ARMENIA. TABLE 1. POPULATION INFORMATION Growth rate (%) a 1979 a b 1999 b to. b Data & Statistics/The World Bank
|
|
|
- Aubrey Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARMENIA
2 50 ARMENIA
3 ARMENIA 1. GENERAL INFORMATION General Overview The Republic of Armenia, the smallest of the three Transcaucasian republics, is a landlocked mountainous country bounded on the north by the Republic of Georgia, on the east and southwest by Azerbaijan, on the south by Iran and on the west by Turkey. The northern border is 196 km long, the border with Azerbaijan is 913 km, the southern border has a length of 42 km and the western 280 km. The land area of the republic is km 2. The terrain is defined by the high Armenian Plateau with mountains, little forest and fast flowing rivers. The average height above sea level is about meters. The climate is highland continental with hot and dry summers and cold winters. Annual average temperature varies from -2.7 C to 13.8 C. The coldest month is January (from 1.2 C to C) and the hottest months are July and August (from 25.8 C to 8.7 C). Summer temperatures may rise up to 42 C, winter cold has maximum of 46 C below zero. Summer relative wetness is 32-45% (July- August), winter relative wetness is 80-90%. Annual rainfall varies from 220 mm (in winter) to 900 mm (May- June). The annual maximum sunshine is hours (Lake Sevan area), and minimum hours (Idgevan). The average intensity of solar radiation on the aclinic plane on a cloudless day is 700 kkal/m 2. The annual average wind velocity varies from 7.7 m/sec to 1.0 m/sec. The population of Armenia is about 3.8 million, of which 70% lives in urban areas. Armenia is a densely populated country with a density of 135 person/km 2. The historical population information is shown in Table 1. TABLE 1. POPULATION INFORMATION Growth rate (%) a 1979 a b 1999 b to Population (millions) Population density (inhabitants/km²) Urban population as percent of total Area (1000 km²) 28.4 a Formal data of the census of population. b Data & Statistics/The World Bank Source: IAEA Energy and Economic Database; Data & Statistics/The World Bank; Country Information. The population growth from 1990 to 2001is about 6%. The concentration of population is not equal in different areas of the republic. The Ararat Valley is the most populated territory of the country with the density of 245 person/km 2. Its area makes about 26.7% of the total territory and its population reach to 58.8% of the total population. Yerevan, the capital of the Republic of Armenia, lays in the Ararat Valley and is home to 1.2 million people, which is about one third of the total population. The highland areas have much less population with the density of 35 person/km Economic Indicators After the disintegration of the Soviet Union, an economic crisis broke out, and Armenia suffered from sharp decline in production during the period The country undertook great efforts to overcome it. Since then, the situation has been gradually stabilized, and the republic is coming out of the crisis following the transition to a market economy. During the period , 2001 ARMENIA 51
4 the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has increased on 63%, and the average growth rate was 5.6% per year. The historical GDP information is shown in Table 2. TABLE 2. GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT (GDP) Growth rate (%) c 1997 c 1998 c 1999 c to 2001 GDP (a) GDP (b) per capita N/A GDP by sector (%) : -Agriculture Industry Services (a) Millions of current US$ at market prices (c) Data & Statistics/The World Bank (b) Current US$ per capita at market prices Source: IAEA Energy and Economic Data Base; Data & Statistics/The World Bank; Country Information. Armenia is not rich in mineral raw materials. There are only a few items of considerable industrial value: copper, bauxite, molybdenum, precious metals, perlite, diatomite and coal. This factor mainly determines the economic structure of the republic. There has traditionally been very little heavy industry. The manufacturing sector has a prevailing share in GDP Energy Situation The main sources of energy, traditionally used in Armenia, are: oil products, natural gas, nuclear energy, hydropower and coal. Hydro and a small amount of brown coal are the only domestic sources of energy, which are exploited. The republic has no oil and some gas reserves (not exploited). There are no uranium resources either. The energy reserves are shown in Table 3. Primary energy sources, in thousand tonnes of oil equivalent, are summarized in Table 4. To meet its energy requirements, Armenia has to import gas, oil products and nuclear fuel. TABLE 3. ESTIMATED ENERGY RESERVES Estimated energy reserves in 1999 (Exajoule) Solid Liquid Gas Uranium Hydro Total (1) (2) Total amount in place (1) This total represents essentially recoverable reserves. (2) For comparison purposes a rough attempt is made to convert hydro capacity to energy by multiplying the gross theoretical annual capability (World Energy Council ) by a factor of 10. Source: IAEA Energy and Economic Data Base TABLE 4. PRIMARY ENERGY SOURCES ktoe Year Coal and Petroleum Gas (Natural Nuclear Hydro Electricity Total Wood Products + LPG) (Imp-Exp.) N/A Source: Country Information. 52 ARMENIA
5 Hydropower is based on the water resources of the republic, including Lake Sevan, one of the largest highland fresh-water lakes in the world (1 900 m above sea level), and the rivers: Arax, Arpa, Hrazdan, Debet and Vorotan. There are six hydropower plants of the Sevan-Hrazdan cascade (556 MW), three plants of the Vorotan cascade (400 MW) and a number of small hydropower plants (60 MW). During the last period of time, several small hydro power plants with the total capacity of 15 MW have been built. Hydro power plants of the Sevan-Hrazdan cascade are operating at a low level capacity, because, after the intense use of the lake water during the last crisis, the Government of Armenia decided to reduce releases from Lake Sevan to restore its potential. At the same time, Armenia has still an unused hydraulic potential of about 300 MW (or 1248 millions kwh of electric energy) that can be developed economically. Natural gas is the most important source of energy covering up to 58% of the total energy supply. It is imported from Russia and used to operate two thermal power plants; a third thermal power plant is not operating, because it was built to supply thermal energy to an industrial factory, which is no longer in operation. However, the plans have been under discussion to restart this thermal power plant together with that industrial factory. The designed capacity of the high-pressure gas transportation network of Armenia is 17 billions m 3 /year. In 1980, the maximum demand for natural gas in Armenia was above 5-6 billions m 3 /year. There have been five main gas pipelines built, which ensured the gas delivery from three sides: Georgia, North and West Azerbaijan. Today, only the first one is operating. Nowadays, the natural gas demand is 1.5 billions m 3 /year, but the expected demand by the year 2015 will be 5 billions m 3 /year. There are underground storage facilities for natural gas with a maximal gas storage volume of 180 million m 3. Gas distribution in Armenia is performed through high, medium and low-pressure distribution networks. Oil products are imported from the neighbouring countries, mostly utilized for transport, industry, residential sector (heating) and as secondary fuel (mazut) in thermal power plants. During the last several years, mazut was not imported into the republic. As to the renewable sources of energy (geothermal, wind, solar and waste burning), they are under study and not yet available. Armenia has a considerable potential of geothermal energy, but a programme has to be developed to explore the geothermal resources and to carry out drilling activities. Wind power projects (the construction of power stations) are still under discussion. The most worth-while regions suitable for the construction are: Vanadzor, Aragats, Lake Sevan basin and Sisian, where the wind velocity reaches 7 m/s. Armenia is a sunny republic with a high level of solar radiation. Nevertheless, it is too expensive to utilize the solar energy, and the republic, which appears to have very good solar radiation potential, cannot afford using it. A waste burning facility project (the construction of a station with a capacity of 10 MW in Yerevan) is under discussion as well. Nuclear energy played a crucial role during the period of recovery from the economical crisis. There is one Armenian nuclear power plant (ANPP), which has two reactor units. Unit 1 is not operating and unit 2 has been re-commissioned in 1995, after 6.5 years of outage. The fuel is supplied by the Russian Federation. In Armenia, the primary energy per capita is around 0.55 toe/capita compared with 0.55 in Georgia, 2.4 in Belarus and 3.2 Toe/capita in Ukraine. The energy statistics are shown in Table 5. The country total energy consumption shows a steady increase at a rate, which is significantly greater than the increase of GDP. Table 6 shows the historical energy consumption data. The data on energy consumption by sector (Table 7) do not show the major changes during the years shown. The energy consumption by region is shown in Table 8. The energy consumption by region shows a prevalence of Yerevan city, which is responsible for about 50% of the total consumption. ARMENIA 53
6 1.4. Energy Policy. In , the Government of RA and the Ministry of Energy started the implementation of a stabilization policy: institutional development and objectives to overcome the energy crisis. The main objectives of that stage were as follows: restructuring the sector to overcome financial crisis and creating premises for further development; developing plans for improvement of the sector taking into consideration the economy as a whole; improvement of the management structure of the Ministry of Energy with the purpose of elimination of the sector operational management and increasing the enterprise independence; minimization of bartering in energy sales and elimination of cross subsidizing of separate enterprises and sectors; carrying out a suspended and targeted privatization policy; participation and encouraging major investments in the energy sector. The following results were achieved during that period: the Energy Law and the Law on Responsibility for the Violations in the Area of Utilization of Nuclear Energy have been adopted; number of laws affecting investment in energy were adopted: the Law on Foreign Investment; the Law on Enterprises and Entrepreneurial Activities; the Law on Privatization and Demonopolization; the Law on Real Estate; the Law on Taxes (enables more favourable treatment for foreign investors); the Energy Regulatory Commission was established in 1997; high voltage transmission line Iran-Armenia has been commissioned and the intersystem HVL 220 kv with Georgia was rehabilitated; 11 regional distribution enterprises have been consolidated into 4 companies; measures on modernizing the accounting, billing and collecting systems have been implemented; HV Transmission Company has been established; dispatch and wholesale functions were assigned to Armenergo State Closed Joint Stock Company; 15 small HPPs have been privatized till 1997, two of which are the property of French citizens; normative schedules of major overhaul are renewed; Joint-Venture Stock Company - ArmRosgasprom has been founded; central heating and gas-supply to the consumers has been restored; Armenia became a member of European Energy Charter, Black Sea Economic Co-operation and others. During the period of , changes were made in the Armenian legislation with respect to the country s energy policy. The Ministry of Energy was preparing the new edition of Law On Energy of the Republic of Armenia which was to replace the previous one that was in use since The National Assembly, in March 2001, adopted the new edition of Law On Energy of the Republic of Armenia. In March 2000, the National Assembly adopted the Law On Amendments and Additions to the Law On safe Use of Nuclear Energy for Peaceful Purposes. In particular, one of the amendments reads: Those objects which are of safety importance shall be constructed and decommissioned by the law, being submitted to the Government. 54 ARMENIA
