EWEA response on the ERGEG Position Paper on Smart Grids
|
|
|
- Antonia Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EWEA response on the ERGEG Position Paper on Smart Grids
2 EWEA response on the ERGEG Position Paper on Smart Grids Question 1: Do you consider that networks, transmission and distribution, are facing new challenges that will require significant innovation in the near future? Several factors require the significant upgrade of transmission and distribution networks, and the paper addresses most of these challenges. With respect to renewable variable generation and more specifically wind power, the paper does not consider the challenges in a balanced way; it over-emphasizes potential problems due to the so-called intermittent characteristics (whereas aggregated variable generation is not intermittent) and ignores the technological opportunities and benefits that these renewable technologies bring, in terms of savings in operational costs of power generation, and improvements in network efficiency and security. The main challenges in transmission with respect to variable generation are the need for additional capacity both within, and between, EU countries, more coordinated planning for accelerated implementation of transmission upgrades and new network topologies and technologies (for example HV DC) that enable accessing the huge indigenous offshore wind energy potential in the European seas. The upgraded interconnection capacity is notably required to take full advantage of the continental character of wind power (predictability and capacity credit of wind generation). Furthermore, upgrades are needed for an improved interactive operation of decentralised plants and the system, and for an adaptation to a more flexible operation of the entire generation mix for a massive integration of variable generation interacting securely with a more responsive demand side. The main challenge at distribution level is a modernisation of networks to adapt to the new realities where generation is implemented closer to demand and where there is a need and opportunity thanks to technical developments for improved end-user participation and massive demand-side response. Technical innovations are enabling the creation of micro grids which under certain critical circumstances (for example during a serious fault at transmission level) would be able to disconnect from transmission network and still satisfy consumer demand in a reliable way. In our opinion, this modernised distribution level is the main area for using the terminology Smart Grids. With the creation of ENTSO-E it can be reasonably expected that the international operation of the interconnected systems in Europe will substantially improve. This process is expected to be facilitated / enabled by the adoption of European Network Codes which set out the required minimum network standards in the area of security, operation, planning as intended by the Third Package. The first discussions are taking place already (Framework Guidelines for Grid Connection) and it is clear that the scope of the network codes will extend to cross border network management for both the transmission and distribution system level. It is highly surprising that the ERGEG paper ignores the opportunities offered by the process of Network Codes creation for spelling out smart grid type requirements which in fact is the only relevant pathway to formulate the technical minimum 2
3 standards for the networks to meet the future challenges, including the necessary network intelligence at the relevant levels. Principles and ingredients of the smart grid concept as outlined in the paper should be just essential requirements for the relevant Network Codes. It would not make sense to develop policies and regulation with respect to Smart Grids outside the framework as set out by the intended development of European Network Codes. Question 2: Do you agree with the ERGEG s understanding of smart grid? If not, please specify why not. The scope and definitions of the smart grids concept as developed in the paper especially the figure 1) - are too broad to be a workable concept to be applied for regulatory purposes. In fact, the understanding presented in the ERGEG paper extends to almost all aspects of network development one can think of. The definition of smart grids as developed by IEC on the other hand is a quite good start: it is clear, and not complicated to measure (verify if a network complies to the definition by looking at its essential components). Furthermore it is inadequate that the analysis in the ERGEG paper looks at smarter distribution networks without taking into account smart metering. The figure 2 illustrates that the ERGEG view developed in the paper on smart grids should be considered as work in progress, as it does not recognise the possible existence of storage, only considers residential demand (and not industry or transport) and excludes interactions with non-electric energy uses (for example heating). The definition of ERGEG (in view of developing regulation) as developed in the paper is a panacea of solutions at all levels. Consequently the scope of regulation with respect to smart grids becomes so broad that it is very unlikely to get any agreement with all stakeholders involved in a reasonable time. The way out of this is as highlighted above to connect and embed smart grid principles (some of which are described in the paper) in the relevant Network Code processes where applicable. But then the purpose of the document should be reformulated, and its link with specific Network Codes (planning, operation etc.) should be explicitly stated where relevant. In the light of the implementation of the Third Package, it does not make sense to maintain a process for regulation (including consultations etc.) on smart grids independent of, and parallel with, the development of network codes. Question 3: Do you agree that objectives of reducing energy consumption impose the need for decoupling regulated companies profit from the volume of energy supplied? How can this be implemented? The principle of decoupling profits of companies (like grid operators) from the volumes they process seems quite strange, if this applies to network companies in the pure sense of the word. This at least should be better explained including the link with the subject of the paper. 3
4 Drivers Question 4: Do you agree with the drivers that have been identified in the consultation document? If not, please offer your comments on the drivers including additional ones. The analysis of how to reach the objectives has several shortcomings. The position of renewable energy in the networks is incorrectly described in the ERGEG paper. Wind power the principal variable renewable generation - is connected both at distribution and at transmission level. In this moment, a significant share of the presently 75 GW installed wind power capacity is connected at distribution level, however, this does not correspond to the concept of distributed generation outlined in the consultation paper. In fact distributed generation has several sizes, which also determine the impacts on the networks. More active management of distributed networks is one of the major drivers for smart grids. In the list of drivers the numbers 1 and 2 are the same driver, namely increased distributed generation and variable (not intermittent) generation at transmission and distribution level. That ERGEG mentions the need for new smart technologies for connecting offshore wind again illustrates the ERGEG concept of smart grids is very confusing and ill defined. Strong drivers for the implementation of smart grid technologies which are not mentioned in the list are recent innovations in the ICT sector. End-user participation in modernised networks is essential. However, when mentioning Electrical Vehicles (EVs) as a form of energy storage on distribution level, it should be mentioned that this requires additional technical developments and metering requirements. As it is going now, EVs only draw electricity from the grid (which could be time shifted) but are not designed to feed this energy back in the grid at moments of higher demand. Market: besides the fact that better integrated markets require more information flow, it should be mentioned that faster markets (with shorter gate-closure times) also require a more intensified information exchange. Operational security: in addition the more universal use of dynamic line rating to optimise the utilisation of existing transmission capacity should be mentioned as an example of more intelligence in transmission networks. Opportunities and regulatory challenges Question 5: Do you agree that a user-centric approach should be adopted when considering the deployment of smart grids? User centric approach from SOs: This should be reflected in the Network Codes. (and hence should be spelled out in the relevant Framework Guidelines). The so-called user centric approach does not only apply for Smart Grid principles. Question 6: How should energy suppliers and energy service companies act in the process of deploying smart grids solution? 4
5 The role and duties of energy suppliers and energy service companies can only become more clear if the concept of smart grids is defined in a more focused and clear way. Question 7: Do you think that the current and future needs of network users have been properly identified in Section 3.3? Several of the (listed) new services should be clarified / added - Services needed by generators: which generators do need balancing services that manage intermittent generation? Normally it is a system operator who needs balancing services, and then only the net system unbalance has to be cared for, not unpredicted production of individual generation. (again an erroneous use of the term intermittent). What are access products for intermittent generation? The ERGEG paper should clarify this point, in particular in relation to wind power generation. - Services needed by customers: essential services enabled by smart grid solutions and not mentioned in the list are (a) the possibility of more flexibly choosing a supplier and (b) shifting parts of the load to other point of time triggered by price signals. - Services provided by network operators: if decarbonisation will lead to price increases, then this is caused by improper market functioning By the same token European Energy regulators should acknowledge that insufficient decarbonisation will lead to price increases due to the expected shortage of fossil fuel. Question 8: Do you think that the main future network challenges and possible solutions have been identified in Section 3.4 and 3.5 respectively? If not, please provide details of additional challenges/solutions. Challenges are adequately described (if the term intermittent is replaced by variable). As to the described smart grid solutions, we would like to make the following remarks: - Network planning does not seem an area for smart grids in the proper sense of the word. Again, intelligence obviously should be a basic ingredient for planning and should be embedded in the network planning codes. - As regarding the network operation solutions only the 1 st, 5 th and 8 th bullet are really typical smart grid solutions the other bullet points are objectives or main tasks/actions requiring a range of technical and management solutions. Again this illustrates the confused use of the definition in the paper. - Regarding the solution for generators, the second and third bullet point mentioned (voltage control) as such are not smart grid solutions but aspects that can benefit from improved intelligence in the network. The first bullet point with respect to variable (not intermittent) generation includes the exchange of forecast information. - Regarding the solutions for end-users, the second bullet point is typically a higher level solution, closer to the system operator than to the customer. 5
