E-marketplaces and Risk Management: Implementation on Greek para-pharmaceutical industry
|
|
|
- Philomena Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E-marketplaces and Management: Implementation on Greek para-pharmaceutical industry Vrassidas LEOPOULOS 1 Dimitra VOULGARIDOU 1 Konstantinos KIRYTOPOULOS 1 1 Mechanical Engineer Dpt National Technical University of Athens Iroon Polytechniou 9 GREECE Abstract: Aim of this paper is to attempt an integration of risk management in e-business practices, such as the e-marketplaces. The model proposed here is based on the development of an e-marketplace where the owner will act as the link among the points of sales (Pharmacies), the s and the para-pharmaceutical Production Companies. Moreover, the owner/ operator will use an information system that will use risk management as a criterion for suppliers/ buyers selection. The model is thoroughly described as well as its benefits. Some of them are: improved vendor selections process, in depth knowledge of temporary partners (vendors or customers) and strategic advantage of the e-marketplace itself. Key-Words: risk management, e-business, e-marketplace, para-pharmaceutical industry 1 Introduction The popularisation of the internet and the diversity of e-business practices facilitate the development of an e-supply chain bringing together manufacturers, suppliers and customers and leveraging the web technologies to smooth logistical co-ordination across the links [1]. The participation in an e-supply chain should be a win-win endeavour for each participant. Each one of the links of the chain adds value in the network, and expects to receive significant value from it. In order to achieve the expected benefits the e-supply chain partners have to co-ordinate the flow of information and further the physical logistics system not only among individual partners but throughout the chain. On the other hand, risk management is a technique that leads to better management of any process [2], thus, why not, the e-supply chain. Aim of this paper is to provide a model for the integration of e-business practices in the para-pharmaceutical industry in Greece, as well as to support these practices with a risk management module. The current supply chain channel, the e-marketplace concept and the typical risk management process are investigated and then a model is proposed for the co-ordination of the whole channel. Finally, the benefits for each participant are presented. The rest of this paper is organised as follows: In Section 2, 3 and 4, the current situation of the parameters that consist the model proposed, are presented. Section 2 describes the purchasing process of the para-pharmaceutical industry. Section 3 describes some of the typical e-commerce practices related to the model proposed and Section 4 presents the typical risk management process. The model is presented in Section 5 along with the expected benefits. Finally, in Section 6 the conclusions and opportunities for further research in the topic are presented. 2 Purchasing process in the parapharmaceutical industry The players of the purchasing process in the parapharmaceutical industry are depicted on a high level in Fig. 2. These players are: Para-pharmaceutical Production Companies. s, who operate, store and distribute products, acting as links between Production companies and the points of sales (either a or a Brand ). s are also importing products, which distribute are distributed afterwards. All those stores that are allowed to sell drugs (Pharmacies and Brand Pharmacies). Unlikely to other countries, the Greek law does not 1
2 permit drugs and related stuff to be sold in any store. Pharmacies are small and very small enterprises owned by individuals, where Brand Pharmacies are Unions. These Unions are formed by several independent (or not) Pharmacies under the same Brand. Greek legislation does not allow chains of pharmacies owned by a company. In the model described in Fig. 2, one can make out two categories that sell (Production Companies, s) and three categories that buy (s, Pharmacies, Brand Pharmacies). Pharmacies and Brand Pharmacies have the opportunity to buy either from a or the main vendor who is the Production Company. Although independent Pharmacies can buy from any vendor, it is often noticed that they develop an exclusive relationship with one of them. The transactions between buyers and sellers are, mostly, executed through conventional means, such as fax, telephone or face to face contact. The penetration of information systems in the sector is presented as follows: 9200 licences have been issued by the State for Pharmacies and the 8500 are active. Only 300 use an electronic procurement system. On the other hand, the majority of sellers (Production Companies and s) has either installed an ERP system or is moving towards this direction. In other words, the buyers (Pharmacies) lack technological evolution and this is explained by their limited size that cannot afford investments in information systems and the lack of know how to operate them. In the Model description part, the authors of this paper present how the e-commerce practises may enhance these transactions. 3 E-marketplaces The technology that links organisations through electronic means is known as e-commerce. E- business covers any form of transaction and information exchange among companies, customers and government, which take place using new information technologies mainly the internet [3]. Initially, e-commerce used the traditional fixed pricing models that grew out many years ago as mass production and extended distribution chains encouraged the economies of scale. Fixed prices met the necessity to manage the increase in both volume and variety of products over large geographic areas. However, fixed prices are slow to adjust to market conditions, thereby causing a gap between a price that is charged for a good and its actual market value. The second tier of e-commerce was the dynamic commerce. This type of e-commerce is the ability to buy and sell goods and services over the internet where price is changing depending on supply and demand [1]. Dynamic commerce, as any type of e-commerce, eliminates the need for many layers of intermediaries and reduces the overall cost of sales. For buyers, these markets provide a wider variety of suppliers and better, more widely available, information. For sellers, participation in these markets translates into higher revenues and quicker inventory turn over. The third tier, negotiated e-commerce, is the ability to map complex negotiation structures in business transaction, including multiple stages of negotiations with more than one bidding parameter, such as price, delivery time, and condition of goods or payment terms. The form of e-business that fits in the parapharmaceutical industry and can lead in tangible benefits is the e-marketplace (EM this point forward). EMs are becoming the new business venue for buying, selling and supporting customers, products and services. Still in their early evolutionary stages, they are primarily focused on bringing together buyers and sellers, but as their rapid development goes on, they will evolve from simple matchmaking services focused on transactions and e-commerce to new value-based business models. The main goal for the EM will be the integration of the transaction exchange, the value-added services, and the knowledge services into Value Trust Networks that offer secure collaboration to the members of the community. EMs can be categorised in three different ways. The first type of categorisation is Public vs Private EMs. At a Public EM, independent companies assume the responsibility of creating an electronic marketplace in which the participants, buyers and sellers, are free to take part in. At a private EM, a company installs the marketplace in order to manage its own supply processes and defines the participants access level. Each of these two versions has grown fast in the last two years, although the private one outnumbers. The second categorisation type is Vertical vs Horizontal EMs. Vertical are called the EMs which concern a specific sector, are industry-specific and aggregate supply or demand in vertical industries. Horizontal EMs concern a great range of industries and their purpose is to facilitate the exchange of products, information and services. For instance, according to ICAP study [4], an EM that deals with MRO (Materials, Repair and Operation) products is a horizontal EM where a participant can find several goods ranging from office machinery to furniture and software systems. The last categorisation type is Open vs Closed 2
