Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics. Department of Civil Engineering College of Science and Engineering
|
|
|
- Joy Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Department of Civil Engineering College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis, MN Dept. Main Office: Fax: Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects Contract Number: RD3-42 Milestone Number: 3 Report Date: 11/29/10 Principal Investigator: Fotis Sotiropoulos Contract Contact: Bridget Foss fotis@umn.edu Congressional District: (Corporate office) Minnesota 5 th Congressional District: (Project location) Minnesota 5 th MILESTONE REPORT Executive Summary: This project aims at developing a Virtual Wind Simulator (VWS) for the prediction of atmospheric boundary layer flow and its interactions with wind turbines and wind farms. The use of the simulator will assist in the improved design of potential wind energy projects by providing more accurate predictions of local and wind turbulence at site and turbine levels. Additionally, the VWS will help increase the level of wind energy utilization and reduce the cost of energy production. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) methods are used in this project to develop a computational framework for conducting high-resolution simulations of wind turbulence at the meso and micro scales. In particular, the Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) technique will allow for accurate simulations of the turbulent flow at spatial resolutions as small as one to ten meters, and temporal resolutions of just a few seconds. Parameterizations for wind turbine forces will also be developed in the LES framework. In addition, three-dimensional, time-evolving flow fields obtained from LES at any location within a potential wind farm site could then be used as the inflow condition for even more detailed simulations of the turbulent flow around the blades of specific wind turbines using a hybrid Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS)/LES technique. The SAFL computational models will be coupled to macro-scale regional models to develop a powerful multi-scale computational tool, the VWS. The VWS will integrate the latest advancements in computational fluid dynamics research and provide reliable, high-resolution descriptions of wind turbulence across the entire range of scales that are relevant to wind power production. This information will provide objective, scientifically based criteria that can be used by wind energy project developers for the site-specific, optimal selection and placement (micrositing) of wind turbines. 1
2 As planned, during this reporting period (quarter) activities have been carried out that address three of the specific objectives of the project: (a) Development of a multi-scale computational fluid dynamics (CFD) framework for accurate simulation of high-resolution wind and turbulence fields and their effects on wind turbine operation and energy output. (b) Validation of the proposed Virtual Wind Simulator using high-resolution wind and turbulence measurements collected in an atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel. (c) Testing the Virtual Wind Simulator using wind and turbulence measurements collected at an operational wind farm. Project funding provided by customers of Xcel Energy through a grant from the Renewable Development Fund. Technical Progress: We have made substantial progress in Task 1, Task 2 and Task 3. The progress made in the three tasks is discussed below. Task 1. Development of the Virtual Wind Simulator for high-resolution simulations of wind, turbulence and their effect on energy production Progress has continued on the development and testing of two of the components of the Virtual Wind Simulator: the Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) code and the RANS/LES code. Subtask 1.1. LES of the atmospheric boundary layer and turbine models Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) can potentially provide the kind of high-resolution spatial and temporal information needed to maximize wind energy production and minimize fatigue loads in wind farms. However, the accuracy of LES in simulations of atmospheric boundary layer flow and its interactions with wind turbines hinges on our ability to parameterize subgrid-scale (SGS) turbulent fluxes as well as turbine-induced forces. Below we summarize our most recent efforts to develop and validate a LES framework to simulate atmospheric boundary layer flow and the interaction with wind turbines and wind farms. (a) Subgrid-scale turbulence modeling Progress has continued on the improvement, implementation and testing of the state-of-the-art subgrid-scale (SGS) models recently developed by Prof. Porte-Agel s research group. These include the Lagrangian scale-dependent dynamic models for both momentum and scalar fluxes (Stoll and Porte-Agel, 2006; Wan and Porte-Agel, 2010) and the new modulated gradient model (Lu and Porte-Agel, 2010). The new models allow for tuning-free simulations and are found to perform better than the existing LES models, including the standard Smagorinsky model and the scale-invariant dynamic model (Germano et al., 1991). (b) Modeling turbine-induced forces in LES Three models have been implemented to parameterize turbine-induced forces (e.g., thrust, lift and drag) in LES: (a) the `standard' actuator-disk model (ADM-NR), which calculates only the thrust force and distributes it uniformly over the rotor area; (b) the newly developed actuator-disk model with rotation (ADM-R), which uses blade element momentum theory to calculate the lift and drag forces (thus producing both thrust and rotation), and distribute them over the rotor disk based on the local blade and flow characteristics (for more details on this model, see Wu and Porte-Agel, 2010); and (c) an actuator-line model (ALM) that distributes the forces only at the position of the 2
3 blades. Even though it requires more computational resources, the ALM model is capable of capturing some important flow features such as helicoidal vortices. The three models are currently being used to simulate flow through wind farms, including the Mower County Wind Farm. Figure 1 shows simulation results from a simple neutral atmospheric boundary layer through the SW corner of the wind farm. The flow simulated with the ADM-R and ALM agrees well with the SODAR measurements collected inside the wind farm. Current efforts are focused on extending the development and validation of the new-generation LES (including new SGS models and wind-turbine parameterizations) to more realistic atmospheric conditions such as stable and unstable conditions as well as wind farm configurations. Fig. 1: Left: Layout of the SW the Mower County wind farm and placement of the wind turbines and SODARs. Right: Two dimensional contour plots of the simulated time-averaged streamwise velocity (m/s) 3
4 on a horizontal plane at hub height. Comparison between different wind-turbine models: (a) ADM-NR, (b) ADM-R, (c) ALM. Subtask 1.2 URANS/LES model for wind turbine flow We have developed a computational framework that enables us to perform high resolution simulations of a wind turbine on a complex terrain. To accomplish this we have generalized our fluid/structure interaction curvilinear/immersed boundary (FSI- CURVIB) method [Borazjani et al., J. Comp. Phys. 227, , 2008] to incorporate overset (CHIMERA) grids to increase grid resolution locally near complex immersed boundaries, such as topographic features and multiple turbine rotors. The computational domain (say a section of a wind farm) can be discretized with a Cartesian grid within which a complex topography and/or multiple turbine rotors can be treated either as sharpinterface immersed boundaries. We have developed novel interpolation techniques for satisfying mass conservation in the resulting composite grids in conjunction with an efficient fractional step method. The numerical methodology has been generalized to include both inertial and non-inertial frame formulations as well as to enable simulations with hybrid formulations. We have implemented dynamic subgrid scale model for largeeddy simulations (LES) and k-ω model for unsteady Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes (URANS) simulations. We have carried out turbulent as well as inviscid simulations for the two-blade NREL phase VI wind turbine rotor rotating at 72 rpm and wind velocity 7 and 15 m/s. A coarse and a fine overset grid arrangements with 8.6 and 12.5 million grid nodes, respectively, has been used for these simulations. We compare the simulation results against the NREL phase VI experiments in terms of pressure coefficient distribution on the blades as shown in Fig 3. Fig 4 shows the kinetic energy in the LES wake in the midplane of the blade. Fig 5 and 6 show the 3D wake structure visualized by the iso-surfaces of q-criteria for the instantaneous and averaged flow fields obtained from LES. Fig. 2. Blade-geometry-resolving LES. 4
