Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
|
|
|
- Zoe Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP TITLE: Layer-By-Layer Printing of Cells and its Application to Tissue Engineering DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited This paper is part of the following report: TITLE: Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings. Volume 845, Nanoscale Materials Science in Biology and Medicine, Held in Boston, MA on 28 November-2 December 2004 To order the complete compilation report, use: ADA The component part is provided here to allow users access to individually authored sections f proceedings, annals, symposia, etc. However, the component should be considered within [he context of the overall compilation report and not as a stand-alone technical report. The following component part numbers comprise the compilation report: ADP thru ADP UNCLASSIFIED
2 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol Materials Research Society AA4.5 Layer-by-layer printing of cells and its application to tissue engineering Priya Kesari 1, Tao Xul, Thomas Boland'* 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina ABSTRACT Tissues and organs exhibit distinct shapes and functions nurtured by vascular connectivity. In order to mimic and examine these intricate structure-function relationships, it is necessary to develop efficient strategies for assembling tissue-like constructs. Many of the top-down fabrication techniques used to build microelectromechanical systems, including photolithography, are attractive due to the similar feature sizes, but are not suitable for delicate biological systems or aqueous environments. A layer-by layer approach has been proposed by us to pattern functional cell structures in three dimensions. Freeform cell structures are created by the inkjet method, in which cells are entrapped within hydrogels and crosslinked on demand. The cells are viable, functional and show potential for cell maturation as exemplified by the diversion of hematopoietic stem cells into multiple cell types. These results show promise for many tissue engineering applications. INTRODUCTION Tissue engineering may be defined as a multidisciplinary specialty applying the methods and principles of engineering and the life sciences toward the development of biological substitutes for the restoration, maintenance and improvement of organ function [1]. Traditionally this has been done by the seeding of cellular material onto a suitable scaffold material to create three dimensional (3D) constructs. [2] However there are currently a number of drawbacks to this technique. Organs consist of multiple cellular phenotypes in specific locations and this is hard to replicate. In addition, the degree of cellular permeation is variable and may not proceed uniformly. The volume of tissue that can be constructed is limited by diffusion and osmosis. Finally, though there have been large advances in scaffold technology the construction of contractile structures like the myocardium and vascular conduits continues to be a challenge. An alternative approach to tissue construction is a genuine challenge. Since the first application of fused deposition modeling for tissue engineering scaffolds [3], considerable effort has been focused on printing synthetic biodegradable scaffolds [4]. Concurrently a variety of rapid prototyping techniques have been developed to define macroscopically the shapes of 111
3 deposited biomaterials, including photolithography [5], syringe-based gel deposition [6], and solid freeform fabrication [7;8]. That these approaches have not yet led to the construction of harmonically organized complex tissues may be due to the difficulty to embed the various cell types within the intricate designs. Bottom up construction processes may offer a possible solution. Such processes have combined soft lithography and self-assembly to construct hierarchical non-living materials [9], and may be applied to the self-assembly of tissues or the study of cooperative effects in developmental biology [10]. Our approach combines rapid prototyping procedures with micro encapsulation to print viable freeform structures using custom modified printers [11-13]. We have previously shown that cell aggregates fuse when placed near each other on collagen hydro gel surfaces. This model system was chosen in an attempt to construct more complex three-dimensional tissue blocks by the combination of computer programmed deposition of cells or cell aggregates into macroscopically defined shapes. Moreover, this process known as computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE) [14] is based on the observation that cells have a biologically-programmed capacity for selfassembly and will differentiate during a short maturation process if provided a suitable environment, exemplified by the behavior of embryonic tissue explants [15]. We report here the fabrication of tubular cell structures that exhibit form and function. MATERIALS AND METHODS Preparation of Alginate For fabricating the composite construct, sodium alginate (2% w/v) (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) and gelatin (0.1 w/v) was dissolved in Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS) (Sigma Chemicals, St. Louis, MO) overnight and the solution was filtered using 0.22 gm filter (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA). As a cross linking solution, 0.25 M of CaCI 2 in double-distilled water was used. When CaCi 2 and sodium alginate are in contact, cross linking takes place forming a chemically reversible gel [ 16]. Thermal ink-jet printer For this study we modified a HP697c inkjet printer to engineer freeform constructs. In brief, the paper feed mechanism of the printer was disabled and a z-axis module was incorporated. Since the z-axis control is very essential to build a 3-dimensional structure, an electronically controlled elevator chamber was designed and constructed using a stepper motor assembly. For the elevator stage a 2.5 cm round glass cover slip (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) was fixed to the tip of a metallic rod, which was connected to the stepper motor. A DC power supply (Hewlett-Packard Corp., Palo Alto, CA) was used to generate a 4V signal to operate the stepper motor through a series of four toggle switches. A sterile 50 ml conical tube (Fischer Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) was customized and used as the elevator chamber and filled with of sterile alginate solution. A commercial inkjet cartridge (HP51629A, 40ml) was emptied and rinsed thoroughly with double distilled water and 100 % ethanol several times till completely free of ink. It was then immersed in an ultrasonic sonicator to remove any ink or blockages. The cartridge was sprayed with 100 % ethanol and the whole assembly of the printer along with the cartridge was placed overnight in a Class II hood under ultraviolet light prior to use. 112