3 EMs. A useful distinction of EMs based on their accessibility is that of open and closed EMs [5,6]. An open (global) EM, created among companies, companies and consumers or among companies and authorities, is characterised by low degree of information sharing and collaboration. However, the number of participants is unlimited, the network is open and unprotected, partners are not assessed and therefore security and authenticity is necessary. In an open EM the net is the market. On the contrary, closed EMs (often industry-specific clubs ) is created among companies, limited in number. Their main characteristic is the high degree of information sharing and collaboration since they are closed company-owned networks (with firewalls) and the partners are known and connected with high security level through networking. 4 Management management, as presented in the 6th WSEAS International Multiconference by the same authors, is not a new field of science [7]. The first approach of the formal introduction of Management (RM) techniques in the scientific community, was the effort put by Hammer [8] to apply it on technical solutions. There is also quite extended bibliography of RM in the theory of investments and financial risk field [9]. Recent trends have involved RM in the project management sector [10]. However, there is no literature considering the risk management as a tool embedded in the e-marketplaces services. This is what the authors are ambitious to achieve through this paper. The steps of Management can be summarised as in Fig. 1 [11]. The first step of the process is the Development of a Management Plan. This Plan sets the base for the other Management steps. The second step of the process is the identification of risks that might affect the project (in our case the procurement process). Identification is an important step of the process since one cannot cope with problems that have not been identified. There are many techniques indicating the way to identify risks, such as checklists, experts interviews, etc [12]. The third and fourth steps of the process address the analysis issue. Depending on the amount of information available or desirable, analysis could be either qualitative or quantitative. Next step for RM is the Mitigation Action Plan, i.e. the definition of specific and effective response, in order to smooth or completely eliminate the risk. Preventive or corrective actions maybe used in order to obtain the minimisation of risk [11]. The last step, which is the Follow Up and Control of risks, aims to assure that the outcome from the previous steps is still valid as the time passes by, the mitigation actions defined are really efficient and that every new risk is registered. Follow up Mgt Plan Identification Mitigation Qualitative Quantitative Fig. 1: Management Steps Analysis 5 E-marketplaces and the risk management tool 5.1 Model description The model presented in this paper aims to propose an integrated framework of risk management practices and e-marketplaces of the parapharmaceutical industry in Greece. The model is based on the development of an EM where the owner will act as the link among the points of sales (Pharmacies), the s and the parapharmaceutical Production Companies. The EM model proposed here is a vertical and closed EM belonging in the negotiated e-commerce practice (see section 3). Fig. 2 summarises the concept of the model. As it can be seen, all the interactions, apart from the physical distribution, are carried out through the marketplace, which is run by the operator (one of the links of the supply chain or an individual company). The development of an e-marketplace is described in the 8 th WSEAS Conference by the same authors (the paper has been accepted for publication) [13]. In a nutshell, one should follow three steps in order to set up the marketplace. First, select the operation type. Second, find the critical mass of participants. Third, initiate transactions. One of the most important aspects that has to be taken into consideration for the success of this endeavour are the so-called success factors. Some of these success factors are: The support from the top management, right systems infrastructure, internet site of high quality that meets or exceeds user expectations, etc. [14,15]. 3
4 Production Brand buyer did not succeed in paying on time, as well as the amount not paid. y product characteristics, such as vulnerability in environmental conditions (heat, light, etc). The operator provides risk cases that have been identified so that the potential buyer knows the most applicable vendor. For instance a product sensitive to heat should be bought from a vendor as near as possible to the point of sale or the vendor should have proven that delivery without problems is ensured. Information flow Supply Fig. 2: Proposed model for the Para- Pharmaceutical Industry From the strategic point of view, the role of the operator is to link the needs of the points of sales (Pharmacies) to the offers of the s and the producers. The core concept of this model is that Pharmacies do not negotiate by themselves but the operator runs the negotiation on their behalf. The strategic advantage of the operator is that since the needs of many Pharmacies or Brand Pharmacies may be aggregated, a scale economy can be achieved, when the or the Production Company is asked for goods. On the other hand, sellers have advantages, as well. The benefits for each participant of the electronic market are presented in sub-section 5.2. The innovative part of this paper is the use of risk management in the EM. The core conception is the creation of a Corporate Memory that includes all the products that can be sold in the EM, as well as all the participants. Each element of this memory is linked to the related risks that have been experienced in the past (Fig. 3). So, the operator of the EM offers to the participants the risk management module. The benefit that stems from this service is that the operator knows the problems that have been encountered by a specific vendor, customer or product, and takes them into account when deciding for a new deal (contract). A typical list of risks that the operator of the EM has to record in risk sheets is the following: Inability of a supplier (Production Company or ) to deliver on time (Number of occurrences, Delay in hours/ days, Type of product) Wrong shipments or improper products (Number of occurrences, Type of product) Insolvent Buyer ( or ). The operator may have data on how many times the Product Product CORPORATE MEMORY Production Company Product Fig. 3: Structure of Corporate Memory The aforementioned Corporate Memory is the tool that lets the operator of the EM to perform risk management, as well. However, the risk management steps followed are somehow different. Identification step: All the transactions among sellers and buyers, apart from the physical transportation of goods, take place through the EM. This means that the operator knows at any time the problems that have been faced in any phase of the supply chain. These problems are recorded and form the risk catalogue for each participant and product. Analysis step: The analysis of risks is semiquantitative. Scales are used in order to determine the exposure of a risk. The exposure is the probability of occurrence times the impact if the risk occurs and it is the measure of the seriousness of a risk. Fig. 4 shows an indicative scale for the aforementioned figures. Mitigation step: As stated earlier, the operator of the EM is also the negotiator that bridges the gap among Pharmacies, s and Production Companies. Taking the buyer s or the seller s side should be avoided. On the contrary effort should be put on an overall improvement process for the whole chain. This means that risks should be allocated to the participant that is most capable to deal with 4
5 them. Furthermore, when the operator is about to decide about a contract he should always take into account the risks that may affect either the buyer (low quality of the product, delivery delays, etc) or the seller (payments delays, refusal to receive certain product quantities, etc). Fig.4: Indicative scales for risk analysis Follow up step: This process is the continuous improvement step for the corporate memory. The operator tracks the transactions that take place in the EM and changes the Probability or the Impact for each risk, eliminates risks or adds new risks in the memory. 5.2 Benefits for each participant in the marketplace Although the benefits to buyers usually exceed those to suppliers [16], to date, business-to-business (B2B) technologies have been predominantly exploited by larger firms down-stream in the supply chain rather than by upstream SMEs [17]. This gives rise to our syllogism that Pharmacies (typical SMEs) should be involved in the aforementioned EM. However, tangible benefits occur for each and every participant of the EM. Furthermore, this specific EM proposed here includes a risk management module. Having such a module may rescue participants from misunderstandings, bad relations and above all, it is able to improve efficiency. The benefits from the use of this model are as follows: E-marketplace owner: EM operator (owner) holds the leading role of these new B2B relationships. In return for delivering this service, the operator gets substantial rewards by sharing the returns achieved by buyers and suppliers and increases the income by giving web space in the companies to advertise themselves. Moreover, instead of a fixed fee for their services, EM operators may have earnings calculated as a percentage of the decrease in cost that they achieve for Pharmacies. Since the operator acts as a negotiator between a and a vendor, sharing a part of the savings of the is normal. Moreover, the addition of a risk management module will improve participants selection for a deal (contract) by the operator, thus it will lead to high performance that will make participants happy. From another point of view, one can see the risk management module as a strategic advantage that will attract new participants and enlarge the e-market. Suppliers Production Companies: Suppliers can shorten sales channel and decrease prospecting costs by turning to the internet technologies. In addition, they can access new customers through B2B e- commerce and present their products while significantly reduce the promotional and advertising costs. Their benefits can reach further by creating close collaboration between trading partners in a secure environment and promoting price discovery. Last but not least, they will take advantage of the risk management tool as the operator will secure them from the buyers who do not hold to their payment agreements etc. s: One of the leading problems for a is the inventory. This problem can be directly attributed to a problem with reliable information exchange, by replacing goods based on information instead of estimation. Additionally, the EM will offer them a great range of suppliers, better quality of products, improved and fast information flow, as well as reduced cost for the procurements and less time spent in finding the right supplier or buyer Pharmacies: Pharmacies can use EMs to reduce direct and indirect supply chain costs by participating in bulk orders (through the EM operator) and buying from qualified new suppliers that were unknown before. The risk management done by the operator improves the procurement process and is something that could not be done by a small enterprise such as independent Pharmacies. In addition, they can manage their exchanges through 5
