EVALUATION OF THE MICROSATELLITE POLYMORPHISM IN INTRON I OF THE MYOSTATIN GENE (MSTN) IN LATVIAN BLUE CATTLE BREED
|
|
|
- Dustin Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EVALUATION OF THE MICROSATELLITE POLYMORPHISM IN INTRON I OF THE MYOSTATIN GENE (MSTN) IN LATVIAN BLUE CATTLE BREED Mazvērsīte, J. 1, Grīslis, Z. 2, Sugoka, O. 1, Sokolovska, J. 1 and Sjakste, T. 1 1 Institute of Biology of the University of Latvia, Miera 43, Salaspils, LV2169, Latvia; 2 Latvia University of Agriculture, Liela iela 2, Jelgava, Latvia, LV-3001, phone: , tanja@ .lubi.edu.lv Abstract Myostatin (MSTN), a member of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily, is a highly conserved, potent negative regulator of skeletal muscle growth in many species from rodents to humans. Loss of MSTN activity in cattle, mice, and humans leads to a profound phenotype of muscle overgrowth associated with more numerous and larger fibers and enhanced regenerative capacity. Several MSTN gene structural variations have been reported as potentially significant in cattle phenotype performance. Here we report preliminary data on the microsatellite polymorphism of the first intron of the MSTN gene in Latvian Blue cattle breed. Key words Cattle, myostatin, microsatellite, polymorphism. Introduction Growth and differentiation factors (GDF) specifically regulate tissue and cell growth and differentiation. One of GDF proteins, GDF-8, also called myostatin (MSTN) has been considered as a novel and unique regulator of muscle growth (Tajbakhsh et al., 1996; Rudnicki et al., 1993; Zhu & Miller, 1997; Kassar-Duchaaussoy et al., 2004). MSTN gene is highly conserved across species and is expressed both in developing and mature skeletal muscle (McPherron, 1997). Multiple experimental findings on mice overall suggests that low or moderate inhibition of myostatin levels leads to muscle hypertrophy whereas total myostatin suppression leads to muscle hyperplasia (Joulia-Ekasa & Cabello, 2006). The bovine MSTN gene is located at 2q11 (Bovmap Database, ) and consists of three exons and two introns. Phenotype of several cattle breeds, such as Belgian Blue, exhibiting an obviously increased muscle mass (double muscled phenotype), was correlated with mutations at the MSTN locus (Charlier et al., 1995). Several MSTN gene inactivating mutations that naturally occur in bovine strains are associated to the increased total muscle mass associated to hyperplasia (Grobet et al., 1997; Kambadur et al., 1997; McPherron & Lee, 1997; Karim et al., 2000). In many species belonging to the Artiodactila (pig, goat, sheep, cattle), first intron of the MSTN gene is characterized by the presence T-mononucleotide microsatellite (MS). High variability of T-repeat units as well as its 5 flanking sequence was identified within and between some bovine breeds (De la Rosa-Reina et al., 2006). The origin, evolutional conservatism and/or variability and biological function of MS concerning genomic regions are not well understood. However, in recent years it has become clear that MS and their flanking regions are functionally active participants of gene and genome function. They could code for regulatory elements, participate in hairpins and Z-fingers and other secondary structures influencing the gene transcription and processing (Lewin, 2004). Our findings on barley beta-amylase gene indicate that MS motif is in strong correlation with the whole intron haplotype and trait responsible SNPs in neighboring exons (Sjakste & Zhuk, 2006). Therefore, studies of MS polymorphism of the corresponding genes could give information on the population variability as well as to precisely characterize haplotypes, their association with the phenotypes and to establish MS functional implications. The goal of this pilot study was to characterize MSTN gene intron I haplotype on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and MS polymorphisms in Latvian Blue cattle breed, developed from indigenous Latvian cattle breed and one of the rarest cattle breeds in the world (Grislis, 2006). 267
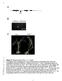
2 Materials and Methods The blood of the seven animals was obtained from Latvian farmers as part of the common contract project Nr /S386 between Latvia University of Agriculture and Latvian Ministry of Agriculture. DNA was isolated from 500 µl of blood of each animal using K0512 Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Fermentas, Lithuania) according to producer protocol. DNA quality and quantity were visualized with electrophoresis in 1% agarose gel. The 5 region of the intron I of the MSTN gene was amplified with forward primer AMXaF: 5 -TCA TTA CCA TGC CCA CGG AGT GTG-3 and reversal primer AMXaR: 5 -TTT ACT TCC TTA TTG CTC TTA CTA-3. PCR reactions were performed in total volume of 30 µl containing 1.5 mm MgCl 2, 10 mm dntp, 0.6 mm of each primer, 3 µl of 10 x PCR buffer, 0.75 U Taq DNA Polymerase (Fermentas, Lithuania ), and 100 ng of genomic DNA. The PCR reaction was carried out in an Eppendorf Mastercycler gradient thermocycle under the following conditions: initial denaturing of 94 C, 3 min, 35 cycles of denaturing 94 C for 30 sec, annealing 54 C for 30 sec and extension of 72 C for 1min, and final extension of 72 C for 5 min. Amplification was followed by direct sequencing in both directions with forward primer AMBsF: 5 -CCACGGAGTGTGAGTAGTCCT G-3 and reversal primer AMBsR: 5 -TTGCTCTACTAATACATTAAGT-3. DNA sequencing was carried out in Latvian Biomedical Center on Abi Prism 3100 Genetic Analyzer. The strategy of amplification is presented in Fig. 1. Primer design was performed by the Primer 3.0 program using the highly conserved regions of exon I and intron I generated from database available MSTN genomic sequence (GeneBank accession AB076403). Alignments of the previously published MSTN intron 1 genomic sequences and sequences obtained in this study were generated by the multiple alignment service ClustalW ( Bos taurus MSTN gene stucture 5' AMBaF AMBaR 3' Figure 1. The MSTN gene structure and the strategy of amplification. Nucleotide numbering is given according to the sequence reported previously as MSTN gene for Bos taurus (GeneBank accession AB076403). Exons are indicated in grey. Star shows location of MS in the first intron of the gene. Results and Discussion The amplification of the 5 region of the intron I of the MSTN gene resulted in the product of expected size (approximately 635 bp) for all 7 animals of Latvian Blue cattle breed used in pilot study. All amplification products were sequenced in both forward and reversal direction. Two alleles of MS of different (T)n mononucleotide repeat number and different sequence motif were detected (Table 1, Fig. 2). Longest allele 1 was detected in homozygous condition (Fig. 2A) in 3 animals and characterized by sequence motif A 773 (GG) 2 (GT) 2 TG(T) 18 C (Table 1). Sequence of the allele 1 differs from corresponding gene portion of reported previously MSTN genomic sequence (GeneBank: AB ) only in (T)n repeat number ((T) 18 and (T) 19 correspondingly). Practically the same MS motif A 773 (G) 2 (GT) 2 TG(T) n T was described for MSTN gene of Beefmaster and Chianin cattle breeds (De la Rosa-Reina et al., 2006), the difference is limited to (T) n repeat number and SNP C 798 T flanking MS from 3 end. 268