7 The level of electricity average tariff was increased from 12 drams in 1995 to 21.6 drams, and the residential tariff to 25 drams (US $1= 560 Dram now). The energy sector cost analysis has shown that in short-term perspective it is possible to stabilize the level of costs and restrain the increase of tariffs through promotion of the efficiency of power generation, transmission and distribution, extension of the electricity market, loss reduction and other measures. TABLE 5. ENERGY STATISTICS Exajoule Energy consumption - Total (1) Solids (2) N/A Liquids Gases Primary electricity (3) Energy production - Total Solids N/A Liquids Gases N/A N/A N/A N/A Primary electricity (3) N/A Net import (import - export) - Total Solids Liquids Gases (1) Energy consumption = Primary energy consumption + Net import (Import - Export) of secondary energy. (2) Solid fuels include coal, lignite and commercial wood. (3) Primary electricity = Hydro + Geothermal + Nuclear + Wind. Source: IAEA Energy and Economic Database and Country Information. TABLE 6. TOTAL FINAL ENERGY CONSUMPTION Total final consumption Ktoe Consumption increase % 10.6% 9.0% GDP increase % 5.8% 3.1% 7.2% 3.3% 6.0% 7.2% Source: Country Information. TABLE 7. ENERGY CONSUMPTION BY ECONOMY SECTOR ktoe Economy Sector Industry Transport Agriculture Commerce and public service Residential Non specified Non-energy use Total energy consumption Source: Country Information. ARMENIA 55
8 TABLE 8. ENERGY CONSUMPTION BY REGION Macro Regions Year North Centre South Yerevan Total Final Consumption Source: Country Information. A programme for improvement of metering, billing and collection of payments for electricity, heat and natural gas is being implemented, together with the transfer of accounting to international norms and standards and annual auditing of the company s financial reports by independent auditors. A programme has been implemented to organize collections through banks. Though there are difficulties in the whole economy of the country, the Government gives priority to budget payments for the electricity provided to budget organizations as well as compensation for the electricity consumed by irrigation, drinking water, industry and electrical transport companies. In the district heating sector there are number of problems concerning physical wear of heating networks equipment, lack of industrial heat consumption and low level of payment collection in the residential sector. The Government of the Republic of Armenia and the WB are developing a project for district heating rehabilitation. The following measures were undertaken in the year 2001: fully commercialized and transparent relationships between the enterprises; creation of the wholesale market of energy and power; rehabilitation and modernization of transmission and distribution networks; modernization of the metering system, which will exclude the non-measured losses and decrease the technical losses. The results of asset revaluation show that the sector s main assets resources have already expired. The equipment is worn out and requires major overhaul, 38% of installed capacities are already over 30 years old. It is necessary to take all due measures to renew the energy sector of Armenia. The strategy for the National Energy Sector development is based on: three-level energy diversification policy: Generation side: - HPP, TPP, NPP; Fuel supply side: - natural gas, oil, nuclear fuel; Fuel transportation side: - gas pipelines, oil product delivery; domestic fuel resource exploration; regional co-operation. The Development Programme specifies: In Hydro power: rehabilitation of the existing Hydro Power Plants (HPP); development of economically feasible new hydro potential on the base of small HPPs with private investments; establishment of Pump Storage Plants with comparatively small investments. In Thermal power: 56 ARMENIA
9 operation of existing aggregates and units to complete exhaustion of their technical resource; commissioning of new Unit N5 on Hrazdan TPP; refurbishment of Yerevan TPP on the basis of modern Combined Cycle units. Development of the nuclear power sector using modern technologies; Development of renewable energy with participation of private investments; Implementation of planned energy efficiency campaign. Along with the refurbishment and development of generating capacities, the main attention is paid to rehabilitation of transportation and distribution networks, interconnections, implementation of dispatch control and communication devices in the Power Sector. 2. ELECTRICITY SECTOR. The total installed capacity of the Armenian Power System is about 3600 MW, which includes: the installed capacity of the Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) MW; Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) with designed capacity of 815 MW, which was decommissioned after the earthquake in 1988 and recommissioned with MW in 1995; two HPPs cascades of 1000 MW. The high-voltage transmission network of Armenia consists of kv lines. There are 14 substations of 220 kv and 119 substations of 110 kv. The capacity of the existing high voltage network is considered sufficient for the current and forecasted loads. The high-voltage transmission network has the interconnections with the all neighbouring countries: Azerbaijan: 330 and 220 kv, Georgia: 220 kv, Turkey: 220 kv, Iran: 220 kv Structure of the Electricity Sector. At present, aiming to increase operation efficiency and profitability of energy enterprises, the following structure of the Energy Sector has been elaborated : 11 regional distribution enterprises have been consolidated to 4 companies; transmission function was separated from Armenergo and HV Transmission Company has been created; dispatch and wholesale functions were assigned to Armenergo State Closed Joint Stoke Company. Thus, a basis for the creation of a real energy wholesale market was established. The Energy Commission is responsible for the antimonopoly regulation. The key functions of the antimonopoly regulation are tariff regulation and licensing of entities in the energy sector. Armenergo is a wholesale buyer-reseller of generated electricity and takes responsibility to realize dispatching with the purpose of efficient delivery of the electricity. The structure of the energy sector is shown in Figure Decision Making Process Privatization of state companies was implemented to encourage market competition. For this purpose, separation of generation, transmission, and distribution systems was established. Within this framework, the Ministry of Energy is responsible for: defining the policies for the electricity sector; establishing the rules with which the electricity supply industry must comply; authorizing the allocation of funds to state companies; ARMENIA 57
10 deciding on the respective awards during the privatization process. Presently Armenia plans to develop an integrated resource planning and decision-making process aiming in co-ordinating the functions of its diverse institutional system and assuring thorough participation of all sectors, public and private. Mechanisms related to the electrical system expansion, economic management and regulation with mitigating impact on the environment have not been defined. Policy Strategy Regulations Dispatch/ Power Market Management Government of RA Ministry of Energy ANRA National Dispatching Centre Pricing Generation NPP TPPs HPPs Transmission Distribution HV Transmission Import/Export Energy Regulating Body Consumption C o n s u m e r s FIG. 1. Structure of the Energy Sector Foreign interconnected utility companies have to apply for authorization from the Ministry of Energy to participate in the wholesale electricity market. In this way they are assured of their reserve and do not resort to sell at dumping prices. Payment to transmission companies includes a charge for the energy actually transmitted. Distributors and large users may enter into supply contracts at the prices defined in their contracts Main Indicators In 2001, the total installed capacity of the generating stations in Armenia was MW. The annual electricity production was 5.74 billion kwh. Table 9 shows the historical statistics of the electricity production balance and Table 10 - the energy related ratios. In addition, Figures 2 to 5 show the total electricity production, the electrical energy balance, the annual electrical energy consumption per capita and the share of the electricity in the total energy consumption Impact on Open Electricity Market in the Nuclear Sector Before the disintegration of the USSR, Armenia, as a part of the Soviet Union, was under the unified All-Union energy policy. The electricity generated by Armenian Power Plants joined the Transcaucasien Energy System before being distributed to the consumers in accordance with the existing plans. After becoming an independent state, Armenia had to meet the open market requirements in all the branches of the industry. The energy sector and the nuclear sector in particular were deeply affected by the economic difficulties during the market transition and were in need of reorganization and de-regulation. 58 ARMENIA
11 TABLE 9. ELECTRICITY PRODUCTION AND INSTALLED CAPACITY Electricity production (TW h) - Total (1) Thermal Hydro Nuclear Capacity of electrical plants (GW(e)) - Total Thermal Hydro Nuclear (1) Electricity losses are not deducted. Source: IAEA Energy and Economic Database; Country Information. TABLE 10. ENERGY RELATED RATIOS Energy consumption per capita (GJ/capita) Electricity per capita (MW h/capita) Electricity production/energy production (%) Nuclear/total electricity (%) Ratio of external dependency (%) (1) Load factor of electricity plants - Total (%) Thermal Hydro Nuclear N/A (1) Net import / Total energy consumption. Source: IAEA Energy and Economic Database; Country Information. GWh Nuclear Termal Hydro FIG. 2. Total Electricity Production ARMENIA 59
12 GWh Import Export Consumption Generation kwh per capita FIG. 3. Electrical Energy Balance FIG. 4. Electrical Energy Consumption 100% 80% 60% Electricity Other 40% 20% 0% FIG. 5. Share of Electricity in Total Energy Consumption 60 ARMENIA
13 A new energy policy was developed by the Government of Armenia, with the evaluation of the National Energy Balance as a main factor and a starting point for a National Energy Strategic Plan. Special attention was paid to restructuring the energy sector. A number of laws in energy were adopted. Several small HPPs have been privatized. The implementation of a stabilization policy with the crucial role of restarting the ANPP allowed the country to overcome the energy crisis of the post- Soviet period. Now Armenia is covering its electricity demand completely and can ensure the export of power to neighbouring countries. In the nearest future, however, additional energy sources may be required as the economy of the republic is recovering and the living standard is increasing steadily. 3. NUCLEAR POWER SITUATION 3.1. Historical Development The Armenian Nuclear Power Plant was commissioned in 1976, with achieving the initial criticality for Unit 1 on 22 December, 1976, and for Unit 2 - on 5 January, The units were put into commercial operation on 6 October 1977 and on 3 May 1980, respectively. The units are of the WWER type, and the design of the ANPP was developed between 1968 and It was based on the project of Units 3 and 4 of the Novovoronezh NPP. The plant was constructed under the industry documentation of Mechanical Engineering Ministry of the former USSR, the permissions for site selection and construction were formalized in accordance with the acting at that time normative documents. Fig. 6. Map of locations of all electricity generating power plants and main high voltage interconnections with the neighbouring countries After the 1988 earthquake, though the Power Plant was not damaged, the Council of the USSR Ministers decreed to shut down the ANPP as a precautionary measure. Unit 1 was shut down on 25 February 1989 and Unit 2 on 18 March The units were not decommissioned but kept in prolonged shut down condition. As mentioned earlier, the Government of Armenia decided in April 1993 to restart Unit 2 of the ANPP, in order to overcome the severe economic crisis and taking into ARMENIA 61
