Investment Evaluation of a Suburban Coastal Transport System
|
|
|
- Arron Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Investment Evaluation of a Suburban Coastal Transport System Evangelos Sambracos University of Piraeus 2002 Online at MPRA Paper No , posted 24. June :48 UTC
2 INVESTMENT EVALUATION OF A SUBURBAN COASTAL TRANSPORT SYSTEM SAMBRACOS Evangelos Associate Professor of Transport Economics Dept. of Maritime Studies University of Piraeus sambra@unipi.gr Summary This paper aims at determining the optimum viable solution of an investment on a suburban coastal shipping system in the area of Athens. More specifically it refers to the development of a sea transport system, alternative to the existing road one, that would connect Piraeus with the southern suburban coastal area of Athens. The best viable solution of such an undertaking is considered to be the one, which under the existing constraints maximises the total profit that derives from this investment. The variables used for the formation of the constraints are the number of vessels used, the routing and the price of the services. The article after presenting the methodology of the market analysis, focuses on the financing alternatives of the project and their impact on its economic efficiency and concludes with the best viable scenarios and optimum solution. 1. Introduction The paper s main objective is to determine the optimum solution of an investment undertaking that includes an alternative transportation system, that is a suburban coastal transport system in the south region of Athens. Such a system is believed that can offer a possible solution to the transport problems of congestion, which characterise the existing overloaded road network of Athens. Suburban coastal shipping has a special character. First there are not many examples of cities that use an analogous transport system. Secondly, the main competitor of sea transport is road transport or fixed track systems (train, tram). It should be mentioned that the current transportation system despite its deficiencies in terms of time, cost as well as externalities remains a strong travel alternative and consequently a constraint for the development of the proposed seaborne transport. This is due to the several advantages it offers to its users like door to door services, flexibility and speed. City of Athens disposes a road system as the main one satisfying the transport demand to and from the suburban areas.
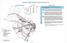
3 The best economic solution for an investment of this kind is determined as the one that maximises the profit of the investor, under the constraints that the current transport system sets. In this context, in order to format the constrains of the system, a market analysis has been conducted taking all the above into consideration in order to examine the possible demand for such a system versus the existing road transport one (Greek Bank of Industrial Development, 1995). However, the question is whether an enterprise in this field would be economically viable and which would be the required demand of that service, in order to be able to equalise the marginal costs with the marginal revenue. 2. A methodology for the development of a suburban coastal transportation system in Athens urban area 2.1 The survey It is obvious that the greatest part of the demand for sea transportation would come from the coastal suburbs that lie mostly in the eastern and southern part of Piraeus and their most important feature is that they constitute areas of permanent residence. These suburbs include Alimos, Voula, Vouliagmeni, Glyfada, Elliniko, Kalithea, Moschato, Piraeus and P. Faliro. They constitute the districts of direct interest for this analysis (see figure 1). The case of the nearby districts that are situated northern than the coastal ones is also examined (Ag. Dimitrios, Argyroupolis, Vari, Ilioupolis, Koukaki, N. Smirni etc). This case obviously refers to the current car owners who can drive their cars up to the terminal station and then embark on the sea vessels after parking their cars (park and ride). The first step in estimating the potential demand for a suburban coastal transportation system was to proceed to the determination of the total movements in the above mentioned area. This led to the development of the analogous Trip Distribution Model (Sambracos 2001) that shows the movements between the examined suburbs by private car and by bus. Data for the creation of the model was gathered by several origin destination surveys that have taken place over the last years in addition with the records of the National Statistics Services on the population of the suburbs.
4 Figure 1: Suburban coastal shipping operation in the south region of Athens The second step was to proceed to a Modal Split Model (Abacoumcin 1990, Giannopoulos 1981) and to determine the alternative means of transport that could satisfy the transport demand in and between the suburbs in question. In order to create such a model, the 'stated preference' method was used, a technique that uses and analyses the alternative scenarios, the questioned passengers state that they would prefer (Pearmain et.al, 1990, Bristow et.al, 2000). The questioned person is asked to choose between alternative situations/solutions, some of which may not yet be known to him, such as the proposed coastal transport system. The reason for using this method is mainly the fact that it can show results based on small samples (Koppelman et al, 1983). Thus the classic revealed preference method show disadvantages since it cannot be used in demand forecasting under existing conditions and cannot use qualitative criteria (such as the comfort of a transport means). The survey was conducted with the use of questionnaires on June 1994 in the two main centres of interest, Piraeus and Glyfada. The questionnaire included 13 questions that had to do with: - the used transport means, - the origin and destination of the trip, - the purpose of the trip, - the frequency of the movement,
5 - the preference towards sea transport, - the ability to use a car, - the minimum and maximum time for the users of private cars and buses, - the parking fees, - the walking distance between the parking area or the bus station and the final destination. Besides the questions there were six different scenarios, that referred to combinations of four main factors that determine the choice of a transport means. These are: - the time of the trip (from door to door), - the price of the ticket, - the possible delays in the arrival of the vessel, - the sea/weather condition. Additionally, data regarding the sex, age and other demographic characteristics were taken into consideration. In order to determine the demand allocation between the alternative transport means the Logit analysis was conducted (Ortuzar et. al., 1990) using as inputs the mentioned six scenarios and as variables the time of the trip (by bus/car and ship), the cost of the trip (by bus/car and ship), the delays (by ship), and the weather conditions of the coastal shipping alternative as well as the characteristics of the users (age, sex, purpose of the trip etc). Above them the time, cost of the trip and the weather conditions were statistically the most important variables Designing the system In order to design the suburban coastal shipping system there are several factors of both quantitative and qualitative character to consider, using as data the outputs of the origin-destination model and the conducted survey (stated preferences). The first factor was the ports that should be used to format the system, the number of stops between the main ports of Piraeus and Glyfada in combination with several levels of ticket prices. Three scenarios were examined: 1. Piraeus port P. Faliro Glyfada 2. Piraeus port Zea port P. Faliro Glyfada and 3. Piraeus - Glyfada The results from the survey showed that more mid stops would make the system unattractive and inefficient compared to the existing road one since they would increase the travel time. Additionally, more vessels would be required increasing therefore the cost of the system.
6 The price levels examined for each scenario referred to a sea fare of 300, 400, 500, 600 and 700 GRDrh respectively. The results of the stated preference model for a 12 hour and a peak hour transport work showed that the higher the number of mid stops the higher the demand for travelling. Based in that conclusion the third alternative was abandoned. The second factor was the vessels type and the necessary number of vessels to cover the two and three mid stops alternatives. The number of vessels depends on the demand for each alternative on a 12h and peak hour (PD) basis, the time of the trip and consequently the maximum number of trips the vessel can perform (FB), the frequency of embarkations (FL), the capacity of the vessel (C = PD/FL) and equals to the ratio: FL n = FB As for the type of the vessels, the choice was based on four factors: - the purchase and operational cost - the operational reliability, speed and flexibility - the friendliness towards the environment - the safety and comfort for the passenger The proposed type of the vessel based on the above factors was the flying dolphin type. Its characteristics on speed (33knots/h) and capacity (110 pas.) prove that for the one mid stop scenario two vessels are requested and for the two mid stop scenario three vessels. 3. Defining the optimum solution The best viable solution of such an undertaking is determined as the solution that maximises the Profit (P) of the undertaker. According to the economic theory maximising the Profit means maximising the difference between Revenues (R) and the Cost (C) that derive form the operation of the company. In other words it is: P = R-C max (P) = max (R-C) The constraints of the above profit maximisation consist of the existing alternative solutions, which derive from the market analysis on demand patterns towards the undertaking.
