Army Innovation Strategy
|
|
|
- Gwen Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 U.S. Department of the Army Army Innovation Strategy INFORMATION COMPILED BY: The Office of Business Transformation
2 The reference to commercial or nongovernmental entities or products in this document does not constitute an official endorsement or approval. i
3 FOREWORD The Army has always been an innovative organization, owing past successes in large part to.the indomitable spirit of the American Soldier who continuously finds new solutions to solve pressing tactical problems. However, the pace of change in the geopolitical and fiscal environments, rapid adversary adaptations, and accelerated technology capabilities demand more innovation at a faster rate to ensure the Army's ability to win in a complex world. Increasing the frequency and speed of innovation will require a structured, systematic, top-and bottom-driven approach to promoting entrepreneurship and innovation across the entire force. That is the intent of the Army Innovation Strategy (AIS). Innovation will enable the Army to obtain capabilities ahead of competitors and adversaries; address the use of disruptive, asymmetric tools that decrease the value of U.S. conventional weapons and equipment; and streamline processes and systems within the institutional Army. When efforts toward these ends are aligned and focused through unifying, overarching strategic direction, the Army can optimize resources (time, money, technology, and manpower) dedicated toward their accomplishment. Yet, although the AIS provides this overarching direction, Army leaders are reminded that their role in fostering a culture of innovation is pivotal and must not be grounded solely in this document. In the execution of their individual missions, leaders must unambiguously commit to promoting and encouraging innovation, thus creating the freedom to share ideas and take prudent risk. Army leaders must continuously communicate the importance of innovation to the long-term success of the Army. They must also reinforce the fact that failed innovation initiatives are learning opportunities and they must reward, recognize, and share successes. Since the 2014 Defense Innovation Initiative, military and civilian leaders within the Department of Defense have been calling for accelerated innovation, identifying it as a component of the next offset strategy that will put competitive advantage firmly in the hands of American power projection over the coming decades. To this end, the Army will contribute by doing what it has done so well in the past by unleashing the creativity, ingenuity, and adaptability of the uniformed and civilian workforce. Innovation is part of the Army's rich tradition and will be indispensable to meeting our global mission requirements in the future. ~ft.jcs!1 V~eral, U.S. Army Vice Chief of Staff ~ K~~ Senior Official Performing the Duties of the Under Secretary of the Army ii
4 The Army Innovation Vision The Army gains competitive advantage today and into the future by embracing an enduring culture of innovation and entrepreneurship that drives solutions to win in a changing world. I. Purpose Supporting the Department of Defense Agency Strategic Plan, the Army Plan, and the Army Vision, the Army Innovation Strategy (AIS) creates the culture, structures, and systems that will unleash the creativity of the entire force and enable the Army to obtain capabilities ahead of competitors and adversaries; address the use of disruptive, asymmetric tools that decrease the value of U.S. conventional weapons and equipment; and streamline processes and systems within the institutional Army. Innovation is the result of critical and creative thinking and the conversion of new ideas into valued outcomes. The U.S. Army Operating Concept, II. Strategic Intent Until now, the Army has lacked authoritative strategic direction for the creation of a culture of innovation. A successful, sustainable innovation effort that drives key, strategic outcomes requires an approach that is grounded in the mutually dependent roles of entrepreneurship, creativity and invention, and innovation itself (figure 1), through three lines of effort that support these concepts. Figure 1. Entrepreneurship and Innovation 1
5 These lines of effort are Innovation Leadership and Strategy, Managing for Innovation, and Innovation Tools (figure 2). Figure 2. The Army s Three Pronged Approach to Innovation Innovation tools are the programs and processes used to systematically promote the generation of ideas and to track and monitor their progress to implementation. Some of these tools are suggestion programs, problem repositories, innovation cells, and crowdsourcing. Managing for innovation addresses how management in organizations creates a culture that values innovation and entrepreneurship, such as criteria for rewarding and recognizing the workforce; approaches to training, recruitment, and resourcing; and what leaders pay attention to, measure, and control. Innovation leadership and strategy is about establishing and clearly communicating an innovation vision that is aligned to, and supportive of, organizational strategic direction. It includes the development and articulation of goals and objectives as well as formalized assessments of performance in support of achievement. When fully deployed and integrated across the enterprise, these approaches work systematically to advance the Army toward a level of innovation maturity marked by consistent success that results from dynamic, repeatable, and adaptable practices and processes. The AIS provides the framework and direction to advance the Army toward Level 5 innovation maturity (figure 3) by It establishes both a vision and key outcomes for innovation activities and investments across Doctrine, Organization, Training, Materiel, Leadership and Education, Personnel, Facilities and Policy (DOTMLPF-P). It provides the underpinnings for policy, establishing managerial practices to encourage innovation and entrepreneurship at the individual and organizational levels. Finally, the AIS will align innovation efforts through a distributed community of practice with the strategic direction of the Army; promote alignment among diverse offices and agencies within the Army; establish and communicate objectives and priorities, and help focus efforts around them; help in adjudicating conflicting or competing innovation priorities and allow for the distribution of resources in support of established priorities; and serve as an embedding mechanism in advancing a culture of 2
6 innovation and entrepreneurship across the Army. Table 1 addresses, within the context of the three pronged approach, the organizational characteristics and indicators of innovation maturity. As such, it acts as a roadmap for the Army in advancing innovation as a core capability that is strategy focused and people driven, with a return on investment that can be articulated and that makes the case for continued investment self-evident. Figure 3. The Innovation Maturity Model Paul R. Williams, Think for a Change III. Strategic Narrative The Army addresses the imperative for systematic, accelerated innovation across the generating and operating forces through leadership committed to challenging and changing cultural norms, the institutionalization of management practices and processes that support the rapid conversion of new ideas into valued outcomes, and leveraging the diverse talents and capabilities of the Total Force, key partners, suppliers, and other collaborators. Approaches to this accelerated innovation include programs and tools to generate and elevate new ideas or solutions for consideration; increased tolerance for risk and failure in experimentation; changing the way that the Army is managed, including innovation and entrepreneurship as key considerations in attracting, recruiting, retaining, developing, and promoting both the civilian and uniformed forces; focusing innovation efforts on key strategic outcomes that impart competitive advantage on the battlefield; and finally by relentlessly pursuing opportunities for cooperation and collaboration in developing solutions to the Army s strategic challenges and removing bureaucratic obstacles to such initiatives. Innovation is the result of critical and creative thinking and the conversion of new ideas into valued outcomes. Innovation drives the development of new tools or methods that permit Army forces to anticipate future demands, stay ahead of determined enemies, and accomplish the mission. Army Operating Concept,
7 Table 1. The Army Innovation Maturity Matrix Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Innovation Leadership and Strategy Managing for Innovation Innovation Tools Culture Strategic Planning Leadership People Processes Training Performance Measurement Idea Capture Other Tools Innovation Deficiencies Culture is risk-averse, and closed to new ideas Stratetgic planning focuses on past performance, maintaining status quo Leaders focused on past performance and current initiatives only People viewed as productivity units and not idea sources Innovation-related processes not present Innovation-related training not provided No established innovation-related metrics Ideas from employees are not captured and idea management systems not present Innovation tools and techniques are not present Innovation Structure Culture recognizes ideas but systems to move the ideas forward are lacking Ideas generated not aligned to strategy Leaders understand the difference between continuous improvement efforts and innovation People are encouraged to submit ideas Innovation-specific reward and recognition systems are established Employees and managers are introduced to creative problem solving and innovation concepts Leading indicators established and reported (number of ideas submitted, percentage of awards linked to innovation) Employee ideas are captured by mid and front line management General idea submission systems are established to collect and store ideas Innovation Processes Culture is risktolerant and new ideas are documented Ideas aligned with subordinate strategies Senior leaders rely on middle management to communicate innovation goals and processes People are encouraged to cooperate and collaborate to move ideas forward Idea management process and related systems established Senior leaders and executives are offered creativity and innovation training Metrics aligned to innovation goals and success factors (percentage of employees and managers with innovation training, ratio of implemented to submitted ideas) Ideas are captured and processes exist to advance ideas toward implementation General idea campaigns are launched to harvest ideas, regardless of problem(s) to be solved Innovation Standards Culture encourages risk-taking Innovation systems and approaches aligned to strategy Leaders create and market targeted idea campaign and communicate innovation strategy and processes People are encouraged to take calculated risks when problem solving Goals related to innovation system are established Advanced innovation process and Idea champion training to employees and management Lagging indicators established and reported (overall cost savings or avoidance or improved capabilities from innovation) Formal processes and tools exist to track and monitor idea status through the process Targeted idea campaigns are launched to solve specific problems Innovation Optimized Culture encourages collaborative innovation efforts Governance established to ensure ideas are aligned to strategy before implementation Senior management position dedicated to innovation program (Chief Innovation Officer) People are regarded as key providers of innovation ideas and are encouraged to use work time to generate them Innovation program formally established Advanced creative problem solving, idea generation and innovation training provided to employees and management Positive correlation of innovation goals with other key/operational outcomes Centralized idea database is established supported by formal implementation systems Idea generation sessions are sponsored and facilitated 4 Paul R. Williams, Think for a Change
