Influence of Situational Constraints and Public Transport Incentives on Acceptability of Car Use Restrictions in Lahore, Pakistan
|
|
|
- Roberta Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 52 (2): (2015) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: (print), (online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Influence of Situational Constraints and Public Transport Incentives on Acceptability of Car Use Restrictions in Lahore, Pakistan Muhammad A. Javid Department of Civil Engineering, National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Faisal Town, Lahore, Pakistan Abstract: The rapid increase in private car ownership and its usage has resulted in traffic congestion on road infrastructure in Lahore city. It is very important to explore the potential of some travel demand management policies under local socio-economic context. This paper aims to explore the influence of situational constraints and public transport incentives on acceptability of car use restrictions. A questionnaire survey was conducted in Lahore city to obtain the required data. Data was analyzed using structural equation modeling technique. Results revealed that situational constraints and public transport incentives have significant influence on people s travel behavior and acceptability of mobility restrictions on car use. The findings of this study would be useful for local planners in making decision regarding transit improvements and implementing car use reduction measures. Keywords: Travel demand management (TDM), structural equation modeling (SEM), situational constraints, traffic congestion, public transport 1. INTRODUCTION The rapid increase in private vehicle ownership and its usage has resulted in traffic congestions on road infrastructure in most of the developing countries. The traffic jams tend to increase social cost in terms of increase in energy congestion and air pollution, increase in travel time and cost, and increase in accidents. Building more road infrastructure results inequitable solutions for the reduction of traffic congestion because it just facilitates the private vehicle users. It does not provide any appropriate mobility options for the poor people such as non-motorized and public transport modes users. Moreover, such supply side measures encourage more private vehicle ownership and its usage, and tend to increase social cost. In developing countries, the main focus is on supply side measures in order to reduce the gap between demand and supply. However, lack of financial, technical and institutional resources and environment sustainability related problems argue from planners and policy makers to look for demand side solutions with supply side measures. In this perspective, travel demand management (TDM) strategies are considered as effective tools in reducing the traffic congestion and its related social and environmental problems. The TDM strategies tend to influence the individual s travel behavior for the reduction of traffic congestion and have impact on reduction in travel time and cost, and convenience of travel options [1]. Garling and Schuitema [2] believe that it is vital to promote such policies that should reduce the advantage of car use and increase benefits of public transport usage. The TDM strategies are mainly classified into two types such as push or disincentive measures aiming to reduce the advantages of car use (e.g., increase in fuel and road taxes), and pull or incentive measures where alternative travel choices are provided (e.g., improved public transport, van pooling, HOVs lanes) [3]. Another classification includes hard measures such as road pricing, parking charges, Received, December 2014; Accepted, April 2015 *Corresponding author: M.A. Javid; ma.javid@hotmail.com
2 110 Muhammad A. Javid new public transport service and soft measures such as workplace travel plans, personalized travel planning, public transport marketing and travel awareness campaigns [4]. According to Meyer [5], it is required to manage travel demand efficiently for commuting and non-commuting trips and for recurring and non-recurring congestion events in order to optimize the performance of existing transportation system. It is argued that those TDM strategies will be effective in developing countries which offer cheaper travel alternative to the majority of the residents [6]. The TDM measures such as support for ridesharing, public transport improvements and implementation of land use policies can reduce the private vehicle trips. Implementation of parking control measures, and support for pedestrians and cyclists can also be effective in altering the travel demand and pattern [7]. Faiz et al [8] argue that imposing vehicle ownership and other usage related taxes like road tax and parking charges may discourage both car ownership and usage. It is very important to evaluate the public acceptability for the specific TDM strategies before implementing [9] because commuter s behavior will be key factor in their success and effectiveness. In some studies, push measures like road pricing and parking charges perceived low acceptance from public compared with pull measures like public transport improvements [10-11]. However, it is believed that commuters normally perceive pull measures to be more suitable; though push measures are often believed to influence car use reduction to a greater extent [12, 3]. In addition, the acceptability of a measure is important if its objectives have to be achieved [9, 13]. Different factors can influence the acceptability of TDM policies. These factors include individual s socio-economic demographics (SED), lifestyle, attitudes and intentions [3, 12, 17-18]. It is vital to explore the influence of such factors on acceptability of TDM strategies in the local context. Therefore, the objective of this paper is to diagnose the influence of situational constraints or coupling constraints and public transport incentives on acceptability of car use restrictions. The findings of this study are based on results of a questionnaire survey and structural equation modeling. This paper organized in the following manner. Section 2 describes the characteristics of study area and data collection methods. Section 3 presents the results and analysis part and last section summarize the key findings of this study. 2. STUDY AREA AND DATA COLLECTION In this study, Lahore city selected for case study. It is the second largest city of Pakistan after Karachi and largest one of Punjab Province. The population of Lahore city is almost 8.65 million and area about 1792 km 2 [14]. The urban population growth rate is almost 3% per annum [14]. It is concentrated with educational, economic and medical facilities. The people from other parts of the country travel to Lahore in order to enjoy the culture and better living facilities. The presence of such facilities attracts many people from suburban areas and generates huge travel demand. The number of trips generated is very high from the inner zones of the city due to high density development. Population density varies from 450 persons per hectare in the inner zone to 100 persons per hectare in the outer zone and almost 80% of population is living within a radius of 7-8 km from the city centre [14]. Considering the number of trips generated and attracted due to this high density development in the inner zone and concentration of facilities, it can be argued that Lahore city has high potential for mass transit development. On the other hand, the rapidly growing population and traffic demand has resulted persistent traffic congestion on roads despite significant supply of related infrastructure in the last decade. The ownership of private vehicles is increasing at an alarming rate of 17 % per annum [14]. Insufficient and inefficient existing public transport system is one of the main reasons for this increase. Other main elements in the rapid increase of car ownership and usage are banking leasing policy to own a car, changing lifestyles, status symbol and low ownership and usage cost. It
3 Acceptability of Car Use Restrictions in Lahore 111 is believed that motorized traffic also threatens the safety of non-motorized modes users in the busy urban areas [15]. The increased social costs due to heavy traffic congestion in terms of increase in travel time and cost increase in energy consumption and air pollution demands the provision of sustainable travel options. In the context of these stated issues it is required to consider and implement demand management measures in order to solve the congestion oriented problems, and ensure the sustainability of the city. A questionnaire survey was conducted in Lahore to obtain the required data in order to accomplish the study objectives. A comprehensive questionnaire was designed consisting of following two parts. Part one included only personal and trip information of the respondents i.e. gender, marital status, age, income, education, occupation, vehicle ownership, possesses driving license or not, etc. In part two of the questionnaire respondents were requested to state their behavioral intentions for the use of improved public transport under some situational constraints, mobility restrictions on car use, and public transport incentives. A five point Likert scale was used in this part to evaluate the respondents stated intentions, i.e., never (1), almost never (2), sometimes (3), almost every time (4) and every time/always (5). There were fourteen conditional statements as presented in Table 2 and respondents needed to show their intentions for the use of public transport against each statement using five point Likert scales as mentioned above. The respondents were asked to show their preferences to use public transport under different situational constraints such as travelling alone, travelling with family members or friends, and travelling with elder family members. Some incentives were given to the respondents on public transport usage such as reliable service, direct access to important destinations along transit route, low travel cost and less travel time as compared to private car. Some mobility restrictions on car use were included such as limited car parking space at destination; parking is very far from the destination, imposition of road tax and heavy parking fees on car use, and entry restrictions on car in public transport service area. This questionnaire survey was conducted in the various private and civil organizations and educational institutions located in Lahore city. The survey locations were selected keeping in view the target groups of respondents. The target groups were included the current and potential car users. Therefore, only those locations were selected for survey where such kinds of travelers were easily available and accessible. These locations included some engineering departments of University of Engineering and Technology and the University of the Punjab, National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, NESPAK Pvt. Ltd., Transportation Planning Unit (TPU), and some other private organizations. It was assumed that such professional workers and students belonging to engineering fields have more potential to use car. The questionnaire was equipped with the objectives and details of the conducting authority. The filling guidelines were also mentioned at the start of each part. The respondents were selected randomly at each survey location. The survey was conducted with the help of university graduate students and they were properly trained for this purpose. A pilot survey was conducted before the actual survey in order to assure the clarity of designed questionnaire items. Selfcompletion approach by respondents was used in this survey. The questionnaires were distributed at selected locations, and instructions were given to the respondents regarding the contents of the questionnaire and the procedure to answer the questions. The respondents were requested to return the completed questionnaire after two weeks, and completed questionnaires were collected with the help of the survey team. An additional one week was given to those respondents who were not able to complete the questionnaire in the initial period. 3. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS 3.1. Distribution of Respondents Socio-economic Demographics (SEDs) A total of 550 questionnaires were used in the