6 Question 9: Do you expect smarter grid solutions to be essential and/or lower cost than conventional solutions in the next few years? Do you have any evidence that they already are? If so, please provide details. In the implementation of technical innovations, the overall cost/benefit ratio should be considered. For reasons mentioned above, more intelligence in the network, especially at distribution level is essential to enable a smooth and economic cooperation of generation and consumers. More intelligent networks will enable the integration of more renewables, which will lead to lower generation costs. This justifies the use of higher quality (and probably more expensive) infrastructure. On the other hand at distribution level, a more intelligent grid could be helpful in optimisation processes and lead to reduction of investment costs. Question 10: No opinion Priorities for regulation Question 11: Do you agree that regulators should focus on outputs (i.e. the benefits of smart grids) rather than inputs (i.e. the technical details)? The regulators in the first place should facilitate and not obstruct the process that proper standards and proper minimum requirements are implemented for the network infrastructure. The appropriate road towards this goal seems to be (a) the development of Network Codes and (b) the development of specific additional international standards by CEN/CENELEC, to be implemented through the relevant legislation. Furthermore, continued R&D efforts are needed in line with the recommendations of the relevant technology platforms. Questions 12 and 13: Which effects and benefits of smartness could be added to the list (1) - (7) presented in Section 4.1, Table 1? Which effects in this list are more significant to achieving EU targets? How can medium and long-term benefits (e.g. generation diversification and sustainability) be taken into account and measured in a future regulation? Which output measures should be in place to incentivise the performance of network companies? Which performance indicators can easily be assessed and cleansed of grid external effects? Which are suitable for European-level benchmarking and which others could suffer significant differences due to peculiar features of national/regional networks? The Consultation process on the Network Codes is the proper process to provide input on the items of the list which are not directly related to Smart Grids in the proper sense of the term (IEC). This regards more specifically items 3, 6 and 7. For the other items, there is a need for a more focused analysis of the application of the Smart Grids concept on distribution level to identify aspects that are not covered by the Third Package process of Network Code development. 6
7 Questions 14-15: Do you think that network companies need to be incentivised to pursue innovative solutions? How and what output measures could be set to ensure that the network companies pursue innovative solutions/technologies? Do you consider that existing standards or lack of standards represent a barrier to the deployment of smart grids? The modernisation of the networks, especially at distribution level, in order to enable a more effective interaction between the network users and achieving higher levels of network security, should be accompanied by a process of standardisation. There is a need to make an inventory of the gaps in the existing standards. The process of Network Code development in principle offers an opportunity for the stakeholders to identify the relevant standards, and need for further standardisation. The issue is that this process might have to be accelerated to timely achieve solutions necessary for reaching the 2020 targets. Question 16: Do you think that other barriers to deployment than those mentioned in this paper can be already identified? An important barrier in this moment is the present confusion on the scope and definition of the term smart grids. This should be resolved as a matter of urgency. Question 17: No opinion Question 18: What do you consider to be the regulatory priorities for electricity networks in relation to meeting the 2020 targets? With respect to 2020 targets the following priorities are perceived as the most important: At system level: - Interconnection: regulatory measures that facilitate the necessary upgrade of land and sea interconnection capacity and facilitate cross-border trade of electricity - Transmission planning onshore: regulatory measures that facilitate the implementation of identified required upgrades to integrate variable renewable generation - Transmission planning offshore: regulatory measures that facilitate power exchanges together with combined trade and transport of marine renewable generation (offshore wind power etc.) - Flexible generation: regulatory measures that support the development of future generation mix towards higher flexibility to adequately complement increased variable generation As mentioned above, the proper forum to formulate adequate regulatory measures at European level complementing the codes of practice and standards is the Network Code development. At distribution level: - Regulatory measures that support the modernisation of distribution grids, creation of micro grids etc. a.o. by implementation of so-called smart grid solutions. 7
8 It should be investigated where in the process of Network Code development this area could get sufficient attention. Conclusion Integration of a significant share of variable renewable generation should be considered in the frame of a modernisation of the power system towards more sustainable generation, higher security, and fair energy prices for the network users. Whereas at transmission level this modernisation process should be actively taken up by ENTSO-E to be supported by the regulators by adequate measures enabling the necessary innovation - the development at distribution level is much more dispersed. There is a need for workable set of minimum technical requirements in order to implement more intelligence and micro-grid concepts at distribution level, accompanied by a consistent set of regulation at European level in order to ensure the proper interoperability of the networks and achieve a traceable level of security. In this domain there is obviously a task for the European regulators. The present ERGEG paper should be refocused in order to provide a workable start to formulate the scope of this task. ERGEG/CEER should see that network intelligence (the so-called smart grid concepts) is implemented in the Network Codes formulation process where relevant. In addition, there is a need for a more realistic and technically justified view of ERGEG on the impact of variable renewable generation on the networks. There is sufficient experience and literature available in the public domain to underpin such a view. For further information please contact: Paul Wilczek, EWEA: pw@ewea.org or Frans van Hulle, EWEA: fvh@ewea.org The European Wind Energy Association (EWEA) is the voice of the wind industry, actively promoting the utilisation of wind power in Europe and worldwide. It now has over 600 members from 60 countries, including manufacturers with a 90% share of the world wind power market, plus component suppliers, research institutes, national wind and renewables associations, developers, electricity providers, finance and insurance companies and consultants. This combined strength makes EWEA the world s largest and most powerful wind energy network. 8
COMMENTS ON ERGEG POSITION PAPER ON SMART GRIDS
 COMMENTS ON ERGEG POSITION PAPER ON SMART GRIDS INTRODUCTION EDP Distribuição, Energia, SA, referred to as EDPD in the remaining of this document, welcomes the position paper on Smart Grids by the ERGEG
COMMENTS ON ERGEG POSITION PAPER ON SMART GRIDS INTRODUCTION EDP Distribuição, Energia, SA, referred to as EDPD in the remaining of this document, welcomes the position paper on Smart Grids by the ERGEG
Svensk Energi (Swedish Energy Association) response to the public consultation on ERGECs Position Paper on Smart Grids
 SVENSK ENERGI Anders Pettersson +46 8 6772649 Anders.pettersson@svenskenergi.se Datum 2010-03-01 1(5) smartgrids@ieraeq.ora Svensk Energi (Swedish Energy Association) response to the public consultation
SVENSK ENERGI Anders Pettersson +46 8 6772649 Anders.pettersson@svenskenergi.se Datum 2010-03-01 1(5) smartgrids@ieraeq.ora Svensk Energi (Swedish Energy Association) response to the public consultation
2050: Facilitating 50% Wind Energy. Recommendations on transmission infrastructure, system operation and electricity market integration
 2050: Facilitating 50% Wind Energy Recommendations on transmission infrastructure, system operation and electricity market integration 2050: 50% Wind Energy Recommendations on transmission infrastructure,
2050: Facilitating 50% Wind Energy Recommendations on transmission infrastructure, system operation and electricity market integration 2050: 50% Wind Energy Recommendations on transmission infrastructure,
Network of DER Laboratories and Pre-Standardisation. Comments on ERGEG Position Paper on Smart Grids (E09- EQS-30-04)
 Network of Excellence co-funded by the European Commission under the 6 th Framework Programme within the thematic programme Sustainable Energy Systems Contract No. SES6-CT-518299 NoE DERlab Network of
Network of Excellence co-funded by the European Commission under the 6 th Framework Programme within the thematic programme Sustainable Energy Systems Contract No. SES6-CT-518299 NoE DERlab Network of
2 nd STRATEGIC ENERGY REVIEW
 2 nd STRATEGIC ENERGY REVIEW EU ENERGY SECURITY AND SOLIDARITY ACTION PLAN: 2 nd STRATEGIC ENERGY REVIEW 1. Why the strategic energy review? Europe has agreed a forward-looking political agenda to achieve
2 nd STRATEGIC ENERGY REVIEW EU ENERGY SECURITY AND SOLIDARITY ACTION PLAN: 2 nd STRATEGIC ENERGY REVIEW 1. Why the strategic energy review? Europe has agreed a forward-looking political agenda to achieve
Responses are given here with the section references from the consultation document.
