Study on Anaerobic Landfill Leachate Treatability by Membrane Bioreactor
|
|
|
- Jewel Clark
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2010 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry IPCBEE vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Study on Anaerobic Landfill Leachate Treatability by Membrane Bioreactor Rouhallah Mahmoudkhani, Amir Hessam Hassani, Seyed Mahdi Borghei Department of Environmental and Energy Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University Tehran, Iran Ali Torabian Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Tehran Tehran, Iran Abstract This study was undertaken to examine feasibility of biological treating of landfill leachate that was collected from Tehran municipal landfill with about year old. Average COD of the leachate in aerobic submerged membrane bioreactor is mg/l. The reactor with a working volume of 175 L, having membrane module (Hollow fiber) with pore size of 0.1 µm was used in this study. The dissolved oxygen concentration (DO) was maintained at 3.2 mg/l and solid retention times (SRTs) and hydraulic retention times (HRT) were controlled at 55 and 15 days respectively. Following that the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) was stabilized at 6.3 g/l. Under condition of COD/N ratio of 46 and COD/PO 4 -P ratio of 455 and BOD/COD ratio of 0.65, the average effluent COD was 1733 mg/l with average removal efficiency of 97.46%. The average NH 4 N removal efficiencies was 99% which was reached to 99.7% at maximum level. Keywords-Municipal landfill; leachate; Membrane bioreactor; Nutrient removal I. INTRODUCTION The method of anaerobic sanitary landfill for the disposal of municipal solid wastes continues to be widely used in the most countries in the world [3, 17 and 19]. Leachate is a high-strength wastewater formed as a result of percolation of rain-water and moisture through waste in landfills [1]. During the formation of leachate, organic and inorganic compounds are transferred from waste to the liquid medium [21] and pose a hazard to the receiving water bodies. Production of landfill leachate begins with introducing moisture waste into disposal area and continues for several decades following the landfill closure. Leachate contains high organic matter and ammonium nitrogen and varies from site to site and its composition depends upon the landfill age, the quality and quantity of waste, biological and chemical processes that took place during disposal, rainfall density, and water percolation rate through the waste in the landfill. Depending upon what was placed in the landfill, leachate may contain many types of contaminants, and if not removed by treatment, these contaminants may be toxic to life or simply alter the ecology of receiving streams. leachate should be treated before reaching surface water or ground water bodies, because it can accelerate algae growth due to its high nutrient content, deplete dissolved oxygen in the streams, and cause toxic effects in the surrounding water life. Since the composition of a leachate consists of a wide range of contaminants, it cannot be easily treated by conventional methods. Therefore, a number of scientists around the world have intensively focused on the combination of biological and physico-chemical treatment systems for effective leachate treatment [18, 1]. Alternative treatments have been reviewed. Briefly, leachate can be recirculated to the same landfill or treated by different methods: biological, aerobic, anaerobic methods and/or nitrification denitrification to remove organic matter and ammonium nitrogen. Biological processes to remove organic matter can be effective for young leachate with a high BOD5/COD ratio [2]. Many researchers reported that the membrane bioreactors are effective treatment alternatives for the young leachates [1] Landfill leachate is characterized by its generation rate and composition, both of which are affected by the age of the landfill site [22]. In particular,.leachate consists of many different organic and inorganic compounds that may be either dissolved or suspended and which are biodegradable and nonbiodegradable [22]. In addition to this, the characteristic of the leachate varies with regard to its composition and volume, and biodegradable matter present in the leachate with time. For this reason, young and old landfill leachates have very different features. Calace et al. reported that the young landfill leachate fractions have low molecular weight distributions (<500 Da) at the rate of 70%, while the high molecular weight distribution (>10,000 Da) is 18%. Besides, the low and high molecular weight distributions are 28 and 67%, respectively, in old landfill leachate samples [3]. According to this result, easily biodegradable components of leachate reduce, and constituents having high molecular weights and that are nonbiodegradable increase in the course of time. These factors make leachate treatment difficult and these factors needed to be taken into account when different treatment processes are considered. The treatment requirements for leachate from sanitary landfills can vary depending on the discharge limits and contaminants present [3]. Among advanced biological treatment processes, membrane bioreactor (MBR) is the most important process [1]. MBR are considered as a good integration of conventional activated sludge (CAS) system and advanced membrane separation, thus enabling the independent control of sludge retention time (SRT) and hydraulic retention time (HRT) and retaining a high concentration of sludge biomass 5
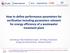
2 in the reactors. Compared with CAS processes, MBR process has great advantages including a smaller footprint, less sludge production and better effluent quality [23]. MBR can be operated at very long sludge ages and can extend greatly the field of application of biological processes for concentrated streams, such as leachate [18], The combination of membrane separation technology and bioreactors has led to a new focus on wastewater treatment. It contributes to very compact systems working with a high biomass concentration and achieving a low sludge production with an excellent effluent quality. Membrane bioreactors have been widely applied at full scale on industrial wastewater treatment and some plants have been adapted to leachate treatment [7, 8]. The process efficiencies were in the range of 95 98% in terms of TOC reduction, and exceeded 97% for specific organic pollutants. Contrary to conventional systems, organisms such as nitrifiers or organisms which are able to degrade slowly biodegradable substances are not washed out of the system and no loss of process activity occurs [8]. II. MATERIALS AND METHODS A. leachate feed The leachate used in this study was collected from a municipal landfill located in Kahrizak near Tehran city in the Tehran province. The landfill has been in operation since 1985, the old of landfill for sampling is years old. The large volume samples (200 L) were collected and stored in a retention tank every week. The characteristics of the landfill leachate investigated are shown in Table 1. Leachate used during this study was young because it contained readily biodegradable organic matter [1]. TABLE I. AVERAGE QUALITY OF LANDFILL LEACHATE USED AS FED Parameter Values COD, mg/l 68250±8000 BOD, mg/l 44500±3000 NH3+NH4-N, mg/l 1470±90 NO3+ NO2-N, mg/l 150±50 ph 6.9±0.2 PO4-P, mg/l 130±40 BOD/COD 0.65 COD/N Cl-, mg/l 14800±1000 SO4, mg/l 5500±300 Conductivity, ms/m 44±6.5 Turbidity, Ntu 3896±270 B. process configuration and system design The investigations were carried out at a laboratory scale in a MBR reactor. The reactor with a working volume of 175 L was made of Plexiglas. Dissolved oxygen was supplied using 2 fine bubble disc diffusers (Ecoflex 250 CV). Made by USA diffuser tech Co. Placed at the bottom of the reactor, producing bubbles of pour size. The amount of oxygen supplied to the reactor was regulated in order to maintain the oxygen concentration at a level of 3 mg/l, one blower pump with capacity of 190 m3h-1 and pressure of 320 mbar, supplied system air requirement, an adjustable air valve controlled. To startup the reactor, we used the returned activated sludge of Gitarieh wastewater treatment plant, which is located in north of Tehran. After each time of aeration rates changes we gave minimum 55 day (SRT) to system to adapt with new condition, analyses were done, when the system reached steady state condition, MLSS at the end of operation in the reactor is assumed as the steady state index, samples were taken from feed and treated leachate, samples were stored in polyethylene cap bottles with capacity of about 100 ml, temperature and dissolved oxygen is measured online air volumetric flow rate in aeration reactor was measured by a volumetric contour in a defined time. Due to importance of timely stages control in MBR system as well as setting feeding, vacuuming, backwashing and measuring and recording of dissolve oxygen and temperature, we used a PLC and computerized system with essential accessories, includes control and relays boards, dissolved oxygen and temperature probes, electrical valves, feed pump, figure 1 present system schematic, which