7 3.1 Cost of the suburban coastal transport system The total cost, that such a transport company will face is a function of (Karvounis 2000: - the investment cost (i), - the operating cost (o) - the financial cost (m) - the depreciation cost (d) Therefore we have, C = f(i, o, m, d) The total cost depends on the number of stops the vessels make. The more the stops the bigger the roundtrip time and consequently a bigger number of vessels is required in order to maintain a high level of service. This increases the investment cost since more capital is required to cover not only the acquisition of the vessels but also their operating expenses. Therefore, it is essential to determine the level up to which we must invest. There are different alternative scenarios that are based on the market analysis on origin destination in order to determine the best alternatives for this system. The market survey already indicated two main alternatives using as a variable (i) the number of stops and the number of vessels to be employed: Scenario 1: one stop between the ports of origin and destination, using two vessels on pick hours Scenario 2: two stops between the ports of origin and destination, using three vessels on pick hours That is Si, where i= 1,2 stops Considering these scenarios, the main cost elements are estimated as following: a. Investment and operating costs The estimation of the investment and operating costs is presented in the table 1 below. The investment cost consists of Founding & Organisation cost, Fixed investments (facilities etc), Working Capital, Unforseen expenses The operating cost consists of Fuels, lubricans etc, Personnel, Office expenses, Maintenance Expenses, Port duties, Insurance, Advertisement
8 Table: 1 Investment and operating cost for the two scenarios (in 000GRDrh)* Costs Scenario 1 Scenario 2 a. Total investment costs Founding - Organization Fixed investments Starting Capital Unforeseen expenses b. Total Annual Operating Cost Fuels Personnel Office expenses Maintenance Expenses Port duties Insurance Advertisement Unforeseen *The estimation of the costs is based on market prices as of 1995 b. Depreciation cost The cost of depreciation is estimated for both scenarios, using the depreciation rates, 4% for building and offices, 10% for the vessels and 20% for the rest equipment, as following: Scenario 1: annual depreciation for the first five years is 93,2mil.GRDrh and for the other five 91,2 mil.grdrh. Scenario 2: annual depreciation for the first five years is 123,2mil.GRDrh and for the other five 121,2mil.GRDrh. c. Financial cost The financial cost for the development of this transport system deals with the financing of the investment costs for its development. Several scenarios of financing are proposed that include: - different % of loaning and own capital - several levels of loaning interest
9 3.2 Revenues of a suburban coastal transport system The revenues from the operation of this system are a function of the demand (q) and the price of the ticket (p). R = f (p, q) The level of demand and the possible ticket price levels were examined during the market research. Although all price levels are possible the research showed that a range between 500GRDrh and 700GRDrh is the most viable one. Above this level the demand is low in favour of road transport and below it is economically unprofitable for the company. The two scenarios therefore are: Sj, where j= 700GRDrh, 500GRDrh It is assumed that for the working days the total revenues are: 2 x Ν x Ρ where, Ρ is the price of the ticket and Ν the corresponding total daily number of passengers. For the weekends (2 X 52=104 days per year) the passenger traffic is estimated to be 70% of the traffic during working days. Therefore the total annual income is: (261+0,7 x 104) x 2 x Ν x Ρ = 667,6 x Ν x Ρ Using the above mentioned scenarios Si and Sj, four cases result: -Case Α: S 1,700 (1 mid-stop & price of the ticket 700GRDrh) -Case Β: S 2,700 (2 mid-stops & price of the ticket 700GRDrh) -Case C: S 1,500 (1 mid-stop & price of the ticket 500GRDrh) -Case D: S 2,500 (2 mid-stops & price of the ticket 500GRDrh) Taking the above into consideration the total annual revenues are for each case: - S 1,700: 913 mil. GRDrh. - S 2,700: 961 mil. GRDrh. - S 1,500: 828 mil. GRDrh. - S 2,500: 875 mil. GRDrh. In order to forecast the total revenues for the years to come there is the assumption that the traffic natural increase rate is 1,5% annually, therefore all the above amounts for the future year e should be multiplied by 1,015 (e-1) (e=1, the first year of evaluation).
10 4. Financial analysis of the system 4.1 Evaluation of the financial cost The determination of the best financial solution that maximises the profit of the Coastal Transport Company is the next step of the investment evaluation of the system. The financial cost (m) of the undertaking is determined by two variables: - l: the percentage (%) of a loan to cover the investment cost and - n: the level of the interest rate Therefore m is a function of l and n, or m = f (l, n) and so C= f (i, o, l, n, d) All cost components have been determined for all S ij. Assuming that the variables in the above function are l and n, we will try to maximise it by using all possible combinations of l and n. In order to evaluate the financial efficiency (Goulielmos 1997) based on the above variables of this initiative we use the method of the Net Present Value and the Internal Rate of Return. Using a discount factor of 4%, the target is to find the alternative S ij that gives the higher Net Present Value (NPV) as well as IRR. Using the above variables we proceed to a 10 years simulation in order to format the equation that proves the relationship between the percentage of loan for all possible levels of loan interest and the NPV, IRR results. The results for all cases and the final equations are included for each case in table 2. The general form of the derived equations, as resulted from the simulation, is a first degree one, with the following formation: Y = a - bx Where Y = NPV X = the percentage of loan at different levels of interest rate a, b = constants
11 The main conclusion is that S 1,700 is the optimum solution, since it shows the greatest Net Present Value and Internal Rate of Return for all different levels of interest (Table 2). Regarding the financing of the project, it is concluded that in every level of the interest rate, the best solution is to self-finance the project. Another important observation is that in S 1,700, the percentage of loan that makes the NPV equal or less than zero (which means that the project is economically a non viable solution) is the highest, in comparison with the other Cases. For example for S 1,700 (see table 2 and figure 2), in the case of a loan interest of 4% the company can take a loan that does not exceed 97,62% of the investment cost. In all other cases, this percentage is much lower, which means bigger financial risk and danger, in the case of inability to self-finance a significant proportion of the investment cost. The same conclusion can be derived for all levels of interest loan. Taking the above into consideration, the second viable solution is S 1,500, where for a 4% of loan interest, the total loan must not exceed 70,03% of the investment cost. Table 2: Financial viability of the project for S ij S 1,700 S 2,700 Loaning Equation % of Loan Equation % of Loan Interest (y=a-bx) that makes (y=a-bx) that makes Rate NPV=0 NPV=0 2% Y= X 99,53% y= x 42,14% 4% Y= X 97,62% y= x 41,33% 6% Y= X 95,78% y= x 40,55% 8% Y= X 94,00% y= x 39,80% 10% y= x 92,29% y= x 39,08% 15% y= x 88,28% y= x 37,38% S 1,500 S 2,500 Loaning Equation % of Loan Equation % of Loan Interest (y=a-bx) that makes (y=a-bx) that makes Rate NPV=0 NPV=0 2% y= x 71,41% y= x 20,33% 4% y= x 70,03% y= x 19,9% 6% y= x 68,71% y= x 19,56% 8% y= x 67,44% y= x 19,20% 10% y= x 66,21% y= x 18,85% 15% y= x 63,34% y= x 18,03%
12 NPV % of Loan Figure 2: Financial viability of the project Loan Interest and % of Loan 100,00% 80,00% 60,00% 40,00% 20,00% Case A Case B Case C Case D 0,00% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 15% Loan Interest 4.2 Sensitivity analysis Another important relationship is observed between the level of the loan and the economic effectiveness of the project (Theofanides, 1985). It is also essential to recognise the risk of such an investment (we choose the optimum solution S 1,700). Since the calculation of the costs is based on real data, while the approach of the revenues is based on demand forecasts, a sensitivity analysis is performed, on different levels of demand. The results are presented in figure 3. Figure 3 shows that, the lower the loan, the lower the danger for all different levels of demand, which we normally expected. A 10% reduction in revenues has no impact on the viability of the project. On the other hand a loan of 30% or more of the investment cost shows great sensitivity if the revenues reduce for 20% and higher. Figure 3: Sensitivity analysis for S 1, Sensitiviry Analysis 0 30% 50% 70% 100% % of Loan 40% reduction in Revenues 30% reduction in Revenues 20% reduction in Revenues 10% Reduction in Revenues