14 account the lack in national energy resources. After 6.5 years of outage, with the technical and financial help of the Russian Federation, Unit 2 of the ANPP was restarted in November 5, Unit 1 remains in a stand still regime for the time being. Locations of all electricity generating power plants and main high voltage interconnections with the neighbouring countries are shown in Figure Status and Trends of Nuclear Power Only Unit 2 of the ANPP is currently in operation. The installed gross capacity is MW. The total production of electricity in Armenia during 2001 amounted to 5740 billion kw h. The nuclear share in overall production along with comparative figures for the other power plants are shown in Table 9. Table 11 shows the status of the nuclear power plants. TABLE 11. STATUS OF NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS Station Type Net Operator Status Reactor Capacity Supplier ARMENIA-2 WWER 376 JSC Operational MNE ARMENIA-1 WWER 376 JSC Shut Down MNE Station Turbogenerato r Construction Criticality Grid Commercial Shutdown Supplier Date Date Date Date Date ARMENIA-2 KHTP 01-Jul Jan Jan May-1980 ARMENIA-1 KHTP 01-Jan Dec Dec Oct Feb-1989 Note: Armenia 2 was shutdown in 1989 and restarted operation in November 1995 Source: IAEA Power Reactor Information System as of 31 December 2001 In 1999, Unit 2 of the ANPP had one emergency shutdown and one event of level 1 on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES). In 2000, there were 3 events reported, one event was rated level 1, and two events were rated level 0. In 2001, there were 7 emergency events occurred at the ANPP, including: 3 of level 1, 4 of level 0 on the INES scale. During the last two years, Unit 2 operated without any emergency shutdown. The following safety upgrading measures were implemented within the period of : Completion of the nuclear service water system project. This is a highly reliable system for cooling safety related loads, which were previously cooled by the cooling towers. It eliminates seismic concerns for cooling. These loads allow cooling in an autonomous regime, separately from the cooling towers. This system is intended to endure earthquakes of high magnitude. Also seismic pumps and other equipment have been installed; 7 Fast closing main steam isolation valves (MSIV) were installed. They will provide better control in the event of a steam line accident and will reduce the risk of a more serious accident involving overcooling of the primary coolant system and reactor vessel; 12 Steam generator safety valves (SGSV) were replaced by new ones; 2 Safety valves of the pressurizer were replaced by new ones; A new fire detection and alarm system was put into operation. 700 Smoke/fire type detectors were installed, of which 70 are blow resistant; An analysis of the material structure of the reactor vessel and primary circuit piping has been carried out by using various modern methods; The installation of a leak detecting system from the primary to the secondary circuit was implemented; The bearing metallic structures (columns) in the turbine hall building and in the emergency diesel-generator room have been coated with fire-resistant material; 62 ARMENIA
15 A seismic safety related re-evaluation programme for Unit 2 has been developed; A multifunctional simulator, for training the operators, was put into operation. Reconstruction of feed-water distribution headers inside the SG 1 and 6. Review of SIAZ logic and scope in regard with the Service Water System implementation. Replacement of emergency condenser tubing in low-pressure cooling system (AK). Commissioning of new system for RCP shaft seal. Installation and commissioning of diesel-pump for feeding SG in the event of full deenergizing. Reconstruction of TG-3 shaft seal system. Development and implementation of Feed-and-Bleed procedure. Scenario development for reactor transfer to safe controlled condition in seismic event. The activity completed and is in a stage of approval. Installation of a compressor for annual pressure tests of SG and RCP compartment tightness. Replacement of DG start-up oil pumps. Implementation of automatic cold overpressure protection equipment for Reactor Vessel cold overpressure protection. The equipment has been installed, but the system has not yet been commissioned. Implementation of automatic cold overpressure protection equipment for RV cold overpressure protection. All these measures were carried out with the assistance of the US DOE and EC TASIC Technical Assistance programmes, which began early 1997 and were completed during These measures assure that the safety of the ANPP increased one level and that the plant can withstand emergency situations without failures Current Policy Issues Apart from the short period of regaining independence, there have been no strong antinuclear movements in Armenia. The current sentiment of the public can be explained not by lack of awareness of the risks involved by the utilization of nuclear energy, but, in the face of the difficult economic conditions, by the considerably lower price of nuclear electricity which outweighs its possible risks. Before independence, the ANPP had a status of State Enterprise. Now there are strong opinions against its partial privatization, so the status of the plant has remained the same. The safety level of the ANPP during the times of very limited financial resources is one of the main concerns of the Armenian Government. After numerous consultations with Western, Russian and Armenian experts, a safety-upgrading programme has been developed. Currently, a new list called List of measures for Unit 2 of the Armenian NPP safety and reliability upgrading for the period of , replaced the previous list. Special attention is focused on financing for spent fuel and radioactive waste storage and funding for decommissioning of the nuclear power plant Organizational Chart The Armenian NPP has been under the State ownership. It is under subordination of the Ministry of Energy, and the Government of Armenia has designated the ANPP with the rights of operator organization. ARMENIA 63
16 4. NUCLEAR POWER INDUSTRY 4.1. Supply of NPPs. Both units of the ANPP with the WWER- 440 (V-270) type reactors, were designed and constructed by organizations of the former Soviet Union, under the supervision of the Ministry of Energy and Electrification of the USSR. The first phase design was developed in The main operator of the project was All-Union Scientific Research and Design Institute for Power Technologies (VNIAEP). The chief scientific supervisor was Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy (Moscow). Now it is called RNC Kurchatov Institute. The chief design organization was Thermoelectroproject (TEP), Gorki. Now it is called NIAEP, Nizhny Novgorod. The main reactor construction organization was OKB Gidropress, Podolsk. The building-construction work was realized by the Gidroenergostroy, Yerevan Operation of NPPs The Republic of Armenia through the Ministry of Energy owns the Armenian NPP. At the present time, the ANPP entitles the rights as operator of a nuclear installation. For other purposes, such as liability to foreign countries, the State is assumed to be the operator. The electricity produced by the ANPP is sold to the Armenergo Joint Stock Company Fuel Cycle, Spent Fuel and Waste Management Service Supply Armenia has no fuel cycle industry. Up to now, all the nuclear fuel has been supplied by Russia. Originally, spent nuclear fuel from the ANPP was to be managed by central Soviet agencies for reprocessing and final disposal of the radioactive wastes. The recovered uranium and plutonium were to be retained by the central agencies in the Soviet Union. However, with the disintegration of the Soviet Union, Armenia had to find other solutions. In 1998, the construction of the first stage of spent fuel dry storage was completed. The spent fuel dry storage facility has eventually been put into operation, and all the transportations of spent fuel are fulfilled according to the requirements of the license given by the ANRA (Armenian Nuclear Regulatory Authority). During the ANPP outage in 2000, the first portion - six fuel canisters containing 336 fuel assemblies, was successfully transferred to and stored in the facility Research and Development Activities There are no major R&D activities in the country International Co-operation in the Field of Nuclear Power Development and Implementation Armenia has multilateral and bilateral projects, mostly concerning safety of the ANPP, with the highly developed counties, including Italy, Germany, France, Russian Federation and USA. Armenia also participates in several international projects developed in framework of co-operation under the aegis of TACIS (EC), IAEA and USAID. Very close co-operation is established with the IAEA. Armenia has become a member of this organization since IAEA experts have been participating in many various assistance projects since then. When in April of 1993 the Government of Armenia made the decision to restart Unit 2 of the ANPP, the IAEA experts participated actively in pre-commissioning investigations and evaluation of the condition of plant equipment. Moreover, they elaborated the whole concept of Unit 2 recommissioning. Armenia has also collaborated with the IAEA in the field of ensuring nuclear safety. At present, several national programmes of the ANPP Unit 2 safety upgrading are in different phases of implementation. 64 ARMENIA
17 The Russian Federation is also an active partner of Armenia. There are many joint projects within the framework of the Nuclear Safety Assistance Programme, realized in close co-operation with the Russian experts. They also took active part in pre-commissioning and restart of Unit2 of the ANPP. In 1996, an agreement was signed between the ANPP and ROSENERGOATOM on industrial and technical-scientific co-operation. In 2000, the agreement was signed between the Governments of RA and RF on Cooperation in the field of peaceful use of nuclear energy. Since 1996, the ANPP is a member of WANO. Since 1996, the EC started, within the framework of TACIS Assistance Programmes, the implementation of projects aiming in modernization of the technological equipment, construction of a multifunctional simulator, technical assistance for upgrading a level of operation of the ANPP, etc. There are a number of projects financed by the US Department of Energy (US DOE). Since 1996/97, in the framework of a Nuclear Safety Assistance Programme for Armenia, the USA specialists have implemented many technical assistance projects at the ANPP aiming to improve, in particular, the fire protection systems, purchase of equipment for the new cooling system, computerization of the safety system and procurement of the equipment for its safety operation. The experts from US DOE are also participating in the development of a programme for future decommissioning of the ANPP. French experts from FRAMATOM were involved in a joint project of constructing the first stage of the spent fuel dry storage system, which started in 1996 and has been completed. The Armenian Nuclear Regulatory Authority (ANRA) has agreements for co-operation with Nuclear Regulatory Authorities of the following countries: Russia, USA, Argentina and Ukraine. The ANRA is member of the organization FORUM, which members are the nuclear regulatory authorities from the countries operating WWERs. The ANRA participates also in the work of the CONCERT Group. In 2000, the implementation of joint projects with the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) of the United Kingdom started. They covered an assistance programme relevant to the ANPP safety upgrading. This includes, in particular, the elaboration of plant operational procedures and development of a quality assurance programme. In 2001, the Italian Government allocated its grant for the development of a part of the Probability Safety Analysis. 5. REGULATORY FRAMEWORK Safety Authority and Licensing Process The state authority for regulation of issues of nuclear and radiation safety - Armenian Nuclear Regulatory Authority (ANRA) - was established by a resolution of the Government of the Republic of Armenia in November The ANRA Statute was approved by Government decree N573 of 16 November It was further reviewed and approved by Government decree N385, dated 22 of June, The main responsibilities of the ANRA are: development of principles and criteria of safe utilization of atomic energy, nuclear and radioactive materials, their transportation and storage; development and introduction of safety rules and regulations; ARMENIA 65