4 Construction of cell tubes Vital to cell patterning procedures is the use of stable, aqueous non-cytotoxic inks that act as cross linking agents delivered using the inkjet method into a rapid prototyping chamber. For this purpose we use ionic cross linking additives such as CaCI 2 in saline cell suspensions at hypertonic concentrations, thereby facilitating the passage of the cells through the printer nozzles as well as rapid local gelling of the pattern. Saline alginate solution was used in the chamber, ensuring biocompatibility of the structures. As a pattern of ink is printed onto the alginate meniscus, ion exchange causes cross linking of alginate, thereby facilitating cell encapsulation within the droplets ranging in diameter from 30 to 50 Itm. Alginate tube constructs of Rat smooth muscle cells (SMCs) were printed. The ink-jet cartridge was filled with 1.5 ml of 0.25 M CaC1 2 solution. Hybond paper (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Ireland) was placed on the cover slip of the z- stage and the tubes were printed on this paper. A tube pattern was designed in a MS Word document (Microsoft, Redmond, WA) using circles of 2 mm diameter and 2 mm width. After every print action a re-coating procedure was performed by lowering the elevator platform into the alginate filled chamber and brought back 100 microns below the original position utilizing the stepper motor assembly. This step was done to ensure the gelling of the printed rings. In order to maximize the amount of SMC cells used, 0.25 ml of the cell suspensions were manually pipetted onto the gelled rings after each re-coating procedure. The stacked rings gelled atop each other to create a cylindrical tube entrapping the cells. The tubes were carefully detached from the Hybond paper and individually placed in small polystyrene dishes (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) filled with 3 ml DMEM, which was changed every 24 hours. To test the viability of the encapsulated cells, a live dead assay (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) was done after 8 days of culture. Confocal Microscopy Cell distribution and morphology in the three dimensional constructs were examined under an LSM-5 spectral confocal microscope. The reconstruction of the top-down and side views and the color depth coding for the entrapped cells were accomplished using Zeiss LSM Image Examiner and Browser software. The SMC cell constructs were fixed on day 18 in 100 % ethanol for 1 hour. They were then rinsed well in DPBS. The cells were tagged with mouse monoclonal anti-actin, a-smooth muscle- FITC antibody (F3777-Fisher Scientific, PA) that was diluted in PBS at a ratio of 1:100 overnight at 4 'C. The constructs with the QCE6 cells were fixed on day 8 in 100 % ethanol for 1 hour. Since these cells express green fluorescent proteins, they were not tagged for viewing under the microscope. Both these samples were then cover slipped and stored in a cool dark place. Functional testing of smooth muscle cell tubes A 50riM solution of Endothelin-1 (ET-1, American peptide Company, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA) was prepared in serum free DMEM. The contractile response of smooth muscle cells encapsulated in the alginate tubes to ET-1 stimulation was evaluated over a period of 5 days at regular time intervals. The SMC tubes were incubated in 5 ml of DMEM supplemented with 10% of FBS in a culture dish at 370 C for 24h. The culture medium 113
5 was then replaced with serum free DMEM to arrest cell growth. After 24h of incubation in serum free medium, 50nM ET-1 solution was administered and after 48h, the tube was re-incubated in 5 ml of serum free media. The lumen area of the tube was measured daily up to 5 days by imaging the dishes with a digital scanner (Perfection 1640SU Photo, Epson) throughout the experiments. The lumen area was calculated using Scion Image software (Scion Corporation, Frederick, MD) and plotted against the time intervals for triplicate experiments. RESULTS Alginate tubes with encapsulated smooth muscle cells are shown in Figure 1 on days 0, 13 and 18. This figure depicts a distinct difference attributed to cellular activity. The smooth muscle cell phenotype was maintained and the cells were distributed evenly throughout the structure as judged by immunostaining confocal microscopy. Within the structure, the cells reached a density of 14x106 cells/ml with 80% viability, as determined by a vital stain at day 18 of the culture. Morphological analysis of histological slides corroborated these findings. Although the morphological evidence for cell viability and distribution of cells in the tube is very compelling, development of vasomotor reactivity in the constructs should be a clear indication that the tubes are becoming a functional in vitro. In an attempt to show the function of the printed tubes, we studied the response of the tubes when challenged with the vasoconstricting agonist Endothelin-I (ET-1). The tubes contracted in a dosedependent manner upon exposure to the agonist with the responses shown in Figure 2, and complete closure of the lumen after 43 hrs in a 50 nm ET-I solution. Although it is difficult to make a direct comparison with contractile responses of other tissue engineered vessels, the tubes clearly showed a functional response. In addition to this contractile response, a relaxation to the initial lumen diameter was seen after removal of the agonist. Clearly, both the challenge and the potential of organ printing technology lie in the design of functional tissues. These cell tubes exhibited vasoreactivity to agonists, while maintaining sufficient mechanical strength, demonstrating the potential utility of this technology to construct functional tissues from the bottom-up. Tissue engineering has progressed in areas relevant to the developments of novel biomaterials [17], the designs of bioreactors for dynamic in vitro culture systems [18], and the uses of diverse cell sources including appropriate multi-potent stem cells [19]. For the construction of soft tissues or even entire organs, however, huge technical challenges remain to be overcome. Among them, the very important problem of how to combine and orchestrate cells, growth factors, and scaffolds into the tissue's architecture, especially where distinct cell types are required in anatomically exact locations to attain biological function. The inkjet printing technology offers a possible solution. 114
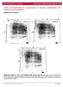
6 Figure 1. Macroscopic and microscopic images of printed cell tubes. (A) Constructs with SMC cells as seen on day 0 immediately after printing (B) a SMC cell tube incubated in media on day 13, (C) Cell tubes on day 8 (D) vital stain of SMC cells on day, (E) 1 vital stain of SMC cells on day 18, and (F) confocal image of SMC cell tubes tagged with FTIC labeled monoclonal anti-actin, a-smooth muscle antibody on day 18. Figure 2. Effect 50 nm of ET-1 on of lumen size of a short SMC tube. (A) Construct after 24 h in DMEM augmented with 10% FBS, (B) Construct after 12 h incubation in serum free medium augmented with 50 nm of ET-1, (C) Construct after 24 h in the ET-1 containing medium, (D) Construct after 45 h in the ET-1 containing medium, (E) Construct after an additional 12 h in the FBS containing medium, (F) Construct after 24 h in the FBS medium. I A B C 2 mm D E F 115
7 CONCLUSIONS To our knowledge no other group has sought to use a commercial inkjet printer as a tool to print alternate layers of hydrogels and cells. We have previously shown that mammalian cells can be printed using inkjet printers [20]. The results presented here show promise in constructing more complex three dimensional shapes. This method, when combined with cell printing offers the capability of arranging viable cells directly into specific patterns, which is critical for building engineered tissue or in vitro models to study cooperative effects in systems biology. We conclude that a combined approach using freeform fabrication techniques aided by the self-assembly nature of cells may be a viable approach to construct building blocks for soft tissues. REFERENCES 1. Fuchs JR, Nasseri BA, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering: a 21st century solution to surgical reconstruction. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2001; 72(2): Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering. Science 1993; 260(5110): Hutmacher DW. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials 2000; 21(24): Yang S, Leong KF, Du Z, Chua CK. The design of scaffolds for use in tissue engineering. Part 11. Rapid prototyping techniques. Tissue Engineering 2002; 8(l): Vozzi G, Flaim C, Ahluwalia A, Bhatia S. Fabrication of PLGA scaffolds using soft lithography and microsyringe deposition. Biomaterials 2003; 24(14): Landers R, Hubner U, Schmelzeisen R, Mulhaupt R. Rapid prototyping of scaffolds derived from thermoreversible hydrogels and tailored for applications in tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2002; 23(23): Sachlos E, Czernuszka JT. Making tissue engineering scaffolds work. Review: the application of solid freeform fabrication technology to the production of tissue engineering scaffolds. European Cells & Materials 2003; 5: Sachlos E, Reis N, Ainsley C, Derby B, Czernuszka JT. Novel collagen scaffolds with predefined internal morphology made by solid freeform fabrication. Biomaterials 2003; 24(8): Whitesides GM, Grzybowski B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science 2002; 295(5564): Salazar-Ciudad I, Jernvall J, Newman SA. Mechanisms of pattern formation in development and evolution. Development 2003; 130(10): Wilson WC, Jr., Boland T. Cell and organ printing 1: protein and cell printers. Anatomical Record 2003; 272A(2):
