Lecture Seeds. Topics. Fertilization
|
|
|
- Emil Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture Seeds Topics Generalized seed structure Where the seed comes from Parts of the seed Kinds of seeds Dicots Monocots Fertilization The seed represents one of the most significant plant adaptations. The Seed develops from the Ovule. When a pollen grain lands on the stigma of the same species, it germinates, forming a pollen tube. Passes between the stigma and style to reach the micropyle of the ovule. Double fertilization occurs. One sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus, producing a zygote. Other unites with the polar nuclei, forming a 3n endosperm cell. The Ovule's Integuments form the Seed Coat. The ability to spread reproduction over a long time-span also contributes to long distance transport of seeds which helps to extend their range. In many cases this was aided by animal dispersal. This can be due to ingestion or by adherence to the feathers of birds or other beasts. Some seeds float and can withstand long exposure to salt water. The coconut is a good example of this and it can spread naturally over the ocean. Parts of seed Structure of Seeds Seeds are mature, fertilized ovules. Embryo: Young sporophyte, diploid (2n), result of fertilization. The mature embryo consists of cotyledons (seed leaves), hypocotyl (stem-like embryonic axis below the cotyledons), radicle (embryonic root). Endosperm: Food storage tissue, triploid (3n), result of fertilization. Testa (seed coat): Outer protective layer of the seed, developed from the integuments of the ovule, maternal dipoid tissue. 1
2 Structure of Seeds Seed Coat Hilum: place where seed was attached to plant Micropyle: small opening in the integuments -The hilum is a mark where the bean was once attached to a plant. - Below it is the micropyle, the tube where the male nucleus first entered the ovule. - micropyle: A small canal in the integument surrounding the ovule of a flowering plant, through which the pollen tube usually enters the ovule on the way to the embryo sac. Water enters the seed via the micropyle prior to germination. - The hypocotyl is the seedling s root, while the epicotyl is its stem. - Inside the pod, the seeds are arranged in an alternate manner 2
3 When the seed is torn apart, two cotyledons are seen, together with the embryonic shoot (= plumule) and the embryonic root (= radicle). - Nature is imperfect. Some ovules are not fertilized, and those that are may not get the same amount of nutrients. - Nature is imperfect. Some ovules are not fertilized, and those that are may not get the same amount of nutrients. This pod has three seeds. The micropyle and hilum 3
4 What are p and r? The structure of a seed consists of: Cotyledons - Food storage organs that function as first seed leaves. Plumule - Embryo shoot. Epicotyl - Stem above cotyledon. Hypocotyl - Stem below attachment point. Radicle - Stem tip developing into a root. Dicot seed and seedling Kinds of seeds Dicot seeds endosperm is partially or completely absorbed by the embryo by cotyledons Monocot seeds endosperm is a discrete, major structural seed unit Monocot Seed and Seedling Dicot seeds endosperm is partially or completely absorbed by the embryo by cotyledons Monocot seeds endosperm is a discrete, major structural seed unit Kinds of seeds Mature Capsella Seed Capsella is used as a model for Dicot Embryo development and helps to show the dynamic relationship between the Embryo and the Endosperm. 4
5 Mature Capsella Seed The Seed consists of: Seed Coat (Testa) Endosperm Embryo The Embryo consists of: Root Apical Meristem (RAM) Hypocotyl Shoot Apical Meristem(SAM) Two Cotyledons (Dicot) Legume seeds tremendous agronomic significance Fabaceae is one of the largest and most important families of flowering plants. The Mature Seed has no visible Endosperm. This is consumed by the Cotyledons. Legume seeds: Honey Locust (Gleditisia) Legume seeds: Honey Locust (Gleditisia) Complete Embryo with both Cotyledons visible as well as the Hypocotyl.. The Hypocotyl is the region of the stem BELOW the Cotyledons. Immature Gleditisia Fruit Immature Seed Split Open: A Cotyledon and Root Apex are readily visible. Immature Seed External View Immature Gleditisia Fruit Dissected Seed: Note the presence of a semitransparent Endosperm plus the Embryo. Embryo with one Cotyledon Removed: The Epicotyl with macroscopic Leaves is visible. The SAM is located at the base of the leaf primordia.. The Cotyledon Scar is visible. This marks the Cotyledonary Node! H = Hypocotyl. Bean (Phaseolus sp.) Bean (Phaseolus sp.) Longitudinal Section through a Bean (Phaseolus) Seed: Note the Funiculus (F) which attaches the Ovule (a.k.a. the Seed) to the Placenta. The Cotyledons fill most of the seed's volume. Fragments of the Endosperm may occur between the Cotyledons and the Testa. Diagram of a typical Legume Seed: The Plumule represents the "Bud" or Shoot Tip of the Embryo. The Epicotyl includes the Plumule and any other stem tissue above the Hypocotyl. Cross-Section of a Bean Seed above the level of the Plumule: The Cotyledons are the only visible Structures. Cross-Section of a Bean Seed through the middle of the Embryonic Axis which lies close to the Funiculus. The Axis consists of everything from the SAM to the RAM 5
6 Bean (Phaseolus sp.) Bean (Phaseolus sp.) Cotyledons may contain large quantities of Starch which has stained brown with IKI. Phaeolus Cotyledons contain a lot of starch. In some cases like Soybean (Glycine max) the Cotyledons contain large amounts of Protein in Protein Vacuoles (Blue). This is the reason why Soybean is such an important crop. High Magnification View of the Funiculus: Note the presence of the Tracheid Bar (T) near the opening (Hilum) in the Testa. Note the Aerenchyma which surrounds the tracheids. These probably assist in the uptake of air and water. There are two Palisade (P) layers composed of Macrosclereids. One of these develops from the Funiculus. The Embryonic Axis is composed of a central Vascular Cylinder (VC) which is Diarch. This suggests that it is the region of the Root. The Vascular Cylinder is surrounded by Ground Tissue (G) and a unicellular Epidermis (E). One layer of Macrosclereids is clearly visible in the Testa (T) 6
BIOLOGY. TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants)
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the ripe anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower. Pollination
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the ripe anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower. Pollination
Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0uepq1w9c_e Prior learning
 Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0uepq1w9c_e Prior learning Working in Partnership draw a diagram of a flowering plant and write out the functions of the parts
Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0uepq1w9c_e Prior learning Working in Partnership draw a diagram of a flowering plant and write out the functions of the parts
DID YOU KNOW that the double coconut palm produces the largest
 Seed Germination Processes and Requirements DID YOU KNOW that the double coconut palm produces the largest seed in the world? It weighs about 50 pounds. The smallest seeds are like dust. Whatever the size
Seed Germination Processes and Requirements DID YOU KNOW that the double coconut palm produces the largest seed in the world? It weighs about 50 pounds. The smallest seeds are like dust. Whatever the size
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify the major parts
Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify the major parts
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN
 DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN Keith Glewen, Nebraska Extension Educator 1 Restrictions for Use of Adjuvants on Corn 2 3 3 Yield Protecting Factors Yield Building Factors WHY DETERMINE STAGES? 1.
