[ 1.1 ] Principles of Government
|
|
|
- Scott Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government
2 [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government Key Terms - Use your book to define these in your notebook. government public policies legislative power executive power dictatorship democracy state(country or nation) sovereign judicial power
3 [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government The State (Country or Nation)
4 [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government How States Arose There are four theories as to how the state came to be. Analyze Charts Which of the theories best describes the origins of the United States? Why?
5 [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government The Purpose of a Government Form a More Perfect Union Establish Justice Insure Domestic Tranquility Provide for the Common Defense Promote the General Welfare Secure the Blessings of Liberty Patriotism
6 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government
7 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Key Terms - Use your book to define these in your notebook. autocracy presidential government oligarchy parliamentary unitary government federal government division of powers confederation
8 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Classifying Governments All governments are classified based on three questions Who can participate in the government? What is the geographic distribution of power? What is the relationship between the Legislative Power (making the laws) and Executive Power (enforcing the laws)?
9 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Who Can Participate? Democracy Direct Democracy - Every person can create and vote on public policies. Direct Democracy doesn t exist at the national level anywhere, is only used in small groups. Indirect Democracy - People vote for representatives to run the government on their behalf. The United States is an Indirect Democracy
10 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Who Can Participate? Republic, Dictatorship and Theocracy Republic - Government is run by representatives of the people. Dictatorship / Authoritarian - A single person (autocracy) or small group of people (oligarchy) run the government and the people have no say. Theocracy - Government based on religious law
11 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Geographic Distribution of Power Centralized / Unitary Government Only having one government in a country Example - Great Britain Central and Local / Federal Government - Having multiple levels of government (ie National, State and Local) Example - United States Confederate States - A loose association of sovereign states Example - The European Union
12 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Geographic Distribution of Power
13 [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Legislative and Executive Branches Presidential or Separation of Powers Between Branches of Government Voters elect a President (Chief Executive) and Legislature (Congress) separately Written Constitution are used to outline the separations of powers within a government Parliamentary Government Voters elect a Legislature (Parliament), that then selects a Prime Minister (Chief Executive)
14 [ 1.4 ] The Basics of Democracy
15 [ 1.4 ] The Basics of Democracy Key Terms - Use your book to define these in your notebook. majority rule compromise citizen free enterprise system
16 [ 1.4 ] The Basics of Democracy Foundations of Democracy American Democracy relies on 5 Basic Concepts Worth of the Individual Equality of All Persons Majority Rule, Minority Rights Necessity of Compromise Insistence upon Individual Freedom
17 [ 1.4 ] The Basics of Democracy Democracy and the Free Enterprise System Free Enterprise System - An economic system, not a political system, based on four concepts: Private Ownership, Individual Initiative, Profit, and Competition. (aka Capitalism) The US has a mixed economy based on the Free Enterprise System. The main role of government in our mixed economy is to Regulate and Promote the economy.
18 [ 1.4 ] The Basics of Democracy Democracy and the Free Enterprise System The four pillars are the basis for free enterprise, or capitalism, in the United States.
19 [ 1.4 ] The Basics of Democracy Citizens Responsibility in a Democracy In order for a democracy to thrive, the citizens involved must be informed and educated. A multitude of news sources are available today through the internet, television and radio. Citizens must use critical thinking skills to make sure the information they receive is valid and useful.
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. S E C T I O N 1 Government and the State How is government defined? What are the basic
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. S E C T I O N 1 Government and the State How is government defined? What are the basic
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify different
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify different
CH. 1: PRINCIPLES OF GOVERNMENT S E C T I O N 1 : G O V E R N M E N T A N D T H E S T A T E
 CH. 1: PRINCIPLES OF GOVERNMENT S E C T I O N 1 : G O V E R N M E N T A N D T H E S T A T E A. WHAT IS GOVERNMENT? is a system that we use to make and enforce public policies Public policies are anything
CH. 1: PRINCIPLES OF GOVERNMENT S E C T I O N 1 : G O V E R N M E N T A N D T H E S T A T E A. WHAT IS GOVERNMENT? is a system that we use to make and enforce public policies Public policies are anything
Name Date MOD. Each government is unique, but into. categories according to. governments of the. , while in the. The. divide power among
 Name Date MOD Government Section 1:2 [Slide 2] Guiding Question: What are some forms of government in the world today? [Slide 3] Objectives: Classify governments according to 3 sets of characteristics.