4 112 Muhammad A. Javid survey, and only 372 samples were obtained, which represented a return rate of 67.7%. Eighteen samples were discarded because of incomplete information and double answers on some questions. Therefore, the results of only 354 samples were used in further analysis. The proportions of male and female respondents in the sample were 67.5% and 32.5%, respectively. There were fewer female respondents because they do not ride motorcycles, and the proportion of working women is also lower in Lahore city. Almost 84% of respondents were aged years, and only 48% had a driving license. Details of socioeconomic demographics (SEDs) are given in Table Average Response on Stated Preferences Average response was calculated for respondent s behavioral intentions to use public transport under stated conditions. For this purpose, respondents response was coded on bipolar scale, i.e., -2 (never), -1 (almost never), 0 (sometimes), 1 (almost every time) and 2 (every time). It can be seen from results presented in Table 2 that respondent s intentions to use public transport vary under different situational constraints. Travelling with family members accounts less average response. It can be said that people feel insecure and less privacy while travelling with family members especially with female. In acceptability of mobility restrictions on use, estimated average response depicts that restriction on car entry in public transport service area has more potential of reducing car use compared to fiscal and parking restrictions. It can be said that improvement in service quality of public transport with car entry restrictions is an effective policy to reduce the traffic congestion in highly congested areas. Parking charges and road tax on car use have almost same influence on car use reduction. In public transport incentives, average response shows that direct access to destination and reliability are the most influencing attributes of public transport along with less travel cost. It looks that sitting has less significance in defining the service quality level of public transport for target group of people Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) Analyses were conducted using structural equation modeling technique to evaluate influence of public transport incentives and situational constraints on acceptability of car use restrictions. Many studies in the field of transportation research have applied SEM technique to diagnose casual relationship between different factors [16-19]. The SEM is a multivariate statistical analysis tool which can elaborate direct and indirect relationships between Table 1. Descriptive statistics of respondents socioeconomic demographics. Characteristics Distribution (%) Marital status Single (65), Married (35) Occupation Students (22.7), private employees (30.6), civil employees (43.1), entrepreneurs (3.6) Personal income per month (PKR) Household income per month (PKR) < 10,000 (19.5), 11,000 20,000 (13.8), 21,000 30,000 (16.7), 31,000 40,000 (17.2), 41,000 60,000 (17.8), 61,000 80,000 (8.8), > 80,000 (6.2) < 20,000 (4.5), 21,000 30,000 (11.6), 31,000 40,000 (10.5), 41,000 60,000 (24.9), 61,000 80,000 (17.0), > 80,000 (31.2) Vehicle ownership None (9.9), Motorcycle (60.2), Car (52.0) Vehicle driven None (23.2), Motorcycle (43.2), Car (40.0) Modal share (usual daily travel mode) Frequency of usual travel mode Walk (7.3), Bicycle (1.5), car (31.2), motorcycle (27.6), auto-rickshaw/taxi (12.3), campus/office transport (7.1), Qingqi/wagon (7.2), bus (5.8) 5 7 days a week (86), 3 4 days a week (9), 1 2 days a week (2), a few times a month or less (3)
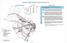
5 Acceptability of Car Use Restrictions in Lahore 113 Table 2. Average response for public transport usage under incentives and restrictions. Description of items Mean Situational Constraints (SC) Commuting with family members (SC-1) Travelling with elder family members (SC-2) Commuting with friends (SC-3) Public transport incentives (PTI) If public transport is reliable than car (PTI-1) When travel cost by public transport is half of car (PTI-2) When travel time by public transport is 10 minutes less than car travel time (PTI-3) When seat is assured in public transport with same travel time as car (PTI-4) When seat is assured in public transport with same travel cost as car (PTI-5) When you can directly access many important places by public transport (PTI-6) Acceptability of mobility restrictions on car use (AMR) When parking is limited at destination (AMR-1) When you need to pay Rs. 100 parking fee at destination (AMR-2) When you need to pay road tax Rs.100 for use of car (AMR-3) When entry of car is restricted in public transport service area (AMR-4) Fig. 1. A typical structural model diagram. the variables. In a SEM model, it is possible to include latent variables. The SEM technique permits the researcher to interpret the covariance structure without considering the multicollinearity issue. For this purpose various users friendly software are available such as SPSS AMOS A typical structural model diagram for this study is shown in Fig. 1. This diagram shows the influence
6 114 Muhammad A. Javid Table 3. Results of structural equation modeling. Limited parking at destination (AMR-1) Rs. 100 parking free (AMR-2) Rs. 100 road tax (AMR-3) Car entry restriction (AMR-4) PTI **.26***.32*** PTI-2.21***.24***.24***.26*** PTI ** PTI *** -.10** PTI-5.14***.07*.11***.37*** PTI-6.12**.15***.16***.12** SC-1.24*** SC-2.29*** SC *** ** Note: PTI: public transport incentive, SC: social constraints, AMR: acceptability of mobility restrictions, *** significant at 1%, ** Significant at 5%, * Significant at 10% of public transport incentive (PTI) variables and various situational constraints (SC) variables on a particular car use reduction measures. Table 3 gives the details of significant structural relationships between influencing factors and car use reduction measure. Next sub-sections discuss the results one by one Limited Car Parking Space at Destination (AMR-1) The less travel cost of public transport compared to car has significant and positive relationship with limited parking restriction policy at destination. It implies that limited parking policy has some impact on car use reduction if the public transport travel cost is less. Similarly, in public transport incentives seat assurance and direct access by public transport to most of the destination have positive and significant impact on reduction of car use under limited parking policy. In situational constraints, travelling with family members has positive association with limited parking policy. It means that limited parking policy has significant influence on reduction of car use even when people travelling with family members. The negative relationship between this policy and SC-3 depict that people would prefer to use private car instead of public transport while travelling with friends Rs. 100 Parking Fee on Car Use (AMR-2) The halved travel cost of public transport as compared to car and direct access to important destinations by public transport have very strong association with acceptance of Rs. 100 parking fee on use of private car. It implies that reduced travel cost of public transport along with imposition of parking charges would have significant influence on reduction of private vehicle usage Rs. 100 Road Tax Imposition on Car Use (AMR-3) The provision of public transport incentives has positive influence on acceptability of Rs. 100 road tax on car use. These incentives include reliability, less travel cost compared to car, and higher access of public transport service. The negative relationship of assured seat with same travel time with road tax policy imply that people would prefer to use their private vehicle even if they need to pay Rs. 100 road tax on car use. In situational constraints, none of the relationship is significant with this policy Car Entry Restriction in Public Transport Service Area (AMR-4) The incentives of reliability, less travel cost compared to car and higher access of public transport have positive influence on acceptability of this
