In Vivo Evaluation of Vena Caval Filters: Can Function Be Linked to Design Characteristics?
|
|
|
- Shawn Houston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CardioVascular and Interventional Radiology Springer-Verlag New York, Inc Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (2000) 23: DOI: /s LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS In Vivo Evaluation of Vena Caval Filters: Can Function Be Linked to Design Characteristics? Mary C. Proctor, 1 Kyung J. Cho, 2 Lazar J. Greenfield 1 1 Department of Surgery, University of Michigan Hospitals, 1500 East Medical Center Drive, Ann Arbor, MI , USA 2 Department of Radiology, University of Michigan Hospitals, 1500 East Medical Center Drive, Ann Arbor, MI , USA Abstract Purpose: To compare the five vena caval filters marketed in the United States and one investigational vena caval filter and to determine whether there is an association between their design and their in vivo function. Methods: Four of each type of filter Simon Nitinol (SN), Bird s Nest (BN), Vena Tech (VT), Greenfield stainless steel (PSGF), Greenfield titanium (TGF), and the investigational stent cone filter (NGF) were studied for 60 days in 12 sheep. Radiographic and pathologic outcomes to be assessed included clot capture and resolution, vena caval penetration, position of the filter, thrombogenicity, and vessel wall reaction. Results: Filters differed with respect to the number of clottrapping levels and the interdependence of the legs. All devices were successfully placed. Intentionally embolized clot was captured. One VT and two SN filters migrated in response to clot capture. Resolution of thrombus was variable, and related to the design of the device. Fibrin webbing was widely present with the VT, BN, and SN filters but limited in the others. The VT and NGF filters demonstrated the most stable filter base diameter. Conclusions: The performance of vena caval filters differs with respect to clot resolution and mechanical stability. Interdependent filter limbs and single-stage conical capture sites appear to result in more favorable performance in in vivo studies. Key words: Animal study Design Performance Thrombus resolution Vena cava filter An ideal vena caval filter must combine the ability to capture clinically significant emboli while maintaining the patency of the vena cava. In addition, it must be mechanically stable. An investigational filter has been developed by the Boston Correspondence to: M.C. Proctor, M.S., Department of Surgery, University of Michigan Hospitals, 2101 Taubman Center/Box 0346, Ann Arbor, MI , USA Scientific Vascular Division (BSC, Natick, MA, USA) and in this study we compared it with the filters currently approved for the US market to determine the extent to which it meets these criteria (Table 1). The investigational stent cone filter, referred to as the NGF, has a unique design incorporating the traditional Greenfield cone combined with a stent base. It is manufactured of nitinol wire to allow compression into a 9 Fr delivery system. The cone portion of the NGF is comparable in volume to the original Greenfield filter. At 55 mm it is the longest of the BSC filters. Its 32-mm resting base diameter is similar to the titanium Greenfield filter (TGF) at 38 mm and the percutaneous stainless steel Greenfield filter (PSGF) at 32 mm (Fig. 1). Our purpose was to compare performance with respect to clot capture, clot resolution, thrombogenicity, migration, filter stability, and histologic effects on the vena cava. Materials and Methods The study was conducted in the Greenfield Vascular Research Laboratory under approval by the University Committee on the Use and Care of Animals and according to Federal regulations. The six devices included the Bird s Nest filter (BN; Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA), the Greenfield filters (PSGF, TGF, NGF, Boston Scientific/Meditech, Natick, MA, USA), the Simon Nitinol filter (SN; Bard, Boston, MA, USA) and the VenaTech filter (VT; Braun, Evanston, IL, USA). Two devices of each type were placed in each of 12 sheep weighing at least 34 kg, one above and one below the renal vein according to the matrix in Table 2. All were placed via the right femoral vein using a prototype 9 Fr transit delivery system. Plain films and cavograms with intravenous contrast were obtained in the anteroposterior and lateral projections both prior to and following filter placement, following intentional embolization and just prior to necropsy. Autologous clot for embolization was produced by adding thrombin to 20 ml of blood drawn from each animal. The blood was placed in a 35-cm 9-mm-diameter tube and aged for 24 hr. Five grams of clots were divided into 100- mm 9-mm segments and released into the femoral vein of six animals via a 50-ml syringe with a modified tip inserted through a femoral venotomy (Table 2) at the time of filter placement. Move-
2 M.C. Proctor et al.: Vena Caval Filter Evaluation 461 Table 1. The study devices and their major design characteristics Device Abbreviation Trapping level(s) Filter leg attachment Percutaneous Stainless Steel PSGF Single Independent a Greenfield (Boston Scientific) Titanium Greenfield TGF Single Independent (Boston Scientific) Next Generation (Boston NGF Single Dependent Scientific) Bird s Nest (Cook) BN Multiple Independent Simon Nitinol (Bard) SN Dual Independent VenaTech (B. Braun) VT Single Dependent a See Materials and Methods Table 2. Study design for placement and clot challenge: study design matrix with type of filter location and whether it underwent intentional clot embolization. In each animal, a Boston Scientific device was paired with another marketed device Filter Location a Intentionally embolized 1 NGF IR Yes VT SR No 2 NGF IR No SN SR No 3 PSGF IR Yes BN SR No 4 PSGF IR No VT SR No 5 TGF IR Yes SN SR No 6 TGF IR No BN SR No 7 VT IR Yes TGF SR No 8VT IR No PSGF SR No 9 SN IR Yes NGF SR No 10 SN IR No TGF SR No 11 BN IR Yes PSGF SR No 12 BN IR No NGF SR No a IR infrarenal; SR suprarenal Fig. 1. A The three traditional Greenfield filters: original stainless steel (left), titanium (center), percutaneous steel (right), and the investigational device (far right) which combines the advantages of a cone with the reduced delivery profile. B The Vena Tech (left), Simon Nitinol (center) and Bird s Nest (right) filters marketed in the United States. ment of the filter during clot challenge was observed under fluoroscopy and measured from post-capture plain films. The animals were recovered and returned to the housing facility for a 60-day survival period. At necropsy, the vena cavas were perfusion-fixed with formalin. After explant, they were photographed from a lateral, cranial and caudal aspect, then opened lengthwise. All filters were examined by a pathologist who was responsible for characterizing thrombus, caval penetration by filter components, filter leg distribution, and fixation site tissue reaction. Histology samples were prepared of tissue found at the fixation site and trapped on or within the filter. The BN filter differs from the others in that it is free-formed continuous wire without a defined shape. For this reason, we did not include it in assessments of centering or symmetry. Filter leg attachment was characterized as being independent if the legs were free of one another, while dependent indicated a physical connection in such a manner that movement of one leg resulted in movement of the others (Table 1). Criteria for determining clinically important movement were based on standards accepted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the 1995 Greenfield Stainless Steel Filter marketing approval submission and included longitudinal movement 20 mm or filter base increase 7 mm. Data were entered into case reporting forms and analyzed using Systat 5.1 (Systat, Evanston, IL, USA). The study was designed to identify large differences among the devices. Due to the small sample size, nonparametric tests were used to analyze continuous variables while likelihood ratio chi-squares or Fisher s Exact test were used with dichotomous data. A nonparametric ANOVA was performed initially to determine whether there were differences among the devices. When significant, further comparisons were done to identify the direction of the differences. Results Animals were comparable in weight (48 52 kg) and caval diameter (17 20 mm) ( p 0.05), thus avoiding potential
