Media backgrounder: 8 facts about energy this summer
|
|
|
- Diana Jackson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 17 January 2018 There is a lot of media interest in how the electricity system that connects Australia s eastern states will cope this summer. Many industry bodies, government agencies and academic institutions have published detailed reports on this topic, and plenty of data exists, but not all of this can be readily decoded. This backgrounder explains recent developments in Australia s National Electricity Market in a more accessible style for the media and the general public. All sources are linked for finding more detail. Contents: : 1) Coal power stations have become a major cause of unreliability ) The Tesla big battery is proving its worth ) Rooftop solar is reducing strain on the grid ) Demand is just as important as supply ) The biggest threat to energy security is climate change ) Solar and wind are the cheapest form of new supply ) Risk to the grid drops after this summer ) Electricity remains the number one source of climate pollution in Australia For further information contact: Mark Wakeham, CEO, Environment Victoria E: m.wakeham@environmentvictoria.org.au P: (03) M: Dr Nicholas Aberle, Campaigns Manager, Environment Victoria E: n.aberle@environmentvictoria.org.au P: (03) M:
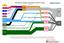
2 1) Coal power stations have become a major cause of unreliability In the space of one week in December last year, coal power stations in Australia failed without warning, or 'tripped', four times: Millmerran coal power station (QLD), 420 MW unit, failed on 12 December 2017 Mt Piper power station (NSW), 700 MW, failed on 13 December 2017 Loy Yang A power station (VIC), 560 MW unit, failed on 14 December 2017 Eraring coal power station (NSW), 700 MW unit, failed on 18 December Many other sudden and unexpected failures have occurred, including ongoing problems at Loy Yang A in Victoria, which has now had six failures in three weeks. This sudden loss of hundreds of megawatts (MW) from coal burning power stations represents a far bigger risk to energy security than any other energy source: The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) has identified the unforeseen material reduction in generation capacity as one of the most likely causes of failing to meet reliability standards (ie. have a blackout). Leading energy economist Bruce Mountain said: The biggest single source of insecurity to the power system is a trip of a major coal thermal generator unit simply because they are so large [it's] not the wind or the sun, or people switching on their air conditioners. Dylan McConnell from the Melbourne University Climate and Energy College said: It is these instantaneous losses of large amounts of capacity that would be causing [the Australian Energy Market Operator] most concern about power system security as we move through summer. Thermal generators like coal are particularly vulnerable to faults and breakdowns in extreme heat (for further detail, see Fact 5). Heatwaves often coincide with peak electricity demand, so coal is failing precisely when it is needed most. The Australia Institute report Can t Stand the Heat notes that Australia s aging coal and gas fleet is not designed to operate in extreme weather conditions. During the February 2017 heatwave, 3600 MW failed during peak demand periods in South Australia, New South Wales and Queensland, equivalent to 14 percent of Australia s coal and gas generation in those states. 2
3 Figure 1 shows the sudden loss of 560 MW of output from Victoria s Loy Yang A power station on 14 December 2017: While wind and solar have variable output, this output can now be predicted days in advance, which gives AEMO time to prepare, and is typically a smaller and less sudden loss of capacity. These coal failures are unpredictable, representing a much larger risk of blackouts. 2) The Tesla big battery is proving its worth South Australia s new lithium ion battery, currently the world s largest, is already demonstrating its value to the National Electricity Market (NEM). (The NEM is Australia s east coast grid linking Queensland, NSW, Victoria, South Australia and Tasmania.) An important part of a renewable energy powered grid is the ability to store energy while it is sunny and windy so it can be used when it is dark and still. Rapid advances in storage technology, especially batteries, are making this possible. The benefits of the Tesla big battery is not just providing dispatchable (ie. on demand) supply. It is also providing lightning fast frequency control to the grid. When a major coal unit trips, the frequency in the grid can fall rapidly. If it falls too far, the grid can become unstable and fail. The battery isn t providing the full frequency response. Rather it is reacting quickly and holding things together briefly while other generators respond a very valuable role (and one for which it isn t currently being paid). 3
4 The chart below shows how the Tesla battery (officially known as the Hornsdale Power Reserve) responded as the frequency in the NEM fell after a unit at Loy Yang A failed. As the frequency returns to the normal range, the battery reduces its output. The above chart is taken from this article by Melbourne University s Dylan McConnell, which explains the battery s summer performance in detail. More large scale batteries are on their way, including a battery linked to a Victorian wind farm and glasshouse at Nectar Farms and possibly an even bigger battery in Queensland. Energy market reform is needed to encourage more large scale battery storage. Specifically, current rules that average pricing out over 30 minutes rather than 5 minutes act as a drag on investment in fast response batteries. For more information on the need for quicker introduction of a 5 minute settlement rule, see here. 3) Rooftop solar is reducing strain on the grid The growth in rooftop solar over the last ten years has been phenomenal. Victoria now has more than 1100 MW of solar panel systems smaller than 100 kw (data available here). This is all likely to be behind the meter, meaning it is not counted towards total supply in the National Electricity Market. In a case of many hands make light work, large numbers of relatively small solar panel systems (mostly on residential homes) are adding up to play an important role in reducing the strain on our energy grid. 4
5 The graph below (from The Australia Institute s Gas and Coal Watch) shows how, on a very hot day this January, Victoria s rooftop solar: Reduced the highest point of peak demand from the grid (at 4pm) by almost 600 MW Delayed the moment of peak demand from the grid by almost three hours, meaning the grid was under strain for less time. The Victorian Essential Services Commission is in the process of introducing a peak feed in tariff for rooftop solar (in addition to a recent increase in the standard feed in tariff). This acknowledges the role solar plays in supporting the grid at critical times, providing an incentive for more households to repower their homes with clean energy. Rooftop solar capacity also plays an important role in reducing the costs of electricity. To meet moments of peak demand, typically on hot summer afternoons, the grid normally requires peaking gas plants to fire up. These generators can turn on relatively quickly but are expensive to operate, and the costs flow through to consumers. Most of Victoria s gas generators, for example, only run a few times each year when demand gets very high. With more rooftop solar shaving off the high points of peak demand, there is much less need for gas peaking plants to turn on, or they will run for much less time. The upshot is fewer price spikes in the wholesale market, which helps lower average prices for consumers. 5
