INTRODUCTION. Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 18, Issue 1, Jan. 2017, pages DOI: / /66243.
|
|
|
- Norman Clifton Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 18, Issue 1, Jan. 2017, pages DOI: / /66243 Research Article THE EFFECT OF ORGANIC FERTILISATION OF LIQUID MANURE AND THE PRP FIX PREPARATION ON THE YIELD AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF WINTER RAPE SEEDS AND SPRING WHEAT GRAIN Ewa Możdżer 1, Edward Meller 1, Adam Sammel 1 1 Department of Soil Science, Grassland Management and Environmental Chemistry Faculty of Environmental Management and Agriculture, Western Pomeranian University of Technology in Szczecin, Słowackiego 17 Str., Szczecin, Poland, ewa.mozdzer@zut.edu.pl Received: Accepted: Published: ABSTRACT In , a field experiment was carried out at the Experimental Station of Cultivar Evaluation in Szczecin-Dąbie. The experiment aimed at determining the effect of slurry without and with addition of increasing PRP Fix preparation doses on the crop yields and some of their qualitative traits. The soil where the experiment was set up was slightly acidic (ph KCL 5.95); nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents were 0.86, 1.55 and 2.70 g kg -1 d.m., respectively. The total content of macro-elements for this type of soil was average. The content of bioavailable forms of phosphorus, magnesium and sulphur was average, while that of potassium was high. The content of organic carbon in soil was low, while the C:N ratio was 10.2:1 and was average for that type of soils. The obtained results show that the applied with slurry combined with PRP Fix preparation and PK increased the yield of winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain and the content of macro-elements being examined in them. The yields of the test plants were larger in the objects where with slurry with addition of 8 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry was applied, when compared to those where only mineral or slurry was used. Winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain usually contained more nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium and sulphur in the objects being fertilised with slurry with PRP Fix preparation in the amount of 8 or 12 kg per 1 m 3 slurry with additional PK (experimental series II) compared to experimental series I without additional PK. Differences in the content of macro-elements in test plants after application of the scheme being used varied. These differences were not always significant. Keywords: slurry, PRP Fix, crops, content of macro-elements, rape seeds, wheat grain INTRODUCTION Over the last dozen or so years, the production of natural fertilisers in Poland has decreased, as well as the range of mineral fertilisers has changed and their prices have increased very clearly. As a result of these circumstances, the doses of natural and mineral fertilisers per unit area have been reduced. This may lead to a reduction in soil fertility and productivity. These arguments have contributed to searching for new, moderately cheap and environmentally sound sources of organic matter and nutrients for plants [Krzywy 2005, Możdżer and Krzywy 2014]. At present, there are large amounts of slurry produced, the chemical composition of which indicates the possibility of using it for purposes. The use by plants is high because most of the nutrient is present in the form of the mineral, eg. nitrogen derived from slurry is better used by plants than from manure [Schepers and et al. 139
2 2008]. According to applicable legislation, slurry cannot be introduced into soil from early November to late February [Journal of Laws, 2008, No. 119, item 765]. Therefore, farms should be equipped with tanks of adequate capacity to store it at that time. Improper storage and use of slurry in spring, summer and autumn may result in environmental pollution (air, soil and water) and contribute to a reduction in plant crop quality. Properly stored slurry with simultaneous recovery of biogas has broad economic and ecological benefits, which inlude a reduction of odors [Nettmann and et. 2010]. According to the date presented by a French company Procedes Roland Pigeon, PRP Fix preparation being produced by it reduces odour emissions to atmosphere by 30% (including NH 3, H 2 S and CH 4 ), increases the manurial value of animal dung, stimulates development of aerobic microorganisms in soils which decompose organic matter, and positively affects the environment. Taking the above data into account, the study was undertaken which aimed at determining the effect of slurry with addition of increasing PRP Fix preparation doses on winter rape and spring wheat yields and some of their qualitative traits. MATERIAL AND RESEARCH METHODS A field vegetation experiment was carried out at the Experimental Station of Cultivar Evaluation in Szczecin-Dąbie in The experiment aimed at determining the effect of slurry without and with addition of increasing PRP Fix preparation doses on the crop yield and qualitative traits and soil fertility indicators. The Experimental Station of Cultivar Evaluation in Szczecin-Dąbie is situated in the southeastern part of the city of Szczecin. The land of the ESCE in Szczecin-Dąbie belongs to very good, good and poor rye complexes of agricultural suitability, and IV a to VI soil quality classes. The experimental soil was characterised by slightly acidic reaction (ph KCL 5.95); total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents were 0.86, 1.55 and 2.70 g kg -1 d.m., respectively. The total content of macro-elements for this type of soil was average. The content of bioavailable forms of phosphorus, magnesium and sulphur was average (55.3, 49.3 and 11.0 mg kg -1 d.m., respectively), while that of potassium was high (132 mg kg -1 d.m.). The content of organic carbon in soil was low (8.80 g kg -1 d.m), while the C:N ratio was 10.2:1 and was average for that type of soils. In early autumn 2011, a two-factor field experiment was set up according to a design presented in Table 1. The dose of slurry introduced into soil in experimental series I and II was determined based on its nitrogen content which corresponded to 100 kg N ha -1. Slurry without and with increasing doses of PRP Fix preparation was introduced on experimental plots on the following dates on for winter rape and on for spring wheat. Three days after slurry input to soil, mineral was applied according to the study design. Table 1 presents the scheme of the experiment being carried out. In spring 2012 and 2013, top dressing with nitrogen in the form of urea (46% N), at a dose of 45 kg N ha -1 for winter rape and 30 kg N ha -1 for spring wheat each, was applied on all objects of experiment series I and II. In experimental series II, based on phosphorus and potassium contents in slurry, additional mineral was determined which amounted to 90 kg P 2 O 5 ha -1 in the form of granular triple super phosphate, containing 46% P 2 O 5, which corresponded to a dose of 0.65 kg per plot and 100 kg K 2 O ha -1 in the form of potassium chloride (KCl), containing 60% K 2 O, which corresponded to a dose of 0.55 kg KCl. Test plants was winter rape, cultivar PR 46 W14, in , and spring wheat, cultivar Bombona, in Table 1. Testing diagram Fertilisation objects without additional mineral with additional PK Mineral fertilisers corresponding to a slurry dose + + Slurry without PRP Fix + + Slurry + 4 kg of PRP Fix + + Slurry + 8 kg of PRP Fix + + Slurry + 12 kg of PRP Fix
3 After agro-technical treatments and application of fertilisers, winter rape seeds, cultivar PR 46 W14, were sown on , and spring wheat grain, cultivar Bombona, on Winter rape was harvested on , while spring wheat on Each year, after reaching production maturity by test plants, they were harvested and crop yield was determined in Mg ha -1. From each replications for a given object, a sample of winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain was collected. An average sample was prepared which were subjected to laboratory examination. Spring wheat and winter rape straws were not sampled for examination because they were left on experimental plots as a source of organic matter for soil. The samples of winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain were dried and ground. Thereafter, they were combined, forming average samples from four replications for each object. The average samples of test plants were subjected to chemical analyses in three replications. In the plant material, dry matter was determined by oven-dry method at C, nitrogen by Kjeldahl distillation method after mineralisation in concentrated sulphuric(vi) acid PN-75/A-04018/Az 3, phosphorus by the method of Burton, potassium and calcium by flame spectrophotometry after wet mineralisation, total sulphur by nephelometric method, magnesium by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) PN-EN ISO and PN-EN ISO after wet mineralisation in the mixture of nitric(v) acid and chloric(vii) acid in a 3:1 ratio. The yield of winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain and the content of macro-elements were analysed statistically. Two-factor analysis of variance for the split-block design was used in statistical calculations. Confidence semi-intervals were determined for p = 0.05, using the Tuckey s test. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION When analysing the yield of winter rape seeds obtained in 2012, it was shown that its highest yields in experimental series I without additional mineral were observed in the object with slurry without addition of PRP Fix preparation ( object 2) and next in that with slurry with 8 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry ( object 4). These yields were significantly higher compared to those from other objects. The significantly lowest yield of winter rape seeds was obtained after application of slurry with addition of 12 kg PRP Fix per 1 m 3 slurry (Table 2). Additional mineral in experimental series II (PK ) increased the yield of winter rape seeds by 7.60% compared to experimental series I without these fertilisers. In this experimental series, the highest yield of winter seed seeds was obtained after application of slurry with addition of 8 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry ( object 9). This yield was significantly higher compared to those from other objects. The highest yield of spring wheat grain (in 2013) was obtained after application of slurry with addition of 4 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry ( object 8) in experimental series II. This yield was significantly higher compared to those of other objects. A significantly lower yield of spring wheat grain was obtained after application of slurry in the where 12 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry was introduced ( object 5) Table 2. An addition of mineral fertilisers significantly increased the yield of its grain in all objects. In experimental series II, where additional PK was applied, the highest yields of spring wheat grain were obtained after application of slurry with addition of 4 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry ( object 8), while the least one after application of slurry with addition of 12 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry ( object 10). An increase in the yield of spring wheat grain between these objects was 11.2%. Differences in the yield of spring wheat grain between particular objects were significant. An average increase in the yield of spring wheat grain between experimental series I and II amounted to 12.5%. On the other hand, the biggest difference in the yield of spring wheat grain was obtained between objects 1 and 6 (17.7%). On average, more powerful effects in the yields of these test plants were obtained in experimental series II (with PK ) Table 2. Fertilisation with slurry with addition of PRP Fix preparation and combined application of PK fertilisers not only had a favourable effect on the yield of winter rape and spring wheat but also positively affected the quality of test plant seeds and grain. The yield-forming effect of biological [organic] on cultivated plants has been 141
4 Table 2. The influence of the liquid manure and the PRP Fix preparation on crop volume of the winter rape seeds of PW 46 W 14 subspecies and spring wheat of Bombona subspecies in Mg ha -1 obtained with influence of the liquid manure and the PRP Fix preparation Exsperiment series Without PK With additional PK LSD 0,05 for: I-dose PRP Fix II- with and without of PK interaction Fertilisation objects Yares of study rape seeds wheat grain mean mean * Explanation of objects experimental series I: 1 mineral fertilisers corresponding to a slurry dose, 2 slurry without PRP Fix, 3 slurry + 4 kg PRP Fix, 4 slurry + 8 kg PRP Fix, 5 slurry + 12 kg PRP Fix; experimental series II: 6 mineral fertilisers corresponding to a slurry dose with additional PK, 7 slurry without PRP Fix + PK, 8 slurry+ 4 kg PRP Fix + PK, 9 slurry + 8 kg PRP Fix + PK, 10 slurry + 12 kg PRP Fix + PK confirmed by the studies conducted by Jamroz et al. [2004] and Łabętowicza et al. [2000]. The results of this study are also confirmed by the experiments of Kalembasy and Kuziemskiej [1993], Harasimowicz-Herman and Herman [2004]. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF TEST PLANTS Literature data show that excessive content or deficiency of macro-elements in plants, obtained as a result of, decreases the fodder and nutritional quality of crop yields [Ciećko and Harnisz 2002, Czyżyk and Strzelczyk 2008, Lipiński 2007, Mattsson 1999]. Table 4 presents average contents of macroelements in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain according to Panak [1995], whereas the recorded contents of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulphur in test plants obtained in 2012 and 2013 are compared in Tables 4, 5 and 6. When comparing the results obtained in this study (Table 5 to 7) with the data from Table 3, it can be conclude that: contents of macro-elements in winter rape seeds were lower than the average values given in Table 3, whereas those in spring wheat grain were higher (Table 4 to 6), magnesium, calcium and sulphur contents in winter rape seeds were lower, whereas nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium ones were larger (Table 4 and 5) compared to the average values given in Table 3, spring wheat grain contained more nitrogen and potassium (except objects 1, 2 and 3) and less phosphorus and calcium (except objects 9 and 10) and magnesium compared to the average values given in Tables 3 and 6. The content of potassium and magnesium in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain was within average content range with an upward trend, that of calcium in winter rape seeds was lower than the average value, and sulphur content in spring wheat grain was within average content range or slightly higher only in objects with addition of PK (experimental series II), whereas in winter rape seeds was lower. 142
5 Table 3. Average nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulphur contents in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain in g kg -1 d.m. [Panak 1995] Plant nitrogen phosphorus potassium calcium magnesium sulphur Rape Wheat Table 4. Content of nitrogen and phosphorus in the winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain obtained due to influence of the liquid manure and PRP Fix preparation Exsperiment series Without PK With additional PK LSD 0,05 for: I-dose PRP Fix II- with and without of PK interaction Fertilisation objects nitrogen total content in g kg -1 d.m. phosphorus winter rape wheat grain winter rape wheat grain mean mean * Explanation of objects is given under Table Table 5. Content of phosphorus and calcium in the winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain obtained due to influence of the liquid manure and PRP Fix preparation Exsperiment series Without PK With additional PK LSD 0,05 for: I-dose PRP Fix II- with and without of PK interaction Fertilisation objects phosphorus total content in g kg -1 d.m. calcium winter rape wheat grain winter rape wheat grain mean mean * Explanation of objects is given under Table
6 Table 6. Content of magnesium and sulphur in the winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain obtained due to influence of the liquid manure and PRP Fix preparation Exsperiment series Without PK With additional PK LSD 0,05 for: I-dose PRP Fix II- with and without of PK interaction Fertilisation objects magnesium total content in g kg -1 d.m. sulphur winter rape wheat grain winter rape wheat grain mean mean * Explanation of objects is given under Table When analysing the effect of slurry with PRP Fix preparation in the amount of 8 kg per 1 m 3 slurry, both in experimental series I and II, an increase was observed in nitrogen content in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain between objects 4 and 9, by 2.79% and 1.75%, respectively (Tab. 4). The highest increase in nitrogen content in winter rape seeds was obtained between object 2 (slurry without PRP Fix) and object 9 (slurry + 8 kg PRP Fix + PK), by 4.62%, whereas in spring wheat grain between objects 1 and 9, by 5.43%. The results of this study show that PK applied with PRP Fix preparation in experimental series II contributed to an increase in nitrogen content in winter rape seeds by 7.10% compared to experimental series I. On the other hand, an increase in nitrogen content in spring wheat grain between experimental series I and II was slight (Table 4). The highest increase in phosphorus content was obtained in winter rape seeds between object 1 and object 9, by 17.8%, whereas in spring wheat grain between objects 1 and 10, by 9.42% (Table 4). When comparing experimental series I with experimental series II, it can be conclude that additional PK with PRP Fix preparation induced an increase in phosphorus content in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain by 13.6% and 2.32%, respectively. In the objects with slurry combined with PRP Fix preparation in experimental series I and II ( objects 3, 4, 5, 8, 9 and 10), potassium content in test plants increased compared to object 1 (Table 5). The application of slurry with addition of PRP Fix in the amount of 8 kg per 1 m 3 slurry in experimental series I and II contributed to an increase in potassium content in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain between object 4 and object 9 by 7.69% and 14.2%, respectively. The highest increase in the content of chemical element being discussed was observed in test plants between objects 1 and 9, by 12.0% and 22.0%, respectively. On the other hand, the lowest potassium level was obtained in the object where only mineral was applied corresponding to a slurry dose introduced into soil ( object 1). Summing up, it can be concluded that there was an average drop in potassium content in winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain between experimental series I and II, by 9.44% and 12.8%, respectively. Slurry with PRP Fix preparation in the amount of 12 kg per 1 m 3 slurry in experimental series I and II induced an increase n calcium content in winter rape seeds between objects 5 and 10, by 6.22% (Table 5). The highest increase in the content of chemical element under discussion was observed both in winter rape seeds and 144