had a working volume of approximately 175 L, in which the membrane module was directly submerged, is shown in Fig. 1. The dissolved oxygen concentration (DO) was maintained at 3.2 mg/l by adjusting the air flow to 4 m 3 h/l. The water level in the bioreactor was controlled with a level controller and a level sensor. The concentration of the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) was 6300 mg/l. The sludge was withdrawn continuously with a pump set at different solid retention times (SRTs). HRT was controlled at 15 days by a rotary flow meter under the operational condition of invariable membrane flux, The effluent of the bioreactor was connected to an automatic vacuum effluent system directly by a rotary flow meter. When the vacuum pump started, part of the gas in the MBR was pumped out to create a negative pressure, and then the wastewater in the bioreactor was drained out through the membrane module and entered into the treated wastewater tank. Backwash electrical gate valve (1 minute in 1 hour) and vacuum pump (3 minutes in 1 hour) periodically run in the automatic vacuum effluent system. However minimum vacuum level was kept by a floater, whether feeding or vacuum pumps were operating or not. Therefore, wastewater noncontinuous entered the bioreactor through the flowed into the submerged membrane module. Feeding pump operate noncontinuous at operating time. C. Membrane characteristics In this pilot-plant test, a hollow-fiber pp microfiltration (MF) membrane was used with pore size of 0.1µm and the effective surface area of a MF membrane module at 4m2. Membrane flux was between 0.5 and 0.8 m 3 /d. TABLE II. TECHNICAL DATA OF POLY PROPYLENE HOLLOW FIBER. Parameter Hollow fiber Raw material PP Diameter inside µm Diameter outside µm Pore size µm Pore density 40-50% 6
3 Membrane area Pressure minus 4 m Mpa ph 0-14 Available temp ºc D. Analytical methods and leachates A lab-scale MBR was set up for COD and biological nutrient removal with a flow rate of 12 L/day. and operated under a total SRT of 55 days, and an HRT of 15 days. Influent characteristics were measured once per week. The effluent BOD5, COD, NO3-N, and PO4-P, NH4 -N, NO2-N, EC, turbidity, Cl-, SO4 were monitored for six week. All experiments were conducted under conditions of constant temperature (21 ºC) and controlled ph (9.5).Determination of COD, BOD5, nitrite, nitrate, ammonium, phosphate, sulfate, CL-, conductivity, MLSS and turbidity were performed according to standard methods, 20th ed. [4] Were used for measurement of total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), volatile fatty acids (VFA), ammonia nitrogen (NH4 ), chloride, total alkalinity and ph. Chemical oxidation demand was analyzed colorimetrically using tests and photometer of the HACH firm (DR 2010). III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. COD removal The average COD concentrations in the influent are mg/l. During the operation, removal efficiencies of COD were above 97.0% suggesting that it was irrespective of COD/N ratios. With high COD/N ratio of 45, the nutrient requirements decrease as the sludge age increases because net sludge production decreases as sludge age increases generally, for sludge ages greater than 10 days, the nitrogen removal attributable to net sludge production is less than 40 mg COD/mg N applied [5]. The maximum value for percent COD removal was obtained around COD/P-PO4 =160 and then dropped above 160 indicating phosphate limitation at high COD [10]. Increasing COD/N-NH4 ratios from 10 to 50 resulted in decreases in COD removal efficiencies steadily possibly because of ammonium and PO4 limitations at high COD/N-NH4 and COD/P-PO4 ratio [10]. in this study the sludge age (SRT) regulate at 55 days then the MLSS was stabilized at 6.3 g/l, Despite the fluctuations of average influent COD concentration ranging from mg/l to mg/l, the effluent COD concentrations were always lower than 1935 mg/l. as shown in Fig. 2 (a), The average effluent COD concentrations was 1733 mg/l, with the average efficiency of 97.46%, under COD/N ratio of 46 and COD/PO4-P ratio of 455 and BOD/COD ratio of 0.65 These data indicated that the system could provide a consistent high efficiency of COD removal. B. Nitrogen removal Removal efficiency for ammonium-nitrogen increased with COD/NH4-N ratio between 10 and 40, because of high ammonium concentrations at low COD/NH4-N ratio, ammonium removal efficiencies were low [10]. Increasing COD/PO4-P ratio resulted in steady increases in NH4-N removal efficiencies for COD/PO4-P values between 40 and 250 indicating adverse effects of high phosphate levels or COD limitations at low COD/PO4-P values [10]. During the whole operation, the removal efficiencies of NH 4 N and TN were as good as COD removal, as shown in Fig. 2 (b). During the operation of COD/N is 46.42, the NH 4 N and TN concentrations removal in effluent were almost the same, indicating no NOx N accumulation was observed in the reactor. Produces of nitrification were almost completely denitrified to nitrogen gas. The average NH 4 N and TN removal efficiencies were 99% while the average NH 4 N effluent concentrations were 10 mg/l, initially, nitrification activity increased gradually, and the highest NH 4 N removal efficiency was 99.7%. However, an almost completely nitrification was achieved during this period. These data showed that mg/l NOx N was remained after days, which implying that the denitrification was accomplished completely. From 20 d to 40 d, the effluent NH 4 N concentration was increased to above 10 mg/l, Initially, the effluent NH 4 N and TN concentrations increased drastically, due to that the microorganism need a period to acclimate the change. Afterwards, effluent concentrations were decreased gradually, suggesting that the nitrification and denitrification capacities were strengthened gradually. C. PO4-P removal Increasing COD/PO4-P values from 40 and 160 resulted in increases in phosphate removal efficiency. Because of excess phosphate or COD limitations at low COD/PO4-P values the phosphate removal efficiency was low. The efficiency decreased for COD/PO4-P values above 200 because of phosphate limitations at high COD/PO4-P values [10]. Fig. 2 (c) presents the PO4 P concentrations in the effluent during the whole operation period. With COD/PO4- P ratio of 455, although the PO4 P concentration in the effluent was low and the average PO4 P removal efficiency was as high as 90%.with increasing COD/N ratio, the PO4 P concentrations in anoxic and aerobic zones decreased insignificantly, and effluent concentration between 1d and 20d was as high as mg/l and the average PO4 P removal efficiency was 85.3%, especially during operation period The PO4 P removal process was stabilized between 20 d and 40 d, with average PO4 P effluent concentration of 6.1 mg/l and removal efficiency of 96%.Additionally, PO4 P release process ceased in anoxic zone. Results indicated that low COD/N ratio decreased PO4 P removal efficiency. And increasing sludge age increasing the PO3_ 4 P removal efficiency. IV. CONCLUSIONS The present study contains results of landfill leachate treatability by membrane bioreactor that is important for modeling, design, and operation of landfill leachate treatment MBRs and determination of discharge limits. Suitable treatment strategy depends on two major criteria: 1. the initial leachate quality and 2. the final requirements given by local discharge water standards [17] the presented data indicate that the landfill leachate composition has a 7
4 significant effect on treatability, in the young landfills and composting units leachate that organics concentration (expressed COD), BOD/COD, Ph, COD/NH4-N ratio is high. The membrane bioreactor has to operate with sludge age greater than 50 days, hydraulic retention times (HRT) 15 days. MBR was developed and demonstrated herein to treat landfill leachate. In order to evaluate the biological treatability of the landfill leachate, the removal efficiency of COD, NH4-N and PO4 P were investigated, These data indicated that The system provided high removals in terms COD, NH4-N and PO4 P removal equal to 97%, 99% and 90.5% respectively. However after treatment in the MBR. The average effluent concentrations of COD, NH 4 N and PO4 P were 1733, 10 and 13 mg/l, respectively, all of them over the permissible limit for IRAN discharge standards (COD < 200 mg/l, NH 4 -N < 2.5 mg/l, PO4 P< 6 mg/l), quality of the effluent from MBR system was not appropriate for discharging into receiving waters requiring an additional aerobic post treatment regarding polishing purposes. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors thank the Islamic Azad University Tehran medical branch, Iran municipalities and rural organization and Tehran municipality for supporting the study. REFERENCES [1] H. Hasar, S. A. Unsal, U. Ipek, S. Karatas, O. Cınar, C. Yaman, C. Kınac, Stripping/ flocculation/ membrane bioreactor/reverse osmosis treatment of municipal landfill leachate, Journal of Hazardous Materials,vol. 171,pp , [2] E. Maranon, L. Castrillon, Y. Fernandez-Nava, A. Fernandez-M endez, A. Fernandez-Sanchez, Coagulation flocculation as a pretreatment process at a landfill leachate nitrification denitrification plant, Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 156, pp , [3] M. S. Bilgili, A. Demir, E. Akkaya, B. Ozkaya, COD fractions of leachate from aerobic and anaerobic pilot scale landfill reactors, Journal of Hazardous Materials,vol. 158,pp , [4] standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th ed., [5] Marais, G.V.R., Wastewater treatment by activated sludge process. Lecture notes. University of Cape Town. South Africa. International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, the Netherlands, [6] USEPA., fine pore aeration systems. Design Manual. EPA/625/1-89/ [7] L. Van Dijk, G.C.G. Roncken, Membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: the state of the art and new developments,water Sci. Technol., vol. 35, pp , [8] S. Renou, J.G. Givaudan, S. Poulain, F. Dirassouyan, P. Moulin, Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity, Journal of Hazardous Materials,vol. 150, pp , (2008). [9] A.K. Azimi, S.H. Hashemi, G.N. Bidhendi, R. Mahmoodkhani, Aeration ratio effect on efficiency of materials removal in sequencing batch reactors, Pakistan journal of biological sciences,vol. 8(1), pp , [10] F. Kargi, A. Uygur, Nutrient removal per formance of a five-step sequencing batch reactor as a function of waste water composition, Elsevier science ltd, process biochemistry,vol. 38, pp , [11] D. Kulikowska, E. Klimiuk, The effect of landfill age on municipal leachate composition, Bioresource Technology,vol. 99,pp , [12] Ew. Klimiuk, D. Kulikowska, Organics removal from landfill leachate and activated sludge production in SBR reactors, Waste Management,vol. 26,pp , [13] Won-Young Ahn, Moon-Sun Kang, Seong Keun Yim, Kwang-Ho Choi, Advanced landfill leachate treatment using an integrated membrane process, Desalination,vol. 149,pp , [14] Z. Fu, F. Yang, F. Zhou, Y. Xue, Control of COD/N ratio for nutrient removal in a modified membrane bioreactor (MBR) treating high strength wastewater, Bioresource Technology,vol. 100, pp , [15] N. Laitinen, A. Luonsi, J. Vilen, Landfill leachate treatment with sequencing batch reactor and membrane bioreactor, Desalination, vol. 191, pp , [16] I. Ozturk, M. Altinbas, I. Koyuncu, O. Arikan, C. Gomec-Yangin, Advanced physic-chemical treatment experiences on young municipal landfill leachates, Waste Management, vol. 23, pp., , [17] S. Renou, J.G. Givaudan, S. Poulain, F. Dirassouyan, P. Moulin, Landfill leachate treatment : Review and opportunity, Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 150, pp , [18] R. Canziani, V. Emondi, M. Garavaglia, F. Malpei, E. Pasinetti, G. Buttiglieri, Effect of oxygen concentration on biological nitrification and microbial kinetics in a cross-flow membrane bioreactor (MBR) and moving-bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) treating old landfill leachate, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 286, pp , [19] L. Hongjiang, Z. Youcai1, S. Lei, G. Yingying, Three-stage aged refuse biofilter for the treatment of landfill leachate, Journal of Environmental Sciences, vol. 21, pp , [20] C. Visvanathan, M. K. Choudhary, M. T. Montalbo, V. Jegatheesan, Landfill leachate treatment using thermophilic membrane bioreactor, Desalination, vol. 204, pp. 8 16, [21] J. Bohdziewicz, E. Neczaj, A. Kwarciak, Landfill leachate treatment by means of anaerobic membrane bioreactor, Desalination, vol. 221, pp , [22] M. Bodzek, E. Lobos-Moysa, M. Zamorowska, Removal of organiccompounds from municipal landfill leachate in a membrane bioreactor, Desalination, vol. 198, pp , [23] Z. Wang, Z. Wu, S. Mai, C.Yang, X. Wang, Y. An, Z. Zhou, Research and applications of membrane bioreactors in China: Progress and prospect, Separation and Purification Technology,vol. 62, pp ,
5 Control and recording system probes Feed tank MBR Air supply system Treated wastewater Excess sludge tank Figure 1. Schematic diagram for MBR process (a) (b) (c) Figure 2. COD concentrations in the effluent and removal in MBR (a) NH4-N concentrations in the effluent and removal in MBR (b) PO4 P concentrations in the effluent and removal in MBR (c) 9
NEW BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL CONCEPT SUCCESSFULLY APPLIED IN A T-DITCH PROCESS WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT
 NEW BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL CONCEPT SUCCESSFULLY APPLIED IN A T-DITCH PROCESS WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT ABSTRACT C. Yang*, L. Zhou**, W. Luo***, and L. Johnson**** *Corstar International Corp. 111
NEW BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL CONCEPT SUCCESSFULLY APPLIED IN A T-DITCH PROCESS WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT ABSTRACT C. Yang*, L. Zhou**, W. Luo***, and L. Johnson**** *Corstar International Corp. 111
Removal of High C and N Contents in Synthetic Wastewater Using Internal Circulation of Anaerobic and Anoxic/Oxic Activated Sludge Processes
 Removal of High C and N Contents in Synthetic Wastewater Using Internal Circulation of Anaerobic and Anoxic/Oxic Activated Sludge Processes Nittaya Boontian School of Environmental Engineering, Institute
Removal of High C and N Contents in Synthetic Wastewater Using Internal Circulation of Anaerobic and Anoxic/Oxic Activated Sludge Processes Nittaya Boontian School of Environmental Engineering, Institute
TWO YEARS OF BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL WITH AN ADVANCED MSBR SYSTEM AT THE SHENZHEN YANTIAN WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT
 TWO YEARS OF BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL WITH AN ADVANCED MSBR SYSTEM AT THE SHENZHEN YANTIAN WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT Chester Yang, Ph.D., Gaowei Gu, Baowei Li, Hongyuan Li, Wanshen Lu, Lloyd Johnson,
TWO YEARS OF BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHORUS REMOVAL WITH AN ADVANCED MSBR SYSTEM AT THE SHENZHEN YANTIAN WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT Chester Yang, Ph.D., Gaowei Gu, Baowei Li, Hongyuan Li, Wanshen Lu, Lloyd Johnson,
Short-term and long-term studies of the co-treatment of landfill leachate and municipal wastewater
 This paper is part of the Proceedings of the 8 International Conference th on Waste Management and The Environment (WM 2016) www.witconferences.com Short-term and long-term studies of the co-treatment
This paper is part of the Proceedings of the 8 International Conference th on Waste Management and The Environment (WM 2016) www.witconferences.com Short-term and long-term studies of the co-treatment
Evaluation of Conventional Activated Sludge Compared to Membrane Bioreactors
 Evaluation of Conventional Activated Sludge Compared to Membrane Bioreactors Short Course on Membrane Bioreactors 3/22/06 R. Shane Trussell, Ph.D., P.E. shane@trusselltech.com Outline Introduction Process
Evaluation of Conventional Activated Sludge Compared to Membrane Bioreactors Short Course on Membrane Bioreactors 3/22/06 R. Shane Trussell, Ph.D., P.E. shane@trusselltech.com Outline Introduction Process
COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN INTEGRATED FIXED FILM ACTIVATED SLUDGE (IFAS), MEMBRANE BIOREACTOR (MBR) AND CONVENTIONAL ACTIVATED SLUDGE (AS) PROCESSES
 Sixteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 16 2012, Istanbul, Turkey 1 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN INTEGRATED FIXED FILM ACTIVATED SLUDGE (IFAS), MEMBRANE BIOREACTOR (MBR) AND CONVENTIONAL
Sixteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 16 2012, Istanbul, Turkey 1 COMPARISON STUDY BETWEEN INTEGRATED FIXED FILM ACTIVATED SLUDGE (IFAS), MEMBRANE BIOREACTOR (MBR) AND CONVENTIONAL
Kirill Ukhanov, GE Water & Process Technologies, Russia, describes how advanced membrane technology is helping a Russian refinery to meet stringent
 Kirill Ukhanov, GE Water & Process Technologies, Russia, describes how advanced membrane technology is helping a Russian refinery to meet stringent wastewater requirements. In Russia, there are strict
Kirill Ukhanov, GE Water & Process Technologies, Russia, describes how advanced membrane technology is helping a Russian refinery to meet stringent wastewater requirements. In Russia, there are strict
Dr Martin Peter *, Joachim Scholz & Victor Ferre. Contents
 Feedback from a metal processing industry MBR Plant in its 3rd Year of Operation:- An Analysis of the Flux, Effluent Quality and Membrane Lifetime Data to date Authors: Dr Martin Peter *, Joachim Scholz
Feedback from a metal processing industry MBR Plant in its 3rd Year of Operation:- An Analysis of the Flux, Effluent Quality and Membrane Lifetime Data to date Authors: Dr Martin Peter *, Joachim Scholz
Advantages & Applications of MBBR Technologies
 Advantages & Applications of MBBR Technologies Wastewater Technologies Attached Growth Suspended Growth Static Fixed film Trickling filters Rope media Web media Biological active filters (BAF) Dynamic
Advantages & Applications of MBBR Technologies Wastewater Technologies Attached Growth Suspended Growth Static Fixed film Trickling filters Rope media Web media Biological active filters (BAF) Dynamic
Operation of a small scale MBR system for wastewater reuse
 Operation of a small scale MBR system for wastewater reuse K. Azis, Ch. Vardalachakis, P. Melidis and S. Ntougias Laboratory of Wastewater Management and Treatment Technologies, Department of Environmental
