Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. A. Fire et al. (1998) Nature Vol 391:
|
|
|
- Marybeth Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans A. Fire et al. (1998) Nature Vol 391:
2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Objective 3. Results 4. Mechanism 5. Summary 6. Take-Home-Lesson 7. Discussion and current questions 2
3 1.1 Introduction History of gene silencing , Richard Jorgensen tried to manipulate petunia plants - Goal: to intensify purple color by introduction of an additional pigment gene - Result: plants with paler or white flowers ; 17:51 MEZ 3
4 1.1 Introduction - History of gene silencing - In other experiments it was tried to make plants resistant to viral infection - over expressed protein should block replication of the virus - replication was restricted - but: the protein was not necessary - just the RNA 4
5 1.1 Introduction - History of gene silencing - antisense RNA was used to knockdown gene-expression - sense RNA had a same effect - RNA-gene-relation in sequence was necessary 5
6 1.2 Introduction - C. elegans - nematode - model organism - rapid generation time - hermaphrodite and sexual reproduction - simple body plan - exact known number of somatic cells 6
7 7
8 ; 17:50 MEZ 8
9 ssrna und asrna equal effect can persist in next generation, even though native RNA transcripts are degraded in progeny cells 2. Objective Investigation of requirements for structure and delivery of the interfering RNA. 9
10 3.1 Results - surmised double stranded-character - injected RNA was synthesized by bacteriophage RNA polymerase: random transcripts - aberrant RNA products were found in DNA transgene assays 10
11 3.2 Results - Comparing interference activities - unc-22 gene: encodes myofilament protein in striated muscle cells - decrease of unc-22 gene expression: twitching phenotype thousand copies of unc-22 mrna are present in these muscel cells - null mutant: strong twitching 11
12 3.2 Results - Comparing interference activities - antisense and sense RNA: small-scale interference - sense-antisense mixture: effective interference - electrophoretic analysis: the injected mixture was double-stranded 12
13 3.3 Results - conditions of annealing - Annealing of ds RNA before injection was not necessary - Mixing the as and s RNA in low-salt conditions: interference - rapid sequential injection of as and s RNA: interference - sequential injection (interval > 1h): marginal interference - conclusion: ss RNA may be degraded 13
14 3.4 Results - Specificity - Co-injection of unc-22 unrelated ds RNA: no increased interference - Injection of construct with ds segment in cis to ss segment: no increased interference - Conclusion: Interference is not potentiated by unspecific panic-response mechanism 14
15 3.5 Results - unc-54, fem-1 and hlh-1 - unc-54: body-wall-muscle heavy-chain isoform of myosin, required for full muscle contraction - fem-1: ankyrin-repeat-containing protein, required in hermaphrodites for sperm production - hlh-1: myod-family protein, required for proper body shape and motility 15
16 3.5 Results - unc-54, fem-1 and hlh-1 - injection of related ds RNA: progeny broods showed null-mutant phenotype - injection of related as or s RNA: progeny broods showed no significant interference 16
17 3.5 Results - unc-54, fem-1 and hlh-1 - Exception: unc-54c showed a larval arrest phenotype (not similar to null-mutant) - explanation: unc-54c segment encodes a highly conserved myosin-motor domain - interference may be knocked down genes with same or homologous motor domain 17
18 3.6 Results - fluorescent reporter proteins 18
19 3.6 Results - fluorescent reporter proteins - embryonically derived muscle cells: no resistance to interference - postembryonically derived striated muscle cells: more resitance to interference - non-striated vulval muscels (late larval growth): resitance to interference 19
20 20
21 3.7 Results - Effects of RNA interference on mrna levels - mex-3 is abundant in early embryos and gonads - ds mex-3 RNA for elimination of endogenous mex-3 mrna - verification by in situ hybridization 21
22 3.8 Results - dsrna is able to cross cellular boundaries 22
23 4. Mechanism 23
24 4. Mechanism 24
25 5. Summary as and srna cause equal marginal downregulation by interference dsrna is able to knock down genes by effective interference dsrna must be related to an endogenous Exon-sequence (related genes may be silenced too) Interfering Effects persist in progeny brood interfering effects are not related to panic-response-mechanism dsrna mediated interference is able to cross cellular boundaries a few cells will escape from these interfering effects Fire and Mello received the Nobelprize in 2006 "for their discovery of RNA interference - gene silencing by double-stranded RNA" 25
26 6. Take-Home-Lesson - RNAi by double-stranded RNA is a potent and specific tool to regulate gene expression in eucaryotes 26
27 7. Discussion and current questions - What is RNAi? - What is the mechanism of mrna down regulation by double-stranded RNA? 27
Nobel Laureate Assignment: Craig Mello. From an early age, Craig Mello was an explorer. He spent much of his
 1 Brett Habermehl December 4, 2014 BIO-583-001 Nobel Laureate Assignment: Craig Mello From an early age, Craig Mello was an explorer. He spent much of his childhood exploring nature and playing in the