7 Acceptability of Car Use Restrictions in Lahore 115 policy. However, the incentive of assured seat with same travel time as car has negative relationship with this policy. It depict that this incentive would not help in reducing the use of private vehicle. In situational constraints, people would prefer to use private vehicle while travelling with friends even with the imposition of this policy as relationship is negative. 4. CONCLUSIONS Reliability of service, less travel cost of public transport and direct access to important destinations by public transport are significant incentives in order to enhance the acceptability of imposed mobility restrictions on car use in Lahore city. It was also revealed that assurance of seat in using public transport with same travel time as private car would not have any impact on reduction of car use even in the presence of mobility restrictions. These findings imply that before imposition of such restrictions on car use we need to enhance the reliability and accessibility of public transport service. It is also required to keep travel cost of public transport on lower side in order to make it attractive for car and non-car users. It was observed that some situational constraints have significant influence on acceptability of car use restrictions such as travelling with friends and family members. People would prefer to use their private vehicle while travelling with friends because they feel better in the society. These findings would be helpful in taking preparatory steps for the improvements of public transport system before imposing above mentioned restrictions on car use. 5. REFERENCES 1. Garling, T., D. Eek, Loukopoulos, S. Fujii, O.J. Stenman, R. Kitamura, R. Pendyala & B. Vilhelmson. A conceptual analysis of the impact of travel demand management on private car use. Transport Policy 9: (2002). 2. Garling, T. & G. Schuitema. Travel demand management targeting reduced private car use: effectiveness, public acceptability, and political feasibility. Journal of Social Issues 63(1): (2007). 3. Steg, L. & C. Vlek. The Role of Problem Awareness in Willingness to Change Car Use and Evaluating Relevant Policy Measures. In: Traffic and Transport Psychology: Theory and Application. J.A. Rothengatter & E. Carbonell Vaya (Ed.), Elsevier, Oxford, UK, p (1997). 4. Garling, T. & S. Fujii. Travel behaviour modification: theories, methods, and programs. Resource Paper presented at IATBR Conference. Kyoto University, Japan (2006). 5. Meyer, M. Demand Management as an Element of Transportation Policy: Using Carrots and Sticks to Influence Travel Behaviour. Transportation Research Record 33(7-8): (1999). 6. Litman, T. Efficient Vehicles versus Efficient Transportation: Comparing Transportation Energy Conservation Strategies. Transport Policy 12(2): (2005). 7. Auckland Regional Council. Travel Demand Management Strategies (2000). Retrieved from 8. Faiz, A., K. Sinha, M. Walsh, & A. Varma. Automatic Air Pollution: Issues and Options for Developing Countries. Working Paper 492, Infrastructure and Urban Development Department. The World Bank, Washington, DC (1990). 9. J. Schade, & B. Schlag. Acceptability of urban transport pricing strategies. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour 6(1): (2003). 10. Schlag, B. & J. Schade. Public acceptability of traffic demand management in Europe. Traffic Engineering and Control 41: (2000). 11. Bhattacharjee, D., S.W. Haider, & Y. Tanaboriboon. Commuter's attitudes towards travel demand management in Bangkok. Transport Policy 4(3): (1997). 12. Javid, M.A., T. Okamura, F. Nakamura, S. Tanaka & R. Wang. Public perceptions to travel demand management measures in Lahore, Pakistan: Analysis and implications. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51(1): (2014). 13. Thorpe, N., P. Hills & S. Jaensirisak. Public attitudes to TDM measures: a comparative study. Transport Policy 7(4): (2000). 14. JICA. Lahore Urban Transport Master Plan in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, Final Report, Vol. I & II, March Retrieved from JICA online library: Esmael, M.O., K. Sasaki & K. Nishii. Road Traffic Accident Trend in Developing Countries The Policy Implications. Proceedings of 13 th World Conference on Transport Research, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, July 2014 (2014). 16. Javid, M.A., T. Okamura, F. Nakamura, S. Tanaka & R. Wang. Comparison of commuters' satisfaction
8 116 Muhammad A. Javid and preferences with public transport: a case of wagon service in Lahore. Jordon Journal of Civil Engineering 7(4): (2013). 17. Javid, M.A., T. Okamura, F. Nakamura, S. Tanaka & R. Wang. Methodology for evaluating the driver s attitudes towards transportation demand management measures in Lahore, Pakistan. Journal of Recent Trends in Civil Engineering and Technology 2(2): (2012). 18. Choocharukul, K., H.T. Van & S. Fujii. Psychological determinants of moral obligation of car use reduction and acceptance of car use restriction in Japan and Thailand. IATSS Research 30(2): (2006). 19. Golob, T. Structural equation modelling for travel behaviour research. Transportation Research Part B 37(1): 1 25 (2003).
Keywords Travel demand management, traffic congestion, travel behavior, perceptions, Lahore
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering & Management (IJIREM) Travel Demand Management Policies Prospects for Lahore: Rating and Classification Muhammad Ashraf Javid College of Engineering
International Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering & Management (IJIREM) Travel Demand Management Policies Prospects for Lahore: Rating and Classification Muhammad Ashraf Javid College of Engineering
Public Perceptions to Travel Demand Management Measures in Lahore, Pakistan: Analysis and Implications
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (1): 17 29 (2014) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Public
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (1): 17 29 (2014) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Public
PUBLIC ATTITUDES TOWARDS TRAVEL DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM) STRATEGIES IN LAHORE, PAKISTAN IMPORTANCE OF LIFESTYLES, SOCIAL AND TRAVEL RELATED BELIEFS
 PUBLIC ATTITUDES TOWARDS TRAVEL DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM) STRATEGIES IN LAHORE, PAKISN IMPORNCE OF LIFESTYLES, SOCIAL AND TRAVEL RELATED BELIEFS JAVID, M. ASHRAF, DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, YOKOHAMA
PUBLIC ATTITUDES TOWARDS TRAVEL DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM) STRATEGIES IN LAHORE, PAKISN IMPORNCE OF LIFESTYLES, SOCIAL AND TRAVEL RELATED BELIEFS JAVID, M. ASHRAF, DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, YOKOHAMA
INTEGRATED ROAD PRICING AND BUS RAPID TRANSIT: THE EFFECT OF HABITUAL BEHAVIOUR AND CAPTIVE ATTITUDE
 INTEGRATED ROAD PRICING AND BUS RAPID TRANSIT: THE EFFECT OF HABITUAL BEHAVIOUR AND CAPTIVE ATTITUDE Abstract Sittha Jaensirisak 1 and Sermsak Pongmesa 2 This paper presents the possibility of using Bus
INTEGRATED ROAD PRICING AND BUS RAPID TRANSIT: THE EFFECT OF HABITUAL BEHAVIOUR AND CAPTIVE ATTITUDE Abstract Sittha Jaensirisak 1 and Sermsak Pongmesa 2 This paper presents the possibility of using Bus
Paradox between public transport and private car as a modal choice in policy formulation
 University of Wollongong Research Online SMART Infrastructure Facility - Papers Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2009 Paradox between public transport and private car as a modal choice in
University of Wollongong Research Online SMART Infrastructure Facility - Papers Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2009 Paradox between public transport and private car as a modal choice in
Transportation Cost Analysis:
 Victoria Transport Policy Institute www.vtpi.org info@vtpi.org 1250 Rudlin Street, Victoria, BC, V8V 3R7, CANADA Phone & Fax (250) 360-1560 Efficiency - Equity - Clarity Transportation Cost Analysis: Techniques,
Victoria Transport Policy Institute www.vtpi.org info@vtpi.org 1250 Rudlin Street, Victoria, BC, V8V 3R7, CANADA Phone & Fax (250) 360-1560 Efficiency - Equity - Clarity Transportation Cost Analysis: Techniques,
Influences of Commuters' Personality and Preferences on Travel Intention in Developing Countries: A case of Bangkok
 Influences of Commuters' Personality and Preferences on Travel Intention in Developing Countries: A case of Bangkok Akkarapol TANGPHAISANKUN Transportation and Logistics Advisor Habitus Co., Ltd. 338/212
Influences of Commuters' Personality and Preferences on Travel Intention in Developing Countries: A case of Bangkok Akkarapol TANGPHAISANKUN Transportation and Logistics Advisor Habitus Co., Ltd. 338/212
Regional Travel Demand Management Plan
 Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 Quality for life Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 For more information, contact: Greater Wellington 142 Wakefield
Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 Quality for life Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 For more information, contact: Greater Wellington 142 Wakefield
Exploring Activity-Travel Patterns in Xiamen, China
 Exploring Activity-Travel Patterns in Xiamen, China Xin Ye 1, Ram M. Pendyala 1, Xiaoguang Yang 2 and Wei Ding 2 Abstract Recent research in travel demand modeling has increasingly focused on the analysis
Exploring Activity-Travel Patterns in Xiamen, China Xin Ye 1, Ram M. Pendyala 1, Xiaoguang Yang 2 and Wei Ding 2 Abstract Recent research in travel demand modeling has increasingly focused on the analysis
Transit System Survey
 Denver Moves: Transit SUMMARY Build Your Own Transit System Survey March-July 2017 ABOUT THE SURVEY The Denver Moves: Transit Build Your Own Transit System (BYOTS) survey invited people to share their
Denver Moves: Transit SUMMARY Build Your Own Transit System Survey March-July 2017 ABOUT THE SURVEY The Denver Moves: Transit Build Your Own Transit System (BYOTS) survey invited people to share their
Cities, Transport and Climate Change August 2009
 www.unhabitat.org 1 EXPERT GROUP MEETING (EGM) ON TRANSPORT FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT United Nations Headquarters, 27-28 August 2009 Cities, Transport and Climate Change: Problems and Opportunities for
www.unhabitat.org 1 EXPERT GROUP MEETING (EGM) ON TRANSPORT FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT United Nations Headquarters, 27-28 August 2009 Cities, Transport and Climate Change: Problems and Opportunities for
Shaping our future. A summary of BC TRANSIT S STRATEGIC PLAN 2030
 Shaping our future A summary of BC TRANSIT S STRATEGIC PLAN 2030 INTRODUCTION: THE NEED TO SHAPE OUR FUTURE Many different factors energy constraints, an aging society, the desire for better personal health
Shaping our future A summary of BC TRANSIT S STRATEGIC PLAN 2030 INTRODUCTION: THE NEED TO SHAPE OUR FUTURE Many different factors energy constraints, an aging society, the desire for better personal health
Secretaría Confederal de Medio Ambiente CCOO. Manel Ferri, Mobility Dptº CC OO responsible
 Secretaría Confederal de Medio Ambiente CCOO Manel Ferri, Mobility Dptº CC OO responsible Brussels, 5th February 2013 European Commuters for Sustainable Mobility Strategies secretaría mº ambiente CS CCOO
Secretaría Confederal de Medio Ambiente CCOO Manel Ferri, Mobility Dptº CC OO responsible Brussels, 5th February 2013 European Commuters for Sustainable Mobility Strategies secretaría mº ambiente CS CCOO
Summary Final version of questionnaire and cover letter
 Work Package 2 Status: Final Date of preparation: March 2009 Author(s): Horários do Funchal Contributions from: All project partners Contract number: EIE/05/095/SI2.420185 Summary WP2 Description of the
Work Package 2 Status: Final Date of preparation: March 2009 Author(s): Horários do Funchal Contributions from: All project partners Contract number: EIE/05/095/SI2.420185 Summary WP2 Description of the
That will also contribute to achievement of a number of objectives and policies in the Regional Policy Statement.
