San Mateo/Cristianitos Creek Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Subproject Data Report. Orange County Coastkeeper. August
|
|
|
- Ruth Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 San Mateo/Cristianitos Creek Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Subproject Data Report Orange County Coastkeeper August
2 Table of Contents Page Project Map 3 Executive Summary 4 Background 6 Project Description 6 Quality Control 7 Site Selection 7 Physical and Chemical Analysis 7 Analysis Methods 8 Data Results Discussion 8 Site Comparisons 11 Conclusion 14 2
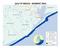
3 Project Map 3
4 Executive Summary In 2006 Orange County Coastkeeper (OCCK) and Inland Empire Waterkeeper began researching the water quality of streams in the Cleveland National Forest to determine baseline water quality in light of the several major development projects proposed for the forest. After examining the data available, it became apparent that this data was insufficient to determine the baseline water quality in most of the streams. To fill this data gap, O.C. Coastkeeper developed a proposal to monitor water quality of the forest streams to document baseline conditions. In 2007, the Inland Empire Canyons Baseline Monitoring Project was funded for one year. The San Mateo Creek and Cristianitos Creek monitoring project was added as a sub project due to the impending development of the Foothill South Tollroad and the lack of data for these creeks. The project began with the creation of a Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) made up of water quality experts from the Elsinore Valley Water District, the U.S. Forest Service, and the University of California Riverside. The TAC had the charge of reviewing the monitoring plan and Quality Assurance Project Plan (QAPP) to insure that the data collected was of sufficient quality to be used by the Regional Water Quality Control Boards and other entities for planning and permitting purposes. The next step for the San Mateo/ Cristianitos Creek project was to conduct a reconnaissance of the two creeks within the confines of San Onofre State Park (which affords the only public access to Cristianitos Creek and the lower reach of San Mateo Creek) to identify sampling sites and dry weather flow conditions. Eventually five sampling sites were identified, with two each on San Mateo and Christianitos Creeks and one stormdrain under the old highway 1 bridge. Dry weather water samples were collected from all five sites during the one year duration of the project (wet weather samples were not collected due to hazardous conditions and lack of sufficient rain for significant flow) and analyzed for standard water quality parameters such as ph, temperature, conductivity, and dissolved oxygen. Additional analysis were run for nutrients and indicator bacteria. All of these tests were run in the field (standard parameters) or in the Coastkeeper lab (nutrients and bacteria) using state accepted methods. We also analyzed a subset of the samples for Total Suspended Solids, Hardness, Metals and Hydrocarbons. These tests were run by a contract lab, also using state approved methods. Sample collection began in July 2007 and was completed in June After the samples were analyzed, the data generated was entered into an Excel spreadsheet. Each sample and the overall mean results were compared to the objectives for inland surface waters detailed in the San Diego Regional Board s Basin Plan. The Basin Plan objectives cover bacteria, ammonia, nitrate, phosphorus, dissolved oxygen and ph. The data for metals was compared to the California Toxics Rule criteria developed by the US EPA for California. The results of the data analysis are mixed; the creeks are generally in good shape but they are beginning to show the impact of the land uses around them. The creeks do not meet 4
5 the basin plan objectives for ammonia and phosphate. All five sample sites exceeded the ammonia and phosphate objectives almost every time they were sampled. The exceedence for phosphate can explained by the fact that phosphate naturally occurs at high levels in Orange County waters. However, we do not have an explanation for the ammonia exceedence other than the fact that the ammonia objective in the San Diego Basin Plan is quite low. Bacteria also showed the effects that even limited development can cause for water quality. The two urban runoff sites, Cristianitos and the San Mateo Stormdrain outlet, had a higher number of exceedences (33% to 82% of samples exceeded single sample objectives) and higher average bacteria concentrations than the other three sites that are natural waters (0% to 33% of samples exceeded single sample objectives). The metals analysis metals showed that the only exceedences were at the Cristianitos site, where Cadmium, Nickel, and Selenium were in exceedence. This is not surprising, as urban runoff is a common source of metals. Twenty three of the twenty five tests run for Total Recoverable Hydrocarbons all came back with non-detects, which indicates that the creeks are not currently affected by Hydrocarbons. 5
6 Background The San Mateo Creek watershed covers approximately 20 square miles of Orange and San Diego Counties, beginning in the Santa Ana Mountains and terminating at San Onofre State Beach just south of the city of San Clemente. Its headwaters are in the San Mateo Wilderness of the Cleveland National Forest, where it is a perennial stream. From there its course leads through the Camp Pendleton Marine Corps Base, where it becomes intermittent. The creek then springs back to the surface and becomes perennial just above the I-5 freeway, and forms an estuary at San Onofre Beach State Park. The upper reach of the stream is undisturbed wilderness and is critical habitat for wildlife, including steelhead trout. The lower section of the stream runs through an area of Camp Pendleton that has seen some disturbance from military operations and farming, but is largely undeveloped with the riparian habitat intact. This area is critical habitat to endangered species, including the pacific pocket mouse, arroyo toad, coastal California Gnatcatcher, and least Bell s vireo. The area below the I-5 freeway is estuarine, and the creek is blocked from discharge to the ocean by a sand berm that is broken during storm events. This area is critical habitat for the tidewater goby and many migratory waterfowl. Overall, the creek is part of one of the last largely undeveloped coastal watersheds in Southern California and is a critical component of a complex ecosystem. Cristianitos Creek is the major tributary to San Mateo Creek. It begins in Orange County just south of Ortega Highway on Rancho Mission Viejo land, and continues through the Donna O Neal Land Conservancy to Camp Pendleton. Here the creek forms the southern boundary of San Onofre State Park before it merges with San Mateo Creek near Cristianitos Road. The creek is intermittent in its lower reach. The Cristianitos Creek watershed has experienced some disturbance from cattle grazing, farming, military activities and urban runoff from nearby development. However, the watershed remains undeveloped and overall the ecosystem and riparian area is intact. This watershed is critical habitat to a wide range of wildlife and provides recreational opportunities to visitors. Project Description In 2006 Orange County Coastkeeper (OCCK) and Inland Empire Waterkeeper began researching the water quality of streams in the Cleveland National Forest. The project s goal was to determine baseline water quality in light of the many major development projects proposed for the forest. After examining the data available, Coastkeeper determined it was insufficient to determine the baseline water quality in most of the streams. To fill this data gap, Coastkeeper developed a proposal to monitor water quality of the forest streams to document baseline conditions. In 2007 the project was funded for one year of monitoring as the Inland Empire Canyons Baseline Monitoring Project. The San Mateo Creek and Cristianitos Creek monitoring project was added as a subproject, due to the impending development of the Foothill South Tollroad and the lack of data for these creeks. 6
7 Quality Control Quality Control for the data developed by the project was maintained by adhering to the Inland Empire Canyons Baseline Monitoring Project Quality Assurance Project Plan developed for the larger project. The QAPP was created with the assistance of a Technical Advisory Committee (TAC), which included water quality experts from the Elsinore Valley Water District, the U.S. Forest Service, and the University of California Riverside. The TAC was responsible for reviewing and approving the QAPP to insure that the data collected was of sufficient quality to be used by the Regional Water Quality Control Boards and other entities for planning and permitting purposes. Site Selection The next step for the San Mateo/ Cristianitos Creek project was to conduct a reconnaissance of the two creeks within the confines of San Onofre State Park (which affords the only public access to Cristianitos Creek and the lower reach of San Mateo Creek) to identify sampling sites and document dry weather flow conditions. During our initial reconnaissance, perennial flow was identified at two selected sites: Cristianitos: at Cristianitos creek near the end of Avenida Pico (due to a steady flow of urban runoff from the Talega housing development) San Mateo: on San Mateo Creek just above the I-5 Freeway bridge, where a spring re-establishes perennial flow. Eventually three other sites were added, one in Cristianitos Creek and two below the San Mateo spring site: Upper Cristianitos: above the urban runoff into Cristianitos creek (added after rain events established water in the creek) San Mateo Outlet: at an outlet under the old highway 101 bridge San Mateo Confluence: at the head of the estuary where two spring fed branches of San Mateo Creek converge (See Project map for site locations). Site Name Latitude Longitude Upper Cristianitos 33 o o Cristianitos 33 o o San Mateo 33 o o San Mateo Outlet 33 o o San Mateo Confluence 33 o o All coordinates are WGS 84 Physical and Chemical Analysis The parameters selected for the monitoring of San Mateo and Cristianitos creeks include nutrients and bacteria, and standard physical parameters including ph, conductivity dissolved oxygen, temperature and a visual observation of flow. Additionally, we selected TRPH (Total Recoverable Petroleum Hydrocarbons) and dissolved metals, 7