6 contracts, avoiding the cost of special orders (emergencies). It has been calculated the 35% of the procurements take place without existing contracts, resulting in a cost increase at about 20% [18]. Especially the local low-turnover Pharmacies can take advantage of the EM since they cannot achieve better prices otherwise.. 6 Conclusion further research There are several benefits not only for one of the links of the chain but for every organisation involved in the EM as shown in the previous sections. However, there are some points that need attention and might also be the spark for further research. As every information system, the EM has an installation and operation cost. Moreover, expenses for the education of the personnel are required and a period of time is needed for the company to adapt to the new operating system. Another issue that should be taken into consideration is the impartiality (neutral attitude) of the operator, as buyers and suppliers should be confronted equally. If the operator lays emphasis on the buyer s side, the suppliers profits are affected and vice versa. As far as the risk management module is concerned, the operator should be very careful. The scope of the process is not to eliminate some suppliers or buyers from the market as this will shrink the market. Aim of the risk management module is to be a criterion for the selection of the right mix of suppliers/ buyers for the right deal (contract). The aforementioned concepts are not consider to be major problems but techniques to overcome them should be developed/ investigated. References: [1] R.Warren The emarketplace Strategies for Success in B2B ecommerce, McGraw-Hill, [2] Tatsiopoulos I., Leopoulos V., Kirytopoulos K., 2001, as a strategic decision factor for the competitive bidding process in contract manufacturing, IFIP Conference, Aalborg, Denmark. [3] Ponis Stavros, A reference model for the Apparel Industry-Reengineering the Greek Apparel Virtual Enterprise, Ph.D. Thesis, National Technical University of Athens, [4] ICAP study, E-marketplaces 2001, Greece, [5] R. Steyer, Okonomische Analyse elektornischer Markte, Working paper, Johannes Gutenberg-University, Mainz, [6] B.F. Schmid, Electronische Markte-Merkmale, Organisation und Potentiale, The mcm institute, University of St.Gallen, Switzerland, [7] Leopoulos V. and Kirytopoulos K., 2002, Methodology for risk management in systems development, Recent advances in Computers, Computing and Communications, WSEAS Press, pp [8] Hammer R.W., 1972, Handbook of system and product safety, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall. [9] Alexander C., 1999, Management and Analysis: Measuring and Modelling Financial, John Wiley & Son Ltd. [10] Kliem R, Ludin I., 1997, Reducing Project, Gower Publishing Ltd, UK. [11] Project Management Institute, 2000, Project management book of knowledge. PMI. [12] R.Wideman, 1992, Project and program risk management: a guide to managing project risks and opportunities. PMI. [13] Leopoulos V., Kirytopoulos K. and Voulgaridou D., 2004, The benefits of e- commerce: A case study of the Greek parapharmaceutical industry, Transactions on Circuits and Systems, Accepted paper in print, World Scientific and Engineering Society Press. [14] E. Turban, J. Lee, M. Warkentin and H. Chung, Electronic Commerce 2002: A Managerial Perspective. Upper Saddle River, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, [15] D. Phan, E-business development for competitive advantages: A case study. Information & Management, Vol. 40, 2003, pp [16] T. Eng, The role of EMs in supply chain management. Industrial Marketing Management, Vol. 33, 2004, pp [17] J. Zheng, N. Caldwell, C. Harland, P. Powell, M. Woerndl and S. Xu, Small firms and e- business: cautiousness, contingency and costbenefit. Journal of Purchasing & Supply Management Vol. 10, 2004, pp [18] Credit Suisse, B2B evolution, 5/2000. Acknowledgements The model presented in this paper is currently developing for a major para-pharmaceutical company in Greece. The project is partly funded by the General Secretariat for Research and Technology, Ministry of Development. 6
Electronic alliances and the (para)pharmaceutical supply chain: Identification of Risks
 Electronic alliances and the (para)pharmaceutical supply chain: Identification of Risks Vrassidas LEOPOULOS Mechanical Engineer Dpt National Technical University of Athens Iroon Polytechniou 9 GREECE Konstantinos
Electronic alliances and the (para)pharmaceutical supply chain: Identification of Risks Vrassidas LEOPOULOS Mechanical Engineer Dpt National Technical University of Athens Iroon Polytechniou 9 GREECE Konstantinos
Methodology for risk management in systems development
 Methodology for risk management in systems development Vrassidas LEOPOULOS Mechanical Engineer Dpt National Technical University of Athens Iroon Polytechniou 9 GREECE Konstantinos KIRYTOPOULOS Mechanical
Methodology for risk management in systems development Vrassidas LEOPOULOS Mechanical Engineer Dpt National Technical University of Athens Iroon Polytechniou 9 GREECE Konstantinos KIRYTOPOULOS Mechanical
Reducing risks of Power Plants development
 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on ENVIRONMENT, ECOSYSTEMS and DEVELOPMENT, Tenerife, Spain, December 14-16, 2007 315 Reducing risks of Power Plants development LAMPRIDOU ANNA Researcher Moschonision 10, Athens GREECE
5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on ENVIRONMENT, ECOSYSTEMS and DEVELOPMENT, Tenerife, Spain, December 14-16, 2007 315 Reducing risks of Power Plants development LAMPRIDOU ANNA Researcher Moschonision 10, Athens GREECE
SWOT analysis in supply chain clustering
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on SYSTEMS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 23-25, 2007 110 SWOT analysis in supply chain clustering VRASSIDAS LEOPOULOS 1 KONSTANTINOS
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on SYSTEMS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 23-25, 2007 110 SWOT analysis in supply chain clustering VRASSIDAS LEOPOULOS 1 KONSTANTINOS
Presentation by: Supichaya Smerchuar
 Chapter 6 B2B Exchanges, Directories, and Other Support Services Presentation by: Supichaya Smerchuar This presentation is part of : Faculty of Information and Computer Technology, Mae Fah Luang University.
Chapter 6 B2B Exchanges, Directories, and Other Support Services Presentation by: Supichaya Smerchuar This presentation is part of : Faculty of Information and Computer Technology, Mae Fah Luang University.
CIPS Positions on Practice P&SM: E-procurement
 CIPS Positions on Practice P&SM: E-procurement Introduction The CIPS' practice documents are written as a statement in time. They are a collection of views on good practice within a particular subject
CIPS Positions on Practice P&SM: E-procurement Introduction The CIPS' practice documents are written as a statement in time. They are a collection of views on good practice within a particular subject
KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI
 KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BBA VI (Hons.) Course Title : COMPUTER APPLICATION TO BUSINESS (E COMMERCE) Course Number : BA (H) 512 Credit Hours : 03 Objective Globalization
KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BBA VI (Hons.) Course Title : COMPUTER APPLICATION TO BUSINESS (E COMMERCE) Course Number : BA (H) 512 Credit Hours : 03 Objective Globalization
CIPS POSITIONS ON PRACTICE PURCHASING AND SUPPLY MANAGEMENT: E-PROCUREMENT
 CIPS POSITIONS ON PRACTICE PURCHASING AND SUPPLY MANAGEMENT: E-PROCUREMENT INTRODUCTION The CIPS' practice documents are written as a statement in time. They are a collection of views on good practice
CIPS POSITIONS ON PRACTICE PURCHASING AND SUPPLY MANAGEMENT: E-PROCUREMENT INTRODUCTION The CIPS' practice documents are written as a statement in time. They are a collection of views on good practice
KARACHI UNVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI
 KARACHI UNVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BBA V (Hons.) Course Title : Computer Application To Business (E Commerce) Course Number : BA (H) 561 Credit Hours : 03 Objectives Globalization
KARACHI UNVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BBA V (Hons.) Course Title : Computer Application To Business (E Commerce) Course Number : BA (H) 561 Credit Hours : 03 Objectives Globalization
Chapter 1. Overview of Electronic Commerce
 Chapter 1 Overview of Electronic Commerce Learning Objectives 1. Define electronic commerce (EC) and describe its various categories. 2. Describe and discuss the content and framework of EC. 3. Describe
Chapter 1 Overview of Electronic Commerce Learning Objectives 1. Define electronic commerce (EC) and describe its various categories. 2. Describe and discuss the content and framework of EC. 3. Describe
E- Publishing: Successful e-commerce efforts to e- publishing online newspapers and independent and independent publication through the internet.