5 30% span 47% span 63% span 80% span 95% span Fig. 3. Pressure coefficient on different airfoil cross sections at different span locations for wind speed 7m/s. Figure 4. Non-dimensional kinetic energy in the midplane of the blade in the LES wake for wind speed 7m/s (left) and 15m/s (right). 5
6 Figure 5. Instantaneous wake (left) vs. averaged wake for speed 7m/s (LES). Figure 6. Instantaneous wake (left) vs. averaged wake for speed 15m/s (LES). 6
7 Task 2. Validation of the Virtual Wind Simulator using wind tunnel measurements Wind tunnel experiments Progress has continued on the fundamental understanding of the turbulent flow properties around wind farms. In particular, we have performed wind tunnel experiments to study fundamental properties of the turbulent flow around a perfectly aligned wind farm placed in a boundary layer flow. Main flow properties of the turbulent flow within and above the aligned wind farm will be compared with the case of a staggered wind turbine array to infer the effect of the layout on the overall wind farm efficiency. High-resolution spatial and temporal fields of velocity and turbulence statistics, collected at different locations (see Fig. 7) using a hotwire sensor anemometer have been used to characterize the wind-turbine wake and guide the development of parameterizations of wind turbines in computational fluid dynamic models (e.g., Fig. 8, 9). Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) experiments are being planned to complement the current information obtained with the hotwire and 3-wire data. Results suggest that the turbulent flow in a wind farm (under an align configuration) can be characterized in two broad regions. The first, located below the turbine top tip height, has a direct effect on the performance of the turbine. The mean flow statistics appear to reach equilibrium as close as the third to fourth row of wind turbines independent of the layout, but turbulence statistics showed dependence with the wind farm configuration. In the second region, located right above the first region, flow adjusts slowly. There, two layers were found: an internal boundary layer where flow is affected by the wind turbine array and an equilibrium layer, where flow statistics are adjusted. The role of these layers on the overall power production in the wind farm will be analyzed. Fig. 7: Photograph of the test section with the model wind turbines (left) and measurement locations right). 7
8 Fig. 8: Miniature wind farm (align configuration) placed in a turbulent boundary layer flow at the SAFL wind tunnel. Measurement locations. Fig. 9. Non-dimensional velocity distribution in the wind farm (Δx/d=5). Fig. 10. Turbulence intensity distribution around the wind farm. Inter-turbine separations of 5 (top) and 7 rotor diameters. 8
9 Task 3. Testing the Virtual Wind Simulator using wind and turbulence measurements collected at an operational wind farm Field experiments Measurements continue in collaboration with our partners from WindLogics, Inc. and Barr Engineering in a wind farm located in Mower County. Two Sodars provided by WindLogics have collected three months of data, which complete the current phase of experiments. A new LiDAR has been purchased and will be used to support the current filed campaign. Field campaign (WindLogics activities) included further data analysis of the SODAR and SCADA data collected from the Mower County wind farm during the summer of 2010 and refinements of quality control and quality assurance procedures for the SCADA data. The sodar data were composited to form turbine wake cross sections. Prior analyses formed the composite cross-sections for all data in the sampling period, but the more recent analyses categorize the cross sections according to atmospheric stability. The data collected during the Summer 2010 has added samples from the set of profiles from which the composites are constructed, allowing for better composites to be calculated. Fig. 11 shows the cross section of the ratio of the waked sodar wind speed to the free stream (upstream from the turbine wake) wind speed and vertical velocity for stable conditions during summer All three sodars at the site have collected data that are capable of resolving the rotation of the flow within the turbine wake. In Fig. 11, the vertical velocity is upward to the left of the wake centerline (Y=0) and downward to the right of the centerline. These results are qualitatively consistent with large eddy simulations that have been conducted. Fig. 11. Y-Z cross section of turbine wake measured by the Triton sodars for stable atmospheric conditions during summer Shading indicates the ratio of wind speeds of the waked to unwaked sodar (the waked sodar is downstream from Turbine 41), and the contour lines show vertical velocity (contour interval of 0.05 m/s, dashed lines are negative, zero line is bold). 9
10 Barr continued to monitor and QA/QC data from Barr ASC Sodar unit deployed at Mower County, post data on project web site, and coordinate analysis with WindLogics. In July and August, final monitoring adjustments for Mower County site, including Natural Power Lidar and ASC Sodar relocations to new sites within the wind farm were performed. Barr coordinated final high-resolution data burst from ASC SoDAR at Mower County site, retrieved ASC SoDAR for review and re-deployment at Prairie Island complex terrain site. In mid-september, Barr installed the meteorological tower and associated equipment near the Prairie Island Indian Community Treasure Island Casino, in preparation for monitoring at complex terrain site. Data collection from that site is ongoing. Plans for lidar, SoDAR, and CSAT-3 deployment at Prairie Island site were also developed in September, Fig. 12. Wind Farm in the Mower county area (top) and LiDAR in operation in the wake of a wind turbine (bottom). 10
11 Additional Milestones: Work is in progress towards Milestone 4. Project Status: The project is ahead of schedule due to the fact that work on the project started before the contract was finalized. LEGAL NOTICE THIS REPORT WAS PREPARED AS A RESULT OF WORK SPONSORED BY NSP. IT DOES NOT NECESSARILY REPRESENT THE VIEWS OF NSP, ITS EMPLOYEES, OR THE RENEWABLE DEVELOPMENT FUND BOARD. NSP, ITS EMPLOYEES, CONTRACTORS, AND SUBCONTRACTORS MAKE NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AND ASSUME NO LEGAL LIABILITY FOR THE INFORMATION IN THIS REPORT; NOR DOES ANY PARTY REPRESENT THAT THE USE OF THIS INFORMATION WILL NOT INFRINGE UPON PRIVATELY OWNED RIGHTS. THIS REPORT HAS NOT BEEN APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED BY NSP NOR HAS NSP PASSED UPON THE ACCURACY OF ADEQUACY OF THE INFORMATION IN THIS REPORT. Appendix: List publications Papers in Refereed Journals 1. Chamorro, L.P., Arndt, REA and Sotiropoulos F. Turbulent flow properties around a staggered wind farm. To be submitted. 2. Chamorro, L.P., Arndt, REA and Sotiropoulos F. Reynolds number dependence of turbulence statistics in the wake of wind turbines. Under Review. 3. Chamorro, L.P., and F. Porté-Agel, Thermal stability and boundary-layer effects on wind turbine wakes. A wind tunnel study. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 136: Lu, H., and F. Porté-Agel, A modulated subgrid-scale model for large-eddy simulation: Application to a neutral atmospheric boundary layer. Physics of Fluids, in press. 5. Wu, Y.-T., and F. Porté-Agel, Large-eddy simulation of wind-turbine wakes: Evaluation of turbine parameterizations. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, in press. 6. Chamorro, L.P., and F. Porté-Agel, A wind tunnel investigation of wind turbines wakes: Boundary-layer turbulence and surface roughness effects. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 132: Conference Presentations 1. Porté-Agel, F., F. Sotiropoulos, R. Conzemius, L. Chamorro, Y.-T. Wu, S. Behara, H. Lu, Development of a high-resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for optimal design of wind energy projects. E3 -Energy, Economic and Environmental- Conference. Minneapolis, MN. 11