1 Brett Habermehl December 4, 2014 BIO-583-001 Nobel Laureate Assignment: Craig Mello From an early age, Craig Mello was an explorer. He spent much of his childhood exploring nature and playing in the
Experimental genetics - 2 Partha Roy
 Partha Roy Experimental genetics - 2 Making genetically altered animal 1) Gene knock-out k from: a) the entire animal b) selected cell-type/ tissue c) selected cell-type/tissue at certain time 2) Transgenic
Partha Roy Experimental genetics - 2 Making genetically altered animal 1) Gene knock-out k from: a) the entire animal b) selected cell-type/ tissue c) selected cell-type/tissue at certain time 2) Transgenic
RNAi minilecture and Using Genetics to Explore Complex Biological Processes
 RNAi minilecture and Using Genetics to Explore Complex Biological Processes 2 American Worm People Win Nobel for RNA Work New York Times Oct. 2, 2006 The 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was
RNAi minilecture and Using Genetics to Explore Complex Biological Processes 2 American Worm People Win Nobel for RNA Work New York Times Oct. 2, 2006 The 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was
Introduction to C. elegans and RNA interference
 Introduction to C. elegans and RNA interference Why study model organisms? The problem: In order to understand biology, we need to learn about the function of the underlying genes How can we find out what
Introduction to C. elegans and RNA interference Why study model organisms? The problem: In order to understand biology, we need to learn about the function of the underlying genes How can we find out what
Learning Objectives. Define RNA interference. Define basic terminology. Describe molecular mechanism. Define VSP and relevance
 Learning Objectives Define RNA interference Define basic terminology Describe molecular mechanism Define VSP and relevance Describe role of RNAi in antigenic variation A Nobel Way to Regulate Gene Expression
Learning Objectives Define RNA interference Define basic terminology Describe molecular mechanism Define VSP and relevance Describe role of RNAi in antigenic variation A Nobel Way to Regulate Gene Expression
Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi
 Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi I. Model systems 1. Caenorhabditis elegans Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (~1 mm) nematode (roundworm) that normally lives in soil. It has become one
Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi I. Model systems 1. Caenorhabditis elegans Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (~1 mm) nematode (roundworm) that normally lives in soil. It has become one
Lecture 9. RNA interference and micrornas. 3rd December
 Lecture 9 RNA interference and micrornas 3rd December 2012 1 Therapeutic nucleic acids DNA RNA Genes (delivered by DNA vectors) Non-coding sequences Genes (delivered by RNA vectors) Non-coding sequences
Lecture 9 RNA interference and micrornas 3rd December 2012 1 Therapeutic nucleic acids DNA RNA Genes (delivered by DNA vectors) Non-coding sequences Genes (delivered by RNA vectors) Non-coding sequences
The first experiments
 RNA interference So that I don t get myself into any trouble, most of the following text is verbatim from the Ambion website, which nicely summarizes a lot of what I will talk about in class. I ve edited
RNA interference So that I don t get myself into any trouble, most of the following text is verbatim from the Ambion website, which nicely summarizes a lot of what I will talk about in class. I ve edited
RNA folding and its importance. Mitesh Shrestha
 RNA folding and its importance Mitesh Shrestha Diseases Caused due to Protein Misfolding Alzheimer s Disease Parkinson s Disease Cataracts Sickle Cell Disease Prion Diseases Cystic Fibrosis Ribozymes Ribonucleic
RNA folding and its importance Mitesh Shrestha Diseases Caused due to Protein Misfolding Alzheimer s Disease Parkinson s Disease Cataracts Sickle Cell Disease Prion Diseases Cystic Fibrosis Ribozymes Ribonucleic
RNAi info from the Fire Lab Version February 1998
 RNAi info from the Fire Lab Version 1.0 1 February 1998 Contents: I. A very short introduction to RNA-mediated interference II. Use of dsrna versus older procedures involving ssrna preparations: III. Is
RNAi info from the Fire Lab Version 1.0 1 February 1998 Contents: I. A very short introduction to RNA-mediated interference II. Use of dsrna versus older procedures involving ssrna preparations: III. Is
Caenorhabditis elegans: The Heavyweight Champ of Gene Knockout Technology
 Caenorhabditis elegans: The Heavyweight Champ of Gene Knockout Technology Rachel Pan The nematode (worm) Caenorhabditis elegans was the first multicellular organism to have its genome, or complete DNA
Caenorhabditis elegans: The Heavyweight Champ of Gene Knockout Technology Rachel Pan The nematode (worm) Caenorhabditis elegans was the first multicellular organism to have its genome, or complete DNA
Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish
 Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-formolecular-cell-biology-7th-edition-by-lodish/ Chapter 5 Molecular Genetic Techniques
Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-formolecular-cell-biology-7th-edition-by-lodish/ Chapter 5 Molecular Genetic Techniques
A Survey of Genetic Methods
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology A Survey of Genetic Methods January 24, 2008 DNA RNA Hybridization ** * radioactive probe reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction RT PCR DNA
