A new approach for the determination of hydrologic prefectures in Greece for the water framework directive
|
|
|
- Cora Matilda Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A new approach for the determination of hydrologic prefectures in Greece for the water framework directive Evangelos A. BALTAS* 1. Introduction The Water Framework Directive constitutes the tool for the long-term, sustainable management of water resources and eco - systems in Europe. The success in the application of the directive is expected to depend on two crucial factors: the coordination between the physical procedures and the human activities that affect the water cycle inside the boundaries of a basin and the early taking of appropriate management measures, which will ensure the desired good condition of surface and groundwater resources for the next few years (EU, 2000). The economic gro - wth of the last few decades has formed new conditions for the use of water resources, since they allow reaching various sector e- conomic objectives, by constantly remaining one of the most important factors for human survival and ecological balance conservation (Koumouli, 2001). Greece is a country of small extent (area of 132,000 km 2 ) with intense ground relief, limited back land and great extent of coasts. The result of this special geomorphologic structure is the division of the area into a plethora of small basins and a large number of water districts (14), (Figure 1), a fact that does not keep up with its small extent (Ministry of Development, 1987). France, which is much larger in extent than Greece, consists of 4 water districts, while Spain consists of 9 (Ministry of Development, 1997). After having assessed that there is a diversity of conditions and needs that demand different special attention, the European Parliament decided that this diversity should have been taken into account during the planning phase and the implementation of measures for the protection and sustainable use of water, on a basin frame (CSI- WFD, 2001; EC, 2001). Decisions should be made as closer as possible to the places where the water is used or affected. (WWF /EC, 2001; /irc /env/ Home / main). Water is not uniformly distributed in space and time. In Greece, there are regions with big water reserves and others suffering from intense water deficiency (Sofios et al., 2007). The mean hyperannual surface precipitation constitutes an important characteristic for the evaluation of a region s hydrologic identity and response, so its examination provides reliable results on the hydrologic status of each water district. The mean annual surface precipitation of a thirty-year period ( ) is depicted in Figure 2. it is possible to observe the high variability of precipitation varying from 1,150 mm in the north-western part of the country to 350 mm in the eastern part. This is attributed to the presence of the Pindos mountain range, which interrupts the prevailing eastern movement of weather systems, thus dividing the country into two major parts: the windward, high precipitation, western areas and the leeward, low precipitation, eastern areas. Abstract The Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council issued a new legislation for the sustainable management of water resources on the basis of drainage basins. The implementation of such policy in Greece would encounter great difficulties due to the fact that the region is split into a large number of drainage areas. Especially in Northern Greece the implementation is more difficult due to transnational water resources. The aggregation of the fourteen water districts of Greece into four hydrologic prefectures is suggested in the present study. The determination of the hydrologic prefectures is based on hydrologic criteria and takes into account the existing management problems regarding internal, coastal and transnational water resources, as well as the existing administrative structure. A smaller number of hydrologic prefectures would meet the EU requirements and would mean better organization and flexibility, as well as more systematic control, supervision and management of water resources. Key words: water districts, hydrologic prefectures, water management. Résumé La Directive 2000/60 /CE du Parlement européen et du Conseil a établi une nouvelle législation pour la gestion durable des ressources en eau sur la base des bassins versants. L application d une telle politique en Grèce rencontrerait de grandes difficultés, étant donné que la région présente un grand nombre de bassins versants. Surtout en Grèce du nord, l application de la Directive est encore plus difficile comme il y a des ressources en eau transfrontalières. Cette é- tude propose l agrégation des quatorze secteurs hydriques de la Grèce en quatre préfectures hydrologiques. La détermination des préfectures est basée sur des critères hydrologiques et prend en compte des problèmes de gestion existants en ce qui concerne les ressources en eau intérieures, côtières et transfrontalières ainsi que la structure administrative existante. Une diminution du nombre des préfectures hydrologiques répondrait aux exigences de l UE et signifierait une meilleure organisation et flexibilité, ainsi qu un contrôle, une surveillance et une gestion des ressources en eau plus systématiques. * Department of Hydraulics, Soil Science and Agricultural Engineering, School of Agriculture, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece. Jel classification: Q250, Q280 Mots-clés: districts hydriques, préfectures hydrologiques, gestion de l eau. 41
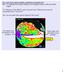
2 The determination of four hydrologic prefectures is attempted in this study, based on the hydrologic identity of the 14 existing water districts, the important management problems regarding the internal and the transnational water resources, as well as the existing administrative structure. The smaller number of hydrologic prefectures entirely complying with the Directive would enable their easier and more complete study and organization, as well as their more systematic control, supervision and management. Figure 1 The 14 water districts in Greece (Source: National Data Bank of Hydrological and Meteorological Information). Figure 2 The mean annual ( ) surface precipitation (mm). 2. Difficulties in the implementation of the directive The difficulty in the implementation of the directive derives among others from the principles that are included in the directive, regarding the water resources and their relations with the environment and other relevant sectors. Authorities with different roles, jurisdictions, responsibilities and interests are involved in the management of water resources (Mimikou, 2000). This diversity of jurisdictions is often the foremost factor in the bad management and for this reason a different approach is necessary to the management practices. In each case, the adaptation of planning and management actions on an appropriate scale is a necessary principle that should be implemented in all the directive s components, by following a bottom-up (e.g. the actions should be effectively coordinated on a local level so that the aim of good condition of water on a basin level can be achieved) and top-down direction. Greece has a geomorphologic peculiarity, owing to the intense relief, the great extent of coasts and the high number of small basins, each one demanding a different management plan. In particular, the most important problems to highlight that concern the state of water resources are: - The difficulty and deficiency in the systematic and reliable recording and evaluation of physical and artificial water systems from a quantitative and qualitative point of view, as well as the deficiency in adequate measurements of hydrologic, meteorological, hydrogeological and qualitative parameters; - The deficiency and difficulty in the alignment of independent hydrogeological basins inside the boundaries of each water district; - The interaction between coastal waters owing to nearby streams or rivers that end up to the sea; - The difficulty and deficiency in the recording of the existing uses of water and in the measurement of the water quantity that is consumed in each use; - The difficulty in the coordination of the authorities at a national and peripheral level, regarding studies and research on the infrastructure relating to the water resources; - The occasional and uncontrolled exploitation of specific water resources beyond the boundaries of one water district, without established knowledge of its capabilities, which leads to the gradual degradation of quality and quantity; - The difficulty in making long-term predictions about hydrologic, population and economic trends, production sectors etc., in the framework of the developing program, 42
3 so that corresponding predictions about utilization structures could be made; - The difficulty in solving problems concerning the planning and management of water resources; - The need for assuring the rational management of transnational water resources and their common utilization on the basis of the water needs of involved countries; - The lack of a single management authority in the water sector. 3. Determination of the hydrologic prefectures to satisfy the directive s needs The criteria that were taken into account for the determination of the hydrologic prefectures are: The surplus of water resources in the western regions of the country should be used to fulfil the needs in the eastern regions; The transnational water resources should be under the control of a single authority; All islands, which constitute small independent hydrological units, should be managed by a single authority. More specifically, the great water potential in western regions that stays unutilized should be integrated into a common management plan for the rational satisfaction of the needs of the eastern part of the country, where the natural supply does not suffice to cover the growing demand. According to the Directive, the transnational water resources of the country require a single and special treatment for the implementation of the most rational management policy, in order that their best utilization inside the national boundaries is achieved, and the disruption of the relationships with the neighbouring countries is prevented. The collaboration between involved countries is necessary together with the creation of complementary agreements and with the renewal of the existing ones according to the directive. The feature that characterizes the development identity of the islands is the limited natural water supply and the increased seasonal demand. A management aiming at the development of infrastructure and the rational use and protection of the existing water resources is necessary in order to overcome the specific problem. The description of characteristics of each water district, examined only for ancillary reasons, proved to be particularly useful for the evaluation, as it showed the connections between the different water districts, as well as their developing peculiarities that will be taken into account in their final integration in a single prefecture. The hydrologic prefectures that resulted by taking into account the above-mentioned criteria are the following four and are shown in Figure 3. - Hydrologic Prefecture of Macedonia-Thrace; - Hydrologic Prefecture of Sterea-Epirus-Thessaly; - Hydrologic Prefecture of Peloponnesus; - Hydrologic Prefecture of Islands. The above separation constitutes a proposal based on Figure 3 The four hydrologic prefectures. scientific data, available today thanks to the use of new technology and mainly geographic information systems, on the infrastructure of the National Data Bank of Hydrological and Meteorological information (NDBHM) (Mimikou, 2000). This proposal constitutes an approach to the complicated issue of the total management of the country s water resources, covering the hydrologic aspect. That management should be planned by considering a plethora of other parameters, such as the water consumption and the utilization structures of the country s water potential. In each case, the hydrologic data and the conclusions that resulted from the study that was accomplished within the NDBHM will be the base towards that direction. 3.1 Hydrologic prefecture of Macedonia-Thrace This prefecture resulted from the union of the following water districts that present common boundaries, similar geomorphologic structure and several affinities between their hydrologic conditions (the number in parenthesis is shown in Figure 1): - Western Macedonia (09); - Central Macedonia (10); - Eastern Macedonia (11); - Thrace (12). The management of transnational water resources, which are valuable for the fulfilment of basic needs, constitutes a crucial issue in this hydrologic prefecture. The lake of Big Prespa with FYROM and Albania and the Small Prespa lake with Albania in the water district of Western Macedonia, Axios river and Doirani lake with FYROM in the water district of Central Macedonia, Strimonas river 43