 National Grid House Warwick Technology Park Gallows Hill, Warwick CV34 6DA European Commission Directorate General Energy Unit A1 Energy Policy Rue De Mot 24 B-1049 Bruxelles Belgium Paul Whittaker Director,
National Grid House Warwick Technology Park Gallows Hill, Warwick CV34 6DA European Commission Directorate General Energy Unit A1 Energy Policy Rue De Mot 24 B-1049 Bruxelles Belgium Paul Whittaker Director,
EWEA response on the CEER consultation on regulatory aspects of the integration of wind generation in European electricity markets
 EWEA response on the CEER consultation on regulatory aspects of the integration of wind generation in European electricity markets EWEA response on the CEER consultation on regulatory aspects of the integration
EWEA response on the CEER consultation on regulatory aspects of the integration of wind generation in European electricity markets EWEA response on the CEER consultation on regulatory aspects of the integration
The intelligent cooperation between consumption and generation at the heart of the Smart Grid.
 Smart Energy Demand Coalition Position Paper The intelligent cooperation between consumption and generation at the heart of the Smart Grid. The SEDC Vision: To promote the active participation by the demand
Smart Energy Demand Coalition Position Paper The intelligent cooperation between consumption and generation at the heart of the Smart Grid. The SEDC Vision: To promote the active participation by the demand
Leadership Through Innovation. Asia Clean Energy Forum 2016
 Leadership Through Innovation Asia Clean Energy Forum 2016 Vision for smart grid deployment to 2050 Juergen Bender Managing Director Bender-IS Co., Ltd. Page: 2 Rationale for smart grid technology The
Leadership Through Innovation Asia Clean Energy Forum 2016 Vision for smart grid deployment to 2050 Juergen Bender Managing Director Bender-IS Co., Ltd. Page: 2 Rationale for smart grid technology The
TC8 cooperates also with several organizations active in the field of electricity supply such as CIGRE, CIRED, IEEE, AFSEC, IEA.
 SMB/6318/R STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLAN (SBP) IEC/TC OR SC: SECRETARIAT: DATE: Please ensure this form is annexed to the Report to the Standardization Management Board if it has been prepared during a meeting,
SMB/6318/R STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLAN (SBP) IEC/TC OR SC: SECRETARIAT: DATE: Please ensure this form is annexed to the Report to the Standardization Management Board if it has been prepared during a meeting,
Options for 2030 infrastructure targets
 Options for 2030 infrastructure targets Infrastructure and the EU 2030 climate and energy framework Discussion paper, December 2013 Highlights > A major expansion of European grid infrastructure is foreseen
Options for 2030 infrastructure targets Infrastructure and the EU 2030 climate and energy framework Discussion paper, December 2013 Highlights > A major expansion of European grid infrastructure is foreseen
TRILOGUE on Market Design Directive and Regulation. CEDEC Key Priorities
 TRILOGUE on Market Design Directive and Regulation CEDEC Key Priorities 22 May 2018 MARKET DESIGN DIRECTIVE Key priority 1 - DSO & flexibility FLEXIBILITY SERVICES - Due to the decentralisation of the
TRILOGUE on Market Design Directive and Regulation CEDEC Key Priorities 22 May 2018 MARKET DESIGN DIRECTIVE Key priority 1 - DSO & flexibility FLEXIBILITY SERVICES - Due to the decentralisation of the
Position Paper for Energy Policy T&D Europe WG1 - V3
 26 June 2008 Position Paper for Energy Policy T&D Europe WG1 - V3 Electricity is the backbone of every modern society and economy and is the most intelligent and flexible carrier of energy. Electricity
26 June 2008 Position Paper for Energy Policy T&D Europe WG1 - V3 Electricity is the backbone of every modern society and economy and is the most intelligent and flexible carrier of energy. Electricity
CBI Response to BEIS Call for Evidence
 CBI Response to BEIS Call for Evidence Smart, Flexible Power System The CBI welcomes the opportunity to respond to the BEIS Call for Evidence on A Smart, Flexible Energy System. Across the UK, the CBI
CBI Response to BEIS Call for Evidence Smart, Flexible Power System The CBI welcomes the opportunity to respond to the BEIS Call for Evidence on A Smart, Flexible Energy System. Across the UK, the CBI
ELECTRICITY NETWORK TRANSFORMATION ROADMAP: KEY CONCEPTS REPORT SUMMARY DECEMBER 2016
 ELECTRICITY NETWORK TRANSFORMATION ROADMAP: KEY CONCEPTS REPORT SUMMARY DECEMBER 2016 A partnership between Energy Networks Australia and CSIRO A TRANSFORMED ELECTRICITY SYSTEM BY» Customers retain security
ELECTRICITY NETWORK TRANSFORMATION ROADMAP: KEY CONCEPTS REPORT SUMMARY DECEMBER 2016 A partnership between Energy Networks Australia and CSIRO A TRANSFORMED ELECTRICITY SYSTEM BY» Customers retain security
Council conclusions on Energy 2020: A Strategy for competitive, sustainable and secure energy
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Council conclusions on Energy 2020: A Strategy for competitive, sustainable and secure energy 3072th TRANSPORT, TELECOMMUNICATIONS and ERGY Council meeting Brussels, 28 February
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Council conclusions on Energy 2020: A Strategy for competitive, sustainable and secure energy 3072th TRANSPORT, TELECOMMUNICATIONS and ERGY Council meeting Brussels, 28 February
A VISION FOR THE SMART GRID
 The Modern Grid Strategy A VISION FOR THE SMART GRID Developed for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability by the National Energy Technology Laboratory June
The Modern Grid Strategy A VISION FOR THE SMART GRID Developed for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability by the National Energy Technology Laboratory June
[R]enewables 24/7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
![[R]enewables 24/7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY [R]enewables 24/7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY](/thumbs/91/106622492.jpg) [R]enewables 24/7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Infrastructure needed to save the climate Grids keep power systems working The electricity grid' is a collective name for all wires, transformers and infrastructure
[R]enewables 24/7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Infrastructure needed to save the climate Grids keep power systems working The electricity grid' is a collective name for all wires, transformers and infrastructure
September 2018 THOUGHT LEADERSHIP: INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTING IN A DISRUPTED WORLD Part 2: POWER SYSTEMS
 September 2018 THOUGHT LEADERSHIP: INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTING IN A DISRUPTED WORLD Part 2: POWER SYSTEMS INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTING IN A DISRUPTED WORLD POWER SYSTEMS As discussed in the first article in this
September 2018 THOUGHT LEADERSHIP: INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTING IN A DISRUPTED WORLD Part 2: POWER SYSTEMS INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTING IN A DISRUPTED WORLD POWER SYSTEMS As discussed in the first article in this
Electricity System Operator Forward Plan 2018/19
 Electricity System Operator Forward Plan 2018/19 Contents 1. Our vision 2. An ambitious plan 3. A changing landscape 4. Value for consumers 5. A plan built with our customers and stakeholders 6. Our roles,
Electricity System Operator Forward Plan 2018/19 Contents 1. Our vision 2. An ambitious plan 3. A changing landscape 4. Value for consumers 5. A plan built with our customers and stakeholders 6. Our roles,
Generation Adequacy. Generation Adequacy. market measures to secure it and methodology for assessment