3 462 M.C. Proctor et al.: Vena Caval Filter Evaluation Fig. 2. Clot is seen under the wire of the BN filter and around the spindle of the SN filter. There is clot debris on the struts of the VT filter and a small clot at the apex of the NGF. bias. All filters were successfully placed according to the manufacturer s directions. Clot Capture, Thrombogenicity, and Resolution Each of the challenged filters trapped all the autologous emboli while maintaining vena cava flow. There was proximal movement of an infrarenal VT and SN filter of 9 mm and 5 mm respectively in response to the challenge as observed under fluoroscopy and measured from pre- and post-challenge plain films. Thrombus resolution was evaluated by venacavography and visual inspection at 60 days. Residual clot was found in two SN, one BN, one NGF, and one TGF filters ( p 0.58) (Fig. 2). In all but two cases, the pathologist characterized the thrombus as post-mortem due to its lack of organization. However, two SN filters had pathologic evidence of organized thrombus, one of which had been challenged with autologous clot and one formed spontaneously. Filter Position and Stability Centering of the filter within the vena cava was determined from cavograms, on the basis of the relationship between the apex of the filter and walls of the vena cava. The VT filter demonstrated the most optimal centering based on the cavograms. Symmetric distribution of the filter legs was determined in two ways: contrast venacavography and actual measurement of inter-leg spacing of specimens obtained at necropsy. Following placement, there was a difference among the devices with respect to the leg distribution, with the NGF having the poorest performance ( p 0.014). However, at explant, the filter legs were well distributed and we failed to find differences among devices by either measurement technique ( p 0.09). The PSGF, NGF, and VT filters demonstrated the greatest overall resistance to movement. Table 3 demonstrates the mean movement, which was not statistically different among filters. We also measured changes in base diameter of the filters and failed to find a statistical difference ( p 0.07). However, there was a trend favoring the NGF (1.7 mm) while the BN filter had the greatest change (7.3 mm). One characteristic of the BN device not previously reported is the possible distortion it causes to the vena cava. Figure 3 Table 3. Summary of mean movement of filters documented over a 60-day observation period (direction not considered) Filter Mean (SD) movement (mm) a demonstrates the manner in which it twists the cava as it becomes incorporated in the wall. Pathology and Histology Mean (SD) filter base change (mm) Mean (SD) intraleg distance (mm) SN 9 (16.9) 4.3 (3.8) 3.8 (2.2) VT 4 (4.1) 1.7 (1.1) 5.5 (3) BN 12 (16.4) 7.3 (3.2) N/A NGF 1 (2.7) 1.7 (1.3) 4.3 (1.9) PSGF 1 (1.4) 4 (4.2) 5.86 (3.8) TGF 20 (17.9) 4.4 (0.5) 5.3 (3.5) a Movement less than 21 mm is considered to be clinically insignificant Fig. 3. cava. The wires of the BN filter appear to distort the vena Examination of the apex of each filter demonstrated a variable degree of fibrin covering (Fig. 4) which was confirmed by the pathologist. The amount varied with the design of the device and was increased when the apex was in direct contact with the vessel wall. The effect of attachment of the filter to the vessel wall differed among devices. The VT and NGF filters were associated with the least disruption to the external surface of the cava (Fig. 5) while the hooks of the PSGF, TGF, SN, and BN filters had various degrees of externalization [1]. The cava frequently appeared to be tent-
4 M.C. Proctor et al.: Vena Caval Filter Evaluation 463 Fig. 4. A fibrin cap develops at the apex in most cases. Note the limited film on the NGF, PSGF, TGF, and VT filters as compared with the heavy layering of the SN and BN filters. Fig. 5. The dependent legs and short hooks of the VT filter limit caval penetration. ed in response to radial force. If a hook penetrated slowly it became encapsulated in a fibrous nodule which protected adjacent tissue, as we have previously reported [2]. Often, the caval wall stretched behind the independent filter limbs and enclosed them, which also provided protection to external organs. In these cases, the measured filter base diameter increased but the true caval diameter remained unchanged. Discussion The similarity of vena caval filters is frequently suggested [3 5]. The SN and VT devices even obtained FDA approval based on inferred equivalence to the Greenfield filters during a 510K approval process. This prospective in vivo study suggests that this may not be true in all areas. All the devices were successfully deployed and captured clinically significant emboli. However, the VT and SN filters moved following clot capture. This tendency may result in clinical sequelae if the final resting place is inappropriate [6 10]. Cavograms obtained immediately prior to necropsy failed to show any retained clot. However, at necropsy, several filters had clot in various stages of resolution and the extent of fibrin deposition in response to resolution differed significantly (Fig. 6). The higher rates of filter and caval occlusion reported in the literature with the VT and SN filters may be related to fibrin webbing, the extent of which can limit caval blood flow [11, 12]. It is unclear whether a filter needs to be perfectly centered within the vena cava to be effective [13], but with respect to this criterion, the NGF and VT filters were the most consistently centered. These devices share the design characteristic of inter-leg dependence: movement of one leg results in movement of one or more of the others but also limits the total amount of movement that can occur. The fixed base appears to promote centering as well as limiting caval penetration. Changes in filter base diameter are frequently used as a surrogate for caval penetration. Devices with independent legs (PSGF, TGF, SN, BN) tended to have greater variability than did the VT and NGF filters, whose diameters are fixed by design. We were unable to correlate actual caval penetration found at necropsy with change in filter base diameter based on radiographs. Figure 7 depicts why the filter base measurement overestimates the actual change in caval diameter based on cavograms. The NGF and VT filters were also associated with the least disruption to the wall of the vena
5 464 M.C. Proctor et al.: Vena Caval Filter Evaluation Fig. 6. The clean wires of the BN filter are a contrast to the resolving thrombus of the SN and the advanced fibrin webbing of the VT filters. Fig. 7. Necropsy specimens increase our understanding of how filter limbs are distributed and point out the weakness of reliance on plain radiographs. cava. These designs involve less intrusive attachment points with greater reliance on radial force resulting in a more stable diameter. We did note a tendency for the base of the VT filter to pull away from the caval wall toward the center of the cava as has previously been demonstrated [14, 15] (Fig. 5). At the other extreme, the tip on the apex of two SN filters had penetrated through the caval wall and a third caused extreme tenting. Tilting of the second clot-trapping level appeared to be responsible as it forced the apex tip through the wall. The significance of symmetric deployment of the filter legs is discussed frequently [16 19]. Determination of leg distribution at necropsy was much more informative than radiographic images, which failed to account for the shape of the vena cava and did not predict whether the cava was well protected. The NGF had the highest incidence of asymmetry at placement, but at explant and at necropsy there was no difference among the devices. This may be due to the characteristics of nitinol that favor its original configuration and is not unlike the response we have seen with the titanium filter. It may also signify early adjustment to the shape of a vena cava that is not perfectly oval. The gross pathologic examination showed other differences among the devices not previously reported. Both the SN and BN filters are designed with more than one level for clot capture. When these devices trap an embolus, it is often in contact with the vessel wall and, as resolution takes place, significant fibrin disposition develops. In the single-level devices (PSGF, TGF, NGF), thrombus is held in the apex allowing circumferential flow and increased resolution with little webbing as the thrombus is not in contact with the vessel wall. In vitro flow studies by Couch et al [20] have provided an explanation for this effect. They found that the design of a filter significantly affects flow velocity and wall shear stress. A broad blunt face with near-wall contact leads to reduced near-wall velocities and wall stress which can increase the risk for thrombogenesis and vena caval occlusion. They concluded that a centered cone provides optimal flow. In conclusion, vena caval filters differ with respect to performance characteristics in this in vivo study. Our study suggests that two design characteristics are associated with these differences: the interdependence of the leg attachment and the number of clot-trapping levels. The investigational filter incorporates a single level of apical clot trapping in addition to a stent base which limits change in filter base diameter. Its smaller attachment points result in less disruption of the caval wall. Unlike the VT filter with a cone apex and stabilizing leg, the stent base reduces flow disturbance within the vena cava, which reduces the risk of caval occlusion. By relating experience with existing filter devices to their design characteristics, new devices can be developed that are closer to ideal. Acknowledgment. Laboratory support was provided by Boston Scientific Corporation. References 1. McCowan TC, Ferris EJ, Carver DK, Molpus WM (1992) Complications of the nitinol vena caval filter. J Vasc Interv Radiol 3: Proctor MC, Greenfield LJ (1997) Apparent vena caval penetration by the Greenfield filter. J Vasc Interv Radiol 8: Ferris E, McCowan T, Carver DK, McFarland DR (1993) Percutaneous inferior vena caval filters: Follow-up of seven designs in 320 patients. Radiology 188: Grassi CJ (1991) Inferior vena caval filters: Analysis of five currently available devices. AJR 156: Mohan CR, Hoballah JJ, Sharp WJ, Kresowik T, Lu CT, Corson JD