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN Keith Glewen, Nebraska Extension Educator 1 Restrictions for Use of Adjuvants on Corn 2 3 3 Yield Protecting Factors Yield Building Factors WHY DETERMINE STAGES? 1.
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN AND SOYBEANS
 DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN AND SOYBEANS Keith Glewen, UNL Extension Educator 3 HOW TO DETERMINE STAGES CORN Vegetative - Count Collars Reproductive - Kernel Characteristics SOYBEANS Vegetative
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN AND SOYBEANS Keith Glewen, UNL Extension Educator 3 HOW TO DETERMINE STAGES CORN Vegetative - Count Collars Reproductive - Kernel Characteristics SOYBEANS Vegetative
Alfalfa. Seed Germination Seedling Growth Vegetative Development. North Dakota State University NDSU Extension Service
 North Dakota State University NDSU Extension Service Alfalfa Seed Germination Seedling Growth Vegetative Development R-648, (Revised), January 1999 Dwain Meyer, Professor of Plant Sciences, Agricultural
North Dakota State University NDSU Extension Service Alfalfa Seed Germination Seedling Growth Vegetative Development R-648, (Revised), January 1999 Dwain Meyer, Professor of Plant Sciences, Agricultural
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE EMBRYO=SAC AND EMBRYO OF AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO.*
 Feb., 1903.] Agrostemma githago. 365 THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE EMBRYO=SAC AND EMBRYO OF AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO.* MELVILLE THURSTON COOK. Agrostemma githago L,. was selected as a plant for comparison with Claytonia
Feb., 1903.] Agrostemma githago. 365 THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE EMBRYO=SAC AND EMBRYO OF AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO.* MELVILLE THURSTON COOK. Agrostemma githago L,. was selected as a plant for comparison with Claytonia
Tree Seed Components. Fdc
 Tree Seed Components A conifer seed has three main components: the seed coat, embryo, and megagametophyte. These components are shown dissected from a longitudinal section of a Douglas-fir seed in Figure
Tree Seed Components A conifer seed has three main components: the seed coat, embryo, and megagametophyte. These components are shown dissected from a longitudinal section of a Douglas-fir seed in Figure
Seeds are central to life on Earth:
 Seeds Part 1 Seeds are central to life on Earth: 1. Establish a new plant (propagation) 2. Food for humans and animals 3. Genetic repository 4. Some things are not possible without seeds Seeds Part 1 Seeds
Seeds Part 1 Seeds are central to life on Earth: 1. Establish a new plant (propagation) 2. Food for humans and animals 3. Genetic repository 4. Some things are not possible without seeds Seeds Part 1 Seeds
Seed Germination and Stand Establishment. Thomas G Chastain CROP 200 Crop Ecology and Morphology
 Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Thomas G Chastain CROP 200 Crop Ecology and Morphology Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Seed Germination Seed Germination is defined as the following: A
Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Thomas G Chastain CROP 200 Crop Ecology and Morphology Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Seed Germination Seed Germination is defined as the following: A
SEED GERMINATION. James C. Delouche 1
 SEED GERMINATION James C. Delouche 1 Germination is the crucial and final event in the life of a seed. It represents both the fulfillment and the completion of the basic function of seed - propagation.
SEED GERMINATION James C. Delouche 1 Germination is the crucial and final event in the life of a seed. It represents both the fulfillment and the completion of the basic function of seed - propagation.
Tetrazolium test procedure for Sorghum bicolor x S. sudanense
 Tetrazolium test procedure for Sorghum bicolor x S. sudanense Topics: TZ Test according to ISTA Rules (2004) TZ Test according to ISTA Working Sheets on Tetrazolium Testing 2003 TZ Test according to Handbook
Tetrazolium test procedure for Sorghum bicolor x S. sudanense Topics: TZ Test according to ISTA Rules (2004) TZ Test according to ISTA Working Sheets on Tetrazolium Testing 2003 TZ Test according to Handbook
Plant Reproduction and Multiplication. 1. Sexual Reproduction 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Micropropagation
 Plant Reproduction and Multiplication 1. Sexual Reproduction 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Micropropagation Sexual Versus Asexual Propagation Sexual propagation - plants are propagated from seeds - gives
Plant Reproduction and Multiplication 1. Sexual Reproduction 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Micropropagation Sexual Versus Asexual Propagation Sexual propagation - plants are propagated from seeds - gives
Alejandra Petinari Augusto Martinelli. Tetrazolium test procedure for Glycine max
 Tetrazolium test procedure for Glycine max Topics One of the methods used in Argentina TZ Test according to ISTA Working Sheets on Tetrazolium Testing 2003, Volume I TZ Test according to Handbook On Tetrazolium
Tetrazolium test procedure for Glycine max Topics One of the methods used in Argentina TZ Test according to ISTA Working Sheets on Tetrazolium Testing 2003, Volume I TZ Test according to Handbook On Tetrazolium
Now we turn our attention to the Coniferales, another great assemblage of seed plants. First let's compare the conifers with the cycads:
 X. The Conifers and Ginkgo Now we turn our attention to the Coniferales, another great assemblage of seed plants. First let's compare the conifers with the cycads: Cycads few apical meristems per plant
X. The Conifers and Ginkgo Now we turn our attention to the Coniferales, another great assemblage of seed plants. First let's compare the conifers with the cycads: Cycads few apical meristems per plant
The Seed of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. A Criticism. Abd El Rahman+Kadry. {received August 9th, 1959) to Guerin s observation (1901).