6 4) Demand is just as important as supply Too often commentators fall into considering only the supply side of electricity. But it really is an electricity market, and markets need to consider both supply and demand. Often, reducing demand is a much better solution than increasing supply. Rooftop solar is one way to reduce demand and strain on the grid. Another is energy efficiency. While less visible to the public, this hidden saviour is helping families and businesses slash their running costs, cut energy waste and maintain reliable supply. Energy efficiency simply means using less energy for the same result. Over the last 20 years improved efficiency standards for appliances and new buildings have saved around 5,000 MW of coal fired generation capacity. That s roughly the equivalent of Loy Yang A and B plus Hazelwood that s no longer needed to power our appliances. But while that s good progress, we ve hardly scratched the surface of what s possible, with Victorian homes built before 2005 averaging only 2 stars compared with 6 stars required for new homes. Recent research concluded that efficiency improvements in buildings plus higher standards for new buildings could deliver more than one quarter of Australia s emission reduction commitments under the Paris Agreement. The majority of household energy use goes towards keeping our homes warm in winter and cool in summer, and heating hot water. So cutting waste through simple measures like insulation, draughtsealing and low flow shower heads can reduce annual energy costs by 40 percent delivering savings of up to $1,000 per year for an average pre 2005 home. This doesn t just benefit individual users. Residential and business users account for the vast majority of electricity consumption, so energy efficiency in the home and at work also benefits the system as a whole. Energy efficiency can play an especially important role in reducing demand at peak times, reducing the need for expensive peaking generation capacity. In a heatwave, for example, an energy efficient home will be able to maintain a comfortable temperature with less electricity consumed for airconditioning. As noted in Fact 3 above, there are peaking generators (typically gas power stations) that only turn on for very short times to meet peak demand on hot days. These cost money to build, operate and maintain, for just a few hours of actually generating electricity. The load duration curve below (via Dylan McConnell from Melbourne University Climate Energy College) shows that Victoria s demand very rarely goes above 7000 MW, the low percentage of 6
7 duration on the far left of the graph. Conversely, demand is almost always above 4000 MW, as shown by the right side of the graph: In 2016, approximately 1700 MW of generation capacity was used for just 43 hours across the entire year. Another measure ramping up this summer is demand management or demand side response. This essentially involves payments to consumers to reduce their energy use for a short period (ie. paying to reduce demand). The Australian Renewable Energy Agency has an excellent post explaining the concept here. This is often a much cheaper option than paying a generator to add more supply. AEMO s Summer Readiness report (pages 14 15) indicates there is 884 MW available from demand response programs, including 143 MW of demand under a new trial with the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. Demand response programs can involve any energy users whether a large number of individual households or a small number of large industrial users. 5) The biggest threat to energy security is climate change People often raise concerns about energy security in summer. During long spells of hot weather, people and businesses run their air conditioners, increasing electricity demand (explained in more detail above) and strain on the grid. However another important concern is that our electricity grid infrastructure, especially aging coal power plants, are vulnerable to faults and breakdowns in the heat. The NSW Energy Security Taskforce drew similar conclusions, flagging that large coal thermal plants generally will not perform as well in extreme hot weather and can also have output limited by environmental constraints, for example, cooling pond temperature limits. 7
8 Their infographic below is a helpful guide to the many ways fossil fuel and energy infrastructure can fail in the heat: What often goes unsaid is that extreme summer weather events like heatwaves can now be directly attributed to human caused climate change. Two graphs highlighted in AEMO s Summer Readiness report indicate how climate events feed into their energy planning. The first shows a high likelihood of temperatures going over median maximums: The second graph demonstrates the role of climate change in increasing the number of extreme heat days the times when the energy grid is under the most strain and when coal and gas power stations are most likely to fail: 8
9 Other climate driven weather events can affect the electricity system. In September 2016, an extreme storm knocked over 22 transmission towers in South Australia, causing a system black event. Low rainfall or prolonged droughts have also reduced the ability to use hydroelectricity generators. 6) Solar and wind are the cheapest form of new supply Analysis by Bloomberg New Energy Finance indicates that wind and solar are now the cheapest options for new electricity supply. They forecast that within 15 years, it will be cheaper to build new solar than it will be to operate existing coal power stations. Other energy market analysts at Reputex found that renewables are the cheapest new supply, based on the Levelised Cost Of Electricity (LCOE). LCOE represents the cost per megawatt hour for building and operating a power station in order to breakeven over its assumed lifetime. Below is their chart showing wind and solar as the cheapest option. (The vertical axis represents cost per megawatt hour in dollars.) 9
10 10
11 A second chart shows solar plus battery storage as the cheapest form of flexible/peaking capacity: More renewable energy projects are in the pipeline. Analysis by Green Energy Markets indicates that, nationally, there are over 12,000 MW of wind farms and 15,000 MW of solar farms planned (with approximately half of each type already holding planning approvals) a list that has grown spectacularly in the last 12 months. 7) Risk to the grid drops after this summer As noted above, there are a lot of renewable energy projects in the pipeline. Any supply shortfall this year is temporary, not a representation of our future electricity system. AEMO has indicated that this summer will be the biggest test for the grid partly because Hazelwood power station has closed but new renewable energy capacity is not yet online. The chart on the next page, from AEMO s 2017 Electricity Statement of Opportunities, shows that the possibility of unserved energy (ie. supply shortfalls) drops significantly in Victoria and South Australia after 2017/18: 11
12 It is also worth noting that the reliability standard of less than 0.002% of unserved energy equates to 10 minutes and 30 seconds of shortfalls over an entire year. A large part of the delay in a number of renewable energy projects can be attributed to the destabilisation of the industry under Prime Minister Tony Abbott, whose numerous reviews of the Federal Renewable Energy Target sapped project proponents of confidence. Had those projects gone ahead several years ago, there would be more supply in place this summer. One of the short term stop gap measures in place in Victoria is 110 MW of temporary diesel generators installed in the Latrobe Valley. While diesel is not an ideal measure from an environmental perspective, there is an estimated 61 percent chance that the generators won t even be needed. If they are needed, it is likely to be in the range of 4 8 hours total. This is a far better environmental outcome than the high levels of constant, daily pollution from Hazelwood power station. A media backgrounder that Environment Victoria produced in March 2016, in the lead up to Hazelwood s closure, is here. 12
13 8) Electricity remains the number one source of climate pollution in Australia Electricity is the largest single source of climate pollution in Australia. The chart below from the Guardian, shows the contribution our electricity consumption makes to total greenhouse gas emissions. Recent federal government data (released in late December under the cover of Christmas for the second year in a row) indicates that greenhouse gas emissions from electricity went down by just over 2 percent from last year. A significant amount of this reduction can be attributed to the closure of Hazelwood, which was until March 2017 the most polluting power station in Australia. A useful summary analysis of the data is available here. If Australia is to take meaningful action on climate change and contribute to international efforts under the Paris Agreement, we need to accelerate the shift away from dirty coal power to clean renewable energy. Reducing emissions from other sectors (such as transport and agriculture) is comparatively difficult, whereas zero emission and low cost alternatives to polluting electricity supply already exist. (Authorised by Nicholas Aberle, Acting CEO, Environment Victoria, Lvl 2, 60 Leicester Street, Carlton VIC 3053.) 13