8 pollutants commonly associated with developed areas and roads. Testing began at San Mateo and Cristianitos creeks in July 2007 and continued on a monthly basis, concluding in June The Upper Cristianitos site was monitored whenever water was present. The San Mateo Confluence site was added in October 2007 and monitored from then on. The San Mateo Outlet was monitored three times and discontinued, since we could not identify the source of water from the outlet, which was suspected to be the I-5 Freeway. Site Visits Location Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Jan Jan Mar Mar Apr May Jun San Mateo x x x x x x x x x x x x Confluence x x x x x x x x x Outlet x x x Chrisitianos x x x x x x x x x x x Upper Chrisitianos x x x x x x Analysis Methods Temperature, ph, dissolved oxygen, and conductivity were measured in the field using pre-calibrated Oakton meters. Bacteria samples were run at the Coastkeeper office using the IDEXX method using colilert 18 reagent for Total Coliform and E.Coli and Enterolert reagent for Enterococci. Nutrient analysis was run at the Coastkeeper lab with a Hach colorimeter, using methods meeting the Inland Empire Canyons Baseline Monitoring Project QAPP requirements. Nitrate-Nitrogen samples were filtered through a.45µm filter and then tested using a variation of the cadmium reduction method detailed in Standard Method 4500-NO 3 E. This test has a range of mg/l, a detection limit of 0.5mg/l and a standard deviation of 0.3 mg/l The Ammonia- Nitrogen samples were tested using a salicylate method adapted from Clin.Chim (1966). This test has a range of mg/l, a detection limit of 0.02 and a standard deviation of The Orthophosphate test was done using a procedure equivalent to USEPA method and Standard Method 4500-PE. This test has a range of mg/l, a detection limit of 0.05mg/l and a standard deviation of 0.05 mg/l. Testing for metals, hardness (as CaCO 3 ), Total Suspended Solids, and Total Recoverable Petroleum Hydrocarbons was done by Test America Labs using EPA method 6020 for metals, SM 2340B for hardness, and SM 2540D for TSS. Testing for TRPH was done using EPA method Data Results Discussion: All data results are in a project database available from Orange County Coastkeeper on request. 8
9 Individual Parameters Water Temperature The temperature of water affects aquatic life because most species can only thrive within a certain temperature range. Other factors, such as dissolved oxygen, can be affected by the temperature which in turn affects the rate of photosynthesis in aquatic plants. As temperatures increase, the quantity of dissolved oxygen in a water body will increase accordingly. Human intervention can affect temperature by removing canopy cover and building or removing water diversions along or in the streams, causing a rise in water temperature. The temperatures we measured were not at levels that would affect the beneficial uses of these streams. Dissolved Oxygen Dissolved oxygen is necessary to sustain aquatic life. Dissolved oxygen shall not be less than 5.0mg/L in inland surface waters, as stated in the San Diego Regional Water Quality Control Board s (SWRCB) Basin Plan. The San Mateo site proved to be the only monitored site to have low levels of dissolved oxygen, with all of the measurements below the basin plan objective. These low dissolved oxygen levels are not surprising at this site as it is a spring and groundwater typically has low levels of dissolved oxygen. Conductivity An estimate of the amount of dissolved solids in the water can be made by measuring conductivity. Dissolved solids include acids, minerals, salts and metals. Conductivity varies for many reasons but high conductivity may be an indicator of bigger problems. Conductivity over 1.0 ms/cm for fresh water can be a sign of problems. None of the sites tested for conductivity exceeded the acceptable limit. ph ph is a measure of hydrogen ions that control the acidity and the alkalinity of the water. Most aquatic life can only survive within a narrow range of ph, thus it is important to monitor. The acceptable level for ph in the San Diego Basin Plan is between 6.5 and 8.6. The sample taken from Cristianitos creek on August 23, 2007 had a ph of 3.16, significantly lower (more acidic) than the recommended ph level of 6.5. All other monitoring dates and sites had ph levels within the acceptable levels. Orthophosphate Orange County soils have naturally high levels of phosphate, phosphates also commonly enter water bodies through lawn and garden fertilizer with run-off or soil erosion. Increased phosphate concentrations can lead to increased growth of algae and plants, which then deplete dissolved oxygen in the water. The San Diego Basin Plan states that phosphates should not exceed 0.1mg/L in order to prevent plant nuisances in streams and other flowing waters. Phosphate levels exceeded the recommended set standard at all five sites. San Mateo, San Mateo Outlet, and Cristianitos had 100% exceedance; San Mateo Confluence and Cristianitos Upper had slightly less exceedance. The highest phosphate level of 2.75 mg/l was sampled at San Mateo Outlet on November 20,
10 Nitrate-Nitrogen Similar to phosphate, nitrate is a plant nutrient that usually enters water bodies through overuse of fertilizer. Excessive Nitrate promotes algal blooms and aquatic plant growth that can suffocate other life. The San Diego Basin Plan states that nitrate levels should not exceed phosphate levels by more than a ten to one ratio. None of the samples exceeded the standard. Ammonia-Nitrogen Ammonia is another plant nutrient, the primary urban runoff sources are fertilizer and animal waste. Ammonia is an important chemical to monitor because it can accumulate to toxic levels and affect the metabolism of fish and other aquatic organisms. This toxin can also affect organisms at higher levels in the food chain. According to the San Diego Basin Plan, the discharge of wastes shall not cause concentrations of ammonia to exceed mg/l in inland surface waters, enclosed bays and estuaries and coastal lagoons. All five monitoring sites exceeded the ammonia standard the majority of the time ranging from 75% (San Mateo) to 100% (San Mateo Outlet and Cristianitos Upper). San Mateo Confluence had an 85% exceedance and Cristianitos had a 93% exceedance of ammonia among all testing dates. San Mateo Outlet had the highest exceedance on November 20, 2007 with an ammonia level of 0.73 mg/l.while there are many exceedences of the ammonia standard it is important to note thet the basin plan states that the standard should nt be exceeded due to the discharge of wastes. Due to the undeveloped nature of these watersheds it is likely that the exceedences found are due to natural conditions. Turbidity/Total Suspended Solids (TSS) Turbidity is attributable to suspended and colloidal matter, the effect of which is to disturb water clarity and diminish the penetration of light. High turbidity levels indicate a large amount of suspended particles in the water. Total Suspended Solids is the measurement of the amount of solid material in a sample. Particles can block sunlight and impede respiration and adversely affect photosynthesis, having a major effect on organisms. Additionally, high levels of turbidity create concern since suspended particles often carry pollutants. Natural turbidity varies from site to site but is generally below 100 NTU. If turbidity is above average, this may indicate erosion, nutrient loading, or excessive algae growth. Turbidity levels exceeding 100 FAU or TSS above 100mg/L fresh water would be considered abnormal and would be a level of concern. None of the sampled sites exceeded the limit for turbidity or TSS. Bacteria (E. coli, and Enterococcus) High levels of these indicator bacteria imply a high probability of pathogens harmful to humans in the water. Total Coliform comes from a broad range of environmental sources including plants and animals. The presence of E.coli is an indicator of fecal contamination from warm-blooded animals and in some cases can cause severe illness. The water quality objective for E.coli in the San Diego Basin Plan for infrequently used areas is (recommended by the U.S. EPA) are 576 MPN/ 100mL (single sample) and 126 MPN/100mL (geomean). All monitored sites had some exceedences of the E.Coli standards. San Mateo had an 9% exceedance in E.Coli; San Mateo Outlet had a 33% exceedance in E. Coli; San Mateo Confluence had a 22% exceedence 10
