Business Process Analysis of Export of Plastic Kitchenware and Tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan
|
|
|
- Giles Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism in Bangladesh: Baseline study series #1 Business Process Analysis of Export of Plastic Kitchenware and Tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan
2 The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is the regional development arm of the United Nations and serves as the main economic and social development centre for the United Nations in Asia and the Pacific. Its mandate is to foster cooperation between its 53 members and 9 associate members. ESCAP provides the strategic link between global and country-level programmes and issues. It supports Governments of countries in the region in consolidating regional positions and advocates regional approaches to meeting the region s unique socioeconomic challenges in a globalizing world. The ESCAP secretariat is in Bangkok. Please visit the ESCAP website at < for further information. The darker areas of the map are ESCAP members and associate members.
3 Business Process Analysis of export of plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan The 1 st report of a series of 5 studies on Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism (TTFMM) in Bangladesh Copyright United Nations 2017 June 2017, Bangkok, Thailand Disclaimers All rights reserved. The opinions, figures and estimates set forth in this publication are the responsibility of the authors and should not be considered as reflecting the views of carrying the endorsement of the United Nations or the Asian Development Bank. Any errors are the responsibility of the authors. Mention of firms names and commercial products does not imply the endorsement of the United Nations or the Asian Development Bank. The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the United Nations or the Asian Development Bank concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area, or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Where the designation country or area appears, it covers countries, territories, cities or areas. References to dollars ($) are to United States dollars unless otherwise stated. Bibliographical and other references have, wherever possible, been verified. The United Nations and the Asian Development Bank bear no responsibility for the availability or functioning of URLs. All the material in this publication may be freely quoted or reprinted, but acknowledgement is required, and a copy of the publication containing the quotation of reprint should be sent to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) Publications Office. The use of this publication for any commercial purposes, including resale, is prohibited unless permission is first obtained from ESCAP and the Asian Development Bank. Requests for permission should state the purpose and the extent of reproduction. This publication has been issued without formal editing. i P a g e
4 CONTENTS Figures and Tables iii Preface vi Acknowledgements vii Executive Summary viii Chapter 1. Introduction 1 Chapter 2. Overview of Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation 3 Chapter 3. Data Collection and Validation 6 Chapter 4. Analysis and Findings As-is trade process and procedures Use-case diagram Core Business Processes Analysis of key indicators Time for export Costs for export Number of procedures for export Number of documents for export Diagnosis and Recommendations for improvement 57 Chapter 5. Summary and Conclusions Proposed interventions to improve trade facilitation Short-term interventions Long-term interventions Utilisation of the Report 74 Appendix 1. List of participants of workshops for the TTFMM baseline study in Bangladesh _ 75 ii P a g e
5 Figures and Tables Figures Figure 2. 1 A Step-by-step approach to implementing trade facilitation measures...3 Figure 2. 2 Buy-Ship-Pay Model...4 Figure 2. 3 Examples of Use-Case and Activity Diagrams...5 Figure 4. 1 Use-Case Diagram of Exporting Plastic kitchenware and tableware to Bhutan...8 Figure 4. 2 Conclude sales contract and trade terms use-case diagram...9 Figure 4. 3 Conclude sales contract and trade terms activity diagram...9 Figure 4. 4 Use-case diagram of core business processes in ship process area Figure 4. 5 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority use-case diagram Figure 4. 6 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority activity diagram Figure 4. 7 Obtain Tax Identification Number use-case diagram Figure 4. 8 Obtain Tax Identification Number activity diagram Figure 4. 9 Open Bank Account against the Trade License use-case diagram Figure Open Bank Account against the trade license activity diagram Figure Obtain Membership in a local business association use-case diagram Figure Obtain Membership in a local business association/chamber activity diagram Figure Obtain Export Registration Certificate use-case diagram Figure Obtain Export Registration Certificate activity diagram Figure Obtain VAT Registration Certificate use-case diagram Figure Obtain VAT Registration Certificate activity diagram Figure Prepare export documents use-case diagram Figure Prepare export documents activity diagram Figure Arrange Transport use-case diagram Figure Arrange Transport activity diagram Figure Arrange Certificate of Origin use-case diagram Figure Arrange Certificate of Origin activity diagram Figure Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin use-case diagram Figure Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin activity diagram Figure Arrange VAT Declaration use-case diagram Figure Arrange VAT Declaration activity diagram Figure Appointment of C&F Agent use-case diagram Figure Appointment of C&F Agent activity diagram Figure Transport goods to Port of Departure use-case diagram Figure Transport goods to Port of Departure activity diagram Figure Provide Customs Declaration use-case diagram Figure Provide Customs Declaration activity diagram Figure Customs Inspection and Clear Goods use-case diagram Figure Customs Inspection and Clear Goods activity diagram Figure Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer use-case diagram Figure Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer activity diagram 41 iii P a g e
6 Figure Border Crossing of Export goods use-case diagram Figure Border Crossing of Export goods activity diagram Figure Sending signed export documents back to Exporter use-case diagram Figure Sending signed export documents back to Exporter activity diagram Figure Use case diagram of core business processes in Pay process area Figure Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer use-case diagram Figure Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer activity diagram Figure Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) use-case diagram Figure Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) activity diagram Figure Time-procedure chart for export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware to Bhutan through Burimari Land Port Figure Costs of the trade procedures excluding one-time procedures Tables Table 3. 1 Time frame for implementing TTFMM baseline study...6 Table 4. 1 Conclude sales contract and trade terms Process Description Table 4. 2 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority Process Description Table 4. 3 Obtain Tax Identification Number Process Description Table 4. 4 Open Bank Account against the trade license Process Description Table 4. 5 Obtain Membership in a local business association/chamber Process Description Table 4. 6 Obtain Export Registration Certificate Process Description Table 4.7 Obtain VAT Registration Certificate Process Description Table 4. 8 Prepare export documents Process Description Table 4. 9 Arrange Transport Process Description Table Arrange Certificate of Origin Process Description Table Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin Process Description Table Arrange VAT Declaration Process Description Table Appointment of C&F Agent Process Description Table Transport goods to Port of Departure Process Description Table Provide Customs Declaration Process Description Table Customs Inspection and Clear Goods Process Description Table Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer Process Description Table Border Crossing of Export goods Process Description Table Sending signed export documents back to Exporter Process Description Table Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer Process Description Table Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) Process Description Table Processes involved and time required in the export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan Table Costs involved in the export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan iv P a g e
7 Table Documents required for export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan Table Documents submission procedures of export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan Table Export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan by Burimari: Diagnosis and Recommendation v P a g e
8 Preface In the process of undertaking the baseline study of Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism (TTFMM) in Bangladesh, five studies are carried out to provide multiple facets of trade and transport facilitation covering export and import of specific products, corridors and border crossings. A synthesis report is also produced based on five study reports. The current report examines trade process of exporting Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan using Business Process Analysis (BPA) approach. It is a stand-alone document itself and in the meantime the 1 st report of a series of 5 studies that feeds the synthesis report. As such, it needs to be read along with other reports to fully understand the background, key findings and conclusions of the TTFMM baseline study. vi P a g e
9 Acknowledgements In preparing this report, great support was received from the host country which was essential for completion of the study. Contribution from Md Nojibur Rahman, Firoz Shah Alam and Abdul Hakim is gratefully acknowledged. The baseline study and the underlying project were managed by Tengfei Wang from ESCAP and Aileen Pangilinan from ADB under the guidance of Yann Duval and Ronald Antonio Q. Butiong. Tanya E. Marin, Linel Ann Reyes-Tayag, and Alona Mae Agustin from ADB provided support for the logistical arrangement of the workshops. The report was prepared by Mohammad Farhad and Tengfei Wang. Data collection was carried out by Mohammad Farhad and study design and supervision were provided by Tengfei Wang. Participants of the various workshops under the project, as detailed in Appendix 1, substantially contributed their expertise to enhance the quality of the project. Mashuk Al Hossain and Muhammad Minhaz Uddin Pahloan played a crucial role for organizing the TTFMM national validation workshop on 31 July-1 August 2016 in Dhaka, Bangladesh 1. Vyonna Bondi and Ekaterina Silanteva reviewed the report. The TTFMM baseline study is funded under both ADB s Technical Assistance Special Fund and the Japan Fund for Poverty Reduction. 1 vii P a g e
10 Executive Summary The report is focused on analyzing trade process of exporting Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan using Business Process Analysis (BPA) approach. It analyzes as-is trade facilitation, provides diagnosis of bottlenecks and offers a set of recommendations. Mapping current trade procedures is beneficial in the following ways. First, the information presented in this document can be used as instruction for traders, especially the new traders, to carry out the trade process. Second, the information can be directly used when a trade portal is established; and finally, the information provides a fundamental basis for diagnosis of bottlenecks along the trade process. Bottlenecks identified in this report include, among others, repeated submission of the same documents to various government agencies; manual rather than automated or online submission of documents; existence of repetitive or redundant processes and high costs for some trade procedures. Key Recommendations in this report are twofold. In the short term, the key recommendation includes 1) Implementation of online application, approval, issuance and renewal of license/certificate/permit in a number of similar processes; 2) Full operationalisation of all the components of ASYCUDA World at Burimari border crossing points; 3) Removal of repetitive or redundant processes; 4) Reduction of costs burden; and 5) Harmonisation of data and documentary requirements. In the long term, the key measures include 1) Introduction of SWIFT (Single Window Interface for Facilitating Trade); 2) Ensuring legal consistency for the introduction of Single Window/electronic procedures; 3) Transparency in legal requirements; and 4) Establishment of authorized economic operator/ trusted trader program. viii P a g e
11 Chapter 1. Introduction The TTFMM baseline study in Bangladesh was conducted as a part of a broad initiative to establish sustainable trade and transport facilitation monitoring mechanisms (TTFMM) in the country in the long term. The TTFMM project covers not only Bangladesh but also Bhutan and Nepal under the South Asia Sub-regional Economic Cooperation (SASEC) Program. In particular, the TTFMM baseline study aims to: 1) Explain the rationale for establishing TTFMM and key methodology for data collection and analysis. 2) Provide a set of indicators and underlying data on trade and transport facilitation performance in Bangladesh. Such baseline data will ensure that the progress or setback in trade facilitation performance in the country can be benchmarked. 3) Diagnose key bottlenecks and recommendations for removing bottlenecks and simplifying trade procedures. In this respect, the study provides policy recommendations to policy makers and stakeholders. 4) Propose way forward to maintain the sustainability of TTFMM. Sustainability is at the core of the design of TTFMM. The scope of the baseline studies of TTFMM was decided through a series of regional and national training workshops held in Bangkok, Thailand in November 2013, in Dhaka, Bangladesh in April, 2014, Wuhan, China in October 2015 and in Bangkok, Thailand in January A wide range of stakeholders were consulted in this process, as shown in the lists of participants of different meetings in Appendix 1. After extensive exercise and discussion with the relevant stakeholders, it was agreed that the TTFMM baseline study in Bangladesh would cover the following processes, products and trade routes and corridors: (i) Export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan through Dhaka- Rangpur- Burimari- Changrabandha- Jaigaon- Phuentsholing- Thimphu; and (ii) Import of lentil from Nepal to Bangladesh through Kathmandu-Kakarvitta-Fulbari- Banglabandha-Dhaka. More specifically, it was decided that the Business Process analysis (BPA) would cover all the above-mentioned products and corridors, Time Release Study (TRS) would cover border crossings at Burimari and Banglabandha LCS and Time-Cost-Distance (TCD) /Corridor Performance Measurement 1 P a g e
12 and Monitoring (CPMM) would cover the corridors from Dhaka to Burimari and from Banglabandha to Dhaka trade corridors. The report is focused on analysis of trade process and procedures of export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan. It is a stand-alone document itself and the 1 st report of a series of 5 studies and feeds the synthesis TTFMM baseline report on Bangladesh. As such, it needs to be read along with other reports to fully understand the background, key findings and conclusions of the TTFMM baseline study. 2 P a g e