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology A Survey of Genetic Methods January 24, 2008 DNA RNA Hybridization ** * radioactive probe reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction RT PCR DNA
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Concepts and Methods in Developmental Biology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Concepts and Methods in Developmental Biology June 16, 2009 Conceptual and Methodological Tools Concepts Genomic equivalence Differential gene expression Differentiation/de-differentiation
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Concepts and Methods in Developmental Biology June 16, 2009 Conceptual and Methodological Tools Concepts Genomic equivalence Differential gene expression Differentiation/de-differentiation
BCH Graduate Survey of Biochemistry
 BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Glen Graham Lecture 30 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Glen Graham Lecture 30 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
Plants Fight it out Intrinsic defence mechanism The magic world of Gene silencing
 I LOVE YOU Plants Fight it out Intrinsic defence mechanism The magic world of Gene silencing Over expression of Chalcone synthase gene to get Purple Petunias Napoli, Lemieux & Jorgensen,1990 Desired Effect
I LOVE YOU Plants Fight it out Intrinsic defence mechanism The magic world of Gene silencing Over expression of Chalcone synthase gene to get Purple Petunias Napoli, Lemieux & Jorgensen,1990 Desired Effect
sirna Overview and Technical Tips
 1 sirna Overview and Technical Tips 2 CONTENTS 3 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 14 18 19 20 21 Introduction Applications How Does It Work? Handy Tips Troubleshooting Conclusions Further References Contact Us 3 INTRODUCTION
1 sirna Overview and Technical Tips 2 CONTENTS 3 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 14 18 19 20 21 Introduction Applications How Does It Work? Handy Tips Troubleshooting Conclusions Further References Contact Us 3 INTRODUCTION
Name AP Biology Mrs. Laux Take home test #11 on Chapters 14, 15, and 17 DUE: MONDAY, DECEMBER 21, 2009
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Inducible genes are usually actively transcribed when: A. the molecule degraded by the enzyme(s) is present in the cell. B. repressor molecules bind to the promoter. C. lactose
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Inducible genes are usually actively transcribed when: A. the molecule degraded by the enzyme(s) is present in the cell. B. repressor molecules bind to the promoter. C. lactose
New microribbon production
 New microribbon production In vitro transformation Excystation brief exposure to acidic ph (~2) flagellar activity within 5-10 min after return to neutral ph breakdown of cyst wall (proteases) trophozoite
New microribbon production In vitro transformation Excystation brief exposure to acidic ph (~2) flagellar activity within 5-10 min after return to neutral ph breakdown of cyst wall (proteases) trophozoite
Genome research in eukaryotes
 Functional Genomics Genome and EST sequencing can tell us how many POTENTIAL genes are present in the genome Proteomics can tell us about proteins and their interactions The goal of functional genomics
Functional Genomics Genome and EST sequencing can tell us how many POTENTIAL genes are present in the genome Proteomics can tell us about proteins and their interactions The goal of functional genomics
New Plant Breeding Technologies
 New Plant Breeding Technologies Ricarda A. Steinbrecher, PhD EcoNexus / ENSSER Berlin, 07 May 2015 r.steinbrecher@econexus.info distributed by EuropaBio What are the NPBTs? *RNAi *Epigenetic alterations
New Plant Breeding Technologies Ricarda A. Steinbrecher, PhD EcoNexus / ENSSER Berlin, 07 May 2015 r.steinbrecher@econexus.info distributed by EuropaBio What are the NPBTs? *RNAi *Epigenetic alterations
Transgene-assisted genetic screen identifies rsd-6 and novel genes as key components
 JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 27 June 2018 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00416-18 Copyright 2018 Long et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 27 June 2018 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00416-18 Copyright 2018 Long et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
OmicsLink shrna Clones guaranteed knockdown even in difficult-to-transfect cells
 OmicsLink shrna Clones guaranteed knockdown even in difficult-to-transfect cells OmicsLink shrna clone collections consist of lentiviral, and other mammalian expression vector based small hairpin RNA (shrna)
OmicsLink shrna Clones guaranteed knockdown even in difficult-to-transfect cells OmicsLink shrna clone collections consist of lentiviral, and other mammalian expression vector based small hairpin RNA (shrna)
RNA Interference and the World of Small RNAs
 RNA Interference and the World of Small RNAs O, I die, Horatio; The potent poison quite o'er-crows my spirit: I cannot live to hear the news from England; But I do prophesy the election lights On Fortinbras:
RNA Interference and the World of Small RNAs O, I die, Horatio; The potent poison quite o'er-crows my spirit: I cannot live to hear the news from England; But I do prophesy the election lights On Fortinbras:
Warm-Up. Describe how the Hershey-Chase experiment proved that DNA is the heritable molecule of genes.