7 spring wheat grain between objects 1 and 9, by 13% and 40.9%, respectively. An average increase in calcium content in spring wheat grain by 12.2% was observed between experimental series I and II. The highest increase in magnesium content was obtained in winter rape seeds between object 1 and object 9, by 5.70%, whereas in spring wheat grain between by 25.4% (Table 6).When comparing experimental series I with experimental series II, it was found that additional PK with PRP Fix preparation contributed to an increase in magnesium content in both test plants to a small extent (3.28% and 2.50%). Slurry with PRP Fix preparation in the amount of 8 and 12 kg per 1 m 3 slurry in experimental series I and II induced and increase in sulphur content in spring wheat grain between objects 4 and 9 and objects 5 and 10, by 5.62 and 5.1%, respectively (Tab. 6). On the other hand, when analysing the content of sulphur in winter rape seeds, there was an increase in it at almost the same level in objects 4, 5, 9 and 10 compared to object 1. It was found that an average increase in sulphur content occurred in spring wheat grain between experimental series I and II, by 3.97%, whereas its increase in winter rape seeds remained at the same level of 12.4 g kg -1 d.m. Both in experimental series I and II, without and with additional PK, the highest content of macro-elements (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium calcium, magnesium and sulphur) was observed in test plants from the object where slurry with addition of 8 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry was applied. The lowest level of macro-elements being discussed was observed in object 1 (only mineral corresponding to a slurry dose being introduced into soil). Differences in the content of macro-elements in test plants after application of the scheme being used varied. These differences were not always significant. Taking into account the findings of Korzeniowska and Stanisławska-Glubiak [2007], Mazur and Maćkowiak [1998], Krzywy [2005], Kutera [2004] and Maćkowiak [2000], as well as Mercik et al. [2003], which characterise the indicators of crop yield quality depending on the content of micro-elements in plants, it can be concluded that supplementary phosphorus and potassium with increasing PRP Fix preparation doses had no negative effect on the quality of harvested test plant yields. CONCLUSIONS 1. The applied with slurry combined with PRP Fix preparation and PK increased the yields of test plants (winter rape seeds and spring wheat grain) and the content of macro-elements in them (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium calcium, magnesium and sulphur). 2. The yields of test plants were larger in the objects where with slurry with addition of 8 kg PRP Fix preparation per 1 m 3 slurry was applied compared to those where only mineral or slurry was used ( objects 1 and 2). 3. Test plants usually contained more nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium and sulphur in the objects being fertilised with slurry with PRP Fix preparation in the amount of 8 or 12 kg per 1 m 3 slurry with additional PK (experimental series II) than in experimental series I without additional PK. 4. The applied scheme had no significant effect on an increase in sulphur content in winter rape seeds between experimental series I and II. 5. The yields of test plants and the content of macro-elements in them depended to a large extent on the content of macro-elements in slurry and mineral fertilisers (additional PK experimental series II). Acknowledgements The study performed within the project of NCN no N N REFERENCES 1. Ciećko Z., Harnisz M., The impact of compost from sewage sludge on the content of potassium, calcium and magnesium MW of selected crops. Zesz. Prob. Post. Nauk Rol. 484(1), [In Polish] 2. Czyżyk F., Strzelczyk M., Pollution of the aquatic environment due to the use of manure on the soil light and heavy. Wyd. IMUZ [In Polish] 3. Harasimowicz-Hermann G., Hermann J., Comparison of subsequent bovine manure and compost from municipal sludge Biotope in the 145
8 cultivation of wheat Zesz. Prob. Post. Nauk Rol., 499, [In Polish] 4. Jamroz E., Drozd J., Licznar M., Weber J., The influence of soil fertilization with compost from municipal waste (KOM) on the yield and quality PTSH. Praca zbiorowa. Red. J. Drozd, [In Polish] 5. Kalembasa S., Kuziemska B., The impact of the origin and date of application of sewage sludge on the yield of some crops on the soil medium. Zesz. Prob. Post. Nauk Rol. 409, [In Polish] 6. Krzywy E., The slurry again. Wyd. Sigma Aura 4, [In Polish] 7. Kutera J., Gospodarka gnojowicą. Wrocław. Wyd. AR Wroc. pp Lipiński W., The ph of the soil and wealth in the light of the chemical-agricultural station. Nawozy i nawożenie. 3A, [In Polish] 9. Łabętowicz J., Ożararowski G., Comparison of compost from municipal waste (Dano) and manure and the terms of the influence on the yield and content of heavy metals in plants. Folia Univ. Agric. Stetin. Agricultura 211(84), [In Polish] 10. Maćkowiak Cz Slurry properties and rules for the application of environmental protection. Mater. Szkol. 75 Puławy IUNG, [In Polish] 11. Mattsson L., Systems of plant nutrient application and their impacts on soil fertility development at three Swedish long-term experimental sites. Zesz. Probl. Post. Nauk Rol. 465, Mazur T., Maćkowiak M., Nawożenie gnojowicą. Application of slurry. PWRiL 13. Mercik M., Sommer K., Rossing K., Standards assessment of nutritional status of winter wheat in different stages of development method DRIS. Rocz. Nauk. Rol. Ser. AT 110(1 2), [In Polish] 14. Możdżer E. Krzywy E., The impact of the active substance PRP Fix added to the slurry from pig to issue fetorów during storage and after the introduction of the soil on the size and quality of crop yields and soil environment. Sprawozdanie końcowe z projektu badawczego NCN nr N pp. 94. [In Polish] 15. Nettmann E., Bergman I., Pramschűfer S., Mundt K., Plogsties V., Hermann C., Klocke M., Ployphasic analyses of methanogenic archael communities in agricultural biogas plants. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, Panak H.,1995. Methodological Guide to the exercise of agricultural chemistry. Wyd. ART. Olsztyn, pp [In Polish] 17. Schepers J.S., Raun W., Nitrogen in agricultural systems. Agronomy Monograph, 49, Stanisławska-Glubiak E., Korzeniowska J., Principles of fertilization with microelements crops. Studia i Raporty. IUNG-POB Puławy, [In Polish] 146
Scientific registration n o : 2587 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation: poster. OLEK Jolanta, FILIPEK Tadeusz
 Scientific registration n o : 587 Symposium n o : 5 Presentation: poster Content and uptake of cadmium and lead by spring under conditions of sewage application Contenu et consommation de cadmium et plomb
Scientific registration n o : 587 Symposium n o : 5 Presentation: poster Content and uptake of cadmium and lead by spring under conditions of sewage application Contenu et consommation de cadmium et plomb
Crop Research Institute in Prague, Drnovská 507/73, Prague 6, Czech Republic
 TESTING OF SOIL PROPERTIES BASIC TOOL FOR RATIONAL NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT IN AGRICULTURE Pavel Čermák 1, Věra Přenosilová 1, Gabriela Mühlbachová 1, Tomáš Lošák 2, Jaroslav Hlušek 2 1 Crop Research Institute
TESTING OF SOIL PROPERTIES BASIC TOOL FOR RATIONAL NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT IN AGRICULTURE Pavel Čermák 1, Věra Přenosilová 1, Gabriela Mühlbachová 1, Tomáš Lošák 2, Jaroslav Hlušek 2 1 Crop Research Institute
Application of meat and bone meals in agricultural ecosystems and their effect on the aquatic environment
 Ecosystems and Sustainable Development VII 449 Application of meat and bone meals in agricultural ecosystems and their effect on the aquatic environment A. Stepien 1 & S. Szymczyk 2 1 Department of Agriculture
Ecosystems and Sustainable Development VII 449 Application of meat and bone meals in agricultural ecosystems and their effect on the aquatic environment A. Stepien 1 & S. Szymczyk 2 1 Department of Agriculture
THE USE OF COVER CROPS AFTER A MAIZE CROP IN THE NORTH OF SPAIN. Dpto. Biología Vegetal y Ecología, UPV. Apdo. 644, Bilbao, Spain.
 ID # 04-03 THE USE OF COVER CROPS AFTER A MAIZE CROP IN THE NORTH OF SPAIN D. Báez 1, M. Pinto 1, M. Rodríguez 2, G. Besga 1 and J. M Estavillo 3 1 NEIKER, Berreaga 1,48160 Derio, Spain 2 Dpto. Sanidad.
ID # 04-03 THE USE OF COVER CROPS AFTER A MAIZE CROP IN THE NORTH OF SPAIN D. Báez 1, M. Pinto 1, M. Rodríguez 2, G. Besga 1 and J. M Estavillo 3 1 NEIKER, Berreaga 1,48160 Derio, Spain 2 Dpto. Sanidad.
Managing nutrient needs in organic farming. Judith Nyiraneza
 Managing nutrient needs in organic farming Judith Nyiraneza Managing nutrient supply One of the main challenge facing the organic farmer: In short-term: supply sufficient nutrient to the crop to achieve
Managing nutrient needs in organic farming Judith Nyiraneza Managing nutrient supply One of the main challenge facing the organic farmer: In short-term: supply sufficient nutrient to the crop to achieve
Dynamics of the soil organic matter in crop rotation and long-term monoculture
 Dynamics of the soil organic matter in crop rotation and long-term monoculture B. Rychcik, J. Adamiak, H. Wójciak University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland ABSTRACT The field experiment, focused
Dynamics of the soil organic matter in crop rotation and long-term monoculture B. Rychcik, J. Adamiak, H. Wójciak University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland ABSTRACT The field experiment, focused
Piotr Szulc, 2 Jan Bocianowski. Department of Agronomy, Poznań University of Life Sciences, Dojazd 11, Poznań, Poland 2
 65 Polish Journal of Agronomy 212, 11, 65 8 Effects of application of different nitrogen fertilizer forms and magnesium on dynamics of dry matter accumulation in two maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids in their
65 Polish Journal of Agronomy 212, 11, 65 8 Effects of application of different nitrogen fertilizer forms and magnesium on dynamics of dry matter accumulation in two maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids in their