Name Date MOD Government Section 1:2 [Slide 2] Guiding Question: What are some forms of government in the world today? [Slide 3] Objectives: Classify governments according to 3 sets of characteristics.
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 1 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 1 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify
January 11, Why do we have Government? In your opinion is it doing what it is supposed to do? (why or why not)
 January 11, 2016 Why do we have Government? In your opinion is it doing what it is supposed to do? (why or why not) What are the three ways We classify governments? What Is Government? Government is the
January 11, 2016 Why do we have Government? In your opinion is it doing what it is supposed to do? (why or why not) What are the three ways We classify governments? What Is Government? Government is the
A State is defined as having the following characteristics: Population, Territory, Sovereignty, and Government.
 January 8, 2016 A State is defined as having the following characteristics: Population, Territory, Sovereignty, and Government. Could the following be properly described as a state? Why or Why not? Taylor
January 8, 2016 A State is defined as having the following characteristics: Population, Territory, Sovereignty, and Government. Could the following be properly described as a state? Why or Why not? Taylor
Further Exploration of Forms of Government. Unit 7, Lesson 3
 Further Exploration of Forms of Government Unit 7, Lesson 3 Forms of Government Who holds the power? Who is sovereign? One Person A Select Group of People The People Forms of Government Who holds the power?
Further Exploration of Forms of Government Unit 7, Lesson 3 Forms of Government Who holds the power? Who is sovereign? One Person A Select Group of People The People Forms of Government Who holds the power?
Three Levels of Power Distribution Ø Unitary Ø Ø
 SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3)
 Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3)
 Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Chapter 1: Foundations of Government
 Chapter 1: Foundations of Government Section 1: The Purposes of Government Section 2: Forms of Government Section 3: Democracy in the United States Section 1 at a Glance The Purposes of Government Government
Chapter 1: Foundations of Government Section 1: The Purposes of Government Section 2: Forms of Government Section 3: Democracy in the United States Section 1 at a Glance The Purposes of Government Government
CHAPTER 1.2. FORMS OF GOVERNMENT:
 CHAPTER 1.2. FORMS OF GOVERNMENT: Objectives: o Outline the characteristics of unitary, federal, and confederate system of government. o Describe differences between presidential and parliamentary systems
CHAPTER 1.2. FORMS OF GOVERNMENT: Objectives: o Outline the characteristics of unitary, federal, and confederate system of government. o Describe differences between presidential and parliamentary systems
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government.
 SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
A. Unitary B. Parliamentary Democracy C. Democracy D. Federal E. Confederation F. Presidential Democracy G. Oligarchy I. Autocracy
 Name: Class Period: 2 3 Governments: Anticipation Guide Directions: You will make predictions about the answers to the following questions BEFORE learning about this unit. Write the letter of the vocabulary
Name: Class Period: 2 3 Governments: Anticipation Guide Directions: You will make predictions about the answers to the following questions BEFORE learning about this unit. Write the letter of the vocabulary
COUNTRY CARD VOCABULARY FLASH CARDS
 COUNTRY CARD VOCABULARY FLASH CARDS Learning Objective(s): The student will understand vocabulary by using flash cards. TEKS: 6.22A Social Studies Skills Materials Needed: Vocabulary Flash Cards Vocabulary:
COUNTRY CARD VOCABULARY FLASH CARDS Learning Objective(s): The student will understand vocabulary by using flash cards. TEKS: 6.22A Social Studies Skills Materials Needed: Vocabulary Flash Cards Vocabulary:
Principles of Government. Unit 1- Foundations of Government
 Principles of Government Unit 1- Foundations of Government Why learn about government? What are some things you could do if government did not exist? What are some things you could not do without the government?
Principles of Government Unit 1- Foundations of Government Why learn about government? What are some things you could do if government did not exist? What are some things you could not do without the government?