 m. ««i t 1 * Acta Botanica Neerlandica 9 (I960) 330-332 The Seed of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. A Criticism Abd El Rahman+Kadry (.Faculty of Agriculture, Ain Shams University, Quobbah Palace, Egypt) {received
m. ««i t 1 * Acta Botanica Neerlandica 9 (I960) 330-332 The Seed of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. A Criticism Abd El Rahman+Kadry (.Faculty of Agriculture, Ain Shams University, Quobbah Palace, Egypt) {received
Grain Yield. Soybean Growth and Development. Yield Components of Soybean. Plants/Branches per area Lauer
 Soybean yield is a complex series of interactions Soybean Growth and Development Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weather YIELD Weeds Insects Variety Diseases SCN Yield Components of Soybean Soybean
Soybean yield is a complex series of interactions Soybean Growth and Development Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weather YIELD Weeds Insects Variety Diseases SCN Yield Components of Soybean Soybean
Development of a guideline for seedling evaluation of Glycine max. Ing. Agr. (M. Sc.) Ignacio Aranciaga Instituto Nacional de Semillas Argentina
 Development of a guideline for seedling evaluation of Glycine max Instituto Nacional de Semillas Argentina Introduction Processed soybeans are the world's largest source of animal protein feed and the
Development of a guideline for seedling evaluation of Glycine max Instituto Nacional de Semillas Argentina Introduction Processed soybeans are the world's largest source of animal protein feed and the
2012 FFA CDE Agronomy Lab Practical
 2012 FFA CDE Agronomy Lab Practical VEGETATIVE WEED ID 1. This weed is NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY 2. The yellowing (chlorosis) and dying (necrosis) along the margins on the leaves of this corn plant are typical
2012 FFA CDE Agronomy Lab Practical VEGETATIVE WEED ID 1. This weed is NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY 2. The yellowing (chlorosis) and dying (necrosis) along the margins on the leaves of this corn plant are typical
This presentation is available at Borges, University of Wisconsin Agronomy
 SOYBEAN YIELD IS A COMPLEX SERIES OF INTERACTIONS Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weeds YIELD Weather Insects Variety Diseases SCN WISCONSIN SOYBEAN PRODUCTION KEYS TO SUCCESS Fertilize and lime
SOYBEAN YIELD IS A COMPLEX SERIES OF INTERACTIONS Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weeds YIELD Weather Insects Variety Diseases SCN WISCONSIN SOYBEAN PRODUCTION KEYS TO SUCCESS Fertilize and lime
CORESTA Guide N 7 February 2009 A Scale For Coding Growth Stages In Tobacco Crops Task Force Growth Stages and Identification Keys for Tobacco
 CORESTA Guide N 7 February 2009 A Scale For Coding Growth Stages In Tobacco Crops Task Force Growth Stages and Identification Keys for Tobacco A Scale for Coding Growth Stages in Tobacco Crops 1. Introduction
CORESTA Guide N 7 February 2009 A Scale For Coding Growth Stages In Tobacco Crops Task Force Growth Stages and Identification Keys for Tobacco A Scale for Coding Growth Stages in Tobacco Crops 1. Introduction
Soybean Seed Protein Genes Are Regulated Spatially during Embryogenesis
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 1, 1095-1 109, November 1989 O 1989 American Society of Plant Physiologists Soybean Seed Protein Genes Are Regulated Spatially during Embryogenesis Luis Perez-Grau and Robert B. Goldberg
The Plant Cell, Vol. 1, 1095-1 109, November 1989 O 1989 American Society of Plant Physiologists Soybean Seed Protein Genes Are Regulated Spatially during Embryogenesis Luis Perez-Grau and Robert B. Goldberg
Biology BY5. D = Urethra (correct spelling required) 1. E = Epididymis 1. F = Seminiferous tubule 1
 Biology BY5 (a) A = Seminal vesicle B = Vas deferens (not: sperm duct) C = Prostate (gland) (not: Prostrate) D = Urethra (correct spelling required) E = Epididymis F = Seminiferous tubule (b) Seminiferous
Biology BY5 (a) A = Seminal vesicle B = Vas deferens (not: sperm duct) C = Prostate (gland) (not: Prostrate) D = Urethra (correct spelling required) E = Epididymis F = Seminiferous tubule (b) Seminiferous
Early Development of the Seed Coat of Soybean (Glycine max)
 Annals of Botany 84: 297 304, 1999 Article No. anbo.1999.0915, available online at http: www.idealibrary.com on Early Development of the Seed Coat of Soybean (Glycine max) S. SHEA MILLER*, LU-ANN A. BOWMAN*,
Annals of Botany 84: 297 304, 1999 Article No. anbo.1999.0915, available online at http: www.idealibrary.com on Early Development of the Seed Coat of Soybean (Glycine max) S. SHEA MILLER*, LU-ANN A. BOWMAN*,
Canola in the Classroom
 Canola in the Classroom Teacher s Guide (Ontario Edition) Science & Technology: Grades 1-3 Learning Expectations All About Canola Plants Grade 1, Understanding Life Systems Needs and Characteristics of
Canola in the Classroom Teacher s Guide (Ontario Edition) Science & Technology: Grades 1-3 Learning Expectations All About Canola Plants Grade 1, Understanding Life Systems Needs and Characteristics of
2017 Kansas State FFA CDE Agronomy Event Lab Practical
 2017 Kansas State FFA CDE Agronomy Event Lab Practical PLANT STRUCTURE - SEEDLINGS 1. TWO PARTS Use the seedlings shown to identify the parts marked by the pins. a. The structure marked by the WHITE pin
2017 Kansas State FFA CDE Agronomy Event Lab Practical PLANT STRUCTURE - SEEDLINGS 1. TWO PARTS Use the seedlings shown to identify the parts marked by the pins. a. The structure marked by the WHITE pin
Crop Proje Soybean & Corn 4H 381A January 2004
 1 4-H Crop Soybean Projects & Corn 4H 381A January 2004 The revision and design of this manual were made possible by a grant from the Iowa Soybean Promotion Board. Note to the Project Helper What a wonderful
1 4-H Crop Soybean Projects & Corn 4H 381A January 2004 The revision and design of this manual were made possible by a grant from the Iowa Soybean Promotion Board. Note to the Project Helper What a wonderful
Identifying Seed Germination Processes and Requirements
 Lesson C3 1 Identifying Seed Germination Processes and Requirements Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 3. Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 1. Identifying Seed Germination Processes
Lesson C3 1 Identifying Seed Germination Processes and Requirements Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 3. Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 1. Identifying Seed Germination Processes
PUBLISHED BY. The Biological Club of the Ohio State University. TABLE OF CONTENTS THE EMBRYO-SAC AND EMBRYO OF NELUMBO.* HARLAN H. YORK.