Operation of a small scale MBR system for wastewater reuse K. Azis, Ch. Vardalachakis, P. Melidis and S. Ntougias Laboratory of Wastewater Management and Treatment Technologies, Department of Environmental
Preparing for Nutrient Removal at Your Treatment Plant
 Summer Seminar Emerging Issues in the Water/Wastewater Industry Preparing for Nutrient Removal at Your Treatment Plant Rajendra P. Bhattarai, P.E., BCEE Austin Water Utility Ana J. Peña-Tijerina, Ph.D.,
Summer Seminar Emerging Issues in the Water/Wastewater Industry Preparing for Nutrient Removal at Your Treatment Plant Rajendra P. Bhattarai, P.E., BCEE Austin Water Utility Ana J. Peña-Tijerina, Ph.D.,
W O C H H O L Z R E G I O N A L W A T E R R E C L A M A T I O N F A C I L I T Y O V E R V I E W
 Facility Overview The recently upgraded and expanded Henry N. Wochholz Regional Water Reclamation Facility (WRWRF) treats domestic wastewater generated from the Yucaipa-Calimesa service area. The WRWRF
Facility Overview The recently upgraded and expanded Henry N. Wochholz Regional Water Reclamation Facility (WRWRF) treats domestic wastewater generated from the Yucaipa-Calimesa service area. The WRWRF
Pilot Studies on Performance of Membrane Bio-Reactor in Treating Hong Kong Freshwater and Saline Sewage and Its Virus Rejection Ability and Mechanism
 Pilot Studies on Performance of Membrane Bio-Reactor in Treating Hong Kong Freshwater and Saline Sewage and Its Virus Rejection Ability and Mechanism G. H. Chen and C. Shang The Hong Kong University of
Pilot Studies on Performance of Membrane Bio-Reactor in Treating Hong Kong Freshwater and Saline Sewage and Its Virus Rejection Ability and Mechanism G. H. Chen and C. Shang The Hong Kong University of
Application of the AGF (Anoxic Gas Flotation) Process
 Application of the AGF (Anoxic Gas Flotation) Process Dennis A. Burke Environmental Energy Company, 6007 Hill Road NE, Olympia, WA 98516 USA (E-mail: dennis@makingenergy.com http//www.makingenergy.com)
Application of the AGF (Anoxic Gas Flotation) Process Dennis A. Burke Environmental Energy Company, 6007 Hill Road NE, Olympia, WA 98516 USA (E-mail: dennis@makingenergy.com http//www.makingenergy.com)
BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHOROUS REMOVAL AN OPERATOR S GUIDE
 BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHOROUS REMOVAL AN OPERATOR S GUIDE ABSTRACT If you have ever faced a rising effluent phosphorous concentration and you are relying on biological phosphorous removal, the information offered
BIOLOGICAL PHOSPHOROUS REMOVAL AN OPERATOR S GUIDE ABSTRACT If you have ever faced a rising effluent phosphorous concentration and you are relying on biological phosphorous removal, the information offered
Aqua MSBR MODIFIED SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR
 MODIFIED SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR MODIFIED SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR For over three decades, Aqua-Aerobic Systems has led the industry in sequencing batch reactor technology with performance proven and
MODIFIED SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR MODIFIED SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR For over three decades, Aqua-Aerobic Systems has led the industry in sequencing batch reactor technology with performance proven and
Increasing of leachate quality using an integrated aerobic membrane bioreactor
 Increasing of leachate quality using an integrated aerobic membrane bioreactor Hassan Hashemi 1, Mahdi Safari 2, Asghar Ebrahimi 3, Abbas Khodabakhshi 4 1 Research Center for Health Sciences, Shiraz University
Increasing of leachate quality using an integrated aerobic membrane bioreactor Hassan Hashemi 1, Mahdi Safari 2, Asghar Ebrahimi 3, Abbas Khodabakhshi 4 1 Research Center for Health Sciences, Shiraz University
General Information on Nitrogen
 General Information on Nitrogen What is nitrogen? Nitrogen was discovered in 1772 by Daniel Rutherford in Scotland Nitrogen gas makes up nearly 80% of the air we breathe Nitrogen gas is not toxic Nitrogen
General Information on Nitrogen What is nitrogen? Nitrogen was discovered in 1772 by Daniel Rutherford in Scotland Nitrogen gas makes up nearly 80% of the air we breathe Nitrogen gas is not toxic Nitrogen
COD REMOVAL OF CARDBOARD FACTORY WASTEWATER BY UPFLOW ANAEROBIC FILTER
 COD REMOVAL OF CARDBOARD FACTORY WASTEWATER BY UPFLOW ANAEROBIC FILTER Khajornsak Sopajaree Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, 50200 Thailand.
COD REMOVAL OF CARDBOARD FACTORY WASTEWATER BY UPFLOW ANAEROBIC FILTER Khajornsak Sopajaree Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, 50200 Thailand.
AquaNereda Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology
 Aerobic Granular Sludge AquaNereda Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology The AquaNereda Aerobic Granular Sludge (AGS) Technology is an innovative biological wastewater treatment technology that provides advanced
Aerobic Granular Sludge AquaNereda Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology The AquaNereda Aerobic Granular Sludge (AGS) Technology is an innovative biological wastewater treatment technology that provides advanced
ADVANCED CONTROL SYSTEM OF ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESSES USING IN- SITU AMMONIUM AND NITRATE PROBES
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 205 ADVANCED CONTROL SYSTEM OF ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESSES USING IN- SITU AMMONIUM
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 205 ADVANCED CONTROL SYSTEM OF ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESSES USING IN- SITU AMMONIUM
Biological Short-Cut Nitrogen Removal from Anaerobic Digestate in a Demonstration Sequencing Batch Reactor
 Biological Short-Cut Nitrogen Removal from Anaerobic Digestate in a Demonstration Sequencing Batch Reactor Francesco Fatone 1, Mario Dante 2, Elisa Nota 1, Silvia Di Fabio 1, Nicola Frison 1, Paolo Pavan
Biological Short-Cut Nitrogen Removal from Anaerobic Digestate in a Demonstration Sequencing Batch Reactor Francesco Fatone 1, Mario Dante 2, Elisa Nota 1, Silvia Di Fabio 1, Nicola Frison 1, Paolo Pavan
Environmental Biotechnology Cooperative Research Centre Date submitted: March 2008 Date published: March 2011
 final report Project code: A.ENV.0044 Prepared by: Environmental Biotechnology Cooperative Research Centre Date submitted: March 2008 Date published: March 2011 PUBLISHED BY Meat & Livestock Australia
final report Project code: A.ENV.0044 Prepared by: Environmental Biotechnology Cooperative Research Centre Date submitted: March 2008 Date published: March 2011 PUBLISHED BY Meat & Livestock Australia
BEING GOOD STEWARDS: IMPROVING EFFLUENT QUALITY ON A BARRIER ISLAND. 1.0 Executive Summary
 BEING GOOD STEWARDS: IMPROVING EFFLUENT QUALITY ON A BARRIER ISLAND Brett T. Messner, PE, Tetra Tech, Inc., 201 E Pine St, Suite 1000, Orlando, FL 32801 Brett.Messner@tetratech.com, Ph: 239-851-1225 Fred
BEING GOOD STEWARDS: IMPROVING EFFLUENT QUALITY ON A BARRIER ISLAND Brett T. Messner, PE, Tetra Tech, Inc., 201 E Pine St, Suite 1000, Orlando, FL 32801 Brett.Messner@tetratech.com, Ph: 239-851-1225 Fred
Module 19 : Aerobic Secondary Treatment Of Wastewater. Lecture 24 : Aerobic Secondary Treatment Of Wastewater
 1 P age Module 19 : Aerobic Secondary Treatment Of Wastewater Lecture 24 : Aerobic Secondary Treatment Of Wastewater 2 P age 19.1 Activated Sludge Process Conventional biological treatment of wastewater
1 P age Module 19 : Aerobic Secondary Treatment Of Wastewater Lecture 24 : Aerobic Secondary Treatment Of Wastewater 2 P age 19.1 Activated Sludge Process Conventional biological treatment of wastewater
AquaPASS. Aqua MixAir System. Phase Separator. System Features and Advantages. Anaerobic. Staged Aeration. Pre-Anoxic.
 PHASED ACTIVATED SLUDGE SYSTEM PHASED ACTIVATED SLUDGE SYSTEM Aqua-Aerobic Systems has led the industry in time-managed, biological technology since 1984. In 2004, Aqua-Aerobic applied its expertise in
PHASED ACTIVATED SLUDGE SYSTEM PHASED ACTIVATED SLUDGE SYSTEM Aqua-Aerobic Systems has led the industry in time-managed, biological technology since 1984. In 2004, Aqua-Aerobic applied its expertise in
Nutrient Removal Processes MARK GEHRING TECHNICAL SALES MGR., BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT
 Nutrient Removal Processes MARK GEHRING TECHNICAL SALES MGR., BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT Presentation Outline 1. Nutrient removal, treatment fundamentals 2. Treatment strategies Treatment methods: CAS, SBR,
Nutrient Removal Processes MARK GEHRING TECHNICAL SALES MGR., BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT Presentation Outline 1. Nutrient removal, treatment fundamentals 2. Treatment strategies Treatment methods: CAS, SBR,
WASTEWATER TREATMENT
 WASTEWATER TREATMENT Every community produces both liquid and solid wastes. The liquid portion-wastewater-is essentially the water supply of the community after it has been fouled by a variety of uses.
WASTEWATER TREATMENT Every community produces both liquid and solid wastes. The liquid portion-wastewater-is essentially the water supply of the community after it has been fouled by a variety of uses.