4 with Bulgaria in the water district of Eastern Macedonia, Nestos river with Bulgaria and Evros river with Bulgaria and Turkey in the water district of Thrace. Their management should involve the following actions: promotion of transnational meetings to secure the demanded capacity and quality of water, collaboration with the upstream countries on water issues (common networks for monitoring quantitative and qualitative parameters, common automatic systems warning of floods), minimization of the dependence on other countries and forecasting alternative ways of development. The water district of Central Macedonia was joined to that of Western Macedonia due to the provision of water to the city of Thessalonica from the Aliakmona river. Furthermore, the basin of Thessalonica city connects to basins of Western Macedonia through ground waters, due to the favorable conditions of common aquifers. These aquifers connect on a hydraulic base and contribute to the urban and agricultural demand for water. Moreover, as the rivers end up at the Gulf of Thermaikos in close proximity, there is an interaction between the river deltas, as well as between the coastal waters. The effect of a coastal area, situated near the boundaries of a water district, on another area of the neighbouring water district is more rationally controlled by a s- ingle authority then by several authorities that may have d- ifferent criteria, programs, equipment, etc. Another remarkable feature of this hydrologic prefecture is the production of hydroelectric energy from the utilization of the water potential of the Aliakmona river. The uses of water for the total hydrologic prefecture are shown in Table 1. The water district of Western Macedonia covers the biggest area (13,624 km 2 ) and is characterized by intense relief with small flat areas. The climate is continental with harsh winter and snowfalls and the mean annual temperature is 13 o C. This district presents a sufficiency in water. A great part of the water demand is met thanks to the transnational lakes of Small and Big Prespa, while Aliakmonas river is used for the water supply of Thessalonica. The mean annual rainfall depth is 640 mm and the mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 8,692 hm 3 (Ministry of Development, 1997). The river basin of Aliakmonas is the biggest (8,847 km 2, 65% of the extent of water district) and the river length is 93 km. A percentage equal to 28% of the total Table 1 Uses of water in the hydrologic prefecture of Macedonia- Thrace. extent corresponds to watersheds with an area smaller than 40 km 2. These watersheds directly drain to the sea, they are characterized by ephemeral low flow and do not contribute to the water potential of the district. The water district of Central Macedonia covers an area of 10,171 km 2 and presents a deficiency in water resources; it is the second poorest in water resources, after the Attica district. However, the water demand is great. The crop productivity of this district is remarkable, second after Thessaly. Additionally, the city of Thessalonica constitutes the second most important centre of industrial development, after Athens. The water demand is satisfied by the Aliakmonas river, as well as by transnational water resources, like the Axios river and the Doirani lake. The mean annual temperature is 14 o C. The mean annual rainfall depth is 577 mm and the corresponding volume is estimated at 5,867 hm 3. The river basin of Axios covers an area of 1,644 km 2 and the length of the river is 100 km within the Greek boundaries. The river basins presenting an area bigger than 1,000 km 2 are those of Axios, Loudias and Gallikos. They cover nearly 38% of the total area of the district, while the same percentage corresponds to watersheds with an area s- maller than 40 km 2. The water district of Eastern Macedonia covers a surface of 7,323 km 2 in area. It is characterized by mild relief with great flat areas and major development in the agricultural sector. The water resources are sufficient to meet the demand. The Strimonas river, which is a transnational river and flows from Bulgaria, constitutes the basic water resource of the district. The mean annual rainfall is 609 mm and the corresponding rainfall volume is estimated at 4,460 hm 3. The river basin of Strimonas covers an area of 5,925 km 2 (81% of the total extent) within Greek boundaries, with a length of 105 km. The remaining 19% of the total extent does not contribute to the water resources, since it consists of small watersheds (<40 km 2 ). The water district of Thrace is 11,117 km 2 in area. The water resources of the district suffice to meet the water demand. The major water resources are the rivers of Evros and Nestos, which are transnational and this means that a special management policy should be set up. The district presents a remarkable crop productivity and there is great potential for further development. The mean annual temperature varies between 14.5 and 16.5º C. The rainfall depth ranges between 500 and 600 mm in the coastal areas and it exceeds 1,000 mm towards the northern mountainous areas. The mean annual rainfall depth is 694 mm and the corresponding volume is estimated at 8,262 hm 3. The total volume of surface runoff is estimated at 10,200 hm 3, while the contribution from the Greek part is about 2,700 hm 3. The length of the Nestos river is 102 km within Greek boundaries. 3.2 Hydrologic prefecture of Sterea Thessaly Epirus This hydrologic prefecture resulted from the union of the water districts of: 44
5 - Western Sterea (04); - Epirus (05); - Eastern Sterea (07); - Thessaly (08) and - Attica (06). The water districts of Western Sterea and Epirus present common boundaries, nearly the same extent and similar geomorphologic, climatologic and hydrologic conditions. They are located at the western part of the country, which is remote from the eastern developed continental axis. It is an agricultural area that is characterized by a dearth of development and isolation. These water districts present a surplus of water resources, the highest in the whole country. The great water potential that stays unutilized should be integrated into a common management plan for the rational fulfilment of the needs inside the boundaries of the water district, but also for increasing the water potential of the eastern part of the country, where the natural supply does not suffice to cover the growing demand. The water resources are mainly used for irrigation and for the production of hydroelectric energy. Ground waters belong to different aquifers that make up a part of the water basins and are fed by the mountainous areas of the basins. In coastal areas (e.g. Gulf of Ambrakikos, Arta), where the waters have been qualitatively downgraded due to the fertilization of crops, the administration from a single central authority is much more efficient. The water districts of Western Sterea, Eastern Sterea and Attica were merged into a single hydrologic prefecture. Eastern Sterea has a greater water potential than that of Attica. Additionally, the river basins of Evinos and Mornos in the water district of Western Sterea, supply potable water to the Metropolis. These actions allow the utilization of water resources of the areas that are water self-sufficient to the benefit of areas presenting a deficiency in water resources (solution to the urgent problem of water supply in Attica), on an efficient base. Eastern Sterea and part of western Sterea should be supported by a specific policy for the contribution of their privileges. The uses of water for the hydrologic prefecture of Sterea Thessaly Epirus are shown in Table 2. The water district of Western Sterea covers a surface of 10,199 km 2 and is located in the part of the country with the highest precipitation. The rivers Acheloos, Evinos and Mornos and the lake Trichonida constitute the biggest water resources of the district, apart from the underground water resources, which generally stay unutilized. At present, a part (equal to 8.6%) of the district s water potential is used for the water supply of Attica. A small part is also transferred to Thessaly via the Plastiras lake. Four hydroelectric plants at the Acheloos river basin have been constructed for the production of electrical energy. The mean annual rainfall depth is about 800-1,000 mm in coastal and flat areas, 1,400 mm in mountainous areas, while it exceeds 1,800 mm in high-elevation areas. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 8,680 hm 3, based on the mean annual rainfall depth and the extent of the water district (Ministry of Development, 1997). The surface runoff is about 5,296 hm 3. The river basins with area greater than 1,000 km 2 are those of Acheloos (5,635 km 2 ) and Evinos, which cover 65% of the total extent of the district. A percentage equal to 23% corresponds to the watersheds that are smaller than 40 km 2. The water district of Epirus has an area of 10,026 km 2 and is located in the part of the country with the highest precipitation. It is characterized by a surplus of water balance and a low development rate. The mean annual rainfall ranges from 1,000-1,200 mm in coastal areas to 2,000 mm in mountainous areas. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 15,878 hm 3. The volume of surface runoff is 5,523 hm 3. The river basins with an area greater than 1,000 km 2 are those of Aoos, Arachthos and Kalamas, covering about 58% of the total extent of the district. Aoos is a river of great hydrologic importance and flows towards the Albanian territory. The Aoos river basin is 2,083 km 2 in area within the Greek boundaries. The Arachthos river has the greatest length, 146 km. A percentage equal to 22% of the total extent of the district corresponds to watersheds with an area smaller than 40 km 2. The water district of Eastern Sterea is 12,321 km 2 in area. It is situated along the eastern developed axis of the country with relatively balanced development of the three production sectors. The water resources are sufficient to meet the demand. The lakes Iliki and Paralimni contribute to the water supply of the Metropolis and the contribution of the underground water is also remarkable. The ground waters belong to independent aquifers that are located in the flat areas of the basins. The mean annual rainfall varies from 500 mm in Asopos basin to 1,200 mm at the mountainous areas of Evias. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 9,383 hm 3. 2,547 hm 3 correspond to the surface runoff. The river basins with area greater than 1,000 km 2 are those of Boiotikos Kifisos (1,913 km 2 ) and Sperchios (1,649 km 2 ). They cover 29% of the total extent of the district. A great percentage, equal to 43%, corresponds to watersheds smaller than 40 km 2 that do not contribute to the water potential. The water district of Attica is the poorest in water resources. The high water demand of the capital of Athens is Table 2 Uses of water in the hydrologic prefecture of Sterea-Thessaly-Epirus. 45
