Chapter 2: Requirements Elicitation. Requirements Engineering
|
|
|
- Lester Blair
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2: Requirements Elicitation Requirements Engineering
2 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Eliciting Requirements Your Stakeholders Sample stakeholder s analysis template Case Study Gus Requirements Engineering 2
3 Requirements Elicitation is the first step in Requirements Engineering You need to use a variety of techniques to determine what the endusers and customers really want, because: Customers are not always good at describing their needs (litany of business jargons/assumptions) Technologists/Computer Scientists/SW Engineers are not always good at understanding/appreciating someone else s business concerns (we have jargons too!) Words/jargons are contextual Gus Requirements Engineering 3
4 Interviewing Techniques 1. Discuss requirements with all who have a stake in the system then: Create a coherent set of requirements that reflect the different stakeholder views Who are your stakeholders? Next, review the requirements document with stakeholders [to reach a consensus] Each stakeholder has a particular view of the system and how it should work RE captures concerns of each stakeholders. How do you resolve conflicting stakeholders views? Examples of Stakeholders: People who have something to contribute to a new system Customer (Clients) Ultimately stakeholders pay for the development End-users Interact with and Purchase the software after it is developed Users already familiar with the current system and will use the new system Problem Domain Experts People who are familiar with the problem that the software must solve Subject Matter Experts Ensures that product is technically feasible; understand innovative software/hardware technologies, protocols; can educate the customer Market Researchers People who have conducted surveys to determine trends and customer needs Software Engineers Gus Requirements Engineering 4
5 Interviewing Techniques How to resolve conflicting stakeholders views Ask customer to prioritize requirements into categories Example Prioritization Scheme: Requirements that absolutely must be met Essential Requirements that are highly desirable but not necessary Desirable Requirements that are possible, but could be eliminated Optional Be a good listener Do not argue with the customer Gus Requirements Engineering 5
6 Interviewing Techniques Sample questions when you interview stakeholders Functional Requirements Functionality: What will the system do? When will the system do it? Are there several modes of operation? What kinds of computations or data transformations must be performed? What are the appropriate reactions to possible stimuli? Data For both input and output, what should be the format of the data? Must any data be retained for any period of time? Design Constraints Physical Environment Where is the equipment to be located? Is there one or several location? Are there constraints on size of the system (Handheld/Server/PC etc)? Are there any COTS or other constraints on programming language, OS because of existing software components? Interfaces Is input coming from one or more other systems ( upstream )? Is output going to one or more other systems ( downstream )? What is the protocol for the upstream and downstream systems? End-Users Who will use the system? Will there be several types of users? What is the skill level of each user? Gus Requirements Engineering 6
7 Interviewing Techniques Sample questions when you interview stakeholders Quality Requirements Performance Are there constraints on execution speed, response time or throughput? How much data will flow through the system? How often will data be received or sent? Usability and Human Factors What kind of training will be required for each type of user? How easy should it be for a user to understand and use the system? Security Must access to the system or information be controlled? Should each user s data be isolated from other users? Should user programs be isolated from other programs and from the OS? Reliability and Availability Must the system detect and isolate faults? What is the prescribed Mean Time between Failures? Is there a maximum time allowed for restarting the system after a failure? How often will the system be backed up? Must back up copies be stored at a different location Maintainability When and in what ways might the system be changed in the future? How easy should it be to add features to the system? How easy should it be to port (or migrate) the system from one platform to another? Precision and Accuracy Timeline /Cost Gus Requirements Engineering 7
8 Techniques 2. Review available documentation Procedures of manual tasks, specifications, manuals 3. Observe current system Gather info about how end-users perform their tasks 4. Apprentice with users Learn users tasks in detail as they are performed 5. Use domain-specific strategies Joint Application Design (JAD) for information systems 6. Use Requirements template Volere stakeholders requirements template Gus Requirements Engineering 8
9 Volere Stakeholders Requirements Template It is Ok (but not necessary) to adapt the Volere Template to your requirements elicitation process: Let s review the template: Additional Reading: Volere Specification manual: Reference Text: Mastering the Requirements Process, second edition, Suzanne Robertson, James Robertson, Addison Wesley, ISBN-13: Gus Requirements Engineering 9
10 Summary Existing Documents Stakeholders wants/needs Domain Models Current organization and systems Elicit Requirements Current situation Model Requirements Template Reuse library Gus Requirements Engineering 10
11 Case Study: Source of requirements Existing Documents Current system Elicit Requirements Current situation Model Stakeholders wants/needs Source of Requirements Gus Requirements Engineering 11
12 Example: Case Study Case Study Case Study materials will be presented in class Gus Requirements Engineering 12
Dr. Aldo Dagnino ABB, Inc. US Corporate Research Center October 21 st, Requirements Engineering
 Dr. Aldo Dagnino ABB, Inc. US Corporate Research Center October 21 st, 2003 Requirements Engineering Class Objectives Students will be able to define the two process areas associated with the Requirements
Dr. Aldo Dagnino ABB, Inc. US Corporate Research Center October 21 st, 2003 Requirements Engineering Class Objectives Students will be able to define the two process areas associated with the Requirements
Requirements Engineering. Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB
 Requirements Engineering Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB 0131 650 5899 mfelici@inf.ed.ac.uk Administration SEOC1 Tutorials start in week 3 SEOC1 Communications: Mailing List: seoc1-students@inf.ed.acuk
Requirements Engineering Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB 0131 650 5899 mfelici@inf.ed.ac.uk Administration SEOC1 Tutorials start in week 3 SEOC1 Communications: Mailing List: seoc1-students@inf.ed.acuk
Verification and Validation
 System context Subject facet Usage facet IT system facet Development facet Validation Core activities Elicitation Negotiation Context of consideration Execution of RE activities Created requirements artefacts
