GENERAL STUDIES MAINS
|
|
|
- Junior Chase
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GENERAL STUDIES MAINS GEOGRAPHY OF INDIA Previous Year Questions Trend Analysis Answer Format / Synopsis of Mains Questions Expected / Practice : Questions PART I 1
2 INDIA PHYSIOGRAPHY Previous Year Questions: 1. What do you understand by Deccan Trap? Describe its characteristics. (95/20) 2. Why do the Western Ghats receive more rainfall than the Eastern Ghats? (95/3) 3. Mention the advantages which India enjoys being at the head of the Indian Ocean. 4. What are the geo-economic causes of underdevelopment of various regions in India? (96/15) (98/15) 5. How do the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep differ in the geological evolution and topographical conditions? (98/15) 6. How is deforestation of Himalayas disturbing the ecological balance of north India? (99/15) 7. What is the importance of Indian Ocean for India? (99/15) 8. Write note on Linguistic regions of India. (00/10) 9. Had there been no Himalayas, what would have been the winter climate in north India? (01/10) 10. Write short note on Glacier. (01/2) 11. Write short note on Equinox. (01/2) 12. Write short note on Define Terai Region. (03/2) 13. Why are the Aravallis called a divide between Mewar and Marwar? (04/10) 14. Write short note on Karewas. (05/2) 15. Write short note on New Moore Island. (06/2) 16. Explain how the Himalayan and the Tibetan highlands play an important role in the-development of the South - West monsoon. (07/10) 17. Write notes on Indira Point. (07/2) 18. Write notes on Causes of Chambal Ravines. (07/2) 19. Write about Terai Region. (08/2) 20. Assess the significance of coastal regions in the economic development of India. ( 09/15) 2
3 Lets select this question asked in 2009 mains- ANSWER FORMAT/ SYNOPSIS OF QUESTIONS (Source- previous year Q papers) Q- Assess the significance of coastal regions in the economic development of India. ( 09/15) We have to give a brief introduction about coastal regions first, and then main answer would be their significance in the economic development (Hidden-as compared to the regions which are present in the hinterland, so you have to actually give extra benefits which coastal regions enjoy as compared to the regions in mainland) Synopsis- - India- Prominent country in Indian ocean - Coastal regions- from Gujarat to W.Bengal - Vast coastline, 2.02 million sq km EEZ ( exclusive economic zone) - Economic significancea) Trade with foreign countries(being on coast-coastal regions have easy access to foreign countries) b) Fishery & other sea food potential c) Hydrocarbon production(mumbai high, Gujarat s coast,kg delta) d) Renewable methods of energy production through tidal energy, OTEC. e) Tourist attraction- coral reefs, mangroves, beaches, etc- generate economy. f) Coastal regions suitable for the growth of some crops like sugarcane Let s take another question- Q- Explain how the Himalayan and the Tibetan highlands play an important role in the-development of the South - West monsoon. (07/10) Synopsis- HIMALAYAS- in foothills of Himalayas is location of sub-tropical high pressure(sthp) belt. In summers, pressure belts shift to north so STHP belt also move to the north, which disintegrates the jet stream(which was blowing originally over northern plains), thus causing a monsoonal trough (vacuum) in this region, thus sucking the SW monsoonal winds. In addition, Himalayas also prevent the further northward movement of the monsoons and hence confine them to Indian landmass. TIBETAN HIGHLANDS- also strengthen SW monsoons by giving birth to tropical easterly jet stream. In summers, the surface of Tibetan plateau become very warm ( warm air always rise) and the warm air rising from Tibet move south towards Indian ocean because of the precence of STHP belt north of Tibet. These currents of warm air deflect to their right as they move due to coriolis force and hence sink over Arabian sea. This air picks up moisture from Arabian sea and joins SW monsoonal winds. 3
4 QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE Q- Coastal pollution has increased now a days Comment. What are the major contents of pollutants. Q- Bay of Bengal islands are the extension of Himalayas. Comment. Q- Write a short note on bhabhar. Q- Deccan plateau is geologically different from chhota-nagpur plateau. Explain. 4
5 NATURAL VEGETATION Previous Year Questions: 1. Where do mangrove forests occur in India? Describe their main characteristics. (96/15) 2. Why has there been opposition from the North-Eastern States to the Supreme Court ban on all activities inside forests? (97/10) 3. Which parts of India have been identified as draught-prone? Mention the norms for such identification. (98/15) 4. What is waste land? Write a note on prospects of waste land development in India. (00/10) 5. What are mangroves and in what way are they useful to us? (00/10) 6. Mention the area of Shola forests in India. (03/2) 7. Write short note on the following: (a) The Sambhar lake (b) The Sundarbans (c) Bombay High (d) Sabarkantha & Banaskantha (04/2) 8. Discuss the wetlands and their role in the ecological conservation in India. (09/15) 5
6 ANSWER FORMAT/SYNOPSIS Q- Discuss the wetlands and their role in the ecological conservation in India. (09/15) Synopsis: Definition of wetland- According to the Wetland Conservation Act of 1991 a wetland is defined by the following criteria: 1) it has mostly hydric soils; 2) it must generally be inundated or saturated above or below the surface; and 3) support vegetation adapted to wet soil conditions. Floodplains, marshes, deltas, swamps, peatlands, dambos and lakes are all types of wetland. Role in ecological conservation- REGULATING SERVICES Water storage Groundwater recharge & discharge Flood control& river regulation Water purification Sediment retention PROVISIONING SERVICES Water supply - domestic & animals Agriculture resources Fisheries Forage resources Craft materials Medicinal plants CULTURAL SERVICES Biodiversity- IMPORTANT (expand it) Cultural sites Wetlands are part of a wider hydrological system, the services and benefits they provide can play a key role in sustaining the livelihoods of communities and the survival of wildlife and biodiversity both in the catchment and downstream..(also resting and breeding place of migratory birds). 6
7 Q- Where do mangrove forests occur in India? Describe their main characteristics. (96/15) Mangroves are marine tidal forests and they are most luxuriant around the mouths of large rivers and in sheltered bays. Distribution in India- Sunderbans- Ganga delta, W.Bengal, Goa, Andaman & Nicobar IS, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Orissa, Karnataka, Kerala Characteristics- Mangrove forests are one of the most productive and bio diverse wetlands on earth. Growing in the inter-tidal areas and estuary mouths between land and sea, mangroves provide critical habitat for a diverse marine and terrestrial flora and fauna. Mangrove plants include trees, shrubs, ferns and palms. These plants are found in the tropics and sub-tropics on riverbanks and along coastlines, being unusually adapted to anaerobic conditions of both salt and fresh water environments. These plants have adapted to muddy, shifting, saline conditions. They produce stilt roots, which project above the mud and water in order to absorb oxygen. Mangrove plants form communities which help to stabilize banks and coastlines and become home to many types of animals. Mangrove forests fix more carbon dioxide per unit area than phytoplankton in tropical oceans. 7