8 IV. Strategic Alignment The U.S. Department of Defense Agency Strategic Plan underscores the criticality of innovation in its strategic goal to achieve dominant capabilities through innovation, technical excellence, and defense institutional reform. Echoing this priority, Department of Defense (DoD) leaders frequently point to accelerated innovation across the department as critical to putting competitive advantage firmly in the hands of American power projection over the coming decades. This need is supported by the 2016 Army Vision, which cites innovation s importance in obtaining capabilities ahead of competitors and adversaries, and in streamlining processes within the institutional Army. Figure 4. The AIS Integration in the Army Planning Hierarchy Further, the 2014 Army Operating Concept specifically identifies innovation as one of eight key tenets for guiding the application of combat power. The concepts underpinning the philosophy and principles of Mission Command, specifically, mutual trust, disciplined initiative, and prudent risk-taking, are consistent with and supportive of the conditions necessary for successful and sustained innovation and entrepreneurship. Similarly, innovation and entrepreneurship are central to the achievement of goals and objectives contained in the Army s Business Strategy, , that governs the management of the institutional Army in delivering its Title 10, United States Code (U.S.C) responsibilities. To this end, the AIS is an enabling strategy to the Army s Vision of Strategic Advantage in a Complex World, and also supports the strategic direction and plans of subordinate Army functions. At the same 5
9 time, the AIS provides overarching and unifying strategic direction for operations, programs, and policies that depend on innovation and entrepreneurial management for their execution such as the Army Operating Concept, the Army Directive (Changing Management Behavior: Every Dollar Counts), and the 2016 Army Ideas for Innovation Implementation Plan (figure 4). Strategic direction established by the AIS will be translated to action through the development and active management of an implementing plan. V. Governance and Assessment The Army Office of Business Transformation (OBT) is responsible for development and coordination of the AIS and oversees the assessment of performance related to the accomplishment of its objectives. Senior leaders review progress in the achievement of AIS goals and objectives through the 2- and 3-Star Army Business Council (ABC) meetings and updates are provided as appropriate to the Senior Review Group (SRG), chaired by the Vice Chief of Staff of the Army (VCSA) and the Under Secretary of the Army (USA). Although the primary purpose for the reviews is to monitor progress, ABC venues provide Army senior leaders with the opportunity to engage in overcoming obstacles or necessary decision making in the achievement of AIS goals. The strategy has a 5 year planning horizon but is reviewed and updated bi-annually to ensure continued responsiveness to the Army s evolving strategic environment. OBT publishes updates to the AIS during the first quarter of the fiscal year. The Army s Strategic Management System (SMS) is the primary enterprise-level tool used to manage Army and organizational strategy execution, to include the AIS. The SMS facilitates measurement of progress against strategic objectives and allows organization leaders to communicate strategy; demonstrate strategic alignment; build goals, objectives, measures and targets; and assess performance in objective accomplishment. VI. Strategic Challenges, Goals, and Objectives Following are goals and objectives responsive to the key innovation challenges that must be addressed in achieving the Army s innovation vision. These challenges were identified by cross-functional teams of Army leaders, subject matter experts, and other stakeholders across the Army commands. A. The Army Culture s Low Tolerance for Risk Challenge: A culture that promotes repeatable and sustainable innovation in any organization requires prudent risk-taking and a reasonable tolerance for failure. However, the Army, like most Federal Government agencies, has a deeply ingrained culture of risk aversion, particularly within the institutional Army where this is reflected in approaches to managing the Total Army and the prioritization of both money and time. Innovation and entrepreneurship are not universally valued across the Army. Instead, adherence to standards is the foundation upon which individual and organizational performance are assessed. As a result, entrepreneurial behavior and the innovation it engenders are discouraged and opportunities to improve the Army and its operations are lost. Goal 1: Innovation and entrepreneurship are valued across the depth and breadth of the Army. Increased and accelerated innovation that directly contributes to the achievement of the Army s vision is the result of uniformed and civilian leaders at all echelons empowering and rewarding experimentation, prudent risk-taking, and learning from mistakes. 6
10 In order for innovation to thrive, there needs to be a fundamental acceptance to experimentation, iteration of ideas, and willingness to allow an idea forward that may be contrary to corporate thinking. David Westfall Objective 1.1: Facilitate the surfacing, vetting, refinement, and implementation of workforcegenerated ideas. Performance Measure 1.1a: Number of Army Ideas for Innovation (AI2) accepted monthly. Target: 10% growth monthly in first year and 2% each subsequent year through fiscal year 2021 (FY21). Performance Measure 1.1b: Number of substantiated complaints received monthly through AI2 on timeliness of idea advancement. Target: 0. Objective 1.2: Incentivize, reward, and recognize innovation that supports the current needs and future objectives of the Army through formal approaches such as Army Materiel Command s Army Greatest Innovation awards program. Performance Measure 1.2a: Formal innovation-related reward and/or recognition programs established at Army command/army service component command/direct reporting unit levels. Target: Programs established by second quarter Performance Measure 1.2b: Army-level ceremony held to recognize top innovators. Target: One ceremony annually. Performance Measure 1.2c: Army score on annual Federal Employee Viewpoint Survey for Creativity and Innovation are Rewarded. Target: 10% increase annually from 2016 baseline through Objective 1.3: Remove bureaucratic and technical barriers to solution emergence with approaches such as the Army Rapid Capabilities Office and Army Cyber Challenges. Performance Indicator 1.3: New, formalized programs that promote unobstructed emergence of solutions to challenges across functional domains are established throughout the enterprise. Objective 1.4: Incorporate innovation and entrepreneurship in Army doctrine as key characteristics of the military profession. Performance Measure 1.4: Army Doctrine Publication 1 includes innovation and entrepreneurship as key characteristics of the military profession. Target: With first revision cycle after publication of this document. B. Programming and Resourcing of Innovation across DOTMLPF-P Challenge: Successful innovation initiatives often require collaboration across functional and organizational lines that necessitate cost sharing, flexible spending approaches, and the flow of money 7
11 to promising opportunities that is not overly obstructed. Such flexibility is inconsistent with the Army s traditional approach to planning, programming, and budgeting where priority is given to codified requirements for meeting standards and achieving specific and predictable outcomes. The lack of deliberate, dedicated, and systematic funding for innovation and innovative ideas outside of Research, Development, Testing and Evaluation (RDT&E) and inflexible funding processes that inhibit the rapid reprogramming and flow of resources to new opportunities often discourages innovation and constrains the Army s ability to collaborate with external agencies in problem-solving for its continued success. Goal 2: The Army systematically plans and programs funding that promotes and supports innovation and entrepreneurial behavior throughout the enterprise, facilitates cost sharing across organizational lines, and provides the means for rapid application of funding to new opportunities as they emerge. Innovation...is seldom the product of a single individual s intellectual brilliance. Innovation is the product of connections between individuals and their ideas. Gary Hamel Objective 2.1: Develop new approaches to planning, programming, and execution that adapt to and support emerging ideas and changing operational demands such as the Army Venture Capital Initiative. Performance Indicator 2.1: Funding is approved with flexible budget justification that allows availability and rapid application of funds to support innovation initiatives and ideas in the year of execution. Target: FY19. Objective 2.2: Develop and submit proposals for Secretary of Defense and congressional consideration that support new approaches to planning, programming, and executing innovation activities that support changing operational demands across DOTMLPF-P. Performance Indicator 2.2: Proposals developed, approved and submitted for consideration. Target: NLT EOY Objective 2.3: Identify and report measures that facilitate an objective assessment of Return on Innovation Investment to rationalize future funding in support of innovation. Performance Measure 2.3: Simple, meaningful criteria to effectively measure desired innovationrelated behaviors and outcomes for leaders, organizations, and individuals are established and used for routine reporting and review by the ABC. Target: Annual reviews conducted beginning in 2nd Quarter FY18. Objective 2.4: Foster creative cost sharing approaches with other Federal agencies; international, state, and local organizations; and the private sector to support collaborative innovation initiatives. Performance Indicator 2.4: Innovation funding (Performance Indicator 2.1a) is unobstructed by execution rules and guidance that preclude mutually beneficial cost sharing arrangements. 8