11 in E. Coli; Cristianitos had a 27% exceedance in E.Coli; and Cristianos Upper had a 17% exceedance in E. Coli. San Mateo Outlet had the highest E.Coli exceedance on November 20, 2007 with an E.Coli level of 7, MPN/100ml. Enterococcus standards are low accepted levels, because the correlation between it and human pathogens is high. The accepted sample limits in the San Diego Basin Plan for infrequently used areas is (recommended by the U.S. EPA) are 151 MPN/100mL (single sample) and 33 MPN/100mL (geomean). Cristianitos Upper was the only site without exceedance in Enterococcus. San Mateo had an exceedance of 27%; San Mateo Confluence had an exceedance of 33%; and Cristianitos had and exceedance of 82%. The highest level of enterococcus was 2, MPN/100mL and was found at both San Mateo on October 29, 2007, and Cristianitos on August 23, Total and Dissolved Metals/Hardness- Metals are naturally occurring elements that are also have a variety of uses in many of the products that we use in a daily basis. Hardness is the measurement of Calcium Carbonate in water and is used to estimate the naturally occurring levels of metals in water. Elevated levels of metals (above natural concentrations) such as copper and zinc are often found in urban runoff and are harmful to aquatic life. The criteria used for metals were developed for California by the USEPA and are detailed in the California Toxics Rule (CTR). These criteria run on a sliding scale in relation to the hardness of the water. There were no exceedences of the CTR for metals at any of the sites although the sites composed of urban runoff (Cristianitos and San Mateo Outlet) had higher values than the other sites. Total Recoverable Hydrocarbons-Total Recoverable Hydrocarbons (TRPH) is used to identify the level of all hydrocarbons, this includes oil and grease, gasoline, asphalt residue and other compounds that are indicative of developed areas and automobile use. This measurement is a good indicator of the impact of development on a waterway. Except of the first sample taken from both the Cristianitos and San Mateo sites all samples had no detectable amounts of Hydrocarbons. Site Comparisons The sites selected for monitoring can be broken down into two basic categories for comparison; The first category is sites on each stream, San Mateo and Cristianitos. The second category is sites that are primarily comprised of urban runoff (Cristianitos and San Mateo Outlet) and sites that are primarily composed of naturally occurring water (upper Cristianitos, San Mateo, San Mateo Confluence). A discussion of the individual sites and then the two streams follows. Cristianitos Creek Sites Upper Cristianitos- This site is located on Cristianitos Creek near the end of Avenida 11
12 Pico upstream of the county detention basin. At this site the stream is intermittent (its natural state) with water present from October 2007 through May The water at this site meets all water quality standards except for ammonia and phosphate (which are exceeded at all of the project sites). This site has clear ponded water with very low flow. Other than ammonia, it exhibits all the characteristics of an undisturbed Orange County stream. Upper Cristianitos had the lowest concentrations of metals, bacteria and nutrients of all the sites tested, and had no exceedences of Enterococcus or metals. ENTEROCOCCUS RESULTS FOR CRISTIANITOS UPPER ENTEROCOCCUS RESULTS (MPN/100 ML) 1/9/ /27/ /28/ /29/ /28/ TESTING DATES Cristianitos- This site is located near the end of Avenida Pico downstream from the county detention basin. At this site the creek receives a constant flow (the highest of all the sites) of urban runoff from the Talega housing development, which continues downstream from the site for about a quarter mile before infiltrating. This site had the highest percentage of exceedences of the bacteria objectives of all the sites with 82% of the Enterococcus exceeding basin plan objectives. Metals were also much higher here than at the Upper Cristianitos site with copper 433% higher and Zinc 675% higher. There were also exceedences of the metals objectives for Cadmium, Nickel, and Selenium. As with all the sites, samples from the Cristianitos site exceeded the ammonia and phosphate objectives almost every time. Nitrate levels were below basin plan standards but still four times higher than the Upper Cristianitos site. ENTEROCOCCUS RESULTS FOR CRISTIANITOS ENTEROCOCCUS RESULTS (MPN/100 ML) 8/23/2007 2, /27/ /29/ /20/ /9/ /28/ /29/ /28/ /28/2008 6/25/ /25/ TESTING DATES San Mateo Creek Sites San Mateo- This site is located on San Mateo Creek just upstream of the I-5 freeway 12
13 bridge. This is the most upstream point where the creek springs back to the surface before flowing downstream to form the estuary. It has low levels of metals with no exceedences of CTR criteria and fairly low levels of bacteria with 27% of the Enterococcus samples exceeding basing plan objectives Dissolved oxygen is low at this site which is consistent with rising groundwater. Flow here is constant but quite low. S ENTEROCCOCUS RESULT (MPN/100 ML) 8/23/ /29/2007 2, /20/2007 ENTEROCOCCUS RESULTS FOR SAN MATEO 1, /9/ /27/ /28/ /29/2008 5/28/ /25/ /25/ TESTING DATES San Mateo Outlet- This site is located under the old highway 1 bridge on the north side. This was the only stormdrain we could find that drained into the creek near the I-5 freeway. The actual sampling site is about 20 feet above the creek bed at the end of the concrete apron from the stormdrain. We monitored it for three months while we tried to determine its source and then stopped after Caltrans refused to provide information on its source. While our testing of this site was limited, what we saw was not good. Enterococcus exceeded the basin plan objective in 67% of the samples. The 24 micrograms per liter of total copper measured was the highest of all the sites. ph was also the highest of all the sites. Luckily the dry weather flow here is very low, so the pollutant load this stormdrain contributes during dry weather is not large. San Mateo Confluence- This site is located at the upstream end of the San Mateo estuary, where the creek begins to pond up behind the beach sand berm. The water here is ponded and there is no flow. There are many waterfowl in the area and it is wetland, not riparian, habitat. There are no exceedences of the metals criteria at this site. The Enterococcus exceedence is 33%, only slightly higher than the San Mateo spring site and much lower than the sites containing urban runoff. As with all the sites, ammonia and phosphate exceed the basin plan standards. Nitrate levels here are the highest of all the sites, but do not exceed basin plan standards. T ENTEROCOCCUS RESULTS FOR SAN MATEO CONFLUENT ENTEROCOCCUS RESUL (MPN/100 ML) 10/29/ /20/ /9/ /27/ /5/ /29/ /28/ /25/ /25/ TESTING DATES Creek Comparisons Both San Mateo Creek and Cristianitos Creek are intermittent streams with relatively 13
14 undeveloped and undisturbed watersheds. Both creeks receive some inputs of urban runoff during the wet and dry season, with Cristianitos Creek getting the most. While the urban flows into these creeks have a number of pollutants at levels that raise concern, the dry weather flows into the creeks are not currently at levels that have a substantial impact on their overall integrity. San Mateo Creek at the sampling area has higher natural flow and a low dry weather input of urban runoff, so the water quality of this creek is still good overall. The dry weather urban runoff seems to be diluted enough by the base flow of the creek to maintain water quality downstream. However, the natural creek flow is low enough that if inputs of urban runoff were to increase substantially, it would affect the downstream estuary. Cristianitos Creek at the sampling area has very low natural flow (and only during the wet season) and is receiving a relatively large amount of urban runoff from nearby homes. While the water quality of the creek is excellent above the urban flows, it rapidly deteriorates where the urban runoff makes up the majority of the creek water. The part of the creek dominated by urban runoff is highly impaired at the site we monitored. Luckily, the urban flow runs along a relatively short length of the creek before infiltrating, so the overall flow regime of the creek is intact. Any additional flows of urban runoff will have drastic consequences for this creek. As seen from the area affected by the Talega runoff, excessive flows from urban runoff can change the flow regime from intermittent to perennial and overwhelm the ability of the low natural flows to dilute the pollutants in urban runoff to acceptable levels. Conclusion Over the last year, O.C Coastkeeper has collected a sufficient amount of data from the five selected sites on Cristianitos and San Mateo Creeks to determine the dry weather water quality of these waterbodies. Overall, the water quality and flow regimes of both streams are good. Except for the sites that are entirely composed of urban runoff, the creeks have low levels of metals and bacteria, there is no substantial evidence of hydrocarbons, and their flow regimes are intact. Both creeks exceed the ammonia and phosphate objectives in the San Diego Basin Plan, most likely due to natural sources considering the consistently high number of exceedences at all sites. Nitrate levels are not currently at levels that are impacting the streams. While both streams are able to maintain their integrity with the current stresses on their systems, it is clear from our monitoring that their current equilibrium could be easily overwhelmed by excessive volumes of water or pollutants from development in their watersheds. 14
Wood Canyon Emergent Wetland Project. City of Aliso Viejo 12 Journey, Suite 100 Aliso Viejo, CA 92656
 Wood Canyon Emergent Wetland Project City of Aliso Viejo 12 Journey, Suite 100 Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 Introduction Wood Canyon is located within Aliso and Wood Canyon Regional Park in southwest Orange County,
Wood Canyon Emergent Wetland Project City of Aliso Viejo 12 Journey, Suite 100 Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 Introduction Wood Canyon is located within Aliso and Wood Canyon Regional Park in southwest Orange County,
Acidity and Alkalinity:
 Evaluation of Pollution Sources to Lake Glenville Quarterly Report December 2018 Kimberlee K Hall, PhD Environmental Health Program, Western Carolina University Summary Chemical and microbial analysis