6 M.C. Proctor et al.: Vena Caval Filter Evaluation 465 (1995) Comparative efficacy and complications of vena caval filters. J Vasc Surg 21: LaPlante J, Contractor F, Kiproff P, Khoury M (1993) Migration of the Simon Nitinol vena cava filter to the chest. AJR 160: Queriroz R, Waldman DL (1998) Transvenous retrieval of a Greenfield filter lodged in the tricuspid valve. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 44: Salamipour H, Rivitz SM, Kaufman JA (1996) Percutaneous transfemoral retrieval of a partially deployed Simon-nitinol filter misplaced into the ascending lumbar vein. J Vasc Interv Radiol 7: Shlansky-Goldberg RD, Wing CM, Leveen RF, Cope C (1993) Effectiveness of a prolapsed Bird s Nest Filter. J Vasc Interv Radiol 4: White KE, McLean GK (1996) Bird s Nest filter: Inferior strut migration during massive thromboembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 7: Crochet DP, Brunel P, Trogrlic S, Grossetete R, Auget JL, Dary C (1999) Long-term follow-up of vena tech-lgm filter: Predictors and frequency of caval occlusion. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10: Grassi CJ, Matsumoto AH, Teitelbaum GP (1992) Vena caval occlusion after Simon Nitinol filter placement: Identification with MR imaging in patients with malignancy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 3: Kinney TB, Rose SC, Weingarten KE, Valji K, Oglevie SB, Roberts AC (1997) IVC filter tilt and asymmetry: Comparison of the over-thewire stainless-steel and titanium Greenfield IVC filters. J Vasc Interv Radiol 8: Crochet DP, Bach-Lijour B, Grossetete R, Raffin T, Nguyen JM, Hurtrel M, Dalulsi G, LeNihouannen JC (1997) Caval incorporation of the LGM Vena Tech filter: An experimental study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 8: Dupin N, Meyer G, Diehl JL (1992) Late total closure and caudal migration of an LGM caval filter. (letter) AJR 159: Dorfman GS (1993) Risks and benefits of manipulation of the Titanium Greenfield inferior vena cava filter after deployment: Filter facts and filter fantasies. J Vasc Interv Radiol 4: Greenfield LJ, Proctor MC (1992) Experimental embolic capture by asymmetric Greenfield filters. J Vasc Surg 16: Greenfield LJ, Proctor MC, Cho KJ, Wakefield TW (1997) Limb asymmetry in titanium Greenfield filters: Clinically significant? J Vasc Surg 26: Kinney TB (1998) Regarding Limb asymmetry in titanium Greenfield filters: Clinically significant? J Vasc Surg 27: Couch GG, Kim H, Ojha M (1997) In vitro assessment of the hemodynamic effects of a partial occlusion in a vena cava filter. J Vasc Surg 25:
THE OPTIONAL ALN VENA CAVA FILTER
 ALN VENA CAVA FILTERS INTENDED TO BE RETRIEVABLE AT ANY TIME THE OPTIONAL ALN VENA CAVA FILTER PERMANENT AND/OR TEMPORARY Prevention of thrombus migration Proven clinical effectiveness High performance
ALN VENA CAVA FILTERS INTENDED TO BE RETRIEVABLE AT ANY TIME THE OPTIONAL ALN VENA CAVA FILTER PERMANENT AND/OR TEMPORARY Prevention of thrombus migration Proven clinical effectiveness High performance
The Optional ALN Vena Cava Filters
 The Optional ALN Vena Cava Filters Devices intended to be retrievable at any time Prevention of thrombus migration Proven clinical effectiveness High performance design INNOVATION New ALN Vena Cava Filter
The Optional ALN Vena Cava Filters Devices intended to be retrievable at any time Prevention of thrombus migration Proven clinical effectiveness High performance design INNOVATION New ALN Vena Cava Filter
The Optional ALN Vena Cava Filters
 The Optional ALN Vena Cava Filters Devices intended to be retrievable at any time Prevention of thrombus migration Proven clinical effectiveness High performance design INNOVATION New ALN Vena Cava Filter
The Optional ALN Vena Cava Filters Devices intended to be retrievable at any time Prevention of thrombus migration Proven clinical effectiveness High performance design INNOVATION New ALN Vena Cava Filter
United States Patent 19 Simon et al.
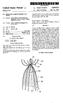 United States Patent 19 Simon et al. 54 REMOVABLE EMBOLUS BLOOD CLOT FLTER 75 Inventors: Morris Simon, Boston; Stephen J. Kleshinski, Scituate; Thomas F. Kinst, Chelsea, all of Mass. 73) Assignee: Nitinol
United States Patent 19 Simon et al. 54 REMOVABLE EMBOLUS BLOOD CLOT FLTER 75 Inventors: Morris Simon, Boston; Stephen J. Kleshinski, Scituate; Thomas F. Kinst, Chelsea, all of Mass. 73) Assignee: Nitinol
ISO Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 2: Vascular stents Part 2: Vascular stent
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 25539-2 Second edition 2012-12-01 Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 2: Vascular stents Part 2: Vascular stent Implants cardiovasculaires Dispositifs endovasculaires
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 25539-2 Second edition 2012-12-01 Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 2: Vascular stents Part 2: Vascular stent Implants cardiovasculaires Dispositifs endovasculaires
Development of a Finite Element Model to Analyse the Proximal Ring of an Endovascular Device
 Development of a Finite Element Model to Analyse the Proximal Ring of an Endovascular Device Emma McCummiskey Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Strathclyde Glasgow, UK. Overview Medical
Development of a Finite Element Model to Analyse the Proximal Ring of an Endovascular Device Emma McCummiskey Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Strathclyde Glasgow, UK. Overview Medical
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety for Boston Scientific Products. 1. WALLSTENT Iliac Endoprosthesis with Unistep Plus Delivery System
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety for Boston Scientific Products Table of Contents 1. WALLSTENT Iliac Endoprosthesis with Unistep Plus Delivery System.1 2. WALLSTENT RP Endoprosthesis (Transhepatic
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety for Boston Scientific Products Table of Contents 1. WALLSTENT Iliac Endoprosthesis with Unistep Plus Delivery System.1 2. WALLSTENT RP Endoprosthesis (Transhepatic
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 3: Vena cava filters
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 25539-3 First edition 2011-12-01 Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 3: Vena cava filters Implants cardiovasculaires Dispositifs endovasculaires Partie 3: Filtres
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 25539-3 First edition 2011-12-01 Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 3: Vena cava filters Implants cardiovasculaires Dispositifs endovasculaires Partie 3: Filtres
Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University Health System,
 Young-Guk Ko, M.D., First EVAR Endograft in Human 1991 Annals of Vascular Surgery Dr. Juan Carlos Parodi, Surgeon Dr. Julio Palmaz, Radiologist Parodi-Palmaz endograft: Dacron + modified Palmaz stents
Young-Guk Ko, M.D., First EVAR Endograft in Human 1991 Annals of Vascular Surgery Dr. Juan Carlos Parodi, Surgeon Dr. Julio Palmaz, Radiologist Parodi-Palmaz endograft: Dacron + modified Palmaz stents
Clinical Experience Using SONIALVISION G4 Multi-Purpose R/F System for Angiographic Examinations
 R/F Clinical Experience Using SONIALVISION G4 Multi-Purpose R/F System for Angiographic Examinations Department of Central Radiology, Takasago Municipal Hospital Naoki Shioya Mr. Naoki Shioya 1. Introduction
R/F Clinical Experience Using SONIALVISION G4 Multi-Purpose R/F System for Angiographic Examinations Department of Central Radiology, Takasago Municipal Hospital Naoki Shioya Mr. Naoki Shioya 1. Introduction
TREAT SMARTER. ACHIEVE MORE. When Treating Thrombus
 TREAT SMARTER. ACHIEVE MORE. When Treating Thrombus Treat Smarter When you want fast, safe, predictable results EKOS Ultrasound Accelerated Thrombolysis Unlocks The Clot Without Ultrasonic Energy With
TREAT SMARTER. ACHIEVE MORE. When Treating Thrombus Treat Smarter When you want fast, safe, predictable results EKOS Ultrasound Accelerated Thrombolysis Unlocks The Clot Without Ultrasonic Energy With
Reliability into. for Biomedical. Devices: Finite Elelment Analyses. Applications CAE Associates
 Designing i Reliability into Biomedical Devices: Finite Elelment Analyses for Biomedical Applications 2005 CAE Associates Designing Reliability into Biomedical Devices: Finite Element Analyses for Bio-Medical
Designing i Reliability into Biomedical Devices: Finite Elelment Analyses for Biomedical Applications 2005 CAE Associates Designing Reliability into Biomedical Devices: Finite Element Analyses for Bio-Medical
Zenith Alpha System, Designed for Easy and Durable repairs. Prof. Elixène JEAN-BAPTISTE (Nice)
 Zenith Alpha System, Designed for Easy and Durable repairs Prof. Elixène JEAN-BAPTISTE (Nice) Aortic Disease Can Progress AFTER Repair Resulting in: Stent migration Endoleaks Sac enlargement Secondary
Zenith Alpha System, Designed for Easy and Durable repairs Prof. Elixène JEAN-BAPTISTE (Nice) Aortic Disease Can Progress AFTER Repair Resulting in: Stent migration Endoleaks Sac enlargement Secondary
First Experiences with the Ziehm Vision FD Mobile C-Arm with Flat-Panel Detector
 01 White Paper No. 02/2009 First Experiences with the Ziehm Vision FD Mobile C-Arm with Flat-Panel Detector Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC) in the Netherlands is the first hospital in the world
01 White Paper No. 02/2009 First Experiences with the Ziehm Vision FD Mobile C-Arm with Flat-Panel Detector Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC) in the Netherlands is the first hospital in the world
TRUFILL DCS ORBIT Detachable Coil System
 ORBIT Conforming to Your Complex Needs Excellent Conformability and Concentric Filling for Outstanding Packing Density ORBIT Full range of Mini Complex and new Tight Distal Loop Technology coils Our Complex
ORBIT Conforming to Your Complex Needs Excellent Conformability and Concentric Filling for Outstanding Packing Density ORBIT Full range of Mini Complex and new Tight Distal Loop Technology coils Our Complex
What makes the technology unique?
