Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots
|
|
|
- Janice Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 12, Nos. 5/6/7, Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots Pham Thu Nga*, Nguyen Hai Yen, Dinh Hung Cuong, Nguyen Ngoc Hai and Nguyen Xuan Nghia Institute of Materials Science, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Road, Cau Giay District, Hanoi, Vietnam Fax: *Corresponding author Vu Thi Hong Hanh Faculty of Physics, Thai nguyen University of Education, Luong Ngoc Quyen Street, Thai Nguyen City, Vietnam Le Van Vu Center for Materials Science, University of Natural Science, VNU, Hanoi, 334 Nguyen Trai St, Thanh Xuan Dist. Hanoi, Vienam Laurent Coolen Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 06, CNRS, UMR 7588, Institut de NanoSciences de Paris (INSP), F-75005, Paris, France Copyright 2015 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
2 526 P.T. Nga et al. Abstract: In an effort to search for new compositions and structures of quantum dots with suppressed blinking photoluminescence (random switching between states of high (on) and low (off) emissivity under continuous photo-excitation) and to serve application purposes in biosensors and in optoelectronic devices, we have studied the fabrication of new CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots (QD). In this work, we present new results on the fabrication of the alloy core/shell quantum dots having a shell thickness of about 1.52 nm and a varied shell composition in Se/S ratio. The influence of the growth temperature on the structural properties (crystalline phase and cell), size and elemental compositions of the core and core/shell QDs is presented. Analysis and in-depth comparison of the calculated ternary QDs composition are performed based on the energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) data and the first exciton absorption peak position and size. Interpretation of the experimental results is also provided. Keywords: ternary quantum dots; structural properties; CdZnSe/ZnSeS; crystalline phase; alloy composition; size. Reference to this paper should be made as follows: Nga, P.T., Yen, N.H., Cuong, D.H., Hai, N.N., Nghia, N.X., Hanh, V.T.H., Vu, L.V. and Coolen, L. (2015) Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots, Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 12, Nos. 5/6/7, pp Biographical notes: Pham Thu Nga is an Associate Professor, PhD in the Physics at the Institute of Materials Science, of Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST). Her research interests include colloidal semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) from synthesis, optical spectroscopy to device fabrication, aimed for different applications fields such as biosensor, quantum dot-light emitting diode (QD-LED) and quantum dots-sensitised solar cell (QDSSC). She is also interested in the interaction of light in nano-sized solids and opal photonic crystals. Nguyen Hai Yen obtained her Master s degree in Physics in Currently, she is a PhD student at Institute of Materials Science-VAST. Her research focuses on the structural and optical properties of the alloy quantum dots. Dinh Hung Cuong was a Bachelor of Engineering Physics at University of Engineering and Technology, Vietnam National University, Hanoi (VNUH). From 2008 to 2013, he was a Master and PhD student at Graduate School, Division of Energy System Research at Ajou University, Korea. His interests are synthesis and characterisation of electrode materials, quantum dots and photonic crystals, electrochemistry, nanoparticle morphology and orientation crystal. Nguyen Ngoc Hai graduated from the Faculty of Physics of Thai Nguyen University of Education, in He obtained his Master s degree in Physics of Solid States (2008) at Hanoi National University of Education. He is PhD student at Institute of Materials Science, VAST. Currently, he is focusing on the fabrication and the optical properties of the II-VI group quantum dots and the application in biosensors for the detection of pesticide residues. Nguyen Xuan Nghia obtained his PhD in Solids Physics in His research focuses on the field of nanomaterials including the synthesis of differently shaped nanocrystals, their optical and vibrational properties, and the application of nanostructures in optoelectronics.
3 Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots 527 Vu Thi Hong Hanh obtained her PhD in Solids Physics in 2012 at the Institute of Physics at Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology. Her research focuses on the optical properties of quantum dots and the effect of the shells thickness on spectroscopic properties of semiconductor nanocrystals. Le Van Vu is an Associate Professor, PhD and lecturer at the Department of Physics and the Centre of Materials Science, University of Natural Science, VNUH, Hanoi, Vietnam. He research focuses on the structural properties of nano materials. Laurent Coolen acquired a PhD in Solids Physics at the Université Denis Diderot, Paris 7 (Laboratoire Kastler-Brossel) in 2006 on nanocrystal photophysics (advisor: J.-P. Hermier). He worked as a post-doctoral researcher at Stanford University in W.E. Moerner s group in He has been since 2007 a Lecturer at the Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6 and studies nanophotonics at the Institute de NanoSciences de Paris. This paper is a revised and expanded version of a paper entitled Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots presented at 4th International Workshop on Nanotechnology and Application, Vung Tau, Vietnam, November, Introduction Nanocrystal quantum dots (QDs) have great potential as a unique optical material in a broad range of applications that rely on downshifting light, especially those which rely on achieving spectral purity at high optical flux [1]. High particle uniformity, high photoluminescence quantum yields, narrow and symmetric emission spectral line shapes and minimal single-dot emission intermittency (known as blinking) have been recognised as universal requirements for the successful use of colloidal quantum dots in nearly all optical applications. However, synthesising samples that simultaneously meet all these four criteria has proven challenging [1]. The colloidal core/shell ternary QD nanocrystals of CdZnSe were reported as non-blinking semiconductor nanocrystals [2]. Thus, the synthesis of continuously emitting single nanocrystals would have profound influences on the usage of nanocrystals in applications for biology, quantum optics and optoelectronics [2]. On the other hand, research on band gap engineering via control of nanocrystal composition, which is achieved by adjusting the constituent stoichiometry of alloyed semiconductors, is still in its infancy [3]. For alloy nanocrystal quantum dots, their optical properties depend on both parameters: their size and composition. There have been some reports on alloy QDs like Zn x Cd 1 x Se [4 7]. To better confine the electron-hole pairs in CdZnSe QD core, the shielding with an extra layer of a wider band gap semiconducting material, such as ZnS, ZnSeS, and CdZnS is necessary in order to ensure carrier confinement to the core regions. Wang et al. [2] described non-blinking core/shell CdZnSe/ZnSe QDs that have an alloy composition core. By using the hightemperature reaction route, at temperatures slightly lower than that used for the core growth, the shell layer is formed. In an effort to study the monitoring of CdZnSe alloy QDs optical properties and their photoluminescence blinking when shielded with an extra shell, which has changes in band-gap different from a ZnSe binary composition layer, we have studied the fabrication of ZnSeS ternary composition shell. In this work,
4 528 P.T. Nga et al. we have used our familiar synthesis method [8,9] to prepare the CdZnSe/ZnSeS QDs whose structural characterisation and properties will be presented in this paper. In order to create CdZnSe alloy QDs, Zhong et al. [6] presented in the process of forming a CdSe seed, then forming alloys, following the mechanisms of embryonic nuclei-induced alloying process. In our fabrication process, the ZnSe seeds were pre-prepared then formed alloys with Cd 2+ ions at intermediate temperatures, following the mechanisms of embryonic nuclei-induced alloying process to obtain CdZnSe alloy QDs. The synthesis method of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy QDs along with some new results on the effects of the growing temperature to structural properties (crystalline phase, shape), size and composition of the CdZnSe ternary QDs are presented in this paper. For different synthesis temperatures, we discuss the obtained QD size and alloy composition, as well as their photo physical properties. We demonstrate perfect shape and size distribution of the CdZnSe/ZnSeS QDs and discuss their structural properties. 2 Experimental 2.1 Materials Cadmium acetate (Cd (Ac) 2, 99.9%), zinc acetate (Zn (Ac) 2, 99.9%), selenium powder (Se, 99.99%), hexamethyl disilthiane (TMS) 2 S, trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO, 99%), trioctylphosphine (TOP, 90%) and hexadecylamine (HDA, 99%) and organic solvents (chloroform, toluene, methanol, hexane, etc.) were purchased from Aldrich. The chemicals were used as received unless otherwise specified. 2.2 Synthesis of CdZnSe ternary core quantum dots For a typical synthesis of 0.5 mm of CdZnSe ternary nanocrystal QDs, the molar ratio of the precursors for the reaction is: Cd/Zn/Se = 0.2/0.8/3.33; TOPO/HAD = 55/45. The core fabrication process is performed through two steps. For the synthesis of CdZnSe QDs samples, g of TOPO and g of HDA are poured into a three-neck reaction flask. Nitrogen gas was used to remove water vapour and oxygen from the reaction flask at room temperature for 30 min, then at 120 C for one hour. The TOP-Se precursor is injected into the flask under vigorous stirring and heating at temperatures up to 100 C in N 2 atmosphere. After heating the reactor up to 190 C under continuous stirring, the zinc precursor solution is injected into the reaction flask. Then the temperature of the flask is increased up to 280 C, at which temperature the cadmium stock solution is injected into the reactor. As the temperature of the liquid in the reaction flask drops to ~260 C, the nucleation of CdZnSe alloy quantum dot nanocrystals starts quickly. After growing CdZnSe alloy quantum dots for 20 min at different temperatures from 260 C to 310 C, we then obtain CdZnSe ternary QDs core with the x value of Zn varied from 0.5 to 0.7. The growing time of 28 min gives the same result as for 20 min. 2.3 Method of growing ZnSeS shell on CdZnSe core The molar ratio of the precursors for growing the ZnSeS shell is: Zn/(Se + S) = 1.37/1. The shells are grown following a modified version of the successive ion layer adsorption