 The Ohio Naturalist PUBLISHED BY The Biological Club of the Ohio State University. Volume IV. JUNE, 1904. No. 8. TABLE OF CONTENTS YORK The Embryo-sac and Embryo of Nelumbo 167 OSBOKN Formal Opening of
The Ohio Naturalist PUBLISHED BY The Biological Club of the Ohio State University. Volume IV. JUNE, 1904. No. 8. TABLE OF CONTENTS YORK The Embryo-sac and Embryo of Nelumbo 167 OSBOKN Formal Opening of
4-H Crop Projects 1: Soybean and Corn Seedy Business
 4-H Youth Development Publications 4-H Youth Development 1-2004 4-H Crop Projects 1: Soybean and Corn Seedy Business Denise L. Schwab Iowa State University, dschwab@iastate.edu Judith M. Levings Iowa State
4-H Youth Development Publications 4-H Youth Development 1-2004 4-H Crop Projects 1: Soybean and Corn Seedy Business Denise L. Schwab Iowa State University, dschwab@iastate.edu Judith M. Levings Iowa State
CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation
 CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS IN PLANT SCIENCE The plants we cultivate for our survival and pleasure all originated from wild plants. However, most of our domesticated plants
CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS IN PLANT SCIENCE The plants we cultivate for our survival and pleasure all originated from wild plants. However, most of our domesticated plants
VEGETATIVE WEED ID. 1. This weed is
 VEGETATIVE WEED ID 1. This weed is NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY 2. The interveinal chlorosis on the upper leaves is typical of the following nutrient deficiency: A) Nitrogen B) Potassium C) Phosphorus D) Iron E)
VEGETATIVE WEED ID 1. This weed is NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY 2. The interveinal chlorosis on the upper leaves is typical of the following nutrient deficiency: A) Nitrogen B) Potassium C) Phosphorus D) Iron E)
Plant Growth: Germinating Seeds
 Plant Growth: Germinating Seeds SC Academic Standards: 4.L.5A; 5.L.4A; 6.L.5B; 7.L.3A; 7.EC.5A- B; H.B.3A; H.B.2D; H.B.6A- D NGSS DCI: 4- LS1.A; 5- LS1.C; 5- LS2.A; 5- ESS3.C; MS- LS1- C; MS- PS3.D; MS-
Plant Growth: Germinating Seeds SC Academic Standards: 4.L.5A; 5.L.4A; 6.L.5B; 7.L.3A; 7.EC.5A- B; H.B.3A; H.B.2D; H.B.6A- D NGSS DCI: 4- LS1.A; 5- LS1.C; 5- LS2.A; 5- ESS3.C; MS- LS1- C; MS- PS3.D; MS-
Amaranthaceae imbibe on moist media overnight soak 18 hours in water Amaranthus bisect (0.1% overnight 20-25)
 AOSA and ISTA Tetrazolium Testing References: Excerpts from methods and evaluation statements (Some paraphrased for easier comparison): (Prepared in 2004 by Annette Miller, AOSA TZ Subcommittee Chairman)
AOSA and ISTA Tetrazolium Testing References: Excerpts from methods and evaluation statements (Some paraphrased for easier comparison): (Prepared in 2004 by Annette Miller, AOSA TZ Subcommittee Chairman)
Hartmann and Kester s Principles and Practices of Plant Propagation: A
 Hartmann and Kester s Principles and Practices of Plant Propagation: A Sneak Preview of the 9 th Edition Sandra B. Wilson 1, Fred T. Davies, Jr 2 and Robert L. Geneve 3 1 University of Florida, Department
Hartmann and Kester s Principles and Practices of Plant Propagation: A Sneak Preview of the 9 th Edition Sandra B. Wilson 1, Fred T. Davies, Jr 2 and Robert L. Geneve 3 1 University of Florida, Department
CROSS COUNTRY EXAMS 2015
 Name: Index No:.. Candidate s Signature:. Date:... 231/1 BIOLOGY Paper 1 Time: 2 Hours CROSS COUNTRY EXAMS 2015 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E) BIOLOGY Paper 1 Time: 2 Hours INSTRUCTIONS
Name: Index No:.. Candidate s Signature:. Date:... 231/1 BIOLOGY Paper 1 Time: 2 Hours CROSS COUNTRY EXAMS 2015 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E) BIOLOGY Paper 1 Time: 2 Hours INSTRUCTIONS
HOW THE ALFALFA PLANT GROWS: IMPACT ON MANAGEMENT
 HOW THE ALFALFA PLANT GROWS: IMPACT ON MANAGEMENT S. Ray Smith Forage Extension Specialist University of Kentucky Contact: raysmith1@uky.edu Introduction Alfalfa is the premier forage crop with high yield,
HOW THE ALFALFA PLANT GROWS: IMPACT ON MANAGEMENT S. Ray Smith Forage Extension Specialist University of Kentucky Contact: raysmith1@uky.edu Introduction Alfalfa is the premier forage crop with high yield,
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/62 Paper 6 (Alternative to Practical), maximum raw mark 40
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 (Alternative to Practical), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 (Alternative to Practical), maximum
Evaluating Seedling Quality: The Basics By Diane Haase and Robin Rose, Winter 2004
 Evaluating Seedling Quality: The Basics By Diane Haase and Robin Rose, Winter 2004 Each year, several million forest seedlings are outplanted. However, many do not survive or grow well. There are many
Evaluating Seedling Quality: The Basics By Diane Haase and Robin Rose, Winter 2004 Each year, several million forest seedlings are outplanted. However, many do not survive or grow well. There are many
REGENERATION IN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS SEEDLINGS 1
 REGENERATION IN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS SEEDLINGS 1 CARL D. LA RUE (Received for publication September 13, 1933) The experiments described in this paper were made for comparison with those conducted by the writer
REGENERATION IN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS SEEDLINGS 1 CARL D. LA RUE (Received for publication September 13, 1933) The experiments described in this paper were made for comparison with those conducted by the writer
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
Vegetative and Cutting Propagation
 15 Vegetative and Cutting Propagation Text Pages: 597 601; 623 628. Objectives: 1. Be able to describe and explain the origins of clones. 2. Be able to describe, explain, and summarize managing sources
15 Vegetative and Cutting Propagation Text Pages: 597 601; 623 628. Objectives: 1. Be able to describe and explain the origins of clones. 2. Be able to describe, explain, and summarize managing sources
Assessment of mechanical damage in sweet corn seeds by image analysis
 UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO Luiz de Queiroz College of Department of Crop Science Assessment of mechanical damage in sweet corn seeds by image analysis Francisco G GOMES-JUNIOR & Silvio M CICERO Introduction
UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO Luiz de Queiroz College of Department of Crop Science Assessment of mechanical damage in sweet corn seeds by image analysis Francisco G GOMES-JUNIOR & Silvio M CICERO Introduction