 The VirtuoSaph Endoscopic Vein Harvesting System is designed to elevate standards for patient safety, conduit quality, and ergonomics. When developing the VirtuoSaph System, Terumo spent significant resources
The VirtuoSaph Endoscopic Vein Harvesting System is designed to elevate standards for patient safety, conduit quality, and ergonomics. When developing the VirtuoSaph System, Terumo spent significant resources
Get a Closer Look. Continuing Support
 Get a Closer Look Terumo s Centers of Excellence bring together clinicians interested in evaluating Terumo s endoscopic vein harvesting products and experienced clinicians already successfully using them.
Get a Closer Look Terumo s Centers of Excellence bring together clinicians interested in evaluating Terumo s endoscopic vein harvesting products and experienced clinicians already successfully using them.
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 2: Vascular stents
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 25539-2 First edition 2008-09-01 Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 2: Vascular stents Implants cardiovasculaires Dispositifs endovasculaires Partie 2: Endoprothèses
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 25539-2 First edition 2008-09-01 Cardiovascular implants Endovascular devices Part 2: Vascular stents Implants cardiovasculaires Dispositifs endovasculaires Partie 2: Endoprothèses
Inferior Vena Cava Filters - Europe Analysis and Market Forecasts
 Inferior Vena Cava Filters - Europe Analysis and Market Forecasts Inferior Vena Cava Filters - Europe Analysis and Market Forecasts BioPortfolio has been marketing business and market research reports
Inferior Vena Cava Filters - Europe Analysis and Market Forecasts Inferior Vena Cava Filters - Europe Analysis and Market Forecasts BioPortfolio has been marketing business and market research reports
S.M.A.R.T. Our inspiration came right from the source. Feeling is believing. S.M.A.R.T. Flex Vascular Stent System. LinkedIn page
 to receive our latest news and key activities. S.M.A.R.T. Flex Vascular System Our inspiration came right from the source. S.M.A.R.T. Flex Vascular System Feeling is believing. LinkedIn page Follow us
to receive our latest news and key activities. S.M.A.R.T. Flex Vascular System Our inspiration came right from the source. S.M.A.R.T. Flex Vascular System Feeling is believing. LinkedIn page Follow us
Harvesting a New Standard of Care
 Harvesting a New Standard of Care The handoff. Be confident what you re passing along is of the highest quality. What do you need to deliver the optimal conduit? Is it knowing that you controlled hemostasis?
Harvesting a New Standard of Care The handoff. Be confident what you re passing along is of the highest quality. What do you need to deliver the optimal conduit? Is it knowing that you controlled hemostasis?
Stent-based anastomotic coupler
 Stent-based anastomotic coupler Design Team Nick Cote, Ryan Myers Matthew Ouellette, Jessica Patel David Schecter Design Advisor Prof. Jeffrey Ruberti Email: J.Ruberti@neu.edu Abstract Microvascular anastomosis
Stent-based anastomotic coupler Design Team Nick Cote, Ryan Myers Matthew Ouellette, Jessica Patel David Schecter Design Advisor Prof. Jeffrey Ruberti Email: J.Ruberti@neu.edu Abstract Microvascular anastomosis
The evolution of stent design for chronic iliac vein obstruction
 The evolution of stent design for chronic iliac vein obstruction Stephen Black Consultant Vascular Surgeon Clinical Lead for Venous and Lymphoedema Surgery Guys and St Thomas Hospital London They Not
The evolution of stent design for chronic iliac vein obstruction Stephen Black Consultant Vascular Surgeon Clinical Lead for Venous and Lymphoedema Surgery Guys and St Thomas Hospital London They Not
The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
 Accepted Manuscript Cameron D. Wright, MD PII: S0022-5223(18)31749-5 DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.06.017 Reference: YMTC 13140 To appear in: The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Received Date:
Accepted Manuscript Cameron D. Wright, MD PII: S0022-5223(18)31749-5 DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.06.017 Reference: YMTC 13140 To appear in: The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Received Date:
Disclosure. Lowell Kabnick, M.D., FACS, FACPh. I disclose the following financial relationship(s):
 Disclosure Lowell Kabnick, M.D., FACS, FACPh I disclose the following financial relationship(s): Research Grant: BTG; Ownership Interest: AngioDynamics, Vascular Insights; Consultant/Advisory Board: AngioDynamics,
Disclosure Lowell Kabnick, M.D., FACS, FACPh I disclose the following financial relationship(s): Research Grant: BTG; Ownership Interest: AngioDynamics, Vascular Insights; Consultant/Advisory Board: AngioDynamics,
Bivalirudin (Angiomax ) vs. Heparin during Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Which is Better and How to Decide?
 Bivalirudin (Angiomax ) vs. Heparin during Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Which is Better and How to Decide? Vinod Nair MD FACC FSCAI Cardiovascular Ins6tute of the South, Houma Financial Disclosure:
Bivalirudin (Angiomax ) vs. Heparin during Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Which is Better and How to Decide? Vinod Nair MD FACC FSCAI Cardiovascular Ins6tute of the South, Houma Financial Disclosure:
Palindrome Precision Chronic Dialysis Catheter Family
 Precision Chronic Dialysis Family Dialysis is Critical... Precision Family of s Increased tip visualisation 1 to aid in preserving access with initial placement. Promoting optimised patient care. From
Precision Chronic Dialysis Family Dialysis is Critical... Precision Family of s Increased tip visualisation 1 to aid in preserving access with initial placement. Promoting optimised patient care. From
TOBA II and TOBA III Clinical Programme Updates
 TOBA II and TOBA III Clinical Programme Updates Michael K. W. Lichtenberg MD, FESC Vascular Center Arnsberg, Germany Conflict of Interest - Disclosure Within the past 12 months, I or my spouse/partner
TOBA II and TOBA III Clinical Programme Updates Michael K. W. Lichtenberg MD, FESC Vascular Center Arnsberg, Germany Conflict of Interest - Disclosure Within the past 12 months, I or my spouse/partner
Power of BRANSIST safire in Neuroendovascular Therapy
 Vascular Power of BRANSIST safire in Neuroendovascular Therapy Department of Radiology, Kinki University Hospital Suguru Ueda Mr. Suguru Ueda 1. Introduction Kinki University Hospital is located in the
Vascular Power of BRANSIST safire in Neuroendovascular Therapy Department of Radiology, Kinki University Hospital Suguru Ueda Mr. Suguru Ueda 1. Introduction Kinki University Hospital is located in the
OR NOT TO OUTSOURCE. Omar Merhi, PhD Director, Clinical Research Operations ABIOMED, INC.