12 2. Chamorro, L.P., and F. Porté-Agel, A wind tunnel investigation of wind turbine wakes: Boundary-layer turbulence and surface roughness effects. American Geophysical Union. San Francisco, CA. 3. Wu, Y.-T.., H. Lu, and F. Porté-Agel, Large-eddy simulation of wind-turbine wakes. American Geophysical Union. San Francisco, CA. 4. Chamorro, L.P., and F. Porté-Agel, A wind tunnel investigation of wind turbine wakes: Boundary-layer turbulence and surface roughness effects. European Geophysical Union. Vienna. 5. Porté-Agel, F., Y.-T. Wu, Y.-T.., H. Lu, Parameterization of turbulent fluxes and wind-turbine forces in large-eddy simulation. European Geophysical Union. Vienna. 6. Porté-Agel, F., F. Sotiropoulos, R. Conzemius, L. Chamorro, Y.-T. Wu, S. Behara, H. Lu, Development of a high-resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for optimal design of wind energy projects. E3 -Energy, Economic and Environmental- Conference. Minneapolis, MN. 7. Chamorro, L.P., and F. Porté-Agel, A wind tunnel investigation of wind turbine wakes. American Physical Society Meeting. Minneapolis, MN. 8. Porté-Agel, F., Y.-T. Wu, and H. Lu, Large-eddy simulation of wind-turbine wakes. American Physical Society Meeting. Minneapolis, MN. 7. Chamorro, L.P., R.E.A. Arndt and F. Sotiropoulos, Turbulence characteristics around a staggered wind farm configuration. A wind tunnel study. American Physical Society Meeting. Minneapolis, Long Beach, CA. 12
College of Science and Engineering. Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
RD3-42: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 RD3-42: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects Principal Investigator: Fotis Sotiropoulos St. Anthony Falls laboratory and Department of Civil
RD3-42: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects Principal Investigator: Fotis Sotiropoulos St. Anthony Falls laboratory and Department of Civil
Visualization of the tip vortices in a wind turbine wake
 J Vis (2012) 15:39 44 DOI 10.1007/s12650-011-0112-z SHORT PAPER Zifeng Yang Partha Sarkar Hui Hu Visualization of the tip vortices in a wind turbine wake Received: 30 December 2010 / Revised: 19 September
J Vis (2012) 15:39 44 DOI 10.1007/s12650-011-0112-z SHORT PAPER Zifeng Yang Partha Sarkar Hui Hu Visualization of the tip vortices in a wind turbine wake Received: 30 December 2010 / Revised: 19 September
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013](/thumbs/90/101817614.jpg) arxiv:1310.3294v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013 Wake Turbulence of Two NREL 5-MW Wind Turbines Immersed in a Neutral Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Flow Jessica L. Bashioum, Pankaj K. Jha, Dr. Sven Schmitz
arxiv:1310.3294v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013 Wake Turbulence of Two NREL 5-MW Wind Turbines Immersed in a Neutral Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Flow Jessica L. Bashioum, Pankaj K. Jha, Dr. Sven Schmitz
Wind Turbine Engineering R&D
 Wind Turbine Engineering R&D at Los Alamos National Laboratory Curtt Ammerman Applied Engineering & Technology Division U N C L A S S I F I E D Operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC for the U.S.
Wind Turbine Engineering R&D at Los Alamos National Laboratory Curtt Ammerman Applied Engineering & Technology Division U N C L A S S I F I E D Operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC for the U.S.
Interaction between large wind farms and the atmospheric boundary layer
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia IUTAM 10 (2014 ) 307 318 23rd International Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Interaction between large wind farms and the atmospheric
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia IUTAM 10 (2014 ) 307 318 23rd International Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Interaction between large wind farms and the atmospheric
Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine
 42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 25-28 June 2012, New Orleans, Louisiana AIAA 2012-2719 Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine Ahmet Ozbay 1,
42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 25-28 June 2012, New Orleans, Louisiana AIAA 2012-2719 Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine Ahmet Ozbay 1,
H POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH. Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu*
 H14-117 POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu* Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong
H14-117 POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu* Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong
INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM
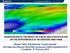 INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM Mandar Tabib, Adil Rasheed, Trond Kvamsdal 12th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind'2015,
INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM Mandar Tabib, Adil Rasheed, Trond Kvamsdal 12th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind'2015,
Towards Simulating the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Wind Farm Flows
 Towards Simulating the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Wind Farm Flows 6 th OpenFOAM Workshop Matthew J. Churchfield Patrick J. Moriarty June 15, 2011 NREL is a national laboratory of the U.S. Department
Towards Simulating the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Wind Farm Flows 6 th OpenFOAM Workshop Matthew J. Churchfield Patrick J. Moriarty June 15, 2011 NREL is a national laboratory of the U.S. Department
OpenFOAM in Wind Energy
 OpenFOAM in Wind Energy GOFUN 2018, Braunschweig Matthias Schramm Fraunhofer IWES and ForWind Oldenburg University started with wind physics Research on wind fields, aerodynamics and turbulence CFD is
OpenFOAM in Wind Energy GOFUN 2018, Braunschweig Matthias Schramm Fraunhofer IWES and ForWind Oldenburg University started with wind physics Research on wind fields, aerodynamics and turbulence CFD is
INVESTIGATIONS ON PERFORMANCE OF A SAVONIUS HYDROKINETIC TURBINE
 INVESTIGATIONS ON PERFORMANCE OF A SAVONIUS HYDROKINETIC TURBINE Ph.D. THESIS by ANUJ KUMAR ALTERNATE HYDRO ENERGY CENTRE INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE-247667 (INDIA) AUGUST, 2017 INVESTIGATIONS
INVESTIGATIONS ON PERFORMANCE OF A SAVONIUS HYDROKINETIC TURBINE Ph.D. THESIS by ANUJ KUMAR ALTERNATE HYDRO ENERGY CENTRE INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE-247667 (INDIA) AUGUST, 2017 INVESTIGATIONS
Limits to the power density of very large wind farms
 Draft (18th September 213) Short Communication Limits to the power density of very large wind farms Takafumi Nishino Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3PJ, UK ABSTRACT
Draft (18th September 213) Short Communication Limits to the power density of very large wind farms Takafumi Nishino Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3PJ, UK ABSTRACT
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine
 Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine N. Tabatabaei 1, M.J. Cervantes 1,2, C. Trivedi 2, J-O Aidanpää 1 1 Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 2 Norwegian University of Science
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine N. Tabatabaei 1, M.J. Cervantes 1,2, C. Trivedi 2, J-O Aidanpää 1 1 Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 2 Norwegian University of Science
Chapter 20 Large Eddy Simulation of Wind Farm Aerodynamics with Energy-Conserving Schemes
 Chapter 20 Large Eddy Simulation of Wind Farm Aerodynamics with Energy-Conserving Schemes Dhruv Mehta Abstract In order to truly realise the potential of wind power, it is vital to understand the aerodynamic
Chapter 20 Large Eddy Simulation of Wind Farm Aerodynamics with Energy-Conserving Schemes Dhruv Mehta Abstract In order to truly realise the potential of wind power, it is vital to understand the aerodynamic
Modeling for Wind Farm Control
 Modeling for Wind Farm Control A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Jennifer Annoni IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
Modeling for Wind Farm Control A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Jennifer Annoni IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
Principal Investigator: Christopher A. Kopchynski Contract Contact: Christopher A. Kopchynski
 Project Title: Development of Health Assessment Tools for Utility-Scale Wind Turbine Towers and Foundations Contract Number: RD4-14 Milestone Number: 3 Report Date: Principal Investigator: Christopher
Project Title: Development of Health Assessment Tools for Utility-Scale Wind Turbine Towers and Foundations Contract Number: RD4-14 Milestone Number: 3 Report Date: Principal Investigator: Christopher
A Study of Twin Co- and Counter-Rotating Vertical Axis Wind Turbines with Computational Fluid Dynamics
 The 16th World Wind Energy Conference, Malmö, Sweden. June 12-15, 217. A Study of Twin Co- and Counter-Rotating Vertical Axis Wind Turbines with Computational Fluid Dynamics PENG, Hua Yi* and LAM, Heung
The 16th World Wind Energy Conference, Malmö, Sweden. June 12-15, 217. A Study of Twin Co- and Counter-Rotating Vertical Axis Wind Turbines with Computational Fluid Dynamics PENG, Hua Yi* and LAM, Heung
Content. 0 Questionnaire 87 from Max Frisch
 Content 0 Questionnaire 87 from Max Frisch 1 Introduction to Wind Energy... 1 1.1 Wind Energy in the year 2010... 1 1.2 The Demand for Electricity... 4 1.3 Energy Policy and Governmental Instruments...