6 covered through the conveyance of water capacities from the water districts of western and eastern Sterea (river basins of Mornos and Evinos and lake Iliki). The mean annual rainfall ranges from 350 mm in flat areas to 1,000 mm at the mountainous areas. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 1,642 hm 3, based on the mean annual rainfall depth (512 mm) and the extent of the water district. 251 hm 3 correspond to surface runoff. The river basin of Kifisos is the greatest in extent (332 km 2 ). A great percentage, equal to 58%, corresponds to watersheds smaller than 40 km 2 that do not contribute to the water potential of the district. The water district of Thessaly has an extent of 13,377 km 2 and includes the greatest flat terrain of the entire country, with the highest crop productivity. The development of the region depends on the promotion of intensive, irrigated agriculture and tourism. There is a dearth of water resources in the region and the demand for water of the existing crops is not satisfied. The refore, a special management policy should be applied in order to reinforce the water potential through the rational use of water resources (extension and modernization of the irrigation network), as well as through the conveyance of water capacities from other water districts. Geomorphologically, the water district is divided into th ree sections: - the eastern coastal and mountainous sector characterized by a Mediterranean climate; - the central flat section, with continental climate; - the western mountainous sector, with mountainous climate. The mean annual temperature varies between 16 and 17º C. The rainfall depth is greater in the western part, it decreases in the flat area and increases in the eastern mountainous areas. The mean annual rainfall depth is estimated at 858 mm and its corresponding volume at 4,175 hm 3. The surface runoff is estimated at 3,202 hm 3. The Pinios river basin is the biggest of the country, with an area equal to 10,628 km 2, which corresponds to 81% of the total area of the water district. The length of the river is 255 km. 3.3 Hydrologic prefecture of Peloponnesus This hydrologic Prefecture of Peloponnesus resulted from the union of the water districts of: - Western Peloponnesus (01); - Eastern Peloponnesus (03); - Northern Peloponnesus (02). These water districts present relevant differences regarding the geomorphologic structure, the climate, the availability of water resources, but also significant common characteristics, such as common boundaries, similar extent, type and rate of development. Their aquifers are independent; spatially, they constitute subgroups of the three water districts and satisfy the urban and mainly the agricultural water demand. The union of the three districts may help in totally managing the water resources and solving problems concerning the ground waters, due to the decrease of the water level, which is attributed to the overexploitation of the aquifers. The groundwater is downgraded in many coastal areas, due to the movement of sea towards the interior. The hydrologic prefecture of Peloponnesus has a long coastline and the effect of a coastal area on another area of the neighbouring water district is more rationally controlled by a single authority. The water uses for the hydrologic prefecture of Peloponnesus and the corresponding percentages are shown in Table 3. Table 3 Uses of water in the hydrologic prefecture of Peloponnesus. The water district of western Peloponnesus is 7,301 km 2 in area and poorly to moderately developed. It is rich in precipitation, surface and underground water resources. The naturally available water potential (surface and underground) is estimated at 4,400 hm 3 /year (Ministry of Development, 1997). The mean annual precipitation ranges between 800 mm at flat areas and 1600 mm at the mountainous areas with an average value equal to 1100 mm. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 8,034 hm 3 (Ministry of Development, 1997). The Alfios river basin has the greatest extent (3,561 km 2 or 49% of the total area) and the length of the river is 60 km. 19% of the total extent of the district consists of small watersheds with area under 40 km 2. These watersheds directly drain to the sea, they are characterized by ephemeral low flow and do not contribute to the water potential of the region. The water district of eastern Peloponnesus is 8,423 km 2 in area and moderately developed. It is poorer in precipitation depth than the western district. The mean annual precipitation ranges between 600 mm in flat areas and 850 mm in mountainous areas, with an average value equal to 808 mm. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 6,805 hm 3. The Evrotas river basin is the greatest in extent (1,765 km 2 or 20% of the total area) and the length of the river is 56 km. A great percentage, equal to 51% of the total extent of the district, consists of small watersheds (<40 km 2 ) that do not contribute to the water potential. The water district of northern Peloponnesus is 7,310 km 2 in area and moderately developed. It presents a sufficiency in water resources. The prevailing climate is Mediterranean in coastal and flat areas, whereas inland there is a more mountainous climate. The duration of the warm period is from 5 up to over 6 months. The mean annual precipitation ranges between 500 mm in flat areas and 1,200 mm in mountainous areas, with an average value equal to 680 mm. The mean annual rainfall volume is estimated at 5,163 hm 3 (Ministry of Development, 1997). The river basin of Pinios is the greatest in extent (960 km 2 ) and the length of the river is 84 km. A great percentage (49%) of the total extent of the district consists of small watersheds. 46
7 3.4 Hydrologic prefecture of Islands This prefecture consists of the water districts of: - Crete (13); - Aegean Sea islands (14); - the rest of the islands (e.g. Eptanisa, etc.) that presently constitute parts of the nearby water districts. The feature that characterizes the identity of this hydrologic prefecture is the limited natural supply of water and the increased seasonal demand. The problem is not intense during the winter months, but it becomes serious in summer. A single authority is required for the encounter of the peculiarity of this situation. The development of infrastructure, the rational use and protection of the existing water resources are both necessary in order to overcome the problem. The water district of Crete is 8,336 km 2 in area. The major and almost exclusive axis of the Crete s development is the northern part of the island that constitutes the island s internal front towards the continental part of the country. The climate is from temperate to Mediterranean warm-semi humid and makes the island ideal for an eight-month tourist activity, as well as for early and late crops. In the mountainous areas especially of the western side, the climate is mountainous. The mean annual temperature varies from 18.5º C in the west to 20º C in the south. The southern and south-eastern coasts of Crete are among the warmest regions of the whole country. The duration of the warm period exceeds 6 months. The island is rich in water resources that could satisfy the growing demand. The greatest problem is their spatial distribution in relation to the needs. More specifically, the western part is rich in surface and underground water resources. The precipitation depth decreases towards the eastern side of the island and, in combination with the salinity of ground waters, it leads to a deficit in the supply-demand balance, posing problems even for the water supply needs (e.g. Iraklio). The mean annual rainfall is estimated at 900 mm, while the rainfall depth is about 1,700 mm in the western part (White Mountains). The annual rainfall volume is estimated at 7,500 hm 3, 1,558 hm 3 of which is surface runoff. The uses of water for the water district of Crete and the corresponding percentages are shown in Table 4. The Water district of Aegean Islands consists of the islands of Cyclades, Dodekanisa, Lesvos, Chios, Samos and stretches over a surface of 9,104 km 2. The water resources do not suffice to meet the demand, with an exception in the eastern Aegean islands, where the rainfall depth is greater. The climate is mild Mediterranean with the mean annual temperature ranging from 16.9 to 19.9 o C. The mean annual rainfall ranges from 350 to 818 mm and the estimated mean annual rainfall volume is 5,200 hm 3. Regarding the water use, 68% of water is used for irrigation. 4. Conclusions In the present study, an approach was suggested to aggregate the fourteen water districts of Greece into four hydrologic prefectures, based on hydrologic criteria, the rational management of internal, coastal and transnational water resources and taking into account the existing administrative structure. A small number of hydrologic prefectures is necessary for better organization and flexibility in solving the existing management problems. The difficulties in the implementation of the Water Framework Directive in Greece, and particularly in Northern Greece (due to the presence of transnational rivers), were assessed and discussed. The management of water resources should be planned by bearing in mind a series of other parameters, such as the spatial precisely defined consumptions of water, the land cover and land use, the country s water potential and the structures for its u- tilization. References CSI-WFD-Project 2.9, Guidance on Best Practices in River Basin Management Planning, Work Package 1: Guidance on the Identification of River Basin Districts, Issue Paper, Valencia, December EC, Common Strategy on the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive. Strategic Document, 2 May European Union, «The Water Framework Directive. (2000/60/EC)». Κoumouli V.D. (2001) Geomorphologic and Hydrologic investigation for redefinition of Water Sections in Greece. N.T.U.A. Interdisciplinary Interdepartmental program of postgraduate studies N.T.U.A. Water resources science & technology. Mimikou, A. M., 2000, National Data Bank of Hydrological and Meteorological Information. Ministry of Development: Law 1739/1987 (φek A 201). «Water Resources Management and other instrumentation». Ministry of Development: Law 2503/1997 (φek A 107). «Administration, Organization of the Periphery, arrangement of local administrative affairs and other instrumentation». Ministry of Development, «Study for the water resources management in Greece». Ministry of Development: Presidential decree 60/1998 (φek A 61). «Assessment of the spatial initiative of the water Resources management of the Periphery». Sofios S., Arabatzis G., Baltas E., Policy for management of water resources in Greece, The Environmentalist, Springer Netherlands, , /s WWF/EC, Elements of Good Practice in Integrated River Basin Management, Key issues, lessons learned and good practice examples from the WWF/EC Water Seminar Series 2000/2001, October 2001, Brussels, Belgium. 47
DEVELOPMENT OF A REGIONAL MODEL FOR HYDROPOWER POTENTIAL IN WESTERN GREECE
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 14, No 4, pp 442-449, 2012 Copyright 2012 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved DEVELOPMENT OF A REGIONAL MODEL FOR HYDROPOWER POTENTIAL IN WESTERN GREECE E.A. BALTAS
Global NEST Journal, Vol 14, No 4, pp 442-449, 2012 Copyright 2012 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved DEVELOPMENT OF A REGIONAL MODEL FOR HYDROPOWER POTENTIAL IN WESTERN GREECE E.A. BALTAS
GROUNDWATER AND NITRATES IN GREECE - AN OVERVIEW. George Stournaras. Hydrology and Engineering Geology Athens University Athens, Greece
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 6 1998 GROUNDWATER AND NITRATES
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 6 1998 GROUNDWATER AND NITRATES
COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT. Report on the implementation of the Water Framework Directive River Basin Management Plans Member State: GREECE
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 9.3.2015 SWD(2015) 54 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Report on the implementation of the Water Framework Directive River Basin Management Plans Member State: GREECE
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 9.3.2015 SWD(2015) 54 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Report on the implementation of the Water Framework Directive River Basin Management Plans Member State: GREECE
APPLICATION OF THE SWAT (SOIL AND WATER ASSESSMENT TOOL) MODEL IN THE RONNEA CATCHMENT OF SWEDEN
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 7, No 3, pp 5-57, 5 Copyright 5 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved APPLICATION OF THE SWAT (SOIL AND WATER ASSESSMENT TOOL) MODEL IN THE RONNEA CATCHMENT OF SWEDEN
Global NEST Journal, Vol 7, No 3, pp 5-57, 5 Copyright 5 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved APPLICATION OF THE SWAT (SOIL AND WATER ASSESSMENT TOOL) MODEL IN THE RONNEA CATCHMENT OF SWEDEN
CORRIGENDUM This document corrects document SWD(2015) 54 final of [Document updated with River Basin Districts GR13 and GR14 in Greece].