HEATWAVES AND ELECTRICITY SUPPLY
 HEATWAVES AND ELECTRICITY SUPPLY is the time of heatwaves in many parts of Australia. Hot weather places significant demand on the electricity system, increasingly so over the last decade with the increased
HEATWAVES AND ELECTRICITY SUPPLY is the time of heatwaves in many parts of Australia. Hot weather places significant demand on the electricity system, increasingly so over the last decade with the increased
Watt on a hot tin roof
 Watt on a hot tin roof How rooftop solar increases reliability and reduces electricity prices Rooftop solar generates best on hot sunny days, exactly the conditions that see gas and coal generation at
Watt on a hot tin roof How rooftop solar increases reliability and reduces electricity prices Rooftop solar generates best on hot sunny days, exactly the conditions that see gas and coal generation at
Impact of small solar PV on the NSW wholesale electricity market. Approved for Public Release 12 October 2017
 Impact of small solar PV on the NSW wholesale electricity market Approved for Public Release 12 October 2017 Disclaimer This report (Report) has been produced by Energy Synapse Pty Ltd ABN 34 616 603 082
Impact of small solar PV on the NSW wholesale electricity market Approved for Public Release 12 October 2017 Disclaimer This report (Report) has been produced by Energy Synapse Pty Ltd ABN 34 616 603 082
Renewable Energy Index. February 2018
 Renewable Energy Index February 2018 Green Energy Markets, March 2018 Key highlights Over summer renewable energy generated more power than brown coal, gas or oil Over summer renewables supplied more power
Renewable Energy Index February 2018 Green Energy Markets, March 2018 Key highlights Over summer renewable energy generated more power than brown coal, gas or oil Over summer renewables supplied more power
Abstract. The renewable energy revolution
 Pumped Hydro Energy Storage and the Renewable Energy Revolution Professor Andrew Blakers Australian National University Andrew.blakers@anu.edu.au Ph 02 6125 5905 September 2015 Abstract In Australia and
Pumped Hydro Energy Storage and the Renewable Energy Revolution Professor Andrew Blakers Australian National University Andrew.blakers@anu.edu.au Ph 02 6125 5905 September 2015 Abstract In Australia and
Renewable Energy Index. December 2018
 Renewable Energy Index December 2018 Green Energy Markets, January 2019 Key highlights This edition of the Renewable Energy Index provides a special focus review of the 2018 year. 2018 will go down as
Renewable Energy Index December 2018 Green Energy Markets, January 2019 Key highlights This edition of the Renewable Energy Index provides a special focus review of the 2018 year. 2018 will go down as
CLEAN COAL: FACTSHEET
 CLEAN COAL: CLIMATECOUNCIL.ORG.AU 1 CLEAN COAL: Clean Coal: Factsheet COAL IS ALWAYS POLLUTING Building new fossil fuel power plants is expensive, polluting and damaging for community health. FACT CHECK
CLEAN COAL: CLIMATECOUNCIL.ORG.AU 1 CLEAN COAL: Clean Coal: Factsheet COAL IS ALWAYS POLLUTING Building new fossil fuel power plants is expensive, polluting and damaging for community health. FACT CHECK
Renewable Energy Index. October 2018
 Renewable Energy Index October 2018 Green Energy Markets, November 2018 Key highlights The recent rapid rate of wind and solar installations puts Australia s main grids on track to have three-quarters
Renewable Energy Index October 2018 Green Energy Markets, November 2018 Key highlights The recent rapid rate of wind and solar installations puts Australia s main grids on track to have three-quarters
Renewable Energy Index Benchmark Report
 Renewable Energy Index 2016-2017 Benchmark Report Green Energy Markets, August 2017 Key findings Renewable energy is on the way to producing as much power as Australian households consume. In fact, between
Renewable Energy Index 2016-2017 Benchmark Report Green Energy Markets, August 2017 Key findings Renewable energy is on the way to producing as much power as Australian households consume. In fact, between
Renewable Energy Index. January 2018
 Renewable Energy Index January 2018 Green Energy Markets, February 2018 Key highlights Solar passes 10,000 jobs mark as it becomes significant source of power Large scale solar farms under construction,
Renewable Energy Index January 2018 Green Energy Markets, February 2018 Key highlights Solar passes 10,000 jobs mark as it becomes significant source of power Large scale solar farms under construction,
Thank you, Chairman, and good morning. I m going to begin my presentation by playing a short video that summarises AGL s strategy.
 Thank you, Chairman, and good morning. I m going to begin my presentation by playing a short video that summarises AGL s strategy. [Video plays] 15 I trust you found the video a useful summary of our strategy.
Thank you, Chairman, and good morning. I m going to begin my presentation by playing a short video that summarises AGL s strategy. [Video plays] 15 I trust you found the video a useful summary of our strategy.
Renewable Energy Index. December 2017
 Renewable Energy Index December 2017 Green Energy Markets, January 2018 Key highlights Wind farm construction exceeds 10,000 job mark as Victoria surges past NSW in renewable energy construction jobs There
Renewable Energy Index December 2017 Green Energy Markets, January 2018 Key highlights Wind farm construction exceeds 10,000 job mark as Victoria surges past NSW in renewable energy construction jobs There
SOLAR PV MYTHS AND FACTS Household solar power in Australia
 Many myths exist about solar power around what it costs, what it can do and whether governments should support households and businesses in going solar. This fact sheet helps set the record straight. THE
Many myths exist about solar power around what it costs, what it can do and whether governments should support households and businesses in going solar. This fact sheet helps set the record straight. THE
Submission to IPART on Solar Feed-in Tariffs 2018/19. April Page 1. Central NSW Councils (Centroc) Submission
 Submission to IPART on Solar Feed-in Tariffs 2018/19 April 2018 Page 1 Centroc PO Box 333 Forbes NSW 2871 Phone: 0428 690 935 Email: jennifer.bennett@centroc.com.au Chairman: Cr John Medcalf, Mayor, Lachlan
Submission to IPART on Solar Feed-in Tariffs 2018/19 April 2018 Page 1 Centroc PO Box 333 Forbes NSW 2871 Phone: 0428 690 935 Email: jennifer.bennett@centroc.com.au Chairman: Cr John Medcalf, Mayor, Lachlan
Renewable Energy Index. April 2018
 Renewable Energy Index April 2018 Green Energy Markets, May 2018 Key highlights Rooftop solar PV installs 56% above last year s record-breaking rate, with employment in solar installations making up more
Renewable Energy Index April 2018 Green Energy Markets, May 2018 Key highlights Rooftop solar PV installs 56% above last year s record-breaking rate, with employment in solar installations making up more
High PV penetration in Australia, Challenges and Opportunities
 High PV penetration in Australia, Challenges and Opportunities Navid Haghdadi 1,2,4 Iain MacGill 1,2 Anna Bruce 1,3,4 1 Centre for Energy and Environmental Market, UNSW 2 School of Electrical Engineering
High PV penetration in Australia, Challenges and Opportunities Navid Haghdadi 1,2,4 Iain MacGill 1,2 Anna Bruce 1,3,4 1 Centre for Energy and Environmental Market, UNSW 2 School of Electrical Engineering
Summer operations November 17
 Summer operations 2017-18 November 17 A report for the National Electricity Market Important notice PURPOSE AEMO has prepared this document to provide information about its preparations for summer 2017-18.
Summer operations 2017-18 November 17 A report for the National Electricity Market Important notice PURPOSE AEMO has prepared this document to provide information about its preparations for summer 2017-18.