 1 TO OUTSOURCE OR NOT TO OUTSOURCE Striking the balance between outsourcing and using in-house resources to improve efficiencies in your trial: which model offers the most value to sponsors? Omar Merhi,
1 TO OUTSOURCE OR NOT TO OUTSOURCE Striking the balance between outsourcing and using in-house resources to improve efficiencies in your trial: which model offers the most value to sponsors? Omar Merhi,
Unique technologies for the endoluminal treatment of complex PAD lesions
 Unique technologies for the endoluminal treatment of complex PAD lesions Athanasios D Giannoukas, MD, MSc, PhD, FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences, University
Unique technologies for the endoluminal treatment of complex PAD lesions Athanasios D Giannoukas, MD, MSc, PhD, FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences, University
Endovascular Device Testing A Survey of Requirements for Product Validation
 MET A4 1p Endovascular Device Testing Info Sheet-02.qxp_MET A4 1p Endovascular Device Testing Info Sheet.qxp 05/04/2016 09:58 Page 1 Endovascular Device Testing A Survey of Requirements for Product Validation
MET A4 1p Endovascular Device Testing Info Sheet-02.qxp_MET A4 1p Endovascular Device Testing Info Sheet.qxp 05/04/2016 09:58 Page 1 Endovascular Device Testing A Survey of Requirements for Product Validation
Protect the Neck. Lieven Maene, MD. Marc Bosiers Koen Deloose Joren Callaert. Patrick Peeters Jürgen Verbist. Lieven Maene Roel Beelen.
 A.Z. Sint-Blasius, Dendermonde Marc Bosiers Koen Deloose Joren Callaert Imelda Hospital, Bonheiden Protect the Neck Patrick Peeters Jürgen Verbist OLV Hospital, Aalst Lieven Maene Roel Beelen R.Z. Heilig
A.Z. Sint-Blasius, Dendermonde Marc Bosiers Koen Deloose Joren Callaert Imelda Hospital, Bonheiden Protect the Neck Patrick Peeters Jürgen Verbist OLV Hospital, Aalst Lieven Maene Roel Beelen R.Z. Heilig
LINC James F. McKinsey, M.D.
 Two-Year Evaluation of Fenestrated and Parallel Branch Endografts for the Treatment of Juxtrarenal, Suprarenal and Thoracoabdominal Aneurysms at a Single Institution LINC 2018 James F. McKinsey, M.D. The
Two-Year Evaluation of Fenestrated and Parallel Branch Endografts for the Treatment of Juxtrarenal, Suprarenal and Thoracoabdominal Aneurysms at a Single Institution LINC 2018 James F. McKinsey, M.D. The
Statement of the. Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions. Presented by. Augusto D. Pichard, MD, FSCAI. Before the
 The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions 2400 N Street NW, Suite 604, Washington, DC 20037-1153 Main: 202.741.9854 Toll Free: 800.992.7224 Fax: 202.689.7224 E-mail: info@scai.org Statement
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions 2400 N Street NW, Suite 604, Washington, DC 20037-1153 Main: 202.741.9854 Toll Free: 800.992.7224 Fax: 202.689.7224 E-mail: info@scai.org Statement
EkoSonic MACH4 Endovascular Device Instructions for Use
 EkoSonic MACH4 Endovascular Device Instructions for Use Indications for Use The EkoSonic Endovascular System is indicated for the: Ultrasound facilitated, controlled and selective infusion of physician-specified
EkoSonic MACH4 Endovascular Device Instructions for Use Indications for Use The EkoSonic Endovascular System is indicated for the: Ultrasound facilitated, controlled and selective infusion of physician-specified
3/17/2016. Antithrombin and heparin dose effects on measures of anticoagulation in first five days of infant-pediatric ECLS.
 Antithrombin and heparin dose effects on measures of anticoagulation in first five days of infant-pediatric ECLS Kirk R. Bingham, BS; Jeffrey B. Riley, CCP; Gregory J. Schears, MD *Division of Cardiovascular
Antithrombin and heparin dose effects on measures of anticoagulation in first five days of infant-pediatric ECLS Kirk R. Bingham, BS; Jeffrey B. Riley, CCP; Gregory J. Schears, MD *Division of Cardiovascular
Inferior Vena Cava Filters (IVCF) - Medical Devices Pipeline Assessment, 2017
 Inferior Vena Cava Filters (IVCF) - Medical Devices Pipeline Assessment, 2017 Inferior Vena Cava Filters (IVCF) - Medical Devices Pipeline Assessment, 2017 BioPortfolio has been marketing business and
Inferior Vena Cava Filters (IVCF) - Medical Devices Pipeline Assessment, 2017 Inferior Vena Cava Filters (IVCF) - Medical Devices Pipeline Assessment, 2017 BioPortfolio has been marketing business and
1. Until the CE Mark suspension has been lifted, the AFX product should not be implanted in patients.
 2 Musick Irvine, CA 92618 949 595 7200 endologix.com Field Safety Notice AFX TM Endovascular AAA System: Suspension of CE Mark 29744/29731 and Patient Follow-up Advice Type of Action: Product Codes: Customer
2 Musick Irvine, CA 92618 949 595 7200 endologix.com Field Safety Notice AFX TM Endovascular AAA System: Suspension of CE Mark 29744/29731 and Patient Follow-up Advice Type of Action: Product Codes: Customer
V. Riambau and G. Mestres Vascular Surgery Division. Cardiovascular Institute Hospital Clinic. University of Barcelona
 V. Riambau and G. Mestres Vascular Surgery Division. Cardiovascular Institute Hospital Clinic. University of Barcelona Consultant/Advisor Bolton Medical Cordis Bard Medtronic Aptus Lombard Medical ivascular
V. Riambau and G. Mestres Vascular Surgery Division. Cardiovascular Institute Hospital Clinic. University of Barcelona Consultant/Advisor Bolton Medical Cordis Bard Medtronic Aptus Lombard Medical ivascular
Part I FEA of Metallic Stents (F2514)
 Part I FEA of Metallic Stents (F2514) PERU Workshop on Medical Device Regulation: Policy and Technical Aspects Kenneth E. Perry, Ph.D. ECHOBIO LLC Bainbridge Island, WA ASTM F2514 1.1 Purpose This guide
Part I FEA of Metallic Stents (F2514) PERU Workshop on Medical Device Regulation: Policy and Technical Aspects Kenneth E. Perry, Ph.D. ECHOBIO LLC Bainbridge Island, WA ASTM F2514 1.1 Purpose This guide
8: IV/SQ Maintenance
 Section 8: IV/SQ Maintenance Section Author(s): abalmforth & wbethurum Field Guide Section 8: IV/SQ Maintenance 1 Section 8: IV & SQ Maintenance 2 Section 8: IV/SW Maintenance Field Guide Section Contents
Section 8: IV/SQ Maintenance Section Author(s): abalmforth & wbethurum Field Guide Section 8: IV/SQ Maintenance 1 Section 8: IV & SQ Maintenance 2 Section 8: IV/SW Maintenance Field Guide Section Contents
Evolution of Embolization
 Evolution of Embolization WITH JAFAR GOLZARIAN, MD; FRANCOIS CORNELIS, MD, PhD; COREY L. TEIGEN, MD; DMITRI E. SAMOILOV, MD; AND FRANK R. ARKO III, MD Jafar Golzarian, MD Professor of Radiology Department
Evolution of Embolization WITH JAFAR GOLZARIAN, MD; FRANCOIS CORNELIS, MD, PhD; COREY L. TEIGEN, MD; DMITRI E. SAMOILOV, MD; AND FRANK R. ARKO III, MD Jafar Golzarian, MD Professor of Radiology Department
CapSure Permanent Fixation System
 CapSure Permanent Fixation System Permanent Fixation Redefined Advancing the Fixation Experience Recipient of 2015 SLS Innovations of the Year recognition. SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product.
CapSure Permanent Fixation System Permanent Fixation Redefined Advancing the Fixation Experience Recipient of 2015 SLS Innovations of the Year recognition. SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product.