 E- Advertising: Advertising and information are currently the largest commercial activities on the web. EXAMPLE: WEBSITES, BANNERS, E- COMMERCE Portals like www.yahoo.com, news groups. E- Catalogs: E-
E- Advertising: Advertising and information are currently the largest commercial activities on the web. EXAMPLE: WEBSITES, BANNERS, E- COMMERCE Portals like www.yahoo.com, news groups. E- Catalogs: E-
E-Business Markets and Models. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 E-Business Markets and Models Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Fundamental Definitions Business and commerce using internet Firms who exist because of the internet (firms born on the net, sometimes referred to
E-Business Markets and Models Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Fundamental Definitions Business and commerce using internet Firms who exist because of the internet (firms born on the net, sometimes referred to
E-procurement and E-markets. E-business lecture 7
 E-procurement and E-markets E-business lecture 7 Outline Intro Purchasing Procurement (E-)markets (E-)Auctions Procurement What is procurement? All activities involved with obtaining items from suppliers:
E-procurement and E-markets E-business lecture 7 Outline Intro Purchasing Procurement (E-)markets (E-)Auctions Procurement What is procurement? All activities involved with obtaining items from suppliers:
A Comparison of Procurement Models for B2B Electronic Commerce
 A Comparison of Procurement Models for B2B Electronic Commerce 1 A Comparison of Procurement Models for B2B Electronic Commerce Avijeet Chauhan School of Computer Science and Engineering University of
A Comparison of Procurement Models for B2B Electronic Commerce 1 A Comparison of Procurement Models for B2B Electronic Commerce Avijeet Chauhan School of Computer Science and Engineering University of
MAXIMIZE PROFITS VAR BUSINESS
 HOW TO MAXIMIZE PROFITS IN A LOW MARGIN VAR BUSINESS Introduction With each passing day, VAR business is getting more and more competitive. As a result, margins have shrunk considerably which has reduced
HOW TO MAXIMIZE PROFITS IN A LOW MARGIN VAR BUSINESS Introduction With each passing day, VAR business is getting more and more competitive. As a result, margins have shrunk considerably which has reduced
Enterprise Systems MIT 21043, Technology Management and Applications Lecturer in Charge S. Sabraz Nawaz
 Chapter 8 Enterprise Systems MIT 21043, Technology Management and Applications Lecturer in Charge S. Sabraz Nawaz Lecturer in Management & IT 1 Learning Objectives Understand the essentials of enterprise
Chapter 8 Enterprise Systems MIT 21043, Technology Management and Applications Lecturer in Charge S. Sabraz Nawaz Lecturer in Management & IT 1 Learning Objectives Understand the essentials of enterprise
/// YOUR GUIDE TO MAGENTO MAGENTO S B2B MODULE
 /// YOUR GUIDE TO MAGENTO MAGENTO S B2B MODULE VOLUME NO. 2 MAGENTO B2B MODULE SUCCEED What are some of the biggest time-wasters in your daily routine? Chances are, it s the little things. When small inefficiencies
/// YOUR GUIDE TO MAGENTO MAGENTO S B2B MODULE VOLUME NO. 2 MAGENTO B2B MODULE SUCCEED What are some of the biggest time-wasters in your daily routine? Chances are, it s the little things. When small inefficiencies
SCM Systems: HP Example HP: largest supply chain among IT manufacturers 9 steps in HP s web-based order-driven SCM:
 SCM Systems: HP Example HP: largest supply chain among IT manufacturers 9 steps in HP s web-based order-driven SCM: 1. Customer or dealer places order 2. Order goes from order entry system to HP s production
SCM Systems: HP Example HP: largest supply chain among IT manufacturers 9 steps in HP s web-based order-driven SCM: 1. Customer or dealer places order 2. Order goes from order entry system to HP s production
Chapter 2. E-Marketplaces: Structures, Mechanisms, Economics, and Impacts
 Chapter 2 E-Marketplaces: Structures, Mechanisms, Economics, and Impacts E-Marketplaces Markets (electronic or otherwise) have three main functions: 1. Matching buyers and sellers; 2. Facilitating the
Chapter 2 E-Marketplaces: Structures, Mechanisms, Economics, and Impacts E-Marketplaces Markets (electronic or otherwise) have three main functions: 1. Matching buyers and sellers; 2. Facilitating the
Disclaimer The material contained in the following presentation is intended to be general background information on Westpac Banking Corporation and it
 B2B Marketplace ebusiness Strategy 16 June 2000 Disclaimer The material contained in the following presentation is intended to be general background information on Westpac Banking Corporation and its activities
B2B Marketplace ebusiness Strategy 16 June 2000 Disclaimer The material contained in the following presentation is intended to be general background information on Westpac Banking Corporation and its activities
SPENDLINK White Paper
 SPENDLINK White Paper Driving Cash Flow and Bottom Line Results From Procurement Excellence September 2008 Steve Tucker Grant Oliver Hubwoo Spendlink TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3 1.1 Definition
SPENDLINK White Paper Driving Cash Flow and Bottom Line Results From Procurement Excellence September 2008 Steve Tucker Grant Oliver Hubwoo Spendlink TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3 1.1 Definition
CHAPTER 11: SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT TRUE/FALSE
 CHAPTER 11: SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT TRUE/FALSE 1. Volkswagen's Rio de Janeiro plant is an excellent example of traditional supply chain management. 2. The key to effective supply chain management is to
CHAPTER 11: SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT TRUE/FALSE 1. Volkswagen's Rio de Janeiro plant is an excellent example of traditional supply chain management. 2. The key to effective supply chain management is to
BSC (Hons.) Business Information Systems, BSc (Hons) Computing and Information Systems. Cohort: BIS/09/FT, BIS/08/PT & BCISR/11/FT
 BSC (Hons.) Business Information Systems, BSc (Hons) Computing and Information Systems Cohort: BIS/09/FT, BIS/08/PT & BCISR/11/FT Examinations for 2011-2012 / Semester 2 MODULE: E-Business MODULE CODE:
BSC (Hons.) Business Information Systems, BSc (Hons) Computing and Information Systems Cohort: BIS/09/FT, BIS/08/PT & BCISR/11/FT Examinations for 2011-2012 / Semester 2 MODULE: E-Business MODULE CODE:
Mini-Project on M-Commerce
 Mini-Project on M-Commerce Structure Migration: From E-Business to M-Business (Chicago) Trends Shaping the Mobile Economy (Bloomington) The M-Commerce Landscape (Peoria/Bloomington) Breakthrough Platform
Mini-Project on M-Commerce Structure Migration: From E-Business to M-Business (Chicago) Trends Shaping the Mobile Economy (Bloomington) The M-Commerce Landscape (Peoria/Bloomington) Breakthrough Platform
Chapter 2 The External Environment. 1. Individual organizations typically have only a marginal impact on the broad environment.