GREENHOUSE INDICATOR SERIES ELECTRICITY GENERATION REPORT 2009
 GREENHOUSE INDICATOR SERIES ELECTRICITY GENERATION REPORT 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction and overview page 2 Charts and graphs for all five states page 4 Victoria analysis page 10 Victoria charts
GREENHOUSE INDICATOR SERIES ELECTRICITY GENERATION REPORT 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction and overview page 2 Charts and graphs for all five states page 4 Victoria analysis page 10 Victoria charts
Australia s renewable energy industry
 1 Australia s renewable energy industry is delivering rapid and deep emissions cuts Ken Baldwin, Andrew Blakers and Matthew Stocks kenneth.baldwin@anu.edu.au; andrew.blakers@anu.edu.au; matthew.stocks@anu.edu.au
1 Australia s renewable energy industry is delivering rapid and deep emissions cuts Ken Baldwin, Andrew Blakers and Matthew Stocks kenneth.baldwin@anu.edu.au; andrew.blakers@anu.edu.au; matthew.stocks@anu.edu.au
Quarterly Energy Dynamics Q4 2017
 MARCH 2018 Quarterly Energy Dynamics Q4 2017 Author: Market Insights Markets Purpose AEMO has prepared this new report to provide energy market participants and governments with information on the market
MARCH 2018 Quarterly Energy Dynamics Q4 2017 Author: Market Insights Markets Purpose AEMO has prepared this new report to provide energy market participants and governments with information on the market
Meeting Australia s Paris greenhouse commitment at zero net cost
 Meeting Australia s Paris greenhouse commitment at zero net cost Andrew Blakers, Matt Stocks and Bin Lu, Australian National University, November 2017 Andrew.blakers@anu.edu.au, 0417 390 139 matthew.stocks@anu.edu.au,
Meeting Australia s Paris greenhouse commitment at zero net cost Andrew Blakers, Matt Stocks and Bin Lu, Australian National University, November 2017 Andrew.blakers@anu.edu.au, 0417 390 139 matthew.stocks@anu.edu.au,
Colossal fossil failures
 Colossal fossil failures 100 breakdowns at gas and coal plants so far in 2018 Bill Browne researcher Mark Ogge project lead, Gas & Coal Watch September 2018 Summary So far in 2018 there have been 100 major
Colossal fossil failures 100 breakdowns at gas and coal plants so far in 2018 Bill Browne researcher Mark Ogge project lead, Gas & Coal Watch September 2018 Summary So far in 2018 there have been 100 major
Victorian Temporary Standby Emergency Power Supply
 Victorian Temporary Standby Emergency Power Supply Community Presentation Morwell, Victoria January 2018 Introduction Temporary standby emergency power supply is needed to help meet Victoria s power needs
Victorian Temporary Standby Emergency Power Supply Community Presentation Morwell, Victoria January 2018 Introduction Temporary standby emergency power supply is needed to help meet Victoria s power needs
A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia
 Engineers Australia Eminent Speaker Presentation, February April 2015 A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia Dr Mark Diesendorf Why do we need Sustainable Energy? Our Climate is Changing! 2 Additional
Engineers Australia Eminent Speaker Presentation, February April 2015 A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia Dr Mark Diesendorf Why do we need Sustainable Energy? Our Climate is Changing! 2 Additional
Energy Market Policy & Challenges
 Energy Market Policy & Challenges API Summer School - 22 February 2016 Dr Brian Spalding, Commissioner AUSTRALIAN ENERGY MARKET COMMISSION AEMC PAGE 1 Energy Market Policy & Challenges Governance and AEMC
Energy Market Policy & Challenges API Summer School - 22 February 2016 Dr Brian Spalding, Commissioner AUSTRALIAN ENERGY MARKET COMMISSION AEMC PAGE 1 Energy Market Policy & Challenges Governance and AEMC
AEMO and ARENA demand response trial to provide 200 megawatts of emergency reserves for extreme peaks
 Media Release 11 OCTOBER 2017 AEMO and ARENA demand response trial to provide 200 megawatts of emergency reserves for extreme peaks The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) and the Australian Energy
Media Release 11 OCTOBER 2017 AEMO and ARENA demand response trial to provide 200 megawatts of emergency reserves for extreme peaks The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) and the Australian Energy
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS
 SOUTH AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: November 2017 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The purpose of this publication is to provide information to the South Australian
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: November 2017 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The purpose of this publication is to provide information to the South Australian
Australia s clean energy: The future is now
 Australia s clean energy: The future is now Clean Energy Council 3 November 2010 The Energy Equation 2 Australia has some of the best renewable energy resources in the world We also have plentiful fossil
Australia s clean energy: The future is now Clean Energy Council 3 November 2010 The Energy Equation 2 Australia has some of the best renewable energy resources in the world We also have plentiful fossil
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS
 SOUTH AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: December 2016 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The purpose of this publication is to provide information about renewable
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: December 2016 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The purpose of this publication is to provide information about renewable
ISSUE to
 ISSUE 16 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1) INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1) THE ROLE OF FORECASTING IN THE NEM... 4 2) FUTURE CHALLENGES FACING THE MARKET... 6 2.1) 2012-13: A YEAR OF TRANSITION?... 6 2.1.1) Carbon Pricing and
ISSUE 16 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1) INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1) THE ROLE OF FORECASTING IN THE NEM... 4 2) FUTURE CHALLENGES FACING THE MARKET... 6 2.1) 2012-13: A YEAR OF TRANSITION?... 6 2.1.1) Carbon Pricing and
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN DEMAND FORECASTS SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS
 SOUTH AUSTRALIAN DEMAND FORECASTS SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: July 2017 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The South Australian Advisory Functions are independent reports prepared by the Australian
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN DEMAND FORECASTS SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: July 2017 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The South Australian Advisory Functions are independent reports prepared by the Australian
National Energy Emissions Audit Electricity Update. July Providing a comprehensive, up-to-date indication of key electricity trends in Australia
 National Energy Emissions Audit Electricity Update July 2018 Providing a comprehensive, up-to-date indication of key electricity trends in Australia Author: Hugh Saddler 2 ABOUT THE AUSTRALIA INSTITUTE
National Energy Emissions Audit Electricity Update July 2018 Providing a comprehensive, up-to-date indication of key electricity trends in Australia Author: Hugh Saddler 2 ABOUT THE AUSTRALIA INSTITUTE
Thank you for the opportunity to make a formal submission responding to the All things considered options paper.
 CO2CRC Limited Building 290 p: +61 (0)3 8595 9600 University of Melbourne e: info@co2crc.com.au Level 1, 700 Swanston Street www.co2crc.com.au VIC 3010, Australia https://twitter.com/ccs_research PO Box
CO2CRC Limited Building 290 p: +61 (0)3 8595 9600 University of Melbourne e: info@co2crc.com.au Level 1, 700 Swanston Street www.co2crc.com.au VIC 3010, Australia https://twitter.com/ccs_research PO Box
About Environment Victoria. Overview. 28 February, By
 28 February, 2017 By email: energymarket.review@delwp.vic.gov.au RE: Review of electricity and gas retail markets in Victoria Environment Victoria submission on the Discussion Paper Thank you for the opportunity
28 February, 2017 By email: energymarket.review@delwp.vic.gov.au RE: Review of electricity and gas retail markets in Victoria Environment Victoria submission on the Discussion Paper Thank you for the opportunity
SOLAR REPORT QUARTER 1, 2018
 SOLAR REPORT MARCH 2016 Australian Energy Council SOLAR REPORT QUARTER 1, 2018 Australian Energy Council DD MM YYYY Australian Energy Council Level 14, 50 Market Street, 2 Table of contents STATE OF SOLAR
SOLAR REPORT MARCH 2016 Australian Energy Council SOLAR REPORT QUARTER 1, 2018 Australian Energy Council DD MM YYYY Australian Energy Council Level 14, 50 Market Street, 2 Table of contents STATE OF SOLAR
SOLAR REPORT QUARTER 3, 2018
 SOLAR REPORT MARCH 2016 Australian Energy Council SOLAR REPORT QUARTER 3, 2018 Australian Energy Council DD MM YYYY Australian Energy Council Level 14, 50 Market Street, Melbourne 2 Table of contents STATE
SOLAR REPORT MARCH 2016 Australian Energy Council SOLAR REPORT QUARTER 3, 2018 Australian Energy Council DD MM YYYY Australian Energy Council Level 14, 50 Market Street, Melbourne 2 Table of contents STATE
SOLAR REPORT JANUARY 2018
 SOLAR REPORT MARCH 2016 Australian Energy Council SOLAR REPORT JANUARY 2018 Australian Energy Council DD MM YYYY Australian Energy Council Level 14, 50 Market Street, Melbourne 2 Table of contents STATE
SOLAR REPORT MARCH 2016 Australian Energy Council SOLAR REPORT JANUARY 2018 Australian Energy Council DD MM YYYY Australian Energy Council Level 14, 50 Market Street, Melbourne 2 Table of contents STATE
Demand Side Management: Who should take Control?