5.5. Multicellular Life. Multicellular organisms depend on interactions among different cell types.
 5.5 Multiular Life VOCABULARY tissue organ organ system differentiation stem 5b, 5c, 5B examine specialized s, including roots, stems, and leaves of plants; and animal s such as blood, muscle, and epithelium;
5.5 Multiular Life VOCABULARY tissue organ organ system differentiation stem 5b, 5c, 5B examine specialized s, including roots, stems, and leaves of plants; and animal s such as blood, muscle, and epithelium;
2 5 AVW. 191T'fj. D. P. TAYLOR 1) : Histopdthology of Meloidogyne-indzzced gdh on the stems of roselle, Hibiscus sabdariffa.
 D. P. TAYLOR 1) : Histopdthology of Meloidogyne-indzzced gdh on the stems of roselle, Hibiscus sabdariffa. Although species of Meloidogyite typically produce root galls on susceptible plants, galls are
D. P. TAYLOR 1) : Histopdthology of Meloidogyne-indzzced gdh on the stems of roselle, Hibiscus sabdariffa. Although species of Meloidogyite typically produce root galls on susceptible plants, galls are
BOMET DISTRICT M-CATS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education
 NAME INDEX NO SCHOOL. Candidate s signature Date.. 231/1 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 (Theory) JULY/AUGUST 2010 BOMET DISTRICT M-CATS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education 231/1 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES.
NAME INDEX NO SCHOOL. Candidate s signature Date.. 231/1 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 (Theory) JULY/AUGUST 2010 BOMET DISTRICT M-CATS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education 231/1 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES.
Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function.
 (4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
(4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
Effect of Growth Regulators on Seed Germination and Its Significance in the Management of Aeginetia indica L. A Root Holoparasite
 American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2012, 3, 1490-1494 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2012.310179 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps) Effect of Growth Regulators on Seed Germination
American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2012, 3, 1490-1494 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2012.310179 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps) Effect of Growth Regulators on Seed Germination
Rosary Pea. Abrus precatorius (L.) Fabaceae
 Rosary Pea Abrus precatorius (L.) Fabaceae Other common names include: crab s eyes Jequiriti precatory pea licorice vine Biology Climbing or trailing woody vine Non-native, native to India Biology Considered
Rosary Pea Abrus precatorius (L.) Fabaceae Other common names include: crab s eyes Jequiriti precatory pea licorice vine Biology Climbing or trailing woody vine Non-native, native to India Biology Considered
Ovule development in seeded and seedless grapes 1 )
 Vitis 9, 7-14 (197) N. Y. State Agricultural Experiment Station, Geneva, USA Ovule development in seeded and seedless grapes 1 ) by Introduction Descriptions of female gametophyte, endosperm and embryo
Vitis 9, 7-14 (197) N. Y. State Agricultural Experiment Station, Geneva, USA Ovule development in seeded and seedless grapes 1 ) by Introduction Descriptions of female gametophyte, endosperm and embryo
Seed Condition. damage to resin vesicles will result in decreased germination. Visual Observation. Morphology
 Seed Condition Seed condition refers to the physical and physiological state of being and health of seeds. Seeds are a living biological end-product of genetic and environmental interaction and their behaviour
Seed Condition Seed condition refers to the physical and physiological state of being and health of seeds. Seeds are a living biological end-product of genetic and environmental interaction and their behaviour
Supplementary Information. c d e
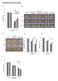 Supplementary Information a b c d e f Supplementary Figure 1. atabcg30, atabcg31, and atabcg40 mutant seeds germinate faster than the wild type on ½ MS medium supplemented with ABA (a and d-f) Germination
Supplementary Information a b c d e f Supplementary Figure 1. atabcg30, atabcg31, and atabcg40 mutant seeds germinate faster than the wild type on ½ MS medium supplemented with ABA (a and d-f) Germination
Plant Propagation PLS 3223/5222
 Plant Propagation PLS 3223/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Techniques of Seed Production and Handling Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Objectives are to Understand: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Different sources for seeds
Plant Propagation PLS 3223/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Techniques of Seed Production and Handling Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Objectives are to Understand: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Different sources for seeds
Seedlings may be counted when they have reached a stage of growth at which all essential structures can be evaluated
 Proposals for 2019 Edition of Canadian Methods and Procedures for Testing Seed (M&P) to become effective 1 July 2019 Changes to 2019 Edition shown as: Deleted text: deleted Inserted text: inserted Proposals:
Proposals for 2019 Edition of Canadian Methods and Procedures for Testing Seed (M&P) to become effective 1 July 2019 Changes to 2019 Edition shown as: Deleted text: deleted Inserted text: inserted Proposals:
Contents of Module 2
 Contents of Module 2 Structures and Functions of Seeds 4 Seed Structures 4 Seed Coat 5 The Embryo 5 Radicle 5 Plumule 5 Cotyledon 5 Endosperm 5 Seed Germination 6 Imbibition 6 Start of Metabolism 7 Radicle
Contents of Module 2 Structures and Functions of Seeds 4 Seed Structures 4 Seed Coat 5 The Embryo 5 Radicle 5 Plumule 5 Cotyledon 5 Endosperm 5 Seed Germination 6 Imbibition 6 Start of Metabolism 7 Radicle
No matter the weather conditions, there will be problematic diseases every year. Which disease may change from year to year.