 market measures to secure it and methodology for assessment Introduction Power markets are at a crossroad. The structure of power generation capacity is changing towards more intermittent renewable energy,
market measures to secure it and methodology for assessment Introduction Power markets are at a crossroad. The structure of power generation capacity is changing towards more intermittent renewable energy,
1. How can Ofgem ensure that sharper Cash Out incentives from the Significant Code Review:
 1. How can Ofgem ensure that sharper Cash Out incentives from the Significant Code Review: encourage generators and suppliers to balance their own positions before gate closure, thus reducing the call
1. How can Ofgem ensure that sharper Cash Out incentives from the Significant Code Review: encourage generators and suppliers to balance their own positions before gate closure, thus reducing the call
We appreciate your feedback
 Publishing date: 22/09/2014 Document title: We appreciate your feedback Please click on the icon to take a 5 online survey and provide your feedback about this document ACER Trg Republike 3 1000 Ljubljana
Publishing date: 22/09/2014 Document title: We appreciate your feedback Please click on the icon to take a 5 online survey and provide your feedback about this document ACER Trg Republike 3 1000 Ljubljana
Energy Technology Perspectives 2014 Harnessing Electricity s Potential
 The Global Outlook An active transformation of the energy system is essential to meet long-term goals. (ETP 2014) charts a course by which policy and technology together become driving forces in transforming
The Global Outlook An active transformation of the energy system is essential to meet long-term goals. (ETP 2014) charts a course by which policy and technology together become driving forces in transforming
EWEA Response to the European Wind Integration Study (EWIS) Report Main Conclusions in a Nutshell
 EWEA Response to the European Wind Integration Study (EWIS) Report Main Conclusions in a Nutshell A consortium of Transmission System Operators (TSOs) carried out the European Wind Integration Study (EWIS)
EWEA Response to the European Wind Integration Study (EWIS) Report Main Conclusions in a Nutshell A consortium of Transmission System Operators (TSOs) carried out the European Wind Integration Study (EWIS)
Smart grids: flexibility from new sources needed to make renewable power work
 Smart grids: flexibility from new sources needed to make renewable power work A policy brief from the Policy Learning Platform on low-carbon economy July 2017 Introduction Renewable energy is key in the
Smart grids: flexibility from new sources needed to make renewable power work A policy brief from the Policy Learning Platform on low-carbon economy July 2017 Introduction Renewable energy is key in the
Strategic Research Agenda Market Deployment Strategy From 2008 to 2030
 Strategic Research Agenda Market Deployment Strategy From 2008 to 2030 SYNOPSIS Preliminary discussion document Table of contents page A 2030 Vision for the Wind Energy Sector 1 Realising the 2030 Vision:
Strategic Research Agenda Market Deployment Strategy From 2008 to 2030 SYNOPSIS Preliminary discussion document Table of contents page A 2030 Vision for the Wind Energy Sector 1 Realising the 2030 Vision:
Adapting Distribution Network Planning Practices and Design Standards to Accommodate Distributed Energy Resources
 21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2016 Grid of the Future Symposium Adapting Distribution Network Planning Practices and Design Standards to Accommodate
21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2016 Grid of the Future Symposium Adapting Distribution Network Planning Practices and Design Standards to Accommodate
Towards a sustainable Romanian energy sector: Roadmap to RES in 2030 Deloitte Romania, June 2018
 Towards a sustainable Romanian energy sector: Roadmap to RES in 2030 Deloitte Romania, June 2018 Content Background 03 1. Development scenarios 04 2. Impact & benefits 09 Key messages 12 2 Background Romania
Towards a sustainable Romanian energy sector: Roadmap to RES in 2030 Deloitte Romania, June 2018 Content Background 03 1. Development scenarios 04 2. Impact & benefits 09 Key messages 12 2 Background Romania
SET PLAN and HORIZON Helder Gonçalves LNEG 29 September 2015
 SET PLAN and HORIZON 2020 Helder Gonçalves LNEG 29 September 2015 Energy Union Built with the ambition to achive in a cost efective way a fundamental transformation of Europe s Energy System. Smarter,
SET PLAN and HORIZON 2020 Helder Gonçalves LNEG 29 September 2015 Energy Union Built with the ambition to achive in a cost efective way a fundamental transformation of Europe s Energy System. Smarter,
Integration of Renewable Energy Resources: a European Perspective
 Patrick Van Hove Research Policy Officer European Commission Research & Innovation Integration of Renewable Energy Resources: a European Perspective International Conference on Integration, Kyoto, 18 November
Patrick Van Hove Research Policy Officer European Commission Research & Innovation Integration of Renewable Energy Resources: a European Perspective International Conference on Integration, Kyoto, 18 November
IEA Technology Roadmaps: Pathways for the Energy Transition
 IEA Technology Roadmaps: Pathways for the Energy Transition APEC EGNRET Jeju, Republic of Korea - 29 March 2017 Simone Landolina Head, International Partnerships and Initiatives (IPI) IEA supports the
IEA Technology Roadmaps: Pathways for the Energy Transition APEC EGNRET Jeju, Republic of Korea - 29 March 2017 Simone Landolina Head, International Partnerships and Initiatives (IPI) IEA supports the
The role of smart grids in integrating variable Renewable Energy sources
 The role of smart grids in integrating variable Renewable Energy sources Dr. Mustapha Taoumi Energy Technology Expert, EU GCC Clean Energy Technology Network Content 1. Smart Grids 2. Renewables in Cities
The role of smart grids in integrating variable Renewable Energy sources Dr. Mustapha Taoumi Energy Technology Expert, EU GCC Clean Energy Technology Network Content 1. Smart Grids 2. Renewables in Cities
UNIÃO AFRICANA ELECTRICITY SMART GRID
 AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA ELECTRICITY SMART GRID 1. Background/context AFSEC The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 7 Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy
AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA ELECTRICITY SMART GRID 1. Background/context AFSEC The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 7 Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy
How to Meet the EU's Greenhouse Gas Emission Targets PRIMES modelling for the Winter Package
 E3MLab www.e3mlab.eu PRIMES Model 1 How to Meet the EU's Greenhouse Gas Emission Targets PRIMES modelling for the Winter Package By Professor Pantelis Capros, E3MLab central@e3mlab.eu CLEAN ENERGY FOR
E3MLab www.e3mlab.eu PRIMES Model 1 How to Meet the EU's Greenhouse Gas Emission Targets PRIMES modelling for the Winter Package By Professor Pantelis Capros, E3MLab central@e3mlab.eu CLEAN ENERGY FOR
5 key policy asks to ensure that market design proposals within the Clean Energy for all Europeans package deliver a sustainable, affordable and
 5 key policy asks to ensure that market design proposals within the Clean Energy for all Europeans package deliver a sustainable, affordable and secure power system. The successful transition to an efficient,
5 key policy asks to ensure that market design proposals within the Clean Energy for all Europeans package deliver a sustainable, affordable and secure power system. The successful transition to an efficient,