In-Service Presentation
 In-Service Presentation 12016 2016 Boston Boston Scientific. Scientific. Corporation or its or Affiliates. its Affiliates. All rights All rights reserved. reserved. PI-379301-AA EU MAR2016 Agenda WallFlex
In-Service Presentation 12016 2016 Boston Boston Scientific. Scientific. Corporation or its or Affiliates. its Affiliates. All rights All rights reserved. reserved. PI-379301-AA EU MAR2016 Agenda WallFlex
REBOA. Todd E. Rasmussen, MD
 REBOA Todd E. Rasmussen, MD Development & Implantation of REBOA within the Military Learning Health System February 8 th, 2018 Todd E. Rasmussen, MD, FACS Colonel, USAF MC Associate Dean for Research Shumacker
REBOA Todd E. Rasmussen, MD Development & Implantation of REBOA within the Military Learning Health System February 8 th, 2018 Todd E. Rasmussen, MD, FACS Colonel, USAF MC Associate Dean for Research Shumacker
ACCESS OPTIONS FOR PATIENTS WITH VENOUS OUTFLOW INSUFFICIENCY SYSTEM MERIT IS COMMITTED TO DIALYSIS ACCESS
 ACCESS OPTIONS FOR PATIENTS WITH VENOUS OUTFLOW INSUFFICIENCY SYSTEM MERIT IS COMMITTED TO DIALYSIS ACCESS SYSTEM When end stage renal disease patients are catheter-dependent or are approaching catheter
ACCESS OPTIONS FOR PATIENTS WITH VENOUS OUTFLOW INSUFFICIENCY SYSTEM MERIT IS COMMITTED TO DIALYSIS ACCESS SYSTEM When end stage renal disease patients are catheter-dependent or are approaching catheter
Whitepaper: Precision Micro-Braiding for Implantable Devices
 Whitepaper: Precision Micro-Braiding for Implantable Devices Keys to Design Success When Contemplating Medical Device Braids By: Robert Kiefer and Keith Smith Braided textile structures are among the most
Whitepaper: Precision Micro-Braiding for Implantable Devices Keys to Design Success When Contemplating Medical Device Braids By: Robert Kiefer and Keith Smith Braided textile structures are among the most
VASCULAR ACCESS PRELUDE SHEATH INTRODUCERS. Merit Medical s Innovative Family of Vascular Access Products A GREAT INTRODUCTION
 VASCULAR ACCESS PRELUDE SHEATH INTRODUCERS Merit Medical s Innovative Family of Vascular Access Products A GREAT INTRODUCTION THE PRELUDE FAMILY OF SHEATH INTRODUCERS A comprehensive product line offering
VASCULAR ACCESS PRELUDE SHEATH INTRODUCERS Merit Medical s Innovative Family of Vascular Access Products A GREAT INTRODUCTION THE PRELUDE FAMILY OF SHEATH INTRODUCERS A comprehensive product line offering
Registry Assessment of Peripheral Interventional Devices (RAPID)
 Registry Assessment of Peripheral Interventional Devices (RAPID) Pablo Morales, MD FDA Division of Cardiovascular Devices MDEpiNet Annual Meeting October 20, 2017 RAPID moving into full SPEED Pablo Morales,
Registry Assessment of Peripheral Interventional Devices (RAPID) Pablo Morales, MD FDA Division of Cardiovascular Devices MDEpiNet Annual Meeting October 20, 2017 RAPID moving into full SPEED Pablo Morales,
Clinical Evaluation of a New In-Line Continuous Blood Gas Monitor
 THE JOURNAL OF EXTRA-CORPOREAL TECHNOLOGY Original Article Clinical Evaluation of a New In-Line Continuous Blood Gas Monitor Rhonda Southworth, MHA, CCP*; Robin Sutton, MS, CCP*; Sam Mize, CCP*; Alfred
THE JOURNAL OF EXTRA-CORPOREAL TECHNOLOGY Original Article Clinical Evaluation of a New In-Line Continuous Blood Gas Monitor Rhonda Southworth, MHA, CCP*; Robin Sutton, MS, CCP*; Sam Mize, CCP*; Alfred
Decide, guide, treat and confirm: The Philips Volcano CLI solution
 Decide, guide, treat and confirm: The Philips Volcano CLI solution Trademarks are the property of Koninklijke Philips N.V. or their respective owners Critical Limb Ischemia Affects the Lives of Many Patients
Decide, guide, treat and confirm: The Philips Volcano CLI solution Trademarks are the property of Koninklijke Philips N.V. or their respective owners Critical Limb Ischemia Affects the Lives of Many Patients
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of the extrahepatic collateral arteries in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
 Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of the extrahepatic collateral arteries in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma Poster No.: C-1945 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit Interventional
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of the extrahepatic collateral arteries in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma Poster No.: C-1945 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit Interventional
V. Riambau, MD, PhD. Professor and Chief of Vascular Surgery Division CardioVascular Institute, Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona
 V. Riambau, MD, PhD Professor and Chief of Vascular Surgery Division CardioVascular Institute, Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona vriambau@clinic.ub.es Consultant/Advisor Bolton Medical Cordis Bard
V. Riambau, MD, PhD Professor and Chief of Vascular Surgery Division CardioVascular Institute, Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona vriambau@clinic.ub.es Consultant/Advisor Bolton Medical Cordis Bard
Comfort your patient deserves. Strength you demand.
 POLYSITE LOW PROFILE HYBRID PORTS Comfort your patient deserves. Strength you demand. We never settle because you never settle. Throughout our 35-year history, clinicians and patients have benefited from
POLYSITE LOW PROFILE HYBRID PORTS Comfort your patient deserves. Strength you demand. We never settle because you never settle. Throughout our 35-year history, clinicians and patients have benefited from
ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF COMPLEX ABDOMINAL AND THORACOABDOMINAL
 Editors G. TORsello - K. P. DONAs M. Austermann B. Berekoven T. Bisdas Contributors M. Lachat F. Marques de Azevedo G. Panuccio ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF COMPLEX ABDOMINAL AND THORACOABDOMINAL ANEURYSMS
Editors G. TORsello - K. P. DONAs M. Austermann B. Berekoven T. Bisdas Contributors M. Lachat F. Marques de Azevedo G. Panuccio ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF COMPLEX ABDOMINAL AND THORACOABDOMINAL ANEURYSMS
Vascular. Making Best Use of Trinias Applications for Lower Extremity Interventional Procedures. 1. Introduction
 Vascular Making Best Use of Trinias Applications for Lower Extremity Interventional Procedures Yasuhiro Takahashi, M.D. Department of Cardiology, The Fraternity Memorial Hospital Yasuhiro Takahashi 1.
Vascular Making Best Use of Trinias Applications for Lower Extremity Interventional Procedures Yasuhiro Takahashi, M.D. Department of Cardiology, The Fraternity Memorial Hospital Yasuhiro Takahashi 1.
Great Saphenous Vein Occlusion with Cyanoacrylate: An Alternative to Endovenous Laser Ablation?
 acta medica orıgınal artıcle Great Saphenous Vein Occlusion with Cyanoacrylate: An Alternative to Endovenous Laser Ablation? Fatma Gonca Eldem*, [MD] Selin Ardalı 1, [MD] Bora Peynircioğlu 1, [MD] 1, Hacettepe
acta medica orıgınal artıcle Great Saphenous Vein Occlusion with Cyanoacrylate: An Alternative to Endovenous Laser Ablation? Fatma Gonca Eldem*, [MD] Selin Ardalı 1, [MD] Bora Peynircioğlu 1, [MD] 1, Hacettepe
CT post processing and low dose scanning
 CT post processing and low dose scanning Gabor Szell GE Healthcare CT Modality Manager EE Annual Scientific and Educational Meeting Innovations in Cardiothoracic Imaging 201 13-14 May 2011, Tokuda Hospital
CT post processing and low dose scanning Gabor Szell GE Healthcare CT Modality Manager EE Annual Scientific and Educational Meeting Innovations in Cardiothoracic Imaging 201 13-14 May 2011, Tokuda Hospital
Human Research Protection Program Guidance for Human Research Determination
 Human Research Protection Program Guidance for Human Research Determination I.1.A The sole purpose of the Institutional Review Board (IRB), as defined in federal statutes, is the protection of human subjects
Human Research Protection Program Guidance for Human Research Determination I.1.A The sole purpose of the Institutional Review Board (IRB), as defined in federal statutes, is the protection of human subjects
Accuracy and Safety of Carbon Dioxide Inferior Vena Cavographyl
 Accuracy and Safety of Carbon Dioxide Inferior Vena Cavographyl Robin Boyd-Kranis, MD' Kevin L. Sullivan, MD David J. Eschelman, MD Joseph Bonn, MD Geoffrey A. Gardiner, MD Index terms: Carbon dioxide
Accuracy and Safety of Carbon Dioxide Inferior Vena Cavographyl Robin Boyd-Kranis, MD' Kevin L. Sullivan, MD David J. Eschelman, MD Joseph Bonn, MD Geoffrey A. Gardiner, MD Index terms: Carbon dioxide
Applications Catheters. Polymer Tube Processing Catheter Hole Drilling
 Applications Catheters Polymer Tube Processing Catheter Hole Drilling Stainless Steel Tube Processing Laser Light Technologies can achieve virtually burr-free cuts in stainless steel tubing of various
Applications Catheters Polymer Tube Processing Catheter Hole Drilling Stainless Steel Tube Processing Laser Light Technologies can achieve virtually burr-free cuts in stainless steel tubing of various
EkoSonic Endovascular System
 EkoSonic Endovascular System Nursing In-Service EKOS Corporation is a BTG International group company US-EKO-1800192 Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to
EkoSonic Endovascular System Nursing In-Service EKOS Corporation is a BTG International group company US-EKO-1800192 Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to
Modular branched endograft system for aortic aneurysm repair: evaluation in a human cadaver circulation model
 Modular branched endograft system for aortic aneurysm repair: evaluation in a human cadaver circulation model Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 2007 41: 126 9 M.A.M. Linsen A.W.F. Vos J. Diks J.A. Rauwerda
Modular branched endograft system for aortic aneurysm repair: evaluation in a human cadaver circulation model Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 2007 41: 126 9 M.A.M. Linsen A.W.F. Vos J. Diks J.A. Rauwerda
A UNIQUE POLYESTER DRUG/DEVICE VASCULAR GRAFT INTERGARD HEPARIN
 A UNIQUE POLYESTER DRUG/DEVICE VASCULAR GRAFT INTERGARD HEPARIN FACTS ON INTERGARD HEPARIN Most frequent causes of vascular graft failure and associated limb loss 1 Graft occlusion due to the development
A UNIQUE POLYESTER DRUG/DEVICE VASCULAR GRAFT INTERGARD HEPARIN FACTS ON INTERGARD HEPARIN Most frequent causes of vascular graft failure and associated limb loss 1 Graft occlusion due to the development
Interventional radiology suite or hybrid operating room: Which is the best for lung nodule localization?