3 Table 1. Result of MSTN MS polymorphism analysis in Latvian Blue cattle. Nucleotide numbering is given according to the sequence reported previously as MSTN gene for Bos Taurus (GeneBank accession AB076403) Number of animals MS allele Allele sequence Homozygote on allele 1 Homozygote on allele 2 Heterozygote on allele 1/allele 2 Allele 1 A 773 (GG) 2 (GT) 2 TG(T) 18 C 3 3 Allele 2 A 773 (G) 2 (T) 14 C 1 SNP A 766 T MS (T)n Figure 2. The sequencing results on the MSTN gene MS region in Latvian Blue cattle. A homozygote on MS allele 1; B homozygote on MS allele 2; C heterozygote. Shortest allele 2 of Latvian Blue cattle of core motif A 773 (G) 2 (T) 14 C was detected in homozygous condition (Fig. 2B) only in one case (Table 1). Similar MS motif A 773 (G) 2 (T) n T with repeat number variation from 11 till 14 and T nucleotide at position 798 was described previously for MSTN gene of Beefmaster, Brahman, Charolais, Simmental cattle breeds (De la Rosa-Reina et al., 2006). Allele 2 is different from the reported sequence (GeneBank: AB076403) variant not only in MS core motif but also in several SNPs including SNP A 766 T in 5 region from the MS repeated portion (Fig. 2B). 269
4 The comparison of sequence results of the both allele 1 and allele 2 (Fig. 2A and B) allowed us to read the sequences we have obtained for resting three animals (Fig. 2C) and to make conclusion on heterozygote genotype of gene portion analyzed (Table 1, Fig. 2). Based on the analysis of both homozygote and heterozygote conditions of allele 2 we suggest that SNP A 766 T could be linked with MS motif in one linkage block. In our pilot study we demonstrated that MSTN gene MS polymorphism is represented in Latvian Blue cattle breed at least by two alleles of different repeated portion motifs and neighbouring SNPs polymorphisms. In set of 7 animals analyzed allele 1 was more frequent (6 and 3 alleles for 3 homozygotes and 3 heterozygotes correspondingly) and allele 2 was revealed as less frequent ( 2 and 3 alleles for 1 homozygote and 3 heterozygotes). As animals were not selected specially for any traits we could suggest that the same allele presentation and distribution could characterize Latvian Blue cattle breed in general. However, broad population study is necessary to prove all our suggestions. Conclusions MSTN gene MS polymorphism is represented in Latvian Blue cattle breed at least by two alleles of different repeated portion motifs and neighbouring SNPs polymorphisms. Allele 2 is different from the reported sequence (GeneBank: AB076403) variant not only in MS core motif but also in several SNPs including SNP A 766 T in 5 region from the MS repeated portion. Longest allele 1 was more frequent and shortest allele 2 was revealed as less frequent. As animals were not selected specially for any traits we could suggest that the same allele presentation and distribution could characterize Latvian Blue cattle breed in general. Acknowledgements Authors are grateful to Latvian Ministry of Agriculture for financial support, contract works No /S386 and No /C-266. We thank Ilva Poudziunas for assistance. References 1. Charlier, C., Coppiters, W., Farnir, F., Grobet, L., Leroy, P., Michaux, C., Mni, M., Schwers, A., Vanmanshoven, P., Hanset, R. (1995) The mh gene causing double muscling in cattle maps to bovine chromosome 2. Mamm. Genome 6, ; 2. De la Rosa-Reyna, X. F., Perez, M. A. R., Sifuentes-Rincon, A. M. (2005) Microsattelite polymorphism in intron 1 of the bovine myostatin gene. J. Appl. Genet., 47, 1 3; 3. Grislis, Z. (2006). Zilās Govs Vidzemē. Biedrība Širnes saglabāšanas apvienība Zilā Govs. Jelgava, Grobet, L., Martin, L., Poncelet, D., Pirottin, D., Brouwers, B., Riquet, J., Schoeberlein, A., Dunner, S., Mienissier, J., Joulia-Ekaza, D., Cabello, G. (2006) Myostatin regulation of muscle development: Molecular basis natural mutations, physiopathological aspects. Exp. cell research 312, ; 5. Kambadur, R., Sharma, M., Smith, T. P., Bass, J. J. (1997) Mutations in myostatin (GDF8) in doublemuscled Belgian Blue and Piedmontese cattle. Genome Res. 7, ; 6. Karim, L., Coppieters, W., Grobet, L., Valentini, A., Georges, M. (2000) Convenient genotyping of six myostatin mutations causinf double-muscling in cattle a multiplex oligonucleotide ligation assay. Anim.Genet. 31, ; 7. Kassar-Duchaaussoy, L., Gayraud-Morel, B., Gomes, D., Rocancourt, D., Buckingham, M., Shinin, V., Tajbakhsh, S. (2004) Mrf4 determines skeletal muscle identity in Myf5: MyoD double-mutant mice. Nature 431, ; 8. Lewin, B. (2004) Genes VΙΙΙ.Pearson,Prentice Hall. 9. McPherron, A., Lee, S. (1997) Double muscling in cattle due to mutations in the myostatin gene. Proceeding of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 94, ; 10. Rudnicki, M., Braun, T., Hinuma, S., Jaenisch, R. (1992) Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to upregulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell 71, ; 11. Sjakste, T., Zhuk, A. (2006) Novel haplotype description and structural background of the eventual functional significance of the barley beta-amylase gene intron rearrangements. Theor.Appl.Genet. 113, ; 270
5 12. Tajbakhsh, S., Rocancourt, D., Buckingham, M. (1996) Muscle progenitor cells failing to respond to positional cues adopt non-myogenic fates in myf-5 null mice. Nature 384, ; 13. Zhu, Z., Miller, B. (1997) MRF4 can substitute for myogenin during early stages of myogenesis. Dev. Dyn.209, KOMBINĒTĀS DUBULTIEDARBĪBAS PIEDEVU IETEKME UZ ZĀLES FERMENTĀCIJU UN IEGŪTĀS SKĀBBARĪBAS KVALITĀTI INFLUENCE OF COMBINED CONSERVATION ADDITIVES ON GRASS FERMENTATION AND OBTAINED SILAGE QUALITY Ošmane B., JemeĜjanovs A., Konošonoka I. Latvijas Lauksaimniecības Universitāte Biotehnoloăijas un Veterinārmedicīnas Zinātniskais Institūts Sigra, Zinātnes iela 1, Latvija, LV-2150, Fakss: , e-pasts: Latvian University of Agriculture Research Institute of Biotechnology and Veterinary Medicine Sigra, Zinātnes iela 1, Latvia, LV-2150, Fax: , Abstract Aerobic instability is a problem on many farms. Use of biological inoculant can improve silage fermentation, but is not effective in protecting silage exposed to air. Aerobic deterioration generates looses and reduces hygienic quality during the feed-out. A combination of inoculant and chemical treatment has the potential to enhance aerobic stability. The aim of experiment was to evaluate the effect of combined use of biological inoculant and chemical additives Na benzoate and K sorbate on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of red clover/galega silage during the feed out. The application of an additives Na benzoate and K sorbate enhanced lactic acid content, reduced ph and eliminated butyric acid fermentation in silage. When the silages were open to air, a diference in the ph and mould growth was significant. After 6 days exposure in open air ph level on control variant (untreated silage) increased from 4,00 to 4,75, but of silage with inoculant and additives ph level was stable. After 8 days, when silage was open, the untreated silage contained higher count of moulds ( 1x10-8 CFU g -1 colony forming units), than silage with inoculant and additives (0 CFU g -1 ). The treated silage quality and aerobic stability was not significantly (p>0,05) different between silage which open in 1, 3, 8 days. Silage with biological inoculant and Na benzoate or K sorbate provides significantly (p<0,05) increasing of milk yield about 1,1 kg per day from cow, comporision with not treated silage. It was concluded that the improvements in fermentation and aerobic stability resulted in a higher performance of dairy cows. Key words Combined additives, second fermentation, silage quality. Ievads Nepareizas fermentācija procesu rezultātā skābbarībā zūd barības vērtība, un tajā var rasties nevēlamas vielas kā, piemēram, sviestskābe, kas samazina barības apēdamību, līdz ar to tā ietekmē dzīvnieku veselību un iegūtās lopkopības produkcijas kvalitāti. Būtisks skābējamības rādītājs ir zaĝmasas mikrobiālais spektrs (pienskābes, sviestskābes, enterobaktērijas, pelējumsēnes un raugveida sēnes) un tā procentuālais sastāvs. Sausnas satura palielināšana vienmēr izmaina fermentācijas procesus skābbarībā. Labas skābbarības gatavošanas procesā būtiska nozīme ir katra auga skābēšanas kritiskajam sausnas saturam. Pienskābes baktērijas labi darbojas arī masā ar paaugstinātu sausnas saturu, kad citu mikroorganismu darbības diapazons ierobežots (JemeĜjanovs, 2005; Kravale, 2005). Svarīgs nosacījums zaĝmasas skābēšanā ir tās ātra iekonservēšana pēc nopĝaušanas. Skābējot masu ar augstāku barotājvērtību, t.i. pirmajās augu attīstības fāzēs, augos esošās olbaltumvielas, to skaldprodukti, minerālvielas u.c. masas skābšanas laikā neitralizē organiskās skābes (sevišėi pienskābi). Šādi procesi neĝauj masai normāli ieskābt. Pirmajās attīstības fāzēs zaĝmasa grūtāk apvīst, ko izraisa osmotiskā spiediena izmaiħas augā. TādēĜ, lai iekonservētu grūtāk skābstošu zāli, jālieto skābēšanas piedevas (Ošmane, 2005; piena lopkopība, 2001). 271
Comparative analysis of myostatin gene and promoter sequences of Qinchuan and Red Angus cattle
 Comparative analysis of myostatin gene and promoter sequences of Qinchuan and Red Angus cattle Y.L. He 1,2 *, Y.H. Wu 1,2 *, F.S. Quan 1, Y.G. Liu 1 and Y. Zhang 1 1 Key Laboratory of Animal Reproductive
Comparative analysis of myostatin gene and promoter sequences of Qinchuan and Red Angus cattle Y.L. He 1,2 *, Y.H. Wu 1,2 *, F.S. Quan 1, Y.G. Liu 1 and Y. Zhang 1 1 Key Laboratory of Animal Reproductive
GENOTYPING BY PCR PROTOCOL FORM MUTANT MOUSE REGIONAL RESOURCE CENTER North America, International
 Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
ANALYSIS OF CANDIDATE GENES FOR MEAT PRODUCTION TRAITS IN DOMESTIC RABBIT BREEDS
 Genetics ANALYSIS OF CANDIDATE GENES FOR MEAT PRODUCTION TRAITS IN DOMESTIC RABBIT BREEDS Fontanesi L.*, Tazzoli M., Scotti E., Russo V. DIPROVAL, Sezione di Allevamenti Zootecnici, University of Bologna,
Genetics ANALYSIS OF CANDIDATE GENES FOR MEAT PRODUCTION TRAITS IN DOMESTIC RABBIT BREEDS Fontanesi L.*, Tazzoli M., Scotti E., Russo V. DIPROVAL, Sezione di Allevamenti Zootecnici, University of Bologna,
Real Time TaqMan PCR technique: a valid tool for the meat quality certification
 Real Time TaqMan PCR technique: a valid tool for the meat quality certification Anna Pozzi, Andrea Galli & Graziella Bongioni. Istituto Sperimentale Italiano L. Spallanzani Milano Italy Abstract The myostatin
Real Time TaqMan PCR technique: a valid tool for the meat quality certification Anna Pozzi, Andrea Galli & Graziella Bongioni. Istituto Sperimentale Italiano L. Spallanzani Milano Italy Abstract The myostatin
HLA-DR TYPING OF GENOMIC DNA
 HLA-DR TYPING OF GENOMIC DNA Zofia SZCZERKOWSKA, Joanna WYSOCKA Institute of Forensic Medicine, Medical University, Gdañsk, Poland ABSTRACT: Advances in molecular biology techniques allowed for introduction
HLA-DR TYPING OF GENOMIC DNA Zofia SZCZERKOWSKA, Joanna WYSOCKA Institute of Forensic Medicine, Medical University, Gdañsk, Poland ABSTRACT: Advances in molecular biology techniques allowed for introduction
STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR
 STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR Ref. PCR1 1. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR Ref. PCR1 1. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Myostatin Mutations Cause Double Muscling in Cattle
 MUSCLE BOCHEMSTRY Myostatin Mutations Cause Double Muscling in Cattle Timothy P. Smith* Eduardo Casas, Scott C. Fahrenkrug, Roger T. Stone, Steven M. Kappes, and John W. Keele ntroduction The differences
MUSCLE BOCHEMSTRY Myostatin Mutations Cause Double Muscling in Cattle Timothy P. Smith* Eduardo Casas, Scott C. Fahrenkrug, Roger T. Stone, Steven M. Kappes, and John W. Keele ntroduction The differences
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/direct_detection_of_genotype.html 1 Like most other model organism Arabidopsis thaliana has a sequenced genome? What do we mean by sequenced genome? What sort of info
http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/direct_detection_of_genotype.html 1 Like most other model organism Arabidopsis thaliana has a sequenced genome? What do we mean by sequenced genome? What sort of info
Some Motifs Were Important for Myostatin Transcriptional Regulation in Sheep (Ovis aries)
 Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Vol. 40, No. 4, July 2007, pp. 547-553 Some Motifs Were Important for Myostatin Transcriptional Regulation in Sheep (Ovis aries) Rong Du 1,2, Xiao-Rong An
Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Vol. 40, No. 4, July 2007, pp. 547-553 Some Motifs Were Important for Myostatin Transcriptional Regulation in Sheep (Ovis aries) Rong Du 1,2, Xiao-Rong An
Carcass Traits Association with GH/AluI Gene Polymorphism in Indonesian Aceh Cattle
 Carcass Traits Association with GH/AluI Gene Polymorphism in Indonesian Aceh Cattle Eka Meutia Sari¹,*, Ronny Rachman Noor 2, Cece Sumantri 2 & Endang Tri Margawati 3 ¹ Department of Animal Production,
Carcass Traits Association with GH/AluI Gene Polymorphism in Indonesian Aceh Cattle Eka Meutia Sari¹,*, Ronny Rachman Noor 2, Cece Sumantri 2 & Endang Tri Margawati 3 ¹ Department of Animal Production,
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
Agricultural University, al. Mickiewicza 24/28, Kraków, Poland
 Genetic Polymorphism Of Zatorska Geese Flock Estimated Through RAPD Markers Krzysztof Andres 1, Ewa Kapkowska 1, Urszula Kaczor 2 1 Department of Poultry and Fur Animals Breeding and Animal Hygiene, 2
Genetic Polymorphism Of Zatorska Geese Flock Estimated Through RAPD Markers Krzysztof Andres 1, Ewa Kapkowska 1, Urszula Kaczor 2 1 Department of Poultry and Fur Animals Breeding and Animal Hygiene, 2
High-Resolution Melting analysis as a tool for rapid and sensitive detection of genotypes in cattle population
 Research and Development Station for Bovine, Arad, Romania High-Resolution Melting analysis as a tool for rapid and sensitive detection of genotypes in cattle population Daniela Elena Ilie, Ada Cean, Ioan
Research and Development Station for Bovine, Arad, Romania High-Resolution Melting analysis as a tool for rapid and sensitive detection of genotypes in cattle population Daniela Elena Ilie, Ada Cean, Ioan
MUTAGENESIS OF THE PROMOTER OF THE OIL PALM HOMOGENTISATE GERANYLGERANYL TRANSFERASE GENE (HGGT) BY PCR-DRIVEN OVERLAP EXTENSION
 ICBAA2017-30 MUTAGENESIS OF THE PROMOTER OF THE OIL PALM HOMOGENTISATE GERANYLGERANYL TRANSFERASE GENE (HGGT) BY PCR-DRIVEN OVERLAP EXTENSION Mohd Shahrul Nizwanshah Karim and Siti Nor Akmar Abdullah Laboratory
ICBAA2017-30 MUTAGENESIS OF THE PROMOTER OF THE OIL PALM HOMOGENTISATE GERANYLGERANYL TRANSFERASE GENE (HGGT) BY PCR-DRIVEN OVERLAP EXTENSION Mohd Shahrul Nizwanshah Karim and Siti Nor Akmar Abdullah Laboratory
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017, 303 307 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) GENETIC DIVERSITY AND BOTTLENECK STUDIES IN PUNGANUR CATTLE THROUGH MICROSATELLITE
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017, 303 307 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) GENETIC DIVERSITY AND BOTTLENECK STUDIES IN PUNGANUR CATTLE THROUGH MICROSATELLITE
Authors: Vivek Sharma and Ram Kunwar
 Molecular markers types and applications A genetic marker is a gene or known DNA sequence on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Why we need Molecular Markers There will be
Molecular markers types and applications A genetic marker is a gene or known DNA sequence on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Why we need Molecular Markers There will be
E-Supporting Information-1 (ESI-1) Ionic liquids promote PCR amplification of DNA
 E-Supporting Information-1 (ESI-1) Ionic liquids promote PCR amplification of DNA Yugang Shi, ab Yen-Liang Liu, a Peng-Yeh Lai, c Ming-Chung Tseng, a Min-Jen Tseng, c Yudong Li, b and Yen-Ho Chu* a a Department
E-Supporting Information-1 (ESI-1) Ionic liquids promote PCR amplification of DNA Yugang Shi, ab Yen-Liang Liu, a Peng-Yeh Lai, c Ming-Chung Tseng, a Min-Jen Tseng, c Yudong Li, b and Yen-Ho Chu* a a Department
IDENTIFICATION OF BETA- LACTOGLOBULIN AND KAPPA-CASEIN GENOTYPES USING PCR-RFLP IN HOLSTEIN CATTLE
 IDENTIFICATION OF BETA- LACTOGLOBULIN AND KAPPA-CASEIN GENOTYPES USING PCR-RFLP IN HOLSTEIN CATTLE Yasemin GEDİK, Mehmet Ali YILDIZ, Orhan KAVUNCU Ankara University Agriculture Faculty Animal Science Biometry
IDENTIFICATION OF BETA- LACTOGLOBULIN AND KAPPA-CASEIN GENOTYPES USING PCR-RFLP IN HOLSTEIN CATTLE Yasemin GEDİK, Mehmet Ali YILDIZ, Orhan KAVUNCU Ankara University Agriculture Faculty Animal Science Biometry
FAQs: PCR Polymerases from Takara Bio
 FAQs: PCR Polymerases from Takara Bio Contents: PCR Basics Q1 Q2 Q3 What parameters do I need to consider when designing primers? What is the optimum amount of template to use? Which conditions are particularly
FAQs: PCR Polymerases from Takara Bio Contents: PCR Basics Q1 Q2 Q3 What parameters do I need to consider when designing primers? What is the optimum amount of template to use? Which conditions are particularly
Biotechnology. Explorer Program. Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1
 Biotechnology Explorer Program Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1 Chromosome 8: PCR TM PCR Workshop Kirk Brown,, Tracy High School; Tracy, Ca Stan Hitomi,, Monte Vista High School; Danville, CA
Biotechnology Explorer Program Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1 Chromosome 8: PCR TM PCR Workshop Kirk Brown,, Tracy High School; Tracy, Ca Stan Hitomi,, Monte Vista High School; Danville, CA
FastGene Optima. Products for PCR. proof-reading. ReadyMix. cdna SNP. routine PCR. polymerase. optimized blend complex templates. N gene knock out B O
 Products for PCR www.nippongenetics.eu efficiency polymerase convenience endpoint PCR incl. loading dye direct PCR incl. dntps engineered enzyme archeal type B polymerase high GC content FastGene tissuebest
Products for PCR www.nippongenetics.eu efficiency polymerase convenience endpoint PCR incl. loading dye direct PCR incl. dntps engineered enzyme archeal type B polymerase high GC content FastGene tissuebest
Development of transcript-associated microsatellite markers in Ancherythoculter nigrocauda and cross-amplification in Culter alburnus
 Development of transcript-associated microsatellite markers in Ancherythoculter nigrocauda and cross-amplification in Culter alburnus Y. Sun 1,2, Q. Li 1, G. Wang 1, D. Zhu 1, J. Chen 1 and P. Li 1 1 Wuhan
Development of transcript-associated microsatellite markers in Ancherythoculter nigrocauda and cross-amplification in Culter alburnus Y. Sun 1,2, Q. Li 1, G. Wang 1, D. Zhu 1, J. Chen 1 and P. Li 1 1 Wuhan
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Molecular LDT in Newborn Screening Laboratories
 Molecular LDT in Newborn Screening Laboratories APHL/CDC Newborn Screening Molecular Workshop Atlanta, GA June 28-30, 2011 Mei Baker, M.D., FACMG Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics University
Molecular LDT in Newborn Screening Laboratories APHL/CDC Newborn Screening Molecular Workshop Atlanta, GA June 28-30, 2011 Mei Baker, M.D., FACMG Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics University
Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism
 Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism Outline of this chapter Gene Mutation DNA Polymorphism Gene Mutation Definition Major Types Definition A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence that composes
Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism Outline of this chapter Gene Mutation DNA Polymorphism Gene Mutation Definition Major Types Definition A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence that composes
Overview. Background ~30 min. Lab activity ~50 min. DNA profiling Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Gel Electrophoresis PCR
 Overview Day 1: Tuesday Introduction to DNA profiling How do we use DNA to solve crimes? Background Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Gel Electrophoresis Set up PCR Day 2: Wednesday Make and Run Agarose
Overview Day 1: Tuesday Introduction to DNA profiling How do we use DNA to solve crimes? Background Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Gel Electrophoresis Set up PCR Day 2: Wednesday Make and Run Agarose
BENG 183 Trey Ideker. Genotyping. To be covered in one 1.5 hr lecture
 BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genotyping To be covered in one 1.5 hr lecture Genetic variation: Some basic definitions Allele Alternative form of a genetic locus inherited separately from each parent Polymorphism
BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genotyping To be covered in one 1.5 hr lecture Genetic variation: Some basic definitions Allele Alternative form of a genetic locus inherited separately from each parent Polymorphism
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
DETERMINATION OF THE Rh FACTOR BY PCR
 DETERMINATION OF THE Rh FACTOR BY PCR Ref.: PCR2 1. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE The aim of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) by studying
DETERMINATION OF THE Rh FACTOR BY PCR Ref.: PCR2 1. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE The aim of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) by studying
Barley Bmy1 gene intron III inter- and intra-haplotype variability
 Barley Bmy1 gene intron III inter- and intra-haplotype variability Sjakste T.G., Zhuk A.F. in Molina-Cano J.L. (ed.), Christou P. (ed.), Graner A. (ed.), Hammer K. (ed.), Jouve N. (ed.), Keller B. (ed.),
Barley Bmy1 gene intron III inter- and intra-haplotype variability Sjakste T.G., Zhuk A.F. in Molina-Cano J.L. (ed.), Christou P. (ed.), Graner A. (ed.), Hammer K. (ed.), Jouve N. (ed.), Keller B. (ed.),
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.20 - BIOTECHNOLOGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals
 Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals Types of mutations: point mutations indels (insertion/deletion) copy number variation structural rearrangements
Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals Types of mutations: point mutations indels (insertion/deletion) copy number variation structural rearrangements
Genetic characterization and polymorphism detection of casein genes in Egyptian sheep breeds
 Genetic characterization and polymorphism detection of casein genes in Egyptian sheep breeds Othman E. Othman and Samia A. El-Fiky Cell Biology Department - National Research Center - Dokki - Egypt Corresponding
Genetic characterization and polymorphism detection of casein genes in Egyptian sheep breeds Othman E. Othman and Samia A. El-Fiky Cell Biology Department - National Research Center - Dokki - Egypt Corresponding
INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA
 E BMT Guidelines (proj.4) ORIGINAL: English DATE: December 21, 2005 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND
E BMT Guidelines (proj.4) ORIGINAL: English DATE: December 21, 2005 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND
What is DNA? Deoxyribonucleic Acid The inherited genetic material that makes us what we are
 DNA Basic Genetics What is DNA? DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid The inherited genetic material that makes us what we are DNA in the Cell Human Genome ~3 billion base pairs of DNA 30,000-35,000 genes Population-each
DNA Basic Genetics What is DNA? DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid The inherited genetic material that makes us what we are DNA in the Cell Human Genome ~3 billion base pairs of DNA 30,000-35,000 genes Population-each
1) (15 points) Next to each term in the left-hand column place the number from the right-hand column that best corresponds:
 1) (15 points) Next to each term in the left-hand column place the number from the right-hand column that best corresponds: natural selection 21 1) the component of phenotypic variance not explained by
1) (15 points) Next to each term in the left-hand column place the number from the right-hand column that best corresponds: natural selection 21 1) the component of phenotypic variance not explained by
POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the
 POPULATION GENETICS POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic composition of populations and how it changes with time. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the change of the genetic constitution)
POPULATION GENETICS POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic composition of populations and how it changes with time. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the change of the genetic constitution)
Lab #4 Polymerase Chain Reaction
 BE60, 011 Lab #4 Polymerase Chain Reaction In this laboratory work you will perform an allelespecific PCR. Allelic variants mean that the two genes (two alleles) are present in one DNA sample. These alleles
BE60, 011 Lab #4 Polymerase Chain Reaction In this laboratory work you will perform an allelespecific PCR. Allelic variants mean that the two genes (two alleles) are present in one DNA sample. These alleles
PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System
 PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0178 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 3 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0178 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 3 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
PREDICT Host DNA Barcoding Guide
 PREDICT Host DNA Barcoding Guide Contents: 1. Rationale for Barcoding.. Page 2 2. Implementation... Page 2 3. PCR Protocols.... Page 3 4. Data Interpretation... Page 5 5. Data Entry into EIDITH.... Page
PREDICT Host DNA Barcoding Guide Contents: 1. Rationale for Barcoding.. Page 2 2. Implementation... Page 2 3. PCR Protocols.... Page 3 4. Data Interpretation... Page 5 5. Data Entry into EIDITH.... Page
A NOTE ON LINKAGE BETWEEN THE ANGORA AND fgf5 GENES IN RABBITS
 W ORLD R ABBIT SCIENCE World Rabbit Sci. 2004, 2: - 6 WRSA, UPV, 2003 A NOTE ON LINKAGE BETWEEN THE ANGORA AND fgf5 GENES IN RABBITS MULSANT P., ROCHAMBEAU H. DE, THÉBAULT R. G. * INRA, Laboratoire de
W ORLD R ABBIT SCIENCE World Rabbit Sci. 2004, 2: - 6 WRSA, UPV, 2003 A NOTE ON LINKAGE BETWEEN THE ANGORA AND fgf5 GENES IN RABBITS MULSANT P., ROCHAMBEAU H. DE, THÉBAULT R. G. * INRA, Laboratoire de
Midterm 1 Results. Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median Number of Students. Exam Score
 Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
PCR in the Classroom. UC Davis - PCR Workshop Friday, September 26, 2003
 PCR in the Classroom UC Davis - PCR Workshop Friday, September 26, 2003 A little history In 1983, Kary B. Mullis conceived the procedure. He went on to Cetus Corp in Emeryville, CA where it was developed
PCR in the Classroom UC Davis - PCR Workshop Friday, September 26, 2003 A little history In 1983, Kary B. Mullis conceived the procedure. He went on to Cetus Corp in Emeryville, CA where it was developed
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1.
 FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
Comparative study of EST-SSR, SSR, RAPD, and ISSR and their transferability analysis in pea, chickpea and mungbean
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Comparative study of EST-SSR, SSR, RAPD, and ISSR and their transferability
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Comparative study of EST-SSR, SSR, RAPD, and ISSR and their transferability
CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory
 CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to amplify specific segments of DNA. If one knows the DNA sequence of regions of DNA that flank
CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to amplify specific segments of DNA. If one knows the DNA sequence of regions of DNA that flank
Amplicon size (bp) E ± SD
 Development of a probe-based qpcr assay for the detection of constitutional and somatic deletions in the NF1 gene. Application to genetic testing and tumor analysis. Terribas E, Garcia-Linares C, Lázaro
Development of a probe-based qpcr assay for the detection of constitutional and somatic deletions in the NF1 gene. Application to genetic testing and tumor analysis. Terribas E, Garcia-Linares C, Lázaro
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods SMAP Assay Detailed Protocol I. Technology Description SMAP is a novel gene amplification method with high sensitivity and single-nucleotide precision, enabling rapid detection of
Supplementary Methods SMAP Assay Detailed Protocol I. Technology Description SMAP is a novel gene amplification method with high sensitivity and single-nucleotide precision, enabling rapid detection of
2. Pyrosequencing Assay Design
 2. Pyrosequencing Assay Design 2.1 Guidelines for PCR set-up and primer design 2.1.1 PCR primer design Design of PCR primers follows standard rules, i.e. calculated Tm of 62-65 C, primer length of about
2. Pyrosequencing Assay Design 2.1 Guidelines for PCR set-up and primer design 2.1.1 PCR primer design Design of PCR primers follows standard rules, i.e. calculated Tm of 62-65 C, primer length of about
10x Hot-Taq Buffer 1 ml 1 ml x 2ea 1 ml x 10ea. dntp Mix (each 10 mm) None / 0.2 ml None / 0.4 ml None / 0.4 ml x 5ea
 HelixAmp TM Hot-Taq Polymerase (Ver. 2.0) CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS (1603-V01R03) Contents HelixAmp TM Hot-Taq Polymerase (Ver. 2.0) Cat. No. HT250/HT250N HT500/HT500N HT2500/HT2500N Hot-Taq (2.5 units/μl)
HelixAmp TM Hot-Taq Polymerase (Ver. 2.0) CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS (1603-V01R03) Contents HelixAmp TM Hot-Taq Polymerase (Ver. 2.0) Cat. No. HT250/HT250N HT500/HT500N HT2500/HT2500N Hot-Taq (2.5 units/μl)
Code: IDK-006 Ver: 1 MTHFR A1298C. Detection system of the A1298C mutation in the human Methylen-tetraydrofolate reductase gene. Reg.
 Detection system of the A1298C mutation in the human Methylen-tetraydrofolate reductase gene Reg. MSP 21199 Valdense 3616, Montevideo 11700, Uruguay Phone (598) 2 336 83 01 Fax (598) 2 336 71 60 info@atgen.com.uy
Detection system of the A1298C mutation in the human Methylen-tetraydrofolate reductase gene Reg. MSP 21199 Valdense 3616, Montevideo 11700, Uruguay Phone (598) 2 336 83 01 Fax (598) 2 336 71 60 info@atgen.com.uy
Sensitivity vs Specificity
 Viral Detection Animal Inoculation Culturing the Virus Definitive Length of time Serology Detecting antibodies to the infectious agent Detecting Viral Proteins Western Blot ELISA Detecting the Viral Genome
Viral Detection Animal Inoculation Culturing the Virus Definitive Length of time Serology Detecting antibodies to the infectious agent Detecting Viral Proteins Western Blot ELISA Detecting the Viral Genome
Inter-simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) Analysis of Somaclonal Variation in Date Palm Plantlets Regenerated from Callus
 2012 2nd International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation IPCBEE vol.35 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Inter-simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) Analysis of Somaclonal Variation in Date
2012 2nd International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation IPCBEE vol.35 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Inter-simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) Analysis of Somaclonal Variation in Date
Beef Cattle Genomics: Promises from the Past, Looking to the Future
 Beef Cattle Genomics: Promises from the Past, Looking to the Future A.D. Herring 1, D.G. Riley 1, J.O. Sanders 1, P.K. Riggs 1, C.A. Gill 1 1 Department of Animal Science, Texas A&M University, College
Beef Cattle Genomics: Promises from the Past, Looking to the Future A.D. Herring 1, D.G. Riley 1, J.O. Sanders 1, P.K. Riggs 1, C.A. Gill 1 1 Department of Animal Science, Texas A&M University, College
PCR. CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D.
 PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
DNA amplification and analysis: minipcr TM Food Safety Lab
 Science for everyone, everywhere DNA amplification and analysis: minipcr TM Food Safety Lab Release date: 09 September 2014 Welcome Our goals for today: Review DNA amplification theory Solve a public health
Science for everyone, everywhere DNA amplification and analysis: minipcr TM Food Safety Lab Release date: 09 September 2014 Welcome Our goals for today: Review DNA amplification theory Solve a public health
Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1
 Bio 212 Lab Name: Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1 OBJECTIVES: Review the following terms and concepts presented in Biology 211: enzymes, DNA structure and replication, role
Bio 212 Lab Name: Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1 OBJECTIVES: Review the following terms and concepts presented in Biology 211: enzymes, DNA structure and replication, role
Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Host-Plant Resistance to Root-knot Nematodes and Fusarium Wilt in Cotton
 Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Host-Plant Resistance to Root-knot Nematodes and Fusarium Wilt in Cotton Phil Roberts & Congli Wang, Department of Nematology Univ. of California, Riverside Project
Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Host-Plant Resistance to Root-knot Nematodes and Fusarium Wilt in Cotton Phil Roberts & Congli Wang, Department of Nematology Univ. of California, Riverside Project
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
ABAH BIOFLUX Animal Biology & Animal Husbandry International Journal of the Bioflux Society
 ABAH BIOFLUX Animal Biology & Animal Husbandry International Journal of the Bioflux Society Polymorphism within growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene in Romanian Black and White and Romanian Grey Steppe cattle
ABAH BIOFLUX Animal Biology & Animal Husbandry International Journal of the Bioflux Society Polymorphism within growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene in Romanian Black and White and Romanian Grey Steppe cattle
Marker types. Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, Allen Van Deynze
 Marker types Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, 2009 Allen Van Deynze Use of DNA Markers in Breeding Germplasm Analysis Fingerprinting of germplasm Arrangement of diversity (clustering,
Marker types Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, 2009 Allen Van Deynze Use of DNA Markers in Breeding Germplasm Analysis Fingerprinting of germplasm Arrangement of diversity (clustering,
BIOTECHNOLOGY. Sticky & blunt ends. Restriction endonucleases. Gene cloning an overview. DNA isolation & restriction
 BIOTECHNOLOGY RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY Recombinant DNA technology involves sticking together bits of DNA from different sources. Made possible because DNA & the genetic code are universal. 2004 Biology
BIOTECHNOLOGY RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY Recombinant DNA technology involves sticking together bits of DNA from different sources. Made possible because DNA & the genetic code are universal. 2004 Biology