 Board of Inquiry MacKays to Peka Peka Expressway Proposal Submitters Evidence Public Transport Voice 5 October 2012 Executive Summary Increasing modal share for public transport is a key outcome in the
Board of Inquiry MacKays to Peka Peka Expressway Proposal Submitters Evidence Public Transport Voice 5 October 2012 Executive Summary Increasing modal share for public transport is a key outcome in the
1996, TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT FOR INTERPROVINCIAL TRAVEL
 1996, TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT FOR INTERPROVINCIAL TRAVEL Executive Summary: Introduction In recent years, the demand for transportation in the National Capital Region has outpaced the ability
1996, TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT FOR INTERPROVINCIAL TRAVEL Executive Summary: Introduction In recent years, the demand for transportation in the National Capital Region has outpaced the ability
UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK
 Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
PUBLIC BEHAVIOR TOWARDS DIFFERENT MEANS OF COMMUTATION WITH REFERENCE TO DEHRADUN
 372 PUBLIC BEHAVIOR TOWARDS DIFFERENT MEANS OF COMMUTATION WITH REFERENCE TO DEHRADUN TADAMARLA.ANUPAMA*; INUMULA KRISHNA MURTHY**; K.DEEPPA*** ABSTRACT *Assistant Professor, College of Management and
372 PUBLIC BEHAVIOR TOWARDS DIFFERENT MEANS OF COMMUTATION WITH REFERENCE TO DEHRADUN TADAMARLA.ANUPAMA*; INUMULA KRISHNA MURTHY**; K.DEEPPA*** ABSTRACT *Assistant Professor, College of Management and
Impact of Social Media on Purchasing Decision of Consumerwith Special Reference to Lahore, Pakistan
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Social Sciences www.rroij.com Impact of Social Media on Purchasing Decision of Consumerwith Special Reference to Lahore, Pakistan Muhammad Yasir Rafiq 1 and Abdullah Malik
Research & Reviews: Journal of Social Sciences www.rroij.com Impact of Social Media on Purchasing Decision of Consumerwith Special Reference to Lahore, Pakistan Muhammad Yasir Rafiq 1 and Abdullah Malik
27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004
 27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004 Paper title: Author(s) name(s): Passengers perspective of bus service quality in Bangkok: an ordered probabilistic modeling
27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004 Paper title: Author(s) name(s): Passengers perspective of bus service quality in Bangkok: an ordered probabilistic modeling
Pima County Travel Reduction Ordinance
 Pima County Travel Reduction Ordinance Source: http://www.municode.com/resources/gateway.asp?pid=16119&sid=3 Chapter 17.40 TRAVEL REDUCTION ORDINANCE Sections: Article I. General Provisions 17.40.010 Short
Pima County Travel Reduction Ordinance Source: http://www.municode.com/resources/gateway.asp?pid=16119&sid=3 Chapter 17.40 TRAVEL REDUCTION ORDINANCE Sections: Article I. General Provisions 17.40.010 Short
ON TRAVEL BEHAVIOUR DYNAMICS FROM THE LONDON CONGESTION CHARGING PANEL SURVEY
 UTSG MA & CHATTERJEE: Travel behaviour dynamics INSIGHTS ON TRAVEL BEHAVIOUR DYNAMICS FROM THE LONDON CONGESTION CHARGING PANEL SURVEY Dr Kang-Rae Ma Research Associate UWE, Bristol Dr Kiron Chatterjee
UTSG MA & CHATTERJEE: Travel behaviour dynamics INSIGHTS ON TRAVEL BEHAVIOUR DYNAMICS FROM THE LONDON CONGESTION CHARGING PANEL SURVEY Dr Kang-Rae Ma Research Associate UWE, Bristol Dr Kiron Chatterjee
ROAD TRANSPORT CONTRIBUTING TO A SUSTAINABLE SOCIETY: VISION OF THE FUTURE
 ROAD TRANSPORT CONTRIBUTING TO A SUSTAINABLE SOCIETY: VISION OF THE FUTURE Prof. G. A. Giannopoulos Hellenic Institute of Transport Chairman, European Conference of Transport Research Institutes (ECTRI)
ROAD TRANSPORT CONTRIBUTING TO A SUSTAINABLE SOCIETY: VISION OF THE FUTURE Prof. G. A. Giannopoulos Hellenic Institute of Transport Chairman, European Conference of Transport Research Institutes (ECTRI)
Transportation and Utilities
 4 Section 4 Transportation and Utilities 4.0 Introduction Transportation and utility systems are essential to accommodate and support development proposed in the Future Land Use Map. The following pages
4 Section 4 Transportation and Utilities 4.0 Introduction Transportation and utility systems are essential to accommodate and support development proposed in the Future Land Use Map. The following pages
Northern Virginia Region Draft Needs Summary
 Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Application of system dynamics with GIS for assessing traffic emission management policy
 Application of system dynamics with GIS for assessing traffic emission management policy L. Chen and W.-L. Yang Department of Water Resources & Environmental Engineering, Tamkang University, Tam-Shui,
Application of system dynamics with GIS for assessing traffic emission management policy L. Chen and W.-L. Yang Department of Water Resources & Environmental Engineering, Tamkang University, Tam-Shui,
Transportation. Sustainability Plan Transportation. Help Us Create a Sustainable Lakewood: Work Group Challenge. Topics. Vision
 Plan 1 Help Us Create a Sustainable Lakewood: Work Group Challenge The work group will be comprised of City staff, industry experts, interested citizens, and other community stakeholders. The work group
Plan 1 Help Us Create a Sustainable Lakewood: Work Group Challenge The work group will be comprised of City staff, industry experts, interested citizens, and other community stakeholders. The work group
Goal 3: To ensure that Vaughan is a city that is easy to get around with a low environmental impact
 How we get around Goal 3: To ensure that Vaughan is a city that is easy to get around with a low environmental impact Vaughan is committed to making choices that will reduce automobile dependency, traffic
How we get around Goal 3: To ensure that Vaughan is a city that is easy to get around with a low environmental impact Vaughan is committed to making choices that will reduce automobile dependency, traffic
Summary of transportation-related goals and objectives from existing regional plans
 SMTC 2050 Long Range Transportation Plan Appendix A: Summary of transportation-related goals and objectives from existing regional plans SMTC 2050 Long Range Transportation Plan Summary of transportation-related
SMTC 2050 Long Range Transportation Plan Appendix A: Summary of transportation-related goals and objectives from existing regional plans SMTC 2050 Long Range Transportation Plan Summary of transportation-related
EXAMPLES OF COMPREHENSIVE PLAN POLICIES HOW TO ESTIMATE THE BENEFITS OF THE CTR PROGRAM
 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... I BACKGROUND OF THE COMMUTE TRIP REDUCTION EFFICIENCY ACT... II MAKING THE CONNECTION BETWEEN COMMUTE TRIP REDUCTION AND THE GROWTH MANAGEMENT ACT... IV CTR PLANNING AND
TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... I BACKGROUND OF THE COMMUTE TRIP REDUCTION EFFICIENCY ACT... II MAKING THE CONNECTION BETWEEN COMMUTE TRIP REDUCTION AND THE GROWTH MANAGEMENT ACT... IV CTR PLANNING AND
The evolution of public transport policy in Hong Kong since 1981
 Smart Construction Research RESEARCH ARTICLE The evolution of public transport policy in Hong Kong since 1981 Li Zhe Wuhan Organize Research, Hubei, Wuhan Abstract: Counting only the usable land, the population
Smart Construction Research RESEARCH ARTICLE The evolution of public transport policy in Hong Kong since 1981 Li Zhe Wuhan Organize Research, Hubei, Wuhan Abstract: Counting only the usable land, the population
Sustainable Urban Mobility Planning. Dr. Toe Aung Director of Urban Planning Division Yangon City Development Committee
 Sustainable Urban Mobility Planning Dr. Toe Aung Director of Urban Planning Division Yangon City Development Committee Background and Objectives Yangon City, with a population of about 5.21 million as
Sustainable Urban Mobility Planning Dr. Toe Aung Director of Urban Planning Division Yangon City Development Committee Background and Objectives Yangon City, with a population of about 5.21 million as
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017
 APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit - ii - APPENDIX B TRANSIT AND MOBILITY GLOSSARY Amenities, stop or station: Objects or facilities (such as a shelter, bench,
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit - ii - APPENDIX B TRANSIT AND MOBILITY GLOSSARY Amenities, stop or station: Objects or facilities (such as a shelter, bench,
TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM)
 TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM) Presented by Timothy Papandreou, Strategic Planning & Policy Jay Primus, SFpark Program 46 Strategic Goals & Objectives Goal 1: Create a safer transportation experience
TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT (TDM) Presented by Timothy Papandreou, Strategic Planning & Policy Jay Primus, SFpark Program 46 Strategic Goals & Objectives Goal 1: Create a safer transportation experience
Workshop on enabling Inclusive Cities ADB 29 October PAKISTAN: Karachi Mass-Transit Project (KMTP)
 Workshop on enabling Inclusive Cities ADB 29 October 2013 PAKISTAN: Karachi Mass-Transit Project (KMTP) Agenda 1. Karachi - Context 2. Rapid Project Description 3. Urban Transport and Inclusiveness: Different
Workshop on enabling Inclusive Cities ADB 29 October 2013 PAKISTAN: Karachi Mass-Transit Project (KMTP) Agenda 1. Karachi - Context 2. Rapid Project Description 3. Urban Transport and Inclusiveness: Different
Town of Lexington Planning Board
 Town of Lexington Planning Board TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT POLICY Adopted by Vote of the Board, September 16, 1998 Originally Adopted March 10, 1997 OBJECTIVES: This Policy focuses on meeting the
Town of Lexington Planning Board TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT POLICY Adopted by Vote of the Board, September 16, 1998 Originally Adopted March 10, 1997 OBJECTIVES: This Policy focuses on meeting the
Mode Choice Modelling based on Work Trips Artificial Neural Network Model
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
CHAPTER VII SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION. So far, the aspects inspiring the micro entrepreneurship enterprise
 CHAPTER VII SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION 7.1 INTRODUCTION So far, the aspects inspiring the micro entrepreneurship enterprise involvement among the entrepreneurs, constraints faced by
CHAPTER VII SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION 7.1 INTRODUCTION So far, the aspects inspiring the micro entrepreneurship enterprise involvement among the entrepreneurs, constraints faced by
The satisfaction level of Chinese tourists(group tours) in Thailand. Xuefei Qin* Asst.Prof.Dr.Kom Campiranon** Abstract
 The satisfaction level of Chinese tourists(group tours) in Thailand Xuefei Qin* Asst.Prof.Dr.Kom Campiranon** Abstract This research has studied the satisfaction level of Chinese groups traveling to Thailand
The satisfaction level of Chinese tourists(group tours) in Thailand Xuefei Qin* Asst.Prof.Dr.Kom Campiranon** Abstract This research has studied the satisfaction level of Chinese groups traveling to Thailand
Donostia San Sebastian
 Donostia San Sebastian T 23.1 - New Parking Scheme in Donostia - San Sebastian Donostia San Sebastian November 2010 Project no. TREN/FP7TR/218940 ARCHIMEDES Project Name ARCHIMEDES (Achieving Real Change
Donostia San Sebastian T 23.1 - New Parking Scheme in Donostia - San Sebastian Donostia San Sebastian November 2010 Project no. TREN/FP7TR/218940 ARCHIMEDES Project Name ARCHIMEDES (Achieving Real Change
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): URBAN TRANSPORT 1
 Greater Dhaka Sustainable Urban Transport Project (RRP BAN 42169) Sector Road Map SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): URBAN TRANSPORT 1 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Dhaka, the capital
Greater Dhaka Sustainable Urban Transport Project (RRP BAN 42169) Sector Road Map SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): URBAN TRANSPORT 1 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Dhaka, the capital
Transportation Concurrency
 2015 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
2015 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
Transportation Concurrency
 2017 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
2017 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
VIA Long Range Plan Glossary
 VIA Long Range Plan Glossary Accessibility. Accessibility is the ability to reach opportunities (economic, social, etc.) within a certain geographical area. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Passed
VIA Long Range Plan Glossary Accessibility. Accessibility is the ability to reach opportunities (economic, social, etc.) within a certain geographical area. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Passed
A Win/Win Strategy: Fixing Transportation and Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Massachusetts
 Northeastern University Dukakis Center for Urban & Regional Policy A Win/Win Strategy: Fixing Transportation and Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Massachusetts E2/T4MA/NRDC EcoSalon Full Speed Ahead:
Northeastern University Dukakis Center for Urban & Regional Policy A Win/Win Strategy: Fixing Transportation and Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Massachusetts E2/T4MA/NRDC EcoSalon Full Speed Ahead:
8: Transportation Demand &
 GPATS Long-Range Transportation Plan 8: Transportation Demand & Emerging Technologies INTRODUCTION The transportation systems of cities, states, and nations are undergoing a period of transformation. As
GPATS Long-Range Transportation Plan 8: Transportation Demand & Emerging Technologies INTRODUCTION The transportation systems of cities, states, and nations are undergoing a period of transformation. As
International Journal on Emerging Technologies 8(1): 43-48(2017) Analysis of Service Quality Attributes for Jaipur Urban Bus Transportation
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 8(1): 43-48(2017) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Analysis of Service Quality Attributes for Jaipur Urban Bus Transportation
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 8(1): 43-48(2017) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Analysis of Service Quality Attributes for Jaipur Urban Bus Transportation
Appendix B - Description of question variables and response scales in the empirical research
 Appendix B - Description of question variables and response scales in the empirical research This section describes in detail the characteristics of the questionnaires: the questions/variables and the
Appendix B - Description of question variables and response scales in the empirical research This section describes in detail the characteristics of the questionnaires: the questions/variables and the
Urban Transportation Planning Prof Dr. V. Thamizh Arasan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras
 Urban Transportation Planning Prof Dr. V. Thamizh Arasan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 14 Modal Split Analysis Contd. This is lecture 14 on urban
Urban Transportation Planning Prof Dr. V. Thamizh Arasan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 14 Modal Split Analysis Contd. This is lecture 14 on urban
Chapter 4 Research Methodology
 Research Methodology 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Research Objectives 4.3 Research Design 4.4 Definition of Target Population 4.5 Sampling Methods 4.6 Determination of Necessary Sample Size 4.7 Instrument development
Research Methodology 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Research Objectives 4.3 Research Design 4.4 Definition of Target Population 4.5 Sampling Methods 4.6 Determination of Necessary Sample Size 4.7 Instrument development
DIFFERENT APPROACHES TO THE MODAL SPLIT CALCULATION IN URBAN AREAS
 DIFFERENT APPROACHES TO THE MODAL SPLIT CALCULATION IN URBAN AREAS Marko Matulin, dipl. ing. Professor Ivan Bošnjak, D. Sc. Ljupko Šimunović, D. Sc. University of Zagreb Faculty of Transport and Traffic