 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS Chapter 2 The External Environment 1. Individual organizations typically have only a marginal impact on the broad environment. 2. The broad environment consists of sociocultural forces,
TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS Chapter 2 The External Environment 1. Individual organizations typically have only a marginal impact on the broad environment. 2. The broad environment consists of sociocultural forces,
Chapter by Prentice Hall
 Chapter 9 E-Commerce: Digital it Markets, Digital Goods 9.1 2007 by Prentice Hall STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the unique features of e-commerce, digital markets, and digital goods? How has Internet
Chapter 9 E-Commerce: Digital it Markets, Digital Goods 9.1 2007 by Prentice Hall STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the unique features of e-commerce, digital markets, and digital goods? How has Internet
A model for Supply Chain Management when. the balance of power between buyer and supplier is not clearly defined
 A model for Supply Chain Management when the balance of power between buyer and supplier is not clearly defined Fabio Frigo-Mosca is Professor of Logistics, University of Applied Sciences of Southern Switzerland
A model for Supply Chain Management when the balance of power between buyer and supplier is not clearly defined Fabio Frigo-Mosca is Professor of Logistics, University of Applied Sciences of Southern Switzerland
Chapter 1. Overview of Electronic Commerce
 Chapter 1 Overview of Electronic Commerce Electronic Commerce: Definitions and Concepts electronic commerce (EC) The process of buying, selling, or exchanging products, services, or information via computer
Chapter 1 Overview of Electronic Commerce Electronic Commerce: Definitions and Concepts electronic commerce (EC) The process of buying, selling, or exchanging products, services, or information via computer
The Expressway to. B2B E-Commerce World. The Leading e-marketplace Service Provider
 The Expressway to B2B E-Commerce World The Leading e-marketplace Service Provider ïïïkåçãoäkåçã ïïïkåçãoäkåéí is a joint venture founded by Compaq Computer, Commerce One, and several leading industrial
The Expressway to B2B E-Commerce World The Leading e-marketplace Service Provider ïïïkåçãoäkåçã ïïïkåçãoäkåéí is a joint venture founded by Compaq Computer, Commerce One, and several leading industrial
BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 1 KNOWLEDGE ORGANISERS
 BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 1 KNOWLEDGE ORGANISERS MARKETING 1.1 Part 1 BUSINESS A business is an organisation whose purpose is to produce goods and services to meet the needs of customers. QUALITATIVE DATA
BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 1 KNOWLEDGE ORGANISERS MARKETING 1.1 Part 1 BUSINESS A business is an organisation whose purpose is to produce goods and services to meet the needs of customers. QUALITATIVE DATA
PERCEPTIONS OF BARRIERS TO E-COMMERCE. Anthony Flynn and Sharon Purchase University of Western Australia. Abstract. Introduction
 PERCEPTIONS OF BARRIERS TO E-COMMERCE Anthony Flynn and Sharon Purchase University of Western Australia Abstract An exploratory survey of supply personnel from the mining industry in Australia indicated
PERCEPTIONS OF BARRIERS TO E-COMMERCE Anthony Flynn and Sharon Purchase University of Western Australia Abstract An exploratory survey of supply personnel from the mining industry in Australia indicated
B2B Customer Surveys. Unique Aspects of B2B Marketing and Research
 B2B Customer Surveys Unique Aspects of B2B Marketing and Research Priority Metrics Group Helping businesses grow through insight South Carolina New York London www.pmgco.com The Business-to-Business (B2B)
B2B Customer Surveys Unique Aspects of B2B Marketing and Research Priority Metrics Group Helping businesses grow through insight South Carolina New York London www.pmgco.com The Business-to-Business (B2B)
Presentation by: Supichaya Smerchuar
 Chapter 5 B2B E-Commerce: E Selling and Buying in Private E-MarketsE Presentation by: Supichaya Smerchuar This presentation is part of : Faculty of Information and Computer Technology, Mae Fah Luang University.
Chapter 5 B2B E-Commerce: E Selling and Buying in Private E-MarketsE Presentation by: Supichaya Smerchuar This presentation is part of : Faculty of Information and Computer Technology, Mae Fah Luang University.
CESIM SIMFIRM Introduction. Simulation for general business management
 CESIM SIMFIRM Introduction Simulation for general business management What is Cesim SimFirm? Cesim SimFirm is an online business simulation game that develops students understanding of the complexity of
CESIM SIMFIRM Introduction Simulation for general business management What is Cesim SimFirm? Cesim SimFirm is an online business simulation game that develops students understanding of the complexity of
SUPPLY CHAIN RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES PRACTISED IN DELL COMPUTERS INC
 SUPPLY CHAIN RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES PRACTISED IN DELL COMPUTERS INC Ramachandran Sampath 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Management Studies and Research, Coimbatore Institute of Management and
SUPPLY CHAIN RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES PRACTISED IN DELL COMPUTERS INC Ramachandran Sampath 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Management Studies and Research, Coimbatore Institute of Management and
The World of e-business Management Information Systems
 The World of e-business 406.306 Management Information Systems Jonghun Park jonghun@snu.ac.kr Dept. of Industrial Engineering Seoul National University 9/20/2007 electronic commerce The buying and selling
The World of e-business 406.306 Management Information Systems Jonghun Park jonghun@snu.ac.kr Dept. of Industrial Engineering Seoul National University 9/20/2007 electronic commerce The buying and selling
BLOCKCHAIN HOW WILL SIMPLIFY AND TRANSFORM THE SUPPLY CHAIN.
 HOW BLOCKCHAIN WILL SIMPLIFY AND TRANSFORM THE SUPPLY CHAIN. Second only to finance, supply chain is arguably the fastest evolving area in business technology. Managing inventory, shipping and trading,
HOW BLOCKCHAIN WILL SIMPLIFY AND TRANSFORM THE SUPPLY CHAIN. Second only to finance, supply chain is arguably the fastest evolving area in business technology. Managing inventory, shipping and trading,
CAR BUYER OF THE FUTURE STUDY ATCBOF14
 ATCBOF14 CAR BUYER OF THE FUTURE STUDY CONSUMERS WANT CHANGE IN THE CAR-BUYING PROCESS ONLY 17 OUT OF 4,000 prefer the CURRENT CAR BUYING PROCESS Autotrader s Car Buyer of the Future Study looked at the
ATCBOF14 CAR BUYER OF THE FUTURE STUDY CONSUMERS WANT CHANGE IN THE CAR-BUYING PROCESS ONLY 17 OUT OF 4,000 prefer the CURRENT CAR BUYING PROCESS Autotrader s Car Buyer of the Future Study looked at the
Policy, Economic, and Industry Repercussions of Current E-Business Diffusion Rate In European Food Industry
 Policy, Economic, and Industry Repercussions of Current E-Business Diffusion Rate In European Food Industry Ilias P. Vlachos a a Agricultural University of Athens, Iera Odos 75, Botanikos 118 55, Athens,
Policy, Economic, and Industry Repercussions of Current E-Business Diffusion Rate In European Food Industry Ilias P. Vlachos a a Agricultural University of Athens, Iera Odos 75, Botanikos 118 55, Athens,
E-Business and E- Commerce
 Chapter 5 E-Business and E- Commerce Information Technology For Management 6 th Edition Turban, Leidner, McLean, Wetherbe Lecture Slides by L. Beaubien, Providence College John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter
Chapter 5 E-Business and E- Commerce Information Technology For Management 6 th Edition Turban, Leidner, McLean, Wetherbe Lecture Slides by L. Beaubien, Providence College John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter
Lesson 1 Foundations of Electronic Commerce
 Lesson 1 Foundations of Electronic Commerce 1 Learning Objectives Define electronic commerce and describe its various categories Distinguish between electronic markets and interorganizational systems Describe
