Modelling Absorption Capacity Performance of Hygienic Product
|
|
|
- Gladys Lorin Casey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 2013, 3, doi: /ojapps Published Online June 2013 ( Modelling Absorption Capacity Performance of Hygienic Product Soumaya Sayeb, Mohamed Ben Hassen, Faouzi Sakli Textile Engineering Laboratory, Monastir University, Monastir, Tunisia Received January 3, 2013; revised February 4, 2013; accepted February 12, 2013 Copyright 2013 Soumaya Sayeb et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT The performance prediction of hygienic products can be a major advantage for manufacturers. Among the interesting performances to be expected, we find the absorption capacity. This is a parameter governed by the composition of the absorbent core, particularly the fibrous component and the characteristics of the superabsorbent polymer (SAP). Thus, various theoretical models have been established to predict the absorption capacity. All these models have taken into account the nature of the fibrous support and the ratio of superabsorbent polymer. Certainly, other factors, less obvious in their modelling, are involved in determining the performance such as the homogeneity of the mixture formed by the fluff and SAP, the distribution of polymer particles in the entire structure, the porous structure, the shape of the capillary, the nature of the nonwoven webs used, etc. Various theoretical models are proposed here to describe the absorption capacity and we will outline the model which best describes this performance. The experimental test results are discussed to verify if the theoretical model selected can be confirmed. Keywords: Model; Absorption Capacity; Hygienic Product; Superabsorbent 1. Introduction Hygienic products have as main component an absorbent core that contains cellulosic fibers from wood pulp (fluff) in which super absorbent particles are spread. The ability of the final product to absorb rapidly and to transport the liquid through the absorbent core is an important requirement. Thus absorbency has been always regarded as one of the most important features desired by consumers in disposable diapers [1-3]. Absorptive capacity is largely determined by the storage capacity and the structure parameters. However, the rate of diffusion of the liquid is influenced by the structure permeability and the capillary shape. The liquid movement in any fibrous structure is influenced by its porosity. The shape of the pores in the fiber structure depends significantly on the type of fiber and the assembly method [4-7]. Based on these findings, Hsieh [5] assumed that the absorption capacity is the ratio between the mass of the liquid absorbed and structure weight before absorption. Absorption capacity can be considered as: C absorption ρl ε = ρ 1 ε (1) f where l is the liquid density, f is the fiber density and ε is the porosity of the structure. Nevertheless, Gupta et al. [7] consider the absorption capacity as the sum of the amount of liquid held within the pores and the amount diffused and held within the structure of the fibers. Absorption capacity can be expressed by the following equation: T 1 V d C = A + ( 1 α ) (2) W f d f W f with: C: the absorption capacity of the structure (in cm 3 /g), A: area structure (cm 2 ), T: thickness of the structure (in cm), W f : dry fiber weight (in g), d f : fiber density (g/cm 3 ), α: the ratio of the increase in volume of a fiber upon wetting to the volume of the liquid diffused into fiber. V d : amount of liquid diffused into the structure of the fibers (in cm 3 ). In this equation (Equation (2)), it was found that the second term is negligible compared to the first. The third term is nearly zero assuming that a fiber swells strictly by exchanging fiber volume with liquid volume. The
2 170 S. SAYEB ET AL. most important factor in this Equation (2) is therefore the thickness structure [8]. Any factors that affect structure thickness will affect the absorbent capacity. The expression of absorptive capacity is reduced to: T C = A (3) W However, the liquid movement in the porous structure is influenced by the capillary forces which in turn are governed by the properties of the liquid (surface tension, viscosity, and density), the fiber surface wetting characteristics, and the geometric configuration of the porous structure [5,9]. Since, it is convenient to divide the mechanism of liquid absorption by a porous structure into 3 basic categories: acquisition, retention and distribution. First, the liquid should be quickly acquired before it is transferred to other parts of the absorbent core. Therefore, sufficient void volume is required for efficient liquid acquisition. Combining super absorbent polymer (SAP) particles with fiber results is an increase of the void volume. Dutkiewicz [4] has established a model expressing the change in the void volume ΔVv in the absorbent structure: 13 α SAP 1.24 ρsap S Δ Vv = S ρ ( ρw0 ) α SAP with: α SAP : SAP ratio in the structure (%), ρ SAP : SAP density (g/cm 3 ), ρ w0 : the initial density of the structure (g/cm 3 ), S is saturation of the structure (ml/g). Equation 4 illustrates many factors that can permit the prediction of the maximum absorption capacity which is the saturation of the absorbent core. In fact it is based on précised parameters referring to the SAP (ρ SAP and α SAP ) and to the fibrous material (ρ w0 ). To verify the theoretical model shown above and to decide if this model corresponds to real absorption phenomenon, we made experimental measurements. 2. Materiel and Methods 2.1. Material Charcteristics This work used bleached soft wood fibre from STORA fluff LKC (mean length 2.7 mm), HySorb B7160 super absorbent polymer based on sodium acrylate (BASF), commercial fibre of viscose (1.7 dtex) and acrylic (1.3 dtex). f SAP (4) 2.2. Experiments Total absorption capacity were realised according to STN2: 117/87 standards for total absorbency measurement. The liquid test used is a 0.9% NaCl solution. The absorption capacity measures the liquid quantity remained associated to the material after a time of impregnation and draining. Figure 1 shows the model of the absorbent structure that has been developed. For these structures, we proceeded to the determination of the maximum absorption capacity. The maximum of absorption capacity determine the saturation of the structure. To demonstrate the previously described model (Equation (4)), we perform two sets of tests. For both sets of tests, all parameters (ρ SAP, α SAP and ρ w0 ) will be varied. For first set, density will be varied by changing the total compression of the structure. In second one, it is varied by changing the nature of the fibers used. 3. Results and Discussion 3.1. SAP Ratio and Absorbent Structure Density Variation For these tests, we will vary the super absorbent polymer ratio and the density of the absorbent structure. The last parameter will be varied by changing the compression of the structure i.e. the structure thickness. We conducted a series of 18 tests where the ratio of super absorbent polymer is varied according to 6 levels and the compression according to 3 levels. Table 1 shows the values corresponding to each level. Non woven Webs Absorbent core: Fluff + (Viscose/acrylic) SAP Particles Figure 1. Model of the absorbent structure tested. Factor 1: SAP ratio 2: thickness Table 1. Levels factor. Levels 1 = 5% 2 = 10% 3 = 15% 4 = 20% 5 = 25% 6 = 30% 1 = 8 mm 2 = 6 mm 3 = 4 mm
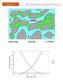
3 S. SAYEB ET AL. 171 The 18 tests were conducted by combining different levels of each factor. Table 2 shows the distribution of tests according to the previously established levels. Once the saturation of the various samples was determined, we proceeded to calculate the variation of the void volume. The obtained results are shown in Figure 2. It illustrates the variation of void volume as a function of SAP ratio and thus for different levels of compression that has been fixed. These curves reveal the effect of compression on the void volume within the porous structure. An increase in compression causes a considerable decrease in interstitial space between fibers. It also reduces the size of capillaries and thus a decline of the structure porosity, which explains the observed results. Moreover, we note that for different levels of compression, the fibrous structure shows an increase in the interstitial space due to the augmentation in SAP ratio. Then we note that this volume is practically constant even after the increase in SAP ratio. However, with varying levels of compression, different structures reach an equal maximum of void volume. This behaviour suggests also that the SAP particles swell considerably and generate a decrease of the permeability of the absorbent core and thus resulting in a Test Table 2. Tests plan. SAP ratio (%) Parameter Thickness (mm) Figure 2. Variation of void volume in absorbent structure in function of thickness. reduction in the void volume. Consequently, the fibrous structure limits its absorption. Therefore, structure saturation occurs beyond a certain threshold of SAP ratio. This threshold value inhibits any absorption or liquid diffusion through the absorbent structure Fiber Structure Variation During these experiments, we proceeded to the variation of the structure density by changing the nature of the fibrous support. SAP ratio is also varied. The experimental procedure adopted is as follows: for different SAP ratios, we inserted viscose and acrylic fiber in to the mixture of fluff. As result, density structure (ρ w0 ) and SAP ratio (α SAP ) are varied. Here, the experiments were carried out in two stages. The first corresponds to structure prepared with an absorbent core made of mixtures of fluff + (viscose or acrylic) fiber which are realized according to a fixed ratio 80% fluff + 20% (viscose or acrylic). Obviously, to determine the saturation of the absorbent core, SAP ratio is varied. The second stage will be conducted as follows: we fixed the SAP ratio (α SAP = constant = 25%) and we varied the mixture ratios constituting the fibrous support. It is to find the fibrous structure that offers best distribution of void volume which leads to improved acquisition and consequently allows less saturation of the absorbent core. Results are described in Figure 3. The curves illustrate the variation of void volume within the different structures realized with SAP ratio increase. We notice that the SAP ratio increase results in void volume augmentation within the absorbent core until reaching a certain threshold of SAP. Indeed, the curves start with an initial growth phase for which any increase in SAP ratio generates a rise in the void volume, then these curves show a phase of stabilization where void volume remains unchanged.
4 172 S. SAYEB ET AL. Figure 3. Variation of void volume in absorbent structure in function of fiber composition of the absorbent structure. However, we observe that the fibrous structure, which provides better void volume while increasing SAP ratio, consists of a mixture of fluff + acrylic. The structure that provides the minimum of void volume is made by a fibrous core containing fluff + viscose. Indeed, we confirm that adding acrylic fiber to fluff diminishes the contact between the swollen SAP particles and inhibits the occurrence of the phenomenon of gel blocking resulting from the decrease in void volume within the absorbent core. This points out the importance of physical structure: acrylic which is more resilient than fluff is not prone to clotting in wet state, indeed and due to this property, physical structure is kept after wet deformation [10]. Consequently the distribution of liquid is improved. When we fixed SAP ratio (α SAP = constant = 25%) and vary mixtures ratio, we obtain Figure 4. Figure 4 shows that fixing the SAP ratio results in a maximum of void volume in both structures consisting of a mixture 80% fluff + 20% (acrylic or viscose). As mentioned, this ratio provides a better arrangement of SAP particles within the absorbent core and consequently larger voids volume that promotes better absorption. Nevertheless, acrylic fiber improves absorption as compared to viscose due to the ability of acrylic to form the physical structure more resilient and stable in the wet state. 4. Conclusions Different models describing the absorption capacity performance within a fibrous structure are presented. The key parameters needed to predict this performance are: the superabsorbent polymer ratio, the structure compression, and the fiber support properties. Indeed, these parameters affect the performances: super absorbent polymer and fibrous support permit the absorption of the liquid, pore volume presented in the structure assure the acquisition of liquid. We selected a model that describes the variation of void volume in the structure during liquid absorption: it Figure 4. Variation of void volume in absorbent structure in function of fiber mixture ratios (α SAP = 25%). illustrates the changes that occur in the structure due to the swelling of the superabsorbent polymer particles. Through the experiments carried out in this study, we tried to verify the theoretical model and to decide if this model corresponds to real absorption phenomenon. The investigated tests revealed a high correlation between the experimental tests conducted and the results described by the model. Thus, for a structure containing fixed super absorbent ratio, the incorporation of synthetic fibers such us acrylic can significantly improve the behaviour of the fiber structure and therefore the absorption. The gel blocking occurrence is largely limited. REFERENCES [1] R. Saminathan and B. W. Steven, Modern Diaper Technology, Tappi Journal, Vol. 79, No. 6, 1996, pp [2] EDANA, Absorbent Hygiene Products, Training Course: Baby Diapers, Sanitary Protection and Adult Incontinence, European Disposables and Nonwovens Association, Vol. 1, 1997, pp , [3] P. Wiertz, Sustainability Report : Absorbent hygiene Products, ent-library/sustainability-report-absorbent-hygiene-produ cts pdf?sfvrsn=2 [4] J. Dutkiewicz, Some Abvances in Nonwovens Structures for Absorbency, Confort and Aesthetics, Autex Research Journal, Vol. 2, No. 3, 2002, pp [5] B. S. Gupta and C. J. Hong, Changes in Web Dimensions during Fluid Uptake and the Impact on Absorbency, Tappi Journal, Vol. 77, No. 12, 1994, pp [6] L. Darry, Nonwovens Containing Immobilized Super Absorbent Polymer Particles, International Nonwovens Journal, Vol. 12, No. 3, 2003, pp [7] M. G. Kamath and A. Dahiya, Absorption Properties, 2004.
5 S. SAYEB ET AL [8] Y. L. Hsieh, Liquid Transport in Fabric Structures, Textile Research Journal, Vol. 65, No. 5, 1995, pp doi: / [9] A. Patnaik, R. S. Rengasamy, et al., Wetting and Wick- ing in Fibrous Materials, Textile Progress, Vol. 38, No. 1, 2006, pp doi: /jotp [10] C. Rosinskaya, Effect of Synthetic Fibres on Absorption Properties of Pads, International Nonwovens Journal, Vol. 11, No. 2, 2002, pp
SOME ADVANCES IN NONWOVEN STRUCTURES FOR ABSORBENCY, COMFORT AND AESTHETICS
 AUTEX Research Journal, Vol. 2, No3, September 2002 AUTEX SOME ADVANCES IN NONWOVEN STRUCTURES FOR ABSORBENCY, COMFORT AND AESTHETICS Jacek Dutkiewicz Buckeye Technologies Inc., Memphis, TN, USA Abstract
AUTEX Research Journal, Vol. 2, No3, September 2002 AUTEX SOME ADVANCES IN NONWOVEN STRUCTURES FOR ABSORBENCY, COMFORT AND AESTHETICS Jacek Dutkiewicz Buckeye Technologies Inc., Memphis, TN, USA Abstract
USE OF SUPER ABSORBENT POLYMERS (SAPs) IN CONCRETE.