13 5. Conclusion From the above analysis it is concluded that the implementation of a suburban coastal transport system in the southern Athens area is economically viable. This can be achieved with one or two mid stops and different price ticket levels. The optimum though economic solution is accomplished when we apply the smallest number of mid stops and the higher ticket price level. In the examined case study, an one mid stop system with a 700GRDRh ticket (S 1,700 ), is the most efficient financial solution since it shows the higher NPV and IRR. That means that the investor has bigger profit by offering the minimum service (1 mid. stop) with the highest price of the range examined ( GRDrh). If he increased the stops and offer more service, and if he reduced the ticket price, then he would attract more customers. But, according to the above analysis the best solution is S 1,700, that means less service, less passengers and higher ticket price. Thus, the percentage of Loan that makes NPV=0 is higher in case S 1,700, in every level of loan interest. That means that offering lower service with the higher price holds minimum financial risk for the investor. Additionally, the sensitivity analysis shows that the higher the level of uncertainty in the total revenues (reduction in demand) the lower the percentage of the loan, that the investor should take. From that point of view the case S 1,700, proves to be the most secure one. 6. References - Bibliography 1. Abacoumkin K. (1990) Transport Systems Planning, Symmetria, pp Bristow A., Nellthorp J. (2000) Transport project appraisal in the European Union, Transport Policy, Volume 7, Issue 1, pp Giannopoulos G. (1981) Transport Planning and Traffic techniques Athens pp Goulielmos A. (1997) Financing Maritime Companies Publ. Stamoulis, Athens, pp (in Greek) 5. Greek Bank of Industrial Development (1994) Investigation of the operation of a coastal shipping transport network between Piraeus and the South suburban area 6. Karvounis S. (2000) Economic & Technical Studies, Publ. Stamoulis (in Greek), pp Koppelman F.S., Chu C. (1983) Effect of Sample Size on Disaggregate Choice Model Estimation and Prediction, Transportation Research Record 944, Washington D.C. 8. Ortuzar J, Willumsen L.G. (1990) Modeling Transport, John Wiley and Sons 9. Pearmain D., Kroes E., (1990) Stated Preference Techniques: a guide to practice, Steer Davies & Gleave Ltd, Hague consulting Group
14 10. Sambracos E. (2001) Introduction on Transport Economics Publ. Stamoulis, Athens, pp (in Greek) 11. Theofanides S. (1985) Manual for the Evaluation of Investment Projects, Greek Bank of Industrial Development, Publ. Papazisis, pp (in Greek)
PDF created with FinePrint pdffactory Pro trial version
 Air - Sea Transport: Competitiveness or Complementarity in the Greek insular market? International Conference on Air Transport-University of Patras 2002 E. Sambracos Associate Professor in Transport Economics
Air - Sea Transport: Competitiveness or Complementarity in the Greek insular market? International Conference on Air Transport-University of Patras 2002 E. Sambracos Associate Professor in Transport Economics
Munich Personal RePEc Archive. Evangelos Sambracos and Harilaos Harissis. University of Piraeus. December 2003
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Advanced Transport Telematics Systems and user requirements: An approach based on the experience gained in the port of from the EUROSCOPE Project Evangelos Sambracos
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Advanced Transport Telematics Systems and user requirements: An approach based on the experience gained in the port of from the EUROSCOPE Project Evangelos Sambracos
Mobility on Demand for Improving Business Profits and User Satisfaction
 Mobility on Demand for Improving Business Profits and User Satisfaction Takuro Ikeda Takushi Fujita Moshe E. Ben-Akiva For a sustainable society, we need to design a mobility management system that does
Mobility on Demand for Improving Business Profits and User Satisfaction Takuro Ikeda Takushi Fujita Moshe E. Ben-Akiva For a sustainable society, we need to design a mobility management system that does
CASE STUDY 5. Extension of the Adriatic-Ionian ferry corridor from Peloponnese to Crete" University of the Aegean Dpt. Shipping, Trade & Transport
 Lisbon, 15 December 2011 CASE STUDY 5 Extension of the Adriatic-Ionian ferry corridor from Peloponnese to Crete" University of the Aegean Dpt. Shipping, Trade & Transport The concept of the Case Study
Lisbon, 15 December 2011 CASE STUDY 5 Extension of the Adriatic-Ionian ferry corridor from Peloponnese to Crete" University of the Aegean Dpt. Shipping, Trade & Transport The concept of the Case Study
ALTERNATIVE PUBLIC TRANSPORT IN AUSTRIA
 ALTERNATIVE PUBLIC TRANSPORT IN AUSTRIA FACTUM OHG traffic and social analyses Danhausergasse 6/4 A-1040 Wien Phone: +43 1 5041546 Fax: +43 1 5041548 e-mail: clemens.kaufmann@factum.at INTRODUCTION Clemens
ALTERNATIVE PUBLIC TRANSPORT IN AUSTRIA FACTUM OHG traffic and social analyses Danhausergasse 6/4 A-1040 Wien Phone: +43 1 5041546 Fax: +43 1 5041548 e-mail: clemens.kaufmann@factum.at INTRODUCTION Clemens
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017
 APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit - ii - APPENDIX B TRANSIT AND MOBILITY GLOSSARY Amenities, stop or station: Objects or facilities (such as a shelter, bench,
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit - ii - APPENDIX B TRANSIT AND MOBILITY GLOSSARY Amenities, stop or station: Objects or facilities (such as a shelter, bench,
Transportation Theory and Applications
 Fall 2017 - MTAT.08.043 Transportation Theory and Applications Lecture I: Introduction A. Hadachi Course Syllabus Lecturer: Amnir Hadachi Course website: https://courses.cs.ut.ee/2017/transport/fall Office
Fall 2017 - MTAT.08.043 Transportation Theory and Applications Lecture I: Introduction A. Hadachi Course Syllabus Lecturer: Amnir Hadachi Course website: https://courses.cs.ut.ee/2017/transport/fall Office
PUBLIC TRANSPORT LONG TERM VISION FOR MILTON KEYNES
 PUBLIC TRANSPORT LONG TERM VISION FOR MILTON KEYNES CONSULTATION January 2004 We are seeking comments on the final results and recommendations from a study (November 2003) of a long term vision for public
PUBLIC TRANSPORT LONG TERM VISION FOR MILTON KEYNES CONSULTATION January 2004 We are seeking comments on the final results and recommendations from a study (November 2003) of a long term vision for public
Content of the module
 Content of the module Methodology approach Planning process Definition of working area Population and territorial context Supply Infrastructure Transport service Demand On board / at the stations or bus
Content of the module Methodology approach Planning process Definition of working area Population and territorial context Supply Infrastructure Transport service Demand On board / at the stations or bus
POLICY FORECASTS USING MIXED RP/SP MODELS: SOME NEW EVIDENCE
 Advanced OR and AI Methods in Transportation POLICY FORECASTS USING MIXED / MODELS: SOME NEW EVIDENCE Elisabetta CHERCHI 1, Italo MELONI 1, Juan de Dios ORTÚZAR Abstract. The application of discrete choice
Advanced OR and AI Methods in Transportation POLICY FORECASTS USING MIXED / MODELS: SOME NEW EVIDENCE Elisabetta CHERCHI 1, Italo MELONI 1, Juan de Dios ORTÚZAR Abstract. The application of discrete choice
LATVIAN EXPERIENCES WITH PSC
 LATVIAN EXPERIENCES WITH PSC 9 OCTOBER 2008 Prague RUDITE REVELINA RIGA CITY COUNCIL Riga the heart of Latvia Riga the capital of Latvia Riga - the geographical centre of the Baltic States Latvia - the
LATVIAN EXPERIENCES WITH PSC 9 OCTOBER 2008 Prague RUDITE REVELINA RIGA CITY COUNCIL Riga the heart of Latvia Riga the capital of Latvia Riga - the geographical centre of the Baltic States Latvia - the
Park and Ride Action Plan Summary. A Catalyst for Change The Regional Transport Strategy for the west of Scotland
 Park and Ride Action Plan Summary A Catalyst for Change The Regional Transport Strategy for the west of Scotland 2007-2021 Strathclyde Partnership for Transport Contents Purpose...2 Issues, Constraints
Park and Ride Action Plan Summary A Catalyst for Change The Regional Transport Strategy for the west of Scotland 2007-2021 Strathclyde Partnership for Transport Contents Purpose...2 Issues, Constraints
Transit Demand Analysis
 Transit Demand Analysis Purpose To determine impact on ridership and revenues of any change in service policy. Need to know how demand estimates will be used. May not require an elaborate analysis in many
Transit Demand Analysis Purpose To determine impact on ridership and revenues of any change in service policy. Need to know how demand estimates will be used. May not require an elaborate analysis in many
car pool mass transportation schedule carrier transfer
 How will I get to where I m going? Chapter 30 Transportation Chapter Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to identify two forms of self-powered transportation. determine the pros and
How will I get to where I m going? Chapter 30 Transportation Chapter Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to identify two forms of self-powered transportation. determine the pros and
IMPROVING URBAN PUBLIC OPERATION: ROSTOV-ON-DON (RUSSIA) R. Sanamov Municipal transport company "Rostovpassagirtrans" Rostov-on-Don, Russia
 IMPROVING URBAN PUBLIC OPERATION: ROSTOV-ON-DON (RUSSIA) EXPERIENCE OF V. Zyryanov Rostov State Civil Engineering University Rostov-on-Don, Russia R. Sanamov Municipal transport company "Rostovpassagirtrans"
IMPROVING URBAN PUBLIC OPERATION: ROSTOV-ON-DON (RUSSIA) EXPERIENCE OF V. Zyryanov Rostov State Civil Engineering University Rostov-on-Don, Russia R. Sanamov Municipal transport company "Rostovpassagirtrans"
Presentation To: HRTPO Passenger Rail Task Force
 Presentation To: HRTPO Passenger Rail Task Force HRTPO Norfolk-Richmond Passenger Rail Ridership and Revenue Forecasts Presentation By December 17, 2013 Transportation Economics & Management Systems, Inc.
Presentation To: HRTPO Passenger Rail Task Force HRTPO Norfolk-Richmond Passenger Rail Ridership and Revenue Forecasts Presentation By December 17, 2013 Transportation Economics & Management Systems, Inc.
MOBILITICS. Scenario Planning and Modeling Connected & Automated Vehicles. June 12, 2018
 MOBILITICS Scenario Planning and Modeling Connected & Automated Vehicles June 12, 2018 Connected and Automated Vehicles are everywhere. Light Duty (personal or shared) Shuttles Bus Freight Parcel Delivery
MOBILITICS Scenario Planning and Modeling Connected & Automated Vehicles June 12, 2018 Connected and Automated Vehicles are everywhere. Light Duty (personal or shared) Shuttles Bus Freight Parcel Delivery
IPSWICH NORTHERN ROUTES STUDY. Stage 1 Progress
 IPSWICH NORTHERN ROUTES STUDY Stage 1 Progress 17 th January 2017 STUDY CONTEXT 2 The study is being funded in partnership with the Suffolk district and borough councils. Work forms part of the Suffolk
IPSWICH NORTHERN ROUTES STUDY Stage 1 Progress 17 th January 2017 STUDY CONTEXT 2 The study is being funded in partnership with the Suffolk district and borough councils. Work forms part of the Suffolk
Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources)
 Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources) A Transportation Modeling Primer May, 1995 Edward A. Beimborn Center for Urban Transportation Studies University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee http://www.uwm.edu/dept/c
Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources) A Transportation Modeling Primer May, 1995 Edward A. Beimborn Center for Urban Transportation Studies University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee http://www.uwm.edu/dept/c
9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT
 9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT To examine the existing transportation system and accurately predict impacts of future growth, a travel demand model is necessary. A travel demand model is a computer
9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT To examine the existing transportation system and accurately predict impacts of future growth, a travel demand model is necessary. A travel demand model is a computer
Macroscopic and Microscopic Simulation for the Evaluation of People Mover Systems. Dr.-Ing. Peter Mott Sven Beller PTV AG, Karlsruhe, Germany
 Macroscopic and Microscopic Simulation for the Evaluation of People Mover Systems Dr.-Ing. Peter Mott Sven Beller PTV AG, Karlsruhe, Germany 1. Introduction This paper is intended to show how a comprehensive
Macroscopic and Microscopic Simulation for the Evaluation of People Mover Systems Dr.-Ing. Peter Mott Sven Beller PTV AG, Karlsruhe, Germany 1. Introduction This paper is intended to show how a comprehensive
Munenori SHIBATA Transport Planning and Marketing Laboratory, Signalling and Transport Information Technology Division
 PAPER A Study on Passengers Train Choice Model in Urban Railways Noriko FUKASAWA Munenori SHIBATA Transport Planning and Marketing Laboratory, Signalling and Transport Information Technology Division This
PAPER A Study on Passengers Train Choice Model in Urban Railways Noriko FUKASAWA Munenori SHIBATA Transport Planning and Marketing Laboratory, Signalling and Transport Information Technology Division This
Estimates of costs of road congestion in Wellington
 Estimates of costs of road congestion in Wellington Dave Grimmond October 2017 For more information, contact the Greater Wellington Regional Council: www.gw.govt.nz info@gw.govt.nz Contents 1. Executive
Estimates of costs of road congestion in Wellington Dave Grimmond October 2017 For more information, contact the Greater Wellington Regional Council: www.gw.govt.nz info@gw.govt.nz Contents 1. Executive
VRE Gainesville-Haymarket Alternatives Analysis Report
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY VRE Gainesville-Haymarket Alternatives Analysis Report Prepared for Virginia Railway Express (VRE) Alexandria, Virginia Prepared by Vienna, Virginia in association with AECOM The Perspectives
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY VRE Gainesville-Haymarket Alternatives Analysis Report Prepared for Virginia Railway Express (VRE) Alexandria, Virginia Prepared by Vienna, Virginia in association with AECOM The Perspectives
Air Pollution Zoning based on Land use and Traffic of Vehicles
 Air Pollution Zoning based on Land use and Traffic of Vehicles Elnaz Irannezhad Transportation Planning Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology elnaziran@gmail.com Seyed Hossein Mousavi
Air Pollution Zoning based on Land use and Traffic of Vehicles Elnaz Irannezhad Transportation Planning Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology elnaziran@gmail.com Seyed Hossein Mousavi
Transport Economics. Energy Summer School, 2017 Selena Sheng Energy Centre, Business School, UoA 27/02/2017
 Transport Economics Energy Summer School, 2017 Selena Sheng Energy Centre, Business School, UoA 27/02/2017 Transport Economics Transport demand Transport supply Congestion pricing Econometric modelling
Transport Economics Energy Summer School, 2017 Selena Sheng Energy Centre, Business School, UoA 27/02/2017 Transport Economics Transport demand Transport supply Congestion pricing Econometric modelling
Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion
 Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion Andrew Wall VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 1 Introduction Congestion is an unavoidable aspect of most urban cities. However, there
Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion Andrew Wall VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 1 Introduction Congestion is an unavoidable aspect of most urban cities. However, there
Intermodality of Network Points The planners view Author(s): Publication Date: Permanent Link: Rights / License:
 Research Collection Conference Paper Intermodality of Network Points The planners view Author(s): Keller, Peter Publication Date: 2001 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004231975 Rights /
Research Collection Conference Paper Intermodality of Network Points The planners view Author(s): Keller, Peter Publication Date: 2001 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004231975 Rights /
Analysis of Sydney Public-Private Partnership Road Tunnels
 Analysis of Sydney Public-Private Partnership Road Tunnels Introduction Geoff Phillips Mathematics Learning Centre, Sydney University The Sydney Cross City Tunnel and the Lane Cove Tunnel have generated
Analysis of Sydney Public-Private Partnership Road Tunnels Introduction Geoff Phillips Mathematics Learning Centre, Sydney University The Sydney Cross City Tunnel and the Lane Cove Tunnel have generated
8.0 Chapter 8 Alternatives Analysis
 8.0 Chapter 8 Alternatives Analysis The primary purpose for using CORSIM in the context of this manual is to guide the design process and program delivery. To this point in the manual, you have been given
8.0 Chapter 8 Alternatives Analysis The primary purpose for using CORSIM in the context of this manual is to guide the design process and program delivery. To this point in the manual, you have been given
THE CONTINUING ROLE OF THE STRATHCLYDE TRANSPORTATION AND LAND-USE MODEL IN STRATEGIC PLANNING. Paul Emmerson and Dr Andrew Ash TRL
 THE CONTINUING ROLE OF THE STRATHCLYDE TRANSPORTATION AND LAND-USE MODEL IN STRATEGIC PLANNING Paul Emmerson and Dr Andrew Ash TRL Jim Dunlop Strathclyde Partnership for Transport Andy Dobson David Simmonds
THE CONTINUING ROLE OF THE STRATHCLYDE TRANSPORTATION AND LAND-USE MODEL IN STRATEGIC PLANNING Paul Emmerson and Dr Andrew Ash TRL Jim Dunlop Strathclyde Partnership for Transport Andy Dobson David Simmonds
Maharashtra Rail Infrastructure Development Limited. Pune Nasik Double Line
 Maharashtra Rail Infrastructure Development Limited (MRIDL) Name of the project Pune Nasik Double Line (With electrification) Term of Reference For Traffic Study and Financial Analysis for Green Field
Maharashtra Rail Infrastructure Development Limited (MRIDL) Name of the project Pune Nasik Double Line (With electrification) Term of Reference For Traffic Study and Financial Analysis for Green Field
AND WASTEFUL" IN BUS TRANSPORT
 "UNNECESSARY COMPETITION AND WASTEFUL" IN BUS TRANSPORT By Ian P. Savage* Many commentators, for example Gwilliam (1964), report that a common reason for regulating local bus services has been that competition
"UNNECESSARY COMPETITION AND WASTEFUL" IN BUS TRANSPORT By Ian P. Savage* Many commentators, for example Gwilliam (1964), report that a common reason for regulating local bus services has been that competition
Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan)
 Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan) 1. Name of the Project Country: Federative Republic of Brazil Project: Belem Metropolitan Trunk Bus System Project Loan Agreement: September
Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan) 1. Name of the Project Country: Federative Republic of Brazil Project: Belem Metropolitan Trunk Bus System Project Loan Agreement: September
That will also contribute to achievement of a number of objectives and policies in the Regional Policy Statement.
 Board of Inquiry MacKays to Peka Peka Expressway Proposal Submitters Evidence Public Transport Voice 5 October 2012 Executive Summary Increasing modal share for public transport is a key outcome in the
Board of Inquiry MacKays to Peka Peka Expressway Proposal Submitters Evidence Public Transport Voice 5 October 2012 Executive Summary Increasing modal share for public transport is a key outcome in the
Application of system dynamics with GIS for assessing traffic emission management policy
 Application of system dynamics with GIS for assessing traffic emission management policy L. Chen and W.-L. Yang Department of Water Resources & Environmental Engineering, Tamkang University, Tam-Shui,
Application of system dynamics with GIS for assessing traffic emission management policy L. Chen and W.-L. Yang Department of Water Resources & Environmental Engineering, Tamkang University, Tam-Shui,
P2 Performance Management September 2014 examination
 Management Level Paper P2 Performance Management September 2014 examination Examiner s Answers Note: Some of the answers that follow are fuller and more comprehensive than would be expected from a well-prepared
Management Level Paper P2 Performance Management September 2014 examination Examiner s Answers Note: Some of the answers that follow are fuller and more comprehensive than would be expected from a well-prepared
Developing islands passenger transport connectivity indices
 Developing islands passenger transport connectivity indices Maria Lekakou, George Remoundos DEPARTMENT OF SHIPPING, TRADE & TRANSPORT Athens, May 2016 The agenda The Greek Coastal Shipping Assesement of
Developing islands passenger transport connectivity indices Maria Lekakou, George Remoundos DEPARTMENT OF SHIPPING, TRADE & TRANSPORT Athens, May 2016 The agenda The Greek Coastal Shipping Assesement of
Linking Gaza and the West Bank: Convoys
 Prepared by the World Bank Technical Team, September 30, 2005 Linking Gaza and the West Bank: Convoys This note proposes how convoys for people and goods might operate between the West Bank and Gaza. Technical
Prepared by the World Bank Technical Team, September 30, 2005 Linking Gaza and the West Bank: Convoys This note proposes how convoys for people and goods might operate between the West Bank and Gaza. Technical
ALBION FLATS DEVELOPMENT EXISTING TRAFFIC CONDITIONS AND POTENTIAL IMPACTS
 EXISTING TRAFFIC CONDITIONS AND POTENTIAL IMPACTS FINAL REPORT SEPTEMBER 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1 2.0 EXISTING TRAFFIC CONDITIONS 2 3.0 FUTURE TRAFFIC CONDITIONS 3 4.0 POTENTIAL IMPACTS
EXISTING TRAFFIC CONDITIONS AND POTENTIAL IMPACTS FINAL REPORT SEPTEMBER 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1 2.0 EXISTING TRAFFIC CONDITIONS 2 3.0 FUTURE TRAFFIC CONDITIONS 3 4.0 POTENTIAL IMPACTS
Presentation of Dakar BRT Project. Abuja, July 3th 2018
 Presentation of Dakar BRT Project Abuja, July 3th 2018 Key figures Dakar : a peninsula of 550 km² 23% of the country's population on 0.3% of the national territory 2.6 M inhabitants in 2005 / 3.5 M in
Presentation of Dakar BRT Project Abuja, July 3th 2018 Key figures Dakar : a peninsula of 550 km² 23% of the country's population on 0.3% of the national territory 2.6 M inhabitants in 2005 / 3.5 M in
THE APPLICATION OF COMPENSATORY RULES TO MODEL PRIVATE SECTOR LAND USE INVESTMENT
 THE APPLICATION OF COMPENSATORY RULES TO MODEL PRIVATE SECTOR LAND USE INVESTMENT van de Wetering, A. and Del Mistro, R. 1 Africon Engineering 1040 Burnett Street, Hatfield. Tel: (012) 427-2724. E-mail:
THE APPLICATION OF COMPENSATORY RULES TO MODEL PRIVATE SECTOR LAND USE INVESTMENT van de Wetering, A. and Del Mistro, R. 1 Africon Engineering 1040 Burnett Street, Hatfield. Tel: (012) 427-2724. E-mail:
This document has been developed to provide context to the Board as part of the strategic planning process. Regional development and travel trends
 1 This document has been developed to provide context to the Board as part of the strategic planning process. Regional development and travel trends and forecasts are provided, including population, employment,
1 This document has been developed to provide context to the Board as part of the strategic planning process. Regional development and travel trends and forecasts are provided, including population, employment,
Overview of Alternatives Analysis
 Red Line/HealthLine Extension Major Transportation Improvement Analysis Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority Public Meeting: February 11, 2016 Final Report Overview of Alternatives Analysis Public
Red Line/HealthLine Extension Major Transportation Improvement Analysis Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority Public Meeting: February 11, 2016 Final Report Overview of Alternatives Analysis Public
Presentation of the practical exercise on traffic forecasting
 Presentation of the practical exercise on traffic forecasting During this session you are going to be assigned a task aimed at making you more familiar with traffic forecasting for High Speed Rail lines.
Presentation of the practical exercise on traffic forecasting During this session you are going to be assigned a task aimed at making you more familiar with traffic forecasting for High Speed Rail lines.