13 Chapter 2. Overview of Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Business Process Analysis (BPA) of Trade Procedures, developed by UNNExT 2 has proved to be an effective tool for providing a detailed understanding of international trade transactions. More than 50 import and export processes in Asia and other regions of the world have been studied since 2009 using BPA. 3 Similar to the existing studies, the UNNExT Business Process Analysis Guide to Simplify Trade Procedures 4 was used to study export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan. According to UN/CEFACT (see Figure 2.1) 5, BPA is recommended as the first step before undertaking other trade facilitation measures related to the simplification, harmonization and automation of trade procedures and documents. Figure 2. 1 A Step-by-step approach to implementing trade facilitation measures E-Single Window & paperless trading Cross-border data harmonization & exchange National data harmonization Documents simplification and alignment Process simplification and harmonization Business Process Analysis Source: UNECE, 2006, Background Paper for UN/CEFACT Symposium on Single Window Common Standards and Interoperability The trade procedures covered by BPA largely fall in the category of Buy-Ship-Pay model recommended by UN/CEFACT (as shown in figure 2.2). In some cases the scope could be confined to selected process(es) according to the priority of the country. 2 More information is available at 3 A summary of the existing studies is available at 4 Detailed information is available at < 5 United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), 2006, Background Paper for UN/CEFACT Symposium on Single Window Common Standards and Interoperability. 3 P a g e
14 Figure 2. 2 Buy-Ship-Pay Model Supplier Intermediary Authorities Customer Buy Ship Pay Prepare for export Export Transport Prepare for import Import Commercial Procedures Transport Procedures Regulatory Procedures Financial Procedures Establish contract Order goods Advise on delivery Request payment Establish transport contract Collect, transport and deliver goods Provide waybill, gods receipt and status reports Obtain export/import licenses, etc. Provide customs declaration Provide cargo declaration Apply trade security procedures Clear goods for import/export Provide credit rating Provide insurance Provide credit Execute payment Issue statements UN/CEFACT Recommendation No. 18 illustrates a simplified view of the international supply chain in the Buy- Ship-Pay model (Box 1). The model identifies the key commercial, logistical, regulatory and payment procedures involved in the international supply chain and provides an overview of the information exchanged between the parties throughout its various steps. Source: One of the key features of the UNNExT Business Process Analysis Guide to Simplify Trade Procedures is the introduction of the Unified Modelling Language (UML) as a standard way to graphically represent the various procedures involved in the trade process (Figure 2. 3). Use of this common standard is essential to providing a systematic description and common language of a procedure that can be understood by all stakeholders involved in international trade transactions, both domestic and foreign. 4 P a g e
15 Figure 2. 3 Examples of Use-Case and Activity Diagrams UML Use-Case Diagram UML Activity Diagram UML Use-Case and Activity Diagrams are used to visualize the captured knowledge of the business processes. The Use-Case Diagram illustrates high-level business processes and the actors associated with each of them. It serves as a frame of reference for further elaboration of business process modelling work. The Activity Diagram, on the other hand, describes activities, inputs, and outputs associated with each business process listed in the Use-Case Diagram. Source: 5 P a g e
16 Chapter 3. Data Collection and Validation The timeframe for implementing TTFMM baseline study in Bangladesh was approximately 14 months and is shown in Table 3.1. The key activities are highlighted below. Sub-regional meeting to plan the baseline study in Wuhan, China Workshop to finalize the plan of the baseline study in Bangkok, Thailand Data collection on BPA Data collection on TRS Data collection on TCD/CPMM TTFMM database, analysis and draft report National results validation meeting Refine TTFMM data and analysis, and finalize study report Table 3. 1 Time frame for implementing TTFMM baseline study The workshops to plan the baseline study in Wuhan, China and Bangkok, Thailand A sub-regional meeting in October 2015 in Wuhan, China to plan the baseline study and discuss the next steps was attended by national consultants and government officials from Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal, and experts from ADB and UNESCAP. Another study planning workshop during which methodologies for BPA, TRS and TCD/CPMM were discussed in detail was held in Bangkok on January Present at the workshop were national consultants of the project, government officers and logistics operators from Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal. Draft questionnaires used for TRS and CPMM were distributed and comprehensively discussed at the workshop, which was instrumental for the actual study. Data collection on BPA The ADB national consultant conducted data collection on selected BPA during October 2015 March 2016 and interviewed key stakeholders located in Dhaka, Rangpur, Burimari and Banglabandha. Following the UNNExT s BPA methodology, information on import and export processes was collected, essentially, through repeated interviews of a number of key informants: exporters, importers, and 6 P a g e
17 intermediaries including public and private sector institutional participants directly involved in the processes being analysed. Whenever required, there were also interviews and consultations with relevant government agencies. Websites of different organisations were also studied to collect published information related to specific procedural requirements, including documents, time and costs and related laws and regulations. National results validation meeting and follow-up activities A national validation workshop was organized by the Bangladesh National Board of Revenue (NBR), in collaboration with ADB and ESCAP from 31 July to 1 August, 2016 in Dhaka, Bangladesh and attended by representatives from relevant government departments and private sector agencies. The project study team presented preliminary study findings and results to stakeholders. The project team considered comments from the workshop in their decision to revise the report. Approximately one month after the meeting, the study team shared the revised reports with the NBR and meeting participants and incorporated further feedback for revision. 7 P a g e
18 Chapter 4. Analysis and Findings 4.1 As-is trade process and procedures Use-case diagram As shown in figure 4.1, there are in total 20 actors involved in exporting Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan. A regular exporter has to complete 15 distinct procedures for exporting Plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan through Burimari LCS. Furthermore, additional 6 one-time procedures are required for a new trader. In other words, a new trader needs to go through 21 procedures to complete export process. Figure Use-case diagram of exporting Plastic Kitchenware and Tableware to Bhutan 8 P a g e
19 4.1.2 Core Business Processes Process area 1: Buy Core business process area 1.1: Conclude sales contract and trade terms Figure 4. 2 Conclude sales contract and trade terms use-case diagram Conclude sales contract and trade terms is the only core business process under the Buy process area for export of Plastic kitchenware and tableware. The Use Case diagram as shown in Figure 4.2 suggests that this core business process requires participation from: Bhutanese importer Bangladeshi exporter Figure 4. 3 Conclude sales contract and trade terms activity diagram 9 P a g e
20 Table Conclude sales contract and trade terms process description Name of the process area 1. Buy Name of the business process 1.1 Conclude sales contract and trade terms Related laws, rules and Incoterms 2010, The Export and Import Control Act 1950, Export regulations Policy , Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1947, Foreign Exchange Regulations (Amendment) Act 2015 Process participant(s) Bhutanese importer Bangladeshi exporter (or Representative) Input and criteria to enter/ Bangladeshi exporter has a list of potential buyers of Plastic begin the business process kitchenware and tableware; Exporter is eligible to export in Bangladesh; Exporter has obtained an ERC (Export Registration Certificate) Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process from CCIE (Office of the Chief Controller of Imports & Exports) Bangladeshi exporter prepares Offer/Quotation comprising price list and sales/delivery terms to inform Bhutanese importer(s) about quoted price and sales terms; Bhutanese Importer receives price offer and sales/delivery terms from the exporter; Importer evaluates exporter s price offer in terms of products cost, quality, quantity and sales/delivery terms; Importer determines whether the offered price and sales/delivery terms are acceptable; If the offered price and sales/delivery terms not acceptable, importer requests exporter to revise the offer; In case of consensus between both the parties, importer confirms intent to purchase; Bangladeshi exporter receives purchase order; Exporter prepares Proforma Invoice and confirms that the plastic kitchenware and tableware will be delivered according to conditions and terms by sending the Proforma Invoice to the Importer; Importer receives the Proforma Invoice. Both sides (Exporter & Importer) have concluded trade contact and sales/delivery terms. Bhutanese Importer received the Proforma Invoice from the Bangladeshi Exporter according to his/her Purchase Order. 3 days 10 P a g e
21 Process Area 2: Ship In the context of export of plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan, the Ship process area consists of 18 core business processes including 6 business processes to meet the general regulatory requirement to export from Bangladesh. As shown in Figure 4.4, these core business processes deal with regulatory requirements to export, transport and customs procedures. They involve the arrangement for cargo movement as well as the completion of customs formalities and necessary actions to meet export of plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan. Figure 4.4 Use-case diagram of core business processes in Ship process area 11 P a g e
22 Core Business Process Area 2.1 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority Figure 4.5 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority use-case diagram Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority is the first core business process under the Ship process area and it is a general requirement in Bangladesh to do any kind of business. The use-case diagram, as shown in Figure 4.5, shows that this core business process requires participation from: Exporter Local Government Authority (City Corporation/ Municipality/ Union Parishad) Figure 4.6 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority activity diagram 12 P a g e
23 Table 4. 2 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority process description Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 2. Ship 2.1 Obtain Trade License from Local Government Authority The City Corporations (Taxation) Rules, 1986 Local Government (Paurashava)(Amended) Act, 2015 Local Government (Union Parishad) Act 2009 Union Parishad (Tax Schedule) Rules 2012 Process participant(s) Bangladeshi exporter (or Representative) Local Government Authority (City Corporation/ Municipality/ Union Parishad) Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Exporter has an ownership or leased property Exporter/Representative collects the prescribed Application Form (Form-K) from concerned Local Authority and fills-out the Form with required information; Exporter/Representative submits the filled Form along with applicant s 3 copies of Photo, Copy of National ID, copy of ownership/lease documents and applicable fees (based on the nature of business entity-for export fee is BDT % VAT+ BDT 150 for Book) to the concerned Local Authority; Local Government Authority (City Corporation/ Municipality/ Union Parishad) verify the applicant s information. If all provided information found correct Concerned Local Authority visit the spot and verify the applicant s information and existence of the business entity; If all provided information found correct, concerned Local Authority issues Trade License to the Exporter; Exporter (or Representative) receives the Trade License. N.B.- Trade license needs to be renewed every year by depositing applicable renewal fees Exporter (or Representative) received the Trade License Average time 3 days; if verification is required from Health or other division required time is 7 days 13 P a g e
24 Core Business Process Area 2.2: Obtain Tax Identification Number Figure 4.7 Obtain Tax Identification Number use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.7 shows that Obtain Tax Identification Number process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) National Board of Revenue (NBR) Figure 4.8 Obtain Tax Identification Number activity diagram 14 P a g e
25 Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations Table 4. 3 Obtain Tax Identification Number process description 2. Ship 2.2 Obtain Tax Identification Number The Income Tax Ordinance, 1984 Process participant(s) Bangladeshi exporter (or Representative) National Board of Revenue (NBR) Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Having a National Identity Card Having a mobile phone number Exporter/Representative fills-out the online application form at ( ; NBR (server) receives the application and verifies; if correct sends verification code to the Exporter/Representative s mobile; Exporter/Representative receives a verification code on his/her mobile phone; Exporter/Representative completes the application process by providing the verification code; NBR receives the completed application form (online); NBR issues tax identification number TIN (online); Exporter/Representative receives the e-tin (online) Exporter/Representative received the e-tin 30 minutes Core Business Process Area 2.3: Open Bank Account against the Trade License Figure 4. 9 Open Bank Account against the Trade License use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.9 suggests that Open Bank Account against the Trade License process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Scheduled Bank 15 P a g e
26 Figure 4.10 Open Bank Account against the trade license activity diagram Table 4. 4 Open Bank Account against the trade license process description Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 2. Ship 2.3 Open Bank Account against the trade license Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Scheduled Bank Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Bank Company Act 1991, Bank Company (amendment) Act 2013 Having a Trade License Exporter/Representative collects the prescribed application form from any scheduled bank ; and fills-out the Form with required information Exporter/Representative submits the filled Form along with applicant s 3 copies of Photo, copy of Trade License, copy of TIN, Copy of NID, Introducer Information, Copy of Nominee s (who will be the successor of the account holder) NID & Photo and minimum deposit to the Bank Manager; Bank verifies the applicant s information and address of the business entity; 16 P a g e
27 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.4 Continued If all provided information found correct, Bank opens the account and issues the Bank Account Number and Cheque Book and bank certificate (if necessary). Exporter/Representative received the account number, Cheque Book and bank certificate (if necessary). Opening bank account requires average time of 1 day; however, receiving cheque book requires 5-10 days. Core Business Process Area 2.4: Obtain Membership in a local business Association/Chamber Figure Obtain Membership in a local business Association use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.11 suggests that Obtain Membership in a local business association/chamber process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Local Business Association/ Chamber 17 P a g e
28 Figure Obtain Membership in a local business Association/Chamber activity diagram Table 4. 5 Obtain Membership in a local business association/chamber process description Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 2. Ship 2.4 Obtain Membership in a local business Association/Chamber Trade Organization Ordinance 1961 Companies Act 1994 Memorandum of Association and Article of Association of respective business association/chamber Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Local Business Association/ Chamber Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Having a Trade License and engaged in trade, industry or any other kind of business Exporter/Representative collects the prescribed application form from Local Business Association/ Chamber and fills-out the Form with required information; The membership application must be proposed by a member and seconded by another, of the membership class to which the applicant wants to be admitted; 18 P a g e
29 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.5. Continued Exporter/Representative submits the filled Form along with applicant s 1 copy of Photo, Copy of Trade License, Copy of TIN Certificate, Copy of Bank Certificate, Copy of Business Name Card of the Exporter, Copy of National Identity Card, A pay order of the fees in favor of Association/ Chamber (i.e Dhaka Chamber of Commerce & Industry (DCCI) Membership fee is BDT. 28,850/-); If all provided information found correct, Local Business Association/Chamber Secretariat issues membership certificate; Exporter receives the Membership Certificate. Exporter received the Membership Certificate. Average time 15 days Core Business Process Area 2.5: Obtain Export Registration Certificate (ERC) Figure Obtain Export Registration Certificate use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.13 shows that Obtain Export Registration Certificate process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Office of the Chief Controller of Imports & Exports (CCI & E) 19 P a g e
30 Figure 4.14 Obtain Export Registration Certificate activity diagram Name of the process area Table 4. 6 Obtain Export Registration Certificate process description Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 2. Ship 2.5 Obtain Export Registration Certificate (ERC) The Imports and Exports (Control) Act 1950; The Importers, Exporters Indentors (Registration) Order, 1981; Review, Appeal and Revision Order Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Office of the Chief Controller of Imports & Exports (CCI & E) Input and criteria to enter/ Having a Trade License and membership of a Local Business begin the business process Association/ Chamber. Activities and associated documentary requirements Exporter/Representative collects the prescribed Application Form from the Office of the Chief Controller of Imports & Exports (CCI&E) and fills-out the Form with required information; Exporter/Representative Submits the filled Form along with Copy of Trade License, Copy of TIN Certificate, Copy of Bank Certificate, Copy of National Identity Card, Copy of Membership Certificate from local chamber and Initial Registration fees (BDT. 8000/- + 15% VAT); CCI&E verifies the submitted documents; and if all provided information found correct, CCI&E issues the ERC; 20 P a g e
31 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.6 Continued Exporter/Representative receives the Export Registration Certificate (ERC). Exporter/Representative received the Export Registration Certificate (ERC). Average time 2 days Core Business Process Area 2.6: Obtain VAT Registration Certificate Figure Obtain VAT Registration Certificate use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure shows that Obtain VAT Registration Certificate process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Local VAT Circle Figure Obtain VAT Registration Certificate activity diagram 21 P a g e
32 Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations Table 4. 7 Obtain VAT Registration Certificate process description 2. Ship 2.6 Obtain VAT Registration Certificate Value Added Tax Act, 1991 Value Added Tax Rules 1991 Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Local VAT Circle Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Having a Trade License, TIN, and a bank account Exporter/Representative collects the prescribed application form (Mushak-6) from concerned Local VAT circle; and fills-out the Form with required information; Exporter/Representative submits the filled Form along with applicant s 2 copies of Photo, copy of NID, copy of TIN, copy of Ownership/Lease documents, copy of ERC and Bank certificate to the concerned VAT Authority; If all provided information found correct, concerned Local VAT Authority issues the VAT Registration Certificate (Concerned VAT Authority performs post verification about applicant s information and existence of the business entity); Exporter/Representative receives the VAT Registration Certificate. Exporter/Representative received the VAT Registration Certificate 2 days Core Business Process Area 2.7: Prepare export documents Figure Prepare export documents use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.17 shows that Prepare export documents process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Beneficiary Bank/ Exporter Bank 22 P a g e
33 Figure Prepare export documents activity diagram Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations Table 4. 8 Prepare export documents process description 2. Ship 2.7 Prepare export documents Incoterms 2010, The Export and Import Control Act 1950, Export Policy , Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1947, Foreign Exchange Regulations (Amendment) Act 2015, Bank Company Act 1991, Bank Company (amendment) Act 2013 Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Beneficiary Bank/ Exporter Bank Input and criteria to enter/ Exporter/Representative received advance payment by begin the business process Telegraphic Transfer (TT). Activities and associated documentary requirements Exporter/Representative collects EXP Form from the Beneficiary Bank/ Exporter Bank ; Exporter/Representative fills-out the EXP Form with required information; 23 P a g e
34 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.8 Continued Exporter/Representative submits filled EXP Form other export documents including Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), copy of TT/LC (15 copies of each documents) to the Bank; Bank assigns a EXP number to the EXP Form and endorse all the documents and returns to the Exporter/Representative; Exporter/Representative receives EXP form with EXP number and other export documents including Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI) and copy of TT/LC endorsed by Bank. Exporter/Representative received EXP form with EXP number and other export documents including Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI) and copy of TT/LC endorsed by Bank. Average time 1 day Core Business Process Area 2.8: Arrange Transport Figure Arrange Transport use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.19 shows that Arrange Transport process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Local Transport Agency 24 P a g e
35 Figure Arrange Transport activity diagram Name of the process area Name of the business process Table 4. 9 Arrange Transport process description 2. Ship 2.8 Arrange Transport Related laws, rules and Incoterms 2010, UCP 600, Negotiable Instruments Act 1881, regulations Negotiable Instruments (Amendment) Act, 1994 Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Local Transport Agency Input and criteria to enter/ Importer and exporter have agreed about the delivery schedule of begin the business process the export products Activities and associated documentary requirements Exporter/Representative calculates the space (CBM) requirement and covered van requirement; Exporter/Representative requests booking requirement to the local transport company; Local transport company prepares Negotiable Bill and Truck Receipt; Exporter accepts the fare and pays the fare in advance; Local transport company confirms the booking upon receipt of the payment; 25 P a g e
36 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.9 Continued Exporter/Representative receives booking confirmation form the transport company Exporter/Representative received booking confirmation form the transport company 2 hours Core Business Process Area 2.9: Arrange Certificate of Origin Figure Arrange Certificate of Origin usecase diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.21 suggests that Arrange Certificate of Origin process requires the participation from the: Exporter (or Representative) Metropolitan Chamber of Commerce & Industry (MCCI) 26 P a g e
37 Figure Arrange Certificate of Origin activity diagram Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations Table Arrange Certificate of Origin process description 2. Ship 2.9 Arrange Certificate of Origin The Export and Import Control Act 1950, Trade Organization Ordinance 1961, Memorandum of Association and Article of Association of respective business association/chamber, Bilateral and multilateral agreements. Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Metropolitan Chamber of Commerce & Industry (MCCI) Input and criteria to enter/ begin Exporter or Representative has export documents including the business process Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), Packing and Weight List (PW) and Truck Receipt Activities and associated Exporter/Representative collects Certificate of Origin Form documentary requirements from MCCI ; Exporter/Representative fills-out the Certificate of Origin Form with required information; Exporter/Representative submits the Certificate of Origin Form along with copies of Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), Packing and Weight List (PW), Truck Receipt and Fees (BDT 75); MCCI receives CO application; 27 P a g e
38 Table 4.10 Continued Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process MCCI verifies submitted documents; If all provided information found correct, MCCI issues the Certificate of Origin certificate; Exporter/Representative receives the Certificate of Origin certificate Exporter/Representative received the Certificate of Origin Average time 1 day Core Business Process Area 2.10: Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin Figure Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.23 shows that Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Export Promotion Bureau (EPB) 28 P a g e
39 Figure Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin activity diagram Name of the process area Table Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin process description Name of the business process 2. Ship 2.10 Arrange SAFTA Certificate of Origin Related laws, rules and The Export and Import Control Act 1950, SAFTA Agreement regulations Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Export Promotion Bureau (EPB) Input and criteria to enter/ Exporter or Representative has export documents including begin the business process Country of Origin, Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), Packing and Weight List (PW), Truck Receipt and cost breakdown of export product. Activities and associated Exporter/Representative collects SAFTA Country of Origin documentary requirements Form from EPB; Exporter/Representative fills-out the SAFTA Country of Origin Form with required information; 29 P a g e
40 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.11 Continued Exporter/Representative submits the SAFTA Country of Origin Form along with copies of Country of Origin, Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), Packing and Weight List (PW), Truck Receipt, EXP Form, cost breakdown of export product, undertaking in Company Pad by the EPB authorized signatory from the exporting company and Fees (BDT 923); EPB receives SAFTA Country of Origin application; EPB verifies submitted documents; If all provided information found correct and export product needs the value addition criteria, EPB issues the SAFTA Certificate of Origin certificate; Exporter/Representative receives the SAFTA Certificate of Origin certificate Exporter/Representative received the SAFTA Certificate of Origin 1 day Core Business process area 2.11: Arrange VAT Declaration Figure Arrange VAT Declaration use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.25 suggests that Arrange VAT Declaration process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Local VAT Circle 30 P a g e
41 Figure Arrange VAT Declaration activity diagram Name of the process area Name of the business process Table Arrange VAT Declaration process description 2. Ship 2.11 Arrange VAT Declaration Related laws, rules and Value Added Tax Act 1991, Value Added Tax Rules 1991, regulations Customs Act 1969 Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Local VAT Circle Input and criteria to enter/ Exporter or Representative has export documents including begin the business process Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), Packing and Weight List (PW), Copy of EXP Form and TT Copy of export product. Activities and associated documentary requirements (Non-Bond) Commercial Department of Exporter sends documents (Proforma Invoice (PI), Commercial Invoice (CI), Packing and Weight List (PW), Copy of EXP Form and TT Copy) to VAT Department (Internal); VAT Department (Internal) prepares VAT-11and VAT 20 based on above documents; 31 P a g e
42 Output criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process VAT Circle official inspects the goods in the factory premises and verifies goods against VAT declaration If all provided information found correct against VAT declaration, Local VAT Circle issues VAT-11 & VAT-20 with seal & signature; Exporter/Representative receives VAT-11 & VAT-20 certificate. Exporter/Representative received VAT-11 & VAT-20 certificate 1 day Core Business process area 2.12: Appointment of Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Figure Appointment of C&F Agent use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.27 shows that Appointment of C&F Agent process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent 32 P a g e
43 Figure Appointment of C&F Agent activity diagram Name of the process area Name of the business process Table Appointment of C&F Agent process description 2. Ship 2.12 Appointment of Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Related laws, rules and Customs Act 1969 regulations Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Input and criteria to enter/ Exporter and Importer have agreed about the delivery date of the begin the business process export products and Exporter has made necessary arrangement for transport of export products to the Port of departure. Activities and associated Exporter/Representative expresses his/her intention to appoint documentary requirements C&F agent for specific export transaction and request quotation for that; C&F Agent calculates the cost and prepare and submit the quotation to the Exporter; (Note: C&F Agent normally takes commission based on assessed value of the export products. The rate of commission is as follows: Assessed value up to BDT 1 1%, Assessed value over BDT 1 Lakh up to BDT 5 0.5%, Assessed value over BDT 5 Lakh up to BDT %, and Assessed value over BDT 50 Lakh 0.2%,) 33 P a g e
44 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.13 Continued Exporter/Representative decides whether or not quotation is acceptable; If Exporter/Representative finds quotation is acceptable, he/she issues an appointment letter to the C&F agent; C&F agent receives letter of appointment. C&F agent received letter of appointment 1/2 day Core Business process area 2.13: Transport goods to Port of Departure Figure Transport goods to Port of Departure use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.29 shows that Transport goods to Port of Departure process requires participation from: Exporter (or Representative) Transport Company Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Land Port Authority (Burimari) 34 P a g e
45 Figure Transport goods to Port of Departure activity diagram Name of the process area Table Transport goods to Port of Departure process description Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 2. Ship 2.13 Transport goods to Port of Departure Process participant(s) Exporter or Representative Transport Company Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Land Port Authority (Burimari) Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Exporter and Importer have agreed about the delivery date of the export products and Exporter has appointed C&F agent to handle customs procedures at the port of departure Exporter/Representative loads the export products into the truck(s) of the previously appointed Local Transport Company; Local Transport Company transports the loaded truck(s) to the Port of Departure; 35 P a g e
46 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.14 Continued C&F Agent (appointed by the Exporter) prepares the Bill of Export and arrange entry of loaded truck(s) into the Land port yard (Burimari); Land Port Authority (Burimari) records the date and time of entry of loaded Truck(s) and send loaded truck(s) to the point of inspection. Land Port Authority (Burimari) records the date and time of entry of loaded Truck(s) 1.5 days Core Business process area 2.14: Provide Customs Declaration Figure Provide Customs Declaration usecase diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure shows that Provide Customs Declaration process requires participation from: Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Customs (Bangladesh) 36 P a g e
47 Figure Provide Customs Declaration activity diagram Name of the process area Name of the business process Table Provide Customs Declaration process description 2. Ship 2.14 Provide Customs Declaration Related laws, rules and Customs Act 1969 and all other allied Acts, Rules and Regulation regulations The Export and Import Control Act 1950, Export Policy Process participant Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) Input and criteria to enter/ Exporter has appointed C&F agent to handle customs procedures begin the business process at the port of departure. Exporter has appointed C&F agent prepared the Bill of Export and all other supporting documents. Export Products reached at Burimari Land Port. 37 P a g e
48 Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Table 4.15 Continued Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent prepares and submits Bill of Export to Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) with all other supporting documents (Filled Bill of Export Form, Export Registration Certificate, TT/LC copy, Certificate of Origin, SAFTA Certificate of Origin, Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Packing and Weight List, Track Receipt, VAT certificate and EXP Form-15 copies of all documents) Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) receives Bill of Export and all supporting documents Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) verifies Bill of Export and all other supporting documents according to the declaration and determines if submitted Export Declaration meets Customs requirements. If it does not, they notify the Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent informing the error(s) in the Export Declaration. It is important that Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent/ exporter revise Bill of Export accordingly If submitted Export Declaration meets Customs requirements, Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) enters all the information in the ASYCUDA World online Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) Issue a Bill of Export number ( C number) Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent receives Bill of Export number ( C number) from Bangladesh Customs as an acknowledgement of acceptance of successful submission of Bill of Export. Customs declaration has been accepted. Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent receives Bill of Export number ( C number) from Bangladesh Customs (Burimari). Average time 30 minutes Core Business process area 2.15: Customs Inspection and Clear Goods Figure Customs Inspection and Clear Goods use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 33 suggests that Customs Inspection and Clear Goods process requires participation from: Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) Customs Bank Land Port Authority (Burimari) 38 P a g e
49 Figure Customs Inspection and Clear Goods activity diagram 39 P a g e
50 Name of the process area Table Customs Inspection and Clear Goods process description Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations Process participant Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process 2. Ship 2.15 Customs Inspection and Clear Goods Customs Act 1969 and all other allied Acts, Rules and Regulation VAT Act 1991, VAT Rules 1991 The Export and Import Control Act 1950, Export Policy Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) Customs Bank Land Port Authority (Burimari) Customs declaration has been accepted. Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent receives Bill of Export number ( C number) from Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) C&F Agent submits Bill of Export with all supporting import documents (TT/LC Copy, ERC, Certificate of Origin, SFAT CO, Proforma Invoice, Commercial Invoice, Packing and Weight List, Track Receipt, VAT Certificate, EXP Form) to Bangladesh Customs (Burimari); Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) retrieves declaration information in ASCYUDA World; Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) verifies all the documents; if all the documents found correct and acceptable against customs declaration, Customs examine the export goods against declaration; If any misconduct found, customs file case against that consignment and related parties; If products found as per declaration, Customs assesses the export goods and provide assessment notice (duty and taxes; if any) to C&F Agent; C&F Agent receives assessment notice and deposits assessed duty (if any) and VAT and AIT on C&F services charges through TR Challan to the Sonali Bank and submits the TR Challan to the Customs; Upon receipt of TR Challan, Customs issues Customs Release Order Following Customs Release, C&F Agent submits export files to the Land Port Authority (BLPA); BLPA calculates port dues and inform C&F Agent; C&F agent pays port dues and collects warehouse charges challan and submit the complete export file to Customs; Customs verifies the export file and sign Out Pass (EXP Form) and Gate Pass; C&F Agent receives signed Out Pass (EXP Form) and Gate Pass; Upon receipt of the clearance, C&F arrange unloading of export goods from Exporter s truck (Bangladeshi) and loading to Importer s truck (Bhutanese/Indian) at the Land Port yard. C&F Agent received signed Out Pass (Customs singed EXP Form) and Gate Pass 2.5 hours 40 P a g e
51 Core Business process area 2.16: Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer Figure Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.35 shows that Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer process requires participation from: Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent (Bangladesh) Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) Representative of Bhutanese Importer Figure Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer activity diagram 41 P a g e
52 Table Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer process description Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 2. Ship 2.16 Handover Export documents to Representative of Bhutanese Importer South Asian Free Trade Agreement and trilateral arrangement between Bangladesh, India and Bhutan Process participant Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent (Bangladesh) Bangladesh Customs (Burimari) Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process C&F Agent received customs clearance and signed export documents Export goods loaded to importer s truck (Bhutanese/Indian) Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs come to the Burimari LCS Bangladesh Customs returns customs clearance of export consignment and signed export documents to C&F Agent; C&F Agent receives customs clearance of export consignment and signed export documents; Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs come to the Burimari LCS crossing the Indian Border; Exporter s C&F Agent handover export documents and export consignment to the Representative of Bhutanese Importer in the presence of Bangladesh Customs; Representative of Bhutanese Importer receives and checks export documents (Bill of Export and 2 sets of all Export documents) and export consignment. Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs received export documents and export consignment. 30 Minutes 42 P a g e
53 Core Business process area 2.17: Border Crossing of Export goods Figure Border Crossing of Export goods use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.37 shows that Border Crossing of Export goods process requires the participation from: Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent (Bangladesh) Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs Border Security (Bangladesh) Border Security (India) Figure Border Crossing of Export goods activity diagram 43 P a g e
54 Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations Table Border Crossing of Export goods process description 2. Ship 2.17 Border Crossing of Export goods Customs Act 1969 and all other allied Acts, Rules and Regulation Process participant Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent (Bangladesh) Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs Border Security (Bangladesh) Border Security (India) Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Export consignment received clearance from Bangladesh Customs and BLPA Export goods loaded to importer s truck (Bhutanese/Indian) Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs received export documents and export consignment Upon receipt of Customs and Port clearance and export documents from Exporter s C&F Agent (Bangladesh), Representative of Bhutanese Importer authorized by Bhutan Customs arrange border crossing of export goods with assistance from Importer s C&F Agent (Bangladesh); Border Security (Bangladesh) verifies export documents and examine export consignment where necessary at the Zero point; Export consignment crosses the border; Border Security (India) verifies export documents and consignment at the entry point of India. Export consignment crossed the border and entered Indian territory 30 minutes 44 P a g e
55 Core Business process area 2.18: Sending signed export documents back to Exporter Figure Sending signed export documents back to Exporter use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.39 shows that Sending signed export documents back to Exporter process requires the participation from: Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent (Bangladesh) Exporter Figure Sending signed export documents back to Exporter activity diagram 45 P a g e
56 Table Sending signed export documents back to Exporter process description Name of the process area Name of the business process 2. Ship 2.18 Sending signed export documents back to Exporter Related laws, rules and Incoterms 2010 regulations Process participant Clearing and Forwarding (C&F) Agent (Bangladesh) Exporter Input and criteria to enter/ Export consignment successfully crossed the border and C&F begin the business process Agent received export documents (including original EXP form) signed by Bangladesh Customs Activities and associated Exporters C&F Agent collects export documents (including documentary requirements original EXP form) signed from Bangladesh Customs Send back export documents (including original EXP form) signed by Bangladesh Customs to exporters Exporter receives export documents (including original EXP form) signed by Bangladesh Customs Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Exporter received export documents (including original EXP form) signed by Bangladesh Customs as a proof of completion export 3 days Process Area 3: Pay For the export of plastic kitchenware and tableware from Bangladesh to Bhutan, Pay process area consists of 2 core business processes. Here Pay process area deals with receiving Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer and obtaining Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) by the Exporter, as shown in Figure Figure Use case diagram of core business processes in Pay process area 46 P a g e
57 Core Business Process Area 3.1: Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer Figure Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer usecase diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.42 shows that Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer process requires the participation from: Bhutanese importer Importer s Bank Exporter s Bank Bangladeshi exporter Figure Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer activity diagram 47 P a g e
58 Table Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer process description Name of the process area Name of the business process Related laws, rules and regulations 3. Pay 3.1 Receive Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1947, Foreign Exchange Regulations (Amendment) Act 2015 Uniform Customs and Practices for Documentary Credit publication number 600. Process participant Bhutanese Importer Importer s Bank (issuing bank) Exporter s Bank (advising bank) Bangladeshi Exporter Input and criteria to enter/ begin the business process Activities and associated documentary requirements Output and criteria to exit the business process Average time required to complete this business process Exporter and importer have already concluded trade contract and terms Importer applies for Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) to importer s bank; Importer s bank reviews submitted documents and evaluates Importer s business and credit profile; If Importer s business and credit is in good standing and Importer has sufficient fund in his bank account, importer s bank approves the application and transfer the payment to exporter s bank by Telegraphic Transfer (TT); Exporter s bank establishes authenticity of the Telegraphic Transfer (TT); deduct service charges and notifies exporter about the arrival of TT form Importer; Exporter submits Advance Receivable Voucher (ARV) to the Bank; Upon receipt of the ARV, Bank transfer the fund to Exporter s account and informs Exporter that fund has been is ready for collection; Exporter receives the payment in his account and makes necessary arrangements for the delivery of goods. Exporter received Advance Payment by Telegraphic Transfer (TT) from the Importer 2 day 48 P a g e
59 Core Business Process Area 3.2: Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) Figure Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) use-case diagram The use-case diagram as shown in Figure 4.44 shows that Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) process requires the participation from: Bangladeshi Exporter Exporter s Bank Figure Obtain Proceed Realization Certificate (PRC) activity diagram 49 P a g e
Business Process Analysis of
 Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism in Nepal Baseline study series #3 Business Process Analysis of The Import Economic and Social Commission of Fabrics for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism in Nepal Baseline study series #3 Business Process Analysis of The Import Economic and Social Commission of Fabrics for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP)
National Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism (TTFMM)
 National Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism (TTFMM) Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer Trade Facilitation Unit United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
National Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism (TTFMM) Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer Trade Facilitation Unit United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
ADB-ESCAP Workshop on TTFMM Baseline Studies in Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal
 ADB-ESCAP Workshop on TTFMM Baseline Studies in Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal Review of the Key Issues on BPA Prabir De 13-15 January 2015, Bangkok BPA to implement paperless trade BPA is the first technical
ADB-ESCAP Workshop on TTFMM Baseline Studies in Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal Review of the Key Issues on BPA Prabir De 13-15 January 2015, Bangkok BPA to implement paperless trade BPA is the first technical
Trade Facilitation in SASEC: Experiences with BPA 1
 Trade Facilitation in SASEC: Experiences with BPA 1 Prabir De RIS, New Delhi Inception Workshop ADB-ESCAP Trade and Transport Facilitation Performance Monitoring System (TTFPM) 26-27 November 2013, Bangkok
Trade Facilitation in SASEC: Experiences with BPA 1 Prabir De RIS, New Delhi Inception Workshop ADB-ESCAP Trade and Transport Facilitation Performance Monitoring System (TTFPM) 26-27 November 2013, Bangkok
Trade facilitation as a key to unlocking trade potential in LLDCs
 Trade facilitation as a key to unlocking trade potential in LLDCs Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer Trade, Investment and Innovation Division UNESCAP wangt@un.org Expert group meeting on the regional
Trade facilitation as a key to unlocking trade potential in LLDCs Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer Trade, Investment and Innovation Division UNESCAP wangt@un.org Expert group meeting on the regional
Agenda. Business Process Analysis (BPA): Introduction and foundation. Business process in the context of trade facilitation can be complex. What is..
 Business Process Analysis (BPA): Introduction and foundation Workshop on National Trade Facilitation Strategy of Kyrgyzstan and Business Process Analysis (BPA) Foundation Training 14 June 2013, Kyrgyzstan
Business Process Analysis (BPA): Introduction and foundation Workshop on National Trade Facilitation Strategy of Kyrgyzstan and Business Process Analysis (BPA) Foundation Training 14 June 2013, Kyrgyzstan
Trade facilitation as a key to unlocking trade potential along OBOR
 Trade facilitation as a key to unlocking trade potential along OBOR Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer Trade, Investment and Innovation Division UNESCAP wangt@un.org GIZ-ESCAP Workshop on promoting
Trade facilitation as a key to unlocking trade potential along OBOR Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer Trade, Investment and Innovation Division UNESCAP wangt@un.org GIZ-ESCAP Workshop on promoting
UNNExT workshop on Paperless trade facilitation for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
 UNNExT workshop on Paperless trade facilitation for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises 2-4 February 2015 United Nations Conference Center (UNCC) Bangkok, Thailand A journey from BPA to TTFMM key issues
UNNExT workshop on Paperless trade facilitation for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises 2-4 February 2015 United Nations Conference Center (UNCC) Bangkok, Thailand A journey from BPA to TTFMM key issues
BPA of Orange Juice and Fresh Orange through Corridor 2: Preliminary Findings from Bangladesh Segment
 BPA of Orange Juice and Fresh Orange through Corridor 2: Preliminary Findings from Bangladesh Segment Mohammad Yunus Bangladesh Presented at SASEC Stakeholder Workshop on Subregional Trade and Transit
BPA of Orange Juice and Fresh Orange through Corridor 2: Preliminary Findings from Bangladesh Segment Mohammad Yunus Bangladesh Presented at SASEC Stakeholder Workshop on Subregional Trade and Transit
UNNExT Workshop on Implementation of e-sps and Automation for Agriculture Trade Facilitation. 1-3 November 2016 Bangkok, Thailand
 UNNExT Workshop on Implementation of e-sps and Automation for Agriculture Trade Facilitation 1-3 November 2016 Bangkok, Thailand Business Process Analysis (BPA) Somnuk Keretho, PhD UNNExT Expert 2 Kasetsart
UNNExT Workshop on Implementation of e-sps and Automation for Agriculture Trade Facilitation 1-3 November 2016 Bangkok, Thailand Business Process Analysis (BPA) Somnuk Keretho, PhD UNNExT Expert 2 Kasetsart
Trade Facilitation in Eastern South Asia: Towards Paperless Trade
 Trade Facilitation in Eastern South Asia: Towards Paperless Trade Prabir De RIS, New Delhi 5 December 2013 Bali, Indonesia South Asia yet to witness regional Period trade facilitation Regional trade* (US$
Trade Facilitation in Eastern South Asia: Towards Paperless Trade Prabir De RIS, New Delhi 5 December 2013 Bali, Indonesia South Asia yet to witness regional Period trade facilitation Regional trade* (US$
Overview of Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in SASEC Countries
 Cluster 3: South Asia Overview of Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in SASEC Countries On-behalf of ADB ESCAP BPA Study Team Prabir De RIS, New Delhi Asia Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum
Cluster 3: South Asia Overview of Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in SASEC Countries On-behalf of ADB ESCAP BPA Study Team Prabir De RIS, New Delhi Asia Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum
Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation
 Inception Workshop on Trade and Transport Facilitation Performance Monitoring System (TTFPM): BPA+ Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Mr. Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer UNESCAP wangt@un.org
Inception Workshop on Trade and Transport Facilitation Performance Monitoring System (TTFPM): BPA+ Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Mr. Tengfei Wang Economic Affairs Officer UNESCAP wangt@un.org
BPA of Lead Acid Accumulator and Lentil through Corridor 1: Preliminary Findings from Bangladesh Segment
 BPA of Lead Acid Accumulator and Lentil through Corridor 1: Preliminary Findings from Bangladesh Segment Mohammad Yunus Bangladesh Presented at SASEC Stakeholder Workshop on Subregional Trade and Transit
BPA of Lead Acid Accumulator and Lentil through Corridor 1: Preliminary Findings from Bangladesh Segment Mohammad Yunus Bangladesh Presented at SASEC Stakeholder Workshop on Subregional Trade and Transit
Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement. Introduction to Business Process Analysis
 Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement Introduction to Business Process Analysis Conducted by Yann Duval, Chief, Trade Facilitation Unit, UNESCAP WCO-UNESCAP 3 rd UNNExT Masterclass:
Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement Introduction to Business Process Analysis Conducted by Yann Duval, Chief, Trade Facilitation Unit, UNESCAP WCO-UNESCAP 3 rd UNNExT Masterclass:
by Mohammad Farhad Research Fellow, Bangladesh Foreign Trade Institute ACJ Cl
 Presentation at UNNExT National Workshop on Agriculture Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis for Bangladesh Jointly organised by BFTI and UNESCAP 27 October 2015, Dhaka, Bangladesh by Mohammad
Presentation at UNNExT National Workshop on Agriculture Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis for Bangladesh Jointly organised by BFTI and UNESCAP 27 October 2015, Dhaka, Bangladesh by Mohammad
South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation : SASEC Trade Facilitation
 South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation : SASEC Trade Facilitation Presentation at the UNCTAD South Asia Regional Forum on Trade Facilitation 7-8 October 2013 Regional Cooperation and Operations Coordination
South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation : SASEC Trade Facilitation Presentation at the UNCTAD South Asia Regional Forum on Trade Facilitation 7-8 October 2013 Regional Cooperation and Operations Coordination
Nepal Trade Facilitation Workshop: Towards a National Single Window* Kathmandu, Nepal 8 February 2011
 Business Process Analysis to Identify Trade Bottlenecks Nepal Trade Facilitation Workshop: Towards a National Single Window* Kathmandu, Nepal 8 February 2011 Dr. Somnuk Keretho Director, Institute for
Business Process Analysis to Identify Trade Bottlenecks Nepal Trade Facilitation Workshop: Towards a National Single Window* Kathmandu, Nepal 8 February 2011 Dr. Somnuk Keretho Director, Institute for
High Level Business Process Analysis Workshop for South Asian Logistics and Connectivity
 The United Nations Network of Experts for Paperless Trade High Level Business Process Analysis Workshop for South Asian Logistics and Connectivity 16 October 2012 UNCC, Bangkok Objectives of this workshop
The United Nations Network of Experts for Paperless Trade High Level Business Process Analysis Workshop for South Asian Logistics and Connectivity 16 October 2012 UNCC, Bangkok Objectives of this workshop
UNNExT Workshop on Agricultural Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in Bangladesh October Dhaka, Bangladesh
 UNNExT Workshop on Agricultural Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in Bangladesh 27-29 October Dhaka, Bangladesh UNNExT National Workshop on Agriculture Trade Facilitation and Business Process
UNNExT Workshop on Agricultural Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in Bangladesh 27-29 October Dhaka, Bangladesh UNNExT National Workshop on Agriculture Trade Facilitation and Business Process
Topics of this session. What is. What is a Business Process? 25/05/2016. Why conduct a Business Process Analysis?
 /0/06 Topics of this session Business Process Analysis to Simplify Trade Procedures Myanmar Capacity Building Programme Training Workshop on Trade Facilitation: Global Agenda and Regional Priorities Yangon,
/0/06 Topics of this session Business Process Analysis to Simplify Trade Procedures Myanmar Capacity Building Programme Training Workshop on Trade Facilitation: Global Agenda and Regional Priorities Yangon,
Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring and UN/CEFACT Recommendation 42
 ESCAP-OECD Workshop on Measuring and Monitoring Trade Facilitation Performance, 7 September 2017 As a side event of Asia-Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2017 Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring
ESCAP-OECD Workshop on Measuring and Monitoring Trade Facilitation Performance, 7 September 2017 As a side event of Asia-Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2017 Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring
Insights from ESCAP s Trade Process Analysis Database (Version 1.0; )
 Brief No. 11, September 2014 Insights from ESCAP s Trade Process Analysis Database (Version 1.0; 2009-2014) Trade facilitation has become a crucial area of focus for countries seeking continuous growth
Brief No. 11, September 2014 Insights from ESCAP s Trade Process Analysis Database (Version 1.0; 2009-2014) Trade facilitation has become a crucial area of focus for countries seeking continuous growth
Business Process Analysis of Import of Wheat in Bangladesh
 Business Process Analysis of Import of Wheat in Bangladesh By Mr. Mohammad Yunus Presented at the National Stakeholder Consultation Meeting Jointly Organized by UN-ESCAP, and SATNET, Dhaka, 14 March, 2013
Business Process Analysis of Import of Wheat in Bangladesh By Mr. Mohammad Yunus Presented at the National Stakeholder Consultation Meeting Jointly Organized by UN-ESCAP, and SATNET, Dhaka, 14 March, 2013
Paperless trade facilitation for SMEs
 Paperless trade facilitation for SMEs Mark GOH Prepared for UNNExT workshop on paperless trade facilitation for SMEs 2-3 Feb 2015, Bangkok, UN Conference Centre Paperless trade facilitation 1 Agenda Overview
Paperless trade facilitation for SMEs Mark GOH Prepared for UNNExT workshop on paperless trade facilitation for SMEs 2-3 Feb 2015, Bangkok, UN Conference Centre Paperless trade facilitation 1 Agenda Overview
Business Process Modeling and Analysis
 Business Process Modeling and Analysis High-level Business Process Analysis Workshop for South Asian Logistics and Connectivity 16 October 2012 UNCC, Bangkok, Thailand Sangwon Lim Trade Facilitation Section
Business Process Modeling and Analysis High-level Business Process Analysis Workshop for South Asian Logistics and Connectivity 16 October 2012 UNCC, Bangkok, Thailand Sangwon Lim Trade Facilitation Section
TRADE AND TRANSPORT FACILITATION MONITORING MECHANISM IN NEPAL BASELINE STUDY
 TRADE AND TRANSPORT FACILITATION MONITORING MECHANISM IN NEPAL BASELINE STUDY Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism IN Nepal Baseline Study Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 IGO license
TRADE AND TRANSPORT FACILITATION MONITORING MECHANISM IN NEPAL BASELINE STUDY Trade and Transport Facilitation Monitoring Mechanism IN Nepal Baseline Study Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 IGO license
UNNExT Workshop on Agricultural Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in Bangladesh October Dhaka, Bangladesh
 UNNExT Workshop on Agricultural Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in Bangladesh 27-29 October Dhaka, Bangladesh UNNExT National Workshop on Agriculture Trade Facilitation and Business Process
UNNExT Workshop on Agricultural Trade Facilitation and Business Process Analysis in Bangladesh 27-29 October Dhaka, Bangladesh UNNExT National Workshop on Agriculture Trade Facilitation and Business Process
Objectives of this session
 Training Workshop on Business Process Analysis in International Trade Module 3. Assessment of business processes and drafting the report with conclusions and recommendations for improvement 3.1. Analyzing
Training Workshop on Business Process Analysis in International Trade Module 3. Assessment of business processes and drafting the report with conclusions and recommendations for improvement 3.1. Analyzing
1. Defining Scope of and Planning a BPA Project
 Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement 1. Defining Scope of and Planning a BPA Project WCO-UNESCAP 3 rd UNNExT Masterclass: Digital Customs and Single Windows in the context of WTO
Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement 1. Defining Scope of and Planning a BPA Project WCO-UNESCAP 3 rd UNNExT Masterclass: Digital Customs and Single Windows in the context of WTO
1. Defining Scope of and Planning a BPA Project
 Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement 1. Defining Scope of and Planning a BPA Project Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation.... Kasetsart University, Bangkok
Business Process Analysis for Trade Facilitation Improvement 1. Defining Scope of and Planning a BPA Project Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation.... Kasetsart University, Bangkok
SASEC Trade and Transit Corridors
 ADB ESCAP BPA Study SASEC Trade and Transit Corridors Priority of Implementations on Major Recommendations Corridor 1 [Kakarvitta Panitanki Phulbari Banglabandh] agency Assumptions and Risks involved,
ADB ESCAP BPA Study SASEC Trade and Transit Corridors Priority of Implementations on Major Recommendations Corridor 1 [Kakarvitta Panitanki Phulbari Banglabandh] agency Assumptions and Risks involved,
Workshop on import and export
 Workshop on import and export By: Mr. Muhammad Ali Workshop Co-ordinator: Mr. Owais Shafique MUHAMMAD ALI - ACCA 1 Types of shipments.. Shipment of imports Shipment of exports Shipment for re-export under
Workshop on import and export By: Mr. Muhammad Ali Workshop Co-ordinator: Mr. Owais Shafique MUHAMMAD ALI - ACCA 1 Types of shipments.. Shipment of imports Shipment of exports Shipment for re-export under
FACILITATION PANEL (FALP)
 International Civil Aviation Organization WORKING PAPER FALP/8-WP/10 30/10/14 English only FACILITATION PANEL (FALP) EIGHTH MEETING Montréal, 24-28 November 2014 Agenda Item 2: Amendments to Annex 9 FACILITATION
International Civil Aviation Organization WORKING PAPER FALP/8-WP/10 30/10/14 English only FACILITATION PANEL (FALP) EIGHTH MEETING Montréal, 24-28 November 2014 Agenda Item 2: Amendments to Annex 9 FACILITATION
Agricultural Trade Facilitation for Bangladesh and Findings from Business Process Analysis (BPA) Study
 Agricultural Trade Facilitation for Bangladesh and Findings from Business Process Analysis (BPA) Study Khan Salehin Trade and Investment Division, ESCAP Dhaka, 7 April 2014 OUTLINE Agriculture trade in
Agricultural Trade Facilitation for Bangladesh and Findings from Business Process Analysis (BPA) Study Khan Salehin Trade and Investment Division, ESCAP Dhaka, 7 April 2014 OUTLINE Agriculture trade in
United. United. Trade
 United Nations Economic Commission for Europe United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business Trade Summary of UNECE Facilitation s UNITED NATIONS New York and Geneva, 2015 SUMMARY
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business Trade Summary of UNECE Facilitation s UNITED NATIONS New York and Geneva, 2015 SUMMARY
Single Window Experiences Hong Kong
 Single Window Experiences Hong Kong United Nations Development Account Project (4th Tranche) Interregional partnership for promoting trade as an engine of growth through knowledge management and information
Single Window Experiences Hong Kong United Nations Development Account Project (4th Tranche) Interregional partnership for promoting trade as an engine of growth through knowledge management and information
Overview of the SATNET Project and Introduction to Business Process Analysis (BPA) as a tool for Trade Facilitation
 Overview of the SATNET Project and Introduction to Business Process Analysis (BPA) as a tool for Trade Facilitation Khan Salehin Trade and Investment Division, ESCAP Don Chan Palace, Vientiane, Lao PDR,
Overview of the SATNET Project and Introduction to Business Process Analysis (BPA) as a tool for Trade Facilitation Khan Salehin Trade and Investment Division, ESCAP Don Chan Palace, Vientiane, Lao PDR,
Trade Facilitation and Supply Chain Competitiveness
 Trade Facilitation and Supply Chain Competitiveness Malcolm McKinnon Chief Executive, Ltd 24 February 2009 Presentation Objectives To demonstrate the link between transport and trade facilitation To present
Trade Facilitation and Supply Chain Competitiveness Malcolm McKinnon Chief Executive, Ltd 24 February 2009 Presentation Objectives To demonstrate the link between transport and trade facilitation To present
EXPORT OF MAIZE FROM LAOS
 Business Process Analysis EXPORT OF MAIZE FROM LAOS By THANOMVONG KHAMVONGSA, MR. Agenda I. Introduction to BPA process II. Actual finding for Export of maize from Laos III. Bottleneck IV. Preliminary
Business Process Analysis EXPORT OF MAIZE FROM LAOS By THANOMVONG KHAMVONGSA, MR. Agenda I. Introduction to BPA process II. Actual finding for Export of maize from Laos III. Bottleneck IV. Preliminary
Updated September 2012
 Updated September 2012 The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is the regional development arm of the United Nations and serves as the main economic and social
Updated September 2012 The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is the regional development arm of the United Nations and serves as the main economic and social
Single Window in the Republic of Azerbaijan
 unofficial translation (original - Russian) Single Window in the Republic of Azerbaijan (replies to an UNECE Questionnaire on single window -2011) Preface What has motivated the single window (SW) implementation
unofficial translation (original - Russian) Single Window in the Republic of Azerbaijan (replies to an UNECE Questionnaire on single window -2011) Preface What has motivated the single window (SW) implementation
Customs Approval to Stuff Container. Freight Forwarder Books Space on Vessel. Permission to Stuff Container. Book Space. Container Made Available
 High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 3 4 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Scans Commercial Invoice Freight Forwarder Books Space on Vessel Book Space Customs Approval to Stuff
High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 3 4 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Scans Commercial Invoice Freight Forwarder Books Space on Vessel Book Space Customs Approval to Stuff
APTFF Capacity Building Workshop on Facilitating Trade in Agricultural Products in the Context of the WTO TFA
 APTFF Capacity Building Workshop on Facilitating Trade in Agricultural Products in the Context of the WTO TFA 7 September 2017 Maame Agyeben Trade, Investment and Innovation Division United Nations ESCAP
APTFF Capacity Building Workshop on Facilitating Trade in Agricultural Products in the Context of the WTO TFA 7 September 2017 Maame Agyeben Trade, Investment and Innovation Division United Nations ESCAP
Warehousing Process - Sea
 High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 3 4 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Bond Process Shipping Agent Process Pre-clearance Movement Process Scans Bill of Lading (BL) and Commercial
High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 3 4 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Bond Process Shipping Agent Process Pre-clearance Movement Process Scans Bill of Lading (BL) and Commercial
SINGLE WINDOW AND TRADE FACILITATION
 SINGLE WINDOW AND TRADE FACILITATION Erich Kieck March 2018 OUTLINE Why? What? How? WHY? Members shall endeavour to establish or maintain a single window, enabling traders to submit documentation and/or
SINGLE WINDOW AND TRADE FACILITATION Erich Kieck March 2018 OUTLINE Why? What? How? WHY? Members shall endeavour to establish or maintain a single window, enabling traders to submit documentation and/or
UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation
 UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation UNNExT Workshop on Trade Facilitation and Paperless Systems for Agrifood Products Almaty, Kazakhstan 4-6 May 2015 1 Page 1 Streamlining and Automating Procedures
UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation UNNExT Workshop on Trade Facilitation and Paperless Systems for Agrifood Products Almaty, Kazakhstan 4-6 May 2015 1 Page 1 Streamlining and Automating Procedures
UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation
 UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation UNNExT Workshop on Trade Facilitation and Paperless Systems for Agrifood Products Almaty, Kazakhstan 4-6 May 2015 1 BUSINESS PROCESS ANALYSIS OF THE EXPORT OF PROCESSED
UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation UNNExT Workshop on Trade Facilitation and Paperless Systems for Agrifood Products Almaty, Kazakhstan 4-6 May 2015 1 BUSINESS PROCESS ANALYSIS OF THE EXPORT OF PROCESSED
UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation
 UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation UNNExT Workshop on Paperless Trade Facilitation for Small and Medium-Sized Entreprises Almaty, Kazakhstan 4-6 May 2015 Buy-Ship-Pay Model 2 International Trade Is
UNNExT Workshops on Trade Facilitation UNNExT Workshop on Paperless Trade Facilitation for Small and Medium-Sized Entreprises Almaty, Kazakhstan 4-6 May 2015 Buy-Ship-Pay Model 2 International Trade Is
Freight Forwarders: (Agente Transitario) The International Bank IMPORTER-EXPORTER FREIGHT FORWARDER IT- 2: PARTIES INVOLVED IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE.
