Water Resources in Spain. The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer Project and the "Programa Agua".
|
|
|
- Ross Bishop
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hydrology Days 2005 Water Resources in Spain. The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer Project and the "Programa Agua". Roberto Arranz 1 MS Graduate Student. Water Resources Planning and Management Division, Civil Engineering Department, Colorado State University, Fort Collins Abstract. The objective of this paper is to offer a "big picture" of water resources in Spain (including general information about the geography, hydrography, climatology, and hydrology), give a brief description of issues such as water use, legislation, and water institutions, and present the two main alternatives being considered to solve the water scarcity problems existing in the Spanish Mediterranean area: the Ebro River Interbasin Transfer Project, based on the diversion of excess water from the Ebro River Basin to the rest of the Mediterranean basins, and the "Programa Agua," based on the reuse of water, seawater desalination, and institutional reforms. The first alternative was planned and was being constructed by the Popular Party administration, but was abandoned after the political turnover of Since the presidential elections of March 2004, the new government has proposed the "Programa Agua". 1. Introduction Due to the climatologic, hydrologic, and geographic characteristics of Spain, the country can utilize only 8% of its natural water resources without the assistance of storage and diversion facilities (El libro blanco del agua en España, 1998). However, with the help of such facilities, including more than 1,200 large dams, Spain is able to use 40% of its water resources. This contrasts with the situation in most European countries, which are able to use an average of 40% of their water resources without any regulation facilities. With the exception of some major cities, Spain's population is concentrated along the coasts. The Mediterranean coast, in particular, attracts Spaniards and millions of foreigners, who wish to live near or visit the sunny beaches. The country's most productive farmland is also located in this Mediterranean area. However, the region has the country's lowest rate of rainfall (~300 mm/year). Most of this precipitation occurs during late summer storms, which cause floods and damage crops. In the Jucar and Segura basins nearly 90% of the water resources are already regulated (Plan hidrológico nacional, 2000). As a result of this situation, water resources are in serious danger. Aquifer depletion, dried wetlands, farmland salinization, insufficient water in rivers to support wildlife, saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers, and point and non-point pollution of surface and groundwater resources are some of the 1 Graduate Research Assistant Integrated Decision Support Group Civil Engineering Department Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO Tel: (970) roberto.arranz@colostate.edu Hydrology Days 43
2 Arranz, Roberto main problems facing this region. Conflicts among users, ecologists, politicians, power groups, speculators and different agencies involved in water planning and management are reported regularly in the media. To solve Spain's water-related problems, the central government along with the River Basin Authorities (the most important water management agencies in Spain) developed 14 river basin plans, or Planes Hidrologicos de Cuenca (PHCs), and a nationwide plan, the Plan Hidrologico Nacional (PHN). As part of the central government's efforts, water resources were evaluated (surface and groundwater, quality and quantity), current and future demands were estimated, and a balance was done. Structural and nonstructural measures were planned to address the water issues. The cornerstone of the PHN was the Ebro River Interbasin Transfer Project. However, the presidential elections of March 2004 resulted in the development of a different plan for water resources, the "Programa Agua." The main components of the "Programa Agua" include desalination, reuse, and institutional and legal reforms. 2. Water Resources in Spain. The general picture 2.1 Geographical situation of Spain Spain is located in the southwest corner of Europe. Spain is bordered on the north by the Cantabric Sea and France, on the west by the Atlantic Ocean and Portugal, on the east by the Mediterranean Sea, and on the south by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Morocco is a close African neighbor to Spain, just 12 km away across the Strait of Gibraltar. The total surface area of Spain is approximately 505,988 km2, having a north-south length of about 700 km and an east-west length from 650 to 1000 km (south and north sides respectively). Spain has got more than 3,500 km of coastline. Spain's geographical location along with the complexity of its orography strongly impacts the country's climate and the availability of water resources. 2.2 Spanish socio-economy and water use Around 40 million people live in Spain, and 90% of this population lives in 30% of the country. More than 43% of the population lives in cities of more than 100,000 people. Most of the population is concentrated in the coastal areas and in some major cities in the interior (Madrid, Zaragoza, Valladolid, and Sevilla). In the future it is expected that Spain's population will not grow but will become even more concentrated in urban areas and that there will be more migration to the coasts, mainly to the Mediterranean area. This situation has consequences for water resources. Although the total demand for water is not expected to increase, the pattern of population migration will impact water resources. The population is moving from areas with abundant water to places where water is scarce and of worse quality. Tourists also impact Spain's water resources. Each year more than 40 million foreign tourists visit Spain, often staying in the Mediterranean area and the Balear and Canary Islands. Over half of the foreign tourists visit during the summer and stay for an average of 12 days. The distribution of the interior tourism (Spanish tourists in Spain) is approximately the same. The absolute 44
3 Water Resources in Spain: The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer and the Programa Agua value of the water demand generated by the tourists is not relevant; it can be evaluated as a 10% increase in the total population of Spain, or ~4,000,000 people. The problem lies in the seasonality of these demands, which can cause guaranty problems in the water supply and can limit the development of certain areas ((El libro blanco del agua en España, 1998). Irrigation is the main consumptive use of water in Spain (~80% of the total consumptive uses and 68% of the total uses, consumptive or not. However, due to its complex orography, Spain has only got a small proportion of its territory (~20% of the total surface) below an altitude of 300 m, an altitude where the climatologic conditions are better for irrigated agriculture and the highest productivity is achieved. 50% of Spain's irrigated areas are located in these limited low altitude regions, mainly in the Mediterranean area and the lower Ebro and Guadalquivir River valleys). At the beginning of the 20th century, more than 65% of Spain's active population worked in the agricultural sector. Now, less than 10% of the active population works in agriculture (El libro blanco del agua en España, 1998). Spanish agriculture is heavily subsidized by the European Union. Subsidies account for approximately 30% of the income of Spanish farmers. Yet the intensive and irrigated agriculture developed in the Mediterranean area (called "Seas of Plastic" because of the greenhouses) is one of the most profitable agricultures in Europe, obtaining three crops of vegetables and other high value products yearly. An indication of how profitable this agriculture can be is that on their own initiative Water User Associations (WUA) are starting to build desalination plants to obtain water for their drip irrigation systems. 1 m3 of this water costs about $0.80. (Torres, 2004). More than 73% of industrial activities are located in 4 principal regions: the Mediterranean area, from Gerona to Murcia (~38%); Madrid (~13.5%); the Northern area, from Asturias to the Basque Country (12.5%); and the Ebro River Valley (8.5%). Electric energy production is a non-consumptive use of water. The water is used for hydropower or to cool thermal power plants. In the 1960s, more than 70% of Spain's electric energy was from hydropower. Now, due to the development of nuclear and fuel powered plants, only 15 to 25% of Spain's energy is derived from hydropower. Electric energy now makes up only 18% of the total energy used in Spain. The Atlantic (Duero, Tajo), Cantabric (North), and Ebro river basins are the most important producers of hydropower (El libro blanco del agua en España, 1998). In summary, the Mediterranean area has high population density (permanent residents and tourists), a high level of industrial development, and intensive irrigated agriculture, but the region does not have abundant water resources. 2.3 Orography and hydrography of Spain There are several mountain systems in Spain that shape the river basins and determine climatic conditions (Figure 1). The Cordillera Cantabrica starts in Galicia on the northwest border of Spain and ends in the Basque Country in north-central Spain. It is located between the Cantabric Sea and the North Meseta. The short, steep and wet North river basins emerge from the north face of 45