Effect of the start-up length on the biological nutrient removal process
 Water Pollution IX 521 Effect of the start-up length on the biological nutrient removal process F. J. Fernández 1, J. Villaseñor 1 & L. Rodríguez 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, ITQUIMA, University
Water Pollution IX 521 Effect of the start-up length on the biological nutrient removal process F. J. Fernández 1, J. Villaseñor 1 & L. Rodríguez 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, ITQUIMA, University
Activated Sludge Treatment Extended Aeration (EA) and Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Systems
 1 Activated Sludge Treatment Extended Aeration (EA) and Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Systems General Features KEE Process packaged and purpose-built activated sludge process systems are suitable for
1 Activated Sludge Treatment Extended Aeration (EA) and Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Systems General Features KEE Process packaged and purpose-built activated sludge process systems are suitable for
Application of MBR Technology in Municipal Wastewater Treatment
 Arab J Sci Eng (20) 36:3 DOI.7/s3369-0-0007-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE - CHEMISTRY A. Naghizadeh A. H. Mahvi A. R. Mesdaghinia M. Alimohammadi Application of MBR Technology in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Received:
Arab J Sci Eng (20) 36:3 DOI.7/s3369-0-0007-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE - CHEMISTRY A. Naghizadeh A. H. Mahvi A. R. Mesdaghinia M. Alimohammadi Application of MBR Technology in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Received:
Impact of Petroleum Refinery Wastewater on Activated Sludge
 Impact of Petroleum Refinery Wastewater on Activated Sludge M. A. R. M. M. Amin, S. R. M. Kutty, H. A. Gasim, M. H. Isa Civil Engineering Department, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS Bandar Seri Iskandar,
Impact of Petroleum Refinery Wastewater on Activated Sludge M. A. R. M. M. Amin, S. R. M. Kutty, H. A. Gasim, M. H. Isa Civil Engineering Department, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS Bandar Seri Iskandar,
EFFECT OF DYE CONCENTRATION ON SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR PERFORMANCE
 Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 2009, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 11-16 EFFECT OF DYE CONCENTRATION ON SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR PERFORMANCE 1 A. A. Vaigan, *1 M. R. Alavi Moghaddam, 2 H. Hashemi 1 Faculty
Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 2009, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 11-16 EFFECT OF DYE CONCENTRATION ON SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR PERFORMANCE 1 A. A. Vaigan, *1 M. R. Alavi Moghaddam, 2 H. Hashemi 1 Faculty
Membrane bioreactor and promising application for textile industry in Vietnam
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 00 (2014) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 13th Global Conference on Sustainable Manufacturing Membrane bioreactor and promising
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 00 (2014) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 13th Global Conference on Sustainable Manufacturing Membrane bioreactor and promising
Nitrogen removal during the treatment of wastewater and landfill leachate in a biological aerated filter
 Nitrogen removal during the treatment of wastewater and landfill leachate in a biological aerated filter G.D. Jojoa-Unigarro, S. González-Martínez Institute of Engineering, National University of Mexico
Nitrogen removal during the treatment of wastewater and landfill leachate in a biological aerated filter G.D. Jojoa-Unigarro, S. González-Martínez Institute of Engineering, National University of Mexico
Choices to Address Filamentous Growth
 Michigan Water Environment Association Process Seminar November 12, 2015 Choices to Address Filamentous Growth Richard Beardslee City of Battle Creek Nathan Cassity Donohue & Associates Outline Battle
Michigan Water Environment Association Process Seminar November 12, 2015 Choices to Address Filamentous Growth Richard Beardslee City of Battle Creek Nathan Cassity Donohue & Associates Outline Battle
GRANULAR ACTIVATED SLUDGE
 CLARKE PRIZE CONFERENCE ON WATER SUSTAINABILITY GRANULAR ACTIVATED SLUDGE THE FUTURE OF BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT REMOVAL JAMES BARNARD CONTENTS Early observations of granular sludge Selection processes in activated
CLARKE PRIZE CONFERENCE ON WATER SUSTAINABILITY GRANULAR ACTIVATED SLUDGE THE FUTURE OF BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT REMOVAL JAMES BARNARD CONTENTS Early observations of granular sludge Selection processes in activated
TWO YEAR CASE STUDY OF INTEGRATED FIXED FILM ACTIVATED SLUDGE (IFAS) AT BROOMFIELD, CO WWTP West 124th Street Broomfield, CO 80020
 ABSTRACT TWO YEAR CASE STUDY OF INTEGRATED FIXED FILM ACTIVATED SLUDGE (IFAS) AT BROOMFIELD, CO WWTP Mr. Ken Rutt 1, Jim Seda 1 and Mr. Chandler H. Johnson 2 1 City & County of Broomfield 2985 West 124th
ABSTRACT TWO YEAR CASE STUDY OF INTEGRATED FIXED FILM ACTIVATED SLUDGE (IFAS) AT BROOMFIELD, CO WWTP Mr. Ken Rutt 1, Jim Seda 1 and Mr. Chandler H. Johnson 2 1 City & County of Broomfield 2985 West 124th
LABORATORY PROJECT: IMPACT OF VARIABLE LOADING ON A FIXED FILM REACTOR VERSUS A SUSPENDED GROWTH REACTOR
 LABORATORY PROJECT: IMPACT OF VARIABLE LOADING ON A FIXED FILM REACTOR VERSUS A SUSPENDED GROWTH REACTOR DUE: MAY 6, 2008 PROFESSOR: DR. BELINDA MCSWAIN-STURM TA: ERIN BELLASSAI 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 BACKGROUND
LABORATORY PROJECT: IMPACT OF VARIABLE LOADING ON A FIXED FILM REACTOR VERSUS A SUSPENDED GROWTH REACTOR DUE: MAY 6, 2008 PROFESSOR: DR. BELINDA MCSWAIN-STURM TA: ERIN BELLASSAI 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 BACKGROUND
Study of Kinetic coefficients of a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) for municipal wastewater treatment
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Arch Hyg Sci 213;2(3):18-113 Journal Homepage: http://jhygiene.muq.ac.ir Study of Kinetic coefficients of a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) for municipal wastewater treatment Ali Naghizadeh
RESEARCH ARTICLE Arch Hyg Sci 213;2(3):18-113 Journal Homepage: http://jhygiene.muq.ac.ir Study of Kinetic coefficients of a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) for municipal wastewater treatment Ali Naghizadeh
CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment
 CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment W3b Trickling filters Jules van Lier Bacteria and other microorganisms have the ability to form biofilms on inert support media. Can we use these biofilm systems
CTB3365x Introduction to Water Treatment W3b Trickling filters Jules van Lier Bacteria and other microorganisms have the ability to form biofilms on inert support media. Can we use these biofilm systems
N2O EMISSION FROM A NITRITATION DOUBLE-SLUDGE SYSTEM TREATING WASTEWATER WITH A HIGH CONCENTRATION OF AMMONIUM
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 18, No X, pp XX-XX, 216 Copyright 216 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved N2O EMISSION FROM A NITRITATION DOUBLE-SLUDGE SYSTEM TREATING WASTEWATER WITH A HIGH CONCENTRATION
Global NEST Journal, Vol 18, No X, pp XX-XX, 216 Copyright 216 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved N2O EMISSION FROM A NITRITATION DOUBLE-SLUDGE SYSTEM TREATING WASTEWATER WITH A HIGH CONCENTRATION
Wastewater Treatment Processes
 Wastewater Treatment Processes (Sep 27 th and 28 th, 2016) by Dr. Arun Kumar (arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in) Objective: To learn about processes used in tertiary treatment Courtesy: Dr. Irene Xagoraraki, MSU,
Wastewater Treatment Processes (Sep 27 th and 28 th, 2016) by Dr. Arun Kumar (arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in) Objective: To learn about processes used in tertiary treatment Courtesy: Dr. Irene Xagoraraki, MSU,
Outline. Municipal Wastewater Engineering. Advanced wastewater treatment. Advanced wastewater treatment. Advanced wastewater treatment
 epartment of Chemical and Environmental Engineering Municipal Wastewater Engineering (4) Prof. Ján erco, Sc. Faculty of Chemical and Food Technology, SUT, SK http://kchbi.chtf.stuba.sk/ http://www.chtf.stuba.sk/kei/
epartment of Chemical and Environmental Engineering Municipal Wastewater Engineering (4) Prof. Ján erco, Sc. Faculty of Chemical and Food Technology, SUT, SK http://kchbi.chtf.stuba.sk/ http://www.chtf.stuba.sk/kei/
Use of Biowin for Process Troubleshooting / Design for a Unique Wastewater
 Use of Biowin for Process Troubleshooting / Design for a Unique Wastewater OWEA Plant Operations and Lab Analysis Workshop W. James Gellner Outline Introduction / Problem Overview Plant Issues Biowin Overview
Use of Biowin for Process Troubleshooting / Design for a Unique Wastewater OWEA Plant Operations and Lab Analysis Workshop W. James Gellner Outline Introduction / Problem Overview Plant Issues Biowin Overview
SOLUTIONS AND EQUIPMENT FOR LEACHATE TREATMENT
 ICAMS 2016 6 th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems SOLUTIONS AND EQUIPMENT FOR LEACHATE TREATMENT IOANA CORINA MOGA 1, FLOAREA PRICOP 2, GABRIEL PETRESCU 1, ALINA DIANA DIACONU
ICAMS 2016 6 th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems SOLUTIONS AND EQUIPMENT FOR LEACHATE TREATMENT IOANA CORINA MOGA 1, FLOAREA PRICOP 2, GABRIEL PETRESCU 1, ALINA DIANA DIACONU
Examples of Studies conducted by
 Examples of Studies conducted by Page Oxygen Uptake Rate (OUR) Fingerprints 1 Toxicity Assessment Using a Dilution Series 4 Assessment of Acute Toxicity to Treatment Plants 5 Biodegradation Tests for Wastewater
Examples of Studies conducted by Page Oxygen Uptake Rate (OUR) Fingerprints 1 Toxicity Assessment Using a Dilution Series 4 Assessment of Acute Toxicity to Treatment Plants 5 Biodegradation Tests for Wastewater
Biological Nitrogen and COD Removal of Nutrient-Rich Wastewater Using Aerobic and Anaerobic Reactors
 J. Water Resource and Protection, 29, 1, 376-38 doi:1.4236/jwarp.29.1545 Published Online November 29 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) Biological Nitrogen and COD Removal of Nutrient-Rich Wastewater
J. Water Resource and Protection, 29, 1, 376-38 doi:1.4236/jwarp.29.1545 Published Online November 29 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) Biological Nitrogen and COD Removal of Nutrient-Rich Wastewater
IWA Publishing 2012 Water Practice & Technology Vol 7 No 3 doi: /wpt
 IWA Publishing 2012 Water Practice & Technology Vol 7 No 3 Comparison of denitrification-nitrification and step-feed activated sludge processes with dynamic simulation K. Sahlstedt a, H. Haimi b and J.