 Warm-Up Describe how the Hershey-Chase experiment proved that DNA is the heritable molecule of genes. Yesterday s Pictures 3D χ " = $ (o e)" e DNA protein protein protein protein protein Host Cell DNA
Warm-Up Describe how the Hershey-Chase experiment proved that DNA is the heritable molecule of genes. Yesterday s Pictures 3D χ " = $ (o e)" e DNA protein protein protein protein protein Host Cell DNA
RNAi HTS and Data Analysis
 Part I RNAi HTS and Data Analysis 1 Introduction to Genome-Scale RNAi Research 1.1 RNAi: An Effective Tool for Elucidating Gene Functions and a New Class of Drugs RNAi is a mechanism in living cells that
Part I RNAi HTS and Data Analysis 1 Introduction to Genome-Scale RNAi Research 1.1 RNAi: An Effective Tool for Elucidating Gene Functions and a New Class of Drugs RNAi is a mechanism in living cells that
MISSION shrna Library: Next Generation RNA Interference
 Page 1 of 6 Page 1 of 6 Return to Web Version MISSION shrna Library: Next Generation RNA Interference By: Stephanie Uder, Henry George, Betsy Boedeker, LSI Volume 6 Article 2 Introduction The technology
Page 1 of 6 Page 1 of 6 Return to Web Version MISSION shrna Library: Next Generation RNA Interference By: Stephanie Uder, Henry George, Betsy Boedeker, LSI Volume 6 Article 2 Introduction The technology
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Lecture 4. The Genetic Core of Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Lecture 4. The Genetic Core of Development The only way to get from genotype to phenotype is through developmental processes. - Remember the analogy that the zygote contains
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Lecture 4. The Genetic Core of Development The only way to get from genotype to phenotype is through developmental processes. - Remember the analogy that the zygote contains
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Optimization of RNAi Targets on the Human Transcriptome Ahmet Arslan Kurdoglu Computational Biosciences Program Arizona State University
 Optimization of RNAi Targets on the Human Transcriptome Ahmet Arslan Kurdoglu Computational Biosciences Program Arizona State University my background Undergraduate Degree computer systems engineer (ASU
Optimization of RNAi Targets on the Human Transcriptome Ahmet Arslan Kurdoglu Computational Biosciences Program Arizona State University my background Undergraduate Degree computer systems engineer (ASU
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Two classes of silencing RNAs move between Caenorhabditis elegans tissues.
 Two classes of silencing RNAs move between Caenorhabditis elegans tissues. Antony M Jose, Giancarlo A Garcia, and Craig P Hunter. Supplementary Figures, Figure Legends, and Tables. Supplementary Figure
Two classes of silencing RNAs move between Caenorhabditis elegans tissues. Antony M Jose, Giancarlo A Garcia, and Craig P Hunter. Supplementary Figures, Figure Legends, and Tables. Supplementary Figure
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle G2# )
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle G2#13709-01) SMALL RNA REGULATORS OF GENE EXPRESSION RG. Clerc May 05, 2010 www.fmi.ch/training/teaching RNAi for RNA interference : discovered
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle G2#13709-01) SMALL RNA REGULATORS OF GENE EXPRESSION RG. Clerc May 05, 2010 www.fmi.ch/training/teaching RNAi for RNA interference : discovered
Lectures 28 and 29 applications of recombinant technology I. Manipulate gene of interest
 Lectures 28 and 29 applications of recombinant technology I. Manipulate gene of interest C A. site-directed mutagenesis A C A T A DNA B. in vitro mutagenesis by PCR T A 1. anneal primer 1 C A 1. fill in
Lectures 28 and 29 applications of recombinant technology I. Manipulate gene of interest C A. site-directed mutagenesis A C A T A DNA B. in vitro mutagenesis by PCR T A 1. anneal primer 1 C A 1. fill in
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. transient. stable. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Experimental Tools and Resources Available in Arabidopsis. Manish Raizada, University of Guelph, Canada
 Experimental Tools and Resources Available in Arabidopsis Manish Raizada, University of Guelph, Canada Community website: The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) at http://www.arabidopsis.org Can order
Experimental Tools and Resources Available in Arabidopsis Manish Raizada, University of Guelph, Canada Community website: The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) at http://www.arabidopsis.org Can order
METODOLOGIE INTEGRATE PER LA SELEZIONE GENOMICA DI PIANTE ORTIVE
 CORSO GENHORT METODOLOGIE INTEGRATE PER LA SELEZIONE GENOMICA DI PIANTE ORTIVE Marzo 2014 Docente: e-mail: Pasquale Termolino termolin@unina.it Posttranscriptional gene silencing Transcriptional gene silencing
CORSO GENHORT METODOLOGIE INTEGRATE PER LA SELEZIONE GENOMICA DI PIANTE ORTIVE Marzo 2014 Docente: e-mail: Pasquale Termolino termolin@unina.it Posttranscriptional gene silencing Transcriptional gene silencing
A Genetic Screen to Identify Mammalian Chromatin Modifiers In Vivo.