4 Arranz, Roberto the mountain range while the big basins of the Duero (west) and Ebro (east) flow from its south face. These mountains are a natural obstacle for the wet winds coming from the north (Cantabric Sea). Rainfall occurs at a high rate throughout the year. The Pyrenees, located in the northeast, constitute the natural frontier between Spain and France. The Spanish side of the Pyrenees is the dry south side. Winds blowing from the north are retained on the French side of the Pyrenees where they produce rain. In Spain, there are several deserts south of the Pyrenees, while other parts of the country at the same latitude are wet. Most of the rivers that originate in the Spanish Pyrenees are tributaries of the Ebro River. Spain's most important hydropower facilities are located in the Pyrenees. The Sistema Central divides the North and South Mesetas (~600 to 1000 m height and flat lands) and the Duero and Tajo river basins. The Sistema Iberico divides the Ebro (northeast), Duero (west), Tajo (southwest) and Jucar (east) river basins. The Montes de Toledo divide the Tajo and Guadiana river basins. The Sierra Morena divides the Guadiana (north-west) and Guadalquivir (southeast) river basins. The Sistema Betico, home to the Iberian Peninsula's highest mountain, Mulhacen Peak (~3,450 m), divides the Guadalquivir (west), Segura (east) and the South (short, steep and extremely dry) river basins. Most of Spain's rivers drain towards the Atlantic Ocean. The exception is the Ebro River Basin, Spain's largest river basin in terms of surface and water resources, which drains to the Mediterranean Sea. NORTE R.B. CORDILLERA CANTABRICA PYRENEES SISTEMA CENTRAL DUERO R.B. MONTES DE TOLEDO TAJO R.B. NORTH MESETA SOUTH MESETA INTERNAS DE CATA- EBRO LOW- LUNA R.B. LANDS EBRO R.B. JUCAR R.B. SISTEMA IBERICO SIERRA GUADIANA R.B. GUADALQUIVIR R.B. GUADALQUIVIR LOWLANDS SUR R.B. SEGURA R.B. SISTEMA Figure 1. General orography and hydrology of Spain 46
5 Water Resources in Spain: The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer and the Programa Agua 2.4 Climatology and hydrology of Spain Due to its geographic location between two huge bodies of water (the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea) and two continents (Europe and Africa), Spain has a diverse climate. Figure 2 shows that there is a gradient of "dryness" from the northwest (wettest) to the southeast (driest). There are 5 different climates in Spain. In the north of Spain (from Galicia to the Catalan Pyrenees) there is a Wet Oceanic climate, characterized by cool temperatures and precipitation of around 1000 mm/year, with maximum precipitation in winter and minimum precipitation in summer. In the center of Spain (the two mesetas) and the Ebro Valley there is a Continental Mediterranean climate, characterized by cold winters, hot and dry summers, and precipitation of 600 mm/year. In this area it usually rains torrentially a few days a year. In the north half of the Mediterranean area (from Gerona to Alicante), there is a Coastal Mediterranean climate, characterized by 700 mm/ year precipitation (mainly torrential rains in spring and autumn), dry winters and summers, and constant hot temperatures (no freezing period). In the southern half of the Mediterranean area (from Murcia to Almeria), there is a Dry Subtropical climate, characterized by low and irregular precipitations of less than 300 mm/year and high temperatures year-round. In southwestern Spain (western Andalucia) there is a Southwest Mediterranean climate, influenced by the cool and wet Atlantic winds. It is characterized by precipitations of 800mm/year (mainly in the spring and autumn), cool and dry winters, and comfortable summers. Figure 2. Mean yearly precipitation (darkest color about 1000 mm and clearest color about 300 mm) 47
6 Arranz, Roberto Without storage and regulation infrastructures, Spain could only use 8% of its water resources versus the 40% available in the rest of Europe with the same conditions. Thanks to more than 1,200 large dams Spain can regulate nearly 40% of its resources. In some areas like the Segura and Sur Basins, 80-90% of water resources are being regulated. 2.5 Water planning and management In Spain, water is not privately owned. According to the 1985 Water Law, the Hydraulic Public Domain (surface, groundwater and atmospheric water and their territory: lakes, wetlands, aquifers, etc.) belongs to the nation. Water use permits (concessions) and pollution permits are issued by the River Basin Authorities. Currently there are more than 500,000 "intakes." Only half of these intakes are declared and less than a quarter are registered (El libro blanco del agua en España, 1998). Water has been managed by River Basin Authorities since the 1920's. Figure 3 shows the 14 administrative divisions and 14 River Basin Authorities. Although there are other federal, state and local institutions with competences in water, the River Basin Authorities (Confederaciones Hidrograficas) are the most important institutions for water planning and management in Spain. Some of their most important functions of the River Basin Authorities are: - Administration and control of the "hydraulic public domain". - Administration of concessions and permits. - Planning, construction and management of their own and nationally owned water systems. - Elaboration of the Basin Scale Framework Plans. Figure 3. River Basin Authorities (Confederaciones Hidrograficas) 48
7 Water Resources in Spain: The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer and the Programa Agua The basins shared between Spain and Portugal represent 41% of Spain's and 72% of Portugal's total surface water resources. The total resources available in these shared basins amount to 60,000 hm3, two-thirds of which is produced in Spain. The most important rivers shared are the: Mino/Minho, Limia/Lima, Duero/Douro, Tajo/Tejo and Guadiana). The first agreements between Spain and Portugal for the management of these rivers were signed in 1964 and 1968 and were only used to distribute hydropower production. In 1998 an agreement was reached for the integral and sustainable use of the shared water resources (El libro blanco del agua en España, 1998). 2.6 Water law The first Spanish Water Law was passed in the late 1870's. The 1879 Water Law was in use until Increasing problems with water quality and quantity, social conflicts, and resource degradation made it necessary to update and elaborate on the old water law. Among other important provisions, the 1985 water law stated the necessity of developing basin scale framework plans (14 plans for the 14 basins, called the Planes Hidrologicos de Cuenca) to evaluate the quantity and quality of water resources and current and future water demands as well as to plan the necessary actuations (structural and nonstructural) to achieve a sustainable use of the water resources. Also the law authorized the development of a nationwide framework plan to address issues concerning two of more river basin authorities. 2.7 Findings of the Mediterranean Basins Framework Plans (Planes Hidrologicos de las Cuencas Mediterraneas) These basin framework plans for the Mediterranean area have determined that there are structural deficits in some of the basins (Segura and Sur for example). A deficit is called structural when the natural resources are less than the demands, so these demands cannot be satisfied with only intra-basin resources. In these areas the current use of water is not sustainable. Aquifers are being overdrawn resulting in seawater intrusion problems in the coastal aquifers, surface water is over-regulated and the natural systems are degraded so that some streams and rivers only convey sewage. The national framework plan, the Plan Hidrologico Nacional, proposed an interbasin transfer project from the Ebro River to the other mediterrranean basins (Internas de Cataluna, Sucar, Segura and Sur) in order to solve the structural deficits mentioned above (Plan hidrológico nacional, 2000). 3. The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer Project 3.1 Technical characteristics The Ebro River ITB project is basically a water diversion project designed to transfer 1050 hm3 yearly from the Ebro River to the other Mediterranean basins (Internas de Cataluna, Jucar, Segura and Sur Basins). It is composed of 49