8 QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE Q- Write a short note on the natural vegetation of India with map. Q- Demarcate the areas of tropical evergreen forests. What relationship they share with south-west monsoon? Q- What is wasteland? What steps govt of India is taking for its remuneration? 8
9 CLIMATE OF INDIA Previous Year Questions: 1. What is intensity of rainfall? Discuss its importance to Indian farmers. (95/15) 2. Discuss the origin of Monsoon in India. (97/15) 3. Mention the agro-climatic regions of India stating the basis of classification. (00/10) 4. Write short note on Mango Showers. (00/2) 5. Explain the causes of the Indian Monsoon. (01/10) 6. Discuss the distribution of winds and rainfall over India in the summer monsoon season. (02/10) 7. Write note on winter rains in India. (06//2) 8. The winter rains in North India are largely related to Jet Streams and Western Disturbances. Bring out the relationship. (08/15) 9. Write about Nor westers. (08/2) 10. Bring out the Significance of the various activities of the Indian Metrological Department. ( 09,15) 11. List the significant local storms of the hot-weather season in the country and bring out their socioeconomic impact. (10,15) 9
10 ANSWER FORMAT/SYNOPSIS Q-. Bring out the Significance of the various activities of the Indian Metrological Department. ( 09,15) Synopsis- The India Meteorological Department was established in It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology, seismology and allied subjects. Various activities it performs-& their Significance- Take meteorological observations and provide forecast meteorological information for optimum operation of weather-sensitive activities like agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, offshore oil explorations, etc. Warn against severe weather phenomena like tropical cyclones, norwesters, duststorms, heavy rains and snow, cold and heat waves, etc., which cause destruction of life and property, thus protect life & property. Provide meteorological statistics required for agriculture, water resource management, industries, oil exploration and other nation-building activities. Conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines. Detect and locate earthquakes and to evaluate seismicity in different parts of the country for development projects. Q- Discuss the distribution of rainfall in India in summer monsoon season. The rainfall in India is seasonal, uncertain and unevenly distributed. Most of the rain comes during the South- West Monsoon period. Rainfall may be too much or too little. There are also long dry periods in between. On the basis of the quantity of rainfall, we can divide India into five major rainfall regions. 1)Very low rainfall region (Less than 30 cms per year). It is found in Karakoram ranges, northern Kashmir and western parts of Kachchh and Rajasthan (Thar desert). 2) Low rainfall region (30 cms. to 60 cms. per year). It is found in Zaskar range, parts of Punjab and Haryana, Central Rajasthan, Western Gujarat and the rain-shadow areas of the Western Ghats. 3) Moderate rainfall (60 cms. to 100 cms. per year). It is found over a greater part of India, excluding the areas of low rainfall and heavy rainfall. Most of the rain is from the South-West Monsoon winds. 4) Heavy rainfall region (100 cms. to 200 cms. per year). It is found in four separate areas, including a narrow belt of the western coast, eastern coastal belt, the foothills of the Himalayas and a part of north-east India. 5) Very heavy rainfall region (over 200 cms. per year). It is found on the western side of the Western Ghats, the foothills of Himalayas, Meghalaya plateau (Shillong plateau) and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Mawsynram in Meghalaya plateau has recorded 1141 cms. of rainfall per year and it is the place which gets the heaviest rainfall in India/world 10
11 QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE Q- Why Tamil Nadu coast receive rainfall during retreating monsoon and not during SW monsoon? Q- What are the factors responsible for variability of rainfall over India? Q- Why tropical cyclones mostly hit the east coast of India and not the west coast? Q- Write a short note on ENSO. 11
12 SOILS IN INDIA Previous Year Questions: 1. Write short note on India s Literate soils. (00/2) 2. Write short note on Regurs. (05/2) 3. Write note on Causes of Soil erosion and its control in India. (05/10) 4. Write notes on Inceptisol. (07/2) 12
13 ANSWER FORMAT/SYNOPSIS Q- Write notes on Inceptisol. (07/2) (This is asked for two marks..examiner can ask vertisol, alfisol, mollisol, etc next year for 2 marks so below I am giving the short answer for USDA taxonomy)- USDA Soil Taxonomy developed by United States Department of Agriculture and the National Cooperative Soil Survey provides an elaborate classification of soil types according to several parameters (most commonly their properties) and in several levels: Order, Suborder, Great Group, Subgroup, Family, and Series. Alfisols form in semiarid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. Andisols soils formed in volcanic ash and defined as soils containing high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, including allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite Aridisols (from the Latin aridus, for dry ) form in an arid or semi-arid climate. Entisols are soils that do not show any profile development other than an A horizon Gelisols are soils of very cold climates which are defined as containing permafrost within two meters of the soil surface. Histosols a soil consisting primarily of organic materials Inceptisols form quickly through alteration of parent material Mollisols form in semi-arid to semi-humid areas, typically under a grassland cover Oxisols are best known for their occurrence in tropical rain forest Spodosols are the typical soils of coniferous, or boreal forests Ultisols commonly known as red clay soils Vertisols a soil in which there is a high content of expansive clay. Q- Write note on Causes of Soil erosion and its control in India. (05/10) 1)Heavy population pressure on land: - forest cover as low as 20.55% of total area population continues to rise at a rapid rate more forests are destroyed heavy pressure on land. 2)Nature of Rainfall:- receives 80 to 90 per cent of rainfall in the monsoon season. heavy downpour during during monsoon months causes floods. - remaining months droughts these affect soils. 3)Overgrazing number of domestic animals, esp cattle highest in world cattle freely graze in open lands making them bare of vegetation-winds carry away dry soil particles Rajasthan 4). Bad farming techniques plough fields in traditional ways small size of holdings, absence of terracing, contour cultivation, crop rotation, improper use of manure have caused erosion 13