Content 0 Questionnaire 87 from Max Frisch 1 Introduction to Wind Energy... 1 1.1 Wind Energy in the year 2010... 1 1.2 The Demand for Electricity... 4 1.3 Energy Policy and Governmental Instruments...
Increasing the Power Production of Vertical-Axis Wind-Turbine Farms Using Synergistic Clustering
 Boundary-Layer Meteorology (2018) 169:275 296 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-018-0368-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Increasing the Power Production of Vertical-Axis Wind-Turbine Farms Using Synergistic Clustering
Boundary-Layer Meteorology (2018) 169:275 296 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-018-0368-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Increasing the Power Production of Vertical-Axis Wind-Turbine Farms Using Synergistic Clustering
Modelling Wind Turbine Inflow:
 Modelling Wind Turbine Inflow: The Induction zone Alexander R Meyer Forsting Main Supervisor: Niels Troldborg Co-supervisors: Andreas Bechmann & Pierre-Elouan Réthoré Why wind turbine inflow? Inflow KE
Modelling Wind Turbine Inflow: The Induction zone Alexander R Meyer Forsting Main Supervisor: Niels Troldborg Co-supervisors: Andreas Bechmann & Pierre-Elouan Réthoré Why wind turbine inflow? Inflow KE
H AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL. Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi
 H13-198 AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi FLUIDYN France, Saint-Denis, France Abstract: The air
H13-198 AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi FLUIDYN France, Saint-Denis, France Abstract: The air
Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting
 Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting Wei Zuo a, Shun Kang b Key Laboratory of Condition Monitoring and Control for Power Plant Equipment, Ministry
Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting Wei Zuo a, Shun Kang b Key Laboratory of Condition Monitoring and Control for Power Plant Equipment, Ministry
Spacing dependence on wind turbine array boundary layers
 Spacing dependence on wind turbine array boundary layers Raúl Bayoán Cal 1,*, Angelisse Ramos 2, Nicholas Hamilton 1, and Dan Houck 3 1 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Portland State
Spacing dependence on wind turbine array boundary layers Raúl Bayoán Cal 1,*, Angelisse Ramos 2, Nicholas Hamilton 1, and Dan Houck 3 1 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Portland State
On the Effects of Directional Bin Size when Simulating Large Offshore Wind Farms with CFD
 On the Effects of Directional Bin Size when Simulating Large Offshore Wind Farms with CFD Peter Argyle, Simon Watson CREST, Loughborough University, ENGLAND p.argyle@lboro.ac.uk ABSTRACT Computational
On the Effects of Directional Bin Size when Simulating Large Offshore Wind Farms with CFD Peter Argyle, Simon Watson CREST, Loughborough University, ENGLAND p.argyle@lboro.ac.uk ABSTRACT Computational
Tuning turbine rotor design for very large wind farms
 Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. Tuning turbine rotor design for very large wind farms Takafumi Nishino 1,* and William Hunter 2 1 Cranfield University, Cranfield, Bedfordshire MK43
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. Tuning turbine rotor design for very large wind farms Takafumi Nishino 1,* and William Hunter 2 1 Cranfield University, Cranfield, Bedfordshire MK43
Wind Farms 1. Wind Farms
 Wind Farms 1 Wind Farms Wind farms are a cluster of wind turbines that are located at a site to generate electricity. Wind farms are also sometimes referred to as a plant, array or a park. The first onshore
Wind Farms 1 Wind Farms Wind farms are a cluster of wind turbines that are located at a site to generate electricity. Wind farms are also sometimes referred to as a plant, array or a park. The first onshore
Effect of turbine alignment on the average power output of wind-farms
 Effect of turbine alignment on the average power output of wind-farms Richard J. A. M. Stevens 1,2, Dennice F. Gayme 1 and Charles Meneveau 1 1 Dept. of Mech. Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore,
Effect of turbine alignment on the average power output of wind-farms Richard J. A. M. Stevens 1,2, Dennice F. Gayme 1 and Charles Meneveau 1 1 Dept. of Mech. Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore,
Aerodynamic Design of 2.5 MW Horizontal Wind Turbine Blade in Combination with CFD Analysis
 Aerodynamic Design of 2.5 MW Horizontal Wind Turbine Blade in Combination with CFD Analysis Seul-Ki Yeom *, Tae-Jin Kang *, Warn-Gyu Park 1) School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University,
Aerodynamic Design of 2.5 MW Horizontal Wind Turbine Blade in Combination with CFD Analysis Seul-Ki Yeom *, Tae-Jin Kang *, Warn-Gyu Park 1) School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University,
768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES
 768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES Sue Ellen Haupt 1,2, Susan W. Stewart 2, Julia A. Cole 2, Frank J. Zajaczkowski, and Kerrie J. Schmehl 2
768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES Sue Ellen Haupt 1,2, Susan W. Stewart 2, Julia A. Cole 2, Frank J. Zajaczkowski, and Kerrie J. Schmehl 2
Boundary-Layer Meteorology Increasing VAWT Wind Farm Power Density using Synergistic Clustering
 Boundary-Layer Meteorology Increasing VAWT Wind Farm Power Density using Synergistic Clustering --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords: Corresponding Author: Increasing
Boundary-Layer Meteorology Increasing VAWT Wind Farm Power Density using Synergistic Clustering --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords: Corresponding Author: Increasing
Numerical simulation of atmospheric boundary layer and wakes of horizontal-axis wind turbines
 Numerical simulation of atmospheric boundary layer and wakes of horizontal-axis wind turbines Ali M AbdelSalam Ramalingam Velraj Institute for Energy Studies, Anna University, Chennai, India Abstract Simulations
Numerical simulation of atmospheric boundary layer and wakes of horizontal-axis wind turbines Ali M AbdelSalam Ramalingam Velraj Institute for Energy Studies, Anna University, Chennai, India Abstract Simulations