Lesson 1 Foundations of Electronic Commerce 1 Learning Objectives Define electronic commerce and describe its various categories Distinguish between electronic markets and interorganizational systems Describe
Chapter 5. Objectives. Business-to-Business Strategies: From Electronic Data Interchange to Electronic Commerce
 Chapter 5 Business-to-Business Strategies: From Electronic Data Interchange to Electronic Commerce Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Strategies that businesses use to improve purchasing,
Chapter 5 Business-to-Business Strategies: From Electronic Data Interchange to Electronic Commerce Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Strategies that businesses use to improve purchasing,
SOLUTIONS FOR CHAPTER 2
 Accounting Information Systems, 10e 1 SOLUTIONS FOR CHAPTER 2 Discussion Questions DQ 2-1 After the core of an ERP system has been implemented, any of the modules may then be implemented separately. What
Accounting Information Systems, 10e 1 SOLUTIONS FOR CHAPTER 2 Discussion Questions DQ 2-1 After the core of an ERP system has been implemented, any of the modules may then be implemented separately. What
E Business and E Commerce
 E Business and E Commerce Management Information Code: 164292-02 Course: Management Information Period: Autumn 2013 Professor: Sync Sangwon Lee, Ph. D D. of Information & Electronic Commerce 1 00. Contents
E Business and E Commerce Management Information Code: 164292-02 Course: Management Information Period: Autumn 2013 Professor: Sync Sangwon Lee, Ph. D D. of Information & Electronic Commerce 1 00. Contents
DO NOT DISTRIBUTE. B2B Exchanges: The next industrial revolution? Paul Farris, Darden School
 B2B Exchanges: The next industrial revolution? Paul Farris, Darden San Diego, 9/26/00 Sponsored by: NRF - PricewaterhouseCoopers - Darden Survey: Respondent Roles Seller/Potential Seller 20% Buyer/Potential
B2B Exchanges: The next industrial revolution? Paul Farris, Darden San Diego, 9/26/00 Sponsored by: NRF - PricewaterhouseCoopers - Darden Survey: Respondent Roles Seller/Potential Seller 20% Buyer/Potential
14. E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures
 14. (Contents) E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures Contents 14. E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures Building E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures Code: 166140-01+02 Course: Electronic
14. (Contents) E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures Contents 14. E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures Building E-Commerce Applications and Infrastructures Code: 166140-01+02 Course: Electronic
E-Commerce: An Emerging Approach in Modern Era. Annu Assistant Professor, G.B.N.K.M.V. Anjanthali (Karnal), Haryana, INDIA
 E-Commerce: An Emerging Approach in Modern Era Annu Assistant Professor, G.B.N.K.M.V. Anjanthali (Karnal), Haryana, INDIA Abstract: E-Commerce or Electronic Commerce is a methodology of modern business,
E-Commerce: An Emerging Approach in Modern Era Annu Assistant Professor, G.B.N.K.M.V. Anjanthali (Karnal), Haryana, INDIA Abstract: E-Commerce or Electronic Commerce is a methodology of modern business,
Lecture 4. E-Marketplace & Business to Busines E-Commerce
 Lecture 4 E-Marketplace & Business to Busines E-Commerce B2B E-Commerce The use of digital technologies to support inter-firm relationships Organisations doing business with other organisations electronically
Lecture 4 E-Marketplace & Business to Busines E-Commerce B2B E-Commerce The use of digital technologies to support inter-firm relationships Organisations doing business with other organisations electronically
Informática Administrativa
 Informática Administrativa Mtro. Josué R. Sánchez Martínez Universidad del Valle de México Learning Objectives 1. Define electronic commerce (EC) and describe its various categories. 2. Describe and discuss
Informática Administrativa Mtro. Josué R. Sánchez Martínez Universidad del Valle de México Learning Objectives 1. Define electronic commerce (EC) and describe its various categories. 2. Describe and discuss
Follow-Up on VFM Section 3.13, 2016 Annual Report RECOMMENDATION STATUS OVERVIEW
 Chapter 1 Section 1.13 Supply Chain Ontario and Procurement Practices Follow-Up on VFM Section 3.13, 2016 Annual Report RECOMMENDATION STATUS OVERVIEW # of Status of Actions Recommended Actions Fully In
Chapter 1 Section 1.13 Supply Chain Ontario and Procurement Practices Follow-Up on VFM Section 3.13, 2016 Annual Report RECOMMENDATION STATUS OVERVIEW # of Status of Actions Recommended Actions Fully In
Issues in Information Systems
 VALUE INCREASING ELECTRONIC COMMERCE SOLUTIONS IN THE APPAREL INDSUTRY Kathleen M. DiIorio, University of West Florida, kmd24@students.uwf.edu June Wei, University of West Florida, jwei@uwf.edu ABSTRACT
VALUE INCREASING ELECTRONIC COMMERCE SOLUTIONS IN THE APPAREL INDSUTRY Kathleen M. DiIorio, University of West Florida, kmd24@students.uwf.edu June Wei, University of West Florida, jwei@uwf.edu ABSTRACT
Management Information Systems. B14. Acquiring IT Applications and Infrastructure
 Management Information Systems Management Information Systems B14. Acquiring IT Applications and Infrastructure Code: 166137-01+02 Course: Management Information Systems Period: Spring 2013 Professor:
Management Information Systems Management Information Systems B14. Acquiring IT Applications and Infrastructure Code: 166137-01+02 Course: Management Information Systems Period: Spring 2013 Professor:
7. Service Systems [4] -- Information Flow & Exchange Models
![7. Service Systems [4] -- Information Flow & Exchange Models 7. Service Systems [4] -- Information Flow & Exchange Models](/thumbs/79/79478361.jpg) 1 of 38 7. Service Systems [4] -- Information Flow & Exchange Models INFO 210-24 September 2007 Bob Glushko 2 of 38 Plan for Today's Lecture Information Flow and Exchange Models Between enterprises (e.g,,
1 of 38 7. Service Systems [4] -- Information Flow & Exchange Models INFO 210-24 September 2007 Bob Glushko 2 of 38 Plan for Today's Lecture Information Flow and Exchange Models Between enterprises (e.g,,
Emerging Information Technology Issues in Leasing
 Emerging Information Technology Issues in Leasing EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Rapid changes in information technology will trigger profound changes in the leasing industry. That is the conclusion of the Emerging
Emerging Information Technology Issues in Leasing EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Rapid changes in information technology will trigger profound changes in the leasing industry. That is the conclusion of the Emerging
Implications of E-commerce for Competition Policy - Note by Romania
 Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development DAF/COMP/WD(2018)40 DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL AND ENTERPRISE AFFAIRS COMPETITION COMMITTEE English - Or. English 23 May 2018 Implications of E-commerce
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development DAF/COMP/WD(2018)40 DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL AND ENTERPRISE AFFAIRS COMPETITION COMMITTEE English - Or. English 23 May 2018 Implications of E-commerce
Commerce One Global Procurement Report
 1 / 19 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. METHODOLOGY...4 3. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 5 3.1 Characteristics of Global High Performers...5 3.2 Factors Driving Global High Performance...5 4. CHARACTERISTICS OF
1 / 19 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. METHODOLOGY...4 3. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 5 3.1 Characteristics of Global High Performers...5 3.2 Factors Driving Global High Performance...5 4. CHARACTERISTICS OF
Procurement Management Processes
 Procurement Management Processes Olga Botero PM630-1004A-01 Contracting and procurement in project management Dr. Tony Prensa October 8 th 2010 Project Procurement Management includes the processes necessary
Procurement Management Processes Olga Botero PM630-1004A-01 Contracting and procurement in project management Dr. Tony Prensa October 8 th 2010 Project Procurement Management includes the processes necessary
Are you in need of a tool to help you do SO MUCH MORE with the TIME, STAFF and BUDGET you have?