COGEN Europe. Micro CHP: Empowering people today for a smarter future tomorrow. 17 December 2010
 COGEN Europe Micro CHP: Empowering people today for a smarter future tomorrow 17 December 2010 Europe s energy infrastructure is facing important challenges. As outlined in the recent Commission Communication
COGEN Europe Micro CHP: Empowering people today for a smarter future tomorrow 17 December 2010 Europe s energy infrastructure is facing important challenges. As outlined in the recent Commission Communication
Medium voltage products. Technical Application Papers No. 17 Smart grids 1. Introduction
 Medium voltage products Technical Application Papers No. 17 Smart grids 1. Introduction Contents 2 1. Introduction 8 2 The different components and functions of a smart grid 8 2.1 Integration of distributed
Medium voltage products Technical Application Papers No. 17 Smart grids 1. Introduction Contents 2 1. Introduction 8 2 The different components and functions of a smart grid 8 2.1 Integration of distributed
European Commission, SWG(2014)15 final, Impact Assessment to 2030 climate and energy framework
 Wind energy will be key in delivering a decarbonised power sector by 2050. Today wind energy can meet 10.4% of the EU s electricity demand. And in 2030 it meets 23.9% of the EU s electricity demand, making
Wind energy will be key in delivering a decarbonised power sector by 2050. Today wind energy can meet 10.4% of the EU s electricity demand. And in 2030 it meets 23.9% of the EU s electricity demand, making
Opportunities to Accelerate Smart Grid Deployment through Innovative Market Design
 2018-05-28 Opportunities to Accelerate Smart Grid Deployment through Innovative Market Design A discussion document prepared for the workshop and high-level panel discussion, Intelligent market design
2018-05-28 Opportunities to Accelerate Smart Grid Deployment through Innovative Market Design A discussion document prepared for the workshop and high-level panel discussion, Intelligent market design
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in the Electricity System - Grid Issues -
 Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in the Electricity System - Grid Issues - Brussels, 30 March 2005 Background At European and national level mid-term plans exist to increase the share of electricity
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in the Electricity System - Grid Issues - Brussels, 30 March 2005 Background At European and national level mid-term plans exist to increase the share of electricity
The Future of Electricity Networks. Smart Grids Pier Nabuurs Technology Platform SmartGrids Advisory Council Chairman CEO N.V.
 The Future of Electricity Networks 6 May, 2009 Dubai, UAE Smart Grids Pier Nabuurs Technology Platform SmartGrids Advisory Council Chairman CEO N.V. KEMA Agenda Why SmartGrids? Europe s System What is
The Future of Electricity Networks 6 May, 2009 Dubai, UAE Smart Grids Pier Nabuurs Technology Platform SmartGrids Advisory Council Chairman CEO N.V. KEMA Agenda Why SmartGrids? Europe s System What is
European Perspectives in implementing Smart Grids
 European Perspectives in implementing Smart Grids 03 March 2015, NEW DELHI Vittalkumar A. Dhage Energy Sector Specialist Contents 1. EBTC 2. EU Electricity Grid 3. European actions 4. Smart Grid pilots
European Perspectives in implementing Smart Grids 03 March 2015, NEW DELHI Vittalkumar A. Dhage Energy Sector Specialist Contents 1. EBTC 2. EU Electricity Grid 3. European actions 4. Smart Grid pilots
CEOs OF LEADING EUROPEAN ENERGY COMPANIES CONTRIBUTION TO THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL, MARCH 2014
 CEOs OF LEADING EUROPEAN ENERGY COMPANIES CONTRIBUTION TO THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL, 20-21 MARCH 2014 The European energy and climate policy is at a crossroads. The three key pillars of competitiveness, security
CEOs OF LEADING EUROPEAN ENERGY COMPANIES CONTRIBUTION TO THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL, 20-21 MARCH 2014 The European energy and climate policy is at a crossroads. The three key pillars of competitiveness, security
IRENA s perspective on the energy sector transformation Opportunities for Russian in new energy segment
 IRENA s perspective on the energy sector transformation Opportunities for Russian in new energy segment Prof. Dr. Roland Roesch Deputy Director IITC AtomExpo Renewable Energy Roundtable 15. May 2018 Sochi,
IRENA s perspective on the energy sector transformation Opportunities for Russian in new energy segment Prof. Dr. Roland Roesch Deputy Director IITC AtomExpo Renewable Energy Roundtable 15. May 2018 Sochi,
Consultation on an EU strategy for liquefied natural gas and gas storage
 Consultation on an EU strategy for liquefied natural gas and gas storage (EBA) Rue d Arlon 63-65 1040 Brussels BELGIUM Identification number in the transparency register: 18191445640-83 QUESTIONS & s responses
Consultation on an EU strategy for liquefied natural gas and gas storage (EBA) Rue d Arlon 63-65 1040 Brussels BELGIUM Identification number in the transparency register: 18191445640-83 QUESTIONS & s responses
Engage Consulting Briefing Note: Smart Metering Implementation Programme: Prospectus
 Engage Consulting Briefing Note: Smart Metering Implementation Programme: Prospectus Introduction This briefing note summarises the content from the Smart Metering Implementation Programme: Prospectus
Engage Consulting Briefing Note: Smart Metering Implementation Programme: Prospectus Introduction This briefing note summarises the content from the Smart Metering Implementation Programme: Prospectus
Bulk Power System Integration of Variable Generation - Program 173
 Program Description Program Overview Environmentally driven regulations such as state-mandated renewable energy standards and federal air and water standards, along with improved economic viability for
Program Description Program Overview Environmentally driven regulations such as state-mandated renewable energy standards and federal air and water standards, along with improved economic viability for
Scottish Enterprise Supporting the Scottish Energy Systems Approach. Seonaid Vass. Scottish Enterprise Head of Energy, Renewables
 Scottish Enterprise Supporting the Scottish Energy Systems Approach Seonaid Vass Scottish Enterprise Head of Energy, Renewables About Scottish Enterprise Scottish Enterprise is Scotland's main economic
Scottish Enterprise Supporting the Scottish Energy Systems Approach Seonaid Vass Scottish Enterprise Head of Energy, Renewables About Scottish Enterprise Scottish Enterprise is Scotland's main economic
Improving Renewables Integration in the European Power Systems. Simon Müller Analyst System Integration of Renewables Renewable Energy Division
 Improving Renewables Integration in the European Power Systems Simon Müller Analyst System Integration of Renewables Renewable Energy Division European Utility Week, 4 November 2015, Vienna OECD/IEA 2015
Improving Renewables Integration in the European Power Systems Simon Müller Analyst System Integration of Renewables Renewable Energy Division European Utility Week, 4 November 2015, Vienna OECD/IEA 2015
Proposed Smart Grid Vision for South Africa Presented to AMEU Members by Dr. M Bipath presented on behalf of SASGI
 Proposed Smart Grid Vision for South Africa Presented to AMEU Members by Dr. M Bipath presented on behalf of SASGI Policy Work Group Members Dr. M Bipath-SANEDI-(chair) Dr. Clinton Carter-Brown-ESKOM-vice
Proposed Smart Grid Vision for South Africa Presented to AMEU Members by Dr. M Bipath presented on behalf of SASGI Policy Work Group Members Dr. M Bipath-SANEDI-(chair) Dr. Clinton Carter-Brown-ESKOM-vice