8 Arranz, Roberto two main transmission lines (north and south), with pumping intakes placed a few kilometers upstream from the Ebro River Delta. The north line (168 km long and 11m3/s of capacity) is a closed conduit that diverts 190 hm3 yearly towards the basins of Cataluna, which primarily serve the metropolitan area of Barcelona. Water must be pumped about 250 m. The south line (746 km long and 50 m3/s of capacity) is an open canal that diverts 860 hm3 yearly towards the Jucar, Segura and Sur basins. Water must be pumped about 750 m, and about 450 m of hydropower can be produced. An intermediate reservoir has been planned for this south line. The projected capital cost of this infrastructure is ~4.2 billion euros and the project will be managed by a public agency called TRASAGUA (Plan hidrológico nacional, 2000). Figure 4. North and South branches of the Ebro River IBT Project 3.2 Philosophy of the Project The philosophy behind this project is that only excess water will be transferred. The current and future water rights of the donor basin and its environment will have priority. The water systems in the donor basin (more that 60 reservoirs) won't be affected and the water users in the donor basin won't notice the operation of this project. Only the operation of two hydropower reservoirs a few kilometers upstream of the intakes will be slightly modified, because only excess water will be diverted a few kilometers before it enters the Mediterranean Sea in the Ebro River Delta. The ecologic effects of the project in the Ebro River Delta have been addressed and a minimum flow requirement downstream of the project's intakes has been established to prevent the intrusion of sea water in the Delta (Horne et al, 2003). The water diverted will only be used to satisfy currently existing demands ensuring that the overdrawn aquifers and surface resources will be used in a sustainable way and never will 50
9 Water Resources in Spain: The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer and the Programa Agua be used to satisfy demands due to new irrigated agriculture or land development. Since its conception, this project has been very controversial. Communities in the donor basin (Ebro Basin) objected to the project while communities in the other Mediterranean basins strongly supported it. Furthermore, politicians and the scientific community didn't agree on the effectiveness and the social, economic and environmental impacts of the project. Despite the fact the Mediterranean states governed by the Socialist party strongly supported the project, the Socialist Party promised to abandon the project if they won the presidential elections. 3.3 Political turnover, March 2004 By the beginning of March 2004, construction had been started on the Ebro River Interbasin Transfer Project (Santos, 2004). At great expense, most of the detailed designs for the infrastructure had been done by engineering firms. The contracts for pipe and valve supplies were scheduled to be signed within a few weeks. The general elections were coming and the conservative ruling Popular Party government wanted to show its position. The future of water had been one of the cornerstone issues of the election. On March 14, 2004 the Socialist Party won the presidential elections. A few days later, the new president, Rodriguez Zapatero, announced that the Ebro River IBT project was going to be abandoned. Soon thereafter Zapatero presented an alternative called the "Programa AGUA". 4. The alternative: the "Programa Agua" The "Programa AGUA " is the alternative to the Ebro River IBT presented by the Socialist Party government. It is intended to solve the water scarcity problem in the Mediterranean area and create institutional and legal reforms that are applicable to the whole country. Instead of diverting water from the Ebro River, the program advocates water reuse and seawater desalination. The main proposals of the "Programa AGUA" are: Reform of the river basin authorities ("Confederaciones Hidrograficas") to promote autonomous government and public participation. Water banks will be created in every river basin to promote the equitable, sustainable, and efficient reassignment of water rights. Water charges will reflect the real cost of providing the service, according to the European Framework Law. No subsidies will be allowed. Rather than developing conventional sources, reuse and desalination of water will be promoted to solve existing problems. The specific problem addressed by the Ebro River IBT will be solved with a series of more than 100 actions (mainly WWTP improvement to promote the reuse and seawater desalination, see figure 5). The estimated cost of these actuations is about 3.9 billion euros. 51
10 Arranz, Roberto Figure 5. The Programa Agua proposed to substitute the Ebro River IBT Project 5. Conclusions In Spain, political parties have determined the course of nationwide water planning. The pros and cons of the Ebro River IBT and the "Programa Agua" have been frequently exaggerated by politicians, decision makers and other stakeholders depending on their own interests or political affiliations. 52
11 Water Resources in Spain: The Ebro River Interbasin Transfer and the Programa Agua References Horne, A. J., Dracup, J., Hanemann, M., Rodriguez-Iturbe, I., Means, E. and Roth, J.C., 2003: A technical review of the Spanish Hydrological Plan (Ebro River outof-basin diversion). Unpublished manuscript. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid, 1998: El libro blanco del agua en España. (Spanish Ministry of Environment, 1998: The white book of water in Spain). Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid, 2000: Plan hidrológico nacional (PHN). Volúmenes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. (Spanish Ministry of Environment, 2000: National hydrological plan, Volumes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5). Santos, R. Revista Ambienta. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Marzo-Abril 2004: Comienzan las obras. (Santos, R. Ambienta Magazine. Spanish Ministry of Environment, March-April 2004: Comienan las obras) Torres, M. Revista Ambienta. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Julio-Agosto 2004: La desalacion de agua de mar y el vertido de la salmuera. (Torres, M.Ambienta Magazine. Spanish Ministry of Environment, July-August 2004: La desalacion de agua de mar y el vertido de la salmuera). Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, 2004: pagina web del Programa Agua. (Spanish Ministry of Environment, 2004: website of the "Programa Agua") 53
INTERNATIONAL NETWORKS of BASIN ORGANIZATIONS Debrecen (Hungary) June 2007
 INTERNATIONAL NETWORKS of BASIN ORGANIZATIONS Debrecen (Hungary) June 2007 Flood Management in Spain: case of Tagus River Justo Mora A.-Muñoyerro Tagus River Basin Authority Spanish Ministry of Environment
INTERNATIONAL NETWORKS of BASIN ORGANIZATIONS Debrecen (Hungary) June 2007 Flood Management in Spain: case of Tagus River Justo Mora A.-Muñoyerro Tagus River Basin Authority Spanish Ministry of Environment
Water Governance in Spain and Risk Management.
 WORLD BANK Workshop on water security Sofia, Bulgaria 18 th -19 th September 2017 Water Governance in Spain and Risk Management. José-Ángel Rodríguez-Cabellos Head of the Planning Office Guadiana River
WORLD BANK Workshop on water security Sofia, Bulgaria 18 th -19 th September 2017 Water Governance in Spain and Risk Management. José-Ángel Rodríguez-Cabellos Head of the Planning Office Guadiana River
The case of the Guadalquivir River Basin in Spain
 Victor Juan Cifuentes Sanchez. Head of Hydrological Planning Office Guadalquivir River Basin Authority (CHG) Roma, 23/10/2017 Great Rivers of the world International Summit The case of the Guadalquivir
Victor Juan Cifuentes Sanchez. Head of Hydrological Planning Office Guadalquivir River Basin Authority (CHG) Roma, 23/10/2017 Great Rivers of the world International Summit The case of the Guadalquivir
Leading Issues in Water Supply Sustainability in Catalonia (NE Spain)
 Leading Issues in Water Supply Sustainability in Catalonia (NE Spain) Lluís Sala Consorci Costa Brava (Girona, Spain) lsala@ccbgi.org Meeting Centre for Integrated Water Research - Prince Khaled Chair
Leading Issues in Water Supply Sustainability in Catalonia (NE Spain) Lluís Sala Consorci Costa Brava (Girona, Spain) lsala@ccbgi.org Meeting Centre for Integrated Water Research - Prince Khaled Chair
An overview of the main water conflicts in Spain: Proposals for problem-solving
 An overview of the main water conflicts in Spain: Proposals for problem-solving Lucila Candela 1, Francisco Domingo 2, Julio Berbel 3 and Juan José Alarcón 4 1 Dep. of Geotechnical Engineering and Geoscience-UPC.
An overview of the main water conflicts in Spain: Proposals for problem-solving Lucila Candela 1, Francisco Domingo 2, Julio Berbel 3 and Juan José Alarcón 4 1 Dep. of Geotechnical Engineering and Geoscience-UPC.