IWA Publishing 2012 Water Practice & Technology Vol 7 No 3 Comparison of denitrification-nitrification and step-feed activated sludge processes with dynamic simulation K. Sahlstedt a, H. Haimi b and J.
Case Study. BiOWiSH Aqua. Biological Help for the Human Race. Municipal Wastewater Bathurst Waste Water Treatment Works Australia.
 Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua Municipal Wastewater Bathurst Waste Water Treatment Works Australia BiOWiSH Aqua Executive Summary The main objective of the validation was to quantify cost savings in using BiOWiSH.
Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua Municipal Wastewater Bathurst Waste Water Treatment Works Australia BiOWiSH Aqua Executive Summary The main objective of the validation was to quantify cost savings in using BiOWiSH.
A Roadmap for Smarter Nutrient Management in a Carbon and Energy Constrained World. Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE
 A Roadmap for Smarter Nutrient Management in a Carbon and Energy Constrained World Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE 91 st Annual Conference 21 June 2016 The Importance of Carbon Without carbon, life as
A Roadmap for Smarter Nutrient Management in a Carbon and Energy Constrained World Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE 91 st Annual Conference 21 June 2016 The Importance of Carbon Without carbon, life as
Innovating Water Treatment Technologies in Managing Water-Energy Demand
 Innovating Water Treatment Technologies in Managing Water-Energy Demand L.Y. Lee, S.L. Ong, J.Y. Hu and H.Y. Ng Centre for Water Research, Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering; NUS Environmental
Innovating Water Treatment Technologies in Managing Water-Energy Demand L.Y. Lee, S.L. Ong, J.Y. Hu and H.Y. Ng Centre for Water Research, Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering; NUS Environmental
Characterization of Ammonia Removal from Municipal Wastewater Using Microwave Energy: Batch Experiment
 Environment and Natural Resources Research; Vol. 3, No. 1; 213 ISSN 1927-488 E-ISSN 1927-496 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Characterization of Ammonia Removal from Municipal Wastewater
Environment and Natural Resources Research; Vol. 3, No. 1; 213 ISSN 1927-488 E-ISSN 1927-496 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Characterization of Ammonia Removal from Municipal Wastewater
MBBR Pack. The modular plug & play wastewater treatment solution WATER TECHNOLOGIES
 MBBR Pack The modular plug & play wastewater treatment solution WATER TECHNOLOGIES MBBR Pack A complete modular, The stakes Local authorities and industries have to deal quickly with rapid increases -
MBBR Pack The modular plug & play wastewater treatment solution WATER TECHNOLOGIES MBBR Pack A complete modular, The stakes Local authorities and industries have to deal quickly with rapid increases -
Presence And Effects Of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On Sewage Treatment Efficiency
 Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy Volume 14 Article 2 January 21 Presence And Effects Of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On Sewage Treatment Efficiency Bozena
Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy Volume 14 Article 2 January 21 Presence And Effects Of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On Sewage Treatment Efficiency Bozena
MBBR Wastewater Treatment Processes
 MBBR Wastewater Treatment Processes by Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. 1. Introduction The Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) wastewater treatment process is a relatively recent addition in the wastewater
MBBR Wastewater Treatment Processes by Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. 1. Introduction The Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) wastewater treatment process is a relatively recent addition in the wastewater
COMPARING THE EFFICIENCY OF UAFF AND UASB WITH HYBRID REACTOR IN TREATING WOOD FIBER WASTEWATER
 Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 26, Vol. 3, No., pp. 39-44 COMPARING THE EFFICIENCY OF UAFF AND UASB WITH HYBRID REACTOR IN TREATING WOOD FIBER WASTEWATER B. Ayati, *H. Ganjidoust Department of Civil
Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 26, Vol. 3, No., pp. 39-44 COMPARING THE EFFICIENCY OF UAFF AND UASB WITH HYBRID REACTOR IN TREATING WOOD FIBER WASTEWATER B. Ayati, *H. Ganjidoust Department of Civil
Water and Environmental Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Lund University
 New leachate treatment methods Jude Ifeanyichukwu Madu Water and Environmental Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Lund University P.O. Box 4, SE00, Lund, Sweden, Phone: +46 46 89 99, Email:
New leachate treatment methods Jude Ifeanyichukwu Madu Water and Environmental Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Lund University P.O. Box 4, SE00, Lund, Sweden, Phone: +46 46 89 99, Email:
Activated Sludge Process Control: Nitrification
 Activated Sludge Process Control: Nitrification 60 th Annual KWWOA Conference, Session 1: April 11, 2017 Dan Miklos, Senior Associate, Midwest Region, Hazen and Sawyer Agenda Overview of the Utopia Plant
Activated Sludge Process Control: Nitrification 60 th Annual KWWOA Conference, Session 1: April 11, 2017 Dan Miklos, Senior Associate, Midwest Region, Hazen and Sawyer Agenda Overview of the Utopia Plant
How to define performance parameters for verification including parameters relevant for energy efficiency of a wastewater treatment plant
 Project Partners: How to define performance parameters for verification including parameters relevant for energy efficiency of a wastewater treatment plant Ewa Neczaj, Chief Verification Expert, ETV Body,
Project Partners: How to define performance parameters for verification including parameters relevant for energy efficiency of a wastewater treatment plant Ewa Neczaj, Chief Verification Expert, ETV Body,
Renovation of secondary treatment facility into the Step-feed Biological Nitrogen Removal Process by the effective use of the existing structure
 Renovation of secondary treatment facility into the Step-feed Biological Nitrogen Removal Process by the effective use of the existing structure Kiyohiko Hayashi Director, Toba Wastewater Treatment Plant,
Renovation of secondary treatment facility into the Step-feed Biological Nitrogen Removal Process by the effective use of the existing structure Kiyohiko Hayashi Director, Toba Wastewater Treatment Plant,
Proposal by Russia to delete hot sub-spot Hot sub-spot name South-West Wastewater Treatment Plant
 Proposal by Russia to delete hot sub-spot 18.4 LAND 14/2009, Document 6/3/Rev.1 ATTACHMENT 1. Hot sub-spot name South-West Wastewater Treatment Plant 2. Location Block 2, 123, Volkhonskoye shosse, St.
Proposal by Russia to delete hot sub-spot 18.4 LAND 14/2009, Document 6/3/Rev.1 ATTACHMENT 1. Hot sub-spot name South-West Wastewater Treatment Plant 2. Location Block 2, 123, Volkhonskoye shosse, St.