 Gus Frangou, Stephanie Palmer & Mark Groudine Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle- USA A Genetic Screen to Identify Mammalian Chromatin Modifiers In Vivo. During mammalian development and differentiation
Gus Frangou, Stephanie Palmer & Mark Groudine Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle- USA A Genetic Screen to Identify Mammalian Chromatin Modifiers In Vivo. During mammalian development and differentiation
Applicazioni biotecnologiche
 Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Technical tips Session 4
 Technical tips Session 4 Biotinylation assay: Streptavidin is a small bacterial protein that binds with high affinity to the vitamin biotin. This streptavidin-biotin combination can be used to link molecules
Technical tips Session 4 Biotinylation assay: Streptavidin is a small bacterial protein that binds with high affinity to the vitamin biotin. This streptavidin-biotin combination can be used to link molecules
Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ
 Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Introduction to Microarray Analysis
 Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.)
 Biochemistry 412 RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.) April 4, 2006 The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by anti-sense
Biochemistry 412 RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.) April 4, 2006 The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by anti-sense
Branches of Genetics
 Branches of Genetics 1. Transmission genetics Classical genetics or Mendelian genetics 2. Molecular genetics chromosomes, DNA, regulation of gene expression recombinant DNA, biotechnology, bioinformatics,
Branches of Genetics 1. Transmission genetics Classical genetics or Mendelian genetics 2. Molecular genetics chromosomes, DNA, regulation of gene expression recombinant DNA, biotechnology, bioinformatics,
RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also mirna, sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.)
 Biochemistry 412 RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also mirna, sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.) April 8, 2008 The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by
Biochemistry 412 RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also mirna, sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.) April 8, 2008 The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by
DNA Microarrays & RNAi
 Biochemistry 412 DNA Microarrays & RNAi April 7, 2009 DNA Microarrays The development of DNA microarrays led to an explosion in mrna profiling studies. Stolovitky (2003) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 13, 370.
Biochemistry 412 DNA Microarrays & RNAi April 7, 2009 DNA Microarrays The development of DNA microarrays led to an explosion in mrna profiling studies. Stolovitky (2003) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 13, 370.
DOWNLOAD OR READ : RNA INTERFERENCE CURRENT TOPICS IN MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : RNA INTERFERENCE CURRENT TOPICS IN MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 rna interference current topics in microbiology and immunology rna interference current
DOWNLOAD OR READ : RNA INTERFERENCE CURRENT TOPICS IN MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 rna interference current topics in microbiology and immunology rna interference current
WORKING WITH THE FIGURES. 1. In Figure 8-3, why are the arrows for genes 1 and 2 pointing in opposite directions?
 8 RNA: Transcription and Processing WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 8-3, why are the arrows for genes 1 and 2 pointing in opposite directions? The arrows for genes 1 and 2 indicate the direction
8 RNA: Transcription and Processing WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 8-3, why are the arrows for genes 1 and 2 pointing in opposite directions? The arrows for genes 1 and 2 indicate the direction
RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.)
 Biochemistry 412 RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.) April 3, 2007 The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by anti-sense
Biochemistry 412 RNA Interference (RNAi) (see also sirna, micrna, shrna, etc.) April 3, 2007 The Discovery of the RNA Interference (RNAi) Phenomenon 1. Gene-specific inhibition of expression by anti-sense
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
The Silence of the Genes
 The Silence of the Genes Initial Observation: Plant geneticists aim to turn pink petunia to purple by over-expression of chalcone synthetase wt wt + Chalcone synthetase cdna driven by cauliflower mosaic
The Silence of the Genes Initial Observation: Plant geneticists aim to turn pink petunia to purple by over-expression of chalcone synthetase wt wt + Chalcone synthetase cdna driven by cauliflower mosaic
Lac Operon contains three structural genes and is controlled by the lac repressor: (1) LacY protein transports lactose into the cell.
 Regulation of gene expression a. Expression of most genes can be turned off and on, usually by controlling the initiation of transcription. b. Lactose degradation in E. coli (Negative Control) Lac Operon
Regulation of gene expression a. Expression of most genes can be turned off and on, usually by controlling the initiation of transcription. b. Lactose degradation in E. coli (Negative Control) Lac Operon
Genetics Faculty of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Topic 16: Biotechnology
 Genetics 10201232 Faculty of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Topic 16: Biotechnology 1 Biotechnology is defined as the technology that involves the use of living organisms
Genetics 10201232 Faculty of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Topic 16: Biotechnology 1 Biotechnology is defined as the technology that involves the use of living organisms
Intragenic suppressors: true revertants
 Suppressor Genetics: intragenic and informational suppressors We have covered one approach used in genetics to study gene function: classical forward genetics where an investigator selects or screens for
Suppressor Genetics: intragenic and informational suppressors We have covered one approach used in genetics to study gene function: classical forward genetics where an investigator selects or screens for
2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry and Medicine
 2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry and Medicine Lin Wang and Xianfeng Song Adviser: Sima Setayeshgar Outline o Background: transcription of genes into proteins o 2006 Nobel prizes in chemistry and medicine
2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry and Medicine Lin Wang and Xianfeng Song Adviser: Sima Setayeshgar Outline o Background: transcription of genes into proteins o 2006 Nobel prizes in chemistry and medicine
MMG 301, Lec. 25 Mutations and Bacteriophage
 MMG 301, Lec. 25 Mutations and Bacteriophage Questions for today: 1. What are mutations and how do they form? 2. How are mutant bacteria used in research? 3. What are the general properties of bacteriophage
MMG 301, Lec. 25 Mutations and Bacteriophage Questions for today: 1. What are mutations and how do they form? 2. How are mutant bacteria used in research? 3. What are the general properties of bacteriophage
BACTERIAL GENETICS. How does the DNA in the bacterial cell replicate
 BACTERIAL GENETICS Bacterial genetics is the study of gene structure and function in bacteria. Genetics itself is concerned with determining the number, location, and character of the genes of an organism.