14 5) Topography North Eastern parts of India, Shiwaliks and the hilly regions in south India are affected by soil erosion because of steep slopes and heavy rainfall. During heavy rainfall, soils are washed away by running water down the slope. 6) Deforestation: destruction of forests for cultivation cutting of trees exposes the soil to water and wind which leads to soil erosion SOIL CONSERVATION SCHEMES 1.The centrally sponsored scheme of Integrated Watershed Management in the catchments of flood-prone rivers was launched during sixth Plan in eight flood-prone rivers of the Gangetic Basin covering seven States and one Union Territory. It aims at enhancing the ability of the catchment by absorbing larger quantity of rainwater, reducing erosion and consequent silt load in the stream and river beds and thus helping to mitigate the fury of floods in the productive plains. 2.A scheme for reclamation and development of ravine areas was launched in in MP, UP and Rajasthan. included prepheral bunding to halt further ingress of ravines, afforestation of ravines, aforestaton of ravines for fuel, fodder and reclamation of shallow ravines. 3. Control of shifting cultivation is implemented since in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura The integrated programme envisages settling of families practising shifting cultivation. it helps them to practise terraced cultivation, raising of horticultural palantations and afforestation to support animal husbandry and to meet fuel and fodder requirements. 4) In urban areas, rain water harvesting is means of checking soil erosion, besides recharging ground water. Alongwith it- new farming techniques- contour bunding, ploughing, terrace farming, strip cropping, shelter belts and afforestation. (shorten it, keep with in word limits). 14
15 QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE Q- Laterite soils occur in regions of alternative wet and dry conditions. Explain. Q- Name the regions of soil erosion in India. What is the effect of soil erosion and what measures should be adopted to prevent it. Q- Write a short note on black cotton soils. Why they are known as cotton soils? 15
16 DRAINAGE SYSTEM OF INDIA Previous Year Questions: 1. Why have the rivers of the peninsular India well-defined rigid channels in sharp contrast to the Himalayan rivers? (95/20) 2. Write short note on Two prominent left bank tributaries of river Ganges. (01/2) 3. Describe the major characteristics of the rivers of Peninsular India. (03/10) 4. Elucidate the factors contributing to the growing need for water harvesting in India, both rural and urban. (05/10) 5. Write note on Significance of Lake Chilka. (05/2) 6. Why do the rivers of west coast not form a delta? (06/10) 7. Write note on Hussain Sagar. (06/2) 8. Write about Buckingham Canal. (08/2) 9. Causes for dominant dendritic pattern of drainage in the Gangetic plains (10,5 ) 16
17 ANSWER FORMAT/SYNOPSIS Q- Write short note on Two prominent left bank tributaries of river Ganges. (01/2) Map is just to assist you in learning various right and left bank tributaries of ganga and from where they originate. Two left bank tributaries- lets take ghaghra and kosi Ghaghra- Karnali or Ghaghara is a perennial trans-boundary river originating on the Tibetan Plateau near Lake Mansarovar. It cuts through the Himalayas in Nepal and joins the Sarda River at Brahmaghat in India. Together they form the Ghaghra River, a major left bank tributary of the Ganges. Kosi river- or sapta-kosi for its seven Himalayan tributaries is a trans-boundary river flowing through Nepal and India. Some of the rivers of the Koshi system, such as the Arun, the Sun Kosi and the Bhote Koshi, originate in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It is one of the largest tributaries of the Ganges. Also known as sorrow of Bihar for its frequest floods it cause in Bihar. 17
18 Q- Why have the rivers of the peninsular India well-defined rigid channels in sharp contrast to the Himalayan rivers? (95/20) Peninsular rivers- Show all the characteristics of the mature rivers- less erosion, graded & shallow valleys, short courses, low waterfalls, etc These are Geologically older, Flow through hard granitic soils of peninsular India. Himalayan rivers- young, more erosion, high valleys, long courses, meanders- because they pass through northern plains- through region of soft alluvial soils, thus often change their courses (eg kosi). 18
19 QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE Q- what are the differences between west flowing rivers and east flowing rivers of India? Q- write a short note on lake sambhar. Q- Write a short note on National waterways of India. Q- Which pattern does streams in peninsular India follows? Q- What are the benefits of inter-linkages of rivers Q- Write a short note on river water pollution and its mitigation efforts by GOI. INTERACTIVE DISTANCE LEARNING PROGRAMME [ STUDY MATERIAL & MAINS TEST SERIES ] UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF EXPERTS (Expert Guidance, Feedback & Discussion) # General Studies # Sociology # Public Administration # Geography # Philosophy # Psychology # Hindi Lit. REGISTRATION OPEN -THE TEAM VISION IAS - Contact No. : , ajay_uor@yahoo.com
Forest Resources. Unit III Population & Natural Resources
 Forest Resources Unit III Population & Natural Resources Topics Forest resources Forest resources-indian Scenario Functions of forests Importance of forests Ecological and Economical Importance Types of
Forest Resources Unit III Population & Natural Resources Topics Forest resources Forest resources-indian Scenario Functions of forests Importance of forests Ecological and Economical Importance Types of
CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES
 Natural Resources CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES NATURAL RESOURCES Exhaustible natural resources Inexhaustible natural resources Renewable Partly renewable Nonrenewable Inexhaustible Conditionally
Natural Resources CLASSIFICATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES NATURAL RESOURCES Exhaustible natural resources Inexhaustible natural resources Renewable Partly renewable Nonrenewable Inexhaustible Conditionally
DROUGHT (INDIA) SURINDER KAUR INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT
 DROUGHT (INDIA) SURINDER KAUR INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT WATER AVAILIBILITY IN INDIA AREA OF THE COUNTRY 32,87,263 SQ. KMs RAINFALL 4000 KM³ SURFACE WATER POTENTIAL 684 KM³ GROUND WATER POTENTIAL
DROUGHT (INDIA) SURINDER KAUR INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT WATER AVAILIBILITY IN INDIA AREA OF THE COUNTRY 32,87,263 SQ. KMs RAINFALL 4000 KM³ SURFACE WATER POTENTIAL 684 KM³ GROUND WATER POTENTIAL
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
GEOGRAPHY. H.C.G. Paper 2 (Two hours)
 GEOGRAPHY H.C.G. Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
GEOGRAPHY H.C.G. Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones
 3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
Chapter 1 Resources and Development
 Chapter 1 Resources and Development Resources Substances available in our environment that can be used for specific purposes and are technologically accessible, economically viable and culturally acceptable
Chapter 1 Resources and Development Resources Substances available in our environment that can be used for specific purposes and are technologically accessible, economically viable and culturally acceptable
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
RIVER BASIN PENNAR [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN PENNAR [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS ORGANISATIONS (RBOs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
RIVER BASIN PENNAR [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS ORGANISATIONS (RBOs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
MC 17 G 10 PART I (30 MARKS)
 PART I (30 MARKS) Attempt all questions from this Part Question 1. Study the extract of the Survey of India Map sheet No. 45D/10 and answer the following questions. (Easting - 14 to 24, Northing - 02 to
PART I (30 MARKS) Attempt all questions from this Part Question 1. Study the extract of the Survey of India Map sheet No. 45D/10 and answer the following questions. (Easting - 14 to 24, Northing - 02 to
Status, Quality and Management of Groundwater in India
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 717-722 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Status,
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 717-722 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Status,
LAND AND SOIL RESOURCES Chapter 1
 Humans through technology and institutions transform things available with nature. Resources are of two types natural and human. Resources can be classified in the following ways (a) On the basis of origin
Humans through technology and institutions transform things available with nature. Resources are of two types natural and human. Resources can be classified in the following ways (a) On the basis of origin
Life Sciences For NET & SLET Exams Of UGC-CSIR. Section B and C. Volume-23. Contents
 Section B and C Volume-23 Contents 12. APPLIED BIOLOGY E. BIO-RESOURCE AND USES OF BIODIVERSITY 1 F. BREEDING IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS, INCLUDING MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION 1. PLANT BREEDING 34 2. MARKER ASSISTED
Section B and C Volume-23 Contents 12. APPLIED BIOLOGY E. BIO-RESOURCE AND USES OF BIODIVERSITY 1 F. BREEDING IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS, INCLUDING MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION 1. PLANT BREEDING 34 2. MARKER ASSISTED
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT OF LAND RESOURCES LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION NO. 70 TO BE ANSWERED ON
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT OF LAND RESOURCES LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION NO. 70 TO BE ANSWERED ON 20.07.2017 Development of Wasteland *70. SHRI KUNWAR PUSHPENDRA SINGH
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT OF LAND RESOURCES LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION NO. 70 TO BE ANSWERED ON 20.07.2017 Development of Wasteland *70. SHRI KUNWAR PUSHPENDRA SINGH
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture.
 1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION. help rebalance the water cycle, mitigate the effects of climate change and improve human health and livelihoods.
 1 FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION World Water Day, on 22 March every year, is about focusing attention on the importance of water. This year s theme, Nature for Water, explores nature-based solutions (NBS) to the
1 FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION World Water Day, on 22 March every year, is about focusing attention on the importance of water. This year s theme, Nature for Water, explores nature-based solutions (NBS) to the
Background Paper Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Asia
 Background Paper Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Asia Mozaharul Alam, Research Fellow Bangladesh Centre for Advanced Studies Hotel Crowne Plaza, Beijing, China 11-13 April 2007
Background Paper Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Asia Mozaharul Alam, Research Fellow Bangladesh Centre for Advanced Studies Hotel Crowne Plaza, Beijing, China 11-13 April 2007
VISION DOCUMENT FOR 12TH FIVE YEAR PLAN
 National Afforestation & Eco-development Board, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India VISION DOCUMENT FOR 12TH FIVE YEAR PLAN RCNAEB, BHOPAL Indian Institute of Forest Management, Bhopal
National Afforestation & Eco-development Board, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India VISION DOCUMENT FOR 12TH FIVE YEAR PLAN RCNAEB, BHOPAL Indian Institute of Forest Management, Bhopal
Test Paper Set I Subject : Social Science - II
 Test Paper Set I Subject : Social Science - II Time : Hr. Marks : 0 Geography : Chapter - 5; Economics : Chapter - A.. (A) Complete the following sentences using words from the brackets : The foothills
Test Paper Set I Subject : Social Science - II Time : Hr. Marks : 0 Geography : Chapter - 5; Economics : Chapter - A.. (A) Complete the following sentences using words from the brackets : The foothills
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]
![AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]](/thumbs/79/79737240.jpg) AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems
 3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems 3.1 Natural Environment The goals, issues and programmes regarding the natural environment of the Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001-2011 are shown
3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems 3.1 Natural Environment The goals, issues and programmes regarding the natural environment of the Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001-2011 are shown
CLIMATE CHANGE. Noor Haslizawati Abu Bakar Farahiyah Ilyana Jamaludin. Malaysia
 CLIMATE CHANGE Noor Haslizawati Abu Bakar Farahiyah Ilyana Jamaludin Malaysia Where is Malaysia? Malaysia Is a tropical country consists 2 land masses (West and East). West Malaysia: 11 states, East Malaysia:
CLIMATE CHANGE Noor Haslizawati Abu Bakar Farahiyah Ilyana Jamaludin Malaysia Where is Malaysia? Malaysia Is a tropical country consists 2 land masses (West and East). West Malaysia: 11 states, East Malaysia:
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR INTEGRATED LAND MANAGEMENT: CASE OF INDIA
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR INTEGRATED LAND MANAGEMENT: CASE OF INDIA R.B.Singh and Dilip Kumar Department of Geography Delhi School of Economics University of Delhi Delhi-110007, India E-mail:rbsgeo@hotmail.com
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR INTEGRATED LAND MANAGEMENT: CASE OF INDIA R.B.Singh and Dilip Kumar Department of Geography Delhi School of Economics University of Delhi Delhi-110007, India E-mail:rbsgeo@hotmail.com
WIND ENERGY FOR POWER GENERATION
 International Journal of Mechanical, Robotics and Production Engineering. Volume VI, Special Issue, 2016, ISSN 2349-3534, www.ijmpe.com, email editor@ijmpe.com WIND ENERGY: AN ATTEMPT TO ANALYZE AND REVIEW
International Journal of Mechanical, Robotics and Production Engineering. Volume VI, Special Issue, 2016, ISSN 2349-3534, www.ijmpe.com, email editor@ijmpe.com WIND ENERGY: AN ATTEMPT TO ANALYZE AND REVIEW
CHAPTER 4 STUDY AREA DESCRIPTION
 88 CHAPTER 4 STUDY AREA DESCRIPTION 4.1 GENERAL For the purpose of evaluating the impact of tank restoration on livelihoods, three restored tanks in two districts of Kancheepuram and Thiruvallur in Tamil
88 CHAPTER 4 STUDY AREA DESCRIPTION 4.1 GENERAL For the purpose of evaluating the impact of tank restoration on livelihoods, three restored tanks in two districts of Kancheepuram and Thiruvallur in Tamil
RIVER BASIN GHAGARA [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN GHAGARA [ INDIA ] Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names. 1.2 Relief Map and Index Map of RB with Country/ State/ Province
RIVER BASIN GHAGARA [ INDIA ] Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names. 1.2 Relief Map and Index Map of RB with Country/ State/ Province
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT
 DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT Cropping Seasons in India Agriculture in India also follows three distinct cropping seasons i.e. rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown from October to December
DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT Cropping Seasons in India Agriculture in India also follows three distinct cropping seasons i.e. rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown from October to December
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
area of land with steep sides that rise sharply from surrounding land gently raised areas of land
 Mountains area of land with steep sides that rise sharply from surrounding land Hills gently raised areas of land Mountains/Hills ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES -protection from invasion -lack of farmable land
Mountains area of land with steep sides that rise sharply from surrounding land Hills gently raised areas of land Mountains/Hills ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES -protection from invasion -lack of farmable land
IPCC FOURTH ASSESSMENT CLIMATE CHANGE 2007: IMPACTS, ADAPTATION AND VULNERABILITY
 IPCC FOURTH ASSESSMENT CLIMATE CHANGE 2007: IMPACTS, ADAPTATION AND VULNERABILITY THE PROCESS! 394 Authors! 45 Review Editors! 4 Review Cycles! 1,183 Expert Reviewers! 49,610 Review Comments! Five year
IPCC FOURTH ASSESSMENT CLIMATE CHANGE 2007: IMPACTS, ADAPTATION AND VULNERABILITY THE PROCESS! 394 Authors! 45 Review Editors! 4 Review Cycles! 1,183 Expert Reviewers! 49,610 Review Comments! Five year
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE CHANGE. LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION No. 334 TO BE ANSWERED ON
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE CHANGE LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION No. 334 TO BE ANSWERED ON 09.08.2016 Ecological Impact of Mining *334. SHRI JANARDAN SINGH SIGRIWAL state:
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE CHANGE LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION No. 334 TO BE ANSWERED ON 09.08.2016 Ecological Impact of Mining *334. SHRI JANARDAN SINGH SIGRIWAL state:
Climate Change: The India and UK contexts
 Climate Change: The India and UK contexts Dr. Suresh Rohilla Visiting Research Fellow Dr. Geraint Ellis Senior Lecturer School of Planning, Architecture and Civil Engineering Planning Queen s University,
Climate Change: The India and UK contexts Dr. Suresh Rohilla Visiting Research Fellow Dr. Geraint Ellis Senior Lecturer School of Planning, Architecture and Civil Engineering Planning Queen s University,
Popular Kheti. Volume-2, Issue-3 (July-September), 2014 Available online at popularkheti.info ISSN:
 Watershed Management- Solution to Water Crisis Rahul Chopra*, Ajeet Singh, Pravisha Lahoty and Manisha Rana Rajasthan College of Agriculture, MPUAT, Udaipur-313001 *Email of corresponding author: rahulrockingcool969@gmail.com
Watershed Management- Solution to Water Crisis Rahul Chopra*, Ajeet Singh, Pravisha Lahoty and Manisha Rana Rajasthan College of Agriculture, MPUAT, Udaipur-313001 *Email of corresponding author: rahulrockingcool969@gmail.com
SSLC SOCIAL SCIENCE IMPORTANT 5 MARKS QUESTION & ANSWERS SSLC SOCIAL SCIENCE IMPORTANT 5 MARKS QUESTION & key ANSWER GEROGRAPHY
 SSLC SOCIAL SCIENCE IMPORTANT 5 MARKS QUESTION & key ANSWER GEROGRAPHY 1. India is a Sub continent Justify A continent possesses distinct characteristics of diverse 1. Physical features 2. Climate conditions
SSLC SOCIAL SCIENCE IMPORTANT 5 MARKS QUESTION & key ANSWER GEROGRAPHY 1. India is a Sub continent Justify A continent possesses distinct characteristics of diverse 1. Physical features 2. Climate conditions
Climate Change Challenges faced by Agriculture in Punjab
 Climate Change Challenges faced by Agriculture in Punjab Dr. M. Mohsin Iqbal and Dr. Arshad M. Khan Global Change Impact Studies Centre (GCISC), Islamabad Seminar on Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture
Climate Change Challenges faced by Agriculture in Punjab Dr. M. Mohsin Iqbal and Dr. Arshad M. Khan Global Change Impact Studies Centre (GCISC), Islamabad Seminar on Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture
Forest Cover and Forest Area
 Forest Cover and Forest Area Chapter 3 FOREST COVER AND FOREST AREA The term 'Forest Area' (or recorded forest area) generally refers to all the geographic areas recorded as forest in government records.
Forest Cover and Forest Area Chapter 3 FOREST COVER AND FOREST AREA The term 'Forest Area' (or recorded forest area) generally refers to all the geographic areas recorded as forest in government records.
Managing Living Soils Workshop
 Managing Living Soils Workshop Status and Priorities of Soil Management in Kenya Hamisi Mzoba African Conservation Tillage Network (ACT) Email: hamisi.mzoba@act-africa.org Background Information: Kenya
Managing Living Soils Workshop Status and Priorities of Soil Management in Kenya Hamisi Mzoba African Conservation Tillage Network (ACT) Email: hamisi.mzoba@act-africa.org Background Information: Kenya
Page 1 of 6. Agriculture. I. Answer the Following
 Agriculture Page 1 of 6 I. Answer the Following Q1. What is the importance of agriculture in the Indian economy? Ans. Two-thirds of India s population is engaged in agricultural activities. Agriculture
Agriculture Page 1 of 6 I. Answer the Following Q1. What is the importance of agriculture in the Indian economy? Ans. Two-thirds of India s population is engaged in agricultural activities. Agriculture
Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands
 Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
Climate change Adaptation in South Asia
 Climate change Adaptation in South Asia SREEJA NAIR TERI South Asia Climate Change Focal Points and Experts Consultation Meeting, Thimphu, 16-17 November 2011 Global mean temperatures rising faster with
Climate change Adaptation in South Asia SREEJA NAIR TERI South Asia Climate Change Focal Points and Experts Consultation Meeting, Thimphu, 16-17 November 2011 Global mean temperatures rising faster with
Introduction to Ecology p
 Introduction to Ecology 19-1 p. 359-365 Essential Question 1. Identify three ways in which the expanding human population impacts the environment. 2. Describe the hierarchical levels of organization in
Introduction to Ecology 19-1 p. 359-365 Essential Question 1. Identify three ways in which the expanding human population impacts the environment. 2. Describe the hierarchical levels of organization in
Foundation for Ecological Security, India Structure of the presentation
 Foundation for Ecological Security, India Structure of the presentation The Indian context Watershed Mgt in India Issues in Watershed Mgt What we do How we work Results Challenges 1 The Indian context
Foundation for Ecological Security, India Structure of the presentation The Indian context Watershed Mgt in India Issues in Watershed Mgt What we do How we work Results Challenges 1 The Indian context
CORAL REEFS. Coral reefs are home to many organisms Provide habitat and shelter for 25 percent of all fish species in the deeper parts of the ocean.
 CORAL REEFS We have looked at the development of coral reefs starting with a volcanic island on which coral starts to appear. Coral is a kind of animal that needs to be in water. Being an animal, it also
CORAL REEFS We have looked at the development of coral reefs starting with a volcanic island on which coral starts to appear. Coral is a kind of animal that needs to be in water. Being an animal, it also
Questions 3-6 refer to the diagram of surface currents in the oceans. 3. A current responsible for moving heat away from the equator.
 1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
The State of the World s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific
 The State of the World s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Resources availability land and water availability in high income countries land
The State of the World s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Resources availability land and water availability in high income countries land
Soil Health Management in India
 Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management In order to improve the soil health of the Indian soils, gov- The nature and extent of deficiencies of nutrients in
Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management In order to improve the soil health of the Indian soils, gov- The nature and extent of deficiencies of nutrients in
CLASS X GEOGRAPHY QUESTION BANK. Mr.THOMAS.K.J Holy Angel s Sr. Sec. School Sahibabad
 CLASS X GEOGRAPHY QUESTION BANK Mr.THOMAS.K.J Holy Angel s Sr. Sec. School Sahibabad CLASS X GEOGRAPHY QUESTION BANK 1. DEFINITIONS FROM TOPO MAPS 1. REPRESENTATIVE FRACTION (RF): It is the ratio between
CLASS X GEOGRAPHY QUESTION BANK Mr.THOMAS.K.J Holy Angel s Sr. Sec. School Sahibabad CLASS X GEOGRAPHY QUESTION BANK 1. DEFINITIONS FROM TOPO MAPS 1. REPRESENTATIVE FRACTION (RF): It is the ratio between
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 11 Living Systems
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology
 Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology 1.Coral Reefs: the aquatic equal to the tropical rain forests 2.The two major aquatic life zones A. saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs, coastal marshes, mangrove
Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology 1.Coral Reefs: the aquatic equal to the tropical rain forests 2.The two major aquatic life zones A. saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs, coastal marshes, mangrove
Environmental and Climate change in Mongolia
 Environmental and Climate change in Mongolia D. Azzaya Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology (IMH), Mongolia Juulchny gudamj-5, Ulaanbaatar-46, 210646, Mongolia A.Khaulenbek Desertification study center,
Environmental and Climate change in Mongolia D. Azzaya Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology (IMH), Mongolia Juulchny gudamj-5, Ulaanbaatar-46, 210646, Mongolia A.Khaulenbek Desertification study center,
MT MT 154 SOCIAL SCIENCE (73) GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS PRELIM I PAPER II (E) Preliminary Model Answer Paper Max.
 MT 5 08...... 00 MT 5 SOCIAL SCIENCE (73) GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS PRELIM I PAPER II (E) Time : Hours Preliminary Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 0 A.. (A) Complete and write the following statements by choosing
MT 5 08...... 00 MT 5 SOCIAL SCIENCE (73) GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS PRELIM I PAPER II (E) Time : Hours Preliminary Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 0 A.. (A) Complete and write the following statements by choosing
What are Wetlands? Wetland Ecology Fall 2017
 What are Wetlands? Wetland Ecology Fall 2017 Ingredients to make a wetland Water Topography Soil Plants Animals Definitions Transition zone between upland and permanently flooded ecosystems Isolated basins
What are Wetlands? Wetland Ecology Fall 2017 Ingredients to make a wetland Water Topography Soil Plants Animals Definitions Transition zone between upland and permanently flooded ecosystems Isolated basins
How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island?
 How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island? Do you think for a moment that humans altering the Hydrologic Cycle would also change the Weather? Precipitation
How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island? Do you think for a moment that humans altering the Hydrologic Cycle would also change the Weather? Precipitation
Climate Variability, Urbanization and Water in India
 Climate Variability, Urbanization and Water in India M. Dinesh Kumar Executive Director Institute for Resource Analysis and Policy Hyderabad-82 Email: dinesh@irapindia.org/dineshcgiar@gmail.com Prepared
Climate Variability, Urbanization and Water in India M. Dinesh Kumar Executive Director Institute for Resource Analysis and Policy Hyderabad-82 Email: dinesh@irapindia.org/dineshcgiar@gmail.com Prepared
6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE
 6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE 38 MT EDUCARE LTD. Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and rewrite the statements : 1. India ranks... in the world regarding area under cultivation.
6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE 38 MT EDUCARE LTD. Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and rewrite the statements : 1. India ranks... in the world regarding area under cultivation.
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh
 12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
Climate Change Impact and Adaptation in South Asia
 Regional Conference Climate Change: Challenges and Opportunities for South Asia Climate Change Impact and Adaptation in South Asia Ajaya Dixit Nepal Water Conservation Foundation/ISET-N Ministry of Environment
Regional Conference Climate Change: Challenges and Opportunities for South Asia Climate Change Impact and Adaptation in South Asia Ajaya Dixit Nepal Water Conservation Foundation/ISET-N Ministry of Environment
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
River Talk Patterns. Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3. Human nervous system. Waters and drainage patterns. Road system.