 USE OF SUPER ABSORBENT POLYMERS (SAPs) IN CONCRETE. An overview of some aspects of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) in concrete technology. The use of superabsorbent polymers as a crack sealing and crack
USE OF SUPER ABSORBENT POLYMERS (SAPs) IN CONCRETE. An overview of some aspects of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) in concrete technology. The use of superabsorbent polymers as a crack sealing and crack
Luquafleece. The superabsorbent fabric
 Luquafleece The superabsorbent fabric General Particulate superabsorbent polymers (superabsorbents, SAP) are well known for their capability to absorb and retain many times their own weight in aqueous
Luquafleece The superabsorbent fabric General Particulate superabsorbent polymers (superabsorbents, SAP) are well known for their capability to absorb and retain many times their own weight in aqueous
ORIGINAL PAPER/Peer Reviewed Pore Size and Air Permeability Of Four Nonwoven Fabrics
 ORIGINAL PAPER/Peer Reviewed Pore Size and Air Permeability Of Four Nonwoven Fabrics By Helen H. Epps and Karen K. Leonas, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA Abstract The relationship between pore size
ORIGINAL PAPER/Peer Reviewed Pore Size and Air Permeability Of Four Nonwoven Fabrics By Helen H. Epps and Karen K. Leonas, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA Abstract The relationship between pore size
Active Flow Control in a VARTM Process Using Localized Induction Heating
 247 Active Flow Control in a VARTM Process Using Localized Induction Heating Richard J. Johnson and Ranga Pitchumani 1, 2 1, 2 Composites Processing Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University
247 Active Flow Control in a VARTM Process Using Localized Induction Heating Richard J. Johnson and Ranga Pitchumani 1, 2 1, 2 Composites Processing Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University
Harmonized Test Methods Nonwovens and Related Industries. Table of Contents
 INDA and EDANA are pleased to answer the industry needs by publishing the 2012 edition of our Harmonized Test Methods Manual for the nonwoven and related industry. This 2012 edition contains the most complete
INDA and EDANA are pleased to answer the industry needs by publishing the 2012 edition of our Harmonized Test Methods Manual for the nonwoven and related industry. This 2012 edition contains the most complete
Air Permeability & Porosity in Spun-laced Fabrics
 Omer Berk Berkalp Istanbul Technical University Textile Technologies and Design Faculty, Textile Engineering Department Inonu cad. No.87 Gumussuyu/Beyoglu 34437 Istanbul, Turkiye E-mail: berkalpo@itu.edu.tr
Omer Berk Berkalp Istanbul Technical University Textile Technologies and Design Faculty, Textile Engineering Department Inonu cad. No.87 Gumussuyu/Beyoglu 34437 Istanbul, Turkiye E-mail: berkalpo@itu.edu.tr
Abstract Process Economics Program Report 194A SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS (April 2002)
 Abstract Process Economics Program Report 194A SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS (April 2002) Superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) represent a class of organic chemicals defined primarily by the their functional capability
Abstract Process Economics Program Report 194A SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS (April 2002) Superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) represent a class of organic chemicals defined primarily by the their functional capability
Utilization of Air Permeability In Predicting The Thermal Conductivity
 ORIGINAL PAPER/PEER-REVIEWED Utilization of Air Permeability In Predicting The Thermal Conductivity By Pamela Banks-Lee a *, Massoud Mohammadi b, Parviz Ghadimi c Abstract: General linear regression models
ORIGINAL PAPER/PEER-REVIEWED Utilization of Air Permeability In Predicting The Thermal Conductivity By Pamela Banks-Lee a *, Massoud Mohammadi b, Parviz Ghadimi c Abstract: General linear regression models
SIMULATION OF INFUSION PROCESS FOR COMPOSITES MATERIALS COUPLING STOKES, DARCY AND SOLID FINITE DEFORMATION
 SIMULATION OF INFUSION PROCESS FOR COMPOSITES MATERIALS COUPLING STOKES, DARCY AND SOLID FINITE DEFORMATION ARNAUD DEREIMS ESI GROUP (LYON) & CLAUDE GOUX LABORATORY UMR CNRS5146 - ECOLE NATIONALE SUPÉRIEURE
SIMULATION OF INFUSION PROCESS FOR COMPOSITES MATERIALS COUPLING STOKES, DARCY AND SOLID FINITE DEFORMATION ARNAUD DEREIMS ESI GROUP (LYON) & CLAUDE GOUX LABORATORY UMR CNRS5146 - ECOLE NATIONALE SUPÉRIEURE
Water-entrained cement-based materials by superabsorbent polymers On the fundamentals Esteves, Luis Pedro
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: January 11, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Water-entrained cement-based materials by superabsorbent polymers On the fundamentals Esteves, Luis Pedro Published in: International
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: January 11, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Water-entrained cement-based materials by superabsorbent polymers On the fundamentals Esteves, Luis Pedro Published in: International
USE OF MULTIPLE TEST TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATION OF COMPLEX PORE STRUCTURE ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION NON-MERCURY LIQUID EXTRUSION POROSIMETRY
 USE OF MULTIPLE TEST TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATION OF COMPLEX PORE STRUCTURE Akshaya Jena and Krishna Gupta Porous materials, Inc. 83 Brown Road Ithaca, NY 14850 ABSTRACT Pore structures of a ceramic filtration
USE OF MULTIPLE TEST TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATION OF COMPLEX PORE STRUCTURE Akshaya Jena and Krishna Gupta Porous materials, Inc. 83 Brown Road Ithaca, NY 14850 ABSTRACT Pore structures of a ceramic filtration
Research Article Experimental Study on Forecasting Mathematical Model of Drying Shrinkage of Recycled Aggregate Concrete
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 212, Article ID 567812, 14 pages doi:1.1155/212/567812 Research Article Experimental Study on Forecasting Mathematical Model of Drying Shrinkage of Recycled
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 212, Article ID 567812, 14 pages doi:1.1155/212/567812 Research Article Experimental Study on Forecasting Mathematical Model of Drying Shrinkage of Recycled
J. F. Hunt M. Tamasy-Bano and H. Nyist ABSTRACT
 Part II - Modelling the Drying of Three-Dimensional Pulp Moulded Structures - Drying Data Obtained from Flat Panels using Virgin and Recycled Paper Fibre J. F. Hunt M. Tamasy-Bano and H. Nyist USDA, Forest
Part II - Modelling the Drying of Three-Dimensional Pulp Moulded Structures - Drying Data Obtained from Flat Panels using Virgin and Recycled Paper Fibre J. F. Hunt M. Tamasy-Bano and H. Nyist USDA, Forest
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 19699-1 First edition 2017-08 Superabsorbent polymer Sodium polyacrylate resin for absorbing blood Part 1: Test methods Résines super-absorbantes Polyacrylate de sodium pour
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 19699-1 First edition 2017-08 Superabsorbent polymer Sodium polyacrylate resin for absorbing blood Part 1: Test methods Résines super-absorbantes Polyacrylate de sodium pour
FLEXIBLE INJECTION: A NOVEL LCM TECHNOLOGY FOR LOW COST MANUFACTURING OF HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPOSITES. PART II NUMERICAL MODEL
 FPCM-9 (2008) The 9 th International Conference on Flow Processes in Composite Materials Montréal (Québec), Canada 8 ~ 10 July 2008 FLEXIBLE INJECTION: A NOVEL LCM TECHNOLOGY FOR LOW COST MANUFACTURING
FPCM-9 (2008) The 9 th International Conference on Flow Processes in Composite Materials Montréal (Québec), Canada 8 ~ 10 July 2008 FLEXIBLE INJECTION: A NOVEL LCM TECHNOLOGY FOR LOW COST MANUFACTURING
Study of cyclic bursting loading on needle-punched nonwovens: Part II Change in air permeability and compression behavior
 Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 43, June 2018, pp. 203-208 Study of cyclic bursting loading on needle-punched nonwovens: Part II Change in air permeability and compression behavior Bipin
Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 43, June 2018, pp. 203-208 Study of cyclic bursting loading on needle-punched nonwovens: Part II Change in air permeability and compression behavior Bipin
"Pulp and Paper Testing" Edited by Jan-Erik Levlin And Liva Sōderhjeln
 Item Number: 0202FIN17 ISBN: 952-5216-17-9 287 pages Contents include: Single fibers and pulp testing Paper testing Uncertainty of testing Standardization Chapter 1 - Aim of pulp and paper testing 1 Why
Item Number: 0202FIN17 ISBN: 952-5216-17-9 287 pages Contents include: Single fibers and pulp testing Paper testing Uncertainty of testing Standardization Chapter 1 - Aim of pulp and paper testing 1 Why
Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for self-healing concrete. JEONG Yeonung, Ph.D. Research Fellow National University of Singapore
 Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for self-healing concrete JEONG Yeonung, Ph.D. Research Fellow National University of Singapore Content 1. Background 2. Concept of self-healing concrete 3. Introduction to
Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for self-healing concrete JEONG Yeonung, Ph.D. Research Fellow National University of Singapore Content 1. Background 2. Concept of self-healing concrete 3. Introduction to
Numerical Calculation of Viscous-Elastic Fluid Flooding Residual Oil Film in the Complex Pore
 Open Journal of Fluid Dynamics,,, 47-5 http://dx.doi.org/.46/ojfd..9 Published Online September (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd) Numerical Calculation of Viscous-Elastic Fluid Flooding Residual Oil
Open Journal of Fluid Dynamics,,, 47-5 http://dx.doi.org/.46/ojfd..9 Published Online September (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd) Numerical Calculation of Viscous-Elastic Fluid Flooding Residual Oil
Global Fluff Pulp Outlook
 Global Fluff Pulp Outlook RISI North American Conference San Francisco, USA October 218 Patrick Cavanagh Economist, Pulp Presentation Overview Fluff pulp basics Demand Steady growth trends for both mature
Global Fluff Pulp Outlook RISI North American Conference San Francisco, USA October 218 Patrick Cavanagh Economist, Pulp Presentation Overview Fluff pulp basics Demand Steady growth trends for both mature
Open Access Experimental Study on Road Properties of High Liquid Limit Soil in Yunfu Highway
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 46 The Open Construction and Building Technology Journal, 2015, 9, 46-51 Open Access Experimental Study on Road Properties of High Liquid Limit Soil
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 46 The Open Construction and Building Technology Journal, 2015, 9, 46-51 Open Access Experimental Study on Road Properties of High Liquid Limit Soil
CHAPTER 5 APPLICATION OF AGAVE FIBRE REINFORCED EPOXY MATERIALS
 157 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATION OF AGAVE FIBRE REINFORCED EPOXY MATERIALS 5.1 FABRICATION OF HOUSEHOLD TABLE The increasing environmental awareness in the world new global agreement, and international governmental
157 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATION OF AGAVE FIBRE REINFORCED EPOXY MATERIALS 5.1 FABRICATION OF HOUSEHOLD TABLE The increasing environmental awareness in the world new global agreement, and international governmental
A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF META-ARAMID FIBRID FORMATION
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2017, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 1651-1655 1651 A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF META-ARAMID FIBRID FORMATION by Li-Rong YAO *, Xiao-Juan LI, Ye-Qun JIANG, and Shan-Qing XU School of Textile and
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2017, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 1651-1655 1651 A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF META-ARAMID FIBRID FORMATION by Li-Rong YAO *, Xiao-Juan LI, Ye-Qun JIANG, and Shan-Qing XU School of Textile and
Nanofibrillated Cellulose Fibers:
 Nanofibrillated Cellulose Fibers: Where Size Matters in Opening New Markets to Nanofiber Usage Presentation to 2008 TAPPI Nanotechnology Conference June 25-27, 27, 2008 St Louis, MO By E.C. Homonoff, R.E.
Nanofibrillated Cellulose Fibers: Where Size Matters in Opening New Markets to Nanofiber Usage Presentation to 2008 TAPPI Nanotechnology Conference June 25-27, 27, 2008 St Louis, MO By E.C. Homonoff, R.E.
L Manufacturing of Polymer Composites FS 17 Exercise 6. Exercise 6: Solution PROCESSING
 Exercise 6: Solution OUT-OF-AUTOCLAVE PROCESSING Source: http://www.virgingalactic.com/multimedia/album/graphics-and-illustrations Exercise responsible: Max Volk, mvolk@ethz.ch, LEE O224 ETH Zürich Composite
Exercise 6: Solution OUT-OF-AUTOCLAVE PROCESSING Source: http://www.virgingalactic.com/multimedia/album/graphics-and-illustrations Exercise responsible: Max Volk, mvolk@ethz.ch, LEE O224 ETH Zürich Composite
Asian Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6, Issue 07, pp , July, 2015 RESEARCH ARTICLE
 Available Online at http://www.journalajst.com ASIAN JOURNAL OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSN: 0976-3376 Asian Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6, Issue 07, pp. 1579-1583, July, 2015 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Available Online at http://www.journalajst.com ASIAN JOURNAL OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSN: 0976-3376 Asian Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6, Issue 07, pp. 1579-1583, July, 2015 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of Elastic Polylactic Acid Material Using Electron Beam Radiation
 ELECTRONICS Development of Elastic Polylactic Acid Material Using Electron Beam Radiation Shinichi KANAZAWA Sumitomo Electric Fine Polymer has developed a technology for fabricating a brand new elastic
ELECTRONICS Development of Elastic Polylactic Acid Material Using Electron Beam Radiation Shinichi KANAZAWA Sumitomo Electric Fine Polymer has developed a technology for fabricating a brand new elastic
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 12, December -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Development
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 12, December -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Development
NATURAL POLYMER AS WATERPROOFING COMPOUND IN CEMENT CONCRETE
 NATURAL POLYMER AS WATERPROOFING COMPOUND IN CEMENT CONCRETE Remya V 1 and Hima Elizabeth Koshy 2 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department Of Civil Engineering, Mount Zion College of Engineering, Pathanamthitta
NATURAL POLYMER AS WATERPROOFING COMPOUND IN CEMENT CONCRETE Remya V 1 and Hima Elizabeth Koshy 2 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department Of Civil Engineering, Mount Zion College of Engineering, Pathanamthitta
SIMULATION AND CONTROL OF THE VACUUM ASSISTED RESIN TRANSFER MOULDING PROCESS BY MEANS OF FLEXIBLE PERMEABILITY MODELS
 SIMULATION AND CONTROL OF THE VACUUM ASSISTED RESIN TRANSFER MOULDING PROCESS BY MEANS OF FLEXIBLE PERMEABILITY MODELS Enrique Díaz a, Concha Sanz a, J. Antonio García-Manrique b a AIMPLAS, Instituto Tecnológico
SIMULATION AND CONTROL OF THE VACUUM ASSISTED RESIN TRANSFER MOULDING PROCESS BY MEANS OF FLEXIBLE PERMEABILITY MODELS Enrique Díaz a, Concha Sanz a, J. Antonio García-Manrique b a AIMPLAS, Instituto Tecnológico
Global Fluff Pulp Market: Industry Analysis & Outlook ( )
 Industry Research by Koncept Analytics Global Fluff Pulp Market: Industry Analysis & Outlook ----------------------------------------- (2017-2021) October 2017 1 Executive Summary Fluff Pulp, also known
Industry Research by Koncept Analytics Global Fluff Pulp Market: Industry Analysis & Outlook ----------------------------------------- (2017-2021) October 2017 1 Executive Summary Fluff Pulp, also known
Characteristics of Solder Paste
 Characteristics of Solder Paste Flow Solder paste is a viscous non-newtonian fluid, whose resistance to flow is not constant, and which exhibits shear thinning. This is an essential requirement for printing,
Characteristics of Solder Paste Flow Solder paste is a viscous non-newtonian fluid, whose resistance to flow is not constant, and which exhibits shear thinning. This is an essential requirement for printing,
Sound absorbing properties of materials made of rubber crumbs
 Sound absorbing properties of materials made of rubber crumbs F. Asdrubali, F. D Alessandro and S. Schiavoni Università degli studi di Perugia, Via G. Duranti 67, 06125 Perugia, Italy fasdruba@unipg.it
Sound absorbing properties of materials made of rubber crumbs F. Asdrubali, F. D Alessandro and S. Schiavoni Università degli studi di Perugia, Via G. Duranti 67, 06125 Perugia, Italy fasdruba@unipg.it
Effect of Optical Brightening Agent (OBA) on Bleaching Process on Paper of Eucalyptus Kraft Pulp
 Natural Resources, 013, 4, 378-38 http://d.doi.org/10.436/nr.013.45046 Published Online September 013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/nr) Effect of Optical Brightening Agent (OBA) on Bleaching Process on
Natural Resources, 013, 4, 378-38 http://d.doi.org/10.436/nr.013.45046 Published Online September 013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/nr) Effect of Optical Brightening Agent (OBA) on Bleaching Process on
COMPACTION BEHAVIOUR AND PERMEABILITY OF CELLULOSIC FIBRE FOR RTM APPLICATIONS
 COMPACTION BEHAVIOUR AND PERMEABILITY OF CELLULOSIC FIBRE FOR RTM APPLICATIONS Loleï Khoun, Frédéric Busnel and Damien Maillard National Research Council Canada 75 bd de Mortagne, Boucherville, QC, J4B
COMPACTION BEHAVIOUR AND PERMEABILITY OF CELLULOSIC FIBRE FOR RTM APPLICATIONS Loleï Khoun, Frédéric Busnel and Damien Maillard National Research Council Canada 75 bd de Mortagne, Boucherville, QC, J4B
Copyright 2015 by Fatemeh Bateny. All Rights Reserved
 ABSTRACT BATENY, FATEMEH. Fluid Absorption and Release of Nonwovens and their Response to Compression. (Under the direction of Dr. Eunkyoung Shim and Dr. Behnam Pourdeyhimi). Fluid handling is a key property
ABSTRACT BATENY, FATEMEH. Fluid Absorption and Release of Nonwovens and their Response to Compression. (Under the direction of Dr. Eunkyoung Shim and Dr. Behnam Pourdeyhimi). Fluid handling is a key property
Global Pulp Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts ( ) June 2018
 Global Pulp Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts (2018-2022) June 2018 Global Pulp Market: Coverage Executive Summary and Scope Introduction/Market Overview Market Analysis Regional Analysis Market Dynamics