DIFFERENT APPROACHES TO THE MODAL SPLIT CALCULATION IN URBAN AREAS Marko Matulin, dipl. ing. Professor Ivan Bošnjak, D. Sc. Ljupko Šimunović, D. Sc. University of Zagreb Faculty of Transport and Traffic
Attitudes and Behavioral Responses to Parking Measures
 Attitudes and Behavioral Responses to Parking Measures Peter van der Waerden, Aloys Borgers and Harry Timmermans Urban Planning Group Eindhoven University of Technology P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven
Attitudes and Behavioral Responses to Parking Measures Peter van der Waerden, Aloys Borgers and Harry Timmermans Urban Planning Group Eindhoven University of Technology P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven
Service Quality and Consumer Behavior on Metered Taxi Services
 Service Quality and Consumer Behavior on Metered Taxi Services Nattapong Techarattanased Abstract The purposes of this research are to make comparisons in respect of the behaviors on the use of the services
Service Quality and Consumer Behavior on Metered Taxi Services Nattapong Techarattanased Abstract The purposes of this research are to make comparisons in respect of the behaviors on the use of the services
MOBILE APP-BASED TAXI SERVICES AND CUSTOMER SATISFACTION: AN EMPIRICAL REVIEW FROM LAHORE CITY, PAKISTAN
 International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. VI, Issue 5, May 2018 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 MOBILE APP-BASED TAXI SERVICES AND CUSTOMER SATISFACTION: AN EMPIRICAL
International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. VI, Issue 5, May 2018 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 MOBILE APP-BASED TAXI SERVICES AND CUSTOMER SATISFACTION: AN EMPIRICAL
Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links
 Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links Reference Bok, D. (2018). Transportation policy and planning. https://www.hks.harvard.edu/courses/transportation-policy-and-planning Transportation
Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links Reference Bok, D. (2018). Transportation policy and planning. https://www.hks.harvard.edu/courses/transportation-policy-and-planning Transportation
Exploring the Relationship between Undergraduate Education and Sustainable Transport Attitudes
 Exploring the Relationship between Undergraduate Education and Sustainable Transport Attitudes Junghwa Kim a, Jan-Dirk Schmöcker b*, Satoshi Fujii c a,b, c Department of Urban Management, Kyoto University,
Exploring the Relationship between Undergraduate Education and Sustainable Transport Attitudes Junghwa Kim a, Jan-Dirk Schmöcker b*, Satoshi Fujii c a,b, c Department of Urban Management, Kyoto University,
INTEGRATED MOBILITY PLAN
 Re: Item No. 3 INTEGRATED MOBILITY PLAN Committee of the Whole December 5, 2017 halifax.ca/integratedmobility Presentation Outline Why the IMP Now? Big Transportation Moves in HRM IMP Vision and Transportation
Re: Item No. 3 INTEGRATED MOBILITY PLAN Committee of the Whole December 5, 2017 halifax.ca/integratedmobility Presentation Outline Why the IMP Now? Big Transportation Moves in HRM IMP Vision and Transportation
Content of the module
 Content of the module Methodology approach Planning process Definition of working area Population and territorial context Supply Infrastructure Transport service Demand On board / at the stations or bus
Content of the module Methodology approach Planning process Definition of working area Population and territorial context Supply Infrastructure Transport service Demand On board / at the stations or bus
OWNERS SATISFACTION AND THE WILLINGNESS OVER THE IMPLEMENTATION OF EASY AUTOMATED CAR PARKING SYSTEM (GPS AND DIALOG GSM) IN SRI LANKA- CASE STUDY
 OWNERS SATISFACTION AND THE WILLINGNESS OVER THE IMPLEMENTATION OF EASY AUTOMATED CAR PARKING SYSTEM (GPS AND DIALOG GSM) IN SRI LANKA- CASE STUDY S. Rajivkanth 1 1 Masters in Information Technology, University
OWNERS SATISFACTION AND THE WILLINGNESS OVER THE IMPLEMENTATION OF EASY AUTOMATED CAR PARKING SYSTEM (GPS AND DIALOG GSM) IN SRI LANKA- CASE STUDY S. Rajivkanth 1 1 Masters in Information Technology, University
A STUDY ON CONSUMER AWARENESS AND DETERMINANTS OF ONLINE SHOPPING Dr. R. Kavitha* 1. TamilNadu, India.
 ISSN: 29-7196 IJMRR/Aug 15/ Volume 5/Issue /Article -6/636-6 Dr. R. Kavitha et. al., / International Journal of Management Research & Review A STUDY ON CONSUMER AWARENESS AND DETERMINANTS OF ONLINE SHOPPING
ISSN: 29-7196 IJMRR/Aug 15/ Volume 5/Issue /Article -6/636-6 Dr. R. Kavitha et. al., / International Journal of Management Research & Review A STUDY ON CONSUMER AWARENESS AND DETERMINANTS OF ONLINE SHOPPING
UNDERSTANDING TRAVEL BEHAVIOR AND MODE CHOICE OF URBAN UNIVERSITY CAMPUS EMPLOYEES
 Sisiopiku and Ramadan 1 UNDERSTANDING TRAVEL BEHAVIOR AND MODE CHOICE OF URBAN UNIVERSITY CAMPUS EMPLOYEES Virginia P. Sisiopiku, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental
Sisiopiku and Ramadan 1 UNDERSTANDING TRAVEL BEHAVIOR AND MODE CHOICE OF URBAN UNIVERSITY CAMPUS EMPLOYEES Virginia P. Sisiopiku, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental
Relationship between Socio-Economic Status and Post-Purchase Behaviour of Maruti car customers
 Relationship between Socio-Economic Status and Post-Purchase Behaviour of Maruti car customers R.Sivakumar Asst. Professor Management Wing, Directorate of Distance Education Annamalai University, Annamalainagar
Relationship between Socio-Economic Status and Post-Purchase Behaviour of Maruti car customers R.Sivakumar Asst. Professor Management Wing, Directorate of Distance Education Annamalai University, Annamalainagar
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 195 ( 2015 ) World Conference on Technology, Innovation and Entrepreneurship
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 195 ( 2015 ) 2896 2904 World Conference on Technology, Innovation and Entrepreneurship Expert System on
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 195 ( 2015 ) 2896 2904 World Conference on Technology, Innovation and Entrepreneurship Expert System on
International Journal of Engineering Research and Modern Education (IJERME) ISSN (Online): (www.rdmodernresearch.com) Volume I, Issue II,
 A RESEARCH ON QUALITY FACTORS INFLUENCING ONLINE SHOPPING K. Veerakumar Assistant Professor in Commerce - BPS, NGM College (Autonomous), Pollachi, Tamilnadu Abstract: There are many reasons why people
A RESEARCH ON QUALITY FACTORS INFLUENCING ONLINE SHOPPING K. Veerakumar Assistant Professor in Commerce - BPS, NGM College (Autonomous), Pollachi, Tamilnadu Abstract: There are many reasons why people
Commission for Travel Demand Submission from Transport for London March 2017
 Commission for Travel Demand Submission from Transport for London March 2017 Introduction TfL is the strategic transport authority for London, governed by the Mayor of London and responsible for delivering
Commission for Travel Demand Submission from Transport for London March 2017 Introduction TfL is the strategic transport authority for London, governed by the Mayor of London and responsible for delivering
(1)Background. (2)Methodology CURRENT SITUATION. Pollution situation report 2016, Pollution Control Department
 (1)Background (2)Methodology (3)Results (4)Analysis CURRENT SITUATION Pollution situation report 216, Pollution Control Department (1)Background (2)Methodology (3)Results (4)Analysis POINT SOURCE Unexplained
(1)Background (2)Methodology (3)Results (4)Analysis CURRENT SITUATION Pollution situation report 216, Pollution Control Department (1)Background (2)Methodology (3)Results (4)Analysis POINT SOURCE Unexplained
Asian Research Consortium
 Asian Research Consortium International Journal of Research in Organizational Behavior and Human Resource Management, Vol. 1, No. 3, 2013, pp. 107-115. ISSN 2320-8724 International Journal of Research
Asian Research Consortium International Journal of Research in Organizational Behavior and Human Resource Management, Vol. 1, No. 3, 2013, pp. 107-115. ISSN 2320-8724 International Journal of Research
Transit Demand Analysis