CFD ANALYSIS OF CONVECTIVE FLOW IN A SOLAR DOMESTIC HOT WATER STORAGE TANK
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 4, Issue 1, January-2013 1 CFD ANALYSIS OF CONVECTIVE FLOW IN A SOLAR DOMESTIC HOT WATER STORAGE TANK Mr. Mainak Bhaumik M.E. (Thermal
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 4, Issue 1, January-2013 1 CFD ANALYSIS OF CONVECTIVE FLOW IN A SOLAR DOMESTIC HOT WATER STORAGE TANK Mr. Mainak Bhaumik M.E. (Thermal
EFFECTS OF TURBULENCE MODELLING ON THE PREDICTIONS OF THE PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION AROUND THE WING OF A SMALL SCALE VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK EFFECTS OF TURBULENCE MODELLING ON THE PREDICTIONS
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK EFFECTS OF TURBULENCE MODELLING ON THE PREDICTIONS
A Parametric Study on Power Variation for Model Wind Turbine Arrays
 Portland State University PDXScholar Dissertations and Theses Dissertations and Theses Summer 8-28-2013 A Parametric Study on Power Variation for Model Wind Turbine Arrays Dominic DeLucia Portland State
Portland State University PDXScholar Dissertations and Theses Dissertations and Theses Summer 8-28-2013 A Parametric Study on Power Variation for Model Wind Turbine Arrays Dominic DeLucia Portland State
Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms. Stefan Ivanell Director, Stand Up for Wind Centre
 Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms Stefan Ivanell Director, Stand Up for Wind Centre Planning of lectures Lecture 1: Energy extraction and flow close to the blades Lecture 2: Flow behind the turbine, i.e.,
Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms Stefan Ivanell Director, Stand Up for Wind Centre Planning of lectures Lecture 1: Energy extraction and flow close to the blades Lecture 2: Flow behind the turbine, i.e.,
An Experimental Investigation on the Wake Interference of Wind Turbines Sited Over Complex Terrains
 5th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition 9-12 January 212, Nashville, Tennessee AIAA 212-169 An Experimental Investigation on the Wake Interference
5th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition 9-12 January 212, Nashville, Tennessee AIAA 212-169 An Experimental Investigation on the Wake Interference
Prediction of Pollutant Emissions from Industrial Furnaces Using Large Eddy Simulation
 Paper # B03 Topic: Turbulent Flames 5 th US Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and Hosted by the University of California at San Diego March 25-28, 2007.
Paper # B03 Topic: Turbulent Flames 5 th US Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and Hosted by the University of California at San Diego March 25-28, 2007.
Lidar Measurements at SWIFT
 Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Lidar Measurements at SWIFT David Maniaci and Thomas Herges IEA Task 31 + 32 Meeting October 4, 2016 Sandia
Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Lidar Measurements at SWIFT David Maniaci and Thomas Herges IEA Task 31 + 32 Meeting October 4, 2016 Sandia
Wind Energy. Wind Engineering and Renewable Energy Laboratory (WIRE) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology - Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland
 Wind Energy Majid Bastankhah Fernando Porté Ágel Wind Engineering and Renewable Energy Laboratory (WIRE) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology - Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland Overview I. History of Wind
Wind Energy Majid Bastankhah Fernando Porté Ágel Wind Engineering and Renewable Energy Laboratory (WIRE) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology - Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland Overview I. History of Wind
Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software To cite this article: D Zahariea 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical analysis of eccentric orifice plate using ANSYS Fluent software To cite this article: D Zahariea 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
CERC activities under the TOPFARM project: Wind turbine wake modelling using ADMS
 CERC activities under the TOPFARM project: Wind turbine wake modelling using ADMS Final report Prepared for Risø DTU, National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy 13 th January 211 Report Information FM766
CERC activities under the TOPFARM project: Wind turbine wake modelling using ADMS Final report Prepared for Risø DTU, National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy 13 th January 211 Report Information FM766
FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION MODELLING OF WIND TURBINE BLADES BASED ON COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5769 FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5769 FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION
COMPUTATIONAL SIMULATION OF TIDAL ENERGY GENERATION ESTUARY-SCALE SCENARIOS
 COMPUTATIONAL SIMULATION OF TIDAL ENERGY GENERATION ESTUARY-SCALE SCENARIOS 1corresponding Danny Sale1, Alberto Aliseda University of Washington Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Seattle, WA, U.S.A. author:
COMPUTATIONAL SIMULATION OF TIDAL ENERGY GENERATION ESTUARY-SCALE SCENARIOS 1corresponding Danny Sale1, Alberto Aliseda University of Washington Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Seattle, WA, U.S.A. author:
Performance of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine under Accelerating and Decelerating Flows
 Performance of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine under Accelerating and Decelerating Flows Atif Shahzad, Taimoor Asim*, Rakesh Mishra, Achilleos Paris School of Computing & Engineering, University of Huddersfield,
Performance of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine under Accelerating and Decelerating Flows Atif Shahzad, Taimoor Asim*, Rakesh Mishra, Achilleos Paris School of Computing & Engineering, University of Huddersfield,
Lecture # 14: Wind Turbine Aeromechanics. Dr. Hui Hu. Department of Aerospace Engineering Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011, U.S.