8 12. Mironov V, Boland T, Trusk T, Forgacs G, Markwald RR. Organ printing: computer-aided jet-based 3D tissue engineering. Trends in Biotechnology 2003; 21(4): Boland T, Mironov V, Gutowska A, Roth EA, Markwald RR. Cell and organ printing 2: fusion of cell aggregates in three-dimensional gels. Anatomical Record 2003; 272A(2): Sun W, Lal P. Recent development on computer aided tissue engineering--a review. Computer Methods & Programs in Biomedicine 2002; 67(2): Foty RA, Pfleger CM, Forgacs G, Steinberg MS. Surface tensions of embryonic tissues predict their mutual envelopment behavior. Development 1996; 122(5): Lim F, Sun AM. Microencapsulated islets as bioartificial endocrine pancreas. Science 1980; 210(4472): Griffith LG, Naughton G. Tissue engineering--current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science 2002; 295(5557): Cabrita GJ, Ferreira BS, da Silva CL, Goncalves R, Almeida-Porada G, Cabral JM. Hematopoietic stem cells: from the bone to the bioreactor. Trends in Biotechnology 2003; 21(5): Stock UA, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering: current state and prospects. Annual Review of Medicine 2001; 52: Xu T, Jin J, Gregory C, Hickman JJ, Boland T. Inkjet printing of viable mammalian cells. Biomaterials 2005; 26:
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP019695 TITLE: Fabricating Neural and Cardiomyogenic Stem Cell Structures by a Novel Rapid Prototyping--the Inkjet Printing Method
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP019695 TITLE: Fabricating Neural and Cardiomyogenic Stem Cell Structures by a Novel Rapid Prototyping--the Inkjet Printing Method
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis. 1. General Information. Application Note 19
 Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview... 3 4. Preparation of the Gel and the Slide... 4 4.1. Gel Application... 4 4.2.
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview... 3 4. Preparation of the Gel and the Slide... 4 4.1. Gel Application... 4 4.2.
Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation
 Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation In vitro neurological research presents many challenges due to the difficulty in establishing high-yield neuronal
Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation In vitro neurological research presents many challenges due to the difficulty in establishing high-yield neuronal
Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ashley B. Allen, Hazel Y. Stevens, Robert E. Guldberg. Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. Disclosures:
Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ashley B. Allen, Hazel Y. Stevens, Robert E. Guldberg. Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. Disclosures:
3D Endothelial Pericyte Coculturing Kit Product Description Kit Components
 3D Endothelial Pericyte Coculturing Kit (3D-EPC) Cat #8728 Product Description Blood vessels are responsible for transporting blood throughout the body as part of the circulatory system. Their main components
3D Endothelial Pericyte Coculturing Kit (3D-EPC) Cat #8728 Product Description Blood vessels are responsible for transporting blood throughout the body as part of the circulatory system. Their main components
1 Electronic Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 1 Electronic Supporting information 2 3 Replicating 3D printed structures into hydrogels
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 1 Electronic Supporting information 2 3 Replicating 3D printed structures into hydrogels
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Matrix 6-well Plates for Embryonic Stem (ES) Cell Culture. Catalog Number Guidelines for Use
 Corning BioCoat Matrigel Matrix 6-well Plates for Embryonic Stem (ES) Cell Culture Catalog Number 354671 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Matrix 6-well Plates for Embryonic Stem (ES) Cell Culture Catalog Number 354671 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200
Leaf-inspired Artificial Microvascular Networks (LIAMN) for Threedimensional
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Leaf-inspired Artificial Microvascular Networks (LIAMN) for Threedimensional
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Leaf-inspired Artificial Microvascular Networks (LIAMN) for Threedimensional
VitroGel ready-to-use tunable hydrogel for 3D cell culture and beyond
 VitroGel ready-to-use tunable hydrogel for 3D cell culture and beyond Cat No: TWG001 VItroGel 3D (10 ml high concentration) Cat No: TWG002 VitroGel 3D-RGD (10 ml high concentration) Handbook Rev. June
VitroGel ready-to-use tunable hydrogel for 3D cell culture and beyond Cat No: TWG001 VItroGel 3D (10 ml high concentration) Cat No: TWG002 VitroGel 3D-RGD (10 ml high concentration) Handbook Rev. June
2. Precision Extrusion Deposition Previous research has focused on Fuse Deposition Modeling (FDM) for the fabrication of
 PRECISION EXTRUSION DEPOSITION OF POLYCAPROLACTONE/ HYDROXYAPATITE TISSUE SCAFFOLDS L. Shor, S. Güçeri, W. Sun Laboratory for Computer-Aided Tissue Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering and
PRECISION EXTRUSION DEPOSITION OF POLYCAPROLACTONE/ HYDROXYAPATITE TISSUE SCAFFOLDS L. Shor, S. Güçeri, W. Sun Laboratory for Computer-Aided Tissue Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering and
A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING
 A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING Umadevi Kandalam, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry College of Dental Medicine Nova Southeastern University Fort Lauderdale, Florida
A NANOFIBROUS HYDROGEL FOR BONE TISSUE ENGINEERING Umadevi Kandalam, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry College of Dental Medicine Nova Southeastern University Fort Lauderdale, Florida
Table of Contents. 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components Additional Required Reagents Required Equipment...
 i Table of Contents 1.0 Overview of the NeuroCult NCFC Assay 2.0 Materials 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components... 4 2.2 Additional Required Reagents... 4 2.3 Required Equipment... 4 3.0 Preparation
i Table of Contents 1.0 Overview of the NeuroCult NCFC Assay 2.0 Materials 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components... 4 2.2 Additional Required Reagents... 4 2.3 Required Equipment... 4 3.0 Preparation
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis
 Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Related topics: Application Note 27 Data Analysis of Tube Formation Assays. Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview...
Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex
 Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex 1.0. Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigen-specific antibodies coupled
Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex 1.0. Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigen-specific antibodies coupled
Bioreactors in tissue engineering
 Bioreactors in tissue engineering S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative
Bioreactors in tissue engineering S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
Methods in Bioengineering: 3D Tissue Engineering
 Methods in Bioengineering: 3D Tissue Engineering Berthiaume, Francois ISBN-13: 9781596934580 Table of Contents Preface Chapter 1. Chemical Modification of Porous Scaffolds Using Plasma Polymers 1.1. Introduction
Methods in Bioengineering: 3D Tissue Engineering Berthiaume, Francois ISBN-13: 9781596934580 Table of Contents Preface Chapter 1. Chemical Modification of Porous Scaffolds Using Plasma Polymers 1.1. Introduction
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit: 2 color immunocytochemistry of cytochrome c and mitochondria.
 PROTOCOL ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSA07 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit: 2 color immunocytochemistry
PROTOCOL ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSA07 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit: 2 color immunocytochemistry
TractionsForAll. v1.0. September 1 st, Created by Aleksandar Marinković, Sc.D. & Daniel Tschumperlin, Ph.D.
 TractionsForAll v1.0 September 1 st, 2013 TractionsForAll v1.0 is freely distributed program that calculates tractions exerted by an adherent cell on the soft hydrogel substrate underneath. It is created
TractionsForAll v1.0 September 1 st, 2013 TractionsForAll v1.0 is freely distributed program that calculates tractions exerted by an adherent cell on the soft hydrogel substrate underneath. It is created
Tube formation assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis
 Tube formation assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis 1. General Information The µ-slide Angiogenesis is designed for tube formation observation on an inverse microscope. It can be used with all common gel matrices
Tube formation assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis 1. General Information The µ-slide Angiogenesis is designed for tube formation observation on an inverse microscope. It can be used with all common gel matrices
Inkjet printing of viable mammalian cells
 Biomaterials 26 (2005) 93 99 Inkjet printing of viable mammalian cells Tao Xu, Joyce Jin, Cassie Gregory, James J. Hickman*, Thomas Boland* Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, 502 Rhodes
Biomaterials 26 (2005) 93 99 Inkjet printing of viable mammalian cells Tao Xu, Joyce Jin, Cassie Gregory, James J. Hickman*, Thomas Boland* Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, 502 Rhodes
Human ipsc-derived Renal Proximal Tubular Cells. Protocol version 1.0
 Human ipsc-derived Renal Proximal Tubular Cells Protocol version 1.0 Protocol version 1.0 Table of Contents Product Information 2 Preparation of Reagents 3 Culture of Human ipsc-derived Renal Proximal
Human ipsc-derived Renal Proximal Tubular Cells Protocol version 1.0 Protocol version 1.0 Table of Contents Product Information 2 Preparation of Reagents 3 Culture of Human ipsc-derived Renal Proximal
Computer Aided Tissue Engineering for Modeling and Design of Novel Tissue Scaffolds
 633 Computer Aided Tissue Engineering for Modeling and Design of Novel Tissue Scaffolds J. Nam, B. Starly, A. Darling and W. Sun Drexel University, jae.h.nam@drexel.edu, bs49@drexel.edu, andrew.leete.darling@drexel.edu,
633 Computer Aided Tissue Engineering for Modeling and Design of Novel Tissue Scaffolds J. Nam, B. Starly, A. Darling and W. Sun Drexel University, jae.h.nam@drexel.edu, bs49@drexel.edu, andrew.leete.darling@drexel.edu,
Modular bioink for 3D printing of biocompatible hydrogels: sol-gel polymerization of hybrid peptides and polymers
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Modular bioink for 3D printing of biocompatible hydrogels: sol-gel
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Modular bioink for 3D printing of biocompatible hydrogels: sol-gel
Supporting Information. Self-Supporting Nanoclay as Internal Scaffold Material for Direct Printing of Soft Hydrogel Composite Structures in Air
 Supporting Information Self-Supporting Nanoclay as Internal Scaffold Material for Direct Printing of Soft Hydrogel Composite Structures in Air Yifei Jin 1, Chengcheng Liu 2, Wenxuan Chai 1, Ashley Compaan
Supporting Information Self-Supporting Nanoclay as Internal Scaffold Material for Direct Printing of Soft Hydrogel Composite Structures in Air Yifei Jin 1, Chengcheng Liu 2, Wenxuan Chai 1, Ashley Compaan
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells
 Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Care Manual: Maintenance and Differentiation from Myoblasts to Myocytes
 Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Care Manual: Maintenance and Differentiation from Myoblasts to Myocytes STORAGE CONDITIONS Media: Short Term 4 C 6 months -20 C F or research use only. Not approved for human
Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Care Manual: Maintenance and Differentiation from Myoblasts to Myocytes STORAGE CONDITIONS Media: Short Term 4 C 6 months -20 C F or research use only. Not approved for human
Thirupathi Kumara Raja. S, 1 Thiruselvi. T, 1 Asit Baran Mandal, 1 Gnanamani. A, 1* Adyar, Chennai Tamil Nadu, India
 Supplementary File ph and redox sensitive albumin hydrogel : A self-derived biomaterial Thirupathi Kumara Raja. S, 1 Thiruselvi. T, 1 Asit Baran Mandal, 1 Gnanamani. A, 1* 1 CSIR-CLRI Adyar, Chennai Tamil
Supplementary File ph and redox sensitive albumin hydrogel : A self-derived biomaterial Thirupathi Kumara Raja. S, 1 Thiruselvi. T, 1 Asit Baran Mandal, 1 Gnanamani. A, 1* 1 CSIR-CLRI Adyar, Chennai Tamil
Mechano-dependent biosynthetic response of microintegrated cells in elastomeric scaffolds.