Fishermans Bend Integrated Transport Plan Peer Review John Kiriakidis, GTA Consultants 28/03/2018
 Fishermans Bend Integrated Transport Plan Peer Review John Kiriakidis, GTA Consultants 28/03/2018 GTA creating transport that works 01 Preliminaries GTA creating transport that works Review scope : Review
Fishermans Bend Integrated Transport Plan Peer Review John Kiriakidis, GTA Consultants 28/03/2018 GTA creating transport that works 01 Preliminaries GTA creating transport that works Review scope : Review
Transportation Report to SPC on Transportation and Transit 2017 March 15. ISC: UNRESTRICTED TT Page 1 of 7 ROUTEAHEAD UPDATE
 Page 1 of 7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report provides Council with an update on the status of implementation of RouteAhead, a 30-year strategic plan for public transit in Calgary. The report also highlights
Page 1 of 7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report provides Council with an update on the status of implementation of RouteAhead, a 30-year strategic plan for public transit in Calgary. The report also highlights
2016 transit accessibility plan
 2016 transit accessibility plan This document is available in alternate formats upon request. 905-864-4141 transit@milton.ca miltontransit.ca Table of Contents Section 1 Executive Summary 3 Section 2 Milton
2016 transit accessibility plan This document is available in alternate formats upon request. 905-864-4141 transit@milton.ca miltontransit.ca Table of Contents Section 1 Executive Summary 3 Section 2 Milton
PUBLIC TRANSIT IMPROVEMENTS THAT WOULD BETTER SERVE OLDER PERSONS
 7 PUBLIC TRANSIT IMPROVEMENTS THAT WOULD BETTER SERVE OLDER PERSONS What makes some transit services better than others in terms of their abilities to meet the needs of older travelers? The first step
7 PUBLIC TRANSIT IMPROVEMENTS THAT WOULD BETTER SERVE OLDER PERSONS What makes some transit services better than others in terms of their abilities to meet the needs of older travelers? The first step
Public Transport Infrastructure
 Christchurch City Council Public Transport Infrastructure Activity Management Plan Long Term Plan 2015 2025 3 December 2014 Christchurch City Council Quality Assurance Statement Christchurch City Council
Christchurch City Council Public Transport Infrastructure Activity Management Plan Long Term Plan 2015 2025 3 December 2014 Christchurch City Council Quality Assurance Statement Christchurch City Council
2004 FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE
 Austin-San Antonio Intermunicipal Commuter Rail District 2004 FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE December 2004 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY INTRODUCTION Almost 3 million people in Central Texas, living and working between
Austin-San Antonio Intermunicipal Commuter Rail District 2004 FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE December 2004 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY INTRODUCTION Almost 3 million people in Central Texas, living and working between
The Victorian Transport Plan (Department of Transport, 2008).
 18 TRANSPORT Planning should ensure an integrated and sustainable transport system that provides access to social and economic opportunities, facilitates economic prosperity, contributes to environmental
18 TRANSPORT Planning should ensure an integrated and sustainable transport system that provides access to social and economic opportunities, facilitates economic prosperity, contributes to environmental
THE P+R SYSTEM WITH VMS INFORMATION TABASCO
 CAPE - GOOD PRACTICE EXAMPLES IN TRANSPORT TELEMATICS 1 DEMONSTRATION SITE: (FROTTMANING P+R STATION, MUNICH ON THE A9 MOTORWAY) MUNICH/GERMANY NAME OF THE DEMONSTRATION PROJECT (CASE STUDY): DURATION
CAPE - GOOD PRACTICE EXAMPLES IN TRANSPORT TELEMATICS 1 DEMONSTRATION SITE: (FROTTMANING P+R STATION, MUNICH ON THE A9 MOTORWAY) MUNICH/GERMANY NAME OF THE DEMONSTRATION PROJECT (CASE STUDY): DURATION
MODELLING FREIGHT DEMAND. John de Pont, TERNZ
 MODELLING FREIGHT DEMAND John de Pont, TERNZ ABSTRACT Over the last 10 years, road freight in New Zealand has grown at approximately 1.3 times the rate of growth of real gross domestic product (RGDP) and
MODELLING FREIGHT DEMAND John de Pont, TERNZ ABSTRACT Over the last 10 years, road freight in New Zealand has grown at approximately 1.3 times the rate of growth of real gross domestic product (RGDP) and
UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK
 Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): URBAN TRANSPORT 1
 Greater Dhaka Sustainable Urban Transport Project (RRP BAN 42169) Sector Road Map SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): URBAN TRANSPORT 1 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Dhaka, the capital
Greater Dhaka Sustainable Urban Transport Project (RRP BAN 42169) Sector Road Map SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): URBAN TRANSPORT 1 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Dhaka, the capital
TAXI has been an important mode of transportation
 , March 12-14, 2014, Hong Kong Virtual Taxi Stand Management System Kar Leong TEW, Jessie CAI, Elliot CHIAM, Ziheng LIN, Bernice NG, Manning ZHANG, Steve LEE Abstract Taxi is an important mode of transportation
, March 12-14, 2014, Hong Kong Virtual Taxi Stand Management System Kar Leong TEW, Jessie CAI, Elliot CHIAM, Ziheng LIN, Bernice NG, Manning ZHANG, Steve LEE Abstract Taxi is an important mode of transportation
Development of urban public transport in Kazakhstan POLICY OVERVIEW AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 Development of urban public transport in Kazakhstan POLICY OVERVIEW AND RECOMMENDATIONS CAST project chief technical advisor ALMATY 16 November 2017 Public Transport Improvement is not an option STUDY:
Development of urban public transport in Kazakhstan POLICY OVERVIEW AND RECOMMENDATIONS CAST project chief technical advisor ALMATY 16 November 2017 Public Transport Improvement is not an option STUDY:
Strategic noise mapping of Adelaide CBD
 Strategic noise mapping of Adelaide CBD Valeri V. Lenchine 1, Jonathan Song 1 1 Science, Assessment & Planning Division, SA Environment Protection Authority, Adelaide, Australia ABSTRACT The Adelaide Central
Strategic noise mapping of Adelaide CBD Valeri V. Lenchine 1, Jonathan Song 1 1 Science, Assessment & Planning Division, SA Environment Protection Authority, Adelaide, Australia ABSTRACT The Adelaide Central
Travel Forecasting Tutorial
 Travel Forecasting Tutorial Travel Demand Modeling/Forecasting Process by which relationships among causal factors and travel decisions are analyzed and mathematically modeled. Decisions include: Travel
Travel Forecasting Tutorial Travel Demand Modeling/Forecasting Process by which relationships among causal factors and travel decisions are analyzed and mathematically modeled. Decisions include: Travel
New challenges in mobility services: business trends, forms and success factors
 New challenges in mobility services: business trends, forms and success factors Dr. Dimitrios J. DIMITRIOU Planning, Management & Economics in Transport Development Professor Assistant, Department of Economics,
New challenges in mobility services: business trends, forms and success factors Dr. Dimitrios J. DIMITRIOU Planning, Management & Economics in Transport Development Professor Assistant, Department of Economics,
ROUTE CHOICE MODELLING USING ADAPTIVE NEURAL FUZZY INTERFACE SYSTEM AND LOGISTIC REGRESSION METHOD
 ROUTE CHOICE MODELLING USING ADAPTIVE NEURAL FUZZY INTERFACE SYSTEM AND LOGISTIC REGRESSION METHOD Soumya R. Nayak Department of Civil Engineering, Indira Gandhi Institute of Technology, India Sandeep
ROUTE CHOICE MODELLING USING ADAPTIVE NEURAL FUZZY INTERFACE SYSTEM AND LOGISTIC REGRESSION METHOD Soumya R. Nayak Department of Civil Engineering, Indira Gandhi Institute of Technology, India Sandeep
Commonwealth Transportation Board I-66 Corridor Briefing Outside the Beltway Route 15 to I-495
 Commonwealth Transportation Board I-66 Corridor Briefing Outside the Beltway Route 15 to I-495 January 13, 2015 1 Project Status Update Transit P3 Procurement I-66 Corridor Briefing Overview Major Project
Commonwealth Transportation Board I-66 Corridor Briefing Outside the Beltway Route 15 to I-495 January 13, 2015 1 Project Status Update Transit P3 Procurement I-66 Corridor Briefing Overview Major Project
Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004
 Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004 Introduction : Overview of Presentation - Option Appraisal Policy Context - Potential PRISM Applications - Use of the Model / Scale of the
Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004 Introduction : Overview of Presentation - Option Appraisal Policy Context - Potential PRISM Applications - Use of the Model / Scale of the
Transportation Economics and Decision Making. L e c t u r e - 4
 Transportation Economics and Decision Making L e c t u r e - 4 Example of Mutually Exclusive Alternatives Problem definition A certain section of highway is now in location A. Number of perspective designs
Transportation Economics and Decision Making L e c t u r e - 4 Example of Mutually Exclusive Alternatives Problem definition A certain section of highway is now in location A. Number of perspective designs
Effectively Using the QRFM to Model Truck Trips in Medium-Sized Urban Communities
 Effectively Using the QRFM to Model Truck Trips in Medium-Sized Urban Communities By Dr. Michael Anderson and Mary Catherine Dondapati Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering The University of
Effectively Using the QRFM to Model Truck Trips in Medium-Sized Urban Communities By Dr. Michael Anderson and Mary Catherine Dondapati Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering The University of
SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow
 Preliminary Report SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow WP 03: Multi-modal Transportation Modelling D03.3 User Manual and Example Test Data Sets First Draft Karlsruhe, January
Preliminary Report SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow WP 03: Multi-modal Transportation Modelling D03.3 User Manual and Example Test Data Sets First Draft Karlsruhe, January
VIA Long Range Plan Glossary
 VIA Long Range Plan Glossary Accessibility. Accessibility is the ability to reach opportunities (economic, social, etc.) within a certain geographical area. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Passed
VIA Long Range Plan Glossary Accessibility. Accessibility is the ability to reach opportunities (economic, social, etc.) within a certain geographical area. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Passed
Buzz Rides: A Dorm Room Name in College Transportation
 Cameron Winders Buzz Rides: A Dorm Room Name in College Transportation The Buzz Rides mission is to provide safe, eco-friendly, and free transportation to students. Buzz Rides started in 2013 at the University
Cameron Winders Buzz Rides: A Dorm Room Name in College Transportation The Buzz Rides mission is to provide safe, eco-friendly, and free transportation to students. Buzz Rides started in 2013 at the University
1. Background to the West Midlands 1.1 West Midlands and Future Transport
 1. Background to the West Midlands 1.1 West Midlands and Future Transport The West Midlands is at the heart of the UK s motorway network with the M6, M5, M40, M42 converging on and passing through the
1. Background to the West Midlands 1.1 West Midlands and Future Transport The West Midlands is at the heart of the UK s motorway network with the M6, M5, M40, M42 converging on and passing through the
An integrated scheme for Olympic Village traffic and parking arrangements. Abstract: The present study deals with the development of an integrated
 An integrated scheme for Olympic Village traffic and parking arrangements George Yannis 1, John Golias 2, Ioanna Spyropoulou 3, Adelkis Rogan 4 Abstract: The present study deals with the development of
An integrated scheme for Olympic Village traffic and parking arrangements George Yannis 1, John Golias 2, Ioanna Spyropoulou 3, Adelkis Rogan 4 Abstract: The present study deals with the development of
Methodological Approach
 Appendix B Methodological Approach This section sets out the methodology which was utilised in the production of this analysis. It is informed by international literature and knowledge of the Irish transport
Appendix B Methodological Approach This section sets out the methodology which was utilised in the production of this analysis. It is informed by international literature and knowledge of the Irish transport
1) Operating costs, such as fuel and labour. 2) Maintenance costs, such as overhaul of engines and spraying.
 NUMBER ONE QUESTIONS Boni Wahome, a financial analyst at Green City Bus Company Ltd. is examining the behavior of the company s monthly transportation costs for budgeting purposes. The transportation costs
NUMBER ONE QUESTIONS Boni Wahome, a financial analyst at Green City Bus Company Ltd. is examining the behavior of the company s monthly transportation costs for budgeting purposes. The transportation costs
Melbourne Airport heavy rail line MAH
 Melbourne Airport heavy rail line MAH Option type New assets Location Melbourne central subregion, Melbourne western subregion and Melbourne northern subregion Melbourne Airport north west state-significant
Melbourne Airport heavy rail line MAH Option type New assets Location Melbourne central subregion, Melbourne western subregion and Melbourne northern subregion Melbourne Airport north west state-significant
Creating a Transit Supply Index. Andrew Keller Regional Transportation Authority and University of Illinois at Chicago
 Creating a Transit Supply Index Andrew Keller Regional Transportation Authority and University of Illinois at Chicago Presented at Transport Chicago Conference June 1, 2012 Introduction This master's project
Creating a Transit Supply Index Andrew Keller Regional Transportation Authority and University of Illinois at Chicago Presented at Transport Chicago Conference June 1, 2012 Introduction This master's project
Travel Demand Modelling [T1]
![Travel Demand Modelling [T1] Travel Demand Modelling [T1]](/thumbs/80/82313377.jpg) This publication was prepared by the National Guidelines for Transport System Management in Australia Steering Committee and approved by the Transport and Infrastructure Senior Officials' Committee. The
This publication was prepared by the National Guidelines for Transport System Management in Australia Steering Committee and approved by the Transport and Infrastructure Senior Officials' Committee. The
Zenith Model Framework Papers - Version Paper G Mode Choice Model
 Zenith Model Framework Papers - Version 3.0.1 Paper G Mode Choice Model May 2014 Page Intentionally Left Blank Paper G Mode Choice Model Draft Report COPYRIGHT: The concepts and information contained in
Zenith Model Framework Papers - Version 3.0.1 Paper G Mode Choice Model May 2014 Page Intentionally Left Blank Paper G Mode Choice Model Draft Report COPYRIGHT: The concepts and information contained in
Demand Response: How cities around the world have responded to this global phenomenon
 Demand Response: How cities around the world have responded to this global phenomenon Nov 2017 l Mel Pecen, Managing Director, ANZ Demand Response: How cities around the world have responded to this global
Demand Response: How cities around the world have responded to this global phenomenon Nov 2017 l Mel Pecen, Managing Director, ANZ Demand Response: How cities around the world have responded to this global
Low Emission Bus Workshop: Local Challenges in Leeds. Gwyn Owen
 Low Emission Bus Workshop: Local Challenges in Leeds Gwyn Owen Summary of Key Transport Challenges Significant population growth of up to 15% by 2028 to 860,000 Most congested part of the Leeds highway
Low Emission Bus Workshop: Local Challenges in Leeds Gwyn Owen Summary of Key Transport Challenges Significant population growth of up to 15% by 2028 to 860,000 Most congested part of the Leeds highway
APPENDIX A. Analysis Of The High Speed Rail Authority s Planned Pricing William H. Warren July 2, Management Summary
 APPENDIX A Objective: Analysis Of The High Speed Rail Authority s Planned Pricing William H. Warren July 2, 2010 Management Summary To analyze the pricing used in the HSR Authority s Ridership Forecasts
APPENDIX A Objective: Analysis Of The High Speed Rail Authority s Planned Pricing William H. Warren July 2, 2010 Management Summary To analyze the pricing used in the HSR Authority s Ridership Forecasts
TRANSIT SERVICE GUIDELINES
 CHATHAM AREA TRANSIT AUTHORITY FEBRUARY 2014 Table of Contents 1. PURPOSE... 3 2. CAT SERVICE GUIDELINES... 3 3. TRAVEL MARKETS... 4 4. TRANSIT COVERAGE... 4 5. TRANSIT ACCESS... 4 6. BUS STOP SPACING
CHATHAM AREA TRANSIT AUTHORITY FEBRUARY 2014 Table of Contents 1. PURPOSE... 3 2. CAT SERVICE GUIDELINES... 3 3. TRAVEL MARKETS... 4 4. TRANSIT COVERAGE... 4 5. TRANSIT ACCESS... 4 6. BUS STOP SPACING
2017 TRANSPORTATION POLICY STATEMENT