12 C. Leveraging the Total Force: People, Diversity, Experience, Partners, and Collaborators Challenge: Openness to new ideas, a willingness to experiment and take risks, workforce engagement, and diversity are values most closely correlated with strong performance in innovation. Yet the Army s approaches to recruiting, developing, managing, retaining, and recognizing the uniformed and civilian force do not fully support these values. Further, as an enterprise, the Army lacks a systemic approach for the discovery, rapid evaluation, accreditation, integration, and acquisition of promising ideas, technologies and processes that may be realized through collaboration with partners, suppliers, and collaborators internal and external to the Federal Government. Goal 3: The Army optimizes and aligns the diverse talent, skills, backgrounds, and ideas from the Total Army as well as partners from other nations, industry, and academia to systematically explore, incentivize, and adopt new concepts, technologies, and processes that positively impact the Army and its operations. The Army will work with all stakeholders across the Department of Defense, other services, industry, research laboratories, and civilian innovators to develop new operating concepts and technologies. GEN Mark A. Milley, CSA Objective 3.1: Build the Army s innovation network. Strengthen linkages with external idea creators and invest in collaboration forums which connect innovators across traditional organizational lines with such approaches as the Army Research Laboratory s Open Campus Initiative. Performance Measure 3.1: An entity at the Headquarters, Department of the Army (HQDA) level is designated identify and implement opportunities for partnerships to optimize innovation capacity. Target: End of year (EOY) FY17. Objective 3.2: Integrate innovation and entrepreneurship into the Army s talent management practices. Performance Indicator 3.2a: The Army establishes measurable objectives for and rates individual behaviors and leadership actions in innovation and entrepreneurship. These objectives and behaviors are included in Army approaches to recruiting, performance evaluations, professional development, and promotion. Target: EOY FY20. Performance Indicator 3.2b: The Secretary of the Army (SECARMY)/Chief of Staff, Army (CSA) with other senior leadership personally and routinely spotlight and recognize individuals and initiatives demonstrating innovation and entrepreneurship. Objective 3.3: Better leverage the Continuous Process Improvement (CPI) community, including Lean Six Sigma as Business Process Re-Engineering (BPR) practitioners and related infrastructure (e.g., the Army s BPR Center of Excellence) for the identification of institutional challenges and solutions. 9
13 Performance Indicator 3.3: Lean Six Sigma practitioners and leaders within the CPI community work systematically and synergistically with idea capture and idea management programs across the enterprise to facilitate the implementation of innovative solutions to Army challenges. Target: EOY FY18. Diverse backgrounds and experiences bring inherently different outlooks and ways of thinking, the key to innovation in organizations. We gain a strategic advantage by leveraging the diversity of all members and creating an inclusive environment in which each member is valued and encouraged to provide ideas critical to innovation, optimization, and organizational mission success. DoD Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan, Objective 3.4: Understand, promote, and set conditions to exploit the positive correlation between force diversity and innovation. Performance Measure 3.4a: Army score on annual Federal Employee Viewpoint Survey for Policies and Programs Promote Diversity in the Workplace. Target: 5% increase annually from 2016 baseline through Performance Indicator 3.4b: The Army actively supports in strategy and policy the recommendations contained in the 2011 Military Leadership Diversity Commission Report to the President of the United States and Congress. Objective 3.5: Cultivate intrinsic motivation. Performance Measure 3.5: Army score on annual Federal Employee Viewpoint Survey for I Feel Encouraged to Come Up with New and Better Ways of Doing Things. Target: 10% increase annually from 2016 baseline through D. Demonstrated, Sustained Leadership Commitment to Innovation Challenge: Leaders who encourage innovation and who invest time and other resources in actively driving and managing it are the primary motivators of innovation and entrepreneurial behavior germane to all organizations in all industries. Army leaders acknowledge and often support the criticality of innovation to the effectiveness and efficiency of the operational and institutional Army. However, to ensure this support remains responsive to the evolving needs of the Army, continuous evaluation of their approaches innovation (e.g., prudent risk-taking, openness to new ideas, rewards and recognition, workforce development, and resource commitment) is necessary. Goal 4: Uniformed and civilian Army leaders possess a strong personal bias for intelligent risk-taking as well as a demonstrated commitment to improvement and innovation. They combine these attributes with a resolute approach to drive necessary changes that create an environment for workforce engagement, entrepreneurship, and technological and organizational innovation, holding subordinate leaders accountable for the same. 10
14 Innovation is the military imperative and the leadership opportunity of this generation Quadrennial Defense Review Objective 4.1: Issue direction from SECARMY/CSA stating engagement in and facilitation of ideation and problem solving as a basic competency expected of all within the Army. Performance Measure 4.1: SECARMY/CSA direction defining desired behaviors for innovation is issued. Target: First quarter, FY18. Objective 4.2: Incorporate in the performance objectives, reviews, and counseling of uniformed and civilian leaders their effectiveness in promoting a culture of prudent risk-taking, improvement, and innovation in their units and organizations. Performance Measure 4.2: Uniformed and civilian supervisors have included in their performance objectives their effectiveness in promoting prudent risk-taking and innovation. Target: EOY Objective 4.3: Incentivize, reward, and recognize leadership in innovation. Performance Measure 4.3: Leadership in innovation is formally recognized at HQDA level. Target: Annually at recognition ceremonies (see Performance Measure 1.2b). E. Aligning Innovation Processes with Strategically Important Outcomes Challenge: In the evolution of innovation processes over the past three decades, Outcome-Driven Innovation is proven to have the highest success rate. However, at all echelons of the Army, performance assessment is grounded largely in measures of performance where the focus is on processes rather than measures of effectiveness that are reflective of key operational and institutional outcomes. When desired outcomes are not clearly defined, communicated, and measured, then approaches to innovation and entrepreneurship lack the necessary focus to optimize their benefits and meaningful impacts and to meet the current and future needs of the Army. Goal 5: Innovation processes and entrepreneurial behavior in the Army are driven by well-defined, clearly articulated, measurable outcomes whose achievement meaningfully impacts the Army s effectiveness and efficiency. Objective 5.1: Identify and aggregate Army challenges through the development and maintenance of a repository or repositories available to innovators across DoD, key partners, and suppliers. Performance Indicator 5.1: Problem repository or repositories are established and active. Target: Second quarter, FY18. Objective 5.2: Align enterprise-level recognition and rewards to innovation that is successful in addressing these challenges. 11
15 Performance Measure 5.2: Innovation rewards and recognition given at HQDA level ceremonies are grounded in clearly articulated, high-impact Army challenges. Target: 100%. [The DoD will] fuel entrepreneurship and innovation and improve government efficiency and effectiveness by unlocking the value of government data. The DoD Agency Strategic Plan, Objective 5.3: Leverage emerging data analytics capabilities in identifying opportunities for innovation. Performance Indicator 5.3: Data analytics are increasingly used to drive innovation across the enterprise. Objective 5.4: Develop an enterprise-wide, scalable business process for innovation. Performance Measure 5.4: Enterprise-wide, scalable business process for innovation is developed and deployed across the enterprise. Target: EOY VII. Goals and Objectives Summary Table 2 summarizes the Army Innovation Strategy goals and objectives. VII. Conclusion In preparation for framing and writing the AIS, OBT met with leaders and innovators from industry, academia, private organizations, other Service branches and Federal agencies, and the Army. Two key learnings came from these engagements that became foundational concepts of the AIS. The first of these is that across the Army the call for innovation has not gone unheard. Army agencies and organizations at all echelons are systematically developing and implementing innovative solutions to solve the Army s greatest challenges with velocity that until now has only been seen in times of war. Accordingly, the intent of the AIS is not to supplant these efforts, but rather to set the conditions for advancing a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship across the Army. The second learning from these engagements is that successful, sustainable innovation with demonstrable outcomes requires a three-pronged approach, driven from both top-down and bottomup, that includes innovation tools, managing for innovation, and innovation leadership and strategy. To this end, the AIS establishes, through goals and objectives responsive to the Army s most fundamental innovation challenges, a trajectory for the maturation of these approaches. Through the accomplishment of these objectives and achievement of the targeted maturity level, the Army will institutionalize an enduring culture of innovation and entrepreneurship that drives solutions to win in a complex world. 12
16 Table 2. Summary of Innovation Goals and Objectives Goals Objectives 1: Innovation and entrepreneurship are valued across the depth and breadth of the Army. Increased and accelerated innovation that directly contributes to the achievement of the Army s vision is the result of uniformed and civilian leaders at all echelons empowering and rewarding experimentation, prudent risktaking, and learning from mistakes. 2: The Army systematically plans and programs funding that promotes and supports innovation and entrepreneurial behavior throughout the enterprise, facilitates cost sharing across organizational lines, and provides the means for rapid application of funding to new opportunities as they emerge. 3: The Army optimizes and aligns the diverse talent, skills, backgrounds, and ideas from the Total Army as well as partners from other nations, industry, and academia to systematically explore, incentivize, and adopt new concepts, technologies, and processes that positively impact the Army and its operations. 4: Uniformed and civilian Army leaders possess a strong personal bias for intelligent risk-taking as well as a demonstrated commitment to improvement and innovation. They combine these attributes with a resolute approach to drive necessary changes that create an environment for workforce engagement, entrepreneurship, and technological and organizational innovation, holding subordinate leaders accountable for the same. 5: Innovation processes and entrepreneurial behavior in the Army are driven by well-defined, clearly articulated, measurable outcomes whose achievement meaningfully impacts the Army s effectiveness and efficiency. 1.1: Facilitate the surfacing, vetting, refinement, and implementation of workforcegenerated ideas. 1.2: Incentivize, reward, and recognize innovation that supports the current needs and future objectives of the Army through formal approaches such as Army Materiel Command s Army Greatest Innovation awards program. 1.3: Remove bureaucratic and technical barriers to solution emergence with approaches such as the Army Rapid Capabilities Office and Army Cyber Challenges. 1.4: Incorporate innovation and entrepreneurship in Army doctrine as key characteristics of the military profession. 2.1: Develop new approaches to planning, programming, and execution that adapt to and support emerging ideas and changing operational demands such as the Army Venture Capital Initiative. 2.2: Develop and submit proposals for Secretary of Defense and congressional consideration that support new approaches to planning, programming, and executing innovation activities that support changing operational demands across DOTMLPF-P. 2.3: Identify and report measures that facilitate an objective assessment of Return on Innovation Investment to rationalize future funding in support of innovation. 2.4: Foster creative cost sharing approaches with other Federal agencies; international, state, and local organizations; and the private sector to support collaborative innovation initiatives. 3.1: Build the Army s innovation network. Strengthen linkages with external idea creators and invest in collaboration forums which connect innovators across traditional organizational lines with such approaches as the Army Research Laboratory s Open Campus Initiative. 3.2: Integrate innovation and entrepreneurship into the Army s talent management practices. 3.3: Better leverage the Continuous Process Improvement (CPI) community, including Lean Six Sigma as Business Process Re-Engineering (BPR) practitioners and related infrastructure (e.g., the Army s BPR Center of Excellence) for the identification of institutional challenges and solutions. 3.4: Understand, promote, and set conditions to exploit the positive correlation between force diversity and innovation. 3.5: Cultivate intrinsic motivation. 4.1: Issue direction from the Secretary of the Army (SECARMY)/Chief of Staff of the Army (CSA) stating engagement in and facilitation of ideation and problem solving as a basic competency expected of all within the Army. 4.2: Incorporate in the performance objectives, reviews, and counseling of uniformed and civilian leaders their effectiveness in promoting a culture of prudent risk-taking, improvement, and innovation in their units and organizations. 4.3: Incentivize, reward. and recognize leadership in innovation. 5.1: Identify and aggregate Army challenges through the development and maintenance of a repository or repositories available to innovators across DoD, key partners, and suppliers. 5.2: Align enterprise-level recognition and rewards to innovation that is successful in addressing these challenges. 5.3: Leverage emerging data analytics capabilities in identifying opportunities for innovation. 5.4: Develop an enterprise-wide, scalable business process for innovation. 13
17 VIII. References 1. Department of Defense, Agency Strategic Plan, Memorandum, Secretary of Defense, November 15, 2014, subject: The Defense Innovation Initiative 3. Headquarters, Department of the Army, The Army Business Strategy Headquarters, Department of the Army, The Army Vision Memorandum, Secretary of the Army, 15 April, 2016, subject: Army Directive (Changing Management Behavior: Every Dollar Counts). 6. Memorandum, Under Secretary of the Army, 14 December, 2016, Army Ideas for Innovation (AI2) Program Implementation Plan. 7. U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command Pamphlet , The U.S. Army Operating Concept, Winning in a Complex World
18 Army Innovation Strategy
National Defense University. Strategic Plan 2012/2013 to 2017/18 One University Evolution
 National Defense University The Chairman s University: Inspiring Creative, Critical and Collaborative Thinkers For Leadership Through Academic Excellence Strategic Plan 2012/2013 to 2017/18 One University
National Defense University The Chairman s University: Inspiring Creative, Critical and Collaborative Thinkers For Leadership Through Academic Excellence Strategic Plan 2012/2013 to 2017/18 One University
3Z0Z 0? W7? TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT MASTER PLAN* (S)l\f> v^n. 0 Department of Defense. AUG 2 ego, August O/ A./ \o V* TECHNICAL LIBRARY
 3Z0Z O/ A./ \o V* ^V TIME y>- v^n 0? W7? TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT MASTER PLAN* 0 Department of Defense August 1988 (S)l\f> TECHNICAL LIBRARY AUG 2 ego, u i ACCESSION NO AD DoD TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
3Z0Z O/ A./ \o V* ^V TIME y>- v^n 0? W7? TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT MASTER PLAN* 0 Department of Defense August 1988 (S)l\f> TECHNICAL LIBRARY AUG 2 ego, u i ACCESSION NO AD DoD TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
Finance Division Strategic Plan
 Finance Division Strategic Plan 2018 2022 Introduction Finance Division The Finance Division of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) provides financial management, enterprise planning and stewardship in support
Finance Division Strategic Plan 2018 2022 Introduction Finance Division The Finance Division of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) provides financial management, enterprise planning and stewardship in support
DEFENSE THREAT REDUCTION AGENCY STRATEGIC PLAN FY
 DEFENSE THREAT REDUCTION AGENCY STRATEGIC PLAN FY 2018-2022 DEFENSE THREAT REDUCTION AGENCY Message from the Director Our Nation and the Department of Defense (DoD) face an increasingly complex and uncertain
DEFENSE THREAT REDUCTION AGENCY STRATEGIC PLAN FY 2018-2022 DEFENSE THREAT REDUCTION AGENCY Message from the Director Our Nation and the Department of Defense (DoD) face an increasingly complex and uncertain
CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT AND INNOVATION (CP2I)
 CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT AND INNOVATION (CP2I) CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT AND INNOVATION THE CHALLENGE: ENSURING SUCCESS FOR TOMORROW Leaders of federal government organizations today face a
CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT AND INNOVATION (CP2I) CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT AND INNOVATION THE CHALLENGE: ENSURING SUCCESS FOR TOMORROW Leaders of federal government organizations today face a
ICMI PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATION
 ICMI PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATION Contact Center Management Competencies The ICMI Professional Certification Contact Center Management Competencies specify job role-specific knowledge, skills and abilities
ICMI PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATION Contact Center Management Competencies The ICMI Professional Certification Contact Center Management Competencies specify job role-specific knowledge, skills and abilities
Continuous Process Improvement Organizational Implementation Planning Framework
 Continuous Process Improvement Organizational Implementation Planning Framework This implementation planning framework can be used by any organization from a military service or other major organization
Continuous Process Improvement Organizational Implementation Planning Framework This implementation planning framework can be used by any organization from a military service or other major organization
The Ohio State University Human Resources Strategic Plan
 Human Resources 2018-2023 Strategic Plan Finalized: May 16, 2018 Delivering HR Excellence. Inspiring People. Leading Change. HR.OSU.EDU 1590 N. High Street, Suite 300 Columbus, OH 43201 614-292-1050 Table
Human Resources 2018-2023 Strategic Plan Finalized: May 16, 2018 Delivering HR Excellence. Inspiring People. Leading Change. HR.OSU.EDU 1590 N. High Street, Suite 300 Columbus, OH 43201 614-292-1050 Table
Supply Management Three-Year Strategic Plan
 Supply Management Three-Year Strategic Plan 2010-2012 Message From the Vice President, Supply Management I am pleased to present our new three-year strategic plan for fiscal years 2010 2012. The plan
Supply Management Three-Year Strategic Plan 2010-2012 Message From the Vice President, Supply Management I am pleased to present our new three-year strategic plan for fiscal years 2010 2012. The plan
Core Values and Concepts
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in highperforming organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in highperforming organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
STRATEGIC PLANNING: IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP
 STRATEGIC PLANNING: IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP MOVING FROM THE STRATEGIC PLAN TO AN OPERATIONAL PLAN Strategic plans provide broad guidance and direction for a higher education institution s immediate future.
STRATEGIC PLANNING: IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP MOVING FROM THE STRATEGIC PLAN TO AN OPERATIONAL PLAN Strategic plans provide broad guidance and direction for a higher education institution s immediate future.