Questions and answers on 2030 framework on climate and energy
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION MEMO Brussels, 22 January 2014 Questions and answers on 2030 framework on climate and energy 1. Why does the EU need a new climate and energy framework for the period up to 2030? The
EUROPEAN COMMISSION MEMO Brussels, 22 January 2014 Questions and answers on 2030 framework on climate and energy 1. Why does the EU need a new climate and energy framework for the period up to 2030? The
Decarbonization pathways and the new role of DSOs
 Decarbonization pathways and the new role of DSOs Kristian Ruby Secretary General Eurelectric 3 April 2019 We have modelled 3 deep decarbonization scenarios based on electrification of key economic sectors
Decarbonization pathways and the new role of DSOs Kristian Ruby Secretary General Eurelectric 3 April 2019 We have modelled 3 deep decarbonization scenarios based on electrification of key economic sectors
BENELUX TALANOA DECLARATION
 BENELUX TALANOA DECLARATION Recalling 60 years of successful cooperation following the adoption of the Benelux Treaty in 1958; Stressing the common willingness to further improve cross border cooperation,
BENELUX TALANOA DECLARATION Recalling 60 years of successful cooperation following the adoption of the Benelux Treaty in 1958; Stressing the common willingness to further improve cross border cooperation,
Speech of Commissioner Günther H. Oettinger
 Check against delivery Speech of Commissioner Günther H. Oettinger Dear Members of the European Parliament, Ladies and Gentlemen, I am glad to be here and to speak to you today. Today, that we inaugurate
Check against delivery Speech of Commissioner Günther H. Oettinger Dear Members of the European Parliament, Ladies and Gentlemen, I am glad to be here and to speak to you today. Today, that we inaugurate
European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids. Retail energy market: Supplementary response to the European Commission s public consultation
 European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids Retail energy market: Supplementary response to the European Commission s public consultation April 2014 EDSO supplementary response to the European
European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids Retail energy market: Supplementary response to the European Commission s public consultation April 2014 EDSO supplementary response to the European
European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids
 European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids Response to ACER public consultation on Energy regulation: a bridge to 2025 June 2014 EDSO s response to ACER public consultation on Energy regulation:
European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids Response to ACER public consultation on Energy regulation: a bridge to 2025 June 2014 EDSO s response to ACER public consultation on Energy regulation:
SET Plan Declaration of Intent on Strategic Targets in the context of an Initiative for Global Leadership in Ocean Energy
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Energy, Transport and Climate SET Plan Secretariat Purpose of this document SET Plan Declaration of Intent on Strategic Targets
EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Energy, Transport and Climate SET Plan Secretariat Purpose of this document SET Plan Declaration of Intent on Strategic Targets
DOMESTIC COGENERATION OF HEAT AND ELECTRICITY
 DOMESTIC COGENERATION OF HEAT AND ELECTRICITY Henrik Weldingh DEFU - Denmark 1 hw@defu.dk INTRODUCTION CHP, Combined Heat and Power, or Cogeneration of Heat and Power, is the simultaneous production of
DOMESTIC COGENERATION OF HEAT AND ELECTRICITY Henrik Weldingh DEFU - Denmark 1 hw@defu.dk INTRODUCTION CHP, Combined Heat and Power, or Cogeneration of Heat and Power, is the simultaneous production of
The Energy Technologies Institute (ETI) Submission to the BERR Consultation on Renewable Energy Strategy
 The Energy Technologies Institute (ETI) Submission to the BERR Consultation on Renewable Energy Strategy 26 th September 2008 1. Introduction to the Energy Technologies Institute The Energy Technologies
The Energy Technologies Institute (ETI) Submission to the BERR Consultation on Renewable Energy Strategy 26 th September 2008 1. Introduction to the Energy Technologies Institute The Energy Technologies
Future Energy Scenarios in five minutes. July 2017
 Future Energy Scenarios in five minutes July 2017 Executive summary About FES National Grid has an important role to play in leading the debate on the energy revolution across the industry and working
Future Energy Scenarios in five minutes July 2017 Executive summary About FES National Grid has an important role to play in leading the debate on the energy revolution across the industry and working
Annex E: Energy supplementary material
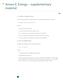 Annex E: Energy supplementary material E.1 Model formulat i o n For these three variables, energy demand is calculated using elasticities as follows: Q = Q 0 [N N / N 0 ] EN [P N / P 0 ] EP [Y N / Y 0
Annex E: Energy supplementary material E.1 Model formulat i o n For these three variables, energy demand is calculated using elasticities as follows: Q = Q 0 [N N / N 0 ] EN [P N / P 0 ] EP [Y N / Y 0
Energy Policy for Communities event. Errol Close Decarbonisation Policy and Co-ordination
 Energy Policy for Communities event Errol Close Decarbonisation Policy and Co-ordination Presentation Overview Introduction to energy policy 2020 2030 The Energy Policy Paper Community Energy Introduction
Energy Policy for Communities event Errol Close Decarbonisation Policy and Co-ordination Presentation Overview Introduction to energy policy 2020 2030 The Energy Policy Paper Community Energy Introduction
Secure, clean and efficient energy system Smart Citizen Centered Energy System Smart Cities
 Rémy Dénos Mark van Stiphout Jean-Marie Bemtgen DG ENER New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal Energy Info Days 2017 Secure, clean and efficient energy system Smart Citizen Centered Energy System Smart
Rémy Dénos Mark van Stiphout Jean-Marie Bemtgen DG ENER New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal Energy Info Days 2017 Secure, clean and efficient energy system Smart Citizen Centered Energy System Smart
Robyn Jenkins May 2012
 UK Future Energy Scenarios Robyn Jenkins May 2012 The UK energy landscape is changing Sustainability Existing power station closures ~25% Affordability Security of supply of total capacity by 2020 Gas
UK Future Energy Scenarios Robyn Jenkins May 2012 The UK energy landscape is changing Sustainability Existing power station closures ~25% Affordability Security of supply of total capacity by 2020 Gas
RGI Strategic Plan. 1. Background. 2. The Role of RGI. RGI Strategic Plan 2016
 RGI Strategic Plan 1. Background Europe s energy system is passing through an exciting period. Building a competitive European electricity market, maintaining security of supply and tackling climate change
RGI Strategic Plan 1. Background Europe s energy system is passing through an exciting period. Building a competitive European electricity market, maintaining security of supply and tackling climate change
D2.2 Implementation Status and Market Focused Diagnosis of the Target Model
 D2.2 Implementation Status and Market Focused Diagnosis of the Target Model Luis Olmos, Pablo Rodilla, Camila Fernandes, Pablo Frias, Ove Wolfgang, Ricardo Loureiro, Bruno Caetano, Bettina Burgholzer,
D2.2 Implementation Status and Market Focused Diagnosis of the Target Model Luis Olmos, Pablo Rodilla, Camila Fernandes, Pablo Frias, Ove Wolfgang, Ricardo Loureiro, Bruno Caetano, Bettina Burgholzer,