 Mechano-dependent biosynthetic response of microintegrated cells in elastomeric scaffolds. Lauren Anderson, Department of Bioengineering, The Pennsylvania State University Dr. Michael Sacks, Mentor, Department
Mechano-dependent biosynthetic response of microintegrated cells in elastomeric scaffolds. Lauren Anderson, Department of Bioengineering, The Pennsylvania State University Dr. Michael Sacks, Mentor, Department
If protein coating is acceptable in the planned experiments, there is another quick and simple way to render the surface hydrophilic.
 1 MEA Handling Warning: Use only liquids or cleaning solutions with a neutral ph (7) on MEAs with a silicon nitride insulation type. Otherwise, the MEAs may be irreversibly damaged. Warning: Do not to
1 MEA Handling Warning: Use only liquids or cleaning solutions with a neutral ph (7) on MEAs with a silicon nitride insulation type. Otherwise, the MEAs may be irreversibly damaged. Warning: Do not to
Protocol for Small-Scale Microcarrier Culture
 Protocol for Small-Scale Microcarrier Culture Hillex II Microcarriers This document provides a general protocol for initiation of small-scale mammalian cell spinner cultures. This procedure is based upon
Protocol for Small-Scale Microcarrier Culture Hillex II Microcarriers This document provides a general protocol for initiation of small-scale mammalian cell spinner cultures. This procedure is based upon
Supporting Information. Physiological ph-dependent gelation for 3D printing based on the. phase separation of gelatin and oxidized dextran
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Physiological ph-dependent gelation for 3D printing based on the phase separation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Physiological ph-dependent gelation for 3D printing based on the phase separation
Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit
 Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit Catalog No. SCR019 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23 8026 2233
Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit Catalog No. SCR019 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23 8026 2233
HUMAN IPSC CULTURE PROTOCOLS
 HUMAN IPSC CULTURE PROTOCOLS FOR TRAINING COURSE IXCELLS BIOTECHNOLOGIES USA, LLC 10340 CAMINO SANTA FE, SUITE C, SAN DIEGO, CA 92121 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 BEFORE STARTING 2-7 SECTION 1.1 COATING
HUMAN IPSC CULTURE PROTOCOLS FOR TRAINING COURSE IXCELLS BIOTECHNOLOGIES USA, LLC 10340 CAMINO SANTA FE, SUITE C, SAN DIEGO, CA 92121 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 BEFORE STARTING 2-7 SECTION 1.1 COATING
MagniSort Mouse Hematopoietic Lineage Depletion Kit Catalog Number: RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse Hematopoietic Lineage Depletion Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse bone marrow cells were unsorted (top row) or sorted with the MagniSort
Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse Hematopoietic Lineage Depletion Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse bone marrow cells were unsorted (top row) or sorted with the MagniSort
Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Fibronectin Coated)
 Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Fibronectin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-FN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Fibronectin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-FN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated)
 Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Instructions. Fuse-It-siRNA. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Modeling Cardiomyocyte Differentiation:
 icell Cardiac Progenitor Cells Prototype Application Protocol Wnt- and Activin/TGFβ-inhibitor Induction with Flow Cytometry Analysis Introduction The ability of cardiac progenitor cells to proliferate
icell Cardiac Progenitor Cells Prototype Application Protocol Wnt- and Activin/TGFβ-inhibitor Induction with Flow Cytometry Analysis Introduction The ability of cardiac progenitor cells to proliferate
StemXVivo. Mesoderm Kit. Catalog Number SC030B. Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm.
 StemXVivo Mesoderm Kit Catalog Number SC030B Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
StemXVivo Mesoderm Kit Catalog Number SC030B Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
ThiolTracker Violet (Glutathione Detection Reagent)
 ThiolTracker Violet (Glutathione Detection Reagent) Catalog nos. T10095, T10096 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability ThiolTracker Violet 180 assays
ThiolTracker Violet (Glutathione Detection Reagent) Catalog nos. T10095, T10096 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability ThiolTracker Violet 180 assays
Radius 384-Well Cell Migration Assay
 Product Manual Radius 384-Well Cell Migration Assay Catalog Number CBA-127 CBA-127-5 384 assays 5 x 384 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is
Product Manual Radius 384-Well Cell Migration Assay Catalog Number CBA-127 CBA-127-5 384 assays 5 x 384 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is
ELISPOT antibody pair Technical Data Sheet
 ELISPOT antibody pair Technical Data Sheet 10-plate and 20-plate format For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. This Technical Data Sheet applies for the following U-CyTech
ELISPOT antibody pair Technical Data Sheet 10-plate and 20-plate format For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. This Technical Data Sheet applies for the following U-CyTech
L6 Cell Growth Protocol
 L6 Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells were subcloned for high fusion (1, 2). Materials: 1. α-minimal Essential Medium (α-mem) Life Technologies #12571-063 2. Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Life
L6 Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells were subcloned for high fusion (1, 2). Materials: 1. α-minimal Essential Medium (α-mem) Life Technologies #12571-063 2. Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Life
T ECHNICAL MANUAL. Culture of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using MesenCult -XF Medium
 T ECHNICAL MANUAL Culture of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using MesenCult -XF Medium i Table of Contents 1.0 Materials... 1 1.1 MesenCult -XF Medium and Required Products... 1 1.2 Additional Required
T ECHNICAL MANUAL Culture of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using MesenCult -XF Medium i Table of Contents 1.0 Materials... 1 1.1 MesenCult -XF Medium and Required Products... 1 1.2 Additional Required
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit
 ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and non-apoptotic
ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and non-apoptotic
Supporting Protocols
 Supporting Protocols This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec ECM Hydrogels. Introduction Cells and organoids may form complex
Supporting Protocols This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec ECM Hydrogels. Introduction Cells and organoids may form complex
Materials and Methods Materials Required for Fixing, Embedding and Sectioning