 IT- 2: PARTIES INVOLVED IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE. SALES CONTRACTS. CUSTOMS PROCEDURES. DOCS. IMPORTER-EXPORTER FREIGHT FORWARDER PARTIES INVOLVED IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE CUSTOMS BROKER INTERNATIONAL BANKER
IT- 2: PARTIES INVOLVED IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE. SALES CONTRACTS. CUSTOMS PROCEDURES. DOCS. IMPORTER-EXPORTER FREIGHT FORWARDER PARTIES INVOLVED IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE CUSTOMS BROKER INTERNATIONAL BANKER
Implementing, Strengthening and Expanding Services and New Projects in TTBizLink
 Implementing, Strengthening and Expanding Services and New Projects in TTBizLink Contents Background Achievements in the last Year Future Developments How did it begin? In 2009, the GoRTT through the MTI
Implementing, Strengthening and Expanding Services and New Projects in TTBizLink Contents Background Achievements in the last Year Future Developments How did it begin? In 2009, the GoRTT through the MTI
Process Analysis for Developing A Single Window - Case of Thailand
 Process Analysis for Developing A Single Window - Case of Thailand Dr. Somnuk Keretho UNESCAP Consultant Advisor to Ministry of Transport, and Minister of Information and Communications Technology for
Process Analysis for Developing A Single Window - Case of Thailand Dr. Somnuk Keretho UNESCAP Consultant Advisor to Ministry of Transport, and Minister of Information and Communications Technology for
Warehousing Process - Land
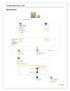 High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Scans Commercial Invoice Unique Consignment Reference (UCR) Bond Process Removal Bond Premises Bond MDA Permit
High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Scans Commercial Invoice Unique Consignment Reference (UCR) Bond Process Removal Bond Premises Bond MDA Permit
FACILITATION OF THE CROSS-BORDER TRANSPORT OF GOODS AND PEOPLE IN THE GREATER MEKONG SUBREGION (September 2004)
 FACILITATION OF THE CROSS-BORDER TRANSPORT OF GOODS AND PEOPLE IN THE GREATER MEKONG SUBREGION (September 2004) A. Cross-Border Facilitation: A Critical Component of Subregional Cooperation in the Transport
FACILITATION OF THE CROSS-BORDER TRANSPORT OF GOODS AND PEOPLE IN THE GREATER MEKONG SUBREGION (September 2004) A. Cross-Border Facilitation: A Critical Component of Subregional Cooperation in the Transport
Facilitating & Automating Trade in Agriculture: Challenges and emerging trends
 Facilitating & Automating Trade in Agriculture: Challenges and emerging trends 26 May 2017, Bangkok, Thailand Maame Agyeben Trade Facilitation Unit, Trade, Investment and Innovation Division, United Nations
Facilitating & Automating Trade in Agriculture: Challenges and emerging trends 26 May 2017, Bangkok, Thailand Maame Agyeben Trade Facilitation Unit, Trade, Investment and Innovation Division, United Nations
UNNExT workshop on Paperless trade facilitation for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
 UNNExT workshop on Paperless trade facilitation for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises 2-4 February 2015 United Nations Conference Center (UNCC) Bangkok, Thailand ACJ Cl ACJ Cl By Mohammad Farhad Research
UNNExT workshop on Paperless trade facilitation for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises 2-4 February 2015 United Nations Conference Center (UNCC) Bangkok, Thailand ACJ Cl ACJ Cl By Mohammad Farhad Research
Progress and key challenges for connecting agricultural sector to global market in the region
 Progress and key challenges for connecting agricultural sector to global market in the region Session 3: Re-thinking Trade Facilitation Strategies for More Inclusive Regional Integration: Focusing on SMEs
Progress and key challenges for connecting agricultural sector to global market in the region Session 3: Re-thinking Trade Facilitation Strategies for More Inclusive Regional Integration: Focusing on SMEs
From Transport Connectivity to Social Networking. Dr.Esmaeil Tekyeh Sadat Advisor to Deputy Minister MFA iran
 From Transport Connectivity to Social Networking Dr.Esmaeil Tekyeh Sadat Smaeils@yahoo.com Advisor to Deputy Minister MFA iran three key challenges out of five, (1) Lack of coordination between government
From Transport Connectivity to Social Networking Dr.Esmaeil Tekyeh Sadat Smaeils@yahoo.com Advisor to Deputy Minister MFA iran three key challenges out of five, (1) Lack of coordination between government
 CHAPTER 10 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Introduction In this lesson we are going to have overall idea of International Business i.e., how to sell goods and services to other countries traders/users and how to
CHAPTER 10 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Introduction In this lesson we are going to have overall idea of International Business i.e., how to sell goods and services to other countries traders/users and how to
and trade facilitation measures, including business process simplification, data harmonization, and Single Window implementation.
 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The original version of this Guide was prepared by a team coordinated by Shamika Sirimanne, Chief, Trade Facilitation Section, and consisting of Maria Misovicova, Peng Bin of ESCAP, Markus
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The original version of this Guide was prepared by a team coordinated by Shamika Sirimanne, Chief, Trade Facilitation Section, and consisting of Maria Misovicova, Peng Bin of ESCAP, Markus
Business Process Analysis for Agriculture Supply Chains Improvement
 Business Process Analysis for Agriculture Supply Chains Improvement Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation... Kasetsart University, Bangkok UNNExT Workshop on Promoting Cross-border
Business Process Analysis for Agriculture Supply Chains Improvement Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation... Kasetsart University, Bangkok UNNExT Workshop on Promoting Cross-border
Asia Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum September 2014, BITEC Bangkok, Thailand
 Asia Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2014 24 25 September 2014, BITEC Bangkok, Thailand APTFF 2014 Trade facilitation for inclusive development 24-25 25 September 2014 National experience in stakeholder
Asia Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2014 24 25 September 2014, BITEC Bangkok, Thailand APTFF 2014 Trade facilitation for inclusive development 24-25 25 September 2014 National experience in stakeholder
Trade Facilitation in South Asia: A Nepalese Perspective
 Trade Facilitation in South Asia: A Nepalese Perspective Purushottam Ojha Secretary Ministry of Commerce and Supplies, Government of Nepal. Asia-Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2009: Setting the Regional
Trade Facilitation in South Asia: A Nepalese Perspective Purushottam Ojha Secretary Ministry of Commerce and Supplies, Government of Nepal. Asia-Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2009: Setting the Regional
TRADE FACILITATION & PLANT HEALTH RECENT LESSONS
 TRADE FACILITATION & PLANT HEALTH RECENT LESSONS Bill Gain Global Lead Trade Facilitation & Border Management Trade & Competitiveness Global Practice World Bank Group TRADE AND COMPETITIVENESS GLOBAL PRACTICE
TRADE FACILITATION & PLANT HEALTH RECENT LESSONS Bill Gain Global Lead Trade Facilitation & Border Management Trade & Competitiveness Global Practice World Bank Group TRADE AND COMPETITIVENESS GLOBAL PRACTICE
ESCAP-ADB Capacity Building Workshop on Sub-regional Trade and Transit Cooperation for SASEC Countries
 ESCAP-ADB Capacity Building Workshop on Sub-regional Trade and Transit Cooperation for SASEC Countries (Tentative as of 7 June 2012) 21-26 June 2012 Kathmandu, Nepal In cooperation with Ministry of Commerce
ESCAP-ADB Capacity Building Workshop on Sub-regional Trade and Transit Cooperation for SASEC Countries (Tentative as of 7 June 2012) 21-26 June 2012 Kathmandu, Nepal In cooperation with Ministry of Commerce
GOVERNMENT OF PAKISTAN MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT
 Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) National Operational Strategy GOVERNMENT OF PAKISTAN MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT (January, 2006) CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1 2.0 DESIGNATED NATIONAL AUTHORITY FOR CLEAN DEVELOPMENT
Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) National Operational Strategy GOVERNMENT OF PAKISTAN MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT (January, 2006) CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1 2.0 DESIGNATED NATIONAL AUTHORITY FOR CLEAN DEVELOPMENT
Single Window (SW) and Paperless Trade Implementation
 Single Window (SW) and Paperless Trade Implementation Success Factors, Lessons Learned & Emerging Trends Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation Kasetsart University ESCAP-ARTNET/ITD
Single Window (SW) and Paperless Trade Implementation Success Factors, Lessons Learned & Emerging Trends Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation Kasetsart University ESCAP-ARTNET/ITD
Regional Study on Improving Regional Trade Procedures and Processes: Sri Lanka
 Regional Study on Improving Regional Trade Procedures and Processes: Sri Lanka Suwendrani Jayaratne, Dharshani Premaratne & Deshal de Mel Institute of Policy Studies, Sri Lanka 1 Outline - Objectives of
Regional Study on Improving Regional Trade Procedures and Processes: Sri Lanka Suwendrani Jayaratne, Dharshani Premaratne & Deshal de Mel Institute of Policy Studies, Sri Lanka 1 Outline - Objectives of
Free Zone Process - Sea
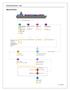 High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 3 4 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Free Zone eexemption Process Shipping Agent Process Pre-clearance Movement Process Scans Bill of Lading
High Level Process Pre-clearance Process 1 2 3 4 Ministries Departments and Agencies (MDA) Process Free Zone eexemption Process Shipping Agent Process Pre-clearance Movement Process Scans Bill of Lading
UN/CEFACT United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business
 UN/CEFACT United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business ICAO Air Cargo Development Forum (IACD) Session 4: Improving Air Cargo Connectivity and Supply Chain Zhengzhou, China, 7 September
UN/CEFACT United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business ICAO Air Cargo Development Forum (IACD) Session 4: Improving Air Cargo Connectivity and Supply Chain Zhengzhou, China, 7 September
Trade Logistics and Facilitation
 Trade Logistics and Facilitation Customs and Border Management: New insights on an old problem Gerard McLinden International Trade Department Typical perspectives My goods were stuck in Customs for 3 weeks
Trade Logistics and Facilitation Customs and Border Management: New insights on an old problem Gerard McLinden International Trade Department Typical perspectives My goods were stuck in Customs for 3 weeks
Fundamental Transit Policy Issues
 MIDTERM REVIEW OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE VIENNA PROGRAMME OF ACTION FOR LLDCs FOR THE DECADE 2014-2024 IN THE EURO-ASIAN REGION Fundamental Transit Policy Issues Ms. Azhar Jaimurzina Chief, Transport
MIDTERM REVIEW OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE VIENNA PROGRAMME OF ACTION FOR LLDCs FOR THE DECADE 2014-2024 IN THE EURO-ASIAN REGION Fundamental Transit Policy Issues Ms. Azhar Jaimurzina Chief, Transport
SINGLE WINDOW, E-CERTS & AUTOMATION: LESSONS, EXPERIENCES & PATHWAYS FOR SPS..