Evaluation of Pollution Sources to Lake Glenville Quarterly Report December 2018 Kimberlee K Hall, PhD Environmental Health Program, Western Carolina University Summary Chemical and microbial analysis
El Dorado Hydroelectric Project FERC Project No Water Quality Monitoring Report
 El Dorado Hydroelectric Project FERC Project No. 184 21 Water Quality Monitoring Report EL DORADO IRRIGATION DISTRICT 289 Mosquito Road Placerville, CA 95667 March 211 1. Introduction The El Dorado Irrigation
El Dorado Hydroelectric Project FERC Project No. 184 21 Water Quality Monitoring Report EL DORADO IRRIGATION DISTRICT 289 Mosquito Road Placerville, CA 95667 March 211 1. Introduction The El Dorado Irrigation
Factsheet: City of West Haven Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: City of West Haven Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: City of West Haven Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
Factsheet: Town of Deep River Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Deep River Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Deep River Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
Factsheet: Town of Hamden Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Hamden Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each town
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Hamden Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each town
Little Cypress Bayou Special Study - Subwatershed 1.10
 - Subwatershed 1.1 Sabine River Authority of Texas August 31, 21 Prepared in Cooperation with the Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission Under the Authorization of the Texas Clean Rivers Act Table
- Subwatershed 1.1 Sabine River Authority of Texas August 31, 21 Prepared in Cooperation with the Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission Under the Authorization of the Texas Clean Rivers Act Table
Factsheet: Town of East Lyme Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of East Lyme Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of East Lyme Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each
Grants Pass Water Quality Monitoring
 Grants Pass Water Quality Monitoring 2003-2005 Rogue Valley Council of Governments April 2005 Rogue Valley Council of Governments Natural Resources Department 155 North First Street Central Point, Oregon
Grants Pass Water Quality Monitoring 2003-2005 Rogue Valley Council of Governments April 2005 Rogue Valley Council of Governments Natural Resources Department 155 North First Street Central Point, Oregon
Factsheet: Town of Trumbull Water Quality and Stormwater Summary
 79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Trumbull Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each town
79 Elm Street Hartford, CT 06106-5127 www.ct.gov/deep Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer Factsheet: Town of Trumbull Water Quality and Stormwater Summary This document was created for each town
Santa Rosa Creek Water Quality Results 2004
 Santa Rosa Creek Water Quality Results 24 Community Clean Water Institute Site Description: SRC4: Off 3rd Street in downtown Santa Rosa. Behind the Vineyard Hotel just West of Highway 11 along the Prince
Santa Rosa Creek Water Quality Results 24 Community Clean Water Institute Site Description: SRC4: Off 3rd Street in downtown Santa Rosa. Behind the Vineyard Hotel just West of Highway 11 along the Prince
The Snapshot CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT
 CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT ABOVE: CONODOGUINET CREEK AT RT 74 BRIDGE FACING DOWNSTREAM The Snapshot The Conodoguinet Watershed Snapshot was a collaborative effort to engage local citizens in
CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT ABOVE: CONODOGUINET CREEK AT RT 74 BRIDGE FACING DOWNSTREAM The Snapshot The Conodoguinet Watershed Snapshot was a collaborative effort to engage local citizens in
4.0 SAN GABRIEL RIVER WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA
 4.0 SAN GABRIEL RIVER WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA 4.1 Watershed Description 4.1.1 Watershed Land Use, Percent Impervious, and Population Land use in the San Gabriel River Watershed Management Area is approximately
4.0 SAN GABRIEL RIVER WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA 4.1 Watershed Description 4.1.1 Watershed Land Use, Percent Impervious, and Population Land use in the San Gabriel River Watershed Management Area is approximately
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014
 Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
First Flush Water Quality Results 2016
 First Flush Water Quality Results 2016 First big rain of the season Freshwater runoff enters storm drains High pollution Sample at outfalls to ocean Oct 14 th : 0.45 in What is First Flush? Partners Objectives
First Flush Water Quality Results 2016 First big rain of the season Freshwater runoff enters storm drains High pollution Sample at outfalls to ocean Oct 14 th : 0.45 in What is First Flush? Partners Objectives
Morro Bay National Estuary Program s Implementation Effectiveness Program For the Morro Bay Watershed. Stormwater Monitoring Report 2015
 Morro Bay National Estuary Program s Implementation Effectiveness Program For the Morro Bay Watershed Stormwater Monitoring Report 215 Loan Agreement Number 12-81-55 Task 3.4 Submitted by Morro Bay National
Morro Bay National Estuary Program s Implementation Effectiveness Program For the Morro Bay Watershed Stormwater Monitoring Report 215 Loan Agreement Number 12-81-55 Task 3.4 Submitted by Morro Bay National
Texas Watch Volunteer Water Quality Monitoring Program 2006 Mary s Creek Data Summary
 Texas Watch Volunteer Water Quality Monitoring Program 26 Mary s Creek Data Summary Narrative Summary of Mary s Creek Mary s Creek is an unclassified, perennial stream flowing 6 miles southwest from Pearland,
Texas Watch Volunteer Water Quality Monitoring Program 26 Mary s Creek Data Summary Narrative Summary of Mary s Creek Mary s Creek is an unclassified, perennial stream flowing 6 miles southwest from Pearland,
Redwood Shores Lagoon February 2019 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report
 Redwood Shores Lagoon February 2019 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes,
Redwood Shores Lagoon February 2019 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes,
Redwood Shores Lagoon November 2016 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report
 Redwood Shores Lagoon November 2016 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes,
Redwood Shores Lagoon November 2016 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes,
MRSWMP Dry Run/ First Flush Summary
 Monterey Bay Sanctuary Citizen Watershed Monitoring Network 299 Foam Street Monterey, CA 93940 Bus. (831) 647-4227 Fax (831) 647-4250 2009-2010 MRSWMP Dry Run/ First Flush Summary Prepared by: Lisa Emanuelson,
Monterey Bay Sanctuary Citizen Watershed Monitoring Network 299 Foam Street Monterey, CA 93940 Bus. (831) 647-4227 Fax (831) 647-4250 2009-2010 MRSWMP Dry Run/ First Flush Summary Prepared by: Lisa Emanuelson,
MARK CREEK DEMONSTRATION PROJECT
 MARK CREEK DEMONSTRATION PROJECT OCC Tasks 20 and 21 FY 1990 319(h) Task 210 EPA Grant # C9-006704-90-0 Submitted by: Oklahoma Conservation Commission Water Quality Division 413 NW 12 th Oklahoma City,
MARK CREEK DEMONSTRATION PROJECT OCC Tasks 20 and 21 FY 1990 319(h) Task 210 EPA Grant # C9-006704-90-0 Submitted by: Oklahoma Conservation Commission Water Quality Division 413 NW 12 th Oklahoma City,
Redwood Shores Lagoon May 2017 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report
 Redwood Shores Lagoon May 2017 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes, Inc.
Redwood Shores Lagoon May 2017 Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes, Inc.
Environmental Services
 215 Environmental Services River Water Quality Summary for the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area In 215, Metropolitan Council Environmental Services (MCES) river monitoring was conducted at six automated and
215 Environmental Services River Water Quality Summary for the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area In 215, Metropolitan Council Environmental Services (MCES) river monitoring was conducted at six automated and
Results from the 2017 Water Quality Monitoring Program
 Results from the 217 Water Quality Monitoring Program As part of a larger project, this summer the BWC conducted water sampling throughout the Belleisle Bay to get a baseline of data and determine the
Results from the 217 Water Quality Monitoring Program As part of a larger project, this summer the BWC conducted water sampling throughout the Belleisle Bay to get a baseline of data and determine the
Environmental Services
 Environmental Services 14 River Water Quality Summary for the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area This document is a summary of the 14 water quality of major rivers in the Twin Cities metropolitan area (metro
Environmental Services 14 River Water Quality Summary for the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area This document is a summary of the 14 water quality of major rivers in the Twin Cities metropolitan area (metro
APPENDIX N Guidance for Preparing/Reviewing CEQA Initial Studies and Environmental Impact Reports
 APPENDIX N N.1 Guidance for Preparing and Reviewing CEQA Initial Studies Step 1: Consider the Project Characteristics as Provided by the Project Applicant Review the project application and draft plan
APPENDIX N N.1 Guidance for Preparing and Reviewing CEQA Initial Studies Step 1: Consider the Project Characteristics as Provided by the Project Applicant Review the project application and draft plan
Redwood Shores Lagoon August Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report
 Redwood Shores Lagoon August Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes, Inc. P.