November CFPB Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan
 November 2016 CFPB Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2016-2020 Message from Richard Cordray Director of the CFPB At the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), we are dedicated to making sure
November 2016 CFPB Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2016-2020 Message from Richard Cordray Director of the CFPB At the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), we are dedicated to making sure
AUDIT ADVANTAGE: IMPROVING MISSION READINESS
 AUDIT ADVANTAGE: IMPROVING MISSION READINESS AUDIT ADVANTAGE: IMPROVING MISSION READINESS THE CHALLENGE: MOVING FROM AUDIT READINESS TO SUSTAINED AUDIT SUCCESS Everything you have heard about the size
AUDIT ADVANTAGE: IMPROVING MISSION READINESS AUDIT ADVANTAGE: IMPROVING MISSION READINESS THE CHALLENGE: MOVING FROM AUDIT READINESS TO SUSTAINED AUDIT SUCCESS Everything you have heard about the size
Visionary Leadership. Systems Perspective. Student-Centered Excellence
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
The practice of constantly assessing personal knowledge and skills and following paths for improvement. have been done by
 Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Brand Knowledge & Advocacy: Understanding the brand s essence, values and vision to build advocacy among stakeholders
 Consumer Insight & Empathy: Developing an understanding of consumers behaviors and underlying motivation Brand Knowledge & Advocacy: Understanding the brand s essence, values and vision to build advocacy
Consumer Insight & Empathy: Developing an understanding of consumers behaviors and underlying motivation Brand Knowledge & Advocacy: Understanding the brand s essence, values and vision to build advocacy
Finance Division. Strategic Plan
 Finance Division Strategic Plan 2014-2019 Introduction FINANCE DIVISION The Finance Division of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) provides financial management, enterprise planning and stewardship in support
Finance Division Strategic Plan 2014-2019 Introduction FINANCE DIVISION The Finance Division of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) provides financial management, enterprise planning and stewardship in support
National Defense University
 National Defense University Strategic Plan AV 2012-2013 to AV 2017-18 22 January 2013 Contents President's Vision and Intent 3 Mission, Vision, and Core Values/Guiding Principles 5 Mission 5 Vision 5 NDU
National Defense University Strategic Plan AV 2012-2013 to AV 2017-18 22 January 2013 Contents President's Vision and Intent 3 Mission, Vision, and Core Values/Guiding Principles 5 Mission 5 Vision 5 NDU
Simitec N 67th Ave Suite 1186 Glendale, Arizona (484)
 Simitec 20250 N 67th Ave Suite 1186 Glendale, Arizona (484) 686-5189 info@simitecinc.com 2013 Simitec, Inc. and/or affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of this publication in
Simitec 20250 N 67th Ave Suite 1186 Glendale, Arizona (484) 686-5189 info@simitecinc.com 2013 Simitec, Inc. and/or affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of this publication in
EMPLOYEE EXPERIENCE CONSULTING: ALM 2017
 EMPLOYEE EXPERIENCE CONSULTING: ALM 2017 BEST-IN-CLASS PROVIDER Cited as the "best-in-class provider" in strategy. "North Highland applies the five core principles of its EX philosophy to a common approach
EMPLOYEE EXPERIENCE CONSULTING: ALM 2017 BEST-IN-CLASS PROVIDER Cited as the "best-in-class provider" in strategy. "North Highland applies the five core principles of its EX philosophy to a common approach
Task Force Innovation Working Groups
 Task Force Innovation Working Groups Emerging Operational Capabilities Adaptive Workforce Information VISION Manage the Innovation Talent of the DON Workforce. ADAPTIVE WORKFORCE WORKING GROUP The Department
Task Force Innovation Working Groups Emerging Operational Capabilities Adaptive Workforce Information VISION Manage the Innovation Talent of the DON Workforce. ADAPTIVE WORKFORCE WORKING GROUP The Department
Identifying Governance Best Practices in Systems-of-Systems Acquisition
 Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive DSpace Repository Reports and Technical Reports All Technical Reports Collection 2014-05-15 Identifying Governance Best Practices in Systems-of-Systems Acquisition
Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive DSpace Repository Reports and Technical Reports All Technical Reports Collection 2014-05-15 Identifying Governance Best Practices in Systems-of-Systems Acquisition
Democratized Data Driving Discovery RENCI Strategic Plan 2017
 Democratized Data Driving Discovery RENCI Strategic Plan 2017 Stanley C. Ahalt, Ph.D. Director, Renaissance Computing Institute (RENCI) Professor, Department of Computer Science, UNC-Chapel Hill Associate
Democratized Data Driving Discovery RENCI Strategic Plan 2017 Stanley C. Ahalt, Ph.D. Director, Renaissance Computing Institute (RENCI) Professor, Department of Computer Science, UNC-Chapel Hill Associate
Sid Koslow Winner of the 2015 Glen A. Gilbert Memorial Award
 Fall 2015 VOLUME 57, NO. 3 Sid Koslow Winner of the 2015 Glen A. Gilbert Memorial Award Plus Big Data Flows Through NextGen Change is Tantalizingly Close for the FAA Coping with Adverse Winter Weather
Fall 2015 VOLUME 57, NO. 3 Sid Koslow Winner of the 2015 Glen A. Gilbert Memorial Award Plus Big Data Flows Through NextGen Change is Tantalizingly Close for the FAA Coping with Adverse Winter Weather
PORTLAND PUBLIC SCHOOLS HUMAN RESOURCE SERVICES AND DELIVERY
 PORTLAND PUBLIC SCHOOLS HUMAN RESOURCE SERVICES AND DELIVERY January 2013 Overview Portland Public School District (the District or PPS) contracted with AKT to create a new vision and values for their
PORTLAND PUBLIC SCHOOLS HUMAN RESOURCE SERVICES AND DELIVERY January 2013 Overview Portland Public School District (the District or PPS) contracted with AKT to create a new vision and values for their
ITS STRATEGIC PLAN. ITS Strategic Plan
 2017 2020 ITS STRATEGIC PLAN ITS Strategic Plan 2017 2020 p. 1 ITS Strategic Plan 2017 2020 p. 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Letter Of Introduction... 4 Who We Are... 6 Our Vision... 6 Our Mission... 6 Our Principles...
2017 2020 ITS STRATEGIC PLAN ITS Strategic Plan 2017 2020 p. 1 ITS Strategic Plan 2017 2020 p. 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Letter Of Introduction... 4 Who We Are... 6 Our Vision... 6 Our Mission... 6 Our Principles...
D E P A R T M E N T O F T H E N A V Y I N T E R N A T I O N A L P R O G R A M S OFFICE STRATEGIC GUIDANCE 2019
 D E P A R T M E N T O F T H E N A V Y I N T E R N A T I O N A L P R O G R A M S OFFICE STRATEGIC GUIDANCE 2019 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for Public Release; distribution is unlimited. 1 VISION
D E P A R T M E N T O F T H E N A V Y I N T E R N A T I O N A L P R O G R A M S OFFICE STRATEGIC GUIDANCE 2019 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for Public Release; distribution is unlimited. 1 VISION
President and Chief Executive Officer Seattle, Washington
 President and Chief Executive Officer Seattle, Washington EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Group Health Foundation, a new, groundbreaking 501(c)(4) philanthropic organization committed to shaping and advancing the work
President and Chief Executive Officer Seattle, Washington EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Group Health Foundation, a new, groundbreaking 501(c)(4) philanthropic organization committed to shaping and advancing the work
Levers of Organizational Change
 Levers of Organizational Change 2 The Impact of Performance Management and First-Line Leaders: On Culture and Organizational Change Overcoming the Barriers Organizations, regardless of institutional size
Levers of Organizational Change 2 The Impact of Performance Management and First-Line Leaders: On Culture and Organizational Change Overcoming the Barriers Organizations, regardless of institutional size
Miles CPA Review: BEC Q Updates for 2017 Edition
 Miles CPA Review Miles CPA Review: BEC Q2 2018 Updates for 2017 Edition Summary of updates: - New version CPA exam structure (w.e.f. April 2017) Time management on the exam - BEC-1.3 Enterprise Risk Management
Miles CPA Review Miles CPA Review: BEC Q2 2018 Updates for 2017 Edition Summary of updates: - New version CPA exam structure (w.e.f. April 2017) Time management on the exam - BEC-1.3 Enterprise Risk Management
Strengthening Organizational Health and Performance in Government
 A Working Paper by the Standing Panel on Executive Organization and Management NATIONAL ACADEMY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION January 2018 Strengthening Organizational Health and Performance in Government Accompanying
A Working Paper by the Standing Panel on Executive Organization and Management NATIONAL ACADEMY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION January 2018 Strengthening Organizational Health and Performance in Government Accompanying
Chicagoland Learning Leaders' Copy
 How the New Workplace Analytics Will Revitalize Your Organization 2012 Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation Adapted by permission of Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation ISBN: 978-1-4221-6639-0
How the New Workplace Analytics Will Revitalize Your Organization 2012 Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation Adapted by permission of Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation ISBN: 978-1-4221-6639-0
CSR / Sustainability Governance and Management Assessment By Coro Strandberg President, Strandberg Consulting
 Introduction CSR / Sustainability Governance and Management Assessment By Coro Strandberg President, Strandberg Consulting www.corostrandberg.com November 2015 Companies which adopt CSR or sustainability
Introduction CSR / Sustainability Governance and Management Assessment By Coro Strandberg President, Strandberg Consulting www.corostrandberg.com November 2015 Companies which adopt CSR or sustainability
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
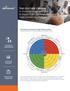 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Transformatio. competency model. Health Leadership Competency Model 3.0. updated, career-spanning. for health sector leaders
 Transformatio National Center Healthcare Leadership Health Leadership Competency Model 3.0 updated, career-spanning competency model for health sector leaders Executive Summary The National Center for
Transformatio National Center Healthcare Leadership Health Leadership Competency Model 3.0 updated, career-spanning competency model for health sector leaders Executive Summary The National Center for
Department of Defense INSTRUCTION
