki 2, Norie Matsuda 2, Akio Nomoto 2, Tetsuro
Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit Mariko Suzuki 1, Saki Kondo 1, Manabu Yamasaki 2, Norie Matsuda 2, Akio Nomoto 2, Tetsuro
Lezione 10. Bioinformatica. Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi
 Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins
Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins