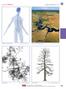 River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
International Journal of Advance ISSN and Applied Research (IJAAR) Impact Factor 0.899
 International Journal of Advance ISSN 2347-7075 and Applied Research (IJAAR) Impact Factor 0.899 Peer Reviewed Bi-Monthly Vol.2 No.1 Sept- Oct 2014 INSTALLATION OF OFF-GRID RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS IN
International Journal of Advance ISSN 2347-7075 and Applied Research (IJAAR) Impact Factor 0.899 Peer Reviewed Bi-Monthly Vol.2 No.1 Sept- Oct 2014 INSTALLATION OF OFF-GRID RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS IN
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
The natural environment Upper grade of Primary Education (10-12 years old)
 Slide 1 1 and 2 The climate in Anantapur The school with which we are having the exchange is located in the State of Andhra Pradesh, a wet and hot Indian region. As this State is quite big, we will focus
Slide 1 1 and 2 The climate in Anantapur The school with which we are having the exchange is located in the State of Andhra Pradesh, a wet and hot Indian region. As this State is quite big, we will focus
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
The Role and Opportunities Of Water Environment in the. Republic of the Union of Myanmar
 The Role and Opportunities Of Water Environment in the Republic of the Union of Myanmar Presented by SOE MYINT Director General (Rtd;) Directorate of Water Resources and Improvement of River Systems (DWIR)
The Role and Opportunities Of Water Environment in the Republic of the Union of Myanmar Presented by SOE MYINT Director General (Rtd;) Directorate of Water Resources and Improvement of River Systems (DWIR)
8/7/18. UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere
 UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project Republic of India
 Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project Republic of India Restoration and conservation of mangroves, coral reefs transplantation along the coastline of Gujarat and Orissa regions Abstract The ICZM project
Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project Republic of India Restoration and conservation of mangroves, coral reefs transplantation along the coastline of Gujarat and Orissa regions Abstract The ICZM project
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes
 BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine
 Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PLAN OF BEN TRE PROVINCE
 30. C l i m a t e C h a n g e A d a p t a t i o n P l a n o f B e n T r e P r o v i n c e PRESENTATION CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PLAN OF BEN TRE PROVINCE November 09 Mr. Truong Duy Hai Ben Tre DONRE TOPOGRAPHY
30. C l i m a t e C h a n g e A d a p t a t i o n P l a n o f B e n T r e P r o v i n c e PRESENTATION CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PLAN OF BEN TRE PROVINCE November 09 Mr. Truong Duy Hai Ben Tre DONRE TOPOGRAPHY
India. India Grain Voluntary Update - October 2017
 THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 10/3/2017 GAIN Report Number:
THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 10/3/2017 GAIN Report Number:
Downloaded from
 SET 3 Series : GBM/1,)- Code No. 64/1/3 # 9 : ' +, - $2 -! Candidates must write the Code on the title page of the answer-book. Roll No. 8 2! " # $ "%& % ' ( )* +, - -! 22!!"#$%! &'()"*+./ %15 0 " & 1!
SET 3 Series : GBM/1,)- Code No. 64/1/3 # 9 : ' +, - $2 -! Candidates must write the Code on the title page of the answer-book. Roll No. 8 2! " # $ "%& % ' ( )* +, - -! 22!!"#$%! &'()"*+./ %15 0 " & 1!
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
India s Readiness for REDD+
 INDIA@COP22 India s Readiness for REDD+ Dr. T.P. Singh Sustainable Lifestyle = Positive Climate Action www.indiaatcop22.org Forests Cover in India Class Area (sq km) % of geo area Very Dense Forest 85,904
INDIA@COP22 India s Readiness for REDD+ Dr. T.P. Singh Sustainable Lifestyle = Positive Climate Action www.indiaatcop22.org Forests Cover in India Class Area (sq km) % of geo area Very Dense Forest 85,904
Ecology. Climate. Global Climate. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
SUMMARY INITIAL ENVIRONMENTAL EXAMINATION REPORT. for the TALA-DELHI POWER TRANSMISSION PROJECT (INDIA)
 SUMMARY INITIAL ENVIRONMENTAL EXAMINATION REPORT for the TALA-DELHI POWER TRANSMISSION PROJECT (INDIA) This report was prepared by the Barrower and is not an ADB document. The IEE is available on request.
SUMMARY INITIAL ENVIRONMENTAL EXAMINATION REPORT for the TALA-DELHI POWER TRANSMISSION PROJECT (INDIA) This report was prepared by the Barrower and is not an ADB document. The IEE is available on request.
GIS STUDY OF THE DIVERSITY OF GINGER CULTIVATION IN INDIA Utpala P, Johny A.K, V.A.Parthasarathy, K.Jayarajan and M.S.Madan
 GIS STUDY OF THE DIVERSITY OF GINGER CULTIVATION IN INDIA Utpala P, Johny A.K, V.A.Parthasarathy, K.Jayarajan and M.S.Madan Ginger is reported to have originated in Southern China. Today, it is cultivated
GIS STUDY OF THE DIVERSITY OF GINGER CULTIVATION IN INDIA Utpala P, Johny A.K, V.A.Parthasarathy, K.Jayarajan and M.S.Madan Ginger is reported to have originated in Southern China. Today, it is cultivated
Chapter 23 Test on South Asia
 Name Score Chapter 23 Test on South Asia Part 1 - Multiple Choice (26 pts.) Read the following statements carefully. Select and circle the most correct choice from among the choices provided. 1. The northern
Name Score Chapter 23 Test on South Asia Part 1 - Multiple Choice (26 pts.) Read the following statements carefully. Select and circle the most correct choice from among the choices provided. 1. The northern
1/16/2008. Too little rain Too much rain. Major Diversion Routes. Modified from Dr. J. Rao, 2003
 Rainfall Distribution in India The Indian River-linking Project: A Geologic, Ecological, and Socio-economic Perspective Too little rain Too much rain Diversion from Surplus to Deficit Regions Major Diversion
Rainfall Distribution in India The Indian River-linking Project: A Geologic, Ecological, and Socio-economic Perspective Too little rain Too much rain Diversion from Surplus to Deficit Regions Major Diversion
Potential Gains from Regional Cooperation and Trade of Electricity in South Asia
 Potential Gains from Regional Cooperation and Trade of Electricity in South Asia Govinda R. Timilsina and Mike Toman The World Bank, Washington, DC 5 th Asian Conference of IAEE University of Western Australia
Potential Gains from Regional Cooperation and Trade of Electricity in South Asia Govinda R. Timilsina and Mike Toman The World Bank, Washington, DC 5 th Asian Conference of IAEE University of Western Australia
VECTOR BORNE DISEASES AND CLIMATIC CHANGES
 VECTOR BORNE DISEASES AND CLIMATIC CHANGES Dr. Neeraj Dhingra Additional Director National Vector Borne Disease Control Porgramme (NVBDCP Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India PREVENTION
VECTOR BORNE DISEASES AND CLIMATIC CHANGES Dr. Neeraj Dhingra Additional Director National Vector Borne Disease Control Porgramme (NVBDCP Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India PREVENTION
THE CONCEPT OF ORGANIC FARMING:
 INTRODUCTION : Agriculture is one of the oldest and most fundamental primary occupation of all human beings since stone age. It is a foundation of all social Cultural and Economical condition of mankind.
INTRODUCTION : Agriculture is one of the oldest and most fundamental primary occupation of all human beings since stone age. It is a foundation of all social Cultural and Economical condition of mankind.
VEGETATIVE, WATER, FISH AND WILDLIFE RESOURCES POLICIES
 VEGETATIVE, WATER, FISH AND WILDLIFE RESOURCES POLICIES The County will: GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1.1 Conserve, Enhance, Protect, Maintain and Manage Vegetative, Water, Fish and Wildlife Resources Promote
VEGETATIVE, WATER, FISH AND WILDLIFE RESOURCES POLICIES The County will: GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1.1 Conserve, Enhance, Protect, Maintain and Manage Vegetative, Water, Fish and Wildlife Resources Promote
Ramsar Advisory Mission Pakistan 29 October 5 November, 2012
 Ramsar Advisory Mission Pakistan 29 October 5 November, 2012 What are wetlands? Wetlands are areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that
Ramsar Advisory Mission Pakistan 29 October 5 November, 2012 What are wetlands? Wetlands are areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that
Water Resources Management in Bhutan. G.Karma Chhopel
 Water Resources Management in Bhutan G.Karma Chhopel Introduction China Area 38,394km 2 Nepal Bhutan Bangladesh India Population 634,982 (2005) Altitude range from 100m above 7500m above msl State of Environment
Water Resources Management in Bhutan G.Karma Chhopel Introduction China Area 38,394km 2 Nepal Bhutan Bangladesh India Population 634,982 (2005) Altitude range from 100m above 7500m above msl State of Environment
The various activities and structures covered under Water Harvesting are:
 Technologies for enhancing ground water recharge Subhra Chakravarty CSIR, New Delhi E-mail: asubhra@hotmail.com Abstract In countries like India, with an ever-increasing demand for water, the importance
Technologies for enhancing ground water recharge Subhra Chakravarty CSIR, New Delhi E-mail: asubhra@hotmail.com Abstract In countries like India, with an ever-increasing demand for water, the importance
Theme : (10) - The role of forestry in poverty alleviation and in supporting human livelihoods in developing countries.
 Theme : (10) - The role of forestry in poverty alleviation and in supporting human livelihoods in developing countries. THE ROLE OF SOCIAL FORESTRY IN POVERTY ALLEVIATION A CASE STUDY FROM INDIA ABSTRACT
Theme : (10) - The role of forestry in poverty alleviation and in supporting human livelihoods in developing countries. THE ROLE OF SOCIAL FORESTRY IN POVERTY ALLEVIATION A CASE STUDY FROM INDIA ABSTRACT
Foundation Course. Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT
 Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Water Resources. Ms. Sarika Karda
 Water Resources Ms. Sarika Karda Introduction Being a renewable resource, water is the most important natural resource. It is needed for all forms of life. It helps in movement, circulation and cycling
Water Resources Ms. Sarika Karda Introduction Being a renewable resource, water is the most important natural resource. It is needed for all forms of life. It helps in movement, circulation and cycling
Humid Tropical Environments
 Humid Tropical Environments Alison J. Reading Russell D. Thompson Andrew C. Millington BLACKWELL Oxford UK & Cambridge USA Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Defining the humid
Humid Tropical Environments Alison J. Reading Russell D. Thompson Andrew C. Millington BLACKWELL Oxford UK & Cambridge USA Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Defining the humid
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS The base of the ocean s food chains is formed by A. blue whales. B. plankton. C. coral reefs. D. sargassums. The place where the ocean meets the land is the The
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS The base of the ocean s food chains is formed by A. blue whales. B. plankton. C. coral reefs. D. sargassums. The place where the ocean meets the land is the The
Status of Soil Resources and Priorities towards Sustainable Soil Management
 NENA Soil Partnership Conference: towards a regional implementation plan on sustainable management of soil resources 1-3 June 2015, Amman, Jordan Status of Soil Resources and Priorities towards Sustainable
NENA Soil Partnership Conference: towards a regional implementation plan on sustainable management of soil resources 1-3 June 2015, Amman, Jordan Status of Soil Resources and Priorities towards Sustainable
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Davood Nikkami (PhD)
 Country Report of The IR. Iran 28-30 Jan., 2009, Bangkok, Thailand Workshop on Improving Agricultural Productivity, Water Use Efficiency & Strengthening Rural Livelihoods Davood Nikkami (PhD) Soil Conservation
Country Report of The IR. Iran 28-30 Jan., 2009, Bangkok, Thailand Workshop on Improving Agricultural Productivity, Water Use Efficiency & Strengthening Rural Livelihoods Davood Nikkami (PhD) Soil Conservation
SOIL MOISTURE CHARACTERISTICS IN UPPER PART OF HINDON RIVER CATCHMENT
 SOIL MOISTURE CHARACTERISTICS IN UPPER PART OF HINDON RIVER CATCHMENT C. P. Kumar * Vijay Kumar ** Vivekanand Singh *** ABSTRACT Knowledge of the physics of soil water movement is crucial to the solution
SOIL MOISTURE CHARACTERISTICS IN UPPER PART OF HINDON RIVER CATCHMENT C. P. Kumar * Vijay Kumar ** Vivekanand Singh *** ABSTRACT Knowledge of the physics of soil water movement is crucial to the solution
Intense Revision Plan for Prelims 2018 Day 8 Ecology and Environment
 Intense Revision Plan for Prelims 2018 Day 8 Ecology and Environment 1. Consider the following statements. 1. Distribution of natural vegetation depends upon temperature and moisture. 2. The amount of
Intense Revision Plan for Prelims 2018 Day 8 Ecology and Environment 1. Consider the following statements. 1. Distribution of natural vegetation depends upon temperature and moisture. 2. The amount of