Case Study for the 2006 HDR WATER TRANSFER FROM THE EBRO RIVER
 Case Study for the 2006 HDR WATER TRANSFER FROM THE EBRO RIVER Cecilia Tortajada 1 Vice President Third World Centre for Water Management Atizapán, Mexico ctortajada@thirdworldcentre.org The transfer of
Case Study for the 2006 HDR WATER TRANSFER FROM THE EBRO RIVER Cecilia Tortajada 1 Vice President Third World Centre for Water Management Atizapán, Mexico ctortajada@thirdworldcentre.org The transfer of
U.S. Water Budget. Figure Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources , Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council.
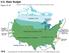 U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
Climate Change Adaptation in Europe and Spain. Cities.
 Climate Change Adaptation in Europe and Spain. Cities. Overview Introduction City Adaptation in Europe City Adaptation in Spain Barcelona Madrid Final reflections Overview Introduction City Adaptation
Climate Change Adaptation in Europe and Spain. Cities. Overview Introduction City Adaptation in Europe City Adaptation in Spain Barcelona Madrid Final reflections Overview Introduction City Adaptation
Definition of environmental objectives in relation with nitrate pollution in the aquifers of Spain. Simulation model and scenarios used.
 International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive 6th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software - Leipzig, Germany - July
International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive 6th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software - Leipzig, Germany - July
Techneau March Spain, a TECHNEAU case study - phase 1 Climate Change
 Techneau March 2007 Spain, a TECHNEAU case study - phase 1 Climate Change Techneau March 2007 Spain, a TECHNEAU case study - phase 1 Climate Change 2007 TECHNEAU TECHNEAU is an Integrated Project Funded
Techneau March 2007 Spain, a TECHNEAU case study - phase 1 Climate Change Techneau March 2007 Spain, a TECHNEAU case study - phase 1 Climate Change 2007 TECHNEAU TECHNEAU is an Integrated Project Funded
Kos,, 6 th September 2007 WATER AGENDA (LIFE04/ENV/GR/000099) EURO-MEDITERRANEAN COOPERATION NETWORK
 Kos,, 6 th September 2007 Sustainable Water Management in Spain: steps forward to implement WFD in Catalonia Xavier Cazorla i Clarisó Environmental Science and Technology Institute (ICTA-UAB) Autonomous
Kos,, 6 th September 2007 Sustainable Water Management in Spain: steps forward to implement WFD in Catalonia Xavier Cazorla i Clarisó Environmental Science and Technology Institute (ICTA-UAB) Autonomous
Water Management in Spain: An example of changing paradigms. Alberto Garrido Associate Professor, Technical University of Madrid
 Spain: An example of Alberto Garrido Associate Professor, Technical University of Madrid M.Ramón Llamas Emeritus Professor, Complutense University Paper presented at the Engelberg Academy Conference on
Spain: An example of Alberto Garrido Associate Professor, Technical University of Madrid M.Ramón Llamas Emeritus Professor, Complutense University Paper presented at the Engelberg Academy Conference on
water resources action project, inc.
 water resources action project, inc. www.wrapdc.org A Comparative Study of Water Data Across Israel, West Bank, and Jordan Water Resources Action Project (WRAP) December 2013 Introduction Water is necessary
water resources action project, inc. www.wrapdc.org A Comparative Study of Water Data Across Israel, West Bank, and Jordan Water Resources Action Project (WRAP) December 2013 Introduction Water is necessary
DECLARATION OF MALTA
 DECLARATION OF MALTA 11 th GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF THE MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANISATIONS 22 nd -24 th March 2017 St. Julians, Malta PERMANENT TECHNICAL SECRETARIAT MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN
DECLARATION OF MALTA 11 th GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF THE MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANISATIONS 22 nd -24 th March 2017 St. Julians, Malta PERMANENT TECHNICAL SECRETARIAT MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN
Climate and Biodiversity
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
Water Account, Mauritius 2013
 Republic of Mauritius Water Account, Mauritius 2013 Statistics Mauritius, Ministry of Finance and Economic Development June 15 Contents Foreword... III List of Symbols and Abbreviations... IV 1. Introduction...
Republic of Mauritius Water Account, Mauritius 2013 Statistics Mauritius, Ministry of Finance and Economic Development June 15 Contents Foreword... III List of Symbols and Abbreviations... IV 1. Introduction...
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet, 8th Edition APES- Chapter #18- Water Supply, Use and Management.
 Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet, 8th Edition APES- Chapter #18- Water Supply, Use and Management Name: Learning Objectives: At the end of this chapter, students will understand:
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet, 8th Edition APES- Chapter #18- Water Supply, Use and Management Name: Learning Objectives: At the end of this chapter, students will understand:
Drought Situations and Management in Vietnam
 Drought Situations and Management in Vietnam Background: In Vietnam, drought is one of the most frequent natural disasters, only after flood and storm, and has been becoming more severe due to the impact
Drought Situations and Management in Vietnam Background: In Vietnam, drought is one of the most frequent natural disasters, only after flood and storm, and has been becoming more severe due to the impact
Public participation in the implementation of the Water framework directive in Spain. Alba Ballester Ciuró February, 19, 2015
 Public participation in the implementation of the Water framework directive in Spain Alba Ballester Ciuró February, 19, 2015 Table of contents 1. Introduction Conceptual framework Institutional framework
Public participation in the implementation of the Water framework directive in Spain Alba Ballester Ciuró February, 19, 2015 Table of contents 1. Introduction Conceptual framework Institutional framework
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS
 WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
EFFECTS OF UPSTREAM HYDROPOWER DAMS AND WATER DIVERSION PROJECTS TO THE DROUGHT AND SALINE INTRUSION OF THE MEKONG RIVER DELTA IN VIETNAM
 EFFECTS OF UPSTREAM HYDROPOWER DAMS AND WATER DIVERSION PROJECTS TO THE DROUGHT AND SALINE INTRUSION OF THE MEKONG RIVER DELTA IN VIETNAM Le Anh Tuan Can Tho Univerity E mail: latuan@ctu.edu.vn The Mekong
EFFECTS OF UPSTREAM HYDROPOWER DAMS AND WATER DIVERSION PROJECTS TO THE DROUGHT AND SALINE INTRUSION OF THE MEKONG RIVER DELTA IN VIETNAM Le Anh Tuan Can Tho Univerity E mail: latuan@ctu.edu.vn The Mekong
Environmental Geography
 Environmental Geography Lecture 13 Water Pollution Lecture 13: Water Pollution I. Water Pollution A. Groundwater B. Surface Water C. Regulation II. Water Use in California 1 I. Water Pollution Types of
Environmental Geography Lecture 13 Water Pollution Lecture 13: Water Pollution I. Water Pollution A. Groundwater B. Surface Water C. Regulation II. Water Use in California 1 I. Water Pollution Types of
DESALINATION: AN ALTERNATIVE TO EBRO WATER TRANSFER?