Redwood Shores Lagoon August Monthly Water Quality Monitoring Report Prepared for Redwood City Public Works Services Department 1400 Broadway Redwood City, CA 94063-2594 Prepared by Clean Lakes, Inc. P.
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality
 Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
REPORT. Report No: 2013/0958 Prepared For: Natural Resources Committee Prepared By: Dean Olsen, Environmental Resource Scientist Date: 11 July 2013
 REPORT Document Id: A544088 Report No: 2013/0958 Prepared For: Natural Resources Committee Prepared By: Dean Olsen, Environmental Resource Scientist Date: 11 July 2013 Subject: Waianakarua River Water
REPORT Document Id: A544088 Report No: 2013/0958 Prepared For: Natural Resources Committee Prepared By: Dean Olsen, Environmental Resource Scientist Date: 11 July 2013 Subject: Waianakarua River Water
Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed
 Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed Linda Green URI Watershed Watch 1-87-95, lgreen@uri.edu WATER QUALITY IS A REFLECTION OF THE ACTIVITIES IN THE LANDS AND WATERS
Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed Linda Green URI Watershed Watch 1-87-95, lgreen@uri.edu WATER QUALITY IS A REFLECTION OF THE ACTIVITIES IN THE LANDS AND WATERS
Middle Santa Ana River Bacterial Indicator TMDL 2009 Dry Season Report
 Middle Santa Ana River Bacterial Indicator TMDL 2009 Dry Season Report December 31, 2009 on behalf of Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority San Bernardino County Stormwater Program County of Riverside
Middle Santa Ana River Bacterial Indicator TMDL 2009 Dry Season Report December 31, 2009 on behalf of Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority San Bernardino County Stormwater Program County of Riverside
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary
 Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
CARLYLE LAKE WATER QUALITY REPORT. for
 CARLYLE LAKE WATER QUALITY REPORT for 1997 U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS, ST. LOUIS DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY SECTION - Water Quality Ted Postol, Section Chief Tori Foerste, Environmental Engineer
CARLYLE LAKE WATER QUALITY REPORT for 1997 U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS, ST. LOUIS DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY SECTION - Water Quality Ted Postol, Section Chief Tori Foerste, Environmental Engineer
Gilleland Creek Intensive Bacteria Survey Addendum. March 18, 2010
 Gilleland Creek Intensive Bacteria Survey Addendum March 18, 21 Prepared by: Texas Stream Team Texas State University San Marcos PREPARED IN COOPERATION WITH THE TEXAS COMMISSION ON ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY
Gilleland Creek Intensive Bacteria Survey Addendum March 18, 21 Prepared by: Texas Stream Team Texas State University San Marcos PREPARED IN COOPERATION WITH THE TEXAS COMMISSION ON ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY
EUTROPHICATION. Student Lab Workbook
 EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
2009 First Flush Program Final Report
 2009 First Flush Program Final Report City Purchase Order #25-10001 Prepared for: City of Santa Cruz Department of Public Works Prepared by: Greg Pepping Executive Director Coastal Watershed Council 345
2009 First Flush Program Final Report City Purchase Order #25-10001 Prepared for: City of Santa Cruz Department of Public Works Prepared by: Greg Pepping Executive Director Coastal Watershed Council 345
Eutrophication: Tracing Nutrient Pollution Back to Penns Creek
 Eutrophication: Tracing Nutrient Pollution Back to Penns Creek Nutrients are substances that life depends on for growth and reproduction. However, when these nutrients enter our planets waterways in excess,
Eutrophication: Tracing Nutrient Pollution Back to Penns Creek Nutrients are substances that life depends on for growth and reproduction. However, when these nutrients enter our planets waterways in excess,
5.0 LOS ANGELES RIVER WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA
 5.0 LOS ANGELES RIVER WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA 5.1 Watershed Description 5.1.1 Watershed Land Use, Percent Impervious, and Population The Los Angeles Watershed Management Area has more than half its area
5.0 LOS ANGELES RIVER WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA 5.1 Watershed Description 5.1.1 Watershed Land Use, Percent Impervious, and Population The Los Angeles Watershed Management Area has more than half its area
Rainbow Creek TMDL Monitoring Program Report for October 2016 through September 2017
 Rainbow Creek TMDL Monitoring Program Report for October 2016 through September 2017 Introduction The Rainbow Creek monitoring program has been developed to provide water quality data in support of the
Rainbow Creek TMDL Monitoring Program Report for October 2016 through September 2017 Introduction The Rainbow Creek monitoring program has been developed to provide water quality data in support of the
2011 Central Coast Regional Snapshot Day Summary Report
 2011 Central Coast Regional Snapshot Day Summary Report Prepared for: City of Santa Cruz Department of Public Works Prepared by: Debie Chirco-Macdonald Program Coordinator Coastal Watershed Council 345
2011 Central Coast Regional Snapshot Day Summary Report Prepared for: City of Santa Cruz Department of Public Works Prepared by: Debie Chirco-Macdonald Program Coordinator Coastal Watershed Council 345
Water Quality Assessment for the Town of Caswell Beach, 2008
 Water Quality Assessment for the Town of Caswell Beach, 2008 UNCW-CMS Report 08-02 Report to: Town of Caswell Beach 1100 Caswell Beach Rd. c/o Mr. Jim Carter, Town Administrator Caswell Beach, N.C. 28465
Water Quality Assessment for the Town of Caswell Beach, 2008 UNCW-CMS Report 08-02 Report to: Town of Caswell Beach 1100 Caswell Beach Rd. c/o Mr. Jim Carter, Town Administrator Caswell Beach, N.C. 28465
Monitoring Stormwater Best Management Practices: Why Is It Important and What To Monitor
 Monitoring Stormwater Best Management Practices: Why Is It Important and What To Monitor Scott D. Struck, Ph.D. US EPA, Urban Watershed Management Branch New Jersey Water Monitoring Workshop 4/20/2006
Monitoring Stormwater Best Management Practices: Why Is It Important and What To Monitor Scott D. Struck, Ph.D. US EPA, Urban Watershed Management Branch New Jersey Water Monitoring Workshop 4/20/2006
PROTECTING OUR WATERWAYS: STORMWATER POLLUTION REDUCTION EFFORTS
 PROTECTING OUR WATERWAYS: STORMWATER POLLUTION REDUCTION EFFORTS Public Information Meeting ~ May 2, 2018 Public Works Stormwater Management Division OVERVIEW Surface Water Quality Protection Municipal
PROTECTING OUR WATERWAYS: STORMWATER POLLUTION REDUCTION EFFORTS Public Information Meeting ~ May 2, 2018 Public Works Stormwater Management Division OVERVIEW Surface Water Quality Protection Municipal
Summary of Basin Characteristics and Facilities. General Land-use Characteristics: Withdrawal and Discharge Sites: Sampling Site Statistics:
 -Digit Watershed Identity Number: 28 This report was prepared by the Kentucky Water Research Institute as a product of the statewide Kentucky Watershed Management process. Information presented in this
-Digit Watershed Identity Number: 28 This report was prepared by the Kentucky Water Research Institute as a product of the statewide Kentucky Watershed Management process. Information presented in this
Hydrology and Water Quality. Water. Water 9/13/2016. Molecular Water a great solvent. Molecular Water
 Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
City of Daphne, Alabama Water Quality Monitoring Plan For Phase II MS4
 City of Daphne, Alabama Water Quality Monitoring Plan For Phase II MS4 2016-2021 Permit # ALR 040039, Expiration Date: September 30, 2021 I. Introduction This document presents the City of Daphne s Stormwater
City of Daphne, Alabama Water Quality Monitoring Plan For Phase II MS4 2016-2021 Permit # ALR 040039, Expiration Date: September 30, 2021 I. Introduction This document presents the City of Daphne s Stormwater
Portland Water District Sebago Lake Watershed Monitoring Programs Crooked River Monitoring (1977 to 2016) Brie Holme
 Portland Water District Sebago Lake Watershed Monitoring Programs Crooked River Monitoring (1977 to 2016) Brie Holme Introduction Sebago Lake is the primary drinking water supply for 200,000 people in
Portland Water District Sebago Lake Watershed Monitoring Programs Crooked River Monitoring (1977 to 2016) Brie Holme Introduction Sebago Lake is the primary drinking water supply for 200,000 people in
GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501
 GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 LAND COVER BACTERIA CHLOROPHYLL A Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 OTHER IMPAIRMENTS Bays & Estuaries
GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 LAND COVER BACTERIA CHLOROPHYLL A Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 OTHER IMPAIRMENTS Bays & Estuaries
State of the San Lorenzo River Symposium Saturday, April 11, 2015 Greg Pepping, Executive Director Coastal Watershed Council
 State of the San Lorenzo River Symposium Saturday, April 11, 2015 Greg Pepping, Executive Director Coastal Watershed Council Coastal Watershed Council Santa Cruz-based 501(c)(3) Established 1995 Science-based