BACTERIAL GENETICS Bacterial genetics is the study of gene structure and function in bacteria. Genetics itself is concerned with determining the number, location, and character of the genes of an organism.
Epigenetics. Medical studies in English, Lecture # 12,
 Epigenetics Medical studies in English, 2018. Lecture # 12, Epigenetics Regulation of gene activity in eukaryotes Correlation of chromatin structure with transcription stably heritable phenotype resulting
Epigenetics Medical studies in English, 2018. Lecture # 12, Epigenetics Regulation of gene activity in eukaryotes Correlation of chromatin structure with transcription stably heritable phenotype resulting
Introducing new DNA into the genome requires cloning the donor sequence, delivery of the cloned DNA into the cell, and integration into the genome.
 Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
Molecular Genetics Student Objectives
 Molecular Genetics Student Objectives Exam 1: Enduring understanding 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Essential knowledge 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source
Molecular Genetics Student Objectives Exam 1: Enduring understanding 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Essential knowledge 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information SI Materials and Methods RT-qPCR The 25 µl qrt-pcr reaction mixture included 1 µl of cdna or DNA, 12.5 µl of 2X SYBER Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems ), 5 µm of primers and
Supporting Information SI Materials and Methods RT-qPCR The 25 µl qrt-pcr reaction mixture included 1 µl of cdna or DNA, 12.5 µl of 2X SYBER Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems ), 5 µm of primers and
Lecture 15: Functional Genomics II
 Lecture 15: Functional Genomics II High-throughput RNAi screens High-throughput insertional/chemical screens Homologous recombination (yeast and mouse) - Other methods in discerning gene function Activation
Lecture 15: Functional Genomics II High-throughput RNAi screens High-throughput insertional/chemical screens Homologous recombination (yeast and mouse) - Other methods in discerning gene function Activation
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 7 Cellular differentiation and the regulation of gene expression. In this lecture we looked at two main questions: How is gene expression regulated? (revision
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 7 Cellular differentiation and the regulation of gene expression. In this lecture we looked at two main questions: How is gene expression regulated? (revision
BCH Graduate Survey of Biochemistry
 BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Marsha Durosier Lecture 29 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Marsha Durosier Lecture 29 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Overview of Genetics Lecture outline (Chpt 1, Genetics by Brooker) #1
 AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Overview of Genetics Lecture outline (Chpt 1, Genetics by Brooker) #1 - Genetics: Progress from Mendel to DNA: Gregor Mendel, in the mid 19 th century provided the
AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Overview of Genetics Lecture outline (Chpt 1, Genetics by Brooker) #1 - Genetics: Progress from Mendel to DNA: Gregor Mendel, in the mid 19 th century provided the
New Plant Breeding Techniques Group 3 Transgenic construct driven breeding
 WORKSHOP COMPERATIVE SITUATION OF NEW PLANT BREEDING TECHNIQUES 12-13 SEPTEMBER 2011 SEVILLE, SPAIN 1 New Plant Breeding Techniques Group 3 Transgenic construct driven breeding Maria Lusser Joint Research
WORKSHOP COMPERATIVE SITUATION OF NEW PLANT BREEDING TECHNIQUES 12-13 SEPTEMBER 2011 SEVILLE, SPAIN 1 New Plant Breeding Techniques Group 3 Transgenic construct driven breeding Maria Lusser Joint Research
The Ups & Downs of Gene Expression:
 The Ups & Downs of Gene Expression: Using Lipid-Based Transfection and RT-qPCR to Deliver Perfect Knockdown and Achieve Optimal Expression Results Hilary Srere, Ph.D. Topics What is RNAi? Methods of Delivery
The Ups & Downs of Gene Expression: Using Lipid-Based Transfection and RT-qPCR to Deliver Perfect Knockdown and Achieve Optimal Expression Results Hilary Srere, Ph.D. Topics What is RNAi? Methods of Delivery
Chapter 20 Biotechnology
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology Manipulation of DNA In 2007, the first entire human genome had been sequenced. The ability to sequence an organisms genomes were made possible by advances in biotechnology, (the
Chapter 20 Biotechnology Manipulation of DNA In 2007, the first entire human genome had been sequenced. The ability to sequence an organisms genomes were made possible by advances in biotechnology, (the
Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications
 Chapter Outline Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications Section 1: The Human Genome KEY IDEAS > Why is the Human Genome Project so important? > How do genomics and gene technologies affect
Chapter Outline Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications Section 1: The Human Genome KEY IDEAS > Why is the Human Genome Project so important? > How do genomics and gene technologies affect
Experimental genetics - I
 Experimental genetics - I Examples of diseases with genetic-links Hemophilia (complete loss or altered form of factor VIII): bleeding disorder Duchenne muscular dystrophy (altered form of dystrophin) muscle
Experimental genetics - I Examples of diseases with genetic-links Hemophilia (complete loss or altered form of factor VIII): bleeding disorder Duchenne muscular dystrophy (altered form of dystrophin) muscle
17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites
 17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites 1 Section 17.5 Transcription regulatory proteins, transcription factors, target cis-acting sites
17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites 1 Section 17.5 Transcription regulatory proteins, transcription factors, target cis-acting sites
1 Enhancing RNAi efficiency by inserting Nuclear factor- B binding sequence into SiRNA expression. cassette. Jianzhong Yi 1*,Chenqian Liu
 1 Enhancing RNAi efficiency by inserting Nuclear factor- B binding sequence into SiRNA expression 2 cassette 3 4 Jianzhong Yi 1*,Chenqian Liu 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20Address for Correspondence:
1 Enhancing RNAi efficiency by inserting Nuclear factor- B binding sequence into SiRNA expression 2 cassette 3 4 Jianzhong Yi 1*,Chenqian Liu 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20Address for Correspondence:
Chapter 13: Biotechnology
 Chapter Review 1. Explain why the brewing of beer is considered to be biotechnology. The United Nations defines biotechnology as any technological application that uses biological system, living organism,
Chapter Review 1. Explain why the brewing of beer is considered to be biotechnology. The United Nations defines biotechnology as any technological application that uses biological system, living organism,
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype. CBS520 Eric Nabity
 Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Concept 13.1 Recombinant DNA Can Be Made in the Laboratory
 13 Biotechnology Concept 13.1 Recombinant DNA Can Be Made in the Laboratory It is possible to modify organisms with genes from other, distantly related organisms. Recombinant DNA is a DNA molecule made
13 Biotechnology Concept 13.1 Recombinant DNA Can Be Made in the Laboratory It is possible to modify organisms with genes from other, distantly related organisms. Recombinant DNA is a DNA molecule made
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr. Faculty of Sciences Lebanese University Beirut, Lebanon.
 Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Faculty of Sciences Lebanese University Beirut, Lebanon https://yeastwonderfulworld.wordpress.com/ Biol328 - B3212 Molecular Biotechnology Partial Exam Question I Explain the procedure
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Faculty of Sciences Lebanese University Beirut, Lebanon https://yeastwonderfulworld.wordpress.com/ Biol328 - B3212 Molecular Biotechnology Partial Exam Question I Explain the procedure
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster
 Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques
 Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Methods for Reverse genetics References:
 Methods for Reverse genetics References: 1. Alonso JM, Ecker JR. Moving forward in reverse: genetic technologies to enable genomewide phenomic screens in Arabidopsis. Nat Rev Genet. 2006 Jul;7(7):524-36.
Methods for Reverse genetics References: 1. Alonso JM, Ecker JR. Moving forward in reverse: genetic technologies to enable genomewide phenomic screens in Arabidopsis. Nat Rev Genet. 2006 Jul;7(7):524-36.
Optimizing RNA interference for application in mammalian cells
 Biochem. J. (2004) 380, 593 603 (Printed in Great Britain) 593 REVIEW ARTICLE Optimizing RNA interference for application in mammalian cells René H. MEDEMA 1 Division of Molecular Biology, H8, Netherlands
Biochem. J. (2004) 380, 593 603 (Printed in Great Britain) 593 REVIEW ARTICLE Optimizing RNA interference for application in mammalian cells René H. MEDEMA 1 Division of Molecular Biology, H8, Netherlands
3. human genomics clone genes associated with genetic disorders. 4. many projects generate ordered clones that cover genome
 Lectures 30 and 31 Genome analysis I. Genome analysis A. two general areas 1. structural 2. functional B. genome projects a status report 1. 1 st sequenced: several viral genomes 2. mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lectures 30 and 31 Genome analysis I. Genome analysis A. two general areas 1. structural 2. functional B. genome projects a status report 1. 1 st sequenced: several viral genomes 2. mitochondria and chloroplasts
32 Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Lecture Outline 11/28/05. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes and Eukarykotes
 3 Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Lecture Outline /8/05 Gene regulation in eukaryotes Chromatin remodeling More kinds of control elements Promoters, Enhancers, and Silencers Combinatorial control Cell-specific
3 Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Lecture Outline /8/05 Gene regulation in eukaryotes Chromatin remodeling More kinds of control elements Promoters, Enhancers, and Silencers Combinatorial control Cell-specific
Application Note sirna dependent gene silencing in HeLa cells cultivated on various cell culture surfaces
 Application Note sirna dependent gene silencing in HeLa cells cultivated on various cell culture surfaces 1 Introduction 1.1 RNA interference (RNAi) One of the most important advances in biology in the
Application Note sirna dependent gene silencing in HeLa cells cultivated on various cell culture surfaces 1 Introduction 1.1 RNA interference (RNAi) One of the most important advances in biology in the
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/333/6047/1311/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Epigenetic Licensing of Germline Gene Expression by Maternal RNA in C. elegans Cheryl L. Johnson and Andrew M. Spence*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/333/6047/1311/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Epigenetic Licensing of Germline Gene Expression by Maternal RNA in C. elegans Cheryl L. Johnson and Andrew M. Spence*
3.a.1- DNA and RNA 10/19/2014. Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes.