18 implementation of licensing activities and licensing of physical persons, implementing activities and holding posts important for safety provision aspect in the area of atomic energy utilization; conduction of safety assessment of activities, objects and equipment in the area of atomic energy utilization; supervision on compliance with the requirements of the legislation in the area of atomic energy utilization and of the issued licenses by the legal and physical persons and applying sanctions where the requirements are not complied with; supervision on preparedness of enterprises and operating organizations included on the national emergency response system to extreme situations at the objects of atomic energy utilization and mitigation of the consequences; controlling the fulfilment of the commitments by Armenia on ratified international agreements jointly with a state authority entitled by the government with issues of international relations; controlling the safeguarding of nuclear and special material, special equipment and technologies; fulfilling freely inspection of objects of atomic energy, implemented activities and so on. The ANRA is under a direct subordination of the Armenian Government and independent from those organizations responsible for development and utilization of atomic energy. According to its Statute, the ANRA organizes and performs state supervision and inspections over utilization of nuclear energy, as well as its regulation. On 24 of May, 2001, according to the Government decision N 452, the ANRA was awarded with the authorisation for the regulatory activity on protection against the irradiation from ionisation sources and their safety. On 25 of April, 2001, according to the Government decision N 342, the Science-Research Centre of Nuclear and Radiation Safety was established at the ANRA. On the basis of the Governmental decree issued in 1994, all regulations, norms, etc. applicable to nuclear power in Russia have been accepted in Armenia. The ANRA is aware of the fact that many of these regulations need revision. This process is to a limited extent underway. Armenia has a single stage licensing process for NPPs and the licensing authority is the ANRA. The ANRA is reporting to the Vice Premier once a month on the safety of the licensed facilities. The licensee is responsible for the safety of the NPP. The licensee is obliged by the license to: Guarantee the keeping of principles, criteria and requirements on the nuclear and radiation safety, as well as the conditions or acts of the temporary exploitation permission; Inform ANRA about the deviations of the conditions of the temporary exploitation permission, as well as the incidents and emergencies during NPP Unit exploitation Main National Laws and Regulations The following laws and governmental decrees concerning the activities in the field of atomic energy use are in force in Armenia: Law on Implementation of modifications and additions both in the Code of RA on administrative and criminal legal violations, entered into force on 30 November Law on Energy of the Republic of Armenia, entered into force on 1 July The new Law on Energy of the Republic of Armenia entered into force in March, 2001, and replaced an old one which entered into force on 1 July Law on Safe Use of Nuclear Energy for Peaceful Purposes entered into force on 1 March ARMENIA
19 The amendment to the law on Safe Use of Nuclear Energy for Peaceful Purposes entered into force on 21 March The Government Decree N-389, , on the Implementation in Armenia of Regulations and Standards on Nuclear and Radiation Safety which are in force in the Russian Federation. The Government Decree N-401, dated on Introduction of Additions in the Government Decree N-161, dated (about the types of activities that are subject to licensing). The Government Decree N-331, dated on Restart of the ANPP Unit 2, and the Measures for Ensuring its Further Safe and Uninterrupted Operation. The Government Decree N 465, dated , approved the list of objects, which are of safety importance in the field of nuclear energy use. The Government Decree N 769, dated , approved the list of operations and work positions, which are of safety importance in the field of nuclear energy use. The Government Decree N-746, dated , approved the Order of Evacuation of Population from the Contaminated Territories. The Government Decree N-679, dated , approved the Order of Providing the Population with the Individual Protection Means. The Government Decree N-640, dated , approved the Rules for Organizing and Conducting the Safety Expertise in a field of Nuclear Energy Utilization. The Government Decree N-1263, dated , approved Special Rules for Nuclear and Radioactive Materials Transportations. The Government Decree N-765, dated , approved the Order of State Registration of Ionisation Irradiation Sources. The Government Protocol N-51, dated , adopted the Principal Positions on Planning and Realisation Activities for the Nuclear and Radiation Accidents Resistance International, Multilateral and Bilateral Agreements AGREEMENTS WITH THE AGENCY NPT related agreement INFCIRC No: 455 Entry into force: 5 May 1994 Additional protocol Signed: 29 September 1997 GOV/2948 Improved procedures for designation of safeguards inspectors No reply Supplementary agreement Signed: 30 September 1999 on provision of technical assistance by the IAEA Agreement on privileges and immunities Non-Party RELEVANT INTERNATIONAL TREATIES OR AGREEMENTS NPT Acceded: 15 July 1993 Convention on the physical Entry into force: 23 September 1993 protection of nuclear material ARMENIA 67
20 Convention on early notification Entry into force: 24 September 1993 of a nuclear accident Convention on assistance in Entry into force: 24 September 1993 case of a nuclear accident or radiological emergency Vienna convention on civil Entry into force: 24 November 1993 liability for nuclear damage Joint protocol Protocol to amend the Vienna convention on civil liability for nuclear damage Convention on supplementary compensation for nuclear damage Non-Party Not signed Not signed Convention on nuclear safety Entry into force: 20 December 1998 Joint convention on the safety of spent fuel management and on the safety of radioactive waste management ZANGGER committee Nuclear export guidelines Acceptance of NUSS codes Not signed Non-Member Not adopted No reply Comprehensive nuclear-test-ban treaty 1 October 1996 BILATERAL AGREEMENTS Agreement with the Russian Federation Entry into force 17 March 1994 on restarting operation of ANPP Agreement with Republic of Argentine Entry into force: 22 April 1999 on co-operation for the peaceful uses of nuclear energy Agreement with the Government of the Signed: 26 September 2000 Russian Federation on co-operation in the field of peaceful use of nuclear energy 68 ARMENIA
21 REFERENCES [1] Armenian Economic Trends issued by the European Commission, DGIA, NIS/TACIS services. [2] Investment Guide of Armenian Development Agency (1998). [3] Specifics and Phases of the Economic Reforms in Armenia in , Ministry of the State Statistics. [4] Manual on the Climate Data for the Construction Design in Armenia. [5] Data & Statistics/The World Bank, [6] IAEA Energy and Economic Database (EEDB). [7] IAEA Power Reactor Information System (PRIS). ARMENIA 69
22 Appendix DIRECTORY OF THE MAIN ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS AND COMPANIES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR POWER RELATED ACTIVITIES NATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AUTHORITY Ministry of Energy Tel: Government House Fax: , Republic Square minenr@arminco.com Yerevan, Republic of Armenia Atomic Energy Department Tel: Fax: atomen@freenet.am Armenian Nuclear Regulatory Authority Tel: ; Tigran Mets av. 4 Fax: Yerevan, Republic of Armenia head@asas.asrmenia.su MAIN POWER UTILITY Armenian Nuclear Power Plant Tel: Metsamor, Fax: Armavir region 6 Lmusoyan@arm.r.am Republic of Armenia MANUFACTURES AND SERVICES Armatom Tel: Admiral Isakov, 50 Fax: Yerevan, Republic of Armenia armatom@freenet.am Atomservice Tel/Fax: Metsamor, Armavir region 6 Republic of Armenia HIGH ENERGY RESEARCH INSTITUTES, UNIVERSITIES AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS Institute of Energy Tel: Amaranotsayin, 127, Yerevan, Republic of Armenia Atomenergoseysmoproject Tel: Hrazdan Defile, YerGes-2 Fax: Yerevan, Republic of Armenia Yerevan Physics Institute Yerevan State University National Academy of Sciences of Armenia ARMENIA
Armenia Nuclear Power Profile. IAEA, Vienna May
 Armenia Nuclear Power Profile IAEA, Vienna 10-13 May General Information The referendum for independence of Armenia was held on 21 September 1991. Based on the results of the referendum (99% voted for
Armenia Nuclear Power Profile IAEA, Vienna 10-13 May General Information The referendum for independence of Armenia was held on 21 September 1991. Based on the results of the referendum (99% voted for
Nuclear energy development in the Republic of Armenia. IAEA, Amsterdam June
 Nuclear energy development in the Republic of Armenia IAEA, Amsterdam 21-23 June Geography and Climate The Republic of Armenia is a landlocked mountainous country bordered on the north by the Republic
Nuclear energy development in the Republic of Armenia IAEA, Amsterdam 21-23 June Geography and Climate The Republic of Armenia is a landlocked mountainous country bordered on the north by the Republic
DESIGN AND SAFETY PRINCIPLES LEONTI CHALOYAN DEPUTY CHIEF ENGINEER ON MODERNIZATION
 DESIGN AND SAFETY PRINCIPLES LEONTI CHALOYAN DEPUTY CHIEF ENGINEER ON MODERNIZATION VIENNA OKTOBER 3-6, 2016 1 ANPP * ANPP is located in the western part of Ararat valley 30 km west of Yerevan close to
DESIGN AND SAFETY PRINCIPLES LEONTI CHALOYAN DEPUTY CHIEF ENGINEER ON MODERNIZATION VIENNA OKTOBER 3-6, 2016 1 ANPP * ANPP is located in the western part of Ararat valley 30 km west of Yerevan close to
REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA. Flag. Map. Coat of Arms. Republic of Armenia. Tatever Ropeway. Yerevan /Capital/ Cross-stone
 REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA Flag Map Coat of Arms Republic of Armenia Tatever Ropeway Yerevan /Capital/ Cross-stone Energy Policy B /23 June-13 July, 2013 JICA/ Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of The
REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA Flag Map Coat of Arms Republic of Armenia Tatever Ropeway Yerevan /Capital/ Cross-stone Energy Policy B /23 June-13 July, 2013 JICA/ Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of The
Transition Towards Sustainable Energy Armenia by Artashes Sargsyan; August 21, 2017 EcoTeam
 INFORSE-Europe Sustainable Energy Seminar August 21-24, 2017 Nordic Folkecenter for Renewable Energy, Denmark Transition Towards Sustainable Energy Armenia by Artashes Sargsyan; August 21, 2017 EcoTeam
INFORSE-Europe Sustainable Energy Seminar August 21-24, 2017 Nordic Folkecenter for Renewable Energy, Denmark Transition Towards Sustainable Energy Armenia by Artashes Sargsyan; August 21, 2017 EcoTeam
THEME Country profile Current state of energy sector Outlook of energy demand and supply The energy policy Documents and its implementation. Short ter
 IEEJ : June 2012 NATIONAL DISPATCHING CENTER OF POWER SYSTEMS,MONGOLIA TRAINING AND DIALOGUE PROGRAMS OF JICA www.energy.mn COUNTRY PRESENTATION: MONGOLIA ENERGY POLICY (B) THEME Country profile Current
IEEJ : June 2012 NATIONAL DISPATCHING CENTER OF POWER SYSTEMS,MONGOLIA TRAINING AND DIALOGUE PROGRAMS OF JICA www.energy.mn COUNTRY PRESENTATION: MONGOLIA ENERGY POLICY (B) THEME Country profile Current
ON THERMAL ENERGY. Based on Article 65 (1) of the Constitution of the Republic of Kosovo, LAW ON THERMAL ENERGY CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISIONS
 LAW No. No. 05/L 05/L -058-052 ON ON INDUSTRIAL THERMAL ENERGY DESIGN LAW No. 05/L -052 ON THERMAL ENERGY Assembly of the Republic of Kosovo, Based on Article 65 (1) of the Constitution of the Republic
LAW No. No. 05/L 05/L -058-052 ON ON INDUSTRIAL THERMAL ENERGY DESIGN LAW No. 05/L -052 ON THERMAL ENERGY Assembly of the Republic of Kosovo, Based on Article 65 (1) of the Constitution of the Republic
NATIONAL REPORT OF THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA CONVENTION ON NUCLEAR SAFETY
 NATIONAL REPORT OF THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA CONVENTION ON NUCLEAR SAFETY YEREVAN, AUGUST 2004 CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 4 CHAPTER 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS 1.1. Existing Nuclear Installations 5 CHAPTER 2.
NATIONAL REPORT OF THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA CONVENTION ON NUCLEAR SAFETY YEREVAN, AUGUST 2004 CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 4 CHAPTER 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS 1.1. Existing Nuclear Installations 5 CHAPTER 2.