 Accepted Manuscript Interventional radiology suite or hybrid operating room: Which is the best for lung nodule localization? Robert B. Cameron PII: S0022-5223(18)31813-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.06.063
Accepted Manuscript Interventional radiology suite or hybrid operating room: Which is the best for lung nodule localization? Robert B. Cameron PII: S0022-5223(18)31813-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.06.063
DEC DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control Room -W066-G609 Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 Ms. Victoria Rendon Senior
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control Room -W066-G609 Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 Ms. Victoria Rendon Senior
Contrast media administration - Alternatives to the cubital vein
 Contrast media administration - Alternatives to the cubital vein Radiologists must be prepared for administration of contrast media via the intraosseous route & CVC Hampus Eklöf MD, PhD CMO Unilabs radiology
Contrast media administration - Alternatives to the cubital vein Radiologists must be prepared for administration of contrast media via the intraosseous route & CVC Hampus Eklöf MD, PhD CMO Unilabs radiology
Pulmonary Nodule Localization - Best Method. Jay M. Lee, M.D. Chief and Associate Professor Division of Thoracic Surgery, UCLA
 Pulmonary Nodule Localization - Best Method Jay M. Lee, M.D. Chief and Associate Professor Division of Thoracic Surgery, UCLA 1 Localization of pulmonary nodules Lung cancer screening has lead to frequent
Pulmonary Nodule Localization - Best Method Jay M. Lee, M.D. Chief and Associate Professor Division of Thoracic Surgery, UCLA 1 Localization of pulmonary nodules Lung cancer screening has lead to frequent
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium fondaparinux, 2.5mg/0.5ml, solution for injection (Arixtra ) No. (287/06) GlaxoSmithKline 7 July 2006 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the
Scottish Medicines Consortium fondaparinux, 2.5mg/0.5ml, solution for injection (Arixtra ) No. (287/06) GlaxoSmithKline 7 July 2006 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the
Valiant Navion device enhancements: a case-based approach to Navion s clinical value
 Valiant Navion device enhancements: a case-based approach to Navion s clinical value Luigi Lovato Cardiovascular Radiology Unit Program In collaboration with Cardiac Surgery Unit S. Orsola University Hospital
Valiant Navion device enhancements: a case-based approach to Navion s clinical value Luigi Lovato Cardiovascular Radiology Unit Program In collaboration with Cardiac Surgery Unit S. Orsola University Hospital
PICC TIP TRACKING & CONFIRMATION WITHOUT CHEST X-RAY
 GETTING TO THE HEART OF THE MATTER Using x-ray to confirm picc tip placement wastes clinical care time, exposes patients to harmful radiation, and delays medical therapy. The Sherlock 3cg* Tip Confirmation
GETTING TO THE HEART OF THE MATTER Using x-ray to confirm picc tip placement wastes clinical care time, exposes patients to harmful radiation, and delays medical therapy. The Sherlock 3cg* Tip Confirmation
Uncompromised Handling with Tri-layer Sealing Properties
 Uncompromised Handling with Tri-layer Sealing Properties The Dialysis Access Graft with a Low Bleed Barrier The GORE ACUSEAL Vascular Graft is a tri-layer vascular graft which includes an elastomeric membrane
Uncompromised Handling with Tri-layer Sealing Properties The Dialysis Access Graft with a Low Bleed Barrier The GORE ACUSEAL Vascular Graft is a tri-layer vascular graft which includes an elastomeric membrane
Merit Medical s Innovative Family. of Vascular Access Products. A Great Introduction
 Merit Medical s Innovative Family of Vascular Access Products A Great Introduction Sheath Introducers The Prelude family of sheath introducers is a comprehensive product line offering excellent transitions,
Merit Medical s Innovative Family of Vascular Access Products A Great Introduction Sheath Introducers The Prelude family of sheath introducers is a comprehensive product line offering excellent transitions,
MECH ENG 762 Computational Modeling of Circulatory System Term 1 (September - December 2018)
 Department of Mechanical Engineering School of Computational Science and Engineering School of Biomedical Engineering McMaster University MECH ENG 762 Computational Modeling of Circulatory System Term
Department of Mechanical Engineering School of Computational Science and Engineering School of Biomedical Engineering McMaster University MECH ENG 762 Computational Modeling of Circulatory System Term
Development of a patient-specific modular vascular phantom with clinically relevant mechanical properties. Academic Year:
 Development of a patient-specific modular vascular phantom with clinically relevant mechanical properties Student: 852517 Supervisor: Co-Supervisor: Prof. Elena De Momi Dr. Helge Wurdemann Academic Year:
Development of a patient-specific modular vascular phantom with clinically relevant mechanical properties Student: 852517 Supervisor: Co-Supervisor: Prof. Elena De Momi Dr. Helge Wurdemann Academic Year:
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY D-DIMER UPDATE
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY D-DIMER UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits see the Continuing
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY D-DIMER UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits see the Continuing
Placement of peripherally inserted central catheter by imaging. Experience in a children's hospital
 Placement of peripherally inserted central catheter by imaging. Experience in a children's hospital Poster No.: C-0226 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Albi Rodríguez, I. Solis Muniz,
Placement of peripherally inserted central catheter by imaging. Experience in a children's hospital Poster No.: C-0226 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Albi Rodríguez, I. Solis Muniz,
Placement of peripherally inserted central catheter by imaging. Experience in a children's hospital
 Placement of peripherally inserted central catheter by imaging. Experience in a children's hospital Poster No.: C-0226 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Albi Rodríguez, I. Solís Muñiz,
Placement of peripherally inserted central catheter by imaging. Experience in a children's hospital Poster No.: C-0226 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Albi Rodríguez, I. Solís Muñiz,
American College of Radiology Detailed Summary of the CY 2017 Final Rule for the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System
 American College of Radiology Detailed Summary of the CY 2017 Final Rule for the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released its final rule
American College of Radiology Detailed Summary of the CY 2017 Final Rule for the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released its final rule
From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery
 From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery Midterm pivotal trial results of the Talent Low Profile System for repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm: Analysis of complicated versus uncomplicated aortic
From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery Midterm pivotal trial results of the Talent Low Profile System for repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm: Analysis of complicated versus uncomplicated aortic
White Paper. Dose Tracking System. Patient Skin Dose Estimates in Real Time
 White Paper Dose Tracking System Patient Skin Dose Estimates in Real Time INTRODUCTION In an era of increased utilization of ionizing radiation for medical diagnostic and interventional procedures and
White Paper Dose Tracking System Patient Skin Dose Estimates in Real Time INTRODUCTION In an era of increased utilization of ionizing radiation for medical diagnostic and interventional procedures and
Virtual scaffolding and radial strength testing of stents
 Virtual scaffolding and radial strength testing of stents M. De Beule, P. Mortier, G. De Santis, M. Conti, P. Segers, P. Verdonck, and B. Verhegghe biommeda - IBiTech, Ghent University, Belgium Abstract:
Virtual scaffolding and radial strength testing of stents M. De Beule, P. Mortier, G. De Santis, M. Conti, P. Segers, P. Verdonck, and B. Verhegghe biommeda - IBiTech, Ghent University, Belgium Abstract:
Conformability without Compromise
 Conformability without Compromise THE STANDARD IN Conformability AND Designed for flexibility and conformability in tortuous anatomy. Optimized aortic wall apposition in angulated arch anatomy without
Conformability without Compromise THE STANDARD IN Conformability AND Designed for flexibility and conformability in tortuous anatomy. Optimized aortic wall apposition in angulated arch anatomy without
Clinical Evaluation of the Hemotec Heparin Dose Response Cartridge
 Clinical Evaluation of the Hemotec Heparin Dose Response Cartridge Mark Dumond, BS, CCT, David Dumond, BS, CCT, Cheryl Cook, BS, Brett Duffner, BS The Ohio State University Hospital Columbus, OH Keywords:
Clinical Evaluation of the Hemotec Heparin Dose Response Cartridge Mark Dumond, BS, CCT, David Dumond, BS, CCT, Cheryl Cook, BS, Brett Duffner, BS The Ohio State University Hospital Columbus, OH Keywords:
Radiography Curriculum Analysis
 Program Number Program Name Date / /20 Radiography Curriculum Analysis DIRECTIONS: Determine the course(s) in which each of the following content area is covered and enter the course number(s) and/or title(s).