 Demand Side Management: Who should take Control? When a large number of people use their high-energy appliances simultaneously, it can result in a peak in electricity demand and a corresponding rise in
Demand Side Management: Who should take Control? When a large number of people use their high-energy appliances simultaneously, it can result in a peak in electricity demand and a corresponding rise in
3.2 Energy efficiency and renewable energy
 3.2 Energy efficiency and renewable energy Background Ongoing electricity price rises coupled with Australian consumers desire to decrease their carbon footprints has created a new interest and landscape
3.2 Energy efficiency and renewable energy Background Ongoing electricity price rises coupled with Australian consumers desire to decrease their carbon footprints has created a new interest and landscape
A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia
 A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia Dr Mark Diesendorf Institute of Environmental Studies University of New South Wales m.diesendorf@unsw.edu.au Collapse of Larsen B ice shelf, Antarctica 1 Australian
A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia Dr Mark Diesendorf Institute of Environmental Studies University of New South Wales m.diesendorf@unsw.edu.au Collapse of Larsen B ice shelf, Antarctica 1 Australian
Submission to the Victorian Competition and Efficiency Commission Feed in Tariff Inquiry
 Submission to the Victorian Competition and Efficiency Commission Feed in Tariff Inquiry March 19, 2012 Beyond Zero Emissions Kindness House Suite 10, Level 1 288 Brunswick Street Fitzroy, Victoria 3065
Submission to the Victorian Competition and Efficiency Commission Feed in Tariff Inquiry March 19, 2012 Beyond Zero Emissions Kindness House Suite 10, Level 1 288 Brunswick Street Fitzroy, Victoria 3065
Re: RIT-T Market Modelling, high level review. Introduction & background. June Mr R Korte, Executive Manager Asset Management
 Oakley Greenwood Pty Ltd 2/20 Baynes Street Margate Beach QLD 4019 PO Box 125 Margate Beach QLD 4019 Phone +617 3283 3249 Fax +617 3112 5068 June 2018 Mr R Korte, Executive Manager Asset Management ElectraNet
Oakley Greenwood Pty Ltd 2/20 Baynes Street Margate Beach QLD 4019 PO Box 125 Margate Beach QLD 4019 Phone +617 3283 3249 Fax +617 3112 5068 June 2018 Mr R Korte, Executive Manager Asset Management ElectraNet
WIND AND SOLAR FARMS TESTING REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTINGENCY FCAS REGISTRATION
 WIND AND SOLAR FARMS TESTING REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTINGENCY FCAS REGISTRATION PREPARED BY: AEMO Operations Department Systems Performance & Commercial VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 5 October 2018 STATUS:
WIND AND SOLAR FARMS TESTING REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTINGENCY FCAS REGISTRATION PREPARED BY: AEMO Operations Department Systems Performance & Commercial VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 5 October 2018 STATUS:
ENABLING EMBEDDED GENERATION
 APRIL 2014 ENABLING EMBEDDED GENERATION Turning Australian electricity on its head WHAT IS EMBEDDED GENERATION? Energy supply systems around the world are being transformed by embedded (or distributed)
APRIL 2014 ENABLING EMBEDDED GENERATION Turning Australian electricity on its head WHAT IS EMBEDDED GENERATION? Energy supply systems around the world are being transformed by embedded (or distributed)
Residential Demand Response using a Single Variable Information System-
 Residential Demand Response using a Single Variable Information System- The Wind Number ABSTRACT Renewable energy has become cost-competitive with natural gas and coal-fired power plants as a source of
Residential Demand Response using a Single Variable Information System- The Wind Number ABSTRACT Renewable energy has become cost-competitive with natural gas and coal-fired power plants as a source of
ADVICE TO COMMONWEALTH GOVERNMENT ON DISPATCHABLE CAPABILITY
 ADVICE TO COMMONWEALTH GOVERNMENT ON DISPATCHABLE CAPABILITY Published: September 2017 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose AEMO has prepared this document to provide advice to the Commonwealth Government on matters
ADVICE TO COMMONWEALTH GOVERNMENT ON DISPATCHABLE CAPABILITY Published: September 2017 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose AEMO has prepared this document to provide advice to the Commonwealth Government on matters
Sustainable Energy. Ecologically Sustainable Energy. Implications for the Sydney Region
 Sustainable Energy Implications for the Sydney Region Dr Mark Diesendorf Institute of Environmental Studies, UNSW m.diesendorf@unsw.edu.au 1 Ecologically Sustainable Energy Efficient energy use and energy
Sustainable Energy Implications for the Sydney Region Dr Mark Diesendorf Institute of Environmental Studies, UNSW m.diesendorf@unsw.edu.au 1 Ecologically Sustainable Energy Efficient energy use and energy
Renewable Technologies in the Future NEM
 Renewable Technologies in the Future NEM 100% Renewables for Australia? Dr Jenny Riesz Australian Power Institute (API) Summer School Wednesday 24 th February 2016 Who am I? Overview 100% Renewables: Worth
Renewable Technologies in the Future NEM 100% Renewables for Australia? Dr Jenny Riesz Australian Power Institute (API) Summer School Wednesday 24 th February 2016 Who am I? Overview 100% Renewables: Worth
South Australia s business community is paying the price for a grid that is no longer fit for purpose.
 Executive Summary South Australia s business community is paying the price for a grid that is no longer fit for purpose. The meeting of COAG s Energy Council on 19 August must take action to start the
Executive Summary South Australia s business community is paying the price for a grid that is no longer fit for purpose. The meeting of COAG s Energy Council on 19 August must take action to start the
MODELLING THE MARKET IMPACT OF BATTERY STORAGE IN ASIA-PACIFIC ELECTRICITY MARKETS
 MODELLING THE MARKET IMPACT OF BATTERY STORAGE IN ASIA-PACIFIC ELECTRICITY MARKETS DISCLAIMER THIS PAPER HAS BEEN PREPARED BASED ON OUR PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE AND INFORMATION WHICH IS AVAILABLE IN THE
MODELLING THE MARKET IMPACT OF BATTERY STORAGE IN ASIA-PACIFIC ELECTRICITY MARKETS DISCLAIMER THIS PAPER HAS BEEN PREPARED BASED ON OUR PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE AND INFORMATION WHICH IS AVAILABLE IN THE
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN AUSTRALIA OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES
 RENEWABLE ENERGY IN AUSTRALIA OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES SLIDE 1 Jane Hider 21 June 2018 WWW.CORRS.COM.AU 3448-2583-2970v1 OVERVIEW SLIDE 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 Setting the scene Current Renewables market in
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN AUSTRALIA OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES SLIDE 1 Jane Hider 21 June 2018 WWW.CORRS.COM.AU 3448-2583-2970v1 OVERVIEW SLIDE 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 Setting the scene Current Renewables market in
Energy Matters The Little Green Book
 Energy Matters The Little Green Book Contents 2 Introduction 5 Making the switch 6 Home and business 8 Schools 11 Community buildings 12 Remote areas 14 Grid connect and off-grid 19 Solar panels 21 Wind
Energy Matters The Little Green Book Contents 2 Introduction 5 Making the switch 6 Home and business 8 Schools 11 Community buildings 12 Remote areas 14 Grid connect and off-grid 19 Solar panels 21 Wind
Western Australia electricity price trends
 EMBARGOED UNTIL 12.01AM (AEST) ON 14 DECEMBER 2016 Western Australia electricity price trends 2016 Residential Electricity Price Trends report Average residential electricity prices in Western Australia
EMBARGOED UNTIL 12.01AM (AEST) ON 14 DECEMBER 2016 Western Australia electricity price trends 2016 Residential Electricity Price Trends report Average residential electricity prices in Western Australia