![CORRIGENDUM This document corrects document SWD(2015) 54 final of [Document updated with River Basin Districts GR13 and GR14 in Greece]. CORRIGENDUM This document corrects document SWD(2015) 54 final of [Document updated with River Basin Districts GR13 and GR14 in Greece].](/thumbs/93/117988174.jpg) EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 17.7.2018 SWD(2015) 54 final/2 CORRIGENDUM This document corrects document SWD(2015) 54 final of 09.03.2015. [Document updated with River Basin Districts GR13 and GR14 in
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 17.7.2018 SWD(2015) 54 final/2 CORRIGENDUM This document corrects document SWD(2015) 54 final of 09.03.2015. [Document updated with River Basin Districts GR13 and GR14 in
Chapter Climatic changes and impacts on Greece s water systems** Introduction
 Chapter 2 The risks and impacts of climate change by sector* 2.1 Climatic changes and impacts on Greece s water systems** 2.1.1 Introduction The concept of water resources derives from the relationship
Chapter 2 The risks and impacts of climate change by sector* 2.1 Climatic changes and impacts on Greece s water systems** 2.1.1 Introduction The concept of water resources derives from the relationship
CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION
 CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2 INTRODUCTION 3 DESERTIFICATION FACTORS IN CYPRUS CLIMATE 5 SOIL 5 WATER MANAGEMENT 5 ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS 6 GENERAL MEASURES TO
CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2 INTRODUCTION 3 DESERTIFICATION FACTORS IN CYPRUS CLIMATE 5 SOIL 5 WATER MANAGEMENT 5 ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS 6 GENERAL MEASURES TO
HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANTS of PPC S.A. in GREECE
 HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANTS of PPC S.A. in GREECE Ioannis Argyrakis Director Hydroelectric Generation Department 1 A GENERAL INFORMATION FOR HPP s of PPC SA 2 HPPs location 3 The Hydroelectric development
HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANTS of PPC S.A. in GREECE Ioannis Argyrakis Director Hydroelectric Generation Department 1 A GENERAL INFORMATION FOR HPP s of PPC SA 2 HPPs location 3 The Hydroelectric development
HYDROELECTRIC PRODUCTION OF PPC S.A.
 HYDROELECTRIC PRODUCTION OF PPC S.A. HIGH AVAILABILITY RELIABILITY FLEXIBILITY Ioannis Argyrakis Director Hydroelectric Generation Department 1 A GENERAL INFORMATION FOR HPP s of PPC SA 2 HPPs location
HYDROELECTRIC PRODUCTION OF PPC S.A. HIGH AVAILABILITY RELIABILITY FLEXIBILITY Ioannis Argyrakis Director Hydroelectric Generation Department 1 A GENERAL INFORMATION FOR HPP s of PPC SA 2 HPPs location
Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin
 Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin Spain and Algeria are active members of the United Nations, the Union for the Mediterranean and the 5+5 Dialogue for
Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin Spain and Algeria are active members of the United Nations, the Union for the Mediterranean and the 5+5 Dialogue for
COUNTRY LEVEL IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE (CLICC) PILOT PROJECT- GHANA
 COUNTRY LEVEL IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE (CLICC) PILOT PROJECT- GHANA National Circumstances: Major Developments Since 2006 Ghana s population has tripled, from 6.7million in 1960 to 24.9million in 2010
COUNTRY LEVEL IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE (CLICC) PILOT PROJECT- GHANA National Circumstances: Major Developments Since 2006 Ghana s population has tripled, from 6.7million in 1960 to 24.9million in 2010
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT. Annex to the
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 22.3.2007 SEC(2007) 363 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Annex to the COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL 'Towards
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 22.3.2007 SEC(2007) 363 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Annex to the COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL 'Towards
HYDRODIPLOMACY IN PRACTICE: TRANSBOUNDARY WATER MANAGEMENT IN NORTHERN GREECE
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 10, No 3, pp 287-294, 2008 Copyright 2008 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved HYDRODIPLOMACY IN PRACTICE: TRANSBOUNDARY WATER MANAGEMENT IN NORTHERN GREECE Y. MYLOPOULOS
Global NEST Journal, Vol 10, No 3, pp 287-294, 2008 Copyright 2008 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved HYDRODIPLOMACY IN PRACTICE: TRANSBOUNDARY WATER MANAGEMENT IN NORTHERN GREECE Y. MYLOPOULOS
CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT
 Convention on Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes SEMINAR ON THE ROLE OF ECOSYSTEMS AS WATER SUPPLIERS (Geneva, 13-14 December 2004) CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT Water Management
Convention on Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes SEMINAR ON THE ROLE OF ECOSYSTEMS AS WATER SUPPLIERS (Geneva, 13-14 December 2004) CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT Water Management
IRRIGATION CHALLENGES IN NORTH WEST GREECE: PERSPECTIVES AND SOLUTIONS FOR FLOOD PRONE REGIONS
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 IRRIGATION CHALLENGES IN NORTH WEST GREECE: PERSPECTIVES AND SOLUTIONS FOR FLOOD
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 IRRIGATION CHALLENGES IN NORTH WEST GREECE: PERSPECTIVES AND SOLUTIONS FOR FLOOD
Kallikrates The New Architecture for Local Government in Greece in an Environment of Economic Crisis
 Kallikrates The New Architecture for Local Government in Greece in an Environment of Economic Crisis Du 26 au 28 novembre 2014 Montpellier Dr. Michalis Christakis CONTENTS 1. The Reform Itself. 2. The
Kallikrates The New Architecture for Local Government in Greece in an Environment of Economic Crisis Du 26 au 28 novembre 2014 Montpellier Dr. Michalis Christakis CONTENTS 1. The Reform Itself. 2. The
IRRIGATION CHALLENGES IN NORTH WEST GREECE: PERSPECTIVES AND SOLUTIONS FOR FLOOD PRONE REGIONS
 CEST2015 Rhodes, Greece Ref no: XXX IRRIGATION CHALLENGES IN NORTH WEST GREECE: PERSPECTIVES AND SOLUTIONS FOR FLOOD PRONE REGIONS D. SERBIS, C. PAPATHANASIOU, and N. MAMASSIS Laboratory of Hydrology and
CEST2015 Rhodes, Greece Ref no: XXX IRRIGATION CHALLENGES IN NORTH WEST GREECE: PERSPECTIVES AND SOLUTIONS FOR FLOOD PRONE REGIONS D. SERBIS, C. PAPATHANASIOU, and N. MAMASSIS Laboratory of Hydrology and
! Ural Mountains. Please SAVE and PRINT the document file transferred to you when you logged in to help you take notes during class. !