AZERBAIJAN COUNTRY PROFILE 83
 AZERBAIJAN COUNTRY PROFILE 83 Overview The Republic of Azerbaijan has a GDP of USD 46,259 million lviii and a population of approximately 8.57 million. lix The total primary energy supply in 2007 was 11.91
AZERBAIJAN COUNTRY PROFILE 83 Overview The Republic of Azerbaijan has a GDP of USD 46,259 million lviii and a population of approximately 8.57 million. lix The total primary energy supply in 2007 was 11.91
Decommissioning and Site Release Problems for Georgian Nuclear Research Reactor IRT-M
 Decommissioning and Site Release Problems for Georgian Nuclear Research Reactor IRT-M Giorgi Nabakhtiani Grigol Kiknadze Nuclear and Radiation Safety Service Ministry of Environment Protection and Natural
Decommissioning and Site Release Problems for Georgian Nuclear Research Reactor IRT-M Giorgi Nabakhtiani Grigol Kiknadze Nuclear and Radiation Safety Service Ministry of Environment Protection and Natural
Contents. Introduction. Introduction. First Power Plant based on AC Tesla s s principles 1900! Recent Energy Sector Development
 ENERGY AGENCY OF THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA Contents Recent Energy Sector Development and AERS Responsibilities Ljiljana Hadžibabić Head of the Energy Department NARUC Energy Regulatory Partnership Program
ENERGY AGENCY OF THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA Contents Recent Energy Sector Development and AERS Responsibilities Ljiljana Hadžibabić Head of the Energy Department NARUC Energy Regulatory Partnership Program
General Overview Area km2 Population-3,5 mln Situated south-east of Europe Density of population 121.9/km2 Economy- based on sevices 75% agricul
 IEEJ : June 2012 JICA Training and Dialogue Program Moldova: Energy Security Policies and Problems Mircea Suruceanu Senior Expert, Departent for District heating Ministry of Economy of Moldova Tokyo 2012
IEEJ : June 2012 JICA Training and Dialogue Program Moldova: Energy Security Policies and Problems Mircea Suruceanu Senior Expert, Departent for District heating Ministry of Economy of Moldova Tokyo 2012
REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA LAW ON ELECTRICITY 20 July, 2000, No. VIII 1881 as amended by 26 June, 2001, No. IX-408 Vilnius CHAPTER ONE GENERAL PROVISIONS
 Official translation REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA LAW ON ELECTRICITY 20 July, 2000, No. VIII 1881 as amended by 26 June, 2001, No. IX-408 Vilnius CHAPTER ONE GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1. Purpose of the Law This
Official translation REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA LAW ON ELECTRICITY 20 July, 2000, No. VIII 1881 as amended by 26 June, 2001, No. IX-408 Vilnius CHAPTER ONE GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1. Purpose of the Law This
Schedule 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 Schedule 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION This document is intended to provide context to the Haida Gwaii Request for Expressions of Interest (RFEOI) for the potential electricity supply opportunity for clean electricity
Schedule 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION This document is intended to provide context to the Haida Gwaii Request for Expressions of Interest (RFEOI) for the potential electricity supply opportunity for clean electricity
RESULTS OF THE GRADUAL UPGRADING AT BOHUNICE WWER - 440/230 NPP
 RESULTS OF THE GRADUAL UPGRADING AT BOHUNICE WWER - 440/230 NPP P. Krupa Ingeneer, e-mail: Krupa_Peter@ebo.seas.sk Bohunice NPPs Introduction The centre of upgrading activities in VVER NPP is clearly in
RESULTS OF THE GRADUAL UPGRADING AT BOHUNICE WWER - 440/230 NPP P. Krupa Ingeneer, e-mail: Krupa_Peter@ebo.seas.sk Bohunice NPPs Introduction The centre of upgrading activities in VVER NPP is clearly in
DECOMMISSIONING OF NUCLEAR FACILITIES IN UKRAINE
 DECOMMISSIONING OF NUCLEAR FACILITIES IN UKRAINE Tatiana Kilochytska State Nuclear Regulatory Committee of Ukraine Annual Forum for Regulators and Operators in the Field of Decommissioning International
DECOMMISSIONING OF NUCLEAR FACILITIES IN UKRAINE Tatiana Kilochytska State Nuclear Regulatory Committee of Ukraine Annual Forum for Regulators and Operators in the Field of Decommissioning International
World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013
 World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013 www.smallhydroworld.org SPAIN Disclaimer Published in 2013 by United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and International Center on Small
World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013 www.smallhydroworld.org SPAIN Disclaimer Published in 2013 by United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and International Center on Small
Multiple approaches on supporting nuclear program development and contracting of NPPs
 Multiple approaches on supporting nuclear program development and contracting of NPPs STATE NUCLEAR ENERGY CORPORATION ROSATOM Technical Meeting Topical Issues on Infrastructure Development: Development
Multiple approaches on supporting nuclear program development and contracting of NPPs STATE NUCLEAR ENERGY CORPORATION ROSATOM Technical Meeting Topical Issues on Infrastructure Development: Development
NATURAL GAS MARKET IN AZERBAIJAN AND REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
 MULTI-YEAR EXPERT MEETING ON SERVICES, DEVELOPMENT AND TRADE: THE REGULATORY AND INSTITUTIONAL DIMENSION Geneva, 17-19 March 2010 NATURAL GAS MARKET IN AZERBAIJAN AND REGULATORY FRAMEWORK By Yaqub HASANOV
MULTI-YEAR EXPERT MEETING ON SERVICES, DEVELOPMENT AND TRADE: THE REGULATORY AND INSTITUTIONAL DIMENSION Geneva, 17-19 March 2010 NATURAL GAS MARKET IN AZERBAIJAN AND REGULATORY FRAMEWORK By Yaqub HASANOV
VIETNAM. FIG. 1. Map of mainland Vietnam
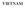 VIETNAM 988 VIETNAM VIETNAM 1. GENERAL INFORMATION 1.1. General Overview Vietnam, a nation located along the eastern coast of the mainland of Southeast Asia, is shaped like a giant letter S, extending
VIETNAM 988 VIETNAM VIETNAM 1. GENERAL INFORMATION 1.1. General Overview Vietnam, a nation located along the eastern coast of the mainland of Southeast Asia, is shaped like a giant letter S, extending
IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS for protecting people and the environment. Predisposal Management of Radioactive Waste from Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facilities
 DS447 Date: 20 February 2015 IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS for protecting people and the environment STATUS: SPESS STEP 12 For submission to CSS Predisposal Management of Radioactive Waste from Nuclear Fuel Cycle
DS447 Date: 20 February 2015 IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS for protecting people and the environment STATUS: SPESS STEP 12 For submission to CSS Predisposal Management of Radioactive Waste from Nuclear Fuel Cycle
Japan s Energy White Paper 2017
 Japan s Energy White Paper 207 Japan s Energy Landscape and Key Policy Measures PART Fukushima Reconstruction Progress PART 2 New Developments in Energy Policy PART 3 Energy System Reform and Bolstering
Japan s Energy White Paper 207 Japan s Energy Landscape and Key Policy Measures PART Fukushima Reconstruction Progress PART 2 New Developments in Energy Policy PART 3 Energy System Reform and Bolstering
Renewable energy: Investing in Africa
 1. Who is responsible for energy policy? 2. To what extent have generation, transmission and distribution activities been unbundled? 3. Who owns and operates the (grid-connected) generation, transmission
1. Who is responsible for energy policy? 2. To what extent have generation, transmission and distribution activities been unbundled? 3. Who owns and operates the (grid-connected) generation, transmission
MEMO 27 June District heating and combined heat and power in China
 MEMO 27 June 2013 File no. Ref. Ole Odgaard Page 1 District heating and combined heat and power in China District heating has expanded rapidly in Northern China since the beginning of the 1990 s. Residential
MEMO 27 June 2013 File no. Ref. Ole Odgaard Page 1 District heating and combined heat and power in China District heating has expanded rapidly in Northern China since the beginning of the 1990 s. Residential
Law of the People's Republic of China on Conserving Energy
 Law of the People's Republic of China on Conserving Energy (Adopted at the 28th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National People's Congress on November 1, 1997, promulgated by Order No.
Law of the People's Republic of China on Conserving Energy (Adopted at the 28th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National People's Congress on November 1, 1997, promulgated by Order No.
IAEA-TECDOC Energy and nuclear power planning study for Armenia
 IAEA-TECDOC-1404 Energy and nuclear power planning study for Armenia July 2004 IAEA-TECDOC-1404 Energy and nuclear power planning study for Armenia July 2004 The originating Section of this publication
IAEA-TECDOC-1404 Energy and nuclear power planning study for Armenia July 2004 IAEA-TECDOC-1404 Energy and nuclear power planning study for Armenia July 2004 The originating Section of this publication
Energy sector in Mongolia. Contents Brief of energy sector Energy sector policy Future trend
 Energy sector in Mongolia Contents Brief of energy sector Energy sector policy Future trend 1 Energy sector in Mongolia Contents Brief of energy sector Energy sector policy Future trend 2 Mongolia-Socioeconomic
Energy sector in Mongolia Contents Brief of energy sector Energy sector policy Future trend 1 Energy sector in Mongolia Contents Brief of energy sector Energy sector policy Future trend 2 Mongolia-Socioeconomic
SNRIU Nuclear installation modifications
 State Nuclear Regulatory Inspectorate of Ukraine SNRIU Nuclear installation modifications Andrii Goroshanskyi Law of Ukraine «On Use of Nuclear Energy and Radiation Safety» of 08-Feb-1995 Article 22. The
State Nuclear Regulatory Inspectorate of Ukraine SNRIU Nuclear installation modifications Andrii Goroshanskyi Law of Ukraine «On Use of Nuclear Energy and Radiation Safety» of 08-Feb-1995 Article 22. The
INSC Assistance on Improvement of Safety of Waste Management and Decommissioning Worldwide
 INSC Assistance on Improvement of Safety of Waste Management and Decommissioning Worldwide B. Batandjieva 1, B. Farrar 2 (JRC-IET, EC), M. Carton 3 (DEVCO, EC) Abstract As part of the Instrument for Nuclear
INSC Assistance on Improvement of Safety of Waste Management and Decommissioning Worldwide B. Batandjieva 1, B. Farrar 2 (JRC-IET, EC), M. Carton 3 (DEVCO, EC) Abstract As part of the Instrument for Nuclear
TRANSPORT OF NUCLEAR MATERIAL AND NUCLEAR WASTE
 GUIDE YVL 6.5 / 4 APRIL 2005 TRANSPORT OF NUCLEAR MATERIAL AND NUCLEAR WASTE 1 GENERAL 3 2 DEFINITIONS 3 3 REGULATIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES CONCERNING TRANSPORTS 4 3.1 General transport regulations for
GUIDE YVL 6.5 / 4 APRIL 2005 TRANSPORT OF NUCLEAR MATERIAL AND NUCLEAR WASTE 1 GENERAL 3 2 DEFINITIONS 3 3 REGULATIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES CONCERNING TRANSPORTS 4 3.1 General transport regulations for
Chapter: 1.1 Energy Scenario
 Chapter: 1.1 Energy Scenario Part-I: Objective type questions and answers 1. The energy sources, that are either found or stored in nature are a) Secondary Energy Sources b) Primary Energy Sources c) both
Chapter: 1.1 Energy Scenario Part-I: Objective type questions and answers 1. The energy sources, that are either found or stored in nature are a) Secondary Energy Sources b) Primary Energy Sources c) both
ECONOMIC TRENDS OF ITALIAN ELECTRICITY SECTOR SHORT TERMS STATISTICS
 NEWSLETTER January - March 2017 ECONOMIC TRENDS OF ITALIAN ELECTRICITY SECTOR SHORT TERMS STATISTICS In the first three months of 2017 data of national electricity sector has shown an increase in electricity
NEWSLETTER January - March 2017 ECONOMIC TRENDS OF ITALIAN ELECTRICITY SECTOR SHORT TERMS STATISTICS In the first three months of 2017 data of national electricity sector has shown an increase in electricity
Renewable Portfolio Standards
 Renewable Portfolio Standards Lisa Schwartz Presentation to Oregon State University Energy Economics Class Feb. 22, 2010 The Regulatory Assistance Project China EU India United States About the Regulatory
Renewable Portfolio Standards Lisa Schwartz Presentation to Oregon State University Energy Economics Class Feb. 22, 2010 The Regulatory Assistance Project China EU India United States About the Regulatory
REGULATORY CONTROL OF SAFETY AT NUCLEAR FACILITIES
 REGULATORY CONTROL OF SAFETY AT NUCLEAR FACILITIES 1 GENERAL 5 2 GOVERNMENT RESOLUTION 5 2.1 Application and its processing 5 2.2 Documents to be submitted to STUK 6 3 CONSTRUCTION LICENCE 6 3.1 Licence
REGULATORY CONTROL OF SAFETY AT NUCLEAR FACILITIES 1 GENERAL 5 2 GOVERNMENT RESOLUTION 5 2.1 Application and its processing 5 2.2 Documents to be submitted to STUK 6 3 CONSTRUCTION LICENCE 6 3.1 Licence
sustainable Energy Deployment in Egypt
 Ministry of Electricity and Renewable Energy sustainable Energy Deployment in Egypt Eng. Ahmed Mohina Undersecretary for Authorities follow up 9/11/2017 contents Where we want to be?. Where are we now?.