Wiśniewska-Kadżajan et al.: Concentrations of K, Mg and Na and their ionic relations in Dactylis glomerata biomass
 - 1269 - CONCENTRATIONS OF K, Mg AND Na AND THEIR IONIC RELATIONS IN DACTYLIS GLOMERATA L. BIOMASS GROWN IN SOIL WITH MUSHROOM SUBSTRATE AND MINERAL FERTILISERS WIŚNIEWSKA - KADŻAJAN, B. * MALINOWSKA,
- 1269 - CONCENTRATIONS OF K, Mg AND Na AND THEIR IONIC RELATIONS IN DACTYLIS GLOMERATA L. BIOMASS GROWN IN SOIL WITH MUSHROOM SUBSTRATE AND MINERAL FERTILISERS WIŚNIEWSKA - KADŻAJAN, B. * MALINOWSKA,
RAKESH KUMAR* ICAR RC NEH Region Nagaland Centre Jharnapani , Nagaland, India
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(1): 67-71, 2017 (March) PRODUCTION POTENTIAL, QUALITY AND NUTRIENT UPTAKE OF LINSEED AS INFLUENCED BY FERTILITY LEVELS AND SEEDING RATES UNDER THE FOOT HILL CONDITION OF NAGALAND
Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(1): 67-71, 2017 (March) PRODUCTION POTENTIAL, QUALITY AND NUTRIENT UPTAKE OF LINSEED AS INFLUENCED BY FERTILITY LEVELS AND SEEDING RATES UNDER THE FOOT HILL CONDITION OF NAGALAND
GOA Trial Site Report
 Phosphorous placement and its effect on establishment and performance of canola Trail ode: GONU55- Season/year: Winter 5 Location: Spicers reek, Wellington ollaborators: Joe and Sam Mason Keywords GONU55-,
Phosphorous placement and its effect on establishment and performance of canola Trail ode: GONU55- Season/year: Winter 5 Location: Spicers reek, Wellington ollaborators: Joe and Sam Mason Keywords GONU55-,
Nordic Association of Agricultural Scientists
 NJF Report Vol. 1 No 1 2005 Nordic Association of Agricultural Scientists NJF-Seminar 369 Organic farming for a new millennium -status and future challenges Published by Nordic Association of Agricultural
NJF Report Vol. 1 No 1 2005 Nordic Association of Agricultural Scientists NJF-Seminar 369 Organic farming for a new millennium -status and future challenges Published by Nordic Association of Agricultural
POLISH JOURNAL OF SOIL SCIENCE VOL. L/ PL ISSN JERZY TERLIKOWSKI*
 POLISH JOURNAL OF SOIL SCIENCE VOL. L/2 2017 PL ISSN 0079-2985 DOI: 10.17951/pjss/2017.50.2.155 JERZY TERLIKOWSKI* Rational productive use of inorganic nitrogen reserves released in permanent meadow situated
POLISH JOURNAL OF SOIL SCIENCE VOL. L/2 2017 PL ISSN 0079-2985 DOI: 10.17951/pjss/2017.50.2.155 JERZY TERLIKOWSKI* Rational productive use of inorganic nitrogen reserves released in permanent meadow situated
The Potash Development Association Oilseed Rape and Potash
 leaflet 13 The Potash Development Association Oilseed Rape and Potash kg/ha K 2 O Nutrient balance Efficient crop nutrition requires the correct balance of all nutrients, and in principle individual plant
leaflet 13 The Potash Development Association Oilseed Rape and Potash kg/ha K 2 O Nutrient balance Efficient crop nutrition requires the correct balance of all nutrients, and in principle individual plant
Piotr Szulc* Department of Agronomy, Poznań University of Life Sciences, Dojazd 11, Poznań, Poland
 Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 22, No. 1 (2013), 239-248 Original Research Effects of Soil Supplementation with Urea and Magnesium on Nitrogen Uptake, and Utilization by Two Different Forms of Maize (Zea
Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 22, No. 1 (2013), 239-248 Original Research Effects of Soil Supplementation with Urea and Magnesium on Nitrogen Uptake, and Utilization by Two Different Forms of Maize (Zea
CHARACTERISTICS OF MUNICIPAL WASTE BIODEGRADABLE FRACTION AND EVALUATION OF ITS PROCESSING
 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 16, Issue 5, Nov. 2015, pages 133 137 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/60469 Research Article CHARACTERISTICS OF MUNICIPAL WASTE BIODEGRADABLE FRACTION AND EVALUATION OF
Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 16, Issue 5, Nov. 2015, pages 133 137 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/60469 Research Article CHARACTERISTICS OF MUNICIPAL WASTE BIODEGRADABLE FRACTION AND EVALUATION OF
IPNS BASED FERTILIZER MANAGEMENT FOR RICE IN COASTAL ZONE OF BANGLADESH. Abstract
 ISSN 0258-7122 (Print), 2408-8293 (Online) Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 41(4): 667-673, December 2016 IPNS BASED FERTILIZER MANAGEMENT FOR RICE IN COASTAL ZONE OF BANGLADESH M. N. ISLAM 1, M. I. U. SARKAR
ISSN 0258-7122 (Print), 2408-8293 (Online) Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 41(4): 667-673, December 2016 IPNS BASED FERTILIZER MANAGEMENT FOR RICE IN COASTAL ZONE OF BANGLADESH M. N. ISLAM 1, M. I. U. SARKAR
Nutrient management on organic cattle farms
 Nutrient management on organic cattle farms Dan Clavin Teagasc Farm Management and Rural Development Department, Athenry, Co. Galway Elaine Leavy Teagasc Farm Management and Rural Development Department,
Nutrient management on organic cattle farms Dan Clavin Teagasc Farm Management and Rural Development Department, Athenry, Co. Galway Elaine Leavy Teagasc Farm Management and Rural Development Department,
Effect of phosphoric fertilizers as a source of sulphur on malt barley total and technological grain yields
 Effect of phosphoric fertilizers as a source of sulphur on malt barley total and technological grain yields J. Potarzycki, W. Grzebisz Department of Agricultural Chemistry, Agricultural University, Poznań,
Effect of phosphoric fertilizers as a source of sulphur on malt barley total and technological grain yields J. Potarzycki, W. Grzebisz Department of Agricultural Chemistry, Agricultural University, Poznań,
5BROCHURE RECYCLE ORGANIC WASTE SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION PRACTICES - ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT -
 5BROCHURE SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION PRACTICES - ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT - RECYCLE ORGANIC WASTE COLEACP makes this brochure available to ACP (African, Caribbean and Pacific) fruit and vegetable growers and
5BROCHURE SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION PRACTICES - ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT - RECYCLE ORGANIC WASTE COLEACP makes this brochure available to ACP (African, Caribbean and Pacific) fruit and vegetable growers and
Tests to predict the potassium requirements of canola
 Tests to predict the potassium requirements of canola R.F. Brennan Department of Agriculture, 444 Albany Highway, Albany, WA 6330, Australia; e-mail: rbrennan@agric.wa.gov.au ABSTRACT Significant increases
Tests to predict the potassium requirements of canola R.F. Brennan Department of Agriculture, 444 Albany Highway, Albany, WA 6330, Australia; e-mail: rbrennan@agric.wa.gov.au ABSTRACT Significant increases
Effect of fertilizer application and the main nutrient limiting factors for yield and quality of sugarcane production in Guangxi red soil
 TROPICS Vol. ( ) Issued July, Effect of fertilizer application and the main nutrient limiting factors for yield and quality of sugarcane production in Guangxi red soil Institute of Soil and Fertilizer,
TROPICS Vol. ( ) Issued July, Effect of fertilizer application and the main nutrient limiting factors for yield and quality of sugarcane production in Guangxi red soil Institute of Soil and Fertilizer,
Fertilization and fertilizers use in the Netherlands
 Fertilization and fertilizers use in the Netherlands Presentation for Stanley Company ir. J.J. (Janjo) de Haan & ir. W. (Wim) van Dijk Program 1. Introduction Wageningen UR 2. Introduction Dutch agriculture
Fertilization and fertilizers use in the Netherlands Presentation for Stanley Company ir. J.J. (Janjo) de Haan & ir. W. (Wim) van Dijk Program 1. Introduction Wageningen UR 2. Introduction Dutch agriculture
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT SOURCES OF NUTRITION AND IRRIGATION LEVELS ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND NUTRIENT USE EFFICIENCY OF WHEAT
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Parvinder Kumar and R K Pannu, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 4, October 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved EFFECT OF DIFFERENT SOURCES
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Parvinder Kumar and R K Pannu, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 4, October 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved EFFECT OF DIFFERENT SOURCES
Nutrient Management for Field Grown Leafy Vegetables a European Perspective Ian G. Burns
 Nutrient Management for Field Grown Leafy Vegetables a European Perspective Ian G. Burns Warwick Crop Centre, School of Life Sciences, University of Warwick, Wellesbourne, Warwick CV35 9EF, United Kingdom
Nutrient Management for Field Grown Leafy Vegetables a European Perspective Ian G. Burns Warwick Crop Centre, School of Life Sciences, University of Warwick, Wellesbourne, Warwick CV35 9EF, United Kingdom
The content of some micronutrients in rendzina soil cultivated using different tillage systems and catch crops
 7 Polish Journal of Agronomy 2011, 4, 7 11 The content of some micronutrients in rendzina soil cultivated using different tillage systems and catch crops Piotr Kraska Department of the Agricultural Ecology,
7 Polish Journal of Agronomy 2011, 4, 7 11 The content of some micronutrients in rendzina soil cultivated using different tillage systems and catch crops Piotr Kraska Department of the Agricultural Ecology,
R. V. JOSHI, B. J. PATEL AND K. M. PATEL*
 Forage Res., 41 (2) : pp. 104-108 (2015) http://forageresearch.in EFFECT OF NITROGEN LEVELS AND TIME OF APPLICATION ON GROWTH, YIELD, QUALITY, NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS CONTENT AND UPTAKE FOR SEED PRODUCTION
Forage Res., 41 (2) : pp. 104-108 (2015) http://forageresearch.in EFFECT OF NITROGEN LEVELS AND TIME OF APPLICATION ON GROWTH, YIELD, QUALITY, NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS CONTENT AND UPTAKE FOR SEED PRODUCTION
Nutrient management. Cassava
 Nutrient management Cassava Fertilizer use By applying mineral fertilizers to their cassava, smallholder farmers can increase their yields from about 10 tonnes to as much as 16 tonnes of fresh roots per
Nutrient management Cassava Fertilizer use By applying mineral fertilizers to their cassava, smallholder farmers can increase their yields from about 10 tonnes to as much as 16 tonnes of fresh roots per
Fondul Social European POS DRU
 Keywords: inoculation, fertilization, harvest time, productivity, CP (crude protein), NDF (neutral detergent fiber), ADF (acid detergent fiber), calcium/phosphorus ratio Biomass productivity and quality
Keywords: inoculation, fertilization, harvest time, productivity, CP (crude protein), NDF (neutral detergent fiber), ADF (acid detergent fiber), calcium/phosphorus ratio Biomass productivity and quality
Agricultural humus management using high quality composts
 Agricultural humus management using high quality s DR. STEFANIE SIEBERT AND DR. BERTRAM KEHRES Bundesgütegemeinschaft Kompost e.v., Germany, biowaste, benefit of use, soil fertilizer, plant nutrition,
Agricultural humus management using high quality s DR. STEFANIE SIEBERT AND DR. BERTRAM KEHRES Bundesgütegemeinschaft Kompost e.v., Germany, biowaste, benefit of use, soil fertilizer, plant nutrition,
Improving supply and phosphorus use efficiency in organic farming systems
 Aspects of Applied Biology 79, 2006 What will organic farming deliver? COR 2006 Improving supply and phosphorus use efficiency in organic farming systems By R L WALKER 1, C A WATSON 1, R M REES 2 & E A
Aspects of Applied Biology 79, 2006 What will organic farming deliver? COR 2006 Improving supply and phosphorus use efficiency in organic farming systems By R L WALKER 1, C A WATSON 1, R M REES 2 & E A
Effects of Reduced Rates of N, P, K, S and Zn on the Growth and Yield of BRRI dhan29
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 5 (4): 58-522, 205 ISSN 88-6769 IDOSI Publications, 205 DOI: 0.5829/idosi.aejaes.205.5.4.2564 Effects of Reduced Rates of N, P, K, S and Zn on the Growth and
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 5 (4): 58-522, 205 ISSN 88-6769 IDOSI Publications, 205 DOI: 0.5829/idosi.aejaes.205.5.4.2564 Effects of Reduced Rates of N, P, K, S and Zn on the Growth and
THE EFFECT OF SOIL AND FOLIAR SULPHUR APPLICATION ON WINTER WHEAT YIELD AND SOIL PROPERTIES. Grzegorz Kulczycki
 THE EFFECT OF SOIL AND FOLIAR SULPHUR APPLICATION ON WINTER WHEAT YIELD AND SOIL PROPERTIES Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences Abstract In the years 2009-2010 the effect of sulphur fertilization
THE EFFECT OF SOIL AND FOLIAR SULPHUR APPLICATION ON WINTER WHEAT YIELD AND SOIL PROPERTIES Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences Abstract In the years 2009-2010 the effect of sulphur fertilization
S. S. Malhi 1, S. A. Brandt 1, C. L. Vera 2 and D. Leach 2. Background
 Potential of Rock Phosphate and Other Organic/Inorganic Amendments in Preventing P Deficiency in Barley on a P-Deficient Soil in Northeastern Saskatchewan S. S. Malhi 1, S. A. Brandt 1, C. L. Vera 2 and
Potential of Rock Phosphate and Other Organic/Inorganic Amendments in Preventing P Deficiency in Barley on a P-Deficient Soil in Northeastern Saskatchewan S. S. Malhi 1, S. A. Brandt 1, C. L. Vera 2 and
Natural fertiliser control and application system in Poland state of the art. The natural manure composition in Poland estimating and verification
 Natural fertiliser control and application system in Poland state of the art. The natural manure composition in Poland estimating and verification Jacek Walczak Department of Technology, Ecology and Economics
Natural fertiliser control and application system in Poland state of the art. The natural manure composition in Poland estimating and verification Jacek Walczak Department of Technology, Ecology and Economics
Effect of diet manipulation on manure characteristics
 Effect of diet manipulation on manure characteristics I: Agronomical features and atmospheric emissions II: Energy recovery of biogas Ministério da Agricultura, do Desenvolvimento Rural e das Pescas Olga
Effect of diet manipulation on manure characteristics I: Agronomical features and atmospheric emissions II: Energy recovery of biogas Ministério da Agricultura, do Desenvolvimento Rural e das Pescas Olga
Mineral Assimilation of Sugar Beets 1
 Mineral Assimilation of Sugar Beets 1 W. E. CARLSONS The rate of mineral assimilation during plant growth can be approximately followed by knowledge of the quantity found in plants taken at intervals throughout
Mineral Assimilation of Sugar Beets 1 W. E. CARLSONS The rate of mineral assimilation during plant growth can be approximately followed by knowledge of the quantity found in plants taken at intervals throughout
NITROGEN MINERALIZATION IN SOME CALCAREOUS SOILS OF IRAQ. Faiz G. Aziz, Hamad M. Salih, Barzan I. Khayatt, M. A. Umran
 Proc. 5th Sci. Conf. / SRC Iraq, Baghdad 7 11 Oct. 1989 Vol. I Part 2 NITROGEN MINERALIZATION IN SOME CALCAREOUS SOILS OF IRAQ Faiz G. Aziz, Hamad M. Salih, Barzan I. Khayatt, M. A. Umran Department of
Proc. 5th Sci. Conf. / SRC Iraq, Baghdad 7 11 Oct. 1989 Vol. I Part 2 NITROGEN MINERALIZATION IN SOME CALCAREOUS SOILS OF IRAQ Faiz G. Aziz, Hamad M. Salih, Barzan I. Khayatt, M. A. Umran Department of
THE IMPACT OF WEATHER CONDITIONS ON THE YIELD OF WINTER TRITICALE AND CONTENT OF MACROELEMENTS IN GRAIN
 ts Journal of Elementology ISSN 1644-2296 Brzozowska I., Brzozowski J., Grabowski J. 2016. The impact of weather conditions on the yield of winter triticale and content of macroelements in grain. J. Elem.,
ts Journal of Elementology ISSN 1644-2296 Brzozowska I., Brzozowski J., Grabowski J. 2016. The impact of weather conditions on the yield of winter triticale and content of macroelements in grain. J. Elem.,
Crop Nutrition Key Points:
 Crop Nutrition Key Points: Apply N fertiliser using the recommendations table (below) but making allowances for N applied in organic manures. N fertiliser applications should be timed to avoid impairing
Crop Nutrition Key Points: Apply N fertiliser using the recommendations table (below) but making allowances for N applied in organic manures. N fertiliser applications should be timed to avoid impairing
Production potential realization and quality enhancement of mung bean through integrated nutrient management
 Journal of Crop and Weed, 0():87-9(04) Production potential realization and quality enhancement of mung bean through integrated nutrient management N. C. BANIK AND K. SENGUPTA Dept. of Agronomy Bidhan
Journal of Crop and Weed, 0():87-9(04) Production potential realization and quality enhancement of mung bean through integrated nutrient management N. C. BANIK AND K. SENGUPTA Dept. of Agronomy Bidhan
MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS, PLANT PHENOLOGY AND YIELD OF SPRING BARLEY (Hordeum sativum L.) DEPENDING ON CULTIVAR PROPERTIES AND SOWING DATE
 ACTA AGROBOTANICA Vol. 65 (2): 171 176 2012 MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS, PLANT PHENOLOGY AND YIELD OF SPRING BARLEY (Hordeum sativum L.) DEPENDING ON CULTIVAR PROPERTIES AND SOWING DATE Institute of Soil
ACTA AGROBOTANICA Vol. 65 (2): 171 176 2012 MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS, PLANT PHENOLOGY AND YIELD OF SPRING BARLEY (Hordeum sativum L.) DEPENDING ON CULTIVAR PROPERTIES AND SOWING DATE Institute of Soil
EVALUATION OF GRAIN FILLING RATE AND PATH ANALYSIS IN DIFFERENT COMBINATIONS OF NITROGEN AND ZINC IN MAIZE
 60 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 22 (No 1) 2016, 60-64 Agricultural Academy EVALUATION OF GRAIN FILLING RATE AND PATH ANALYSIS IN DIFFERENT COMBINATIONS OF NITROGEN AND ZINC IN MAIZE L. SHAFEA
60 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 22 (No 1) 2016, 60-64 Agricultural Academy EVALUATION OF GRAIN FILLING RATE AND PATH ANALYSIS IN DIFFERENT COMBINATIONS OF NITROGEN AND ZINC IN MAIZE L. SHAFEA
NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND YIELD OF ONION AS INFLUENCED BY NITROGEN AND SULPHUR FERTILIZATION
 ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 32(3) : 413-420, September 2007 NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND YIELD OF ONION AS INFLUENCED BY NITROGEN AND SULPHUR FERTILIZATION S. NASREEN 1, M. M. HAQUE 2, M. A. HOSSAIN
ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 32(3) : 413-420, September 2007 NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND YIELD OF ONION AS INFLUENCED BY NITROGEN AND SULPHUR FERTILIZATION S. NASREEN 1, M. M. HAQUE 2, M. A. HOSSAIN
Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers
 Symposium no. 65 Paper no. 246 Presentation: poster Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers KOZLOV A.E., STEPANOV A. and MANUCHAROVA N. Moscow
Symposium no. 65 Paper no. 246 Presentation: poster Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers KOZLOV A.E., STEPANOV A. and MANUCHAROVA N. Moscow
ENVIRONMENTAL AND YIELDING ASPECTS OF CONVERSION TO ORGANIC FARMING - A CASE STUDY
 ENVIRONMENTAL AND YIELDING ASPECTS OF CONVERSION TO ORGANIC FARMING - A CASE STUDY Tyburski Józef 1, Stalenga Jarosław 2, Kopiński Jerzy 2 1 University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, 2 Institute of Soil
ENVIRONMENTAL AND YIELDING ASPECTS OF CONVERSION TO ORGANIC FARMING - A CASE STUDY Tyburski Józef 1, Stalenga Jarosław 2, Kopiński Jerzy 2 1 University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, 2 Institute of Soil
The Potash Development Association Forage Maize Fertiliser Requirements
 leaflet 17 The Potash Development Association Forage Maize Fertiliser Requirements Why Maize? Maize makes high quality silage for dairy cattle, beef and sheep at less cost than silage made from grass.
leaflet 17 The Potash Development Association Forage Maize Fertiliser Requirements Why Maize? Maize makes high quality silage for dairy cattle, beef and sheep at less cost than silage made from grass.
Response of Integrated Nutrient Management on Nutrient Uptake, Economics and Nutrient Status of Soil in Bold Seeded Summer Groundnut
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.019
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.019
Response of sesame to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization in Northern Sudan
 Response of sesame to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization in Northern Sudan Abdel Rahman A. El Mahdi Faculty of Agriculture, Nile Valley University, Darmali, Sudan. Corresponding author email: amahdi54@hotmail.com
Response of sesame to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization in Northern Sudan Abdel Rahman A. El Mahdi Faculty of Agriculture, Nile Valley University, Darmali, Sudan. Corresponding author email: amahdi54@hotmail.com
FERTILISER VALUE AND TRACE ELEMENT CONTENT OF COMPOSTS PRODUCED FROM DIFFERENT WASTES
 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 16, Issue 4, Oct. 2015, pages 154 160 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/59365 Research Article FERTILISER VALUE AND TRACE ELEMENT CONTENT OF COMPOSTS PRODUCED FROM DIFFERENT
Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 16, Issue 4, Oct. 2015, pages 154 160 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/59365 Research Article FERTILISER VALUE AND TRACE ELEMENT CONTENT OF COMPOSTS PRODUCED FROM DIFFERENT
EFFECT OF FOLIAR VS SOIL APPLICATION OF NITROGEN ON YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS OF WHEAT VARIETIES
 Pak. J. Bot., 42(4): 2737-2745, 2010. EFFECT OF FOLIAR VS SOIL APPLICATION OF NITROGEN ON YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS OF WHEAT VARIETIES JEHAN BAKHT 1*, MOHAMMAD SHAFI 2 MOHAMMAD ZUBAIR 2, MOHAMMAD AMAN
Pak. J. Bot., 42(4): 2737-2745, 2010. EFFECT OF FOLIAR VS SOIL APPLICATION OF NITROGEN ON YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENTS OF WHEAT VARIETIES JEHAN BAKHT 1*, MOHAMMAD SHAFI 2 MOHAMMAD ZUBAIR 2, MOHAMMAD AMAN
The Potash Development Association Grain Legumes need Potash
 leaflet 18 The Potash Development Association Grain Legumes need Potash Grain legumes in the UK Field beans and peas are the main grain legume crops in the UK with, between them, around 250,000 ha grown.
leaflet 18 The Potash Development Association Grain Legumes need Potash Grain legumes in the UK Field beans and peas are the main grain legume crops in the UK with, between them, around 250,000 ha grown.
RESPONDING TO THE NEEDS OF EUROPEAN AGRICULTURE
 RESPONDING TO THE NEEDS OF EUROPEAN AGRICULTURE poly4.com BRINGING SCIENCE TO THE FIELD is the trademark name of Sirius Minerals flagship polyhalite product. is a naturally-occurring, low-chloride, multi-nutrient
RESPONDING TO THE NEEDS OF EUROPEAN AGRICULTURE poly4.com BRINGING SCIENCE TO THE FIELD is the trademark name of Sirius Minerals flagship polyhalite product. is a naturally-occurring, low-chloride, multi-nutrient
Using Soil Tests for Soil Fertility Management
 Using Soil Tests for Soil Fertility Management Mark Plunkett, Soil & Plant Nutrition Specialist, Johnstown Castle, Co. Wexford Overview Soil Testing and soil fertility levels Managing soil fertility 5
Using Soil Tests for Soil Fertility Management Mark Plunkett, Soil & Plant Nutrition Specialist, Johnstown Castle, Co. Wexford Overview Soil Testing and soil fertility levels Managing soil fertility 5
Fertility and Crop Nutrition. B. Linquist, R. Mutters, J. Hill and C. vankessel Rice Production Workshop, March 21, 2011
 Fertility and Crop Nutrition B. Linquist, R. Mutters, J. Hill and C. vankessel Rice Production Workshop, March 21, 2011 900 800 Fertilizer costs: 1960-2010 Source: USDA 700 600 Nitrogen solutions (30%)
Fertility and Crop Nutrition B. Linquist, R. Mutters, J. Hill and C. vankessel Rice Production Workshop, March 21, 2011 900 800 Fertilizer costs: 1960-2010 Source: USDA 700 600 Nitrogen solutions (30%)
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online):
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Influence of Integrated Nutrient Management Practices on Yield and Yield
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Influence of Integrated Nutrient Management Practices on Yield and Yield
Fertilizer and Lime Project Final Report Increasing the magnesium concentration of tall fescue leaves with phosphorus and boron fertilization
 Fertilizer and Lime Project Final Report - 24 Increasing the magnesium concentration of tall fescue leaves with phosphorus and boron fertilization Dale G. Blevins, Agronomy Department, University of Missouri
Fertilizer and Lime Project Final Report - 24 Increasing the magnesium concentration of tall fescue leaves with phosphorus and boron fertilization Dale G. Blevins, Agronomy Department, University of Missouri
Environment Protection Engineering
 Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 37 2011 No. 3 LESZEK STYSZKO*, DIANA FIJAŁKOWSKA*, MONIKA SZTYMA-HORWAT* INFLUENCE OF FERTILIZATION WITH COMPOST FROM MUNICIPAL SLUDGE ON THE CONTENT OF DRY MATTER
Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 37 2011 No. 3 LESZEK STYSZKO*, DIANA FIJAŁKOWSKA*, MONIKA SZTYMA-HORWAT* INFLUENCE OF FERTILIZATION WITH COMPOST FROM MUNICIPAL SLUDGE ON THE CONTENT OF DRY MATTER
Response of Alfalfa to Sulphur Application Heartland SCIA Partner Grant Final Report
 Response of Alfalfa to Sulphur Application Heartland SCIA Partner Grant Final Report Purpose: Develop recommendations for source, rate and timing of Sulphur (S) application in alfalfa and refine tools
Response of Alfalfa to Sulphur Application Heartland SCIA Partner Grant Final Report Purpose: Develop recommendations for source, rate and timing of Sulphur (S) application in alfalfa and refine tools
Keeping the Grass Greener on Your Side of the Fence Understanding Pasture Fertility
 Keeping the Grass Greener on Your Side of the Fence Understanding Pasture Fertility Don Green Forage Specialist Soils and Crops Branch Manitoba Agriculture and Food Carman, MB Introduction: Sometimes it
Keeping the Grass Greener on Your Side of the Fence Understanding Pasture Fertility Don Green Forage Specialist Soils and Crops Branch Manitoba Agriculture and Food Carman, MB Introduction: Sometimes it
GENERAL ASPECTS REGARDING WASTE MANAGEMENT IN SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURE
 Scientific Bulletin. Series F. Biotechnologies, Vol. XVII, 2013 ISSN 2285-1364, CD-ROM ISSN 2285-5521, ISSN Online 2285-1372, ISSN-L 2285-1364 Abstract. GENERAL ASPECTS REGARDING WASTE MANAGEMENT IN SUSTAINABLE
Scientific Bulletin. Series F. Biotechnologies, Vol. XVII, 2013 ISSN 2285-1364, CD-ROM ISSN 2285-5521, ISSN Online 2285-1372, ISSN-L 2285-1364 Abstract. GENERAL ASPECTS REGARDING WASTE MANAGEMENT IN SUSTAINABLE
TR02-5. Technical Re.port. Application of Anaerobically Digested Biosolids to Dryland Winter Wheat
 Technical Re.port TR02-5 Agricultural - Department of Cooperative April 2002. Experiment Soil and Crop Extension Station Sciences i Application of Anaerobically Digested Biosolids to Dryland Winter Wheat
Technical Re.port TR02-5 Agricultural - Department of Cooperative April 2002. Experiment Soil and Crop Extension Station Sciences i Application of Anaerobically Digested Biosolids to Dryland Winter Wheat
QUESTIONNAIRE. Application of Chemical Fertilizer in Agriculture a study with special reference to the farmers in Andhra Pradesh, India.
 ANNEXURE QUESTIONNAIRE Application of Chemical Fertilizer in Agriculture a study with special reference to the farmers in Andhra Pradesh, India. I, T. Sudhakar Reddy, Research Scholar (Ph.D) at Acharya
ANNEXURE QUESTIONNAIRE Application of Chemical Fertilizer in Agriculture a study with special reference to the farmers in Andhra Pradesh, India. I, T. Sudhakar Reddy, Research Scholar (Ph.D) at Acharya
NJF Report Vol. 1 No NJF-Seminar 372. Manure - an agronomic and environmental challenge
 NJF Report Vol. 1 No 2 2005 NJF-Seminar 372 Manure - an agronomic and environmental challenge Arranged by NJF sections - Soil, Water and Environment - Engineering Nils Holgersson gymnasiet Skurup, Sweden
NJF Report Vol. 1 No 2 2005 NJF-Seminar 372 Manure - an agronomic and environmental challenge Arranged by NJF sections - Soil, Water and Environment - Engineering Nils Holgersson gymnasiet Skurup, Sweden
Human Urine an Alternative to Chemical Fertilizers in Crop Production
 Human Urine an Alternative to Chemical Fertilizers in Crop Production Dr. C. A. Srinivasamurthy 1, Mr. H. Yogeeshappa 2, Dr. G. Sridevi 3, Mr. Mukund Joshi 4, Mr. S.Vishwanath 5 and Vijayakrishna 6 1 Professor
Human Urine an Alternative to Chemical Fertilizers in Crop Production Dr. C. A. Srinivasamurthy 1, Mr. H. Yogeeshappa 2, Dr. G. Sridevi 3, Mr. Mukund Joshi 4, Mr. S.Vishwanath 5 and Vijayakrishna 6 1 Professor
Comparing N and S sources to improve yield and nutrient efficiency in canola cropping systems in south-eastern Australia.