 Europe s Climate and Environment Teacher: Mrs. Moody Class begins at: 10:05 Learning Targets: I I CAN describe the major environmental concerns facing Europe today. While you wait: Work on your USA Test
Europe s Climate and Environment Teacher: Mrs. Moody Class begins at: 10:05 Learning Targets: I I CAN describe the major environmental concerns facing Europe today. While you wait: Work on your USA Test
TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC EVALUATION OF WATER REUSE FROM WASTEWATER TREATMENTS PLANTS
 TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC EVALUATION OF WATER REUSE FROM WASTEWATER TREATMENTS PLANTS 12 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Dodecanese, Greece, 8 10 September 2011
TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC EVALUATION OF WATER REUSE FROM WASTEWATER TREATMENTS PLANTS 12 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Dodecanese, Greece, 8 10 September 2011
6 th World Water Forum
 International Office For Water PARIS-FRANCE International Network Of Basin Organizations 6 th World Water Forum 12 17 March 2012, Marseille TOWARDS WORLD WATER SOLUTIONS ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES French
International Office For Water PARIS-FRANCE International Network Of Basin Organizations 6 th World Water Forum 12 17 March 2012, Marseille TOWARDS WORLD WATER SOLUTIONS ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES French
Institutional and Policy Framework Analysis GREECE
 INCO-CT-2004-509093 ADU-RES Co-ordination Action for Autonomous Desalination Units Based on Renewable Energy Systems Institutional and Policy Framework Analysis GREECE WP-7: Institutional & Policy Framework
INCO-CT-2004-509093 ADU-RES Co-ordination Action for Autonomous Desalination Units Based on Renewable Energy Systems Institutional and Policy Framework Analysis GREECE WP-7: Institutional & Policy Framework
MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION IN THE AQUIFER OF N. MOUDANIA, GREECE
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Hellenic Agricultural Organization Demeter Land Reclamation Institute Hellas. Forschungzentrum Juelich GmbH Agrosphere Institute (IBG 3) Germany
 Hellenic Agricultural Organization Demeter Land Reclamation Institute Hellas Forschungzentrum Juelich GmbH Agrosphere Institute (IBG 3) Germany Assessing the potential effects of climate change in the
Hellenic Agricultural Organization Demeter Land Reclamation Institute Hellas Forschungzentrum Juelich GmbH Agrosphere Institute (IBG 3) Germany Assessing the potential effects of climate change in the
Challenges & Opportunities in the Water Sector (Mauritius) Manta Devi Nowbuth (Dr) University of Mauritius
 Challenges & Opportunities in the Water Sector (Mauritius) By Manta Devi Nowbuth (Dr) University of Mauritius The island of Mauritius Mauritius The island of Mauritius Geographical location: between longitude
Challenges & Opportunities in the Water Sector (Mauritius) By Manta Devi Nowbuth (Dr) University of Mauritius The island of Mauritius Mauritius The island of Mauritius Geographical location: between longitude
RAINFALL - RUNOFF MODELING IN AN EXPERIMENTAL WATERSHED IN GREECE
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 RAINFALL - RUNOFF MODELING IN AN EXPERIMENTAL WATERSHED IN GREECE KOTSIFAKIS
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 RAINFALL - RUNOFF MODELING IN AN EXPERIMENTAL WATERSHED IN GREECE KOTSIFAKIS
Interview 10 - Kleanthis Kravvaritis, Greece
 Interview 10 - Kleanthis Kravvaritis, Greece Profile Name: Kleanthis Kravvaritis Age: 43 Education: Mechanical Engineer Activity: CEO of «RENEWABLE - KRAVVARITIS & PARTNERS CONSULTING ENGINEERS» Lives
Interview 10 - Kleanthis Kravvaritis, Greece Profile Name: Kleanthis Kravvaritis Age: 43 Education: Mechanical Engineer Activity: CEO of «RENEWABLE - KRAVVARITIS & PARTNERS CONSULTING ENGINEERS» Lives
ACTIVITIES FOR COMBATTING AGRICULTURAL DROUGHT IN TURKEY. I. Introduction
 ACTIVITIES FOR COMBATTING AGRICULTURAL DROUGHT IN TURKEY I. Introduction Turkey is a developing country with rapidly growing economy and its population approximately half of which is under age of thirty.
ACTIVITIES FOR COMBATTING AGRICULTURAL DROUGHT IN TURKEY I. Introduction Turkey is a developing country with rapidly growing economy and its population approximately half of which is under age of thirty.
Drought and water scarcity management plan for the Peloponnese river basin districts
 Drought and water scarcity management plan for the Peloponnese river basin districts S. Michas 1, A. Efstratiadis 2, K. Nikolaou* 1 and Ν. Mamassis 2 1 Hydroexigiantiki Consulting Engineers, 3 Evias Str.
Drought and water scarcity management plan for the Peloponnese river basin districts S. Michas 1, A. Efstratiadis 2, K. Nikolaou* 1 and Ν. Mamassis 2 1 Hydroexigiantiki Consulting Engineers, 3 Evias Str.
Hydrological Observatory description
 Athens, Greece Location The Greater Athens Area hydrological observatory is located in the periphery of Attica, in the south of the country, and covers the part of the greater Athens area, which extends
Athens, Greece Location The Greater Athens Area hydrological observatory is located in the periphery of Attica, in the south of the country, and covers the part of the greater Athens area, which extends
The European soil information system and its extension to the Mediterranean Basin
 The European soil information system and its extension to the Mediterranean Basin Montanarella L. in Zdruli P. (ed.), Steduto P. (ed.), Lacirignola C. (ed.), Montanarella L. (ed.). Soil resources of Southern
The European soil information system and its extension to the Mediterranean Basin Montanarella L. in Zdruli P. (ed.), Steduto P. (ed.), Lacirignola C. (ed.), Montanarella L. (ed.). Soil resources of Southern
Cool waters and atmospheric high pressure
 QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
HELLENIC REPUBLIC REGION OF EPIRUS. Special Advisor in EU affairs at Vice Governor of Region of Epirus
 Grigorios Vangelidis HELLENIC REPUBLIC REGION OF EPIRUS Special Advisor in EU affairs at Vice Governor of Region of Epirus g.vangelidis@php.gov.gr 21 April, 2015 Information seminar in Rome Epirus: geographic
Grigorios Vangelidis HELLENIC REPUBLIC REGION OF EPIRUS Special Advisor in EU affairs at Vice Governor of Region of Epirus g.vangelidis@php.gov.gr 21 April, 2015 Information seminar in Rome Epirus: geographic
UTILIZATION OF ANALYTICAL HIERARCHY PROCESS TO EVALUATE IMPROVEMENT OPTIONS FOR A LOCAL ENERGY SYSTEM
 UTILIZATION OF ANALYTICAL HIERARCHY PROCESS TO EVALUATE IMPROVEMENT OPTIONS FOR A LOCAL ENERGY SYSTEM N. Katsoulakos a, D. Damigos b, D. Kaliampakos c, a National Technical University of Athens, Metsovion
UTILIZATION OF ANALYTICAL HIERARCHY PROCESS TO EVALUATE IMPROVEMENT OPTIONS FOR A LOCAL ENERGY SYSTEM N. Katsoulakos a, D. Damigos b, D. Kaliampakos c, a National Technical University of Athens, Metsovion
SWOT ANALYSIS FOR THE PILOT RIVER BASIN: Irminio River Basin
 Project cofinanced by European Regional Development Fund Project cofinancé par le Fonds européen de développement régional 1G-MED08-515 Sustainable Water Management through Common Responsibility enhancement
Project cofinanced by European Regional Development Fund Project cofinancé par le Fonds européen de développement régional 1G-MED08-515 Sustainable Water Management through Common Responsibility enhancement
DECLARATION OF MALTA
 DECLARATION OF MALTA 11 th GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF THE MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANISATIONS 22 nd -24 th March 2017 St. Julians, Malta PERMANENT TECHNICAL SECRETARIAT MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN
DECLARATION OF MALTA 11 th GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF THE MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANISATIONS 22 nd -24 th March 2017 St. Julians, Malta PERMANENT TECHNICAL SECRETARIAT MEDITERRANEAN NETWORK OF BASIN
Perspectives on water reuse in Europe. Windhoek, October 2018
 Perspectives on water reuse in Europe Windhoek, 18-19 October 2018 How far are we from potable reuse? 1. Very far, it s never going to happen 2. Maybe not so far 3. Well, it s already happening 4. Actually,
Perspectives on water reuse in Europe Windhoek, 18-19 October 2018 How far are we from potable reuse? 1. Very far, it s never going to happen 2. Maybe not so far 3. Well, it s already happening 4. Actually,
Mr. Jean - François DONZIER
 Mr. Jean - François DONZIER General Manager Office for Water - IOWater - Permanent Technical Secretary Network of Basin Organizations - INBO - FRESH WATER IS A TIME BOMB!!! office for Water PARIS Network
Mr. Jean - François DONZIER General Manager Office for Water - IOWater - Permanent Technical Secretary Network of Basin Organizations - INBO - FRESH WATER IS A TIME BOMB!!! office for Water PARIS Network
Water Supply Development in Iran during Recent Drought
 Water Supply Development in Iran during Recent Drought Farid Karimpour 1, Seyed Hamed Alemohammad 2 Abstract Iran is located in one of the arid and semi-arid regions of the world and due to a dry weather,
Water Supply Development in Iran during Recent Drought Farid Karimpour 1, Seyed Hamed Alemohammad 2 Abstract Iran is located in one of the arid and semi-arid regions of the world and due to a dry weather,
Management of Water Resources in Cyprus
 Management of Water Resources in Cyprus CHARLES DEMETRIOU Hydrologist Water Development Department Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources & Environment 9 July, 2012 OUTLINE Mission of the Water Development
Management of Water Resources in Cyprus CHARLES DEMETRIOU Hydrologist Water Development Department Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources & Environment 9 July, 2012 OUTLINE Mission of the Water Development
INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON HARMONISING ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS WITH SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT POTENTIAL OF RIVER BASINS.
 INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON HARMONISING ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS WITH SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT POTENTIAL OF RIVER BASINS 24-26 March 2010 IRBM in Malaysia DID Initiatives by Department of Irrigation
INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON HARMONISING ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS WITH SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT POTENTIAL OF RIVER BASINS 24-26 March 2010 IRBM in Malaysia DID Initiatives by Department of Irrigation
Albanian Power Exchange - Novelties and Impact
 Albanian Power Exchange - Novelties and Impact Abstract Melisa Panariti University of Durres Gloria Çeno University of Durres This article provides an overview related to the establishment of the Albanian
Albanian Power Exchange - Novelties and Impact Abstract Melisa Panariti University of Durres Gloria Çeno University of Durres This article provides an overview related to the establishment of the Albanian
Water ressources in Tunisiaare limitedand characterised by high spatial disparities.
 Tunisia ranks in the category of countries with the least resources water in the Mediterranean. For a population of 11 million, the total renewable water resources per capita is estimated to 415 m 3 (2014)
Tunisia ranks in the category of countries with the least resources water in the Mediterranean. For a population of 11 million, the total renewable water resources per capita is estimated to 415 m 3 (2014)
Water Development and Management Strategy of China
 Water Development and Management Strategy of China Li Yuanyuan Deputy Chief Engineer, General Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Planning and Design General Institute, MWR Abstract: Water is not
Water Development and Management Strategy of China Li Yuanyuan Deputy Chief Engineer, General Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Planning and Design General Institute, MWR Abstract: Water is not
The EXIKONOMO project ΕΦΔ : ΕΞΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΩ
 The EXIKONOMO project Brief Description Objectives of the project Description The project aims to improve energy efficiency at a local level/municipalities, to promote energy saving activities with direct
The EXIKONOMO project Brief Description Objectives of the project Description The project aims to improve energy efficiency at a local level/municipalities, to promote energy saving activities with direct
Hydrology and Water Management. Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar
 Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
What is the Copernicus Climate Change Service?
 What is the Copernicus Climate Service? Copernicus for Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu INTRODUCTION The Copernicus Climate Service (C3S) has
What is the Copernicus Climate Service? Copernicus for Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu INTRODUCTION The Copernicus Climate Service (C3S) has
Manifesto from the Workshop Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater
 Manifesto from the Workshop Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater EU Working Group C workshop October 12th, Warsaw A workshop on Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater was held in Warsaw under the umbrella
Manifesto from the Workshop Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater EU Working Group C workshop October 12th, Warsaw A workshop on Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater was held in Warsaw under the umbrella
Eleni Tryfon & Eva Papastergiadou The Goulandris Natural History Museum, Greek Biotope/Wetland Centre, 57001, Thessaloniki, Greece
 P R E L IM IN A R Y R E V IE W OF W A T E R Q U A L IT Y R E S E A R C H IN G R E E C E Eleni Tryfon & Eva Papastergiadou The Goulandris Natural History Museum, Greek Biotope/Wetland Centre, 57001, Thessaloniki,
P R E L IM IN A R Y R E V IE W OF W A T E R Q U A L IT Y R E S E A R C H IN G R E E C E Eleni Tryfon & Eva Papastergiadou The Goulandris Natural History Museum, Greek Biotope/Wetland Centre, 57001, Thessaloniki,
Use of a conceptual rainfall runoff model in water resources planning
 The influence of man on the hydrological regime with special reference to representative and experimental basins L'influence de l'homme sur le régime hydrologique avec référence particulière aux études
The influence of man on the hydrological regime with special reference to representative and experimental basins L'influence de l'homme sur le régime hydrologique avec référence particulière aux études
VII meeting of the Ministers of agriculture and fisheries of CIHEAM member countries. Final declarations
 VII meeting of the Ministers of agriculture and fisheries of CIHEAM member countries. Final declarations in Basurco B. (ed.). The Mediterranean fisheries sector. A reference publication for the VII meeting
VII meeting of the Ministers of agriculture and fisheries of CIHEAM member countries. Final declarations in Basurco B. (ed.). The Mediterranean fisheries sector. A reference publication for the VII meeting
Project description Environmental issues Beneficiaries Administrative data Read more
 HydroSense - Innovative precision technologies for optimised irrigation and integrated crop management in a water-limited agrosystem LIFE08 ENV/GR/000570 Project description Environmental issues Beneficiaries
HydroSense - Innovative precision technologies for optimised irrigation and integrated crop management in a water-limited agrosystem LIFE08 ENV/GR/000570 Project description Environmental issues Beneficiaries
SWOT ANALYSIS on WATER MANAGEMENT in ANTHEMOUNTAS PILOT RIVER BASIN
 Project cofinanced by European Regional Development Fund Project cofinancé par le Fonds européen de développement régional 1G-MED08-515 Sustainable Water Management through Common Responsibility enhancement
Project cofinanced by European Regional Development Fund Project cofinancé par le Fonds européen de développement régional 1G-MED08-515 Sustainable Water Management through Common Responsibility enhancement
Mapping irrigated areas and water consumption in Crete
 Mapping irrigated areas and water consumption in Crete Eleni Ioannidou Student number: 4520483 Supervisors: Prof.dr. W.G,M. Bastiaanssen Dr. Silvia Alfieri Delft University of Technology, Department of
Mapping irrigated areas and water consumption in Crete Eleni Ioannidou Student number: 4520483 Supervisors: Prof.dr. W.G,M. Bastiaanssen Dr. Silvia Alfieri Delft University of Technology, Department of
Analysis of the hydrological system of Hexi Corridor, Gansu Province. CHEN MENGXIONG Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, Beijing , China
 The Hydrological Basis for Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Beijing Symposium, October 1990). IAHS Publ. no. 197,1990. Analysis of the hydrological system of Hexi Corridor, Gansu Province
The Hydrological Basis for Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Beijing Symposium, October 1990). IAHS Publ. no. 197,1990. Analysis of the hydrological system of Hexi Corridor, Gansu Province
Cohesion Policy of the European Union and Parameterization of. the Level of Development and Hysteresis of Regions
 Cohesion Policy of the European Union and Parameterization of the Level of Development and Hysteresis of Regions George N. Botzoris 1 Panagiotis D. Koudoumakis 2 1. Democritus Thrace University, Department
Cohesion Policy of the European Union and Parameterization of the Level of Development and Hysteresis of Regions George N. Botzoris 1 Panagiotis D. Koudoumakis 2 1. Democritus Thrace University, Department
Solid Waste Management in Greece: large steps forward
 Solid Waste Management in Greece: large steps forward By Mavropoulos Antonios, Head of SWM Dept. of EPEM SA Member of Hellenic Solid Waste Association Solid Waste Management (SWM) in Greece is usually
Solid Waste Management in Greece: large steps forward By Mavropoulos Antonios, Head of SWM Dept. of EPEM SA Member of Hellenic Solid Waste Association Solid Waste Management (SWM) in Greece is usually
CLIMATE CHANGE CHALLENGES TO WATER MANAGEMENT IN JUCAR RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY. Juan José Moragues Terrades President of the Júcar River Basin Authority
 CLIMATE CHANGE CHALLENGES TO WATER MANAGEMENT IN JUCAR RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY Juan José Moragues Terrades President of the Júcar River Basin Authority WATER FRAMEWORK DIRECTIVE Meeting of the European River
CLIMATE CHANGE CHALLENGES TO WATER MANAGEMENT IN JUCAR RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY Juan José Moragues Terrades President of the Júcar River Basin Authority WATER FRAMEWORK DIRECTIVE Meeting of the European River
Risk management of urban rain events in a coastal city. The case of Marseille
 Risk management of urban rain events in a coastal city The case of Marseille Jean Claude GONDART General Secretary of the municipality of Marseille Dominique LAPLACE Manager engineering department SERAM
Risk management of urban rain events in a coastal city The case of Marseille Jean Claude GONDART General Secretary of the municipality of Marseille Dominique LAPLACE Manager engineering department SERAM
ADEME/ Energie-Cités Splash Spatial Planning for Small Hydro Central Macedonia
 Planning for Small Hydro Central Macedonia (Greece) GENERAL ASPECTS Greece has a burgeoning demand for Electricity, but most electricity is currently generated from poor quality coal. Hydroelectricity
Planning for Small Hydro Central Macedonia (Greece) GENERAL ASPECTS Greece has a burgeoning demand for Electricity, but most electricity is currently generated from poor quality coal. Hydroelectricity
DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEMS FROM LIGNITE FIRED POWER PLANTS TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE IN GREECE
 DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEMS FROM LIGNITE FIRED POWER PLANTS TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE IN GREECE E. Karlopoulos 1, D. Pekopoulos 2, E. Kakaras 1 1. Centre for Research and Technology Hellas/Institute for Solid
DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEMS FROM LIGNITE FIRED POWER PLANTS TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE IN GREECE E. Karlopoulos 1, D. Pekopoulos 2, E. Kakaras 1 1. Centre for Research and Technology Hellas/Institute for Solid
This document is meant purely as a documentation tool and the institutions do not assume any liability for its contents
 2000L0060 EN 20.11.2014 007.001 1 This document is meant purely as a documentation tool and the institutions do not assume any liability for its contents B DIRECTIVE 2000/60/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
2000L0060 EN 20.11.2014 007.001 1 This document is meant purely as a documentation tool and the institutions do not assume any liability for its contents B DIRECTIVE 2000/60/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
I. HELLENIC PARLIAMENT
 May 2016 The second e-bulletin of the flagship project of the General Secretariat for Gender Equality (GSGE) on service organisation for the integration, monitoring and evaluation of gender equality policies
May 2016 The second e-bulletin of the flagship project of the General Secretariat for Gender Equality (GSGE) on service organisation for the integration, monitoring and evaluation of gender equality policies
Indicator Fact Sheet (WEC05) Demonstration indicator: biological quality of lakes
 Indicator Fact Sheet (WEC05) Demonstration indicator: biological quality of lakes Author: Attila Lázár, Vituki Consult, Jens Bogestrand, NERI EEA project manager: Niels Thyssen version 01.10.03 Key message
Indicator Fact Sheet (WEC05) Demonstration indicator: biological quality of lakes Author: Attila Lázár, Vituki Consult, Jens Bogestrand, NERI EEA project manager: Niels Thyssen version 01.10.03 Key message
A Method to Estimate Buna River Discharge, Albania
 Hydrology Days 2009 A Method to Estimate Buna River Discharge, Albania Niko PANO 1, Bardhyl AVDYLI 2 Tirana University Faculty of History Philology, Geography Department Tirana, Albania. Abstract Buna
Hydrology Days 2009 A Method to Estimate Buna River Discharge, Albania Niko PANO 1, Bardhyl AVDYLI 2 Tirana University Faculty of History Philology, Geography Department Tirana, Albania. Abstract Buna
Executive summary. Pressures
 6 Groundwater quality and quantity in Europe Executive summary Groundwater is a major source of drinking water all over Europe, and thus the state of groundwater in terms of quality and quantity is of
6 Groundwater quality and quantity in Europe Executive summary Groundwater is a major source of drinking water all over Europe, and thus the state of groundwater in terms of quality and quantity is of
INBO s s REGIONAL NETWORKS
 INTERNATIONAL NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANIZATIONS Created in 1994 to facilitate operational exchanges between BO INBO s s REGIONAL NETWORKS North American Network of Basin Organizations (NANBO) Latin American
INTERNATIONAL NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANIZATIONS Created in 1994 to facilitate operational exchanges between BO INBO s s REGIONAL NETWORKS North American Network of Basin Organizations (NANBO) Latin American
Climate Change and the Eastern Mediterranean Precipitation Regime
 Climate Change and the Eastern Mediterranean Precipitation Regime Manfred A. Lange Energy, Environment and Water Research Center, The Cyprus Institute EWACC2010 Energy, Water & Climate Change in the Mediterranean
Climate Change and the Eastern Mediterranean Precipitation Regime Manfred A. Lange Energy, Environment and Water Research Center, The Cyprus Institute EWACC2010 Energy, Water & Climate Change in the Mediterranean
CCAI Demonstration Projects in Viet Nam. Dr. Nguyen Anh Duc National CCAI Coordinator, Viet Nam National Mekong Committee
 1 CCAI Demonstration Projects in Viet Nam Dr. Nguyen Anh Duc National CCAI Coordinator, Viet Nam National Mekong Committee Outline Project: Preliminary Study on Climate Change Adaptation Plan in Kien Giang
1 CCAI Demonstration Projects in Viet Nam Dr. Nguyen Anh Duc National CCAI Coordinator, Viet Nam National Mekong Committee Outline Project: Preliminary Study on Climate Change Adaptation Plan in Kien Giang
The implementation of Water Framework Directive (WFD) in Greece Linking WFD with coastal water protection
 The implementation of Water Framework Directive (WFD) in Greece Linking WFD with coastal water protection Anastasia Lazarou Dr. Chemist Athens, 19 January 2007 Basic Directives related with the protection
The implementation of Water Framework Directive (WFD) in Greece Linking WFD with coastal water protection Anastasia Lazarou Dr. Chemist Athens, 19 January 2007 Basic Directives related with the protection
Spatial and environmental planning and waste management (some thoughts on the case of Attica)
 Spatial and environmental planning and waste management (some thoughts on the case of Attica) M. Haidarlis Department of Planning and Regional Development, University of Thessaly, Greece Abstract Facing
Spatial and environmental planning and waste management (some thoughts on the case of Attica) M. Haidarlis Department of Planning and Regional Development, University of Thessaly, Greece Abstract Facing
Volume II: Hazard Annex Drought
 Volume II: Hazard Annex Drought Causes and Characteristics of Droughts A drought is a period of drier than normal conditions that results in waterrelated problems. 81 Drought occurs in virtually all climatic
Volume II: Hazard Annex Drought Causes and Characteristics of Droughts A drought is a period of drier than normal conditions that results in waterrelated problems. 81 Drought occurs in virtually all climatic
STUDY GUIDE. Living in Europe. Chapter 13, Section 1. Europe Today. Terms to Know DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCE ORGANIZING YOUR THOUGHTS
 Chapter 13, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 313 319. Living in Europe Terms to Know European Union (EU) A trading community that unites much of western Europe (page 313) Maastricht Treaty The treaty
Chapter 13, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 313 319. Living in Europe Terms to Know European Union (EU) A trading community that unites much of western Europe (page 313) Maastricht Treaty The treaty
The environmental objectives and Programme of Measures of the River Basin Management Plan. The case of Cyprus. Iacovos Papaiacovou
 The environmental objectives and Programme of Measures of the River Basin Management Plan The case of Cyprus Iacovos Papaiacovou General Manager Sewerage Board of Limassol Amathus www.sbla.com.cy The island
The environmental objectives and Programme of Measures of the River Basin Management Plan The case of Cyprus Iacovos Papaiacovou General Manager Sewerage Board of Limassol Amathus www.sbla.com.cy The island
Regional Archive of past Drought Impacts
 Regional Archive of past Drought Impacts Agricultural University of Athens Christos A. Karavitis Stavros Alexandris Vassilia Fassouli Demetrios Stamatakos Demetrios Tsesmelis COUNTRY Slovenia Greece FYROM
Regional Archive of past Drought Impacts Agricultural University of Athens Christos A. Karavitis Stavros Alexandris Vassilia Fassouli Demetrios Stamatakos Demetrios Tsesmelis COUNTRY Slovenia Greece FYROM
A 25 Year Strategic Plan
 A 25 Year Strategic Plan The challenges which face the provision of water services are identified as: Meeting Customer Needs at an Affordable Cost Providing Safe Water Supplies Managing Wastewater Protecting
A 25 Year Strategic Plan The challenges which face the provision of water services are identified as: Meeting Customer Needs at an Affordable Cost Providing Safe Water Supplies Managing Wastewater Protecting
EFC Working Party on the Management of Mountain Watersheds
 EFC Working Party on the Management of Mountain Watersheds 27th Session Štrbské Pleso, Slovak Republic, 7-10 April 2010 NATIONAL REPORT OF TURKEY National Report of TURKEY 1. Introduction Turkey attended
EFC Working Party on the Management of Mountain Watersheds 27th Session Štrbské Pleso, Slovak Republic, 7-10 April 2010 NATIONAL REPORT OF TURKEY National Report of TURKEY 1. Introduction Turkey attended
The Community Initiative Leader +
 The Community Initiative Leader + Georgios Apostolidis Democritus University of Thrace School of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences Department of Forestry and Management of the Environment and Natural
The Community Initiative Leader + Georgios Apostolidis Democritus University of Thrace School of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences Department of Forestry and Management of the Environment and Natural
Please provide the following contact information and complete the grey text boxes:
 Questionnaire according to Commission Decision 94/741/EC for the report of the Member States on the transposition and implementation of Directive 2006/12/EC (Waste Framework Directive) Please provide the
Questionnaire according to Commission Decision 94/741/EC for the report of the Member States on the transposition and implementation of Directive 2006/12/EC (Waste Framework Directive) Please provide the
Pilot Study. Adaptation in water and coastal areas in Puglia, Italy
 THEMATIC CENTRE Drought, Water and Coasts Pilot Study Adaptation in water and coastal areas in Puglia, Italy Three pilot studies were carried out under the OrientGate Thematic Centre on Drought, Water
THEMATIC CENTRE Drought, Water and Coasts Pilot Study Adaptation in water and coastal areas in Puglia, Italy Three pilot studies were carried out under the OrientGate Thematic Centre on Drought, Water
STEP-BY-STEP MONITORING METHODOLOGY FOR