Contents. Introduction. Where We Are At A Snapshot of Solar in Australia. Where We Can Go Opportunities to Grow. Case Study: Maria
 Part one Australia is a world-leader in the residential uptake of solar PV but across the country, we ve only just begun tapping into the extraordinary potential for rooftop solar. Funded by Contents Introduction
Part one Australia is a world-leader in the residential uptake of solar PV but across the country, we ve only just begun tapping into the extraordinary potential for rooftop solar. Funded by Contents Introduction
NATIONAL ELECTRICITY FORECASTING REPORT FOR THE NATIONAL ELECTRICITY MARKET
 NATIONAL ELECTRICITY FORECASTING REPORT FOR THE NATIONAL ELECTRICITY MARKET Published: June 2016 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose AEMO has prepared this document in connection with its national transmission planning
NATIONAL ELECTRICITY FORECASTING REPORT FOR THE NATIONAL ELECTRICITY MARKET Published: June 2016 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose AEMO has prepared this document in connection with its national transmission planning
Capacity Energy Markets: A view from Germany and the United States. by Rebecca Bertram
 Capacity Energy Markets: A view from Germany and the United States by Rebecca Bertram Published by the Heinrich Böll Stiftung Washington, DC, September 2013 Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial-
Capacity Energy Markets: A view from Germany and the United States by Rebecca Bertram Published by the Heinrich Böll Stiftung Washington, DC, September 2013 Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial-
A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia
 Engineers Australia Eminent Speaker Presentation, February April 2015 A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia Dr Mark Diesendorf Why do we need Sustainable Energy? Our Climate is Changing! 2 Additional
Engineers Australia Eminent Speaker Presentation, February April 2015 A Sustainable Energy Future for Australia Dr Mark Diesendorf Why do we need Sustainable Energy? Our Climate is Changing! 2 Additional
Meridian Energy presentation to UBS Australasia Conference
 Meridian Energy presentation to UBS Australasia Conference 16 November 2015 Attached is a presentation Meridian Energy will be giving at UBS's Australasia Conference today in Sydney. ENDS Mark Binns Chief
Meridian Energy presentation to UBS Australasia Conference 16 November 2015 Attached is a presentation Meridian Energy will be giving at UBS's Australasia Conference today in Sydney. ENDS Mark Binns Chief
REVIEW 2018 RESIDENTIAL ELECTRICITY PRICE TRENDS REVIEW FINAL REPORT 21 DECEMBER Australian Energy Market Commission
 FINAL REPORT 2018 RESIDENTIAL ELECTRICITY PRICE TRENDS REVIEW 21 DECEMBER 2018 REVIEW INQUIRIES Australian Energy PO Box A2449 Sydney South NSW 1235 E aemc@aemc.gov.au T (02) 8296 7800 F (02) 8296 7899
FINAL REPORT 2018 RESIDENTIAL ELECTRICITY PRICE TRENDS REVIEW 21 DECEMBER 2018 REVIEW INQUIRIES Australian Energy PO Box A2449 Sydney South NSW 1235 E aemc@aemc.gov.au T (02) 8296 7800 F (02) 8296 7899
CHAPTER 2 - DEFINITIONS, PROCESS AND METHODOLOGY. 2.1 Key definitions of energy and maximum demand
 \ \\ \\ \ \ \ \ \\\ \ \ \ "' \\ I \ \ \ \ \ \ CHAPTER 2 - DEFINITIONS, PROCESS AND METHODOLOGY 2.1 Key definitions of energy and maximum demand This section provides an overview of key definitions and
\ \\ \\ \ \ \ \ \\\ \ \ \ "' \\ I \ \ \ \ \ \ CHAPTER 2 - DEFINITIONS, PROCESS AND METHODOLOGY 2.1 Key definitions of energy and maximum demand This section provides an overview of key definitions and
FORECASTS AND KEY INFLUENCING FACTORS FOR GRID SUPPLIED ENERGY
 FORECASTS AND KEY INFLUENCING FACTORS FOR GRID SUPPLIED ENERGY November 2016 NSW PRESENTED BY NICOLA FALCON MANAGER SUPPLY PLANNING SLIDE 1 CHANGING NATURE OF THE AUSTRALIAN ELECTRICITY INDUSTRY Market
FORECASTS AND KEY INFLUENCING FACTORS FOR GRID SUPPLIED ENERGY November 2016 NSW PRESENTED BY NICOLA FALCON MANAGER SUPPLY PLANNING SLIDE 1 CHANGING NATURE OF THE AUSTRALIAN ELECTRICITY INDUSTRY Market
 The Climate Change Problem Electricity generation is the main source of carbon emissions (25% of carbon emissions globally), followed by deforestation & land use (24%), industry (21%) and transportation
The Climate Change Problem Electricity generation is the main source of carbon emissions (25% of carbon emissions globally), followed by deforestation & land use (24%), industry (21%) and transportation
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ELECTRICITY MARKET ECONOMIC TRENDS REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS
 SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ELECTRICITY MARKET ECONOMIC TRENDS REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: October 2015 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The purpose of this report is to provide information about
SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ELECTRICITY MARKET ECONOMIC TRENDS REPORT SOUTH AUSTRALIAN ADVISORY FUNCTIONS Published: October 2015 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose The purpose of this report is to provide information about
UTS: INSTITUTE FOR SUSTAINABLE FUTURES. Quick Facts
 UTS: INSTITUTE FOR SUSTAINABLE FUTURES Quick Facts 2017 The Institute for Sustainable Futures (ISF) was established by the University of Technology, Sydney in 1996 to work with industry, government and
UTS: INSTITUTE FOR SUSTAINABLE FUTURES Quick Facts 2017 The Institute for Sustainable Futures (ISF) was established by the University of Technology, Sydney in 1996 to work with industry, government and
QUEENSLAND COMPETITION AUTHORITY
 REPORT TO QUEENSLAND COMPETITION AUTHORITY 2 JUNE 2017 WHOLESALE ELECTRICITY SPOT PRICES ESTIMATION OF QUEENSLAND WHOLESALE ELECTRICITY SPOT FOR USE BY THE QUEENSLAND COMPETITION AUTHORITY IN ITS ADVICE
REPORT TO QUEENSLAND COMPETITION AUTHORITY 2 JUNE 2017 WHOLESALE ELECTRICITY SPOT PRICES ESTIMATION OF QUEENSLAND WHOLESALE ELECTRICITY SPOT FOR USE BY THE QUEENSLAND COMPETITION AUTHORITY IN ITS ADVICE
ECONOMICS AND POLICY OF LARGE-SCALE BATTERY STORAGE
 ECONOMICS AND POLICY OF LARGE-SCALE BATTERY STORAGE May 2016 Mark R. Jacobsen ECONOMICS AND POLICY OF LARGE-SCALE BATTERY STORAGE 1 Mark R. Jacobsen, May 2016 kleinmanenergy.upenn.edu IF THE SHARE OF SOLAR
ECONOMICS AND POLICY OF LARGE-SCALE BATTERY STORAGE May 2016 Mark R. Jacobsen ECONOMICS AND POLICY OF LARGE-SCALE BATTERY STORAGE 1 Mark R. Jacobsen, May 2016 kleinmanenergy.upenn.edu IF THE SHARE OF SOLAR
ELECTRICITY STATEMENT OF OPPORTUNITIES For the National Electricity Market
 ELECTRICITY STATEMENT OF OPPORTUNITIES For the National Electricity Market EXECUTIVE BRIEFING 2010 Preface I am pleased to introduce AEMO s 2010 Electricity Statement of Opportunities (ESOO), which presents
ELECTRICITY STATEMENT OF OPPORTUNITIES For the National Electricity Market EXECUTIVE BRIEFING 2010 Preface I am pleased to introduce AEMO s 2010 Electricity Statement of Opportunities (ESOO), which presents
Mr Craig Price Group Manager, Planning Australian Energy Market Operator GPO Box 2008 Melbourne VIC 3001
 ABN 70 250 995 390 180 Thomas Street, Sydney PO Box A1000 Sydney South NSW 1235 Australia T (02) 9284 3000 F (02) 9284 3456 2/02/2018 Mr Craig Price Group Manager, Planning Australian Energy Market Operator
ABN 70 250 995 390 180 Thomas Street, Sydney PO Box A1000 Sydney South NSW 1235 Australia T (02) 9284 3000 F (02) 9284 3456 2/02/2018 Mr Craig Price Group Manager, Planning Australian Energy Market Operator
Energy Market. Insights. Solar Thermal Generation: The Answer To Australia s Renewable Energy Needs? by Adrian Kemp
 Issue No. 3 August 2009 Energy Market Insights Solar Thermal Generation: The Answer To Australia s Renewable Energy Needs? by Adrian Kemp From the Editor In this third edition of our EMI series, Adrian
Issue No. 3 August 2009 Energy Market Insights Solar Thermal Generation: The Answer To Australia s Renewable Energy Needs? by Adrian Kemp From the Editor In this third edition of our EMI series, Adrian
Making Connections Straight Talk About Electricity in Ontario