 0 TRANSPORTATION POLICY STATEMENT 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Critical investments are needed to maintain and improve Virginia s transportation network. The structural imbalance between critical needs and
0 TRANSPORTATION POLICY STATEMENT 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Critical investments are needed to maintain and improve Virginia s transportation network. The structural imbalance between critical needs and
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BUSINESS 9609/1 Paper 1 Short Answer/Essay MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BUSINESS 9609/1 Paper 1 Short Answer/Essay MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme
FinEst Bay Area Development The Tallinn Tunnel Project. Financial indicators
 FinEst Bay Area Development The Tallinn Tunnel Project Financial indicators Passenger traffic volumes Current Assumptions 2030 Helsinki Helsinki- Airport 20 M Tallinn Airport 70 M Espoo 125 M Helsinki
FinEst Bay Area Development The Tallinn Tunnel Project Financial indicators Passenger traffic volumes Current Assumptions 2030 Helsinki Helsinki- Airport 20 M Tallinn Airport 70 M Espoo 125 M Helsinki
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN THE RAILWAYS
 CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN THE RAILWAYS Paper presented at the 9 th Annual Sessions of the Chartered Institute of Transport (Sri Lanka) Amal S. Kumarage Ph.D., MCIT Senior Lecturer, Head Transport Engineering
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN THE RAILWAYS Paper presented at the 9 th Annual Sessions of the Chartered Institute of Transport (Sri Lanka) Amal S. Kumarage Ph.D., MCIT Senior Lecturer, Head Transport Engineering
Performance-Based Technology Scanning for Intercity Rail Passenger Systems
 Performance-Based Technology Scanning for Intercity Rail Passenger Systems Carl D. Martland Lexcie Lu Dalong Shi Joseph M. Sussman Massachusetts Institute of Technology Presented to the Transportation
Performance-Based Technology Scanning for Intercity Rail Passenger Systems Carl D. Martland Lexcie Lu Dalong Shi Joseph M. Sussman Massachusetts Institute of Technology Presented to the Transportation
6.0 CONGESTION HOT SPOT PROBLEM AND IMPROVEMENT TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL ANALYSIS
 6.0 CONGESTION HOT SPOT PROBLEM AND IMPROVEMENT TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL ANALYSIS 6.1 MODEL RUN SUMMARY NOTEBOOK The Model Run Summary Notebook (under separate cover) provides documentation of the multiple
6.0 CONGESTION HOT SPOT PROBLEM AND IMPROVEMENT TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL ANALYSIS 6.1 MODEL RUN SUMMARY NOTEBOOK The Model Run Summary Notebook (under separate cover) provides documentation of the multiple
Input from Engineers Ireland Into the Department of Transport s Statement of Strategy
 Input from Engineers Ireland Into the Department of Transport s Statement of Strategy 2008 2010 Table of Contents Page Executive Summary 3 Department of Transport Mandate and Mission (2005-2007) 4 The
Input from Engineers Ireland Into the Department of Transport s Statement of Strategy 2008 2010 Table of Contents Page Executive Summary 3 Department of Transport Mandate and Mission (2005-2007) 4 The
Northern Virginia Region Draft Needs Summary
 Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Getting around in Essex A bus and passenger transport strategy summary
 Getting around in Essex A bus and passenger transport strategy summary Working in partnership with 2 Contents Introduction 5 Section One Buses are important to Essex 6 Buses make life better for people
Getting around in Essex A bus and passenger transport strategy summary Working in partnership with 2 Contents Introduction 5 Section One Buses are important to Essex 6 Buses make life better for people
Prague Integrated Transport (PID) Contract Management
 Prague Integrated Transport (PID) Contract Management Characteristics of the metropolitan area (PID area of interest) Prague - area 496 km 2 population 1.25 mil. Prague transport region includes a part
Prague Integrated Transport (PID) Contract Management Characteristics of the metropolitan area (PID area of interest) Prague - area 496 km 2 population 1.25 mil. Prague transport region includes a part
G. A. GIANNOPOULOS* AND G. AIFANDOPOULOU-KLIMIS**
 Transport Reviews, Vol. 24, No. 4, 465 483, July 2004 Inland Maritime Transport in Greece after the Lifting of the Cabotage and Full Liberalization: A Review. Part 1: The Situation before and Expected
Transport Reviews, Vol. 24, No. 4, 465 483, July 2004 Inland Maritime Transport in Greece after the Lifting of the Cabotage and Full Liberalization: A Review. Part 1: The Situation before and Expected
Demand Curves in Bangkok
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1395 33 Derivation of Value of Time and Traffic Demand Curves in Bangkok YUICHIRO MOTOMURA AND SURAPONG LAOHA-UNYA A value of time has been calculated by calibrating a traffic
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1395 33 Derivation of Value of Time and Traffic Demand Curves in Bangkok YUICHIRO MOTOMURA AND SURAPONG LAOHA-UNYA A value of time has been calculated by calibrating a traffic
Introduction to Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Transportation Systems 1 PART III: TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION 2 Chapter 28: Urban Public Transportation 3 Urban Public Transportation Introduction LOS Services History Costs Temporal Peaking
Introduction to Transportation Systems 1 PART III: TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION 2 Chapter 28: Urban Public Transportation 3 Urban Public Transportation Introduction LOS Services History Costs Temporal Peaking
Local Transit Service
 Local Transit Service Cochrane Youth Council March 20, 2018 Peer System Review Cities and Towns the size of Cochrane have local and regional transit service. Airdrie (54,000), Spruce Grove (32,000) and
Local Transit Service Cochrane Youth Council March 20, 2018 Peer System Review Cities and Towns the size of Cochrane have local and regional transit service. Airdrie (54,000), Spruce Grove (32,000) and
ANNEX F BRESSAY LINK. STAG 1: APPRAISAL SUMMARY TABLES (ASTs)
 ANNEX F BRESSAY LINK STAG 1: APPRAISAL SUMMARY TABLES (ASTs) Table F1 STAG 1 Appraisal Summary Table: Do Minimum Proposal Details Name and address of authority or organisation promoting the proposal:
ANNEX F BRESSAY LINK STAG 1: APPRAISAL SUMMARY TABLES (ASTs) Table F1 STAG 1 Appraisal Summary Table: Do Minimum Proposal Details Name and address of authority or organisation promoting the proposal:
Urban transport system benchmarking
 Urban Transport XII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 223 Urban transport system benchmarking M. W. Ludema Delft University of Technology, Faculty of Technology, Policy and Management,
Urban Transport XII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 223 Urban transport system benchmarking M. W. Ludema Delft University of Technology, Faculty of Technology, Policy and Management,
Forecasting Intermodal Competition in a Multimodal Environment
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1139 15 Forecasting Intermodal Competition in a Multimodal Environment KEVIN NEELS AND JOSEPH MATHER In this paper, the problem or accurately describing patterns of intermodal
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1139 15 Forecasting Intermodal Competition in a Multimodal Environment KEVIN NEELS AND JOSEPH MATHER In this paper, the problem or accurately describing patterns of intermodal
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. 1.1 Introduction
 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 As part of the Second East Sussex Local Transport Plan (LTP2) an accompanying Accessibility Strategy was published in March 2006. The strategy identified a number
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 As part of the Second East Sussex Local Transport Plan (LTP2) an accompanying Accessibility Strategy was published in March 2006. The strategy identified a number
5 Kapiti Coast: Community, Transport and Travel Behaviour
 5 Kapiti Coast: Community, Transport and Travel Behaviour 5.1 Population Of all territorial authorities in the region, Kapiti Coast has the highest population. It also has the fourth highest population
5 Kapiti Coast: Community, Transport and Travel Behaviour 5.1 Population Of all territorial authorities in the region, Kapiti Coast has the highest population. It also has the fourth highest population