 Page 1 Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigenspecific antibodies coupled to fluorophores. Depending on the antibody or dye used, proteins,
Page 1 Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigenspecific antibodies coupled to fluorophores. Depending on the antibody or dye used, proteins,
Neural Stem Cells (ipsc from Blood Cells; Male)
 Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Neural Stem Cells (ipsc from Blood Cells; Male) Product Information Catalog Number ASE-9234 (Male) Description Applied StemCell's
Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Neural Stem Cells (ipsc from Blood Cells; Male) Product Information Catalog Number ASE-9234 (Male) Description Applied StemCell's
Monoclonal antibodies
 Monoclonal antibodies 1. Boost the best-responded mouse 3-5 days before fusion. 2. Build up frozen stock of myeloma cells (NS-1 or P 3 U 1 etc.) in MEM + 10% FCS containing 0.1
Monoclonal antibodies 1. Boost the best-responded mouse 3-5 days before fusion. 2. Build up frozen stock of myeloma cells (NS-1 or P 3 U 1 etc.) in MEM + 10% FCS containing 0.1
Kit Components (Included) Cat # # of vials Product Name Quantity Storage Human Renal Cortical Epithelial Cells (HRCEpiC)
 3D Renal Tubule Formation Kit 3D-RTF Cat # 3D-4110 Product Description The human kidney is frequently exposed to drugs and toxic compounds, which can result in nephrotoxicity. A drug s uptake and clearance
3D Renal Tubule Formation Kit 3D-RTF Cat # 3D-4110 Product Description The human kidney is frequently exposed to drugs and toxic compounds, which can result in nephrotoxicity. A drug s uptake and clearance
Multi-Nozzle Biopolymer Deposition for Freeform Fabrication of Tissue Constructs
 Multi-Nozzle Biopolymer Deposition for Freeform Fabrication of Tissue Constructs S. Khalil, J. Nam, A. Darling, W. Sun * Laboratory for Computer-Aided Tissue Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
Multi-Nozzle Biopolymer Deposition for Freeform Fabrication of Tissue Constructs S. Khalil, J. Nam, A. Darling, W. Sun * Laboratory for Computer-Aided Tissue Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
BD IMag. Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM. Technical Data Sheet. Product Information
 Technical Data Sheet Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM Product Information Material Number: Size: Storage Buffer: 557812 5 ml Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Description
Technical Data Sheet Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM Product Information Material Number: Size: Storage Buffer: 557812 5 ml Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Description
LabCyte CORNEA-MODEL
 LabCyte CORNEA-MODEL Three-dimensional Cultured Human Cornea Epithelial Model User s Manual For Research Use Only Please read this manual before use Updated March, 2017 Table of contents I Characteristics
LabCyte CORNEA-MODEL Three-dimensional Cultured Human Cornea Epithelial Model User s Manual For Research Use Only Please read this manual before use Updated March, 2017 Table of contents I Characteristics
Perfusion culture and live cell imaging of Hepatitis C Virus Replicon cells in miniature bioreactor and analysis of shape of nuclei
 Perfusion culture and live cell imaging of Hepatitis C Virus Replicon cells in miniature bioreactor and analysis of shape of nuclei Anisha Prasad a, Prof. Saumitra Das b and Prof. G. K. Ananthasuesh c
Perfusion culture and live cell imaging of Hepatitis C Virus Replicon cells in miniature bioreactor and analysis of shape of nuclei Anisha Prasad a, Prof. Saumitra Das b and Prof. G. K. Ananthasuesh c
UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER
 Date: 04 October 2005 Authors: Sally Quataert and Jennifer Hossler Approval: Sally A. Quataert 1. Purpose: To enumerate the total number of or IgM secreting plasma B cells in human peripheral blood mononuclear
Date: 04 October 2005 Authors: Sally Quataert and Jennifer Hossler Approval: Sally A. Quataert 1. Purpose: To enumerate the total number of or IgM secreting plasma B cells in human peripheral blood mononuclear
If protein coating is acceptable in the planned experiments, there is another quick and simple way to render the surface hydrophilic.
 1 MEA Handling Warning: Use only liquids or cleaning solutions with a neutral ph (7) on MEAs with a silicon nitride insulation type. Otherwise, the MEAs may be irreversibly damaged. Warning: Do not to
1 MEA Handling Warning: Use only liquids or cleaning solutions with a neutral ph (7) on MEAs with a silicon nitride insulation type. Otherwise, the MEAs may be irreversibly damaged. Warning: Do not to
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Creating Biomimetic Anisotropic Architectures with Co-Aligned Nanofibers and Macrochannels by Manipulating Ice Crystallization Linpeng Fan, Jing-Liang Li*, Zengxiao Cai, and Xungai
Supporting Information Creating Biomimetic Anisotropic Architectures with Co-Aligned Nanofibers and Macrochannels by Manipulating Ice Crystallization Linpeng Fan, Jing-Liang Li*, Zengxiao Cai, and Xungai
Efficient operation of the HyPerforma 5:1 Single-Use Bioreactor at low working volume
 APPLICATION NOTE HyPerforma : Single-Use Bioreactor Efficient operation of the HyPerforma : Single-Use Bioreactor at low working volume Introduction The Thermo Scientific HyPerforma : Single-Use Bioreactor
APPLICATION NOTE HyPerforma : Single-Use Bioreactor Efficient operation of the HyPerforma : Single-Use Bioreactor at low working volume Introduction The Thermo Scientific HyPerforma : Single-Use Bioreactor
Whole Mount IHC Protocol
 Whole Mount IHC Protocol Authors: Ruth Sullivan, Ryan Trevena and Kyle Wegner Creation Date: 03/17/2016 All steps should be conducted with gentle agitation on an orbital shaker, unless otherwise instructed.
Whole Mount IHC Protocol Authors: Ruth Sullivan, Ryan Trevena and Kyle Wegner Creation Date: 03/17/2016 All steps should be conducted with gentle agitation on an orbital shaker, unless otherwise instructed.
High-throughput automation with the Attune NxT Autosampler: consistent results across all wells and across plates
 APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer with Autosampler High-throughput automation with the Attune NxT Autosampler: consistent results across all wells and across plates Introduction The emerging field
APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer with Autosampler High-throughput automation with the Attune NxT Autosampler: consistent results across all wells and across plates Introduction The emerging field
Supplementary Information:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information: 3D Printed Nervous System on a Chip Blake N. Johnson, a,b Karen
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information: 3D Printed Nervous System on a Chip Blake N. Johnson, a,b Karen
CytoGLOW. IKK-α/β. Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit. Catalog #: CB5358
 CytoGLOW IKK-α/β Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: CB5358 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research Purposes Only.
CytoGLOW IKK-α/β Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: CB5358 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research Purposes Only.
