CHARACTERIZATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL PARAMETERS AND SPECIES RICHNESS IN TIDEPOOLS
|
|
|
- Kellie Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHARACTERIZATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL PARAMETERS AND SPECIES RICHNESS IN TIDEPOOLS Jason Silva Biology Department,, 950 Main Street, Worcester, Ma Abstract The rocky intertidal is full of tide pools at different elevations. These elevations are the high, middle, and low intertidal zone. The higher elevated tide pools would have more exposure time than pools in the middle and lower intertidal. This allows more time for the physical environmental factors to affect the water chemistry. The lower the elevation of the tide pools, the less exposure occurs minimizing the affect of the physical environmental factors on water chemistry. The high intertidal zone would have less species richness because of the increased variation in water chemistry. We investigated whether variation in water chemistry correlated with species richness by measuring salinity, ph, temperature, and species richness at three different zones in the rocky intertidal. Key Words: Salinity, elevation, species richness Introduction The rocky intertidal has an array of species found in the different zones. The intertidal is typically broken up into three parts: high, middle and low. The zones can be differentiated by either measuring the physical height from mean low water level or by identifying the key species (typically algae) of each zone (Doty 1946). During low tide organisms in the higher intertidal are emerged in air for a longer duration than organisms lower in the intertidal. Therefore in high intertidal zones it would be expected to find a community of hardy organisms that could tolerate the fluctuations of these physical factors. A couple physical environmental factors that may affect intertidal communities are outside temperature, rock temperature, wind speed, sunlight intensity (shaded or nonshaded), and rainfall. Each of these factors can increase or decrease the salinity, ph, and temperature of the tide pools. Salinity is a factor highly susceptible to variation due to sun exposure, rain or cloudy weather. The sun intensity causes evaporation, which would lead to a higher concentration of salt in the water increasing the salinity. Also during rainstorms the salinity would be lowered because of the rain water diluting the tide pool water. The focus of this study is to determine observationally whether tide pool exposure to the physical environmental factors would affect the salinity, ph, and temperature of the water and therefore the species richness in the tide pool. Materials and Methods Study Site: The study took place at the rocky shores surrounding the Northeastern University Marine Science Center, Nahant MA. Water analysis was conducted on twenty-seven randomly selected tide pools and five open ocean samples. Nine tide pools were identified in three zones of the intertidal (high, middle, and low). The zones were identified by using key species. This means we used species only found in the
2 certain zone to identify it. Data were collected during three low tides (September 15 th, October 26 th, and November 18 th, 2012). Temperature, ph, salinity, and species richness were measured in each of the tidal pools. A submerged underwater thermometer was used for temperature. The ph was measured using ph strips that were placed in the tidal pool and left there for 5 minutes or until color changes had stopped. The color on the strip was compared to the color/ph chart that ranged from 6> on the ph strip container. To determine the salinity a refractometer was used to read it. A drop of water from the tide pool was placed on the lens and the salinity was read. Species richness was measured by video recording each tide pool and later counting the different species observed. The entire pools were sampled and the video length varied depending on size of tide pool. The different variables were tested for relationships between them using the correlation test. The p values of the correlation were used to test for significant relationships among variables. Results and Discussion Temperature The temperature in the tide pools ranged between 6-20 C. The temperature decreased significantly between September and November. The temperature at high tide varied most from the open water temperature (Figure1). Temperature was affected by the solar radiation, air temperature and rock temperature. Based on figure 1 in earlier trips (September and October) solar radiation had the greatest effect on the water temperature. The higher average temperature of the water showed this. The higher temperature was discovered in the longer exposed zones (high and middle zones). The later trip (November) the rock temperature and air temperature had a greatest effect observed by the low temperatures in the longer exposed tide pools (figure 1). The air temperature and rock temperature was cooled as the months passed. Therefore the air temperature and colder rocks cooled the water in the longer exposed zones. If the study were to continue the rock temperature will note as well. In the correlation tests it was found that temperature had a significant correlation with ph (pvalue of 0.021) and species richness (p-value of 0.032)(Table 1). Journal of Marine Volume 1: Issue 2 Page 25
3 /25/12 Temperature (C) High Middle Low Ocean 0.00 Figure 1. Temperature Variation in Tide Pools Located throughout the Intertidal. The average temperature of the four zones for the three different trips in The temperature dropped every month. The general temperature pattern was that the greatest differences are at high zones and it gradually moves towards the ocean temperature the lower it moves in the intertidal. The error bars show the standard error for each of the averages. Each point signifies the average species found for each of the zones during each trip in 2012 ph The ph was lower in the low intertidal and increased in the tide pools higher in the intertidal on the September and November trips (Figure 2). The October trip showed a slight drop of ph in the lower intertidal zone and then a increase in the ocean ph. After using testing for correlation and correlation significance using excel it was found that ph had significant correlation with temperature. This indicates sun exposure could have an affect on ph. Klugh (1924) showed states that the ph was not affected by elevation of the tide pool but by the proportion of vegetation to animals in the tide pools. Future research could be done on the organism s metabolic rate and its affect on water ph. Metabolic rate is slowed in colder temperature (Johnston et al. 2001) and the ph was lower during the colder water temperature trip. Journal of Marine Volume 1: Issue 2 Page 26