 3.a.1- DNA and RNA Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EU 3.B: Expression
3.a.1- DNA and RNA Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EU 3.B: Expression
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 February 15, 2013 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) 1. Which of the following statements are not true Transcriptomes consist of mrnas Proteomes consist
1 February 15, 2013 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) 1. Which of the following statements are not true Transcriptomes consist of mrnas Proteomes consist
Genetic Modification For Potential Biocontrol
 Genetic Modification For Potential Biocontrol Aquatic Invaders Summit St Cloud, MN 05-October, 2016 Chris Merkes cmerkes@usgs.gov (608) 781-6316 What is genetic control? Genetic control is the exploitation
Genetic Modification For Potential Biocontrol Aquatic Invaders Summit St Cloud, MN 05-October, 2016 Chris Merkes cmerkes@usgs.gov (608) 781-6316 What is genetic control? Genetic control is the exploitation
Manipulating genes and cells (Kap. 10)
 Manipulating genes and cells (Kap. 10) restriction enzymes and agarose gel electrophoresis DNA sequencing nucleic acid hybridization techniques genomic and cdna libraries cloning of DNA PCR and PCR applications
Manipulating genes and cells (Kap. 10) restriction enzymes and agarose gel electrophoresis DNA sequencing nucleic acid hybridization techniques genomic and cdna libraries cloning of DNA PCR and PCR applications
Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome. A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS
 Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS 2 Do Now - Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation The diagram below shows five genes (with their enhancers) from the genome
Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS 2 Do Now - Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation The diagram below shows five genes (with their enhancers) from the genome
Chapter 5 Genetic Analysis in Cell Biology. (textbook: Molecular Cell Biology 6 ed, Lodish section: )
 Chapter 5 Genetic Analysis in Cell Biology (textbook: Molecular Cell Biology 6 ed, Lodish section: 5.1+5.4-5.5) Understanding gene function: relating function, location, and structure of gene products
Chapter 5 Genetic Analysis in Cell Biology (textbook: Molecular Cell Biology 6 ed, Lodish section: 5.1+5.4-5.5) Understanding gene function: relating function, location, and structure of gene products
Giardia RNAi Paper Discussion. Supplemental - VSG clonality. Variant-specific surface protein VSP9B10
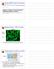 Giardia RNAi Paper Discussion Supplemental - VSG clonality VSP9B10 Green - VSP9B10 antibody Blue - DAPI Demonstration that cell line expresses a single VSP Variant-specific surface protein Outside Inside
Giardia RNAi Paper Discussion Supplemental - VSG clonality VSP9B10 Green - VSP9B10 antibody Blue - DAPI Demonstration that cell line expresses a single VSP Variant-specific surface protein Outside Inside
Genome Engineering. Brian Petuch
 Genome Engineering Brian Petuch Guiding Principles An understanding of the details of gene engineering is essential for understanding protocols when making recommendations on: Risk assessment Containment
Genome Engineering Brian Petuch Guiding Principles An understanding of the details of gene engineering is essential for understanding protocols when making recommendations on: Risk assessment Containment
Fatchiyah
 Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
Value Correct Answer Feedback. Student Response. A. Dicer enzyme. complex. C. the Dicer-RISC complex D. none of the above
 1 RNA mediated interference is a post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanism Which component of the RNAi pathway have been implicated in cleavage of the target mrna? A Dicer enzyme B the RISC-siRNA complex
1 RNA mediated interference is a post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanism Which component of the RNAi pathway have been implicated in cleavage of the target mrna? A Dicer enzyme B the RISC-siRNA complex
Trends in Medical Research -
 RNA Interference Tel : 02-2267-1740 / E-mail : kimys@inje.ac.kr, RNAi (RNA or RNA silencing) ( ) DNA small RNA (srnas) mrna,. DNA small RNA. DNA RNA small RNA. small RNA mirna (microrna), RNA RNAi. 1993
RNA Interference Tel : 02-2267-1740 / E-mail : kimys@inje.ac.kr, RNAi (RNA or RNA silencing) ( ) DNA small RNA (srnas) mrna,. DNA small RNA. DNA RNA small RNA. small RNA mirna (microrna), RNA RNAi. 1993