Program Number Program Name Date / /20 Radiography Curriculum Analysis DIRECTIONS: Determine the course(s) in which each of the following content area is covered and enter the course number(s) and/or title(s).
Discover TruPRP. PRP the way you want it.
 Discover TruPRP PRP the way you want it. Discover TruPRP Discover the quality of Magellan TruPRP. The Magellan technology provides an automated dual spin processing system that can deliver (PRP) Platelet
Discover TruPRP PRP the way you want it. Discover TruPRP Discover the quality of Magellan TruPRP. The Magellan technology provides an automated dual spin processing system that can deliver (PRP) Platelet
New Drugs in the Sky: Coatings & Drug Elution for Improving Stents and Vascular Prostheses Beat H. Walpoth, MD
 New Drugs in the Sky: Coatings & Drug Elution for Improving Stents and Vascular Prostheses Beat H. Walpoth, MD Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland Coatings
New Drugs in the Sky: Coatings & Drug Elution for Improving Stents and Vascular Prostheses Beat H. Walpoth, MD Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland Coatings
Tissue Engineering for Blood Vessels
 Regenerative Medicine Tissue Engineering for Blood Vessels JMAJ 47(6): 288 293, 2004 Narutoshi HIBINO and Toshiharu SHIN OKA Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Heart Institute of Japan, Tokyo Women
Regenerative Medicine Tissue Engineering for Blood Vessels JMAJ 47(6): 288 293, 2004 Narutoshi HIBINO and Toshiharu SHIN OKA Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Heart Institute of Japan, Tokyo Women
Clinical Applications. ImagingRite. Interventional Radiology
 Clinical Applications ImagingRite Interventional Radiology ImagingRite, a comprehensive suite of imaging tools offered with Infinix -i angiographic systems, was designed to assist clinicians in optimizing
Clinical Applications ImagingRite Interventional Radiology ImagingRite, a comprehensive suite of imaging tools offered with Infinix -i angiographic systems, was designed to assist clinicians in optimizing
ASAHI Masters PARKWAY SOFT. ASAHI Masters PARKWAY HF
 ASAHI Masters PARKWAY SOFT Microcatheter ASAHI Masters PARKWAY HF Microcatheter SYMBOLS 1 English 2 AMK-DT207 Ver.1.40 / 11TS028 SYMBOLS Legal manufacturer Consult instructions for use Do not use if package
ASAHI Masters PARKWAY SOFT Microcatheter ASAHI Masters PARKWAY HF Microcatheter SYMBOLS 1 English 2 AMK-DT207 Ver.1.40 / 11TS028 SYMBOLS Legal manufacturer Consult instructions for use Do not use if package
COATING SYSTEMS BIOLINE COATING
 COATING SYSTEMS BIOLINE COATING BIOLINE COATING MIMICKING HUMAN TISSUE MAQUET THE GOLD STANDARD MAQUET is an international synonym for innovative and technological advances in operating rooms and intensive
COATING SYSTEMS BIOLINE COATING BIOLINE COATING MIMICKING HUMAN TISSUE MAQUET THE GOLD STANDARD MAQUET is an international synonym for innovative and technological advances in operating rooms and intensive
A New Endoprosthesis With Sensing Capability
 A New Endoprosthesis With Sensing Capability Isa C.T. Santos, Alexandra Sepúlveda, Luís Rocha & João Manuel R.S. Tavares ICABB 2010 October 14-16 Venice, Italy Outline Aneurysm Treatment options Thoracic
A New Endoprosthesis With Sensing Capability Isa C.T. Santos, Alexandra Sepúlveda, Luís Rocha & João Manuel R.S. Tavares ICABB 2010 October 14-16 Venice, Italy Outline Aneurysm Treatment options Thoracic
Trabecular Metal Technology
 Trabecular Metal Technology Alexandre Nehme Departement of Orthopedic Surgery. Saint Georges University Hospital. Beirut. The cellular structure of Tantallum (Trabecular Metal) resembles bone and approximates
Trabecular Metal Technology Alexandre Nehme Departement of Orthopedic Surgery. Saint Georges University Hospital. Beirut. The cellular structure of Tantallum (Trabecular Metal) resembles bone and approximates
Making the difference with Live Image Guidance
 OncoSuite Interventional X-ray Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Next generation of Image Guided Therapy in Interventional Oncology Live Image Guidance in Interventional Oncology OncoSuite:
OncoSuite Interventional X-ray Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Next generation of Image Guided Therapy in Interventional Oncology Live Image Guidance in Interventional Oncology OncoSuite:
Polidocanol Endovenous Microfoam (PEM) Comprehensive Treatment for Great Saphenous Vein System (GSV) Incompetence
 Polidocanol Endovenous Microfoam (PEM) Comprehensive Treatment for Great Saphenous Vein System (GSV) Incompetence By Ariel D. Soffer, MD, FACC Dr. Ariel David Soffer-Bio NCVH Vein Forum Fellow of the American
Polidocanol Endovenous Microfoam (PEM) Comprehensive Treatment for Great Saphenous Vein System (GSV) Incompetence By Ariel D. Soffer, MD, FACC Dr. Ariel David Soffer-Bio NCVH Vein Forum Fellow of the American
Assessing Intra-procedural Arterial Complications Following Lobar Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 Microsphere
 Assessing Intra-procedural Arterial Complications Following Lobar Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 Microsphere Abdulrahman Masrani, MD ; Bradford J Chong, BS; Osman Ahmed, MD; Sreekumar Madassery, MD;
Assessing Intra-procedural Arterial Complications Following Lobar Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 Microsphere Abdulrahman Masrani, MD ; Bradford J Chong, BS; Osman Ahmed, MD; Sreekumar Madassery, MD;
Innovating to Create Value through New Perspectives and Synthesis
 Feature Article Innovating to Create Value through New Perspectives and Synthesis With the corporate mission of Contributing to Society through Healthcare, the Terumo Group has brought valuable innovation
Feature Article Innovating to Create Value through New Perspectives and Synthesis With the corporate mission of Contributing to Society through Healthcare, the Terumo Group has brought valuable innovation
Conformability without Compromise
 Conformability without Compromise THE STANDARD IN Conformability AND Designed for flexibility and conformability in tortuous anatomy. Optimized aortic wall apposition in angulated arch anatomy without
Conformability without Compromise THE STANDARD IN Conformability AND Designed for flexibility and conformability in tortuous anatomy. Optimized aortic wall apposition in angulated arch anatomy without