Global Pulp Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts (2018-2022) June 2018 Global Pulp Market: Coverage Executive Summary and Scope Introduction/Market Overview Market Analysis Regional Analysis Market Dynamics
CAPILLARY EFFECTS IN VACUUM ASSISTED RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING WITH NATURAL FIBERS
 CAPILLARY EFFECTS IN VACUUM ASSISTED RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING WITH NATURAL FIBERS Gastón Francucci 1, Analía Vázquez 2, Exequiel S. Rodríguez 1, Edu Ruiz 3 1 Materials Science and Technology Research Institute
CAPILLARY EFFECTS IN VACUUM ASSISTED RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING WITH NATURAL FIBERS Gastón Francucci 1, Analía Vázquez 2, Exequiel S. Rodríguez 1, Edu Ruiz 3 1 Materials Science and Technology Research Institute
Particle Size Determination of Porous Powders Using the SediGraph
 Application Note 94 Particle Size Determination of Porous Powders Using the SediGraph Sedimentation analysis based upon Stokes Law provides a convenient method for determining particle size distribution
Application Note 94 Particle Size Determination of Porous Powders Using the SediGraph Sedimentation analysis based upon Stokes Law provides a convenient method for determining particle size distribution
Chapter 11 Compressibility of Soil
 Page 11 1 Chapter 11 Compressibility of Soil 1. The compression of soil layers as a result of foundation or other loadings is caused by (a) deformation of soil particles. (b) relocation of soil particles.
Page 11 1 Chapter 11 Compressibility of Soil 1. The compression of soil layers as a result of foundation or other loadings is caused by (a) deformation of soil particles. (b) relocation of soil particles.
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP019439 TITLE: Simulation of the Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding Process DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP019439 TITLE: Simulation of the Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding Process DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution
The impact of the amount of polypropylene fibres on spalling behaviour and residual mechanical properties of Reactive Powder Concretes
 MATEC Web of Conferences 6, 23 (213) DOI: 1.151/matecconf/213623 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 213 The impact of the amount of polypropylene fibres on spalling behaviour and residual
MATEC Web of Conferences 6, 23 (213) DOI: 1.151/matecconf/213623 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 213 The impact of the amount of polypropylene fibres on spalling behaviour and residual
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Geometrical analysis of Gas Diffusion Layer in a Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Low H.W., and Birgersson E. Engineering Science Programme National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546
Geometrical analysis of Gas Diffusion Layer in a Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Low H.W., and Birgersson E. Engineering Science Programme National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546
PORE VOLUME OF NANOFIBER NONWOVENS. Akshaya Jena and Krishna Gupta Porous Materials Inc., 20 Dutch Mill Road, Ithaca, NY 14850, USA
 PORE VOLUME OF NANOFIBER NONWOVENS Akshaya Jena and Krishna Gupta Porous Materials Inc., 20 Dutch Mill Road, Ithaca, NY 14850, USA ABSTRACT Pore volume, pore diameter, pore volume distribution and pore
PORE VOLUME OF NANOFIBER NONWOVENS Akshaya Jena and Krishna Gupta Porous Materials Inc., 20 Dutch Mill Road, Ithaca, NY 14850, USA ABSTRACT Pore volume, pore diameter, pore volume distribution and pore
Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for self-healing concrete. JEONG Yeonung, Ph.D. Research Fellow National University of Singapore
 Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for self-healing concrete JEONG Yeonung, Ph.D. Research Fellow National University of Singapore Content 1. Background 2. Concept of self-healing concrete 3. Introduction to
Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for self-healing concrete JEONG Yeonung, Ph.D. Research Fellow National University of Singapore Content 1. Background 2. Concept of self-healing concrete 3. Introduction to
INFLUENCE OF TECHNOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON AGROTEXTILES WATER ABSORBENCY USING ANOVA MODEL
 INFLUENCE OF TECHNOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON AGROTEXTILES WATER ABSORBENCY USING ANOVA MODEL LUPU Iuliana G. 1, GROSU Marian C. 2 1. Gheorghe Asachi Technical University from Iaşi, Faculty of Textile-Leather
INFLUENCE OF TECHNOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON AGROTEXTILES WATER ABSORBENCY USING ANOVA MODEL LUPU Iuliana G. 1, GROSU Marian C. 2 1. Gheorghe Asachi Technical University from Iaşi, Faculty of Textile-Leather
New developments to Capture the Manufacturing Process of Composite Structures in LS-DYNA
 New developments to Capture the Manufacturing Process of Composite Structures in LS-DYNA Gregor Knust, Thomas Klöppel, André Haufe, Christian Liebold DYNAmore GmbH, Stuttgart Oasys LS-DYNA Users Meeting
New developments to Capture the Manufacturing Process of Composite Structures in LS-DYNA Gregor Knust, Thomas Klöppel, André Haufe, Christian Liebold DYNAmore GmbH, Stuttgart Oasys LS-DYNA Users Meeting
Improved Oil Recovery by Injection of Water and Gas
 Improved Oil Recovery by Injection of Water and Gas Dr. Amin Azhdarpour Department Of Petroleum Engineering, Marvdasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Marvdasht, Iran. E-mail: aminazh22@gmail.com;amin.azhdarpour@miau.ac.ir
Improved Oil Recovery by Injection of Water and Gas Dr. Amin Azhdarpour Department Of Petroleum Engineering, Marvdasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Marvdasht, Iran. E-mail: aminazh22@gmail.com;amin.azhdarpour@miau.ac.ir
A Finite Element Code for Porous Media Flows
 A Finite Element Code for Porous Media Flows Mold-filling in LCM, a process to make polymer composites Wicking flow in rigid and swelling materials Permeability prediction General laminar flow Hua Tan
A Finite Element Code for Porous Media Flows Mold-filling in LCM, a process to make polymer composites Wicking flow in rigid and swelling materials Permeability prediction General laminar flow Hua Tan
Comparing pulp mill Pulmac fiber quality testing with conventional laboratory pulp evaluation.
 Comparing pulp mill Pulmac fiber quality testing with conventional laboratory pulp evaluation. W.F. Cowan Research Director and CEO Pulmac Instruments International Moretown, Vermont The increasing use
Comparing pulp mill Pulmac fiber quality testing with conventional laboratory pulp evaluation. W.F. Cowan Research Director and CEO Pulmac Instruments International Moretown, Vermont The increasing use
Chapter 2. Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties
 Chapter 2 Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties Table of Contents Pages 1. Introduction... 3 2. Rock and Minerals... 3 3. Porosity... 4 3.1. Porosity Classification... 6 3.2. Range of porosity values for
Chapter 2 Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties Table of Contents Pages 1. Introduction... 3 2. Rock and Minerals... 3 3. Porosity... 4 3.1. Porosity Classification... 6 3.2. Range of porosity values for
Vaahtorainauksen tutkimus VTT:n tutkimusympäristöissä
 Vaahtorainauksen tutkimus VTT:n tutkimusympäristöissä Metsäteollisuuspäivät Savonlinna 19.-20.9.2018 Harri Kiiskinen, VTT Harri.kiiskinen@vtt.fi Phone: +358 40 527 3853 18.09.2018 VTT beyond the obvious
Vaahtorainauksen tutkimus VTT:n tutkimusympäristöissä Metsäteollisuuspäivät Savonlinna 19.-20.9.2018 Harri Kiiskinen, VTT Harri.kiiskinen@vtt.fi Phone: +358 40 527 3853 18.09.2018 VTT beyond the obvious
Numerical Determination of Transport Properties of Catalyst Layer, Microporous Layer and Gas Diffusion Layer
 Numerical Determination of Transport Properties of Catalyst Layer, Microporous Layer and Gas Diffusion Layer Jürgen Becker, Math2Market GmbH, Kaiserslautern 10 th Symposium for Fuel Cell and Battery Modelling
Numerical Determination of Transport Properties of Catalyst Layer, Microporous Layer and Gas Diffusion Layer Jürgen Becker, Math2Market GmbH, Kaiserslautern 10 th Symposium for Fuel Cell and Battery Modelling
Research Article Development of Glass/Jute Fibers Reinforced Polyester Composite
 Indian Materials Science Volume 2013, Article ID 675264, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/675264 Research Article Development of / Fibers Reinforced Polyester Composite Amit Bindal, 1 Satnam Singh,
Indian Materials Science Volume 2013, Article ID 675264, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/675264 Research Article Development of / Fibers Reinforced Polyester Composite Amit Bindal, 1 Satnam Singh,
Diffusion of moisture and chloride ions in repaired concrete subjected to complex deterioration factors
 Journal of Asian Concrete Federation Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. -26, June 17 ISSN 246-7964 / eissn 246-7972 http://dx.doi.org/.1872/acf.17.6.3.1. Technical Paper Diffusion of moisture and chloride ions in repaired
Journal of Asian Concrete Federation Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. -26, June 17 ISSN 246-7964 / eissn 246-7972 http://dx.doi.org/.1872/acf.17.6.3.1. Technical Paper Diffusion of moisture and chloride ions in repaired
Numerical Evaluation of Effective Gas Diffusivity Saturation Dependence of Uncompressed and Compressed Gas Diffusion Media in PEFCs
 Numerical Evaluation of Effective Gas Diffusivity Saturation Dependence of Uncompressed and Compressed Gas Diffusion Media in PEFCs V. P. Schulz a, P. P. Mukherjee b, J. Becker a, A. Wiegmann a, and C.-Y.
Numerical Evaluation of Effective Gas Diffusivity Saturation Dependence of Uncompressed and Compressed Gas Diffusion Media in PEFCs V. P. Schulz a, P. P. Mukherjee b, J. Becker a, A. Wiegmann a, and C.-Y.
Gas measurement method and weighing method to measure the core porosity research and comparative analysis
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 50-0, ISSN (p): 78-879 Vol. 05, Issue 0 (March. 05), V PP 0-6 www.iosrjen.org Gas measurement method and weighing method to measure the core porosity research
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 50-0, ISSN (p): 78-879 Vol. 05, Issue 0 (March. 05), V PP 0-6 www.iosrjen.org Gas measurement method and weighing method to measure the core porosity research
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE WITH SAP PART I: DEVELOPMENT OF COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE WITH SAP PART I: DEVELOPMENT OF COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH Marianne Tange Hasholt (1), Morten H. Seneka Jespersen (1) and Ole Mejlhede Jensen (1) (1) Department of Civil Engineering,
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE WITH SAP PART I: DEVELOPMENT OF COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH Marianne Tange Hasholt (1), Morten H. Seneka Jespersen (1) and Ole Mejlhede Jensen (1) (1) Department of Civil Engineering,
CHAPTER - 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER - 1 INTRODUCTION 1. 1.1 Polymer Matrix Composites Composite materials are formed by combining two or more materials that have different properties. The constituent materials work together to give
CHAPTER - 1 INTRODUCTION 1. 1.1 Polymer Matrix Composites Composite materials are formed by combining two or more materials that have different properties. The constituent materials work together to give
SUPER ABSORBENT POLYMERS TO STIMULATE SELF HEALING IN ECC
 SUPER ABSORBENT POLYMERS TO STIMULATE SELF HEALING IN ECC J.S. Kim (1) and E. Schlangen (1) (1) Delft University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geoscience, Micromechanics Laboratory (MICROLAB),
SUPER ABSORBENT POLYMERS TO STIMULATE SELF HEALING IN ECC J.S. Kim (1) and E. Schlangen (1) (1) Delft University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geoscience, Micromechanics Laboratory (MICROLAB),
Chapter 7. Mechanical properties 7.1. Introduction 7.2. Stress-strain concepts and behaviour 7.3. Mechanical behaviour of metals 7.4.
 Chapter 7. Mechanical properties 7.1. Introduction 7.2. Stress-strain concepts and behaviour 7.3. Mechanical behaviour of metals 7.4. Mechanical behaviour of ceramics 7.5. Mechanical behaviour of polymers
Chapter 7. Mechanical properties 7.1. Introduction 7.2. Stress-strain concepts and behaviour 7.3. Mechanical behaviour of metals 7.4. Mechanical behaviour of ceramics 7.5. Mechanical behaviour of polymers
Large scale fire test on tunnel segment: Real boundary conditions in order to evaluate spalling sensitivity and fire resistance
 MATEC Web of Conferences 6, 04001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/20130604001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Large scale fire test on tunnel segment: Real boundary conditions in
MATEC Web of Conferences 6, 04001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/20130604001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Large scale fire test on tunnel segment: Real boundary conditions in
Forest Biomaterials in Canada: FPInnovations Scientific and Technical Expertise
 Forest Biomaterials in Canada: FPInnovations Scientific and Technical Expertise Jimmy Jong, PhD. Research Manager for Cellulosic Biomaterials FPInnovations, Canada For Oct. 11, 2017, Uruguay (Symposium
Forest Biomaterials in Canada: FPInnovations Scientific and Technical Expertise Jimmy Jong, PhD. Research Manager for Cellulosic Biomaterials FPInnovations, Canada For Oct. 11, 2017, Uruguay (Symposium
EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF THE DURABILITY OF CORK CONCRETE
 Int. Journal for Housing Science, Vol.32, No.2 pp. 149-162, 2008 Published in the United States EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF THE DURABILITY OF CORK CONCRETE Fernando G. Branco, António Tadeu CICC, Department
Int. Journal for Housing Science, Vol.32, No.2 pp. 149-162, 2008 Published in the United States EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF THE DURABILITY OF CORK CONCRETE Fernando G. Branco, António Tadeu CICC, Department
CMY Rev. 0. (01/2017).