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
MICROSATELITTE DNA VARIATION IN THE BLACK SEA STELLATE STURGEON, ACIPENSER STELLATUS
 Lucrări ştiinńifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 41 (1) (2008), Timişoara MICROSATELITTE DNA VARIATION IN THE BLACK SEA STELLATE STURGEON, ACIPENSER STELLATUS VARIAłIA ADN MICROSATELIT LA PASTRUGA
Lucrări ştiinńifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 41 (1) (2008), Timişoara MICROSATELITTE DNA VARIATION IN THE BLACK SEA STELLATE STURGEON, ACIPENSER STELLATUS VARIAłIA ADN MICROSATELIT LA PASTRUGA
MILK PROTEIN GENOTYPE EFFECTS ON MILK PRODUCTION IN BEEF HEIFERS AND CALF PERFORMANCE: PRELIMINARY RESULTS. Story in Brief
 MILK PROTEIN GENOTYPE EFFECTS ON MILK PRODUCTION IN BEEF HEIFERS AND CALF PERFORMANCE: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Gary K. Ziehe1, Daniel Pomp2 and David S. Buchanan3 Story in Brief Genotypes at the j3-lactoglobulinand
MILK PROTEIN GENOTYPE EFFECTS ON MILK PRODUCTION IN BEEF HEIFERS AND CALF PERFORMANCE: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Gary K. Ziehe1, Daniel Pomp2 and David S. Buchanan3 Story in Brief Genotypes at the j3-lactoglobulinand
Genetic Identity. Steve Harris SPASH - Biotechnology
 Genetic Identity Steve Harris SPASH - Biotechnology Comparison of Organisms ORGANISM GENES BASE PAIRS Lambda Phage 40 50,000 E.coli 400 5,000,000 Yeast 13,000 15,000,000 Human 20,000 3,000,000,000 (3 billion)
Genetic Identity Steve Harris SPASH - Biotechnology Comparison of Organisms ORGANISM GENES BASE PAIRS Lambda Phage 40 50,000 E.coli 400 5,000,000 Yeast 13,000 15,000,000 Human 20,000 3,000,000,000 (3 billion)
PCR analysis was performed to show the presence and the integrity of the var1csa and var-
 Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
DIFFERENTIATION OF MEAT SPECIES USING SPECIES-SPECIFIC REPEAT AND PCR-RFLP TECHNIQUE
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 2183 2187 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) DIFFERENTIATION OF MEAT SPECIES USING SPECIES-SPECIFIC REPEAT AND PCR-RFLP TECHNIQUE
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 2183 2187 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) DIFFERENTIATION OF MEAT SPECIES USING SPECIES-SPECIFIC REPEAT AND PCR-RFLP TECHNIQUE
Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of the partial promoter region of κ-casein (CSN3) gene in Iranian Bacterianus and Dromedaries camels
 Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 5, 2014: 1719-1725 Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of the partial promoter
Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 5, 2014: 1719-1725 Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of the partial promoter
PV92 PCR Bio Informatics
 Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
FORENSIC GENETICS. DNA in the cell FORENSIC GENETICS PERSONAL IDENTIFICATION KINSHIP ANALYSIS FORENSIC GENETICS. Sources of biological evidence
 FORENSIC GENETICS FORENSIC GENETICS PERSONAL IDENTIFICATION KINSHIP ANALYSIS FORENSIC GENETICS Establishing human corpse identity Crime cases matching suspect with evidence Paternity testing, even after
FORENSIC GENETICS FORENSIC GENETICS PERSONAL IDENTIFICATION KINSHIP ANALYSIS FORENSIC GENETICS Establishing human corpse identity Crime cases matching suspect with evidence Paternity testing, even after
Using molecular marker technology in studies on plant genetic diversity Final considerations
 Using molecular marker technology in studies on plant genetic diversity Final considerations Copyright: IPGRI and Cornell University, 2003 Final considerations 1 Contents! When choosing a technique...!
Using molecular marker technology in studies on plant genetic diversity Final considerations Copyright: IPGRI and Cornell University, 2003 Final considerations 1 Contents! When choosing a technique...!
Effect of MSTN propeptide protein on the growth and development of Altay lamb muscle
 Effect of MSTN propeptide protein on the growth and development of Altay lamb muscle W. Du 1, Y. Zhang 1, J.Z. Yang 2, H.B. Li 1, J. Xia 1, N. Li 1, J.S. Zhang 1, X.M. Yan 1 and Z.Y. Zhou 1 1 Xinjiang
Effect of MSTN propeptide protein on the growth and development of Altay lamb muscle W. Du 1, Y. Zhang 1, J.Z. Yang 2, H.B. Li 1, J. Xia 1, N. Li 1, J.S. Zhang 1, X.M. Yan 1 and Z.Y. Zhou 1 1 Xinjiang
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Traditional Genetic Improvement. Genetic variation is due to differences in DNA sequence. Adding DNA sequence data to traditional breeding.
 1 Introduction What is Genomic selection and how does it work? How can we best use DNA data in the selection of cattle? Mike Goddard 5/1/9 University of Melbourne and Victorian DPI of genomic selection
1 Introduction What is Genomic selection and how does it work? How can we best use DNA data in the selection of cattle? Mike Goddard 5/1/9 University of Melbourne and Victorian DPI of genomic selection
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis. Mitesh Shrestha
 Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
ANALYSIS OF POLYMORPHISM OF CAST GENE AND CLPG GENE IN SHEEP BY PCR-RFLP METHOD
 Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (2) (2009), Timişoara ANALYSIS OF POLYMORPHISM OF CAST GENE AND CLPG GENE IN SHEEP BY PCR-RFLP METHOD ANALIYA POLIMORFISMULUI GENELOR CAST ŞI CLPG
Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (2) (2009), Timişoara ANALYSIS OF POLYMORPHISM OF CAST GENE AND CLPG GENE IN SHEEP BY PCR-RFLP METHOD ANALIYA POLIMORFISMULUI GENELOR CAST ŞI CLPG
Association between Polymorphisms of MSTN and MYF5 Genes and Growth Traits in Three Chinese Cattle Breeds
 1798 Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci. Vol. 20, No. 12 : 1798-1804 December 2007 www.ajas.info Association between Polymorphisms of MSTN and MYF5 Genes and Growth Traits in Three Chinese Cattle Breeds R. F. Zhang
1798 Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci. Vol. 20, No. 12 : 1798-1804 December 2007 www.ajas.info Association between Polymorphisms of MSTN and MYF5 Genes and Growth Traits in Three Chinese Cattle Breeds R. F. Zhang
1
 1 2 3 4 5 Cosmids are plasmid vectors that contain cos sites. The cos site is the only requirement for DNA to be packaged into a phage particle 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 For de novo sequencing using
1 2 3 4 5 Cosmids are plasmid vectors that contain cos sites. The cos site is the only requirement for DNA to be packaged into a phage particle 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 For de novo sequencing using
Genomic DNA was extracted from 3 to 5 ml of blood collected in EDTA blood collection tubes
 Supplementary information Methods DNA and RNA extraction Genomic DNA was extracted from to ml of blood collected in EDTA blood collection tubes using the Gentra Puregene Blood kit (Qiagen, California,
Supplementary information Methods DNA and RNA extraction Genomic DNA was extracted from to ml of blood collected in EDTA blood collection tubes using the Gentra Puregene Blood kit (Qiagen, California,
Si mon P t e ersen J ones
 Simon Petersen Jones What is a DNA based Test Uses sample of DNA Blood Cheek Swab Identifies the genotype (not phenotype) of the animal There are Two Categories of Test: Mutation Detection Direct detection
Simon Petersen Jones What is a DNA based Test Uses sample of DNA Blood Cheek Swab Identifies the genotype (not phenotype) of the animal There are Two Categories of Test: Mutation Detection Direct detection
5/18/2017. Genotypic, phenotypic or allelic frequencies each sum to 1. Changes in allele frequencies determine gene pool composition over generations
 Topics How to track evolution allele frequencies Hardy Weinberg principle applications Requirements for genetic equilibrium Types of natural selection Population genetic polymorphism in populations, pp.