Flexibility, distributed resources and multi-energy systems
 Patrick Van Hove Research Programme Officer DG RTD Flexibility, distributed resources and multi-energy systems International Institute for Energy System Integration Copenhagen, 28/05/2014 Not legally binding
Patrick Van Hove Research Programme Officer DG RTD Flexibility, distributed resources and multi-energy systems International Institute for Energy System Integration Copenhagen, 28/05/2014 Not legally binding
EDF and Integration of Distributed Energy Resources
 IEEE Power Engineering Society Tuesday, June 20, 2006. Montreal EDF and Integration of Distributed Energy Resources Bruno Meyer (presenter) Director Power Systems Technology and Economics Yves Bamberger,
IEEE Power Engineering Society Tuesday, June 20, 2006. Montreal EDF and Integration of Distributed Energy Resources Bruno Meyer (presenter) Director Power Systems Technology and Economics Yves Bamberger,
Flexibility, distributed resources and multi-energy systems
 Patrick Van Hove Research Programme Officer DG RTD Flexibility, distributed resources and multi-energy systems International Institute for Energy System Integration Copenhagen, 28/05/2014 Not legally binding
Patrick Van Hove Research Programme Officer DG RTD Flexibility, distributed resources and multi-energy systems International Institute for Energy System Integration Copenhagen, 28/05/2014 Not legally binding
MODERATOR: ENEA Consulting: Louis-Marie Jacquelin, Director of Development and Innovation. ENEA Consulting, Louis-Marie Jacquelin
 STAGE 1 2.15PM 3.15PM THE INTEGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGIES IN A SMARTER GRID SPEAKERS: ERDF: Jacques Merley, Head of Network Planning Department Federal Network Agency: Dr. Sascha Falahat, Assistant Head
STAGE 1 2.15PM 3.15PM THE INTEGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGIES IN A SMARTER GRID SPEAKERS: ERDF: Jacques Merley, Head of Network Planning Department Federal Network Agency: Dr. Sascha Falahat, Assistant Head
Analysing grid flow over time as a cornerstone of the Smart Grid strategy
 Analysing grid flow over time as a cornerstone of the Smart Grid strategy European Utility Week 15-17 October 2013 - Amsterdam Einar Hoffmann, Managing IT Architect, DONG Energy, Denmark eihof@dongenergy.dk
Analysing grid flow over time as a cornerstone of the Smart Grid strategy European Utility Week 15-17 October 2013 - Amsterdam Einar Hoffmann, Managing IT Architect, DONG Energy, Denmark eihof@dongenergy.dk
However, this surge comes with a cost.
 1 1. juni 2015 We are at a changing point for the energy industry on several fields, - energy markets are in transition both in Europe and in Japan, as we just learned from Prof. Hatta, - There will be
1 1. juni 2015 We are at a changing point for the energy industry on several fields, - energy markets are in transition both in Europe and in Japan, as we just learned from Prof. Hatta, - There will be
Power Perspectives 2030
 Executive Summary A contributing study to Roadmap 2050: a practical guide to a prosperous, low-carbon europe EXECUTIVE SUMMARY A. CONTEXT In October 2009, the European Council set an economy-wide greenhouse
Executive Summary A contributing study to Roadmap 2050: a practical guide to a prosperous, low-carbon europe EXECUTIVE SUMMARY A. CONTEXT In October 2009, the European Council set an economy-wide greenhouse
Supporting Documentation A Changing Industry and Marketplace 0
 Supporting Documentation A Changing Industry and Marketplace 0 Ergon Energy s Regulatory Proposal is presented in a number of documents to make it easier for our different stakeholders to access the information
Supporting Documentation A Changing Industry and Marketplace 0 Ergon Energy s Regulatory Proposal is presented in a number of documents to make it easier for our different stakeholders to access the information
Making smarter decisions with Smarter metering
 aking smarter decisions with Smarter metering 4 6 ay, 2009 Dubai, UAE Tony Clarke Head of International Sales Siemens etering Services United Kingdom Smart etering is more than just smart meters The drive
aking smarter decisions with Smarter metering 4 6 ay, 2009 Dubai, UAE Tony Clarke Head of International Sales Siemens etering Services United Kingdom Smart etering is more than just smart meters The drive
Nordic Power System. Challenges and Opportunities for the Nordic Power System
 Challenges and Opportunities for the Nordic Power System This report summarises the shared view of the four Nordic Transmission System Operators (TSOs) Svenska kraftnät, Statnett, Fingrid and Energinet.dk,
Challenges and Opportunities for the Nordic Power System This report summarises the shared view of the four Nordic Transmission System Operators (TSOs) Svenska kraftnät, Statnett, Fingrid and Energinet.dk,
REA response to DECC Consultation on Ensuring Regulation Encourages Innovation
 REA response to DECC Consultation on Ensuring Regulation Encourages Innovation The Renewable Energy Association (REA) is pleased to submit this response to the above consultation. The REA represents a
REA response to DECC Consultation on Ensuring Regulation Encourages Innovation The Renewable Energy Association (REA) is pleased to submit this response to the above consultation. The REA represents a
GEODE Position Paper. The Key Role of Distribution System Operators in the New European Energy Efficiency Strategy
 GEODE Position Paper The Key Role of Distribution System Operators in the New European Energy Efficiency Strategy - Groupement Européen des entreprises et Organismes de Distribution d Energie General Delegation:
GEODE Position Paper The Key Role of Distribution System Operators in the New European Energy Efficiency Strategy - Groupement Européen des entreprises et Organismes de Distribution d Energie General Delegation:
The Renewables-Grid-Initiative. Note to DG Budget 20 July 2010
 The Renewables-Grid-Initiative Note to DG Budget 20 July 2010 Summary The mission of the Renewables-Grid-Initiative (RGI) is to promote effective integration of 100% electricity produced from renewable
The Renewables-Grid-Initiative Note to DG Budget 20 July 2010 Summary The mission of the Renewables-Grid-Initiative (RGI) is to promote effective integration of 100% electricity produced from renewable
GIE s answer to Public Consultation on the Renewable Energy Strategy
 Ref.: 12GIE003 January 2012 GIE s answer to Public Consultation on the Renewable Energy Strategy Context The legislative framework as regards renewable energy is laid down in the Renewable Energy Directive
Ref.: 12GIE003 January 2012 GIE s answer to Public Consultation on the Renewable Energy Strategy Context The legislative framework as regards renewable energy is laid down in the Renewable Energy Directive
Energy Networks Association - Response to Call for Evidence from BEIS/Ofgem
 The Voice of the Networks A Smart, Flexible Energy System Energy Networks Association - Response to Call for Evidence from BEIS/Ofgem Background Please find below the response from Energy Networks Association
The Voice of the Networks A Smart, Flexible Energy System Energy Networks Association - Response to Call for Evidence from BEIS/Ofgem Background Please find below the response from Energy Networks Association
INTERACTIVE CUSTOMER GATEWAY FOR ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT, ELECTRICITY MARKET, AND SERVICES FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY
 INTERACTIVE CUSTOMER GATEWAY FOR ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT, ELECTRICITY MARKET, AND SERVICES FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY Pertti Järventausta Jarmo Partanen Seppo Kärkkainen Tampere University of Lappeenranta