State of the San Lorenzo River Symposium Saturday, April 11, 2015 Greg Pepping, Executive Director Coastal Watershed Council Coastal Watershed Council Santa Cruz-based 501(c)(3) Established 1995 Science-based
Ambient Water Quality Objectives For The Tributaries To Okanagan Lake Near Kelowna
 Water Quality Ambient Water Quality Objectives For The Tributaries To Okanagan Lake Near Kelowna Overview Report Water Management Branch Environment And Resource Division Ministry Of Environment, Lands
Water Quality Ambient Water Quality Objectives For The Tributaries To Okanagan Lake Near Kelowna Overview Report Water Management Branch Environment And Resource Division Ministry Of Environment, Lands
SAN BERNARD RIVER ABOVE TIDAL - SEGMENT 1302
 SAN BERNARD RIVER ABOVE TIDAL - SEGMENT 1302 SAN BERNARD RIVER ABOVE TIDAL - SEGMENT 1302 LAND COVER BACTERIA DISSOLVED OXYGEN NUTRIENTS Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns SAN BERNARD RIVER
SAN BERNARD RIVER ABOVE TIDAL - SEGMENT 1302 SAN BERNARD RIVER ABOVE TIDAL - SEGMENT 1302 LAND COVER BACTERIA DISSOLVED OXYGEN NUTRIENTS Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns SAN BERNARD RIVER
Water Pollution Overview. Sewage dumping
 Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Sewage dumping Ocean Pollution Water Pollution Overview Urban Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Water Pollution Overview Urban Runoff Water Pollution Overview
Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Sewage dumping Ocean Pollution Water Pollution Overview Urban Water Pollution Water Pollution Overview Water Pollution Overview Urban Runoff Water Pollution Overview
Impact of Orange County Sanitation District Wastewater Disinfection on Beach Water Quality
 Impact of Orange County Sanitation District Wastewater Disinfection on Beach Water Quality Coastal Coalition March 27, 2014 Presented By: Dr. Samuel Choi Orange County Sanitation District Environmental
Impact of Orange County Sanitation District Wastewater Disinfection on Beach Water Quality Coastal Coalition March 27, 2014 Presented By: Dr. Samuel Choi Orange County Sanitation District Environmental
Hydrology and Water Quality. Water. Water 9/11/2018. Molecular Water a great solvent. Molecular Water
 Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Executive Summary EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. ES.1 Monitoring Program Objectives. ES.2 Summary of Monitoring Results
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ES.1 Monitoring Program Objectives The following are the major monitoring program objectives, as outlined in the Municipal Stormwater Permit: Assess compliance with the Municipal Stormwater
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ES.1 Monitoring Program Objectives The following are the major monitoring program objectives, as outlined in the Municipal Stormwater Permit: Assess compliance with the Municipal Stormwater
ALISO CREEK WATERSHED RUNOFF MANAGEMENT PLAN WATER QUALITY DATA ASSESSMENT 2013 ANNUAL REPORT ORANGE COUNTY STORMWATER PROGRAM
 ALISO CREEK WATERSHED RUNOFF MANAGEMENT PLAN WATER QUALITY DATA ASSESSMENT 2013 ANNUAL REPORT ORANGE COUNTY STORMWATER PROGRAM Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 2.0 Watershed Setting and BMPs... 2 3.0 BMP
ALISO CREEK WATERSHED RUNOFF MANAGEMENT PLAN WATER QUALITY DATA ASSESSMENT 2013 ANNUAL REPORT ORANGE COUNTY STORMWATER PROGRAM Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 2.0 Watershed Setting and BMPs... 2 3.0 BMP
EAST FORK SAN JACINTO RIVER - SEGMENT 1003
 EAST FORK SAN JACINTO RIVER - SEGMENT 1003 EAST FORK SAN JACINTO RIVER - SEGMENT 1003 LAND COVER BACTERIA Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns Perennial Stream Perennial Stream Segment Number:
EAST FORK SAN JACINTO RIVER - SEGMENT 1003 EAST FORK SAN JACINTO RIVER - SEGMENT 1003 LAND COVER BACTERIA Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns Perennial Stream Perennial Stream Segment Number:
Dog River Watershed Management Plan
 Dog River Watershed Management Plan Preliminary Water Quality Data Analysis Doug Robison, PWS ESA is where solutions and service meet. Water Quality - Regulatory Primer Designated Use Categories Swimming
Dog River Watershed Management Plan Preliminary Water Quality Data Analysis Doug Robison, PWS ESA is where solutions and service meet. Water Quality - Regulatory Primer Designated Use Categories Swimming
City of Texarkana, Arkansas. Storm Water Pollution
 City of Texarkana, Arkansas Storm Water Pollution STORM WATER GUIDE What is Storm Water Pollution? Stormwater can provide a toxic discharge which can enter into a lake, river or coastal water system. As
City of Texarkana, Arkansas Storm Water Pollution STORM WATER GUIDE What is Storm Water Pollution? Stormwater can provide a toxic discharge which can enter into a lake, river or coastal water system. As
First Flush 2015: Midcoast Storm Drains
 First Flush 2015: Midcoast Storm Drains What is First Flush? First big rain of the season Freshwater runoff enters storm drains High pollution Sampled at outfall to ocean Nov 2 nd : 0.64 in Partners Objectives
First Flush 2015: Midcoast Storm Drains What is First Flush? First big rain of the season Freshwater runoff enters storm drains High pollution Sampled at outfall to ocean Nov 2 nd : 0.64 in Partners Objectives
Estero Americano Watershed Sediment Reduction Project, Phase II, Sonoma and Marin Counties, CA. Draft Quarterly Monitoring Report Item B.4.
 Estero Americano Watershed Sediment Reduction Project, Phase II, Sonoma and Marin Counties, CA Draft Quarterly Monitoring Report Item B.4.2 This quarterly report summarizes data collected from December
Estero Americano Watershed Sediment Reduction Project, Phase II, Sonoma and Marin Counties, CA Draft Quarterly Monitoring Report Item B.4.2 This quarterly report summarizes data collected from December
SANTA ANA RIVER CITIZENS MONITORING PROJECT FINAL REPORT ORANGE COUNTY COASTKEEPER. for
 SANTA ANA RIVER CITIZENS MONITORING PROJECT FINAL REPORT by ORANGE COUNTY COASTKEEPER for PAVLOVA VITALE Contract Manager Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Control Board 3737 Main St., Suite 500 Riverside,CA
SANTA ANA RIVER CITIZENS MONITORING PROJECT FINAL REPORT by ORANGE COUNTY COASTKEEPER for PAVLOVA VITALE Contract Manager Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Control Board 3737 Main St., Suite 500 Riverside,CA
Aquatic Science Unit 2. Water Quality and Water Pollution
 Aquatic Science Unit 2 Water Quality and Water Pollution What is a healthy water body? In your own words, take a moment to describe what you believe are some of the characteristics of a healthy stream
Aquatic Science Unit 2 Water Quality and Water Pollution What is a healthy water body? In your own words, take a moment to describe what you believe are some of the characteristics of a healthy stream
Continuous records for the Chariton River indicate that 2004 was an average water year, with total flow approximately equal to the average annual
 2004 Rathbun Report Iowa State University Limnology Laboratory John A. Downing, Ph.D. George Antoniou, Assistant Scientist For Rathbun Land and Water Alliance August 31, 2005 A. Tributaries Personnel of
2004 Rathbun Report Iowa State University Limnology Laboratory John A. Downing, Ph.D. George Antoniou, Assistant Scientist For Rathbun Land and Water Alliance August 31, 2005 A. Tributaries Personnel of
West Souris River Technical Water Quality Report Summary
 Page 1 West Souris River Technical Water Quality Report Summary SAMPLING BACKGROUND INFORMATION Surface water quality data have been collected by the Water Quality Management Section, Manitoba Water Stewardship,
Page 1 West Souris River Technical Water Quality Report Summary SAMPLING BACKGROUND INFORMATION Surface water quality data have been collected by the Water Quality Management Section, Manitoba Water Stewardship,
MARK TWAIN LAKE WATER QUALITY REPORT. for
 MARK TWAIN LAKE WATER QUALITY REPORT for 1997 U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS, ST. LOUIS DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY SECTION - Water Quality Ted Postol, Section Chief Tori Foerste, Environmental Engineer
MARK TWAIN LAKE WATER QUALITY REPORT for 1997 U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS, ST. LOUIS DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY SECTION - Water Quality Ted Postol, Section Chief Tori Foerste, Environmental Engineer
Portland Water District Sebago Lake Watershed Monitoring Programs Tributary Monitoring ( ) Kirsten Ness
 Introduction Portland Water District Sebago Lake Watershed Monitoring Programs Tributary Monitoring (1977 2016) Kirsten Ness Sebago Lake is the primary drinking water supply for nearly 200,000 people in
Introduction Portland Water District Sebago Lake Watershed Monitoring Programs Tributary Monitoring (1977 2016) Kirsten Ness Sebago Lake is the primary drinking water supply for nearly 200,000 people in
Water Resources/Water Quality
 Water Resources/Water Quality From where does your drinking water come? How much land should be set aside for aquifer protection? Why should we care about Barton Springs? What are the effects (if any!)