Distribution of Power. Unitary Confederation Federal
 Governments of Asia SS7CG7 a. Compare and Contrast the federal republic of the Republic of India, the communist state of the People s Republic of China, and the constitutional monarchy of Japan, distinguishing
Governments of Asia SS7CG7 a. Compare and Contrast the federal republic of the Republic of India, the communist state of the People s Republic of China, and the constitutional monarchy of Japan, distinguishing
Brain Wrinkles. Africa s. Republic of Kenya & Republic of South Africa
 Africa s Republic of Kenya & Republic of South Africa Government Systems Who has the power? Unitary--power is held by one central authority Confederation--association of independent states that agree to
Africa s Republic of Kenya & Republic of South Africa Government Systems Who has the power? Unitary--power is held by one central authority Confederation--association of independent states that agree to
Chp. 2 Comparing Forms of Government
 Chp. 2 Comparing Forms of Government Objectives p. 002 In this chapter, the students will classify various political systems analyze the advantages and disadvantages of various political systems and compare
Chp. 2 Comparing Forms of Government Objectives p. 002 In this chapter, the students will classify various political systems analyze the advantages and disadvantages of various political systems and compare
Latin American Governments. Brazil, Mexico, & Cuba
 Latin American Governments Brazil, Mexico, & Cuba Let s Review Government Systems Who has the power? Unitary--power is held by one central authority Confederation--association of independent states that
Latin American Governments Brazil, Mexico, & Cuba Let s Review Government Systems Who has the power? Unitary--power is held by one central authority Confederation--association of independent states that
REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT
 REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT DEFINITION people elect delegates to make laws and conduct government HOW PRACTICED People formed government to protect to their natural rights Government required the consent
REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT DEFINITION people elect delegates to make laws and conduct government HOW PRACTICED People formed government to protect to their natural rights Government required the consent
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to
 In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
Government, you say? European governments
 Government, you say? European governments Why do we have governments? All countries require governments to function. Governments provide laws, structure, public services, and national defense. There are
Government, you say? European governments Why do we have governments? All countries require governments to function. Governments provide laws, structure, public services, and national defense. There are
Henry6SS (H6SSGov) 1. An example of economic cooperation among European nations that occurred in the late 1900s was the
 Name: Date: 1. An example of economic cooperation among European nations that occurred in the late 1900s was the A. creation of the United Nations. B. signing of the Treaty of Versailles. C. creation of
Name: Date: 1. An example of economic cooperation among European nations that occurred in the late 1900s was the A. creation of the United Nations. B. signing of the Treaty of Versailles. C. creation of
ROLES, PURPOSES AND TYPES OF GOVERNMENT
 ROLES, PURPOSES AND TYPES OF GOVERNMENT State versus Nation State: A politically organized union that has four essential features: - population (people) - territory - established governmt - sovereignty
ROLES, PURPOSES AND TYPES OF GOVERNMENT State versus Nation State: A politically organized union that has four essential features: - population (people) - territory - established governmt - sovereignty
Chapter 1 Foundations of Government. The purposes of Government Forms of Government Democracy in the United States
 Chapter 1 Foundations of Government The purposes of Government Forms of Government Democracy in the United States Definition of Government The formal institutions and processes through which decisions
Chapter 1 Foundations of Government The purposes of Government Forms of Government Democracy in the United States Definition of Government The formal institutions and processes through which decisions
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship
 SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
Different Democracies. EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy?
 Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 1. World Governments
 Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 1 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 1 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 2. World Governments
 Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 2 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 2 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Governments. How do countries decide how to organize their government, and who gets to make the decisions?