 Transit Demand Analysis Purpose To determine impact on ridership and revenues of any change in service policy. Need to know how demand estimates will be used. May not require an elaborate analysis in many
Transit Demand Analysis Purpose To determine impact on ridership and revenues of any change in service policy. Need to know how demand estimates will be used. May not require an elaborate analysis in many
Transportation Master Plan Introduction
 1. Introduction Building a Liveable Ottawa 2031 has set out a process to guide the completion of a fiveyear update of the City s Official Plan, Transportation Master Plan, Infrastructure Master Plan, Cycling
1. Introduction Building a Liveable Ottawa 2031 has set out a process to guide the completion of a fiveyear update of the City s Official Plan, Transportation Master Plan, Infrastructure Master Plan, Cycling
Tour complexity and transportation demand management: A focus on CBD work tours
 Tour complexity and transportation demand management: A focus on CBD work tours 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 Moein Khaloei M.Sc. of Transportation Planning Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Amirkabir
Tour complexity and transportation demand management: A focus on CBD work tours 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 Moein Khaloei M.Sc. of Transportation Planning Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Amirkabir
BACKGROUNDER #8: Transportation Pricing
 BACKGROUNDER #8: Transportation Pricing Purpose: Why is this topic important to the Regional Transportation Strategy? Transport Demand Management (TDM) is the use of policies, programs, services and products
BACKGROUNDER #8: Transportation Pricing Purpose: Why is this topic important to the Regional Transportation Strategy? Transport Demand Management (TDM) is the use of policies, programs, services and products
Parking is the sacred cow of land uses. It claims privileged status in zoning codes
 Parking Management for Smart Growth R I C H A R D W I L L S O N Parking is the sacred cow of land uses. It claims privileged status in zoning codes and there is simply too much of it in cities. Previous
Parking Management for Smart Growth R I C H A R D W I L L S O N Parking is the sacred cow of land uses. It claims privileged status in zoning codes and there is simply too much of it in cities. Previous
Assumption University-eJournal of Interdisciplinary Research (AU-eJIR) Vol 2. Issue 1
 THE STUDY OF FACTORS AFFECTING INTENTIONS TO USE CAR SHARING SERVICES IN THAILAND Direk Tayakee Assumption University Bangkok, Thailand Email: direk@tayakee.com Abstract: This research is conducted to
THE STUDY OF FACTORS AFFECTING INTENTIONS TO USE CAR SHARING SERVICES IN THAILAND Direk Tayakee Assumption University Bangkok, Thailand Email: direk@tayakee.com Abstract: This research is conducted to
Sample TOR for CMP Preparation
 Annex 6 Sample TOR for CMP Preparation This annex provides a sample terms of reference (TOR) for use in appointing consultants to assist with the preparation of a CMP. The TOR should be amended where necessary
Annex 6 Sample TOR for CMP Preparation This annex provides a sample terms of reference (TOR) for use in appointing consultants to assist with the preparation of a CMP. The TOR should be amended where necessary
Best practice examples and research on passenger intermodality in the European Union. Šibenik - 18/6/2013, DUNEA l.l.c.
 Best practice examples and research on passenger intermodality in the European Union Šibenik - 18/6/2013, DUNEA l.l.c. Why intermodality? Report on passenger intermodality in the EU Policy background behind
Best practice examples and research on passenger intermodality in the European Union Šibenik - 18/6/2013, DUNEA l.l.c. Why intermodality? Report on passenger intermodality in the EU Policy background behind
Transportation, Mobility and Access
 Transportation, Mobility and Access In The City of North Vancouver A Discussion Paper Prepared to Inform the Direction of a New Official Community Plan 2021 & Beyond Dragana Mitic Assistant City Engineer
Transportation, Mobility and Access In The City of North Vancouver A Discussion Paper Prepared to Inform the Direction of a New Official Community Plan 2021 & Beyond Dragana Mitic Assistant City Engineer
CITY OF BRAMPTON TRANSPORTATION MASTER PLAN UPDATE TECHNICAL REPORT #6 - TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT
 CITY OF BRAMPTON TRANSPORTATION MASTER PLAN UPDATE TECHNICAL REPORT #6 - TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT MARCH 2015 Table of Contents 1. Scope of the Technical Memorandum... 1 2. Introduction... 1 2.1
CITY OF BRAMPTON TRANSPORTATION MASTER PLAN UPDATE TECHNICAL REPORT #6 - TRANSPORTATION DEMAND MANAGEMENT MARCH 2015 Table of Contents 1. Scope of the Technical Memorandum... 1 2. Introduction... 1 2.1
UAB COMMUTER SURVEY FINAL REPORT
 UAB COMMUTER SURVEY FINAL REPORT Virginia P. Sisiopiku, PhD Associate Professor of Transportation Engineering Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering Rachael C. Thompson Undergraduate
UAB COMMUTER SURVEY FINAL REPORT Virginia P. Sisiopiku, PhD Associate Professor of Transportation Engineering Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering Rachael C. Thompson Undergraduate
CHAPTER 7. TRAVEL PATTERNS AND TRAVEL FORECASTING
 CHAPTER 7. TRAVEL PATTERNS AND TRAVEL FORECASTING TRAVEL PATTERNS Northwest Arkansas has experienced unprecedented growth in population and employment in the past 25 years. The economic vitality and diversity
CHAPTER 7. TRAVEL PATTERNS AND TRAVEL FORECASTING TRAVEL PATTERNS Northwest Arkansas has experienced unprecedented growth in population and employment in the past 25 years. The economic vitality and diversity
System Dynamics Model of Shanghai Passenger Transportation Structure Evolution
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1110 1118 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scien ce s 96 ( 2013 ) 1110 1118 13th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals (CICTP 2013)
EFFECTIVE DESIGN OF P&R SYSTEM IN METROPLOLITAN AREA
 EFFECTIVE DESIGN OF P&R SYSTEM IN METROPLOLITAN AREA Ljupko Simunovic D.Sc., Prof. Ivan Bosnjak D.Sc., Marko Matulin B.Sc. Department of Intelligent Transport Systems Faculty of Transport and Traffic Sciences
EFFECTIVE DESIGN OF P&R SYSTEM IN METROPLOLITAN AREA Ljupko Simunovic D.Sc., Prof. Ivan Bosnjak D.Sc., Marko Matulin B.Sc. Department of Intelligent Transport Systems Faculty of Transport and Traffic Sciences
The Impact of Advertising on Consumer Purchase Decision with Reference to Consumer Durable Goods in Oman
 International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research (IJMSR) Volume 5, Issue 12, December2017, PP 11-19 ISSN 2349-0330 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0349 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0349.0512002
International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research (IJMSR) Volume 5, Issue 12, December2017, PP 11-19 ISSN 2349-0330 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0349 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0349.0512002
1003 K Street NW, Suite 209 Washington, DC MEMORANDUM. Matthew Ridgway, Nat Bottigheimer, and Alex Rixey, Fehr & Peers
 1003 K Street NW, Suite 209 Washington, DC 20001 202.854.2750 MEMORANDUM Date: To: From: Subject: Eric Graye, M-NCPPC Matthew Ridgway, Nat Bottigheimer, and Alex Rixey, Fehr & Peers Performance Metrics
1003 K Street NW, Suite 209 Washington, DC 20001 202.854.2750 MEMORANDUM Date: To: From: Subject: Eric Graye, M-NCPPC Matthew Ridgway, Nat Bottigheimer, and Alex Rixey, Fehr & Peers Performance Metrics
Increasing Ridership and Efficient Passenger Transit
 Increasing Ridership and Efficient Passenger Transit Final 8/6/13 Summary: This initiative presents an array of measures that can be adopted to decrease GHG emissions from the state's passenger transportation
Increasing Ridership and Efficient Passenger Transit Final 8/6/13 Summary: This initiative presents an array of measures that can be adopted to decrease GHG emissions from the state's passenger transportation
FACTORS INFLUENCING OF STRESS MANAGEMENT AMONG COLLEGE FACULTY IN DHARMAPURI TOWN