 SINGLE WINDOW, E-CERTS & AUTOMATION: LESSONS, EXPERIENCES & PATHWAYS FOR SPS.. Bill Gain Global Lead Trade Facilitation & Border Management World Bank Group TRADE AND COMPETITIVENESS GLOBAL PRACTICE The
SINGLE WINDOW, E-CERTS & AUTOMATION: LESSONS, EXPERIENCES & PATHWAYS FOR SPS.. Bill Gain Global Lead Trade Facilitation & Border Management World Bank Group TRADE AND COMPETITIVENESS GLOBAL PRACTICE The
Skills Assessment Support (SAS) General Occupations - Required Document Checklist
 All uploaded documents need to be high quality colour scans of the original documents. Identity Documents: Passport Bio Page/ Birth Certificate: It is preferable that you upload a coloured copy of your
All uploaded documents need to be high quality colour scans of the original documents. Identity Documents: Passport Bio Page/ Birth Certificate: It is preferable that you upload a coloured copy of your
Fundamental Transit Policy Issues
 MIDTERM REVIEW OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE VIENNA PROGRAMME OF ACTION FOR LLDCs FOR THE DECADE 2014-2024 IN THE EURO-ASIAN REGION Fundamental Transit Policy Issues Ms. Azhar Jaimurzina Chief, Transport
MIDTERM REVIEW OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE VIENNA PROGRAMME OF ACTION FOR LLDCs FOR THE DECADE 2014-2024 IN THE EURO-ASIAN REGION Fundamental Transit Policy Issues Ms. Azhar Jaimurzina Chief, Transport
UN/CEFACT Reference Data Models (Semantic Models) Anticipating and Following Technological Trends in ebusiness Data Exchanges
 UN/CEFACT Reference Data Models (Semantic Models) Anticipating and Following Technological Trends in ebusiness Data Exchanges UN/CEFACT: Who we are and what we do Objectives Simple, transparent and effective
UN/CEFACT Reference Data Models (Semantic Models) Anticipating and Following Technological Trends in ebusiness Data Exchanges UN/CEFACT: Who we are and what we do Objectives Simple, transparent and effective
UN/CEFACT Simple, Transparent and Effective Processes For Global Commerce
 UN/CEFACT Simple, Transparent and Effective Processes For Global Commerce BUSINESS REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION (BRS) Business Domain: Cross Industry Supply Chain Business Process: Invoice Process Document
UN/CEFACT Simple, Transparent and Effective Processes For Global Commerce BUSINESS REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION (BRS) Business Domain: Cross Industry Supply Chain Business Process: Invoice Process Document
STEP BY STEP GUIDE TO EXPORTING WORKSHOP
 STEP BY STEP GUIDE TO EXPORTING WORKSHOP Module 3: Getting Products to Market Shipping & Logistics Available Options Presenter: Beverly Johnson JLB International (Shipping) Ltd March 27, 2014 DEFINITION
STEP BY STEP GUIDE TO EXPORTING WORKSHOP Module 3: Getting Products to Market Shipping & Logistics Available Options Presenter: Beverly Johnson JLB International (Shipping) Ltd March 27, 2014 DEFINITION
LIST OF UNECE UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATIONS ON TRADE FACILITATION
 LIST OF UNECE UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATIONS ON TRADE FACILITATION UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE 2 UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE LIST OF UNECE UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATIONS ON TRADE
LIST OF UNECE UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATIONS ON TRADE FACILITATION UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE 2 UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE LIST OF UNECE UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATIONS ON TRADE
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRADE/C/CEFACT/2017/10 Distr.: General 17 January 2017 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Executive Committee Centre for Trade Facilitation
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRADE/C/CEFACT/2017/10 Distr.: General 17 January 2017 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Executive Committee Centre for Trade Facilitation
Detailed Rules for Implementation of Bonded Delivery of Dalian Commodity Exchange. Chapter I General Provisions
 Detailed Rules for Implementation of Bonded Delivery of Dalian Commodity Exchange Chapter I General Provisions Article 1 These Detailed Rules are formulated subject to the Trading Rules of Dalian Commodity
Detailed Rules for Implementation of Bonded Delivery of Dalian Commodity Exchange Chapter I General Provisions Article 1 These Detailed Rules are formulated subject to the Trading Rules of Dalian Commodity
Enquiries : or tel or fax
 BOOK NOW for one of ITRISA s popular import / export training courses! ITRISA is registered with the Department of Higher Education and Training (reg. no. 2002/HE08/001) and is fully accredited by the
BOOK NOW for one of ITRISA s popular import / export training courses! ITRISA is registered with the Department of Higher Education and Training (reg. no. 2002/HE08/001) and is fully accredited by the
UN/CEFACT Simple, Transparent and Effective Processes For Global Commerce
 UN/CEFACT Simple, Transparent and Effective Processes For Global Commerce BUSINESS REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION (BRS) Business Domain: Cross Industry Supply Chain Business Process: Invoice Process Document
UN/CEFACT Simple, Transparent and Effective Processes For Global Commerce BUSINESS REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION (BRS) Business Domain: Cross Industry Supply Chain Business Process: Invoice Process Document
THE RELEVANT KEY PRINCIPLES OF THE SAFE FRAMEWORK OF STANDARDS, IN FURTHER FACILITATING THE PROCESS OF CLEARING RELIEF CONSIGNMENTS
 THE RELEVANT KEY PRINCIPLES OF THE SAFE FRAMEWORK OF STANDARDS, IN FURTHER FACILITATING THE PROCESS OF CLEARING RELIEF CONSIGNMENTS Introduction 1. The issues surrounding international relief operations
THE RELEVANT KEY PRINCIPLES OF THE SAFE FRAMEWORK OF STANDARDS, IN FURTHER FACILITATING THE PROCESS OF CLEARING RELIEF CONSIGNMENTS Introduction 1. The issues surrounding international relief operations
Concepts and Implementations
 Evolution of National Single Window: Concepts and Implementations Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation... Kasetsart University, Bangkok sk@ku-inova.org Table of Contents 1. Evolutionary
Evolution of National Single Window: Concepts and Implementations Somnuk Keretho, PhD Director, Institute for IT Innovation... Kasetsart University, Bangkok sk@ku-inova.org Table of Contents 1. Evolutionary
ASEAN SINGLE WINDOW POTENTIAL IMPACT SURVEY
 ASEAN SINGLE WINDOW POTENTIAL IMPACT SURVEY WE ARE IN FULL SUPPORT OF ASW IMPLEMENTATION BECAUSE WE EXPECT TRADE FACILITATION AND RELATED COSTS SAVINGS WILL BE OBTAINED TOGETHER WITH IMPROVED TRANSPARENCY
ASEAN SINGLE WINDOW POTENTIAL IMPACT SURVEY WE ARE IN FULL SUPPORT OF ASW IMPLEMENTATION BECAUSE WE EXPECT TRADE FACILITATION AND RELATED COSTS SAVINGS WILL BE OBTAINED TOGETHER WITH IMPROVED TRANSPARENCY
Business Process Analysis Guide To Simplify Trade Procedures
 Business Process Analysis Guide To Simplify Trade Procedures Available at http://www.unescap.org/tid/publication/tipub2558.asp ANNEX 1 (December 2011) BUSINESS PROCESS ANALYSIS OF THE EXPORT OF JASMINE
Business Process Analysis Guide To Simplify Trade Procedures Available at http://www.unescap.org/tid/publication/tipub2558.asp ANNEX 1 (December 2011) BUSINESS PROCESS ANALYSIS OF THE EXPORT OF JASMINE
Business process analysis of trade procedures in selected Central Asian countries
 i Business analysis of trade procedures in selected Central Asian countries Copyright ESCAP and IRTI 2015 All rights reserved Disclaimers All rights reserved. The opinions, figures and estimates set forth
i Business analysis of trade procedures in selected Central Asian countries Copyright ESCAP and IRTI 2015 All rights reserved Disclaimers All rights reserved. The opinions, figures and estimates set forth
GUIDE TO KEY ISSUES IN DEVELOPMENT OF LOGISTICS POLICY
 GUIDE TO KEY ISSUES IN DEVELOPMENT OF LOGISTICS POLICY The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the United Nations Secretariat. The opinions,
GUIDE TO KEY ISSUES IN DEVELOPMENT OF LOGISTICS POLICY The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the United Nations Secretariat. The opinions,
WCO Data Model 3.0 : Implications for Paperless Trade Initiatives
 WCO Data Model 3.0 : Implications for Paperless Trade Initiatives Asia-Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2010 Kuala Lumpur, 5-66 October 2010 Copyright of the World Customs Organization SP SAHU World Customs
WCO Data Model 3.0 : Implications for Paperless Trade Initiatives Asia-Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum 2010 Kuala Lumpur, 5-66 October 2010 Copyright of the World Customs Organization SP SAHU World Customs
Trade Facilitation, Single Window and Data Harmonization: Conceptual framework and standards
 Second Regional Conference on Trade Facilitation, the Single Window and Data Harmonization Tbilisi, 13-14 June 2012 Trade Facilitation, Single Window and Data Harmonization: Conceptual framework and standards
Second Regional Conference on Trade Facilitation, the Single Window and Data Harmonization Tbilisi, 13-14 June 2012 Trade Facilitation, Single Window and Data Harmonization: Conceptual framework and standards
TANZANIA BUREAU OF STANDARDS Pre-Export Verification of Conformity to Standards
 INTRODUCTION The Bureau of Standards (TBS) was established by Act of Parliament in 1975 which was subsequently amended in 1977. TBS is a specialized parastatal organization servicing in the field of standardization,
INTRODUCTION The Bureau of Standards (TBS) was established by Act of Parliament in 1975 which was subsequently amended in 1977. TBS is a specialized parastatal organization servicing in the field of standardization,
Trade Facilitation, Regional Integration & Logistics Liberalization
 Andrew L. Stoler The University of Adelaide Third ARTNeT Consultative Meeting of Policy Makers and Research Institutions Macao, China 1-2 November 2006 1 The Case Studies* Comparative Analysis of Trade
Andrew L. Stoler The University of Adelaide Third ARTNeT Consultative Meeting of Policy Makers and Research Institutions Macao, China 1-2 November 2006 1 The Case Studies* Comparative Analysis of Trade
Chapter 4 Documents Used in International Trade
 Chapter 4 Documents Used in International Trade Documents Used in International Trade Operations Financial documents Used to obtain payment Commercial documents Not intended to obtain payment Both documents
Chapter 4 Documents Used in International Trade Documents Used in International Trade Operations Financial documents Used to obtain payment Commercial documents Not intended to obtain payment Both documents
Getting Ready for Exports/Imports (1 day) Wed 30 January. Wed 13 March. Wed 30 January. Fri 8 February
 ITRISA is registered with the Department of Higher Education and Training (reg. no. 2002/HE08/001) and is fully accredited by the Council on Higher Education. As such, its training is recognised by the
ITRISA is registered with the Department of Higher Education and Training (reg. no. 2002/HE08/001) and is fully accredited by the Council on Higher Education. As such, its training is recognised by the
EXPORT BOOT CAMP KICK START YOUR Knowledge on EXPORTS in 2 days!
 EXPORT BOOT CAMP KICK START YOUR Knowledge on EXPORTS in 2 days! UA SALES & RANDBURG CHAMBER OF COMMERCE & INDUSTRY Report for duty: 24 & 25 APRIL 2017 This two-day workshop will kick start your learning
EXPORT BOOT CAMP KICK START YOUR Knowledge on EXPORTS in 2 days! UA SALES & RANDBURG CHAMBER OF COMMERCE & INDUSTRY Report for duty: 24 & 25 APRIL 2017 This two-day workshop will kick start your learning
International. Standard. Banking Practice. for the Examination of Documenta. under UCP 600
 International Standard Banking Practice for the Examination of Documenta under UCP 600 I INTERNAT I KT CHAMBER OF COMMI The world business Organization Contents INTRODUCTION 9 PRELIMINARY CONSIDERATIONS
International Standard Banking Practice for the Examination of Documenta under UCP 600 I INTERNAT I KT CHAMBER OF COMMI The world business Organization Contents INTRODUCTION 9 PRELIMINARY CONSIDERATIONS
CASE STORIES. Interagency Collaboration for Single Window Implementation: Thailand s Experience TRADE. High-level Architecture of THAINSW
 TRADE FACILITATION IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE CASE STORIES Interagency Collaboration for Single Window Implementation: Thailand s Experience National Single Window (THAINSW) is a successful interagency collaboration.
TRADE FACILITATION IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE CASE STORIES Interagency Collaboration for Single Window Implementation: Thailand s Experience National Single Window (THAINSW) is a successful interagency collaboration.
ASEAN CUSTOMS TRANSIT SYSTEM (ACTS)
 ASEAN CUSTOMS TRANSIT SYSTEM () Customs Transit within ASEAN Member States An Introduction for Customs Authorities one vision one identity one community CONTENTS 1. Background of the...2 2. The movement
ASEAN CUSTOMS TRANSIT SYSTEM () Customs Transit within ASEAN Member States An Introduction for Customs Authorities one vision one identity one community CONTENTS 1. Background of the...2 2. The movement
Electronic Certification in the context of Agricultural Trade
 Electronic Certification in the context of Agricultural Trade Jonathan Koh STDF Seminar on Electronic Sanitary and Phytosanitary Certification Geneva, WTO All rights reserved. CrimsonLogic and the Shell
Electronic Certification in the context of Agricultural Trade Jonathan Koh STDF Seminar on Electronic Sanitary and Phytosanitary Certification Geneva, WTO All rights reserved. CrimsonLogic and the Shell