5 Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots 529 and reaction (SILAR) procedure originally described by Jack Li et al. [10]. For the ZnSeS shell growth, TOP-Se is mixed with (TMS) 2 S (Se/S molar ratio = x/(1 x); x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and 0.8). The zinc stock solution drop-by-drop is injected very slowly (a drop ~50 µl) at a rate of 1 2 drops/second, under vigorous stirring, then the mixture of (TMS) 2 S and TOP-Se is added to the alloy QD core solution. After the end of each turn of Zn precursors and (TOP-Se & S 2 ) mixture s injection, the reaction temperature is kept at 240 C and stirred strongly under N 2 atmosphere for 15 min so that ions can have enough time to stick to the outer layer of the CdZnSe core, thus forming single-layers and giving the best reaction productivity. Several 15-min delays between injection steps are necessary to produce multi-shell QDs. The time for ternary ZnSe x S 1 x shell growth is 15 min. At the end of this step we obtain the CdZnSe/ZnSeS QDs and the expected shell thickness is approximately 1.52 nm. In this experiment, the amount of chemicals for the shell calculated for the estimated cores size is approximately 5 nm. After 15 min after the core/shell ternary quantum dots formed, the heater is removed and the reaction mixture is cooled down to stop the reaction. When the temperature of the reaction mixture cools to below 70 C, the ternary QDs are dispersed in organic solvent (such as chloroform and toluene etc.). A little amount of the sample is extracted after the growth of each shell for optical measurements. 2.4 Methods of characterisation of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary quantum dots Each sample was purified three times to remove excess organic coordinating compounds before powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) measurements. Methanol is used to precipitate the QDs, which are isolated by centrifugation and decantation. The powder X-ray diffraction (Siemens, D5005) is used to identify the wurtzite (w) or zinc-blende (zb) crystal structure with characteristic peaks of the QD samples. The XRD patterns were compared with the tabulated values of bulk CdSe (JCPDS card No (zb) and (w)), ZnSe (JCPDS (zb) and (w)) and ZnS (JCPDS (zb) and (w)). The elemental analysis is carried out using a Nova NanoSEM 450 scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The EDS method has been used to analyse the composition of the elements Cd, Zn, Se and S present in the ternary QD samples. The size of the core QDs and the shell thickness are determined by the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) method, using a JEOL Jem 1010 microscope operating at 100 kv. The absorption characteristics of the QDs were measured by UV-visible absorption spectroscopy (Shimadzu, UV-1800). For optical characterisation of the sample, all the QD samples were diluted with toluene. 3 Result and discussion For the CdZnSe QD cores, during the synthesis process, we noticed that the growth temperature of the nanocrystals is the most important factor, affecting the composition and size of the CdZnSe ternary quantum dots. For the synthesis of different samples, in this fabrication method, all parameters but the nanocrystals growth temperature are kept constant.
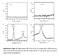
6 530 P.T. Nga et al. 3.1 XRD studies The crystalline phase of the ternary QDs were investigated using powder XRD method. The CdSe as well as ZnSe normally show duality in their crystalline structure, proving that they can be formed with either sphalerite (cubic, zinc blende type) or wurtzite (hexagonal type) structure. The XRD patterns indicate the CdZnSe ternary QDs samples obtained at low temperature (260 C 280 C) possess a cubic structure (zinc-blend (zb)) (curves 4, 6, 7 and 7a in Figure 1). The peak positions are in between those of bulk zb CdSe (JCPDS data) and zb ZnSe (JCPDS data). As a result, these CdZnSe cores show a zinc-blende crystal structure, and the diffraction peaks shifted toward the higher-angle side compared with the pattern of pure zb CdSe. Reflections with the highest intensity observed from CdZnSe QDs originated from (111) and (220) planes. The addition of Zn to CdSe has shown to shift (111) and (220) planes to lower d value (i.e., higher θ values) as reported on the CdZnSe thin films [11]. Peaks corresponding to hexagonal modification of CdSe were observed in small quantities for the obtained sample at 280 C as observable in Figure 1 (curves 7, 7a). For the ternary QD cores fabricated in higher temperatures from 285 C to 310 C, (curves 11, B, 13, C, D and E in Figure 1), we find experimental XRD peaks between the tabulated peaks corresponding to the wurtzite phases of CdSe and ZnSe, which would be in agreement with a wurtzite CdZnSe alloy (although, given the width of the experimental spectra, we cannot exclude a polytype of zinc-blende and wurtzite phases). The wurtzite structure would be consistent with the structure reported in Zhong et al. [12] with a ZnSe-seeded growth process. In ternary QDs samples, the two components CdSe and ZnSe differ only in the cations. As the group II cations diffuse much more easily than the group VI anions in II-VI semiconductors, the Cd 2+ and Zn 2+ can be intermixed to form an alloy. As the Zn 2+ content increased, the diffraction peaks shifted toward the higher-angle side compared to the pattern of pure CdSe. Broad XRD peaks are attributed to the small particle size. The growth time of the QD nanocrystals changes from 20 min to 28 min without changing the properties of the crystallisation phase of the ternary QDs. The ternary CdZnSe all crystallise at the zb-alloy CdZnSe phase (curves 7 and 7a- Figure 1). Therefore, we chose the QDs growing time to be 20 min. When growing the ternary ZnSeS shell on the zb CdZnSe cores, at the temperature of 240 C, we can observe that CdZnSe cores show a zinc blende crystalline structure. With the shell the diffraction peaks shifted toward the higher-angle side compared to the pattern of zb CdZnSe core. The peak positions are in between those of bulk zb ZnS (JCPDS 5-566) and zb ZnSe (JCPDS ) (Figure 2). The peak positions for the core/shell QDs are shifted to higher angles as compared to the core sample because of the ZnSeS shell contribution with smaller lattice constant. Although the samples E1 E4 are synthesised with different Se/S precursor ratios, the XRD patterns look similar, suggesting that Se and S concentrations in the shell did not have clear influence to the structure of the shell. 3.2 EDS measurement Elemental composition analysis by the EDS method enables us to establish a detailed formula of the CdZnSe ternary QD samples and the core/shell structure presented above. On the other hand, in order to determine the accuracy of the ternary QD composition by
7 Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots 531 EDS analysis, we have carried out extra calculations based on the TEM images taken from the samples, and the experimental data Eg of alloy QDs obtained from the absorption spectra. Composition of the CdZnSe cores calculated from EDS data is normalised to Cd+Zn = 1 and rounded up/down to ~0.1. Figure 1 Powder XRD patterns of CdZnSe ternary QD cores with the same reaction time of 20 min but different growing temperature, from 260 C (6) to 310 C (D). Bulk diffraction peaks for zinc blende (zb) ZnSe (top blue sticks) and wurtzite (w) ZnSe (top black sticks) and zb CdSe (bottom red sticks) and w CdSe (bottom blue sticks) are indexed for identification purpose (see online version for colours) Figure 2 Powder XRD patterns of CdZnSe ternary QD cores (sample E) and CdZnSe/ZnSeS core/shell (samples E1, E2, E3 and E4). The sticks patterns show the standard peak position of bulk wurtzite ZnS (top black sticks) and zb ZnS (top blue sticks), zb ZnSe (middle red sticks) and zb CdSe (bottom red sticks) are shown (see online version for colours)