 No matter the weather conditions, there will be problematic diseases every year. Which disease may change from year to year. This presentation focuses on integrated pest management of corn and soybean
No matter the weather conditions, there will be problematic diseases every year. Which disease may change from year to year. This presentation focuses on integrated pest management of corn and soybean
The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. Which part does a sperm use to swim towards an egg?
 Year 9 Exam Biology Practice Questions Q. The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. What are eggs and sperm? Tick the correct box. animals cells organs Which part does a sperm use to
Year 9 Exam Biology Practice Questions Q. The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. What are eggs and sperm? Tick the correct box. animals cells organs Which part does a sperm use to
TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A TUESDAY 17 JUNE 2008 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A222/01
 F GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A222/01 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A UNIT 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier) TUESDAY 17 JUNE 2008 Morning Time: 40 minutes *CUP/T44357* Candidates
F GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A222/01 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A UNIT 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier) TUESDAY 17 JUNE 2008 Morning Time: 40 minutes *CUP/T44357* Candidates
This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation in cooperation with the Fresno Unified School District.
 TM This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science) began in 1981 with a grant from the National Science Foundation. The non-profit
TM This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science) began in 1981 with a grant from the National Science Foundation. The non-profit
Inheritance (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Inheritance (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Key definitions Chromosome Allele Gene Haploid nucleus Diploid nucleus Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive A thread of DNA, made
Inheritance (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Key definitions Chromosome Allele Gene Haploid nucleus Diploid nucleus Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive A thread of DNA, made
CBSE QUESTION PAPER. BIOLOGY (Theory)
 CBSE QUESTION PAPER BIOLOGY (Theory) Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of four sections A, B, C and D. Section
CBSE QUESTION PAPER BIOLOGY (Theory) Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of four sections A, B, C and D. Section
Gregor Mendel. Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants
 Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants A. True Breeding Pea Plants Self pollinate and produce new plants genetically identical to themselves Mendel decides to cross pollinate the plants Offspring
Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants A. True Breeding Pea Plants Self pollinate and produce new plants genetically identical to themselves Mendel decides to cross pollinate the plants Offspring
NQF Level: 1 US No:
 NQF Level: 1 US No: 116199 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Physiology Assessor:............................................ Workplace / Company:.................................. Commodity:...................
NQF Level: 1 US No: 116199 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Physiology Assessor:............................................ Workplace / Company:.................................. Commodity:...................
WATERLOGGING TOLERANCE OF SOYBEAN
 Short Communication Bangladesh Agron. J. 2015, 18(2): 105-109 WATERLOGGING TOLERANCE OF SOYBEAN R. Ara 1, M. A. Mannan 1*, Q. A. Khaliq 1 and M. M. Uddin Miah 2 1 Department of Agronomy, Bangabandhu Sheikh
Short Communication Bangladesh Agron. J. 2015, 18(2): 105-109 WATERLOGGING TOLERANCE OF SOYBEAN R. Ara 1, M. A. Mannan 1*, Q. A. Khaliq 1 and M. M. Uddin Miah 2 1 Department of Agronomy, Bangabandhu Sheikh
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?!
 If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
The Potash Development Association Oilseed Rape and Potash
 leaflet 13 The Potash Development Association Oilseed Rape and Potash kg/ha K 2 O Nutrient balance Efficient crop nutrition requires the correct balance of all nutrients, and in principle individual plant
leaflet 13 The Potash Development Association Oilseed Rape and Potash kg/ha K 2 O Nutrient balance Efficient crop nutrition requires the correct balance of all nutrients, and in principle individual plant
Plant and Soil Science I
 PRECISION EXAMS Plant and Soil Science I EXAM INFORMATION Items 50 Points 50 Prerequisites NONE Grade Level 9-12 Course Length ONE YEAR DESCRIPTION Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in a wide
PRECISION EXAMS Plant and Soil Science I EXAM INFORMATION Items 50 Points 50 Prerequisites NONE Grade Level 9-12 Course Length ONE YEAR DESCRIPTION Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in a wide
a) Which of these is the BEST title for the group of objects shown below? A Heavy Objects B Rough Objects C Wooden Objects D Magnetic Objects
 Name: Year: 3 FIRST TERM SCIENCE REVISION PAPER 1 Circle the correct answer a) Which of these is the BEST title for the group of objects shown below? A Heavy Objects B Rough Objects C Wooden Objects D
Name: Year: 3 FIRST TERM SCIENCE REVISION PAPER 1 Circle the correct answer a) Which of these is the BEST title for the group of objects shown below? A Heavy Objects B Rough Objects C Wooden Objects D
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SCIENCE Class X Time 3hrs Max marks 90
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SCIENCE Class X Time 3hrs Max marks 90 1) Write the SI unit for power of the lens. (1) 2) Name the chemical responsible for depletion of ozone layer. (1) 3) Name any two oxidizing
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SCIENCE Class X Time 3hrs Max marks 90 1) Write the SI unit for power of the lens. (1) 2) Name the chemical responsible for depletion of ozone layer. (1) 3) Name any two oxidizing
PRACTICAL TIPS FOR GROWING, HARVESTING, AND FEEDING HIGH QUALITY SMALL GRAIN CEREAL SILAGE
 PRACTICAL TIPS FOR GROWING, HARVESTING, AND FEEDING HIGH QUALITY SMALL GRAIN CEREAL SILAGE Gene Aksland, George Fohner, Manuel C. Gomes, and Tim Jacobsen 1 ABSTRACT Small grain cereal forages are widely
PRACTICAL TIPS FOR GROWING, HARVESTING, AND FEEDING HIGH QUALITY SMALL GRAIN CEREAL SILAGE Gene Aksland, George Fohner, Manuel C. Gomes, and Tim Jacobsen 1 ABSTRACT Small grain cereal forages are widely
adaptation any structure or behavior of an organism that allows it to survive in its environment (SRB, IG)
 FOSS Structures of Life Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation any structure or behavior of an organism that allows it to survive in its environment (SRB, IG) adult a mature plant (IG) antenna (plural
FOSS Structures of Life Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation any structure or behavior of an organism that allows it to survive in its environment (SRB, IG) adult a mature plant (IG) antenna (plural
B5 Growth and development. B5 Growth and development. Question How many different bases are found in DNA?