 Making Connections Straight Talk About Electricity in Ontario 2018 Energy Conservation Progress Report, Volume One Summary 2005 Download the full report at: eco.on.ca/reports/2018-making-connections Dianne
Making Connections Straight Talk About Electricity in Ontario 2018 Energy Conservation Progress Report, Volume One Summary 2005 Download the full report at: eco.on.ca/reports/2018-making-connections Dianne
25,000. Energy use in Uralla Town and Shire. The energy context. MEGAwatt hours. Firewood in Uralla 45% Uralla's Electricty GRID
 The energy context Energy use in Uralla Town and Shire What energy is used? Uralla's primary energy needs (excluding transport) are meet by electricity and firewood with a modest use of LPG gas. Electricity
The energy context Energy use in Uralla Town and Shire What energy is used? Uralla's primary energy needs (excluding transport) are meet by electricity and firewood with a modest use of LPG gas. Electricity
The viability of electrical energy storage for Lochiel Park households. Peter Pudney, Adrian Grantham, Lesley A Ward, David Whaley, John Boland
 The viability of electrical energy storage for Lochiel Park households Peter Pudney, Adrian Grantham, Lesley A Ward, David Whaley, John Boland Authors Title Peter Pudney, Adrian Grantham, Lesley A Ward,
The viability of electrical energy storage for Lochiel Park households Peter Pudney, Adrian Grantham, Lesley A Ward, David Whaley, John Boland Authors Title Peter Pudney, Adrian Grantham, Lesley A Ward,
South Australia experienced a mild summer with only a few days exceeding 40 C. A relatively short heat wave occurred in late January 2011.
 KEY FINDINGS The South Australian Annual Supply and Demand Outlook (SASDO) is an independent report prepared by the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) about the current state and future development
KEY FINDINGS The South Australian Annual Supply and Demand Outlook (SASDO) is an independent report prepared by the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) about the current state and future development
South Australia Energy Transformation (Riverlink) RIT-T Total Environment Centre Submission
 South Australia Energy Transformation (Riverlink) RIT-T Total Environment Centre Submission 31 August 2018 1/99 Devonshire Street, Surry Hills, NSW 2010 Ph: 02 9211 5022 Fax: 02 9211 5033 www.tec.org.au
South Australia Energy Transformation (Riverlink) RIT-T Total Environment Centre Submission 31 August 2018 1/99 Devonshire Street, Surry Hills, NSW 2010 Ph: 02 9211 5022 Fax: 02 9211 5033 www.tec.org.au
M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3]
![M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3]](/thumbs/85/92444350.jpg) M. allow mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M2. (a) gas (burning) (b) (i) (transmission) cables and (step-up
M. allow mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M2. (a) gas (burning) (b) (i) (transmission) cables and (step-up
Independent review into the future security of the NEM
 Summary of the Independent review into the future security of the NEM The Finkel Review March 2017 Summary of Preliminary Report released December 2016 The national reform blueprint will outline national
Summary of the Independent review into the future security of the NEM The Finkel Review March 2017 Summary of Preliminary Report released December 2016 The national reform blueprint will outline national
Easy Transition to Renewables
 Easy Transition to Renewables Presentation to the Australian Institute of Energy 6-11- 2017 Ben Rose WHY DOES THE WORLD NEED CLEAN ENERGY NOW? We are not doing enough to met our Paris commitments What
Easy Transition to Renewables Presentation to the Australian Institute of Energy 6-11- 2017 Ben Rose WHY DOES THE WORLD NEED CLEAN ENERGY NOW? We are not doing enough to met our Paris commitments What
Most of us are into saving money these days, right?
 Energy Saving Guide Most of us are into saving money these days, right? Surfing the web for the latest deals on everything from mortgages to TVs is a way of life. But have you ever considered the possibility
Energy Saving Guide Most of us are into saving money these days, right? Surfing the web for the latest deals on everything from mortgages to TVs is a way of life. But have you ever considered the possibility
DEMAND SIDE PARTICIPATION 2016 NATIONAL ELECTRICITY FORECASTING REPORT
 2016 NATIONAL ELECTRICITY FORECASTING REPORT Published: September 2016 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose AEMO has prepared this document to provide information about estimated demand side participation in the National
2016 NATIONAL ELECTRICITY FORECASTING REPORT Published: September 2016 IMPORTANT NOTICE Purpose AEMO has prepared this document to provide information about estimated demand side participation in the National
Climate Café: Why is Australia's electricity system in such a mess?
 Climate Café: Why is Australia's electricity system in such a mess? With Honorary Associate Professor Hugh Saddler Monday 27th March, 12.15-1.45pm With power outages across various Australian states and
Climate Café: Why is Australia's electricity system in such a mess? With Honorary Associate Professor Hugh Saddler Monday 27th March, 12.15-1.45pm With power outages across various Australian states and
Providing a comprehensive, up-to-date indication of key greenhouse gas and energy trends in Australia. National Energy Emissions Audit June 2017
 National Energy Emissions Audit June 217 Providing a comprehensive, up-to-date indication of key greenhouse gas and energy trends in Australia Hugh Saddler Introduction Welcome to the first issue of the
National Energy Emissions Audit June 217 Providing a comprehensive, up-to-date indication of key greenhouse gas and energy trends in Australia Hugh Saddler Introduction Welcome to the first issue of the
2017 POLICY DOCUMENT. Powering Queensland s Future: Affordable, Stable and Balanced. Putting Queenslanders First
 2017 POLICY DOCUMENT Powering Queensland s Future: Affordable, Stable and Balanced Putting 2 Powering Queensland s Future: Affordable, Stable and Balanced Contents Message from the Premier 3 Our Commitment
2017 POLICY DOCUMENT Powering Queensland s Future: Affordable, Stable and Balanced Putting 2 Powering Queensland s Future: Affordable, Stable and Balanced Contents Message from the Premier 3 Our Commitment
Solar Power Realities
 Solar Power Realities Supply-Demand Characteristics, Storage and Capital Costs by Peter Lang Abstract This paper provides a simple analysis of the capital cost of solar power and energy storage sufficient
Solar Power Realities Supply-Demand Characteristics, Storage and Capital Costs by Peter Lang Abstract This paper provides a simple analysis of the capital cost of solar power and energy storage sufficient
Renewable Energy A Game Changer. Ross Garnaut President, SIMEC ZEN Energy Professor of Economics, University of Melbourne
 Renewable Energy A Game Changer Ross Garnaut President, SIMEC ZEN Energy Professor of Economics, University of Melbourne CLIMATE AND ENERGY POLICY AFTER THE NEG 2 THREE ESSENTIAL OBJECTIVES: v Emissions
Renewable Energy A Game Changer Ross Garnaut President, SIMEC ZEN Energy Professor of Economics, University of Melbourne CLIMATE AND ENERGY POLICY AFTER THE NEG 2 THREE ESSENTIAL OBJECTIVES: v Emissions
The Energy Trilemma: A cost curve for emissions reductions & energy storage in the Australian electricity sector
 MARKET STUDY March 2017 The Energy Trilemma: A cost curve for emissions reductions & energy storage in the Australian electricity sector SUMMARY REPORT Marginal Abatement Cost (MAC) curve & Storage technology
MARKET STUDY March 2017 The Energy Trilemma: A cost curve for emissions reductions & energy storage in the Australian electricity sector SUMMARY REPORT Marginal Abatement Cost (MAC) curve & Storage technology
Submission to Independent Expert Panel on Interim Targets. May 2018
 Submission to Independent Expert Panel on Interim Targets May 2018 Summary The Victorian Climate Change Act (2017) was an important step forward in re-establishing the state as a climate change leader.