 AerE 344 Lecture Notes Lecture # 14: Wind Turbine Aeromechanics Dr. Hui Hu Department of Aerospace Engineering Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 11, U.S.A Wind Energy Production and Wind Turbine Installations
AerE 344 Lecture Notes Lecture # 14: Wind Turbine Aeromechanics Dr. Hui Hu Department of Aerospace Engineering Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 11, U.S.A Wind Energy Production and Wind Turbine Installations
A Holistic View of Wind Farm Control
 A Holistic View of Wind Farm Control Peter Seiler February 11, 2014 Seminar: Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory James Blyth, 1887: 1 st electric wind turbine in Marykirk, Scotland. (Not Shown) Turbine Shown,
A Holistic View of Wind Farm Control Peter Seiler February 11, 2014 Seminar: Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory James Blyth, 1887: 1 st electric wind turbine in Marykirk, Scotland. (Not Shown) Turbine Shown,
A Large-Eddy Simulation of Wind-Plant Aerodynamics
 A Large-Eddy Simulation of Wind-Plant Aerodynamics Preprint Matthew J. Churchfield, Sang Lee, and Patrick J. Moriarty National Renewable Energy Laboratory Luis A. Martinez and Stefano Leonardi University
A Large-Eddy Simulation of Wind-Plant Aerodynamics Preprint Matthew J. Churchfield, Sang Lee, and Patrick J. Moriarty National Renewable Energy Laboratory Luis A. Martinez and Stefano Leonardi University
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
 40 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW The literature review presented in the thesis are classified into three major domains namely Wind turbine airfoil aerodynamics, Design and performance of wind turbine, Optimization
40 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW The literature review presented in the thesis are classified into three major domains namely Wind turbine airfoil aerodynamics, Design and performance of wind turbine, Optimization
Numerical Simulation of Flow Field around a Darrieus Vertical axis wind turbine to Estimate Rotational wakes Size
 Numerical Simulation of Flow Field around a Darrieus Vertical axis wind turbine to Estimate Rotational wakes Size Milad Babadi Soultanzadeh 1, Babak Mehmandoust Isfahani 2, and Davoud Toghrai Semiromi
Numerical Simulation of Flow Field around a Darrieus Vertical axis wind turbine to Estimate Rotational wakes Size Milad Babadi Soultanzadeh 1, Babak Mehmandoust Isfahani 2, and Davoud Toghrai Semiromi
based on the work of: Mirko Musa Craig Hill Kevin Howard Michael Heislel
 Michele Guala Extracting energy from wind and water based on the work of: Mirko Musa Craig Hill Kevin Howard Michael Heislel with contributions by Arvind Singh Christopher Feist Michael Heisel Fotis Sotiropoulos
Michele Guala Extracting energy from wind and water based on the work of: Mirko Musa Craig Hill Kevin Howard Michael Heislel with contributions by Arvind Singh Christopher Feist Michael Heisel Fotis Sotiropoulos
Aerodynamic Analysis of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Using Blade Element Momentum Theory for Low Wind Speed Conditions
 Aerodynamic Analysis of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Using Blade Element Momentum Theory for Low Wind Speed Conditions Esam Abubaker Efkirn, a,b,* Tholudin Mat Lazim, a W. Z. Wan Omar, a N. A. R. Nik Mohd,
Aerodynamic Analysis of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Using Blade Element Momentum Theory for Low Wind Speed Conditions Esam Abubaker Efkirn, a,b,* Tholudin Mat Lazim, a W. Z. Wan Omar, a N. A. R. Nik Mohd,
CFD model of an aerating hydrofoil
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS CFD model of an aerating hydrofoil To cite this article: D Scott et al 214 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 22 628 View the article
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS CFD model of an aerating hydrofoil To cite this article: D Scott et al 214 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 22 628 View the article
A Study on Design of A High Efficiency Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Blade Using Composite Materials
 Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press SL, vol.7, no.1, pp.59-65, 2013 A Study on Design of A High Efficiency Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Blade Using Composite Materials H. Park 1, H. Lee 2 and G. Park 2 Abstract:
Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press SL, vol.7, no.1, pp.59-65, 2013 A Study on Design of A High Efficiency Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Blade Using Composite Materials H. Park 1, H. Lee 2 and G. Park 2 Abstract:
Optimal and Simulation of HAWT Blade S809
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep- Oct. 2014), PP 83-88 Optimal and Simulation of HAWT Blade S809 Prof. Yogesh
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep- Oct. 2014), PP 83-88 Optimal and Simulation of HAWT Blade S809 Prof. Yogesh
Ontwerpsoftware voor windenergietoepassingen
 CWI, 11 november 2010 Ontwerpsoftware voor windenergietoepassingen Peter Eecen www.ecn.nl Outline Introduction to ECN Introduction to Wind Energy Examples of research activities - Rotor aerodynamics dedicated
CWI, 11 november 2010 Ontwerpsoftware voor windenergietoepassingen Peter Eecen www.ecn.nl Outline Introduction to ECN Introduction to Wind Energy Examples of research activities - Rotor aerodynamics dedicated
WIND-DIESEL-STORAGE PROJECT AT KASABONIKA LAKE FIRST NATION
 WIND-DIESEL-STORAGE PROJECT AT KASABONIKA LAKE FIRST NATION [1] Professor David A. Johnson Wind Energy Group Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering University of Waterloo 2009 Wind-Diesel
WIND-DIESEL-STORAGE PROJECT AT KASABONIKA LAKE FIRST NATION [1] Professor David A. Johnson Wind Energy Group Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering University of Waterloo 2009 Wind-Diesel
[Asif, 4(8): August, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785
![[Asif, 4(8): August, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785 [Asif, 4(8): August, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785](/thumbs/89/97956162.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY CFD ANALYSIS AND FABRICATION OF BLADE OF A HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE USING DIFFERENT T. Mohammed Asif *, G. Praveen Kumar Yadav
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY CFD ANALYSIS AND FABRICATION OF BLADE OF A HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE USING DIFFERENT T. Mohammed Asif *, G. Praveen Kumar Yadav
EFFECT OF COMBINED HOLE CONFIGURATION ON FILM COOLING WITH AND WITHOUT MIST INJECTION
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2018, Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 1923-1931 1923 EFFECT OF COMBINED HOLE CONFIGURATION ON FILM COOLING WITH AND WITHOUT MIST INJECTION by Ke TIAN a, Jin WANG a*, Chao LIU a, Jakov BALETA
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2018, Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 1923-1931 1923 EFFECT OF COMBINED HOLE CONFIGURATION ON FILM COOLING WITH AND WITHOUT MIST INJECTION by Ke TIAN a, Jin WANG a*, Chao LIU a, Jakov BALETA
Wedging Angle Effect on the Aerodynamic Structure of a Rutland 913 Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
 International Journal of Fluid Mechanics & Thermal Sciences 2016; 2(1): 1-9 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijfmts doi: 10.11648/j.ijfmts.20160201.11 ISSN: 2469-8105 (Print); ISSN: 2469-8113 (Online)
International Journal of Fluid Mechanics & Thermal Sciences 2016; 2(1): 1-9 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijfmts doi: 10.11648/j.ijfmts.20160201.11 ISSN: 2469-8105 (Print); ISSN: 2469-8113 (Online)
CFD Analysis of Oil Flooded Twin Screw Compressors
 CFD Analysis of Oil Flooded Twin Screw Compressors Sham RANE, Ahmed KOVACEVIC, Nikola STOSIC City University London, Centre for Compressor Technology, London, EC1V 0HB, UK sham.rane@city.ac.uk July 11-14,
CFD Analysis of Oil Flooded Twin Screw Compressors Sham RANE, Ahmed KOVACEVIC, Nikola STOSIC City University London, Centre for Compressor Technology, London, EC1V 0HB, UK sham.rane@city.ac.uk July 11-14,
Verification and validation of a real-time 3D-CFD wake model for large wind farms
 Verification and validation of a real-time 3D-CFD wake model for large wind farms Presented by: Wolfgang Schlez 1,2 Co-Authors: Philip Bradstock 2, Michael Tinning 2, Staffan Lindahl 2 (1) ProPlanEn GmbH;