APPLICATION SPECIFIC PROTOCOL CELL MIGRATION FOR ADHERENT CELLS
 APPLICATION SPECIFIC PROTOCOL CELL MIGRATION FOR ADHERENT CELLS AIM 3D Cell Culture Chips are very useful for the study of 3D cell invasion and migration. The chips are not only suitable for endpoint measurement;
APPLICATION SPECIFIC PROTOCOL CELL MIGRATION FOR ADHERENT CELLS AIM 3D Cell Culture Chips are very useful for the study of 3D cell invasion and migration. The chips are not only suitable for endpoint measurement;
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION: 1. Supplemental methods 2. Supplemental figure legends 3. Supplemental figures
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008 A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008 A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA
 sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
Differentiation of bone marrow stem cells on inkjet printed silk lines
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 Differentiation of bone marrow stem cells on inkjet printed silk lines
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 Differentiation of bone marrow stem cells on inkjet printed silk lines
Chapter 8. Comparison of static vs dynamic culture
 Chapter 8 Comparison of static vs dynamic culture 8.1. Literature Review Articular cartilage is a load-bearing connective tissue in which its functions not only transmitting the compressive joint loads
Chapter 8 Comparison of static vs dynamic culture 8.1. Literature Review Articular cartilage is a load-bearing connective tissue in which its functions not only transmitting the compressive joint loads
Cell Micropatterning Using Magnetite Nanoparticles and Magnetic Force
 Cell Micropatterning Using Magnetite Nanoparticles and Magnetic Force Kosuke Ino, Kazunori Shimizu, Akira Ito and Hiroyuki Honda, Department of Biotechnology, School of Engineering, Nagoya University,
Cell Micropatterning Using Magnetite Nanoparticles and Magnetic Force Kosuke Ino, Kazunori Shimizu, Akira Ito and Hiroyuki Honda, Department of Biotechnology, School of Engineering, Nagoya University,
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable
 Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Design of scaffolds with computer assistance
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 157 Design of scaffolds with computer assistance H. A. Almeida 1, P. J. Bártolo 1 & J. C. Ferreira 2 1 Centre for Rapid and Sustainable Product Development CDRsp,
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 157 Design of scaffolds with computer assistance H. A. Almeida 1, P. J. Bártolo 1 & J. C. Ferreira 2 1 Centre for Rapid and Sustainable Product Development CDRsp,
3D Transfection System
 3D Transfection System Why 3D Technology? Introduction to Three Dimensional (3D) Cell Culture The goal of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture is to eliminate the stress and artificial responses cells experience
3D Transfection System Why 3D Technology? Introduction to Three Dimensional (3D) Cell Culture The goal of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture is to eliminate the stress and artificial responses cells experience
Hypoxyprobe -1 Green Kit Kit contents:
 Updated 2015 1 PRODUCT INSERT Hypoxyprobe, Inc 121 Middlesex Turnpike Burlington, MA 01803 USA www.hypoxyprobe.com Hypoxyprobe -1 Green Kit Kit contents: Solid pimonidazole HCl (Hypoxyprobe -1) FITC conjugated
Updated 2015 1 PRODUCT INSERT Hypoxyprobe, Inc 121 Middlesex Turnpike Burlington, MA 01803 USA www.hypoxyprobe.com Hypoxyprobe -1 Green Kit Kit contents: Solid pimonidazole HCl (Hypoxyprobe -1) FITC conjugated
CytoSelect 24-Well Wound Healing Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect 24-Well Wound Healing Assay Catalog Number CBA-120 CBA-120-5 24 assays 5 x 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Wounded tissue initiates
Product Manual CytoSelect 24-Well Wound Healing Assay Catalog Number CBA-120 CBA-120-5 24 assays 5 x 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Wounded tissue initiates
CHALLENGES OF 3D BIOPRINTING IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
 CENTRE DE THÉRAPIE TISSULAIRE & CELLULAIRE CHALLENGES OF 3D BIOPRINTING IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Pr. D. Dufrane MD, PhD 3D-BIOPRINTING: MYTH OR REALITY? 2 REGENERATIVE MEDICINE FOR ORGAN AND TISSUE A LARGE
CENTRE DE THÉRAPIE TISSULAIRE & CELLULAIRE CHALLENGES OF 3D BIOPRINTING IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Pr. D. Dufrane MD, PhD 3D-BIOPRINTING: MYTH OR REALITY? 2 REGENERATIVE MEDICINE FOR ORGAN AND TISSUE A LARGE
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Chemical Sporulation and Germination: Cytoprotective Nanocoating of Individual
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Chemical Sporulation and Germination: Cytoprotective Nanocoating of Individual
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody
 ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and nonapoptotic
ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and nonapoptotic
IncuCyte S3 Neuronal Activity Assay
 IncuCyte S3 Neuronal Activity Assay For the kinetic quantification of neuronal activity and functional connectivity This protocol provides an overview of the methodology which uses the lentiviral based
IncuCyte S3 Neuronal Activity Assay For the kinetic quantification of neuronal activity and functional connectivity This protocol provides an overview of the methodology which uses the lentiviral based
Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative received
Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative received
Culture of Human ipsc-derived Neural Stem Cells in a 96-Well Plate Format
 Protocol supplement version 1.0 Culture of Human ipsc-derived Neural Stem Cells in a 96-Well Plate Format Protocol Supplement This protocol supplement is to be used in addition to the Neural Stem Cell
Protocol supplement version 1.0 Culture of Human ipsc-derived Neural Stem Cells in a 96-Well Plate Format Protocol Supplement This protocol supplement is to be used in addition to the Neural Stem Cell
 3D Blood Brain Impedance Assay Using SynBBB Idealized Network (TEER configuration) Kits and Chips Technical Manual Catalog #s 402004, 402003, 102015-SB Schematic of the chip used for the SynBBB Model and
3D Blood Brain Impedance Assay Using SynBBB Idealized Network (TEER configuration) Kits and Chips Technical Manual Catalog #s 402004, 402003, 102015-SB Schematic of the chip used for the SynBBB Model and
Glycoprotein Assay Kit. Green Fluorescence)
 Version 1 Last updated 15 June 2018 ab235629 O-GalNAc Modified Glycoprotein Assay Kit (FACS/Microscopy, Green Fluorescence) For the measurement of O-GalNAc-glycosylated proteins in suspension or adherent
Version 1 Last updated 15 June 2018 ab235629 O-GalNAc Modified Glycoprotein Assay Kit (FACS/Microscopy, Green Fluorescence) For the measurement of O-GalNAc-glycosylated proteins in suspension or adherent
nanoprecipitation mpeg-pla 2 nd Emulsion mpeg-pla in DCM
 THERAPEUTIC NANOTECHNOLOGY LAB MODULE Location: BioNano Lab, 3119 Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory (MNTL) Instructor: Jianjun Cheng, Assistant Professor of Materials Science and Engineering Lab Assistants:
THERAPEUTIC NANOTECHNOLOGY LAB MODULE Location: BioNano Lab, 3119 Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory (MNTL) Instructor: Jianjun Cheng, Assistant Professor of Materials Science and Engineering Lab Assistants:
PKA α/β CAT (Phospho-Thr197)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 PKA α/β CAT (Phospho-Thr197) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG01634 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 PKA α/β CAT (Phospho-Thr197) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG01634 Please read the provided manual
What is a scaffold? A 3D structure which supports 3D tissue growth
 LO SCAFFOLD Outline Scaffold definition Scaffold requirements History of scaffold fabrication New approaches in scaffold design: Bioprinting, Nano-in-Micro Scaffold characterisation What is a scaffold?