 27/07/2004 Num. 3 ENVIRONMENT contents DESALINATION: AN ALTERNATIVE TO EBRO WATER TRANSFER? THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF DESALINATION PLANTS. Melchor Senent Alonso DESALINATION: A REAL ALTERNATIVE? Juan
27/07/2004 Num. 3 ENVIRONMENT contents DESALINATION: AN ALTERNATIVE TO EBRO WATER TRANSFER? THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF DESALINATION PLANTS. Melchor Senent Alonso DESALINATION: A REAL ALTERNATIVE? Juan
Climate Change: Background and Implications
 Climate Change: Background and Implications American Public Works Association Conference on Climate Change Tempe, AZ April 9, 2008 Peter Schultz U.S. Climate Change Science Program Office, Director Outline
Climate Change: Background and Implications American Public Works Association Conference on Climate Change Tempe, AZ April 9, 2008 Peter Schultz U.S. Climate Change Science Program Office, Director Outline
27 29 January Washington DC - USA
 27 29 January Washington DC - USA Paper of Mr. Jean - François DONZIER General Manager International Office for Water Permanent Technical Secretary International Network of Basin Organizations If the greenhouse-effect
27 29 January Washington DC - USA Paper of Mr. Jean - François DONZIER General Manager International Office for Water Permanent Technical Secretary International Network of Basin Organizations If the greenhouse-effect
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance
 Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
ASSESSMENT OF SALINITY INTRUSION IN THE RED RIVER UNDER THE EFFECT OF CLIMATE CHANGE
 ASSESSMENT OF SALINITY INTRUSION IN THE RED RIVER UNDER THE EFFECT OF CLIMATE CHANGE Presented by NGUYEN Trung Viet Water Resources University, Vietnam March 2-4, 2011 Introduction Red River System is
ASSESSMENT OF SALINITY INTRUSION IN THE RED RIVER UNDER THE EFFECT OF CLIMATE CHANGE Presented by NGUYEN Trung Viet Water Resources University, Vietnam March 2-4, 2011 Introduction Red River System is
Chapter 2. Site description. 2.1 Installations
 Chapter 2 Site description The Ebro basin stretches from Spain s intermediate mediterranean coast to the north of the Iberian peninsula. Its area occupies approximately 17% of the total of the Iberian
Chapter 2 Site description The Ebro basin stretches from Spain s intermediate mediterranean coast to the north of the Iberian peninsula. Its area occupies approximately 17% of the total of the Iberian
Institutional and Policy Framework Analysis ALGERIA
 INCO-CT-2004-509093 ADU-RES Co-ordination Action for Autonomous Desalination Units based on Renewable Energy Systems Institutional and Policy Framework Analysis ALGERIA WP-7: Institutional & Policy Framework
INCO-CT-2004-509093 ADU-RES Co-ordination Action for Autonomous Desalination Units based on Renewable Energy Systems Institutional and Policy Framework Analysis ALGERIA WP-7: Institutional & Policy Framework
Hydroelectric power. Made by: Kekoa, Sara, Kupaa and Bree
 Hydroelectric power Made by: Kekoa, Sara, Kupaa and Bree How it s produced General: Hydroelectric power creates kinetic energy by using water to turn a propeller turbine which turns a metal shaft in a
Hydroelectric power Made by: Kekoa, Sara, Kupaa and Bree How it s produced General: Hydroelectric power creates kinetic energy by using water to turn a propeller turbine which turns a metal shaft in a
Name Date Class. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia
 For use with textbook pages 463 468. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia Terms to Know arable Suitable for farming (page 464) commodity An economic product (page 465) petrochemical
For use with textbook pages 463 468. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia Terms to Know arable Suitable for farming (page 464) commodity An economic product (page 465) petrochemical
Flood risk management and land use planning in changing climate conditions Mikko Huokuna Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE
 10th International Drainage Workshop of ICID 06.-11. July 2008 Flood risk management and land use planning in changing climate conditions Mikko Huokuna Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE Background hydrological
10th International Drainage Workshop of ICID 06.-11. July 2008 Flood risk management and land use planning in changing climate conditions Mikko Huokuna Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE Background hydrological
MEDITERRANEAN BASINS. JUCAR RIVER BASIN AS A CASE STUDY
 ROLE OF REGIONS/PROVINCES, OTHER LOCAL AUTHORITIES AND WATER STAKEHOLDERS IN RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT MEDITERRANEAN BASINS. JUCAR RIVER BASIN AS A CASE STUDY MENBO Mediterranean Network of Basin Organisations
ROLE OF REGIONS/PROVINCES, OTHER LOCAL AUTHORITIES AND WATER STAKEHOLDERS IN RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT MEDITERRANEAN BASINS. JUCAR RIVER BASIN AS A CASE STUDY MENBO Mediterranean Network of Basin Organisations
WATER MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR RIBEIRAS DO ALGARVE, PORTUGAL
 WATER MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR RIBEIRAS DO ALGARVE, PORTUGAL arid cyprus, conference may 2005 1 ribeiras do algarve river basin area of the basin: 3837 Km 2 18 municipalities more than 350,000 inhabitants
WATER MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR RIBEIRAS DO ALGARVE, PORTUGAL arid cyprus, conference may 2005 1 ribeiras do algarve river basin area of the basin: 3837 Km 2 18 municipalities more than 350,000 inhabitants
Pact of Paris on water and adaptation to climate change in the basins of rivers, lakes and aquifers From COP21 to COP22
 Task Force on Water and Climate, Geneva, September 15th 2016 Pact of Paris on water and adaptation to climate change in the basins of rivers, lakes and aquifers From COP21 to COP22 Eric TARDIEU Deputy
Task Force on Water and Climate, Geneva, September 15th 2016 Pact of Paris on water and adaptation to climate change in the basins of rivers, lakes and aquifers From COP21 to COP22 Eric TARDIEU Deputy
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions
 Intended Nationally Determined Contributions Objective: The State of Kuwait - November 2015 In accordance with Decision 1/CP.19 and based on the information mentioned in decision 1/CP.20 which invites
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions Objective: The State of Kuwait - November 2015 In accordance with Decision 1/CP.19 and based on the information mentioned in decision 1/CP.20 which invites
Thermal Pollution. Thermal Pollution-Niladri Chakrabarty
 Thermal Pollution Thermal Pollution The basic definition of thermal water pollution is the deterioration of water quality as a result of any process that changes ambient water temperature It is usually
Thermal Pollution Thermal Pollution The basic definition of thermal water pollution is the deterioration of water quality as a result of any process that changes ambient water temperature It is usually
Climate change adaptation in China: national policy and regional practice
 Climate change adaptation in China: national policy and regional practice Guihua WANG, Peter HILLS The Kadoorie Institue, The University of Hong Kong Email: samuelwanggh@gmail.com Addressing climate change
Climate change adaptation in China: national policy and regional practice Guihua WANG, Peter HILLS The Kadoorie Institue, The University of Hong Kong Email: samuelwanggh@gmail.com Addressing climate change
Richmond. Social Science PRIMARY
 Richmond Social Science PRIMARY Contents Unit Reading Topics Know how to 1 The Earth 6 The Earth is round The solar system and the Earth The Earth s movements Our planet Earth Interpret diagrams of the
Richmond Social Science PRIMARY Contents Unit Reading Topics Know how to 1 The Earth 6 The Earth is round The solar system and the Earth The Earth s movements Our planet Earth Interpret diagrams of the
Life in Water. Chapter 3
 Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division
 National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
IRAN GEOGRAPHY AND POPULATION
 IRAN GEOGRAPHY AND POPULATION The Islamic Republic of Iran covers a total area of about 1.65 million km² and is bordered by Azerbaijan, Armenia, the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan
IRAN GEOGRAPHY AND POPULATION The Islamic Republic of Iran covers a total area of about 1.65 million km² and is bordered by Azerbaijan, Armenia, the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan
Colorado Basin. Colorado Scheme - Benefits / Problems
 Colorado Basin By the end of this section you should be able to : Describe and explain the benefits and problems of the Colorado scheme. Use a range of resources. Extract information from given resources.
Colorado Basin By the end of this section you should be able to : Describe and explain the benefits and problems of the Colorado scheme. Use a range of resources. Extract information from given resources.
APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran
 APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran Purpose: Conduct research to analyze the effects of water diversions on surrounding ecosystems and human communities. Compare and contrast the problems and successes
APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran Purpose: Conduct research to analyze the effects of water diversions on surrounding ecosystems and human communities. Compare and contrast the problems and successes
Phyto-technology to reduce water pollution and sustain forestry and agroforestryactivities in the South Mediterranean region
 Phyto-technology to reduce water pollution and sustain forestry and agroforestryactivities in the South Mediterranean region Paolo De Angelis DIBAF University of Tuscia Viterbo- Italy PEOPLE INVOLVED Paolo
Phyto-technology to reduce water pollution and sustain forestry and agroforestryactivities in the South Mediterranean region Paolo De Angelis DIBAF University of Tuscia Viterbo- Italy PEOPLE INVOLVED Paolo
Questions and Answers about the Water Supply and Water Quality bond act for the November, 2018 ballot. Updated November 17, 2017
 Questions and Answers about the Water Supply and Water Quality bond act for the November, 2018 ballot. Updated November 17, 2017 What is the need for more State investment in water resources? What is the
Questions and Answers about the Water Supply and Water Quality bond act for the November, 2018 ballot. Updated November 17, 2017 What is the need for more State investment in water resources? What is the
PAKISTAN BALOCHISTAN SMALL SCALE IRRIGATION PROJECT (SSIP) PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB1661 Project Name
 PAKISTAN BALOCHISTAN SMALL SCALE IRRIGATION PROJECT (SSIP) PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB1661 Project Name Balochistan Small Scale Irrigation Project Region SOUTH ASIA
PAKISTAN BALOCHISTAN SMALL SCALE IRRIGATION PROJECT (SSIP) PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB1661 Project Name Balochistan Small Scale Irrigation Project Region SOUTH ASIA
World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013
 World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013 www.smallhydroworld.org SPAIN Disclaimer Published in 2013 by United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and International Center on Small
World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013 www.smallhydroworld.org SPAIN Disclaimer Published in 2013 by United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and International Center on Small
Alternative Futures for the City of La Paz, Mexico
 O N T H E G R O U N D Alternative Futures for the City of La Paz, Mexico Caroline Dragoo University of Arizona and Robert Faris Harvard University La Paz, Mexico is working hard not to turn into Cabo San
O N T H E G R O U N D Alternative Futures for the City of La Paz, Mexico Caroline Dragoo University of Arizona and Robert Faris Harvard University La Paz, Mexico is working hard not to turn into Cabo San
The many faces of the Niger River
 11 The many faces of the Niger River The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa after the Nile and the Congo; it runs for 4,200 km in West Africa. It presents many different faces along its length.
11 The many faces of the Niger River The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa after the Nile and the Congo; it runs for 4,200 km in West Africa. It presents many different faces along its length.
Application of SWAT Model in land-use. change in the Nile River Basin: A Review
 Application of SWAT Model in land-use change in the Nile River Basin: A Review By: Marwa Ali, Okke Batelaan and Willy Bauwens 15-6-2011 Application of SWAT Model in land-use 1 change in the Nile River
Application of SWAT Model in land-use change in the Nile River Basin: A Review By: Marwa Ali, Okke Batelaan and Willy Bauwens 15-6-2011 Application of SWAT Model in land-use 1 change in the Nile River
Integrated Watershed Management Plan
 mighty peace watershed alliance Integrated Plan SUMMARY What is the Plan? The Mighty Peace Alliance (MPWA) supports the three goals of Alberta s Water for Life Strategy: safe secure drinking water, healthy
mighty peace watershed alliance Integrated Plan SUMMARY What is the Plan? The Mighty Peace Alliance (MPWA) supports the three goals of Alberta s Water for Life Strategy: safe secure drinking water, healthy
Sediment management of hydropower cascade: example of CNR run-of-river developments, French Rhone River, France
 Sediment management of hydropower cascade: example of CNR run-of-river developments, French Rhone River, France Christophe PETEUIL Compagnie Nationale du Rhone Engineering Department, River Systems and
Sediment management of hydropower cascade: example of CNR run-of-river developments, French Rhone River, France Christophe PETEUIL Compagnie Nationale du Rhone Engineering Department, River Systems and
Vulnerability of hydrological ecosystem services to climatic extremes in a Mediterranean river basin
 Vulnerability of hydrological ecosystem services to climatic extremes in a Mediterranean river basin Marta Terrado, Vicenç Acuña, Driss Ennaanay, Heather Tallis, Sergi Sabater CLIMATIC EXTREMES AND HYDROLOGICAL
Vulnerability of hydrological ecosystem services to climatic extremes in a Mediterranean river basin Marta Terrado, Vicenç Acuña, Driss Ennaanay, Heather Tallis, Sergi Sabater CLIMATIC EXTREMES AND HYDROLOGICAL
Paper Reference. 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F. Foundation Tier. Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F Foundation Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F Foundation Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
WATER RESOURCES PROBLEMS IN SOUTHERN EUROPE AN OVERVIEW REPORT
 European Topic Centre on Inland Waters WATER RESOURCES PROBLEMS IN SOUTHERN EUROPE AN OVERVIEW REPORT By T.Estrela, C.Marcuello and A.Iglesias August 1996 This report was prepared under the supervision
European Topic Centre on Inland Waters WATER RESOURCES PROBLEMS IN SOUTHERN EUROPE AN OVERVIEW REPORT By T.Estrela, C.Marcuello and A.Iglesias August 1996 This report was prepared under the supervision
Battle for the Biosphere
 Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Environmental science: An interdisciplinary area of study that includes both applied and theoretical aspects of human impact on the world.