8 532 P.T. Nga et al. The Cd/Zn ratios of the CdZnSe (samples B, C, D and E) are established (Table 1). In pursuit of determining the composition of the shell, with the ternary core/shell QDs, we suppose that the ratios of Cd/Zn and Cd/Se of the core do not change during the shell creation process. From the calculation results of the experimental EDS data, we saw that there is a change in the Se amount in different samples, from 0.2 to 0.5 (with sample series B) from 0.2 to 0.6 with sample series C, etc. Table 1 Cd/Zn ratios from EDS data of the CdZnSe ternary QD samples Sample Cd/Zn amount B 0.3/0.7 C 0.4/0.6 D 0.5/0.5 E 0.3/0.7 We also found that, for the quantum dot samples in powder form, their crystalline phase shows quite clearly that, depending on the fabricating temperature, they either fully crystallise in zb or w crystalline phase with partly crystallise in a zb small amount, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. However, with the same samples, when analysing the elemental composition with the EDS method, we did not get the results on charge balance between atoms with positive valence (like Cd and Zn) and atoms with negative valence (like Se), for CdZnSe core QDs. Calculations showed the same for alloy core/shell QDs. To explain this, we managed to deduce the following reasons: The size of these quantum dots is small (from 4.1 nm to 6.5 nm), making the number of atoms on the surface much larger than that inside the QDs, so the ratio of the atoms with positive charge will be other than 1. This is also observed and reported by the group of Morris-Cohen [13] with CdSe QDs. Since the only experimental analysis method used is EDS, the results on the elemental composition to deduce the formula of ternary QDs that may have little errors. Moreover, the calculated elemental composition with the ternary core/shell QDs may also have small error because of the assumption that during the shell growth process, the composition of the core and the number of atoms on their surface are not changed. However, since the process of shell crystal growth takes place in the solution, we cannot be sure about this. Thus, the ternary QDs formula obtained is actually not balanced in electronic charge. 3.3 TEM images The images from TEM measurement has also been used to clarify the shape, size and uniformity in size of the QDs, as a function of the core crystal growth temperature and the stages of the shell crystal growth with different composition. Figure 3 shows the TEM images of four ternary QD samples grown at temperatures 285 C (B), 290 C (E), 300 C (C) and 310 C (D). From these TEM images, we can see that the QDs of the sample grown at 285 C have a wide range of size distribution. On the other hand, between 290 C and 310 C, the QDs
9 Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots 533 are grown with size uniformity. The average particle diameter of the samples changes accordingly: 5, 5.3, 6.5 and 6.57 nm (the error is approximately ±0.5 1 nm). Figure 3 TEM images of 5 nm (sample B), 6.5 nm (E), 5.3 nm (C) and 6.5 nm (D) CdZnSe core QDs. Scale bars: 20 nm However, while growing the QD samples at 310 C, the organic molecules such as TOPO and HDA in the flask evaporate strongly during the QD growing process. Also, the samples created at this temperature have lower emission intensity than the other samples. Therefore, we choose the temperature condition of 285 C-300 C to synthesise the QD samples. Here, we can also see that when ZnxCd1-xSe QDs are prepared from ZnSe nuclei or ZnSe QD seeds as used in this study, a red-shift in the emission maximum was observed during the alloying stage as a result of the decrease in band gap energy as Cd2+ is progressively incorporated into the ZnSe lattice [6,7]. Alloy formation occurred at temperatures lower than the alloying point for the CdSe-seeded growth, implying that cation exchange reaction between ZnSe nanocrystals and Cd2+ is more favoured than that between CdSe and Zn2+. This is attributed to the much lower bond dissociation energy of Zn-Se (136 kj mol 1) relative to Cd-Se (310 kj mol 1) as reported in Regulacio and Han [3]. From the results on analysing crystalline phase with XRD and all of the analyses above, it can be assumed that the chosen QD synthesis temperature of 2900C or 300 C is suitable. The TEM images of CdZnSe core/shell QDs samples are presented in Figure 4. The ZnSeS shell with a different ratio of Se/S in the precursor was brought into reaction. The Se quantity varied from 2.0 to 0.8 in moles. The pre-calculated precursor amount for
10 534 P.T. Nga et al. the same shell thickness is ~1.52 nm (1 ML is equivalent to 0.38 nm, the a lattice constant of ZnS). We found that, when more layers of ZnSeS shell are grown, the size of the QDs increases a bit, and the average diameter is ~7 nm. Figure 4 TEM images of CdZnSe QDs and CdZnSe/ZnSexS1-x core/shell QDs with the average size of 5.3 nm (C), 5 nm (B) to 6.5 nm (E) for the cores and 6.3 nm (bottom left-b), 5.3 nm (bottom middle-e) and 7 nm (bottom right-c) for the core/shell QDs. Scale bars: 20 nm However, for sample series E, TEM images show that the fabrication of the ZnSeS shell altered the shape of the QDs, from quasi-spherical shape of the core, to an elongated shape, and sometimes include both spherical particles and cubes. Owing to the
11 Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots 535 non-uniformity in shape and size of the QDs, on the absorption spectra of these samples, the first exciton peak of the QDs is not observed (Figure 5, bottom). In contrast, with the sample series B and C, owing to the shape and size uniformity, the first exciton peak is clearly observed in the absorption spectra (Figure 5, top). Figure 5 Absorption spectra of CdZnSe cores and CdZnSe cores capped with the ZnSeS shell, from top to bottom for the cores diameter: sample C (5.3 nm) and E (6.57 nm) and with the same thickness shell of ZnSeS but different Se amount (see online version for colours) From a detailed study of the experimental results obtained, as stated above, we can draw some remarks as follows: The CdZnSe ternary QDs can be obtained at different temperatures, starting from 260 C to 310 C, following the synthesis method as presented in this paper. However, the suitable temperature is 285 C 300 C, allowing the obtainment of the CdZnSe QDs with the most uniform spherical shape, diameter ~5 nm, phase crystalline w CdZnSe.
12 536 P.T. Nga et al. XRD pattern and element composition of the same CdZnSe sample are not fully adequate. This was observed for all samples that we studied. This is a significant surprise for us: with the same CdZnSe QDs powder sample, we identify their crystalline phase through the characteristic diffraction lines and experimental d values obtained from XRD pattern, but the EDS analysis showed that the Cd/Zn ratio or total (Cd+Zn)/Se ratio in CdZnSe is smaller than 1, which means the electronic charge of these nanocrystals composition is not equilibrated. An unexpected consequence of this fact is that the underlying lattice structure change from wurtzite (of ZnSe lattice formed at first moment of the synthesis process) in the ternary centre region to zinc blende in the ternary surface region (formed over the time and at growth temperature). One can account for this lattice structure evolution by noting that the ZnSe nanocrystal at room temperature is zinc blende. Further explanations for this is the small size (~5 nm) of the QDs, making the number of atoms (Cd 2+ and Zn 2+ ) located on the surface much greater than the number of atoms inside the QD and because the group II cations diffuse much more easily than the group VI anions in II-VI semiconductors. The composition analysis of ZnSeS shell gives similar results. It can be observed that raising the growth temperature of CdZnSe QDs is the most important factor, which allows the creation of uniform spherical QDs. At higher temperatures, for example from 300 C 310 C, alloy QD samples have the Cd/Zn composition ratio of 0.4/0.6 and 0.5/0.5. This means that the higher the temperature becomes, the more easily the Cd 2+ ions diffuse into the ZnSe crystal lattice, according to the fabrication method presented in this paper. Simultaneous research of the absorption spectra and TEM images of CdZnSe and CdZnSe/ZnSeS samples of the same series clearly showed that the shape of the absorption spectra depends on the shape and size of the QDs. Photoluminescence and blinking properties of the CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary QDs will be presented in detail in a forthcoming paper. 4 Conclusions Some new results on the creation of ternary core/shell QDs are presented in this work. We were able to fabricate such QDs with high accuracy and reproducible. The study on the fabrication of a series of CdZnSe/ZnSeS QD samples at different growth temperatures, while still retaining most other fabricating conditions, has allowed the determination of the suitable temperature to produce spherical CdZnSe QDs, with high uniformity in size and shape, as 290 C 300 C. The experimental results allow us to confirm the alloy nature of CdZnSe QDs fabricated at 300 C for 20 min, whose Cd/Zn ratio = 0.4/0.6, with an average diameter of ~5 nm. The shielding of ZnSeS with a ~1.5 nm thick shell has increased the average size of the core/shell QDs to approximately 7 nm. The CdZnSe ternary QDs fabricated using this method are Zn-rich QDs. Explanations have been proposed to clarify the collected data. This may be one of the first detailed studies on the relationship between crystalline phase, elemental composition and size shape of the CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary core/shell QDs. The CdZnSe/ZnSeS QDs can be applied for biological purposes and optoelectronic devices.
13 Study on the fabrication of CdZnSe/ZnSeS ternary alloy quantum dots 537 Acknowledgements This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number , by the PICS project No and the support for young researcher from IMS-VAST. The authors thank the National Key Laboratory for Electronic Materials and Devices-IMS for the use of facilities. We sincerely thank Prof. Nguyen Quang Liem for his precious discussions. References 1 Chen, O., Zhao, J., Chauhan, V.P., Cui, J., Wong, C., Harris, D.K., Wei, H., Han, H., Fukumura, D., Jain, R.K. and Bawendi, M.G. (2013) Compact high-quality CdSe CdS core shell nanocrystals with narrow emission linewidths and suppressed blinking, Nat. Mater., Vol. 12, pp Wang, X., Ren, X., Kahen, K., Hahn, M.A., Rajeswaran, M., Zacher, S.M., Silcox, J., Cragg, G.E., Efros, A.L. and Krauss, T.D. (2009) Non-blinking semiconductor nanocrystals, Nature, Vol. 459, pp Regulacio, M.D. and Han, M.Y. (2010) Composition-Tunable Alloyed Semiconductor Nanocrystals, Acc. Chem. Res., Vol. 43, No. 5, pp Kim, J.U., Lee, J.J., Jang, H.S., Jeon, D.Y. and Yang, H.S. (2011) Widely tunable emissions of colloidal Zn x Cd 1-x Se alloy quantum dots using a constant Zn/Cd precursor ratio, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., Vol. 1, pp Zheng, Y.G., Yang, Z.C. and Ying, J.Y. (2007) Aqueous synthesis of glutathione-capped ZnSe and Zn 1-x Cd x Se alloyed quantum dots, Adv. Mater., Vol. 19, pp Zhong, X.H., Zhang, Z.H., Liu, S.H., Han, M.Y. and Knoll, W. (2004) Embryonic nuclei induced alloying process for the reproducible synthesis of blue-emitting Zn x Cd 1-x Se nanocrystals with long-time thermal stability in size distribution and emission wavelength, J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 108, pp Sung, Y.M., Lee, Y.J. and Park, K.S. (2006) Kinetic analysis for formation of Cd 1-x Zn x Se solid-solution nanocrystals, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Vol. 128, pp Nga, P.T., Chinh, V.D., Hanh, V.T.H., Nghia, N.X. and Dzung, P.T. (2011) Optical properties of normal and giant multishell CdSe quantum dots for potential application in material science, Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 8, Nos. 3 5, pp Isnaeni, Kim, K.H., Nguyen, D.L., Lim, H., Nga, P.T. and Cho, Y.H. (2011) Shell layer dependence of photoblinking in CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots, Appl. Phys. Lett., Vol. 98, pp Jack Li, J., Wang, Y.A., Guo, W., Keay, J.C., Mishima, T.D., Johnson, M.B. and Peng, X. (2003) Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Vol. 125, pp Hankare, P.P., Chate, P.A., Asabe, M.R., Delekar, S.D., Mulla, I.S. and Garadkar, K.M. (2006) Characterization of Cd 1 x Zn x Se thin films deposited at low temperature by chemical route, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., Vol. 17, pp Zhong, X.H., Feng, Y.Y., Zhang, Y.L., Gu, Z.Y. and Zou, L. (2007) Nanotechnol., Vol. 18, pp Morris-Cohen, A.J., Donakowski, M.D., Knowles, K.E. and Weiss, E.A. (2010) The effect of a common purification procedure on the chemical composition of the surfaces of CdSe quantum dots synthesized with trioctylphosphine oxide, J. Phys. Chem. C, Vol. 114, pp
Studies on Structural and Optical Properties of Iron doped Cds Nanoparticles ABSTRACT
 Studies on Structural and Optical Properties of Iron doped Cds Nanoparticles Atheek P., Vidhya M. and Balasundaram O. N Department of Physics, PSG College of Arts & Science, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Studies on Structural and Optical Properties of Iron doped Cds Nanoparticles Atheek P., Vidhya M. and Balasundaram O. N Department of Physics, PSG College of Arts & Science, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
CHAPTER 4. SYNTHESIS OF ALUMINIUM SELENIDE (Al 2 Se 3 ) NANO PARTICLES, DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERIZATION
 40 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS OF ALUMINIUM SELENIDE (Al 2 Se 3 ) NANO PARTICLES, DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERIZATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION Aluminium selenide is the chemical compound Al 2 Se 3 and has been used as a precursor
40 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS OF ALUMINIUM SELENIDE (Al 2 Se 3 ) NANO PARTICLES, DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERIZATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION Aluminium selenide is the chemical compound Al 2 Se 3 and has been used as a precursor
Colloidal Synthesis of Homogeneously Alloyed CdSe x S 1-x Nanorods with Compositionally Tunable Photoluminescence
 Colloidal Synthesis of Homogeneously Alloyed CdSe x S 1-x Nanorods with Compositionally Tunable Photoluminescence Shalini Singh, Ajay Singh, Kumaranand Palaniappan,Kevin M. Ryan * Materials and Surface
Colloidal Synthesis of Homogeneously Alloyed CdSe x S 1-x Nanorods with Compositionally Tunable Photoluminescence Shalini Singh, Ajay Singh, Kumaranand Palaniappan,Kevin M. Ryan * Materials and Surface
Tunable band structure in coreshell quantum dots through alloying of the core
 Tunable band structure in coreshell quantum dots through alloying of the core A. Guille ǀ D. Mourad ǀ T. Aubert ǀ A. Houtepen ǀ R. Van Deun ǀ E. Brainis ǀ Z. Hens 1. Introduction Semiconductor nanocrystals
Tunable band structure in coreshell quantum dots through alloying of the core A. Guille ǀ D. Mourad ǀ T. Aubert ǀ A. Houtepen ǀ R. Van Deun ǀ E. Brainis ǀ Z. Hens 1. Introduction Semiconductor nanocrystals
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Radial-Position-Controlled Doping in CdS/ZnS Core/Shell Nanocrystals Yongan Yang, Ou Chen, Alexander Angerhofer and Y. Charles Cao* Department of Chemistry, University of Florida,
Supporting Information: Radial-Position-Controlled Doping in CdS/ZnS Core/Shell Nanocrystals Yongan Yang, Ou Chen, Alexander Angerhofer and Y. Charles Cao* Department of Chemistry, University of Florida,
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 11, November 2009, p
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 11, November 2009, p. 617 622 TUNABILITY OF STRUCTURAL, SURFACE TEXTURE, COMPOSITIONAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF CdZnS THIN FILMS BY PHOTO ASSISTED- CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 11, November 2009, p. 617 622 TUNABILITY OF STRUCTURAL, SURFACE TEXTURE, COMPOSITIONAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF CdZnS THIN FILMS BY PHOTO ASSISTED- CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION
Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles
 Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles R.Hepzi Pramila Devamani 1*, R.Kiruthika, P.Mahadevi and S.Sagithapriya 2 1 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, V.V.Vanniaperumal
Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles R.Hepzi Pramila Devamani 1*, R.Kiruthika, P.Mahadevi and S.Sagithapriya 2 1 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, V.V.Vanniaperumal
Crystal Phase-Controlled Synthesis of Cu 2 FeSnS 4 Nanocrystals with Band Gap around 1.5 ev
 Crystal Phase-Controlled Synthesis of Cu 2 FeSnS 4 Nanocrystals with Band Gap around 1.5 ev Xiaoyan Zhang, a,b Ningzhong Bao,* c Karthik Ramasamy, a Yu-Hsiang A. Wang, a Yifeng Wang, c Baoping Lin b and
Crystal Phase-Controlled Synthesis of Cu 2 FeSnS 4 Nanocrystals with Band Gap around 1.5 ev Xiaoyan Zhang, a,b Ningzhong Bao,* c Karthik Ramasamy, a Yu-Hsiang A. Wang, a Yifeng Wang, c Baoping Lin b and
Ibn Al-Haitham Jour. for Pure & Appl. Sci Vol. 32 (1) 2019
 Novel Co-Precipitation Method for Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide in Accordance to PH: Structural and Optical Properties as an Active Optical Filter Zehraa N. Abdul-Ameer Lecturer Remote Sensing
Novel Co-Precipitation Method for Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide in Accordance to PH: Structural and Optical Properties as an Active Optical Filter Zehraa N. Abdul-Ameer Lecturer Remote Sensing
Efficient CdSe Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells Prepared by Postsynthesis Assembly Approach
 Electronic Supplementary Information Efficient CdSe Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells Prepared by Postsynthesis Assembly Approach H. Zhang, K. Cheng, Y. M. Hou, Z. Fang, Z. X. Pan, W. J. Wu, J. L. Hua
Electronic Supplementary Information Efficient CdSe Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells Prepared by Postsynthesis Assembly Approach H. Zhang, K. Cheng, Y. M. Hou, Z. Fang, Z. X. Pan, W. J. Wu, J. L. Hua
Spectra Chacracterizations of Optical Nanoparticles
 THAI NGUYEN UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION Spectra Chacracterizations of Optical Nanoparticles Chu Viet Ha Department of Physics 18/2018 1 THAI NGUYEN UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION Address 20 Luong Ngoc Quyen Street,
THAI NGUYEN UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION Spectra Chacracterizations of Optical Nanoparticles Chu Viet Ha Department of Physics 18/2018 1 THAI NGUYEN UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION Address 20 Luong Ngoc Quyen Street,
STRUCTURAL AND OPTOELECTRONIC PROPERTIES OF PYRALYTICALLY SPRAYED CdZnS THIN FILMS
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 9, No. 12, December 2012, p. 495-500 STRUCTURAL AND OPTOELECTRONIC PROPERTIES OF PYRALYTICALLY SPRAYED CdZnS THIN FILMS S. RAJATHI *, N. SANKARASUBRAMANIAN *, K. RAMANATHAN, M.
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 9, No. 12, December 2012, p. 495-500 STRUCTURAL AND OPTOELECTRONIC PROPERTIES OF PYRALYTICALLY SPRAYED CdZnS THIN FILMS S. RAJATHI *, N. SANKARASUBRAMANIAN *, K. RAMANATHAN, M.
Supporting Information for Particle-size Dependent Förster Resonance Energy Transfer from Upconversion Nanoparticles to Organic Dyes
 Supporting Information for Particle-size Dependent Förster Resonance Energy Transfer from Upconversion Nanoparticles to Organic Dyes Verena Muhr a, Christian Würth b, Marco Kraft b, Markus Buchner a, Antje
Supporting Information for Particle-size Dependent Förster Resonance Energy Transfer from Upconversion Nanoparticles to Organic Dyes Verena Muhr a, Christian Würth b, Marco Kraft b, Markus Buchner a, Antje
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Materials. GdCl 3 xh 2 O, (99.99%), YCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), YbCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), ErCl 3 6H 2 O (99.9%), NaOH (98+%), NH 4 F (98+%), 1 octadecene (90%), and oleic acid (90%) were all purchased from Sigma
Materials. GdCl 3 xh 2 O, (99.99%), YCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), YbCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), ErCl 3 6H 2 O (99.9%), NaOH (98+%), NH 4 F (98+%), 1 octadecene (90%), and oleic acid (90%) were all purchased from Sigma
for New Energy Materials and Devices; Beijing National Laboratory for Condense Matter Physics,
 Electronic Supplementary Information Highly efficient core shell CuInS 2 /Mn doped CdS quantum dots sensitized solar cells Jianheng Luo, a Huiyun Wei, a Qingli Huang, a Xing Hu, a Haofei Zhao, b Richeng
Electronic Supplementary Information Highly efficient core shell CuInS 2 /Mn doped CdS quantum dots sensitized solar cells Jianheng Luo, a Huiyun Wei, a Qingli Huang, a Xing Hu, a Haofei Zhao, b Richeng
SYNTHESIS, SPECTRAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CYANINE DYE CY3 BONDING CDTE/CDS CORE/SHELL STRUCTURE QUANTUM DOTS
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 8, No. 12, December 211, p. 725-73 SYNTHESIS, SPECTRAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CYANINE DYE CY3 BONDING CDTE/CDS CORE/SHELL STRUCTURE QUANTUM DOTS YIN LIU a, XUENING FEI a, b*, JUN
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 8, No. 12, December 211, p. 725-73 SYNTHESIS, SPECTRAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CYANINE DYE CY3 BONDING CDTE/CDS CORE/SHELL STRUCTURE QUANTUM DOTS YIN LIU a, XUENING FEI a, b*, JUN
Deposited by Sputtering of Sn and SnO 2
 Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 448~453, 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.4191/kcers.2012.49.5.448 Comparative Study of Nitrogen Incorporated SnO 2 Deposited by Sputtering of Sn and
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 448~453, 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.4191/kcers.2012.49.5.448 Comparative Study of Nitrogen Incorporated SnO 2 Deposited by Sputtering of Sn and
Supplementary Figure 1 TEM of external salt byproducts. TEM image of some salt byproducts precipitated out separately from the Si network, with
 Supplementary Figure 1 TEM of external salt byproducts. TEM image of some salt byproducts precipitated out separately from the Si network, with non-uniform particle size distribution. The scale bar is
Supplementary Figure 1 TEM of external salt byproducts. TEM image of some salt byproducts precipitated out separately from the Si network, with non-uniform particle size distribution. The scale bar is
Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide (CdS) Quantum Dots (QDS) for Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cell Applications
 Nano Vision, Vol. 5(7-9), 237-241, July-September 2015 (An International Research Journal of Nano Science & Technology), www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Synthesis and
Nano Vision, Vol. 5(7-9), 237-241, July-September 2015 (An International Research Journal of Nano Science & Technology), www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Synthesis and
The Effect of Annealing Heat Treatment on Structural and Optical Properties of Ce-doped ZnO Thin Films
 4th International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering (ICCMCEE 2015) The Effect of Annealing Heat Treatment on Structural and Optical Properties of Ce-doped Thin Films
4th International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering (ICCMCEE 2015) The Effect of Annealing Heat Treatment on Structural and Optical Properties of Ce-doped Thin Films
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Type-II Core/Crown CdSe/CdTe Semiconductor Nanoplatelets Silvia Pedetti 1,2, Sandrine Ithurria 2, Hadrien Heuclin 1, Gilles Patriarche 3, Benoit Dubertret 2 1 Nexdot, 10 rue Vauquelin
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Type-II Core/Crown CdSe/CdTe Semiconductor Nanoplatelets Silvia Pedetti 1,2, Sandrine Ithurria 2, Hadrien Heuclin 1, Gilles Patriarche 3, Benoit Dubertret 2 1 Nexdot, 10 rue Vauquelin
Supplementary Figure S1. High-resolution XPS spectra in the Cu 2p region and Cu LMM spectra are shown in (A) and (B) respectively for CdSe NCs
 Supplementary Figure S1. High-resolution XPS spectra in the Cu 2p region and Cu LMM spectra are shown in (A) and (B) respectively for CdSe NCs treated with 651 Cu + ions per NC and in (C) and (D) respectively
Supplementary Figure S1. High-resolution XPS spectra in the Cu 2p region and Cu LMM spectra are shown in (A) and (B) respectively for CdSe NCs treated with 651 Cu + ions per NC and in (C) and (D) respectively
QUANTUM SIZE EFFECT IN CHEMOSYNTHESIZED NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 5, No 4, October-December 2010, p. 805-810 QUANTUM SIZE EFFECT IN CHEMOSYNTHESIZED NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS S. A. VANALAKAR, S. S. MALI, M. P.
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 5, No 4, October-December 2010, p. 805-810 QUANTUM SIZE EFFECT IN CHEMOSYNTHESIZED NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS S. A. VANALAKAR, S. S. MALI, M. P.
Supplementary Figure 1. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) of a wide-field of a) 2 nm, b) 4 nm and c) 6 nm Cu 2 Se nanocrystals (NCs),
 Supplementary Figure 1. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) of a wide-field of a) 2 nm, b) 4 nm and c) 6 nm Cu 2 Se nanocrystals (NCs), respectively. To the right of each spectrum us shown a lowmagnification
Supplementary Figure 1. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) of a wide-field of a) 2 nm, b) 4 nm and c) 6 nm Cu 2 Se nanocrystals (NCs), respectively. To the right of each spectrum us shown a lowmagnification
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Improving the Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Activities of Mesoporous Single Crystal Rutile TiO 2 for Water Splitting Wei Jiao, Ying Peng Xie, Run Ze Chen,
Electronic Supplementary Information Improving the Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Activities of Mesoporous Single Crystal Rutile TiO 2 for Water Splitting Wei Jiao, Ying Peng Xie, Run Ze Chen,
Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Magnetite) Nanocrystals. Tan Wenyou. Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore
 ABSTRACT Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Magnetite) Nanocrystals Tan Wenyou Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge, Singapore 119260 Monodispersed iron
ABSTRACT Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Magnetite) Nanocrystals Tan Wenyou Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge, Singapore 119260 Monodispersed iron
Supporting Information. Photoinduced Anion Exchange in Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Photoinduced Anion Exchange in Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals David Parobek, Yitong Dong, Tian Qiao, Daniel Rossi, Dong Hee Son* Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University,
Supporting Information Photoinduced Anion Exchange in Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals David Parobek, Yitong Dong, Tian Qiao, Daniel Rossi, Dong Hee Son* Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University,
Efficiency Enhancement of Bulk-Heterojunction
 Efficiency Enhancement of Bulk-Heterojunction Hybrid Solar Cells Michael Krüger, Yunfei Zhou, Michael Eck Freiburg Materials Research Centre (FMF), University of Freiburg, Germany Institute for Microsystems
Efficiency Enhancement of Bulk-Heterojunction Hybrid Solar Cells Michael Krüger, Yunfei Zhou, Michael Eck Freiburg Materials Research Centre (FMF), University of Freiburg, Germany Institute for Microsystems
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
Deliverable D1.4: Report on QDs with tunable color and high quantum yield. Summary
 Deliverable D.4: Report on QDs with tunable color and high quantum yield Responsible author: Dr Beata Kardynal, FZJ Summary The synthesis of the InP/ZnS nanocrystals with wavelengtnh in the range of green
Deliverable D.4: Report on QDs with tunable color and high quantum yield Responsible author: Dr Beata Kardynal, FZJ Summary The synthesis of the InP/ZnS nanocrystals with wavelengtnh in the range of green
Supporting Information. Solution-Processed 2D PbS Nanoplates with Residual Cu 2 S. Exhibiting Low Resistivity and High Infrared Responsivity
 Supporting Information Solution-Processed 2D PbS Nanoplates with Residual Cu 2 S Exhibiting Low Resistivity and High Infrared Responsivity Wen-Ya Wu, Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, Asim Guchhait, Gloria Yan
Supporting Information Solution-Processed 2D PbS Nanoplates with Residual Cu 2 S Exhibiting Low Resistivity and High Infrared Responsivity Wen-Ya Wu, Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, Asim Guchhait, Gloria Yan
FLUORESCENCE GAS SENSOR BASED ON CdTe QUANTUM DOTS FOR DETECTION OF VOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS GAS
 FLUORESCENCE GAS SENSOR BASED ON CdTe QUANTUM DOTS FOR DETECTION OF VOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS GAS Norhayati Abu Bakar 1, Aidhia Rahmi 1, Akrajas Ali Umar 1. *, Muhamad Mat Salleh 1 and Muhammad Yahaya
FLUORESCENCE GAS SENSOR BASED ON CdTe QUANTUM DOTS FOR DETECTION OF VOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS GAS Norhayati Abu Bakar 1, Aidhia Rahmi 1, Akrajas Ali Umar 1. *, Muhamad Mat Salleh 1 and Muhammad Yahaya
CHAPTER 6 STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF. CdSe/CdTe MULTILAYER THIN FILMS
 CHAPTER 6 STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF CdSe/CdTe MULTILAYER THIN FILMS CHAPTER 6 STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF CdSe/CdTe MULTILAYER THIN FILMS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Quantum size effects in semiconductors
CHAPTER 6 STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF CdSe/CdTe MULTILAYER THIN FILMS CHAPTER 6 STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF CdSe/CdTe MULTILAYER THIN FILMS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Quantum size effects in semiconductors
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry S 1
 2013 S 1 Thermochemical analysis on the growth of NiAl 2 O 4 rods Sang Sub Kim, a Yong Jung Kwon, b Gunju Sun, a Hyoun Woo Kim,* b and Ping Wu* c a Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Inha
2013 S 1 Thermochemical analysis on the growth of NiAl 2 O 4 rods Sang Sub Kim, a Yong Jung Kwon, b Gunju Sun, a Hyoun Woo Kim,* b and Ping Wu* c a Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Inha
Preparation and characterization of Co BaTiO 3 nano-composite films by the pulsed laser deposition
 Journal of Crystal Growth 289 (26) 48 413 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcrysgro Preparation and characterization of Co BaTiO 3 nano-composite films by the pulsed laser deposition Wu Weidong a,b,, He Yingjie
Journal of Crystal Growth 289 (26) 48 413 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcrysgro Preparation and characterization of Co BaTiO 3 nano-composite films by the pulsed laser deposition Wu Weidong a,b,, He Yingjie
ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF CDS THIN FILMS SPIN COATED ON CONDUCTIVE GLASS SUBSTRATES
 UDC: 538.9 Condensed matter Physics, Solid state Physics, Experimental Condensed matter Physics ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF CDS THIN FILMS SPIN COATED ON CONDUCTIVE GLASS SUBSTRATES P. Samarasekara and P.A.S.
UDC: 538.9 Condensed matter Physics, Solid state Physics, Experimental Condensed matter Physics ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF CDS THIN FILMS SPIN COATED ON CONDUCTIVE GLASS SUBSTRATES P. Samarasekara and P.A.S.
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A Green Route to Fabricate MoS 2 Nanosheets in Water/ethanol/CO 2 Yuhang
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A Green Route to Fabricate MoS 2 Nanosheets in Water/ethanol/CO 2 Yuhang
Well-defined Colloidal 2-D Layered Transition Metal Chalcogenide Nanocrystals via Generalized Synthetic Protocols
 Intensity (a.u.) Supporting Information Well-defined Colloidal 2-D Layered Transition Metal Chalcogenide Nanocrystals via Generalized Synthetic Protocols Sohee Jeong, Dongwon Yoo, Jung-tak Jang, Minkyoung
Intensity (a.u.) Supporting Information Well-defined Colloidal 2-D Layered Transition Metal Chalcogenide Nanocrystals via Generalized Synthetic Protocols Sohee Jeong, Dongwon Yoo, Jung-tak Jang, Minkyoung
A general strategy for metallic nanocrystals synthesis in organic medium
 Supplementary Information for A general strategy for metallic nanocrystals synthesis in organic medium Peng Huang, a Jing Lin, b Zhiming Li, a Hengyao Hu, a Kan Wang, a Guo Gao, a Rong He a and Daxiang
Supplementary Information for A general strategy for metallic nanocrystals synthesis in organic medium Peng Huang, a Jing Lin, b Zhiming Li, a Hengyao Hu, a Kan Wang, a Guo Gao, a Rong He a and Daxiang
Internal structure of nanoparticles of Al generated by laser ablation in liquid ethanol
 Internal structure of nanoparticles of Al generated by laser ablation in liquid ethanol G. Viau, a V. Collière, b G.A. Shafeev c a Université de Toulouse, INSA-LPCNO, CNRS UMR 5215, IRSAMC, 135, av. de
Internal structure of nanoparticles of Al generated by laser ablation in liquid ethanol G. Viau, a V. Collière, b G.A. Shafeev c a Université de Toulouse, INSA-LPCNO, CNRS UMR 5215, IRSAMC, 135, av. de
Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes
 Journal of Optoelectronic and Biomedical Materials Volume 1, Issue 1, March 2009, p. 79-84 Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes N. Taşaltin a, S. Öztürk a, H. Yüzer b, Z. Z. Öztürk a,b* a
Journal of Optoelectronic and Biomedical Materials Volume 1, Issue 1, March 2009, p. 79-84 Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes N. Taşaltin a, S. Öztürk a, H. Yüzer b, Z. Z. Öztürk a,b* a
Yanmei Liu, Min Li, Qingqing Fang, Qingrong Lv, Mingzai Wu, and Shuai Cao
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 48, NO. 4 AUGUST 2010 Structural and Photoluminescence Properties of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-Assisted Growth Co-Doped ZnO Nanorod Arrays Compared with Pure ZnO Nanorod
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 48, NO. 4 AUGUST 2010 Structural and Photoluminescence Properties of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-Assisted Growth Co-Doped ZnO Nanorod Arrays Compared with Pure ZnO Nanorod
Emission-Tunable Near-infrared Ag 2 S Quantum Dots
 Supporting Information for: Emission-Tunable Near-infrared Ag 2 S Quantum Dots Peng Jiang, Zhi-Quan Tian, Chun-Nan Zhu, Zhi-Ling Zhang and Dai-Wen Pang* Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Biology
Supporting Information for: Emission-Tunable Near-infrared Ag 2 S Quantum Dots Peng Jiang, Zhi-Quan Tian, Chun-Nan Zhu, Zhi-Ling Zhang and Dai-Wen Pang* Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Biology
Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanocrystals using a reducing amphiphile. Ferdinand Gonzaga, Sherdeep Singh and Michael A. Brook. Department of Chemistry
 Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanocrystals using a reducing amphiphile. Ferdinand Gonzaga, Sherdeep Singh and Michael A. Brook Department of Chemistry 1280 Main St. W. Hamilton ON L8S 4M1 Canada Outline
Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanocrystals using a reducing amphiphile. Ferdinand Gonzaga, Sherdeep Singh and Michael A. Brook Department of Chemistry 1280 Main St. W. Hamilton ON L8S 4M1 Canada Outline
PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 10, No. 2, April - June 2015, p. 715-719 PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD N. EKTHAMMATHAT
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 10, No. 2, April - June 2015, p. 715-719 PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD N. EKTHAMMATHAT
Growth of Hexagonal Phase Sodium Rare Earth Tetrafluorides Induced by Heterogeneous Cubic Phase Core
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Growth of Hexagonal Phase Sodium Rare Earth Tetrafluorides
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Growth of Hexagonal Phase Sodium Rare Earth Tetrafluorides
Linlin Xin a and Xuefeng Liu b. School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, , PR China.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Black TiO 2 Inverse Opals for Visible-Light Photocatalysis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Black TiO 2 Inverse Opals for Visible-Light Photocatalysis
Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration
 International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 5 No. 5, May, 2016 Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration I. B. Obasi 1 and J. C. Osuwa 2
International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 5 No. 5, May, 2016 Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration I. B. Obasi 1 and J. C. Osuwa 2
Bright White Light Emission from Ultrasmall Cadmium Selenide Nanocrystals
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Bright White Light Emission from Ultrasmall Cadmium Selenide Nanocrystals Teresa E. Rosson 1, Sarah M. Claiborne 1, James R. McBride 1, Benjamin S. Stratton 1,3, and Sandra J. Rosenthal
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Bright White Light Emission from Ultrasmall Cadmium Selenide Nanocrystals Teresa E. Rosson 1, Sarah M. Claiborne 1, James R. McBride 1, Benjamin S. Stratton 1,3, and Sandra J. Rosenthal
EFFECT OF GROWTH TEMPERATURE ON THE CATALYST-FREE GROWTH OF LONG SILICON NANOWIRES USING RADIO FREQUENCY MAGNETRON SPUTTERING
 International Journal of Nanoscience Vol. 10, Nos. 1 & 2 (2011) 13 17 #.c World Scienti c Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S0219581X11007594 EFFECT OF GROWTH TEMPERATURE ON THE CATALYST-FREE GROWTH OF LONG
International Journal of Nanoscience Vol. 10, Nos. 1 & 2 (2011) 13 17 #.c World Scienti c Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S0219581X11007594 EFFECT OF GROWTH TEMPERATURE ON THE CATALYST-FREE GROWTH OF LONG
Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films
 Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films H. R. Kulkarni KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: ZnS thin films were prepared by pulsed electrodeposition
Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films H. R. Kulkarni KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: ZnS thin films were prepared by pulsed electrodeposition
Experimental Studies of Thermal Transport in Heat Transfer Fluids Using Infrared Thermography
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
A comparative study on electrorheological properties of various silica/conducting polymer core/shell nanospheres
 Supplementary Information for: A comparative study on electrorheological properties of various silica/conducting polymer core/shell nanospheres Jin-Yong Hong and Jyongsik Jang* World Class University (WCU)
Supplementary Information for: A comparative study on electrorheological properties of various silica/conducting polymer core/shell nanospheres Jin-Yong Hong and Jyongsik Jang* World Class University (WCU)
Structure and optical properties of M/ZnO (M=Au, Cu, Pt) nanocomposites
 Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 8 () 339 38 Structure and optical properties of M/ (M=Au, Cu, Pt) nanocomposites U. Pal a,b, *, J. Garc!ıa-Serrano a, G. Casarrubias-Segura a, N. Koshizaki c, T. Sasaki
Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 8 () 339 38 Structure and optical properties of M/ (M=Au, Cu, Pt) nanocomposites U. Pal a,b, *, J. Garc!ıa-Serrano a, G. Casarrubias-Segura a, N. Koshizaki c, T. Sasaki
Preparation and Characterization of Copper Oxide -Water Based Nanofluids by One Step Method for Heat Transfer Applications
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.976 2015, 4(1), 127-132 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preparation and Characterization of Copper Oxide -Water Based Nanofluids by One Step
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.976 2015, 4(1), 127-132 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preparation and Characterization of Copper Oxide -Water Based Nanofluids by One Step
Characterization of SrAlO:Dy nano phosphors
 International Journal of Materials Physics. ISSN 0974-309X Volume 7, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-13 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Characterization of SrAlO:Dy nano phosphors
International Journal of Materials Physics. ISSN 0974-309X Volume 7, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-13 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Characterization of SrAlO:Dy nano phosphors
Annealing Effects on the Properties of Copper Selenide Thin Films for Thermoelectric Applications
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861. Volume 4, Issue 5 (Sep. - Oct. 2013), PP 65-71 Annealing Effects on the Properties of Copper Selenide Thin Films for Thermoelectric Applications
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861. Volume 4, Issue 5 (Sep. - Oct. 2013), PP 65-71 Annealing Effects on the Properties of Copper Selenide Thin Films for Thermoelectric Applications
GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Preparation and characteristics of LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si thermoluminescent material
 VNU Journal of Science, Mathematics - Physics 23 (2007) 225-231 Preparation and characteristics of LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si thermoluminescent material Vu Thi Thai Ha 1, Nguyen Thi Quy Hai 1, Nguyen Ngoc Long 2,,
VNU Journal of Science, Mathematics - Physics 23 (2007) 225-231 Preparation and characteristics of LiF:Mg,Cu,Na,Si thermoluminescent material Vu Thi Thai Ha 1, Nguyen Thi Quy Hai 1, Nguyen Ngoc Long 2,,
Three-dimensional binary superlattices of magnetic nanocrystals and semiconductor quantum dots
 Supplementary Information Three-dimensional binary superlattices of magnetic nanocrystals and semiconductor quantum dots F.X. Redl*, K.-S. Cho *, C.B. Murray*, S. O Brien *IBM, T. J. Watson Research Center,
Supplementary Information Three-dimensional binary superlattices of magnetic nanocrystals and semiconductor quantum dots F.X. Redl*, K.-S. Cho *, C.B. Murray*, S. O Brien *IBM, T. J. Watson Research Center,
Selective growth of Au nanograins on specific positions (tips, edges. heterostructures.
 Selective growth of Au nanograins on specific positions (tips, edges and facets) of Cu 2 O octahedrons to form Cu 2 O-Au hierarchical heterostructures. Han Zhu b, MingLiang Du* a,b, DongLiang Yu b, Yin
Selective growth of Au nanograins on specific positions (tips, edges and facets) of Cu 2 O octahedrons to form Cu 2 O-Au hierarchical heterostructures. Han Zhu b, MingLiang Du* a,b, DongLiang Yu b, Yin
CHAPTER 8 CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK
 CHAPTER 8 CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK In this thesis an experimental investigation about Magnisium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles and its nanocomposites i.e.mgo-x (X= NiO, CuO, Co3O4, Fe2O3, CeO2,
CHAPTER 8 CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK In this thesis an experimental investigation about Magnisium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles and its nanocomposites i.e.mgo-x (X= NiO, CuO, Co3O4, Fe2O3, CeO2,
Time resolved spectroscopic studies on some nanophosphors
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 31, No. 3, June 2008, pp. 401 407. Indian Academy of Sciences. Time resolved spectroscopic studies on some nanophosphors HARISH CHANDER and SANTA CHAWLA* Electronic Materials Division,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 31, No. 3, June 2008, pp. 401 407. Indian Academy of Sciences. Time resolved spectroscopic studies on some nanophosphors HARISH CHANDER and SANTA CHAWLA* Electronic Materials Division,
How can we describe a crystal?
 How can we describe a crystal? Examples of common structures: (1) The Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Structure (LiH, MgO, MnO, AgBr, PbS, KCl, KBr) The NaCl structure is FCC The basis consists of one Na atom and
How can we describe a crystal? Examples of common structures: (1) The Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Structure (LiH, MgO, MnO, AgBr, PbS, KCl, KBr) The NaCl structure is FCC The basis consists of one Na atom and
Electronic Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information An Au@Ag Nanocube based Plasmonic Nano-sensor for Rapid Detection
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information An Au@Ag Nanocube based Plasmonic Nano-sensor for Rapid Detection
Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates
 Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90 (2006) 753 759 www.elsevier.com/locate/solmat Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, A. Austine
Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90 (2006) 753 759 www.elsevier.com/locate/solmat Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, A. Austine
Graphene/Fe 3 O Quaternary Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Properties
 Graphene/Fe 3 O 4 @Fe/ZnO Quaternary Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Properties Yu Lan Ren, Hong Yu Wu, Ming Ming Lu, Yu Jin Chen, *, Chun Ling Zhu, # Peng Gao *, # Mao
Graphene/Fe 3 O 4 @Fe/ZnO Quaternary Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Properties Yu Lan Ren, Hong Yu Wu, Ming Ming Lu, Yu Jin Chen, *, Chun Ling Zhu, # Peng Gao *, # Mao
Facile ex-situ NaF size/morphology tuning strategy for highly monodisperse sub-5 nm β-nagdf 4 :Yb/Er
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile ex-situ NaF size/morphology tuning strategy for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile ex-situ NaF size/morphology tuning strategy for
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Experimental All the chemicals were of analytical grade and used without
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Experimental All the chemicals were of analytical grade and used without
Synthesis and Laser Processing of ZnO Nanocrystalline Thin Films. GPEC, UMR 6631 CNRS, Marseille, France.
 TH.B 9.45 O Synthesis and Laser Processing of ZnO Nanocrystalline Thin Films I. Ozerov 1, D. Nelson 2, A.V. Bulgakov 3, W. Marine* 1, and M. Sentis 4 1 GPEC, UMR 6631 CNRS, 13288 Marseille, France. 2 A.F.
TH.B 9.45 O Synthesis and Laser Processing of ZnO Nanocrystalline Thin Films I. Ozerov 1, D. Nelson 2, A.V. Bulgakov 3, W. Marine* 1, and M. Sentis 4 1 GPEC, UMR 6631 CNRS, 13288 Marseille, France. 2 A.F.
SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF MgO NANOPARTICLES
 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF MgO NANOPARTICLES Bhagya J 1,2, Dedhila Devadathan 1, Baiju V 1, Biju R 1, Raveendran R 1 1 Nanoscience Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF MgO NANOPARTICLES Bhagya J 1,2, Dedhila Devadathan 1, Baiju V 1, Biju R 1, Raveendran R 1 1 Nanoscience Research Laboratory, Department of Physics,
The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell
 , pp.66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.140.14 The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Don-Kyu Lee Electrical Engineering, Dong-Eui University,
, pp.66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.140.14 The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Don-Kyu Lee Electrical Engineering, Dong-Eui University,
Supporting Information. Trapping the Catalyst Working State by Amber-Inspired Hybrid
 Supporting Information Trapping the Catalyst Working State by Amber-Inspired Hybrid Material and Revealing the Cobalt Nanostructure Evolution in Gas-to- Liquid Processing Bingbing Zhang a, Haiquan Su a*,
Supporting Information Trapping the Catalyst Working State by Amber-Inspired Hybrid Material and Revealing the Cobalt Nanostructure Evolution in Gas-to- Liquid Processing Bingbing Zhang a, Haiquan Su a*,
Supplementary Information. Solution-phase Synthesis of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanowires
 Supplementary Information Solution-phase Synthesis of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanowires Dandan Zhang,,, Samuel W. Eaton,, Yi Yu, Letian Dou,, Peidong Yang*,,,, Department of Chemistry, Department
Supplementary Information Solution-phase Synthesis of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanowires Dandan Zhang,,, Samuel W. Eaton,, Yi Yu, Letian Dou,, Peidong Yang*,,,, Department of Chemistry, Department
STUDY OF CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITED NANOCRYSTALLINE CdZnS THIN FILMS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 3 Issue 2, April-June 2011 p. 39-43 STUDY OF CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITED NANOCRYSTALLINE CdZnS THIN FILMS V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR *Yeshwantrao Chavan
Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 3 Issue 2, April-June 2011 p. 39-43 STUDY OF CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITED NANOCRYSTALLINE CdZnS THIN FILMS V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR *Yeshwantrao Chavan
LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 porous nanorods as high-rate and long-life cathode for Li-ion batteries
 Supporting Information LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 porous nanorods as high-rate and long-life cathode for Li-ion batteries Xiaolong Zhang, Fangyi Cheng, Jingang Yang, Jun Chen* Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy
Supporting Information LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 porous nanorods as high-rate and long-life cathode for Li-ion batteries Xiaolong Zhang, Fangyi Cheng, Jingang Yang, Jun Chen* Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy
Ceramic Processing Research
 Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 536~540 (009) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Electrical and optical properties of MgO films deposited on soda lime glass by a
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 536~540 (009) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Electrical and optical properties of MgO films deposited on soda lime glass by a
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Reduced Carrier Recombination in PbS - CuInS2 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Zhenhua Sun, 1,2,3 Gary Sitbon, 1,2,3 Thomas Pons, 1,2,3 Artem A. Bakulin, 4 and Zhuoying Chen 1,2,3,* 1.
Supplementary Information Reduced Carrier Recombination in PbS - CuInS2 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Zhenhua Sun, 1,2,3 Gary Sitbon, 1,2,3 Thomas Pons, 1,2,3 Artem A. Bakulin, 4 and Zhuoying Chen 1,2,3,* 1.
Applications of Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR) Technique for CZTS Thin Film Solar Cells
 NANO VISION An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Abbr: Nano Vision. 2013, Vol.3(3): Pg.235-239 Applications
NANO VISION An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Abbr: Nano Vision. 2013, Vol.3(3): Pg.235-239 Applications
Solar Cells and Photosensors.