System context Subject facet Usage facet IT system facet Development facet Validation Core activities Elicitation Negotiation Context of consideration Execution of RE activities Created requirements artefacts
Introduction to Software Engineering
 Introduction to Software Engineering 2. Requirements Collection Mircea F. Lungu Based on a lecture by Oscar Nierstrasz. Roadmap > The Requirements Engineering Process > Functional and non-functional requirements
Introduction to Software Engineering 2. Requirements Collection Mircea F. Lungu Based on a lecture by Oscar Nierstrasz. Roadmap > The Requirements Engineering Process > Functional and non-functional requirements
Requirements A Socio Technical Discipline
 Requirements A Socio Technical Discipline This is the fourth article in a series that explains the thinking behind the Volere 1 requirements techniques. Subsequent articles will explore various aspects
Requirements A Socio Technical Discipline This is the fourth article in a series that explains the thinking behind the Volere 1 requirements techniques. Subsequent articles will explore various aspects
REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING
 1 REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING Chapter 4- by Ian Sommerville TOPICS COVERED Functional and non-functional requirements The software requirements document Requirements specification Requirements engineering
1 REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING Chapter 4- by Ian Sommerville TOPICS COVERED Functional and non-functional requirements The software requirements document Requirements specification Requirements engineering
8/30/2010. Lecture 1. Topics covered. Functional and non-functional requirements The software requirements document Requirements specification
 Topics covered Functional and non-functional requirements The software requirements document Chapter 4 Requirements Engineering Requirements specification Requirements engineering processes Lecture 1 Requirements
Topics covered Functional and non-functional requirements The software requirements document Chapter 4 Requirements Engineering Requirements specification Requirements engineering processes Lecture 1 Requirements
Another Elevator System in Volere Pattern
 Another Elevator System in Volere Pattern A software-based system is required to control lifts (elevators) manufactured by Skyhi Lifts. Lifts are constrained to shafts (one lift per shaft) and are moved
Another Elevator System in Volere Pattern A software-based system is required to control lifts (elevators) manufactured by Skyhi Lifts. Lifts are constrained to shafts (one lift per shaft) and are moved
Business Process Oriented Requirements Engineering Process
 Process Oriented Requirements Engineering Process Tomoyuki Arao, Eiji Goto, Tomoko Nagata Nomura Research Institute, Ltd. tarao@alumni.cmu.edu, e-gotou@nri.co.jp, t-nagata@nri.co.jp Abstract Although requirements
Process Oriented Requirements Engineering Process Tomoyuki Arao, Eiji Goto, Tomoko Nagata Nomura Research Institute, Ltd. tarao@alumni.cmu.edu, e-gotou@nri.co.jp, t-nagata@nri.co.jp Abstract Although requirements
Building BA competency in an IT organization
 2014 BA Convention Building BA competency in an IT organization Haresh Chetnani BA CoE, Fiserv India 2014 2014 BA Convention 2 What does this convey? When the delivery does not meet expectation Courtesy
2014 BA Convention Building BA competency in an IT organization Haresh Chetnani BA CoE, Fiserv India 2014 2014 BA Convention 2 What does this convey? When the delivery does not meet expectation Courtesy
[Name] [ ID] [Contact Number]
![[Name] [ ID] [Contact Number] [Name] [ ID] [Contact Number]](/thumbs/76/74089438.jpg) [Name] [Email ID] [Contact Number] THIS IS ONLY MODEL RESUME - DO NOT COPY AND PASTE INTO YOUR RESUME. PROFILE SUMMARY 15+ years of IT experience in Consulting and worked with the Major clients for the
[Name] [Email ID] [Contact Number] THIS IS ONLY MODEL RESUME - DO NOT COPY AND PASTE INTO YOUR RESUME. PROFILE SUMMARY 15+ years of IT experience in Consulting and worked with the Major clients for the
Organising Requirements
 Requirements Organisation, Analysis and Evolution Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 20 CITS4401 Software Requirements and Design 2 Viewpoints Organising Requirements Interactor viewpoints:
Requirements Organisation, Analysis and Evolution Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 20 CITS4401 Software Requirements and Design 2 Viewpoints Organising Requirements Interactor viewpoints:
Requirements Engineering Processes. Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 7 Slide 1
 Requirements Engineering Processes Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 7 Slide 1 Objectives To describe the principal requirements engineering activities and their relationships
Requirements Engineering Processes Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 7 Slide 1 Objectives To describe the principal requirements engineering activities and their relationships
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition
 Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition Learning Objectives Describe the activities of the systems analysis life cycle phase Explain the effect of business process reengineering
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition Learning Objectives Describe the activities of the systems analysis life cycle phase Explain the effect of business process reengineering
Requirements Engineering
 Requirements Engineering Professor Ray Welland Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow E-mail: ray@dcs.gla.ac.uk The Importance of Requirements Identifying (some) requirements is the starting
Requirements Engineering Professor Ray Welland Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow E-mail: ray@dcs.gla.ac.uk The Importance of Requirements Identifying (some) requirements is the starting
Application of Plug-in Technology in Computer Software Technology
 2018 International Conference on Education, Management and Social Science (EMSS 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-554-4 Application of Plug-in Technology in Computer Software Technology Yi-Dan Xu and Li Wang ABSTRACT
2018 International Conference on Education, Management and Social Science (EMSS 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-554-4 Application of Plug-in Technology in Computer Software Technology Yi-Dan Xu and Li Wang ABSTRACT
Requirements Engineering
 Requirements Engineering Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Topics covered Requirements Engineering Requirements Elicitation Requirements Validation Requirements Management 2 2 Requirement Engineering The goal
Requirements Engineering Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Topics covered Requirements Engineering Requirements Elicitation Requirements Validation Requirements Management 2 2 Requirement Engineering The goal
Requirements Knowledge Model. Business. Event. Business. responding. Business. Use Case 1.. Business tracing * * * * Requirement