Submission to Independent Expert Panel on Interim Targets May 2018 Summary The Victorian Climate Change Act (2017) was an important step forward in re-establishing the state as a climate change leader.
Possible Australian perspectives for the EU electricity market in 2025
 Possible Australian perspectives for the EU electricity market in 2025 Iain MacGill Associate Professor, School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications Joint Director (Engineering), CEEM UNSW
Possible Australian perspectives for the EU electricity market in 2025 Iain MacGill Associate Professor, School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications Joint Director (Engineering), CEEM UNSW
Factors Affecting CO 2 Emission Intensity of Power Sector in Australia
 Factors Affecting CO 2 Emission Intensity of Power Sector in Australia Marjan Nazifi Faculty of Business and Economics Macquarie University The 41 st IAEE International Conference Transforming Energy Markets
Factors Affecting CO 2 Emission Intensity of Power Sector in Australia Marjan Nazifi Faculty of Business and Economics Macquarie University The 41 st IAEE International Conference Transforming Energy Markets
VALUING ROOFTOP SOLAR
 INTRODUCTION NET ENERGY METERING VALUING ROOFTOP SOLAR ALTERNATIVES TO NEM 1 INTRODUCTION TURN DISTRIBUTED GENERATION 2 TURN A Consumer Advocacy Organization Fighting for Small Ratepayers since 1973 Founded
INTRODUCTION NET ENERGY METERING VALUING ROOFTOP SOLAR ALTERNATIVES TO NEM 1 INTRODUCTION TURN DISTRIBUTED GENERATION 2 TURN A Consumer Advocacy Organization Fighting for Small Ratepayers since 1973 Founded
Causes of residential electricity bill changes in Victoria, 1995 to prepared for: Victorian Electricity Distribution Businesses
 Causes of residential electricity bill changes in Victoria, 1995 to 2017 prepared for: Victorian Electricity Distribution Businesses DISCLAIMER This report has been prepared for the Victorian Electricity
Causes of residential electricity bill changes in Victoria, 1995 to 2017 prepared for: Victorian Electricity Distribution Businesses DISCLAIMER This report has been prepared for the Victorian Electricity
Minimum electricity feed-in tariffs to apply from 1 July 2018 draft decision
 26 January 2018 By email: fitreview@esc.vic.gov.au Energy Division Essential Services Commission Victoria Level 37, 2 Lonsdale Street Melbourne Victoria 3000 Dear Commission, Minimum electricity feed-in
26 January 2018 By email: fitreview@esc.vic.gov.au Energy Division Essential Services Commission Victoria Level 37, 2 Lonsdale Street Melbourne Victoria 3000 Dear Commission, Minimum electricity feed-in
FULLY CHARGED: RENEWABLES AND STORAGE POWERING AUSTRALIA
 FULLY CHARGED: RENEWABLES AND STORAGE POWERING AUSTRALIA CLIMATECOUNCIL.ORG.AU Thank you for supporting the Climate Council. The Climate Council is an independent, crowd-funded organisation providing quality
FULLY CHARGED: RENEWABLES AND STORAGE POWERING AUSTRALIA CLIMATECOUNCIL.ORG.AU Thank you for supporting the Climate Council. The Climate Council is an independent, crowd-funded organisation providing quality
100% Renewables for Australia?
 100% Renewables for Australia? Challenges and Opportunities Dr Jenny Riesz AEMC 8 th October 2014 Who am I? Overview 100% renewables worth thinking about? 100% renewables technically feasible? 100% renewables
100% Renewables for Australia? Challenges and Opportunities Dr Jenny Riesz AEMC 8 th October 2014 Who am I? Overview 100% renewables worth thinking about? 100% renewables technically feasible? 100% renewables
Renewable Energy: Policy options & integration issues
 Renewable Energy: Policy options & integration issues CEEM 2007 Outline Sustainability context Renewable energy generation: status & costs Renewable energy policy options Integration into competitive electricity
Renewable Energy: Policy options & integration issues CEEM 2007 Outline Sustainability context Renewable energy generation: status & costs Renewable energy policy options Integration into competitive electricity
Answers. Earth s Resources. Year 7 Science Chapter 6
 Answers Earth s Resources Year 7 Science Chapter 6 p132 1 Five of Earth s resources that are vital for human survival: Water, air, plants, animals, salt, soil. 2 Ten of Earth s resources that, while not
Answers Earth s Resources Year 7 Science Chapter 6 p132 1 Five of Earth s resources that are vital for human survival: Water, air, plants, animals, salt, soil. 2 Ten of Earth s resources that, while not
ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE CONSTRUCTION
 ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE CONSTRUCTION Teachers Notes & Worksheets Teachers notes also Available on the DVD As either Word or PDF file Permission is granted for Students to use Teachers Notes And worksheets
ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE CONSTRUCTION Teachers Notes & Worksheets Teachers notes also Available on the DVD As either Word or PDF file Permission is granted for Students to use Teachers Notes And worksheets
The Contribution of Nuclear to a Reliable, Affordable and Low-Emissions Energy Future for Australia
 Governor Macquarie Tower Level 23, 1 Farrer Place Sydney NSW 2000 ABN: 88 160 242 428 The Contribution of Nuclear to a Reliable, Affordable and Low-Emissions Energy Future for Australia A Submission to
Governor Macquarie Tower Level 23, 1 Farrer Place Sydney NSW 2000 ABN: 88 160 242 428 The Contribution of Nuclear to a Reliable, Affordable and Low-Emissions Energy Future for Australia A Submission to
ERCOT in 2018: Challenges & Opportunities
 ERCOT in 2018: Challenges & Opportunities Bill Magness President & CEO ERCOT Texas-Germany Bilateral Dialogue on Challenges and Opportunities in the Electricity Market February 27, 2108 What is ERCOT?
ERCOT in 2018: Challenges & Opportunities Bill Magness President & CEO ERCOT Texas-Germany Bilateral Dialogue on Challenges and Opportunities in the Electricity Market February 27, 2108 What is ERCOT?
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): ENERGY
 Country Partnership Strategy: Philippines, 2011 2016 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): ENERGY 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Challenges. Economic growth has been impeded in the Philippines
Country Partnership Strategy: Philippines, 2011 2016 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): ENERGY 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Challenges. Economic growth has been impeded in the Philippines
SOLARISE NEW ZEALAND
 SOLARISE NEW ZEALAND A plan to install solar and batteries in half a million homes over the next ten years Phil Crawford / Greenpeace SOLARISE NEW ZEALAND 1 AN AMBITIOUS PLAN WHY IT S TIME TO SEIZE THE
SOLARISE NEW ZEALAND A plan to install solar and batteries in half a million homes over the next ten years Phil Crawford / Greenpeace SOLARISE NEW ZEALAND 1 AN AMBITIOUS PLAN WHY IT S TIME TO SEIZE THE