 Are you in need of a tool to help you do SO MUCH MORE with the TIME, STAFF and BUDGET you have? Afaxys is a GPO an established and proven business model Afaxys is UNIQUE because it s dedicated to the public
Are you in need of a tool to help you do SO MUCH MORE with the TIME, STAFF and BUDGET you have? Afaxys is a GPO an established and proven business model Afaxys is UNIQUE because it s dedicated to the public
TIM 50 - Business Information Systems. Lecture 8. Instructor: Terry Allen UC Santa Cruz 10/24/2011
 TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 8 Instructor: Terry Allen UC Santa Cruz 10/24/2011 Outline Announcements CISCO review ERP Student Presentation (news) E-commerce Alibris case 1 Announcements
TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 8 Instructor: Terry Allen UC Santa Cruz 10/24/2011 Outline Announcements CISCO review ERP Student Presentation (news) E-commerce Alibris case 1 Announcements
Outline. Announcements. Announcements. Cisco Summary. Announcements 10/26 10/28. TIM 50 - Business Information Systems. E-commerce
 Outline TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 8 Instructor: Terry Allen UC Santa Cruz 10/24/2011 Announcements CISCO review ERP Student Presentation (news) E-commerce Alibris case Announcements
Outline TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 8 Instructor: Terry Allen UC Santa Cruz 10/24/2011 Announcements CISCO review ERP Student Presentation (news) E-commerce Alibris case Announcements
Advanced B2B Procurement on the Internet
 UDC 621.395.74:658.14:681.32 Advanced B2B Procurement on the Internet VKazuhiro Hosoi (Manuscript received September 18, 2000) Electronic Commerce (EC) is one of the biggest trends on the Internet, and
UDC 621.395.74:658.14:681.32 Advanced B2B Procurement on the Internet VKazuhiro Hosoi (Manuscript received September 18, 2000) Electronic Commerce (EC) is one of the biggest trends on the Internet, and
Costing Logistics Services A. Hatzis 1, A. Koulidou 2, D. Folinas 3
 Costing Logistics Services A. Hatzis 1, A. Koulidou 2, D. Folinas 3 1,2 Department of Accounting, Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Greece 3 Department of Logistics, Alexander
Costing Logistics Services A. Hatzis 1, A. Koulidou 2, D. Folinas 3 1,2 Department of Accounting, Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Greece 3 Department of Logistics, Alexander
TITLE 133 LEGISLATIVE RULE WEST VIRGINIA HIGHER EDUCATION POLICY COMMISSION SERIES 43
 TITLE 133 LEGISLATIVE RULE WEST VIRGINIA HIGHER EDUCATION POLICY COMMISSION SERIES 43 TITLE: PURCHASING EFFICIENCIES SECTION 1 GENERAL 1.1 Scope This rule establishes the guidelines for the Commission
TITLE 133 LEGISLATIVE RULE WEST VIRGINIA HIGHER EDUCATION POLICY COMMISSION SERIES 43 TITLE: PURCHASING EFFICIENCIES SECTION 1 GENERAL 1.1 Scope This rule establishes the guidelines for the Commission
Bachelor of Science (Honours)
 Bachelor of Science (Honours) Business Management Business Management with Communications Business Management with Communications and Year in Industry Business Management with Industrial Placement International
Bachelor of Science (Honours) Business Management Business Management with Communications Business Management with Communications and Year in Industry Business Management with Industrial Placement International
E-Marketing/7E Chapter 11. The Internet for Distribution
 E-Marketing/7E Chapter 11 The Internet for Distribution Chapter 11 Objectives After reading Chapter 11, you will be able to: Describe the three major functions of a distribution channel. Explain how the
E-Marketing/7E Chapter 11 The Internet for Distribution Chapter 11 Objectives After reading Chapter 11, you will be able to: Describe the three major functions of a distribution channel. Explain how the
FAQ: E-Commerce Model and Strategy Formulation
 FAQ: E-Commerce Model and Strategy Formulation Question 1: What type of e-commerce is the most dominant, and why? Answer 1: Though the popular press has focused heavily on B2C e-commerce in recent years,
FAQ: E-Commerce Model and Strategy Formulation Question 1: What type of e-commerce is the most dominant, and why? Answer 1: Though the popular press has focused heavily on B2C e-commerce in recent years,
AM SYLLABUS (2020): Marketing AM SYLLABUS (2020) SYLLABUS
 MARKETING AM SYLLABUS (2020) AM23 SYLLABUS 1 Marketing AM23 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper 1 (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Syllabus objectives The syllabus is intended to encourage candidates to:
MARKETING AM SYLLABUS (2020) AM23 SYLLABUS 1 Marketing AM23 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper 1 (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Syllabus objectives The syllabus is intended to encourage candidates to:
e-commerce WEEK7 Learning Objectives
 IMS9043 IT IN ORGANISATIONS Learning Objectives Describe electronic commerce, its dimensions, benefits, limitations, and process. e-commerce WEEK7 Describe the major applications of e- commerce in the
IMS9043 IT IN ORGANISATIONS Learning Objectives Describe electronic commerce, its dimensions, benefits, limitations, and process. e-commerce WEEK7 Describe the major applications of e- commerce in the
Innovative method for data collection and risk analysis during the bidding process
 Innovative method for data collection and risk analysis during the bidding process V. Belles, K Kirytopoulos, V. Leopoulos &M, Sfantsikopoulos National Technical University of Athens, Mechanical Engineering
Innovative method for data collection and risk analysis during the bidding process V. Belles, K Kirytopoulos, V. Leopoulos &M, Sfantsikopoulos National Technical University of Athens, Mechanical Engineering
n Business Paper Proposal Due 1/29 n Database Assignment 1 Due 2/3 n Reading for Thursday n Messerschmitt Ch 4
 Class Announcements TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 7 n Business Paper Proposal Due 1/29 n Database Assignment 1 Due 2/3 Instructor: John Musacchio UC Santa Cruz n Reading for Thursday n
Class Announcements TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 7 n Business Paper Proposal Due 1/29 n Database Assignment 1 Due 2/3 Instructor: John Musacchio UC Santa Cruz n Reading for Thursday n
THE DIGITAL FIRM: ELECTRONIC COMMERCE AND ELECTRONIC BUSINESS
 Chapter 4 THE DIGITAL FIRM: ELECTRONIC COMMERCE AND ELECTRONIC BUSINESS 4.1 2003 by Prentice Hall OBJECTIVES How has Internet technology changed value propositions and business models? What is electronic
Chapter 4 THE DIGITAL FIRM: ELECTRONIC COMMERCE AND ELECTRONIC BUSINESS 4.1 2003 by Prentice Hall OBJECTIVES How has Internet technology changed value propositions and business models? What is electronic
Research on Middle and Small Manufacture Enterprise E-commerce Application Systems Mingqiang Zhu a, Zuxu Zou b
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-05-21 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 933, pp 819-823 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.933.819 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Research on Middle and Small Manufacture
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-05-21 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 933, pp 819-823 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.933.819 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Research on Middle and Small Manufacture
Transfer Pricing Issues in Business Restructurings
 Transfer Pricing Issues in Business Restructurings Mike Murphy December 6, 2008 L E A D E R S H I P P R O B L E M SO L V I N G V A L U E C R E A T I O N Contents Statement of Objective Business Restructurings
Transfer Pricing Issues in Business Restructurings Mike Murphy December 6, 2008 L E A D E R S H I P P R O B L E M SO L V I N G V A L U E C R E A T I O N Contents Statement of Objective Business Restructurings
Supply Chain Integration Based on Core Manufacturing Enterprise
 Supply Chain Integration Based on Core Manufacturing Enterprise Wenqin Cao 1 and Haiyan Zhu 2 1 School of Mechanical and Electronical Engineering, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang, P.R. China 2
Supply Chain Integration Based on Core Manufacturing Enterprise Wenqin Cao 1 and Haiyan Zhu 2 1 School of Mechanical and Electronical Engineering, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang, P.R. China 2
19/12/2011. Testing 1. Selected crucial definitions for ISO What does ISO 9001 have to say about processes?
 Euro-Med Workshop on Administrative Simplification Strategies for Enterprises: Better Public Services for Competitive Enterprises Brussels 30 November 1 December 2011 Euro-Med Workshop: Administrative
Euro-Med Workshop on Administrative Simplification Strategies for Enterprises: Better Public Services for Competitive Enterprises Brussels 30 November 1 December 2011 Euro-Med Workshop: Administrative
CIPS Purchasing & Supply Management (P&SM) Model
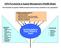 CIPS Purchasing & Supply (P&SM) Model This illustrates the generic P&SM processes and how they contribute to any organisation EXTERNAL FACTORS & IMPACTS Economic Environment Technology Changes Social Environment/
CIPS Purchasing & Supply (P&SM) Model This illustrates the generic P&SM processes and how they contribute to any organisation EXTERNAL FACTORS & IMPACTS Economic Environment Technology Changes Social Environment/
Urban community empowerment: context on supply chain collaboration in the SMEs
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Urban community empowerment: context on supply chain collaboration in the SMEs To cite this article: Y Masnita et al 2018 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Urban community empowerment: context on supply chain collaboration in the SMEs To cite this article: Y Masnita et al 2018 IOP Conf.
Making the Application of E-Marketplace with the Use of Virtual Account on Company
 Making the Application of E-Marketplace with the Use of Virtual Account on Company Hermawan Heriyanto Alexander Setiawan Adi Wibowo Abstract: Indonesia is home to various marketplace sites such as Lazada,
Making the Application of E-Marketplace with the Use of Virtual Account on Company Hermawan Heriyanto Alexander Setiawan Adi Wibowo Abstract: Indonesia is home to various marketplace sites such as Lazada,
MIS and Business Operations
 MIS and Business Operations Problems w/ Textbook? Case 1 due Sunday via email at 24:00. (keep copy of sent messages, cases received after 24:00 are penalized 10% with 10%/day thereafter) See session 1
MIS and Business Operations Problems w/ Textbook? Case 1 due Sunday via email at 24:00. (keep copy of sent messages, cases received after 24:00 are penalized 10% with 10%/day thereafter) See session 1
Design of Controlling Supported Sustainability of Manufacturing Enterprises
 Design of Controlling Supported Sustainability of Manufacturing Enterprises Eryk Głodziński Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Production Engineering, Warsaw, Poland e.glodzinski@wip.pw.edu.pl
Design of Controlling Supported Sustainability of Manufacturing Enterprises Eryk Głodziński Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Production Engineering, Warsaw, Poland e.glodzinski@wip.pw.edu.pl
E-Procurement in a Brazilian Service Company-Accomplishments and Pitfalls.