 Requirements Knowledge Model This model provides a language for communicating the knowledge that you discover during requirements-related activities. We present it here as a guide to the information you
Requirements Knowledge Model This model provides a language for communicating the knowledge that you discover during requirements-related activities. We present it here as a guide to the information you
The software process
 Software Processes The software process A structured set of activities required to develop a software system Specification; Design; Validation; Evolution. A software process model is an abstract representation
Software Processes The software process A structured set of activities required to develop a software system Specification; Design; Validation; Evolution. A software process model is an abstract representation
Volere Requirements: How to Get Started
 Requirements: How to Get Started Since its introduction in 1995, the approach to requirements has been adopted by thousands of organizations around the world. We felt that it was time to summarize some
Requirements: How to Get Started Since its introduction in 1995, the approach to requirements has been adopted by thousands of organizations around the world. We felt that it was time to summarize some
Tradeoffs in Using SOA with
 Architecture-Centric Evolution (ACE) Working Group @ GSAW 2009 Tradeoffs in Using SOA with Legacy Components Scott Tilley stilley@sei.cmu.edu Components of an SOA-Based System End User Application Portal
Architecture-Centric Evolution (ACE) Working Group @ GSAW 2009 Tradeoffs in Using SOA with Legacy Components Scott Tilley stilley@sei.cmu.edu Components of an SOA-Based System End User Application Portal
Version 4.7. CMS Online Quarterly Release Notes. January Copyright 2018 International Human Resources Development Corporation
 Version 4.7 CMS Online Quarterly Release Notes January 2018 Copyright 2018 International Human Resources Development Corporation 4.7 Feature Updates Quarterly Update Version 4.7 was released on January
Version 4.7 CMS Online Quarterly Release Notes January 2018 Copyright 2018 International Human Resources Development Corporation 4.7 Feature Updates Quarterly Update Version 4.7 was released on January
Software Processes. Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1
 Software Processes Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be
Software Processes Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be
CSE 435 Software Engineering. Sept 14, 2015
 CSE 435 Software Engineering Sept 14, 2015 What is Software Engineering Where Does the Software Engineer Fit In? Computer science: focusing on computer hardware, compilers, operating systems, and programming
CSE 435 Software Engineering Sept 14, 2015 What is Software Engineering Where Does the Software Engineer Fit In? Computer science: focusing on computer hardware, compilers, operating systems, and programming
Business Events as a focal point of analysis
 Business Events as a focal point of analysis November 5, 2015 - Las Vegas John Bethke, MBA, CBAP, CPA Bethke Consulting, LLC Purpose of Presentation! To describe an analysis framework using business events
Business Events as a focal point of analysis November 5, 2015 - Las Vegas John Bethke, MBA, CBAP, CPA Bethke Consulting, LLC Purpose of Presentation! To describe an analysis framework using business events
How to Successfully Collect, Analyze and Implement User Requirements Gerry Clancy Glenn Berger
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 24, 2012 How to Successfully Collect, Analyze and Implement User Requirements Gerry Clancy Glenn Berger Requirements Gathering
Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 24, 2012 How to Successfully Collect, Analyze and Implement User Requirements Gerry Clancy Glenn Berger Requirements Gathering
version NDIA CMMI Conf 3.5 SE Tutorial RE - 1
 Requirements Engineering SE Tutorial RE - 1 What Are Requirements? Customer s needs, expectations, and measures of effectiveness Items that are necessary, needed, or demanded Implicit or explicit criteria
Requirements Engineering SE Tutorial RE - 1 What Are Requirements? Customer s needs, expectations, and measures of effectiveness Items that are necessary, needed, or demanded Implicit or explicit criteria
Requirements Engineering and SCRUM. Peter Dolog dolog [at] cs [dot] aau [dot] dk E2-201 Information Systems February 13, 2007
![Requirements Engineering and SCRUM. Peter Dolog dolog [at] cs [dot] aau [dot] dk E2-201 Information Systems February 13, 2007 Requirements Engineering and SCRUM. Peter Dolog dolog [at] cs [dot] aau [dot] dk E2-201 Information Systems February 13, 2007](/thumbs/72/67491645.jpg) Requirements Engineering and SCRUM Peter Dolog dolog [at] cs [dot] aau [dot] dk E2-201 Information Systems February 13, 2007 2 Scrum Larman Ch. 7 3 Scrum Model Start A small group is responsible for picking
Requirements Engineering and SCRUM Peter Dolog dolog [at] cs [dot] aau [dot] dk E2-201 Information Systems February 13, 2007 2 Scrum Larman Ch. 7 3 Scrum Model Start A small group is responsible for picking
What are Requirements? SENG1031 Software Engineering Workshop 1. My Notes. System Overview: The Big Picture
 What are Requirements? SENG1031 Software Engineering Workshop 1 Requirements, An Overview Peter Ho CSE, UNSW 5 Aug 2010 Requirements are a collection of statements defined by the System Stakeholders. These
What are Requirements? SENG1031 Software Engineering Workshop 1 Requirements, An Overview Peter Ho CSE, UNSW 5 Aug 2010 Requirements are a collection of statements defined by the System Stakeholders. These
Software Processes. Objectives. Topics covered. The software process. Waterfall model. Generic software process models
 Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
II. Software Life Cycle. Laurea Triennale in Informatica Corso di Ingegneria del Software I A.A. 2006/2007 Andrea Polini
 II. Software Life Cycle Laurea Triennale in Informatica Corso di Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process
II. Software Life Cycle Laurea Triennale in Informatica Corso di Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process
CCU 2010 / Identifying User Needs and Establishing Requirements. Lesson 7. (Part1 Requirements & Data Collection)
 CCU 2010 / 2011 Lesson 7 Identifying User Needs and Establishing Requirements (Part1 Requirements & Data Collection) Previous Lesson (1) Participative Design Users are active in Developing Discussing and
CCU 2010 / 2011 Lesson 7 Identifying User Needs and Establishing Requirements (Part1 Requirements & Data Collection) Previous Lesson (1) Participative Design Users are active in Developing Discussing and
Objectives. The software process. Topics covered. Waterfall model. Generic software process models. Software Processes
 Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Objectives Software Processes To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Change is constant. Obstacle to RE: Why requirement study? Limitation of the designers Different knowledge domains Not expertise Ubiquitous nature
 Design the right thing! Fang Chen Change is constant Requirement Design Creation What makes the change? Human nature Society Organization i Competitors Human nature: never satisfy ) 4 Why requirement study?