Water Resources/Water Quality From where does your drinking water come? How much land should be set aside for aquifer protection? Why should we care about Barton Springs? What are the effects (if any!)
Anthropogenic Impacts on Bays and Watersheds. HI-MOES Presentation 2009 The Kohala Center Kohala Watershed Partnership
 Anthropogenic Impacts on Bays and Watersheds HI-MOES Presentation 2009 The Kohala Center Kohala Watershed Partnership Some Common Terms Watershed = An area of land that drains into a common destination
Anthropogenic Impacts on Bays and Watersheds HI-MOES Presentation 2009 The Kohala Center Kohala Watershed Partnership Some Common Terms Watershed = An area of land that drains into a common destination
National Science Content Standards: A: Science as Inquiry E: Science and Technology
 National Science Content Standards: A: Science as Inquiry E: Science and Technology To develop an understanding of water quality monitoring and an appreciation of the methods used to keep water safe and
National Science Content Standards: A: Science as Inquiry E: Science and Technology To develop an understanding of water quality monitoring and an appreciation of the methods used to keep water safe and
Multipurpose Wetland Creation and Restoration to Improve Water Quality and Wildlife Habitat in Coastal Urban Bayous
 Multipurpose Wetland Creation and Restoration to Improve Water Quality and Wildlife Habitat in Coastal Urban Bayous CEER 2014 New Orleans, LA George Guillen, Misty Shepard, K. Vale and J. Oakley Environmental
Multipurpose Wetland Creation and Restoration to Improve Water Quality and Wildlife Habitat in Coastal Urban Bayous CEER 2014 New Orleans, LA George Guillen, Misty Shepard, K. Vale and J. Oakley Environmental
ULTRAVIOLET DISINFECTION FOR STORMWATER TREATMENT IN COASTAL CAROLINAS
 ULTRAVIOLET DISINFECTION FOR STORMWATER TREATMENT IN COASTAL CAROLINAS Ronald A. Geiger HDR Engineering, Charlotte, NC Tom Garigen, Horry County Storm Water, Conway, SC BACKGROUND South Carolina's beaches
ULTRAVIOLET DISINFECTION FOR STORMWATER TREATMENT IN COASTAL CAROLINAS Ronald A. Geiger HDR Engineering, Charlotte, NC Tom Garigen, Horry County Storm Water, Conway, SC BACKGROUND South Carolina's beaches
2017 Water Quality Year in Review
 Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Water Quality Program Pontchartrain Basin Sampling Program How Clean is Lake Pontchartrain s Water? 2017 Water Quality Year-in-Review In 2017, LPBF Water Quality Program
Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Water Quality Program Pontchartrain Basin Sampling Program How Clean is Lake Pontchartrain s Water? 2017 Water Quality Year-in-Review In 2017, LPBF Water Quality Program
SOURCE WATER MONITORING
 Monitoring and Protecting Our Water Sources SOURCE WATER MONITORING The Upper Cache la Poudre (UCLP) Watershed Collaborative Monitoring Program was established in 28 between the City of Fort Collins, the
Monitoring and Protecting Our Water Sources SOURCE WATER MONITORING The Upper Cache la Poudre (UCLP) Watershed Collaborative Monitoring Program was established in 28 between the City of Fort Collins, the
OCSD Urban Runoff Program SCAP Collection Systems in Motion
 OCSD Urban Runoff Program SCAP Collection Systems in Motion Tom B. Meregillano Regulatory Specialist Orange County Sanitation District, CA OCSD Service Area Los Angeles Santa Ana San Diego Orange County,
OCSD Urban Runoff Program SCAP Collection Systems in Motion Tom B. Meregillano Regulatory Specialist Orange County Sanitation District, CA OCSD Service Area Los Angeles Santa Ana San Diego Orange County,
Middle Santa Ana River Bacterial Indicator TMDL Implementation Report
 Middle Santa Ana River Bacterial Indicator TMDL Implementation Report February 2013 on behalf of Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority San Bernardino County Stormwater Program County of Riverside Cities
Middle Santa Ana River Bacterial Indicator TMDL Implementation Report February 2013 on behalf of Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority San Bernardino County Stormwater Program County of Riverside Cities
City of Delray Beach MS4 Assessment Program: Part V. Monitoring Requirements MS4 Permit No. FLS
 City of Delray Beach MS4 Assessment Program: Part V. Monitoring Requirements MS4 Permit No. FLS 000018 004 The purpose of this document is to outline the assessment program for the City of Delray Beach
City of Delray Beach MS4 Assessment Program: Part V. Monitoring Requirements MS4 Permit No. FLS 000018 004 The purpose of this document is to outline the assessment program for the City of Delray Beach
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
SNAPSHOT DAY, May 10, 2008
 SNAPSHOT DAY, 2008 Supported by: Mr. Krick and students from La Sierra High School Ms. Hampton, Mr. Pitruzzello and students from King High School May 10, 2008 1 What is Snapshot Day? In honor of Water
SNAPSHOT DAY, 2008 Supported by: Mr. Krick and students from La Sierra High School Ms. Hampton, Mr. Pitruzzello and students from King High School May 10, 2008 1 What is Snapshot Day? In honor of Water
Appendix B: Inventory of Data Sources
 Appendix B: Inventory of Data Sources LIST OF DATA SOURCES AND REFERENCES TO SUPPORT WATER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN FOR THE SOUTH ORANGE COUNTY WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA November 4, 2015 Orange County
Appendix B: Inventory of Data Sources LIST OF DATA SOURCES AND REFERENCES TO SUPPORT WATER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PLAN FOR THE SOUTH ORANGE COUNTY WATERSHED MANAGEMENT AREA November 4, 2015 Orange County
South Carolina Water Quality Standards. Heather Preston DHEC Bureau of Water October 14, 2008
 South Carolina Water Quality Standards Heather Preston DHEC Bureau of Water October 14, 2008 The Water Quality Standards 303 (c) of the Clean Water Act requires all states to have water quality standards
South Carolina Water Quality Standards Heather Preston DHEC Bureau of Water October 14, 2008 The Water Quality Standards 303 (c) of the Clean Water Act requires all states to have water quality standards
Water Chemistry. Water 101
 Water Chemistry Water 101 I. Introduction A. Water is not pure Many different kinds of chemicals dissolved in it Ions, organic chemicals, organic matter, particulate matter, and gases can all be in water
Water Chemistry Water 101 I. Introduction A. Water is not pure Many different kinds of chemicals dissolved in it Ions, organic chemicals, organic matter, particulate matter, and gases can all be in water
Peach Creek Watershed
 SH 304 Peach Creek Watershed Bastrop Peach Cree FM 713 Caldwell Peach Creek, Sandy Fork Copperas Creek 1803C Peach Creek Fayette FM 1054 US 90 Waelder US IH US 90 FM 1680 IH 10 Dry Run Gonzales SH 97 Peach
SH 304 Peach Creek Watershed Bastrop Peach Cree FM 713 Caldwell Peach Creek, Sandy Fork Copperas Creek 1803C Peach Creek Fayette FM 1054 US 90 Waelder US IH US 90 FM 1680 IH 10 Dry Run Gonzales SH 97 Peach
CBF Water Quality Interactive Map
 CBF Water Quality Interactive Map Student and adult groups that take part Often, they measure the water chemistry to evaluate the be doing it when you come out with us! By compiling these points on a map
CBF Water Quality Interactive Map Student and adult groups that take part Often, they measure the water chemistry to evaluate the be doing it when you come out with us! By compiling these points on a map
Cooperative Monitoring Program nutrient monitoring results
 Cooperative Monitoring Program nutrient monitoring results Nutrient Water Quality Symposium, Santa Maria Central Coast Water Quality Preservation, Inc. Executive Director: Kirk Schmidt (831-750-5449, kschmidt@ccwqp.org)
Cooperative Monitoring Program nutrient monitoring results Nutrient Water Quality Symposium, Santa Maria Central Coast Water Quality Preservation, Inc. Executive Director: Kirk Schmidt (831-750-5449, kschmidt@ccwqp.org)
Water Chemistry Monitoring
 Chicago River Fieldtrip Activity Summary Students use basic to advanced water quality monitoring kits and probes to assess the water quality of the Chicago River. Water chemistry kits available for loan
Chicago River Fieldtrip Activity Summary Students use basic to advanced water quality monitoring kits and probes to assess the water quality of the Chicago River. Water chemistry kits available for loan
Bacon Creek Watershed Plan Implementation Chapter 3: Learning More - Monitoring to Secure New Data Draft
 Bacon Creek Watershed Plan Implementation Chapter 3: Learning More - Monitoring to Secure New Data Draft There are two main goals of watershed planning: protect good water quality and improve poor water
Bacon Creek Watershed Plan Implementation Chapter 3: Learning More - Monitoring to Secure New Data Draft There are two main goals of watershed planning: protect good water quality and improve poor water
Impacts to Aquatic Habitats from Land-Use or Is It Polluted?