 Comparing N and S sources to improve yield and nutrient efficiency in canola cropping systems in south-eastern Australia. Tauhid A. Khan 1, Robert Norton 1,2, Robert Edis 1, Charlie Walker 3 and Deli Chen
Comparing N and S sources to improve yield and nutrient efficiency in canola cropping systems in south-eastern Australia. Tauhid A. Khan 1, Robert Norton 1,2, Robert Edis 1, Charlie Walker 3 and Deli Chen
Reed Canarygrass Response to Nitrogen and Chloride Fertilization
 Reed Canarygrass Response to Nitrogen and Chloride Fertilization William H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute P.O Box 90, Chazy, NY 12921 Everett D. Thomas Charlie J. Sniffen Carl J. Majewski Catherine
Reed Canarygrass Response to Nitrogen and Chloride Fertilization William H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute P.O Box 90, Chazy, NY 12921 Everett D. Thomas Charlie J. Sniffen Carl J. Majewski Catherine
Scientific registration n : 178 Symposium n : 40 Presentation : poster YADVINDER-SINGH, BIJAY-SINGH, KHERA T.S., KHIND C.S.
 Scientific registration n : 178 Symposium n : 40 Presentation : poster Crop residue management for improved soil and crop productivity in rice-wheat cropping system in Indo- Gangetic plains of India Gestion
Scientific registration n : 178 Symposium n : 40 Presentation : poster Crop residue management for improved soil and crop productivity in rice-wheat cropping system in Indo- Gangetic plains of India Gestion
The Potash Development Association Why Maintain Soil Potash Reserves?
 leaflet 28 The Potash Development Association Why Maintain Soil Potash Reserves? Introduction Potash is an essential nutrient for all crops and grassland and for livestock. Maintaining soil fertility so
leaflet 28 The Potash Development Association Why Maintain Soil Potash Reserves? Introduction Potash is an essential nutrient for all crops and grassland and for livestock. Maintaining soil fertility so
OPTIMIZATION OF TECHNOLOGICAL MEASURES TO PROMOTE CEREAL STRAW DECOMPOSITION IN THE POST HARVEST PERIOD
 OPTIMIZATION OF TECHNOLOGICAL MEASURES TO PROMOTE CEREAL STRAW DECOMPOSITION IN THE POST HARVEST PERIOD Ausra Arlauskiene, Aleksandras Velykis, Alvyra Slepetiene Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture
OPTIMIZATION OF TECHNOLOGICAL MEASURES TO PROMOTE CEREAL STRAW DECOMPOSITION IN THE POST HARVEST PERIOD Ausra Arlauskiene, Aleksandras Velykis, Alvyra Slepetiene Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture
FACULTY OF AGRICULTURE AND FOOD SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF SARAJEVO DRY MATTER AND PROTEIN YIELDS OF RED CLOVER, ITALIAN RYEGRASS AND THEIR MIXTURES
 FACULTY OF AGRICULTURE AND FOOD SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF SARAJEVO DRY MATTER AND PROTEIN YIELDS OF RED CLOVER, ITALIAN RYEGRASS AND THEIR MIXTURES Senija Alibegovic-Grbic, Muamer Bezdrob and Hamdija Civic
FACULTY OF AGRICULTURE AND FOOD SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF SARAJEVO DRY MATTER AND PROTEIN YIELDS OF RED CLOVER, ITALIAN RYEGRASS AND THEIR MIXTURES Senija Alibegovic-Grbic, Muamer Bezdrob and Hamdija Civic
NUTRIENT CONTENT OF SOME LOCALLY AVAILABLE ORGANIC MATERIALS AND THEIR POTENTIAL AS ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF NUTRIENTS FOR COCONUT
 COCOS (2003), 15 23-30 Printed in Sri Lanka NUTRIENT CONTENT OF SOME LOCALLY AVAILABLE ORGANIC MATERIALS AND THEIR POTENTIAL AS ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF NUTRIENTS FOR COCONUT N. A. Tennakoon and S. D. Hemamala
COCOS (2003), 15 23-30 Printed in Sri Lanka NUTRIENT CONTENT OF SOME LOCALLY AVAILABLE ORGANIC MATERIALS AND THEIR POTENTIAL AS ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF NUTRIENTS FOR COCONUT N. A. Tennakoon and S. D. Hemamala
EFFECT OF INTEGRATED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT ON GROWTH CHARACTERISTIC OF KHARIF MAIZE
 EFFECT OF INTEGRATED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT ON GROWTH CHARACTERISTIC OF KHARIF MAIZE Madane K. T., M. S. Narale and D. M.Sawant Asst. Prof. Department of Agronomy, Shriram College of Agriculture, Paniv Received:
EFFECT OF INTEGRATED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT ON GROWTH CHARACTERISTIC OF KHARIF MAIZE Madane K. T., M. S. Narale and D. M.Sawant Asst. Prof. Department of Agronomy, Shriram College of Agriculture, Paniv Received:
Effect of Phosphorous Nutrition through Foliar and Irrigation on Budgeting of Primary Macro Nutrients in Drip Fertigated Maize
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Harshitha et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (): 028-032 (208) ISSN: 2320 705 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.8782/2320-705.6007 ISSN: 2320 705 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 ():
Available online at www.ijpab.com Harshitha et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (): 028-032 (208) ISSN: 2320 705 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.8782/2320-705.6007 ISSN: 2320 705 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 ():
Yield and Nutrient Accumulation of KDML 105 Rice as Influenced by Farmyard Manure and Wood Vinegar
 368 Yield and Nutrient Accumulation of KDML 105 Rice as Influenced by Farmyard Manure and Wood Vinegar Lyda Hok, Darunee Jothityangkoon* and Anan Polthanee Department of Plant Science and Agricultural
368 Yield and Nutrient Accumulation of KDML 105 Rice as Influenced by Farmyard Manure and Wood Vinegar Lyda Hok, Darunee Jothityangkoon* and Anan Polthanee Department of Plant Science and Agricultural
Aus dem Institut für Betriebswirtschaft, Agrarstruktur und ländliche Räume
 Aus dem Institut für Betriebswirtschaft, Agrarstruktur und ländliche Räume Heike Nitsch Good farming practice - definitions, implementation, experiences : Report on the results of work package 2 within
Aus dem Institut für Betriebswirtschaft, Agrarstruktur und ländliche Räume Heike Nitsch Good farming practice - definitions, implementation, experiences : Report on the results of work package 2 within
Quentin Kelly-Edwards
 PROTECTING THE ENVIRONMENT THROUGH REDUCTION OF AMMONIA EMISSIONS FROM SLURRY. Quentin Kelly-Edwards Regional Manager UK & RoI JH Agro A/S TOPICS 1. The problem and the causes 2. Introduction to slurry
PROTECTING THE ENVIRONMENT THROUGH REDUCTION OF AMMONIA EMISSIONS FROM SLURRY. Quentin Kelly-Edwards Regional Manager UK & RoI JH Agro A/S TOPICS 1. The problem and the causes 2. Introduction to slurry
The influence of different foliar fertilisation on the yield and botanical composition of a meadow sward
 The influence of different foliar fertilisation on the yield and botanical composition of a meadow sward Jankowska-Huflejt H. 1 and Klusek G. 2 1 Department of Meadow and Pasture, Institute for Land Reclamation
The influence of different foliar fertilisation on the yield and botanical composition of a meadow sward Jankowska-Huflejt H. 1 and Klusek G. 2 1 Department of Meadow and Pasture, Institute for Land Reclamation
Global warming potential of Swiss arable and forage production systems
 Federal Department of Economic Affairs DEA Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon Research Station ART Global warming potential of Swiss arable and forage production systems Thomas Nemecek Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon
Federal Department of Economic Affairs DEA Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon Research Station ART Global warming potential of Swiss arable and forage production systems Thomas Nemecek Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon
NUTRIENTS. Nitrogen (N) 15,000 Potassium (K) 10,000 Calcium (Ca) 5,000 Magnesium (Mg) 2,000 Phosphorus (P) 2,000 Sulfur (S) 1,000
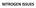 NITROGEN ISSUES NUTRIENTS Macro-nutrients mg/kg* Nitrogen (N) 15,000 Potassium (K) 10,000 Calcium (Ca) 5,000 Magnesium (Mg) 2,000 Phosphorus (P) 2,000 Sulfur (S) 1,000 * Based on Dry Weight of plant tissue
NITROGEN ISSUES NUTRIENTS Macro-nutrients mg/kg* Nitrogen (N) 15,000 Potassium (K) 10,000 Calcium (Ca) 5,000 Magnesium (Mg) 2,000 Phosphorus (P) 2,000 Sulfur (S) 1,000 * Based on Dry Weight of plant tissue
Fifth International Scientific Agricultural Symposium Agrosym 2014
 Original scientific paper 10.7251/AGSY1404138B OAT GRAIN YIELD VARIATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH PRODUCTIVITY PARAMETERS AMONG OAT CULTIVARS GROWN IN LATVIA Linda BRUNAVA 1,2*, Ina ALSIŅA 1, Sanita ZUTE 2 1 Institute
Original scientific paper 10.7251/AGSY1404138B OAT GRAIN YIELD VARIATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH PRODUCTIVITY PARAMETERS AMONG OAT CULTIVARS GROWN IN LATVIA Linda BRUNAVA 1,2*, Ina ALSIŅA 1, Sanita ZUTE 2 1 Institute
Managing Soil Fertility: Targets to maximise production. Dr David P. Wall Teagasc, Johnstown Castle, Co Wexford
 Managing Soil Fertility: Targets to maximise production Dr David P. Wall Teagasc, Johnstown Castle, Co Wexford Outline Soil fertility trends on dairy farms 5 Steps to soil fertility management Soil Testing
Managing Soil Fertility: Targets to maximise production Dr David P. Wall Teagasc, Johnstown Castle, Co Wexford Outline Soil fertility trends on dairy farms 5 Steps to soil fertility management Soil Testing
Wheat trial 2013/2014; KCl application + PN foliar L A N D L A B. PNA Potassium Nitrate Association 2014/08/14. Adriano Altissimo
 L A N D L A B agronomist, biotechnologists 2014/08/14 PNA Potassium Nitrate Association Wheat trial 2013/2014; KCl application + PN foliar Adriano Altissimo Aim of the trial Is the evaluation of the impact
L A N D L A B agronomist, biotechnologists 2014/08/14 PNA Potassium Nitrate Association Wheat trial 2013/2014; KCl application + PN foliar Adriano Altissimo Aim of the trial Is the evaluation of the impact
COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, SUMERPUR Lecture programme -2 ND Year I Sem ( ) Course: AGRON Field Crops-I (Kharif) Credits: 3(2+1)
 COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, SUMERPUR Lecture programme -2 ND Year I Sem (2016-17) Course: AGRON 4211- Field Crops-I (Kharif) Credits: 3(2+1) Teacher: Mr. L. K. Jain Class Time: As per time table Discipline:
COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, SUMERPUR Lecture programme -2 ND Year I Sem (2016-17) Course: AGRON 4211- Field Crops-I (Kharif) Credits: 3(2+1) Teacher: Mr. L. K. Jain Class Time: As per time table Discipline:
Phytomass formation and carbon amount returned to soil depending on green manure crop
 Agronomy Research 7(Special issue I), 517 521, 29 Phytomass formation and carbon amount returned to soil depending on green manure crop L. Talgre 1, E. Lauringson 1, H. Roostalu 2, A. Astover 2 and A.
Agronomy Research 7(Special issue I), 517 521, 29 Phytomass formation and carbon amount returned to soil depending on green manure crop L. Talgre 1, E. Lauringson 1, H. Roostalu 2, A. Astover 2 and A.
Emerging Paradigms in Biosolids Management. Dr Bill Barber 15 th February 2013
 Emerging Paradigms in Biosolids Management Dr Bill Barber 15 th February 2013 TTDSA Biosolids Production Trend in Europe 10000 9500 9000 8500 8000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 1) Increasingly Strict
Emerging Paradigms in Biosolids Management Dr Bill Barber 15 th February 2013 TTDSA Biosolids Production Trend in Europe 10000 9500 9000 8500 8000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 1) Increasingly Strict
STUDIES ON INTEGRATED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT IN WHEAT
 STUDIES ON INTEGRATED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT IN WHEAT THESIS ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO CHAUDHARY CHARAN SINGH UNIVERSITY, MEERUT, U.P. FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN AGRONOMY BY BHUPENDRA KUMAR Enrol.
STUDIES ON INTEGRATED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT IN WHEAT THESIS ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO CHAUDHARY CHARAN SINGH UNIVERSITY, MEERUT, U.P. FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN AGRONOMY BY BHUPENDRA KUMAR Enrol.
AGRONOMIC PERFORMANCE OF ACID - BASED LIQUID FERTILISER ON WINTER WHEAT
 AGRONOMIC PERFORMANCE OF ACID - BASED LIQUID FERTILISER ON WINTER WHEAT Authors J.I. Burke, B. O'Reilly 1 and E.G. Gallagher 1 Crops Research Centre Oak Park, Carlow 1 Faculty of Agriculture, University
AGRONOMIC PERFORMANCE OF ACID - BASED LIQUID FERTILISER ON WINTER WHEAT Authors J.I. Burke, B. O'Reilly 1 and E.G. Gallagher 1 Crops Research Centre Oak Park, Carlow 1 Faculty of Agriculture, University
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT NITROGEN AND POTASSIUM LEVELS AND FOLIAR APPLICATION OF BORON ON WHEAT YIELD
 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT NITROGEN AND POTASSIUM LEVELS AND FOLIAR APPLICATION OF BORON ON WHEAT YIELD Sarwat M. Youssef*, Salah E.-D. A. Faizy, Mohamed H. Hegazy, and Hassan R. El-Ramady ABSTRACT From the present
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT NITROGEN AND POTASSIUM LEVELS AND FOLIAR APPLICATION OF BORON ON WHEAT YIELD Sarwat M. Youssef*, Salah E.-D. A. Faizy, Mohamed H. Hegazy, and Hassan R. El-Ramady ABSTRACT From the present
College of Agriculture, S.K. Rajasthan Agricultural University, Bikaner , India
 Annals of Arid Zone 52(2): 95-99, 2013 Effect of Nitrogen Levels and its Scheduling on Growth, Yield and Grain Quality of Malt Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under Normal and Late Sown Conditions in North-West
Annals of Arid Zone 52(2): 95-99, 2013 Effect of Nitrogen Levels and its Scheduling on Growth, Yield and Grain Quality of Malt Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under Normal and Late Sown Conditions in North-West
In this document we give a brief description of the products, their specifications and suitable applications.
 Superior products, Superior results PRODUCTS REGYP supplies numerous high quality agricultural & industrial products throughout NSW, VIC and QLD for industrial, agricultural and civil applications. In
Superior products, Superior results PRODUCTS REGYP supplies numerous high quality agricultural & industrial products throughout NSW, VIC and QLD for industrial, agricultural and civil applications. In
Chapter 4.3. Manure Test Interpretation. learning objectives
 Chapter 4.3 Manure Test Interpretation learning objectives Convert between units on a manure test report. Estimate available organic nitrogen and total crop available nitrogen from manure test information.
Chapter 4.3 Manure Test Interpretation learning objectives Convert between units on a manure test report. Estimate available organic nitrogen and total crop available nitrogen from manure test information.
Keywords: crop density, dry matter, digestibility, yield
 Effect of Different Animal Manure on Flower Yield and Qualitative and Quantitative Characteristics of Forage Production of Saffron (Crocus sativus) in Mashhad Conditions P. Rezvani-Moghaddam, A.A. Mohammad-Abadi,
Effect of Different Animal Manure on Flower Yield and Qualitative and Quantitative Characteristics of Forage Production of Saffron (Crocus sativus) in Mashhad Conditions P. Rezvani-Moghaddam, A.A. Mohammad-Abadi,
Marek Krysztoforski AAC Poland
 Nutrient balances as an advisory tool, Case Poland Marek Krysztoforski AAC Poland Balancing nutrients and manure management, their impact on water quality Author: Stefan Pietrzak, professor Institute of
Nutrient balances as an advisory tool, Case Poland Marek Krysztoforski AAC Poland Balancing nutrients and manure management, their impact on water quality Author: Stefan Pietrzak, professor Institute of
What is manure worth?
 What is manure worth? Good manure management starts with recognizing and understanding the value of manure as a resource. Livestock manure represents a valuable resource that, if used appropriately provides
What is manure worth? Good manure management starts with recognizing and understanding the value of manure as a resource. Livestock manure represents a valuable resource that, if used appropriately provides
tfirst Monitoring alternative fertilisers demonstration
 tfirst Monitoring alternative fertilisers demonstration Moorooduc Plains 2017 Monitoring alternative fertilisers on the Moorooduc Plains Introduction The aim of this demonstration was to provide some information
tfirst Monitoring alternative fertilisers demonstration Moorooduc Plains 2017 Monitoring alternative fertilisers on the Moorooduc Plains Introduction The aim of this demonstration was to provide some information
Studies on the Effect of Urine on Biogas Production
 Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 41(1-2), 23-32, 2006 Studies on the Effect of Urine on Biogas Production M. Shamsul Haque and M. Naimul Haque Institute of Fuel Research & Development, BCSIR, Dhaka-1205, Bangladesh
Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 41(1-2), 23-32, 2006 Studies on the Effect of Urine on Biogas Production M. Shamsul Haque and M. Naimul Haque Institute of Fuel Research & Development, BCSIR, Dhaka-1205, Bangladesh
Effects of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil and Plants, and on Crop Productivity in Aleppo Governorate
 Effects of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil and Plants, and on Crop Productivity in Aleppo Governorate Abstract M.M. Al-Zoubi 1, A. Arslan 1,2, G. Abdelgawad 2, N. Pejon 1, M. Tabbaa 1
Effects of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil and Plants, and on Crop Productivity in Aleppo Governorate Abstract M.M. Al-Zoubi 1, A. Arslan 1,2, G. Abdelgawad 2, N. Pejon 1, M. Tabbaa 1
FertiliserStatistics2017
 FertiliserStatistics217 Each year AIC gathers together data to provide insight into agricultural practices and crop nutrient usage for policy makers and the industry. Fertiliser Statistics 217 (216 harvest
FertiliserStatistics217 Each year AIC gathers together data to provide insight into agricultural practices and crop nutrient usage for policy makers and the industry. Fertiliser Statistics 217 (216 harvest
IV International Symposium Agrosym 2013
 10.7251/AGSY1303226B EFFECT OF ACID SOILS FERTILIZATION ON MORFOLOGICAL AND PRODUCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF TRITICALE Milan BIBERDZIC 1*, Miodrag JELIC 1, Goran MAKSIMOVIC 1, Sasa BARAC 1, Svetomir STAMENKOVIC
10.7251/AGSY1303226B EFFECT OF ACID SOILS FERTILIZATION ON MORFOLOGICAL AND PRODUCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF TRITICALE Milan BIBERDZIC 1*, Miodrag JELIC 1, Goran MAKSIMOVIC 1, Sasa BARAC 1, Svetomir STAMENKOVIC
Effect of Land Configuration, Irrigation and INM on Quality, Nutrient Content and Uptake of Indian Bean (var. GNIB-21)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 527-537 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.068
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 527-537 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.068