 Chapter 1: Environmental Interrelationships THE NATURE OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Environmental science: An interdisciplinary area of study that includes both applied and theoretical aspects of human impact
Chapter 1: Environmental Interrelationships THE NATURE OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Environmental science: An interdisciplinary area of study that includes both applied and theoretical aspects of human impact
Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living
 Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living organisms that inhabit a geographic area and depend on it
Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living organisms that inhabit a geographic area and depend on it
GROUNDWATER AND ECOSYSTEM SERVICE VULNERABILITY AND RESILIENCE
 GROUNDWATER AND ECOSYSTEM SERVICE VULNERABILITY AND RESILIENCE The View from Europe and Spain IWMI Workshop Managing Smallholder Groundwater-dependent Agrarian Socioecologies using an Ecosystem Service
GROUNDWATER AND ECOSYSTEM SERVICE VULNERABILITY AND RESILIENCE The View from Europe and Spain IWMI Workshop Managing Smallholder Groundwater-dependent Agrarian Socioecologies using an Ecosystem Service
The Elbe River Basin: Preliminary evaluation of the answers. Janos J. Bogardi Executive Officer of GWSP
 GWSP-GCI II Workshop on the Water-Energy-Food Security Nexus The Elbe River Basin: Preliminary evaluation of the answers Janos J. Bogardi Executive Officer of GWSP Winnipeg, Canada, 3-4 May 2012 The Elbe
GWSP-GCI II Workshop on the Water-Energy-Food Security Nexus The Elbe River Basin: Preliminary evaluation of the answers Janos J. Bogardi Executive Officer of GWSP Winnipeg, Canada, 3-4 May 2012 The Elbe
BUSINESS PLAN CEN/TC 92 WATER METERS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 Date : 2010-09-06 Page: 1/8 BUSINESS PLAN CEN/TC 92 WATER METERS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Scope Standardization for meters to measure volume flow of cold potable water and heated water enclosed in full conduits,
Date : 2010-09-06 Page: 1/8 BUSINESS PLAN CEN/TC 92 WATER METERS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Scope Standardization for meters to measure volume flow of cold potable water and heated water enclosed in full conduits,
Option 11. Divert Water from Miocene and Hendricks Canal to Supply the Ridge
 Integrated Water Resources Plan Option 11 Divert Water from Miocene and Hendricks Canal to Supply the Ridge This option would use water from the Miocene Canal and/or Hendricks Canal for municipal supplies
Integrated Water Resources Plan Option 11 Divert Water from Miocene and Hendricks Canal to Supply the Ridge This option would use water from the Miocene Canal and/or Hendricks Canal for municipal supplies
Middle East and North Africa
 IWMI Research Middle East and North Africa Groundwater Revitalizing canal irrigation Sustainability of the Nile Delta and its water and salt balances Reusing saline water and restoring salt-affected land
IWMI Research Middle East and North Africa Groundwater Revitalizing canal irrigation Sustainability of the Nile Delta and its water and salt balances Reusing saline water and restoring salt-affected land
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Reservoir Operations Maria Placht, Institute for Water Resources, USACE 49
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Reservoir Operations Maria Placht, Institute for Water Resources, USACE 49 Context The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (the Corps) is responsible for a variety of water resourcerelated
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Reservoir Operations Maria Placht, Institute for Water Resources, USACE 49 Context The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (the Corps) is responsible for a variety of water resourcerelated
Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia
 Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia DIAGNOSTIC PAPER 1 GUILLAUME LACOMBE, PENNAN CHINNASAMY Regional Conference on Risks and Solutions: Adaptation Frameworks
Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia DIAGNOSTIC PAPER 1 GUILLAUME LACOMBE, PENNAN CHINNASAMY Regional Conference on Risks and Solutions: Adaptation Frameworks
EUROPEAN TERRITORIAL COOPERATION. COOPERATION PROGRAMME Interreg VB SOUTHWEST EUROPE
 EUROPEAN TERRITORIAL COOPERATION COOPERATION PROGRAMME Interreg VB SOUTHWEST EUROPE Adopted by EC 18/06/2015 Adopted version 18/06/2015 1 CCI Title 2014TC16RFTN007 Programme Interreg VB Southwest Europe
EUROPEAN TERRITORIAL COOPERATION COOPERATION PROGRAMME Interreg VB SOUTHWEST EUROPE Adopted by EC 18/06/2015 Adopted version 18/06/2015 1 CCI Title 2014TC16RFTN007 Programme Interreg VB Southwest Europe
Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its Mitigation
 Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 1 (2016) 32-37 doi: 10.17265/2332-8215/2016.01.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 1 (2016) 32-37 doi: 10.17265/2332-8215/2016.01.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its
WEC IWRM Seminar Sana a March 2010
 Components of IWRM study program at WEC and its relevance to water sector in Yemen by Prof. Dr.Abdulla Babaqi WEC IWRM Seminar Sana a 15-16 March 2010 Outline Current situation of the water sector Needs
Components of IWRM study program at WEC and its relevance to water sector in Yemen by Prof. Dr.Abdulla Babaqi WEC IWRM Seminar Sana a 15-16 March 2010 Outline Current situation of the water sector Needs
Vulnerabilities to Climate Change Impacts and Strengthening Disaster Risk Management in East Asian Cities
 Hanoi, Vietnam 2008 Primer Reducing Vulnerabilities to Climate Change Impacts and Strengthening Disaster Risk Management in East Asian Cities I/ CITY DESCRIPTION A. Hanoi Topography and demography characteristics
Hanoi, Vietnam 2008 Primer Reducing Vulnerabilities to Climate Change Impacts and Strengthening Disaster Risk Management in East Asian Cities I/ CITY DESCRIPTION A. Hanoi Topography and demography characteristics
Impacts of Drought in the e Philippines
 Department of Science and Technology Department of Science and Technology Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration Impacts of Drought in the e Philippines by Rosalina
Department of Science and Technology Department of Science and Technology Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration Impacts of Drought in the e Philippines by Rosalina
Geographic context. Hydropower developments on the upper Rhone River
 Environmental friendly flushing downstream Genissiat dam, French upper Rhone River, France Christophe PETEUIL Compagnie Nationale du Rhone Engineering Department, River Systems and Climate Hazards Division
Environmental friendly flushing downstream Genissiat dam, French upper Rhone River, France Christophe PETEUIL Compagnie Nationale du Rhone Engineering Department, River Systems and Climate Hazards Division
The State of the Colorado River
 April 2014 The State of the Colorado River Executive Summary The Colorado River Basin is now in its fifteenth year of drought. System runoff during this period has been comparable to or less than that
April 2014 The State of the Colorado River Executive Summary The Colorado River Basin is now in its fifteenth year of drought. System runoff during this period has been comparable to or less than that
Journal of Water Resource and Hydraulic Engineering Jul. 2015, Vol. 4, Iss. 3, PP
 Water Resources Modelling Using System Dynamic in Vensim (A case study: Risk analysis of Sefīd-Rūd Dam Reservoir intake decrease on downstream agricultural water demand) Hassan Pourfallah Koushali *1,
Water Resources Modelling Using System Dynamic in Vensim (A case study: Risk analysis of Sefīd-Rūd Dam Reservoir intake decrease on downstream agricultural water demand) Hassan Pourfallah Koushali *1,
Uncertainty in hydrologic impacts of climate change: A California case study
 Uncertainty in hydrologic impacts of climate change: A California case study Ed Maurer Civil Engineering Dept. Santa Clara University Photos from USGS Motivating Questions What are potential impacts of
Uncertainty in hydrologic impacts of climate change: A California case study Ed Maurer Civil Engineering Dept. Santa Clara University Photos from USGS Motivating Questions What are potential impacts of
Adaptation Strategy of the Slovak Republic on Adverse Impacts of Climate Change Overview: Executive Summary
 Adaptation Strategy of the Slovak Republic on Adverse Impacts of Climate Change Overview: Executive Summary Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic December 2016 Climate change has caused a wide
Adaptation Strategy of the Slovak Republic on Adverse Impacts of Climate Change Overview: Executive Summary Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic December 2016 Climate change has caused a wide
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007
 Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Hay being cut last week was more of a clipping or hay that either needs to be taken off due to weeds or because. Ellensburg Division - PNW
 Vol. 7 No. 1-2014 May Spring Edition Ellensburg Division - PNW Hay being cut last week was more of a clipping or hay that either needs to be taken off due to weeds or because the field is planted to timothy.
Vol. 7 No. 1-2014 May Spring Edition Ellensburg Division - PNW Hay being cut last week was more of a clipping or hay that either needs to be taken off due to weeds or because the field is planted to timothy.
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges
 Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Case Study: Climate Change Adaptation in the City of Irvine, CA. ND-GAIN Urban Adaptation Assessment Gracie Georgi
 Case Study: Climate Change Adaptation in the City of Irvine, CA ND-GAIN Urban Adaptation Assessment Gracie Georgi 8.11.17 Author Gracie Georgi is a junior at the University of Notre Dame studying Political
Case Study: Climate Change Adaptation in the City of Irvine, CA ND-GAIN Urban Adaptation Assessment Gracie Georgi 8.11.17 Author Gracie Georgi is a junior at the University of Notre Dame studying Political
Carbonic Imbalance in the atmosphere main cause of the Global Warming and Climate Change
 *K.Iskandarova, **M.Karabayev *National Center for Biotechnology, Kazakhstan **International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center CIMMYT, KazAgroInnovation JSC of the Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan
*K.Iskandarova, **M.Karabayev *National Center for Biotechnology, Kazakhstan **International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center CIMMYT, KazAgroInnovation JSC of the Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan
DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEMS FROM LIGNITE FIRED POWER PLANTS TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE IN GREECE
 DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEMS FROM LIGNITE FIRED POWER PLANTS TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE IN GREECE E. Karlopoulos 1, D. Pekopoulos 2, E. Kakaras 1 1. Centre for Research and Technology Hellas/Institute for Solid
DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEMS FROM LIGNITE FIRED POWER PLANTS TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE IN GREECE E. Karlopoulos 1, D. Pekopoulos 2, E. Kakaras 1 1. Centre for Research and Technology Hellas/Institute for Solid
Phil Mashoko(Pr Eng) Director: W & S City of Cape Town South Africa
 Phil Mashoko(Pr Eng) Director: W & S City of Cape Town South Africa SECURITY OF WATER SUPPLY It is the ability to continuously produce and supply safe drinking water to the enduser ASSURANCE RISK LEVEL
Phil Mashoko(Pr Eng) Director: W & S City of Cape Town South Africa SECURITY OF WATER SUPPLY It is the ability to continuously produce and supply safe drinking water to the enduser ASSURANCE RISK LEVEL
INTERACTION BETWEEN CLIMATIC CONDITIONS AND WATER POLLUTION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE TRANSBOUNDARY CATCHMENT OF GUADIANA RIVER.