Ministry of Electricity and Renewable Energy sustainable Energy Deployment in Egypt Eng. Ahmed Mohina Undersecretary for Authorities follow up 9/11/2017 contents Where we want to be?. Where are we now?.
ENERGY AND WATER STATISTICS 2016
 ENERGY AND WATER STATISTICS 216 Introduction This issue of Economic and Social Indicators presents Statistics on Energy and Water for the years 215 and 216. The statistics have been compiled in close collaboration
ENERGY AND WATER STATISTICS 216 Introduction This issue of Economic and Social Indicators presents Statistics on Energy and Water for the years 215 and 216. The statistics have been compiled in close collaboration
IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS for protecting people and the environment. Predisposal Management of Radioactive Waste from Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facilities
 DS447 Date: September 2014 IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS for protecting people and the environment STATUS: SPESS STEP 11 MS comments incorporated Review Committee Member comments due 31 Oct Predisposal Management
DS447 Date: September 2014 IAEA SAFETY STANDARDS for protecting people and the environment STATUS: SPESS STEP 11 MS comments incorporated Review Committee Member comments due 31 Oct Predisposal Management
Slovenia. Key issues. General overview
 Slovenia Key issues Further strengthening of the power grid is needed to ensure the reliable and safe operation of the national electricity system. Planned investments in additional cross-border capacity
Slovenia Key issues Further strengthening of the power grid is needed to ensure the reliable and safe operation of the national electricity system. Planned investments in additional cross-border capacity
Electricity Supply. Monthly Energy Grid Output by Fuel Type (MWh)
 For the first quarter of 2015, Ontario experienced overall demand that was typical for the province in winter, and strong generator output. Demand for Ontario electricity increased as a result of cold
For the first quarter of 2015, Ontario experienced overall demand that was typical for the province in winter, and strong generator output. Demand for Ontario electricity increased as a result of cold
Green Cross Russia Nuclear and Radiation Safety Programme. V. M. Kuznetsov Contemporary state of safety at Russian nuclear installations
 Green Cross Russia Nuclear and Radiation Safety Programme V. M. Kuznetsov Contemporary state of safety at Russian nuclear installations The Russian nuclear complex (1) 213 nuclear installations (industrial
Green Cross Russia Nuclear and Radiation Safety Programme V. M. Kuznetsov Contemporary state of safety at Russian nuclear installations The Russian nuclear complex (1) 213 nuclear installations (industrial
DSS ARGOS AND RODOS WITHIN EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
 DSS ARGOS AND RODOS WITHIN EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT Radiation Emergency Centre NordDSS, Copenhagen, October 1-2, 2009 EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS AND RESPONSE ESSENTIAL REGULATIONS (1) Act of Parliament of 29 November
DSS ARGOS AND RODOS WITHIN EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT Radiation Emergency Centre NordDSS, Copenhagen, October 1-2, 2009 EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS AND RESPONSE ESSENTIAL REGULATIONS (1) Act of Parliament of 29 November
OperatiOn and safety report Of MOchOvce and BOhunice v2 nuclear power plants
 2016 OperatiOn and safety report Of MOchOvce and BOhunice v2 nuclear power plants The company is certified according to three management systems: Certificate stn en iso 9001:2008 Quality management system
2016 OperatiOn and safety report Of MOchOvce and BOhunice v2 nuclear power plants The company is certified according to three management systems: Certificate stn en iso 9001:2008 Quality management system
HYDRO ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL POLICIES IN TURKEY
 Review Article JTEN 2015 94 Journal of Thermal Engineering http://eds.yildiz.edu.tr/journal-of-thermal-engineering/articles Yildiz Technical University Press, Istanbul, Turkey Manuscript Received May 30,
Review Article JTEN 2015 94 Journal of Thermal Engineering http://eds.yildiz.edu.tr/journal-of-thermal-engineering/articles Yildiz Technical University Press, Istanbul, Turkey Manuscript Received May 30,
LAW OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA ON PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF RADIOACTIVE POLLUTION
 LAW OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA ON PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF RADIOACTIVE POLLUTION (Adopted at the 3rd Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People's Congress on June 28, 2003 and
LAW OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA ON PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF RADIOACTIVE POLLUTION (Adopted at the 3rd Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People's Congress on June 28, 2003 and
NATIONAL REPORT OF POLAND ON COMPLIANCE WITH THE OBLIGATIONS OF THE CONVENTION ON NUCLEAR SAFETY
 NATIONAL REPORT OF POLAND ON COMPLIANCE WITH THE OBLIGATIONS OF THE CONVENTION ON NUCLEAR SAFETY Polish 7 th national report as referred To in Article 5 of the Convention on Nuclear Safety (blank page)
NATIONAL REPORT OF POLAND ON COMPLIANCE WITH THE OBLIGATIONS OF THE CONVENTION ON NUCLEAR SAFETY Polish 7 th national report as referred To in Article 5 of the Convention on Nuclear Safety (blank page)
Research on China's power industry investment in Kazakhstan. Gao Yang
 International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP 2016) Research on China's power industry investment in Kazakhstan Gao Yang The Central Asian Economic Research Institute, China (Xinjiang)
International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP 2016) Research on China's power industry investment in Kazakhstan Gao Yang The Central Asian Economic Research Institute, China (Xinjiang)
IEA-DSM Task XVII: Country Report Austria
 IEA-DSM Task XVII: Country Report Austria Matthias Stifter, arsenal research 30. April 2008 AUSTRIA Facts and Figures (2005) 1 Energy consumption in Austria Figure 1 depicts the evolution of gross domestic
IEA-DSM Task XVII: Country Report Austria Matthias Stifter, arsenal research 30. April 2008 AUSTRIA Facts and Figures (2005) 1 Energy consumption in Austria Figure 1 depicts the evolution of gross domestic
CURRENT STATUS AND PERSPECTIVES OF RES DEVELOPMENT IN THE REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA.
 CURRENT STATUS AND PERSPECTIVES OF RES DEVELOPMENT IN THE REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA. National Energy Regulatory Agency ANRE Kiev, Jun 2013 Sector challenges Lack of own energy resources (natural gas, oil, coal);
CURRENT STATUS AND PERSPECTIVES OF RES DEVELOPMENT IN THE REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA. National Energy Regulatory Agency ANRE Kiev, Jun 2013 Sector challenges Lack of own energy resources (natural gas, oil, coal);
PLANT VOGTLE UNITS 3 AND 4
 PLANT VOGTLE UNITS 3 AND 4 ZERO GREENHOUSE GASES Nuclear energy facilities release zero greenhouse gases while producing electricity. A single uranium pellet the size of a pencil eraser produces as much
PLANT VOGTLE UNITS 3 AND 4 ZERO GREENHOUSE GASES Nuclear energy facilities release zero greenhouse gases while producing electricity. A single uranium pellet the size of a pencil eraser produces as much
CBM AND CMM DEVELOPMENT IN MONGOLIA NEW POLICIES TO STIMULATE CLEAN ENERGY PROJECTS
 CBM AND CMM DEVELOPMENT IN MONGOLIA NEW POLICIES TO STIMULATE CLEAN ENERGY PROJECTS Dr. Badarch Mendbayar, Director Mongolia Nature and Environment Consortium Global Methane Forum Washington, DC 29 30
CBM AND CMM DEVELOPMENT IN MONGOLIA NEW POLICIES TO STIMULATE CLEAN ENERGY PROJECTS Dr. Badarch Mendbayar, Director Mongolia Nature and Environment Consortium Global Methane Forum Washington, DC 29 30
NUCLEAR CONSULTING SERVICES
 NUCLEAR CONSULTING SERVICES AN EXPERIENCED DEVELOPER OF NEW NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS ABOUT US Brief history Lithuania has more than 30 years of experience operating and decommissioning the Ignalina NPP and
NUCLEAR CONSULTING SERVICES AN EXPERIENCED DEVELOPER OF NEW NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS ABOUT US Brief history Lithuania has more than 30 years of experience operating and decommissioning the Ignalina NPP and
Nuclear Power Economics and Markets
 Nuclear Power Economics and Markets IBC - Decommissioning of Nuclear Reactors & Materials 29 30 September 2014; Miami, Florida Edward Kee Disclaimer The NECG slides that follow are not a complete record
Nuclear Power Economics and Markets IBC - Decommissioning of Nuclear Reactors & Materials 29 30 September 2014; Miami, Florida Edward Kee Disclaimer The NECG slides that follow are not a complete record
UNMIK REGULATION NO. 2004/22 ON THE PROMULGATION OF A LAW ADOPTED BY THE ASSEMBLY OF KOSOVO ON ELECTRICITY
 UNITED NATIONS United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo UNMIK NATIONS UNIES Mission d Administration Intérimaire des Nations Unies au Kosovo UNMIK/REG/2004/22 30 June 2004 REGULATION NO.
UNITED NATIONS United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo UNMIK NATIONS UNIES Mission d Administration Intérimaire des Nations Unies au Kosovo UNMIK/REG/2004/22 30 June 2004 REGULATION NO.