Nitrogen Transformation within Constructed Wetlands Purifying Secondary Treated Sewage
 Nitrogen Transformation within Constructed Wetlands Purifying Secondary Treated Sewage T. Y. Yeh 1,*, C. M. Kao 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering National University of Kaohsiung Kaohsiung,
Nitrogen Transformation within Constructed Wetlands Purifying Secondary Treated Sewage T. Y. Yeh 1,*, C. M. Kao 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering National University of Kaohsiung Kaohsiung,
Ultrafiltration Technical Manual
 Ultrafiltration Technical Manual Copyright by: inge AG Flurstraße 17 86926 Greifenberg (Germany) Tel.: +49 (0) 8192 / 997 700 Fax: +49 (0) 8192 / 997 999 E-Mail: info@inge.ag Internet: www.inge.ag Contents
Ultrafiltration Technical Manual Copyright by: inge AG Flurstraße 17 86926 Greifenberg (Germany) Tel.: +49 (0) 8192 / 997 700 Fax: +49 (0) 8192 / 997 999 E-Mail: info@inge.ag Internet: www.inge.ag Contents
Determination of design criteria for UASB reactors as a wastewater pretreatment system in tropical small communities
 International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 51-57, Spring 2004 Determination of design criteria for UASB reactors as a wastewater pretreatment system in tropical small
International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 51-57, Spring 2004 Determination of design criteria for UASB reactors as a wastewater pretreatment system in tropical small
Aerofloat specialises in the treatment of greywater and industrial wastewater from a range of industries.
 www.aerofloat.com.au Aerofloat designs, manufactures and installs simple, affordable wastewater treatment systems using its patented Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) products and patent pending MBBR systems
www.aerofloat.com.au Aerofloat designs, manufactures and installs simple, affordable wastewater treatment systems using its patented Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) products and patent pending MBBR systems
Steven Dickey. Abstract
 A Comparison of Anaerobic Treatment Performance of Fish Sludge in High-Saline and Low-Saline Environments Based on Volatile Fatty Acid and Biogas Production Abstract Steven Dickey Mesophilic anaerobic
A Comparison of Anaerobic Treatment Performance of Fish Sludge in High-Saline and Low-Saline Environments Based on Volatile Fatty Acid and Biogas Production Abstract Steven Dickey Mesophilic anaerobic
Thirteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC , Hurghada, Egypt
 Thirteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 13 2009, Hurghada, Egypt COST EFFECTIVE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PROCESSES: ANAEROBIC DOMESTIC WASTEWATER TREATMENT USING FIXED FILM REACTOR AS A
Thirteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 13 2009, Hurghada, Egypt COST EFFECTIVE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PROCESSES: ANAEROBIC DOMESTIC WASTEWATER TREATMENT USING FIXED FILM REACTOR AS A
General Operational Considerations in Nutrient and Wet Weather Flow Management for Wastewater Treatment Facilities Part II
 General Operational Considerations in Nutrient and Wet Weather Flow Management for Wastewater Treatment Facilities Part II Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE Julian Sandino, PhD, PE, BCEE Ohio WEA Plant
General Operational Considerations in Nutrient and Wet Weather Flow Management for Wastewater Treatment Facilities Part II Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE Julian Sandino, PhD, PE, BCEE Ohio WEA Plant
BIOTECTOR TOC Analysers
 BIOTECTOR TOC Analysers Reliable and accurate measurement of Total Organic Carbon in potable and waste water streams Adrian Hughes Process Sales Consultant What is TOC The TOC test measures the amount
BIOTECTOR TOC Analysers Reliable and accurate measurement of Total Organic Carbon in potable and waste water streams Adrian Hughes Process Sales Consultant What is TOC The TOC test measures the amount
Optimizing Nutrient Removal With Instrumentation. John Rutledge Hach RSM-Wastewater in NC & SC
 Optimizing Nutrient Removal With Instrumentation John Rutledge Hach RSM-Wastewater in NC & SC Nutrients Nitrogen & Phosphorus Both are essential for plant & algae growth Both are present in municipal wastewater
Optimizing Nutrient Removal With Instrumentation John Rutledge Hach RSM-Wastewater in NC & SC Nutrients Nitrogen & Phosphorus Both are essential for plant & algae growth Both are present in municipal wastewater
Engineering, NTUA, 15780, Greece Tel: ; Fax: * Correspondence author
 Influence of the backwash cleaning water temperature on the membrane performance in a pilot SMBR unit. L. Lintzos 1, K. Chatzikonstantinou 2, N. Tzamtzis 3*, S. Malamis 4 1 Postgraduate student in the
Influence of the backwash cleaning water temperature on the membrane performance in a pilot SMBR unit. L. Lintzos 1, K. Chatzikonstantinou 2, N. Tzamtzis 3*, S. Malamis 4 1 Postgraduate student in the
WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEM
 WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEM PrintStudioOne.com Nelson Environmental Inc. The Nelson Environmental OPTAER system is an efficient pond-based wastewater treatment solution utilized in a broad spectrum of
WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEM PrintStudioOne.com Nelson Environmental Inc. The Nelson Environmental OPTAER system is an efficient pond-based wastewater treatment solution utilized in a broad spectrum of
membrane bioreactor performance compared to conventional wastewater treatment
 Water Technologies & Solutions technical paper membrane bioreactor performance compared to conventional wastewater treatment Authors: Thomas C. Schwartz and Brent R. Herring, Woodard and Curran Incorporated
Water Technologies & Solutions technical paper membrane bioreactor performance compared to conventional wastewater treatment Authors: Thomas C. Schwartz and Brent R. Herring, Woodard and Curran Incorporated
Modelling of Wastewater Treatment Plants
 Modelling of Wastewater Treatment Plants Nevenka Martinello nevemar@gmail.com Why do we need WWTP models? to build a WWTP model CASE STUDY - WWTP model in Sweden Why do we need WWTP models? Rise awareness
Modelling of Wastewater Treatment Plants Nevenka Martinello nevemar@gmail.com Why do we need WWTP models? to build a WWTP model CASE STUDY - WWTP model in Sweden Why do we need WWTP models? Rise awareness
Efficiency of different coagulants in pretreatment of composting plant leachate
 Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 6, No. 6, p. 21-28, 2015 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Efficiency of different
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 6, No. 6, p. 21-28, 2015 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Efficiency of different
- 1 - Retrofitting IFAS Systems In Existing Activated Sludge Plants. by Glenn Thesing
 - 1 - Retrofitting IFAS Systems In Existing Activated Sludge Plants by Glenn Thesing Through retrofitting IFAS systems, communities can upgrade and expand wastewater treatment without the expense and complication
- 1 - Retrofitting IFAS Systems In Existing Activated Sludge Plants by Glenn Thesing Through retrofitting IFAS systems, communities can upgrade and expand wastewater treatment without the expense and complication
Unit Treatment Processes in Water and Wastewater Engineering
 Unit Treatment Processes in Water and Wastewater Engineering T J Casey AQUAVARRA RESEARCH LIMITED 22A Brookfield Avenue Blackrock Co. Dublin. October 2006 Author s Note Water and wastewater treatment technology
Unit Treatment Processes in Water and Wastewater Engineering T J Casey AQUAVARRA RESEARCH LIMITED 22A Brookfield Avenue Blackrock Co. Dublin. October 2006 Author s Note Water and wastewater treatment technology
ANAEROBIC TREATMENT OF PAPER MILL WASTEWATER
 ANAEROBIC TREATMENT OF PAPER MILL WASTEWATER M. Eeckhaut 1, J.P. Ombregt 1, B. Vanderhaegen 2, M. Bambridge 3, A. Ginnis 4 Abstract In this paper the performance of an anaerobic wastewater treatment plant
ANAEROBIC TREATMENT OF PAPER MILL WASTEWATER M. Eeckhaut 1, J.P. Ombregt 1, B. Vanderhaegen 2, M. Bambridge 3, A. Ginnis 4 Abstract In this paper the performance of an anaerobic wastewater treatment plant
Shortcut Biological Nitrogen Removal for sustainable wastewater treatment and achieving energy neutrality
 METROPOLITAN WATER RECLAMATION DISTRICT OF GREATER CHICAGO Shortcut Biological Nitrogen Removal for sustainable wastewater treatment and achieving energy neutrality Fenghua Yang, P.E., BCEE Outline Nitrogen
METROPOLITAN WATER RECLAMATION DISTRICT OF GREATER CHICAGO Shortcut Biological Nitrogen Removal for sustainable wastewater treatment and achieving energy neutrality Fenghua Yang, P.E., BCEE Outline Nitrogen
Carbon Redirection and its Role in Energy Optimization at Water Resource Recovery Facilities
 Carbon Redirection and its Role in Energy Optimization at Water Resource Recovery Facilities Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE, WEF Fellow Joint Energy Conference NYSAWWA & NYWEA Albany, NY 16 November
Carbon Redirection and its Role in Energy Optimization at Water Resource Recovery Facilities Samuel Jeyanayagam, PhD, PE, BCEE, WEF Fellow Joint Energy Conference NYSAWWA & NYWEA Albany, NY 16 November
Sulaibiya world s largest membrane water reuse project
 Water Technologies & Solutions technical paper Sulaibiya world s largest membrane water reuse project background In May 2001, a consortium including Mohammed Abdulmohsin Al-Kharafi and Sons (The Kharafi
Water Technologies & Solutions technical paper Sulaibiya world s largest membrane water reuse project background In May 2001, a consortium including Mohammed Abdulmohsin Al-Kharafi and Sons (The Kharafi
Evaluation of Laboratory and Plant Scale Membrane Bioreactors in Treating Textile Wastewater
 ( Evaluation of Laboratory and Plant Scale Membrane Bioreactors in Treating Textile Wastewater T. A. Ferdian*, A. Reza* and T. Setiadi** * Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Industrial Technology,
( Evaluation of Laboratory and Plant Scale Membrane Bioreactors in Treating Textile Wastewater T. A. Ferdian*, A. Reza* and T. Setiadi** * Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Industrial Technology,
Module 22 : Sludge Management
 1 P age Module 22 : Sludge Management Lecture 36 : Sludge Management 2 P age 22.1 Introduction In the context of wastewater treatment residual is used to refer sludge. The term sludge refers to the solids
1 P age Module 22 : Sludge Management Lecture 36 : Sludge Management 2 P age 22.1 Introduction In the context of wastewater treatment residual is used to refer sludge. The term sludge refers to the solids
NUTRIENT REMOVAL PROCESSES IN WASTEWATER TREATMENT. We re Glad You re Here!