 INTERACTION BETWEEN CLIMATIC CONDITIONS AND WATER POLLUTION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE TRANSBOUNDARY CATCHMENT OF GUADIANA RIVER. Andrés Olay (*), Nuno Gomes (**), Rodrigo Álvarez (*), Sonia Sousa (**), Jorge
INTERACTION BETWEEN CLIMATIC CONDITIONS AND WATER POLLUTION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE TRANSBOUNDARY CATCHMENT OF GUADIANA RIVER. Andrés Olay (*), Nuno Gomes (**), Rodrigo Álvarez (*), Sonia Sousa (**), Jorge
Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) of the IPCC (2007) on Climate Change. Part II Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability.
 Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) of the IPCC (2007) on Climate Change Part II Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability Summary 06/04/07 The report from Working Group II of the Intergovernmental
Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) of the IPCC (2007) on Climate Change Part II Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability Summary 06/04/07 The report from Working Group II of the Intergovernmental
SUSTAINABLE USE OF OCEANS IN THE CONTEXT OF THE GREEN ECONOMY AND THE ERADICATION OF POVERTY, PRINCIPALITY OF MONACO, NOVEMBER, 2011
 SUSTAINABLE USE OF OCEANS IN THE CONTEXT OF THE GREEN ECONOMY AND THE ERADICATION OF POVERTY, PRINCIPALITY OF MONACO, 28 30 NOVEMBER, 2011 Implementation of Offshore Wind Power & Potential of Tidal, Wave
SUSTAINABLE USE OF OCEANS IN THE CONTEXT OF THE GREEN ECONOMY AND THE ERADICATION OF POVERTY, PRINCIPALITY OF MONACO, 28 30 NOVEMBER, 2011 Implementation of Offshore Wind Power & Potential of Tidal, Wave
Use of the IQQM simulation model for planning and management of a regulated river system
 Integrated Water Resources Management (Proceedings of a symposium held al Davis. California. April 2000). IAHS Publ. no. 272, 2001. 83 Use of the IQQM simulation model for planning and management of a
Integrated Water Resources Management (Proceedings of a symposium held al Davis. California. April 2000). IAHS Publ. no. 272, 2001. 83 Use of the IQQM simulation model for planning and management of a
ESTIMATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON WATER RESOURCES BY USING BILAN WATER BALANCE MODEL
 ESTIMATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON WATER RESOURCES BY USING BILAN WATER BALANCE MODEL Stanislav Horacek, Ladislav Kasparek, Oldrich Novicky T. G. Masaryk Water Research Institute Prague, Czech Republic
ESTIMATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON WATER RESOURCES BY USING BILAN WATER BALANCE MODEL Stanislav Horacek, Ladislav Kasparek, Oldrich Novicky T. G. Masaryk Water Research Institute Prague, Czech Republic
What Are Environmental (Instream) Flows?
 1 What Are Environmental (Instream) Flows? Sustainable water management requires that both human needs and the needs of aquatic and riparian ecosystems be fulfilled. Dams and diversion of water for municipal
1 What Are Environmental (Instream) Flows? Sustainable water management requires that both human needs and the needs of aquatic and riparian ecosystems be fulfilled. Dams and diversion of water for municipal
Review of Saudi Arabia Municipal Water Tariff
 World Environment 213, 3(2): 66-7 DOI: 1.5923/j.env.21332.5 Review of Saudi Arabia Municipal Water Tariff Omar K M Ouda Department of Civil Engineering, Prince Mohamed Bin Fahd University, Al Khobar, Kingdom
World Environment 213, 3(2): 66-7 DOI: 1.5923/j.env.21332.5 Review of Saudi Arabia Municipal Water Tariff Omar K M Ouda Department of Civil Engineering, Prince Mohamed Bin Fahd University, Al Khobar, Kingdom
Outline. Water and sanitation strategy in Morocco Key numbers and main indicators Principal achievement projects
 Water 1 Outline Water and sanitation strategy in Morocco Key numbers and main indicators 2014 Principal achievement projects 2014-2015 Investment program 2015-2017 Perspectives project (2030) Financing
Water 1 Outline Water and sanitation strategy in Morocco Key numbers and main indicators 2014 Principal achievement projects 2014-2015 Investment program 2015-2017 Perspectives project (2030) Financing
Findings from a pan- European assessment of transboundary waters under the UNECE Water Convention Dr. Annukka Lipponen Coordinator of the Assessment
 Findings from a pan- European assessment of transboundary waters under the UNECE Water Convention Dr. Annukka Lipponen Coordinator of the Assessment UNECE About the Second Assessment Covers more than 140
Findings from a pan- European assessment of transboundary waters under the UNECE Water Convention Dr. Annukka Lipponen Coordinator of the Assessment UNECE About the Second Assessment Covers more than 140
Pipelines to Nowhere? Structural Responses to Climate Change and Population
 Pipelines to Nowhere? Structural Responses to Climate Change and Population Presented by James Lochhead, Esq. Brownstein Hyatt Farber Schreck, LLP bhfs.com Evolving Strategies of Water Supply Development
Pipelines to Nowhere? Structural Responses to Climate Change and Population Presented by James Lochhead, Esq. Brownstein Hyatt Farber Schreck, LLP bhfs.com Evolving Strategies of Water Supply Development
Pilot Study. Adaptation in water and coastal areas in Puglia, Italy
 THEMATIC CENTRE Drought, Water and Coasts Pilot Study Adaptation in water and coastal areas in Puglia, Italy Three pilot studies were carried out under the OrientGate Thematic Centre on Drought, Water
THEMATIC CENTRE Drought, Water and Coasts Pilot Study Adaptation in water and coastal areas in Puglia, Italy Three pilot studies were carried out under the OrientGate Thematic Centre on Drought, Water
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016
 SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
Desalination Plans to Solve Water Scarcity
 Desalination Plans to Solve Water Scarcity Thomas Manaugh, PhD Integral Scientific Institute "A new type of thinking is essential if mankind is to survive and move toward higher levels. -- Albert Einstein
Desalination Plans to Solve Water Scarcity Thomas Manaugh, PhD Integral Scientific Institute "A new type of thinking is essential if mankind is to survive and move toward higher levels. -- Albert Einstein
WATER STRATEGY in the WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN
 WATER STRATEGY in the WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN March 2015 1 WATER STRATEGY in the WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN index 1. Preamble... 3 2. Background... 3 3. Rationale... 5 4. Major priority issues for the Strategy...
WATER STRATEGY in the WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN March 2015 1 WATER STRATEGY in the WESTERN MEDITERRANEAN index 1. Preamble... 3 2. Background... 3 3. Rationale... 5 4. Major priority issues for the Strategy...