 Governments How do countries decide how to organize their government, and who gets to make the decisions? The Basics According to Merriam-Webster, a government is a group of people who control and make
Governments How do countries decide how to organize their government, and who gets to make the decisions? The Basics According to Merriam-Webster, a government is a group of people who control and make
Foundations of Government. Section 1: Page 24
 Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
The Federal Democracy of Australia
 The Federal Democracy of Australia Organization- Government can be distributed in three ways Unitary Federal Confederation Citizen Involvement- Citizens can participate in government in three ways Democracy
The Federal Democracy of Australia Organization- Government can be distributed in three ways Unitary Federal Confederation Citizen Involvement- Citizens can participate in government in three ways Democracy
[ 1.2 ] Types of Government
![[ 1.2 ] Types of Government [ 1.2 ] Types of Government](/thumbs/84/89475689.jpg) [ 1.2 ] Types of Government U.S. Congress & Great Britain s Parliament P.M. Theresa May & President Donald Trump [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Learning Objec
[ 1.2 ] Types of Government U.S. Congress & Great Britain s Parliament P.M. Theresa May & President Donald Trump [ 1.2 ] Types of Government Learning Objec
The History of Government. Mr. Cline Civics Marshall High School Marshall, IL Unit One: Presentation One
 The History of Government Mr. Cline Civics Marshall High School Marshall, IL Unit One: Presentation One * Reconciling What Government Should Be With What It Is Throughout the history of government, however,
The History of Government Mr. Cline Civics Marshall High School Marshall, IL Unit One: Presentation One * Reconciling What Government Should Be With What It Is Throughout the history of government, however,
132. What type of government exists in Brazil? A. communist B. monarchy C. presidential democracy D. parliamentary democracy
 SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
UNITARY SYSTEM. (Levels of Government) If one central government runs the nation, the system is said to be a
 UNITARY SYSTEM (Levels of Government) If one central government runs the nation, the system is said to be a unitary system. The central government makes laws for the entire nation; local governments have
UNITARY SYSTEM (Levels of Government) If one central government runs the nation, the system is said to be a unitary system. The central government makes laws for the entire nation; local governments have
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES
 CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
The U.S. Constitution: Basic Structure
 The U.S. Constitution: Basic Structure In the late 1700s, 90% of Americans had a basic understanding of the key concepts relating to the U.S. Constitution. What do you think that figure is today? Have
The U.S. Constitution: Basic Structure In the late 1700s, 90% of Americans had a basic understanding of the key concepts relating to the U.S. Constitution. What do you think that figure is today? Have
Highlights: Comparing Systems of Government SS.7.C.3.2
 Highlights: Comparing Systems of Government SS.7.C.3.2 Compare parliamentary, federal, confederal, and unitary systems of government. Terri Susan Fine, Ph.D. Content Specialist, Florida Joint Center for
Highlights: Comparing Systems of Government SS.7.C.3.2 Compare parliamentary, federal, confederal, and unitary systems of government. Terri Susan Fine, Ph.D. Content Specialist, Florida Joint Center for
';: f ^ g & ^ # f f n s
 Z^cZ^^nt GOVERNMENT/CIVICS UNDERSTANDINGS ';: f ^ g & ^ # f f n s will compare and contrast various forms of government distnbute power: unitary, confederate, andfederat_ m a n f w
Z^cZ^^nt GOVERNMENT/CIVICS UNDERSTANDINGS ';: f ^ g & ^ # f f n s will compare and contrast various forms of government distnbute power: unitary, confederate, andfederat_ m a n f w
Chapter Six. Government and Policymaking
 Chapter Six Government and Policymaking Comparative Politics Today, 9/e Almond, Powell, Dalton & Strøm Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman 2008 Government and Policymaking Government and Policymaking
Chapter Six Government and Policymaking Comparative Politics Today, 9/e Almond, Powell, Dalton & Strøm Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman 2008 Government and Policymaking Government and Policymaking
Thursday April 12,2018
 Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please get the handout Who Rules? from the red basket and copy this Venn Diagram on the back. autocracy democracy Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please
Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please get the handout Who Rules? from the red basket and copy this Venn Diagram on the back. autocracy democracy Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please
SS7 Civics: Ch 1.4. The Forms of Government
 SS7 Civics: Ch 1.4 The Forms of Government The Importance of Government Importance of Government A. A government is the ruling authority for a community. Importance of Government B. There are three primary
SS7 Civics: Ch 1.4 The Forms of Government The Importance of Government Importance of Government A. A government is the ruling authority for a community. Importance of Government B. There are three primary
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship
 SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
Introduction to Comparative Government and Politics. Classwork Study Questions II
 Introduction to Comparative Government and Politics Classwork Study Questions II 1.Differentiate between levels of government. Supranational: a type of multinational political union where negotiated power
Introduction to Comparative Government and Politics Classwork Study Questions II 1.Differentiate between levels of government. Supranational: a type of multinational political union where negotiated power
You the Future Voter Curriculum Map. The Constitution. Topic: Basic Elements of Our Government
 Grade k-1 Topic: Rules are Important Topic: Basic Elements of Our Government Topic: You Are an American Topic: Rights & Responsibilities 1. Rules promote a citizen's safety and happiness. 2. Governments
Grade k-1 Topic: Rules are Important Topic: Basic Elements of Our Government Topic: You Are an American Topic: Rights & Responsibilities 1. Rules promote a citizen's safety and happiness. 2. Governments
Vocabulary. Unit 2 and Unit 3 Study Guide
 Confederacy: Vocabulary Province: Legislature/Congress/Parliament: Economics: Free Market: Laissez- Faire: Mixed- Market Economy: Bourgeoisie: Proletariat: I. Systems of Government A. Unitary System 1.
Confederacy: Vocabulary Province: Legislature/Congress/Parliament: Economics: Free Market: Laissez- Faire: Mixed- Market Economy: Bourgeoisie: Proletariat: I. Systems of Government A. Unitary System 1.
Can you hear me? 10/19/15& Today s Topic: Latin America s Government. Let s go over the class rules:
 Can you hear me? Georgia Cyber Academy s mission is to provide an exemplary individualized and engaging educational experience for all students. Classes begin at: 1st Block 8:35am 2 nd Block 10:05am Learning
Can you hear me? Georgia Cyber Academy s mission is to provide an exemplary individualized and engaging educational experience for all students. Classes begin at: 1st Block 8:35am 2 nd Block 10:05am Learning
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Basic Government Principles & Design Quiz Short Answer 1. Name each of the 4 Defining Activities of Government and explain their function and importance. 2. List and explain the 3 characteristics of a
Basic Government Principles & Design Quiz Short Answer 1. Name each of the 4 Defining Activities of Government and explain their function and importance. 2. List and explain the 3 characteristics of a
MOHANLAL SUKHADIA UNIVERSITY
 MOHANLAL SUKHADIA UNIVERSITY Submitted to: Submitted By: Deepti Sharma Amulya Democracy is a form of govt in which eligible citizens participate equally- either directly or indirectly through representatives.
MOHANLAL SUKHADIA UNIVERSITY Submitted to: Submitted By: Deepti Sharma Amulya Democracy is a form of govt in which eligible citizens participate equally- either directly or indirectly through representatives.
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
What level of government has the most amount of the power?
 Governments Form of Government Confederation What level of government has the most amount of the power? What level of government has the least amount of power? Example Unitary System Federal System Confederation
Governments Form of Government Confederation What level of government has the most amount of the power? What level of government has the least amount of power? Example Unitary System Federal System Confederation
GOVERNMENT & CITIZENSHIP CORE CONCEPT PART 8
 GOVERNMENT & CITIZENSHIP CORE CONCEPT PART 8 FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT Government = a group of people who have the power to make and enforce laws for a country or area. Purpose of Government 1. Protect
GOVERNMENT & CITIZENSHIP CORE CONCEPT PART 8 FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT Government = a group of people who have the power to make and enforce laws for a country or area. Purpose of Government 1. Protect
INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Vocabulary Journal
 INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Vocabulary Journal SET UP YOUR PAPER AS FOLLOWS: Get out notebook paper, OUT OF THE SPIRAL! From the left side, fold the paper vertically, to the center, or draw a line
INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Vocabulary Journal SET UP YOUR PAPER AS FOLLOWS: Get out notebook paper, OUT OF THE SPIRAL! From the left side, fold the paper vertically, to the center, or draw a line
Government Extra Study Practice
 Government Extra Study Practice Name: Period: What is Government? Government 1. I can explain the purpose of government 2. I can identify each of the following for dictatorship, monarchy, constitutional
Government Extra Study Practice Name: Period: What is Government? Government 1. I can explain the purpose of government 2. I can identify each of the following for dictatorship, monarchy, constitutional
The American Anomaly. A Chapter-by-Chapter Synopsis
 The American Anomaly A Chapter-by-Chapter Synopsis Nation, State, and Regime (Chapter 1) The U.S. is a relatively new nation and state, but has a strong sense of national identity. The regime is defined
The American Anomaly A Chapter-by-Chapter Synopsis Nation, State, and Regime (Chapter 1) The U.S. is a relatively new nation and state, but has a strong sense of national identity. The regime is defined
Chapter 6: Government and Policy Making
 Chapter 6: Government and Policy Making Introduction Policymaking The pivotal stage in the political process, the point at which bills become law, or edicts are issued by the rulers, whoever they are Decision
Chapter 6: Government and Policy Making Introduction Policymaking The pivotal stage in the political process, the point at which bills become law, or edicts are issued by the rulers, whoever they are Decision
U.S. Presidents...79
 Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Basics of Government Government in Your Life...5 What Is Government?...6 Authority vs. Power...7 Why Do We Need Government?...8 What Does Government Do?...9 Limited
Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Basics of Government Government in Your Life...5 What Is Government?...6 Authority vs. Power...7 Why Do We Need Government?...8 What Does Government Do?...9 Limited
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name
 CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt United States Government correlated to
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt United States Government 2012 correlated to Indiana Academic for Social Studies (May 2014), United States Government Standard 1 The Nature of Politics and Government Students
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt United States Government 2012 correlated to Indiana Academic for Social Studies (May 2014), United States Government Standard 1 The Nature of Politics and Government Students
2014 Brain Wrinkles. A Federal Parliamentary Democracy
 A Federal Parliamentary Democracy Standards SS6CG6 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
A Federal Parliamentary Democracy Standards SS6CG6 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
European Governments: United Kingdom, Russia, & Germany Brain Wrinkles
 European Governments: United Kingdom, Russia, & Germany 2014 Brain Wrinkles United Kingdom Parliamentary System of the United Kingdom Unitary System: the central government has all the power Democracy:
European Governments: United Kingdom, Russia, & Germany 2014 Brain Wrinkles United Kingdom Parliamentary System of the United Kingdom Unitary System: the central government has all the power Democracy:
The State Popula'on A state must have people, the number of which does not directly relate to its existence.
 The State Popula'on A state must have people, the number of which does not directly relate to its existence. Territory A state must be comprised of land territory with known and recognized boundaries.
The State Popula'on A state must have people, the number of which does not directly relate to its existence. Territory A state must be comprised of land territory with known and recognized boundaries.
2.6 let s be responsible
 CHAPTER 2? 2.6 let s be responsible focus QuesTIOns: what are the purposes and functions of government? how are individual rights protected and challenged within the context of majority rule? what are
CHAPTER 2? 2.6 let s be responsible focus QuesTIOns: what are the purposes and functions of government? how are individual rights protected and challenged within the context of majority rule? what are
Comparing Government Systems 1. Teachers Curriculum Institute
 P r e v i e w Work with your partner to read about six forms of government in today s world. Take turns reading each paragraph, using a low voice. As you read about each form of government, look for advantages
P r e v i e w Work with your partner to read about six forms of government in today s world. Take turns reading each paragraph, using a low voice. As you read about each form of government, look for advantages
Unit Three Word Cards. 1 civics. 2 political scientist. a social scientist who is trained to study government and citizenship
 1 civics the study the rights and duties of citizens and of how the government works Example: In order to preserve democracy for future generations, schools in the United States require courses in civics.
1 civics the study the rights and duties of citizens and of how the government works Example: In order to preserve democracy for future generations, schools in the United States require courses in civics.
United States Government
 Standard 1: The Nature of Citizenship, Politics, and Government Students will identify, define, compare, and contrast ideas regarding the nature of government, politics, and civic life and explain how
Standard 1: The Nature of Citizenship, Politics, and Government Students will identify, define, compare, and contrast ideas regarding the nature of government, politics, and civic life and explain how
Civics/Government Understandings
 Which of these identifies a person as a member of a religious group? A. Same language B. Shared beliefs* C. Same nationality D. Shared physical traits What effect does an increase in a country s literacy
Which of these identifies a person as a member of a religious group? A. Same language B. Shared beliefs* C. Same nationality D. Shared physical traits What effect does an increase in a country s literacy
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
What is Citizenship? A citizen is one who has specific rights and obligations within a political unit such as being a citizen of a country or a state.