 E-Procurement in a Brazilian Service Company-Accomplishments and Pitfalls. GLAUCIA APARECIDA PRATES gprates@hotmail.com ROSALINDA CHEDIAN PIMENTEL chedian@netsite.com.br MARCO TULIO OSPINA PATINO btospina@terra.com.br
E-Procurement in a Brazilian Service Company-Accomplishments and Pitfalls. GLAUCIA APARECIDA PRATES gprates@hotmail.com ROSALINDA CHEDIAN PIMENTEL chedian@netsite.com.br MARCO TULIO OSPINA PATINO btospina@terra.com.br
Part III: eprocurement
 Part III: eprocurement 2 Learning Targets Which are important product categories and procurement processes? How can we structure market relationships? What are the pros and cons of sell side solutions?
Part III: eprocurement 2 Learning Targets Which are important product categories and procurement processes? How can we structure market relationships? What are the pros and cons of sell side solutions?
Financial Accounting. John J. Wild. Sixth Edition. Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Financial Accounting John J. Wild Sixth Edition McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 04 Reporting and Analyzing Merchandising Operations Conceptual
Financial Accounting John J. Wild Sixth Edition McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 04 Reporting and Analyzing Merchandising Operations Conceptual
New revenue guidance Implementation in the technology sector
 No. US2017-08 April 25, 2017 What s inside: Overview..1 Identify the contract.2 Identify performance obligations..6 Determine transaction price 9 Allocate transaction price 12 Recognize revenue. 14 Principal
No. US2017-08 April 25, 2017 What s inside: Overview..1 Identify the contract.2 Identify performance obligations..6 Determine transaction price 9 Allocate transaction price 12 Recognize revenue. 14 Principal
The Agency Guide To Programmatic Buying
 The Agency Guide To Programmatic Buying Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Defining Programmatic Buying 3. How Does Real-Time Bidding Work? 4. The Benefits 5. The Challenges 6. Conclusion The Agency
The Agency Guide To Programmatic Buying Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Defining Programmatic Buying 3. How Does Real-Time Bidding Work? 4. The Benefits 5. The Challenges 6. Conclusion The Agency
Marketing Principles is a nine-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 3 modules.
 Module Specification: Marketing Principles Marketing Principles is a nine-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 3 modules. To gain the CIM Level 3 Foundation Certificate in Marketing
Module Specification: Marketing Principles Marketing Principles is a nine-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 3 modules. To gain the CIM Level 3 Foundation Certificate in Marketing
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright Chapter 5
 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 E-Business and E-Commerce 2 Chapter Outline Overview of E-Business and E-Commerce Major EC Mechanisms
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 E-Business and E-Commerce 2 Chapter Outline Overview of E-Business and E-Commerce Major EC Mechanisms
The Evolution of B2B Distribution Ecommerce and Multi-Channel Strategies 2017
 The Evolution of B2B Distribution Ecommerce and Multi-Channel Strategies 2017 THE TRANSFORMATION OF B2B DISTRIBUTION Technology, ecommerce and customer expectations are dramatically changing the landscape
The Evolution of B2B Distribution Ecommerce and Multi-Channel Strategies 2017 THE TRANSFORMATION OF B2B DISTRIBUTION Technology, ecommerce and customer expectations are dramatically changing the landscape
Supply Chain Management. Keep up with demand and ensure optimal efficiency through real-time monitoring of inventory status
 Supply Chain Management Keep up with demand and ensure optimal efficiency through real-time monitoring of inventory status Contents Purchasing 3 Business Partners and Products 3 Flexible Pricing Rules
Supply Chain Management Keep up with demand and ensure optimal efficiency through real-time monitoring of inventory status Contents Purchasing 3 Business Partners and Products 3 Flexible Pricing Rules
ELECTRONIC PROCUREMENT What does it buy you?
 ELECTRONIC PROCUREMENT What does it buy you? Example: Rocky Flats Environmental Technology Site NWCCC June 27th 2001 Jeff Haight Group CH2M HILL/ Seattle (425) 453-5000 jhaight@ch2m.com This material was
ELECTRONIC PROCUREMENT What does it buy you? Example: Rocky Flats Environmental Technology Site NWCCC June 27th 2001 Jeff Haight Group CH2M HILL/ Seattle (425) 453-5000 jhaight@ch2m.com This material was
AASB 15: Revenue recognition implementation issues. 14 November 2017
 AASB 15: Revenue recognition implementation issues 14 November 2017 Your facilitators today Kim Heng Brendan Doyle Brandon Dalton Joe Rinarelli 2 Where are we at? The day has (almost) arrived JANUARY 2018
AASB 15: Revenue recognition implementation issues 14 November 2017 Your facilitators today Kim Heng Brendan Doyle Brandon Dalton Joe Rinarelli 2 Where are we at? The day has (almost) arrived JANUARY 2018
PMBOK Knowledge Areas. Project Risk Management. Objectives of Risk Management. Factors Influencing Successful Risk Management. Project Risk Management
 PMBOK Knowledge Areas IMS 2000 2 nd Year Studio Seminar 9 Project Management Risk Management and Stakeholder Analysis If we don t succeed, we run the risk of failure. Dan Quayle (1947 - ) During weeks
PMBOK Knowledge Areas IMS 2000 2 nd Year Studio Seminar 9 Project Management Risk Management and Stakeholder Analysis If we don t succeed, we run the risk of failure. Dan Quayle (1947 - ) During weeks
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN
 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN Introduction Information is crucial to the performance of a supply chain because it provides the basis upon which supply chain managers make decisions. Information
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN Introduction Information is crucial to the performance of a supply chain because it provides the basis upon which supply chain managers make decisions. Information
THE CASE FOR CONNECTED MANUFACTURING
 THE CASE FOR CONNECTED MANUFACTURING TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Executive overview 2 A state of emerging opportunities 3 The infrastructure as-is and the infrastructure to-be 3 The transformational challenge
THE CASE FOR CONNECTED MANUFACTURING TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Executive overview 2 A state of emerging opportunities 3 The infrastructure as-is and the infrastructure to-be 3 The transformational challenge
Comparing PMBOK Guide 4 th Edition, PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition, and ISO 21500
 Comparing PMBOK Guide 4 th Edition, PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition, and ISO 21500 Thierry Labriet, STS STS SA, Lausanne, Switzerland +41 21 510 11 50 office@sts.ch www.sts.ch 1 Contents 1 Foreword... 3 2 Executive
Comparing PMBOK Guide 4 th Edition, PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition, and ISO 21500 Thierry Labriet, STS STS SA, Lausanne, Switzerland +41 21 510 11 50 office@sts.ch www.sts.ch 1 Contents 1 Foreword... 3 2 Executive
CIPS Exam Report for Learner Community:
 CIPS Exam Report for Learner Community: Qualification: Diploma in procurement and supply Unit: D1 - Contexts of P&S Exam series: January 2016 Question 1 Learning Outcome 1 (a) Explain, with examples, the
CIPS Exam Report for Learner Community: Qualification: Diploma in procurement and supply Unit: D1 - Contexts of P&S Exam series: January 2016 Question 1 Learning Outcome 1 (a) Explain, with examples, the
E-commerce Mock-exam Questions
 Chapter 1 Page 15 to 16 E-commerce Mock-exam Questions Not every product is suitable for sale online, so the way in which a website is used to market products will vary. It is useful to consider the five
Chapter 1 Page 15 to 16 E-commerce Mock-exam Questions Not every product is suitable for sale online, so the way in which a website is used to market products will vary. It is useful to consider the five
Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition
 Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Electronic and Mobile Commerce and Enterprise Systems Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition 1 Why Learn About Electronic and
Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Electronic and Mobile Commerce and Enterprise Systems Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition 1 Why Learn About Electronic and