 Department of Defense INSTRUCTION NUMBER 1400.25, Volume 2011 May 7, 2016 USD(P&R) SUBJECT: DoD Civilian Personnel Management System: Defense Civilian Intelligence Personnel System (DCIPS) Performance
Department of Defense INSTRUCTION NUMBER 1400.25, Volume 2011 May 7, 2016 USD(P&R) SUBJECT: DoD Civilian Personnel Management System: Defense Civilian Intelligence Personnel System (DCIPS) Performance
Government-Wide Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2011
 Government-Wide Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2011 Our Nation derives strength from the diversity of its population and from its commitment to equal opportunity for all. We are at our best when
Government-Wide Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2011 Our Nation derives strength from the diversity of its population and from its commitment to equal opportunity for all. We are at our best when
The New Engagement: A Bold Statement of Colliding Concepts Transcending Traditional Solutions
 The New Engagement: A Bold Statement of Colliding Concepts Transcending Traditional Solutions North Carolina State University Office of Outreach & Engagement NC STATE UNIVERSITY VISION, MISSION, VALUES
The New Engagement: A Bold Statement of Colliding Concepts Transcending Traditional Solutions North Carolina State University Office of Outreach & Engagement NC STATE UNIVERSITY VISION, MISSION, VALUES
Stephen Welby Director, Systems Engineering Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (AT&L)
 Stephen Welby Director, Systems Engineering Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (AT&L) DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A -- Cleared for public release by OSR on 22 October2010 SR 11-S-0183 10/26/10 1 We are
Stephen Welby Director, Systems Engineering Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (AT&L) DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A -- Cleared for public release by OSR on 22 October2010 SR 11-S-0183 10/26/10 1 We are
Federal Segment Architecture Methodology Overview
 Federal Segment Architecture Methodology Background In January 2008, the Federal Segment Architecture Working Group (FSAWG) was formed as a sub-team of the Federal CIO Council s Architecture and Infrastructure
Federal Segment Architecture Methodology Background In January 2008, the Federal Segment Architecture Working Group (FSAWG) was formed as a sub-team of the Federal CIO Council s Architecture and Infrastructure
ADVISORY COUNCIL SUMMIT
 ADVISORY COUNCIL SUMMIT 9/11/18 Agenda 1. Welcome and Introductions 2. Human Resources Vision, Benefits & Philosophy 3. Project Recalibration Details 4. Job Descriptions & Compensation Infrastructure Development
ADVISORY COUNCIL SUMMIT 9/11/18 Agenda 1. Welcome and Introductions 2. Human Resources Vision, Benefits & Philosophy 3. Project Recalibration Details 4. Job Descriptions & Compensation Infrastructure Development
DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY
 DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY The Nation s Combat Logistics Support Agency PEOPLE AND CULTURE PLAN Human Capital Management in the Defense Logistics Agency DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY MESSAGE FROM THE DIRECTOR
DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY The Nation s Combat Logistics Support Agency PEOPLE AND CULTURE PLAN Human Capital Management in the Defense Logistics Agency DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY MESSAGE FROM THE DIRECTOR
THE WHITE HOUSE. Office of the Press Secretary. For Immediate Release October 5, October 5, 2016
 THE WHITE HOUSE Office of the Press Secretary For Immediate Release October 5, 2016 October 5, 2016 MEMORANDUM FOR THE HEADS OF EXECUTIVE DEPARTMENTS AND AGENCIES SUBJECT: Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
THE WHITE HOUSE Office of the Press Secretary For Immediate Release October 5, 2016 October 5, 2016 MEMORANDUM FOR THE HEADS OF EXECUTIVE DEPARTMENTS AND AGENCIES SUBJECT: Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
NASA Transformation. NASA Transformation. March One TEAM, One JOURNEY, One NASA Building the Future Together
 NASA Transformation March 2005 One TEAM, One JOURNEY, One NASA Building the Future Together NASA Transformation 1 AGENDA IMPERATIVE FOR TRANSFORMATION TRANSFORMATION and THE NASA FAMILY TRANSFORMATION
NASA Transformation March 2005 One TEAM, One JOURNEY, One NASA Building the Future Together NASA Transformation 1 AGENDA IMPERATIVE FOR TRANSFORMATION TRANSFORMATION and THE NASA FAMILY TRANSFORMATION
DIVERSITY & INCLUSION STRATEGIC PLAN,
 DIVERSITY & INCLUSION STRATEGIC PLAN, 2018-2021 October 2018 CONTENTS Message from the Chair 1 Introduction 2 D&I Vision 2 D&I Objectives & Outcomes 3 D&I Strategies & Actions 4 D&I Timelines & Milestones
DIVERSITY & INCLUSION STRATEGIC PLAN, 2018-2021 October 2018 CONTENTS Message from the Chair 1 Introduction 2 D&I Vision 2 D&I Objectives & Outcomes 3 D&I Strategies & Actions 4 D&I Timelines & Milestones
Core Values and Concepts
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Accion Venture Lab Job Description Guide
 Accion Venture Lab Job Description Guide Overview This document intends to demonstrate best practices in crafting a job description - Please be sure to adapt your job description to include skills and
Accion Venture Lab Job Description Guide Overview This document intends to demonstrate best practices in crafting a job description - Please be sure to adapt your job description to include skills and
S & T Management Core Competency Profile
 (Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
(Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
Concept of Operations. Disaster Cycle Services Program Essentials DCS WC OPS PE
 Concept of Operations Disaster Cycle Services Program Essentials DCS WC OPS PE October 2014 Change Log Date Page(s) Section Change Owner: Disaster Cycle Services 2 Change Log... 2 Introduction... 4 Purpose...
Concept of Operations Disaster Cycle Services Program Essentials DCS WC OPS PE October 2014 Change Log Date Page(s) Section Change Owner: Disaster Cycle Services 2 Change Log... 2 Introduction... 4 Purpose...
DOD INSTRUCTION BUSINESS SYSTEMS REQUIREMENTS AND ACQUISITION
 DOD INSTRUCTION 5000.75 BUSINESS SYSTEMS REQUIREMENTS AND ACQUISITION Originating Component: Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment Effective: February 2, 2017 Change
DOD INSTRUCTION 5000.75 BUSINESS SYSTEMS REQUIREMENTS AND ACQUISITION Originating Component: Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment Effective: February 2, 2017 Change
UC Core Competency Model
 UC Core Competency Model Developed and Endorsed by: UC Learning and Development Consortium Chief Human Resources Officers Date: May 2011 University of California Staff Employees Core Competencies Communication
UC Core Competency Model Developed and Endorsed by: UC Learning and Development Consortium Chief Human Resources Officers Date: May 2011 University of California Staff Employees Core Competencies Communication
BBA VIII Semester. Strategic Management. POST RAJ POKHAREL M.Phil. (TU) 01/2010), Ph.D. in Progress
 BBA VIII Semester Strategic Management POST RAJ POKHAREL M.Phil. (TU) 01/2010), Ph.D. in Progress 1 Institutionalizing Strategy Institutionalizing Strategy Concepts, Structuring an effective organization,
BBA VIII Semester Strategic Management POST RAJ POKHAREL M.Phil. (TU) 01/2010), Ph.D. in Progress 1 Institutionalizing Strategy Institutionalizing Strategy Concepts, Structuring an effective organization,
MGM RESORTS INTERNATIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES
 MGM RESORTS INTERNATIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES Mission, Vision, Core Values and People Philosophy Our Mission MGM Resorts International is the leader in entertainment and hospitality - a diverse collection
MGM RESORTS INTERNATIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES Mission, Vision, Core Values and People Philosophy Our Mission MGM Resorts International is the leader in entertainment and hospitality - a diverse collection
CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS
 CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS The Criteria are built on the following set of interrelated core values and concepts: visionary leadership customer-driven excellence organizational and personal learning valuing
CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS The Criteria are built on the following set of interrelated core values and concepts: visionary leadership customer-driven excellence organizational and personal learning valuing
Sponsor/CRO Partnership Optimization
 Insight Brief Sponsor/CRO Partnership Optimization Developing a CRO Governance Model Geoff Garabedian, Vice President and Managing Director, Consulting at Quintiles Josh Samon, Principal Life Sciences
Insight Brief Sponsor/CRO Partnership Optimization Developing a CRO Governance Model Geoff Garabedian, Vice President and Managing Director, Consulting at Quintiles Josh Samon, Principal Life Sciences
Individual Report for Maria Sample
 Individual Report for Maria Sample 360 Table of Contents 2 3 Section 1: The New HR Competency Model 6 Section 2: Understanding Your Report 7 Section 3: Demographic Information 9 Section 4: Summary of Domains
Individual Report for Maria Sample 360 Table of Contents 2 3 Section 1: The New HR Competency Model 6 Section 2: Understanding Your Report 7 Section 3: Demographic Information 9 Section 4: Summary of Domains
Table of Contents. 3 Foreword. 4 Shared Vision and Common Mission. 5 Introduction. 6 Strategic Plan
 Table of Contents 3 Foreword 4 Shared Vision and Common Mission 5 Introduction 6 Strategic Plan 7 Goal 1 - Loss Prevention (Objectives/Action Plans) 8 Goal 2 - Safety Culture (Objectives/Action Plans)
Table of Contents 3 Foreword 4 Shared Vision and Common Mission 5 Introduction 6 Strategic Plan 7 Goal 1 - Loss Prevention (Objectives/Action Plans) 8 Goal 2 - Safety Culture (Objectives/Action Plans)
WELCOME TO THE. PART 2 Creating Lifelong Learning Experiences for the Government Workforce
 WELCOME TO THE PART 2 Creating Lifelong Learning Experiences for the Government Workforce It used to be that you d learn through young adulthood and then enter the workforce. Now, learning and work are
WELCOME TO THE PART 2 Creating Lifelong Learning Experiences for the Government Workforce It used to be that you d learn through young adulthood and then enter the workforce. Now, learning and work are
Five Guiding Principles of a Successful Center of Excellence
 Five Guiding Principles of a Successful Center of Excellence What is a Center of Excellence? At some point in their life cycle, most companies find it beneficial to develop a Center of Excellence (CoE).