Verification and validation of a real-time 3D-CFD wake model for large wind farms Presented by: Wolfgang Schlez 1,2 Co-Authors: Philip Bradstock 2, Michael Tinning 2, Staffan Lindahl 2 (1) ProPlanEn GmbH;
Aerodynamic Investigation of a Wind Turbine using CFD and Modified BEM Methods
 Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 9, Special Issue 1, pp. 107-111, 2016. Selected papers from the 7 th International Exergy, Energy and Environment Symposium, IEEE7-2015 Available online at www.jafmonline.net,
Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 9, Special Issue 1, pp. 107-111, 2016. Selected papers from the 7 th International Exergy, Energy and Environment Symposium, IEEE7-2015 Available online at www.jafmonline.net,
Flow Physics and Performance of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Arrays
 AIAA AVIATION Forum 6- June 4, Atlanta, GA 3nd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference.54/6.4-339 Flow Physics and Performance of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Arrays Downloaded by University of Michigan - Duderstadt
AIAA AVIATION Forum 6- June 4, Atlanta, GA 3nd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference.54/6.4-339 Flow Physics and Performance of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Arrays Downloaded by University of Michigan - Duderstadt
1039 P a g e. Fig 2.2: NREL reverse engineered Wind turbine Blade. Figure 1.2: Lift and Drag on a wind-turbine blade profile
 Design And Analysis Of Wind Turbine Blade Design System (Aerodynamic) A.V.Pradeep*, Kona Ram Prasad**, T.Victor Babu*** * (Department of Mechanical Engineering, S.V.P.Engineering College, Visakhapatnam)
Design And Analysis Of Wind Turbine Blade Design System (Aerodynamic) A.V.Pradeep*, Kona Ram Prasad**, T.Victor Babu*** * (Department of Mechanical Engineering, S.V.P.Engineering College, Visakhapatnam)
Analyzing the Effect of Dimples on Wind Turbine Efficiency Using CFD
 Analyzing the Effect of Dimples on Wind Turbine Efficiency Using CFD Arun K.K 1., Navaneeth V.R 1, Sam Vimal Kumar S 2, Ajay R 2 Associate Professor 1, P.G.Student 2, Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Analyzing the Effect of Dimples on Wind Turbine Efficiency Using CFD Arun K.K 1., Navaneeth V.R 1, Sam Vimal Kumar S 2, Ajay R 2 Associate Professor 1, P.G.Student 2, Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM
 Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM Márton Balczó 1, Tamás Faragó 2, Tamás Lajos 3 PhD Student 1, Student 2, Professor 3 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of
Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM Márton Balczó 1, Tamás Faragó 2, Tamás Lajos 3 PhD Student 1, Student 2, Professor 3 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of
A New Analytical Approach to Improving the Aerodynamic Performance of the Gyromill Wind Turbine
 A New Analytical Approach to Improving the Aerodynamic Performance of the Gyromill Wind Turbine Eiji Ejiri 1,*, Tomoya Iwadate 2 1 Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Chiba Institute of Technology,
A New Analytical Approach to Improving the Aerodynamic Performance of the Gyromill Wind Turbine Eiji Ejiri 1,*, Tomoya Iwadate 2 1 Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Chiba Institute of Technology,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research Literature Review on Blade Design of Hydro-Microturbines
 Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com Literature Review on Blade Design of
Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com Literature Review on Blade Design of
Ontwerpsoftware voor Windenergietoepassingen
 Ontwerpsoftware voor Windenergietoepassingen CWI in Bedrijf: Energy, Mathematics & Computer Science, 11 november 2011, in Amsterdam. P.J. Eecen ECN-M--11-046 April 2011 2 ECN-M--11-046 CWI, 11 november
Ontwerpsoftware voor Windenergietoepassingen CWI in Bedrijf: Energy, Mathematics & Computer Science, 11 november 2011, in Amsterdam. P.J. Eecen ECN-M--11-046 April 2011 2 ECN-M--11-046 CWI, 11 november
CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
Wind turbine performance in shear flow and in the wake of another turbine through high fidelity numerical simulations with moving mesh technique
 WIND ENERGY Wind Energ. (2012) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)..535 RESEARCH ARTICLE Wind turbine performance in shear flow and in the wake of another turbine through
WIND ENERGY Wind Energ. (2012) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)..535 RESEARCH ARTICLE Wind turbine performance in shear flow and in the wake of another turbine through
The modelling of tidal turbine farms using multi-scale, unstructured mesh models
 The modelling of tidal turbine farms using multi-scale, unstructured mesh models Stephan C. Kramer, Matthew D. Piggott, Jon Hill Applied Modelling and Computation Group (AMCG) mperial College London Louise
The modelling of tidal turbine farms using multi-scale, unstructured mesh models Stephan C. Kramer, Matthew D. Piggott, Jon Hill Applied Modelling and Computation Group (AMCG) mperial College London Louise
Wind Energy. ME922/927 Wind energy 1
 Wind Energy 1 Wind source Winds in western Europe tend to be driven by Atlantic weather systems. In some parts of the world, the wind is largely due to thermal effects: it is then fairly predictable. Power
Wind Energy 1 Wind source Winds in western Europe tend to be driven by Atlantic weather systems. In some parts of the world, the wind is largely due to thermal effects: it is then fairly predictable. Power
Reducing Uncertainty in Wind Project Energy Estimates
 www.vaisala.com Reducing Uncertainty in Wind Project Energy Estimates A Cost-Benefit Analysis of Additional Measurement Campaign Methods Wind project energy production estimates are a key element in determining
www.vaisala.com Reducing Uncertainty in Wind Project Energy Estimates A Cost-Benefit Analysis of Additional Measurement Campaign Methods Wind project energy production estimates are a key element in determining
CFD and Wind Tunnel Study of the Performance of a Multi- Directional Wind Tower with Heat Transfer Devices
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 1692 1697 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 CFD and Wind Tunnel Study of the Performance of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 1692 1697 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 CFD and Wind Tunnel Study of the Performance of
Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor
 Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor S.S.Vinay l, S.D.Ravi 2, G PremaKumar 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l M.E Student, Bangalore University, Bangalore. 2 Project Assistant, CGPL, Dept
Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Producer Gas Carburettor S.S.Vinay l, S.D.Ravi 2, G PremaKumar 3 and N.K.S.Rajan 4 l M.E Student, Bangalore University, Bangalore. 2 Project Assistant, CGPL, Dept
Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion
 Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion S. M. Salim, K. C. Ong, S. C. Cheah Abstract The performance of three different numerical techniques, i.e. RANS,
Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion S. M. Salim, K. C. Ong, S. C. Cheah Abstract The performance of three different numerical techniques, i.e. RANS,
Measuring discharge. Climatological and hydrological field work
 Measuring discharge Climatological and hydrological field work 1. Background Discharge (or surface runoff Q s) refers to the horizontal water flow occurring at the surface in rivers and streams. It does
Measuring discharge Climatological and hydrological field work 1. Background Discharge (or surface runoff Q s) refers to the horizontal water flow occurring at the surface in rivers and streams. It does
Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study
 Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study Stéphane SANQUER (1), Julien Berthaut-Gerentes (1), Luis Cosculluela Soteras (2) (1) Meteodyn (2) Iberdrola Renovables Introduction Forested areas
Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study Stéphane SANQUER (1), Julien Berthaut-Gerentes (1), Luis Cosculluela Soteras (2) (1) Meteodyn (2) Iberdrola Renovables Introduction Forested areas
Overview of wind energy research and development at NRC-IAR (Canada)
 Revue des Energies Renouvelables SMEE 10 Bou Ismail Tipaza (2010) 69 80 Overview of wind energy research and development at NRC-IAR (Canada) A. Benmeddour *, A. Wall, B. McAuliffe, P.J. Penna and J.C.