 Impacts to Aquatic Habitats from Land-Use or Is It Polluted? Water Pollution is: The addition of excessive carbon to a system The addition of large amounts of materials to water that causes adverse changes
Impacts to Aquatic Habitats from Land-Use or Is It Polluted? Water Pollution is: The addition of excessive carbon to a system The addition of large amounts of materials to water that causes adverse changes
Lake Elsinore and Canyon Lake Watersheds Nutrient TMDL Monitoring Annual Report
 Lake Elsinore and Canyon Lake sheds Nutrient TMDL Monitoring 2016 2017 Annual Report Prepared for: Lake Elsinore & San Jacinto sheds Project Authority 11615 Sterling Avenue Riverside, California 92503
Lake Elsinore and Canyon Lake sheds Nutrient TMDL Monitoring 2016 2017 Annual Report Prepared for: Lake Elsinore & San Jacinto sheds Project Authority 11615 Sterling Avenue Riverside, California 92503
Fountain Creek Watershed Water Quality Overview. Fountain Creek Watershed Citizen Advisory Committee June 12, 2015
 Fountain Creek Watershed Water Quality Overview Fountain Creek Watershed Citizen Advisory Committee June 12, 2015 Outline Fountain Creek Watershed Strategic Plan - 2009 Regulatory standards and classifications
Fountain Creek Watershed Water Quality Overview Fountain Creek Watershed Citizen Advisory Committee June 12, 2015 Outline Fountain Creek Watershed Strategic Plan - 2009 Regulatory standards and classifications
Pennsylvania Pequea and Mill Creek Watershed Section 319 National Monitoring Program Project
 Pennsylvania Pequea and Mill Creek Watershed Section 319 National Monitoring Program Project Figure 36: Pequea and Mill Creek (Pennsylvania) Watershed Project Location 231 T-1 C-1 T1-3 T-4 C1-2 T2-3 T-2
Pennsylvania Pequea and Mill Creek Watershed Section 319 National Monitoring Program Project Figure 36: Pequea and Mill Creek (Pennsylvania) Watershed Project Location 231 T-1 C-1 T1-3 T-4 C1-2 T2-3 T-2
MS4 Assessment Program to Satisfy Part V. Monitoring Requirements
 MS4 Assessment Program to Satisfy Part V. Monitoring Requirements Submitted by City of Boynton Beach MS4 Permit No. FLS000018-004 The purpose of this document is to outline the City of Boynton Beach Stormwater
MS4 Assessment Program to Satisfy Part V. Monitoring Requirements Submitted by City of Boynton Beach MS4 Permit No. FLS000018-004 The purpose of this document is to outline the City of Boynton Beach Stormwater
Oso Creek and Oso Bay Data Report
 Oso Creek and Oso Bay Data Report February 2011 Prepared by: Texas Stream Team River Systems Institute Texas State University San Marcos This report was prepared in cooperation with the Texas Commission
Oso Creek and Oso Bay Data Report February 2011 Prepared by: Texas Stream Team River Systems Institute Texas State University San Marcos This report was prepared in cooperation with the Texas Commission
Presentation to the District of Central Saanich Hagan-Graham and Tetayut Water Quality Monitoring Programs
 Presentation to the District of Central Saanich Hagan-Graham and Tetayut Water Quality Monitoring Programs April 2 th, 217 Hagan-Graham Summary Modern WQ program undertaken at sites on Hagan-Graham Creeks:
Presentation to the District of Central Saanich Hagan-Graham and Tetayut Water Quality Monitoring Programs April 2 th, 217 Hagan-Graham Summary Modern WQ program undertaken at sites on Hagan-Graham Creeks:
by Keith Kennedy Manager of Environmental Programs North Central Texas Council of Governments
 by Keith Kennedy Manager of Environmental Programs North Central Texas Council of Governments What is NPDES? National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System USEPA outfall permitting program Storm water
by Keith Kennedy Manager of Environmental Programs North Central Texas Council of Governments What is NPDES? National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System USEPA outfall permitting program Storm water
Otter Creek Watershed TMDL Project. Stakeholder Meeting June 6, 2013
 Otter Creek Watershed TMDL Project Stakeholder Meeting June 6, 2013 1 Meeting Purpose Meet with watershed & technical advisory group members and watershed landowners to provide basic Otter Creek TMDL project
Otter Creek Watershed TMDL Project Stakeholder Meeting June 6, 2013 1 Meeting Purpose Meet with watershed & technical advisory group members and watershed landowners to provide basic Otter Creek TMDL project
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION. Stream processes are strongly related to the physical conditions of the
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Stream processes are strongly related to the physical conditions of the watershed from which they flow. Alterations to physical conditions of a watershed manifest themselves through
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Stream processes are strongly related to the physical conditions of the watershed from which they flow. Alterations to physical conditions of a watershed manifest themselves through
Southern California Bight 2008 Regional Monitoring Program: Volume VIII. Estuarine Eutrophication
 Technical Report 0711 Southern California Bight 2008 Regional Monitoring Program: Volume VIII. Estuarine Eutrophication K. McLaughlin 1, M. Sutula 1, L. Busse 2, S. Anderson 3, J. Crooks 4, R. Dagit 5,
Technical Report 0711 Southern California Bight 2008 Regional Monitoring Program: Volume VIII. Estuarine Eutrophication K. McLaughlin 1, M. Sutula 1, L. Busse 2, S. Anderson 3, J. Crooks 4, R. Dagit 5,
MARK TWAIN LAKE 2002 WATER QUALITY
 MARK TWAIN LAKE 2002 WATER QUALITY REPORT U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS, ST. LOUIS DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY SECTION - Water Quality Ted Postol, Section Chief Tori Foerste, Environmental Engineer Donna
MARK TWAIN LAKE 2002 WATER QUALITY REPORT U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS, ST. LOUIS DISTRICT ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY SECTION - Water Quality Ted Postol, Section Chief Tori Foerste, Environmental Engineer Donna
Globeville Landing Outfall Surface Water. December 12, 2017 Andrew Ross, Jon Novick Denver Department of Public Health & Environment
 Globeville Landing Outfall Surface Water December 12, 2017 Andrew Ross, Jon Novick Denver Department of Public Health & Environment Introductions Andrew Ross Environmental Program Manager, DDPHE Jon Novick
Globeville Landing Outfall Surface Water December 12, 2017 Andrew Ross, Jon Novick Denver Department of Public Health & Environment Introductions Andrew Ross Environmental Program Manager, DDPHE Jon Novick