LO SCAFFOLD Outline Scaffold definition Scaffold requirements History of scaffold fabrication New approaches in scaffold design: Bioprinting, Nano-in-Micro Scaffold characterisation What is a scaffold?
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Xeno-Free Culture and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Neurons
 Xeno-Free Culture and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Neurons Publication Part Number MAN0007497 Revision 1.0 Introduction As the field of neuroscience moves closer to the reality of neural stem
Xeno-Free Culture and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Neurons Publication Part Number MAN0007497 Revision 1.0 Introduction As the field of neuroscience moves closer to the reality of neural stem
Implantable hydrogel beads entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Exploring the effects of nearzero-order drug release for intracranial chemotherapy
 Implantable hydrogel beads entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Exploring the effects of nearzero-order drug release for intracranial chemotherapy Abstract ID: 123910 Sudhir H. Ranganath, Alvin Yang,
Implantable hydrogel beads entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Exploring the effects of nearzero-order drug release for intracranial chemotherapy Abstract ID: 123910 Sudhir H. Ranganath, Alvin Yang,
WHITE PAPER: ATELO COLLAGEN. Product Number: FS22001, FS22002, FS22003, FS22004, FS22005, FS22006
 Page 1 of 5 WHITE PAPER: ATELO COLLAGEN 1.0 GENERAL INFORMATION Material Name: Pepsin Soluble Atelo Collagen in 0.01M HCl Product Number: FS22001, FS22002, FS22003, FS22004, FS22005, FS22006 Product Description/
Page 1 of 5 WHITE PAPER: ATELO COLLAGEN 1.0 GENERAL INFORMATION Material Name: Pepsin Soluble Atelo Collagen in 0.01M HCl Product Number: FS22001, FS22002, FS22003, FS22004, FS22005, FS22006 Product Description/
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit Catalog Number SC027B Reagents for the identification of human pluripotent stem cells by in vitro functional differentiation. This package insert
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit Catalog Number SC027B Reagents for the identification of human pluripotent stem cells by in vitro functional differentiation. This package insert
The Design of Droplet Based Bioprinting Systems for Reliable Bioink Delivery
 The Design of Droplet Based Bioprinting Systems for Reliable Bioink Delivery Matthew Benning School of Mechanical in Systems Engineering Newcastle University Introduction Our Research Aim and Objectives
The Design of Droplet Based Bioprinting Systems for Reliable Bioink Delivery Matthew Benning School of Mechanical in Systems Engineering Newcastle University Introduction Our Research Aim and Objectives
Cellular UV-Induced DNA Damage Staining Kit (CPD)
 Cellular UV-Induced DNA Damage Staining Kit (CPD) For the rapid detection of CPDs in genomic DNA of cultured cells Cat. No. KT-918 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Page 1 of
Cellular UV-Induced DNA Damage Staining Kit (CPD) For the rapid detection of CPDs in genomic DNA of cultured cells Cat. No. KT-918 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Page 1 of
Promising Future for Ex vivo Tissue Fabrication. Eiji Kobayashi, MD, PhD Department of Organ Fabrication, Keio University School of Medicine, Japan
 Promising Future for Ex vivo Tissue Fabrication Eiji Kobayashi, MD, PhD Department of Organ Fabrication, Keio University School of Medicine, Japan The research for fabricating tissue/organs through cultivation
Promising Future for Ex vivo Tissue Fabrication Eiji Kobayashi, MD, PhD Department of Organ Fabrication, Keio University School of Medicine, Japan The research for fabricating tissue/organs through cultivation
Which hydrogel preparation for immunostaining protocol should I use?
 Protocol: Preparation of TissueSpec hydrogels for immunostaining This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec matrix hydrogels.
Protocol: Preparation of TissueSpec hydrogels for immunostaining This protocol may be used prior to immunostaining cells, organoids, or patient-derived xenografts cultured in TissueSpec matrix hydrogels.
Mechano-dependent Biosynthetic Response of Micro-integrated Cells in Elastomeric Scaffolds
 Mechano-dependent Biosynthetic Response of Micro-integrated Cells in Elastomeric Scaffolds Lauren Anderson 1,2, John Stella 3, and Dr. Michael Sacks 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute,
Mechano-dependent Biosynthetic Response of Micro-integrated Cells in Elastomeric Scaffolds Lauren Anderson 1,2, John Stella 3, and Dr. Michael Sacks 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute,
Human ipsc-derived Sensory Neuron Progenitors. For the generation of ipsc-derived sensory neurons
 Human ipsc-derived Sensory Neuron Progenitors For the generation of ipsc-derived sensory neurons Product Information Catalog. No. Product Name Format Stock Conc. Storage on Arrival Thawing Instructions
Human ipsc-derived Sensory Neuron Progenitors For the generation of ipsc-derived sensory neurons Product Information Catalog. No. Product Name Format Stock Conc. Storage on Arrival Thawing Instructions
Human ipsc-derived Sensory Neuron Progenitors. For the generation of ipsc-derived sensory neurons
 Human ipsc-derived Sensory Neuron Progenitors For the generation of ipsc-derived sensory neurons Additional Reagents Product Name Supplier Product Code Mitomycin C Sigma-Aldrich M4287 Store at 4 o C for
Human ipsc-derived Sensory Neuron Progenitors For the generation of ipsc-derived sensory neurons Additional Reagents Product Name Supplier Product Code Mitomycin C Sigma-Aldrich M4287 Store at 4 o C for
Protocol Using the Reprogramming Ecotropic Retrovirus Set: Mouse OSKM to Reprogram MEFs into ips Cells
 STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction
STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction
