Invitation to KTH Railway Group seminar (+lunch)
|
|
|
- Curtis Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Invitation to KTH Railway Group seminar (+lunch) When: Thursday 29 th September 216 at Where: KTH, Teknikringen 8, ground floor, Vehicle Engineering Laboratory Coffee etc Welcome Yuyi Li, Roger Enblom, Sebastian Stichel and Wenlin Shen: Prediction and validation of wheel profile wear on a Chinese high-speed train.5-.3 Jennifer Warg: Timetable evaluation with focus on quality for travellers (TET C3) Information from the Director Break Hailong Liu, Ulf Olofsson and Pär Jönsson: Effect of the sliding velocity on the particle emission from dry sliding wheel-rail contacts Carlos Casanueva, Visakh Krishna, Roger Jönsson and Bo-Lennart Nelldal: Novel articulated wagon designs for increased capacity 11.5 Lunch For participation in the seminar and lunch, please inform Mats Berg at mabe@kth.se by 26 September. Welcome! Sebastian Stichel and Mats Berg
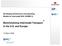
2 Prediction and Validation of Wheel Profile Wear on a Chinese High-Speed Train Yuyi Li*, Roger Enblom*, Sebastian Stichel*, Wenlin Shen + *KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Aeronautical and Vehicle Engineering + Changchun Railway Vehicles Co., Ltd. CRRC The shape of the wheel profile is very important for the performance of the wheel-rail system. Due to the interaction between wheel and rail, the shape of wheel profile changes with the running mileage increasing. The wheel profile wear has influence not only on the vehicle dynamic response but also on the maintenance cost, especially for high-speed wheelsets that achieve high mileages in a very short time. Therefore there is a demand to optimise the wheel profiles on Chinese high speed trains to maximize mileage between reprofiling and to minimize reprofiling cost. Therefore KTH Rail Vehicles was asked to predict the wheel profile wear for a number of different profiles. Evaluation criteria for the investigated wheel profiles are mainly the amount of wear, the conicity development and the dynamic behaviour of the vehicle with worn wheel profiles. The work is divided into two parts. One part is to calibrate the parameters of the wear prediction tool, which has been developed by Jendel and Enblom at KTH. The calibration is based on field measurements of S2CN wheel profiles on a Chinese high-speed train. The second part of the project is to predict the wear behaviour of modified S2CN wheel profiles on the same vehicle. The wear prediction tool includes several parts, the load collective, the vehicle-track interaction, the wear model, the profile update and an iteration loop. To determine the load collective and the wear rate calibration factors a sensitivity analysis with respect to key simulation set parameters is performed. The reference wear rate of S2CN is validated through comparison with in-service measurements at different mileages. The expected simulated tread wear is.2 mm for 37,5 km mileage. It also turns out that a selection of varying worn rails and variable transition curves have to be used in the process of wheel wear prediction. The calibrated prediction model is used to predict wear for modified wheel profiles for a Chinese high-speed train based on the S2CN wheel profile. One of the profiles (S2CN-RF) was tested on one trainset in parallel to the simulations. A comparison between simulations and measurements for this profile shows that the calculated wear distribution and depth are very similar to the measured one after 4, km. The simulation somewhat overestimates the wear after, km though. Thus it can be concluded that the prediction methodology is accurate and can be used to find wheel profiles that reduce maintenance costs for Chinese high-speed trains in the future. S2CN Comparison between simulated and measured profiles S2CN-RF Comparison between simulated and measured profiles at 2,km 6 5 4,km-s,km-m 1,km-s 1,km-m 191,km-s 191,km-m standard Simulated Measured S2CN-RF Comparison between simulated and measured profiles at 4,km standard Simulated Measured Fig. 1 Comparison results of S2CN and S2CN-RF, left: S2CN, right: S2CN-RF
3 Timetable evaluation with focus on quality for travellers Jennifer Warg Department of Transport Science, KTH Royal Institute of Technology Punctuality and reliability are important for travellers. Railway lines with heterogeneous and dense traffic have proved to be prone to generate delays. Faster services and increased traffic have to be counterbalanced with measures for increased reliability. Efficient timetable planning can improve the use of such lines. Usually, that aim is treated from either a capacity or a socio-economic point of view. Because both are important, this thesis aims to combine the fields. A new method to evaluate timetable alternatives is developed. Commonly used methods are combined in a novel way to reveal values for different variables as input for evaluation of alternatives. That enables the comparison of timetable strategies using relevant input data. The idea is to estimate the benefits of a timetable for a traveller by expressing them as a timetable performance index (TTPI). For this purpose, quality indicators and methods to reveal them are identified. In the next step, traditional valuations for relationships between the indicators are used to test different model configurations for evaluation of alternatives, for example alternative departures on the same line or different timetables. To treat this multidisciplinary task, several case studies were performed on the Swedish Southern and Western Main lines. As part of a study focussing on methods to measure and evaluate capacity based on travellers valuations, the importance of delays was analysed in a questionnaire study and relationships between several variables describing the timetable were found. The other case studies aimed to identify relevant variables and use them to evaluate alternatives. Static and dynamic variables are distinguished. The static ones describe the timetable before operation, the dynamic ones the result of operation or estimated outcome revealed by means of, for example, simulation. Empirical delay data is used in one study, simulation with the microscopic tool RailSys in the others. In one of the studies, analysis is combined with the macroscopic timetabling tool TVEM (Lindfeldt, 2). The case studies showed the characteristics of the analysed lines described by the chosen variables and which methods and variables are relevant to use for a comparison of timetable slots or evaluation of effects of changes in the timetable. An evaluation method was developed where simulation and timetable analysis reveal the variables. The idea is to construct an analytical function using traditional weights for relationships between the variables to convert the values of the variables into a performance index (PI). Based on a PI for each train slot (TSPI), the TTPI for the whole timetable is estimated. It describes the quality of a timetable in terms of timetable time, i.e. the resulting value is a time that is comparable to the scheduled travel time of one train departure, but includes additional information. With this method, complex timetables can be evaluated regarding their robustness to perturbations, which is valuable for socio-economic analysis of effects of measures applied on the railway system. As shown in a one of the case studies, quality in terms of punctuality and reliability is important for travellers, at the same time as the design of the timetable has significant impact on these aspects. Timetable analysis and simulation are relevant methods to reveal variables that describe these characteristics and evaluation with the presented method is recommended. The configuration of the TTPI is essential for the outcome whereas it is important to choose variables and parameters adequately. If this is taken into account, the approach can be an efficient way to adjust timetables and choose the best alternative, for instance if a train path or timetable change is to be chosen among several.