INTERACTIVE CUSTOMER GATEWAY FOR ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT, ELECTRICITY MARKET, AND SERVICES FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY Pertti Järventausta Jarmo Partanen Seppo Kärkkainen Tampere University of Lappeenranta
Overview of the financing framework for the German Energiewende
 Overview of the financing framework for the German Energiewende Dr. Urban Rid Director General Energy Policy electricity and grids Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy Berlin, 13 November 2014
Overview of the financing framework for the German Energiewende Dr. Urban Rid Director General Energy Policy electricity and grids Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy Berlin, 13 November 2014
COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE IMPACT ASSESSMENT. Accompanying the document
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 23.7.2014 SWD(2014) 256 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE IMPACT ASSESSMENT Accompanying the document Communication from the Commission to the
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 23.7.2014 SWD(2014) 256 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE IMPACT ASSESSMENT Accompanying the document Communication from the Commission to the
Smart Grids, New Downstream & the New Deal for EU Electricity Consumers
 Smart Grids, New Downstream & the New Deal for EU Electricity Consumers Pavla Mandátová, Advisor Retail Markets, EURELECTRIC European Power Generation Summit Prague, 27 th November 2015 EURELECTRIC represents
Smart Grids, New Downstream & the New Deal for EU Electricity Consumers Pavla Mandátová, Advisor Retail Markets, EURELECTRIC European Power Generation Summit Prague, 27 th November 2015 EURELECTRIC represents
A 2020 Vision for Europe s energy customers Joint Statement
 A 2020 Vision for Europe s energy customers Joint Statement 13 November 2012 updated on 12 December 2013 E nergy is a vital part of our lives; in order to ensure our wellbeing and to participate fully
A 2020 Vision for Europe s energy customers Joint Statement 13 November 2012 updated on 12 December 2013 E nergy is a vital part of our lives; in order to ensure our wellbeing and to participate fully
CIGRE STRATEGY Prelude to next Century
 CIGRE STRATEGY 2017-2022 Prelude to next Century Rob Stephen President of CIGRE CIGRE MISSION AND VISION To be the world s foremost collaborative technical reference organization for all aspects of electric
CIGRE STRATEGY 2017-2022 Prelude to next Century Rob Stephen President of CIGRE CIGRE MISSION AND VISION To be the world s foremost collaborative technical reference organization for all aspects of electric
European Smart Power Market Project
 European Smart Power Market Project Karsten Neuhoff Climate Policy Initiative / DIW Berlin Background and Scope In the EU, at least 200 gigawatts (GWs) of new and additional renewable energy sources may
European Smart Power Market Project Karsten Neuhoff Climate Policy Initiative / DIW Berlin Background and Scope In the EU, at least 200 gigawatts (GWs) of new and additional renewable energy sources may
European Commission s proposal for a revised Electricity Directive
 European Commission s proposal for a revised Electricity Directive ESMIG proposals for amendments 1 : Article 2 paragraph 18 18. smart metering system means an electronic system that can measure energy
European Commission s proposal for a revised Electricity Directive ESMIG proposals for amendments 1 : Article 2 paragraph 18 18. smart metering system means an electronic system that can measure energy
CONTAINER GLASS PRODUCTION UNDER THE EU-ETS REFORM POST-2020:
 AVENUE LOUISE 89, Bte 4 B-1050 BRUXELLES REGISTER 1550133398-72 TEL +32 2 536 00 80 FAX +32 2 539 37 52 E-MAIL secretariat@feve.org BRUSSELS, 18 MAY 2016 CONTAINER GLASS PRODUCTION UNDER THE EU-ETS REFORM
AVENUE LOUISE 89, Bte 4 B-1050 BRUXELLES REGISTER 1550133398-72 TEL +32 2 536 00 80 FAX +32 2 539 37 52 E-MAIL secretariat@feve.org BRUSSELS, 18 MAY 2016 CONTAINER GLASS PRODUCTION UNDER THE EU-ETS REFORM
U N I T E D N A T I O N S. Joint Statement
 U N I T E D N A T I O N S Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Economic Commission for Europe Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean Economic Commission for Africa Economic
U N I T E D N A T I O N S Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Economic Commission for Europe Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean Economic Commission for Africa Economic
European Power sector s perspective on the role of the EU ETS
 European Power sector s perspective on the role of the EU ETS Brussels, 12 January 2016 The European Decarbonisation agenda brings a new reality to the power system Long term EU decarbonisation objectives
European Power sector s perspective on the role of the EU ETS Brussels, 12 January 2016 The European Decarbonisation agenda brings a new reality to the power system Long term EU decarbonisation objectives
Research Projects as of March 27, 2018
 2017-2018 Research Projects as of March 27, 2018 CARBON MANAGEMENT IMPACTS ON ELECTRICITY MARKETS IN CANADA This project is designed to gain insights into challenges and opportunities carbon management
2017-2018 Research Projects as of March 27, 2018 CARBON MANAGEMENT IMPACTS ON ELECTRICITY MARKETS IN CANADA This project is designed to gain insights into challenges and opportunities carbon management
COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE REGIONS
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 15.7.2015 COM(2015) 340 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 15.7.2015 COM(2015) 340 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE
Profound changes underway in energy markets Signs of decoupling of energy-related CO 2 emissions and global economic growth Oil prices have fallen pre
 Keisuke Sadamori Director of Energy Markets and Security, IEA The 88th IEEJ Energy Seminar, 5th October 215 Profound changes underway in energy markets Signs of decoupling of energy-related CO 2 emissions
Keisuke Sadamori Director of Energy Markets and Security, IEA The 88th IEEJ Energy Seminar, 5th October 215 Profound changes underway in energy markets Signs of decoupling of energy-related CO 2 emissions
Connecting an all-electric world
 Connecting an all-electric world eurelectric Power Summit 2018 Ljubljana, June 5, 2018 Session III: New Frontiers of Electrification Ralf Christian, CEO Division siemens.com/energy-management All-electric
Connecting an all-electric world eurelectric Power Summit 2018 Ljubljana, June 5, 2018 Session III: New Frontiers of Electrification Ralf Christian, CEO Division siemens.com/energy-management All-electric
Overcoming RES Permitting and Grid Access Barriers in Greece
 GREEK ASSOCIATION OF RES ELECTRICITY PRODUCERS Overcoming RES Permitting and Grid Access Barriers in Greece A short presentation for the 9 th Workshop of the International Feed-In Cooperation Friday, 27
GREEK ASSOCIATION OF RES ELECTRICITY PRODUCERS Overcoming RES Permitting and Grid Access Barriers in Greece A short presentation for the 9 th Workshop of the International Feed-In Cooperation Friday, 27
Towards a zero-carbon and digital energy system: What policy challenges for Europe?
 Towards a zero-carbon and digital energy system: What policy challenges for Europe? Our preliminary research results on the issue Simone Tagliapietra Research fellow on energy and climate Bruegel, 27.10.2016
Towards a zero-carbon and digital energy system: What policy challenges for Europe? Our preliminary research results on the issue Simone Tagliapietra Research fellow on energy and climate Bruegel, 27.10.2016