Design the right thing! Fang Chen Change is constant Requirement Design Creation What makes the change? Human nature Society Organization i Competitors Human nature: never satisfy ) 4 Why requirement study?
Knowledge Management
 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 9 Knowledge Management 9-1 Learning Objectives Define knowledge. Learn the characteristics of knowledge management. Describe organizational
Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 9 Knowledge Management 9-1 Learning Objectives Define knowledge. Learn the characteristics of knowledge management. Describe organizational
Chapter 6: Software Evolution and Reengineering
 Chapter 6: Software Evolution and Reengineering Harald Gall Software Engineering Group www.ifi.unizh.ch/swe/ Universität Zürich Institut für Informatik Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition.
Chapter 6: Software Evolution and Reengineering Harald Gall Software Engineering Group www.ifi.unizh.ch/swe/ Universität Zürich Institut für Informatik Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition.
SWE 211 Software Processes
 SWE 211 Software Processes These slides are designed and adapted from slides provided by Software Engineering 9 /e Addison Wesley 2011 by Ian Sommerville 1 Outlines Software process models Process activities
SWE 211 Software Processes These slides are designed and adapted from slides provided by Software Engineering 9 /e Addison Wesley 2011 by Ian Sommerville 1 Outlines Software process models Process activities
Topics covered. Software process models Process iteration Process activities The Rational Unified Process Computer-aided software engineering
 Software Processes Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Software Processes Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be used To describe outline process models for requirements engineering, software
Functional and non functional requirements. Requirements elicitation Requirements analysis Requirements validation Requirements management
 Requirements Engineering Eduardo Rodriguez Tello, PhD Cinvestav Tamaulipas 2009 2012 1 Content Requirements engineering Functional and non functional requirements Requirements engineering processes Requirements
Requirements Engineering Eduardo Rodriguez Tello, PhD Cinvestav Tamaulipas 2009 2012 1 Content Requirements engineering Functional and non functional requirements Requirements engineering processes Requirements
Software Processes 1
 Software Processes 1 Topics covered Software process models Process activities Coping with change 2 The software process A structured set of activities required to develop a software system. Many different
Software Processes 1 Topics covered Software process models Process activities Coping with change 2 The software process A structured set of activities required to develop a software system. Many different
Product Requirements. Requirements. Get it Right ASAP. Why Requirements are Difficult. Levels of S/W Requirements. Types of S/W Requirements
 Requirements Overview importance of getting right difficulty of getting right types and levels of characteristics of good the Requirements Development Process inception gathering, classification actors
Requirements Overview importance of getting right difficulty of getting right types and levels of characteristics of good the Requirements Development Process inception gathering, classification actors
Risk Management. Risk Management. Risk Reduction Patterns. Typical Sources of Risk. Dr. James A. Bednar. Dr. David Robertson
 Risk Management Risk Management Dr. James A. Bednar jbednar@inf.ed.ac.uk http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/jbednar Dr. David Robertson dr@inf.ed.ac.uk http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/ssp/members/dave.htm There are
Risk Management Risk Management Dr. James A. Bednar jbednar@inf.ed.ac.uk http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/jbednar Dr. David Robertson dr@inf.ed.ac.uk http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/ssp/members/dave.htm There are
Product Requirements. Requirements. Get it Right ASAP. Why Requirements are Difficult. Types of S/W Requirements. Levels of S/W Requirements
 Requirements Overview importance of getting right difficulty of getting right types and levels of characteristics of good the Requirements Development Process inception gathering, classification evaluation
Requirements Overview importance of getting right difficulty of getting right types and levels of characteristics of good the Requirements Development Process inception gathering, classification evaluation
In this Lecture you will Learn: Requirements Capture. User Requirements. Current System Investigating
 In this Lecture you will Learn: Requirements Capture Chapter 6A The distinction between the current and required systems When and how to apply the main fact finding techniques The roles played by users
In this Lecture you will Learn: Requirements Capture Chapter 6A The distinction between the current and required systems When and how to apply the main fact finding techniques The roles played by users
Lecture 01. Section - A
 Lecture 01 Section - A 1 Software Project Management Chapter 1 4 th Edition An Introduction Robert Hughes and Mike Cotterell 2 Outline of talk In this introduction the main questions to be addressed will
Lecture 01 Section - A 1 Software Project Management Chapter 1 4 th Edition An Introduction Robert Hughes and Mike Cotterell 2 Outline of talk In this introduction the main questions to be addressed will
Architecting Agile Businesses:
 Architecting Agile Businesses: A Guideline for the Business-Oriented Software Architect Kaine Ugwu SATURN 2016 Kaine Ugwu Software Architect Konga Online Shopping Ltd. Planning new technology insertion
Architecting Agile Businesses: A Guideline for the Business-Oriented Software Architect Kaine Ugwu SATURN 2016 Kaine Ugwu Software Architect Konga Online Shopping Ltd. Planning new technology insertion
Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling Twelfth Edition
 Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling Twelfth Edition Chapter Ten Working with Executives Type of Sponsor Involvement Micromanagement Effectiveness Invisibility
Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling Twelfth Edition Chapter Ten Working with Executives Type of Sponsor Involvement Micromanagement Effectiveness Invisibility
Buy:
 C108: DEMO OF QMS 9001:2015 INTERNAL AUDITOR TRAINING PPT PRESENTATION KIT Price 270 USD Buy: www.globalmanagergroup.com C108- Contents of QMS 9001:2015 Internal auditor PPT Presentation Training kit ISO
C108: DEMO OF QMS 9001:2015 INTERNAL AUDITOR TRAINING PPT PRESENTATION KIT Price 270 USD Buy: www.globalmanagergroup.com C108- Contents of QMS 9001:2015 Internal auditor PPT Presentation Training kit ISO
School Leadership Team Review Process Guide
 School Leadership Team Review Process Guide Structuring an Effective School Leadership Team February 15, 2019 February 11, 2019 Page 0 of 112 Structuring an Effective School Leadership Team To know why
School Leadership Team Review Process Guide Structuring an Effective School Leadership Team February 15, 2019 February 11, 2019 Page 0 of 112 Structuring an Effective School Leadership Team To know why
Requirements engineering
 Requirements engineering Paul Jackson School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are requirements? Traditional to distinguish functional from non-functional requirements. Functional requirements
Requirements engineering Paul Jackson School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are requirements? Traditional to distinguish functional from non-functional requirements. Functional requirements
Chapter 3 Prescriptive Process Models
 Chapter 3 Prescriptive Process Models - Generic process framework (revisited) - Traditional process models - Specialized process models - The unified process Generic Process Framework Communication Involves
Chapter 3 Prescriptive Process Models - Generic process framework (revisited) - Traditional process models - Specialized process models - The unified process Generic Process Framework Communication Involves
Role of Requirement Engineering Processes in Software Development
 Role of Requirement Engineering Processes in Software Development Dr Rajinder Singh (Department of Electronics,S.D College, Ambala Cantt Email: rsrana42@rediffmail.com) ABSTRACT The rapid development in
Role of Requirement Engineering Processes in Software Development Dr Rajinder Singh (Department of Electronics,S.D College, Ambala Cantt Email: rsrana42@rediffmail.com) ABSTRACT The rapid development in
Requirements Engineering Unit 4: Requirements modeling, specification & prioritization
 Unit 4: Requirements modeling, specification & prioritization Department of Computer Science / Rijksuniversiteit Groningen (RUG) http://www.cs.rug.nl/~liangp/teaching/courses/re2009fall/ 9/29/2009 1 9/29/2009
Unit 4: Requirements modeling, specification & prioritization Department of Computer Science / Rijksuniversiteit Groningen (RUG) http://www.cs.rug.nl/~liangp/teaching/courses/re2009fall/ 9/29/2009 1 9/29/2009
Lecture 7 Software Product Design and Project Overview
 Lecture 7 Software Product Design and Project Overview Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 16, 2008
Lecture 7 Software Product Design and Project Overview Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 16, 2008
Functional requirements and acceptance testing
 Functional requirements and acceptance testing Lecture 3 Software Engineering TDDC88/TDDC93 autumn 2007 Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Message from the course
Functional requirements and acceptance testing Lecture 3 Software Engineering TDDC88/TDDC93 autumn 2007 Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Message from the course
Knowledge Management Process
 Prepared By Cherwell Software Knowledge Management Process Vanderbilt University June 4, 2018 Knowledge Process Page 1 of 14 Contents Version History... 3 Summary... 4 Knowledge Centered Support (KCS)...
Prepared By Cherwell Software Knowledge Management Process Vanderbilt University June 4, 2018 Knowledge Process Page 1 of 14 Contents Version History... 3 Summary... 4 Knowledge Centered Support (KCS)...
Addressing the Challenges of Medical Content Authoring
 Addressing the Challenges of Medical Content Authoring Five Recommendations for Combining English Content Development with Localization A Publication of Lionbridge Life Sciences INTRODUCTION RECOMMENDATION
Addressing the Challenges of Medical Content Authoring Five Recommendations for Combining English Content Development with Localization A Publication of Lionbridge Life Sciences INTRODUCTION RECOMMENDATION
Now, I wish you lots of pleasure while reading this report. In case of questions or remarks please contact me at:
 Preface Somewhere towards the end of the second millennium the director of Vision Consort bv, Hans Brands, came up with the idea to do research in the field of embedded software architectures. He was particularly
Preface Somewhere towards the end of the second millennium the director of Vision Consort bv, Hans Brands, came up with the idea to do research in the field of embedded software architectures. He was particularly
ETASS II SKILL LEVEL AND LABOR CATEGORY DESCRIPTIONS. Skill Levels
 ETASS II SKILL LEVEL AND LABOR CATEGORY DESCRIPTIONS Skill Levels Level Entry I Intermediate II Senior III Principal IV Knowledge/Skill Description Applies fundamental concepts, processes, practices, and
ETASS II SKILL LEVEL AND LABOR CATEGORY DESCRIPTIONS Skill Levels Level Entry I Intermediate II Senior III Principal IV Knowledge/Skill Description Applies fundamental concepts, processes, practices, and
PMP Exam Preparation Workshop Project Communications Management
 PMP Exam Preparation Workshop 1 Learning Objectives By the end of this session you will understand: The importance of communication for the success of a project; The communication processes as described
PMP Exam Preparation Workshop 1 Learning Objectives By the end of this session you will understand: The importance of communication for the success of a project; The communication processes as described
It Is Still The Requirements Getting Software Requirements Right By James Ward
 A StickyMinds.com Original It Is Still The Requirements Getting Software Requirements Right By James Ward Summary: Why are information systems requirements so difficult to define? What causes the yawning
A StickyMinds.com Original It Is Still The Requirements Getting Software Requirements Right By James Ward Summary: Why are information systems requirements so difficult to define? What causes the yawning
Meltem Özturan
 Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 2 1 Information Systems (IS) Development Environment Systems Information Systems Information Systems Development 3 (Systems) A system is a collection of
Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 2 1 Information Systems (IS) Development Environment Systems Information Systems Information Systems Development 3 (Systems) A system is a collection of
Requirements Organisation, Analysis. Software Requirements & Project Management CITS3220
 Requirements Organisation, Analysis and Negotiation Software Requirements & Project Management CITS3220 Organising Requirements Viewpoints Interactor viewpoints: people or other systems that interact
Requirements Organisation, Analysis and Negotiation Software Requirements & Project Management CITS3220 Organising Requirements Viewpoints Interactor viewpoints: people or other systems that interact
Lecture 1. In practice, most large systems are developed using a. A software process model is an abstract representation
 Chapter 2 Software Processes Lecture 1 Software process descriptions When we describe and discuss processes, we usually talk about the activities in these processes such as specifying a data model, designing
Chapter 2 Software Processes Lecture 1 Software process descriptions When we describe and discuss processes, we usually talk about the activities in these processes such as specifying a data model, designing
Session-2: Deep Drive into Non Functional Requirements (NFRs)
 Session-2: Deep Drive into Non Functional Requirements (NFRs) Important Points to Note All Participating colleges are requested to mute your telephone lines during the webinar session. Participants are
Session-2: Deep Drive into Non Functional Requirements (NFRs) Important Points to Note All Participating colleges are requested to mute your telephone lines during the webinar session. Participants are
T Software Testing and Quality Assurance Test Planning
 T-76.5613 Software Testing and Quality Assurance 10.10.2007 Test Planning Juha Itkonen Outline Test planning, purpose and usage of a test plan Topics of test planning Exercise References: IEEE Std 829-1998,
T-76.5613 Software Testing and Quality Assurance 10.10.2007 Test Planning Juha Itkonen Outline Test planning, purpose and usage of a test plan Topics of test planning Exercise References: IEEE Std 829-1998,
HOW YOUR CAREER BACKGROUND CAN HELP YOU BECOME A BUSINESS ANALYST
 By Laura Brandenburg Lesson Objective: After completing this lesson, you ll be able to identify strengths from your career background that will directly support your transition into business analysis.
By Laura Brandenburg Lesson Objective: After completing this lesson, you ll be able to identify strengths from your career background that will directly support your transition into business analysis.
Software Methodologies
 Question 1: What is a practical method of selecting a software project development methodology? Answer 1: There are many software development methodologies to choose from, so making the choice can be an
Question 1: What is a practical method of selecting a software project development methodology? Answer 1: There are many software development methodologies to choose from, so making the choice can be an
Match the words in A with the definitions in B. Use a dictionary to check your answers. plans to achieve particular objectives
 You are going to listen to an interview for a job. Complete the exercises below. Try not to read the text until you have completed the exercises. Remember, you can listen as many times as you need to,
You are going to listen to an interview for a job. Complete the exercises below. Try not to read the text until you have completed the exercises. Remember, you can listen as many times as you need to,
Requirements Validation and Negotiation
 REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2014/2015 Dr. Sebastian Adam Requirements Validation and Negotiation AGENDA Fundamentals of Requirements Validation Fundamentals of Requirements Negotiation Quality Aspects
REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2014/2015 Dr. Sebastian Adam Requirements Validation and Negotiation AGENDA Fundamentals of Requirements Validation Fundamentals of Requirements Negotiation Quality Aspects
JOB DESCRIPTION. The Subject Position has no responsibility for ongoing and sustained supervision of other staff.
 JOB DESCRIPTION I. JOB IDENTIFICATION Position Title: Business Analyst Job Code: NEW Position Number: Various Linguistic Profile: BBC Group and Level: ADG E Supervisor Title: Chief, Business and Technology
JOB DESCRIPTION I. JOB IDENTIFICATION Position Title: Business Analyst Job Code: NEW Position Number: Various Linguistic Profile: BBC Group and Level: ADG E Supervisor Title: Chief, Business and Technology
making money from customer use of kiosk attracting more customers to the store saving money if the kiosk replaces manual operations
 Business Requirements Business requirements collected from multiple sources might conflict. For example, consider a kiosk product with embedded software that will be sold to retail stores and used by the
Business Requirements Business requirements collected from multiple sources might conflict. For example, consider a kiosk product with embedded software that will be sold to retail stores and used by the
ISO 9001:2015 Internal Auditor Training Présentation kit (Editable) 1. Overview of ISO 9001: ISO 9001 principles 12
 C108: DEMO OF QMS 9001:2015 INTERNAL AUDITOR TRAINING PPT PRESENTATION KIT Price 270 USD Buy: http://www.certificationconsultancy.com/quality-9001-2015-auditor-training-presentation.htm C108- Contents
C108: DEMO OF QMS 9001:2015 INTERNAL AUDITOR TRAINING PPT PRESENTATION KIT Price 270 USD Buy: http://www.certificationconsultancy.com/quality-9001-2015-auditor-training-presentation.htm C108- Contents
Essentials of IBM Rational Requirements Composer, v3. Module 4: Creating a use-case model
 Essentials of IBM Rational Requirements Composer, v3 Module 4: Creating a use-case model Copyright IBM Corporation 2010, 2011 Module overview After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain
Essentials of IBM Rational Requirements Composer, v3 Module 4: Creating a use-case model Copyright IBM Corporation 2010, 2011 Module overview After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain
Case Study: Software Product Integration Practices
 Case Study: Software Product Integration Practices Stig Larsson 1, Ivica Crnkovic 2 1 ABB AB, Corporate Research, Västerås, Sweden 2 Mälardalen University, Department of Computer Engineering, Västerås,
Case Study: Software Product Integration Practices Stig Larsson 1, Ivica Crnkovic 2 1 ABB AB, Corporate Research, Västerås, Sweden 2 Mälardalen University, Department of Computer Engineering, Västerås,
TDT4252 Modelling of Information Systems Advanced Course
 1 TDT4252 Modelling of Information Systems Advanced Course Sobah Abbas Petersen Adjunct Associate Professor sap@idi.ntnu.no 2 Today s Lecture AKM in Industry: an example Purpose: To describe an approach
1 TDT4252 Modelling of Information Systems Advanced Course Sobah Abbas Petersen Adjunct Associate Professor sap@idi.ntnu.no 2 Today s Lecture AKM in Industry: an example Purpose: To describe an approach
Validation of NORM (Needs Oriented Framework for Producing Requirements Decision Material) Framework in Industry
 Master Thesis Software Engineering Thesis no: MSE-2012:102 09 2012 Validation of NORM (Needs Oriented Framework for Producing Requirements Decision Material) Framework in Industry Salman Nazir Rizwan Yousaf
Master Thesis Software Engineering Thesis no: MSE-2012:102 09 2012 Validation of NORM (Needs Oriented Framework for Producing Requirements Decision Material) Framework in Industry Salman Nazir Rizwan Yousaf
Identification of. 2 (25) - SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE ATAM: Method for Architecture Evaluation - Sven Arne Andreasson - Computer Science and Engineering
 ATAM: Method for Architecture Evaluation ATAM Focuses on quality attribute requirements. Critical to have precise characterizations for each quality attribute. Attribute-Based Architectural Styles The
ATAM: Method for Architecture Evaluation ATAM Focuses on quality attribute requirements. Critical to have precise characterizations for each quality attribute. Attribute-Based Architectural Styles The
Domain Understanding and Requirements Elicitation (2)
 Domain Understanding and Requirements Elicitation (2) CS/SE 3RA3 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada Ryszard Janicki Domain Understanding
Domain Understanding and Requirements Elicitation (2) CS/SE 3RA3 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada Ryszard Janicki Domain Understanding
Question 2: Requirements Engineering. Part a. Answer: Requirements Engineering Process
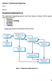 Question 2: Requirements Engineering Part a. Answer: Requirements Engineering Process The requirements engineering process varies from domain to domain. But the general activities involved are: Elicitation
Question 2: Requirements Engineering Part a. Answer: Requirements Engineering Process The requirements engineering process varies from domain to domain. But the general activities involved are: Elicitation
Lectures 2 & 3. Software Processes. Software Engineering, COMP201 Slide 1
 Lectures 2 & 3 Software Processes Software Engineering, COMP201 Slide 1 What is a Process? When we provide a service or create a product we always follow a sequence of steps to accomplish a set of tasks
Lectures 2 & 3 Software Processes Software Engineering, COMP201 Slide 1 What is a Process? When we provide a service or create a product we always follow a sequence of steps to accomplish a set of tasks
! To solve problems. ! To take up new opportunities. ! Requirements - descriptions of. " Behavior. " Data. " Constraints (eg. cost and schedule)
 COMP3110/6311, Software Analysis and Design Why do we Develop Software? To solve problems To take up new opportunities The value of Requirements "#$"%&'(%)#*+"%#)&),'$&+)& '()#-&)'$./,0.&+%/&.%1"*(%2.%#
COMP3110/6311, Software Analysis and Design Why do we Develop Software? To solve problems To take up new opportunities The value of Requirements "#$"%&'(%)#*+"%#)&),'$&+)& '()#-&)'$./,0.&+%/&.%1"*(%2.%#
Requirements Elicitation. Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 17
 Requirements Elicitation Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 17 Lecture Overview What is requirements elicitation? Underlying difficulties Generic Techniques Specific Techniques Requirements
Requirements Elicitation Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 17 Lecture Overview What is requirements elicitation? Underlying difficulties Generic Techniques Specific Techniques Requirements
PRReSE Process of Non-Functional Requirements Reuse for Embedded Systems Based on a NFR-Framework
 PRReSE Process of Non-Functional Requirements Reuse for Embedded Systems Based on a NFR-Framework Cristiano Marçal Toniolo Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences Methodist University of Piracicaba (UNIMEP)
PRReSE Process of Non-Functional Requirements Reuse for Embedded Systems Based on a NFR-Framework Cristiano Marçal Toniolo Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences Methodist University of Piracicaba (UNIMEP)
ATAM. Architecture Trade-off Analysis Method with case study. Bart Venckeleer, inno.com
 ATAM Architecture Trade-off Analysis Method with case study Bart Venckeleer, inno.com SEI Software Architecture Tools and Methods Active Reviews for Intermediate Designs (ARID) Architecture-Based System
ATAM Architecture Trade-off Analysis Method with case study Bart Venckeleer, inno.com SEI Software Architecture Tools and Methods Active Reviews for Intermediate Designs (ARID) Architecture-Based System
B U S I N E S S S Y S T E M S AN AL Y S T Schematic Code (
 I. DESCRIPTION OF WORK B U S I N E S S S Y S T E M S AN AL Y S T Schematic Code 10740 (31000043 Positions in this banded class plan, design, examine, analyze, develop, implement, administer, and monitor
I. DESCRIPTION OF WORK B U S I N E S S S Y S T E M S AN AL Y S T Schematic Code 10740 (31000043 Positions in this banded class plan, design, examine, analyze, develop, implement, administer, and monitor
Analysing client requirements
 Analysing client requirements Before you can start to analyse the information you have gathered you should think about what you are trying to achieve . The client has presented you with a business problem.
Analysing client requirements Before you can start to analyse the information you have gathered you should think about what you are trying to achieve . The client has presented you with a business problem.
9/2/2015. Steering the Course: How to Capture Business Needs vs. Business Processes. What Does Good Business Analysis Take? General Definitions
 9/2/2015 General Definitions Needs circumstances in which something is necessary, or requires some course of action Steering the Course: How to Capture Business Needs vs. Business Processes Processes are
9/2/2015 General Definitions Needs circumstances in which something is necessary, or requires some course of action Steering the Course: How to Capture Business Needs vs. Business Processes Processes are
CSEB233: Fundamentals of Software Engineering. Software Requirements Part 1 Understanding Requirements Engineering
 CSEB233: Fundamentals of Software Engineering Software Requirements Part 1 Understanding Requirements Engineering Objectives Discuss the concept of requirements and the types of requirements Explain what
CSEB233: Fundamentals of Software Engineering Software Requirements Part 1 Understanding Requirements Engineering Objectives Discuss the concept of requirements and the types of requirements Explain what
Implementation of Eurostat Quality Declarations at Statistics Denmark with cost-effective use of standards
 Implementation of Eurostat Quality Declarations at Statistics Denmark with cost-effective use of standards Mogens Grosen Nielsen, Chief Adviser, Statistics Denmark Lars Thygesen, Director, Statistics Denmark
Implementation of Eurostat Quality Declarations at Statistics Denmark with cost-effective use of standards Mogens Grosen Nielsen, Chief Adviser, Statistics Denmark Lars Thygesen, Director, Statistics Denmark
Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description
 Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description Requirements Engineering Project Description This project is student-driven. There will be external sponsors, users, and others that
Requirements Engineering and Software Architecture Project Description Requirements Engineering Project Description This project is student-driven. There will be external sponsors, users, and others that
Chapter 8 Understanding Requirements
 Chapter 8 Understanding Requirements Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, 8th edition by Roger S. Pressman 1 Outline What is RE? RE Tasks RE Process Eliciting Requirements( 需求获取 ) Developing
Chapter 8 Understanding Requirements Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, 8th edition by Roger S. Pressman 1 Outline What is RE? RE Tasks RE Process Eliciting Requirements( 需求获取 ) Developing
Requirements: Into the Mind of the Author
 Requirements: Into the Mind of the Author It seems well-accepted that it is cheaper to find defects earlier in the software development lifecycle than during dynamic testing or in live operation. I don
Requirements: Into the Mind of the Author It seems well-accepted that it is cheaper to find defects earlier in the software development lifecycle than during dynamic testing or in live operation. I don
Requirements Elicitation
 Requirements Elicitation Software Engineering I Lecture 4 14. November 2006 Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen 1 Outline Motivation Requirements elicitation challenges
Requirements Elicitation Software Engineering I Lecture 4 14. November 2006 Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen 1 Outline Motivation Requirements elicitation challenges
Requirements Analysis and Design Definition. Chapter Study Group Learning Materials
 Requirements Analysis and Design Definition Chapter Study Group Learning Materials 2015, International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA ). Permission is granted to IIBA Chapters to use and modify this
Requirements Analysis and Design Definition Chapter Study Group Learning Materials 2015, International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA ). Permission is granted to IIBA Chapters to use and modify this
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Tata Consultancy Services ltd. 12 October
 Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Tata Consultancy Services ltd. 12 October 2006 1 Objectives (1/2) At the end of the presentation, participants should be able to: Realise the need for a systematic
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Tata Consultancy Services ltd. 12 October 2006 1 Objectives (1/2) At the end of the presentation, participants should be able to: Realise the need for a systematic
Syllabus. REQB Certified Professional for Requirements Engineering. Advanced Level Requirements Manager
 Syllabus REQB Certified Professional for Requirements Engineering Requirements Manager Version 1.0 2011 The copyright to this edition of the syllabus in all languages is held by the Global Association
Syllabus REQB Certified Professional for Requirements Engineering Requirements Manager Version 1.0 2011 The copyright to this edition of the syllabus in all languages is held by the Global Association
(c) Addison Wesley Chapter 1. ! Software production is an art. ! Two groups. ! Main causes of software failures
 MACIASZEK, L.A. (2001): Requirements Analysis and System Design. Developing Information Systems with UML, Addison Wesley Chapter 1 Software Process Copyright 2000 by Addison Wesley Version 1.0 Software
MACIASZEK, L.A. (2001): Requirements Analysis and System Design. Developing Information Systems with UML, Addison Wesley Chapter 1 Software Process Copyright 2000 by Addison Wesley Version 1.0 Software
CHAPTER 2: IMPLEMENTATION PHASES AND OFFERINGS
 CHAPTER 2: IMPLEMENTATION PHASES AND OFFERINGS Objectives Introduction The objectives are: Describe the purpose of the phase planning activity, preconditions, and deliverables in the implementation methodology.
CHAPTER 2: IMPLEMENTATION PHASES AND OFFERINGS Objectives Introduction The objectives are: Describe the purpose of the phase planning activity, preconditions, and deliverables in the implementation methodology.
Estimating SW Size and Effort Estimating Size and Effort
 Estimating SW Size and Effort Estimating Size and Effort Dr. James A. Bednar jbednar@inf.ed.ac.uk http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/jbednar Dr. David Robertson dr@inf.ed.ac.uk http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/ssp/members/dave.htm
Estimating SW Size and Effort Estimating Size and Effort Dr. James A. Bednar jbednar@inf.ed.ac.uk http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/jbednar Dr. David Robertson dr@inf.ed.ac.uk http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/ssp/members/dave.htm