4 Effect of the sliding velocity on the particle emission from dry sliding wheel rail contacts Supervisors: Ulf Olofsson and Pär Jönsson PhD student: Hailong Liu, The contact between wheels and rails consists of a mixture of rolling contact and sliding. The sliding takes place on both tangent and curved tracks. As a result, the sliding velocity increases in curves and in particular reach a relative peak when braking in a narrow curve. On one hand, this variation in the sliding velocity affects the wear behavior in the wheel rail system. On the other hand, it may lead to an increased emission of submicron particles (< 1 µm) to an underground railway environment due to a high contact temperature. Thus, it is of interest to investigate the effect of the sliding velocity on wear behavior, contact temperature, and particle emission in a dry sliding wheel rail contact. Experiments have been carried out in a laboratory setup (Fig. 1), which consists of a pin-ondisk tribometer and an environmental chamber. The results show that the value of PNC (particle number concentration) increases remarkably as the sliding velocity increases from.1 to 3.4 m/s. Significantly, a high level of PNC (millions/liter) dominated by submicron particles was observed for high sliding velocities (1.2 and 3.4 m/s). This observation was related to Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the laboratory test setup the variation of the measured contact temperature (Fig. 2a). According to SEM and EDS observations, the oxide layers were detected within the pin worn surface (Fig. 2b) and the collected particles were found to exist in the form of iron oxide (Fig. 2c) for high sliding velocities. As indicated by the above outcomes, an oxidative wear was identified as the dominating mechanism leading to the formation of a substantial number of iron-oxide containing submicron particles. In addition, the formation of oxide layers within the pin surface also avoids a severe wear and results in a low wear rate and a smooth worn surface at high sliding velocities. (a) Oxide layers (b) (c) Iron oxide particles Fig. 2. The experimental results with respect to a sliding velocity of 3.4 m/s: (a) the particle number concentration (FMPS) and the contact temperature, (b) SEM image of the pin surface after the test, (c) SEM image of the collected particles.
5 Novel articulated wagon designs for increased capacity Carlos Casanueva 1, Visakh V Krishna 1, Roger Jönsson 2, Bo-Lennart Nelldal 1 1 Railway Group, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden 2 NTnet AB, Malmö, Sweden Corresponding author: Carlos Casanueva, carlosc@kth.se Capacity4Rail is a EU project whose aims are improving the competitiveness and reliability of rail freight in order to make it more attractive more sophisticated and modern market requirements. This work focuses on increasing the capacity of the overall system by using novel vehicle designs with higher payload per meter, both from the system design and the vehicle dynamics point of view. The proposal is an articulated spine wagon composed by five car bodies and six bogies, of which four of them are shared between one car body and the next one. In the WP, an effort has been made to look into the implications of these type of very long wagons in all aspects of freight operation, and this presentation focuses on three of these: the increase in payload by using different but related configurations, the challenges in vehicle design, and the dynamic analysis of the running gear. The developed new wagon concept is a 12-axle 225ft spine car with 5 frames and Jacobs bogies. The 45ft module has been chosen because there is an increasing demand for these containers. An evaluation has been done of the 12-axle 225ft wagon and a conventional 6-axle 9ft wagon with Jacobs bogie and two frames (class Sgrss). The 225ft 12-axle wagon gives 4% less cost per TEUkilometre than a conventional 6-axle 9ft-wagon. The figures also indicate the savings of longer trains: an extension from 63 to 74m will decrease the cost by %, and increasing it up to 5m would reduce it by 25%. The dynamic analysis of the vehicle starts with the calculation of the critical speed for different vehicles. Figure 3 shows that, for an increasing number of wagons in the articulated system, the critical speed is slightly higher. However, conventional four axle vehicles have a higher axle load available for all the wheelsets, as the load is split evenly amongst them, unlike articulated vehicles where the load of the first and last bogie are lower than the limiting load in intermediate bogies. Thus, the higher load in the lead and trailing 14# wheelsets makes them more stable. With no further changes in the running gear, the proposed vehicles have a reduced critical speed. The conclusion is that, from vehicle performance point of view, it is worth to explore the possibility of increasing payload by slightly reducing the dynamic behavior of the system, as the 12- axle vehicle is much more flexible when it comes to modern multimodal transportation. Cri$cal(Speed((km/h)( 12# # 8# 6# 4# 2# # # 85# 87# 113# 94# 96# 123# 4# 6# 18T_r38# 2T_r42# 22,5T_r46# Load((T)(and(Wheel(radius(mm)( Single#Car# 2#car#wagon#s 5#car#wagon#s
Preprint. This is the submitted version of a paper presented at ICRI Workshop on Wear and RCF.
 http://www.diva-portal.org Preprint This is the submitted version of a paper presented at ICRI Workshop on Wear and RCF. Citation for the original published paper: Casanueva, C., Dirks, B., Enblom, R.,
http://www.diva-portal.org Preprint This is the submitted version of a paper presented at ICRI Workshop on Wear and RCF. Citation for the original published paper: Casanueva, C., Dirks, B., Enblom, R.,
Postprint. This is the accepted version of a paper presented at RailTokyo2015. Citation for the original published paper:
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at RailTokyo15. Citation for the original published paper: Lindfeldt, A. (15) Validation of a simulation model for
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at RailTokyo15. Citation for the original published paper: Lindfeldt, A. (15) Validation of a simulation model for
Evaluation of punctuality on a heavily utilised railway line with mixed traffic
 Computers in Railways XI 545 Evaluation of punctuality on a heavily utilised railway line with mixed traffic O. Lindfeldt Division of Traffic and Logistics, Department of Transport and Economics, Royal
Computers in Railways XI 545 Evaluation of punctuality on a heavily utilised railway line with mixed traffic O. Lindfeldt Division of Traffic and Logistics, Department of Transport and Economics, Royal
Simulation of freight train operations with departures ahead of schedule
 Computers in Railways XIV 239 Simulation of freight train operations with departures ahead of schedule A. Lindfeldt & H. Sipilä Department of Transport Science, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Sweden
Computers in Railways XIV 239 Simulation of freight train operations with departures ahead of schedule A. Lindfeldt & H. Sipilä Department of Transport Science, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Sweden
INNOVATIVE FREIGHT WAGON CONCEPTS FOR EFFICIENT TRANS-EUROPEAN RAIL FREIGHT
 INNOVATIVE FREIGHT WAGON CONCEPTS FOR EFFICIENT TRANS-EUROPEAN RAIL FREIGHT Dr. Gerhard Troche 1 Dipl.-Ing. Armando Carrillo Zanuy 2 Changes in the competitive environment force railways both to improve
INNOVATIVE FREIGHT WAGON CONCEPTS FOR EFFICIENT TRANS-EUROPEAN RAIL FREIGHT Dr. Gerhard Troche 1 Dipl.-Ing. Armando Carrillo Zanuy 2 Changes in the competitive environment force railways both to improve
Simulation and models to support planning and management of railway traffic for improving capacity
 Capacity for Rail Simulation and models to support planning and management of railway traffic for improving capacity Project Workshop & Training, Olomuc 28 April 2017 Magnus Wahlborg, Trafikverket, Petr
Capacity for Rail Simulation and models to support planning and management of railway traffic for improving capacity Project Workshop & Training, Olomuc 28 April 2017 Magnus Wahlborg, Trafikverket, Petr
SP3 Framework development for capability trade-offs C4R Workshop M18 report 11 June 2015
 Capacity for Rail SP3 Framework development for capability trade-offs C4R Workshop M18 report 11 June 2015 Magnus Wahlborg Trafikverket, Swedish transport administration Working status Conclusion research
Capacity for Rail SP3 Framework development for capability trade-offs C4R Workshop M18 report 11 June 2015 Magnus Wahlborg Trafikverket, Swedish transport administration Working status Conclusion research
Chapter 1. Introduction. 1.1 Research motivation
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Research motivation This thesis is about a more sophisticated timetable compilation and capacity analysis for a selected Dutch railway line compared to the existing tools applied
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Research motivation This thesis is about a more sophisticated timetable compilation and capacity analysis for a selected Dutch railway line compared to the existing tools applied
A study of the performance and utilization of the Swedish railway network
 A study of the performance and utilization of the Swedish railway network A. Lindfeldt Division of Traffic and Logistics, Department of Transport and Economics, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm,
A study of the performance and utilization of the Swedish railway network A. Lindfeldt Division of Traffic and Logistics, Department of Transport and Economics, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm,
From single to double track: effects of alternative extension measures
 Computers in Railways XIII 313 From single to double track: effects of alternative extension measures O. Lindfeldt Vectura Consulting AB, Stockholm, Sweden Abstract Extension of single-track lines into
Computers in Railways XIII 313 From single to double track: effects of alternative extension measures O. Lindfeldt Vectura Consulting AB, Stockholm, Sweden Abstract Extension of single-track lines into
Optimisation of Wheelset Maintenance using Whole System Cost Modelling
 RRUKA Annual Conference, 7 November 2012 1 Optimisation of Wheelset Maintenance using Whole System Cost Modelling Adam Bevan, Institute of Railway Research, University of Huddersfield Paul Molyneux-Berry,
RRUKA Annual Conference, 7 November 2012 1 Optimisation of Wheelset Maintenance using Whole System Cost Modelling Adam Bevan, Institute of Railway Research, University of Huddersfield Paul Molyneux-Berry,
Vehicle Track Interaction Strategic Model (VTISM) Overview for ICRI Project (Apr-2016)
 V/T SIC Vehicle / Track System Interface Committee Vehicle Track Interaction Strategic Model (VTISM) Overview for ICRI Project (Apr-2016) Andy Rhodes, Serco Adam Bevan, University of Huddersfield Overview
V/T SIC Vehicle / Track System Interface Committee Vehicle Track Interaction Strategic Model (VTISM) Overview for ICRI Project (Apr-2016) Andy Rhodes, Serco Adam Bevan, University of Huddersfield Overview
WEAR OF RAILWAY BRAKE BLOCK MATERIALS AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES PIN-ON-DISC EXPERIMENTS
 WEAR OF RAILWAY BRAKE BLOCK MATERIALS AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES PIN-ON-DISC EXPERIMENTS 1,2 Vernersson, Tore *, 1 Lundén, Roger, 3 Abbasi, Saeed and 3 Olofsson, Ulf 1 CHALMERS APPLIED MECHANICS / CHARMEC,
WEAR OF RAILWAY BRAKE BLOCK MATERIALS AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES PIN-ON-DISC EXPERIMENTS 1,2 Vernersson, Tore *, 1 Lundén, Roger, 3 Abbasi, Saeed and 3 Olofsson, Ulf 1 CHALMERS APPLIED MECHANICS / CHARMEC,
Arch. Metall. Mater., Vol. 61 (2016), No 4, p
 Arch. Metall. Mater., Vol. 61 (2016), No 4, p. 1833 1838 DOI: 10.1515/amm-2016-0296 T. Giętka*,#, K. Ciechacki** Modeling of railway wheels made of austempered ductile iron A person is forced to travel
Arch. Metall. Mater., Vol. 61 (2016), No 4, p. 1833 1838 DOI: 10.1515/amm-2016-0296 T. Giętka*,#, K. Ciechacki** Modeling of railway wheels made of austempered ductile iron A person is forced to travel
2015 HDR, all rights reserved.
 2015 HDR, all rights reserved. How do you Spell Capacity on a Railroad? - A Primer on Railroad Operations Design Kevin Keller, PE HDR Engineering, Inc. 2015 HDR, all rights reserved. Outline Introduction
2015 HDR, all rights reserved. How do you Spell Capacity on a Railroad? - A Primer on Railroad Operations Design Kevin Keller, PE HDR Engineering, Inc. 2015 HDR, all rights reserved. Outline Introduction
Case Study: KTH Royal Institute of Technology
 Case Study: KTH Royal Institute of Technology Adams Demonstrates Ability to Accurately Evaluate New Logging Machine Design in a fraction of the time required by the build and test method Overview Traditional
Case Study: KTH Royal Institute of Technology Adams Demonstrates Ability to Accurately Evaluate New Logging Machine Design in a fraction of the time required by the build and test method Overview Traditional
- Particulate matter (PM10, 2.5, 1) -Coarse region (2.5µm < dp <10µm)
 - Particulate matter (PM10, 2.5, 1) The Suspension of fine solids particles or liquid droplets or mixture of them in the gas or liquid -Coarse region (2.5µm < dp
- Particulate matter (PM10, 2.5, 1) The Suspension of fine solids particles or liquid droplets or mixture of them in the gas or liquid -Coarse region (2.5µm < dp
Innovative Rail Freight Wagon 2030 the 5L future initiative as a basis for growth in rail freight transportation an example for sector collaboration
 Innovative Rail Freight Wagon 2030 the 5L future initiative as a basis for growth in rail freight transportation an example for sector collaboration Initial Situation In the past the rail freight sector
Innovative Rail Freight Wagon 2030 the 5L future initiative as a basis for growth in rail freight transportation an example for sector collaboration Initial Situation In the past the rail freight sector
The European Freight Rail Experience with Innovation. Nigel Ash Network Rail Consulting
 The European Freight Rail Experience with Innovation Nigel Ash Network Rail Consulting Contents Challenges facing European Freight Rail 3 European Freight Rail Innovation: Interoperability 8 European Freight
The European Freight Rail Experience with Innovation Nigel Ash Network Rail Consulting Contents Challenges facing European Freight Rail 3 European Freight Rail Innovation: Interoperability 8 European Freight
MEGASWING, YOUR VERY OWN INTER- MODAL TERMINAL.
 MEGASWING, YOUR VERY OWN INTER- MODAL TERMINAL. Sdgnss Swingable megatrailer pocket wagon Offer rail transport to all customers and increase rail profits. Use your fleet more efficiently; load an entire
MEGASWING, YOUR VERY OWN INTER- MODAL TERMINAL. Sdgnss Swingable megatrailer pocket wagon Offer rail transport to all customers and increase rail profits. Use your fleet more efficiently; load an entire
RailSys Suite. Innovative IT solution for railway transport. a product by
 RailSys Suite Innovative IT solution for railway transport a product by Timetable construction Simulation Innovation Working timetable Remaining capacity Railway Redundancy-free Graphical timetable Punctuality
RailSys Suite Innovative IT solution for railway transport a product by Timetable construction Simulation Innovation Working timetable Remaining capacity Railway Redundancy-free Graphical timetable Punctuality
MERLIN Project Project
 MERLIN Newsletter Issue 1, November 2014 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in the Rail System Smarter Background This project has received funding from the European Union s Seventh
MERLIN Newsletter Issue 1, November 2014 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in the Rail System Smarter Background This project has received funding from the European Union s Seventh
Building capacity through structured heavy haul operations on single-track shared corridors in North America
 Page 12 Building capacity through structured heavy haul operations on single-track shared corridors in North America D. Mussanov, N. Nishio & C.T. Dick University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Page 12 Building capacity through structured heavy haul operations on single-track shared corridors in North America D. Mussanov, N. Nishio & C.T. Dick University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
ESTIMATION OF ROLLING CONTACT FATIGUE IN RAILWAY VEHICLES
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2014 Goutam Nayak and Piyush Verma, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Special Issue, Vol. 1, No. 1, January 2014 National Conference on Recent Advances in
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2014 Goutam Nayak and Piyush Verma, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Special Issue, Vol. 1, No. 1, January 2014 National Conference on Recent Advances in
IMA Materialforschung und Anwendungstechnik GmbH. Test before you depart
 IMA Materialforschung und Anwendungstechnik GmbH Test before you depart 2 Three test hangars each with more than 5.000 m test area Climatic chambers for environmental simulation Latest measurement and
IMA Materialforschung und Anwendungstechnik GmbH Test before you depart 2 Three test hangars each with more than 5.000 m test area Climatic chambers for environmental simulation Latest measurement and
SHIFT²RAIL Stakeholder meeting Innovations Programs - IP4 & IP5
 SHIFT²RAIL Stakeholder meeting Innovations Programs - IP4 & IP5 Understanding the needs of users and customers, Introduce IT technologies to make railways more attractive Y. Perréal, Thales Transportation
SHIFT²RAIL Stakeholder meeting Innovations Programs - IP4 & IP5 Understanding the needs of users and customers, Introduce IT technologies to make railways more attractive Y. Perréal, Thales Transportation
The SUSTRAIL Project: an Integrated Approach for an Increased Performance of the Freight Rail System
 The SUSTRAIL Project: an Integrated Approach for an Increased Performance of the Freight Rail System General Presentation Clemente Fuggini, Deputy Project Coordinator clemente.fuggini@dappolonia.it Motivations
The SUSTRAIL Project: an Integrated Approach for an Increased Performance of the Freight Rail System General Presentation Clemente Fuggini, Deputy Project Coordinator clemente.fuggini@dappolonia.it Motivations
THE GERMAN TRANSPORT FORUM
 Position of the Rail Technology and Rail Transport steering committees in the German Transport Forum May 2012 THE GERMAN TRANSPORT FORUM Our mission Mobility is one of the most important factors for growth
Position of the Rail Technology and Rail Transport steering committees in the German Transport Forum May 2012 THE GERMAN TRANSPORT FORUM Our mission Mobility is one of the most important factors for growth
Supply and Demand Analysis
 Technical, Socio-economic and Supply/Demand study regarding the transport of the FERRMED Great Rail Network (Scandinavia-Rhine- Rhône-Western Mediterranean) Supply and Demand Analysis Presented by Daniele
Technical, Socio-economic and Supply/Demand study regarding the transport of the FERRMED Great Rail Network (Scandinavia-Rhine- Rhône-Western Mediterranean) Supply and Demand Analysis Presented by Daniele
Automated analysis of train event recorder data to improve micro-simulation models
 Operations Analysis 125 Automated analysis of train event recorder data to improve micro-simulation models S. de Fabris, G. Longo & G. Medeossi Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Operations Analysis 125 Automated analysis of train event recorder data to improve micro-simulation models S. de Fabris, G. Longo & G. Medeossi Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Automated analysis of train event recorder data to improve micro-simulation models
 Computers in Railways XI 575 Automated analysis of train event recorder data to improve micro-simulation models S. de Fabris, G. Longo & G. Medeossi Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Computers in Railways XI 575 Automated analysis of train event recorder data to improve micro-simulation models S. de Fabris, G. Longo & G. Medeossi Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Capacity estimation of new single track stations. Solomon Kinfe
 Capacity estimation of new single track stations Solomon Kinfe Master of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2012 TCS-MT 12-036 Capacity estimation of new single track stations Solomon Kinfe Master thesis
Capacity estimation of new single track stations Solomon Kinfe Master of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2012 TCS-MT 12-036 Capacity estimation of new single track stations Solomon Kinfe Master thesis
How to manage changes in maintenance plan of freight wagon?
 How to manage changes in maintenance plan of freight wagon? Real case study Geoffrey TRESONTANI - ECM Manager CFL cargo CFL cargo - Service Expertise Sécurité Ferroviaire / Cellule ECM - Geoffrey TRESONTANI
How to manage changes in maintenance plan of freight wagon? Real case study Geoffrey TRESONTANI - ECM Manager CFL cargo CFL cargo - Service Expertise Sécurité Ferroviaire / Cellule ECM - Geoffrey TRESONTANI
Strategies for data collection and analysis Submission date: 01/08/2017 Deliverable 41.3
 D3.1.1 Review of existing practices to improve capacity on the European rail network Strategies for data collection and analysis Submission date: Deliverable 41.3 D41.3 Strategies for data collection and
D3.1.1 Review of existing practices to improve capacity on the European rail network Strategies for data collection and analysis Submission date: Deliverable 41.3 D41.3 Strategies for data collection and
Newsletter Issue 2, April 2016
 Newsletter Issue 2, April 2016 Foreword News from the consortium Here is the second issue of the Capacity4Rail project Newsletter. Started in October 2013, Capacity4Rail is now well in its third year.
Newsletter Issue 2, April 2016 Foreword News from the consortium Here is the second issue of the Capacity4Rail project Newsletter. Started in October 2013, Capacity4Rail is now well in its third year.
Perspectives and challenges in operationalizing the
 Distr.: General 18 April 2017 Chinese, English and Russian only Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Working Group on the Trans-Asian Railway Network 5th meeting Busan, Republic of Korea,
Distr.: General 18 April 2017 Chinese, English and Russian only Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Working Group on the Trans-Asian Railway Network 5th meeting Busan, Republic of Korea,
System Dynamics Model of Shanghai Passenger Transportation Structure Evolution
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1110 1118 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1110 1118 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Applying multiscaling analysis to detect capacity resources in railway networks
 Computers in Railways XI 595 Applying multiscaling analysis to detect capacity resources in railway networks A. Gille, M. Klemenz & Th. Siefer Institute of Transport, Railway Construction and Operation,
Computers in Railways XI 595 Applying multiscaling analysis to detect capacity resources in railway networks A. Gille, M. Klemenz & Th. Siefer Institute of Transport, Railway Construction and Operation,
Evaluation of rail wear characteristics on heavy haul track section using measurement data
 track section using measurement data Luleå Railway Research Centre Luleå, Sweden Matthias Asplund Trafikverket Luleå, Sweden Uday Kumar Luleå Railway Research Centre Luleå, Sweden SUMMARY The rail is a
track section using measurement data Luleå Railway Research Centre Luleå, Sweden Matthias Asplund Trafikverket Luleå, Sweden Uday Kumar Luleå Railway Research Centre Luleå, Sweden SUMMARY The rail is a
EXCELLENCE IN RAILWAY & MINING ENGINEERING
 EXCELLENCE IN RAILWAY & MINING ENGINEERING Other equipment reconditioned or manufactured by the company include: Vacuum pumps Compressors Air, hydraulic and mechanical jacks Air and vacuum brake equipment
EXCELLENCE IN RAILWAY & MINING ENGINEERING Other equipment reconditioned or manufactured by the company include: Vacuum pumps Compressors Air, hydraulic and mechanical jacks Air and vacuum brake equipment
Joint design standard for running times, dwell times and headway times
 Computers in Railways X 611 Joint design standard for running times, dwell times and headway times V. A. Weeda & P. B. L. Wiggenraad Department of Transport & Planning, Delft University of Technology,
Computers in Railways X 611 Joint design standard for running times, dwell times and headway times V. A. Weeda & P. B. L. Wiggenraad Department of Transport & Planning, Delft University of Technology,
Timetable management and operational simulation: methodology and perspectives
 Computers in Railways X 579 Timetable management and operational simulation: methodology and perspectives A. Radtke Institut für Verkehrswesen, Eisenbahnbau und betrieb, University of Hannover, Germany
Computers in Railways X 579 Timetable management and operational simulation: methodology and perspectives A. Radtke Institut für Verkehrswesen, Eisenbahnbau und betrieb, University of Hannover, Germany
Service Availability of the Urban Maglev System in Korea
 Service Availability of the Urban Maglev System in Korea No. 014 Yong-Jun Seo, Si-Gweon Choi, Hee-Kap Yang, and Doo-Jong Koh Hyundai-Rotem Company, E&M Engineering & Sales Team, 231, Yangjae-dong, Seoul
Service Availability of the Urban Maglev System in Korea No. 014 Yong-Jun Seo, Si-Gweon Choi, Hee-Kap Yang, and Doo-Jong Koh Hyundai-Rotem Company, E&M Engineering & Sales Team, 231, Yangjae-dong, Seoul
Simulation of Railway Operation on the line from Zagreb to Karlovac by OPENTRACK
 Simulation of Railway Operation on the line from Zagreb to Karlovac by OPENTRACK Hrvoje HARAMINA, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Transport and Traffic Sciences Andreas SCHÖBEL, Vienna University of Technology,
Simulation of Railway Operation on the line from Zagreb to Karlovac by OPENTRACK Hrvoje HARAMINA, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Transport and Traffic Sciences Andreas SCHÖBEL, Vienna University of Technology,
FREIGHT CARS & LOCOMOTIVES
 FREIGHT CARS & LOCOMOTIVES COMPOSITE BRAKE SHOES FOR RAIL VEHICLES TYPE K INFORMATION SHEET Application: UIC 541-4 homologation for freight cars up to 120km/h New-built freight cars designed for brake
FREIGHT CARS & LOCOMOTIVES COMPOSITE BRAKE SHOES FOR RAIL VEHICLES TYPE K INFORMATION SHEET Application: UIC 541-4 homologation for freight cars up to 120km/h New-built freight cars designed for brake
Implementation of the Timetable Planning System STRAX/TPS in Denmark
 Implementation of the Timetable Planning System STRAX/TPS in Denmark A. H. Kaas 1 & R. Goossmann 2 1 Atkins Transportation Scandinavia, Denmark 2 HaCon, Germany Abstract The TPS Timetable Planning System,
Implementation of the Timetable Planning System STRAX/TPS in Denmark A. H. Kaas 1 & R. Goossmann 2 1 Atkins Transportation Scandinavia, Denmark 2 HaCon, Germany Abstract The TPS Timetable Planning System,
THE SWISS EXPERIENCE IN RAIL NOISE MITIGATION IN URBAN AREAS: AN OVERALL APPROACH
 THE SWISS EXPERIENCE IN RAIL NOISE MITIGATION IN URBAN AREAS: AN OVERALL APPROACH Jakob Oertli Infrastructure, Swiss Federal Railways, Bern, Switzerland 1. Abstract Detailed cost-effectiveness analyses
THE SWISS EXPERIENCE IN RAIL NOISE MITIGATION IN URBAN AREAS: AN OVERALL APPROACH Jakob Oertli Infrastructure, Swiss Federal Railways, Bern, Switzerland 1. Abstract Detailed cost-effectiveness analyses
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Intermodal transportation in urban framework: a discrete-events simulative approach A. Di Febbraro", V. Recagno* & S. Sacone" ^Department of Communications, Computer, and System Sciences Dipartimento di
Intermodal transportation in urban framework: a discrete-events simulative approach A. Di Febbraro", V. Recagno* & S. Sacone" ^Department of Communications, Computer, and System Sciences Dipartimento di
Position Paper Technical Innovation Circle for Rail Freight Transport (TIS)
 Position Paper Technical Innovation Circle for Rail Freight Transport (TIS) Berlin, 23 September 2014 About TIS During the Innotrans 2012 trade fair in Berlin, the Technical Innovation Circle for Rail
Position Paper Technical Innovation Circle for Rail Freight Transport (TIS) Berlin, 23 September 2014 About TIS During the Innotrans 2012 trade fair in Berlin, the Technical Innovation Circle for Rail
WP5 PROCESS OPTIMISATION
 This project has received funding from the Shift2Rail Joint Undertaking under the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement no. 777594 (OptiYard) WP5 PROCESS
This project has received funding from the Shift2Rail Joint Undertaking under the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement no. 777594 (OptiYard) WP5 PROCESS
Trends and Topics in Research and Development Related to Transportation and Traffic Planning Technology
 PERSPECTIVE Trends and Topics in Research and Development Related to Transportation and Traffic Planning Technology Kunihiro KAWASAKI Signalling and Transport Information Technology Division Noriko FUKASAWA
PERSPECTIVE Trends and Topics in Research and Development Related to Transportation and Traffic Planning Technology Kunihiro KAWASAKI Signalling and Transport Information Technology Division Noriko FUKASAWA
SUSTAINABLE LOGISTICS
 SUSTAINABLE LOGISTICS What s new in Green Cargo Revenue 2017 SEK4,3 MD +3% (compared to 2016) Earnings SEK 1 M 2017 SEK 748 M NEW FREIGHT AGREEMENTS Evaluate a number of locomotives and wagons More load-efficient
SUSTAINABLE LOGISTICS What s new in Green Cargo Revenue 2017 SEK4,3 MD +3% (compared to 2016) Earnings SEK 1 M 2017 SEK 748 M NEW FREIGHT AGREEMENTS Evaluate a number of locomotives and wagons More load-efficient
The effect of road surface deterioration on pavement service life
 The effect of road surface deterioration on pavement service life Parisa Khavassefat 1* Denis Jelagin 1 Björn Birgisson 2 parisak@kth.se Jelagin@kth.se bjornbir@kth.se 1) Highway and Railway Engineering,
The effect of road surface deterioration on pavement service life Parisa Khavassefat 1* Denis Jelagin 1 Björn Birgisson 2 parisak@kth.se Jelagin@kth.se bjornbir@kth.se 1) Highway and Railway Engineering,
1562. Study on vibration reduction slab track and adjacent transition section in high-speed railway tunnel
 1562. Study on vibration reduction slab track and adjacent transition section in high-speed railway tunnel Qingyuan Xu 1, Xiaoping Chen 2, Bin Yan 3, Wei Guo 4 School of Civil Engineering, Central South
1562. Study on vibration reduction slab track and adjacent transition section in high-speed railway tunnel Qingyuan Xu 1, Xiaoping Chen 2, Bin Yan 3, Wei Guo 4 School of Civil Engineering, Central South
Single-Entry-Point - SEP User Manual
 Index of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Information of bonus applications for Germany 5 3 Information of bonus applications for the Netherlands 6 4 Information of bonus applications for Switzerland 8 5 Information
Index of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Information of bonus applications for Germany 5 3 Information of bonus applications for the Netherlands 6 4 Information of bonus applications for Switzerland 8 5 Information
Material and its influence on the friction coefficient
 APi Pin-on-disc Study of the Rusts on Wheel Rail Material and its influence on the friction coefficient ; Ulf Olofsson Department of Machine Design; KTH Railway Group Royal linstitute t of Technology (KTH)
APi Pin-on-disc Study of the Rusts on Wheel Rail Material and its influence on the friction coefficient ; Ulf Olofsson Department of Machine Design; KTH Railway Group Royal linstitute t of Technology (KTH)
Components Weigh in Motion (WIM) & Wheel Impact Load Detector (WILD) Generic Product Catalog
 Components Weigh in Motion (WIM) & Wheel Impact Load Detector (WILD) Generic Product Catalog Table of Contents Introduction 4 Main Features 4 Application fields 4 System Overview 5 Typical installation
Components Weigh in Motion (WIM) & Wheel Impact Load Detector (WILD) Generic Product Catalog Table of Contents Introduction 4 Main Features 4 Application fields 4 System Overview 5 Typical installation
REDUCING THE OCCURRENCES AND IMPACT OF FREIGHT TRAIN DERAILMENTS. Results of the D-Rail project
 REDUCING THE OCCURRENCES AND IMPACT OF FREIGHT TRAIN DERAILMENTS Results of the D-Rail project WP 5 Integration of Monitoring Concepts D-Rail final seminar, 12.11.2014 Stockholm Matthias Krüger (DB AG)
REDUCING THE OCCURRENCES AND IMPACT OF FREIGHT TRAIN DERAILMENTS Results of the D-Rail project WP 5 Integration of Monitoring Concepts D-Rail final seminar, 12.11.2014 Stockholm Matthias Krüger (DB AG)
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Bevan, Adam and Molyneux Berry, Paul Optimisation of Wheelset Maintenance: Current Research Activities Original Citation Bevan, Adam and Molyneux Berry, Paul (2014)
University of Huddersfield Repository Bevan, Adam and Molyneux Berry, Paul Optimisation of Wheelset Maintenance: Current Research Activities Original Citation Bevan, Adam and Molyneux Berry, Paul (2014)
Catalogue of examples
 Making the railway system work better for society. Examples for the practical arrangements for the vehicle authorisation process Name E. DEL RIO G.TURNER S. YOUNG Drafted by Validated by Approved by H.
Making the railway system work better for society. Examples for the practical arrangements for the vehicle authorisation process Name E. DEL RIO G.TURNER S. YOUNG Drafted by Validated by Approved by H.
Research Article An Alternative Approach for High Speed Railway Carrying Capacity Calculation Based on Multiagent Simulation
 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 216, Article ID 427873, 1 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/427873 Research Article An Alternative Approach for High Speed Railway Carrying Capacity Calculation
Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 216, Article ID 427873, 1 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/427873 Research Article An Alternative Approach for High Speed Railway Carrying Capacity Calculation
Coupled Numerical Modelling of Railway Track Substructure with Vehicle-Track Interaction
 Paper 125 Civil-Comp Press, 2015 Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Civil, Structural and Environmental Engineering Computing, J. Kruis, Y. Tsompanakis and B.H.V. Topping, (Editors),
Paper 125 Civil-Comp Press, 2015 Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Civil, Structural and Environmental Engineering Computing, J. Kruis, Y. Tsompanakis and B.H.V. Topping, (Editors),
ONTIME (Optimal Networks for Train Integration Management across Europe)
 ONTIME (Optimal Networks for Train Integration Management across Europe) Next Generation Railway Traffic Management Dr. Lei Chen L.Chen.3@bham.ac.uk Birmingham Centre for Railway Research and Education
ONTIME (Optimal Networks for Train Integration Management across Europe) Next Generation Railway Traffic Management Dr. Lei Chen L.Chen.3@bham.ac.uk Birmingham Centre for Railway Research and Education
Acoustics Management Predictions Measurements Analysis. Rail vehicle acoustics. Know-how and experience in vibro-acoustics.
 Acoustics Management Predictions Measurements Analysis Rail vehicle acoustics Know-how and experience in vibro-acoustics www.muellerbbm.com Our competence The engineering company Müller-BBM is active in
Acoustics Management Predictions Measurements Analysis Rail vehicle acoustics Know-how and experience in vibro-acoustics www.muellerbbm.com Our competence The engineering company Müller-BBM is active in
General model of railway transportation capacity
 Computers in Railways XIII 335 General model of railway transportation capacity H. E. Boysen Department of Transport Science, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Sweden Abstract A general model of railway
Computers in Railways XIII 335 General model of railway transportation capacity H. E. Boysen Department of Transport Science, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Sweden Abstract A general model of railway
LANDUSE PLANNING, PUBLIC TRANSPORT AND PERSONAL MOBILITY
 1 LANDUSE PLANNING, PUBLIC TRANSPORT AND PERSONAL MOBILITY Entries propose fundamentally different regional scenarios. A commonly agreed principle is increasing building density near rail stops. Challenging
1 LANDUSE PLANNING, PUBLIC TRANSPORT AND PERSONAL MOBILITY Entries propose fundamentally different regional scenarios. A commonly agreed principle is increasing building density near rail stops. Challenging
2.0 Purpose. 3.0 Work Plan. Page 1 of 7
 2.0 Purpose The purpose of this document is to present the findings of the field investigation and concept design study, as well as recommend appropriate track relocation and bridge modifications to provide
2.0 Purpose The purpose of this document is to present the findings of the field investigation and concept design study, as well as recommend appropriate track relocation and bridge modifications to provide
Rail Choice, Modelling and Materials. Brian Whitney Principal - Track Engineer Network Rail 20 th November 2012
 Rail Choice, Modelling and Materials Brian Whitney Principal - Track Engineer Network Rail 20 th November 2012 1 Rail Loading - Surface Damage This type of damage accounts for the majority of defects we
Rail Choice, Modelling and Materials Brian Whitney Principal - Track Engineer Network Rail 20 th November 2012 1 Rail Loading - Surface Damage This type of damage accounts for the majority of defects we
Assessment of Corrosion on Rail Axles
 Assessment of Corrosion on Rail Axles John Rudlin 1, Dorothee Panggabean 2, Antonietta Loconte 3 and Angelique Raude 4 TWI Ltd Cambridge CB1 6AL, UK Telephone 01223 899000 Fax 01223 890689 E-mail john.rudlin@twi.co.uk
Assessment of Corrosion on Rail Axles John Rudlin 1, Dorothee Panggabean 2, Antonietta Loconte 3 and Angelique Raude 4 TWI Ltd Cambridge CB1 6AL, UK Telephone 01223 899000 Fax 01223 890689 E-mail john.rudlin@twi.co.uk
RAILWAY TRAFFIC OPERATION
 doc. Ing. Jozef Gašparík, PhD. prof. Ing. Jozef Majerčák, PhD. doc. Ing. Jaromír Široký, Ph.D. doc. dr. sc. Borna Abramović Ing. Pavol Meško, PhD. Ing. Petr Nachtigall, Ph.D. Ing. Vladislav Zitrický PhD.
doc. Ing. Jozef Gašparík, PhD. prof. Ing. Jozef Majerčák, PhD. doc. Ing. Jaromír Široký, Ph.D. doc. dr. sc. Borna Abramović Ing. Pavol Meško, PhD. Ing. Petr Nachtigall, Ph.D. Ing. Vladislav Zitrický PhD.
MERLIN Project Project
 MERLIN Newsletter Issue 2, December 2015 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in Rail System Smarter A summary of the latest achievements Background Energy management is currently and
MERLIN Newsletter Issue 2, December 2015 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in Rail System Smarter A summary of the latest achievements Background Energy management is currently and
Wheel / Rail Interaction Georg Hettasch
 BACK TO THE FUTURE Biennial Symposium: 10 11 October 2012 Wheel / Rail Interaction Georg Hettasch Presentation overview Why railways work The goal The wheel / rail interaction universe Acknowledgements:
BACK TO THE FUTURE Biennial Symposium: 10 11 October 2012 Wheel / Rail Interaction Georg Hettasch Presentation overview Why railways work The goal The wheel / rail interaction universe Acknowledgements:
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Malmbanan traffic simulations : investments and capacity allocation Magnus Wahlborg Banverket Swedish National Rail Administration Infrastructure Management S-781 85 Borldnge Sweden EMail: magnus. wahlborg
Malmbanan traffic simulations : investments and capacity allocation Magnus Wahlborg Banverket Swedish National Rail Administration Infrastructure Management S-781 85 Borldnge Sweden EMail: magnus. wahlborg
A model for the life expectancy of railway switches and crossings for maintenance and renewal planning in asset management systems
 Computers in Railways XI 765 A model for the life expectancy of railway switches and crossings for maintenance and renewal planning in asset management systems W.-J. Zwanenburg EPFL: École Polytechnique
Computers in Railways XI 765 A model for the life expectancy of railway switches and crossings for maintenance and renewal planning in asset management systems W.-J. Zwanenburg EPFL: École Polytechnique
Assesment of The EMU and Track Condition Monitoring Results from Chosen Track Sections During Normal Operation
 TRANSPORT Assesment of The EMU and Track Condition Monitoring Assesment of The EMU and Track Condition Monitoring Results from Chosen Track Sections During Normal Operation Rafał Melnik, Andrzej Chudzikiewicz
TRANSPORT Assesment of The EMU and Track Condition Monitoring Assesment of The EMU and Track Condition Monitoring Results from Chosen Track Sections During Normal Operation Rafał Melnik, Andrzej Chudzikiewicz
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL FOR MOBILITY AND TRANSPORT DECISION
 Ref. Ares(2018)4510586-03/09/2018 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL FOR MOBILITY AND TRANSPORT Director-General DECISION authorising the use of unit costs for the retrofitting of noisy wagons under
Ref. Ares(2018)4510586-03/09/2018 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL FOR MOBILITY AND TRANSPORT Director-General DECISION authorising the use of unit costs for the retrofitting of noisy wagons under
Calculating the Contact Stress Resulting from Lateral Movement of the Wheel on Rail by Applying Hertz Theory
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 6, No. 4 / December 01, pp. 148-154 The Korean Society for Railway Calculating the Contact Stress Resulting from Lateral Movement of the Wheel on Rail by Applying
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 6, No. 4 / December 01, pp. 148-154 The Korean Society for Railway Calculating the Contact Stress Resulting from Lateral Movement of the Wheel on Rail by Applying
SGF Öst Seminar. Measurement and Improvement of Grout Penetrability in Hard Rock - Current Developments. By: Ali N. Ghafar
 SGF Öst Seminar Measurement and Improvement of Grout Penetrability in Hard Rock - Current Developments By: Ali N. Ghafar Stockholm, 2016 This study was supervised by: Prof. Stefan Larsson Main-Supervisor
SGF Öst Seminar Measurement and Improvement of Grout Penetrability in Hard Rock - Current Developments By: Ali N. Ghafar Stockholm, 2016 This study was supervised by: Prof. Stefan Larsson Main-Supervisor
Wayside train monitoring systems (WTMS). Uncompromising safety.
 Wayside train monitoring systems (WTMS). Uncompromising safety. We keep Switzerland moving. Travel in comfort. Get there on time. The Swiss are world champions in rail travel. Every day, some 10,671 trains
Wayside train monitoring systems (WTMS). Uncompromising safety. We keep Switzerland moving. Travel in comfort. Get there on time. The Swiss are world champions in rail travel. Every day, some 10,671 trains
FAQ: The New East Coast Line
 FAQ: The New East Coast Line Why is a railway in northern Sweden essential for Europe? Sweden is a vast country with enormous natural resources. Our industry has extremely high standards for environmental
FAQ: The New East Coast Line Why is a railway in northern Sweden essential for Europe? Sweden is a vast country with enormous natural resources. Our industry has extremely high standards for environmental
Probabilistic Cost Optimisation of Soil Improvement Strategies
 Probabilistic Cost Optimisation of Soil Improvement Strategies G.B. de Vries 1 ; P.H.A.J.M. van Gelder 2 ; J.K. Vrijling 2 1 Van Oord ACZ, Jan Blankenweg 2, 4200 AL Gorinchem, The Netherlands (E-mail:
Probabilistic Cost Optimisation of Soil Improvement Strategies G.B. de Vries 1 ; P.H.A.J.M. van Gelder 2 ; J.K. Vrijling 2 1 Van Oord ACZ, Jan Blankenweg 2, 4200 AL Gorinchem, The Netherlands (E-mail:
Benchmarking and evaluation of railway operations performance
 Benchmarking and evaluation of railway operations performance Gemma Nicholson, David Kirkwood, Felix Schmid, Clive Roberts Birmingham Centre for Railway Research and Education, UK 25 March 2015 Outline
Benchmarking and evaluation of railway operations performance Gemma Nicholson, David Kirkwood, Felix Schmid, Clive Roberts Birmingham Centre for Railway Research and Education, UK 25 March 2015 Outline
Development Center 1
 Development Center 1 Visually and technologically impressive: the Universal Train Test Rig. 2 A TRADITION OF INNOVATION: EFFICIENCY, SAFETY, SYSTEMS COMPETENCE. For more than 110 years, the engineers at
Development Center 1 Visually and technologically impressive: the Universal Train Test Rig. 2 A TRADITION OF INNOVATION: EFFICIENCY, SAFETY, SYSTEMS COMPETENCE. For more than 110 years, the engineers at
Survey of maintenance practices and costs
 Survey of maintenance practices and costs ESIS TC24 Meeting 1-2 October, 2014, POLIMI (Milano) Aitor Landaberea CAF S.A. Wheels, Axles and Gearboxes Business Unit Contents Objectives RAMS/LCC in railways
Survey of maintenance practices and costs ESIS TC24 Meeting 1-2 October, 2014, POLIMI (Milano) Aitor Landaberea CAF S.A. Wheels, Axles and Gearboxes Business Unit Contents Objectives RAMS/LCC in railways
Development of a Decision Support Model Using MapObjects to Study Transportation Systems
 Title: Development of a Decision Support Model Using MapObjects to Study Transportation Systems Authors: Dr. Hojong Baik. Research Scientist. Virginia Tech. Blacksburg, VA. U.S.A. Nicholas Hinze, Graduate
Title: Development of a Decision Support Model Using MapObjects to Study Transportation Systems Authors: Dr. Hojong Baik. Research Scientist. Virginia Tech. Blacksburg, VA. U.S.A. Nicholas Hinze, Graduate
Planning tomorrow s railway - role of technology in infrastructure and timetable options evaluation
 Planning tomorrow s railway - role of technology in infrastructure and timetable options evaluation D. Wood, S. Robertson Capacity Management Systems, AEA Technology Rail, UK Abstract Whether upgrading
Planning tomorrow s railway - role of technology in infrastructure and timetable options evaluation D. Wood, S. Robertson Capacity Management Systems, AEA Technology Rail, UK Abstract Whether upgrading
Q&A: The New East Coast Line
 Q&A: The New East Coast Line Why is a railway in northern Sweden essential for Europe? Sweden is a vast country with enormous natural resources. Our industry has extremely high standards for environmental
Q&A: The New East Coast Line Why is a railway in northern Sweden essential for Europe? Sweden is a vast country with enormous natural resources. Our industry has extremely high standards for environmental
Simulation of different railway signalling systems
 Simulation of different railway signalling systems M. Grimm', B.Sandbla
Simulation of different railway signalling systems M. Grimm', B.Sandbla
A pin-on-disc study of the rate of airborne wear particle emissions from railway braking materials
 A pin-on-disc study of the rate of airborne wear particle emissions from railway braking materials Saeed Abbasi¹, Anders Jansson², Lars Olander³, Ulf Olofsson¹, Ulf Sellgren¹ 1 KTH Machine Design, SE 100
A pin-on-disc study of the rate of airborne wear particle emissions from railway braking materials Saeed Abbasi¹, Anders Jansson², Lars Olander³, Ulf Olofsson¹, Ulf Sellgren¹ 1 KTH Machine Design, SE 100
UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK
 Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
1. Introduction. 1.1 Project Background. ANTONY JOHNSTONE Transport Associate Aurecon
 ANTONY JOHNSTONE Transport Associate Aurecon Antony.johnstone@aurecongroup.com RAFAEL CARVAJAL Operational Modelling and Visualisation Coordinator Main Roads WA Rafael.CARVAJALCIFUENTES@mainroads.wa.gov.au
ANTONY JOHNSTONE Transport Associate Aurecon Antony.johnstone@aurecongroup.com RAFAEL CARVAJAL Operational Modelling and Visualisation Coordinator Main Roads WA Rafael.CARVAJALCIFUENTES@mainroads.wa.gov.au
Train monitoring systems. Uncompromising safety.
 Train monitoring systems. Uncompromising safety. We keep Switzerland moving. Travel in comfort. Get there on time. The Swiss are world champions in rail travel. Every day, some 11,000 trains travel on
Train monitoring systems. Uncompromising safety. We keep Switzerland moving. Travel in comfort. Get there on time. The Swiss are world champions in rail travel. Every day, some 11,000 trains travel on
Paving the way for increased safety. MULTIRAIL Technology. Measuring, checking, monitoring and sand filling.
 Paving the way for increased safety. MULTIRAIL Technology. Measuring, checking, monitoring and sand filling. A sign of our times: more and more people and materials need to reach their destinations faster
Paving the way for increased safety. MULTIRAIL Technology. Measuring, checking, monitoring and sand filling. A sign of our times: more and more people and materials need to reach their destinations faster
Benchmarking Intermodal Transport in the U.S. and Europe
 Developing Infrastructure and Operating Models for Intermodal Shift (DIOMIS 2) Benchmarking Intermodal Transport in the U.S. and Europe 10 March 2009 Chart 1 Objectives of survey Comparison of American
Developing Infrastructure and Operating Models for Intermodal Shift (DIOMIS 2) Benchmarking Intermodal Transport in the U.S. and Europe 10 March 2009 Chart 1 Objectives of survey Comparison of American
INFRASTRUCTURE SOLUTIONS FOR INCREASED EFFICIENCY AND PRODUCTIVITY OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL TRANSPORTS IN CITIES
 INFRASTRUCTURE SOLUTIONS FOR INCREASED EFFICIENCY AND PRODUCTIVITY OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL TRANSPORTS IN CITIES A. TREIBER TFK Transport Research Institute in Sweden. M.Sc. from Uppsala University, Sweden
INFRASTRUCTURE SOLUTIONS FOR INCREASED EFFICIENCY AND PRODUCTIVITY OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL TRANSPORTS IN CITIES A. TREIBER TFK Transport Research Institute in Sweden. M.Sc. from Uppsala University, Sweden
Network Rail conclusions on the Variable Usage Charge. Ben Worley, Senior Regulatory Economist 8 May 2013
 Network Rail conclusions on the Variable Usage Charge Ben Worley, Senior Regulatory Economist 8 May 2013 The process where we are Consultation issued Jan 2013 Deadline for consultation responses April
Network Rail conclusions on the Variable Usage Charge Ben Worley, Senior Regulatory Economist 8 May 2013 The process where we are Consultation issued Jan 2013 Deadline for consultation responses April
Availability target of the railway infrastructure: an analysis
 Availability target of the railway infrastructure: an analysis Ambika P. Patra, MTech, Luleå University of Technology Uday Kumar, PhD, Luleå University of Technology Per-Olof Larsson Kråik, PhD, Swedish
Availability target of the railway infrastructure: an analysis Ambika P. Patra, MTech, Luleå University of Technology Uday Kumar, PhD, Luleå University of Technology Per-Olof Larsson Kråik, PhD, Swedish
Rail Freight Noise CEF Transport call Virtual Information Day 17 January 2019
 10.30-10.55 Rail Freight Noise 2019 CEF Transport call Virtual Information Day 17 January 2019 Julie Buy, Policy Officer, Transport Investment Unit, Directorate-General Mobility & Transport (DG MOVE) Piotr
10.30-10.55 Rail Freight Noise 2019 CEF Transport call Virtual Information Day 17 January 2019 Julie Buy, Policy Officer, Transport Investment Unit, Directorate-General Mobility & Transport (DG MOVE) Piotr
Macroscopic and Microscopic Simulation for the Evaluation of People Mover Systems. Dr.-Ing. Peter Mott Sven Beller PTV AG, Karlsruhe, Germany
 Macroscopic and Microscopic Simulation for the Evaluation of People Mover Systems Dr.-Ing. Peter Mott Sven Beller PTV AG, Karlsruhe, Germany 1. Introduction This paper is intended to show how a comprehensive
Macroscopic and Microscopic Simulation for the Evaluation of People Mover Systems Dr.-Ing. Peter Mott Sven Beller PTV AG, Karlsruhe, Germany 1. Introduction This paper is intended to show how a comprehensive
Chapter 4. Wheel Load Data Analysis
 Chapter 4 Wheel Load Data Analysis This chapter explains the methods used for analyzing the wheel load data. The analyses of the data in the time and frequency domains are addressed. The effects of various
Chapter 4 Wheel Load Data Analysis This chapter explains the methods used for analyzing the wheel load data. The analyses of the data in the time and frequency domains are addressed. The effects of various