 Available online at http://www.ijasrd.org/in International Journal of Advanced Scientific Research & Development Vol. 03, Iss. 02, Ver. II, Apr Jun 2016, pp. 130 13 e-issn: 2395-609 p-issn: 2394-906 FACTORS
Available online at http://www.ijasrd.org/in International Journal of Advanced Scientific Research & Development Vol. 03, Iss. 02, Ver. II, Apr Jun 2016, pp. 130 13 e-issn: 2395-609 p-issn: 2394-906 FACTORS
According to the results of a new survey by The International Parking Institute
 2015 EMERGING TRENDS Report on a survey conducted by the International Parking Institute Parking isn t just about parking anymore. New parking technology and a focus on sustainability broaden the role
2015 EMERGING TRENDS Report on a survey conducted by the International Parking Institute Parking isn t just about parking anymore. New parking technology and a focus on sustainability broaden the role
Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources)
 Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources) A Transportation Modeling Primer May, 1995 Edward A. Beimborn Center for Urban Transportation Studies University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee http://www.uwm.edu/dept/c
Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources) A Transportation Modeling Primer May, 1995 Edward A. Beimborn Center for Urban Transportation Studies University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee http://www.uwm.edu/dept/c
Workplace Travel Planning Guide
 Workplace Travel Planning Guide Welcome to the Get Healthy at Work Workplace Travel Planning Guide. We hope you find this guide practical and easy to follow. It will help your organisation to develop and
Workplace Travel Planning Guide Welcome to the Get Healthy at Work Workplace Travel Planning Guide. We hope you find this guide practical and easy to follow. It will help your organisation to develop and
SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow
 Preliminary Report SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow WP 03: Multi-modal Transportation Modelling D03.3 User Manual and Example Test Data Sets First Draft Karlsruhe, January
Preliminary Report SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow WP 03: Multi-modal Transportation Modelling D03.3 User Manual and Example Test Data Sets First Draft Karlsruhe, January
NEED ECONOMIC TRANSPORTATION LOCATIONS EXAMPLE
 A. Enhance multimodal networks and facilities around transit access points such as existing and emerging rail stations, high capacity bus stops, and intermodal transfer centers There is a need for improved
A. Enhance multimodal networks and facilities around transit access points such as existing and emerging rail stations, high capacity bus stops, and intermodal transfer centers There is a need for improved
A Plan for Sustainable Transportation at Yale. June 2012 [Updated September 1, 2013] INTRODUCTION
![A Plan for Sustainable Transportation at Yale. June 2012 [Updated September 1, 2013] INTRODUCTION A Plan for Sustainable Transportation at Yale. June 2012 [Updated September 1, 2013] INTRODUCTION](/thumbs/80/81721071.jpg) A Plan for Sustainable Transportation at Yale June 2012 [Updated September 1, 2013] INTRODUCTION Yale Transportation Options has been providing support for members of the Yale community interested in more
A Plan for Sustainable Transportation at Yale June 2012 [Updated September 1, 2013] INTRODUCTION Yale Transportation Options has been providing support for members of the Yale community interested in more
Mobility Management Basics
 Mobility Management Basics Module 5: Transportation for Job Seekers and Low-Income Workers For individuals with limited income or those transitioning from public assistance programs, having access to reliable
Mobility Management Basics Module 5: Transportation for Job Seekers and Low-Income Workers For individuals with limited income or those transitioning from public assistance programs, having access to reliable
AGENT-BASED MODELLING OF A SOCIAL DILEMMA IN MODE CHOICE BASED ON TRAVELERS EXPECTATIONS AND SOCIAL LEARNING MECHANISMS
 Advanced OR and AI Methods in Transportation AGENT-BASED MODELLING OF A SOCIAL DILEMMA IN MODE CHOICE BASED ON TRAVELERS EXPECTATIONS AND SOCIAL LEARNING MECHANISMS Yos SUNITIYOSO 1, Shoji MATSUMOTO 2
Advanced OR and AI Methods in Transportation AGENT-BASED MODELLING OF A SOCIAL DILEMMA IN MODE CHOICE BASED ON TRAVELERS EXPECTATIONS AND SOCIAL LEARNING MECHANISMS Yos SUNITIYOSO 1, Shoji MATSUMOTO 2
Transport Costs and Urban Form: Is There a Connection? H Lansdell, R McKellar
 Abstract Introduction Planning implies direction and organised action to efficiently achieve that direction. Urban transport and land use planning has developed to ensure an efficient arrangement of urban
Abstract Introduction Planning implies direction and organised action to efficiently achieve that direction. Urban transport and land use planning has developed to ensure an efficient arrangement of urban
Keywords: Urban mobility, modal integration; transportation systems; sustainable transport.
 Proposal of urban mobility model from the modal integration Santa Maria do Leme river basin: subsidies for the expansion at São Carlos city, São Paulo State, Brazil Speakers: SOUSA, Isabel 1 ; HANAI, Frederico
Proposal of urban mobility model from the modal integration Santa Maria do Leme river basin: subsidies for the expansion at São Carlos city, São Paulo State, Brazil Speakers: SOUSA, Isabel 1 ; HANAI, Frederico
Seminar on Importance of Transport Infrastructure for National Development Chamber of Construction Industry 26th August 2008
 Amal S. Kumarage kumarage@sltnet.lk Seminar on Importance of Transport Infrastructure for National Development Chamber of Construction Industry 26th August 2008 Constraints for Development Infrastructure
Amal S. Kumarage kumarage@sltnet.lk Seminar on Importance of Transport Infrastructure for National Development Chamber of Construction Industry 26th August 2008 Constraints for Development Infrastructure
UN DESA/DSD Transport Assessment Methodology Meeting
 Asian Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST) Initiative Follow up Proposal on Kyoto Declaration signed by 34 Asian Cities UN DESA/DSD Transport Assessment Methodology Meeting Choudhury R.C. Mohanty,
Asian Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST) Initiative Follow up Proposal on Kyoto Declaration signed by 34 Asian Cities UN DESA/DSD Transport Assessment Methodology Meeting Choudhury R.C. Mohanty,
LINKAGES AMONG DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE AND FACTORS INFLUENCING SOCIALLY CONSCIOUS CONSUMER
 LINKAGES AMONG DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE AND FACTORS INFLUENCING SOCIALLY CONSCIOUS CONSUMER Dr.V.Vasanth 1, Dr.K.Sankar Ganesh 2, Mr.N.Mohamed Syed Alikhan 3 1,3 Assistant Professor, 2 Professor & Head, Department
LINKAGES AMONG DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE AND FACTORS INFLUENCING SOCIALLY CONSCIOUS CONSUMER Dr.V.Vasanth 1, Dr.K.Sankar Ganesh 2, Mr.N.Mohamed Syed Alikhan 3 1,3 Assistant Professor, 2 Professor & Head, Department
CHAPTER 4 FUTURE TRENDS
 CHAPTER 4 FUTURE TRENDS 4.1 LAND USE SCENARIO PLANNING Scenario planning represents the next generation of analytical processes created to evaluate the influence of development intensities and land use
CHAPTER 4 FUTURE TRENDS 4.1 LAND USE SCENARIO PLANNING Scenario planning represents the next generation of analytical processes created to evaluate the influence of development intensities and land use
Porter, D.R., Performance Standards for Growth Management. PAS Report 461. APA Planning Press: Chicago, IL. ed
 Porter, D.R., Performance Standards for Growth Management. PAS Report 461. APA Planning Press: Chicago, IL. ed. 1996. The first five chapters of this report discuss the various performance measures, including
Porter, D.R., Performance Standards for Growth Management. PAS Report 461. APA Planning Press: Chicago, IL. ed. 1996. The first five chapters of this report discuss the various performance measures, including