4 /25/ ph High Middle Low Ocean 6.00 Figure 2. ph variation in the intertidal. Tide pools in three intertidal zones were identified and tested for ph on three different dates in Each point signifies the average ph of one of the four zones for the three different trips. The ph was higher in the high intertidal zones and decreased in the lower zones. The different symbols represent the different trips. The error bars show the standard error for each of the averages. Species Richness Generally there as low species richness in the high intertidal, high in the middle, and again low species richness in the low intertidal. Species richness also was found to have a significant positive correlation with temperature (Table1). This means the higher the temperature the higher the species richness. Salinity and ph were also tested for correlation with species richness. Salinity and species richness were both slightly negatively correlated, but these results were not significant. This indicates that the hypothesis was correct in that temperature affects species richness. In this study it was found that species richness was not significantly correlated with ph and salinity. Further analysis with a larger sample sizes is needed to ascertain what, if any, relationship exists between ph, salinity, and species richness. The same species were typically found throughout each of the zones. This demonstrates that there are limitations to the species in the intertidal zone. In the rocky intertidal organisms are limited by physical factors in the upper intertidal zone and biological factors limits organisms in the lower intertidal (Foster 1971, Underwood et al.1983). Journal of Marine Volume 1: Issue 2 Page 27
5 12.00 Species Richness /25/ High Middle Low Figure 3. Species Richness across the Rocky Intertidal. Tide pools in the three intertidal zones were identified and recorded to count the different species. Each point signifies the average species found for each of the zones during each trip in The error bars show the standard error for each of the averages. Species richness was at its peak during middle tide. In high and low tide it drops with high having the lowest numbers. Salinity The salinity of tide pools in the middle and low intertidal was similar to that measured in the ocean water. However, the salinity in the high intertidal tide pools varied from 30.0 to 37.2 ppt. For example, in September, one tide pool had salinity reading of 25. The other tide pool in that zone that day was 34.5, more consistent with other days sampled. The 25 ppt reading of salinity alters the average, which explains the low point on the graph. The low salinity levels have resulted from rainwater entering the pool earlier in the day. The elevated salinity in the October and November trips showed that evaporation had occurred in the tide pools longer exposed to the solar radiation. The correlation test found that the data didn t significantly demonstrate that salinity can effected species richness. A better correlation might be found if the data were collected within a period of a month, especially during a month of high solar radiation intensity (summer). The study took place during a seasonal change from summer to winter therefore the cooling temperature could have affected salinity(doty 1946). The correlation table shows a negative correlation between temperature and salinity. The correlation was found to almost significant with a p value of Journal of Marine Volume 1: Issue 2 Page 28
6 Salinity (ppt) /26/12 High Middle Low Ocean Figure 4. Salinity levels in selected tide pools and the ocean during fall Tide pools in three intertidal zones were identified and analyzed for salinity on three different dates in Salinity was measured using the refractometer. High tide had a higher salinity and it dropped to around ocean salinity for mid and low zones. The error bars show the standard error for each of the averages. Species richness was at its peak during middle tide. Summary Table 1. Correlation Table. The correlation between the different variables and the significance of those correlations. The bolded Temperature/pH and Temperature/Species richness were found to be significant with values of and The variables were averaged for all three trips. Correlation Standard Error p value Species Richness/pH Temperature/pH Salinity/pH Temperature/Species Richness Temperature/Salinity Salinity/Species richness Zonal species richness distribution may be correlated with daily, monthly, or annual variation. Keeping this in mind it is possible that the main factors effecting zonation may Journal of Marine Volume 1: Issue 2 Page 29
7 shift throughout the seasons. This can be seen through the changes between the different trips (Figure 1-4). The species richness for middle and low tide for the two later trips (October and November) decreased substantially (figure3). It was also noted that the species found during those visits were primarily vegetation and snails. From the analysis conducted temperature is a limiting factor of species richness in the middle intertidal. The analysis of the factors involved correlations between species richness, ph, salinity and temperature. The results showed that the factors correlated with each other therefore in order to get more definite answers to the hypothesis the experiment would have to be brought into the lab where the other variables can be controlled and monitored. Temperature and ph and Temperature and species richness had a significant correlation. Literature Cited Doty S. Maxwell Critical Tide Factors that are Correlated with the Vertical Distribution of Marine Algae and Other Organisms along the Pacific Coast. Ecology, Vol. 27, No. 4 (Oct., 1946), pp Foster, B.A Desiccation as a factor in the intertidal zonation of barnacles. Marine Biology. January 1971, Volume 8, Issue 1, pp Johnston I. A., Clarke A., Ward P., 1991.Temperature and metabolic rate in sedentary fish from the Antarctic, North Sea and Indo-West Pacific Ocean. Marine Biology. Volume 109, Issue 2, pp Klugh A. B Factors Controlling the Biota of Tide-Pools. Ecology. Vol. 5, No. 2 (Apr., 1924), pp Underwood A.J, Denley E.J., Moran M.J Experimental analyses of the structure and dynamics of mid-shore rocky intertidal communities in New South Wales. Oecologia. February 1983, Volume 56, Issue 2-3, pp Journal of Marine Volume 1: Issue 2 Page 30
Rocky Intertidal Ecology
 Rocky Intertidal Ecology The Rocky Intertidal program at the Hatfield Marine Science Center is designed to be a 50-minute inquiry-based program that examines the dynamic environment of rocky shores and
Rocky Intertidal Ecology The Rocky Intertidal program at the Hatfield Marine Science Center is designed to be a 50-minute inquiry-based program that examines the dynamic environment of rocky shores and
Distribution of Ascophyllum nodosum, Mytilus edulis, and Balanus balanoides on Rock Substratum Throughout the Intertidal Zones of New England
 Distribution of Ascophyllum nodosum, Mytilus edulis, and Balanus balanoides on Rock Substratum Throughout the Intertidal Zones of New England Emily Claire Department of Biology,, Worcester, MA 01610 (ebraun@clarku.edu)
Distribution of Ascophyllum nodosum, Mytilus edulis, and Balanus balanoides on Rock Substratum Throughout the Intertidal Zones of New England Emily Claire Department of Biology,, Worcester, MA 01610 (ebraun@clarku.edu)
CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH)
 CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH) Related lesson plan Fresh and Seawater Density What is this sensor? CTD is an acronym for Conductivity, Temperature and Depth. However, this is somewhat misleading
CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH) Related lesson plan Fresh and Seawater Density What is this sensor? CTD is an acronym for Conductivity, Temperature and Depth. However, this is somewhat misleading
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Lab: Ocean Salinity and Density M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
1. Jill made the table below during her research on aquatic zones and living organisms. Based on Jill s observations, which conclusion could you draw?
 1. Jill made the table below during her research on aquatic zones and living organisms. Based on Jill s observations, which conclusion could you draw? A. Organisms in the intertidal zone must be able to
1. Jill made the table below during her research on aquatic zones and living organisms. Based on Jill s observations, which conclusion could you draw? A. Organisms in the intertidal zone must be able to
Life in Water. Chapter 3
 Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Name Hour AP Biology Lab: Dissolved Oxygen in Aquatic Ecosystem: The Relationship between Temperature, DO, and Respiration Rates
 Name Hour AP Biology Lab: Dissolved Oxygen in Aquatic Ecosystem: The Relationship between Temperature, DO, and Respiration Rates Although water is composed of oxygen and hydrogen atoms, biological life
Name Hour AP Biology Lab: Dissolved Oxygen in Aquatic Ecosystem: The Relationship between Temperature, DO, and Respiration Rates Although water is composed of oxygen and hydrogen atoms, biological life
1 INTRODUCTION 2 MOTIVATION FOR THE PRESENT EXPERIMENT. Dynamics of the Salt-Freshwater Mixing Zone in Ocean Beaches. N. Cartwright 1 and P.
 Second International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers Monitoring, Modeling, and Management. Mérida, Mexico, March 3 April, 3 Dynamics of the Salt-Freshwater Mixing Zone in Ocean Beaches
Second International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers Monitoring, Modeling, and Management. Mérida, Mexico, March 3 April, 3 Dynamics of the Salt-Freshwater Mixing Zone in Ocean Beaches
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
Ocean Literacy The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate.
 Freshand Salt Principle 3 Ocean Literacy The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate. Great Lakes Literacy The Great Lakes influence local and regional weather and climate. 49 Fresh Salt and
Freshand Salt Principle 3 Ocean Literacy The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate. Great Lakes Literacy The Great Lakes influence local and regional weather and climate. 49 Fresh Salt and
Chapter Concepts LIFE IN WATER. The Hydrologic Cycle. The Hydrologic Cycle
 Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems?
 Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Causes of Eutrophication and its Effects of on Aquatic Ecosystems. Eutrophication can occur when inorganic nutrients are introduced into an aquatic
 Rachel Nash BIOL 271 Prof. Wagner T.A. Emily Bernhardt Eutrophication Lab Report 4/2/2008 Abstract Causes of Eutrophication and its Effects of on Aquatic Ecosystems Eutrophication can occur when inorganic
Rachel Nash BIOL 271 Prof. Wagner T.A. Emily Bernhardt Eutrophication Lab Report 4/2/2008 Abstract Causes of Eutrophication and its Effects of on Aquatic Ecosystems Eutrophication can occur when inorganic
SCIENCE CURRICULUM FIRST GRADE. 1. Explore using your senses to make observations. 2. Identify the five senses and communicate how they are used.
 SCIENCE CURRICULUM FIRST GRADE PLANTS ARE LIVING THINGS Your Senses 5.1 (Scientific Processes) A.1 1. Explore using your senses to make observations. 2. Identify the five senses and communicate how they
SCIENCE CURRICULUM FIRST GRADE PLANTS ARE LIVING THINGS Your Senses 5.1 (Scientific Processes) A.1 1. Explore using your senses to make observations. 2. Identify the five senses and communicate how they
High Latitude Environment
 9. Habitats: High Latitude Ecosystems High Latitude Environments Seasonal Processes Sea ice Food Fall Reproduction Bentho-pelagic coupling Food Weds Climate Change Effects Dr Rhian G. Waller 26th April
9. Habitats: High Latitude Ecosystems High Latitude Environments Seasonal Processes Sea ice Food Fall Reproduction Bentho-pelagic coupling Food Weds Climate Change Effects Dr Rhian G. Waller 26th April
Day in the Life of the Hudson & Harbor Vocabulary
 Day in the Life of the Hudson & Harbor Vocabulary adapt: to develop a way of dealing with conditions in a particular environment adaptation: a feature that allows an organism to adjust to differing environmental
Day in the Life of the Hudson & Harbor Vocabulary adapt: to develop a way of dealing with conditions in a particular environment adaptation: a feature that allows an organism to adjust to differing environmental
Earth s Water Reservoirs
 Earth s Water Reservoirs Introduction What do you think of when you hear the word reservoir? Living in Utah, most of us will think of a man made lake that stores needed water. Many of us have been swimming,
Earth s Water Reservoirs Introduction What do you think of when you hear the word reservoir? Living in Utah, most of us will think of a man made lake that stores needed water. Many of us have been swimming,
Microhabitats #1: Quantitative Study of Microhabitats
 Microhabitats #1: Quantitative Study of Microhabitats Adapted from: Microhabitats in Environmental Science Activities Kit by Michael Roa. The Center for Applied Research in Education, 1993. Microhabitats
Microhabitats #1: Quantitative Study of Microhabitats Adapted from: Microhabitats in Environmental Science Activities Kit by Michael Roa. The Center for Applied Research in Education, 1993. Microhabitats
Roof mounted solar panels on Bldg L, Verde Valley Campus. 1. One developed Acre can produce approx 100 KW of peak solar power.
 SOLAR OPPORTUNITIES Roof mounted solar panels on Bldg L, Verde Valley Campus There is a growing national commitment to the utilization of sustainable energy sources. Solar, wind, and bio- mass systems
SOLAR OPPORTUNITIES Roof mounted solar panels on Bldg L, Verde Valley Campus There is a growing national commitment to the utilization of sustainable energy sources. Solar, wind, and bio- mass systems
AP Environmental Science II. Unit 2-2: Alternative Energy
 NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 2-2, Alternative Energy AP Environmental Science II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE AP Environmental Science
NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 2-2, Alternative Energy AP Environmental Science II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE AP Environmental Science
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
Modeling Your Water Balance
 Modeling Your Water Balance Purpose To model a soil s water storage over a year Overview Students create a physical model illustrating the soil water balance using glasses to represent the soil column.
Modeling Your Water Balance Purpose To model a soil s water storage over a year Overview Students create a physical model illustrating the soil water balance using glasses to represent the soil column.
Planetary Energy Balance
 Planetary Energy Balance Overview of Planetary Energy Balance Energy coming into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun is always in balance with the energy leaving Earth s atmosphere going back out into
Planetary Energy Balance Overview of Planetary Energy Balance Energy coming into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun is always in balance with the energy leaving Earth s atmosphere going back out into
The Biosphere. GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 CHAPTER 15 The Biosphere GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.2 Climate Climate is a key abiotic factor
CHAPTER 15 The Biosphere GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.2 Climate Climate is a key abiotic factor
Survivability in Hawaii: What s Next After Sustainability? Pete Mouginis-Mark Office Vice Chancellor for Research, UH Manoa
 Survivability in Hawaii: What s Next After Sustainability? Pete Mouginis-Mark Office Vice Chancellor for Research, UH Manoa pmm@hawaii.edu How can we in Hawaii address our sustainability needs for renewable
Survivability in Hawaii: What s Next After Sustainability? Pete Mouginis-Mark Office Vice Chancellor for Research, UH Manoa pmm@hawaii.edu How can we in Hawaii address our sustainability needs for renewable
Chapter 3: Ocean Water
 Chapter 3: Ocean Water CHAPTER 3 PROJECT - DENSITY BOTTLES During the Golf Ball Density lab, you will see the ways in which fresh water interacts with salt water when the two are mixed. The two forms of
Chapter 3: Ocean Water CHAPTER 3 PROJECT - DENSITY BOTTLES During the Golf Ball Density lab, you will see the ways in which fresh water interacts with salt water when the two are mixed. The two forms of
Part I: Salish Sea Introduction. Review:
 Part I: Salish Sea Introduction Review: The Salish Sea The Salish Sea was formed about 20,000 years ago during the last ice age by the carving action of glaciers. There are 3 major parts of the Salish
Part I: Salish Sea Introduction Review: The Salish Sea The Salish Sea was formed about 20,000 years ago during the last ice age by the carving action of glaciers. There are 3 major parts of the Salish