 Q1 How many different bases are found in DNA? Q2 Which DNA bases always pair together? 4 A with T G with C Q3 What is a gene? Q4 What are proteins made of? A gene is a short section of DNA that contains
Q1 How many different bases are found in DNA? Q2 Which DNA bases always pair together? 4 A with T G with C Q3 What is a gene? Q4 What are proteins made of? A gene is a short section of DNA that contains
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9872890822* AGRICULTURE 0600/11 Paper 1 October/November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9872890822* AGRICULTURE 0600/11 Paper 1 October/November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet
 Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet 1 HOMEWORK 1 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are specialised. Describe what this means and
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet 1 HOMEWORK 1 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are specialised. Describe what this means and
PMT GCE BIOLOGY BY5. Marks. Available. 1. (a) A 1. (b) I 1. (c) H/C 1. (d) F 1. (e) G 1. Question total 5. WJEC CBAC Ltd. 49
 GCE BIOLOGY BY5. (a) A (b) I (c) H/C (d) F (e) G total 5 49 . (a) The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. (b) (i) Embryo sac. (ii) Through stigma, style, ovary wall, micropyle. (Must travel
GCE BIOLOGY BY5. (a) A (b) I (c) H/C (d) F (e) G total 5 49 . (a) The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. (b) (i) Embryo sac. (ii) Through stigma, style, ovary wall, micropyle. (Must travel
GCE BIOLOGY BY5. (b) I 1. (c) H/C 1. (d) F 1. (e) G 1
 GCE BIOLOGY BY5. (a) A (b) I (c) H/C (d) F (e) G total 5 49 . (a) The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. (b) (i) Embryo sac. (ii) Through stigma, style, ovary wall, micropyle. (Must travel
GCE BIOLOGY BY5. (a) A (b) I (c) H/C (d) F (e) G total 5 49 . (a) The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. (b) (i) Embryo sac. (ii) Through stigma, style, ovary wall, micropyle. (Must travel
Genetics 1 Star Test
 Name: ate: 1. The accompanying data table summarizes the results of an investigation in which seeds from the same plant were grown under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. 2. The
Name: ate: 1. The accompanying data table summarizes the results of an investigation in which seeds from the same plant were grown under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. 2. The
M P BHOJ (OPEN) UNIVERSITY, BHOPAL ASSIGNMENT QUESTION PAPER
 PAPER : I Plant Development and Reproduction Q.1 Explain use of mutants in understanding seeding development? OR Short note on :- (i) Tropisms (ii) Mobilization of food reserves Q.2 Describe the organization
PAPER : I Plant Development and Reproduction Q.1 Explain use of mutants in understanding seeding development? OR Short note on :- (i) Tropisms (ii) Mobilization of food reserves Q.2 Describe the organization
Cottonsee. Quality Evaluation. f illmrersity. COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE ~ipln1 State
 Cottonsee Quality Evaluation COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE ~ipln1 State f illmrersity Cottonseed Quality Evaluation Introduction There are several tests for evaluating cottonseed quality. Some tests use
Cottonsee Quality Evaluation COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE ~ipln1 State f illmrersity Cottonseed Quality Evaluation Introduction There are several tests for evaluating cottonseed quality. Some tests use
NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT. Figure 1. The availability of P is affected by soil ph.
 NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT FO 0792 F (REVISED 2016) Understanding Phosphorus in Minnesota Soils Paulo H. Pagliari, Daniel E. Kaiser, Carl J. Rosen, and John A. Lamb: Extension Specialists in Nutrient Management
NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT FO 0792 F (REVISED 2016) Understanding Phosphorus in Minnesota Soils Paulo H. Pagliari, Daniel E. Kaiser, Carl J. Rosen, and John A. Lamb: Extension Specialists in Nutrient Management
VEGETATIVE WEED ID CROP GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT. 2. The sorghum plant shown here is in which of the following growth stages: NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY
 2010 FFA Agromony CDE Lab Practical Questions VEGETATIVE WEED ID 1. This weed is CROP GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT 2. The sorghum plant shown here is in which of the following growth stages: A) growing point
2010 FFA Agromony CDE Lab Practical Questions VEGETATIVE WEED ID 1. This weed is CROP GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT 2. The sorghum plant shown here is in which of the following growth stages: A) growing point
Soybean Agronomy. G. Hnatowich, ICDC Research Agronomist
 Soybean Agronomy G. Hnatowich, ICDC Research Agronomist 1 Soybeans Production Shifting Manitoba Soybean Acreage 1000000 900000 800000 700000 600000 500000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 Acres 1996 2001
Soybean Agronomy G. Hnatowich, ICDC Research Agronomist 1 Soybeans Production Shifting Manitoba Soybean Acreage 1000000 900000 800000 700000 600000 500000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 Acres 1996 2001
HUMANITY AGAINST HUNGER
 M A S T E R 4.1 HUMANITY AGAINST HUNGER You have been selected to join Humanity AGAINST Hunger, an international effort dedicated to fighting hunger around the world. Globally, it is estimated that 842
M A S T E R 4.1 HUMANITY AGAINST HUNGER You have been selected to join Humanity AGAINST Hunger, an international effort dedicated to fighting hunger around the world. Globally, it is estimated that 842
Class 10-SA-1-TEST-1
 Class 10-SA-1-TEST-1 1 Section A 1. Write name of the compound: CH3-CH2-CHO 2. Trilobite, Ammonite is which type of fossils? 3. Define biological magnification. 4. Illustrate why there should be equitable