KAZAKHSTAN. Titles for Table: Kazakh 48% Russian34% Ukrainian5% German3% Uzbek2% Tatar2% Korean1% Other 5%
 KAZAKHSTAN 546 KAZAKHSTAN KAZAKHSTAN 1. ENERGY, ECONOMIC AND ELECTRICITY INFORMATION 1.1. General Overview Kazakhstan is a newly independent Euro-Asian republic, created in 1991 with the dissolution of
KAZAKHSTAN 546 KAZAKHSTAN KAZAKHSTAN 1. ENERGY, ECONOMIC AND ELECTRICITY INFORMATION 1.1. General Overview Kazakhstan is a newly independent Euro-Asian republic, created in 1991 with the dissolution of
Use of PSA to Support the Safety Management of Nuclear Power Plants
 S ON IMPLEMENTATION OF THE LEGAL REQUIREMENTS Use of PSA to Support the Safety Management of Nuclear Power Plants РР - 6/2010 ÀÃÅÍÖÈß ÇÀ ßÄÐÅÍÎ ÐÅÃÓËÈÐÀÍÅ BULGARIAN NUCLEAR REGULATORY AGENCY TABLE OF CONTENTS
S ON IMPLEMENTATION OF THE LEGAL REQUIREMENTS Use of PSA to Support the Safety Management of Nuclear Power Plants РР - 6/2010 ÀÃÅÍÖÈß ÇÀ ßÄÐÅÍÎ ÐÅÃÓËÈÐÀÍÅ BULGARIAN NUCLEAR REGULATORY AGENCY TABLE OF CONTENTS
Coal Closure In Ontario
 MINISTRY OF ENERGY Coal Closure In Ontario August 2015 Purpose Ontario has experience in phasing out coal-fired electricity generation. This deck provides insight into Ontario s experience through a thorough
MINISTRY OF ENERGY Coal Closure In Ontario August 2015 Purpose Ontario has experience in phasing out coal-fired electricity generation. This deck provides insight into Ontario s experience through a thorough
Brief Overview of Renewable Energy Regulation in Tanzania
 THE ENERGY AND WATER UTILITIES REGULATORY AUTHORITY (EWURA) Brief Overview of Renewable Energy Regulation in Tanzania Presentation by Anastas P. Mbawala Director of Electricity At the NARUC EWURA Mission
THE ENERGY AND WATER UTILITIES REGULATORY AUTHORITY (EWURA) Brief Overview of Renewable Energy Regulation in Tanzania Presentation by Anastas P. Mbawala Director of Electricity At the NARUC EWURA Mission
Climate change vulnerability and adaptation in the energy sector, focus on the nuclear power sector
 Climate change vulnerability and adaptation in the energy sector, focus on the nuclear power sector Loreta Stankeviciute (IAEA) and Henri Paillère (NEA) OECD Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) and the International
Climate change vulnerability and adaptation in the energy sector, focus on the nuclear power sector Loreta Stankeviciute (IAEA) and Henri Paillère (NEA) OECD Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) and the International
Low temperature cogeneration using waste heat from research reactor as a source for heat pump
 National Centre for Nuclear Research in Poland Low temperature cogeneration using waste heat from research reactor as a source for heat pump Anna Przybyszewska International Atomic Energy Agency 14-16
National Centre for Nuclear Research in Poland Low temperature cogeneration using waste heat from research reactor as a source for heat pump Anna Przybyszewska International Atomic Energy Agency 14-16
Development of renewable energy sector in the Kyrgyz Republic
 Ministry of Energy of the Kyrgyz Republic Development of renewable energy sector in the Kyrgyz Republic Almaz Stomaliev Chief of the Power Generation and Transmission Department September 2013 Almaty 1
Ministry of Energy of the Kyrgyz Republic Development of renewable energy sector in the Kyrgyz Republic Almaz Stomaliev Chief of the Power Generation and Transmission Department September 2013 Almaty 1
GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 79 OF 2014 ON NATIONAL ENERGY POLICY THE PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA,
 GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 79 OF 2014 ON NATIONAL ENERGY POLICY THE PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA, Considering : a. that to implement the provision of Article 11
GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 79 OF 2014 ON NATIONAL ENERGY POLICY THE PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA, Considering : a. that to implement the provision of Article 11
Second Pillar: Energy
 2 nd Pillar: Energy Second Pillar: Energy Overview of Current Situation The energy sector is mainly responsible for providing for the energy needs for all economic sectors as well as families, in addition
2 nd Pillar: Energy Second Pillar: Energy Overview of Current Situation The energy sector is mainly responsible for providing for the energy needs for all economic sectors as well as families, in addition
German contribution on the safety assessment of research reactors
 German contribution on the safety assessment of research reactors S. Langenbuch J. Rodríguez Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) mh. Schwertnergasse 1, D-50667 Köln, Federal Republic
German contribution on the safety assessment of research reactors S. Langenbuch J. Rodríguez Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) mh. Schwertnergasse 1, D-50667 Köln, Federal Republic
MONGOLIA COUNTRY PROFILE 88
 MONGOLIA COUNTRY PROFILE 88 Overview Mongolia has a GDP of USD 5,259 million lxvi and a population of approximately 2.61 million. lxvii The total primary energy supply in 2007 was 3.09 Mtoe (million tons
MONGOLIA COUNTRY PROFILE 88 Overview Mongolia has a GDP of USD 5,259 million lxvi and a population of approximately 2.61 million. lxvii The total primary energy supply in 2007 was 3.09 Mtoe (million tons
RES-E policy and planning in GREECE
 RES-E policy and planning in GREECE Dimitri Lalas face 3 ts S.A. Sofia 17-19Jan2017 1 Questions Posed 1. Present RES-E support scheme Is your country on the path to reach its 2020 RES-E target? Key barriers
RES-E policy and planning in GREECE Dimitri Lalas face 3 ts S.A. Sofia 17-19Jan2017 1 Questions Posed 1. Present RES-E support scheme Is your country on the path to reach its 2020 RES-E target? Key barriers
Cooperation in the Energy Sector
 MINISTRY OF ENERGY AND INDUSTRY OF THE KYRGYZ REPUBLIC Cooperation in the Energy Sector Ministry of Energy and Industry of the Kyrgyz Republic Speaker: Aibek R. Kaliev, Deputy Minister Bishkek, 2014 Following
MINISTRY OF ENERGY AND INDUSTRY OF THE KYRGYZ REPUBLIC Cooperation in the Energy Sector Ministry of Energy and Industry of the Kyrgyz Republic Speaker: Aibek R. Kaliev, Deputy Minister Bishkek, 2014 Following
CIRCULAR GENERAL PROVISIONS
 MINISTRY OF CONSTRUCTION -------- SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness --------------- No. 10/2013/TT-BXD Hanoi, July 25, 2013 CIRCULAR ON CONSTRUCTION QUALITY MANAGEMENT Pursuant
MINISTRY OF CONSTRUCTION -------- SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness --------------- No. 10/2013/TT-BXD Hanoi, July 25, 2013 CIRCULAR ON CONSTRUCTION QUALITY MANAGEMENT Pursuant
Module 05 WWER/ VVER (Russian designed Pressurized Water Reactors)
 Module 05 WWER/ VVER (Russian designed Pressurized Water Reactors) 1.3.2016 Prof.Dr. Böck Technical University Vienna Atominstitut Stadionallee 2, 1020 Vienna, Austria ph: ++43-1-58801 141368 boeck@ati.ac.at
Module 05 WWER/ VVER (Russian designed Pressurized Water Reactors) 1.3.2016 Prof.Dr. Böck Technical University Vienna Atominstitut Stadionallee 2, 1020 Vienna, Austria ph: ++43-1-58801 141368 boeck@ati.ac.at
Gas transmission system of the Republic of Moldova. Regulatory documents for the construction of new pipelines.
 JSC "Moldovagaz" Gas transmission system of the Republic of Moldova. Regulatory documents for the construction of new pipelines. D.N. Bichek Head of Department of the gas complex development and operation
JSC "Moldovagaz" Gas transmission system of the Republic of Moldova. Regulatory documents for the construction of new pipelines. D.N. Bichek Head of Department of the gas complex development and operation
WIND POWER TARGETS FOR EUROPE: 75,000 MW by 2010
 About EWEA EWEA is the voice of the wind industry actively promoting the utilisation of wind power in Europe and worldwide. EWEA members from over 4 countries include 2 companies, organisations, and research
About EWEA EWEA is the voice of the wind industry actively promoting the utilisation of wind power in Europe and worldwide. EWEA members from over 4 countries include 2 companies, organisations, and research
ARMENIA ELECTRICITY DEMAND FORECAST
 ARMENIA ELECTRICITY DEMAND FORECAST ASSISTANCE TO ENERGY SECTOR TO STRENGTHEN ENERGY SECURITY AND REGIONAL INTEGRATION CONTRACT NUMBER EPP-I-08-03-00008-00 NOVEMBER 2012 This publication was produced for
ARMENIA ELECTRICITY DEMAND FORECAST ASSISTANCE TO ENERGY SECTOR TO STRENGTHEN ENERGY SECURITY AND REGIONAL INTEGRATION CONTRACT NUMBER EPP-I-08-03-00008-00 NOVEMBER 2012 This publication was produced for
SB 838: Oregon Renewable Energy Act Establishing an Oregon Renewable Energy Standard
 SB 838: Oregon Renewable Energy Act Establishing an Oregon Renewable Energy Standard Section-by-Section Summary SB 838, C-engrossed version As passed by Oregon House of Representatives, May 23 rd, 2007.
SB 838: Oregon Renewable Energy Act Establishing an Oregon Renewable Energy Standard Section-by-Section Summary SB 838, C-engrossed version As passed by Oregon House of Representatives, May 23 rd, 2007.