Revue des Energies Renouvelables SMEE 10 Bou Ismail Tipaza (2010) 69 80 Overview of wind energy research and development at NRC-IAR (Canada) A. Benmeddour *, A. Wall, B. McAuliffe, P.J. Penna and J.C.
LNG Safety Research: FEM3A Model Development. Quarterly Report to Prepared by:
 1 LNG Safety Research: FEM3A Model Development Quarterly Report 07-01-06 to 09-30-06 Prepared by: Iraj A. Salehi Gas Technology Institute and Jerry Havens and Tom Spicer University of Arkansas October
1 LNG Safety Research: FEM3A Model Development Quarterly Report 07-01-06 to 09-30-06 Prepared by: Iraj A. Salehi Gas Technology Institute and Jerry Havens and Tom Spicer University of Arkansas October
A new approach to wind energy. John O. Dabiri California Institute of Technology
 A new approach to wind energy John O. Dabiri California Institute of Technology jodabiri@caltech.edu Our goal: Develop wind energy technologies that match the global reach of the wind itself Only 4 countries
A new approach to wind energy John O. Dabiri California Institute of Technology jodabiri@caltech.edu Our goal: Develop wind energy technologies that match the global reach of the wind itself Only 4 countries
FLATE Hillsborough Community College - Brandon (813)
 The Florida Advanced Technological Education (FLATE) Center wishes to make available, for educational and noncommercial purposes only, materials relevant to the EST1830 Introduction to Alternative/Renewable
The Florida Advanced Technological Education (FLATE) Center wishes to make available, for educational and noncommercial purposes only, materials relevant to the EST1830 Introduction to Alternative/Renewable
Optimization of Wind Loads Affecting Skyscrapers using ANSYS
 Optimization of Wind Loads Affecting Skyscrapers using ANSYS Kavana B C 1, M S kalappa 2 1MTech student, dept of civil Engineering, MCE, Hassan, Karnataka, India 2Professor, dept of civil Engineering,
Optimization of Wind Loads Affecting Skyscrapers using ANSYS Kavana B C 1, M S kalappa 2 1MTech student, dept of civil Engineering, MCE, Hassan, Karnataka, India 2Professor, dept of civil Engineering,
Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II, WCE, July -,, London, U.K. Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies S. M. Kwa, S. M. Salim Abstract Fluctuating
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II, WCE, July -,, London, U.K. Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies S. M. Kwa, S. M. Salim Abstract Fluctuating
 This document has been downloaded from the library section of www.wind-power-program.com Visit our website for information on the WindPower program and the UK Wind Speed Database program both downloadable
This document has been downloaded from the library section of www.wind-power-program.com Visit our website for information on the WindPower program and the UK Wind Speed Database program both downloadable
MODERN PRACTICES FOR MEASUREMENT OF GAS PATH PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF AN AXIAL TURBINE
 Review of the Air Force Academy No.1 (33)/2017 MODERN PRACTICES FOR MEASUREMENT OF GAS PATH PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF AN AXIAL TURBINE Daniel OLARU, Valeriu VILAG, Gheorghe
Review of the Air Force Academy No.1 (33)/2017 MODERN PRACTICES FOR MEASUREMENT OF GAS PATH PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF AN AXIAL TURBINE Daniel OLARU, Valeriu VILAG, Gheorghe
Wind Energy Chapter 13 Resources and Technologies. Energy Systems Engineering
 Wind Energy Chapter 13 Resources and Technologies Energy Systems Engineering Further Readings David Spera, Ed., Wind Turbine Technology: Fundamental Concepts of Wind Turbine Engineering, ASME Press, New
Wind Energy Chapter 13 Resources and Technologies Energy Systems Engineering Further Readings David Spera, Ed., Wind Turbine Technology: Fundamental Concepts of Wind Turbine Engineering, ASME Press, New
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 6 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 6 Jul 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 6 Jul 2017](/thumbs/85/91865793.jpg) WIND ENERGY Wind Energ. 2015; 00:1 12 This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Stevens, R. J. A. M. (2016) Dependence of optimal wind turbine spacing on wind farm length. Wind Energ.,
WIND ENERGY Wind Energ. 2015; 00:1 12 This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Stevens, R. J. A. M. (2016) Dependence of optimal wind turbine spacing on wind farm length. Wind Energ.,
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION ON PITCH DISTANCE, COMPOUND ANGLE AND TURBULENCE INTENSITY OFDOUBLE CYLINDRICAL FILM COOLING HOLE GEOMETRY
 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION ON PITCH DISTANCE, COMPOUND ANGLE AND TURBULENCE INTENSITY OFDOUBLE CYLINDRICAL FILM COOLING HOLE GEOMETRY Hazim Fadli Aminnuddin and Kamil Abdullah Center for Energy and Industrial
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION ON PITCH DISTANCE, COMPOUND ANGLE AND TURBULENCE INTENSITY OFDOUBLE CYLINDRICAL FILM COOLING HOLE GEOMETRY Hazim Fadli Aminnuddin and Kamil Abdullah Center for Energy and Industrial
On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation
 On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong,
On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong,
College of Science and Engineering
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory College of Science and Engineering 2 Third Ave SE Minneapolis, MN 55414 Main Office: 612-624-4363 Fax: 612-624-4398 http://www.safl.umn.edu Project Title:
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory College of Science and Engineering 2 Third Ave SE Minneapolis, MN 55414 Main Office: 612-624-4363 Fax: 612-624-4398 http://www.safl.umn.edu Project Title:
Wind Turbine Blade Design for Subscale Testing
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Wind Turbine Blade Design for Subscale Testing To cite this article: Arash Hassanzadeh et al 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 753 2248 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Wind Turbine Blade Design for Subscale Testing To cite this article: Arash Hassanzadeh et al 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 753 2248 View the article online
MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD
 MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD J. Allegrini 1,2 ; J. Kämpf 3 ; V. Dorer 1 ; J. Carmeliet 1,2 1: Empa, Laboratory for Building Science
MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD J. Allegrini 1,2 ; J. Kämpf 3 ; V. Dorer 1 ; J. Carmeliet 1,2 1: Empa, Laboratory for Building Science
Energy Performance Systems, Inc.
 Energy Performance Systems, Inc. Owner & Developer of the Whole Tree Energy Technology 13 November 2012 Project Title: Improving the Efficiency of Planting, Tending and Harvesting Farm-Grown Trees for
Energy Performance Systems, Inc. Owner & Developer of the Whole Tree Energy Technology 13 November 2012 Project Title: Improving the Efficiency of Planting, Tending and Harvesting Farm-Grown Trees for
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 ) 692 697 6th BSME International Conference on Thermal Engineering (ICTE 2014) Adjacent wake effect of a vertical
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 ) 692 697 6th BSME International Conference on Thermal Engineering (ICTE 2014) Adjacent wake effect of a vertical
Blade number effect for a ducted wind turbine
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology (8) 984~99 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/738-494x DOI.7/s6-8-743-8 Blade number effect for a ducted wind turbine
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology (8) 984~99 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/738-494x DOI.7/s6-8-743-8 Blade number effect for a ducted wind turbine