 STEP-BY-STEP MONITORING METHODOLOGY FOR INDICATOR 6.5.2 PROPORTION OF TRANSBOUNDARY BASIN AREA WITH AN OPERATIONAL ARRANGEMENT FOR WATER COOPERATION 1. MONITORING CONTEXT 1.1 INTRODUCTION OF THE INDICATOR
STEP-BY-STEP MONITORING METHODOLOGY FOR INDICATOR 6.5.2 PROPORTION OF TRANSBOUNDARY BASIN AREA WITH AN OPERATIONAL ARRANGEMENT FOR WATER COOPERATION 1. MONITORING CONTEXT 1.1 INTRODUCTION OF THE INDICATOR
A WEAP Model of the Kinneret Basin
 A WEAP Model of the Kinneret Basin Illy Sivan 1, Yigal Salingar 1 and Alon Rimmer 2 This is an English translation of the article that originally appeared in Sivan, I., Y. Salingar, and A. Rimmer, A WEAP
A WEAP Model of the Kinneret Basin Illy Sivan 1, Yigal Salingar 1 and Alon Rimmer 2 This is an English translation of the article that originally appeared in Sivan, I., Y. Salingar, and A. Rimmer, A WEAP
CLIMATE CHANGE CHALLENGES TO WATER MANAGEMENT IN JUCAR RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY. Juan José Moragues Terrades President of the Júcar River Basin Authority
 CLIMATE CHANGE CHALLENGES TO WATER MANAGEMENT IN JUCAR RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY Juan José Moragues Terrades President of the Júcar River Basin Authority WATER FRAMEWORK DIRECTIVE Meeting of the European River
CLIMATE CHANGE CHALLENGES TO WATER MANAGEMENT IN JUCAR RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY Juan José Moragues Terrades President of the Júcar River Basin Authority WATER FRAMEWORK DIRECTIVE Meeting of the European River
4. Pressures on groundwater quantity
 Pressures on groundwater quantity 39 4. Pressures on groundwater quantity 4.1 Groundwater abstraction 4.1.1 Geographical situation The vulnerability of an aquifer to overexploitation depends on its type,
Pressures on groundwater quantity 39 4. Pressures on groundwater quantity 4.1 Groundwater abstraction 4.1.1 Geographical situation The vulnerability of an aquifer to overexploitation depends on its type,
STRATEGIC EVALUATION ON ENVIRONMENT AND RISK PREVENTION UNDER STRUCTURAL AND COHESION FUNDS FOR THE PERIOD
 STRATEGIC EVALUATION ON ENVIRONMENT AND RISK PREVENTION UNDER STRUCTURAL AND COHESION FUNDS FOR THE PERIOD 2007-2013 Contract No. 2005.CE.16.0.AT.016. National Evaluation Report for Greece Main Report
STRATEGIC EVALUATION ON ENVIRONMENT AND RISK PREVENTION UNDER STRUCTURAL AND COHESION FUNDS FOR THE PERIOD 2007-2013 Contract No. 2005.CE.16.0.AT.016. National Evaluation Report for Greece Main Report
"EUROPE-INBO DECLARATION OF THESSALONIKI" Draft Working document Version 1.d
 RESEAU INTERNATIONAL DES ORGANISMES DE BASSIN INTERNATIONAL NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANIZATIONS RED INTERNACIONAL DE ORGANISMOS DE CUENCA 13 th EUROPE-INBO 2015 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE WATER FRAMEWORK
RESEAU INTERNATIONAL DES ORGANISMES DE BASSIN INTERNATIONAL NETWORK OF BASIN ORGANIZATIONS RED INTERNACIONAL DE ORGANISMOS DE CUENCA 13 th EUROPE-INBO 2015 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE WATER FRAMEWORK
Establishing the influence of climate, water extraction and tectonics on the water level of the Prespa Lakes (N Greece)
 Establishing the influence of climate, water extraction and tectonics on the water level of the Prespa Lakes (N Greece) Tim van der Schriek & Christos Giannakopoulos National Observatory of Athens Institute
Establishing the influence of climate, water extraction and tectonics on the water level of the Prespa Lakes (N Greece) Tim van der Schriek & Christos Giannakopoulos National Observatory of Athens Institute
REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL AND THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 4.10.2013 COM(2013) 683 final REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL AND THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT on the implementation of Council Directive 91/676/EEC concerning the protection
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 4.10.2013 COM(2013) 683 final REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL AND THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT on the implementation of Council Directive 91/676/EEC concerning the protection
Climate Change & The Water Sector
 & The Water Sector Copernicus for Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu WHY IS COPERNICUS NEEDED IN WATER SECTOR? Climate Climate and the water cycle
& The Water Sector Copernicus for Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu WHY IS COPERNICUS NEEDED IN WATER SECTOR? Climate Climate and the water cycle
ISTAO OBSERVATORY ON MARITIME TRAFFIC IN THE ADRIATIC AND IONIAN SEA
 ISTAO OBSERVATORY ON MARITIME TRAFFIC IN THE ADRIATIC AND IONIAN SEA REPORT ON TRAFFIC TO 2006 by Ida Simonella Portonovo 29 May 2007 INTRODUCTION As usual, the Observatory s annual report is focussed
ISTAO OBSERVATORY ON MARITIME TRAFFIC IN THE ADRIATIC AND IONIAN SEA REPORT ON TRAFFIC TO 2006 by Ida Simonella Portonovo 29 May 2007 INTRODUCTION As usual, the Observatory s annual report is focussed
Spatial and temporal variations of winter discharge under climate change: Case study of rivers in European Russia
 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). 245 Spatial and temporal variations of winter discharge
Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). 245 Spatial and temporal variations of winter discharge
Developing a local flood risk management strategy Annex 1: Flooding, flood sources and flood defences
 Developing a local flood risk management strategy Annex 1: Flooding, flood sources and flood defences Pennine Water Group, University of Sheffield in collaboration with the partners of the FloodResilienCity
Developing a local flood risk management strategy Annex 1: Flooding, flood sources and flood defences Pennine Water Group, University of Sheffield in collaboration with the partners of the FloodResilienCity
Forest Cover Change
 Summary Resources Forest covers less than two fifths of the land area of Albania, a small hilly country in southern Europe bordering the Adriatic Sea. Some areas of other wooded land are included with
Summary Resources Forest covers less than two fifths of the land area of Albania, a small hilly country in southern Europe bordering the Adriatic Sea. Some areas of other wooded land are included with
SIMULATION OF NITRATE CONTAMINATION IN LAKE KARLA AQUIFER
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 SIMULATION OF NITRATE CONTAMINATION IN LAKE KARLA AQUIFER TZIATZIOS G., SIDIROPOULOS
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 SIMULATION OF NITRATE CONTAMINATION IN LAKE KARLA AQUIFER TZIATZIOS G., SIDIROPOULOS
Spatial and temporal variations of winter discharge under climate change: Case study of rivers in European Russia
 doi:10.5194/piahs-368-245-2015 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). 245 Spatial and temporal
doi:10.5194/piahs-368-245-2015 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). 245 Spatial and temporal
Water Resources CHOIR in China
 Water Resources CHOIR in China Strategic research and innovation priorities for water Liu Dengwei 水利部发展研究中心 Development Research Center of the Ministry of Water Resources of China Water Resources CHOIR
Water Resources CHOIR in China Strategic research and innovation priorities for water Liu Dengwei 水利部发展研究中心 Development Research Center of the Ministry of Water Resources of China Water Resources CHOIR
Analysis of Future Discharge in Nakdong River Basin According to Effect on Climate Change
 Hydrology Days 2012 Analysis of Future Discharge in Nakdong River Basin According to Effect on Climate Change Hyun Suk Shin 1, Mi Eun Kim 2, Ji Ye Im, and Tae Seok Shon 3 Department of Civil and Environmental
Hydrology Days 2012 Analysis of Future Discharge in Nakdong River Basin According to Effect on Climate Change Hyun Suk Shin 1, Mi Eun Kim 2, Ji Ye Im, and Tae Seok Shon 3 Department of Civil and Environmental
CHAPTER 6 MEDITERRANEAN WATERSHED MANAGEMENT: OVERCOMING WATER CRISIS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN
 Watershed Management: Water Resources for the Future CHAPTER 6 MEDITERRANEAN WATERSHED MANAGEMENT: OVERCOMING WATER CRISIS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN Luc Dassonville and Luca Fé d Ostiani Plan Bleu, FAO Water
Watershed Management: Water Resources for the Future CHAPTER 6 MEDITERRANEAN WATERSHED MANAGEMENT: OVERCOMING WATER CRISIS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN Luc Dassonville and Luca Fé d Ostiani Plan Bleu, FAO Water
Trends in the Water Industry
 Water networks management optimisation / Energy efficiency Trends in the Water Industry Prof. Dr. Michael Bongards michael.bongards@fh-koeln.de 1 Cologne University of Applied Sciences - CUAS CUAS - Facts
Water networks management optimisation / Energy efficiency Trends in the Water Industry Prof. Dr. Michael Bongards michael.bongards@fh-koeln.de 1 Cologne University of Applied Sciences - CUAS CUAS - Facts
Hydraulic Policy in Spain Teodoro Estrela Deputy Water Director Ministry of Environment, and Rural and Marine Affairs Spain
 Hydraulic Policy in Spain 1902-2008 2008 Teodoro Estrela Deputy Water Director Ministry of Environment, and Rural and Marine Affairs Spain Contents Introduction Historical Evolution Basic principles of
Hydraulic Policy in Spain 1902-2008 2008 Teodoro Estrela Deputy Water Director Ministry of Environment, and Rural and Marine Affairs Spain Contents Introduction Historical Evolution Basic principles of
COST-GRALE-Norwegian Centre in Paris
 COST-GRALE-Norwegian Centre in Paris Joint PhD-Training School The Financial Crisis: Stimulating or Strangling Decentralization? The Greek Case Prof. Dr.N-K. Hlepas National und Kapodistrian University
COST-GRALE-Norwegian Centre in Paris Joint PhD-Training School The Financial Crisis: Stimulating or Strangling Decentralization? The Greek Case Prof. Dr.N-K. Hlepas National und Kapodistrian University