Commercial Nuclear Fuel Leasing The Relationships to Nonproliferation and Repository Site Performance
 Commercial Nuclear Fuel Leasing The Relationships to Nonproliferation and Repository Site Performance D.L. Pentz The Pentz Consulting Company, Inc. 4062 S. Beach Dr., Freeland, WA 98249 USA R.H. Stoll
Commercial Nuclear Fuel Leasing The Relationships to Nonproliferation and Repository Site Performance D.L. Pentz The Pentz Consulting Company, Inc. 4062 S. Beach Dr., Freeland, WA 98249 USA R.H. Stoll
Official Journal of the European Union DIRECTIVE 2003/54/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL. of 26 June 2003
 15.7.2003 L 176/37 DIRECTIVE 2003/54/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 26 June 2003 concerning common rules for the internal market in electricity and repealing Directive 96/92/EC THE EUROPEAN
15.7.2003 L 176/37 DIRECTIVE 2003/54/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 26 June 2003 concerning common rules for the internal market in electricity and repealing Directive 96/92/EC THE EUROPEAN
NATIONAL POLICY FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
 REPUBLIC OF BULGARIA MINISTRY OF ECONOMY, ENERGY AND TOURISM NATIONAL POLICY FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Aleksandrina Dimitrova Head of Department Renewable Energy Sources Energy
REPUBLIC OF BULGARIA MINISTRY OF ECONOMY, ENERGY AND TOURISM NATIONAL POLICY FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Aleksandrina Dimitrova Head of Department Renewable Energy Sources Energy
Oregon Renewable Energy Resources
 Background Brief on September 2012 Inside this Brief Overview of Renewable Energy Renewable Portfolio Standard Energy Facility Siting Renewable Energy Legislation Staff and Agency Contacts State Capitol
Background Brief on September 2012 Inside this Brief Overview of Renewable Energy Renewable Portfolio Standard Energy Facility Siting Renewable Energy Legislation Staff and Agency Contacts State Capitol
2.ENERGY AND OIL #INVESTINGUATEMALA. Industry in Guatemala
 2.ENERGY AND OIL #INVESTINGUATEMALA Industry in Guatemala General information of the country Capital City Currency Exchange Rate (2013) Official Language Population Labor Force (2013) GDP (2013) FDI inflows
2.ENERGY AND OIL #INVESTINGUATEMALA Industry in Guatemala General information of the country Capital City Currency Exchange Rate (2013) Official Language Population Labor Force (2013) GDP (2013) FDI inflows
World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013
 World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013 www.smallhydroworld.org SLOVENIA 4 Europe 4.3 Southern Europe 4.3.10 Slovenia European Small Hydropower Association, Stream Map Key facts Population 1,996,617
World Small Hydropower Development Report 2013 www.smallhydroworld.org SLOVENIA 4 Europe 4.3 Southern Europe 4.3.10 Slovenia European Small Hydropower Association, Stream Map Key facts Population 1,996,617
NUCLEAR SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BSR
 NUCLEAR SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BSR-1.8.2-2015 APPROVED BY Order No. 22.3-99 of The Head of State Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate, of 7 October 2011 (as amended by Order No. 22.3-57 of the Head of State
NUCLEAR SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BSR-1.8.2-2015 APPROVED BY Order No. 22.3-99 of The Head of State Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate, of 7 October 2011 (as amended by Order No. 22.3-57 of the Head of State
THE NEW LAW FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES IN GREECE AND MEASURES FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PHOTOVOLTAIC APPLICATIONS IN THE COUNTRY
 THE NEW LAW FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES IN GREECE AND MEASURES FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PHOTOVOLTAIC APPLICATIONS IN THE COUNTRY C Protogeropoulos CRES Centre for Renewable Energy Sources Department of
THE NEW LAW FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES IN GREECE AND MEASURES FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PHOTOVOLTAIC APPLICATIONS IN THE COUNTRY C Protogeropoulos CRES Centre for Renewable Energy Sources Department of
Lessons Learnt after the Chernobyl Accident 25 Years Later
 Lessons Learnt after the Chernobyl Accident 25 Years Later Helena Janžekovič Slovenian Nuclear Safety Administration P.O. Box 5759, Železna cesta 16 SI-1001, Ljubljana, Slovenia helena.janzekovic@gov.si
Lessons Learnt after the Chernobyl Accident 25 Years Later Helena Janžekovič Slovenian Nuclear Safety Administration P.O. Box 5759, Železna cesta 16 SI-1001, Ljubljana, Slovenia helena.janzekovic@gov.si
Development of Renewable Energies in Tunisia
 Development of Renewable Energies in Tunisia Mr. Mustapha EL HADDAD Introduction This article aims at highlighting development opportunities for renewable energies (RE) in Tunisia. It covers five RE sectors
Development of Renewable Energies in Tunisia Mr. Mustapha EL HADDAD Introduction This article aims at highlighting development opportunities for renewable energies (RE) in Tunisia. It covers five RE sectors
Methodology for calculating subsidies to renewables
 1 Introduction Each of the World Energy Outlook scenarios envisages growth in the use of renewable energy sources over the Outlook period. World Energy Outlook 2012 includes estimates of the subsidies
1 Introduction Each of the World Energy Outlook scenarios envisages growth in the use of renewable energy sources over the Outlook period. World Energy Outlook 2012 includes estimates of the subsidies
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN RUSSIA. CURRENT STATE AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS
 RENEWABLE ENERGY IN RUSSIA. CURRENT STATE AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS Vladimir Karghiev Senior Expert on renewable energies EU Russia Energy Dialogue Technology Centre Solar Energy Center Intersolarcenter Moscow,
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN RUSSIA. CURRENT STATE AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS Vladimir Karghiev Senior Expert on renewable energies EU Russia Energy Dialogue Technology Centre Solar Energy Center Intersolarcenter Moscow,
Assessment of Turkey s Nuclear Energy Policy. Mustafa YAVUZDEMIR 2017
 Assessment of Turkey s Nuclear Energy Policy By Mustafa YAVUZDEMIR 2017 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Past and Current Energy Context 3. Challenges to Achieve Sufficient Nuclear Capacity 4. Current Legal
Assessment of Turkey s Nuclear Energy Policy By Mustafa YAVUZDEMIR 2017 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Past and Current Energy Context 3. Challenges to Achieve Sufficient Nuclear Capacity 4. Current Legal
Legislative Framework for the Regulation of Decommissioning at Egypt. Prof. Dr. Farouk M. A. Rahman
 Legislative Framework for the Regulation of Decommissioning at Egypt Prof. Dr. Farouk M. A. Rahman Egypt Framework for Decommissioning Legal Decree of the president of the United Arab Republic, law 59
Legislative Framework for the Regulation of Decommissioning at Egypt Prof. Dr. Farouk M. A. Rahman Egypt Framework for Decommissioning Legal Decree of the president of the United Arab Republic, law 59
CLASSIFICATION OF SYSTEMS, STRUCTURES AND COMPONENTS OF A NUCLEAR FACILITY
 CLASSIFICATION OF SYSTEMS, STRUCTURES AND COMPONENTS OF A NUCLEAR FACILITY 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope of application 3 3 Classification requirements 3 3.1 Principles of safety classification 3 3.2 Classification
CLASSIFICATION OF SYSTEMS, STRUCTURES AND COMPONENTS OF A NUCLEAR FACILITY 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope of application 3 3 Classification requirements 3 3.1 Principles of safety classification 3 3.2 Classification
Country profile. More from less material resource efficiency in Europe overview of policies, instruments and targets in 32 countries.
 Country profile More from less material resource efficiency in Europe 2015 overview of policies, instruments and targets in 32 countries Lithuania May 2016 This country profile is based on information
Country profile More from less material resource efficiency in Europe 2015 overview of policies, instruments and targets in 32 countries Lithuania May 2016 This country profile is based on information
Reactor Technology: Materials, Fuel and Safety. Dr. Tony Williams
 Reactor Technology: Materials, Fuel and Safety Dr. Tony Williams Course Structure Unit 1: Reactor materials Unit 2. Reactor types Unit 3: Health physics, Dosimetry Unit 4: Reactor safety Unit 5: Nuclear
Reactor Technology: Materials, Fuel and Safety Dr. Tony Williams Course Structure Unit 1: Reactor materials Unit 2. Reactor types Unit 3: Health physics, Dosimetry Unit 4: Reactor safety Unit 5: Nuclear
SCADA/EMS for Unified Power System of Russia
 1 SCADA/EMS for Unified Power System of Russia Oxana Yakovleva Head of SCADA/EMS PIU, System Operator for UES of Russia Vladimir Calovic KEMA Consulting EPCC - les Diablerets, Switzerland, June 8, 2005
1 SCADA/EMS for Unified Power System of Russia Oxana Yakovleva Head of SCADA/EMS PIU, System Operator for UES of Russia Vladimir Calovic KEMA Consulting EPCC - les Diablerets, Switzerland, June 8, 2005
CANADIAN RENEWABLE & CONSERVATION EXPENSE ("CRCE") "CLEAN" ENERGY TAX INCENTIVES MARCH 31, 2016
 CANADIAN RENEWABLE & CONSERVATION EXPENSE ("CRCE") "CLEAN" ENERGY TAX INCENTIVES MARCH 31, 2016 This updated article is an overview of the Canadian income tax considerations relevant to Canadian renewable
CANADIAN RENEWABLE & CONSERVATION EXPENSE ("CRCE") "CLEAN" ENERGY TAX INCENTIVES MARCH 31, 2016 This updated article is an overview of the Canadian income tax considerations relevant to Canadian renewable
ENERGY CHARTER PROTOCOL ON ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RELATED ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS (Annex 3 to the Final Act of the European Energy Charter Conference)
 ENERGY CHARTER PROTOCOL ON ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RELATED ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS (Annex 3 to the Final Act of the European Energy Charter Conference) PREAMBLE THE CONTRACTING PARTIES to this Protocol, Having
ENERGY CHARTER PROTOCOL ON ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND RELATED ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS (Annex 3 to the Final Act of the European Energy Charter Conference) PREAMBLE THE CONTRACTING PARTIES to this Protocol, Having
CHINA 2050 HIGH RENEWABLE ENERGY PENETRATION SCENARIO AND ROADMAP STUDY. Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission
 CHINA 2050 HIGH RENEWABLE ENERGY PENETRATION SCENARIO AND ROADMAP STUDY Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission ENERGY RESEARCH INSTITUTE NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND REFORM COMMISSION
CHINA 2050 HIGH RENEWABLE ENERGY PENETRATION SCENARIO AND ROADMAP STUDY Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission ENERGY RESEARCH INSTITUTE NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND REFORM COMMISSION
Energy Resources and Security of Supply in Serbia
 ENERGY AGENCY OF THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA Energy Resources and Security of Supply in Serbia Energy Balances and Infrastructure Development Ljiljana Hadžibabić Head of the Technical Department Energy Regulatory
ENERGY AGENCY OF THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA Energy Resources and Security of Supply in Serbia Energy Balances and Infrastructure Development Ljiljana Hadžibabić Head of the Technical Department Energy Regulatory
MALAYSIA: OPTIMIZING IAEA & INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION FOR A NEW NUCLEAR POWER PROJECT
 MALAYSIA: OPTIMIZING IAEA & INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION FOR A NEW NUCLEAR POWER PROJECT By Dato Dr Muhamad Lebai Juri Director General Malaysian Nuclear Agency IAEA National Liaison Agency OUTLINE Introduction
MALAYSIA: OPTIMIZING IAEA & INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION FOR A NEW NUCLEAR POWER PROJECT By Dato Dr Muhamad Lebai Juri Director General Malaysian Nuclear Agency IAEA National Liaison Agency OUTLINE Introduction
Independent Power Production Policy
 ENERGY STRATEGY FOR YUKON Independent Power Production Policy October 2015 BACKGROUND The Government of Yukon (YG) released the Energy Strategy for Yukon in January 2009. The strategy sets out YG s energy
ENERGY STRATEGY FOR YUKON Independent Power Production Policy October 2015 BACKGROUND The Government of Yukon (YG) released the Energy Strategy for Yukon in January 2009. The strategy sets out YG s energy
Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its Mitigation
 Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 1 (2016) 32-37 doi: 10.17265/2332-8215/2016.01.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 1 (2016) 32-37 doi: 10.17265/2332-8215/2016.01.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its
DISTRIBUTION DISPATCHING THE MISSING LINK IN ELECTRICAL INDUSTRY IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES
 DISTRIBUTION DISPATCHING THE MISSING LINK IN ELECTRICAL INDUSTRY IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES R.Kalili M. Mehri Tehran South- East Distribution Company Tehran Center Distribution Company Abstract During recent
DISTRIBUTION DISPATCHING THE MISSING LINK IN ELECTRICAL INDUSTRY IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES R.Kalili M. Mehri Tehran South- East Distribution Company Tehran Center Distribution Company Abstract During recent
GEODE S POSITION ON THE EC DIRECTIVE PROPOSAL
 GEODE S POSITION ON THE EC DIRECTIVE PROPOSAL Christian Held, Deputy Chairman of GEODE GEODE Autumn Conference 21 st October 2011 Wien Energie Stromnetz GmbH Mariannengasse 4-6 Vienna 2 Summary I. Introduction
GEODE S POSITION ON THE EC DIRECTIVE PROPOSAL Christian Held, Deputy Chairman of GEODE GEODE Autumn Conference 21 st October 2011 Wien Energie Stromnetz GmbH Mariannengasse 4-6 Vienna 2 Summary I. Introduction
ENERGY BALANCE OF VIETNAM BY 2020
 MINISTRY OF INDUSTRY AND TRADE ENERGY BALANCE OF VIETNAM BY 2020 April-2009 CONTENTS General information about Vietnam s energy resources Current status of Vietnam s energy supply vs. demand Forecasted
MINISTRY OF INDUSTRY AND TRADE ENERGY BALANCE OF VIETNAM BY 2020 April-2009 CONTENTS General information about Vietnam s energy resources Current status of Vietnam s energy supply vs. demand Forecasted