 What is Citizenship? A citizen is one who has specific rights and obligations within a political unit such as being a citizen of a country or a state. All countries have their own definitions and expectations
What is Citizenship? A citizen is one who has specific rights and obligations within a political unit such as being a citizen of a country or a state. All countries have their own definitions and expectations
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT
 UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT United States Government provides a framework for understanding the purposes, principles, and practices of constitutional representative democracy in the United States. Responsible
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT United States Government provides a framework for understanding the purposes, principles, and practices of constitutional representative democracy in the United States. Responsible
Part Three: Political Structures/Institutions
 Part Three: Political Structures/Institutions Our political institutions work remarkably well. They are designed to clang against each other. The noise is democracy at work. -- Michael Novak (American
Part Three: Political Structures/Institutions Our political institutions work remarkably well. They are designed to clang against each other. The noise is democracy at work. -- Michael Novak (American
Wednesday March 22, 2017
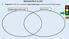 Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Demonstrate skills that enable people to monitor and influence state, local and national affairs.
 1. Civic Skills 1. Democratic government depends on informed and engaged citizens who exhibit civic skills and values, practice civic discourse, vote and participate in elections, apply inquiry and analysis
1. Civic Skills 1. Democratic government depends on informed and engaged citizens who exhibit civic skills and values, practice civic discourse, vote and participate in elections, apply inquiry and analysis
Types of Governments
 Types of Governments Anarchy In an anarchy, nobody is in control or everyone is, depending on how you look at it. Sometimes the word anarchy is used to refer to an out-of control mob. When it comes to
Types of Governments Anarchy In an anarchy, nobody is in control or everyone is, depending on how you look at it. Sometimes the word anarchy is used to refer to an out-of control mob. When it comes to
Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies. Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS
 Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS SS6CG1 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government
Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS SS6CG1 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government
American Civics. Three Objectives: 1. What is Government?
 Syllabus Highlights 1. No Seating chart (avoid the back) 2. Don t ask to go to the bathroom Just take the pass! (do not go to the bathroom at the beginning of the hour) 3. All tests are curved against
Syllabus Highlights 1. No Seating chart (avoid the back) 2. Don t ask to go to the bathroom Just take the pass! (do not go to the bathroom at the beginning of the hour) 3. All tests are curved against
United States Government
 United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
Social Studies Content Area 2014 GED Assessment Targets. Types of modern and historical governments. (CG1.a)
 GED Preparation Lesson Plan Module: Social Studies Lesson Title: Systems and Forms of Government Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education) Social Studies Practices 2014 Assessment Targets High
GED Preparation Lesson Plan Module: Social Studies Lesson Title: Systems and Forms of Government Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education) Social Studies Practices 2014 Assessment Targets High
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4
 Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine elements of the United Kingdom s parliamentary democracy. 2. Describe regional and local government in the United Kingdom. 3. Analyze
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine elements of the United Kingdom s parliamentary democracy. 2. Describe regional and local government in the United Kingdom. 3. Analyze
Central Government. Political Unit. Central Government. Political Unit
 POL 110HA Module 5 Lecture Notes Three Primary Forms of Democratic Governments Let s begin by addressing the three primary forms that democratic governments take, in terms of the relationship between the
POL 110HA Module 5 Lecture Notes Three Primary Forms of Democratic Governments Let s begin by addressing the three primary forms that democratic governments take, in terms of the relationship between the
WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW
 WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW When America was new, every state had its own rules. Money was not the same in all states. Each state had a leader. No one was the leader of all the people. This was not working!
WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW When America was new, every state had its own rules. Money was not the same in all states. Each state had a leader. No one was the leader of all the people. This was not working!
Title: (form of government) A. What is the big idea/definition for this form of government?