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Temperature: Air vs. Water vs. More Water
 Temperature: Air vs. Water vs. More Water Temperature Adapted from: A Change in the Weather? in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Grade Level: basic Duration: 1 class Setting: classroom
Temperature: Air vs. Water vs. More Water Temperature Adapted from: A Change in the Weather? in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Grade Level: basic Duration: 1 class Setting: classroom
Effect of Water Temperature on Manatee Migration into Blue Spring State Park (Adaptations) Grade Level: Elementary 4/5
 Effect of Water Temperature on Manatee Migration into Blue Spring State Park (Adaptations) Grade Level: Elementary 4/5 Subject Area: Earth science, math, biology Duration: 1 hr. instruction/background
Effect of Water Temperature on Manatee Migration into Blue Spring State Park (Adaptations) Grade Level: Elementary 4/5 Subject Area: Earth science, math, biology Duration: 1 hr. instruction/background
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG
 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Environmental Constraints on the Restoration Success of Black Mangrove Habitats in the Northern Gulf of Mexico
 Environmental Constraints on the Restoration Success of Black Mangrove Habitats in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Jonathan M. Willis, Lauren K. Alleman, Christine N. Pickens, Laura C. Hundy, and Mark W. Hester
Environmental Constraints on the Restoration Success of Black Mangrove Habitats in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Jonathan M. Willis, Lauren K. Alleman, Christine N. Pickens, Laura C. Hundy, and Mark W. Hester
CH. 15 THE BIOSPHERE 1
 CH. 15 THE BIOSPHERE 1 15.1 BIOSPHERE Part of Earth where life exists All of Earth s ecosystems Biota all living things in biosphere Abiotic factors NOT included Ex: water, air, rocks 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS
CH. 15 THE BIOSPHERE 1 15.1 BIOSPHERE Part of Earth where life exists All of Earth s ecosystems Biota all living things in biosphere Abiotic factors NOT included Ex: water, air, rocks 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Study of the North-facing Slope. of the Grand Valley State University Ravines. B.M. Hussey. K.J. Sylvester
 Study of the North-facing Slope of the Grand Valley State University Ravines B.M. Hussey K.J. Sylvester Bio 215 Dr. Shontz I. INTRODUCTION The beech-maple climax forest, found in North America, grows only
Study of the North-facing Slope of the Grand Valley State University Ravines B.M. Hussey K.J. Sylvester Bio 215 Dr. Shontz I. INTRODUCTION The beech-maple climax forest, found in North America, grows only
Water Quality Temperature
 Water Quality Computer 10 The temperature of a body of water influences its overall quality. Water temperatures outside the normal range for a stream or river can cause harm to the aquatic organisms that
Water Quality Computer 10 The temperature of a body of water influences its overall quality. Water temperatures outside the normal range for a stream or river can cause harm to the aquatic organisms that
Case Study: Bio-Climatic Building Design for Tropical Climates
 Case Study: Bio-Climatic Building Design for Tropical Climates The project is located in a Development Zone and the objectives include: opening the city towards the sea, to reinvigorate the city centre,
Case Study: Bio-Climatic Building Design for Tropical Climates The project is located in a Development Zone and the objectives include: opening the city towards the sea, to reinvigorate the city centre,
Chapter 4 Guided Notes and presentations
 Module 9: The Unequal Heating of Earth Definitions Troposphere: Chapter 4 Guided Notes and presentations Stratosphere: Albedo: Ozone Graph the following temperature data and corresponding layers of the
Module 9: The Unequal Heating of Earth Definitions Troposphere: Chapter 4 Guided Notes and presentations Stratosphere: Albedo: Ozone Graph the following temperature data and corresponding layers of the
NYS STANDARD/KEY IDEA/PERFORMANCE INDICATOR. LE Core* 1.1a, a-b, 4.1.1d, 4.1.f, 4.6.1a, 4.6.1c, 4.6.1d, 4.6.1g. Conducting an Experiment
 September Environmental Scientists The web of life The scientific method The Biosphere The third planet from the sun The universe Doppler Effect The sun s family The moon Tidal Forces The seasons The Earth
September Environmental Scientists The web of life The scientific method The Biosphere The third planet from the sun The universe Doppler Effect The sun s family The moon Tidal Forces The seasons The Earth
Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats
 Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats Background & Key Concepts Coral reefs grow at rates ranging from 1 cm to 100 cm per year. Over long periods of time, they can form huge structures, making
Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats Background & Key Concepts Coral reefs grow at rates ranging from 1 cm to 100 cm per year. Over long periods of time, they can form huge structures, making
EVALUATING WATER REQUIREMENTS OF DEVELOPING WALNUT ORCHARDS IN THE SACRAMENTO VALLEY
 EVALUATING WATER REQUIREMENTS OF DEVELOPING WALNUT ORCHARDS IN THE SACRAMENTO VALLEY Allan Fulton ABSTRACT Most of the research on irrigation of walnuts has primarily focused on plant water relations and
EVALUATING WATER REQUIREMENTS OF DEVELOPING WALNUT ORCHARDS IN THE SACRAMENTO VALLEY Allan Fulton ABSTRACT Most of the research on irrigation of walnuts has primarily focused on plant water relations and
4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems
 biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and abiotic factors including
biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and abiotic factors including
Keansburg High School Science Department. Pacing Chart. Text: Life on an Ocean Planet; Current Publishing Corporation; 2010
 Keansburg High School Science Department Pacing Chart Course: Marine Science Text: Life on an Ocean Planet; Current Publishing Corporation; 2010 Ice Breaker Unit 1: Importance of Ocean Exploration Unit
Keansburg High School Science Department Pacing Chart Course: Marine Science Text: Life on an Ocean Planet; Current Publishing Corporation; 2010 Ice Breaker Unit 1: Importance of Ocean Exploration Unit
Rena Long-Term Environmental Recovery monitoring programme
 Rena Long-Term Environmental Recovery monitoring programme About the report Q. What is the Rena Long-Term Environmental Recovery Monitoring Programme? A comprehensive scientific sampling and monitoring
Rena Long-Term Environmental Recovery monitoring programme About the report Q. What is the Rena Long-Term Environmental Recovery Monitoring Programme? A comprehensive scientific sampling and monitoring
Intertidal Ecology. Key concepts: intertidal zones, nutrient upwelling, desiccation, holdfasts, water vascular systems, larval recruitment
 Intertidal Ecology Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to do the following: Describe the rocky intertidal zone Differentiate between the four intertidal zones Explain one way that physical processes
Intertidal Ecology Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to do the following: Describe the rocky intertidal zone Differentiate between the four intertidal zones Explain one way that physical processes
Global Warming Science Solar Radiation
 SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
yk4lm (1:26) vd_90 (4:37)
 Properties of Water Video Notes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2vfld5 yk4lm (1:26) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ivu4nl vd_90 (4:37) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0ens nj4zfz8#t=4.4600086 (4:58) new
Properties of Water Video Notes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2vfld5 yk4lm (1:26) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ivu4nl vd_90 (4:37) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0ens nj4zfz8#t=4.4600086 (4:58) new
Electric Forward Market Report
 Mar-01 Mar-02 Jun-02 Sep-02 Dec-02 Mar-03 Jun-03 Sep-03 Dec-03 Mar-04 Jun-04 Sep-04 Dec-04 Mar-05 May-05 Aug-05 Nov-05 Feb-06 Jun-06 Sep-06 Dec-06 Mar-07 Jun-07 Sep-07 Dec-07 Apr-08 Jun-08 Sep-08 Dec-08
Mar-01 Mar-02 Jun-02 Sep-02 Dec-02 Mar-03 Jun-03 Sep-03 Dec-03 Mar-04 Jun-04 Sep-04 Dec-04 Mar-05 May-05 Aug-05 Nov-05 Feb-06 Jun-06 Sep-06 Dec-06 Mar-07 Jun-07 Sep-07 Dec-07 Apr-08 Jun-08 Sep-08 Dec-08
SOLAR PASSIVE DESIGN: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE
 SOLAR PASSIVE DESIGN: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE Understanding Climate and Atmosphere Human impact on global weather Energy outlook in India Energy needs in buildings Comfort zone Solar passive design- Case
SOLAR PASSIVE DESIGN: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE Understanding Climate and Atmosphere Human impact on global weather Energy outlook in India Energy needs in buildings Comfort zone Solar passive design- Case
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4478546470* GEOGRAPHY 0460/43 Paper 4 Alternative to Coursework October/November 2016 Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4478546470* GEOGRAPHY 0460/43 Paper 4 Alternative to Coursework October/November 2016 Candidates
Estuary Adventures. Background. Objective
 Estuary Adventures Objective Students will work in groups to understand the concept of estuaries, their importance, and the role that density plays in the mixing of fresh and salt water. Students will
Estuary Adventures Objective Students will work in groups to understand the concept of estuaries, their importance, and the role that density plays in the mixing of fresh and salt water. Students will
Factors affecting evaporation 3/16/2010. GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology. Several factors affect the rate of evaporation from surfaces:
 GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology Some definitions Evaporation conversion of a liquid to a vapour Transpiration that part of evaporation which enters the atmosphere through plants Total Evaporation
GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology Some definitions Evaporation conversion of a liquid to a vapour Transpiration that part of evaporation which enters the atmosphere through plants Total Evaporation
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS The base of the ocean s food chains is formed by A. blue whales. B. plankton. C. coral reefs. D. sargassums. The place where the ocean meets the land is the The
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS The base of the ocean s food chains is formed by A. blue whales. B. plankton. C. coral reefs. D. sargassums. The place where the ocean meets the land is the The
Biotic and Abiotic Factors
 Biotic and Abiotic Factors Different Approaches to the Study of Ecology Ecology is the study of an organism or organisms and their relationship to the environment. An organism s environment consists of
Biotic and Abiotic Factors Different Approaches to the Study of Ecology Ecology is the study of an organism or organisms and their relationship to the environment. An organism s environment consists of
Think About It (not on notes)
 Aquatic Ecosystems Think About It (not on notes) We call our planet Earth, yet nearly three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered with water. Despite the vital roles aquatic ecosystems play in the biosphere,
Aquatic Ecosystems Think About It (not on notes) We call our planet Earth, yet nearly three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered with water. Despite the vital roles aquatic ecosystems play in the biosphere,
Design Guide for Solar Water Pumping. Dankoff Solar Products, Inc.
 Special advance-publication for the Advanced PV Course Solar Energy International May 2001 Design Guide for Solar Water Pumping Dankoff Solar Products, Inc. The world s most diverse selection of solar
Special advance-publication for the Advanced PV Course Solar Energy International May 2001 Design Guide for Solar Water Pumping Dankoff Solar Products, Inc. The world s most diverse selection of solar
ISPRS Archives XXXVIII-8/W3 Workshop Proceedings: Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture
 IMPACT ANALYSIS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON DIFFERENT CROPS IN GUJARAT, INDIA Vyas Pandey, H.R. Patel and B.I. Karande Department of Agricultural Meteorology, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110, India
IMPACT ANALYSIS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON DIFFERENT CROPS IN GUJARAT, INDIA Vyas Pandey, H.R. Patel and B.I. Karande Department of Agricultural Meteorology, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110, India
Information paper 17. Prepared by: David Clark. book:
 Information paper 17 Thermal comfort standards Prepared by: David Clark A paper referenced in the book: Cundall Johnston & Partners LLP. 2013 Issue 1.0: 29 July 2013 This information paper is one of a
Information paper 17 Thermal comfort standards Prepared by: David Clark A paper referenced in the book: Cundall Johnston & Partners LLP. 2013 Issue 1.0: 29 July 2013 This information paper is one of a
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change
 Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Fairwinds Schooner Cove Redevelopment
 www.archipelago.ca Habitatt Assessment Report April 2017 Habitatt Assessment Report Fairwinds Schooner Cove Redevelopment May 2017 Prepared for: Prepared by: ICR Projects Inc. Leo Mariotto #300 555 Sixth
www.archipelago.ca Habitatt Assessment Report April 2017 Habitatt Assessment Report Fairwinds Schooner Cove Redevelopment May 2017 Prepared for: Prepared by: ICR Projects Inc. Leo Mariotto #300 555 Sixth
Homework for Unit Vocab for Unit 6; due: 2. Pg 333 (1-5), Pg 335 (1-4), Pg 337 (1-4), Pg 339 (1-6), No sentences; due:
 Unit 6 Heat Homework for Unit 6 1. Vocab for Unit 6; due: 2. Pg 333 (1-5), Pg 335 (1-4), Pg 337 (1-4), Pg 339 (1-6), No sentences; due: 3. Temperature change activity; due: 4. Heat Transfer Homework; due:
Unit 6 Heat Homework for Unit 6 1. Vocab for Unit 6; due: 2. Pg 333 (1-5), Pg 335 (1-4), Pg 337 (1-4), Pg 339 (1-6), No sentences; due: 3. Temperature change activity; due: 4. Heat Transfer Homework; due:
Vibrio parahaemolyticus Control Plan
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Control Plan June 1 August 31, 2017 New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Water Monitoring and Standards / Division of Fish & Wildlife and New Jersey Department
Vibrio parahaemolyticus Control Plan June 1 August 31, 2017 New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Water Monitoring and Standards / Division of Fish & Wildlife and New Jersey Department
Climate Change and Coral Bleaching
 Rising ocean temperatures may push coral reefs to their limits. Climate Change and Coral Bleaching http://www.nova.org.au/coral-bleaching Essentials! Corals are animals that live in a mutually beneficial
Rising ocean temperatures may push coral reefs to their limits. Climate Change and Coral Bleaching http://www.nova.org.au/coral-bleaching Essentials! Corals are animals that live in a mutually beneficial
SUCCESSION AND STABILITY
 Chapter Concepts Chapter 20 SUCCESSION AND STABILITY Community changes during succession include increases in species diversity and changes in species composition Ecosystem changes during succession include
Chapter Concepts Chapter 20 SUCCESSION AND STABILITY Community changes during succession include increases in species diversity and changes in species composition Ecosystem changes during succession include
Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems How would you describe your Community? Did you include your family and friends? Did you include your school? Did you include plants and animals? A biological
Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems How would you describe your Community? Did you include your family and friends? Did you include your school? Did you include plants and animals? A biological
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
3 2 Energy Flow. Slide 1 of 41. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
1 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle
 Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin
 The BACC Author Team Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin 4u Springer Contents Preface The BACC Author Team Acknowledgements V VII XIII 1 Introduction and Summary 1 1.1 The BACC Approach
The BACC Author Team Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin 4u Springer Contents Preface The BACC Author Team Acknowledgements V VII XIII 1 Introduction and Summary 1 1.1 The BACC Approach
Climates and Ecosystems
 Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
How Might Global Warming Affect Your Community?
 Climate Change Activity 6 How Might Global Warming Affect Your Community? Goals In this activity you will: Brainstorm the ways that global warming might influence the Earth. List ways that global warming
Climate Change Activity 6 How Might Global Warming Affect Your Community? Goals In this activity you will: Brainstorm the ways that global warming might influence the Earth. List ways that global warming
Curriculum Guide. National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science
 National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
Performance Evaluation of Rainwater Harvesting Systems Toronto, Ontario
 Performance Evaluation of Rainwater Harvesting Systems Toronto, Ontario Prepared by: Toronto and Region Conservation 2010 Toronto, Ontario A final report prepared by: Toronto and Region Conservation Authority
Performance Evaluation of Rainwater Harvesting Systems Toronto, Ontario Prepared by: Toronto and Region Conservation 2010 Toronto, Ontario A final report prepared by: Toronto and Region Conservation Authority
COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER
 COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of dissolved substances. Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater, measured in parts per thousand
COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of dissolved substances. Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater, measured in parts per thousand
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
The Status of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the Stanislaus River Summary report of 2015 snorkel surveys
 The Status of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the Stanislaus River Summary report of 2015 snorkel surveys Prepared By: Matt Peterson Jason Guignard Andrea Fuller Doug Demko FISHBIO 1617 S. Yosemite
The Status of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the Stanislaus River Summary report of 2015 snorkel surveys Prepared By: Matt Peterson Jason Guignard Andrea Fuller Doug Demko FISHBIO 1617 S. Yosemite
Renewable Energy. Visible light. Cool air. Warm air. Condensation. Precipitation. Evaporation
 Renewable Energy All renewable energy sources derive from the Sun. The Sun provides the energy that drives our weather systems and water cycle. It is the prime source of all energy on Earth and it is essential
Renewable Energy All renewable energy sources derive from the Sun. The Sun provides the energy that drives our weather systems and water cycle. It is the prime source of all energy on Earth and it is essential
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline William P. Cunningham University of Minnesota Mary Ann Cunningham Vassar College Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 11 Living Systems
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
A Case Study on Ocean Acidification By Sindia M. Rivera-Jiménez, Ph.D. Department of Natural Science, Santa Fe College, Gainesville Fl
 A Case Study on Ocean Acidification By Sindia M. Rivera-Jiménez, Ph.D. Department of Natural Science, Santa Fe College, Gainesville Fl Please read the following abstract of an article from the journal
A Case Study on Ocean Acidification By Sindia M. Rivera-Jiménez, Ph.D. Department of Natural Science, Santa Fe College, Gainesville Fl Please read the following abstract of an article from the journal
GC2: Components of the Earth System Working Together
 Global Connections: Earth Systems at the Global Scale GC2: Components of the Earth System Working Together Purpose To develop familiarity with interactions among the major components of the Earth system
Global Connections: Earth Systems at the Global Scale GC2: Components of the Earth System Working Together Purpose To develop familiarity with interactions among the major components of the Earth system
Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed
 Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed Linda Green URI Watershed Watch 1-87-95, lgreen@uri.edu WATER QUALITY IS A REFLECTION OF THE ACTIVITIES IN THE LANDS AND WATERS
Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed Linda Green URI Watershed Watch 1-87-95, lgreen@uri.edu WATER QUALITY IS A REFLECTION OF THE ACTIVITIES IN THE LANDS AND WATERS
Macro and Micro Climate Climate
 The following text is taken from University of Strathclyde's Energy Systems Research Unit ESRU's web site (file type '16-Climate.pdf') Macro and Micro Climate Climate The climate of the earth consists
The following text is taken from University of Strathclyde's Energy Systems Research Unit ESRU's web site (file type '16-Climate.pdf') Macro and Micro Climate Climate The climate of the earth consists
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Macmillan/McGraw-Hill
 First Grade Curriculum Science Macmillan/McGraw-Hill -- 2002 LIFE SCIENCE UNIT A-LIFE SCIENCE PLANTS ARE LIVING THINGS ALL ABOUT LIVING THINSGS SENSES: Explore using senses to make observations Identify
First Grade Curriculum Science Macmillan/McGraw-Hill -- 2002 LIFE SCIENCE UNIT A-LIFE SCIENCE PLANTS ARE LIVING THINGS ALL ABOUT LIVING THINSGS SENSES: Explore using senses to make observations Identify
Activities for Exhibit Exploration
 This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
EVALUATION OF THE SOLAR INCOME FOR BRAŞOV URBAN AREA
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. (5) - Series I: Engineering Sciences EVALUATION OF THE SOLAR INCOME FOR BRAŞOV URBAN AREA C. ŞERBAN E. EFTIMIE Abstract: Energy is an essential factor
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. (5) - Series I: Engineering Sciences EVALUATION OF THE SOLAR INCOME FOR BRAŞOV URBAN AREA C. ŞERBAN E. EFTIMIE Abstract: Energy is an essential factor
UNIT V--FUEL MOISTURE
 UNIT V--FUEL MOISTURE The fuel, moisture content in natural fuels is such an important factor to fuels availability for fire ignition and combustion that we have devoted an entire unit to the subject.
UNIT V--FUEL MOISTURE The fuel, moisture content in natural fuels is such an important factor to fuels availability for fire ignition and combustion that we have devoted an entire unit to the subject.
Scientific Consensus Statement on the Likely Impacts of Climate Change on the Pacific Northwest. Executive Summary
 Scientific Consensus Statement on the Likely Impacts of Climate Change on the Pacific Northwest Executive Summary The signatories of this statement seek to describe the state of scientific knowledge regarding
Scientific Consensus Statement on the Likely Impacts of Climate Change on the Pacific Northwest Executive Summary The signatories of this statement seek to describe the state of scientific knowledge regarding
Environmental Principles & Concepts (EP&C)/COSA Correlation of 4 th - 7 th Grade CA Science Standards
 Environmental Principles & Concepts (EP&C)/COSA Correlation of 4 th - 7 th Grade CA Science Standards For ROSS Certifications at least nine of the 14 science standards are addressed during a 5-day program,
Environmental Principles & Concepts (EP&C)/COSA Correlation of 4 th - 7 th Grade CA Science Standards For ROSS Certifications at least nine of the 14 science standards are addressed during a 5-day program,
7.014 Lecture 20: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 2007
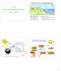 Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
First Grade Science Curriculum
 1.1 (1 st 9 Weeks) enchmarks =Core Knowledge asic text is Harcourt race Supplemental ooks supplied The Human ody 1. Discuss body systems and identify basic parts and functions associated with each a. Skeletal
1.1 (1 st 9 Weeks) enchmarks =Core Knowledge asic text is Harcourt race Supplemental ooks supplied The Human ody 1. Discuss body systems and identify basic parts and functions associated with each a. Skeletal
Table of Contents. Thermal Modeling of Buildings II. Biosphere 2: Original Goals. Biosphere 2: Revised Goals. Biosphere 2: Original goals
 Thermal Modeling of Buildings II This is the second lecture concerning itself with the thermal modeling of buildings. This second example deals with the thermodynamic budget of Biosphere 2, a research
Thermal Modeling of Buildings II This is the second lecture concerning itself with the thermal modeling of buildings. This second example deals with the thermodynamic budget of Biosphere 2, a research