 Folheto_Texart_S.pdf 1 09/01/2017 13:50:25 C M Y CM MY CY CMY 124999118. Rev. 0. (01/2017). K Textart is essentially a reinforced non-woven swab, that combines woven and non-woven technologies in a single
Folheto_Texart_S.pdf 1 09/01/2017 13:50:25 C M Y CM MY CY CMY 124999118. Rev. 0. (01/2017). K Textart is essentially a reinforced non-woven swab, that combines woven and non-woven technologies in a single
John F. Hunt, P.E. Forest Products Laboratory Madison, WI USA ABSTRACT
 3D Structural Panels: A Literature Review John F. Hunt, P.E. Forest Products Laboratory Madison, WI 53726 USA ABSTRACT The world population has surpassed the 6 billion mark and many of these people live
3D Structural Panels: A Literature Review John F. Hunt, P.E. Forest Products Laboratory Madison, WI 53726 USA ABSTRACT The world population has surpassed the 6 billion mark and many of these people live
Influence of CDW Recycled Aggregate on Drying Shrinkage of Mortar
 Open Journal of Civil Engineering, 2012, 2, 53-57 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojce.2012.22009 Published Online June 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojce) Influence of CDW Recycled Aggregate on Drying
Open Journal of Civil Engineering, 2012, 2, 53-57 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojce.2012.22009 Published Online June 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojce) Influence of CDW Recycled Aggregate on Drying
Use of Super Absorbing Polymers (SAP) for Internal Curing of Conventional Concrete with Low W/C Ratio
 Use of Super Absorbing Polymers (SAP) for Internal Curing of Conventional Concrete with Low W/C Ratio K. Letcham *** Assistant Professor in Civil Engineering, KPR Institute of Engineering & Technology,
Use of Super Absorbing Polymers (SAP) for Internal Curing of Conventional Concrete with Low W/C Ratio K. Letcham *** Assistant Professor in Civil Engineering, KPR Institute of Engineering & Technology,
Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers
 Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers S. Grigoriev a, I. Baranov a, P. Millet b, Z. Li c, V. Fateev a a Hydrogen Energy and Plasma Technology Institute of Russian Research
Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers S. Grigoriev a, I. Baranov a, P. Millet b, Z. Li c, V. Fateev a a Hydrogen Energy and Plasma Technology Institute of Russian Research
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 583 587 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 A
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 583 587 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 A
ESI s Composites Simulation Solution
 ESI s Composites Simulation Solution Integrated solution to simulate the manufacturing of structural composites components Dr. Xiaoshi Jin November 2015 1 Copyright ESI Copyright Group, 2015. ESI Group,
ESI s Composites Simulation Solution Integrated solution to simulate the manufacturing of structural composites components Dr. Xiaoshi Jin November 2015 1 Copyright ESI Copyright Group, 2015. ESI Group,
Defect Prediction in Composites Based on Numerical Simulation and Expertise Knowledge
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS Defect Prediction in Composites Based on Numerical Simulation and Expertise Knowledge Li YanXia*, LI Min, GU Yi-Zhuo, Sun Jing and ZHANG Zuo-Guang
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS Defect Prediction in Composites Based on Numerical Simulation and Expertise Knowledge Li YanXia*, LI Min, GU Yi-Zhuo, Sun Jing and ZHANG Zuo-Guang
Composite Materials. In depth look
 Composite Materials In depth look Classification of Composites Metals Materials Polymers Ceramics Composites Metal Matrix Composites Polymer Matrix Composites Ceramic Matrix Composites Classification of
Composite Materials In depth look Classification of Composites Metals Materials Polymers Ceramics Composites Metal Matrix Composites Polymer Matrix Composites Ceramic Matrix Composites Classification of
Lecture 5. Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC)
 Lecture 5 Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC) Surface Tension, Review Physical Model for Capillary The capillary model provides a mathematical relationship between the radius of curvature of the air-water
Lecture 5 Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC) Surface Tension, Review Physical Model for Capillary The capillary model provides a mathematical relationship between the radius of curvature of the air-water
WATER ABSORPTION OF SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS IN A CEMENTITIOUS ENVIRONMENT
 International RILEM Conference on Advances in Construction Materials through Science and Engineering 5-7 September 2011, Hong Kong, China WATER ABSORPTION OF SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS IN A CEMENTITIOUS ENVIRONMENT
International RILEM Conference on Advances in Construction Materials through Science and Engineering 5-7 September 2011, Hong Kong, China WATER ABSORPTION OF SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS IN A CEMENTITIOUS ENVIRONMENT
Abstract. ZAVERI, MITUL DILIP. Absorbency Characteristics of Kenaf Core Particles
 Abstract ZAVERI, MITUL DILIP. Absorbency Characteristics of Kenaf Core Particles (Under the direction of Dr. Behnam Pourdeyhimi). Chopped kenaf core (2 to 4 in length), obtained from Greene Natural Fibers
Abstract ZAVERI, MITUL DILIP. Absorbency Characteristics of Kenaf Core Particles (Under the direction of Dr. Behnam Pourdeyhimi). Chopped kenaf core (2 to 4 in length), obtained from Greene Natural Fibers
POROSITY, SPECIFIC YIELD & SPECIFIC RETENTION. Physical properties of
 POROSITY, SPECIFIC YIELD & SPECIFIC RETENTION Porosity is the the ratio of the voids to the total volume of an unconsolidated or consolidated material. Physical properties of n = porosity as a decimal
POROSITY, SPECIFIC YIELD & SPECIFIC RETENTION Porosity is the the ratio of the voids to the total volume of an unconsolidated or consolidated material. Physical properties of n = porosity as a decimal
SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES GROUNDWATER. Instructor. Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ
 SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES GROUNDWATER Instructor Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus SEES 503 Sustainable Water
SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES GROUNDWATER Instructor Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus SEES 503 Sustainable Water
VOID FORMATION IN AN ANISOTROPIC WOVEN FIBER DURING RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS VOID FORMATION IN AN ANISOTROPIC WOVEN FIBER DURING RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING Daigo Seto 1*, Ryosuke Matsuzaki, Akira Todoroki 1, Yoshihiro Mizutani 1
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS VOID FORMATION IN AN ANISOTROPIC WOVEN FIBER DURING RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING Daigo Seto 1*, Ryosuke Matsuzaki, Akira Todoroki 1, Yoshihiro Mizutani 1
This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT
 This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Foam forming - potential production technology for building materials Author(s) Jetsu, Petri; Pöhler, Tiina Citation 12th
This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Foam forming - potential production technology for building materials Author(s) Jetsu, Petri; Pöhler, Tiina Citation 12th
Influence of Angle Ply Orientation on Tensile Properties of Carbon/Glass Hybrid Composite
 Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 2013, 1, 231-235 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2013.15036 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmmce) Influence
Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 2013, 1, 231-235 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2013.15036 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmmce) Influence
PLASMA SURFACE TREATMENT OF POLYPROPYLENE REINFORCING FIBRES BY DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE
 PLASMA SURFACE TREATMENT OF POLYPROPYLENE REINFORCING FIBRES BY DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE T. Morávek, J. Ráhel Masaryk University, Faculty of Science, Brno, Czech Republic. Z. Szalay Comenius University,
PLASMA SURFACE TREATMENT OF POLYPROPYLENE REINFORCING FIBRES BY DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE T. Morávek, J. Ráhel Masaryk University, Faculty of Science, Brno, Czech Republic. Z. Szalay Comenius University,
STANDARDIZATION IN GEOTECH SECTOR V.K.PATIL
 STANDARDIZATION IN GEOTECH SECTOR V.K.PATIL BOMBAY TEXTILE RESEARCH ASSOCIATION L.B.S.MARG, GHATKOPAR (W),MUMBAI-400086. WEB : btraindia.com e-mail : btra@vsnl.com What are Standards? Standards are published
STANDARDIZATION IN GEOTECH SECTOR V.K.PATIL BOMBAY TEXTILE RESEARCH ASSOCIATION L.B.S.MARG, GHATKOPAR (W),MUMBAI-400086. WEB : btraindia.com e-mail : btra@vsnl.com What are Standards? Standards are published
Research Article Evaluation and Injection Parameter Optimization for Polymer Flooding with Different Kinds of Profile Control Agents
 Chemistry Volume, Article ID 75, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//75 Research Article Evaluation and Injection Parameter Optimization for Polymer Flooding with Different Kinds of Profile Control Agents Yikun
Chemistry Volume, Article ID 75, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//75 Research Article Evaluation and Injection Parameter Optimization for Polymer Flooding with Different Kinds of Profile Control Agents Yikun
ASE SYSTEMS. EPOXY RESIN FLOOR Prep / REPAIR SYSTEM For Air Caster Load Moving Equipment
 ASE SYSTEMS The Ergonomics & Productivity Specialists! 5611 Guhn Road Ste: A1 * Houston Texas 77040 *al@asesystems.com 713-462-3072 * fax: 713-462-3540 * www.asesystems.com The following Epoxy Resins &
ASE SYSTEMS The Ergonomics & Productivity Specialists! 5611 Guhn Road Ste: A1 * Houston Texas 77040 *al@asesystems.com 713-462-3072 * fax: 713-462-3540 * www.asesystems.com The following Epoxy Resins &
Analysis of the Gas Diffusion Layer in a PEM Fuel Cell Teng Zhang, E.Birgersson
 Analysis of the Gas Diffusion Layer in a PEM Fuel Cell Teng Zhang, E.Birgersson Engineering Science Programme, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 7546 ABSTRACT
Analysis of the Gas Diffusion Layer in a PEM Fuel Cell Teng Zhang, E.Birgersson Engineering Science Programme, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 7546 ABSTRACT
SOLUTION IMPREGNATION OF NATURAL FIBRES/ABS MATRIX COMPOSITES
 SOLUTION IMPREGNATION OF NATURAL FIBRES/ABS MATRIX COMPOSITES M. Durante, C. Leone, M. Ussorio, I. Crivelli Visconti 1 Department of Materials and Production Engineering, University of Naples "Federico
SOLUTION IMPREGNATION OF NATURAL FIBRES/ABS MATRIX COMPOSITES M. Durante, C. Leone, M. Ussorio, I. Crivelli Visconti 1 Department of Materials and Production Engineering, University of Naples "Federico
DRILLING FLUIDS & SEALANTS Producers of Bentonite Sealants, Drilling Fluids & Additives with Worldwide Distribution
 DRILLING FLUIDS & SEALANTS Producers of Bentonite Sealants, Drilling Fluids & Additives with Worldwide Distribution BENTONITE SEALANTS GRANULAR SEAL (8 mesh) Granulated bentonite that contains no additives.