 NUTRIENT REMOVAL PROCESSES IN WASTEWATER TREATMENT We re Glad You re Here! Please, put your cell phones on vibrate during sessions and, take calls to the hallway NUTRIENT REMOVAL PROCESSES IN WASTEWATER
NUTRIENT REMOVAL PROCESSES IN WASTEWATER TREATMENT We re Glad You re Here! Please, put your cell phones on vibrate during sessions and, take calls to the hallway NUTRIENT REMOVAL PROCESSES IN WASTEWATER
MODIFIED SEQUENTIAL BATCH REACTOR (MSBR) A NEW PROCESS OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT
 Ninth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC9 2005, Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt 105 MODIFIED SEQUENTIAL BATCH REACTOR (MSBR) A NEW PROCESS OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT Medhat M. A. Saleh * and Usama F.
Ninth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC9 2005, Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt 105 MODIFIED SEQUENTIAL BATCH REACTOR (MSBR) A NEW PROCESS OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT Medhat M. A. Saleh * and Usama F.
SECTION 14.0 BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT REMOVAL
 SECTION 14.0 BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT REMOVAL 14.1 INTRODUCTION Up to this point in the report, the physical and biochemical concepts considered for application to the secondary treatment sections of the three
SECTION 14.0 BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT REMOVAL 14.1 INTRODUCTION Up to this point in the report, the physical and biochemical concepts considered for application to the secondary treatment sections of the three
Innovative Use of Dissolved Air Flotation with Biosorption as Primary Treatment to Approach Energy Neutrality in WWTPs
 Innovative Use of Dissolved Air Flotation with Biosorption as Primary Treatment to Approach Energy Neutrality in WWTPs H.-B. Ding *, M. Doyle **, A. Erdogan **, R. Wikramanayake ***, and P. Gallagher ***
Innovative Use of Dissolved Air Flotation with Biosorption as Primary Treatment to Approach Energy Neutrality in WWTPs H.-B. Ding *, M. Doyle **, A. Erdogan **, R. Wikramanayake ***, and P. Gallagher ***
ANAEROBIC CO-DIGESTION OF DAIRY MANURE WITH POTATO WASTE. Department of Biological & Agricultural Engineering, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID 3
 ANAEROBIC CO-DIGESTION OF DAIRY MANURE WITH POTATO WASTE S. K. R. Yadanaparthi 1,4, L. Chen 2,4, B. Glaze 3,4 1 Environmental Science Program, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID 2 Department of Biological
ANAEROBIC CO-DIGESTION OF DAIRY MANURE WITH POTATO WASTE S. K. R. Yadanaparthi 1,4, L. Chen 2,4, B. Glaze 3,4 1 Environmental Science Program, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID 2 Department of Biological
AMMONIA REMOVAL USING MLE PROCESS EXPERIENCES AT BALLARAT NORTH. David Reyne. Central Highlands Water Authority
 AMMONIA REMOVAL USING MLE PROCESS EXPERIENCES AT BALLARAT NORTH Paper Presented by : David Reyne Author: David Reyne, Plant Operator Wastewater Treatment, Central Highlands Water Authority 65 th Annual
AMMONIA REMOVAL USING MLE PROCESS EXPERIENCES AT BALLARAT NORTH Paper Presented by : David Reyne Author: David Reyne, Plant Operator Wastewater Treatment, Central Highlands Water Authority 65 th Annual
SUSTAINABLE EMISSION REDUCTION OF AMMONIUM FROM A LANDFILL BODY USING THE ANAMMOX-PROCESS AT THE VLAGHEIDE LANDFILL IN SCHIJNDEL (NL)
 SUSTAINABLE EMISSION REDUCTION OF AMMONIUM FROM A LANDFILL BODY USING THE ANAMMOX-PROCESS AT THE VLAGHEIDE LANDFILL IN SCHIJNDEL (NL) W.J. van Vossen*, A. de Vos**, Theo Folmer*** * Royal Haskoning, P.O.
SUSTAINABLE EMISSION REDUCTION OF AMMONIUM FROM A LANDFILL BODY USING THE ANAMMOX-PROCESS AT THE VLAGHEIDE LANDFILL IN SCHIJNDEL (NL) W.J. van Vossen*, A. de Vos**, Theo Folmer*** * Royal Haskoning, P.O.
Innovations in Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal
 1 st Annual Innovative Wastewater Technologies Seminar Innovations in Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Jose A. Jimenez, Ph.D., P.E. Director of Technology and Innovation Brown and Caldwell July 15 th, 2015
1 st Annual Innovative Wastewater Technologies Seminar Innovations in Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Jose A. Jimenez, Ph.D., P.E. Director of Technology and Innovation Brown and Caldwell July 15 th, 2015
ArcelorMittal Monessen operates
 Technical Article 75 Full-Scale Treatment of a Coke Oven Wastewater Using Immersed-Membrane Biological Reactor Technology ArcelorMittal Monessen operates a coke production plant on the Monongahela River
Technical Article 75 Full-Scale Treatment of a Coke Oven Wastewater Using Immersed-Membrane Biological Reactor Technology ArcelorMittal Monessen operates a coke production plant on the Monongahela River
Comparison on the Treatment Performance of Full-scale Sewage Treatment Plants using Conventional and Modified Activated Sludge Processes
 Comparison on the Treatment Performance of Full-scale Sewage Treatment Plants using Conventional and Modified Activated Sludge Processes FATIHAH SUJA 1, RAKMI ABDUL RAHMAN 2 AND OTHMAN JAAFAR 3 1,3 Department
Comparison on the Treatment Performance of Full-scale Sewage Treatment Plants using Conventional and Modified Activated Sludge Processes FATIHAH SUJA 1, RAKMI ABDUL RAHMAN 2 AND OTHMAN JAAFAR 3 1,3 Department
Lagoons Operation and Management in New Brunswick
 Lagoons Operation and Management in New Brunswick Lagoons Provide secondary treatment to domestic wastewater by the action of bacteria stabilizing the organic matter in the wastewater. Benefits of lagoons:
Lagoons Operation and Management in New Brunswick Lagoons Provide secondary treatment to domestic wastewater by the action of bacteria stabilizing the organic matter in the wastewater. Benefits of lagoons:
19. AEROBIC SECONDARY TREATMENT OF WASTEWATER
 19. AEROBIC SECONDARY TREATMENT OF WASTEWATER 19.1 Activated Sludge Process Conventional biological treatment of wastewater under aerobic conditions includes activated sludge process (ASP) and Trickling
19. AEROBIC SECONDARY TREATMENT OF WASTEWATER 19.1 Activated Sludge Process Conventional biological treatment of wastewater under aerobic conditions includes activated sludge process (ASP) and Trickling
EVALUATION OF CERAMNIC MBR TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER REUSE. Abstract. Introduction
 EVALUATION OF CERAMNIC MBR TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER REUSE James F. DeCarolis, P.E., Black & Veatch, 300 Rancheros Drive, Suite 250, San Marcos, CA, 92069, decarolisjf@bv.com, Ph: 619-204-2537 Scott Freeman,
EVALUATION OF CERAMNIC MBR TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER REUSE James F. DeCarolis, P.E., Black & Veatch, 300 Rancheros Drive, Suite 250, San Marcos, CA, 92069, decarolisjf@bv.com, Ph: 619-204-2537 Scott Freeman,
Biological Nutrient Removal Processes
 Chapter 22 Biological Nutrient Removal Processes Overview of Biological Nutrient Removal 22-3 Biological Selectors 22-6 Growth Zones 22-6 Selector Size and Equipment 22-10 Yardsticks for Measuring Biological
Chapter 22 Biological Nutrient Removal Processes Overview of Biological Nutrient Removal 22-3 Biological Selectors 22-6 Growth Zones 22-6 Selector Size and Equipment 22-10 Yardsticks for Measuring Biological
Journal of Separation Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, pp (MBR)
 Journal of Separation Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 71-69 Jafar.moghaddas@sut.ac.ir (MBR).. mg/l MLSS mg/l F/M BOD (SRT) 5-How andsalwomir 1- MBR: membrane Bioreactor 2- MLSS: Mixed Liquor
Journal of Separation Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 71-69 Jafar.moghaddas@sut.ac.ir (MBR).. mg/l MLSS mg/l F/M BOD (SRT) 5-How andsalwomir 1- MBR: membrane Bioreactor 2- MLSS: Mixed Liquor