 Designing Photonic Crystals in Strongly Absorbing Material for Applications in Solar Cells and Photosensors. Minda Wagenmaker 1, Ebuka S. Arinze 2, Botong Qiu 2, Susanna M. Thon 2 1 Mechanical Engineering
Designing Photonic Crystals in Strongly Absorbing Material for Applications in Solar Cells and Photosensors. Minda Wagenmaker 1, Ebuka S. Arinze 2, Botong Qiu 2, Susanna M. Thon 2 1 Mechanical Engineering
Pre-treatment of low temperature GaN buffer layer deposited on AlN Si substrate by hydride vapor phase epitaxy
 Ž. Surface and Coatings Technology 131 000 465 469 Pre-treatment of low temperature GaN buffer layer deposited on AlN Si substrate by hydride vapor phase epitaxy Ha Jin Kim, Ho-Sun Paek, Ji-Beom Yoo Department
Ž. Surface and Coatings Technology 131 000 465 469 Pre-treatment of low temperature GaN buffer layer deposited on AlN Si substrate by hydride vapor phase epitaxy Ha Jin Kim, Ho-Sun Paek, Ji-Beom Yoo Department
Towards High-Safety Potassium-Sulfur Battery Using. Potassium Polysulfide Catholyte and Metal-Free Anode
 Supporting Information Towards High-Safety Potassium-Sulfur Battery Using Potassium Polysulfide Catholyte and Metal-Free Anode Jang-Yeon Hwang, Hee Min Kim, Chong S. Yoon, Yang-Kook Sun* Department of
Supporting Information Towards High-Safety Potassium-Sulfur Battery Using Potassium Polysulfide Catholyte and Metal-Free Anode Jang-Yeon Hwang, Hee Min Kim, Chong S. Yoon, Yang-Kook Sun* Department of
Fabrication and Characterization of a Polypyrrole Coated Copper Nanowire Gas Sensor
 Fabrication and Characterization of a Polypyrrole Coated Copper Nanowire Gas Sensor A.B.Kashyout*, H. Shokry Hassan*, A. A. A. Nasser**, I. Morsy**, and H. Abuklill** *Advanced Technology and New Materials
Fabrication and Characterization of a Polypyrrole Coated Copper Nanowire Gas Sensor A.B.Kashyout*, H. Shokry Hassan*, A. A. A. Nasser**, I. Morsy**, and H. Abuklill** *Advanced Technology and New Materials
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Single Crystal Nanoflowers with Different Chemical Composition and Physical Properties Grown by Limited Ligand Protection Arun Narayanaswamy,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Single Crystal Nanoflowers with Different Chemical Composition and Physical Properties Grown by Limited Ligand Protection Arun Narayanaswamy,
Vacuum, Ar, and O 2 annealing effects on bandgap-tunable semiconducting amorphous Cd Ga O thinfilms
 Full paper Vacuum, Ar, and O 2 annealing effects on bandgap-tunable semiconducting amorphous Cd Ga O thinfilms Chiyuki SATO *, Yota KIMURA * and Hiroshi YANAGI *, **,³ *Interdisciplinary Graduate School
Full paper Vacuum, Ar, and O 2 annealing effects on bandgap-tunable semiconducting amorphous Cd Ga O thinfilms Chiyuki SATO *, Yota KIMURA * and Hiroshi YANAGI *, **,³ *Interdisciplinary Graduate School
In Situ X-ray Scattering Guides the Synthesis of Uniform PtSn Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information In Situ X-ray Scattering Guides the Synthesis of Uniform PtSn Nanocrystals Liheng Wu,, Amanda P. Fournier, Joshua J. Willis,, Matteo Cargnello,,, * and Christopher J. Tassone, *
Supporting Information In Situ X-ray Scattering Guides the Synthesis of Uniform PtSn Nanocrystals Liheng Wu,, Amanda P. Fournier, Joshua J. Willis,, Matteo Cargnello,,, * and Christopher J. Tassone, *
Rapid degradation of methylene blue in a novel
 Title: Rapid degradation of methylene blue in a novel heterogeneous Fe 3 O 4 @rgo@tio 2 -catalyzed photo-fenton system Author names Xiaoling Yang, Wei Chen, Jianfei Huang, Ying Zhou, Yihua Zhu,* and Chunzhong
Title: Rapid degradation of methylene blue in a novel heterogeneous Fe 3 O 4 @rgo@tio 2 -catalyzed photo-fenton system Author names Xiaoling Yang, Wei Chen, Jianfei Huang, Ying Zhou, Yihua Zhu,* and Chunzhong
Surface modification of thermally evaporated CdTe thin films for sensing application of organic compounds
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, October 2017, pp. 701-709 Surface modification of thermally evaporated CdTe thin films for sensing application of organic compounds Sukhvir Singh*, Sandeep
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, October 2017, pp. 701-709 Surface modification of thermally evaporated CdTe thin films for sensing application of organic compounds Sukhvir Singh*, Sandeep
Controlled Fabrication and Optical Properties of Uniform CeO 2 Hollow Spheres
 Controlled Fabrication and Optical Properties of Uniform CeO 2 Hollow Spheres Gen Chen, a Wei Ma, a Xiaohe Liu, a, * Shuquan Liang, b Guanzhou Qiu, a and Renzhi Ma c, * a Department of Inorganic Materials,
Controlled Fabrication and Optical Properties of Uniform CeO 2 Hollow Spheres Gen Chen, a Wei Ma, a Xiaohe Liu, a, * Shuquan Liang, b Guanzhou Qiu, a and Renzhi Ma c, * a Department of Inorganic Materials,
Cubic CeO 2 Nanoparticles as Mirror-like Scattering Layer for Efficient Light Harvesting in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
 Supplementary Material (ESI for Chemical Communications This journal is (c The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Supplementary Material (ESI for Chemical Communications Cubic CeO 2 Nanoparticles as Mirror-like
Supplementary Material (ESI for Chemical Communications This journal is (c The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Supplementary Material (ESI for Chemical Communications Cubic CeO 2 Nanoparticles as Mirror-like
Core/Shell Nanoheterostructures
 High Temperature Photoluminescence of CdSe/CdS Core/Shell Nanoheterostructures Benjamin T. Diroll and Christopher B. Murray Department of Chemistry and Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
High Temperature Photoluminescence of CdSe/CdS Core/Shell Nanoheterostructures Benjamin T. Diroll and Christopher B. Murray Department of Chemistry and Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Morphology controlled synthesis of monodispersed manganese. sulfide nanocrystals and their primary application for supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Morphology controlled synthesis of monodispersed manganese sulfide nanocrystals
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Morphology controlled synthesis of monodispersed manganese sulfide nanocrystals
Influence of In/Sn ratio on nanocrystalline indium tin oxide thin films by spray pyrolysis method
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Physics Research, 2011, 2 (1): 19-25 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-0970 CODEN (USA):
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Physics Research, 2011, 2 (1): 19-25 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-0970 CODEN (USA):
Retarding the crystallization of PbI 2 for highly reproducible planarstructured perovskite solar cells via sequential deposition
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Retarding the crystallization of PbI 2 for highly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Retarding the crystallization of PbI 2 for highly
EFFECT OF DEPOSITION TIME ON CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION PROCESS AND THICKNESS OF BaSe THIN FILMS.
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 3 Issue 4, October-December 2011 p. 81-85 EFFECT OF DEPOSITION TIME ON CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION PROCESS AND THICKNESS OF BaSe THIN FILMS. N.A. OKEREKE
Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 3 Issue 4, October-December 2011 p. 81-85 EFFECT OF DEPOSITION TIME ON CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION PROCESS AND THICKNESS OF BaSe THIN FILMS. N.A. OKEREKE
Growth, Optical and Electrical Properties of zinc tris (thiourea) sulphate (ZTS) Single Crystals
 Volume 7 No.1, May 013 Growth, Optical and Electrical Properties of zinc tris (thiourea) sulphate (ZTS) Single Crystals M.Loganayaki Department of Physics, SRM University, Ramapuram, Chennai-600 089 A.
Volume 7 No.1, May 013 Growth, Optical and Electrical Properties of zinc tris (thiourea) sulphate (ZTS) Single Crystals M.Loganayaki Department of Physics, SRM University, Ramapuram, Chennai-600 089 A.
Synthesis and Characterization of DC Magnetron Sputtered ZnO Thin Films Under High Working Pressures
 Accepted Manuscript Synthesis and Characterization of DC Magnetron Sputtered ZnO Thin Films Under High Working Pressures M. Hezam, N. Tabet, A. Mekki PII: S0040-6090(10)00417-7 DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.03.091
Accepted Manuscript Synthesis and Characterization of DC Magnetron Sputtered ZnO Thin Films Under High Working Pressures M. Hezam, N. Tabet, A. Mekki PII: S0040-6090(10)00417-7 DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.03.091
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Effect of PH on Cobalt Oxide Nano Particles Prepared by Co-Precipitation Method
 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Effect of PH on Cobalt Oxide Nano Particles Prepared by Co-Precipitation Method Ghazaleh
AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Effect of PH on Cobalt Oxide Nano Particles Prepared by Co-Precipitation Method Ghazaleh
Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with high stability and reusability
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with
Growth and Characterization of Cd 1-x Zn x Te Films
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Growth and Characterization of Cd 1-x Zn x Te Films Nway Han Myat Thin 1 and Pho Kaung 2 Abstract The II-VI polycrystalline semiconducting materials have
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Growth and Characterization of Cd 1-x Zn x Te Films Nway Han Myat Thin 1 and Pho Kaung 2 Abstract The II-VI polycrystalline semiconducting materials have