Topics How to track evolution allele frequencies Hardy Weinberg principle applications Requirements for genetic equilibrium Types of natural selection Population genetic polymorphism in populations, pp.
Decoding genomic selection and the benefit for unconventional traits
 Decoding genomic selection and the benefit for unconventional traits Pete Hansen Dept. of Animal Sciences University of Florida Change in Breeding Value for Milk Yield in Holsteins 1957-2013 Breeding Value
Decoding genomic selection and the benefit for unconventional traits Pete Hansen Dept. of Animal Sciences University of Florida Change in Breeding Value for Milk Yield in Holsteins 1957-2013 Breeding Value
Ah, Lou! There really are differences between us!
 Name Per Ah, Lou! There really are differences between us! Introduction The human genome (the total sum of our genetic makeup) is made up of approximately 6 billion base pairs distributed on 46 chromosomes.
Name Per Ah, Lou! There really are differences between us! Introduction The human genome (the total sum of our genetic makeup) is made up of approximately 6 billion base pairs distributed on 46 chromosomes.
Characterization of microsatellites in the fungal plant pathogen, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
 1 2 3 4 Characterization of microsatellites in the fungal plant pathogen, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum 5 6 7 8 9 Caroline Sirjusingh and Linda M. Kohn, Department of Botany, University of Toronto at Mississauga,
1 2 3 4 Characterization of microsatellites in the fungal plant pathogen, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum 5 6 7 8 9 Caroline Sirjusingh and Linda M. Kohn, Department of Botany, University of Toronto at Mississauga,
WORKING GROUP ON BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES AND DNA PROFILING IN PARTICULAR. Eleventh Session Madrid, September 16 to 18, 2008
 ORIGINAL: English DATE: September 16, 2008 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA E WORKING GROUP ON BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES AND DNA PROFILING IN PARTICULAR
ORIGINAL: English DATE: September 16, 2008 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA E WORKING GROUP ON BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES AND DNA PROFILING IN PARTICULAR
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
PCR. What is PCR? What is PCR? Why chain? What is PCR? Why Polymerase?
 What is PCR? PCR the swiss army knife Claudia Stäubert, Institute for biochemistry PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by
What is PCR? PCR the swiss army knife Claudia Stäubert, Institute for biochemistry PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by
Linkage analysis of SNPs in IGFBP-6 and its relation with the body sizes of pig
 Linkage analysis of SNPs in IGFBP-6 and its relation with the body sizes of pig X.B. Fang*, S.C. Liu*, Q.Y. Wu, S.M. Li, Y.Y. Cheng, H.Y. Fu, C. Lu, D. Su, H. Yu and L.L. Hao College of Animal Science,
Linkage analysis of SNPs in IGFBP-6 and its relation with the body sizes of pig X.B. Fang*, S.C. Liu*, Q.Y. Wu, S.M. Li, Y.Y. Cheng, H.Y. Fu, C. Lu, D. Su, H. Yu and L.L. Hao College of Animal Science,
High-Resolution Melting Interactive Workshop AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description
 AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description List of Example Assays Page Technique Example assay 2 Unlabeled probe genotyping HR-1 Factor V Leiden mutation 6 Unlabeled probe genotyping - LightScanner Factor
AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description List of Example Assays Page Technique Example assay 2 Unlabeled probe genotyping HR-1 Factor V Leiden mutation 6 Unlabeled probe genotyping - LightScanner Factor
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE OF HNUE Chemical and Biological Sci., 2012, Vol. 57, No. 8, pp This paper is available online at
 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE OF HNUE Chemical and Biological Sci., 2012, Vol. 57, No. 8, pp. 111-118 This paper is available online at http://stdb.hnue.edu.vn ANALYZING RYR-1 GENOTYPE POLYMORPHISM IN MONG CAI STOCK
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE OF HNUE Chemical and Biological Sci., 2012, Vol. 57, No. 8, pp. 111-118 This paper is available online at http://stdb.hnue.edu.vn ANALYZING RYR-1 GENOTYPE POLYMORPHISM IN MONG CAI STOCK
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Genetics fundamentals and DNA toolkit. Partha Roy
 Genetics fundamentals and DNA toolkit Partha Roy 1 (REVIEW of Terminologies and Concepts) Haploid organism: single copy of chromosome (ex: bacteria, yeast) Diploid organism: two copies of chromosome (paternal
Genetics fundamentals and DNA toolkit Partha Roy 1 (REVIEW of Terminologies and Concepts) Haploid organism: single copy of chromosome (ex: bacteria, yeast) Diploid organism: two copies of chromosome (paternal
INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS
 ORIGINAL: English DATE: October 21, 2010 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA E GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND DATABASE CONSTRUCTION (
ORIGINAL: English DATE: October 21, 2010 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA E GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND DATABASE CONSTRUCTION (
Characterization of novel polymorphic genomic microsatellite markers of Boehmeria tricuspis (Hance) Makino
 Characterization of novel polymorphic genomic microsatellite markers of Boehmeria tricuspis (Hance) Makino Q. Tang, J.H. Chen, G.G. Zang and M.B. Luan Key Laboratory of Stem-fiber Biomass and Engineering
Characterization of novel polymorphic genomic microsatellite markers of Boehmeria tricuspis (Hance) Makino Q. Tang, J.H. Chen, G.G. Zang and M.B. Luan Key Laboratory of Stem-fiber Biomass and Engineering
Functional Genomics Research Stream. Research Meeting: June 19, 2012 SYBR Green qpcr, Research Update
 Functional Genomics Research Stream Research Meeting: June 19, 2012 SYBR Green qpcr, Research Update Updates Alternate Lab Meeting Fridays 11:30-1:00 WEL 4.224 Welcome to attend either one Lab Log thanks
Functional Genomics Research Stream Research Meeting: June 19, 2012 SYBR Green qpcr, Research Update Updates Alternate Lab Meeting Fridays 11:30-1:00 WEL 4.224 Welcome to attend either one Lab Log thanks