DRILLING FLUIDS & SEALANTS Producers of Bentonite Sealants, Drilling Fluids & Additives with Worldwide Distribution BENTONITE SEALANTS GRANULAR SEAL (8 mesh) Granulated bentonite that contains no additives.
DEVELOPMENT AND STUDY OF ANTI-NOISE BARRIERS BASED ON ALTERNATIVE RAW MATERIAL SOURCES
 DEVELOPMENT AND STUDY OF ANTI-NOISE BARRIERS BASED ON ALTERNATIVE RAW MATERIAL SOURCES Jiri ZACH (1), Jiri BROZOVSKY (1), and Jitka HROUDOVA (1) (1) Brno University of technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT AND STUDY OF ANTI-NOISE BARRIERS BASED ON ALTERNATIVE RAW MATERIAL SOURCES Jiri ZACH (1), Jiri BROZOVSKY (1), and Jitka HROUDOVA (1) (1) Brno University of technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
VOID FORMATION DURING PREFORM IMPREGNATION IN LIQUID COMPOSITE MOLDING PROCESSES
 VOID FORMATION DURING PREFORM IMPREGNATION IN LIQUID COMPOSITE MOLDING PROCESSES C. DeValve and R. Pitchumani Advanced Materials and Technologies Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Virginia
VOID FORMATION DURING PREFORM IMPREGNATION IN LIQUID COMPOSITE MOLDING PROCESSES C. DeValve and R. Pitchumani Advanced Materials and Technologies Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Virginia
INVESTIGATING REASONS FOR FILTER BAG FAILURE AND DEVELOPING A METHOD TO IMPROVE ITS LIFE SPAN
 INVESTIGATING REASONS FOR FILTER BAG FAILURE AND DEVELOPING A METHOD TO IMPROVE ITS LIFE SPAN Dr. İbrahim ÇAKMANUS FFT FAN FİLTER SYSTEM CO. LTD. www.filtrefan.com. ABSTRACT This paper reports a study
INVESTIGATING REASONS FOR FILTER BAG FAILURE AND DEVELOPING A METHOD TO IMPROVE ITS LIFE SPAN Dr. İbrahim ÇAKMANUS FFT FAN FİLTER SYSTEM CO. LTD. www.filtrefan.com. ABSTRACT This paper reports a study
A Study of Two-Phase Flow in a Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Tang.M.Z, K.E.Birgersson
 A Study of Two-Phase Flow in a Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Tang.M.Z, K.E.Birgersson Engineering Science Programme, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Singapore, 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore
A Study of Two-Phase Flow in a Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Tang.M.Z, K.E.Birgersson Engineering Science Programme, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Singapore, 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore
Keywords: Drying Shrinkage of Concrete, Autogenous Shrinkage, Design Shrinkage Strain
 A Discussion on the Shrinkage Interpretation from the Experimental Shrinkage Measurement Based on the Australian Testing Procedure AS1012.13 William A. Thomas¹, James Mohammadi² and Dr Warren South³ ¹Chief
A Discussion on the Shrinkage Interpretation from the Experimental Shrinkage Measurement Based on the Australian Testing Procedure AS1012.13 William A. Thomas¹, James Mohammadi² and Dr Warren South³ ¹Chief
CFD analysis of Metallic Foam-Filled Triple Tube Concentric Heat Exchanger
 CFD analysis of Metallic Foam-Filled Triple Tube Concentric Heat Exchanger Abstract Mishra Roshan *, Chaudhari Kiran # * Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, University
CFD analysis of Metallic Foam-Filled Triple Tube Concentric Heat Exchanger Abstract Mishra Roshan *, Chaudhari Kiran # * Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, University
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING CYCLE WITH DUAL- INITIATOR SYSTEMS
 FPCM-9 (2008) The 9 th International Conference on Flow Processes in Composite Materials Montréal (Québec), Canada 8 ~ 10 July 2008 NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING CYCLE
FPCM-9 (2008) The 9 th International Conference on Flow Processes in Composite Materials Montréal (Québec), Canada 8 ~ 10 July 2008 NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF RESIN TRANSFER MOLDING CYCLE
Ceramic and glass technology
 1 Row materials preperation Plastic Raw materials preperation Solid raw materials preperation Aging wet milling mastication Mixing seving Grain size reduction Milling Crushing Very fine milling Fine milling
1 Row materials preperation Plastic Raw materials preperation Solid raw materials preperation Aging wet milling mastication Mixing seving Grain size reduction Milling Crushing Very fine milling Fine milling
Shrinkage Development in High Performance Concrete. Ammar Yahia, P.Eng., Ph.D.,
 Shrinkage Development in High Performance Concrete Ammar Yahia, P.Eng., Ph.D., Outlines 1. Introduction 2. High-performance concrete 3. Autogenous shrinkage 4. Autogenous shrinkage stress 5. Autogenous
Shrinkage Development in High Performance Concrete Ammar Yahia, P.Eng., Ph.D., Outlines 1. Introduction 2. High-performance concrete 3. Autogenous shrinkage 4. Autogenous shrinkage stress 5. Autogenous
Prediction of the spatial occurrence of fire induced spalling in concrete slabs using random fields
 MATEC Web of Conferences 6, 05004 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/20130605004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Prediction of the spatial occurrence of fire induced spalling in concrete
MATEC Web of Conferences 6, 05004 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/20130605004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Prediction of the spatial occurrence of fire induced spalling in concrete
The absorbent solutions provider
 Welcome The absorbent solutions provider The mission of Technical Absorbents (TAL) is to offer a truly world class level of innovation, development and supply of super absorbent products, precisely tailored
Welcome The absorbent solutions provider The mission of Technical Absorbents (TAL) is to offer a truly world class level of innovation, development and supply of super absorbent products, precisely tailored