Five Guiding Principles of a Successful Center of Excellence What is a Center of Excellence? At some point in their life cycle, most companies find it beneficial to develop a Center of Excellence (CoE).
POSITION NARRATIVE Vice President of Integration & Learning First 5 LA
 BACKGROUND POSITION NARRATIVE Vice President of Integration & Learning First 5 LA First 5 LA is a leading early childhood advocate organization created by California voters to invest Proposition 10 tobacco
BACKGROUND POSITION NARRATIVE Vice President of Integration & Learning First 5 LA First 5 LA is a leading early childhood advocate organization created by California voters to invest Proposition 10 tobacco
Competencies. Working in Partnership. Creativity and Innovation Organisational and People Development
 Competencies Leadership Competency Framework - Summary Technical Expertise Demonstrates an avid interest in continuously enhancing current skills and learning new ones; applies advanced functional or technical
Competencies Leadership Competency Framework - Summary Technical Expertise Demonstrates an avid interest in continuously enhancing current skills and learning new ones; applies advanced functional or technical
a GAO GAO DEFENSE MANAGEMENT Tools for Measuring and Managing Defense Agency Performance Could Be Strengthened
 GAO United States Government Accountability Office Report to the Committee on Armed Services, U.S. Senate September 2004 DEFENSE MANAGEMENT Tools for Measuring and Managing Defense Agency Performance Could
GAO United States Government Accountability Office Report to the Committee on Armed Services, U.S. Senate September 2004 DEFENSE MANAGEMENT Tools for Measuring and Managing Defense Agency Performance Could
CACI International Inc. Jefferies Technology Conference May 2017
 CACI International Inc Jefferies Technology Conference May 2017 Forward-looking Statements There are statements made herein which do not address historical facts and, therefore, could be interpreted to
CACI International Inc Jefferies Technology Conference May 2017 Forward-looking Statements There are statements made herein which do not address historical facts and, therefore, could be interpreted to
BUSINESS AND ADMINISTRATIVE (BAS) DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ STRATEGIC PLAN
 BUSINESS AND ADMINISTRATIVE (BAS) DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ STRATEGIC PLAN 2015-20 BAS exists to advance education, exploration and engagement TABLE OF CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 3 I.
BUSINESS AND ADMINISTRATIVE (BAS) DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ STRATEGIC PLAN 2015-20 BAS exists to advance education, exploration and engagement TABLE OF CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 3 I.
Korn Ferry Executive to Leader Institute. Accelerating development for senior executives and enterprise leaders.
 Korn Ferry Executive to Leader Institute Accelerating development for senior executives and enterprise leaders. Are your senior leaders ready for enterprise leadership? The transition from executive to
Korn Ferry Executive to Leader Institute Accelerating development for senior executives and enterprise leaders. Are your senior leaders ready for enterprise leadership? The transition from executive to
International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) CEO
 International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) CEO Profile of CEO with the International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP), The Hague - the Netherlands Organization The International Pharmaceutical Federation
International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) CEO Profile of CEO with the International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP), The Hague - the Netherlands Organization The International Pharmaceutical Federation
U.S. Army Audit Agency
 U.S. Army Audit Agency Strategic Plan With Detailed FYs 2001 2005 Table of Contents Mission and Vision 1 Values 2 Trends and Assumptions 3 Overview of the Goals 4 Strategies, and Performance Measures 5
U.S. Army Audit Agency Strategic Plan With Detailed FYs 2001 2005 Table of Contents Mission and Vision 1 Values 2 Trends and Assumptions 3 Overview of the Goals 4 Strategies, and Performance Measures 5
United States Military Entrance Processing Command Strategic Plan
 United States Military Entrance Processing Command Strategic Plan 2016-2026 January 2016 Table of Contents Item Page No. Commander s Intent 1 USMEPCOM s Mission, Vision, Values, and Goals 2 Strategic Alignment
United States Military Entrance Processing Command Strategic Plan 2016-2026 January 2016 Table of Contents Item Page No. Commander s Intent 1 USMEPCOM s Mission, Vision, Values, and Goals 2 Strategic Alignment
THE STRATEGIC MINDSET
 the THE STRATEGIC MINDSET APPLYING STRATEGIC THINKING SKILLS FOR ORGANIZATIONAL SUCCESS Strategy and its consistent application by managers and leaders are keys to long-term organizational success. Strategy
the THE STRATEGIC MINDSET APPLYING STRATEGIC THINKING SKILLS FOR ORGANIZATIONAL SUCCESS Strategy and its consistent application by managers and leaders are keys to long-term organizational success. Strategy
PART 1: INTRODUCTION. Purpose of the BIZBOK Guide. What is Business Architecture?
 PART 1: INTRODUCTION Purpose of the BIZBOK Guide A Guide to the Business Architecture Body of Knowledge (the BIZBOK Guide) provides a practical guide for business architecture practitioners and individuals
PART 1: INTRODUCTION Purpose of the BIZBOK Guide A Guide to the Business Architecture Body of Knowledge (the BIZBOK Guide) provides a practical guide for business architecture practitioners and individuals
From Dictionary.com. Risk: Exposure to the chance of injury or loss; a hazard or dangerous chance
 Sharon Hale and John Argodale May 28, 2015 2 From Dictionary.com Enterprise: A project undertaken or to be undertaken, especially one that is important or difficult or that requires boldness or energy
Sharon Hale and John Argodale May 28, 2015 2 From Dictionary.com Enterprise: A project undertaken or to be undertaken, especially one that is important or difficult or that requires boldness or energy
DCMA Instruction 4201, Civilian Personnel
 DCMA Instruction 4201 Civilian Personnel Office of Primary Responsibility Human Capital Directorate in concert with Talent Management Capability Effective: July 20, 2018 Releasability: New Issuance: Incorporates:
DCMA Instruction 4201 Civilian Personnel Office of Primary Responsibility Human Capital Directorate in concert with Talent Management Capability Effective: July 20, 2018 Releasability: New Issuance: Incorporates:
Strategic Asset Management Plan
 Strategic Asset Management Plan Prepared for Town of Oakville December 2017 CH2M HILL Canada Limited 245 Consumers Road Suite 400 Toronto, ON M2J 1R3 CA Contents Section Page Acronyms and Abbreviations...
Strategic Asset Management Plan Prepared for Town of Oakville December 2017 CH2M HILL Canada Limited 245 Consumers Road Suite 400 Toronto, ON M2J 1R3 CA Contents Section Page Acronyms and Abbreviations...
INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT. Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture
 INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture June 2011 Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture describes the key elements of organizational culture and business
INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture June 2011 Foundation for an Effective Safety Culture describes the key elements of organizational culture and business
Mid Michigan Community College. Strategic Plan
 Mid Michigan Community College Strategic Plan 2011-2015 The Foundations of Strategic Planning Anything built to last must have a solid foundation. This strategic plan was built on the principles, concepts,
Mid Michigan Community College Strategic Plan 2011-2015 The Foundations of Strategic Planning Anything built to last must have a solid foundation. This strategic plan was built on the principles, concepts,
2018 LeadingAge Texas Awards Program
 2018 LeadingAge Texas Awards Program ALL CATEGORIES & CRITERIA AWARD OF HONOR The Award of Honor, LeadingAge Texas s highest award is presented to one distinguished individual who has provided outstanding
2018 LeadingAge Texas Awards Program ALL CATEGORIES & CRITERIA AWARD OF HONOR The Award of Honor, LeadingAge Texas s highest award is presented to one distinguished individual who has provided outstanding
ORGANIZED FOR BUSINESS: BUILDING A CONTEMPORARY IT OPERATING MODEL
 ORGANIZED FOR BUSINESS: BUILDING A CONTEMPORARY IT OPERATING MODEL Time is running out for the traditional, monopolistic IT model now that users have so many alternatives readily available. Today s enterprises
ORGANIZED FOR BUSINESS: BUILDING A CONTEMPORARY IT OPERATING MODEL Time is running out for the traditional, monopolistic IT model now that users have so many alternatives readily available. Today s enterprises
Our Commitment to Corporate Responsibility
 Our Commitment to Corporate Responsibility At Symantec, corporate responsibility and positive societal impact are core to our business strategy. Integrity is a cornerstone of our mission and values, and
Our Commitment to Corporate Responsibility At Symantec, corporate responsibility and positive societal impact are core to our business strategy. Integrity is a cornerstone of our mission and values, and
Platinum (Organization Award) Based on the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award
 Platinum (Organization Award) Based on the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award PURPOSE: The Mid-South Quality and Productivity Center presents a Regional Quality Cup Award which is aligned with the
Platinum (Organization Award) Based on the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award PURPOSE: The Mid-South Quality and Productivity Center presents a Regional Quality Cup Award which is aligned with the
2017 AIR FORCE MATERIEL COMMAND STRATEGIC PLAN
 i TABLE OF CONTENTS 2017 AIR FORCE MATERIEL COMMAND STRATEGIC PLAN Commander s Intent... ii Purpose... 2 Air Force Strategic Guidance... 3 AFMC Mission and Vision... 4 AFMC Way Ahead Goals and Objectives...
i TABLE OF CONTENTS 2017 AIR FORCE MATERIEL COMMAND STRATEGIC PLAN Commander s Intent... ii Purpose... 2 Air Force Strategic Guidance... 3 AFMC Mission and Vision... 4 AFMC Way Ahead Goals and Objectives...