Class 10-SA-1-TEST-1 1 Section A 1. Write name of the compound: CH3-CH2-CHO 2. Trilobite, Ammonite is which type of fossils? 3. Define biological magnification. 4. Illustrate why there should be equitable
kda
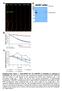 Relative VENUS/RFP fluorescence Relative fluorescence a min 2 min 4 min 6 min 8 min min Jas9-VENUS d kda 8 3 75 63 48 Jas9-VENUS Col- - + - + COR µm Jas9-VENUS 35 28 H2B-RFP 7 b c Overlay,2,8,6,4,2,6,4,2,8,6,4,2
Relative VENUS/RFP fluorescence Relative fluorescence a min 2 min 4 min 6 min 8 min min Jas9-VENUS d kda 8 3 75 63 48 Jas9-VENUS Col- - + - + COR µm Jas9-VENUS 35 28 H2B-RFP 7 b c Overlay,2,8,6,4,2,6,4,2,8,6,4,2
Effect of 2, 4 - Dichlorophenoxyaceticacid on the Linear Growth of Seedlings of Some Weeds S. N. KHOSLA*
 Effect of 2, 4 - Dichlorophenoxyaceticacid on the Linear Growth of Seedlings of Some Weeds S. N. KHOSLA* Several workers (Everson and Dunham, 1951; Graceduenas and Kommedhal 1958; Hamner et al, 1946; Johnson
Effect of 2, 4 - Dichlorophenoxyaceticacid on the Linear Growth of Seedlings of Some Weeds S. N. KHOSLA* Several workers (Everson and Dunham, 1951; Graceduenas and Kommedhal 1958; Hamner et al, 1946; Johnson
Wheat Growth Stages in Relation to Management Practices
 Wheat Growth Stages in Relation to Management Practices Shawna Loper September 19 & 20, 2012 University of Arizona Cooperative Extension 1 According to Large (1954) cereals develop as follow Feekes Growth
Wheat Growth Stages in Relation to Management Practices Shawna Loper September 19 & 20, 2012 University of Arizona Cooperative Extension 1 According to Large (1954) cereals develop as follow Feekes Growth
Purdue Crops Invitational
 Purdue Crops Invitational 2009 2009 Exam 1. Herbicide effectiveness is not dependent upon A. soil organic matter content B. soil ph C. application procedure D. using the maximum rate 2. Manure placed on
Purdue Crops Invitational 2009 2009 Exam 1. Herbicide effectiveness is not dependent upon A. soil organic matter content B. soil ph C. application procedure D. using the maximum rate 2. Manure placed on
Early Endosperm, Embryo, and Ovule Development in Glycine max (L.) Merr.
 Botany Publication and Papers Botany 7-1994 Early Endosperm, Embryo, and Ovule Development in Glycine max (L.) Merr. Mark A. Chamberlin Iowa State University Harry T. Horner Iowa State University, hth@iastate.edu
Botany Publication and Papers Botany 7-1994 Early Endosperm, Embryo, and Ovule Development in Glycine max (L.) Merr. Mark A. Chamberlin Iowa State University Harry T. Horner Iowa State University, hth@iastate.edu
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure S1. Phenotypic comparison of the wild type and mutants.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Phenotypic comparison of the wild type and mutants. Supplementary Figure S2. Transverse sections of anthers. Supplementary Figure S3. DAPI staining and
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Phenotypic comparison of the wild type and mutants. Supplementary Figure S2. Transverse sections of anthers. Supplementary Figure S3. DAPI staining and
Annex. Nutrient Deficiency
 Annex Nutrient Deficiency A- A- Field management of rice High-quality crop management is essential to derive maximum benefit from site-specific management. Photo captions (a) Proper leveling reduces water
Annex Nutrient Deficiency A- A- Field management of rice High-quality crop management is essential to derive maximum benefit from site-specific management. Photo captions (a) Proper leveling reduces water
Intensification and Agroforestry. What solution for cacao systems?
 Intensification and Agroforestry What solution for cacao systems? Intensification for cocoa systems today Intensification or how to produce more and faster on the same piece of land A - To increase the
Intensification and Agroforestry What solution for cacao systems? Intensification for cocoa systems today Intensification or how to produce more and faster on the same piece of land A - To increase the
GraspIT AQA GCSE Cell Biology - ANSWERS
 A. Cell structure part 1 Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and animal and plant cells 1. Describe the similarities and differences between a typical plant and a typical animal cell. (4) Typical animal and plant
A. Cell structure part 1 Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and animal and plant cells 1. Describe the similarities and differences between a typical plant and a typical animal cell. (4) Typical animal and plant
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Friday 21 May 2010 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Nil
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Friday 21 May 2010 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Nil
HERZLIA MIDDLE SCHOOL
 NAME TEACHER S COMMENT TEACHER CLASS MARK PERCENTAGE HERZLIA MIDDLE SCHOOL GRADE 7 NATURAL SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION 28 NOVEMBER 2014 TIME: 90 Minutes MARKS: 150 1 EXAMINERS: MR B.TSHADO & MRS J. AVIS
NAME TEACHER S COMMENT TEACHER CLASS MARK PERCENTAGE HERZLIA MIDDLE SCHOOL GRADE 7 NATURAL SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION 28 NOVEMBER 2014 TIME: 90 Minutes MARKS: 150 1 EXAMINERS: MR B.TSHADO & MRS J. AVIS
TIME : 2 ½ hours permitted CAPE BIOLOGY RESOURCES 12/16/2011
 ADVANCED BIOLOGY RESOURCES FOR CARIBBEAN STUDENTS UNIT 1 BIOLOGY WORKSHEET ONE TIME : 2 ½ hours permitted CAPE BIOLOGY RESOURCES 12/16/2011 - 2 - SECTION A Answer ALL questions. You must write your answers
ADVANCED BIOLOGY RESOURCES FOR CARIBBEAN STUDENTS UNIT 1 BIOLOGY WORKSHEET ONE TIME : 2 ½ hours permitted CAPE BIOLOGY RESOURCES 12/16/2011 - 2 - SECTION A Answer ALL questions. You must write your answers
PAPER 5 Practical Test OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION hour 30 minutes
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/5 PAPER 5 Practical Test OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION 2002 1
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/5 PAPER 5 Practical Test OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION 2002 1