 Types/Forms of Government Notes Create this Outline/Chart on your own notebook paper. Make one for each of the following types of government: I. Autocracy, II. Communism, III. Direct Democracy, IV. Monarchy,
Types/Forms of Government Notes Create this Outline/Chart on your own notebook paper. Make one for each of the following types of government: I. Autocracy, II. Communism, III. Direct Democracy, IV. Monarchy,
The student will demonstrate an understanding of national governments in Southern and Eastern Asia. Compare and contrast:
 Governments of Asia Standard SS7CG7 The student will demonstrate an understanding of national governments in Southern and Eastern Asia. Compare and contrast: the federal republic of the Republic of India,
Governments of Asia Standard SS7CG7 The student will demonstrate an understanding of national governments in Southern and Eastern Asia. Compare and contrast: the federal republic of the Republic of India,
State of Israel, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, & Islamic Republic of Iran
 State of Israel, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, & Islamic Republic of Iran Bell Ringer: Writing to Win Complete the following statement and add supporting details in your writing to win journal. You must have
State of Israel, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, & Islamic Republic of Iran Bell Ringer: Writing to Win Complete the following statement and add supporting details in your writing to win journal. You must have
Organization people set up to protect their community and enforce the rules
 ? Organization people set up to protect their community and enforce the rules Roles: Protect lives, liberties, and property of the community Provide services individuals cannot provide on their own Use
? Organization people set up to protect their community and enforce the rules Roles: Protect lives, liberties, and property of the community Provide services individuals cannot provide on their own Use
Correlation of. EMC Publishing s. American Government, Citizenship and Power. to Indiana s United States Government Academic Standards
 Correlation of EMC Publishing s American Government, Citizenship and Power to Indiana s United States Government Academic Standards Standard 1 The Nature of Politics and Government Students will identify,
Correlation of EMC Publishing s American Government, Citizenship and Power to Indiana s United States Government Academic Standards Standard 1 The Nature of Politics and Government Students will identify,
The Keys to Creating the Perfect Government
 The Keys to Creating the Perfect Government By Amanda Kopp Miramonte High School 2009 WINNER 1 st Place: Thomas Jefferson Chapter SAR Competition 2 nd Place: California Society SAR Competition Political
The Keys to Creating the Perfect Government By Amanda Kopp Miramonte High School 2009 WINNER 1 st Place: Thomas Jefferson Chapter SAR Competition 2 nd Place: California Society SAR Competition Political
CPSD Civics 9 Semester-at-a-Glance (18 weeks)
 CPSD Civics 9 Semester-at-a-Glance (18 weeks) QUARTER 1 Unit 0 Class Intro, Historical Thinking Skills, Geography, and Arkansas ACT 1284 : Mandated Review of Colonization to 1890 (1-2 weeks) Unit 1 Citizenship
CPSD Civics 9 Semester-at-a-Glance (18 weeks) QUARTER 1 Unit 0 Class Intro, Historical Thinking Skills, Geography, and Arkansas ACT 1284 : Mandated Review of Colonization to 1890 (1-2 weeks) Unit 1 Citizenship
correlated to Indiana s Academic Standards Social Studies United States Government
 correlated to Indiana s Academic Standards Social Studies United States Government 6/2002 2001 American Government, eighth edition correlated to Indiana's Academic Standards Social Studies United States
correlated to Indiana s Academic Standards Social Studies United States Government 6/2002 2001 American Government, eighth edition correlated to Indiana's Academic Standards Social Studies United States
Who Rules? Name: Anticipation Activity Mind Map
 Types of Governments. What kinds of governments exist? What kinds of leaders can be in charge of a country? Think about everything you ve ever heard of or learned add it to this mind map. Circle each idea
Types of Governments. What kinds of governments exist? What kinds of leaders can be in charge of a country? Think about everything you ve ever heard of or learned add it to this mind map. Circle each idea
Prentice Hall. American Government: Readings and Cases, 17th Edition (Woll) High School
 Prentice Hall American Government: Readings and Cases, 17th Edition (Woll) 2008 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O High School Standard 1 - The Nature of Politics and Government Students will identify,
Prentice Hall American Government: Readings and Cases, 17th Edition (Woll) 2008 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O High School Standard 1 - The Nature of Politics and Government Students will identify,
Concepts in Comparative Politics
 Concepts in Comparative Politics Power, Sovereignty, & Authority Power The ability to direct the behavior of others through coercion, persuasion, or leadership Authority Legal right to exercise power on
Concepts in Comparative Politics Power, Sovereignty, & Authority Power The ability to direct the behavior of others through coercion, persuasion, or leadership Authority Legal right to exercise power on
Constitution Vocabulary Words. Thursday, September 5, 13
 Constitution Vocabulary Words Government The institutions, people, and processes by which a nation-state or political unit is ruled and its public policy created and administered Nation-State A political
Constitution Vocabulary Words Government The institutions, people, and processes by which a nation-state or political unit is ruled and its public policy created and administered Nation-State A political
Forms of Government. Who Rules?
 Forms of Government Who Rules? What is a Government? A Government is an organized system that makes laws and decisions for the good of the country.» If you compare all the types of governments in the world,
Forms of Government Who Rules? What is a Government? A Government is an organized system that makes laws and decisions for the good of the country.» If you compare all the types of governments in the world,