Ed.D. in Organizational Leadership Core Leadership Understandings. Program Competencies
 Ed.D. in Organizational Leadership Core Leadership Understandings Program Competencies Some thoughts regarding the core leadership understandings follow: The competencies listed for each core leadership
Ed.D. in Organizational Leadership Core Leadership Understandings Program Competencies Some thoughts regarding the core leadership understandings follow: The competencies listed for each core leadership
CORROSION MANAGEMENT MATURITY MODEL
 CORROSION MANAGEMENT MATURITY MODEL CMMM Model Definition AUTHOR Jeff Varney Executive Director APQC Page 1 of 35 TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW... 5 I. INTRODUCTION... 6 1.1 The Need... 6 1.2 The Corrosion
CORROSION MANAGEMENT MATURITY MODEL CMMM Model Definition AUTHOR Jeff Varney Executive Director APQC Page 1 of 35 TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW... 5 I. INTRODUCTION... 6 1.1 The Need... 6 1.2 The Corrosion
Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara
 Leads Innovation Leadership Styles Manages Change Models Integrity, Trust & Transparency Strategic Thinking and Planning Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara Conflict Management
Leads Innovation Leadership Styles Manages Change Models Integrity, Trust & Transparency Strategic Thinking and Planning Manager, Supervisor & CEMA Skill Set Model County of Santa Clara Conflict Management
How a project approach will build change management capability across your organization
 capability across your How a project approach will build change management capability across your Prosci Webinar How a project approach will build change management Enterprise Change Management Organizational
capability across your How a project approach will build change management capability across your Prosci Webinar How a project approach will build change management Enterprise Change Management Organizational
Strategic Plan. Uniting to care & cure
 2017-2020 Strategic Plan Uniting to care & cure Table of Contents Message from the President & CEO Page 2 Overview Page 3 Mission Page 4 Core Values Page 5 2017-2020 Objectives & Strategies Page 6 Mission
2017-2020 Strategic Plan Uniting to care & cure Table of Contents Message from the President & CEO Page 2 Overview Page 3 Mission Page 4 Core Values Page 5 2017-2020 Objectives & Strategies Page 6 Mission
the council initiative on public engagement
 public engagement at the city of edmonton share your voice shape our city the council initiative on public engagement new public engagement practice and implementation roadmap final report CITY OF EDMONTON
public engagement at the city of edmonton share your voice shape our city the council initiative on public engagement new public engagement practice and implementation roadmap final report CITY OF EDMONTON
The School District of Lee County Division of Operations
 The School District of Lee County Division of Operations District Based Administrator Evaluation System 2013-2014 Academic Year Table of Contents District Based Administrator Evaluation System Overview...
The School District of Lee County Division of Operations District Based Administrator Evaluation System 2013-2014 Academic Year Table of Contents District Based Administrator Evaluation System Overview...
Cross-Service Collaboration
 Cross-Service Collaboration Yields Efficiencies for Diminishing Resources Jay Mandelbaum Tina M. Patterson Chris Radford Allen S. Alcorn William F. Conroy III 8 Diminishing manufacturing sources and material
Cross-Service Collaboration Yields Efficiencies for Diminishing Resources Jay Mandelbaum Tina M. Patterson Chris Radford Allen S. Alcorn William F. Conroy III 8 Diminishing manufacturing sources and material
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
ROCKY MOUNTAIN PERFORMANCE EXCELLENCE POSITION DESCRIPTION FOR THE EXECUTIVE/MANAGING DIRECTOR
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN PERFORMANCE EXCELLENCE POSITION DESCRIPTION FOR THE EXECUTIVE/MANAGING DIRECTOR ABOUT THE ORGANIZATION: Rocky Mountain Performance Excellence (RMPEx) is a Colorado nonprofit corporation
ROCKY MOUNTAIN PERFORMANCE EXCELLENCE POSITION DESCRIPTION FOR THE EXECUTIVE/MANAGING DIRECTOR ABOUT THE ORGANIZATION: Rocky Mountain Performance Excellence (RMPEx) is a Colorado nonprofit corporation
2019 LeadingAge Texas Awards Program ALL CATEGORIES & CRITERIA
 2019 LeadingAge Texas Awards Program ALL CATEGORIES & CRITERIA Awards marked * indicate both individuals AND organizations/groups are eligible to be nominated. AWARD OF HONOR The Award of Honor, LeadingAge
2019 LeadingAge Texas Awards Program ALL CATEGORIES & CRITERIA Awards marked * indicate both individuals AND organizations/groups are eligible to be nominated. AWARD OF HONOR The Award of Honor, LeadingAge
Core Element Assessment Tool
 Core Element Assessment Tool The California Accountable Community for Health (CACHI) core element assessment tool was designed to help local collaboratives develop a shared understanding of their strengths,
Core Element Assessment Tool The California Accountable Community for Health (CACHI) core element assessment tool was designed to help local collaboratives develop a shared understanding of their strengths,
Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness
 DOD INSTRUCTION 1400.25, VOLUME 920 DEFENSE CIVILIAN PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SENIOR EXECUTIVE SERVICE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND COMPENSATION POLICY Originating Component: Office of the Under
DOD INSTRUCTION 1400.25, VOLUME 920 DEFENSE CIVILIAN PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SENIOR EXECUTIVE SERVICE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND COMPENSATION POLICY Originating Component: Office of the Under
RESULTS. SAMPLE OF AN ACTUAL REPORT (PART II) Name of site left off. CERTIFIED: No Yes
 MC WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Technical Assistance Report For XXX Center or Organization From the Certification Subcommittee Of the Quality Assurance Committee DATE SAMPLE OF AN ACTUAL REPORT (PART II)
MC WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT BOARD Technical Assistance Report For XXX Center or Organization From the Certification Subcommittee Of the Quality Assurance Committee DATE SAMPLE OF AN ACTUAL REPORT (PART II)
Prepared for: Joe Sample 2/2/15
 Leadership Potential Inventory Report Prepared for: Joe Sample 2/2/ Introduction Your Leadership Potential Inventory Report collects feedback about your behavior and performance from you and your supervisor.
Leadership Potential Inventory Report Prepared for: Joe Sample 2/2/ Introduction Your Leadership Potential Inventory Report collects feedback about your behavior and performance from you and your supervisor.
Strategic Intent ONE AGENCY ONE COMMUNITY
 Strategic Intent 2007-2011 ONE AGENCY ONE COMMUNITY CENTRAL INTELLIGENCE AGENCY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Director s Message This Strategic Intent, which benefited greatly from [employee] comments and suggestions,
Strategic Intent 2007-2011 ONE AGENCY ONE COMMUNITY CENTRAL INTELLIGENCE AGENCY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Director s Message This Strategic Intent, which benefited greatly from [employee] comments and suggestions,
To achieve our vision of helping patients around the world, we are creating an organization that can fully leverage diversity.
 Labor At a Glance To achieve our vision of helping patients around the world, we are creating an organization that can fully leverage diversity. Takeda is endeavoring to attract and develop diverse global
Labor At a Glance To achieve our vision of helping patients around the world, we are creating an organization that can fully leverage diversity. Takeda is endeavoring to attract and develop diverse global
FINANCE & BUSINESS AT PENN STATE...
 Table of Contents FINANCE & BUSINESS AT PENN STATE... 3 Mission & Vision... 3 Organizational Profile... 3 F&B Situational Analysis... 3 F&B Alignment with University Priorities... 4 STRATEGIC PRIORITIES...
Table of Contents FINANCE & BUSINESS AT PENN STATE... 3 Mission & Vision... 3 Organizational Profile... 3 F&B Situational Analysis... 3 F&B Alignment with University Priorities... 4 STRATEGIC PRIORITIES...
DCMA Instruction Stewardship
 DCMA Instruction 4301 Stewardship Office of Primary Responsibility Stewardship Capability Effective: July 18, 2018 Releasability: Cleared for public release Incorporates: DCMA-INST 117, Government Purchase
DCMA Instruction 4301 Stewardship Office of Primary Responsibility Stewardship Capability Effective: July 18, 2018 Releasability: Cleared for public release Incorporates: DCMA-INST 117, Government Purchase
Workshops and Short Session Topics
 Workshops and Short Session Topics We design workshops, short conference sessions and keynotes that fit within your culture and address your specific needs. Below is a list of our most requested topics
Workshops and Short Session Topics We design workshops, short conference sessions and keynotes that fit within your culture and address your specific needs. Below is a list of our most requested topics
